- 1Intelligent Data Mining Laboratory, Department of Medical Research, Taichung Veterans General Hospital, Taichung, Taiwan
- 2Institute of Environmental and Occupational Health Sciences, School of Medicine, National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University, Taipei, Taiwan
- 3Department of Medicinal and Applied Chemistry, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung City, Taiwan
- 4Research Center for Precision Environmental Medicine, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung City, Taiwan
- 5School of Public Health, National Defense Medical Center, Taipei, Taiwan
- 6Department of Chemistry, Tunghai University, Taichung, Taiwan
- 7National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, National Health Research Institutes, Miaoli, Taiwan
- 8Department of Medical Research, China Medical University Hospital, China Medical University, Taichung, Taiwan
- 9Department of Safety, Health and Environmental Engineering, National United University, Miaoli, Taiwan
Background: It is uncertain if exposure to BPA and its substitutes has an impact on renal function, including N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase (NAG), which is an early marker for kidney injury. We aimed to (1) Estimate the daily intakes (DIs) of BPA and its substitutes using individual urinary levels and conduct the cumulative risk assessment of bisphenols. (2) Assessed the association between exposure to BPA and its substitutes with various renal function indices using a dose-based and cumulative risk assessment approach.
Methods: We recruited 366 participants, and three bisphenols (BPA, bisphenol F, and bisphenol S) were analyzed through ultraperformance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. DI levels were calculated for each bisphenol. Hazard index (HI) values were calculated for determining cumulative risk. Using the renal function index, we measured the serum and urinary level (e.g., microalbumin, NAG). The NAG/Creatinine ratio (> 4 IU/g creatinine) and other renal functions indexes based on clinical cut-off points to defined abnormality.
Results: After adjustment for covariates, increased NAG/Creatinine ratios were associated with higher DIs of BPA, showing a dose-response trend (Adjusted Odds Ratio [AOR] tertile2: 3.58, 95% CI = 1.52–8.44; AOR tertile3: 7.34, 95% CI = 2.26–23.81; Ptrend < 0.001). Notably, the HI of bisphenols was positively associated with NAG/Creatinine in adults (AOR tertile2= 2.18, 95% CI = 1.10–4.34; AOR tertile3= 4.27, 95% CI = 2.14–8.51) after adjusted for covariates.
Conclusion: We found a sensitive risk factor for abnormal NAG/creatinine levels after exposure to BPA and its substitute. Further mechanistic studies are needed to clarify these associations.
1 Introduction
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a significant global health issue contributing to increased morbidity (1). Bisphenol A (BPA), an endocrine-disrupting chemical widely used in polycarbonate plastics and epoxy resins (2), applied in products such as thermal paper, toys, tableware, medical devices, polycarbonate bottles, food packaging, and cosmetic and personal care products (PCPs) (54). Notably, BPA concentrations in Taiwanese adults were nearly six times higher than in other countries, with levels of 7.96 μg/L in Taiwan, compared to 1.24 μg/L in the USA and 1.49 μg/L in Korea (3). BPA plays a crucial role in CKD progression as it is eliminated through the kidneys (4, 5).
Exposure to BPA triggers inflammation, leading to kidney injury, glomerular damage, tubular cell harm, and fibrosis. These nephrotoxicants enter cells via endocytosis, causing lipid peroxidation, mitochondrial dysfunction, DNA damage, and increased reactive oxygen species. This results in mutations, impaired cellular proliferation, and protein alterations, ultimately leading to renal damage (55). BPA adversely affects albumin-to-creatinine ratio (ACR) and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) (6), as confirmed by meta-analyses (6, 7). Despite restrictions on BPA use in many countries, substitutes like bisphenol F (BPF) and bisphenol S (BPS) have emerged, raising concerns due to their structural similarity and widespread application (8). Studies indicate BPS and BPF may pose toxicity risks comparable to or greater than BPA (9, 10), yet research on their impact on renal function remains limited (11, 12). Understanding the relationship between these substitutes and renal function is crucial.
Most human population studies have focused on the ACR (13) or on estimating functional parameters (e.g., eGFR) as outcomes of kidney diseases (7). However, the results for eGFR vary depending on the equations applied [e.g., Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration [CKD-EPI] and Modification of Diet in Renal Disease [MDRD-4] equations (11)]. Although urinary N-acetyl-β-glucosaminidase (NAG) is crucial for estimating tubular injury (14, 15) and it has been identified as a sensitive determinant of CKD (16) and type 2 diabetes mellitus [DM (17)], whether exposure to BPA and its substitutes is associated urinary NAG levels remains unclear.
Given the limited literature on how exposure to BPA and its substitutes affects various renal indices in the general population, the present study aim to estimate the daily intakes of BPA and its substitutes using individual urinary levels and conduct the cumulative risk assessment of bisphenols. Using a cumulative risk assessment approach to assess the association between exposure to BPA and its substitutes with various renal function indices (e.g., ACR, eGFR, and NAG).
2 Methods
2.1 Study population
Participants were recruited from the Taiwan Environmental Survey for Toxicants 2013 (18–22) in the present cross-sectional study. The final study population comprised 271 adults (≥18 years) and 95 minors (<18 years).
2.2 Analytical method for detecting bisphenol
The analytical method used in the present study is described in detail in our previous study (19, 23). After >8 h of fasting, spot urine samples were also collected from the participants in the early morning during their visit. These samples were temporarily stored in polypropylene containers and subsequently transferred to amber glass bottles (prewashed with acetonitrile) and stored at −80°C until analysis.
2.3 DI estimation and cumulative risk assessment of BPA and its substitutes
The DI and cumulative risk assessment for BPA and its substitutes utilized methodologies detailed in our previous publications (3) (Specific calculation formulas are provided in the Supplementary Table S1).
2.4 Measurement of renal function and other parameters in serum and urine
We assessed various parameters related to renal function, including those obtained from urine and serum samples. The serum levels of blood creatinine, blood uric acid, and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) were determined. Additionally, concentrations of creatinine, microalbumin, protein, NAG, and uric acid in urine samples were measured. Upon collection in the morning, each participant’s blood and urine samples underwent centrifugation for 20 min at 4°C and were then stored at −80°C until analysis. All analyses were conducted in a blinded and randomized manner by a technician from a laboratory accredited by the Taiwan Accreditation Foundation (No. 1673) (18).
The ACR was determined by dividing the microalbumin level by the urinary creatinine concentration. The NAG-to-creatinine ratio (NAG/creatinine) was calculated by dividing the urine NAG level by the urinary creatinine concentration. eGFR was calculated using CKD-MDRD equation (24, 25) and the CKD-EPI equation (25, 26). Estimated creatinine clearance rate (CCr) was calculated using the Cockcroft–Gault formula (Supplementary Information: The formula of related renal functions, Supplementary Table S1).
Based on the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (27), participants with fasting plasma glucose levels above 126 mg/dL were considered to have type 2 DM. According to the CKD Guideline (28) and the recommended clinical cut-off points for microalbumin (1.9 mg/dL), urine protein (14 mg/dL), ACR (30 mg/g creatinine), BUN (20 mg/dL), NAG/creatinine (4 IU/g creatinine) (29), and eGFR (90 mL/min/1.73 m2). Participants were also stratified into normal or abnormal groups indicative of early renal impairment (30).
2.5 Statistical analysis
BPA levels and renal function indicators were compared across different age groups using Mann–Whitney U or Kruskal-Wallis tests. The natural logarithms for urinary bisphenol levels and renal function indices were used to ensure that the normality assumption was met. The detectable rate was determined by dividing the number of urine samples in which the bisphenol level exceeded the detection limit by the total number of urine samples analyzed. The summary metric for BPs (ΣBPs) was calculated by summing the molar concentrations of the measured BPs (31). All bisphenols measurements, including the molar sum, were divided by urinary creatinine to adjust for urine dilution.
Urinary bisphenol levels, including DI, were categorized into tertiles (0–2), and p-trend tests were conducted to assess dose–response relationships with renal function indices. Covariates were selected on the basis of literature findings, their data availability, and their statistical significance in our models. After adjustment, we used multiple linear regressions and logistic regression models to investigate the associations between bisphenol levels and renal function indices in various models. All statistical analyses were performed using SAS (version 9.4; SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA). A p value of <0.05 was regarded as significant.
Additionally, through the use of the mgcv R-package, log-transformed parameters were incorporated into generalized additive model (GAM)-penalized regression splines to determine the nonlinear associations with the risk pertaining to renal function indices. The optimal number of knots and the smoothing parameter were selected efficiently by conducting generalized cross-validation (32).
3 Results
3.1 Population characteristics
Table 1 summarizes the general and sociodemographic characteristics of the participants. The distribution of sexes was relatively even, with 128 men (47.2%) and 143 women (52.8%) in the adult group, and 55 boys (57.9%) and 40 girls (42.1%) in the minor group. Analysis revealed that males had a significantly higher frequency of abnormalities in urine protein levels (>14 mg/dL) and eGFR (<90 mL/min/1.73 m2) compared to females (urine protein: 11.7% vs. 2.1%, p = 0.002; eGFR: 50.0% vs. 37.1%, p = 0.035). Conversely, abnormalities in NAG/creatinine were more prevalent in females than males (44.4% vs. 35.4%). In contrast, abnormalities in renal function indices among minors were extremely rare (e.g., abnormal eGFR: 0%), and no significant sex differences were observed. Therefore, the investigation into the association between urinary bisphenol levels and renal function indices was limited to adults (Supplementary Table S2).
3.2 Distribution of urinary bisphenol levels and renal function index
The detection rate for BPA and its substitutes was 100% in all urine samples. Notably, the median levels for BPA and its substitutes were significantly higher in the adults than in the minors (BPA, 9.45 vs. 4.08 μg/g creatinine; BPF, 9.63 vs. 6.63 μg/g creatinine; BPS, 2.43 vs. 1.67 μg/g creatinine; ΣBPs, 0.10 vs. 0.06 nmol/g creatinine; all p < 0.001). We also performed comprehensive estimations of DI levels for BPA, BPF, and BPS. In the adults, the median DI level was 2.29 ng/kg/day for BPA, 2.35 ng/kg/day for BPF, and 0.58 ng/kg/day for BPS. These levels were significantly higher than those in the minors (p < 0.001), with median DI levels of 0.60 ng/kg/day for BPA, 0.77 ng/kg/day for BPF, and 0.24 ng/mL for BPS. Furthermore, the median HI values for BPA and its substitutes were significantly higher in the adults than in the minors (1.29 × 10−3 vs. 4.1× 10−4, p < 0.001; Table 2).
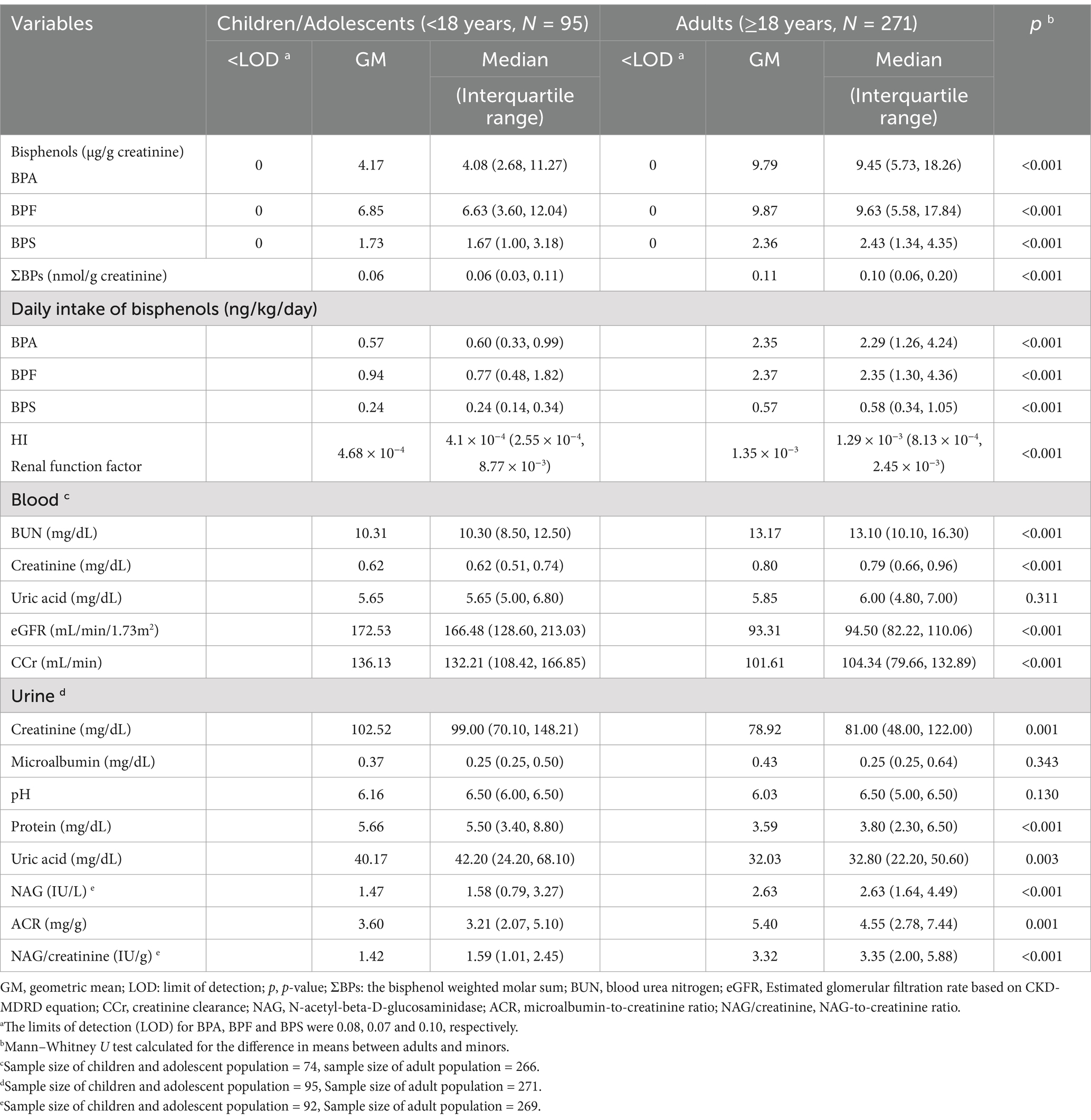
Table 2. Median and geometric mean levels of bisphenols and renal function index among Taiwanese adults and children/adolescents.
Relative to the minors, the adults exhibited significantly higher median levels of blood BUN (13.10 vs. 10.30 mg/dL), blood creatinine (0.79 vs. 0.62 mg/dL), urine NAG (2.63 vs. 1.58 IU/L), ACR (4.55 vs. 3.21 mg/g), and NAG/creatinine (3.35 vs. 1.59 IU/g). By contrast, the median levels of urine creatinine (81 vs. 99 mg/dL), urine protein (3.8 vs. 5.5 mg/dL), uric acid (32.8 vs. 42.2 mg/dL), eGFR (94.50 vs. 166.48 mL/min/1.73 m2), and CCr (104.34 vs. 132.21 mL/min) were significantly lower in the adults than in the minors (Table 2).
3.3 Association between bisphenol levels and renal function index
The DI levels for BPA and its substitutes were significantly and positively associated with the ACR and NAG/creatinine levels (ACR, [BPA, r = 0.25; BPF, r = 0.26; BPS, r = 0.26]; NAG/creatinine, [BPA, r = 0.42; BPF, r = 0.38; BPS, r = 0.35]; all p < 0.05). Additionally, the DI levels for BPA and its substitutes were significantly and negatively associated with urine protein levels and eGFR (urine protein, [BPA, r = −0.39; BPF, r = −0.42; BPS, r = −0.42]; eGFR, [BPA, r = −0.33; BPF, r = −0.20; BPS, r = −0.22]; all p < 0.05) (Supplementary Figure S1).
Supplementary Tables S3, S4 reveal that higher HI values were linked to lower urine protein (β = −0.66, p < 0.001) and NAG (β = −0.25, p < 0.001) levels, but higher ACR (β = 0.39, p < 0.001) and NAG/creatinine (β = 0.32, p < 0.001) levels. Overall, while exposure to BPA and its substitutes appears to mildly affect renal function, no association with eGFR was observed.
Higher bisphenol DI levels were associated with lower NAG levels (p-trend <0.001), but higher NAG/creatinine ratios (p-trend <0.001) among adults. Specifically, adults in the highest DI tertile exhibited notably elevated NAG/creatinine compared to those in the lowest tertile (Supplementary Tables S5, S6, Figure 1). These findings indicate that higher bisphenol exposure levels were linked to increased abnormalities in renal function indices, particularly NAG/creatinine, in adults.
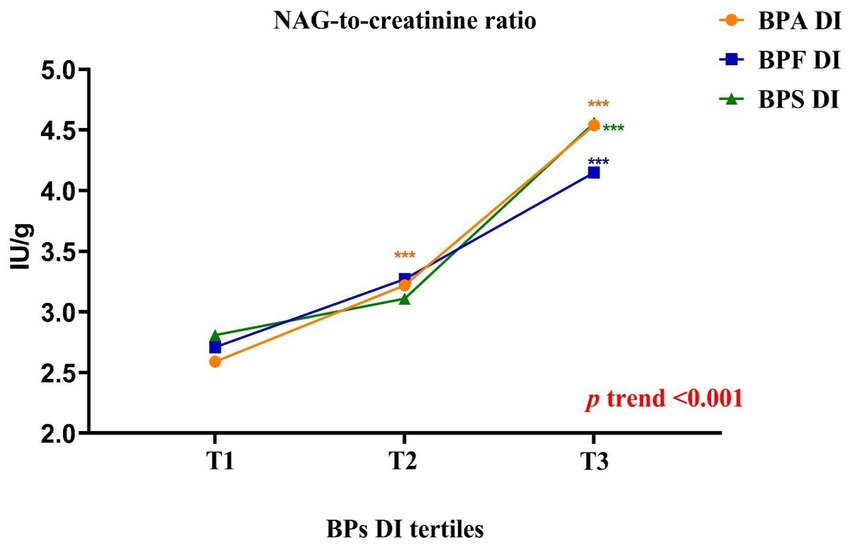
Figure 1. Schematic representation of the results obtained in the parameters related to renal function according to the daily intake of bisphenols tertiles in adults (BPA: [T1 < 1.11; T2 = 1.11–2.83; T3 > 2.83]; BPF: [T1 < 1.24; T2 = 1.24–2.80; T3 > 2.80]; BPS: [T1 < 0.41; T2 = 0.41–0.81; T3 > 0.81]). All results were expressed as median. Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn’s multiple comparisons test. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001.
After adjustments for type 2 DM, BMI age and sex, we discovered that the adjusted odds ratio (AOR) for the adults in the highest tertile (T3) of BPA DI had a 7.34 times higher risk (AOR = 7.34, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 2.26–23.81) of having abnormal NAG/creatinine compared with those in the lowest tertile. Furthermore, those in the second tertile (T2) had a 3.58 times higher risk (AOR = 3.58, 95% CI = 1.52–8.44; Table 3, Figure 2) of having abnormal NAG/creatinine compared with those in the lowest tertile. No similar trend was identified for the other renal function indices. This finding indicates that the risk of having abnormal NAG/creatinine increased by 4 to 7 times with BPA DI, with a dose–response relationship. Although, the third tertile of urinary BPS and BPS DI levels associated with abnormality urine proteins (BPS: AOR = 12.23, 95% CI = 1.61–93.16; BPS DI: AOR = 7.24, 95% CI = 1.00–52.24), however, the 95% CI was rather wide and existed uncertainty relationships, because there was so scanty data on the abnormality protein (n = 18). We also discovered that urinary BPS level in the higher tertile (tertile 2 and 3) of BPS DI had a 5.53 to 5.98 times higher risk of abnormal ACR compared with those in the lowest tertile (p < 0.05).
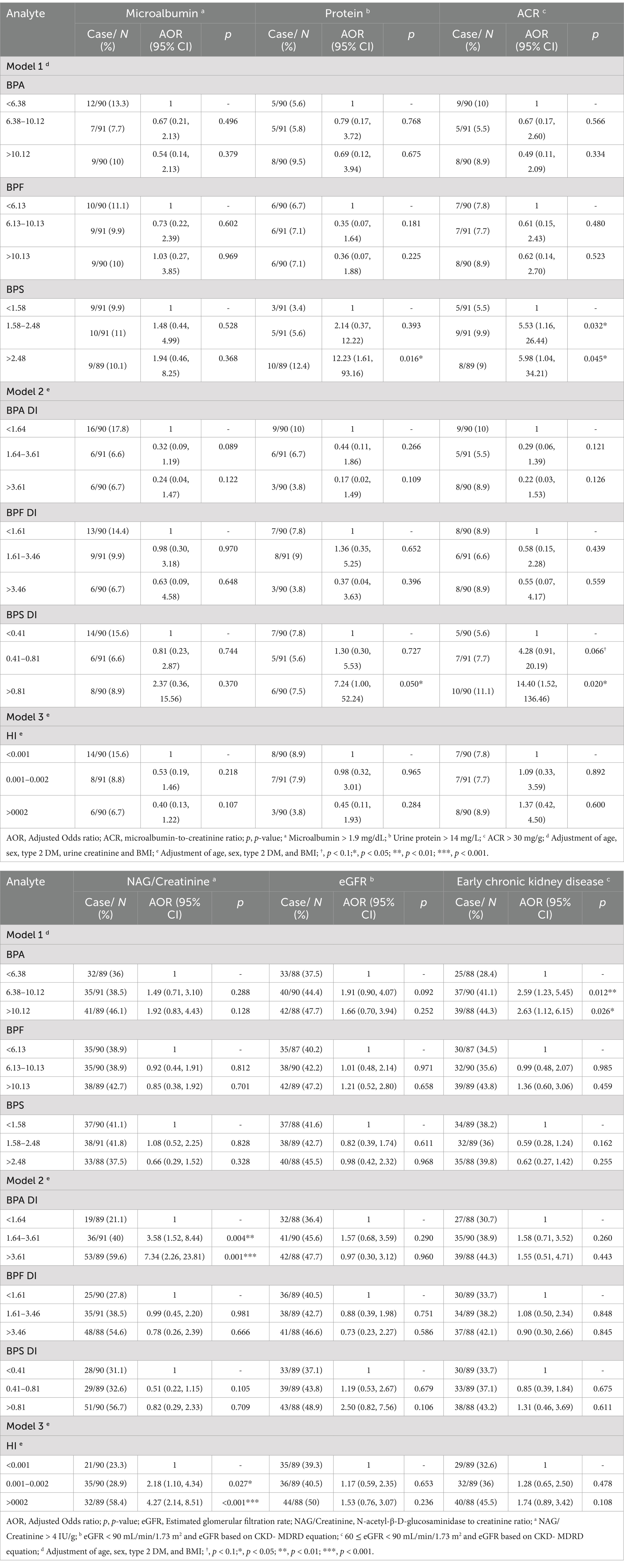
Table 3. Association between bisphenols levels and the risk of higher renal function indexes in adults (n = 271).
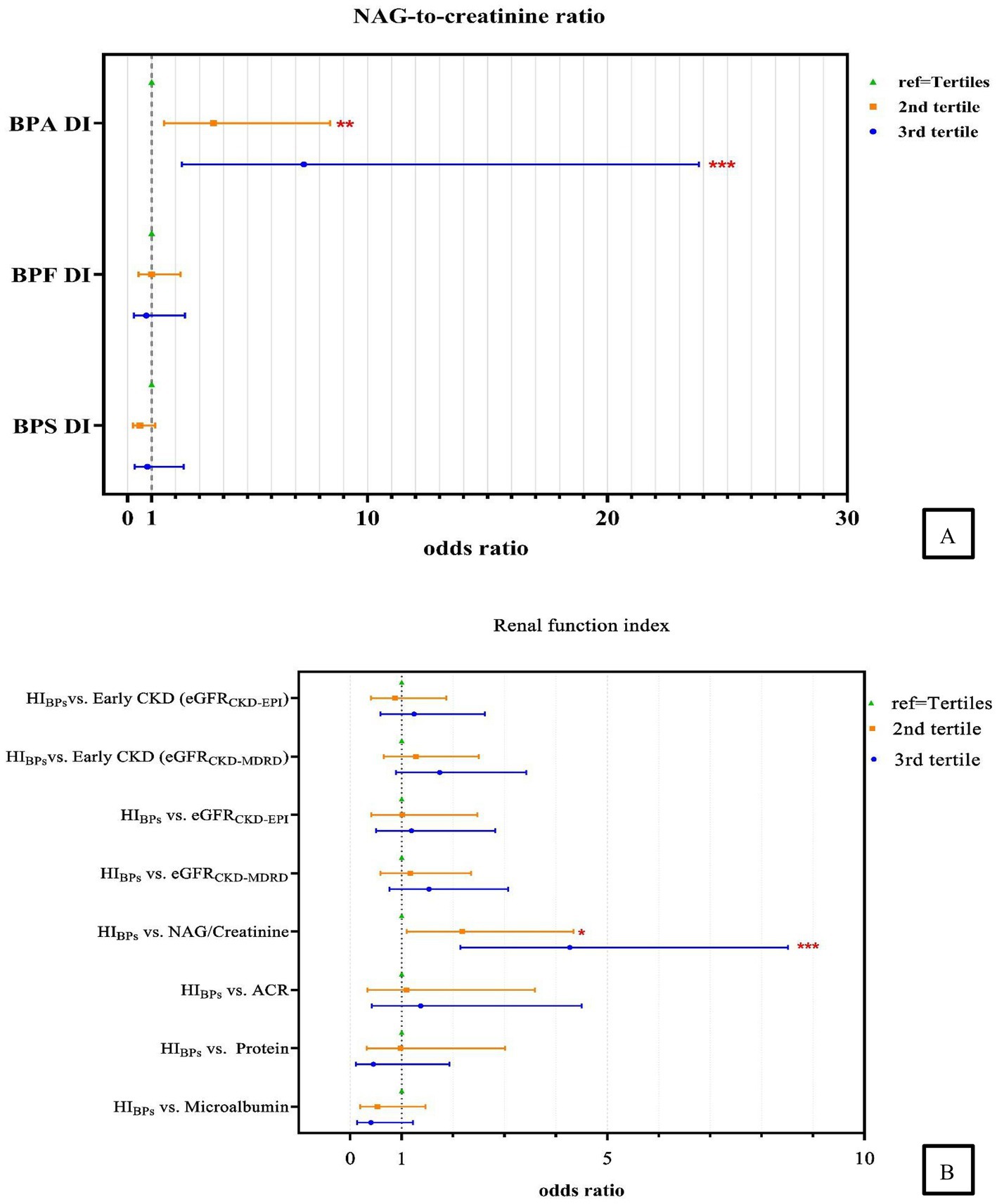
Figure 2. Association between (A) urinary measurement of daily bisphenols intake and the risk of higher NAG-to-creatinine ratio; (B) the HI and renal function indexes. Abnormality: Microalbumin>1.9 mg/dL; Urine protein >14 mg/L; Albumin-to-creatinine ratio (ACR) >30 mg/g; N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase to creatinine ratio (NAG/Creatinine) > 4 IU/g; Estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFRCKD-MDRD/EPI) < 90 mL/min/1.73 m2 and eGFR based on CKD- MDRD, CKD-EPI equation, respectively; Early Chronic Kidney Disease (Early CKDCKD-MDRD/EPI): 60 ≤ eGFR <90 mL/min/1.73 m2 and eGFR based on CKD- MDRD and CKD-EPI equation, respectively; Adjustment of age, sex, type 2 DM, and BMI. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001.
In the highest tertile of BPS DI (third tertile), the risk of having an abnormal eGFR CKD-EPI was 4.06 times higher (AOR = 4.06, 95% CI = 0.97–17.07, p < 0.1) (Supplementary Table S7); this finding was inconsistent to that obtained using the eGFRCKD-MDRD, which is based on the CKD-MDRD equation, no significant differences were observed (AOR = 2.50, 95% CI = 0.82–7.56; Table 3). Furthermore, when early CKD was defined on the basis of abnormalities in eGFR (depend on CKD-MDRD equation), we found that urinary BPA levels increased the risk of early CKD by 2.50 times (AOR = 2.50, 95% CI =1.19–5.24, 2nd tertile) and 2.55 times (AOR = 2.55, 95% CI =1.09–5.95, 3rd tertile), but no significant differences were observed depend on CKD-EPI equation (Supplementary Table S7).
We found that excluding patients with DM or adjusting for this condition did not alter the strength of association between the risks of abnormal NAG/creatinine, whereas highest cumulative HI was significantly positively associated with abnormal NAG/creatinine (models 1–3) (Supplementary Figure S2). After adjustment for covariates, the AOR for adults in the highest tertile of HI value, compared to the lowest tertile group, showed a 4.27 times higher risk (95% CI = 2.14–8.51) of abnormal NAG/creatinine, followed by the second tertile (T2) with a 2.18 times higher risk (95% CI = 1.10–4.34), suggesting that the cumulative risk of bisphenol exposure increases the risk of renal tubular damage (Table 3, Figure 2). Our study also examined the relationship between the cumulative risk of HI calculated based on different tolerable daily intakes (TDIs) and the NAG/creatinine. The cumulative HI for bisphenols were significantly and positively associated with NAG/creatinine, especially the highest tertile of HI, the risk of having an abnormal NAG/creatinine were 3.33 to 4.27 times higher (Model 1: AOR = 4.27, 95% CI = 1.19–8.51; Model 2: AOR = 4.27, 95% CI = 2.14–8.51; Model 3: AOR = 3.33, 95% CI = 1.70–6.52) (Supplementary Table S8, Figure 3).

Figure 3. Association between the HIBPs and NAG-to-creatinine ratio. HI is the cumulative summation of HQs for each compound; Model 1: based on EFSA (46) TDI of BPA (4,000 ng/kg/ay), TDI of 4,000 (ng/kg bw /day) for BPF (56); TDI of 4,400 (ng/kg bw /day) for BPS; Model 2: based on EFSA (47) TDI of BPA (0.2 ng/kg/day) and assume the BPA TDI equal to BPF and BPS; Model 3: based on BfR (48) TDI (200 ng/kg/day) and assume the BPA TDI equal to BPF and BPS; Adjustment of age, sex, type 2 DM and BMI in all models; *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001.
The GAM model and the penalty spline method were applied to determine any significant departure from linearity in this relationship (Supplementary Figure S3). The results revealed that BPA DI and HI values were associated abnormal NAG/creatinine (Psmooth < 0.001). Furthermore, a similar trend was identified between the BPS concentration/DI and renal function indexes, i.e., abnormalities in the early CKD (depend on CKD-MDRD equation) (Psmooth < 0.05).
4 Discussion
We identified a significant dose–response relationship between increasing BPA DI and the likelihood of elevated NAG/creatinine levels in Taiwanese adults aged 18 years and older. Notably, we also discovered that HI value was significantly and positively associated with NAG/creatinine after adjustment for significant covariates.
Studies have reported inconsistent findings regarding the associations between BPA exposure and renal function. Notably, most clinical markers of renal function are based on the ACR or eGFR. An increase in the urinary BPA concentration is significantly associated with an increase in the ACR (6, 33) and a decrease in eGFR (6). By contrast, a positive association between urinary BPA levels and eGFR was reported in female adults from the general population in the United States (5) and in patients with CKD (8). A possible explanation for this association is that declining renal function increases the difficulty of eliminating BPA, resulting in BPA accumulation and a vicious cycle of BPA accumulation, especially in individuals with an eGFR of 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 (34). In the U.S. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey from 2003 to 2016, analysis of data from 12,000 adults based on BPA/creatinine quartiles showed significantly higher ACR in groups with higher urinary BPA levels compared to those with the lowest levels (7). A similar trend was revealed in the BPA substitutes and renal function; the results revealed that individuals with higher urinary BPS levels exhibited higher ACR and eGFR (11), whereas those with higher urinary BPF levels exhibited lower eGFR. These findings were similar to those of the present study; that is, urinary BPS levels are positively associated with an abnormal ACR. In contrast to the findings related to BPA, which showed a significant increase in urea nitrogen, serum creatinine, 24-h proteinuria, and the urine protein-to-creatinine ratio, as well as a significant reduction in creatinine clearance, our study revealed a different outcome. Higher BPS concentrations were associated with an increased risk of proteinuria abnormalities (7). However, few study has assessed the association between bisphenol DI and renal function. We confirmed a significant positive association between BPA exposure and the risk of having higher NAG/creatinine in adults. Furthermore, the highest BPS DI was associated with an increased risk of abnormalities in protein and eGFR by CKD-EPI equation. Due to the short half-life of bisphenols, relying solely on a single urinary marker may not adequately reflect renal function. Hence, we assessed both short-term (concentration and DI) and long-term (cumulative risk) exposures to bisphenol to comprehensively examine the relationships between bisphenol exposure and renal function indices.
Studies examining eGFR by applying various equations (e.g., CKD-EPI or MDRD-4) have obtained inconsistent results (26). Nevertheless, eGFR is a crucial basis for diagnosing CKD (28). In Taiwan, MDRD equations are used to calculate eGFR as part of efforts for the prevention and treatment of CKD (35), and numerous Taiwanese studies have applied the CKD-MDRD equation to calculate eGFR (7, 36). In the present study, we discovered that BPS DI levels were positively associated with abnormalities in eGFR when the CKD-EPI equation was applied; however, no significant differences in eGFR were identified when the CKD-MDRD equation was applied. Additionally, the urinary BPA levels increased the early CKD when early CKD (60 ≤ eGFR<90 mL/min/1.73 m2) depend on CKD-MDRD equation, whereas there was no significant difference between urinary BPA levels and early CKD depend on CKD-EPI equation. This finding is similar to that of Moreno-Gómez-Toledano et al. (7), who identified a significant difference between higher levels of urinary BPA and lowest level only when the CKD-EPI equation was applied (i.e., a significant difference was not identified when the CKD-MDRD equation was applied). Therefore, relying only on clinical indicators such as eGFR and ACR is insufficient as part of efforts for CKD prevention.
Urinary NAG is widely used as a valuable biomarker of both acute kidney injury and CKD (37). Furthermore, urinary NAG is a sensitive indicator of proximal tubular cell injury (38), and an increase in the urinary NAG concentration suggests injury to the proximal tubule. Given the fundamental roles of NAG, it is an essential contributor to chronic diseases such as diabetes (39), resulting in diabetic nephropathy (40). Notably, NAG levels are already elevated in patients with diabetes who have a normal albumin level and a normal eGFR (41). In the present study, after adjustment for covariates (including DM), high BPA DI increased a high risk of NAG/creatinine abnormalities, namely BPA still dominated bisphenol exposure in our study despite restrictions on its use and production (42), possibly because Taiwan banned only BPA used in baby bottles. Nevertheless, researchers are yet to explore the relationship between bisphenol exposure and abnormal NAG/creatinine levels; most research has focused only on the association between phthalate exposure patterns and renal impairment and has reported that high-molecular-weight phthalate pattern scores were positively associated with NAG levels in adults in Shanghai (43). Additionally, an increase in two ubiquitous chemicals (urinary melamine and estimated diethyl hexyl phthalate [DEHP] intake) together may be positively associated with an increase in urinary NAG/creatinine levels in pregnant women in Taiwan (44). This finding is similar to our findings; that is, bisphenols and phthalates exhibit similar properties, and both may cause renal tubular injury. In conclusion, BPA exposure does not appear to be related to glomerular filtration rate, with a significant association found only with its substitute BPS. This suggests that BPA exposure is more likely to cause renal tubular injury. Given the high BPA exposure in the Taiwanese population (3), it is crucial to pay close attention to the potential impact of kidney damage in the future.
Limited studies provide dose- or risk-based predictors for extrapolating the adverse renal effects of bisphenol exposure. Uncertainty in risk assessment arises from factors like exposure scenario characterization, parameter estimates, and model predictions (45). Variations in TDI based on different health effects for the same chemical substance lead to diverse hazard risk calculations. Therefore, we propose a reference range for uncertain risk scenarios. Based on European Food Safety Authority (EFSA)’s TDI for BPA, focused on renal toxicity (46), we utilized HI values to evaluate cumulative bisphenol exposure and its association with reduced renal function indices in Taiwanese adults, consistent with our previous approach (18). After adjusting for covariates such as DM, our analysis indicated that higher HI values were associated with increased risk of abnormal NAG/creatinine, aligning with EFSA’s TDI (47) and contrasting with The German Federal Institute for Risk Assessment, BfR’s TDI (48), which underestimated this risk. BPA is recognized as a biomarker of renal disease with nephrotoxic effects reported (46, 49, 50). However, studies on the nephrotoxicity of BPA substitutes at human exposure levels are sparse. For BPF and BPS, TDIs were calculated assuming their renal effects are similar to BPA (31, 51). More research on the nephrotoxic effects of various BPA substitutes is essential to mitigate uncertainty in risk assessment. As international BPA regulations vary and remain controversial, the EFSA CEP Panel identified BPA’s effect on Th17 cell percentage as the critical effect. After dose conversion to HED, the lowest BMDL of 8.2 ng/kg bw per day was used for risk assessment, with default UFs of 2.5 and 10 applied for inter-species toxicodynamic and intra-human variability (47). The BfR disagrees with the EFSA’s new TDI, citing methodological discrepancies, particularly the lack of evidence that increased Th17 cells in mice cause adverse effects (48). Despite this, we recommend that countries set region-specific BPA management or restriction guidelines based on local exposure situations and economic conditions. Additionally, more stringent regulations for BPA substitutes should be introduced step by step.
The present study has several limitations. Firstly, its cross-sectional design hinders establishing causality despite associations found between BPA and its substitutes with renal function indices. Secondly, potential alternative explanations for our results cannot be ruled out due to unmeasured confounding factors like phthalates, melamine, and other metals in our regression models (18, 51, 52). Thirdly, using single spot urine samples instead of 24-h collections may introduce bias in assessing associations of BPA and its substitutes with renal biomarkers, although some studies suggest single spot samples can indicate long-term exposure when exposure levels are stable (53). To mitigate this, we employed multiple exposure indicators (DI and HI value) and designed our questionnaire to assess exposure frequency assuming participants had similar lifestyles and dietary habits. Fourthly, using serum creatinine to adjust for renal function indices like eGFR or ACR may be limited by differences in serum creatinine levels based on individual characteristics such as age, sex, or race/ethnicity. Finally, the toxicity of BPA substitutes regarding human exposure and renal damage effects remains understudied, with TDIs for BPF and BPS assumed based on their similarity to BPA’s renal effects in HI evaluations from prior research. Prospective studies are needed to conclusively determine whether BPA and its substitutes are nephrotoxic.
Although our study population was smaller compared to other human biomonitoring datasets, we found significant positive associations between higher BPA DI and the cumulative risk of bisphenols with increased NAG/creatinine levels in adults. Elevated NAG/creatinine levels indicate a higher risk of renal tubular injury and early-stage kidney disease. Comprehensive or mechanistic studies are needed to further elucidate this association. Incorporating other renal function indicators such as NAG/creatinine as clinical diagnostic markers in future studies is recommended. Besides, we also suggest that the sample size of participants be continuously increased and future long-term follow-up studies be conducted to establish a clearer causal relationship.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Research Ethics Commit-tee of National Health Research Institutes. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
Y-JL: Formal analysis, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. J-WC: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. VP: Methodology, Supervision, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. H-BH: Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Software, Writing – review & editing. H-CC: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. P-CH: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. We would also like to extend our sincere gratitude to the National Health Research Institutes (Grant No: EM-113-PP-11, EM-114-PP-11), NHRI-KMU joint research project (NHRIKMU-114-I001) and the Ministry of Science and Technology (Grant No: MOST 110-2314-B- 400-039, NSTC 111-2314-B-400-013, NSTC 112-2314-B-400-006) for their financial support. This work was supported partially by the Research Center for Precision Environmental Medicine, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan from The Featured Areas Research Center Program within the framework of the Higher Education Sprout Project by the Ministry of Education (MOE) in Taiwan and by Kaohsiung Medical University Research Center Grant (KMU-TC113A01–1).
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank our research assistants for their assistance in conducting data and specimen collection and sample pretreatment. We are also deeply grateful for the research collaboration involving the Nutrition and Health Survey in Taiwan team, led by Prof. Pan Wen-Harn and Mr. Zheng Chen, and for the support in sampling provided by the Health Promotion Administration, Ministry of Health and Welfare, Taiwan.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpubh.2025.1505578/full#supplementary-material
Abbreviations
BPA, Bisphenol A; BPF, Bisphenol F; BPS, Bisphenol S; CKD, Chronic kidney disease; ACR, Albumin-to-creatinine ratio; eGFR, Estimated glomerular filtration rate; NAG, N-acetyl-β-d-glucosaminidase; NAG/creatinine, N-acetyl-β-d-glucosaminidase to creatinine ratio; BUN, Blood urea nitrogen; CCr, Creatinine clearance rate; CKD-EPI, Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration; MDRD-4, Modification of Diet in Renal Disease; T2DM, Type 2 diabetes mellitus; DIs, Daily intakes; HQ, Hazard quotients; HI, Hazard index; EFSA, European Food Safety Authority; TDIs, Tolerable daily intakes; DEHP, Diethyl hexyl phthalate; BfR, The German Federal Institute for Risk Assessment.
References
1. Jha, V, Al-Ghamdi, SMG, Li, G, Wu, MS, Stafylas, P, Retat, L, et al. Global economic burden associated with chronic kidney disease: a pragmatic review of medical costs for the inside CKD research Programme. Adv Ther. (2023) 40:4405–20. doi: 10.1007/s12325-023-02608-9
2. Hahladakis, JN, Iacovidou, E, and Gerassimidou, S. An overview of the occurrence, fate, and human risks of the bisphenol-a present in plastic materials, components, and products. Integr Environ Assess Manag. (2022) 19:45–62. doi: 10.1002/ieam.4611
3. Lin, YJ, Chen, HC, Chang, JW, Huang, HB, Chang, WT, and Huang, PC. Exposure characteristics and cumulative risk assessment of bisphenol A and its substitutes: the Taiwan environmental survey for toxicants 2013. Front Public Health. (2024) 12:1396147. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1396147
4. González-Parra, E, Herrero, JA, Elewa, U, Bosch, RJ, Arduán, AO, and Egido, J. Bisphenol A in chronic kidney disease. Int J Nephrol. (2013) 2013:437857:1–9. doi: 10.1155/2013/437857
5. You, L, Zhu, X, Shrubsole, MJ, Fan, H, Chen, J, Dong, J, et al. 2011. Renal function, bisphenol A, and alkylphenols: results from the National Health and nutrition examination survey (NHANES 2003-2006). Environ Health Perspect. (2011) 119:527–33. doi: 10.1289/ehp.1002572
6. Kang, H, Lee, JP, and Choi, K. Exposure to phthalates and environmental phenols in association with chronic kidney disease (CKD) among the general US population participating in multi-cycle NHANES (2005-2016). Sci Total Environ. (2021) 791:148343. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148343
7. Moreno-Gómez-Toledano, R, Arenas, MI, Vélez-Vélez, E, Coll, E, Quiroga, B, Bover, J, et al. Bisphenol A exposure and kidney diseases: systematic review, Meta-analysis, and NHANES 03-16 study. Biomol Ther. (2021) 11:1046. doi: 10.3390/biom11071046
8. Shen, Y, Liu, T, Shi, Y, Zhuang, F, Lu, J, Zhu, Q, et al. Bisphenol A analogs in patients with chronic kidney disease and dialysis therapy. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. (2019) 185:109684. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109684
9. Ji, G, Gu, J, Guo, M, Zhou, L, Wang, Z, Shi, L, et al. A systematic comparison of the developmental vascular toxicity of bisphenol A and its alternatives in vivo and in vitro. Chemosphere. (2022) 291:132936. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132936
10. Thoene, M, Dzika, E, Gonkowski, S, and Wojtkiewicz, J. Bisphenol S in food causes hormonal and obesogenic effects comparable to or worse than bisphenol A: A literature review. Nutrients. (2020) 12:532. doi: 10.3390/nu12020532
11. Moreno-Gómez-Toledano, R. Relationship between emergent BPA-substitutes and renal and cardiovascular diseases in adult population. Environ Pollut. (2022) 313:120106. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2022.120106
12. Kataria, A, Levine, D, Wertenteil, S, Vento, S, Xue, J, Rajendiran, K, et al. Exposure to bisphenols and phthalates and association with oxidant stress, insulin resistance, and endothelial dysfunction in children. Pediatr Res. (2017) 81:857–64. doi: 10.1038/pr.2017.16
13. Lee, I, Park, JY, Kim, S, An, JN, Lee, J, Park, H, et al. Association of exposure to phthalates and environmental phenolics with markers of kidney function: Korean National Environmental Health Survey (KoNEHS) 2015-2017. Environ Int. (2020) 143:105877. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2020.105877
14. Tanaka, SI, Fujioka, Y, Tsujino, T, Ishida, T, and Hirata, KI. Association between urinary N-acetyl-β-glucosaminidase activity-urinary creatinine concentration ratio and risk of disability and all-cause mortality. PLoS One. (2022) 17:e0265637. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0265637
15. Liu, Q, Zong, R, Li, H, Yin, X, Fu, M, Yao, L, et al. Distribution of urinary N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminidase and the establishment of reference intervals in healthy adults. J Clin Lab Anal. (2021) 35:e23748. doi: 10.1002/jcla.23748
16. Hong, JD, and Lim, IS. Correlation between glomerular filtration rate and urinary N acetyl-beta-D glucosaminidase in children with persistent proteinuria in chronic glomerular disease. Korean J Pediatr. (2012) 55:136–42. doi: 10.3345/kjp.2012.55.4.136
17. Kim, HK, Lee, M, Lee, YH, Kang, ES, Cha, BS, and Lee, BW. Renal tubular damage marker, urinary N-acetyl-β-D-Glucosaminidase, as a predictive marker of hepatic fibrosis in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab J. (2022) 46:104–16. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2020.0273
18. Chang, JW, Liao, KW, Huang, CY, Huang, HB, Chang, WT, Jaakkola, JJK, et al. Phthalate exposure increased the risk of early renal impairment in Taiwanese without type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int J Hyg Environ Health. (2020) 224:113414. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheh.2019.10.009
19. Huang, PC, Tsai, CH, Liang, WY, Li, SS, Pan, WH, and Chiang, HC. Age and gender differences in urinary levels of eleven phthalate metabolites in general Taiwanese population after a dehp episode. PLoS One. (2015) 10:e0133782. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0133782
20. Huang, PC, Waits, A, Chen, HC, Chang, WT, Jaakkola, JJK, and Huang, HB. Mediating role of oxidative/nitrosative stress biomarkers in the associations between phthalate exposure and thyroid function in Taiwanese adults. Environ Int. (2020) 140:105751. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2020.105751
21. Huang, PC, Chen, HC, Chou, WC, Lin, HW, Chang, WT, and Chang, JW. Cumulative risk assessment and exposure characteristics of parabens in the general Taiwanese using multiple hazard indices approaches. Sci Total Environ. (2022) 843:156821. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.156821
22. Huang, HB, Siao, CY, Lo, YC, Shih, SF, Lu, CH, and Huang, PC. Mediation effects of thyroid function in the associations between phthalate exposure and glucose metabolism in adults. Environ Pollut. (2021) 278:116799. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116799
23. Chen, HC, Chang, JW, Sun, YC, Chang, WT, and Huang, PC. Determination of parabens, bisphenol A and its analogs, Triclosan, and Benzophenone-3 levels in human urine by isotope-dilution-UPLC-MS/MS method followed by supported liquid extraction. Toxics. (2022) 10:21. doi: 10.3390/toxics10010021
24. Levey, AS, Coresh, J, Greene, T, Marsh, J, Stevens, LA, Kusek, JW, et al. Expressing the modification of diet in renal disease study equation for estimating glomerular filtration rate with standardized serum creatinine values. Clin Chem. (2007) 53:766–72. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2006.077180
25. Stevens, LA, Li, S, Kurella Tamura, M, Chen, SC, Vassalotti, JA, Norris, KC, et al. Comparison of the CKD epidemiology collaboration (CKD-EPI) and modification of diet in renal disease (MDRD) study equations: risk factors for and complications of CKD and mortality in the kidney early evaluation program (KEEP). Am J Kidney Dis. (2011) 57:S9–S16. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2010.11.007
26. Levey, AS, Stevens, LA, Schmid, CH, Zhang, YL, Castro, AF 3rd, Feldman, HI, et al. A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann Intern Med. (2009) 150:604–12. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-150-9-200905050-00006
27. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, (2023). Prevent type 2 diabetes. Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/prevent-type-2/index.html (Accessed May 15, 2024).
28. Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes. KDIGO 2012 Clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int Suppl. (2012) 3:1–150.
29. Kim, SR, Lee, YH, Lee, SG, Kang, ES, Cha, BS, Kim, JH, et al. Urinary N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase, an early marker of diabetic kidney disease, might reflect glucose excursion in patients with type 2 diabetes. Medicine. (2016) 95:e4114. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000004114
30. Levin, A, and Stevens, PE. Summary of KDIGO 2012 CKD guideline: behind the scenes, need for guidance, and a framework for moving forward. Kidney Int. (2014) 85:49–61. doi: 10.1038/ki.2013.444
31. Mok, S, Jeong, Y, Park, M, Kim, S, Lee, I, Park, J, et al. Exposure to phthalates and bisphenol analogues among childbearing-aged women in Korea: influencing factors and potential health risks. Chemosphere. (2021) 264:128425. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128425
32. Wood, SN. Generalized additive models: an introduction with R. Boca Raton, FL: Chapman and Hall/CRC Publisher (2017).
33. Li, M, Bi, Y, Qi, L, Wang, T, Xu, M, Huang, Y, et al. Exposure to bisphenol A is associated with low-grade albuminuria in Chinese adults. Kidney Int. (2012) 81:1131–9. doi: 10.1038/ki.2012.6
34. Krieter, DH, Canaud, B, Lemke, HD, Rodriguez, A, Morgenroth, A, von Appen, K, et al. Bisphenol A in chronic kidney disease. Artif Organs. (2013) 37:283–90. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1594.2012.01556.x
35. National Health Insurance Administration, (2017). HPV. Available at: https://www.hpa.gov.tw/Pages/Detail.aspx?nodeid=1115&pid=6472 (Accessed March 12, 2012).
36. Wu, JJ, Weng, SC, Liang, CK, Lin, CS, Lan, TH, Lin, SY, et al. Effects of kidney function, serum albumin and hemoglobin on dementia severity in the oldest old people with newly diagnosed Alzheimer’s disease in a residential aged care facility: a cross-sectional study. BMC Geriatr. (2020) 20:391. doi: 10.1186/s12877-020-01789-0
37. Novak, R, Salai, G, Hrkac, S, Vojtusek, IK, and Grgurevic, L. Revisiting the role of NAG across the continuum of kidney disease. Bioengineering. (2023) 10:444. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering10040444
38. Skálová, S. The diagnostic role of urinary N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminidase (NAG) activity in the detection of renal tubular impairment. Acta Med. (2005) 48:75–80. doi: 10.14712/18059694.2018.35
39. Hart, GW. Nutrient regulation of signaling and transcription. J Biol Chem. (2019) 294:2211–31. doi: 10.1074/jbc.AW119.003226
40. Fiseha, T, and Tamir, Z. Urinary markers of tubular injury in early diabetic nephropathy. Int J Nephrol. (2016) 2016:1–10. doi: 10.1155/2016/4647685
41. Nauta, FL, Boertien, WE, Bakker, SJ, van Goor, H, van Oeveren, W, de Jong, PE, et al. Glomerular and tubular damage markers are elevated in patients with diabetes. Diabetes Care. (2011) 34:975–81. doi: 10.2337/dc10-1545
42. Li, J, Zhang, W, Zhou, Y, Shi, J, Xia, W, Xu, S, et al. Cumulative health risks for bisphenols using the maximum cumulative ratio among Chinese pregnant women. Environ Pollut. (2021) 270:116044. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.116044
43. Chen, J, Shi, X, Zhou, X, Dong, R, Yuan, Y, Wu, M, et al. Renal function and the exposure to melamine and phthalates in Shanghai adults. Chemosphere. (2020) 246:125820. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.125820
44. Tsai, HJ, Kuo, FC, Wu, CF, Sun, CW, Hsieh, CJ, Wang, SL, et al. Association between two common environmental toxicants (phthalates and melamine) and urinary markers of renal injury in the third trimester of pregnant women: the Taiwan maternal and infant cohort study (TMICS). Chemosphere. (2021) 272:129925. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.129925
45. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. (2023). Uncertainty and variability. Available at: https://www.epa.gov/expobox/uncertainty-and-variability (Accessed December 27, 2024).
46. European Food Safety Authority. Scientific opinion on the risks to public health related to the presence of bisphenol A (BPA) in foodstuffs. EFSA J. (2015) 13:3978. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2015.3978
47. European Food Safety Authority. Re-evaluation of the risks to public health related to the presence of bisphenol A (BPA) in foodstuffs. EFSA J. (2023) 21:6857. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2023.6857
48. BfR (German Federal Institute for Risk Assessment), (2023). Bisphenol A: BfR proposes health based guidance value, current exposure data are needed for a full risk assessment. Available at: https://mobil.bfr.bund.de/cm/349/bisphenol-a-bfr-proposes-health-based-guidance-value-current-exposure-data-are-needed-for-a-full-risk-assessment (Accessed April 19, 2023).
49. Priego, AR, Parra, EG, Mas, S, Morgado-Pascual, JL, Ruiz-Ortega, M, and Rayego-Mateos, S. Bisphenol A modulates autophagy and exacerbates chronic kidney damage in mice. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:7189. doi: 10.3390/ijms22137189
50. Gowder, SJ. Nephrotoxicity of bisphenol A (BPA)-an updated review. Curr Mol Pharmacol. (2013) 6:163–72. doi: 10.2174/1874467207666140410115823
51. Huang, HB, Pan, WH, Chang, JW, Chiang, HC, Guo, YL, Jaakkola, JJ, et al. Does exposure to phthalates influence thyroid function and growth hormone homeostasis? The Taiwan environmental survey for toxicants (TEST) 2013. Environ Res. (2017) 153:63–72. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2016.11.014
52. Wu, CF, Hsiung, CA, Tsai, HJ, Tsai, YC, Hsieh, HM, Chen, BH, et al. Interaction of melamine and di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate exposure on markers of early renal damage in children: the 2011 Taiwan food scandal. Environ Pollut. (2018) 235:453–61. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.12.107
53. Jia, LL, Luan, YL, Shen, HM, and Guo, Y. Long-term stability of several endocrine disruptors in the first morning urine samples and their associations with lifestyle characteristics. Sci Total Environ. (2022) 850:157873. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.157873
54. Tarafdar, A, Sirohi, R, Balakumaran, PA, Reshmy, R, Madhavan, A, Sindhu, R, et al. (2022). The hazardous threat of bisphenol A: Toxicity, detection and remediation. J Hazard Mater. 423(Pt A):127097. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127097
55. Yadav, R, Kumar, D, Singh, J, and Jangra, A. Environmental toxicants and nephrotoxicity: Implications on mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Toxicology. (2024) 504:153784. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2024.153784
Keywords: bisphenol A substitutes, hazard index, cumulative risk assessment, renal damage, Taiwan, bisphenol A
Citation: Lin Y-J, Chang J-W, Ponnusamy VK, Huang H-B, Chen H-C and Huang P-C (2025) Urinary bisphenol A and its substitutes exposure increased the risk of renal tubular injury (N-acetyl-β-d-glucosaminidase) in the general Taiwanese population. Front. Public Health. 13:1505578. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1505578
Edited by:
Ahmed Abdeen, Benha University, EgyptReviewed by:
Mustafa Shukry, Kafrelsheikh University, EgyptAfaf Abdelkader, Benha University, Egypt
Copyright © 2025 Lin, Chang, Ponnusamy, Huang, Chen and Huang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Po-Chin Huang, cGNodWFuZ0BuaHJpLmVkdS50dw==
 Yu-Jung Lin
Yu-Jung Lin Jung-Wei Chang
Jung-Wei Chang Vinoth Kumar Ponnusamy3,4
Vinoth Kumar Ponnusamy3,4 Han-Bin Huang
Han-Bin Huang Po-Chin Huang
Po-Chin Huang