
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Public Health, 24 February 2025
Sec. Children and Health
Volume 13 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2025.1513358
Background: Visceral fat accumulation and dyslipidaemia are associated with infertility symptoms. The cardiometabolic index (CMI) is a comprehensive quantitative measure of central obesity and dyslipidaemia. However, the link between the female CMI and the couple infertility needs to be explored further. Hence, this study aimed to dissect this connection.
Methods: The study used a cross-sectional approach to select 1,641 female participants from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), which was conducted between 2013 and 2020. The natural log–transformed CMI (In-CMI) was used to consider the non-normal distribution of CMI. Logistic regression models adjusted for covariates were employed to investigate the association between the In-CMI and couple infertility.
Results: After adjusting for all covariates, each 1 unit increase in the In-CMI was associated with a 34% increase in the incidence of infertility (odds ratio [OR] 1.34, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.10–1.64, p = 0.004). In addition, the association remained statistically significant after dividing the In-CMI into tertiles (T1, T2, and T3). The T3 group, with the highest In-CMI, showed higher odds of infertility compared with the T1 group (OR 2.11, 95% CI 1.38–3.23, p < 0.001). Subgroup and interaction analyses revealed that the association between the In-CMI and infertility depended on a history of treatment for pelvic infection (P for interaction <0.05). The inflection point for a positive linear association between In-CMI and infertility was−0.73.
Conclusion: The female CMI is linked to the incidence of couple infertility. Moreover, the female CMI shows significant medical significance for assessing couple infertility risk of childbearing age.
Infertility is characterized by the inability to achieve a successful pregnancy after 12 months of regular, unprotected sexual intercourse (1). Infertility has been ranked alongside malignant tumors and cardiovascular diseases as one of the top three diseases affecting quality of life (2). The inability to have children affects men and women throughout the world and leads to pain, depression, discrimination and rejection (3, 4). The prevalence of infertility ranges from 3 to 30% (5). Therefore, it is necessary to take appropriate preventive measures to reduce the negative impact of infertility and the pressure on society.
Obesity has become one of the most severe public health issues. As of 2022, more than 1 billion people worldwide are obese. Notably, the prevalence of obesity in women is particularly alarming, especially central obesity (6). Central obesity is characterised by excessive fat accumulation around the stomach and an increase in waist circumference. Central obesity is associated with metabolic disorders, including dyslipidaemia, and infertility (7). Obesity leads to intracellular fat accumulation or elevated circulating lipids, and approximately 45% of women of childbearing age are affected by dyslipidaemia (8). In recent years, several conventional body size assessments, such as waist circumference and body mass index (BMI), have been widely used to measure the increase in obesity. However, these do not consider lipid metabolism as well as visceral and subcutaneous fat deposition (9). It has been argued that these BMI-like metrics are deceptive and ignore lipid metabolic profiles (10).
The cardiometabolic index (CMI) was first introduced by researchers as a comprehensive assessment of abdominal obesity and fat metabolism (11). Moreover, the CMI can be a valuable indicator in people with normal weight but metabolic disorders (10). The CMI may provide a more robust and independent indicator of metabolic abnormalities than traditional anthropometric measurements (12). Recently, there has been increased discussion on the relationship between the CMI and many diseases, such as depression and diabetes, suggesting its value as an indicator of metabolic disorders (13, 14). However, there has been limited exploration of the link between the CMI and infertility. The CMI may play have an as-yet unexplored clinical role in infertility. Therefore, this study explored this link using the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) database.
In the United States, a cross-sectional survey called NHANES, conducted by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, assesses the health and nutrition status; it includes face-to-face interviews and physical examinations of the population. Participants first provide written informed consent and then complete a health interview at home; finally, a physical examination is conducted at a mobile medical centre where urine and blood samples are collected. The present study used data collected from 2013 to 2020 as part of the NHANES. For this period, there were 35,706 people. After excluding minors (< 18 years old) and older individuals (> 45 years old) (n = 25,817), men (n = 4,688), pregnant women and those who were no longer fertile due to ovariectomy or hysterectomy (n = 394) and individuals with incomplete information on the CMI (n = 2,387) or infertility (n = 769), and outlier (n = 10). A total of 1,641 eligible subjects were analysed (Figure 1).
The CMI was available for the 1,641 eligible subjects. It was calculated as follows:
Where TG is the triglyceride level and HDL-C is the high-density lipoprotein cholesterol level, both measured in the blood.
Infertility was assessed based on the responses to two questions of the NHANES: (1) “Have you tried to get pregnant for at least 1 year without getting pregnant?” (2) “Have you ever visited a doctor or other health care provider because you could not get pregnant?” Answers of “refused” or “do not know” to either question were considered as missing information on infertility and were excluded. Women who answered “yes” to either of these questions were considered to have a history of infertility. The remaining participants had no history of infertility.
Various sociodemographic indicators, lifestyle habits and factors related to fertility were considered to be potential confounding factors that could affect the study results. The sociodemographic factors included age, race/ethnicity, education level, marital status and the poverty-to-income ratio (PIR). Lifestyle factors including smoking/alcohol consumption status and physical activity. There were four levels for the drinking status: no drinking, moderate drinking (no more than one drink per day), heavy drinking (1–4 drinks per day), and binge drinking (at least four drinks per day) (15). In the U.S., adults are recommended to perform at least 75 min of high-intensity exercise or 150 min of moderate-intensity physical activity per week to promote health. The 1,641 eligible subjects were divided into three categories according to their physical activity: active, moderate and low. Other covariates included height, age at menarche, use of birth control pills, pregnancy history, and treatment for pelvic infections or pelvic infection drug/PID. Besides, the missing data for categorical variables were coded using missing indicator categories, including marital status (n = 171), education (n = 171), alcohol consumption status (n = 119), ever taken birth control pills (n = 723), and pregnancy history (n = 171). Missing data were subsequently handled using multiple imputation methods.
The continuous demographic data are presented as the mean and standard deviation or median and upper and lower quartiles; the categorical data are described as a number depending on the infertility status. Given that the CMI showed a skewed distribution, a natural logarithmic transformation was used to adjust the data to a normal distribution (the In-CMI). Participants in the 2 groups (group with history of infertility, group without history of infertility) were separately divided into three groups (T1, T2, T3) according to ln-CMI (T1, T2, and T3); T1, with the lowest In-CMI, was set as the benchmark group. The chi-square test and t-test were used to evaluate the socioeconomic information of the subjects based on the In-CMI. Multiple and logistic regression was used to explore the relationship between the In-CMI and infertility. In the model 1, there were no modifications based on the covariates. The model 2 was adjusted for age and race. The model 3 was adjusted for age, race, the PIR, age at menarche, education level, smoking behavior, drinking habits, reproductive history, marital status, use of contraceptives, treatment of pelvic infections/PID, and frequency of physical activity. After converting the In-CMI from continuous to categorical data (tertiles), trend analysis was used to explore whether there was a linear relationship between the In-CMI and infertility, including subgroup analysis of age groups, age at menarche, smoking habits, drinking habits, pregnancy history, contraceptive use and PID treatment history. The nonlinear relationship between infertility and In-CMI was studied. The correlation between infertility and In-CMI was analysed by employing smoothed curve fitting. The threshold effect of each interval was calculated and fitted using a piecewise regression model. R Studio (version 4.2.2) and Empower Stats (version 4.0) were used for statistical analysis. A p < 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant.
This study identified 1,641 women aged between 18 and 45 years who took part in the NHANES study, including 197 with infertility. The mean age of all included women was 31.11 ± 8.27 years, while the mean age of the women with infertility was 34.15 ± 7.07 years. Table 1 provides specific information on the infertility status of the participants. Infertility was more common in women who were older, married or cohabiting, better educated, had a history of alcohol abuse, were current smokers, had a history of pregnancy, had been treated for pelvic infections/PID and had been taking birth control pills. The In-CMI was significantly higher for the women with infertility compared with the women without infertility. We divided the women into three groups based on the In-CMI: T1 (≤ 0.222), T2 (0.222–0.466) and T3 (> 0.466). The rate of infertility increased significantly as the In-CMI increased: 20.81% for T1, 35.53% for T2 and 43.66% for T3 (p < 0.001).
A higher In-CMI was associated with a higher risk of difficulty conceiving. All models indicated a positive association between infertility and the In-CMI. Multivariate logistic regression analysis in the model 1 revealed that the odds of infertility increased by 41% for every 1-unit increase in the In-CMI (odds ratio [OR] 1.41, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.18–1.68, p < 0.001). When considering the three groups based on the IN-CMI, the T2 and T3 groups were more likely to have difficulty conceiving children than the T1 group (T2: OR 1.81, 95% CI 1.21–2.72, p = 0.005; T3: OR 2.30, 95% CI 1.55–3.41, p < 0.001). In the model 3, the probability of infertility increased by 34% when the In-CMI increased by 1 unit (OR 1.34, 95% CI 1.10–1.64, p = 0.004). Besides, the T2 and T3 groups were associated with increased odds of infertility (T2: OR 1.78, 95% CI 1.17–2.72, p = 0.007; T3: OR 2.11, 95% CI 1.38–3.23, p < 0.001) (Table 2). A smooth curve fitting analysis was conducted to explore the relationship between ln-CMI and couple infertility. A standard linear model indicated a positive association between ln-CMI and infertility risk (OR = 1.34, 95% CI: 1.10–1.64, p = 0.004). However, a two-piecewise linear regression model revealed a turning point at ln-CMI = −0.73. For ln-CMI < −0.73, the OR was 1.89 (95% CI: 1.31–2.71, p = 0.001), whereas for ln-CMI ≥ −0.73, the association was not significant (OR = 0.87, 95% CI: 0.56–1.34, p = 0.518) (Figure 2 and Table 3).
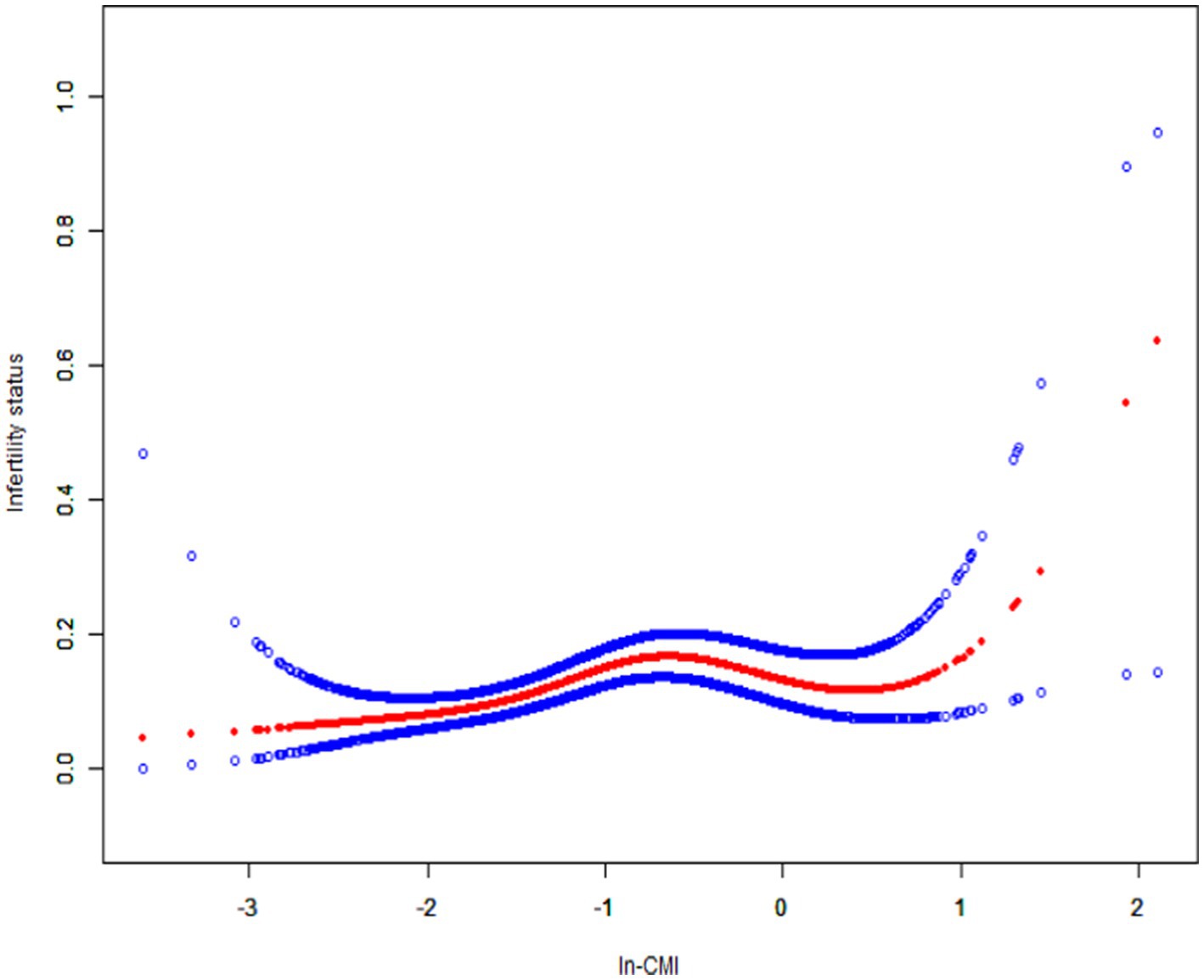
Figure 2. Smoothed curve fitting for In-CMI and infertility. The solid red line represents the smooth curve fit between variables. Blue bands represent the 95% confidence interval from the fit. In-CMI, Natural log-transformed cardiometabolic index.
Subgroup analyses showed that after stratifying patients based on a history of treatment for pelvic infection/PID, the In-CMI was positively associated with the incidence of infertility in women with pelvic infection (OR 5.36, 95% CI 1.39–20.75, p = 0.015) and women without pelvic infection (OR 1.32, 95% CI 1.07–1.62, p = 0.009). The association between the In-CMI and infertility depended on a history of treatment for pelvic infection (P for interaction <0.05). However, the association between the In-CMI and infertility did not depend on age, age at menarche, the smoking status, alcohol use, pregnancy history, use of birth control pills and BMI (Table 4).
To evaluate the efficacy of BMI and CMI in predicting infertility, we constructed receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves. The ROC curve was a graphical tool for assessing the performance of classification models by plotting the true positive rate (degree of sensitivity) and the false positive rate (degree of specificity) across various threshold settings. The area under the curve (AUC) served as a crucial metric for gaging the predictive performance of the model, with an AUC value closer to 1 indicating better predictive performance. In this study, we computed the ROC curves for BMI and CMI, and obtained their respective AUC values. The AUC for BMI was 0.598 (95% CI 0.56–0.64), while the AUC for CMI was 0.585 (95% CI 0.55–0.62) (Supplementary Figure 1).
In this cross-sectional study of 1,641 subjects, it found that a higher In-CMI is associated with a higher incidence of infertility. Subgroup and interaction analyses revealed that the association between the In-CMI and infertility depended on a history of treatment for pelvic infection/PID. This research used a piecewise regression model and found a positive correlation when the In-CMI was < −0.73. When the In-CMI was > −0.73, the association with infertility was no longer statistically significant.
This study is the first to assess the relationship between couple infertility and the female CMI. The CMI is an indicator of centripetal obesity, reflecting the distribution of obesity and lipid metabolism. Abdominal obesity, characterised by visceral fat, is closely related to metabolic disorders and is a significant risk factor for infertility (16). Visceral fat is a crucial indicator of obesity and lipid metabolism (17), and its distribution also significantly affects hormone concentrations. Zhang et al. (18) conducted a retrospective study of 10,424 patients with infertility divided into two groups – one with normal lipid metabolism and one with dyslipidaemia – and found that dyslipidaemia had a negative impact on pregnancy outcomes for in vitro fertilization of patients with infertility but not polycystic ovary syndrome. A study by Tortoriello et al. (19) showed that diet induced a 60% decrease in spontaneous pregnancy rate in obese mice. According to previous studies, abnormalities in lipid cycle metabolism affect the hormonal environment (20), ovarian and uterine function (21), which in turn may contribute to infertility. A randomized, double-blind trial found that reduced fertility was associated with abnormal lipid levels in women (8).
In this exploratory study of 1,641 adult women, it showed that a higher In-CMI may increase the probability of infertility. In model 3, each 1-unit increase in In-CMI was associated with a 34% increase in the probability of infertility after adjusting for age, race, the PIR, age at menarche, education level, smoking status, alcohol consumption status, pregnancy history, marital status, use of birth control pills, a history of treatment for pelvic infection/PID and the physical activity level. Moreover, the T2 and T3 groups with the highest In-CMI had increased odds of infertility compared with the T1 group. In addition, this study validated the association between the In-CMI and infertility based on subgroup analyses. The association depended on a history of treatment for pelvic infection/PID. On the one hand, visceral adipose tissue functions as an active endocrine organ, secreting inflammatory factors such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6). The excessive release of these factors can lead to chronic inflammatory responses, causing damage to vascular endothelial cells and thereby increasing the risk of developing chronic pelvic inflammatory conditions (22, 23). On the other hand, Obesity and PID involve distinct pathological mechanisms but share a common feature of inflammatory responses. For instance, the chronic low-grade inflammation associated with obesity may impact reproductive health through systemic inflammatory pathways, while PID induces localized inflammation that can lead to tubal scarring and dysfunction. Despite these differing mechanisms, both conditions may contribute to infertility through inflammation-related processes.
The mechanisms that underlie the strong association between the female CMI and couple infertility are unclear, but lipid metabolism may be responsible for these results. For example, phospholipids, as a member of lipids, are also an important component of cell membranes. It is involved in membrane fluidity and signaling, thus affecting the process of ovulation by follicular rupture (24, 25). Lipids, on the other hand, as an important source of energy, also provide energy support for cellular functions including follicular rupture (26). Thus lipid metabolism may affect processes such as ovulation and pregnancy. Previous studies have found that gene expression of 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type1 (11β-HSD1) is positively associated with abdominal obesity (27). 11β-HSD1 is considered to be a determinant of local glucocorticoid function, which can be activated by site-specific overexpression and activation of local glucocorticoids. Excess glucocorticoids can malignantly cause visceral adipose tissue accumulation on the one hand and insulin resistance on the other. Insulin resistance leads to increased ovarian testosterone secretion, decreased secretion of sex hormone-binding globulin, and changes in adipokine levels, which disrupts the balance of the hypothalamic–pituitary-ovarian axis, leading to infertility (28). In women with central obesity, excessive abdominal lipid accumulation leads to the breakdown of metabolites such as fatty acids and prostaglandins, which increases ovarian steroid hormone secretion (29). This process predisposes the body to chronic inflammation (30) and localized endometrial autophagy (31). Which affect the process of embryo development during reproduction and lead to infertility (32, 33). Additionally, changes in steroid hormone secretion are closely related to aging. As women age, their fertility declines significantly, accompanied by a decrease in metabolic rate, alterations in fat distribution, and lipid metabolism dysregulation. These changes may affect reproductive health through various mechanisms.
BMI, as a simple and easily accessible anthropometric indicator, facilitates large-scale screening and monitoring, and offers certain reference value in assessing obesity levels and infertility risks. However, BMI solely considers the relationship between weight and height, failing to comprehensively reflect an individual’s metabolic status. It cannot distinguish between the weight of adipose tissue and other types of tissue. Therefore, in some circumstances, BMI may misestimate an individual’s infertility risk. In contrast, CMI integrates multiple metabolic parameters, enabling a more comprehensive assessment of an individual’s degree of metabolic abnormality and thus a more accurate prediction of infertility risk. Despite the slightly lower AUC of CMI compared to BMI in this study, we believe that CMI still holds great potential in predicting infertility. Firstly, CMI requires the results of multiple biochemical indicators and may be influenced by factors such as sample size and measurement errors in certain situations. Secondly, by incorporating multiple metabolic parameters, CMI theoretically provides a more comprehensive reflection of an individual’s metabolic abnormalities, allowing for a more precise prediction of infertility risk. Additionally, CMI may offer unique predictive advantages in specific populations, such as those with polycystic ovary syndrome, which can contribute to a deeper understanding of the pathogenesis of infertility. Due to database limitations, further validation is not possible at this stage, necessitating future research to explore this area further.
In summary, we comprehensively evaluated the relationship between the CMI and infertility and confirmed the predictive value of the CMI for infertility, especially when there is a history of pelvic infection. The optimal critical value of In-CMI for predicting infertility was −0.73. Specific lipidomic changes often predict the onset of clinical symptoms, so the CMI can provide more in-depth and cutting-edge insights for women of reproductive age. The CMI has the advantage of being cost-effective and easily measurable and provides insights into lipid metabolism. The results of this study provide potential new perspectives on infertility treatment and help to deepen the understanding of women’s reproductive health.
However, given the limitations of the study, further in-depth studies and multi-centre validation are still needed to ensure that these findings can be applied more widely in clinical practice. First, the cross-sectional nature of this study precludes the ability to establish a causal relationship between the CMI and infertility. Second, despite considering multiple covariates, it could not rule out all potential confounding influences. Additionally, the measurement of CMI in this study was based on data collected at the time of testing, whereas infertility history reflects a retrospective report of past conditions. This time gap introduces a potential limitation in accurately linking current CMI values with past infertility events, as metabolic changes or other factors influencing fertility may have occurred over time. Therefore, while CMI can provide insights into the current metabolic status, its direct correlation with infertility history may not fully account for all temporal and physiological changes that may have occurred since the infertility event. Lastly, our study has a limitation that reproductive disorders, which may potentially impact fertility as covariates, were not considered in the analysis. This limitation is primarily attributed to the lack of detailed data on common fertility-related conditions (such as endometriosis and polycystic ovary syndrome) in the NHANES database from 2013 to 2020.
The female CMI is linked to the incidence of couple infertility. Moreover, the female CMI shows significant medical significance for assessing couple infertility risk of childbearing age.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
The NHANES agreement has been reviewed and approved by the NCHS Research Ethics Committee. All participants provided written informed consent before participating.
LJ: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – original draft. FZ: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. YW: Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. JW: Supervision, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research received funding from the National Famous Elderly Chinese Medicine Expert Wu Jie Inheritance Workshop.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpubh.2025.1513358/full#supplementary-material
CMI, Cardiometabolic index; In-CMI, The natural log–transformed CMI; NHANES, National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey; OR, Odds ratio; CI, Confidence interval; BMI, Body mass index; TG, Triglycerides; HDL-C, High-density lipoprotein cholesterol; N, Number; PIR, Poverty-to-income ratio; PID, Pelvic inflammatory disease; 11β-HSD1, 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type1; ROC, Receiver operating characteristic; AUC, Area under the curve.
1. Vander Borght, M, and Wyns, C. Fertility and infertility: definition and epidemiology. Clin Biochem. (2018) 62:2–10. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2018.03.012
2. Jie, Q. Assisted reproductive technology: translational medicine from basic to clinical. Peking Univ School J. (2013) 45:835–7.
3. Hecht, LM, Joseph-Mofford, G, Iacobelli, R, Ahmed, M, Haley, E, Loree, AM, et al. Anxiety, depression, and infertility-specific distress among women with female factor infertility. J Health Psychol. (2024) 30:32–9. doi: 10.1177/13591053241235092
4. Hanson, B, Johnstone, E, Dorais, J, Silver, B, Peterson, CM, and Hotaling, J. Female infertility, infertility-associated diagnoses, and comorbidities: a review. J Assist Reprod Genet. (2017) 34:167–77. doi: 10.1007/s10815-016-0836-8
5. Polis, CB, Cox, CM, Tunçalp, Ö, McLain, AC, and Thoma, ME. Estimating infertility prevalence in low-to-middle-income countries: an application of a current duration approach to demographic and health survey data. Hum Reprod. (2017) 32:1064–74. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dex025
6. Ford, ND, Patel, SA, and Narayan, KM. Obesity in low-and middle-income countries: burden, drivers, and emerging challenges. Annu Rev Public Health. (2017) 38:145–64. doi: 10.1146/annurev-publhealth-031816-044604
7. Venkatesh, SS, Ferreira, T, Benonisdottir, S, Rahmioglu, N, Becker, CM, Granne, I, et al. Obesity and risk of female reproductive conditions: a Mendelian randomisation study. PLoS Med. (2022) 19:e1003679. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1003679
8. Pugh, SJ, Schisterman, EF, Browne, RW, Lynch, AM, Mumford, SL, Perkins, NJ, et al. Preconception maternal lipoprotein levels in relation to fecundability. Hum Reprod. (2017) 32:1055–63. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dex052
9. Ramdas Nayak, VK, Nayak, KR, Vidyasagar, S, and P, R. Predictive performance of traditional and novel lipid combined anthropometric indices to identify prediabetes. Diabetes Metab Syndr. (2020) 14:1265–72. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2020.06.045
10. Liu, X, Wu, Q, Yan, G, Duan, J, Chen, Z, Yang, P, et al. Cardiometabolic index: a new tool for screening the metabolically obese normal weight phenotype. J Endocrinol Investig. (202) 44:1253–61.
11. Wakabayashi, I, and Daimon, T. The “cardiometabolic index” as a new marker determined by adiposity and blood lipids for discrimination of diabetes mellitus. Clin Chim Acta. (2015) 438:274–8. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2014.08.042
12. Liu, X, Wu, Q, Yan, G, Duan, J, Chen, Z, Yang, P, et al. Cardiometabolic index: a new tool for screening the metabolically obese normal weight phenotype. J Endocrinol Investig. (2021) 44:1253–61. doi: 10.1007/s40618-020-01417-z
13. Cheng, L, Wu, Q, and Wang, S. Cardiometabolic index is associated with increased depression: a population-based study. J Affect Disord. (2024) 348:259–64. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2023.12.073
14. Song, J, Li, Y, Zhu, J, Liang, J, Xue, S, and Zhu, Z. Nonlinear associations of cardiometabolic index with insulin resistance, impaired fasting glucose, and type 2 diabetes among US adults: a cross-sectional study. Front Endocrinol. (2024) 15:1341828. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1341828
15. Piercy, KL, Troiano, RP, Ballard, RM, Carlson, SA, Fulton, JE, Galuska, DA, et al. The physical activity guidelines for Americans. JAMA. (2018) 320:2020–8. doi: 10.1001/jama.2018.14854
16. Wise, LA, Palmer, JR, and Rosenberg, L. Body size and time-to-pregnancy in black women. Hum Reprod. (2013) 28:2856–64. doi: 10.1093/humrep/det333
17. Musa, S, and Osman, S. Risk profile of Qatari women treated for infertility in a tertiary hospital: a case-control study. Fertil Res Pract. (2020) 6:12. doi: 10.1186/s40738-020-00080-5
18. Zhang, WJ, Bu, ZQ, and Shi, H. Effect of dyslipidemia on pregnancy outcomes of IVF/ICSI-ET in non-PCOS infertile patients. J Reprod Med. (2022) 31:1654–60.
19. Tortoriello, DV, McMinn, J, and Chua, SC. Dietary-induced obesity and hypothalamic infertility in female DBA/2J mice. Endocrinology. (2004) 145:1238–47. doi: 10.1210/en.2003-1406
20. GWYNNE, J, and STRAUSS, J III. The role of lipoproteins in steroidogenesis and cholesterol metabolism in steroidogenic glands. Endocr Rev. (1982) 3:299–329. doi: 10.1210/edrv-3-3-299
21. Bukhari, SA, Zafar, K, Rajoka, MI, İbrahim, Z, Javed, S, Sadiq, R, et al. Oxidative stress-induced DNA damage and homocysteine accumulation may beinvolved in ovarian cancer progression in both young and old patients. Turk J Med Sci. (2016) 46:583–9. doi: 10.3906/sag-1406-17
22. Cai, X, Song, S, Hu, J, Zhu, Q, Yang, W, Hong, J, et al. Body roundness index improves the predictive value of cardiovascular disease risk in hypertensive patients with obstructive sleep apnea: a cohort study. Clin Exp Hypertens. (2023) 45:2259132. doi: 10.1080/10641963.2023.2259132
23. Wang, W, Feng, D, and Ling, B. Biologia Futura: endometrial microbiome affects endometrial receptivity from the perspective of the endometrial immune microenvironment. Biol Futur. (2022) 73:291–300. doi: 10.1007/s42977-022-00134-3
24. Simons, K, and Ikonen, E. Functional rafts in cell membranes. Nature. (1997) 387:569–72. doi: 10.1038/42408
25. Richards, JS. Ovulation: new factors that prepare the oocyte for fertilization. Mol Cell Endocrinol. (2005) 234:75–9. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2005.01.004
26. Sutton-McDowall, ML, Gilchrist, RB, and Thompson, JG. The pivotal role of glucose metabolism in determining oocyte developmental competence. Reproduction. (2010) 139:685–95. doi: 10.1530/REP-09-0345
27. Desbriere, R, Vuaroqueaux, V, Achard, V, Boullu-Ciocca, S, Labuhn, M, Dutour, A, et al. 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 mRNA is increased in both visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue of obese patients. Obesity. (2006) 14:794–8. doi: 10.1038/oby.2006.92
28. Mikhael, S, Punjala-Patel, A, and Gavrilova-Jordan, L. Hy-pothalamic-pituitary-ovarian Axis disorders impacting female fertility. Biomedicines. (2019) 7:5. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines7010005
29. Mazza, E, Troiano, E, Ferro, Y, Lisso, F, Tosi, M, Turco, E, et al. Obesity, dietary patterns, and hormonal balance modulation: gender-specific impacts. Nutrients. (2024) 16:1629. doi: 10.3390/nu16111629
30. Hotamisligil, GS. Inflammation and metabolic disorders. Nature. (2006) 444:860–7. doi: 10.1038/nature05485
31. Choi, AM, Ryter, SW, and Levine, B. Autophagy in human health and disease. N Engl J Med. (2013) 368:651–62. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1205406
32. Krajnik, K, Mietkiewska, K, Skowronska, A, Kordowitzki, P, and Skowronski, MT. Oogenesis in women: from molecular regulatory pathways and maternal age to stem cells. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:6837. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076837
Keywords: cardiometabolic index, obesity, lipid metabolism, infertility, NHANES, cross-sectional study
Citation: Liu J, Zhu F, Wang Y and Wu J (2025) Association between female cardiometabolic index and infertility: a population-based study. Front. Public Health. 13:1513358. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1513358
Received: 18 October 2024; Accepted: 22 January 2025;
Published: 24 February 2025.
Edited by:
Tim S. Nawrot, University of Hasselt, BelgiumReviewed by:
Pauliina Damdimopoulou, Karolinska Institutet (KI), SwedenCopyright © 2025 Liu, Zhu, Wang and Wu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jie Wu, d3VqaWVqaWFvc2hvdUAxNjMuY29t
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.