
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
SYSTEMATIC REVIEW article
Front. Public Health, 27 March 2025
Sec. Aging and Public Health
Volume 13 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2025.1525593
This article is part of the Research TopicReviews and Applications of Implementation Research in Aging and Public HealthView all 13 articles
Objective: To comprehensively and systematically collect the methods used in the evaluation of patients with multiple chronic diseases both domestically and internationally, summarize and analyze the purpose, characteristics and validity of their initial development, and provide reference for health managers to choose appropriate evaluation methods for multiple chronic diseases.
Methods: Analysis of the literature was based on searches conducted across eight electronic databases, including PubMed, EMBASE, Web of Science Core Collection, Scopus, Cochrane Library, CNKI, Wan Fang Database, and the Chinese Biomedical Literature Database (CBM). The initial search was completed on January 8, 2024, and the most recent update was conducted on December 10, 2024, with no restriction on the date of publication. The search process adhered to the 2020 PRISMA guidelines for systematic review.
Results: 54 literatures meeting the criteria were included, involving 54 evaluation methods of multiple chronic diseases. It can be divided into four categories: (1) assessment based on equal weight of disease count and disease severity; (2) based on physiological and psychological health status assessment; (3) evaluation based on drug use; (4) natural language processing evaluation system.
Conclusion: Attention should be paid to the assessment of patients with multiple chronic diseases, and standardized and unified assessment methods should be developed in the future to expand the coverage of diseases and deepen the depth of assessment, so as to provide more comprehensive and accurate health management for the growing number of patients with multiple chronic diseases.
Without patient or public contribution: This systematic review is primarily based on the comprehensive analysis of published literature and did not involve new data collection or direct participation of patients, hence there was no direct contribution from patients or the public.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/, CRD42024530474.
Multiple chronic diseases, as defined by the presence of 2 or more chronic conditions in a single individual, underscore the complexity and variety of health issues faced by individuals. These conditions can significantly impact an individual’s overall health, daily functioning, and quality of life (1). As populations age and the prevalence of chronic diseases rises, the challenge posed by multiple chronic diseases is increasingly becoming a global public health concern. Compared to a single chronic disease, having multiple chronic diseases not only results in more severe health consequences but also increases the complexity of disease treatment and health management. This situation is often linked to functional decline, disability, and premature death (2–4). From a public health perspective, this phenomenon drives total healthcare expenditures while exacerbating health inequities, as vulnerable populations experience earlier multimorbidity onset with poorer outcomes (5). Current clinical practice guidelines, however, remain predominantly single-disease focused, creating implementation barriers in real-world care settings (6).
Therefore, researchers are increasingly focusing on multiple chronic diseases, making related research a prominent topic in the field of health research. However, methodological issues in measuring multiple chronic diseases continue to be a challenge (7). Currently, there exists a range of tools for assessing multiple chronic diseases, however, there is a lack of standardized classification criteria. These tools are typically categorized into four groups: disease counting, organ- or system-based methods, weighted indices, and other assessment methods. While these tools are mainly utilized to gage the prevalence or pattern of multimorbidity, they can also be employed to forecast outcomes or assess interventions (8, 9). Researchers, healthcare providers, and policymakers encounter challenges when choosing the most suitable tool for assessing multiple chronic diseases. Factors such as effectiveness, reliability, feasibility, accessibility, cost, and ease of use of the assessment tool need to be considered.
In addition, the inconsistencies in defining terms related to multiple chronic diseases pose challenges in selecting appropriate assessment methods. The World Health Organization defines multiple chronic diseases as encompassing all conditions impacting an individual’s overall health, rather than focusing on a single disease (1). However, some assessment tools concentrate on comorbidities, which are other diseases co-existing with the primary condition. Different interpretations of ‘health status’ have resulted in various methods for measuring multiple chronic diseases, with debates on whether to incorporate acute illnesses, mental health issues, and so on (10–12). While, the standardization of the measurement of multiple chronic diseases is the basis for quantifying their symptom status, disease burden, treatment effect, etc. Comprehensive measurement studies of multiple chronic diseases are essential to understand their use requirements, advantages, limitations, and applications. This information can help health professionals and researchers to select appropriate measurement tools or develop new methods appropriate for specific health outcomes, thus enhancing the appropriate use of multiple chronic disease assessment tools. This systematic review aims to comprehensively examine the methods used for evaluating patients with multiple chronic diseases, both domestically and internationally. It summarizes and analyzes the objectives, characteristics, and validity of these methods’ initial development, critically assesses and compares their measurement attributes and quality of evidence, and discusses their interpretability and feasibility. The goal is to provide health managers with valuable insights to select appropriate evaluation methods for multiple chronic diseases, while also minimizing implementation barriers.
This review has been registered in the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO registration number: CRD42024530474).
Inclusion criteria: (1) original research content focused on the development, testing, revision, and validation of multiple chronic disease assessment tools; (2) study types included cross-sectional, longitudinal, cohort, case–control studies and randomized controlled trials (RCTs).
Exclusion criteria: (1) comparative studies of multiple chronic disease assessment tools; (2) duplicate data collection; (3) unpublished or non-peer-reviewed literature, such as conference abstracts, preprints, policy papers, and informal publications; (4) inability to access the full text of the literature; (5) literature not in Chinese or English.
The methodology employed in this study is a systematic review that adheres to the PRISMA 2020 Guidelines for Systematic Reviews (13). We conducted comprehensive database searches across several platforms, including The Cochrane Library, PubMed, EMBASE, Web of Science Core Collection, Scopus, CNKI, Wan Fang Database, and the Chinese Biomedical Literature Database (CBM). These searches were performed without applying date restrictions. The initial search was completed on January 8, 2024, and the most recent update was conducted on December 10, 2024.
Before the official search, the research team first conducted a pre-search on PubMed and CNKI, then analyzed and discussed the search results, and adjusted the search strategy as needed to determine the official search terms. The retrieval terms used are ‘Multimorbidity,’ ‘Comorbidity,’ ‘Multiple Chronic Diseases,’ ‘Multiple Chronic Illnesses,’ ‘Multiple Chronic Medical Conditions,’ ‘Multiple Chronic Health Conditions,’ along with ‘Tool,’ ‘Instrument,’ and ‘Measure’. The search strategy incorporates a combination of subject words and free words, along with manual retrospective reference of included studies and relevant systematic reviews, reviews, and guides. All database search strategies are presented in Supplementary Boxes 1.
The collected references were imported into EndNote 20 for literature management, where duplicates were eliminated. Two researchers, trained in systematic evidence-based methods, independently screened the literature in a structured manner based on predetermined inclusion and exclusion criteria. Initially, titles and abstracts were reviewed for screening, with literature failing to meet the criteria being excluded. Subsequently, full-text articles were reviewed.
In the process, the two reviewers also found 18 and 25 relevant articles from the references, respectively. The two reviewers then independently reviewed the 43 papers to ensure the rigor and objectivity of the selection process.
Data relevant to the research questions were extracted from the final set of included literature, such as developer, publication date, country/region, basic characteristics of the research subjects, tool name, and tool validity. Any discrepancies in the literature screening and data extraction process were resolved through discussion between the two researchers; if consensus could not be reached, a third researcher made the final decision.
Two researchers with evidence-based training conducted a qualitative evaluation of the literature across various types of studies, and cross-validated the evaluation results. Any discrepancies were resolved through consultation with a third researcher. The RCTs were assessed for risk of bias using the recommended tool from the Cochrane Handbook 5.1.0, with each study being evaluated independently. Studies that fully met the evaluation criteria were assigned Grade A, indicating the lowest probability of bias. Studies showing partial compliance were assigned Grade B, suggesting a moderate probability of bias. Studies with incomplete results, indicating the highest probability of bias and low study quality, were assigned Grade C. The quality of the cohort studies were assessed using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS), which comprises three parts with a total of 8 items. These items include the selection of research subjects (4 items), between-group comparability (1 item), and exposure or outcome evaluation (3 items). The total score on this scale is 9 points, with studies scoring ≥7 being considered high-quality literature. Cross-sectional studies were assessed using the Australian JBI Evidence-Based Health Care Center (2016) quality evaluation tool, comprising a total of 8 evaluation items. Each item was assessed as “yes”, “no”, “unclear”, or “Not applicable”. The APPRAISE-AI Tool comprises 24 items with a cumulative score of 100. The tool categorizes quality as follows: very low quality (0–19), low quality (20–39), medium quality (40–59), high quality (60–79), and very high quality (80–100).
A total of 2,179 literature sources were identified during the initial search, with 1,436 remaining after the removal of duplicates. Following a thorough screening process based on predefined inclusion and exclusion criteria, two researchers independently reviewed the literature and reached a consensus on 54 relevant studies for final inclusion. The detailed process and outcome of literature screening can be seen in Figure 1.
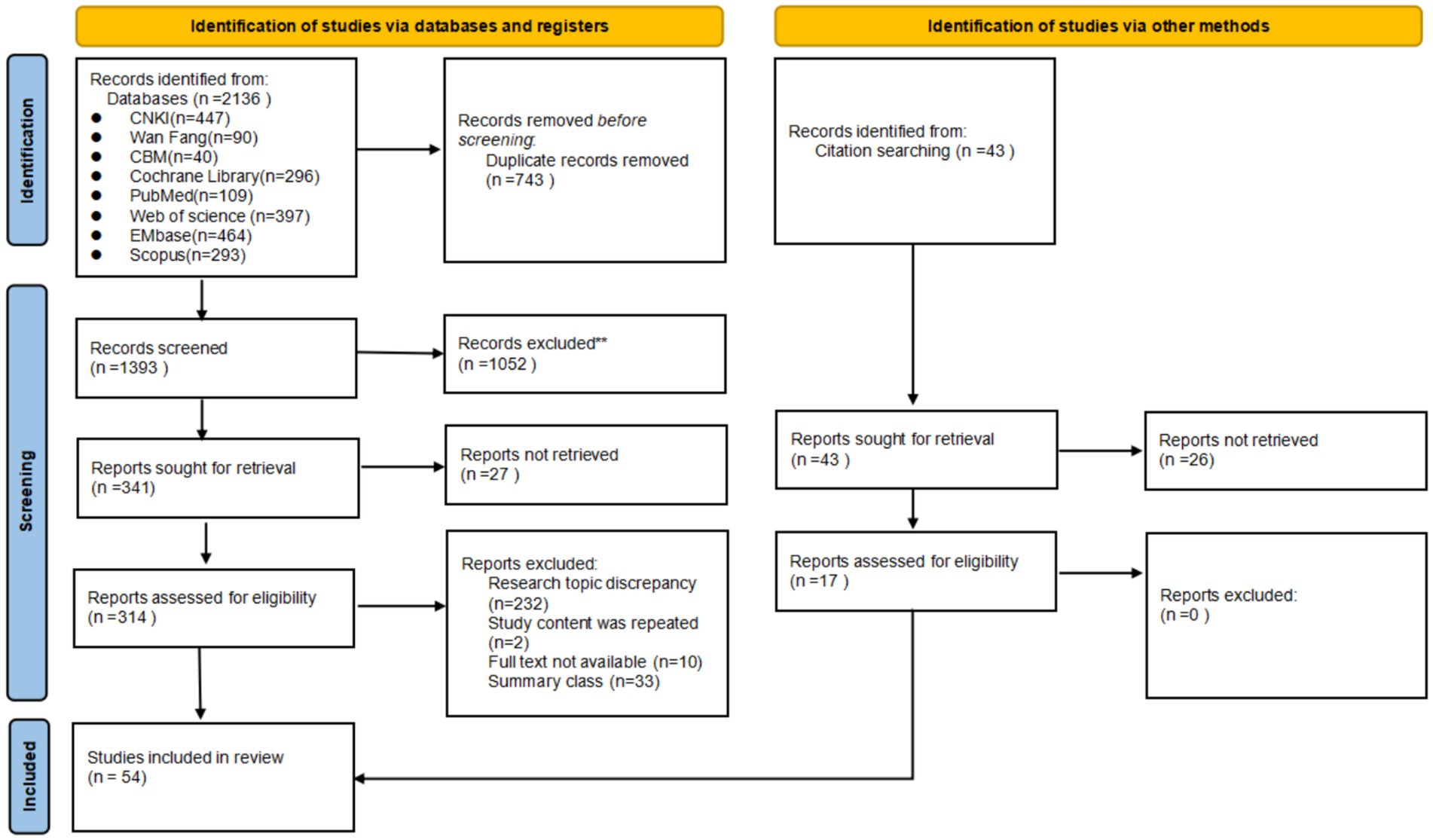
Figure 1. Flow diagram illustrating the original process of screening and identification of studies.
Fifty-four articles were published between 1968 and 2024, across 14 countries. The United States led with 27 articles, followed by Australia with five articles. Among the 54 studies, the development of multiple chronic disease assessment tools aimed to assess patient prognosis, disease status, and their impact and burden. The study participants in the included research encompassed a variety of groups such as community residents, inpatients, outpatients, and patients with specific diseases such as cancer and myeloma. Special groups such as patients with medical insurance, female community residents, and older patients were also included. Outcome indicators examined in the studies comprised mortality, hospitalization costs, medical resource utilization, and functional status. Refer to Table 1 for more details.
Data sources for assessing multiple chronic diseases across the 54 articles included the following categories: (1) Electronic medical records; (2) Insurance database; (3) Self-report; (4) Public health databases; (5) Caregiver report; (6) Administrative database. The majority of studies, 13 in total, utilized data from electronic medical records. Six studies combined data from electronic medical records, self-reports, and other registration databases. Eleven studies relied solely on self-reports, while caregiver reports, including parent reports and medical staff assessments, were used in a total of four studies. Please refer to Table 1 for more specific information.
A total of 54 multi-chronic diseases assessment tools were included in this study, categorized as follows: (1) assessment based on equal weight of disease count and severity; (2) assessment based on physiological and health status; (3) evaluation based on drug use; (4) natural language processing evaluation system. Among the 54 studies, we summarized the reliability and validity of all the evaluation tools as shown in Supplementary Table 1. Thirty-four studies examined the predictive accuracy of various chronic disease assessment tools on outcome indicators. Among them, eight studies were validated by comparing them with established multi-chronic diseases assessment tools like the Elixhauser index and the Charlson comorbidity index. Fourteen studies utilized methods such as the C-statistic to assess the effectiveness of the model. The 54 assessment tools evaluated in these studies covered a range of 4 to 70 disease/health status categories, with only one paper not specifying any particular disease/health status category. As depicted in Figure 2, 85.2% of the assessment tools addressed over 10 disease/health conditions. Supplementary Table 2 provides a detailed breakdown of the types of illnesses/health conditions included. To gain deeper insights into the disease/health status encompassed by the various multiple chronic disease assessment tools, the researchers utilized Python to generate a word cloud map (Figure 3).
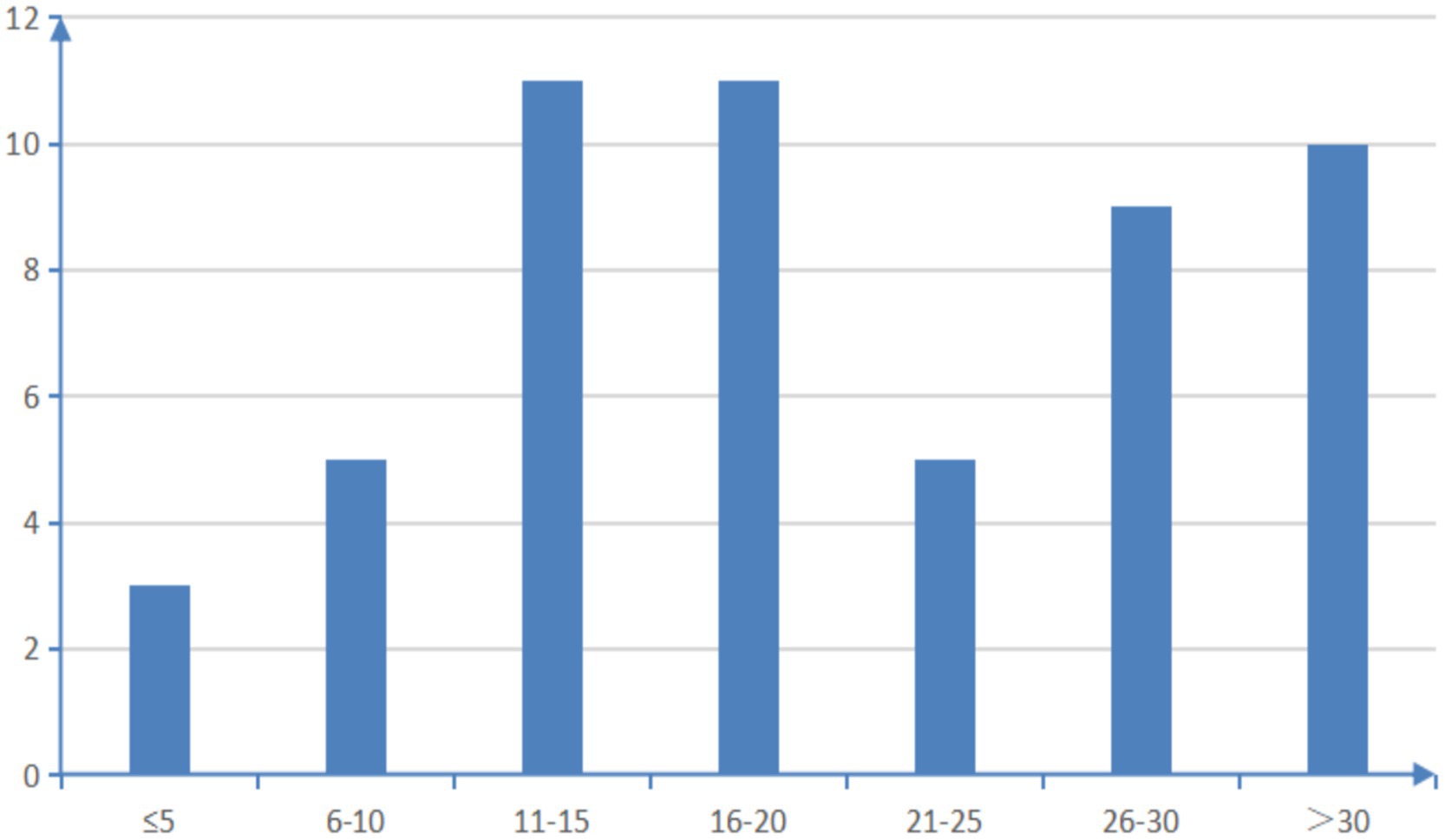
Figure 2. Overview of the number of types of diseases/health conditions covered by the assessment tools.
This study comprised 3 randomized controlled trials and 15 cross-sectional studies, all of which were rated above grade B in quality assessment. Among the 28 cohort studies, 21 scored ≥7 points on the NOS scale. The quality of the included literature was deemed high, as indicated in Supplementary Tables 3–5. The quality of the remaining 8 studies was evaluated using APPRAISE-AI, with 4 studies (14–17) of them being of medium quality. The quality of the included literature deemed medium, as indicated in Supplementary Table 6. Despite some bias related to subject grouping, follow-up duration, and control for confounding factors, such as the lack of a clear randomization method in the studies, all the research was deemed relevant for this review.
Currently, research on multiple chronic diseases is extensively conducted worldwide, encompassing diverse populations and exhibiting significant diversity. Additionally, a broad spectrum of assessment tools for multiple chronic diseases exists, utilizing varied data sources. While most tools exhibit satisfactory reliability, validity, and adaptability in the evaluated populations, some tools still have certain limitations in their applicability. Consequently, existing research conclusions offer valuable reference and practical guidance for the assessment and management of multiple chronic diseases. However, further optimization of these tools is necessary to accommodate a broader range of application scenarios.
As the population ages and lifestyles evolve, the prevalence of patients with multiple chronic diseases is on the rise. In order to optimize the management and treatment of these diseases, this study systematically reviewed multiple chronic disease assessment tools from the 1960s to the present, aiming to evaluate their applicability and effectiveness to patient health status and treatment outcomes in different clinical scenarios. These tools encompass weighted scoring systems, exponential classifications, and natural language processing models. With the popularization of electronic health records and the development of information technology, multiple chronic disease assessment tools are no longer limited to conventional assessment methods (such as disease-specific counting scales and functional status assessments). Some researchers began to integrate artificial intelligence and big data analysis technology to develop an intelligent multiple chronic diseases assessment system. However, the interoperability of these classification evaluation systems still needs to be further verified (10, 18–20). The variety of assessment tools for multiple chronic diseases reflects the intricate nature and varied manifestations of such conditions. These tools may vary in their focus on different risk factors, types of diseases, and prediction models to cater to diverse health management needs (1). For instance, certain tools excel in evaluating cardiovascular disease risk (18), while others are better suited for assessing metabolic syndrome, cancer, or other specific diseases (14, 21–27). This diversity allows for tailored and personalized assessments for particular populations, but it also leads to a wider range of assessment outcomes. To enhance the accuracy of assessment, healthcare personnel may utilize a combination of various assessment tools, including subjective assessment indexes and physiological indicators of comorbidity, to achieve more comprehensive and precise assessment outcomes (8, 28, 29). Although, the combination of different assessment tools can improve the accuracy and completeness of the assessment to some extent. But it also brings a series of challenges: first, it not only reduces the efficiency of assessment, but also requires medical staff to spend more time and effort to familiarize themselves with and understand the use of different assessment tools and the interpretation of results. Second, some assessment tools may require additional resources, such as specialized equipment and trained personnel, leading to a potential waste of medical resources and potential delays in diagnosis and treatment. Therefore, the feasibility and economy of the combined use of multiple chronic disease assessment tools need to be further considered (9). In addition, the absence of standardized evaluation methods hinders the advancement of personalized medicine. A generic assessment approach can effectively combine various types of information to precisely evaluate a patient’s risks and requirements, enabling the development of a more tailored treatment plan. Based on this, a universal assessment method needs to be developed to facilitate the comparison and synthesis of multiple chronic disease assessment tools. The evaluation of multiple chronic diseases should prioritize simplicity, standardization, data compatibility, patient friendliness, and interdisciplinary applicability. Tools should be developed based on reliable evidence and extensive data, taking into account the association and interaction between different diseases. It is important to establish a consistent scoring system, standardized risk calculation formulas, and comparable thresholds to ensure the consistency and comparability of assessment results (30).
Consistent with previous systematic reviews, this systematic review reveals that data on multiple chronic diseases assessments are derived from diverse sources, including medical records, clinical assessments, patient or caregiver reports, public health databases, and administrative databases like insurance claims and health system records (8, 10, 12). Diverse data sources can help achieve personalized assessment, because different assessment purposes and study populations may tend to require different types of data. For example, if you want to accurately assess patient disease burden, an accurate insurance claims database will be the best choice. However, if you want to gain a deeper understanding of the patient’s disease, physical and psychological conditions and needs, based on the patient’s self-reported symptoms and lifestyle, you may obtain more information that is not recorded or coded in the relevant database (31). Furthermore, there are differences in the completeness and accuracy of different data sources. For example, medical records and clinical evaluations in electronic medical records provide detailed medical information but may be subject to subjective physician judgment and recording errors, and do not include undiagnosed health conditions in the patient or conditions not listed on the diagnostic list. Although public health surveys and patient self-reports may be influenced by recall bias, social expectation bias, and subjective assessment, they are portable and can be collected longitudinally throughout the patient’s life cycle, which helps reduce underreporting. In addition, this approach is highly aligned with the promotion of patient self-management, self-care, and a patient-centered healthcare model. Insurance claims data offer extensive data coverage and the flexibility to create various measurement tools, but they are also susceptible to coding and recording errors. In addition, some researchers argue that insurance claims data may be the most practical method currently available to comprehensively evaluate patients with multiple chronic diseases. This approach can provide the large sample sizes necessary to study populations with specific clinical conditions or rare outcomes (8). The insurance claims database contains codes for patient diagnoses, which can be connected to other databases like electronic health records and research data. For instance, the updated version of the Charlson Comorbidity Index utilizes insurance claims databases that rely on ICD and CPT codes to evaluate patients with multiple chronic diseases (32). In contrast, the Elixhauser Index was created using insurance claims databases as its primary data source (33, 34). Studies have highlighted a lack of consistency between the Charlson comorbidity index derived from patient self-reports and medical records. However, despite this inconsistency, the predictive capabilities of both sources remain similar (35). This underscores the importance of considering data sources when creating and utilizing multiple chronic disease assessment tools. A thorough assessment of the reliability of these data sources is essential for the effective and precise multidimensional evaluation of patients with multiple chronic conditions.
In addition, this study evaluated the reliability and adaptability of multiple multimorbidity indices and other related tools. Supplementary Table 1 summarizes the reliability, validity and applicability of these assessment tools. Overall, these tools demonstrated good reliability and adaptability in predicting health outcomes in older patients with multiple chronic diseases. However, some scales have certain limitations in adaptability. Future research needs to conduct empirical verification in larger samples to further evaluate the reliability and validity of these tools. It is also necessary to consider verification in different populations and regions to assess the wide applicability of these tools.
The multi-chronic diseases assessment tool aims to comprehensively evaluate multiple diseases and health states of patients, and provide scientific basis for extensive health assessment and treatment decisions by analyzing their relationships with related outcome indicators such as mortality, medical costs and quality of life. These tools typically include a range of chronic diseases, such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, etc., as well as physiological indicators, related health factors, and other health conditions, such as blood pressure, weight, lifestyle, and activity function. However, it is noted that many existing measures for managing multiple chronic conditions are more geared toward research rather than practical health management (36). The widely used Charlson comorbidity index or disease count is simple to assess and the data is easy to obtain, but it cannot comprehensively reflect the overall experience of multiple chronic diseases (37). Research suggests that factors beyond disease lists, such as social support, coping mechanisms, personal preferences, living environment, and economic status, should also be taken into account when evaluating patients with multiple chronic conditions (30, 38). These additional factors could play a significant role in the development and management of chronic diseases. Researchers have found that disease severity can be included in assessment tools and the subjective impact of the disease on the patient’s social, mental, and physical health can be incorporated into patient reports, such as the Duke Disease Severity Checklist and the Comorbidity Subjective Assessment Index (29, 39, 40). Some studies have also pointed out that simple disease counts are suitable for estimating the prevalence of multiple chronic diseases and examining their clusters or trajectories to explore multimorbidity patterns in more depth, while weighted measures are more suitable for related risk adjustment and outcome prediction of multiple chronic diseases. Therefore, ensuring the accuracy of disease markers is crucial to determine the number of diseases to include in an assessment tool (38). Looking at the current set of multiple chronic disease assessment tools, the diseases and health conditions they cover are diverse, but their breadth and depth require further research. Specifically, although the existing multiple chronic disease assessment tools include many common chronic diseases, the coverage of other chronic diseases may be lower, such as rare diseases or diseases of more specific groups, and the breadth of the assessment tools may be insufficient. Therefore, further research is needed to expand the breadth of assessment tools to include more comprehensive coverage of various chronic diseases and health states. Second, the depth of an assessment tool refers to the degree of detail in which each disease/health state is assessed. Existing multiple chronic disease assessment tools typically focus on basic factors like disease and health, encompassing basic physiological indicators and symptom evaluation (30). Nonetheless, it may be necessary to incorporate more detailed assessment indicators for each specific disease or health condition. For example, in cardiovascular disease assessment, in addition to basic blood pressure and heart rate measurements, consider including results from tests such as electrocardiograms and cardiac ultrasounds. Therefore, further optimization of multiple chronic disease assessment tools is essential through ongoing scientific research, interdisciplinary collaboration, and the application of technology. This will enable the provision of more comprehensive and accurate health management services to patients.
The prevalence of multiple chronic diseases is rising due to the aging population and changes in lifestyle. While these patients may have stable health status, disease progression and new health issues can impact their prognosis. Regular comprehensive assessments are essential to promptly detect any changes in the patient’s health status. For the management and treatment of patients with multiple chronic diseases, it is crucial to conduct thorough research on various assessment methods (38, 41). However, this study identified issues with the existing assessment tools for multiple chronic diseases, including the lack of standardized and universally accepted tools, as well as insufficient breadth and depth of assessment content. In order to build a universal, standardized, intelligent, interdisciplinary, concise and efficient multi-chronic disease assessment tool suitable for the disease spectrum of Chinese patients, it is first necessary to clarify the universal definition of multi-morbidity. Currently, the term “multiple chronic diseases” refers to an individual experiencing two or more chronic health conditions simultaneously (42). Nevertheless, there remains ambiguity regarding whether this definition should encompass various factors linked to multiple diseases, including psychosocial factors, physical risk factors, social networks, disease burden, medical resource utilization, and patient coping strategies (11). Therefore, continuing to carry out large-scale multi-morbidity model research will help understand the special status of patients with multiple chronic diseases and lay a theoretical foundation for constructing multiple chronic disease assessment tools with higher structural validity. The establishment of interdisciplinary teams in medicine, information technology, sociology, psychology, and data science, along with the utilization of advanced technologies like artificial intelligence, machine learning, and natural language processing to integrate diverse data sources for developing a comprehensive multi-chronic disease intelligent assessment tool with robust interoperability, is a key research focus for the future.
This study analyzed a total of 15 cross-sectional studies and 28 cohort studies. The majority of these studies clearly defined the inclusion and exclusion criteria for their research subjects, which were in line with the criteria used in this study. When evaluated using the NOS standard, the cohort studies scored between 5 to 9 points, with 19 studies scoring 8 to 9 points. The 15 cross-sectional studies included in the analysis all received a grade higher than B, indicating a high overall quality of the studies included. The literature elaborates on the research methods and outcome indicators, which help mitigate recall bias and selection bias to some extent. Bias primarily stems from the grouping of research subjects, follow-up duration, and control of confounding variables. For instance, the study lacks a clear randomization method. In general, the quality of the studies was deemed satisfactory.
In this study, various methods for assessing multiple chronic diseases were compared, providing valuable references for health managers in selecting appropriate evaluation techniques for multiple chronic conditions. In addition, this study searched 8 relevant databases with reliable and sufficient data sources. Limitations: primarily, only articles in English and Chinese were considered, excluding evidence published in other languages. Furthermore, the integrated tools come from different literature, and although the quality of the literature has been evaluated, the usability and reliability of the tools have yet to be demonstrated. Lastly, the outcome measures in the studies were reported in scale form, lacking objectivity.
This study critically examined various existing assessment tools for multiple chronic diseases and identified areas for improvement, including versatility, reliability of data sources, and coverage of disease/health conditions. To effectively meet the needs of the increasing number of patients with multiple chronic diseases, future research should focus on creating a universal, standardized, and interdisciplinary multi-chronic disease assessment method. Meanwhile, the reliability of data sources should be further assessed and the range and depth of assessment tools should be expanded. Interdisciplinary collaboration and the integration of advanced technology will be crucial in developing an effective and intelligent tool for assessing multiple chronic diseases. This tool will serve as a methodological and theoretical foundation for offering patients more comprehensive and precise health management services.
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, upon reasonable request.
LY: Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. QiaoL: Conceptualization, Supervision, Methodology, Project administration, Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YL: Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. QinL: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. TW: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. ZZ: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. JY: Methodology, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Humanities and Social Sciences Research Project of Guizhou University, 2024 Digital Transformation and Governance Collaborative Innovation Laboratory Special Project (grant no. GDJD202401); the Key Special Project of the Research Base and Think Tank of Guizhou University (grant no. GDZX2021030); the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 72261005); the National Natural Science Foundation Cultivation Project of the Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University (grant no. gyfynsfc [2023]-35) and the Nursing Evidence-Based Project of the Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University (grant no. gyfyhlxz-2022-3).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpubh.2025.1525593/full#supplementary-material
1. Kernick, D, Chew-Graham, CA, and O'flynn, N. Clinical assessment and management of multimorbidity: NICE guideline. British J General Prac: J Royal College Of General Practitioners. (2017) 67:235–6. doi: 10.3399/bjgp17X690857
2. Gobbens, RJJ, Kuiper, S, Dijkshoorn, H, and van Assen, MALM. Associations of individual chronic diseases and multimorbidity with multidimensional frailty. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. (2024) 117:105259. doi: 10.1016/j.archger.2023.105259
3. Zhong, Y, Qin, G, Xi, H, Cai, D, Wang, Y, Wang, T, et al. Prevalence, patterns of multimorbidity and associations with health care utilization among middle-aged and older people in China [J]. BMC Public Health. (2023) 23:537. doi: 10.1186/s12889-023-15412-5
4. Tran, PB, Kazibwe, J, Nikolaidis, GF, Linnosmaa, I, Rijken, M, and van Olmen, J. Costs of multimorbidity: a systematic review and meta-analyses. BMC Med. (2022) 20:234. doi: 10.1186/s12916-022-02427-9
5. Shaltynov, A, Jamedinova, U, Semenova, Y, Abenova, M, and Myssayev, A. Inequalities in out-of-pocket health expenditure measured using financing incidence analysis (FIA): a systematic review. Healthcare. (2024) 12:1051. doi: 10.3390/healthcare12101051
6. Raghunathan, K, East, C, and Poudel, K. Barriers and enablers for implementation of clinical practice guidelines in maternity and neonatal settings: a rapid review. PLoS One. (2024) 19:e0315588. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0315588
7. Wei, AL, and Feng, W. Visual analysis of research on Multimorbidity of the elderly at home and abroad based on CiteSpace. Med Soc. (2023) 36:1–6. doi: 10.13723/j.yxysh.2023.07.001
8. Suls, J, Bayliss, EA, Berry, J, Bierman, AS, Chrischilles, EA, Farhat, T, et al. Measuring multimorbidity: selecting the right instrument for the purpose and the data source. Med Care. (2021) 59:743–56. doi: 10.1097/MLR.0000000000001566
9. Ho, IS, Azcoaga-Lorenzo, A, and Akbari, A. Examining variation in the measurement of multimorbidity in research: a systematic review of 566 studies. Lancet Public Health. (2021) 6:e587–97. doi: 10.1016/S2468-2667(21)00107-9
10. Lee, ES, Koh, HL, and Ho, EQ. Systematic review on the instruments used for measuring the association of the level of multimorbidity and clinically important outcomes. BMJ Open. (2021) 11:e041219. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-041219
11. Johnston, MC, Crilly, M, Black, C, Prescott, GJ, and Mercer, SW. Defining and measuring multimorbidity: a systematic review of systematic reviews. Eur J Pub Health. (2019) 29:182–9. doi: 10.1093/eurpub/cky098
12. Diederichs, C, Berger, K, and Bartels, DB. The measurement of multiple chronic diseases--a systematic review on existing multimorbidity indices. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. (2011) 66:301–11. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glq208
13. Page, MJ, Mckenzie, JE, and Bossuyt, PM. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ (Clin Res). (2021) 372:n71. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n71
14. Engelhardt, M, Domm, AS, Dold, SM, Ihorst, G, Reinhardt, H, Zober, A, et al. A concise revised myeloma comorbidity index as a valid prognostic instrument in a large cohort of 801 multiple myeloma patients. Haematologica. (2017) 102:910–21. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2016.162693
15. Clark, DO, Von Korff, M, and Saunders, K. A chronic disease score with empirically derived weights [J]. Med Care. (1995) 33:783–95. doi: 10.1097/00005650-199508000-00004
16. Romano, PS, Roos, LL, and Jollis, JG. Adapting a clinical comorbidity index for use with ICD-9-CM administrative data: differing perspectives. J Clin Epidemiol. (1993) 46:1075–9. doi: 10.1016/0895-4356(93)90103-8
17. Bernard, S, Linn, MD, Margaret, W, and Linn, MSSW. Cumulative illness RATING scale. J Am Geriatr Soc. (1968) 16:622–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.1968.tb02103.x
18. Berman, AN, Biery, DW, Ginder, C, Hulme, OL, Marcusa, D, Leiva, O, et al. Natural language processing for the assessment of cardiovascular disease comorbidities: the cardio-canary comorbidity project. Clin Cardiol. (2021) 44:1296–304. doi: 10.1002/clc.23687
19. Tonelli, M, Wiebe, N, Fortin, M, Guthrie, B, Hemmelgarn, BR, James, MT, et al. Methods for identifying 30 chronic conditions: application to administrative data. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. (2015) 15:31. doi: 10.1186/s12911-015-0155-5
20. Dong, YH, Chang, CH, Shau, WY, Kuo, RN, Lai, MS, and Chan, KA. Development and validation of a pharmacy-based comorbidity measure in a population-based automated health care database. Pharmacotherapy. (2013) 33:126–36. doi: 10.1002/phar.1176
21. Shouval, R, Fein, JA, Cho, C, Avecilla, ST, Ruiz, J, Tomas, AA, et al. The simplified comorbidity index: a new tool for prediction of nonrelapse mortality in Allo-HCT. Blood Adv. (2022) 6:1525–35. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2021004319
22. Rotbain, EC, Gordon, MJ, Vainer, N, Frederiksen, H, Hjalgrim, H, Danilov, AV, et al. The CLL comorbidity index in a population-based cohort: a tool for clinical care and research. Blood Adv. (2022) 6:2701–6. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2021005716
23. Gensen, C, Van Loon, SLM, and Van Riel, NA. Assessment of comorbidity in bariatric patients through a biomarker-based model-a multicenter validation of the metabolic health index. J App Laboratory Med. (2022) 7:1062–75. doi: 10.1093/jalm/jfac017
24. Spatola, L, Finazzi, S, Calvetta, A, Angelini, C, and Badalamenti, S. Subjective global assessment-Dialysis malnutrition score and arteriovenous fistula outcome: a comparison with Charlson comorbidity index. J Vasc Access. (2019) 20:70–8. doi: 10.1177/1129729818779550
25. Fenollar-Cortés, J, and Fuentes, LJ. The ADHD concomitant difficulties scale (ADHD-CDS), a brief scale to measure comorbidity associated to ADHD. Front Psychol. (2016) 7:871. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2016.00871
26. Klabunde, CN, Legler, JM, Warren, JL, Baldwin, LM, and Schrag, D. A refined comorbidity measurement algorithm for claims-based studies of breast, prostate, colorectal, and lung cancer patients. Ann Epidemiol. (2007) 17:584–90. doi: 10.1016/j.annepidem.2007.03.011
27. Miskulin, DC, Athienites, NV, Yan, G, Martin, AA, Ornt, DB, Kusek, JW, et al. Comorbidity assessment using the index of coexistent diseases in a multicenter clinical trial. Kidney Int. (2001) 60:1498–510. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.2001.00954.x
28. Newman, AB, Boudreau, RM, Naydeck, BL, Fried, LF, and Harris, TB. A physiologic index of comorbidity: relationship to mortality and disability. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. (2008) 63:603–9. doi: 10.1093/gerona/63.6.603
29. Bayliss, EA, Ellis, JL, and Steiner, JF. Subjective assessments of comorbidity correlate with quality of life health outcomes: initial validation of a comorbidity assessment instrument. Health Qual Life Outcomes. (2005) 3:51. doi: 10.1186/1477-7525-3-51
30. Jiang, HL, Yan, W, and Lu, Y. Research on application and extension of senile comorbidity index. Chronic Dis Prevent Control In China. (2020) 28:548–51. doi: 10.16386/j.cjpccd.issn.1004-6194.2020.07.017
31. Stirland, LE, González-Saavedra, L, Mullin, DS, Ritchie, CW, Muniz-Terrera, G, and Russ, TC. Measuring multimorbidity beyond counting diseases: systematic review of community and population studies and guide to index choice. BMJ (Clin Res). (2020) 368:m160. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m160
32. Sundararajan, V, Henderson, T, Perry, C, Muggivan, A, Quan, H, and Ghali, WA. New ICD-10 version of the Charlson comorbidity index predicted in-hospital mortality. J Clin Epidemiol. (2004) 57:1288–94. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2004.03.012
33. Van Walraven, C, Austin, PC, and Jennings, A. A modification of the Elixhauser comorbidity measures into a point system for hospital death using administrative data. Med Care. (2009) 47:626–33. doi: 10.1097/MLR.0b013e31819432e5
34. Elixhauser, A, Steiner, C, Harris, DR, and Coffey, RM. Comorbidity measures for use with administrative data. Med Care. (1998) 36:8–27. doi: 10.1097/00005650-199801000-00004
35. Susser, SR, Mccusker, J, and Belzile, E. Comorbidity information in older patients at an emergency visit: self-report vs. administrative data had poor agreement but similar predictive validity. J Clin Epidemiol. (2008) 61:511–5. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2007.07.009
36. Xu, HW, Liu, H, Luo, Y, Wang, K, To, MN, Chen, YM, et al. Comparing a new multimorbidity index with other multimorbidity measures for predicting disability trajectories. J Affect Disord. (2024) 346:167–73. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2023.11.014
37. Charlson, ME, Pompei, P, Ales, KL, and MacKenzie, CR. A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: development and validation. J Chronic Dis. (1987) 40:373–83. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(87)90171-8
38. Ho, ISS, Azcoaga-Lorenzo, A, Akbari, A, Davies, J, Khunti, K, Kadam, UT, et al. Measuring multimorbidity in research: Delphi consensus study. BMJ Med. (2022) 1:e000247. doi: 10.1136/bmjmed-2022-000247
39. Mcentee, ML, Gandek, B, and Ware, JE. Improving multimorbidity measurement using individualized disease-specific quality of life impact assessments: predictive validity of a new comorbidity index. Health Qual Life Outcomes. (2022) 20:108. doi: 10.1186/s12955-022-02016-7
40. Parkerson, GRJR, Broadhead, WE, and Tse, CK. The Duke severity of illness checklist (DUSOI) for measurement of severity and comorbidity. J Clin Epidemiol. (1993) 46:379–93. doi: 10.1016/0895-4356(93)90153-R
41. Zhu, ML, Liu, XH, Dong, BR, Qin, MZ, and Chen, Q. Chinese expert consensus on management of elderly patients with multimorbidity. Chinese J Clin Health Care. (2023) 26:577–84. doi: 10.3969/J.issn.1672-6790.2023.05.001
42. Tang, T, Cao, Y, Dong, B, and Wang, J. Chinese Medical Association Geriatrics Branch. Consensus on the Terminology and Definition of Multimorbidity in the Elderly. Chinese J Geriatrics. (2022) 96:1028–1031. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-9026.2022.09.002
43. Kar, D, Taylor, KS, Joy, M, Venkatesan, S, Meeraus, W, Taylor, S, et al. Creating a modified version of the Cambridge multimorbidity score to predict mortality in people older than 16 years: model development and validation. J Med Internet Res. (2024) 26:e56042. doi: 10.2196/56042
44. Harrison, H, Ip, S, and Renzi, C. Implementation and external validation of the Cambridge multimorbidity score in the UK biobank cohort. BMC Med Res Methodol. (2024) 24:71. doi: 10.1186/s12874-024-02175-9
45. Luo, Y, Huang, Z, Liu, H, Xu, H, Su, H, Chen, Y, et al. Development and validation of a multimorbidity index predicting mortality among older Chinese adults. Front Aging Neurosci. (2022) 14:767240. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.767240
46. Hu, WH, Liu, YY, Yang, CH, Zhou, T, Yang, C, Lai, YS, et al. Developing and validating a Chinese multimorbidity-weighted index for middle-aged and older community-dwelling individuals. Age Ageing. (2022) 51:1–9. doi: 10.1093/ageing/afab274
47. Whitney, DG, and Kamdar, NS. Development of a new comorbidity index for adults with cerebral palsy and comparative assessment with common comorbidity indices. Dev Med Child Neurol. (2021) 63:313–9. doi: 10.1111/dmcn.14759
48. Wei, MY, Luster, JE, Ratz, D, Mukamal, KJ, and Langa, KM. Development, validation, and performance of a new physical functioning-weighted multimorbidity index for use in administrative data. J Gen Intern Med. (2021) 36:2427–33. doi: 10.1007/s11606-020-06486-7
49. Wei, MY, Kabeto, MU, Langa, KM, and Mukamal, KJ. Multimorbidity and physical and cognitive function: performance of a new multimorbidity-weighted index. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. (2018) 73:225–32. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glx114
50. Stanley, J, and Sarfati, D. The new measuring multimorbidity index predicted mortality better than Charlson and Elixhauser indices among the general population. J Clin Epidemiol. (2017) 92:99–110. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2017.08.005
51. Fortin, M, Almirall, J, and Nicholson, K. Development of a research tool to document self-reported chronic conditions in primary care. J Comorbidity. (2017) 7:117–23. doi: 10.15256/joc.2017.7.122
52. Corrao, G, Rea, F, and Martino, DI. Developing and validating a novel multisource comorbidity score from administrative data: a large population-based cohort study from Italy. BMJ Open. (2017) 7:e019503. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-019503
53. Thompson, NR, Fan, Y, Dalton, JE, Jehi, L, Rosenbaum, BP, Vadera, S, et al. A new Elixhauser-based comorbidity summary measure to predict in-hospital mortality. Med Care. (2015) 53:374–9. doi: 10.1097/MLR.0000000000000326
54. Tooth, L, Hockey, R, Byles, J, and Dobson, A. Weighted multimorbidity indexes predicted mortality, health service use, and health-related quality of life in older women. J Clin Epidemiol. (2008) 61:151–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2007.05.015
55. George, J, Vuong, T, Bailey, MJ, Kong, DCM, Marriott, JL, and Stewart, K. Development and validation of the medication-based disease burden index. Ann Pharmacother. (2006) 40:645–50. doi: 10.1345/aph.1G204
56. Groll, DL, To, T, and Bombardier, C. The development of a comorbidity index with physical function as the outcome. J Clin Epidemiol. (2005) 58:595–602. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2004.10.018
57. Byles, JE, D'este, C, and Parkinson, L. Single index of multimorbidity did not predict multiple outcomes. J Clin Epidemiol. (2005) 58:997–1005. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2005.02.025
58. Pope, GC, Kautter, J, Ellis, RP, Ash, AS, Ayanian, JZ, Lezzoni, LI, et al. Risk adjustment of Medicare capitation payments using the CMS-HCC model. Health Care Financ Rev. (2004) 25:119–41.
59. Sangha, O, Stucki, G, Liang, MH, Fossel, AH, and Katz, JN. The self-administered comorbidity questionnaire: a new method to assess comorbidity for clinical and health services research. Arthritis Rheum. (2003) 49:156–63. doi: 10.1002/art.10993
60. Fishman, PA, Goodman, MJ, Hornbrook, MC, Meenan, RT, Bachman, DJ, and O’Keeffe Rosetti, MC. Risk adjustment using automated ambulatory pharmacy data: the RxRisk model. Med Care. (2003) 41:84–99. doi: 10.1097/00005650-200301000-00011
61. Rozzini, R, Frisoni, GB, and Ferrucci, L. Geriatric index of comorbidity: validation and comparison with other measures of comorbidity. Age Ageing. (2002) 31:277–85. doi: 10.1093/ageing/31.4.277
62. Fan, VS, Au, D, and Heagerty, P. Validation of case-mix measures derived from self-reports of diagnoses and health. J Clin Epidemiol. (2002) 55:371–80. doi: 10.1016/S0895-4356(01)00493-0
63. Crabtree, HL, Gray, CS, Hildreth, AJ, O'Connell, JE, and Brown, J. The comorbidity symptom scale: a combined disease inventory and assessment of symptom severity. J Am Geriatr Soc. (2000) 48:1674–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2000.tb03882.x
64. Incalzi, RA, Capparella, O, and Gemma, A. The interaction between age and comorbidity contributes to predicting the mortality of geriatric patients in the acute-care hospital. J Intern Med. (1997) 242:291–8. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2796.1997.00132.x
65. Liu, M, Domen, K, and Chino, N. Comorbidity measures for stroke outcome research: a preliminary study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. (1997) 78:166–72. doi: 10.1016/S0003-9993(97)90259-8
66. Shwartz, M, Iezzoni, LI, and Moskowitz, MA. The importance of comorbidities in explaining differences in patient costs. Med Care. (1996) 34:767–82. doi: 10.1097/00005650-199608000-00005
67. Mcgee, D, Cooper, R, and Liao, Y. Patterns of comorbidity and mortality risk in blacks and whites. Ann Epidemiol. (1996) 6:381–5. doi: 10.1016/S1047-2797(96)00058-0
68. Greenfield, S, Apolone, G, and Mcneil, BJ. The importance of co-existent disease in the occurrence of postoperative complications and one-year recovery in patients undergoing total hip replacement. Comorbidity and outcomes after hip replacement. Med Care. (1993) 31:141–54. doi: 10.1097/00005650-199302000-00005
69. Von Korff, M, Wagner, EH, and Saunders, K. A chronic disease score from automated pharmacy data. J Clin Epidemiol. (1992) 45:197–203. doi: 10.1016/0895-4356(92)90016-G
70. Miller, MD, Paradis, CF, Houck, PR, Mazumdar, S, Stack, JA, Rifai, AH, et al. Rating chronic medical illness burden in geropsychiatric practice and research: application of the cumulative illness Rating scale. Psychiatry Res. (1992) 41:237–48. doi: 10.1016/0165-1781(92)90005-N
71. Deyo, RA, Cherkin, DC, and Ciol, MA. Adapting a clinical comorbidity index for use with ICD-9-CM administrative databases. J Clin Epidemiol. (1992) 45:613–9. doi: 10.1016/0895-4356(92)90133-8
72. Weiner, JP, Starfield, BH, Steinwachs, DM, and Mumford, LM. Development and application of a population-oriented measure of ambulatory care case-mix. Med Care. (1991) 29:452–72. doi: 10.1097/00005650-199105000-00006
Keywords: multiple chronic diseases, multimorbidity, assessment methods, systematic review, old people, evaluation tools
Citation: Yao L, Li QX, Liu Y, Li QQ, Wang TR, Zhou ZH and Yin JJ (2025) How to assess multimorbidity: a systematic review. Front. Public Health. 13:1525593. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1525593
Received: 10 November 2024; Accepted: 06 March 2025;
Published: 27 March 2025.
Edited by:
Marcia G. Ory, Texas A&M University, United StatesCopyright © 2025 Yao, Li, Liu, Li, Wang, Zhou and Yin. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Qiaoxing Li, cXhsaUBnenUuZWR1LmNu
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.