
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Public Health , 06 March 2025
Sec. Aging and Public Health
Volume 13 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2025.1517482
This article is part of the Research Topic Enhancing Geriatric Care: International Collaboration and Best Practices for Aging Populations View all 11 articles
Background: The older population in Bangladesh is growing rapidly, from 8.0% in 2020 to 22.0% in 2050. However, the determinants of active aging are scarcely known.
Objective: The study aimed to assess the determinants influencing the active aging situation in Bangladesh.
Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted among 518 older adults aged 60 and over. Following the WHO active aging model, the respondents’ socio-demographic, personal, behavioral, and physical environment and health and social services characteristics were collected using a semi-structured questionnaire. Multiple linear regression was performed to assess the effect of the determinants on active aging, followed by the bivariate level of analysis.
Results: The determinants of active aging were deeply rooted in the respondents’ socio-cultural, economic, and spatial conditions. Nine out of 23 determinants, like marital status, income, decision-making capacity, regular walking/physical exercise, smokeless tobacco consumption, newspaper reading as a leisure activity, use of medicine, and health service accessibility, significantly influence active aging. The active aging score was 10–15% higher among the respondents who regularly adhered to the above determinants.
Conclusion: Effective initiatives are needed to improve the socio-cultural, economic, and health system-related determinants of active aging to enhance the active aging situation. Concerned bodies of the country, ministries, departments, and development partners should take appropriate measures to increase awareness and the participation of people in lifestyle-related determinants to improve the active aging situation in the country.
Population aging is a major global trend that impacts all countries at different rates and levels (1). The number of people aged 60 years and over worldwide was projected to grow from 901 million in 2015 to 2.1 billion by 2050 (2). Population aging is a global phenomenon that requires action at the international, national, regional, and local levels (3).
In Bangladesh, the population aged 60 years and over has risen from 7.7% in 2015 to 9.5% in 2023 (4), with the country’s increasing life expectancy from 57.5 in 1990 to 72.3 in 2023 (4, 5). It has one of the world’s largest older populations and is expected to double from 2001 to 2025. By 2025, one in ten people in Bangladesh will be older adults, increasing to one in five by 2050 (6). The aging population will impact health status, the healthcare system, economic growth, labor markets, consumption, savings, investment, pension, and intergenerational transfers (6, 7). Older adults are among the poorest of the poor. In developing countries like Bangladesh, demographic and related epidemiological transitions occur in the transient socio-economic contexts (8–11). Bangladesh will need more support for the increased number of older adults (12). Increasing modernization and social change contexts confront difficulties in maintaining the honor, security, and dignity of older adults in Bangladesh (13, 14).
Most older people reside in rural areas, with widespread poor health care, economic services, and work opportunities (15, 16). Bangladesh will face a major challenge in providing adequate care and support for the increasing number of older people (15, 17). In recent times, the divorce rate in Bangladesh has been increasing dramatically (18), which will raise the number of separated and lonely aged population (16, 19). Relevant research shows that 95.0% of older people have faced health problems in Bangladesh, and most of them even face multiple health complications (16, 20, 21).
The older population is the most vulnerable group in our society due to their physical weakness, disease burden, lack of job opportunities, lack of property ownership, proper health care, etc. (21, 22). The conditions of older adult women are poorer and deplorable, especially widows and older adult women without sons are suffering more from economic and health vulnerability (16). The older population is the most vulnerable group in our society due to their physical weakness, disease burden, lack of job opportunities, lack of property ownership and proper health care, etc. (20, 22). Given the high impairment rate among older adults in Bangladesh, the link between increasing life expectancy, improved health system, and active aging situation remains inconsistent. Many of the above susceptibilities and sufferings can be reduced by improving the conditions of the determinants of active aging (6).
Enhancing active aging is a global goal aimed at improving the quality of life of older adults by addressing the issues they confront (23). World Health Organization (WHO) defined active aging as “the way of thinking and working on the process of optimizing opportunities for health, participation, and security to enhance the quality of life as people age” (24, 25). Active aging has four dimensions: health, participation, security, and employment (26, 27). Active aging includes economic and non-economic aspects of life (28). The approach has emerged in recognizing older people’s human rights and the principles of the United Nations, including participation, dignity, care, and self-fulfillment (29). Following the WHO model (29), a study used eight indicators of health dimension, three indicators of participation dimension, and seven indicators of security dimension to measure active aging in Bangladesh (30). Active Aging Index (AAI) is the average of the scores of the three dimensions, which has a minimum value of 0 and a maximum value of 1 (30).
The higher score of the active aging index worldwide depends on a society’s socio-economic, personal, behavioral, and psychological determinants (31, 32). ‘Active aging’ results from a society’s socio-economic, cultural, and individual factors. So, based on the literature review, we have chosen the determinants of Active Aging. Considering the context and review of the above literature, a conceptual framework was developed, which included 23 determinants of active aging. The framework incorporated the demographic, socio-economic, personal, behavioral, physical environment, and health and social services contexts that determine the active aging outcome (Figure 1) (27). In these multidimensional determinants, achieving an active aging situation poses several challenges for governments, societies, and older adults regarding opportunities and contributions (33, 34).
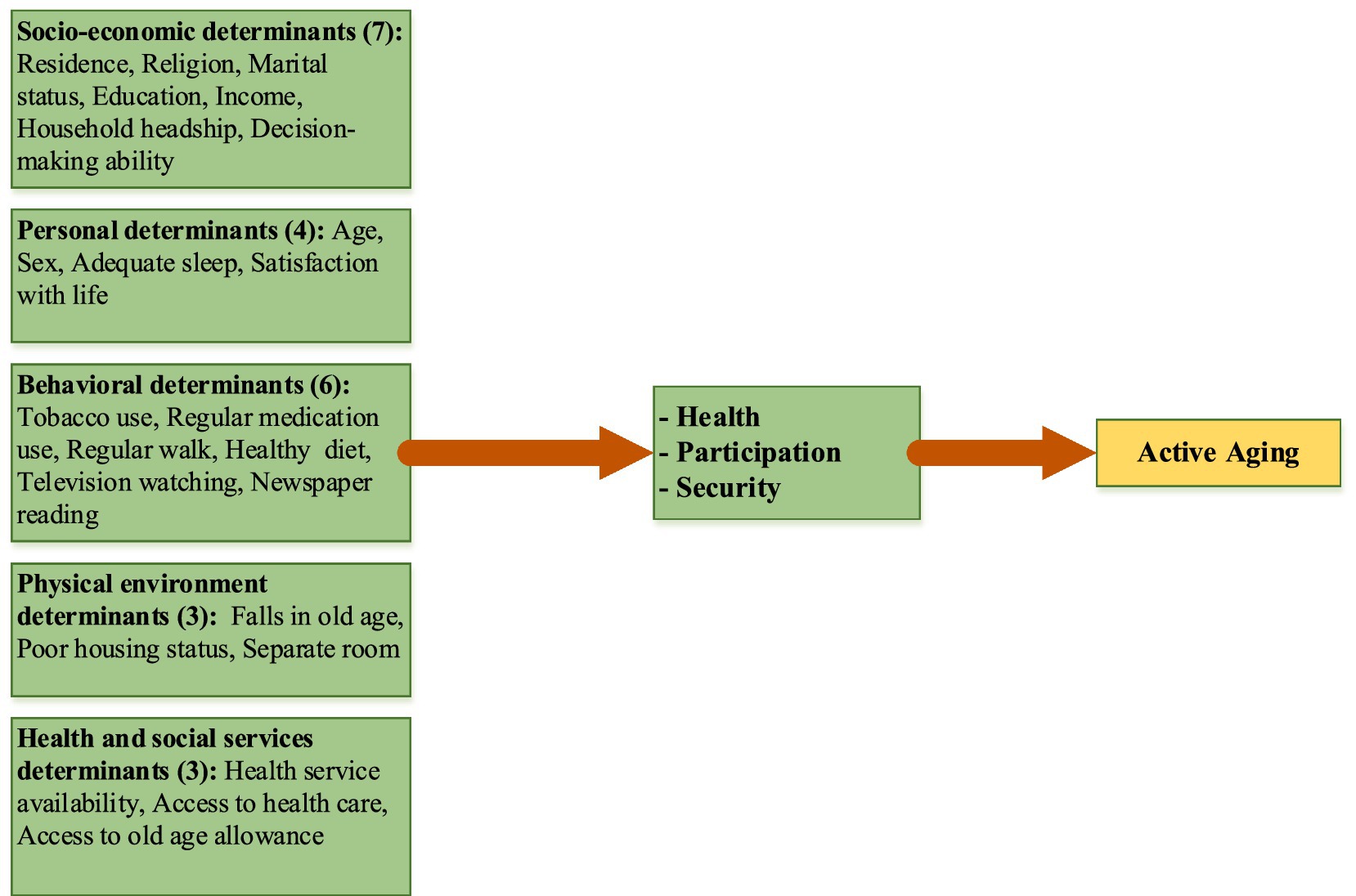
Figure 1. A conceptual framework, based on the WHO model (29), for active aging, including twenty-three determinants.
The concepts of active aging and aging in place are leading the policies and practices of gerontology to meet the diverse needs of the aging population (35). Measuring the active aging situation has become an important research issue in Bangladesh (30), India (36), Pakistan (37), Nepal (38), and 28 European Union (EU) countries (39). This research provides insights into the potential of older adults. It can inform decision-makers to improve government policy to transform the old age group into an economically active population (40). Studies reveal that the active aging level is lower for women than men in almost all countries (41, 42). In India, inactive aging is higher than active aging (27, 36). For Bangladesh, the mean active aging score level for older men and women was 0.62 and 0.66, respectively (30). Rural and urban differentials also exist in active aging situations (43). Bangladesh’s active aging score is lower than many other EU countries (44). Considering the complex multidimensionality of the issues, little is known about the active aging situation and its determinants for older adults in Bangladesh (45, 46). The rapidly changing aging issues demand more attention from researchers and policymakers to assess the context and determinants of the active aging situation for a sustainable (1) and healthy life for the older population in Bangladesh (22, 44, 47, 48). Therefore, it is essential to conduct more research to understand the determinants affecting active aging and its dimensions in Bangladesh (10, 13).
A quantitative research approach was used in this cross-sectional study to determine the determinants of the active aging situation among people 60 years and over. Within the constraints of the research and simultaneously, to make the study more representative by capturing the more diverse scenario of the phenomenon, and with the suggestions of the sampling experts, this research selected two divisions for the study areas. Two divisions, districts and upazilas, were selected later randomly from the divisions. Cochran’s formula (49) was used to calculate the essential sample size for the required precision, confidence, and estimated population, as the total population was larger. The formula for sample size selection was:
where n = sample size; z = z value for the confidence level (e.g., 1.96 for 95% confidence level); p = proportion of the phenomenon under study; q = 1-p = 0.92; d = desired accuracy level, 0.03; df = design effect. The study adopted p = 0.08 as the proportion of older people in Bangladesh was 8.0% (50), and the desired level of precision in the sample was 3.0%. As multistage sampling strategies were used to select the study areas, the design effect was set at 1.65, and thus, the calculated sample size was 518. The probability proportionate sample (PPS) technique was used to distribute the number of samples between the study areas (Table 1). A list of people 60 years and over was prepared, and the sample was selected systematically after every two households.
A semi-structured interview schedule was used for this face-to-face interview to obtain primary data on the socio-economic, personal, behavioral, lifestyle, and health-related twenty-three determinants of active aging. Ethical clearance was obtained from the concerned body, and informed consent was obtained from the respondents. With the help of three trained research assistants (RAs), data were collected from the respondents aged 60 years and over from October to December 2019. The researcher, in person, trained the research assistants (RA) about the research objectives, questions, concepts, wording of the questions, and study settings in detail. RAs participated in pretesting the questionnaire. The RAs stayed in the field with the researcher and collected data through face-to-face interviews. Data were analyzed using univariate and multivariate statistics. The included independent variables for the study (Figure 1) were quantitative, and responses were either dichotomous or continuous, and the dependent variable ‘active aging’ was continuous. The respondents’ responses for each indicator in each dimension of active aging were added to create the composite index for each active aging dimension (30). A multiple linear regression technique was used to assess the effect of the determinants on active aging. SPSS version 18.0 was used to analyze the data. More details of the construction of the AAI can be found in the authors’ earlier paper on Active Aging (30).
Table 2 shows the socio-demographic characteristics of the respondents. Five hundred eighteen respondents were interviewed; 265 were men, and 253 were women. The majority (64.5%) of the older adults were young-old (60–69 years), and 23.5% were middle-old (70–79 years). About 91.0% of the respondents were Muslim, 7.9% were Hindu, and 1.2% were Christian. About 55.0% of the respondents were from rural areas, 45.2% were from urban areas, and 71.2% were married. About 59.0% of the respondents had no formal education, 61.6% had limited income, 67.0% were household heads, and 73.6% were involved in household decision-making.
Following the physical environment, 68.5% of respondents opined that they had better housing status, 86.1% had a separate room, and 27.4% perceived that they had fallen in old age. Regarding health and social services, 60.0% said that health services were available but not accessible (52.5%). Only 15.0% of the respondents reported getting an old age allowance (Table 3).
Table 4 shows that males (0.64), young-old (60–69) (0.61), those who are currently married (0.61), residing in urban (0.63) areas, have higher education (0.63), access to income (0.63), still household heads (0.64), and decision-making capacity (0.64) had a higher mean score of AAI than other groups.
Around 60.0% of the respondents were satisfied with their lives, 37.5% had sufficient sleep (eight hours or more), 45.6% could not consume a balanced diet, and only 24.3% had regular walking as exercise. Most of the older adults (65.0%) were used to smokeless tobacco consumption. Following leisure activities, 45.4% used to watch television, and 8.3% had the habit of newspaper reading. Only 41.1% conform to regular medicine use. The mean scores of active aging were found to be higher among the respondents who had higher personal factors such as perceived life satisfaction (0.64) and sleeping hours more than 8 h (0.65) compared to those who were not satisfied (0.59) and slept less than 8 h (0.59). Similar to personal characteristics, mean scores of active aging were found to be higher for behavioral traits such as older adults having a balanced diet (0.64), practicing regular morning walking (0.65), avoiding tobacco consumption (0.64), watching television (0.65) and reading a newspaper as leisure activities (0.73), regular medicine use (0.59) compared to who did not (Table 5).
Respondents’ active aging condition varied by physical environmental characteristics, including having better, adequate housing status and separate rooms, not being perceived as falling into older age, having availability and accessibility to health services, and getting an old age allowance (Table 6).
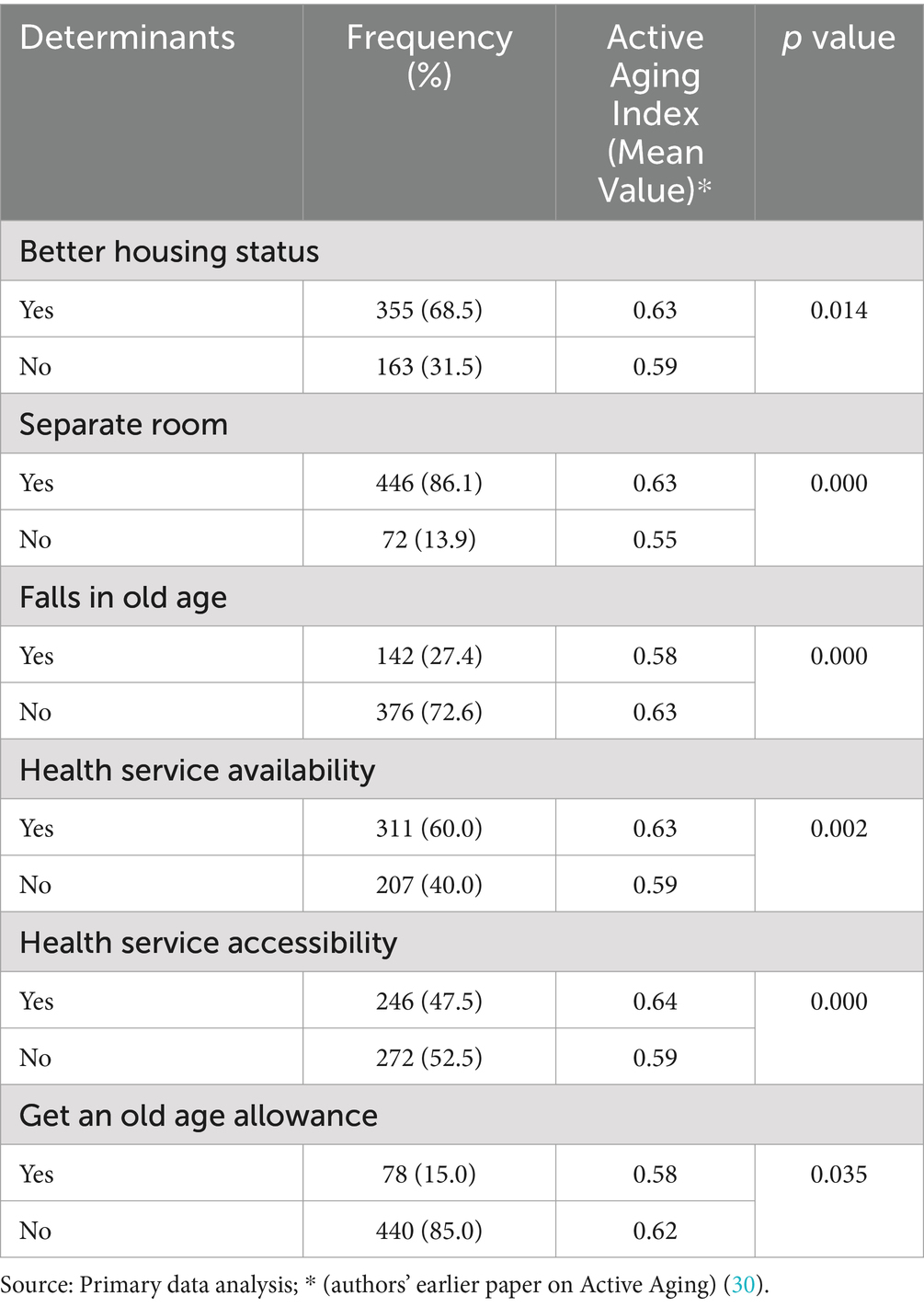
Table 6. Physical environment, health, and social services characteristics of the respondents by AAI.
Figure 2 presented the regression standardized residual, and Figure 3 presented the normal P-P Plot regression standardized residual.
The result of the multiple linear regression model shows that even after controlling all the variables, marital status (AOR = 0.197, 95% CI: 0.018–0.105), income (AOR = 0.121, 95% CI: 0.002—0.042), decision-making ability (AOR = 0.110, 95% CI: 0.001—0.074), regular walking/physical exercise (AOR = 0.120, 95% CI: 0.005—0.067), smokeless tobacco consumption (AOR = −0.110, 95% CI: −0.061— −0.005), newspaper reading (AOR = 0.113, 95% CI: 0.004—0.094) as leisure status, use of medication (AOR = −0.172, 95% CI: −0.076—−0.023), and health service accessibility (AOR = 0.161, 95% CI: 0.015—0.076) had significant effect on the mean score of active aging (Table 7).
This research is one of the very first of its kind in Bangladesh, where behavioral, health, and physical determinants were assessed, and the effects of different socio-demographic, economic, health, personal, behavioral, and physical determinants were evaluated to know the active aging situation of the country. Developed and developing countries have insisted on studying active and healthy aging situations. However, there is a scarcity of research on active aging in Bangladesh (46). The calculated active aging score for rural males and females was 0.65 and 0.58, respectively. For urban males and females, it was 0.65 and 0.57, respectively (46), which is very low compared to many European and East Asian countries (44). The construction of active aging using WHO models and identifying the effects of the determinants on the active aging situation was a unique initiative in Bangladesh, which was earlier applied to other countries’ situations (23, 42). The constructed determinants framework for assessing the active aging situation was new for the country.
The active aging score is influenced by various individual, familial, societal, and national levels determinants (29). In Bangladesh, demographic and socio-economic factors also differentiate active aging, and the findings showed that active aging was higher among young-old people, corroborated by another study (51). Following the findings, it was found that the active aging score was higher among males than females (52), older adults living in urban areas (23), and those who had income and family decision-making abilities (53). Similarly, personal and behavioral characteristics were linked to active aging situations, and the findings were also consistent with those of other studies (54–57). The score for active aging also differed regarding the respondents’ physical environment, health, and social service characteristics, corroborating another study (57).
Considering the global impact of population aging, the United Nations General Assembly declared 2021–2030 as the ‘Decade of Healthy Ageing’ (58, 59). The focus on active aging was growing and was included in the healthy aging umbrella with other important issues of this rights-based approach (60), like no one left behind (61) and social safety net programs for all (62). Active aging issues are broadly circulated in academic, social, political, and media (62). As part of the concern, the findings show insufficient research and contextual evidence on the reality of active aging in Bangladesh. This primary research and its findings reveal the first evidence of systematically identifying the reality of the determinants of the active aging situation in Bangladesh. The study identified, field-tested, and found the significant effects of nine determinants on the active aging index. These determinants are marital status, income, decision-making ability, regular walking/physical exercise, smokeless tobacco consumption, newspaper reading as leisure status, use of medication, and health service accessibility, and they have similarities with the aging situation of other countries (63). Recognition of all the factors may create opportunities for researchers and policy makers to improve active aging situations across different communities and nations.
Findings showed that many socio-demographic, economic, personal, and behavioral determinants are interrelated (31). For example, higher income and education may affect diet, physical exercise, and safe living (45). This inter-relationship between the determinants needs to be accounted for when measuring active aging situations (45). People may value a particular factor more in a given context and culture. It implied that the active aging situation is not isolated from context or static (31). Therefore, a successful measure of active aging situations needs to assess all the known determinants and comprehend the value and importance the individual attaches to each determinant at the individual and community levels (64, 65). The study gained its strengths by introducing an initiative to identify the effect of the determinants on the active aging domains and developing tools for field data collection, which will significantly help future researchers (32).
The study also framed future research directions for assessing active aging situations. Although this study’s cross-sectional methodology allowed for describing relationships between numerous indicators and active aging scores, causal implications cannot be reached. A longitudinal study would be more instrumental in assessing the factors influencing the active aging situation. More qualitative research helps better understand the aspects of active aging. This study did not include older people with psychiatric problems, but they should be included in future studies. Considering the context and reality of a society, different instruments may be used to measure the active aging situation (57).
This study included respondents from only selected rural and urban areas. Thus, further research may be required to generalize the other parts. Furthermore, applying and measuring the WHO policy framework of active aging in Bangladesh to analyze the determinants is quite complex and challenging to quantify in a direct measure. Consequently, some proxy indicators were taken into account.
From the perspective of the continuous growth of older people, ensuring active aging is critical. Determinants of active aging should be considered to enhance the overall wellbeing of older people. Identified determinants can guide policymakers on where to focus and how strategies and action plans must be revisited. Immediate attention is required to improve every aspect of active aging. Based on the identified determining factors of active aging, appropriate programs should be formulated and implemented to increase future active aging levels of the country and countries with similar socio-economic settings. Countries should regularly assess the situation of the active aging determinants to ensure the overall level of active aging and help achieve transformative, inclusive, and sustainable development outcomes. Future studies should include a broader geographic range and a larger, more diverse sample for greater generalizability. Moreover, a follow-up longitudinal study could explore causal relationships and the evolution of active aging determinants over time. Future research may also incorporate older adults with psychiatric and cognitive impairments to provide a more holistic perspective. Actionable strategies such as income-generation programs or community-based health interventions should be taken for the improvement of AAI. The study findings may serve as a benchmark for future research on active aging in similar socio-economic settings.
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by the research evaluation committee of the Department of Population Sciences, University of Dhaka. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
SA: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Writing – original draft. MK: Validation, Writing – review & editing. MH: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Methodology, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. The authors acknowledge the contribution of the University of Dhaka and D4I, University of North Carolina, United States for APC support.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
1. UNDP. Ageing, older persons and the 2030 agenda for sustainable development. New York: UNDP (2017).
3. UNDESA. World social report 2023: Leaving no one behind in an Ageing world. New York: UNDESA (2023).
5. Tareque, MI. Trends in health expectancy at age 60 in Bangladesh from 1996 to 2016. PLoS One. (2022) 17:e0278101. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0278101
6. Kabir, R, Khan, H, Kabir, M, and Rahman, MT. Population ageing in Bangladesh and its implication on health care. Eur Sci J. (2013) 9:34–47. Available at: https://repository.uwl.ac.uk/id/eprint/3436
7. Divo, MJ, Martinez, CH, and Mannino, DM. Ageing and the epidemiology of multimorbidity. Eur Respir J. (2014) 44:1055–68. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00059814
8. Muhammad, T, Srivastava, S, Hossain, B, Paul, R, and Sekher, TV. Decomposing rural–urban differences in successful aging among older Indian adults. Sci Rep. (2022) 12:6430. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-09958-4
9. Salamene, LC, Martins, ELM, Lucchetti, G, and Lucchetti, ALG. Factors associated with successful aging in Brazilian community-dwelling older adults: when physical health is not enough. Geriatr Nurs. (2021) 42:372–8. doi: 10.1016/j.gerinurse.2021.01.009
10. Tan, MP. Healthcare for older people in lower and middle income countries. Age Ageing. (2022) 51:afac016. doi: 10.1093/ageing/afac016
11. Goodman-Palmer, D, Ferriolli, E, Gordon, AL, Greig, C, Hirschhorn, LR, Ogunyemi, AO, et al. Health and wellbeing of older people in LMICs: a call for research-informed decision making. Lancet Glob Health. (2023) 11:e191–2. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(22)00546-0
12. Jahangir, S, Bailey, A, Hassan, MMU, and Hossain, S. Population aging and everyday challenges for older adults in Bangladesh In:. Handbook of aging, health and public policy: Perspectives from Asia. Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore (2022). 1–16.
13. Sarker, AR. Health-related quality of life among older citizens in Bangladesh. SSM Mental Health. (2021) 1:100031. doi: 10.1016/j.ssmmh.2021.100031
14. Hamiduzzaman, M, De Bellis, A, Abigail, W, and Kalaitzidis, E. Elderly women in rural Bangladesh: healthcare access and ageing trends. South Asia Res. (2018) 38:113–29. doi: 10.1177/0262728018767018
15. Barikdar, A, Ahmed, T, and Lasker, S. The situation of the elderly in Bangladesh. Bangladesh J Bioethics. (2016) 7:27–36. doi: 10.3329/bioethics.v7i1.29303
16. Rahman, M. Aging and negligence in Bangladesh. J Gerontol Geriatric Res. (2017) 6:06. doi: 10.4172/2167-7182.1000423
17. Nesa, M. Social status of elderly people in health perspective: a comparison of rural and urban area. IOSR J Human Soc Sci. (2013) 18:83–94. doi: 10.9790/0837-1868394
19. Dahlberg, L, Agahi, N, and Lennartsson, C. Lonelier than ever? Loneliness of older people over two decades. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. (2018) 75:96–103. doi: 10.1016/j.archger.2017.11.004
20. Sara, HH, Chowdhury, MAB, and Haque, MA. Multimorbidity among elderly in Bangladesh. Aging Med. (2018) 1:267–75. doi: 10.1002/agm2.12047
21. Hosain, GM, and Begum, A. Health needs and health status of the elderly in rural Bangladesh. Asia Pac J Public Health. (2003) 15:3–9. doi: 10.1177/101053950301500102
22. Sarker, AR, Zabeen, I, Khanam, M, Akter, R, and Ali, N. Healthcare-seeking experiences of older citizens in Bangladesh: a qualitative study. PLOS Global Public Health. (2023) 3:e0001185. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgph.0001185
23. Haque, MN. Active Ageing level of older persons: regional comparison in Thailand. J Aging Res. (2016) 2016:1–9. doi: 10.1155/2016/9093018
24. WHO. Report of the World Health Organization. Active ageing: a policy framework. Geneva: WHO (2002).
25. Wongsala, M, Anbäcken, EM, and Rosendahl, S. Active ageing - perspectives on health, participation, and security among older adults in northeastern Thailand - a qualitative study. BMC Geriatr. (2021) 21:41. doi: 10.1186/s12877-020-01981-2
26. Urtamo, A, Jyväkorpi, SK, and Strandberg, TE. Definitions of successful ageing: a brief review of a multidimensional concept. Acta Bio-Medica. (2019) 90:359–63. doi: 10.23750/abm.v90i2.8376
27. Irshad, CV, Lekha, PPS, Azeez, EPA, and Rajan, SI. Active and productive ageing in India: evidence from the time use pattern of ageing adults. BMC Geriatr. (2023) 23:718. doi: 10.1186/s12877-023-04428-6
28. Foster, L, and Walker, A. Active Ageing across the life course: towards a comprehensive approach to prevention. Biomed Res Int. (2021) 2021:6650414. doi: 10.1155/2021/6650414
30. Haque, MA, and Afrin, S. Construction of the active aging index in Bangladesh: challenges and opportunities. Heliyon. (2022) 8:e10922. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e10922
31. Abud, T, Kounidas, G, Martin, KR, Werth, M, Cooper, K, and Myint, PK. Determinants of healthy ageing: a systematic review of contemporary literature. Aging Clin Exp Res. (2022) 34:1215–23. doi: 10.1007/s40520-021-02049-w
32. León, LP, Mangin, JP, and Ballesteros, S. Psychosocial determinants of quality of life and active aging. A structural equation model. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2020) 17:6023. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17176023
33. Rudnicka, E, Napierała, P, Podfigurna, A, Męczekalski, B, Smolarczyk, R, and Grymowicz, M. The World Health Organization (WHO) approach to healthy ageing. Maturitas. (2020) 139:6–11. doi: 10.1016/j.maturitas.2020.05.018
34. Zaidi, A, and Sidorenko, A. Features and challenges of population Ageing using the European perspective. St. Gallen: World Demographic and Ageing Forum (2008).
35. Lin, YY, and Huang, CS. Aging in Taiwan: building a Society for Active Aging and Aging in place. The Gerontologist. (2016) 56:176–83. doi: 10.1093/geront/gnv107
36. Pengpid, S, and Peltzer, K. Successful ageing among a national community-dwelling sample of older adults in India in 2017-2018. Sci Rep. (2021) 11:22186. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-00739-z
37. Bibi, R, Yan, Z, Zeb, A, Anwar, N, Mian, N, and Khan, RA. The translation process of the culturally sensitive active aging scale for community-dwelling older adults in Pakistan. BMC Public Health. (2023) 23:1682. doi: 10.1186/s12889-023-16563-1
38. Tausig, M, and Subedi, J. Aging in Nepal. The Gerontologist. (2022) 62:803–8. doi: 10.1093/geront/gnac047
39. Zaidi, A, Gasior, K, Zolyomi, E, Schmidt, A, Rodrigues, R, and Marin, B. Measuring active and healthy ageing in Europe. J Eur Soc Policy. (2017) 27:138–57. doi: 10.1177/0958928716676550
40. Zasimova, L, and Sheluntcova, M. Measuring active aging for government policy planning: A case of Russia. Moscow: National Research University Higher School of Economics (2014).
41. Principi, A, Di Rosa, M, Domínguez-Rodríguez, A, Varlamova, M, Barbabella, F, Lamura, G, et al. The active Ageing index and policy making in Italy. Ageing Soc. (2021) 43:2554–79. doi: 10.1017/S0144686X21001835
42. Guntupalli, A, and Chakraborty, S. Active Ageing index (AAI) in India: Is the approach used in European countries applicable to developing countries? Palgrave Macmillan: Singapore. (2018). p. 437–463.
43. Mapoma, C. Determinants of active ageing in Zambia. Afr Popul Stud. (2014) 28:616. doi: 10.11564/28-3-616
44. Haque, MA, and Afrin, S. Active aging index in Bangladesh: a comparative analysis with a European approach. Ageing Int. (2022) 47:447–64. doi: 10.1007/s12126-021-09429-7
45. Marzo, RR, Khanal, P, Shrestha, S, Mohan, D, Myint, PK, and Su, TT. Determinants of active aging and quality of life among older adults: systematic review. Front Public Health. (2023) 11:1193789. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1193789
46. Tareque, MI, Hoque, N, Islam, TM, Kawahara, K, and Sugawa, M. Relationships between the active aging index and disability-free life expectancy: a case study in the Rajshahi District of Bangladesh. Canadian J Aging. (2013) 32:417–32. doi: 10.1017/S0714980813000494
47. Rahman, MS, Rahman, MA, Afroze, L, and Islam, SMS. Unmet needs for mental care services for older people in Bangladesh during the COVID-19 pandemic. General Psychiatry. (2020) 33:e100294. doi: 10.1136/gpsych-2020-100294
48. Islam, MN, and Nath, DC. A future journey to the elderly support in Bangladesh. J Anthropol. (2012) 2012:752521. doi: 10.1155/2012/752521
51. Perales, J, Martin, S, Ayuso-Mateos, JL, Chatterji, S, Garin, N, Koskinen, S, et al. Factors associated with active aging in Finland, Poland, and Spain. Int Psychogeriatr. (2014) 26:1363–75. doi: 10.1017/S1041610214000520
52. Tajvar, M, Yaseri, M, Mahmoudi, R, and Zaidi, A. Individual-level active aging index and quality of life of older people: a population-based survey in Tehran. Int J Prev Med. (2022) 13:2. doi: 10.4103/ijpvm.IJPVM_358_20
53. Omotara, BA, Yahya, SJ, Wudiri, Z, Amodu, MO, Bimba, JS, and Unyime, J. Assessment of the determinants of healthy Ageing among the rural elderly of north-eastern Nigeria. Health. (2015) 7:754–64. doi: 10.4236/health.2015.76090
54. Uddin, MA. Depression of older persons in rural Bangladesh. Int J Sustain Dev Res. (2017) 3:47–9. doi: 10.11648/j.ijsdr.20170305.11
55. Ahmadi, M, Kazemi-Arpanahi, H, Nopour, R, and Shanbehzadeh, M. Factors influencing quality of life among the elderly: an approach using logistic regression. J Educ Health Promot. (2023) 12:215. doi: 10.4103/jehp.jehp_13_23
56. Uddin, M, Soivong, P, Lasuka, D, and Juntasopeepun, P. Factors influencing quality of life of older persons in Bangladesh. MOJ Gerontol Geriatrics. (2018) 3:203–7. doi: 10.15406/mojgg.2018.03.00115
57. Manasatchakun, P, Chotiga, P, Hochwälder, J, Roxberg, Å, Sandborgh, M, and Asp, M. Factors associated with healthy aging among older persons in northeastern Thailand. J Cross Cult Gerontol. (2016) 31:369–84. doi: 10.1007/s10823-016-9296-y
59. Amuthavalli Thiyagarajan, J, Mikton, C, Harwood, RH, Gichu, M, Gaigbe-Togbe, V, Jhamba, T, et al. The UN decade of healthy ageing: strengthening measurement for monitoring health and wellbeing of older people. Age Ageing. (2022) 51:afac147. doi: 10.1093/ageing/afac147
60. UNSDG. Universal values: Human rights-based approach. New York: United Nations Sustainable Development Group (UNSDG) (2023).
61. SDG U. (2023). Universal Values. principle two: Leave no one behind. New York United Nations sustainable development groups. Available online at: https://unsdg.un.org/2030-agenda/universal-values/leave-no-one-behind (Accessed October 17, 2023)
62. Sifat, RI. Social safety net (SSN) programs in Bangladesh: issues and challenges. J Soc Serv Res. (2021) 47:455–7. doi: 10.1080/01488376.2020.1839627
63. Mandal, K, and Subaiya, L. Co-determinants of Coresidence among older persons in India. Ageing Int. (2024) 49:219–34. doi: 10.1007/s12126-023-09541-w
64. Lu, W, Pikhart, H, and Sacker, A. Domains and measurements of healthy aging in epidemiological studies: a review. The Gerontologist. (2019) 59:e294–310. doi: 10.1093/geront/gny029
Keywords: assessment, determinants of active aging, active aging, Bangladesh, factors of aging
Citation: Afrin S, Khan MMH and Haque MA (2025) Factors affecting the active aging situation in Bangladesh. Front. Public Health. 13:1517482. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1517482
Received: 26 October 2024; Accepted: 17 February 2025;
Published: 06 March 2025.
Edited by:
Peter Crome, Keele University, United KingdomReviewed by:
Srirath Gohwong, Kasetsart University, ThailandCopyright © 2025 Afrin, Khan and Haque. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Md. Aminul Haque, YW1pbnVsLmhhcXVlQGR1LmFjLmJk
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.