
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Public Health , 17 March 2025
Sec. Public Mental Health
Volume 13 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2025.1522877
This article is part of the Research Topic Youth Mental Health, Particularly in Asian Populations View all 66 articles
Purpose: The network theory of mental disorders offers a new perspective for the understanding of comorbidities, but the research on the comorbidities among depression, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is still insufficient. The aim of this study was to explore the internal relationship by establishing and analyzing the comorbidity networks, and to provide suggestions for the intervention after traumatic events.
Methods: We utilized data from the second and third wave of the Chengdu Positive Child Development cohort (N = 3,189, 47.79% female), we estimated to network models of depression, anxiety and PTSD. To assess difference in global connectivity between the two networks, we conducted invariance test.
Results: K27 (Somatic 10), K37 (Generalized Anxiety 9), K15 (Somatic 5), K33 (Generalized Anxiety 7), K24 (Somatic 9) were the most central nodes in both networks, P13 (Sleep problem) had the highest Bridge Expected Influence value. The structural difference between the two networks was statistically significant (M = 0.229, p = 0.010), and the global strength of the network at wave 2 was higher than the network at wave 3 (35.1 vs. 33.9, S = 1.20, p = 0.010).
Conclusion: The correlation in symptoms of the three disorders underscores the need for more comprehensive treatment options for intervention after traumatic events. Central and bridge nodes could inform targeted interventions or policy decisions. Anxiety disorders, especially Som and Gen dimensions, should be the focus of intervention. The Arousal dimension in PTSD, especially sleep disorders, may contribute to the comorbidities. In addition, this study highlights the importance of staged post-traumatic interventions.
Anxiety disorder is a global mental health concern. According to The China Mental Health Survey conducted between July 22, 2013, and March 5, 2015, anxiety disorder has the highest incidence of mental illness, with a lifetime weighted incidence of 6.3% (1). Moreover, it frequently co-occurs with other psychological symptoms, particularly depression and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) (2). Adolescents are more susceptible to mental health issues (3). It is estimated that 14% of adolescents (aged 10–19) experienced mental health problems globally in 2019, with depression disorder and anxiety disorder being significant contributors to adolescent illness and disability (4). Depression and anxiety can impact adolescents’ daily lives and, in severe cases, lead to self-harm or suicide (5–7). Additionally, adolescent mental health are linked to negative long-term outcomes in adulthood, such as physical and mental health, social functioning, and educational achievements (8).
The global COVID-19 pandemic and the associated public health measures implemented to slow down the virus spread, has affected adolescents’ activities and may have long-term negative effects on their mental health (9–11). As a novel and unique global stressor, the fear and uncertainty brought by COVID-19 can lead to symptoms of traumatic stress (12). This stress increases the risk of depression and anxiety (13), often coexisting with PTSD (2). Adolescents are more susceptible to the deteriorating effects on their mental health (14). Considering that the high infection rate and long incubation period (15), the potential traumatic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on adolescents is unlikely to be similar to any disaster outcomes (such as earthquakes or tsunamis) (16). Exploring the coexistence patterns and relationships between depression, anxiety, and PTSD during different stages of the pandemic can inform the development of more effective and context-specific intervention.
Research has shown that PTSD, anxiety, and depression have overlapping risk factors and symptoms. The common trigger factors of PTSD and depression encompass genetic contributors, alongside various environmental influences (11). This phenomenon is caused by the common vulnerability characteristics (17), though evidence remains inconclusive. Anxiety disorder also exhibits significant overlap with PTSD and depression in both triggers and symptoms, including sadness, worry and other emotions, sleep disorders, reduced interest in daily activities, etc. (18, 19). Severe anxiety, depression, and PTSD often present with overlapping symptoms, such as eating disorder, social fear disorder, sleep disorder (20, 21). Adolescents with three conditions all have different degrees of sleep disorders, reduced interest in daily activities and difficulty concentrating. In addition, the three disorders share common risk factors (22), including the family environment (23) and the common vulnerability of individual disease (17).
In previous research on mental disorders, the most popular model is the potential variable model (24). This model shows that the symptoms are caused by unobserved potential variables. The correlation between symptoms can be explained by potential variables. But this may neglect important nuances in how symptoms of each diagnosis affect one another (25). In recent years there has been a shift from a latent-based approach to a network approach, in order to explain the correlation among variables (26). The network structure is an alternative framework for conceptualizing mental disorders, which enables dynamic system modeling programs on the existing links among the three conditions, and emphasis on understanding the strength and nature of associations among symptoms (27, 28). Networks analysis offers powerful empirical tools to visualize symptoms of in large-scale epidemiological studies (29). With this framework, the pathogenesis is tracked according to the symptoms and etiology analysis of existing diseases (30). In addition, contact between diseases enables direct, intuitive, and detailed description of the complex associations between symptoms.
Despite the recognized importance, research investigating the predictors and co-disease relationship between the three disorders is currently limited. Most existing studies are based on cross-sectional data. At the same time, most studies targeted at specific people and populations (31–33), which are less replicable and generalizable. While some have been studies investigating the pairwise relationships between the depression, anxiety, and PTSD two by two in different groups, including randomly selected volunteers (21, 34) and veterans (35), research on young people with a high incidence of the disease is still insufficient (36). Adolescents have a high risk of developing mental disorders, particularly anxiety and depression. Without timely and effective treatment, these conditions can lead to long-term consequences (37). In addition, given China’s unique cultural background, its network structure may be different from that of other countries (38, 39).
To address these research gaps, this study examines the co-occurrence of depression, anxiety, and PTSD using data from a short-term longitudinal cohort of primary school students in Chengdu (n = 3,533). We employ network analysis and network comparison to explore their relationships. The network structure facilitates intuitively and efficiently find the relationship between the three disorders. Furthermore, centrality analysis aids in find the internal connection between the pathogenesis and external manifestations of the three diseases and further study prevention or treatment measures. Network comparison is utilized to explore the vertical relationship between networks. It is speculated that there should be a long-term relationship between the pathogenesis of anxiety disorder, depression disorder and PTSD. Nevertheless, this study acknowledges that the mechanisms linking these disorders may change over time.
Thus, the aims of this study are as follows:
• Aim 1: Model the accurate depression-anxiety-PTSD network structure and identify the most central nodes.
• Aim 2: Analyze the bridge nodes among depression, anxiety, and PTSD to identity key symptoms of comorbidities.
• Aim 3: Compare the comorbid networks at wave 2 and wave 3 to test the hypothesis that comorbidity networks change over time and identify effective interventions for post-traumatic psychological symptoms in different stages.
Data used in this study were derived from the Chengdu Positive Child Development (CPCD) study (40). In CPCD study, data were collected three times from five primary and junior high schools (i.e., from grade 1 to grade 9) in Chengdu during 2019 and 2021. The CPCD using multi-stage stratified cluster sampling method to select five primary and middle schools: one downtown, two suburban in the south and two suburban in the north of Chengdu. The first data collection (Wave 1, did not collect PTSD scale) took place at the end of 2019 before the outbreak of the COVID-19, the second (Wave 2) was between June and July 2020 after the resumption of face-to-face schooling, and the third (Wave 3) was in June 2021. The students were invited to respond to a questionnaire in their classrooms during school hours. Considering the loss of follow-up due to higher education, students from grades 2–5 who participated in the second and third data collection were selected as respondents. After excluding invalid data, 3,189 out of 3,533 students were included in the final analysis. The attrition analyses revealed no significant differences between the sample in age and gender. In terms of ethical approval, this project was reviewed and approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Sichuan university (K2020025). Written informed consent was gained from school principals, students, and parents before the data collection.
Taking into account the specific population selected for this study, our measurement tools are primarily targeted at children and have been commonly applied in prior Chinese research, showing adequate psychometric properties.
Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale (CES-D) is a 20-item self-report questionnaire for screening depression and assessing the frequency of its symptoms (41). Each of the 20 items describes a feeling or behavior related to different depressive symptoms. The participants needed to select how often they having the feeling or engaging in the behavior in the past week through a scale with four points (“0” = “rarely or none of the time (<1 day),” “1” = “some or little of the time (1–2 days),” “2” = “moderately or much of the time (3–4 days),” and “3” = “most or almost all the time (5–7 days)”). The CES-D have been widely used and validated across different age groups, including adolescents (42, 43). Previous studies support the factorial validity of the Chinese CES-D (44). The scale score was the sum of the four items scores, which measure “positive affect” that were reversely coded. Higher composite score indicates higher depression. Scores over 15 can be indicative of significant levels of depression disorder (45). In the present study, the scale showed adequate internal consistency (see Supplementary Table S1).
Anxiety was examined through the questionnaire named “Screen for Child Anxiety Related Emotional Disorders (SCARED)” (46, 47). The SCARED assesses children’s anxiety disorders, and it includes 41 items under five dimensions: “Panic/Somatic (Som),” “Generalized Anxiety (Gen),” “Separation Anxiety (Sep),” “Social Phobia (Soc),” and “School Phobia (Sch).” Being widely validated in different adolescent populations, the scale demonstrated stable factor structure and good reliability (48). Through a 3-point scale, the participants evaluated each item to indicate the level of experiencing the specified anxiety symptom (“0” = “Never,” “1” = “Sometimes,” and “2” = “Often”). A higher score (i.e., the sum of all item scores) refers to a higher level of anxiety disorder. A total score of ≥25 may indicate the presence of an Anxiety Disorder (46). In the present study, the scale showed adequate internal consistency (see Supplementary Table S1).
Adolescents’ PTSD were assessed using the Children’s Revised Impact of Event Scale (CRIES-13) with reliable psychometric properties (49). This scale was used as an objective assessment instrument to screen for PTSD after different traumas (e.g., hurricane) among Chinese children and adolescents, and it includes 13 items under three dimensions: “Intrusion (Int),” “Avoidance (Avo),” and “Arousal (Aro)” (50, 51). Participants were asked to rate the frequency of occurrence of each symptom using a 4-point scale (0 = “never” 1 = “rarely” 3 = “sometimes” and 5 = “a lot”). A cutoff score of 30 was applied to indicate the prevalence of PTSD (49). In the present study, the scale showed adequate internal consistency (see Supplementary Table S1).
Cronbach’s α coefficient was used to assess the internal consistency reliability of the CSE-D, SCARED and CRIES-13 (see Supplementary Table S1) (52).
Mental health variables: depression, anxiety, and PTSD were the key outcomes in the current study. Other demographic variables included grade and gender (1 = Male, 2 = Female). Because the study focused on the complex interactions within comorbidity networks, other confounders were not included.
Our study determined the necessary sample size, accounting for the cluster sampling method used. According the meta-analysis, the pooled prevalence (p) of depression, anxiety, and PTSD among adolescents in China during the pandemic were 29, 26, and 48%, respectively (53). To achieve a relative error (ε) of 10%, we calculated the sample size using the formula described by Huang et al. (1).
The calculated sample size was 1,093 (α = 0.05, p = 26%). Due to the design of cluster sampling, we estimated the necessary sample size at approximately 2,200 participants using a design effect of 2 to account for the cluster sampling design (the final sample size = the calculated sample size * the design effect). To detect an effect size of 0.2 at a significance level of 0.05 with 0.90 statistical power (d = 0.20, α = 0.05), a minimum of 265 participants was required [265 was conducted using G*Power software (version 3.1)] (54). Therefore, the sample size of 3,189 participants in this study was sufficient.
All statistical analyses were conducted using R software (version 4.2.3). Data were cleaned and the multiple imputation method is used to impute these missing data via the “mice” package in R (version 4.2.3) and a total of 5 imputed datasets were obtained and analyzed. Conduct descriptive statistics on the data to summarize the demographic information of participants, as well as the average and standard deviation of the project.
Network structure: A comorbidity network model for two rounds of investigation was constructed using the R package networktools (55) and the GLASSO algorithm (56). The introduction of a LASSO penalty factor to regularize the network and avoid identifying spurious correlations (57). Network analysis was selected as it provides a graphical representation of the conditional relationships between symptoms, offering a nuanced perspective on their interconnections beyond traditional statistical approaches such as regression or factor analysis. The network structure centrally reflects the importance of nodes (58). Nodes in the network structure represent symptoms and edges in this model are interpreted as partial correlation coefficients ranging from −1 to 1, reflecting the paired conditional relationship between two nodes and controlling all other nodes in the network. Red edges signify negative associations and green positive associations. The thicker and more saturated the edge, the stronger the relationship between nodes (58). In this study, the communities were defined based on the theoretical constructs underlying the questionnaires, and symptoms with similar meanings (e.g., sleep problems across different scales) were not merged to maintain interpretability.
Centralities analysis: To determine the bridging effect of symptoms in each comorbidity network, we used the centrality index Expected Influence (EI) to quantify the importance of each symptom node in the network model, as it has a strong correlation with the observed node impact (59). The “central symptom” may have a greater impact on other nodes (60). Another centrality index, bridge centrality, is used to investigate the comorbidity across mental disorders (61). Bridge centrality identifies “bridge symptoms” that connect two mental disorders (62). Bridge Expected Influence (bEI) was calculated as a measure of bridge centrality using the function bridge of the R package networktools (version 1.4.0) (55) to evaluate the significance of a node in connecting external symptom dimensions.
Robustness tests: Tests of robustness comprised 2,500 bootstrapped 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for edge weights and the correlation stability coefficient (CS coefficient) for EI and bEI in subset sample dropping bootstrapping tests (63). Less CI overlap indicates more accurate edge weights (57). CS coefficients above 0.25 are acceptable, and above 0.50 are good (63). The R package bootnet (63) was used to conduct robustness tests, using a non-parametric bootstrap program to estimate edge stability.
Network comparisons: The R packet Network Comparison Test (NCT) (64) was used to test if the two networks differed significantly from each other in global structure and global strength. NCT is a permutation-based network comparison test in which the original group members are repeatedly randomly reassigned to new subsamples that maintain the original sample sizes (1,000 times). A comparison of network structures may yield more information.
Of the 3,189 respondents who screened into the depression, anxiety, and PTSD diagnostic modules, 1,524 were female (47.8%). Supplementary Table S1 shows the mean scores, standard deviations for each symptom and dimensions of symptoms on the depression, anxiety, and PTSD, including a correlation matrix of depression, anxiety and PTSD is presented. Additional descriptive statistics are presented in the Supplementary Table S1.
The network constellations of depression, anxiety and PTSD with bridge symptoms are presented in Figure 1. There are no isolated nodes in the network; all symptoms are connected, either directly or indirectly via other symptoms. The positioning of all network nodes is in similar patterns in both two time-points. While most nodes are clustered together in a single cluster, excepting J4 (Good), J8 (Hopeful), J12 (Happy), J16 (Enjoy). The cluster is comprised of three main groups of sparsely connected symptoms, representing depression, anxiety, and PTSD. The strongest edge connections emerged between symptoms P8 (Flashback) and P9 (Upset by reminders), K13 (Sep 3) and K25 (Sep 6), K17 (Soc 3) and K36 (Soc 4), J6 (Depressed) and J7 (Effort), J12 (Happy) and J16 (Enjoy), J4 (Good) and J8 (Hopeful).
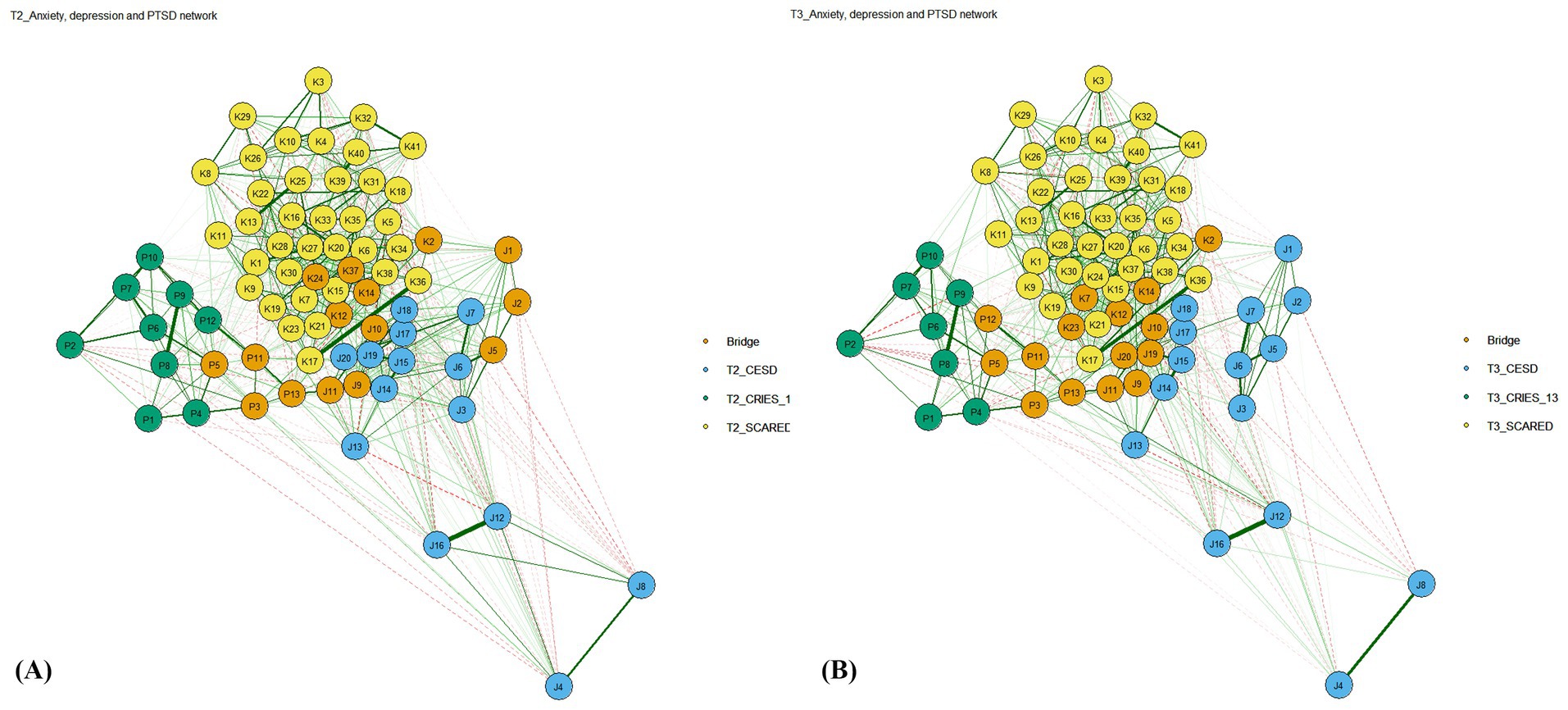
Figure 1. Depression-anxiety-PTSD network in the second and third wave study samples from CPCD. T2: the second wave, T3: the third wave. CESD = Depression SCARED = Anxiety CRIES_13 = PTSD. (A) Depression-anxiety-PTSD network in the second wave. Number of nodes: 74. Number of non-zero edges: 439 / 2701. Mean weight: 0.011426. (B) Depression-anxiety-PTSD network in the second wave. Number of nodes: 74. Number of non-zero edges: 375 / 2701. Mean weight: 0.011446.
Robustness tests were used to assess the stability and accuracy of the two networks (see Supplementary Figures S2, S3). The bootstrapped CIs of edge weights at each wave indicated that the two networks had adequate stability and accuracy.
Figure 2 shows the results of the centrality analysis (The EI difference tests see Supplementary Figure S4). We found that at the network wave 2, K12 (Som 4), K24 (Som 9), K27 (Som 10), K38 (Som 13), K37 (Gen 9), P9 (Upset by reminders), K15 (Som 5), K33 (Gen 7) had the highest EI, at the network 3, K27 (Som 10), K30 (Som 11), J6 (Depressed), K37 (Gen 9), K15 (Som 5), J20 (Get Going), K33 (Gen 7), K24 (Som 9) had the highest EI. This indicated that these six symptoms were the most central symptoms that have strong direct connections to other neighboring symptoms in the present network from a statistical perspective and thus affect them strongly. Targeting these high-EI symptoms in interventions may help disrupt symptom clustering and reduce overall comorbidity.

Figure 2. Expected influence estimates for depression-anxiety-PTSD network in the second and third round study samples from CPCD.
We used a bridge centrality test to assess the bridge symptoms in both networks (see Figures 1, 3; Supplementary Figure S5). The findings indicated that the two networks shared several bridge symptoms, such as P13 (Sleep problem), P11 (Irritability), P3 (Concentration deficit), J11 (Sleep) are bridge symptoms in depression, anxiety, and PTSD. Given the strong bridging role of sleep-related symptoms, interventions focusing on sleep regulation strategies (e.g., CBT-I, sleep hygiene education) may not only alleviate sleep problems but also weaken the connections between anxiety, depression, and PTSD. We also found unique bridge symptoms in each network. The bridge symptoms in the network at wave 2 included K12 (Som 4), K14 (Gen 3), K2 (Sch 1), J2 (Appetite); J20 (Get Going), J10 (Fearful), J11 (Sleep), K23 (Gen 5) were bridge symptoms in the network at wave 3. These findings suggest that intervention strategies should be time-sensitive, addressing key bridge symptoms as they emerge over time.
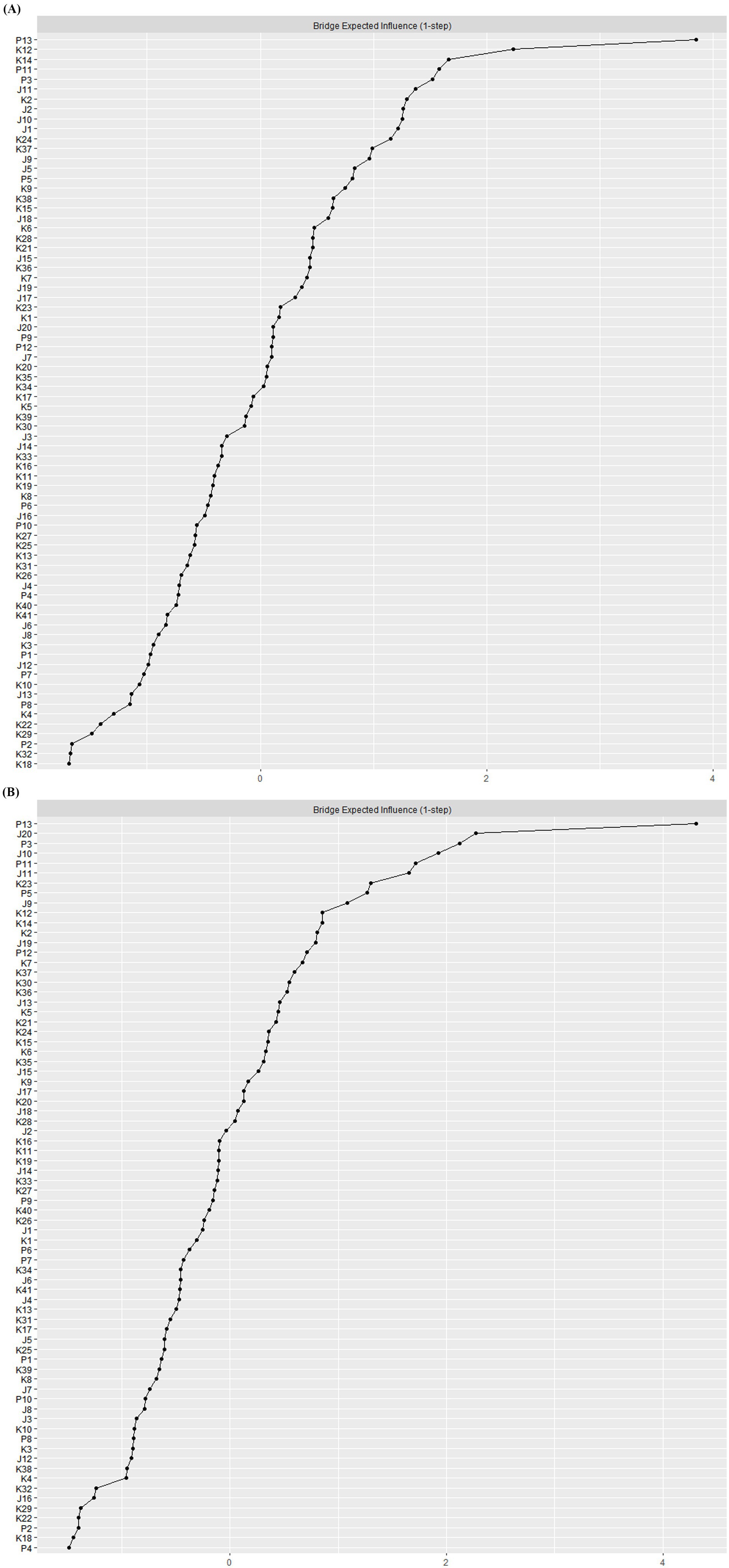
Figure 3. Bridge expected influence estimates for depression-anxiety-PTSD network in the second and third round study samples from CPCD. (A) bEI for network in the second wave. (B) bEI for network in the third wave.
The stability of centrality indices was estimated by the correlation stability coefficients (CS-coefficient), which quantifies the maximum percentage of cases that can be dropped to retain stability. A CS-coefficient above 0.5 indicates an acceptable stability of the centrality indices. According to the results (see Supplementary Figure S1), the stability of centrality indices showed a similar pattern with the CS-coefficients above 0.672 for EI and bEI, indicating that these two centrality indices were stable among subset cases at each time-point.
The network invariance test was used to examine the difference in global connectivity between the two networks. The results showed a significant difference between the structures of the two networks (M = 0.229, p = 0.010), and the global strength of the network at wave 2 was higher than the network at wave 3 (35.1 vs. 33.9, S = 1.20, p = 0.010).
By establishing comorbidity networks, our study found that anxiety disorders, particularly the Som and Gen dimensions, exhibited higher centrality in the network, indicating their significance for intervention focus. Sleep disorders demonstrated the highest bridge centrality within the network, suggesting potential key nodes for comorbidities. In terms of global connectivity, the comorbidity network during early trauma stages appeared more tightly connected, implying greater severity and increased difficulty in intervention (58). Our findings provide evidence for the comorbidity mechanism between these three psychiatric symptoms after the COVID-19 outbreak and offer insights for effective and targeted interventions for child psychopathy in clinical practices.
Our first aim was to model the accurate depression-anxiety-PTSD network structure and identify the most central nodes. We found that the networks in both time-points the overall network comprised three main groups of sparsely connected symptoms, representing depression, anxiety, and PTSD. In addition, the strongest edge connections occur between different symptoms of the same construct. Because depression, anxiety and PTSD structurally represent three independent disorders, symptoms from the same construct are more strongly connected with each other than with items from other constructs (65). This finding is consistent with previous results (25, 65, 66). Although the entire cluster was divided into three groups, the symptom correlations among these three disorders underscore the need for more comprehensive treatment options following traumatic events (67).
The most central nodes of the two networks are the same, K27 (Som 10), K37 (Gen 9), K15 (Som 5), K33 (Gen 7) and K24 (Som 9), indicating that these nodes are strongly connected to other nodes. It shows that anxiety is the more central symptom in the two comorbidity networks, and the occurrence of anxiety is often accompanied by depression and PTSD. This finding validates research by Astill et al. that anxiety disorders may play a key role in the development and maintenance of depression and PTSD (68, 69). Intervention programs targeting these important nodes should be considered to potentially make comorbid interventions more effective. Notably, these five nodes belong to only two dimensions of anxiety—Som and Gen. This may be because Som and Gen are the two most important and closely related dimensions in childhood anxiety (70), and these two dimensions should be the focus of intervention. Moreover, given that cultural differences play a crucial role in shaping mental structures and behaviors, cultural orientation can influence children’s responses to stress and anxiety (71). In collectivist China, anxiety was more strongly associated with eating behavior than physical activity (72). Therefore, the formulation of intervention policies needs to integrate cultural values and social structures.
Our second aim was to analyze of bridge nodes among depression, anxiety, and PTSD. The results indicate that the comorbidity of depression, anxiety and PTSD may be attributable to their shared bridge symptoms, P13 (Sleep problem), P11 (Irritability), P3 (Concentration deficit), J11 (Sleep) are bridge symptoms common to both networks. In both networks, P13 was the most important bridge node, and P13 (Sleep problem) and J11 (Sleep) reflected the sleep disorder of the children from two perspectives. Consistent with most studies, there was a strong co-occurrence between sleep disorder and psychiatric disorders (73–75). Adequate sleep duration is a cornerstones of physical well-being, which serves as the foundation for coping with stressors such as social isolation and academic challenges (76). While socio-cultural could have an impact on sleep patterns (77). For Chinese children, lack of sleep is often linked to different times of going to bed and fear of sleeping alone (78). Notably, P13 (Sleep problem), P11 (Irritability), and P3 (Irritability) all belong to the Arousal dimension of PTSD. It may be that arousal in the face of stressors potentially stimulates certain areas of the brain (hippocampus), making victims of previous traumatic events more susceptible to current life stresses (79).
Different from the findings of Matthew et al. (44), PTSD did not show heterogeneity in our comorbidity network, possibly because the traumatic event in this study was COVID-19 outbreak, while the Matthew’s study did not target a specific traumatic event. The central nodes and the bridge nodes do not coincide because they represent different meanings in the network (80). Furthermore, the central node or bridge node identified by different studies may be different, and this difference may be caused by the differences in traumatic events, measurement tools and sample types (81). This highlights the importance of comorbidity of specific traumatic events for different populations in the development of personalized intervention programs.
Our third aim was to compare the comorbid networks at wave 2 and wave 3. The findings indicate that the structure of the two networks varies, suggesting that the network structure may change with the time of the traumatic event. This is consistent with our hypothesis. The global strength of the network at wave 2 was higher than the network at wave 3, suggesting that the comorbidity characteristics in children are more obvious in the second round than in the third round after the COVID-19 outbreak. This is consistent with the results of Qi et al.’s study (80) on PTSD and depression comorbidity. PTSD and depression became more independent over time, as negative psychological symptoms gradually separated into different disorders over time. After the peak of the COVID-19 outbreak, lockdown and quarantine measures were gradually lifted in most areas and schools reopened; these shifts toward regular routines may have contributed to more attenuated connections between these nodes within the symptom network following the pandemic peak (82–84). These findings suggest that the development of interventions for post-traumatic psychological symptoms should change over time: in the early stages, interventions should focus on comorbid symptoms, whereas in later stage, individualized treatments may be more effective.
Specifically, there were different central nodes and bridge nodes in the two networks. For example, as for the central nodes, P9 (Upset by reminders) appeared in the second round of the network, while J6 (Depressed) appeared in the third round of the network. It may be because the fact that the second round of the survey was at the beginning of the global pandemic of COVID-19, when thinking about the outbreak triggered additional psychological symptoms. This finding aligns with “reliving trauma” being an important symptom in the symptoms of PTSD (69). By the time of the third survey, people had become accustomed to the COVID-19, and thinking about the COVID-19 no longer played a significant role in developing other psychological symptoms. On the contrary, prolonged depression due to the COVID-19 pandemic may play a more important role in the occurrence of other psychological symptoms (85). This is consistent with the comparison of the global strength of the two waves of networks. Regarding bridge nodes, K12 (Som 4) was seen in the second round of the network, while J20 (Get Going) was seen in the third round of the network. This may be because the stress associated with COVID-19 may bring prolonged uncertainty or worry (86), leading to further psychological symptoms, such as feeling low mood, rather than somatic symptoms (87).
Furthermore, stress related to COVID-19 may raise uncertainty and chronic worry, contributing to further psychological symptoms such as fear, restlessness, and irritability rather than somatic symptoms. Multiple studies have also confirmed the delayed impact of the COVID-19 outbreak on mental health, with different symptoms developing in different developmental sequential (88), underscoring the importance of expanding longitudinal studies (89, 90). These findings may enhance our understanding of the comorbidity among depression, anxiety, and PTSD across trauma time, and highlight the need to consider trauma time as a factor in research on comorbidity and clinical practice.
Our study holds both theoretical and practical contributions. Firstly, this study employs network analysis to investigate symptom associations and identify key nodes, providing a fresh perspective on the comorbidity structure of depression, anxiety, and. Secondly, it offers a comprehensive evaluation of the comorbidity network for adolescent psychiatric symptoms, focusing on depression, anxiety, and PTSD. Additionally, we conduct assessments at different stages of the COVID-19 pandemic to explore changes in trauma-related network structures over time. By doing so, we address limitations inherent in cross-sectional studies, and offer evidence supporting comprehensive long-term intervention strategies. These findings may help policy makers in their efforts to develop preparedness plans for future unprecedented events and guide mental health professionals and school personnel to support children now and in the future.
Some limitations of this study also need to be acknowledged. First, while the aim of this study was to examine the comorbidity of depression, anxiety, and PTSD, all the participants were nonclinical samples relying solely on self-reported psychometric data for symptom assessment. As a result, participants may exhibit subliminal symptoms which may not fully reflect the severity and complexity observed in clinical cases. This limitation makes it challenging to assess comorbidity in depth and restricts the generalizability of our findings to clinical populations. Future research should validate these findings in diagnosed clinical samples to enhance applicability. In addition, self-reported bias also affected the accuracy of the study results. Second, our study focused on COVID-19 as a single trauma type and was limited to Chengdu, which limits the exploration of different trauma types and different regions. Third, we aimed to examine the symptom structure of diagnostic categories and so included all symptoms. It is possible that some of the nodes in the network represent the same semantic cluster (e.g., J11: Sleep and P13: Sleep problem), rather than the interaction of otherwise independent constructs. Finally, all analyses were highly exploratory, and as such should be interpreted as hypothesis generating rather than confirming effects.
Further studies should examine whether similar patterns hold in clinical settings, where symptom severity, comorbidities, and treatment histories may introduce additional complexities. Various types (such as car accidents or sexual assaults) and different regions of traumas can also be expanded to broaden the application of comorbidity networks across diverse traumatic experiences and across different regions. Additionally, longitudinal studies are warranted to explore long-term changes in comorbid structures following trauma and furnish stronger evidence for comprehensive long-term intervention strategies.
In conclusion, our findings underscore the importance of prioritizing anxiety disorders when addressing comorbidities associated with depression, anxiety, and PTSD, while also targeting sleep disorders to mitigate their co-occurrence. In addition, post-traumatic intervention strategies need to consider stage-specific approaches as well as encompassing both comprehensive and targeted measures. Future studies should emphasize on long-term monitoring of post-traumatic stress symptoms to provide further evidence. We also call for more future research into other types of trauma and health emergencies.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
The studies involving humans were approved by Ethics Committee of Sichuan University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation in this study was provided by the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin.
HL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Visualization, Writing – original draft. JL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. YW: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Visualization, Writing – original draft. ZL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Writing – review & editing. SM: Conceptualization, Data curation, Writing – review & editing. ZZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Writing – review & editing. LF: Conceptualization, Data curation, Writing – review & editing. LJ: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by Study of Science and Technology Department of Sichuan Province, China [grant number 2020JDKP0021], and The Hong Kong Polytechnic University [grant number 19H0642].
The longitudinal project and the preparation of this paper are financially supported by Daniel T. L. Shek’s research project at the Hong Kong Polytechnic University.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpubh.2025.1522877/full#supplementary-material
PTSD, post-traumatic stress disorder; COVID-19, Corona Virus Disease 2019; CPCD, Chengdu Positive Child Development; CES-D, Depression Scale for Children; SCARED, Child Anxiety Related Emotional Disorders; Som, Panic/Somatic; Gen, Generalized Anxiety; Sep, Separation Anxiety; Soc, Social Phobia; Sch, School Phobia; CRIES, The Children’s Impact of Event Scale; Int, Intrusion; Avo, Avoidance; Aro, Arousal; EI, Expected Influence; bEI, Bridge Expected Influence; CIs, confidence intervals; CS coefficient, correlation stability coefficient; NCT, Network Comparison Test.
1. Huang, Y, Wang, Y, Wang, H, Liu, Z, Yu, X, Yan, J, et al. Prevalence of mental disorders in China: a cross-sectional epidemiological study. Lancet Psychiatry. (2019) 6:211–24. doi: 10.1016/s2215-0366(18)30511-x
2. Spinhoven, P, Penninx, BW, van Hemert, AM, de Rooij, M, and Elzinga, BM. Comorbidity of PTSD in anxiety and depressive disorders: prevalence and shared risk factors. Child Abuse Negl. (2014) 38:1320–30. doi: 10.1016/j.chiabu.2014.01.017
3. Wang, D, Jiang, Q, Yang, Z, and Choi, J-K. The longitudinal influences of adverse childhood experiences and positive childhood experiences at family, school, and neighborhood on adolescent depression and anxiety. J Affect Disord. (2021) 292:542–51. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2021.05.108
4. World Health Organization. Mental health of adolescents. Geneva: World Health Organization (2020).
5. Hu, R, Peng, L, Du, Y, Feng, Y, Xie, L, Shi, W, et al. Reciprocal effect between non-suicidal self-injury and depressive symptoms in adolescence. Front Public Health. (2024) 11:1243885. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1243885
6. Busby Grant, J, Batterham, PJ, McCallum, SM, Werner-Seidler, A, and Calear, AL. Specific anxiety and depression symptoms are risk factors for the onset of suicidal ideation and suicide attempts in youth. J Affect Disord. (2023) 327:299–305. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2023.02.024
7. Guo, X, Wang, L, Li, Z, Feng, Z, Lu, L, Jiang, L, et al. Factors and pathways of non-suicidal self-injury in children: insights from computational causal analysis. Front Public Health. (2024) 12:12. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1305746
8. Alaie, I, Ssegonja, R, Philipson, A, von Knorring, A-L, Möller, M, von Knorring, L, et al. Adolescent depression, early psychiatric comorbidities, and adulthood welfare burden: a 25-year longitudinal cohort study. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. (2021) 56:1993–2004. doi: 10.1007/s00127-021-02056-2
9. Peng, L, Hu, R, Feng, Y, Shi, W, Zhao, L, and Jiang, L. The relationship between family diet consumption, family environment, parent anxiety and nutrition status children during the COVID-19 pandemic: a longitudinal study. Front Public Health. (2023) 11:11. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1228626
10. Zhao, L, Li, X, Yang, Q, Peng, Y, Jiang, L, Jia, P, et al. The longitudinal association between internet addiction and depressive and anxiety symptoms among Chinese adolescents before and during the COVID-19 pandemic. Front Public Health. (2023) 10:10. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.1096660
11. Waszczuk, MA, Zavos, HMS, Gregory, AM, and Eley, TC. The stability and change of etiological influences on depression, anxiety symptoms and their co-occurrence across adolescence and young adulthood. Psychol Med. (2015) 46:161–75. doi: 10.1017/s0033291715001634
12. Sar, V, Bridgland, VME, Moeck, EK, Green, DM, Swain, TL, Nayda, DM, et al. Why the COVID-19 pandemic is a traumatic stressor. PLoS One. (2021) 16:e0240146. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0240146
13. Jenkins, JH, Sanchez, G, Miller, EA, Santillanes Allande, NI, Urano, G, and Pryor, AJ. Depression and anxiety among multiethnic middle school students: age, gender, and sociocultural environment. Int J Soc Psychiatry. (2022) 69:784–94. doi: 10.1177/00207640221140282
14. Pierce, M, Hope, H, Ford, T, Hatch, S, Hotopf, M, John, A, et al. Mental health before and during the COVID-19 pandemic: a longitudinal probability sample survey of the UK population. Lancet Psychiatry. (2020) 7:883–92. doi: 10.1016/s2215-0366(20)30308-4
15. Sun, R, and Zhou, X. Differences in posttraumatic stress disorder networks between young adults and adolescents during the COVID-19 pandemic. Psychol Trauma Theory Res Pract Policy. (2023) 15:S29–36. doi: 10.1037/tra0001252
16. Bowen, AE, Wesley, KL, Cooper, EH, Meier, M, Kaar, JL, and Simon, SL. Longitudinal assessment of anxiety and depression symptoms in U.S. adolescents across six months of the coronavirus pandemic. BMC Psychol. (2022) 10:322. doi: 10.1186/s40359-022-01028-8
17. Angelakis, S, and Nixon, RDV. The comorbidity of PTSD and MDD: implications for clinical practice and future research. Behav Chang. (2015) 32:1–25. doi: 10.1017/bec.2014.26
18. Shi, W, Yuan, GF, Hall, BJ, Liu, X, Su, Y, Zhao, L, et al. Mental disorders and emotional competence among Chinese adolescents before and during COVID-19 pandemic: a longitudinal mediation model. Front Public Health. (2021) 9:767004. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.767004
19. Nyer, M, Farabaugh, A, Fehling, K, Soskin, D, Holt, D, Papakostas, GI, et al. Relationship between sleep disturbance and depression, anxiety, and functioning in college students. Depress Anxiety. (2013) 30:873–80. doi: 10.1002/da.22064
20. Armour, C, Elhai, JD, Richardson, D, Ractliffe, K, Wang, L, and Elklit, A. Assessing a five factor model of PTSD: is dysphoric arousal a unique PTSD construct showing differential relationships with anxiety and depression? J Anxiety Disord. (2012) 26:368–76. doi: 10.1016/j.janxdis.2011.12.002
21. Peel, AJ, Armour, C, Buckman, JEJ, Coleman, JRI, Curzons, SCB, Davies, MR, et al. Comparison of depression and anxiety symptom networks in reporters and non-reporters of lifetime trauma in two samples of differing severity. J Affective Disord Reports. (2021) 6:100201. doi: 10.1016/j.jadr.2021.100201
22. Lamers, F, van Oppen, P, Comijs, HC, Smit, JH, Spinhoven, P, van Balkom, AJLM, et al. Comorbidity patterns of anxiety and depressive disorders in a large cohort study. J Clin Psychiatry. (2011) 72:341–8. doi: 10.4088/JCP.10m06176blu
23. Cao, C, Wang, L, Fang, R, Liu, P, Bi, Y, Luo, S, et al. Anxiety, depression, and PTSD symptoms among high school students in China in response to the COVID-19 pandemic and lockdown. J Affect Disord. (2022) 296:126–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2021.09.052
24. Chevalier, V, Simard, V, and Achim, J. Meta-analyses of the associations of mentalization and proxy variables with anxiety and internalizing problems. J Anxiety Disord. (2023) 95:102694. doi: 10.1016/j.janxdis.2023.102694
25. Price, M, Legrand, AC, Brier, ZMF, and Hébert-Dufresne, L. The symptoms at the center: examining the comorbidity of posttraumatic stress disorder, generalized anxiety disorder, and depression with network analysis. J Psychiatr Res. (2019) 109:52–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2018.11.016
26. Farahani, H, Blagojević, M, Azadfallah, P, Watson, P, Esrafilian, F, and Saljoughi, S. An introduction to artificial psychology, vol. 99. Switzerland: Springer Nature Switzerland AG (2023).
27. Beard, C, Millner, AJ, Forgeard, MJC, Fried, EI, Hsu, KJ, Treadway, MT, et al. Network analysis of depression and anxiety symptom relationships in a psychiatric sample. Psychol Med. (2016) 46:3359–69. doi: 10.1017/s0033291716002300
28. Rouquette, A, Pingault, J-B, Fried, EI, Orri, M, Falissard, B, Kossakowski, JJ, et al. Emotional and behavioral symptom network structure in elementary school girls and association with anxiety disorders and depression in adolescence and early adulthood. JAMA Psychiatry. (2018) 75:1173–81. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2018.2119
29. Berta, A, Miguel Ángel, C, Clara, G-S, and Rubén, H. A bibliometric analysis of 10 years of research on symptom networks in psychopathology and mental health. Psychiatry Res. (2022) 308:114380. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2021.114380
30. Cai, H, Bai, W, Liu, H, Chen, X, Qi, H, Liu, R, et al. Network analysis of depressive and anxiety symptoms in adolescents during the later stage of the COVID-19 pandemic. Transl Psychiatry. (2022) 12:98. doi: 10.1038/s41398-022-01838-9
31. de Feijter, M, Kocevska, D, Blanken, TF, van der Velpen, IF, Ikram, MA, and Luik, AI. The network of psychosocial health in middle-aged and older adults during the first COVID-19 lockdown. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. (2022) 57:2469–79. doi: 10.1007/s00127-022-02308-9
32. Li, J, Jin, Y, Xu, S, Wilson, A, Chen, C, Luo, X, et al. Effects of bullying on anxiety, depression, and posttraumatic stress disorder among sexual minority youths: network analysis. JMIR Public Health Surveill. (2023) 9:e47233. doi: 10.2196/47233
33. Afzali, MH, Sunderland, M, Batterham, PJ, Carragher, N, Calear, A, and Slade, T. Network approach to the symptom-level association between alcohol use disorder and posttraumatic stress disorder. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. (2016) 52:329–39. doi: 10.1007/s00127-016-1331-3
34. Rodrigues, AR, Castro, D, Cardoso, J, Ferreira, F, Serrão, C, Coelho, CM, et al. A network approach to emotion regulation and symptom activation in depression and anxiety. Front Public Health. (2024) 12:12. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1362148
35. Armour, C, Contractor, AA, Palmieri, PA, and Elhai, JD. Assessing latent level associations between PTSD and dissociative factors: is depersonalization and Derealization related to PTSD factors more so than alternative dissociative factors? Psychol Injury and Law. (2014) 7:131–42. doi: 10.1007/s12207-014-9196-9
36. Li, F, Cui, Y, Li, Y, Guo, L, Ke, X, Liu, J, et al. Prevalence of mental disorders in school children and adolescents in China: diagnostic data from detailed clinical assessments of 17,524 individuals. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. (2021) 63:34–46. doi: 10.1111/jcpp.13445
37. Rapee, RM, Oar, EL, Johnco, CJ, Forbes, MK, Fardouly, J, Magson, NR, et al. Adolescent development and risk for the onset of social-emotional disorders: a review and conceptual model. Behav Res Ther. (2019) 123:103501. doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2019.103501
38. Li, M, Wang, Y, Liu, B, Ni, X, Ma, Z, Li, F, et al. Cross-cultural insights into internet addiction and mental health: a network analysis from China and Malawi. BMC Public Health. (2025) 25:251. doi: 10.1186/s12889-025-21496-y
39. Chen, Y, Liu, X, Yan, N, Jia, W, Fan, Y, Yan, H, et al. Higher academic stress was associated with increased risk of overweight and obesity among college students in China. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2020) 17:1715. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17155559
40. Zhao, L, Shek, DTL, Zou, K, Lei, Y, and Jia, P. Cohort profile: Chengdu positive child development (CPCD) survey. Int J Epidemiol. (2022) 51:e95–e107. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyab237
41. Weissman, MM, Orvaschel, H, and Padian, N. Children's symptom and social functioning self-report scales comparison of mothers' and children's reports. J Nerv Ment Dis. (1980) 168:736–40. doi: 10.1097/00005053-198012000-00005
42. Roberts, RE, Andrews, JA, Lewinsohn, PM, and Hops, H. Assessment of depression in adolescents using the Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale. Psycholog Assess: J Consult Clin Psychol. (1990) 2:122–8. doi: 10.1037/1040-3590.2.2.122
43. Wei, Z, Ren, L, Wang, X, Liu, C, Cao, M, Hu, M, et al. Network of depression and anxiety symptoms in patients with epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. (2021) 175:106696. doi: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2021.106696
44. Mathew, AR, Pettit, JW, Lewinsohn, PM, Seeley, JR, and Roberts, RE. Co-morbidity between major depressive disorder and anxiety disorders: shared etiology or direct causation? Psychol Med. (2011) 41:2023–34. doi: 10.1017/s0033291711000407
45. Me, F, Mp, C, and LR,. Assessment of depression in childhood and adolescence: an evaluation of the Center for Epidemiological Studies Depression Scale for children (CES-DC). Am J Psychiatry. (1986) 143:1024–7. doi: 10.1176/ajp.143.8.1024
46. Birmaher, B, Khetarpal, S, Brent, D, Cully, M, Balach, L, Kaufman, J, et al. The screen for child anxiety related emotional disorders (SCARED): scale construction and psychometric characteristics. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. (1997) 36:545–53. doi: 10.1097/00004583-199704000-00018
47. Birmaher, B, Brent, DA, Chiappetta, L, Bridge, J, Monga, S, and Baugher, M. Psychometric properties of the screen for child anxiety related emotional disorders (SCARED): a replication study. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. (1999) 38:1230–6. doi: 10.1097/00004583-199910000-00011
48. Hale, WW, Raaijmakers, Q, Muris, P, and Meeus, W. Psychometric properties of the screen for child anxiety related emotional disorders (SCARED) in the general adolescent population. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. (2005) 44:283–90. doi: 10.1097/00004583-200503000-00013
49. Perrin, S, Meiser-Stedman, R, and Smith, P. The Children's revised impact of event scale (CRIES): validity as a screening instrument for PTSD. Behav Cogn Psychother. (2005) 33:487–98. doi: 10.1017/s1352465805002419
50. Alamdar, S, Lv, Y, Guo, J, Lu, J, and Zhang, Y. Attentional bias effect on post-traumatic outcomes in children after earthquake: mediation role of rumination. PsyCh J. (2020) 9:738–48. doi: 10.1002/pchj.360
51. Chen, X-J, Huang, Y-S, Dang, X-J, and Zheng, X-F. Reduced specificity of autobiographical memory in traumatized adolescents: exploring the contributions of impaired executive control and affect regulation. Acta Psychol Sin. (2013) 44:112–20. doi: 10.3724/sp.J.1041.2012.00112
52. Eisinga, R, Mt, G, and Pelzer, B. The reliability of a two-item scale: Pearson, Cronbach, or spearman-Brown? Int J Public Health. (2012) 58:637–42. doi: 10.1007/s00038-012-0416-3
53. Ma, L, Mazidi, M, Li, K, Li, Y, Chen, S, Kirwan, R, et al. Prevalence of mental health problems among children and adolescents during the COVID-19 pandemic: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Affect Disord. (2021) 293:78–89. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2021.06.021
54. Faul, F, Erdfelder, E, Buchner, A, and Lang, A-G. Statistical power analyses using G*power 3.1: tests for correlation and regression analyses. Behav Res Methods. (2009) 41:1149–60. doi: 10.3758/brm.41.4.1149
55. Jones, P. Networktools: Tools for identifying important nodes in networks. R package version 1.5.2. (2020). Available at: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=networktools
56. Friedman, J, Hastie, T, and Tibshirani, R. Sparse inverse covariance estimation with the graphical lasso. Biostatistics. (2007) 9:432–41. doi: 10.1093/biostatistics/kxm045
57. Cao, X, Wang, L, Cao, C, Fang, R, Chen, C, Hall, BJ, et al. Sex differences in global and local connectivity of adolescent posttraumatic stress disorder symptoms. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. (2018) 60:216–24. doi: 10.1111/jcpp.12963
58. Epskamp, S, Borsboom, D, and Fried, EI. Estimating psychological networks and their accuracy: a tutorial paper. Behav Res Methods. (2017) 50:195–212. doi: 10.3758/s13428-017-0862-1
59. Robinaugh, DJ, Millner, AJ, and McNally, RJ. Identifying highly influential nodes in the complicated grief network. J Abnorm Psychol. (2016) 125:747–57. doi: 10.1037/abn0000181
60. Borsboom, D, and Cramer, AOJ. Network analysis: an integrative approach to the structure of psychopathology. Annu Rev Clin Psychol. (2013) 9:91–121. doi: 10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-050212-185608
61. Guineau, MG, Jones, PJ, Bellet, BW, and McNally, RJ. A network analysis of DSM-5 posttraumatic stress disorder symptoms and event centrality. J Trauma Stress. (2021) 34:654–64. doi: 10.1002/jts.22664
62. Jones, PJ, Ma, R, and McNally, RJ. Bridge centrality: a network approach to understanding comorbidity. Multivar Behav Res. (2019) 56:353–67. doi: 10.1080/00273171.2019.1614898
63. Epskamp, S, and Fried, EI. A tutorial on regularized partial correlation networks. Psychol Methods. (2018) 23:617–34. doi: 10.1037/met0000167
64. van Borkulo, CD, van Bork, R, Boschloo, L, Kossakowski, JJ, Tio, P, Schoevers, RA, et al. Comparing network structures on three aspects: a permutation test. Psychol Methods. (2022) 28:1273–85. doi: 10.1037/met0000476
65. Qi, J, Sun, R, and Zhou, X. Network analysis of comorbid posttraumatic stress disorder and depression in adolescents across COVID-19 epidemic and typhoon Lekima. J Affect Disord. (2021) 295:594–603. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2021.08.080
66. von Hülsen, L, Kenntemich, L, Schäfer, I, Böttche, M, Lueger-Schuster, B, Gallinat, J, et al. Networks of pandemic-specific stressors, risk factors, and clinical symptoms: a comparison between women and men during the early phase of the COVID-19 pandemic. J Psychiatr Res. (2023) 163:391–401. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2023.05.040
67. Jongedijk, RA, Eising, DD, van der Aa, N, Kleber, RJ, and Boelen, PA. Severity profiles of posttraumatic stress, depression, anxiety, and somatization symptoms in treatment seeking traumatized refugees. J Affect Disord. (2020) 266:71–81. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2020.01.077
68. Astill Wright, L, McElroy, E, Barawi, K, Roberts, NP, Simon, N, Zammit, S, et al. Associations among psychosis, mood, anxiety, and posttraumatic stress symptoms: a network analysis. J Trauma Stress. (2023) 36:385–96. doi: 10.1002/jts.22916
69. Liu, N, and Ma, Z. Psychiatric reactions among the non-exposed population who viewed disaster-related short videos: evidence from the 2021 Henan floods. J Psychiatr Res. (2022) 150:21–33. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2022.03.036
70. Vigil-Colet2, A, Canals, J, Cosí, S, Lorenzo-Seva, U, Ferrando, PJ, Hernández-Martínez, C, et al. The factorial structure of the 41-item version of the screen for child anxiety related emotional disorders (SCARED) in a Spanish population of 8 to 12 years-old. Int J Clin Health Psychol. (2009) 92:313–27. Available at: https://ddd.uab.cat/record/143764
71. Chen, P-J, and Antonelli, M. Conceptual models of food choice: influential factors related to foods, individual differences, and society. Food Secur. (2020) 9:912. doi: 10.3390/foods9121898
72. Li, J, Wilczyńska, DM, Lipowska, M, Łada-Maśko, AB, Radtke, BM, Sajewicz-Radtke, U, et al. Beyond Borders: investigating the impact of COVID-19 anxiety and eating attitudes on psychological well-being and physical activity objectives in Poland and China. Nutrients. (2024) 17:41. doi: 10.3390/nu17010041
73. Jin, Y, Xu, S, Shao, Z, Luo, X, Wang, Y, Yu, Y, et al. Discovery of depression-associated factors among childhood trauma victims from a large sample size: using machine learning and network analysis. J Affect Disord. (2024) 345:300–10. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2023.10.101
74. Bai, W, Zhao, Y-J, Cai, H, Sha, S, Zhang, Q, Lei, S-M, et al. Network analysis of depression, anxiety, insomnia and quality of life among Macau residents during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Affect Disord. (2022) 311:181–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2022.05.061
75. Liao, S, Luo, B, Liu, H, Zhao, L, Shi, W, Lei, Y, et al. Bilateral associations between sleep duration and depressive symptoms among Chinese adolescents before and during the COVID-19 pandemic. Sleep Med. (2021) 84:289–93. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2021.06.007
76. Wang, Y, Zhang, Y, Wang, J, Ge, W, Wang, L, Jia, N, et al. Impact of campus closure during COVID-19 on lifestyle, educational performance, and anxiety levels of college students in China. BMC Public Health. (2024) 24:2218. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-19744-8
77. Xiang, Y-T, Ma, X, Lu, J-Y, Cai, Z-J, Li, S-R, Xiang, Y-Q, et al. Relationships of sleep duration with sleep disturbances, basic socio-demographic factors, and BMI in Chinese people. Sleep Med. (2009) 10:1085–9. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2009.03.002
78. Liu, X, Liu, L, Owens, JA, and Kaplan, DL. Sleep patterns and sleep problems among schoolchildren in the United States and China. Pediatrics. (2005) 115:241–9. doi: 10.1542/peds.2004-0815F
79. Jin, Y, Xu, S, Wang, Y, Li, H, Wang, X, Sun, X, et al. Associations between PTSD symptoms and other psychiatric symptoms among college students exposed to childhood sexual abuse: a network analysis. Eur J Psychotraumatol. (2022) 13:2141508. doi: 10.1080/20008066.2022.2141508
80. Qi, J, Ye, Y, Sun, R, Zhen, R, and Zhou, X. Comorbidity of posttraumatic stress disorder and depression among adolescents following an earthquake: a longitudinal study based on network analysis. J Affect Disord. (2023) 324:354–63. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2022.12.119
81. Zhao, C, Jiang, W, Zhang, H, Zhao, Z, Shi, C, and Ren, Z. Exploring the development of posttraumatic stress disorder symptoms in COVID-19 epidemic in China: a network analysis. Curr Psychol. (2023) 43:18701–10. doi: 10.1007/s12144-023-04862-0
82. Fancourt, D, Steptoe, A, and Bu, F. Trajectories of anxiety and depressive symptoms during enforced isolation due to COVID-19 in England: a longitudinal observational study. Lancet Psychiatry. (2021) 8:141–9. doi: 10.1016/s2215-0366(20)30482-x
83. Wang, Y, Hu, Z, Feng, Y, Wilson, A, and Chen, R. Changes in network centrality of psychopathology symptoms between the COVID-19 outbreak and after peak. Mol Psychiatry. (2020) 25:3140–9. doi: 10.1038/s41380-020-00881-6
84. Santana, GL, Lu, P, Li, X, Lu, L, and Zhang, Y. The psychological states of people after Wuhan eased the lockdown. PLoS One. (2020) 15:e0241173. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0241173
85. Houghton, S, Kyron, M, Hunter, SC, Lawrence, D, Hattie, J, Carroll, A, et al. Adolescents' longitudinal trajectories of mental health and loneliness: the impact of COVID-19 school closures. J Adolesc. (2022) 94:191–205. doi: 10.1002/jad.12017
86. Del-Valle, MV, López-Morales, H, Andrés, ML, Yerro-Avincetto, M, Gelpi Trudo, R, Urquijo, S, et al. Intolerance of COVID-19-related uncertainty and depressive and anxiety symptoms during the pandemic: a longitudinal study in Argentina. J Anxiety Disord. (2022) 86:102531. doi: 10.1016/j.janxdis.2022.102531
87. Fan, P, Wang, T, Wang, J, and Wang, J. Network analysis of comorbid depression and anxiety and their associations with response style among adolescents with subthreshold depression. Curr Psychol. (2023) 43:8665–74. doi: 10.1007/s12144-023-04992-5
88. Larsen, L, Schauber, SK, Holt, T, and Helland, MS. Longitudinal Covid-19 effects on child mental health: vulnerability and age dependent trajectories. Child Adolesc Psychiatry Ment Health. (2023) 17:104. doi: 10.1186/s13034-023-00652-5
89. Ravens-Sieberer, U, Kaman, A, Otto, C, Adedeji, A, Napp, A-K, Becker, M, et al. Seelische Gesundheit und psychische Belastungen von Kindern und Jugendlichen in der ersten Welle der COVID-19-Pandemie – Ergebnisse der COPSY-Studie. Bundesgesundheitsbl Gesundheitsforsch Gesundheitsschutz. (2021) 64:1512–21. doi: 10.1007/s00103-021-03291-3
Keywords: longitudinal study, network analysis, post-traumatic stress disorder, depression, anxiety, adolescent health, COVID-19, comorbidities
Citation: Li H, Liu J, Wang Y, Li Z, Mei S, Zhang Z, Fan L and Jiang L (2025) Longitudinal network analysis of depression, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder comorbidities among adolescents in regional China. Front. Public Health. 13:1522877. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1522877
Received: 03 December 2024; Accepted: 26 February 2025;
Published: 17 March 2025.
Edited by:
Wulf Rössler, Charité University Medicine Berlin, GermanyReviewed by:
Carlos Alberto Pereira De Oliveira, Rio de Janeiro State University, BrazilCopyright © 2025 Li, Liu, Wang, Li, Mei, Zhang, Fan and Jiang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Lihua Jiang, bGhqaWFuZ0BzY3UuZWR1LmNu
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.