- 1Department of Nursing, Malayer School of Medical Sciences, Chronic Diseases (Home Care) Research Center, Hamadan University of Medical Sciences, Hamadan, Iran
- 2Department of Nursing, Arak University of Medical Sciences, Arak, Iran
- 3Iranian Social Security Organization, Arak, Iran
- 4Department of Biostatistics, Faculty of Medical Sciences, Arak University of Medical Sciences, Arak, Iran
Objectives: This study examines the impact of social media-based education on health literacy status, self-care, and glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) in individuals with type 2 diabetes (T2D).
Method: This educational intervention study was carried out from March 2022 to June 2022 on diabetic patients visiting the diabetes clinic in Arak, Iran. The patients split into two groups: the virtual education group (n = 38) using the Telegram messaging platform and the control group (n = 38). Patients in the virtual education group received multimedia messages about T2D daily for 4 weeks. Data analysis utilized SPSS version 23 and statistical tests.
Results: The results of this study showed that the overall score of health literacy and the dimensions of reading, understanding, and evaluation were significantly higher in the intervention group than in the control group (p < 0.05). However, the score for the access dimension did not show a significant difference between the two groups (p > 0.05). The Wilcoxon test results indicated that the average HbA1c score significantly decreased in the intervention group before and after the intervention. However, these changes were not significant in the control group. Nevertheless, the Mann–Whitney test did not indicate a significant statistical difference between the groups regarding the average HbA1c score before and after the intervention (p > 0.05).
Conclusion: The findings of this study suggest that social networks provide a suitable platform for delivering self-care education to individuals with T2D. Furthermore, in the long term, it might positively impact the patients’ HbA1c levels. Future studies with larger sample sizes can be beneficial in this area.
Introduction
Diabetes is recognized as one of the most common chronic diseases worldwide (1). The World Health Organization (WHO) even refers to diabetes as a silent epidemic (2). It is predicted that the number of individuals affected by this disease will exceed 592 million by 2035 (3). The prevalence of diabetes is steadily increasing in various countries worldwide (4). Statistics in Iran also show that diabetes affects 7% of the country’s population, and with the current trend, experts estimate that this number will reach 6 million by 2030 (5). Type 2 diabetes (T2D) is the most prevalent form of diabetes globally, accounting for approximately 90% of diabetes cases (6).
Uncontrolled diabetes is associated with the onset of disabilities, cardiovascular diseases, nephropathy, neuropathy, retinopathy, and patient mortality (7). Nevertheless, diligent monitoring and control of the disease can significantly delay or even prevent the onset of diabetes-related complications (6). Any care activity requires patient involvement, and self-care is considered a key component of diabetes management (8). The collection of behaviors adopted by individuals with diabetes or at risk of its complications, enabling them to manage the disease independently, is referred to as self-care activities (7). Proper adherence to self-care activities leads to benefits such as adequate blood sugar control, reduced complications, decreased hospitalizations, and improved quality of life (9). Previous studies have shown that most individuals with diabetes have limited self-care capabilities (10, 11).
In recent years, patients have become significantly more interested in taking responsibility for their disease management, but they need education (11). Therefore, education plays a crucial role in enhancing the self-care abilities of individuals with diabetes (5). Given the chronic and lifelong nature of the disease, self-care for these patients is a lengthy, complex, and challenging process (12). It requires significant lifestyle changes (13). This underscores the growing importance of self-care education (14). Despite their inherent potential, in-person educational sessions have limitations, including impractical transportation for low-income groups, time and location constraints, and a lack of human and financial resources (15).
Recent advancements in information and communication technologies have created opportunities to facilitate learning through multimedia virtual education (16). Social media platforms, in particular, play a significant role in the prevention, care, and management of chronic diseases (8). Their effectiveness in managing various chronic diseases has been well documented (17).
Despite the numerous benefits offered by various social messaging platforms, limited studies have explored their impact on managing type 2 diabetes in developing countries, revealing a gap between the use of these platforms and the understanding of the disease’s management (17). More than three-quarters of individuals with diabetes in low- to middle-income countries face significant challenges in accessing adequate healthcare and treatment (18). According to the World Health Organization, fewer than 50% of patients in these countries benefit from self-care activities (19).
A systematic review and meta-analysis conducted in 2021 also indicated that the self-care score of Iranian diabetic patients is approximately 48.86%, which falls short of the desired level. Based on this finding, the researchers strongly recommend developing interventions aimed at improving self-care among individuals with diabetes (11). The findings of another study in Pakistan demonstrate gaps in individuals with diabetes knowledge and highlight the importance of self-care education. The study also identifies obstacles such as financial constraints and excessive work commitments that hinder patients’ ability to engage in self-care (6).
Obstacles such as high costs, insufficient access to medication, and unequal distribution of healthcare services across different regions are among the challenges faced by developing countries (7, 17). Among the factors affecting the prevention and control of diabetes is having sufficient awareness of the disease, the factors affecting its occurrence and how to prevent this disease. One of the factors that greatly affects the level of awareness and, as a result, more effective control and prevention of the disease, diabetes is health literacy, which is the degree to which individuals have the capacity and ability to acquire, process and understand information related to health and the services they need to make appropriate decisions about their health (9).
Given the direct correlation between health literacy levels and self-care activities (5), we have undertaken the design and implementation of a study on self-care education in virtual spaces to investigate its effects on self-care status, health literacy, and HbA1c levels among individuals with T2D in Iran.
Method
Participants
This educational intervention study was conducted on patients attending the diabetes clinic in Arak, Iran, from March 2022 to June 2022. The sampling method used in this study random sampling’. After acquiring the necessary permissions, eligible individuals were selected from among patients attending the clinic. They were introduced to the research objectives, and upon obtaining their informed consent, they were enrolled in the study.
The inclusion criteria for this study were as follows: a definitive diagnosis of T2D by a specialist endocrinologist, an age range of 30–60 years, a minimum of 6 months of diabetes history, ownership of a smartphone, the ability to use social messaging apps such as Telegram, the absence of psychological disorders, literacy in reading and writing, and Iranian nationality. The exclusion criteria included unwillingness to continue participation, pregnancy, and hospitalization during the study.
The required sample size was calculated based on a similar study, with an effect size of 0.7, α = 0.05, and β = 0.1, resulting in a total sample size of 34 participants per group (20). Considering the attrition rate (10%), 38 individuals were enrolled in each group. The power of the study was calculated to be 80%, ensuring an adequate sample size to detect meaningful differences.
Intervention
In this study, patients were randomly allocated to two groups: the intervention group (n = 38) and the control group (n = 38). After explaining the study and creating a channel on the Telegram messaging platform, the lead author invited all participants to join by sending them an invitation link. Access to this messaging platform was ensured for all participants.
Necessary self-care instructions from credible and up-to-date sources were shared daily through the channel. The content, provided in Persian, included topics related to self-care, such as physical activity, blood glucose monitoring, types of diabetes, dietary guidelines, diabetes complications, and foot care. To ensure participant engagement with the study material, the researcher monitored daily attendance in the channel, tracked the number of views for each message, and contacted any participant who had not accessed the channel for more than 48 h to inquire about the reasons. If a participant failed to engage, they were excluded from the study. The instructional program lasted for 4 weeks. This step was done by the researcher.
Patients in the control group did not receive any educational materials during the study. To adhere to ethical principles, an educational package was provided to these patients after the completion of the study.
Instruments
The researchers developed the self-care questionnaire used in this study by reviewing relevant literature and studies on diabetes. The items in the self-care section of the questionnaire allowed participants to report their self-care activities and the factors affecting their self-care behaviors over the past 7 days. The questionnaire consisted of two sections. The first section included demographic information (age, gender, marital status, education level, occupation, and social media usage) and clinical conditions (duration of diabetes, type of treatment received, and family history of diabetes). The second section contained 16 questions related to diabetes self-care behaviors, compliance diet, exercise, monitoring, treatment, and prevention of complications.
The face validity of the questionnaire was established by presenting it to 10 faculty members with expertise in questionnaire design at Arak University of Medical Sciences. The Cronbach’s alpha coefficient for this questionnaire was 0.91, indicating good internal consistency.
Health literacy was assessed using the Health Literacy for Iranian Adults (HELIA) questionnaire, designed by Montazeri et al. (21), which has demonstrated desirable validity and reliability. The Cronbach’s alpha values for the dimensions of the HELIA questionnaire ranged from 0.72 to 0.89, confirming the reliability of the various dimensions of the instrument (21).
The questionnaire included 33 items assessing patients’ health literacy across five dimensions: access (6 questions), reading (4 questions), understanding (7 questions), evaluation (4 questions), and decision-making and application of health information (12 questions). All items, except those in the reading dimension, were designed on a 5-point Likert scale: (Always: 5, Most of the time: 4, Sometimes: 3, Rarely: 2, Not at all: 1). The items in the “reading skills” dimension used a modified Likert scale: (Very Easy: 5, Easy: 4, Neither easy nor difficult: 3, Difficult: 2, Very Difficult: 1).
The raw score for each participant in each dimension was calculated by summing their responses on each item. To determine the total score, the sum of all item scores was divided by the number of dimensions (5). Scores ranging from 0 to 50 were considered inadequate, scores from 50.1 to 66 were categorized as semi-sufficient, scores from 66.1 to 84 were considered sufficient, and scores from 84.1 to 100 were classified as excellent (22). Participants completed the instrument for evaluation through self-reporting at both the beginning and end of the intervention.
Glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c)
In this study, HbA1c was assessed through laboratory testing at the beginning and end of the intervention. All tests were conducted in a centralized laboratory for all patients.
Data analysis
Data analysis was performed using descriptive statistics, Wilcoxon test, Fisher’s exact test, analysis of covariance (ANCOVA), and the Mann–Whitney U test to compare differences between groups. Data analysis was conducted using SPSS version 23, with a significance level set at 0.05.
Ethical considerations
The design and execution of this research adhered to the Helsinki Declaration. Before beginning the study, all participants were informed about the study’s objectives and were informed that they could withdraw from the study at any time without affecting their relationship with medical professionals or caregivers. The present study has been registered with the Ethics Committee in Research at Arak University of Medical Sciences under the reference number IR.ARAKMU.REC.1398.042.
Results
Two patients withdrew from the study due to a lack of interest, and one patient did not complete the questionnaire. Additionally, three participants were excluded due to inadequate responses on the Telegram messaging platform. Consequently, data analysis was performed with 70 participants. Of these participants, 38.6% were male, and 15.7% resided in rural areas. The demographic characteristics of the study participants are presented in Table 1.
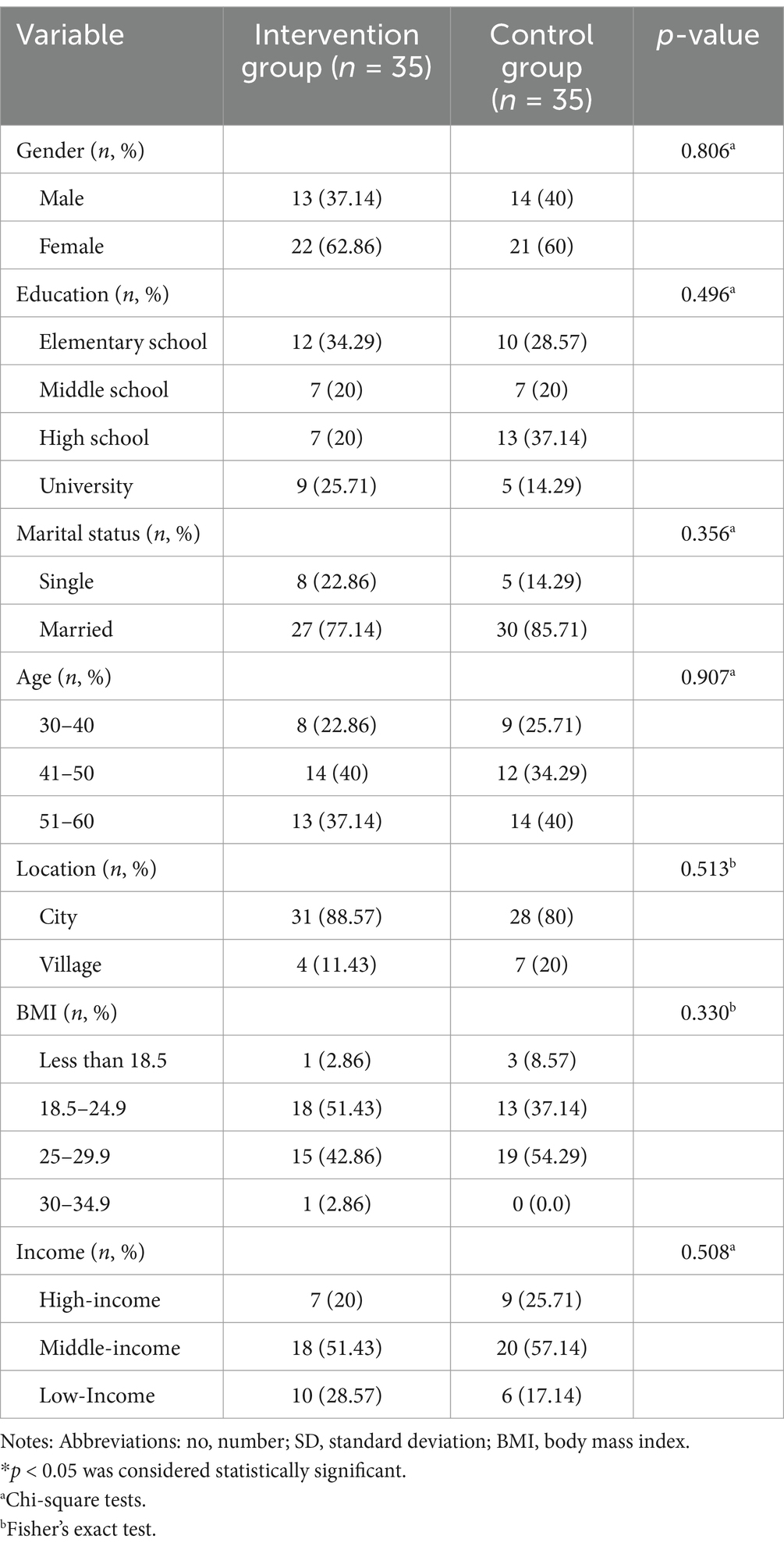
Table 1. Distribution of individual characteristics of the patients in intervention and control groups.
The results indicated that there was no statistically significant difference between the mean scores of reading, access, understanding, evaluation, decision-making, and overall health literacy scores in the two groups before the intervention (p > 0.05). However, after the intervention, the mean scores for reading, understanding, evaluation, decision-making, and total health literacy in the intervention group were significantly higher than in the control group (p < 0.05). The post-intervention access score did not show a statistically significant difference between the two groups (p > 0.05) (Table 2).
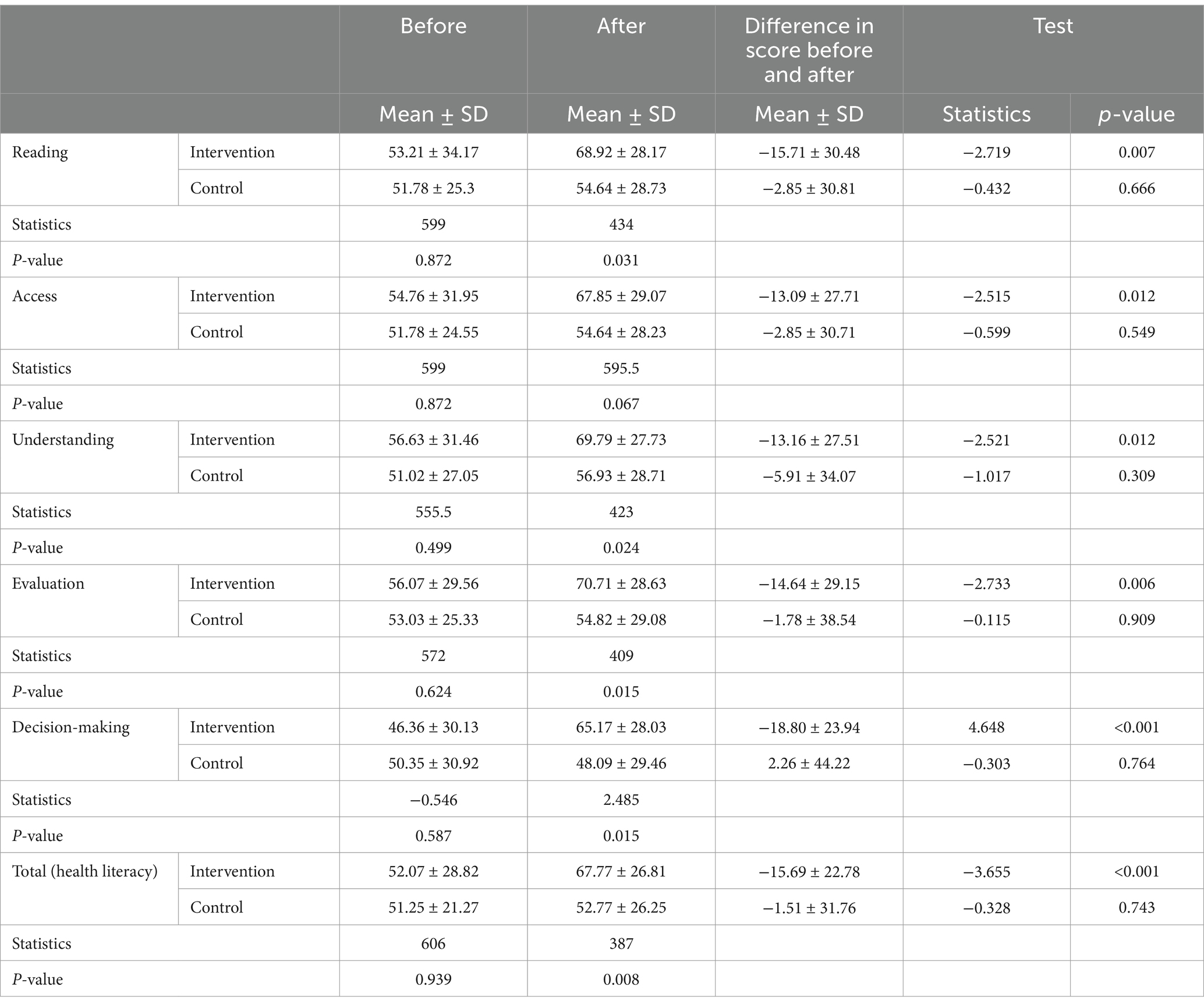
Table 2. Comparison of the mean and standard deviation of health literacy in two groups before and after the intervention.
The results revealed that the changes in the mean scores for reading, access, understanding, evaluation, decision-making, and total health literacy in the intervention group were statistically significant and showed an increase (p < 0.05) (Table 2).
According to the results, there was no statistically significant difference in the mean scores of the self-care questionnaire (follow the diet, physical activity, treatment, control, and prevention of complications) between the control and intervention groups before the intervention (p > 0.05). However, after the intervention, the scores for control and prevention of complications differed significantly between the groups, with the intervention group showing higher scores than the control group (p < 0.05). The average scores for the other dimensions did not show statistically significant differences after the intervention (p > 0.05) (Table 3).
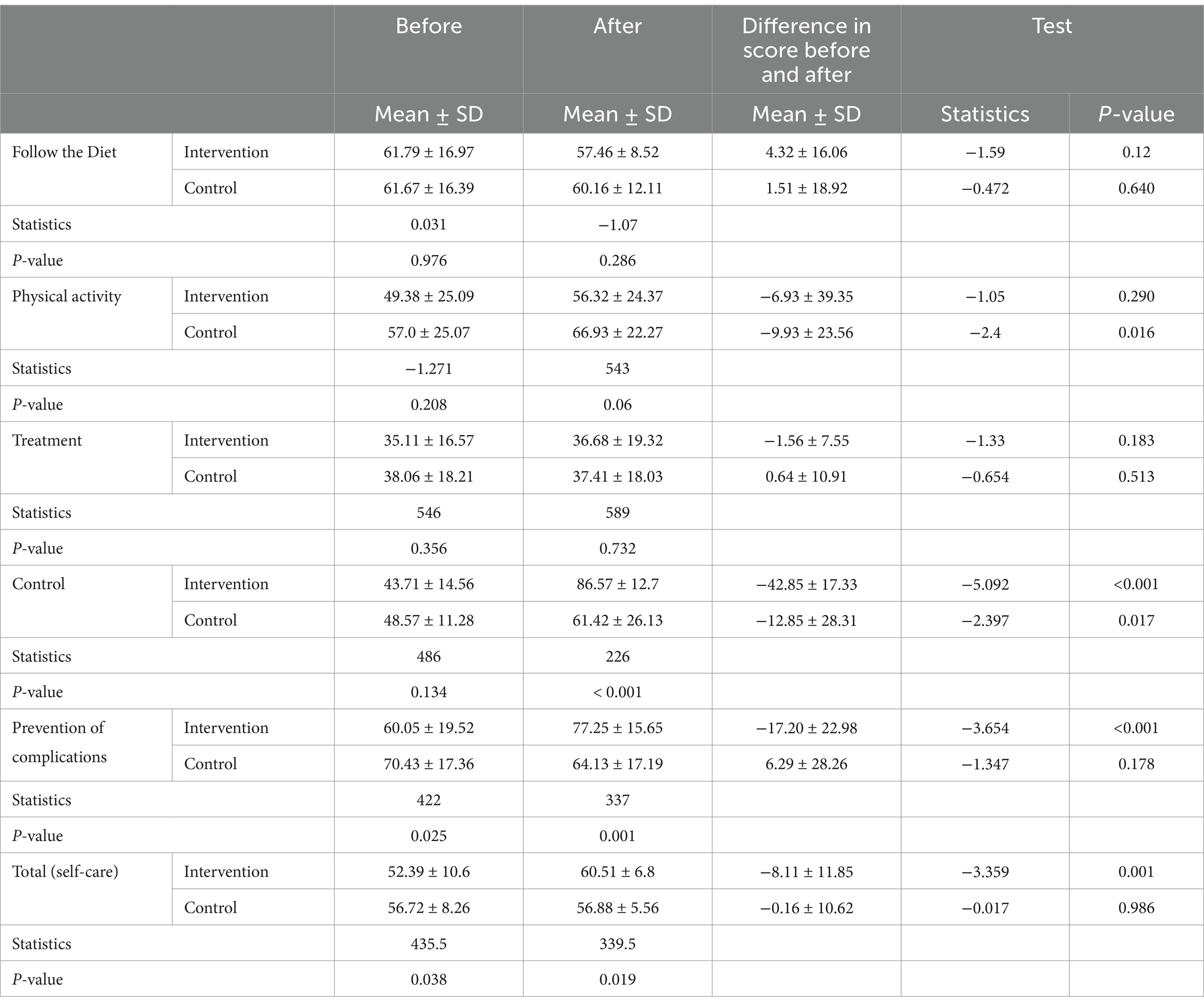
Table 3. Comparison of the mean and standard deviation of self-care in two groups before and after the intervention.
The results indicated that the changes in the average scores for control and prevention of complications in the intervention group were statistically significant and increased (p < 0.05). However, in the control group, the changes in the overall self-care score dimensions were not significant (p > 0.05) (Table 3).
The results showed a significant difference in the mean total score of the self-care questionnaire between the two groups (p < 0.05). To control for confounding variables, analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) was conducted on the baseline self-care total score, revealing a significant difference in the mean self-care total score after the intervention between the two groups, with higher scores observed in the intervention group (p < 0.05). Additionally, the changes in the total self-care score in the intervention group were both statistically significant and increasing (p < 0.05) (Table 3).
The indicated no statistically significant difference in the mean HbA1c levels before and after the intervention between the groups (p > 0.05). However, the Wilcoxon test results showed that the mean HbA1c levels in the intervention group statistically significantly (p < 0.05). This difference was not statistically significant in the control group (Table 4).
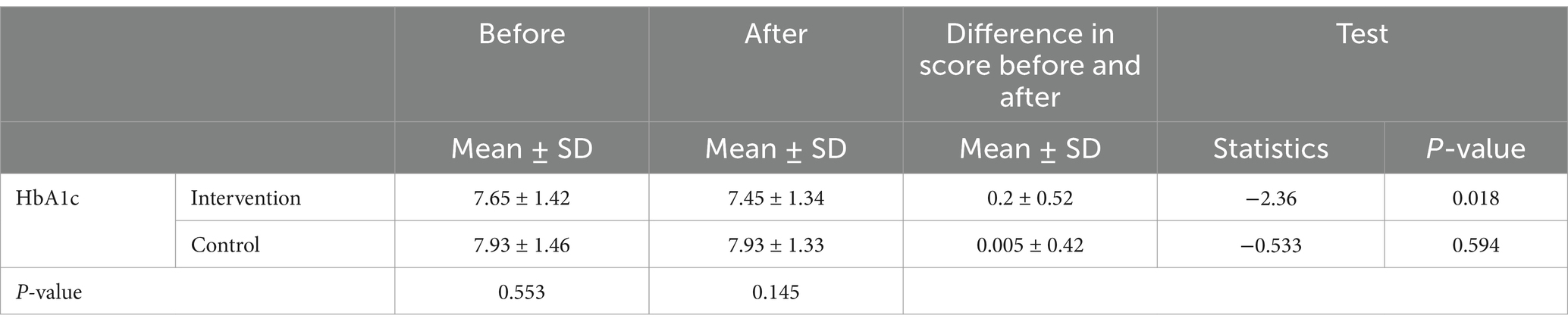
Table 4. Comparison of the mean and standard deviation of HbA1c in two groups before and after intervention.
The results of the correlation analysis indicated that changes in the scores of self-care dimensions did not have a statistically significant relationship with changes in the scores of health literacy dimensions in either group (p > 0.05) (Table 5).
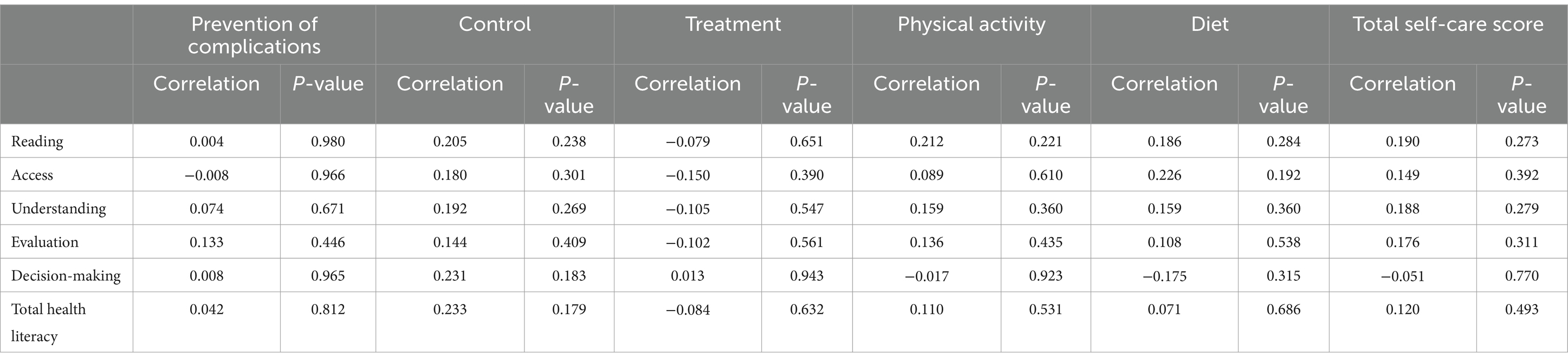
Table 5. Relationship between changes in health literacy level scores and changes in self-care scores in the intervention group.
Discussion
This study aimed to investigate the impact of social media-based education on self-care, health literacy, and glycated hemoglobin levels in individuals with type 2 diabetes. The findings of this study demonstrated that education through social networks effectively enhances health literacy among diabetic patients.
Initially, no statistically significant difference was found in health literacy scores between the intervention and control groups. However, after receiving the education, the intervention group showed significant improvements in reading, understanding, evaluation, decision-making, behavior, and overall health literacy scores. In contrast, the control group did not exhibit such improvements. These findings are consistent with previous studies highlighting the potential of online interventions in enhancing health literacy among individuals with chronic diseases (23, 24).
Health literacy refers to the knowledge and skills necessary to make informed health decisions. It plays a crucial role in managing chronic diseases such as diabetes. Low health literacy is associated with poorer adherence to treatment, worsening medical conditions, increased hospitalization, and higher healthcare costs (25). A meta-analysis has shown that health literacy has a small but significant effect on glycemic management in patients (26). It is important to note that effective self-care in patients is closely linked to adequate health literacy (25).
Our study findings emphasize the effectiveness of virtual education through the Telegram messaging app in improving patients’ health literacy. A cross-sectional study by Moulaei et al. (13) demonstrated that Iranian users obtain more information about their health conditions through social media platforms such as WhatsApp, Telegram, and Instagram. Based on these findings, it is recommended to incorporate social media-based education into routine care programs for individuals with T2D.
Our study findings demonstrated that the mean total score of the self-care questionnaire in the intervention group was significantly higher than that in the control group. These findings are supported by previous studies. Biglar Chopoghlo et al. (17) also showed that self-care education on social media platforms is associated with increased self-efficacy scores in Iranian adolescent girls with type 1 diabetes. Similarly, Alanzi et al. (20) found that using the WhatsApp social network led to a significant increase in knowledge and self-efficacy among T2D patients in the intervention group compared to the control group. Tang et al. (23) reported in a cross-sectional study that the use of innovative technologies, such as mobile phones and multimedia tools, is effective in improving self-care activities in individuals with T2D. These results indicate that social networks should be considered a valuable tool for education due to their benefits, such as accessibility, ease of use, access to up-to-date health information, cost reduction, and the possibility of online interactions in educational programs (13).
In our study, although the overall score of the self-care questionnaire after the intervention was significantly higher in the social media education group compared to the control group, the scores of some self-care dimensions, including physical activity and treatment, in the control group also showed significant improvement after the study, compared to the beginning of the study.
This finding may be attributed to the self-care methods or education received through physicians and other communication channels in the control group. Additionally, this result highlights the complexity of the relationship between health literacy and self-care in diabetic patients. Further research is needed to clarify the influential factors and potential confounding variables in self-care among T2D patients. Existing evidence also supports this finding. For example, Hosseinzadeh et al. (16) demonstrated in their study that both virtual and face-to-face education led to increased self-care in pregnant women with gestational diabetes, compared to the control group. However, no significant difference was found between the two intervention groups.
Aligholipour et al. (19) in a similar study conducted in Iran, demonstrated that although both social network-based and face-to-face education led to increased scores in patients’ self-care activities, no significant difference in outcomes was found between the two intervention groups. Despite the potential effectiveness of education through modern technologies, such as mobile phones, being comparable to face-to-face education (16), researchers emphasize that the interpersonal relationship between the nurse and the patient is a fundamental principle of nursing care. Therefore, virtual education should not entirely replace face-to-face education (19). On the other hand, using virtual networks presents risks, such as exposure to incorrect information, misinterpretation of medical results, and distractions caused by advertisements on these platforms (13).
The findings of the present study indicate that changes in self-care dimension scores do not have a statistically significant relationship with changes in health literacy scores, which contradicts the findings of İlhan et al. (25). Maleki Chollou et al. (27) also demonstrated in their study that there is a positive and almost direct relationship between health literacy dimensions and self-care behaviors in T2D patients across all dimensions. In contrast with our findings, Eyüboğlu and Schulz (28) found no association between health literacy and self-care behaviors in diabetes patients. This discrepancy may be attributed to differences in the implementation methods of educational interventions, measurement tools, and target groups. Some existing evidence also links patients’ demographic characteristics to their self-care activities (23). Education remains an integral part of the care of patients with T2D (29).
İlhan et al. (25) demonstrated in their study that individuals with low health literacy have difficulties in self-care, understanding health information, and adhering to treatment. Therefore, early identification of knowledge deficiencies regarding self-care can lead to better treatment adherence and delay in the onset of complications (29). Social networks allow individuals to utilize educational resources with lower cost and without time and location constraints, while expanding their social interactions (17). RobatSarpooshi et al. (5) also reported an average level of self-care scores in Iranian patients in a study aimed at investigating the relationship between health literacy and self-care behaviors. Furthermore, the results of this study showed that increasing levels of education and awareness among patients were associated with increased adherence to self-care behaviors. The findings of these studies indicate that developing an educational program, especially a self-care program, can be effective in enhancing patient self-efficacy.
To our surprise, we did not find any statistically significant relationship between changes in self-care behaviors and changes in HbA1C levels in the intervention group. This finding contradicts some previous studies that reported a positive correlation between improved self-care behaviors and HbA1C levels (25). Nevertheless, the results of some studies support our findings. Lee et al. demonstrated in a study that assessed the effectiveness of self-care education using a mobile phone program in T2D patients that changes in HbA1c levels between the control and intervention groups at week 26 were not significant (30). Contradictory results regarding the impact of self-care behaviors observed in different countries may be influenced by socio-economic and cultural differences among these countries and the variable levels of self-care status in individuals with diabetes. Additionally, differences in follow-up periods and duration of interventions are other potential reasons for this discrepancy. In our study, although a significant difference in the mean HbA1c levels between the intervention and control groups was not observed, HbA1c levels decreased after the intervention. Some studies have reported significant improvements in blood glucose control in diabetic patients with online interventions, while others have reported limited or no effect (19). Possible reasons for this difference in reported results may include the variability in follow-up durations and different laboratory methods for measuring patients’ blood glucose levels.
One of the strengths of this study is its examination of the impact of social media-based education on health literacy and self-care in individuals with T2D. However, there are several limitations to this study. First, self-care is a complex construct that may be influenced by various confounding factors. For instance, diabetic patients have access to multiple sources of disease-related education, which could potentially affect the study outcomes. Additionally, the relatively short duration of the follow-up and the intervention represents another limitation. Therefore, it is recommended that future research investigate the long-term effects of virtual education on glycemic control and the prevention of diabetes-related complications, with extended follow-up periods. Also, some variables such as personal motivation, family support have an effect on patient self-care that were not measured in this study. Therefore, it is recommended that studies be conducted with the exclusion of these confounding factors.
Conclusion
The results of this study have shown that social networks, such as Telegram, can effectively provide self-care education to a large number of participants, offering broader and more accessible education compared to individual, in-person methods. Given the limited number of healthcare providers in developing countries, this approach is cost-effective, as it does not impose a significant financial burden when compared to other traditional teaching methods. Additionally, considering the varied work schedules and personal commitments of participants, this platform eliminates the time constraints typically associated with in-person education.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
This study has been approved by the Ethics Committee of Arak University of Medical Sciences. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
AS: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. NN: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. AA: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. FM: Conceptualization, Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. FR: Formal analysis, Software, Validation, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Vice-Chancellor of Research Department of Arak University of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
T2D, Type 2 Diabetes; HbA1C, glycosylated hemoglobin.
References
1. Mehrabi, F, Safdari, A, Moslemi, A, Salehi, M, Agharazi, A, and Rezvanfar, MR. Efficacy of Ma'aljobon Aftimouni (Cuscuta Reflexa and whey) on HbA1c and blood glucose levels in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized triple-blind clinical trial. Contemp Clin Trials Commun. (2025) 43:101401. doi: 10.1016/j.conctc.2024.101401
2. Mohammadi, H, Valiee, S, Nouri, B, Fallahi, A, and Zehni, K. The effect of self-care education through social networks on the patients¡¯ quality of life with type 1 diabetes in Sanandaj City, Iran. Creative. Education. (2018) 9:322–32. doi: 10.4236/ce.2018.92022
3. Ausili, D, Barbaranelli, C, Rossi, E, Rebora, P, Fabrizi, D, Coghi, C, et al. Development and psychometric testing of a theory-based tool to measure self-care in diabetes patients: the self-Care of Diabetes Inventory. BMC Endocr Disord. (2017) 17:66. doi: 10.1186/s12902-017-0218-y
4. Jannoo, Z, and Mamode, KN. Medication adherence and diabetes self-care activities among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Value Health Reg Issues. (2019) 18:30–5. doi: 10.1016/j.vhri.2018.06.003
5. RobatSarpooshi, D, Mahdizadeh, M, Alizadeh Siuki, H, Haddadi, M, Robatsarpooshi, H, and Peyman, N. The relationship between health literacy level and self-care behaviors in patients with diabetes. Patient Relat Outcome Meas. (2020) 11:129–35. doi: 10.2147/PROM.S243678
6. Bukhsh, A, Goh, B-H, Zimbudzi, E, Lo, C, Zoungas, S, Chan, K-G, et al. Type 2 diabetes Patients' perspectives, experiences, and barriers toward diabetes-related self-care: a qualitative study from Pakistan. Front Endocrinol. (2020) 11:4873. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.534873
7. Shrivastava, SR, Shrivastava, PS, and Ramasamy, J. Role of self-care in management of diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Metab Disord. (2013) 12:14. doi: 10.1186/2251-6581-12-14
8. Elnaggar, A, Ta Park, V, Lee, SJ, Bender, M, Siegmund, LA, and Park, LG. Patients' use of social Media for Diabetes Self-Care: systematic review. J Med Internet Res. (2020) 22:e14209. doi: 10.2196/14209
9. Aminuddin, HB, Jiao, N, Jiang, Y, Hong, J, and Wang, W. Effectiveness of smartphone-based self-management interventions on self-efficacy, self-care activities, health-related quality of life and clinical outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Nurs Stud. (2021) 116:103286. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2019.02.003
10. Karimy, M, Koohestani, HR, and Araban, M. The association between attitude, self-efficacy, and social support and adherence to diabetes self-care behavior. Diabetol Metab Syndr. (2018) 10:86. doi: 10.1186/s13098-018-0386-6
11. Dehvan, F, Qasim Nasif, F, Dalvand, S, Ausili, D, Hasanpour Dehkordi, A, and Ghanei, GR. Self-care in Iranian patients with diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Prim Care Diabetes. (2021) 15:80–7. doi: 10.1016/j.pcd.2020.08.013
12. Robat Sarpooshi, D, Taghipour, A, Mahdizadeh, M, and Peyman, N. Enablers of and barriers to effective diabetes self-Care in Iran: a qualitative study. Patient Rel Outcome Meas. (2020) 11:109–18. doi: 10.2147/PROM.S241170
13. Moulaei, K, Dinari, Z, Dinari, F, Jahani, Y, and Bahaadinbeigy, K. The role of social networks in diabetes self-care: a cross-sectional study. Health Sci Rep. (2022) 5:e601. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.601
14. Popoviciu, MS, Marin, VN, Vesa, CM, Stefan, SD, Stoica, RA, Serafinceanu, C, et al. Correlations between diabetes mellitus self-care activities and Glycaemic control in the adult population: a cross-sectional study. Healthcare. (2022) 10:174. doi: 10.3390/healthcare10010174
15. Surkan, PJ, Mezzanotte, KS, Sena, LM, Chang, LW, Gittelsohn, J, Trolle Lagerros, Y, et al. Community-driven priorities in smartphone application development: leveraging social networks to self-manage type 2 diabetes in a low-income African American neighborhood. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2019) 16:2715. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16152715
16. Hosseinzadeh, M, Sharifzadeh, G, Hosseinzadeh, M, and Torshizi, M. Comparison of the effect of face-to-face and social media-based training on the self-care of women with gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) in Birjand. Mod Care J. (2022) 19:9456. doi: 10.5812/modernc-119456
17. Biglar Chopoghlo, S, Hosseinkhani, A, Khedmat, L, Zaki-Nejad, M, and Puryaghoob, M. The self-efficacy improvement in adolescent girls with type 1 diabetes mellitus with self-care education through mobile-based social networking. Int J Diabetes Dev Ctries. (2021) 41:676–82. doi: 10.1007/s13410-021-00929-5
18. Letta, S, Aga, F, Yadeta, TA, Geda, B, and Dessie, Y. Barriers to diabetes patients’ self-care practices in eastern Ethiopia: a qualitative study from the health care providers perspective. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. (2021) 14:4335–49. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S335731
19. Aligholipour, M, Feizollahzadeh, H, Ghaffari, M, and Jabbarzadeh, F. Comparison of in-person and MMS -based education in telegram on self-care and fasting blood sugar of patients with diabetes mellitus: a randomized clinical trials. J Caring Sci. (2019) 8:157–64. doi: 10.15171/jcs.2019.023
20. Alanzi, T, Bah, S, Alzahrani, S, Alshammari, S, and Almunsef, F. Evaluation of a mobile social networking application for improving diabetes type 2 knowledge: an intervention study using WhatsApp. J Comp Eff Res. (2018) 7:891–9. doi: 10.2217/cer-2018-0028
21. Montazeri, A, Tavousi, M, Rakhshani, F, Azin Seyed, A, Jahangiri, K, Ebadi, M, et al. Health literacy for Iranian adults (HELIA): development and psychometric properties. Payesh. (2014) 13:589–99.
22. Chahardah-Cherik, SM, Gheibizadeh, MP, Jahani, SP, and Cheraghian, BP. The relationship between health literacy and health promoting behaviors in patients with type 2 diabetes. Int J Community Based Nurs Midwifery. (2018) 6:65–75.
23. Tang, J, Wu, T, Hu, X, and Gao, L. Self-care activities among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a cross-sectional study. Int J Nurs Pract. (2021) 27:e12987. doi: 10.1111/ijn.12987
24. Sentell, TL, Agner, JL, Davis, J, Mannem, S, Seto, TB, Valente, TW, et al. Social networks in patients hospitalized with preventable conditions for heart disease and diabetes in Hawai‘i by health literacy. Chronic Illn. (2022) 18:517–31. doi: 10.1177/1742395320987892
25. İlhan, N, Telli, S, Temel, B, and Aştı, T. Health literacy and diabetes self-care in individuals with type 2 diabetes in Turkey. Prim Care Diabetes. (2021) 15:74–9. doi: 10.1016/j.pcd.2020.06.009
26. Marciano, L, Camerini, A-L, and Schulz, PJ. The role of health literacy in diabetes knowledge, self-care, and glycemic control: a Meta-analysis. J Gen Intern Med. (2019) 34:1007–17. doi: 10.1007/s11606-019-04832-y
27. Maleki Chollou, K, Gaffari-Fam, S, Babazadeh, T, Daemi, A, Bahadori, A, and Heidari, S. The Association of Health Literacy Level with self-care behaviors and glycemic control in a low education population with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a cross-sectional study in Iran. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. (2020) 13:1685–93. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S253607
28. Eyüboğlu, E, and Schulz, PJ. Do health literacy and patient empowerment affect self-care behaviour? A survey study among Turkish patients with diabetes. BMJ Open. (2016) 6:e010186. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2015-010186
29. Krzemińska, S, Lomper, K, Chudiak, A, Ausili, D, and Uchmanowicz, I. The association of the level of self-care on adherence to treatment in patients diagnosed with type 2 diabetes. Acta Diabetol. (2021) 58:437–45. doi: 10.1007/s00592-020-01628-z
Keywords: HbA1c, self-care, health literacy, type 2 diabetes, social networks, Iran
Citation: Safdari A, Nejat N, Abolfathi A, Mehrabi F and Rafiei F (2025) Effect of social media-based education on self-care status, health literacy, and glycated hemoglobin in patients with type 2 diabetes. Front. Public Health. 13:1507726. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1507726
Edited by:
Natalia Świątoniowska-Lonc, 4th Military Hospital of Wroclaw, PolandReviewed by:
Abril Violeta Muñoz Torres, National Autonomous University of Mexico, MexicoHarish Rangareddy, Haveri Institute of Medical Sciences, India
Usha Rani, Manipal Academy of Higher Education, India
Copyright © 2025 Safdari, Nejat, Abolfathi, Mehrabi and Rafiei. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Fatemeh Mehrabi, Zm1laHJhYmkxMzkyQGdtYWlsLmNvbQ==
 Ali Safdari
Ali Safdari Nazi Nejat2
Nazi Nejat2 Fatemeh Mehrabi
Fatemeh Mehrabi