- 1School of Management, Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou, Jiangsu, China
- 2College of Public Health, Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, China
Objective: This study aims to investigate the factors influencing residents' healthcare utilization behavior and provide a scientific basis for enhancing the overall efficiency of healthcare utilization.
Methods: A comprehensive analysis was conducted using data from the China General Social Survey (CGSS) project. Exploratory Factor Analysis (EFA) and Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) were utilized to examine the influences and interrelationships of the three core factors of the Andersen Healthcare Utilization Model (Predisposing Factors, Enabling Resources, and Need), as well as the two extended factors (health behaviors and Medical-service Experience), on residents' decisions regarding the utilization of healthcare services.
Results: A total of 2,230 participants were enrolled in this study. Most were male (55.74%), were married (85.38%), and had junior- and senior-high school educations (45.29%). Mean age was 52.39 years, and 56.32% of participants reported an annual income of <30,000 RMB. EFA distilled influencing factors into four domains: Predisposing and Enabling, Need, Health Behaviors, and Medical-service Experience. The results of the revised SEM indicated that the influence coefficients of Predisposing and Enabling, Need, and Medical-service Experience on Decision to Utilize Health Services (DUHS) were 0.095, −0.104, and 0.093 respectively. Mediation effect test results demonstrated that the indirect effects of Predisposing and Enabling, Need, and Health Behaviors on DUHS were −0.098, 0.024, and −0.017, respectively, all of which were statistically significant. Finally, the fit indices of the modified model indicated an acceptable model fit.
Conclusion: This study showed that unmarried individuals with lower income and job instability exhibit reduced healthcare utilization due to economic barriers and lack of social support. Furthermore, medical service experience is another crucial factor affecting health service utilization. Notably, our findings suggest the need for targeted interventions, including enhanced insurance coverage, improving the quality of medical services and health education campaigns to mitigate disparities in access to health services.
1 Introduction
Due to the fast evolution of society and the exacerbation of population aging, residents' demand for health services has shown a pronounced upward trajectory (1, 2). Healthcare utilization, a pivotal metric gauging the efficacy and responsiveness of a nation's or region's healthcare system, has emerged as a paramount concern. It is particularly salient in China, a populous nation grappling with multifaceted challenges that include a rapidly aging society, profound urban vs. rural disparities in access to healthcare services, and an unequal distribution of medical resources (3, 4). These issues not only significantly affect the health and wellbeing of China's citizens but also pose direct threats to the sustainability of its healthcare system. Therefore, conducting exhaustive research into the patterns and determinants of residents' healthcare utilization behavior is of paramount urgency.
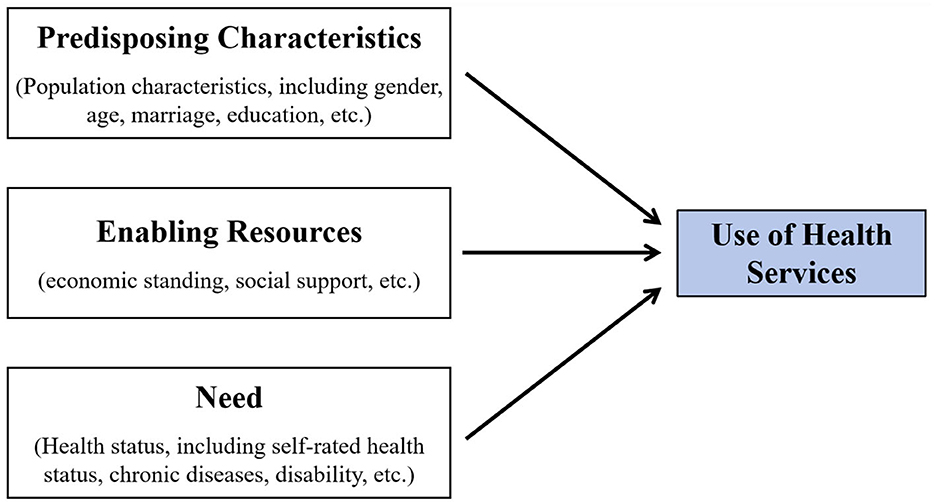
Utilization of healthcare by residents is a dynamic process driven by multiple intricate factors that span individual characteristics, the policy environment, the organizational structure of the healthcare system, and sociocultural contexts (5). To accurately discover the underlying mechanisms of this process and effectively inform policy formulation and practice enhancement, developing a comprehensive, systematic, and scientifically rigorous theoretical framework is imperative. To this end, various conceptual models have been developed and employed to explain and delineate the interrelationships among a series of possible predictive factors for healthcare utilization behavior, and to guide the analysis and evaluation of the study (6–8), including accessibility, availability, acceptability, affordability, adequacy, and the appropriateness of the final decision. Among them, the Andersen Healthcare Utilization Model is one of the most classic and recognized models. The Andersen Healthcare Utilization Model was initially proposed by the eminent American sociologist Ronald Andersen in 1968 (9). It is a multi-layered model that combines the individual and environmental determinants of health service use and has been most widely accepted and adopted in many countries (9–12), with its conclusions being convincing. It now stands as an indispensable, pivotal theoretical foundation for examining healthcare utilization behaviors. While various iterations and extensions of the model have emerged, they consistently emphasize the critical roles of three types of core factors influencing healthcare utilization: Propensity Characteristics (including fundamental demographic attributes such as gender and age), Enabling Resources (e.g., economic standing, social support), and Need (pertaining to an individual's state of health and specific manifestations of service requirements) (13–15). This conceptualization is visualized in Figure 1.
At the same time, there are slight differences in the research on the relationship between the three factors and the strength of their impact on healthcare utilization. Portuguese research has shown that needs and propensity Characteristics determine the use of health services by the older adult (16). A German study also indicates that needs are the main predictors of the cost of health insurance for the older adult (17). For specific populations, research in Australia and Turkey has also demonstrated that needs are the strongest predictors of mental health service use by depressed patients and of inpatients' readmissions (18, 19). Hence, among the three core factors, needs are an important predictor of the use of medical services. Moreover, the effects of the three factors on healthcare utilization vary among ethnic groups and regions (20). In China, through the Andersen Healthcare Utilization Model, researchers have a preliminary understanding of the influencing factors of healthcare utilization in China. It is pointed out that enabling resources can have a greater impact on healthcare utilization than predisposing factors and needs (21). However, a study has also pointed out that needs are the main predictors of rural residents' health service utilization in Guangxi, China (22). As can be seen, the impact of the three factors in the model on healthcare utilization varies by population and region. Additionally, a study has identified that predisposing characteristics, enabling resources, and needs have a local and neighborhood impact, which contributes to disparities in local health services utilization (23). Furthermore, researchers have also included variables such as social capital (24), service utilization experience (25), and social support (26) in the Andersen Healthcare Utilization Model according to specific research purposes to explore the impact of healthcare services utilization. In summary, extensive research on the Andersen Healthcare Utilization Model has been conducted, but the model structure and its results vary across different regions, populations, and research purposes.
The term “Non-utilization” has been referred to in prior researches. It implies that despite the availability of health services, people, due to various reasons such as economic factors, cognitive status, and social support, fail to access these services (22–24). Simultaneously, compared with other health service utilization models, the Anderson healthcare utilization model highlights the impact of individual factors on healthcare utilization, meaning it does not encompass the influence of health service providers. Therefore, this article employed a novel concept, “Intentional Non-utilization”. It indicates that the health service provider has offered the service without a lack thereof, and that when an individual is economically disadvantaged (with inadequate enabling resources) or has a cognitive bias regarding their own health condition (needs), there might be instances of deliberately not utilizing the already provided health-care services.
Therefore, with the Andersen Healthcare Utilization Model as a theoretical basis, this study employs “Intentional Non-utilization” to undertake a comprehensive analysis and systematic decomposition of the multiple factors influencing residents' healthcare utilization from the demand-side perspective. Additionally, a detailed examination of the complex interrelationships among these factors was planned to reveal the patterns governing residents' healthcare utilization behaviors, thereby providing a scientific basis for optimizing healthcare policies, enhancing the healthcare service system, and improving the overall efficiency of healthcare utilization.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Data resources
The data used in this study were sourced from the well-regarded Chinese General Social Survey (CGSS), conducted by the Chinese Survey and Data Center at Renmin University of China (Beijing, China). Initiated in 2003, the CGSS stands as one of China's pioneering nationwide, comprehensive, and continuous academic surveys and is renowned for its authoritative results. The CGSS encompasses all urban and rural households across China's 31 provinces, autonomous regions, and municipalities. The sampling design employs a stratified three-stage probability sampling method, consisting of a mandatory stratum and a selected stratum. The mandatory stratum includes households from the urban districts of leading metropolitan cities, while the selected stratum covers other households nationwide. By employing scientific stratification and sample weighting, a sample of 12,000 households was extracted, maintaining an urban-to-rural ratio of 6:4. For detailed sampling procedures, please refer to the official website of the Chinese General Social Survey (http://cgss.ruc.edu.cn/index.htm). In 2021, the CGSS project systematically and comprehensively gathered data spanning multiple levels of Chinese society, encompassing communities, families, and individuals. This rich dataset, which includes age, gender, income, education, health behaviors, and healthcare utilization, provided a foundation for the detailed analysis in this study.
2.2 Selection and measurement of variables
Participants were queried about their actual past experience of whether they had elected not to utilize a resource or service in a specific situation. Therefore, we chose the question “Do you intentionally avoid seeking medical attention when sick or injured?” as the explanatory variable to understand their decisions and ascertain whether there is “Intentional non-utilization”. The answers were coded as NO (code = 1) and YES (code = 2). Furthermore, we identified five core variables by which to examine factors that influenced residents' healthcare utilization: (1) Predisposing Factors, (2) Enabling Resources, (3) Need, (4) Health Behaviors, and (5) Medical-service Experience.
2.2.1 Predisposing factors
A systematic review of literature that employs Andersen's model revealed the six predisposing variables that are most frequently examined: age, marital status, gender, education, work, and region (12, 27). We incorporated these variables into our research. Age was treated as a continuous variable, while gender, marital status, and region were coded as dichotomous variables: Female (code = 1) vs. Male (code = 2), Unmarried (code = 1) vs. Married (code = 2), and Urban (code = 1) vs. Rural (code = 2), respectively. Respondents' educational levels were categorized in accordance with the 2011 International Standard Classification of Education (ISCED-2011) as follows: Primary education (ISCED 0–2) = 1, including primary and pre-primary education; Middle education (ISCED 3–4) = 2, including junior- and senior-high school education; and Higher education (ISCED 5–8) = 3, including undergraduate, master's, and doctoral studies. We also defined the following work status categories: unstable employment (code = 1), Self-employed (code = 2), and Employed (code = 3).
2.2.2 Enabling resources
In previous research, income or financial status has been the most commonly employed variable in Enabling Resources (28). In addition, social support, defined as the support and assistance individuals receive from their social networks, has been identified as a crucial enabling resource influencing healthcare utilization, as shown by relevant studies on the application and refinement of Andersen's model (29, 30). In the Chinese context, social medical insurance represents a pivotal social-security system established through national and social legislation that aims to reduce the medical burden of insured persons and improve the level of medical security of the people, thereby mitigating the risk of poverty due to illness. Prior research has highlighted the significance of utilizing both public and commercial medical insurance as an economic factor that notably affects residents' utilization of medical services (31). Moreover, medical insurance has consistently emerged as an important predictor in studies using the Andersen model (15, 32). Therefore, in this study we designated Income, Social Support, and Medical Insurance as the core variables representing Enabling Resources. Specifically, Income was quantified using respondents' annual incomes; Social Support was assessed by asking whether respondents had someone to listen to their personal concerns regularly in the past year; and Medical-insurance status was categorized into four groups: No Medical Insurance (code = 1), Commercial Medical Insurance (code = 2), Social Security (code = 3), and Both Social Security and Commercial Insurance (code = 4).
2.2.3 Need
Need pertains to an individual's requirement for healthcare, rooted in their specific state of health, which constitutes the most direct impetus for seeking such care. Currently, the Medical Outcomes Study 36-item Short-form Health Survey (SF-36) is the globally pre-eminent instrument for assessing quality of life (QoL), with its applicability validated across diverse populations (33, 34). The 8-item Short-form Health Survey (SF-8), a streamlined version of the SF-36 (35), covers eight domains essential to evaluating QoL over the preceding 4 weeks: general health (GH), physical functioning (PF), role limitations due to physical health problems (RP), bodily pain (BP), vitality (VT), social functioning (SF), mental health (MH), and role limitations due to emotional problems (RE). The SF-8 scale has been widely adopted in international research due to its brevity, ease of administration, and high response rates (36). Therefore, in this study we used the SF-8 to gauge participants' health characteristics, thereby mirroring their healthcare needs.
2.2.4 Health behaviors
In their assessments of healthcare utilization, scholars have found that in addition to the three core factors posited in the Anderson model, personal-health behaviors strongly correlate with health education or awareness, emerging as a pivotal influence on healthcare demand and service utilization (37, 38). Consequently, in this study we integrated Health Behaviors into the Anderson model. Our review of pertinent literature on Health Behaviors led us to select three representative factors as core variables. First, the detrimental effects of smoking on health and its nexus with healthcare utilization have been amply documented (39, 40); therefore, we deemed respondents' smoking status a crucial health behavior and coded it as Smoking (code = 1) vs. Non-Smoking (code = 2). Second, exercise mitigates the risks of cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes, certain cancers, depression, and anxiety (41); conversely, physical inactivity heightens vulnerability to various health challenges (42), ultimately increasing healthcare utilization (43). Therefore, we gathered data on the frequency of leisure time physical exercise among participants, categorizing them as Never (code = 1), Several Times a Year or Less (code = 2), Several Times a Month (code = 3), Several Times a Week (code = 4), and Every Day (code = 5). Third, undergoing physical examinations demonstrates an individual's concern for their health, constituting a vital Health Behavior. Research indicates that individuals with higher rates of physical-examination utilization tend to adopt healthier lifestyles and behaviors (44); moreover, this population reports better self-assessed state of health (45), and regular physical examinations correlate negatively with healthcare utilization (46). Therefore, we collected data on the frequency of physical examinations sought out by participants in the past 3 years, classifying them as Never (code = 1), Irregular Physical Examination (code = 2), and Regular Physical Examination (code = 3).
2.2.5 Medical-service experience
Due to the high professional standards of healthcare services and the profound lack of medical knowledge among patients, medical personnel often occupy a dominant position in the delivery of medical care, significantly influencing patient experience and satisfaction. Extensive research has emphasized the crucial role of effective communication between patients and medical staff in fostering high satisfaction levels (47). First, positive demeanor, professional commitment, and competence of medical staff have been found to correlate positively with patient satisfaction (48, 49). Second, patients tend to report heightened satisfaction when they receive ample assistance throughout the healthcare process (29). Third, studies have noted the influence of patients' experience or satisfaction on their willingness to reuse health services (50, 51). Therefore, in this study we integrated the concept of Medical-service Experience into the Anderson model to examine how often the following had occurred in previous healthcare visits: (1) failure to comprehend instructions provided by medical staff, (2) uncertainty about how to pose questions to medical staff, and (3) difficulty reading medication instructions or understanding physicians' advice. Answers were classified as Never (code = 1), Rarely (code = 2), Sometimes (code = 3), Often (code = 4), and Always (code = 5). This categorization enabled a nuanced understanding of the challenges patients face in navigating the healthcare system and their resultant satisfaction levels.
2.3 Data analysis
First, we conducted a descriptive analysis of survey participants to examine their demographic characteristics. Next, we conducted exploratory factor analysis (EFA) using SPSS (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA, Version 26) to explore the relationships among the selected variables and ascertain whether the latent variables aligned with the predefined theoretical framework. Specifically, we employed principal component analysis (PCA) to extract item factors and varimax rotation (VR) to enhance the interpretability of the factor solution.
Following this, Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) was implemented in SPSS Amos software, adhering to the two-step approach advocated by Anderson and Gerbing. Within SEM (52), Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA) serves as the measurement component, clarifying the associations between latent variables and their respective indicators. The first step was therefore to conduct CFA on each factor to assess the significance of factor loadings. In the second step, grounded in the Andersen Healthcare Utilization Model and subsequent empirical research, we formulated preliminary hypotheses positing that Predisposing Factors, Enabling Resources, Need, Health Behaviors, and Medical-service Experience would predict Decision to Utilize Health Services (DUHS). Furthermore, we hypothesized that Predisposing Factors and Enabling Resources would predict Need and Medical-service Experience; Predisposing Factors would predict Enabling Resources and Health Behaviors; Health Behaviors would predict Need; and Need would predict Medical-service Experience.
In the process of data analysis, we estimated parameters via the maximum-likelihood method. Concurrently, the bootstrap method was used to test latent mediation effects and quantify total, direct, and indirect effects. The model's significance was initially assessed using the χ2 value; however, given its sensitivity to large sample sizes, we examined additional goodness-of-fit indices (53). Model fit was evaluated based on the following indices and their respective thresholds for acceptable fit (54, 55): (a) root mean square error of approximation (RMSEA) ≤ 0.08, (b) comparative-fit index (CFI) ≥ 0.90, (c) Tucker–Lewis index (TLI) ≥ 0.90, (d) normed-fit index (NFI) ≥ 0.90, and (e) incremental-fit index (IFI) ≥ 0.90. All statistical tests were conducted at a two-sided significance level of P = 0.05.
3 Results
3.1 Demographic characteristics of participants
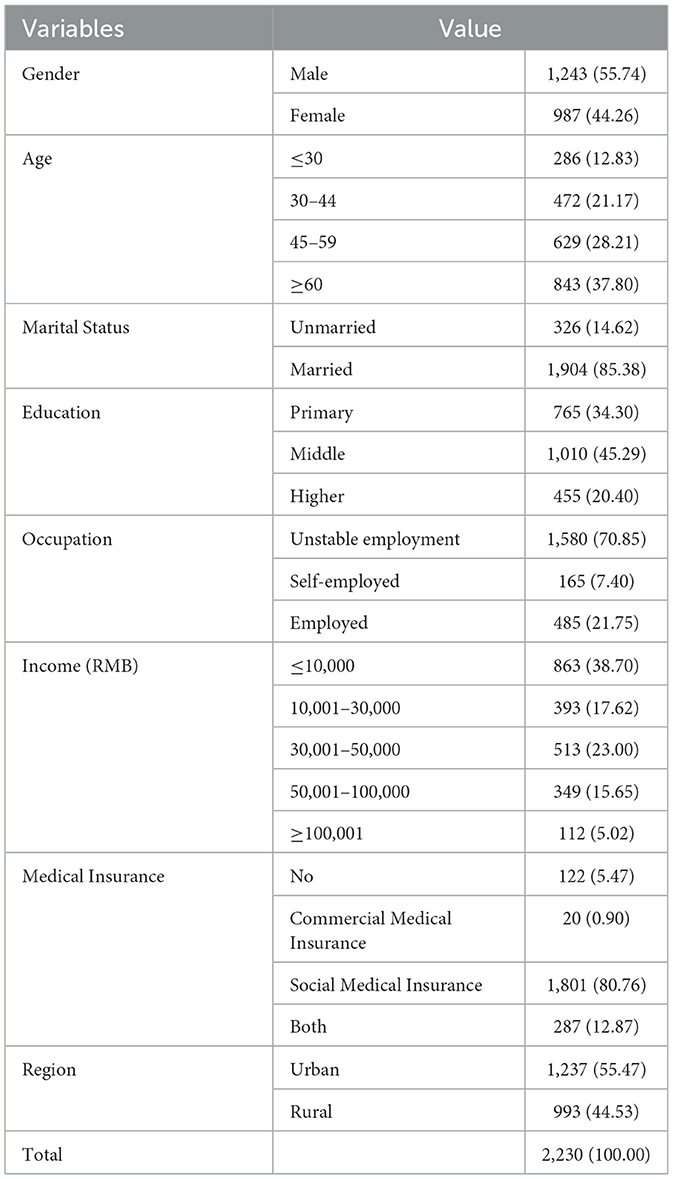
A total of 2230 participants were involved in this study. Most were male (55.74%, n = 1,243), were married (85.38%, n = 1,904), had junior- and senior-high school educations (45.29%, n = 1,010), and were enrolled in social medical insurance (80.76%, n = 1,801). Percentages of participants living in urban and rural areas were 55.47% (n = 1,237) and 44.53% (n = 993), respectively. Mean age was 52.39 years (standard deviation [SD], 17.76), and 56.32% (n = 1,256) of participants reported an annual income of < 30,000 RMB. These details are summarized in Table 1.
3.2 Exploratory factor analysis
All variables attained an EFA value of at least 0.856 on the Kaiser–Meyer–Olkin (KMO) test, exceeding the recommended threshold of 0.6. Bartlett's test result was significant (χ2 = 17,168.54, P < 0.001). Both of these findings demonstrated strong correlations among the variables, indicating that they were suitable for EFA (56).
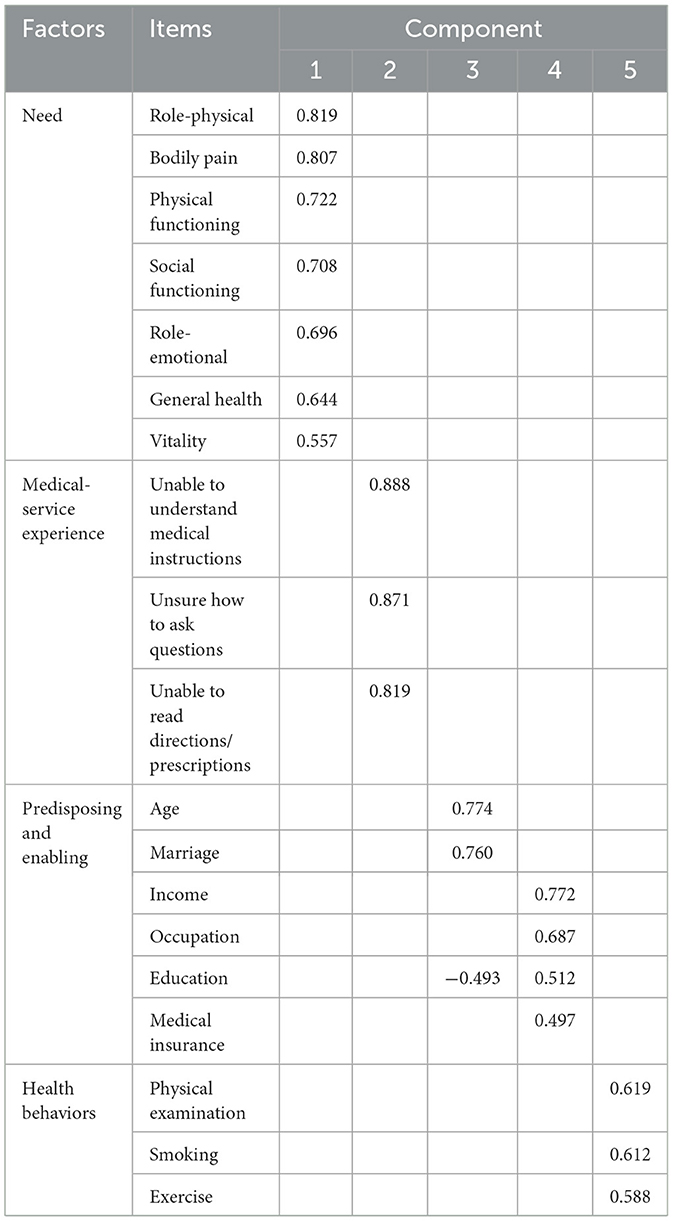
The initial EFA revealed six factors with eigenvalues exceeding 1. However, MH exhibited substantial loadings (>0.4) on two factors, while Social Support had insignificant loadings (< 0.4) on all factors; therefore, we gradually eliminated these two variables from further analysis. In addition, Gender was grouped with Smoking, Exercise, and Examination, variables that inherently represent dimensions of Health Behaviors, and therefore Gender was removed. After these adjustments, we conducted a second EFA on the remaining 19 variables, resulting in the extraction of five factors through rotation. The cumulative contribution rate of these factors amounted to 61.03%, indicating a substantial representation of total variance. Final EFA results are shown in Table 2.
Based on the above-mentioned EFA results, we grouped Age, Marital, Income, Occupation, Education, and Medical Insurance into the third and fourth factors. However, these groupings did not clearly delineate the two dimensions of Propensity Factors and Enabling Resources as predicted by the Anderson Healthcare Utilization Model. Given that these two dimensions are inherently related to participants' demographic and socioeconomic characteristics and that they showed high intercorrelations, distinguishing them during data analysis proved challenging. Therefore, we merged them into one variable designated Propensity and Enabling. Factors 1, 2, and 5 closely aligned with the pre-established dimensions and were therefore retained as Need, Medical-service Experience, and Health Behaviors, respectively.
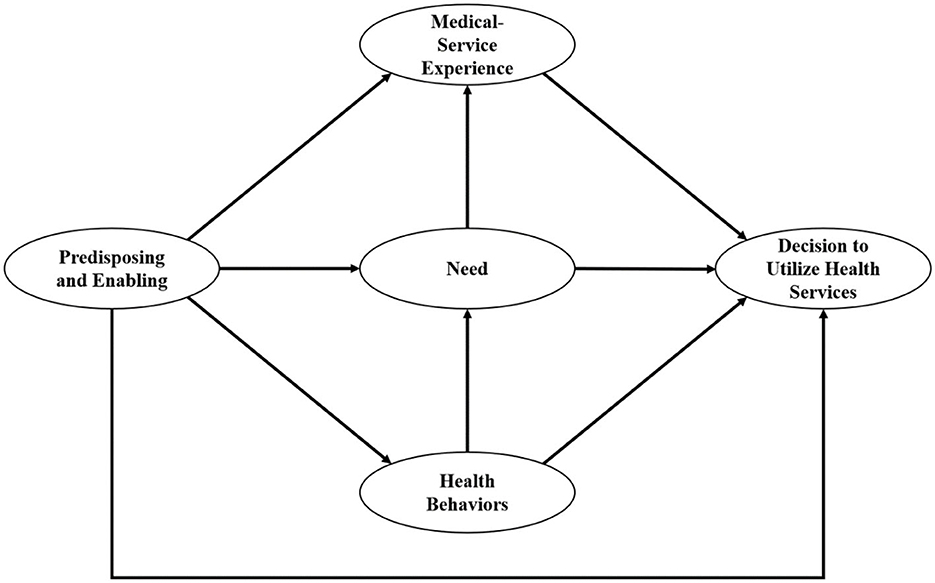
Due to the consolidation of Propensity Factors and Enabling Resources, we revised our hypotheses as follows:
Hypotheses H1–H4: Predisposing and Enabling, Need, Health Behaviors, and Medical-service Experience would predict DUHS.
Hypotheses H5–H7: Predisposing and Enabling would predict Need, Health Behaviors, and Medical-service Experience.
Hypothesis H8: Health Behaviors would predict Need.
Hypothesis H9: Need would predict Medical-service Experience.
The revised hypothetical model is illustrated in Figure 2.
3.3 Confirmatory factor analysis
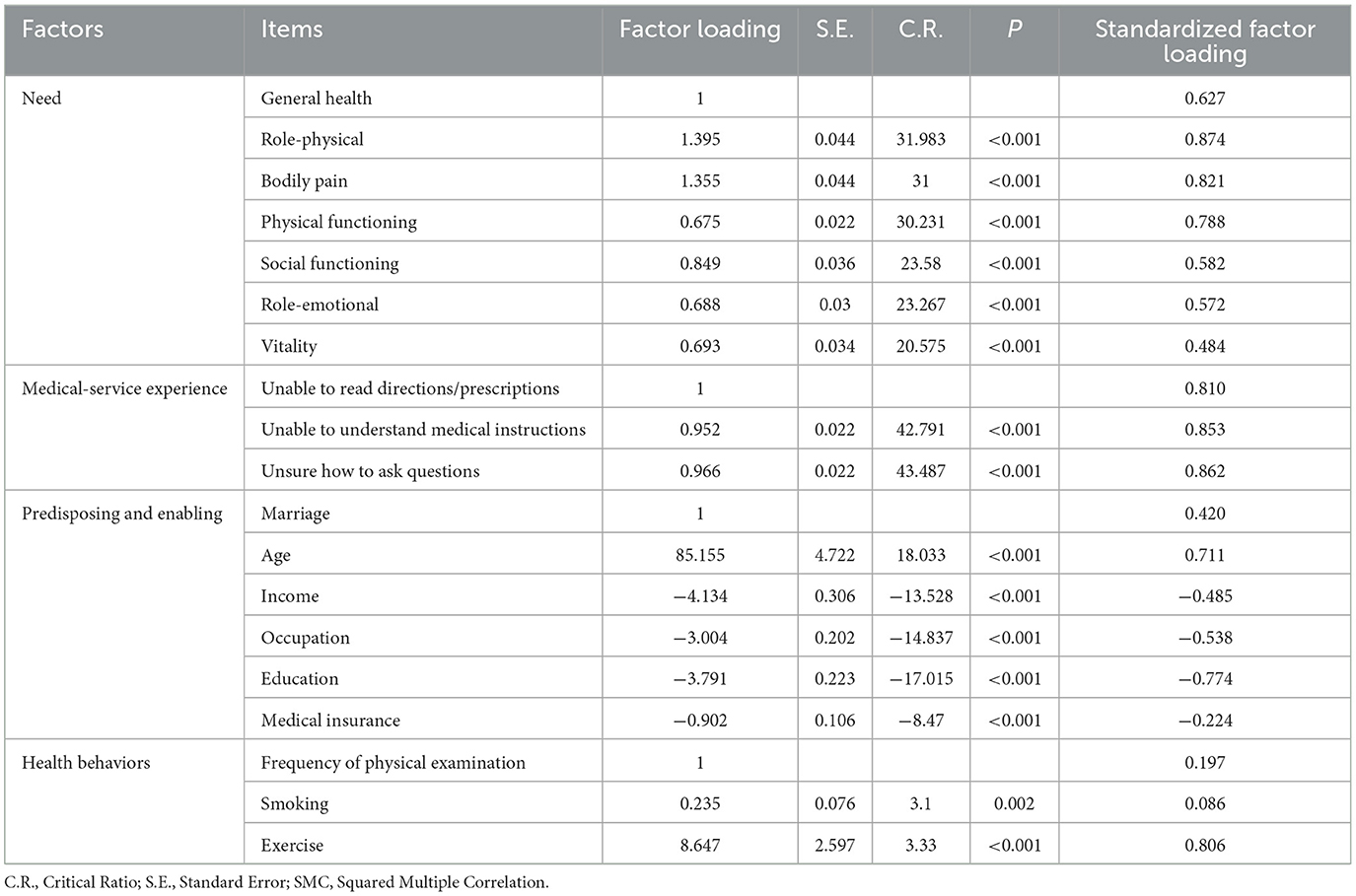
CFA results indicated that standardized factor loading for Smoking was < 0.1, whereas the remaining variables exhibited high factor loadings; furthermore, all variable factor loadings were statistically significant. Given the emphasis placed on the selected variables in Andersen's model by previous research, in this study we aimed to minimize the number of variables excluded, and consequently we retained all variables in the model. The results are shown in Table 3.
3.4 Structural model analysis
In SPSS Amos, we computed the β- and P-values of each path to assess the hypothesized relationships. Model results showed that Predisposing and Enabling (β = 0.090; P = 0.008) and Medical-service Experience (β = 0.093; P < 0.001) had significant positive effects, whereas Need (β = −0.105; P < 0.001) had significant negative effects, on DUHS; therefore, H1, H2, and H4 were supported. However, the hypothetical relationship between Health Behaviors and DUHS (β = 0.011; P = 0.762) was insignificant, and therefore H3 was not supported. Furthermore, Predisposing and Enabling had a significantly positive effect on both Need (β = 0.463; P < 0.001) and Health Behaviors (β = 0.449; P < 0.001), confirming H5 and H6. At the same time, this domain had a significant negative effect on Medical-service Experience (β = −0.336; P < 0.001), validating H7. Health Behaviors had a significant positive effect on Need (β = 0.134; P < 0.001), supporting H8. Finally, Need had a significantly negative effect on Medical-service Experience (β = −0.252; P < 0.001), and therefore H9 was supported. Refer to Supplementary Figure S1 for detail.
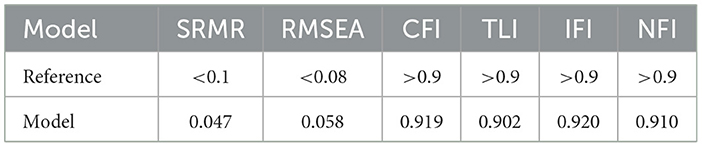
After removing the insignificant path, we reassessed the modified model. Besides, on the premise of ensuring the theoretical significance and empirical validity of the resulting model, we employ the modified index to make appropriate adjustments to the model in order to enhance the model's fitting degree. This can increase the model's accuracy and improve its overall performance. The revised SEM results, presented in Figure 3, indicate minimal changes in path coefficients, supporting the assumption of stability. Specifically, the influence coefficients of Predisposing and Enabling, Need, and Medical-service Experience on DUHS were 0.095, −0.104, and 0.093 respectively. The influence coefficients of Predisposing and Enabling on Need, Health Behaviors, and Medical-service Experience were, respectively, 0.462, 0.452, and −0.336. The influence coefficient of Health Behaviors on Need was 0.134, and that of Need on Medical-service Experience was −0.252. Finally, the fit indices of the modified model, presented in Table 4, indicated an acceptable model fit.
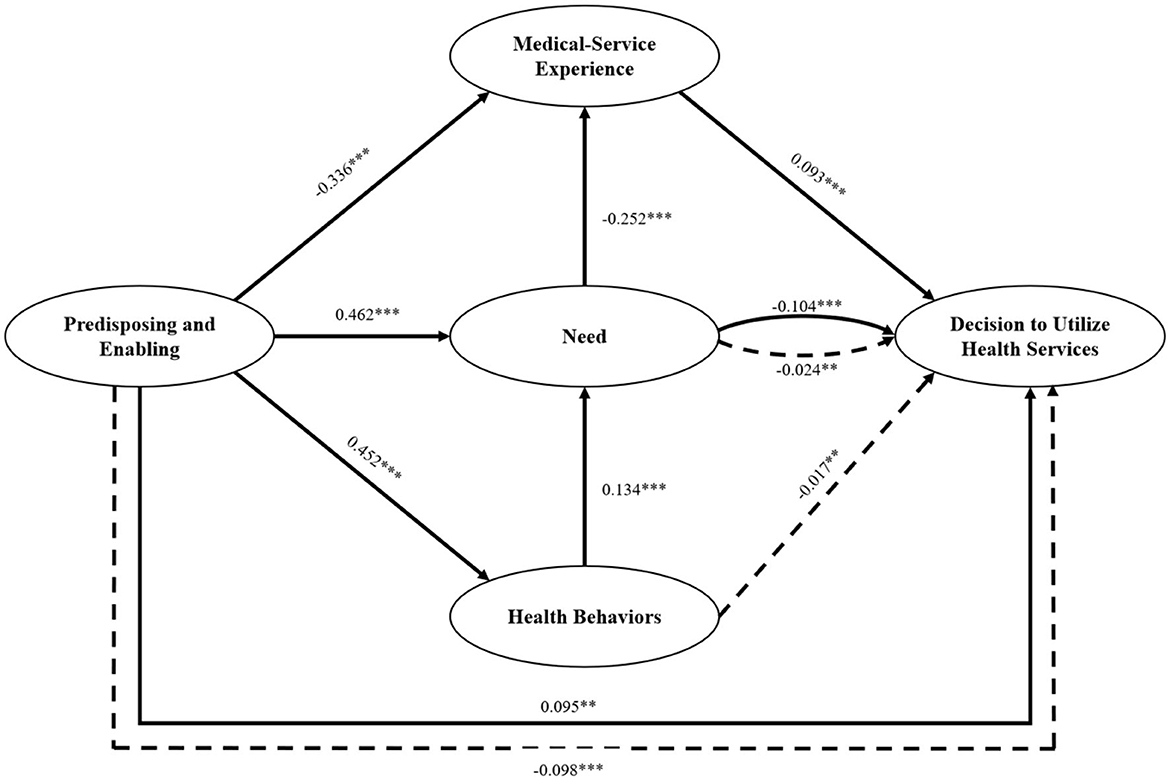
Figure 3. The results of the modified structural equation model. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. Solid lines = direct effect; dashed lines = indirect effect.
3.5 Direct- and indirect-effects analysis
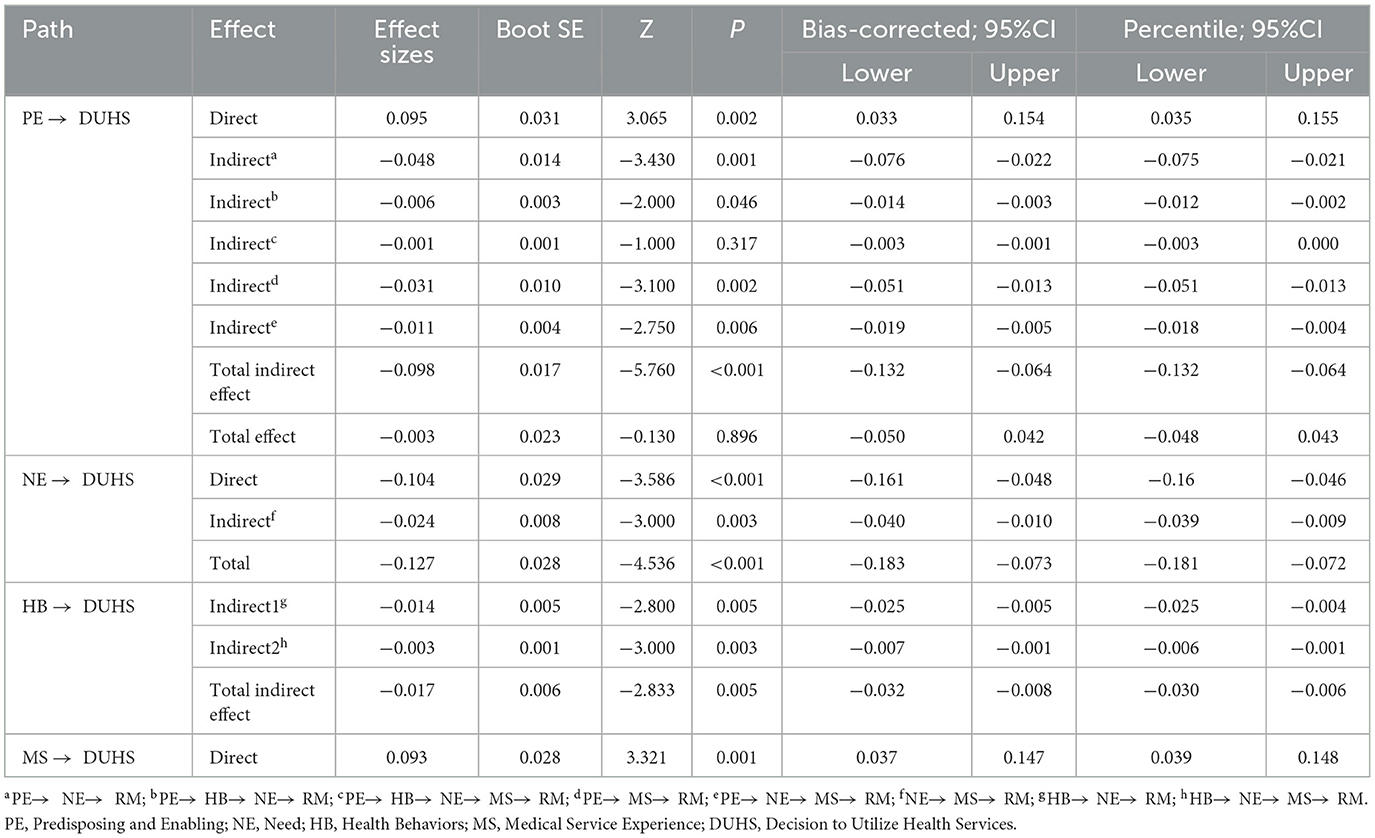
We used the bootstrapping function in Amos to scrutinize the model's mediation effect, examining both the direct and indirect effects of each factor on DUHS. Indirect effects were derived from 5,000 bootstrap samples. Table 5 shows the comprehensive breakdown of each factor's direct and indirect effects on DUHS.
The results showed that the direct and indirect effects of Predisposing and Enabling on DUHS were 0.095 and −0.098, respectively. Notably, the largest indirect path coefficient was that of Need, 0.014, which was statistically significant. However, the aggregate effect of Predisposing and Enabling on DUHS was −0.003, which was not statistically significant. Need exerted a direct effect of −0.104 on DUHS, with an additional indirect effect of −0.024 through Medical-service Experience. The aggregate effect was −0.127, which was statistically significant. Health Behaviors demonstrated a purely indirect influence on DUHS, with a statistically significant value of −0.017. Finally, Medical-service Experience had a statistically significant direct effect of 0.093 on DUHS.
4 Discussion
Based on Anderson's theoretical framework for healthcare utilization, we meticulously synthesized existing literature and constructed a conceptual model, and carried out a systematic analysis. This model offered a scientific examination of how multidimensional factors—including Predisposing Characteristics, Enabling Resources, Need, Health Behaviors, and Medical-service Experience—individually and collectively contributed to the decision-making process informing residents' non-utilization of healthcare. Consequently, it established a comprehensive mechanism underpinning healthcare utilization behaviors. Rigorous controls were enforced throughout the data collection and processing phases of this research. The findings not only extend the Andersen Healthcare Utilization Model by integrating the medical-service experience, but also reveal the factors that influence residents' health care utilization behavior and the interrelationships among them. This study provides a scientific basis for optimizing medical policies, perfecting the medical service system, and enhancing the overall efficiency of medical utilization.
In this study, we combined the Predisposing Factors and Enabling Resources into a single variable, namely Predisposing and Enabling. During the data analysis, the results of the exploratory factor analysis indicated that these two factors are difficult to distinguish. Besides, we observed that the two dimensions of predisposing factors and enabling resources are intrinsically related to the demographic and socio-economic characteristics of the participants and are highly correlated with each other. From the practical needs of the research and the comprehensive consideration of residents' healthcare utilization behavior, combining these two factors into a single variable can more comprehensively reflect the actual situation of residents in healthcare utilization. It helps us to understand and explain the influencing factors of residents' healthcare utilization behavior more concisely and effectively. According to the results, factor loadings for Income, Occupation, Education, and Medical Insurance were negative, whereas those for Age and Marital Status were positive. The direct influence of Predisposing Characteristics and Enabling Resources on the decision not to utilize healthcare was significant and positive (β = 0.095, P < 0.05). This meant that individuals who were older and unmarried and who had lower incomes, less-stable job statuses, lower education levels, and less-comprehensive health insurance coverage exhibited a paradoxical pattern: they had a heightened tendency to require healthcare but were simultaneously more likely to refuse to access it. Research has demonstrated that as individuals age, life and financial stressors tend to intensify, prompting some to adopt cost-saving measures such as delaying seeking medical attention during periods of illness or injury (57). At the same time, human function gradually decreases with age, and older people have cognitive biases about their own states of health (58). On the one hand, they perceive some physical discomfort as a normal phenomenon associated with aging and therefore do not consider medical attention necessary. On the other hand, they may encounter uncomfortable symptoms frequently and attempt to self-diagnose based on their past experiences. Unmarried individuals may face a dearth of direct support and care from partners or family during times of illness or injury (59, 60), resulting in inadequate social support and influencing how they utilize healthcare. Furthermore, compared with married individuals, unmarried people might be more strongly inclined toward independent problem solving and demonstrate less psychological reliance on external support (61). Consequently, they might be more likely to self-manage than to seek medical assistance when dealing with sickness or injury. Conversely, the results showed that individuals with stable jobs, better financial circumstances, and comprehensive health insurance coverage found it easier to access healthcare services without undue concern over financial burdens, similar to previous findings (62–64). Furthermore, those with higher educational attainment tended to have heightened health awareness (65), which facilitated the transformation of healthcare service needs into actual demands. These findings aligned with the results of the existing study. Therefore, health education campaigns and health literacy promotion programme should be targeted at the older adult and unmarried population to reduce “self-diagnosis” behavior. For example, in terms of health education activities, various channels such as community publicity and school education can be used to develop targeted educational content for different age groups and populations In addition, given the relatively low participation rate in commercial insurance, we emphasize the need to provide residents with a diverse range of commercial insurance services, increase participation rates and optimize the reimbursement process, thereby alleviate the economic burden of illness on patients.
Furthermore, our in-depth analysis discovered a nuanced phenomenon: while Enabling Resources made a direct positive contribution to healthcare utilization decisions, these resources unexpectedly exerted a substantial negative indirect influence through mediating factors such as Health Behaviors, Need, and past Medical-service Experience (β = −0.098, P < 0.05). This finding implied that when the overall effect of Predisposing and Enabling Resources on healthcare utilization was evaluated, a notable offset between direct and indirect effects appeared, ultimately resulting in a statistically insignificant total effect. To delve deeper into the reason for this phenomenon, we must consider potential interference from external factors. Specifically, the design and execution of policies and systems, entrenched cultural practices, and the operational efficiency of the healthcare system can significantly influence individuals' healthcare utilization decisions (66, 67). These externalities can intricately and imperceptibly interact with Predisposing and Enabling Resources, giving rise to a “masking effect” that obscures or diminishes otherwise discernible direct effects. In light of this, a more scientific and rigorous approach is imperative when formulating and implementing relevant policies and interventions. First, the diversity of population characteristics and variations in Enabling Resources must be fully acknowledged, since they affect healthcare utilization, which will help researchers avoid generalization or simplification. Second, it is crucial to intensify research efforts on individuals with distinct characteristics to comprehend their unique healthcare needs and service utilization patterns and thereby enable the provision of more precise and personalized intervention strategies.
This study theoretically confirms that need is the most influential factor on the utilization of medical services, which is similar to the results of previous researches on Andersen Healthcare Utilization Model (17–19). In this study, we used Health Status as a proxy measure to quantify the demand for medical services among residents. Our findings indicated that Health Status not only exerted a direct positive influence on residents' propensity to seek medical attention when ill or injured but also reinforced this tendency through an indirect pathway involving Medical-service Experience. Specifically, individuals with superior health demonstrated a greater likelihood of seeking medical services, reflecting their favorable stance toward health preservation and acknowledgment of the significance of medical services.
In addition, Health Behaviors exerted a notable indirect influence on healthcare utilization decisions, mediated through Health Status. Proactive engagement in health-promoting behaviors contributes to the preservation and enhancement of an individual's physiological functions, enabling them to maintain or improve their health (68). This favorable state of health not only mitigates the risk of disease and injury but also heightens individuals' awareness and concern for their own wellbeing (69), empowering them to promptly and effectively utilize healthcare when confronted with health challenges. Furthermore, Health Behaviors play a pivotal role in shaping residents' health awareness and preventive attitudes. The consistent practice of healthy behaviors fosters health literacy in residents, heightening their understanding of health knowledge, reinforcing the significance of disease prevention, and motivating them to proactively safeguard their health in daily life (70). This heightened health awareness and preventive mindset serve as a crucial internal stimulus, propelling residents to actively seek medical services when they are ill or injured (71).
Compared with previous researches, this study extends Andersen Healthcare Utilization Model and emphasizes the important impact of “Medical-service Experience” as an independent dimension on health service utilization. In this study, we found that negative encounters with healthcare services markedly deterred patients from seeking care when ill or injured, manifesting as a pattern of “intentional avoidance.” This emphasized that suboptimal healthcare experiences not only fail to address patients' health concerns but can also negatively affect their future utilization of healthcare services over the long term. In the UK, a healthcare quality investigation study reveals that in the patient-provider relationship, poor medical service experiences (such as disrespect or receiving unfair treatment) are highly prevalent, particularly among minority ethnic/racial groups, and this can impact the utilization of healthcare, thereby leading to health disparities (72). Another survey of outpatient department patients indicates that when patients have a poor medical service experience for any reason (such as feeling powerless or being disrespected), their responses may be extremely negative, including disappointment, fear, and the desire to leave the healthcare system (73). A study in the United States shows that a high-perceived quality of healthcare, which is closely related to the medical service experience, will enhance the utilization of healthcare services (74). The research in Bangladesh also demonstrates that the perception of customers plays a crucial role in the utilization of community clinic services (50). For special populations, studies in the United States and India reveal that the negative experiences of the older adult (75) and transgender individuals (76) are important influencing factors of healthcare utilization. Similarly, prior research has emphasized the pivotal role of positive healthcare experiences in shaping favorable healthcare-seeking behaviors (77). Specifically, when residents receive high-quality medical services and experience effective recovery from prior illnesses or injuries, such positive encounters significantly boost their trust in and satisfaction with the healthcare system (77, 78). In addition, Medical-service Experience is an important measure of patient loyalty, its quality intimately tied to patients' subsequent medical-treatment decisions (79). Consequently, in the face of similar health challenges in the future, they draw on their past positive experiences, which make them more inclined to proactively seek professional medical assistance. Therefore, from a practical perspective, in order to foster the effective utilization of healthcare services and enhance patients' health and wellbeing, medical institutions should continuously enhance the quality of medical services, provide patient-centered services to patients, shape a positive patient experience, and promote a long-term and stable doctor-patient relationship (80). In addition, policymakers ought to establish a safer, more efficacious and more convenient setting for patients through enhancing regulatory mechanisms and intensifying personnel training.
4.1 Strengths and limitations of this study
Firstly, this study systematically explored the effects of multiple dimensions on residents' healthcare utilization decisions based on the Anderson healthcare utilization model. The multi-dimensional framework offers insights into patients' healthcare-seeking behaviors, providing an empirical basis for health policies and medical service optimization. Secondly, strict controls were imposed in data collection and processing. The CGSS data ensured authority and reliability. Various statistical methods were used to test hypotheses, enhancing the scientific nature and reliability of the results. Ultimately, the study integrates medical service experience into the Andersen model and reveals the interactions among factors. It provides a theoretical foundation for healthcare utilization inquiries and clarifies the decision-making mechanism. The findings offer targeted policy suggestions, which are of great practical significance for improving the healthcare system.
However, some limitations of this research should be acknowledged. First, although many significant factors were considered, potential variables, especially psychological and policy factors, might have been omitted from the analysis. Future research can broaden the variable range, for example, by incorporating factors such as regional disparities, provider trust, and telemedicine access into the research, in order to enhance the explanatory power for residents' healthcare utilization behaviors. Second, this study has limitations in causal inference. To better clarify the causal relationships among various factors, future studies can use more rigorous experimental designs or advanced causal inference methods to enhance the causal explanatory power. Third, there might be potential self-report bias in survey responses. Future research can utilize various data collection methods, such as objective measurement and observation, to mitigate the impact of self-report bias on the research results. Finally, it is essential to highlight that the dataset utilized in this research exclusively originates from China. When extrapolating the findings to international contexts, further verification is indeed necessary, but this study nevertheless offers a significant point of reference for analogous inquiries. It is intrinsically arduous for any scholarly endeavor to achieve exhaustive comprehensiveness, and this investigation is no deviation from this norm.
5 Conclusions
In this study, we systematically explored the multi-dimensional factors influencing the healthcare utilization behavior of Chinese residents, effectively validating the applicability and explanatory power of the Anderson Healthcare Utilization Model within this context. Through rigorous empirical analysis, we revealed the intricate interplay among Predisposing Characteristics, Enabling Resources, Health Behaviors, Need, and Medical-service Experience, which collectively molded residents' healthcare-seeking decisions. This study highlights the urgent need for targeted healthcare policies that improve financial accessibility, promote positive healthcare experiences, and support vulnerable groups, particularly older and unmarried individuals. Future research should explore longitudinal trends and intervention efficacy to further refine healthcare access strategies.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
HJ: Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. CM: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. XS: Data curation, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. TF: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. YZ: Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by Humanities and Social Science Fund of Ministry of Education of China [grant number: 24YJCZH111]. The funding agencies had no role in design, analysis, interpretation, or writing of this study.
Acknowledgments
The data utilized in this article originate from the China General Social Survey (CGSS) project, hosted by the China Survey and Data Center at Renmin University of China. The authors extend their gratitude to this esteemed institution and its personnel for their invaluable assistance with the data.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpubh.2025.1503601/full#supplementary-material
Abbreviations
PE, Predisposing and Enabling; NE, Need; HB, Health Behavior; MS, Medical-Service Experience; DUHS, decision to utilize health services; EFA, exploratory factor analysis; CFA, confirmatory factor analysis; SEM, structural equation modeling; VR, varimax rotation; PCA, principal component analysis; RMSEA, root mean square error of approximation; CFI, comparative-fit index; NFI, normed-fit index; TLI, the Tucker-Lewis index; IFI, incremental-fit index.
References
1. Wang Y, Jiang N, Shao H, Wang Z. Exploring unmet healthcare needs and associated inequalities among middle-aged and older adults in Eastern China during the progression toward universal health coverage. Health Econ Rev. (2024) 14:46. doi: 10.1186/s13561-024-00521-7
2. Neill R, Kautsar H, Trujillo A. Is economic growth enough to propel rehabilitation expenditures? An empirical analysis of country panel data and policy implications. BMC Public Health. (2024) 24:1154. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-18601-y
3. Ma M, Shi L, Xie W, Zhu Q, Luo J, Liao S, et al. Coupling coordination degree of healthcare resource supply, demand and elderly population change in China. Int J Equity Health. (2024) 23:147. doi: 10.1186/s12939-024-02236-x
4. Shan L, Gan Y, Yan X, Wang S, Yin Y, Wu X. Uneven primary healthcare supply of rural doctors and medical equipment in remote China: community impact and the moderating effect of policy intervention. Int J Equity Health. (2024) 23:97. doi: 10.1186/s12939-024-02183-7
5. Atanasova E, Panayotova S. Which factors influence health services utilization in Bulgaria? Results of a cross-sectional survey. Eur J Public Health. (2024) 34:646–51. doi: 10.1093/eurpub/ckae095
6. Ricketts TC, Goldsmith LJ. Access in health services research: the battle of the frameworks. Nurs Outlook. (2005) 53:274–80. doi: 10.1016/j.outlook.2005.06.007
7. Levesque J, Harris MF, Russell G. Patient-centred access to health care: conceptualising access at the interface of health systems and populations. Int J Equity Health. (2013) 12:9. doi: 10.1186/1475-9276-12-18
8. Penchansky R, Thomas JW. The concept of access - definition and relationship to consumer satisfaction. Med Care. (1981) 19:127–40. doi: 10.1097/00005650-198102000-00001
9. Andersen RM. Revisiting the behavioral-model and access to medical-care - does it matter. J Health Soc Behav. (1995) 36:1–10. doi: 10.2307/2137284
10. Bradley EH, McGraw SA, Curry L, Buckser A, King KL, Kasl SV, et al. Expanding the Andersen model: the role of psychosocial factors in long-term care use. Health Serv Res. (2002) 37:1221–42. doi: 10.1111/1475-6773.01053
11. Radhamony R, Cross WM, Townsin L, Banik B. Culturally and linguistically diverse community access and utilisation of the mental health service: an explanation using Andersen's behavioural model. Issues Ment Health Nurs. (2024) 45:758–65. doi: 10.1080/01612840.2024.2359602
12. Lin W, Yin W, Yuan D. Factors associated with the utilization of community-based health services among older adults in China-an empirical study based on Anderson's health behavior model. BMC Primary Care. (2022) 23:99. doi: 10.1186/s12875-022-01697-9
13. Alkhawaldeh A, ALBashtawy M, Rayan A, Abdalrahim A, Musa A, Eshah N, et al. Application and use of Andersen's behavioral model as theoretical framework: a systematic literature review from 2012-2021. Iranian J Public Health. (2023) 52:1346–1354. doi: 10.18502/ijph.v52i7.13236
14. Lee S, et al. A comparison of factors associated with unmet healthcare needs in people with disabilities before and after COVID-19: a nationally representative population-based study. BMC Health Serv. Res. (2024) 24:134. doi: 10.1186/s12913-024-10579-y
15. Cai Y, Zhang J, Li Y, Li J, Luo W, Zhang J, et al. Factors associated with oral health service utilization among young people in southern China. BMC Oral Health. (2024) 24:302. doi: 10.1186/s12903-024-03994-4
16. Brandao D, Paul C, Ribeiro O. Health care utilization in very advanced ages: a study on predisposing, enabling and need factors. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. (2022) 98:10. doi: 10.1016/j.archger.2021.104561
17. Heider D, Matschinger H, Müller H, Saum KU, Quinzler R, Haefeli WE, et al. Health care costs in the elderly in Germany: an analysis applying Andersen's behavioral model of health care utilization. BMC Health Serv Res. (2014) 14:12. doi: 10.1186/1472-6963-14-71
18. Graham A, Hasking P, Brooker J, Clarke D, Meadows G. Mental health service use among those with depression: an exploration using Andersen's Behavioral Model of Health Service Use. J Affect Disord. (2017) 208:170–6. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2016.08.074
19. Kaya S, Sain Guven G, Aydan S, Toka O. Predictors of hospital readmissions in internal medicine patients: application of Andersen's Model. Int J Health Plann Manage. (2019) 34:370–83. doi: 10.1002/hpm.2648
20. Amin NS, Driver N. Health care utilization among Middle Eastern, Hispanic/Latino, and Asian immigrants in the United States: an application of Andersen's behavioral model. Ethn Health. (2022) 27:858–76. doi: 10.1080/13557858.2020.1830034
21. Zhang S, Chen Q, Zhang B. Understanding healthcare utilization in china through the andersen behavioral model: review of evidence from the China health and nutrition survey. Risk Manage. Healthc Policy. (2019) 12:209–223. doi: 10.2147/RMHP.S218661
22. Li Y-N, Nong D-X, Wei B, Feng Q-M, Luo H-Y. The impact of predisposing, enabling, and need factors in utilization of health services among rural residents in Guangxi, China. BMC Health Serv Res. (2016). 16:9. doi: 10.1186/s12913-016-1825-4
23. Xin Y, Ren X. Determinants of province-based health service utilization according to Andersen ' s Behavioral Model: a population-based spatial panel modeling study. BMC Public Health. (2023) 23:14. doi: 10.1186/s12889-023-15885-4
24. Peng C, Burr JA, Kim K, Lu N. Home and community-based service utilization among older adults in urban China: the role of social capital. J Gerontol Soc Work. (2020) 63:790–806. doi: 10.1080/01634372.2020.1787574
25. Liu Z, Tan Y, Liang H, Gu Y, Wang X, Hao Y, et al. Factors influencing residents' willingness to contract with general practitioners in Guangzhou, China, during the GP policy trial phase: a cross-sectional study based on Andersen's behavioral model of health services use. Inquiry. (2019) 56:11. doi: 10.1177/0046958019845484
26. Che R, Cheung M. Factors associated with intended utilization of home-based long-term care among older adults in China: the moderating effect of community support. J Gerontol Series B-Psychol Sci Social Sci. (2024) 79:10. doi: 10.1093/geronb/gbae146
27. Suo Z, Shao L, Lang Y. A study on the factors influencing the utilization of public health services by China's migrant population based on the Shapley value method. BMC Public Health. (2023) 23:3. doi: 10.1186/s12889-023-17193-3
28. Chang E, Chan KS, Han H. Effect of acculturation on variations in having a usual source of care among Asian Americans and Non-Hispanic Whites in California. Am J Public Health. (2015) 105:398–407. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2014.301950
29. Fortin M, Bamvita J, Fleury M. Patient satisfaction with mental health services based on Andersen's Behavioral Model. Can J Psychiat. (2018) 63:103–14. doi: 10.1177/0706743717737030
30. Murtha JA, Alagoz E, Breuer CR, Finn A, Raffa SD, Voils CI, et al. Individual-level barriers to bariatric surgery from patient and provider perspectives: a qualitative study. Am J Surg. (2022). 224:429–36. doi: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2021.12.022
31. Shu Z, Liu Y, Li M, Li J. The effects of health system reform on medical services utilization and expenditures in China in 2004-2015. Int Health. (2021) 13:640–7. doi: 10.1093/inthealth/ihab041
32. Rahmawati T, Hsieh H. Appraisal of universal health insurance and maternal health services utilization: pre- and post-context of the Jaminan Kesehatan Nasional implementation in Indonesia. Front Public Health. (2024) 12:1301421. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1301421
33. Ware JE, Gandek B. Overview of the SF-36 health survey and the International Quality of Life Assessment (IQOLA) project. J Clini Epidemiol. (1998) 51:903–12. doi: 10.1016/S0895-4356(98)00081-X
34. Ware JE. Improvements in short-form measures of health status: Introduction to a series. J Clini Epidemiol. (2008) 61:1–5. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2007.08.008
35. Lang L, Zhang L, Zhang P, Li Q, Bian J, Guo Y. Evaluating the reliability and validity of SF-8 with a large representative sample of urban Chinese. Health Qual Life Outcomes. (2018) 16:55. doi: 10.1186/s12955-018-0880-4
36. Turner-Bowker DM. Usefulness of the SF−8TM Health Survey for comparing the impact of migraine and other conditions. Qual Life Res. (2003) 12:1003–12. doi: 10.1023/A:1026179517081
37. Pan L, Wang C, Cao X, Zhu H, Luo L. Unmet healthcare needs and their determining factors among unwell migrants: a comparative study in Shanghai. Int J Environm Res Public Health. (2022) 19:5499. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19095499
38. Shao S, Zhang H, Chen X, Xu X, Zhao Y, Wang M, et al. Health education services utilization and its determinants among migrants: a cross-sectional study in urban-rural fringe areas of Beijing, China. BMC Family Pract. (2021) 22:23. doi: 10.1186/s12875-021-01368-1
39. Baumeister SE, Schumann A, Meyer C, John U, Völzke H, Alte D. Effects of smoking cessation on health care use: is elevated risk of hospitalization among former smokers attributable to smoking-related morbidity? Drug Alcohol Depend. (2007) 88:197–203. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2006.10.015
40. Keto J, Ventola H, Jokelainen J, Timonen M, Linden K, Ylisaukko-Oja T, et al. Primary health care utilisation and its costs among middle-aged smokers. Eur J Health Econ. (2017) 18:351–60. doi: 10.1007/s10198-016-0793-2
41. Coombes JS, Law J, Lancashire B, Fassett RG. “Exercise is medicine”: curbing the burden of chronic disease and physical inactivity. Asia Pac J Public Health. (2015) 27:NP600–5. doi: 10.1177/1010539513481492
42. Hou Z, Zhang X, Gao F. Prospective advances in beneficial effects of exercise on human health. Physical Exercise For Human Health. (2020) 1228:455–9. doi: 10.1007/978-981-15-1792-1_31
43. Lordan G, Pakrashi D. Make time for physical activity or you may spend more time sick! Social Indicat Res. (2014) 119:1379–91. doi: 10.1007/s11205-013-0545-y
44. Ge D, Chu J, Zhou C, Qian Y, Zhang L, Sun L. Rural-urban difference in the use of annual physical examination among seniors in Shandong, China: a cross-sectional study. Int J Equity Health. (2017) 16:86. doi: 10.1186/s12939-017-0585-z
45. Ma X, Fan W, Zhang X, Zhang S, Feng X, Song S, et al. The urban-rural disparities and factors associated with the utilization of public health services among diabetes patients in China. BMC Public Health. (2023) 23:198. doi: 10.1186/s12889-023-17198-y
46. Matsuda S Regulatory Regulatory effects of health examination programs on medical expenditures for the elderly in Japan. Soc Sci Med. (1996) 42:661–70. doi: 10.1016/0277-9536(95)00197-2
47. Kitts RL, Gallagher K, Ibeziako P, Bujoreanu S, Garcia G, Demaso DR. Parent and young adult satisfaction with psychiatry consultation services in a children's hospital. Psychosomatics, (2013). 54:575–84. doi: 10.1016/j.psym.2013.01.008
48. McCallum SL, Andrews JM, Gaughwin MD, Turnbull DA, Mikocka-Walus AA. Patient satisfaction with treatment for alcohol use disorders: comparing patients with and without severe mental health symptoms. Patient Prefer Adherence. (2016) 10:1489–500. doi: 10.2147/PPA.S92902
49. Fang J, Liu L, Fang P. What is the most important factor affecting patient satisfaction - a study based on gamma coefficient. Patient Prefer Adherence. (2019) 13:515–25. doi: 10.2147/PPA.S197015
50. Karim RM, Abdullah MS, Rahman AM, Alam AM. Identifying role of perceived quality and satisfaction on the utilization status of the community clinic services; Bangladesh context. BMC Health Serv Res. (2016) 16:204. doi: 10.1186/s12913-016-1461-z
51. Parker T, et al. Consumer awareness and utilization of clinical services, and their satisfaction and loyalty with community pharmacies: Analysis of a US nationwide survey. J Am College Clini Pharm. (2019) 2:335–342. doi: 10.1002/jac5.1137
52. Anderson JC, Gerbing DW. Structural equation modeling in practice - a review and recommended 2-step approach. Psychol Bullet. (1988) 103:411–23. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.103.3.411
53. Bufquin D, Park J-Y, Back RM, Meira JVd, Hight SK. Employee work status, mental health, substance use, and career turnover intentions: an examination of restaurant employees during COVID-19. Int J Hospit Manage. (2021) 93:102764. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhm.2020.102764
54. Fan N. Strategy use in second language vocabulary learning and its relationships with the breadth and depth of vocabulary knowledge: a structural equation modeling study. Front Psychol. (2020) 11:752. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.00752
55. Golini N, Egidi V. The latent dimensions of poor self-rated health: how chronic diseases, functional and emotional dimensions interact influencing self-rated health in Italian elderly. Soc Indicat Res. (2016) 128:321–39. doi: 10.1007/s11205-015-1033-3
56. Harerimana A, Mtshali NG. Using exploratory and confirmatory factor analysis to understand the role of technology in nursing education. Nurse Educ Today. (2020) 92:104490. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2020.104490
57. Gong CH, Kendig H, He X. Factors predicting health services use among older people in China: An analysis of the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study 2013. BMC Health Serv Res. (2016). 16:1307. doi: 10.1186/s12913-016-1307-8
58. Spitzer S, Weber D. Reporting biases in self-assessed physical and cognitive health status of older Europeans. PLoS ONE. (2019) 14:e0223526. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0223526
59. Warner DF, Adams SA, Anderson RK. The good, the bad, and the indifferent: physical disability, social role configurations, and changes in loneliness among married and unmarried older adults. J Aging Health. (2019) 31:1423–53. doi: 10.1177/0898264318781129
60. Zhang J, Li X, Su S, Liu M. The influence of marital status on the stage at diagnosis, treatment, and survival of adult patients with gastric cancer: a population-based study. Oncotarget. (2017) 8:22385–22405. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7399
61. Sang LT, Thanh V. Understanding the high rates of unmarried Chinese-Vietnamese women: a case study of Cai Rang. Asian Women. (2019) 35:1–18. doi: 10.14431/aw.2019.03.35.1.1
62. Gea-Sánchez M, Gastaldo D, Molina-Luque F, Otero-García L. Access and utilisation of social and health services as a social determinant of health: the case of undocumented Latin American immigrant women working in Lleida (Catalonia, Spain). Health Soc Care Commun. (2017) 25:424–34. doi: 10.1111/hsc.12322
63. Su M, Zhang T, Zhang W, Li Z, Fan X. Decomposition analysis on the equity of health examination utilization for the middle-aged and elderly people in China: based on longitudinal CHARLS data from 2011 to 2018. BMC Public Health. (2024) 24:998. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-18068-x
64. Fan X, Su M, Si Y, Zhao Y, Zhou Z. The benefits of an integrated social medical insurance for health services utilization in rural China: evidence from the China health and retirement longitudinal study. Int J Equity Health. (2021) 20:126. doi: 10.1186/s12939-021-01457-8
65. Besiroglu E, Lutfioglu M. Relations between periodontal status, oral health - related quality of life and perceived oral health and oral health consciousness levels in a Turkish population. Int J Dent Hygiene. (2020) 18:251–60. doi: 10.1111/idh.12443
66. Gage AD, Leslie HH, Bitton A, Jerome JG, Joseph JP, Thermidor R, et al. Does quality influence utilization of primary health care? Evidence from Haiti. Global Health. (2018) 14:59. doi: 10.1186/s12992-018-0379-0
67. Zou Q, He X, Li Z, Xu W, Zhang L. The effects of poverty reduction policy on health services utilization among the rural poor: a quasi-experimental study in central and western rural China. Int J Equity Health. (2019) 18:186. doi: 10.1186/s12939-019-1099-7
68. Allegrante JP, Wells MT, Peterson JC. Interventions to support behavioral self-management of chronic diseases. Annu Rev Public Health. (2019) 40:127–46. doi: 10.1146/annurev-publhealth-040218-044008
69. Beyer A, Wolff JK, Warner LM, Schüz B, Wurm S. The role of physical activity in the relationship between self-perceptions of ageing and self-rated health in older adults. Psychol Health. (2015) 30:671–85. doi: 10.1080/08870446.2015.1014370
70. Ghosh T, Lane DS. The role of preventive medicine in improving societal health. Am J Prevent Med. (2022) 62:653–55. doi: 10.1016/j.amepre.2021.12.005
71. Hai-YanYu, Wu W-L, Yu L-W, Wu L. Health literacy and health outcomes in China ' s floating population: mediating effects of health service. BMC Public Health. (2021) 21:691. doi: 10.1186/s12889-021-10662-7
72. Blanchard J, Lurie N. R-E-S-P-E-C-T: Patient reports of disrespect in the healthcare setting and its impact on care. J Family Pract. (2004) 53:721–30.
73. Staniszewska SH, Henderson L. Patients ' evaluations of the quality of care: influencing factors and the importance of engagement. J Adv Nurs. (2005) 49:530–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2648.2004.03326.x
74. Sellars B, Garza MA, Fryer CS, Thomas SB. Utilization of health care services and willingness to participate in future medical research: the role of race and social support. J Nat Med Assoc. (2010) 102:776–86. doi: 10.1016/S0027-9684(15)30674-X
75. Ambade M, Kim R, Subramanian SV. Experience of health care utilization for inpatient and outpatient services among older adults in India. Public Health Pract. (2024) 8:10. doi: 10.1016/j.puhip.2024.100541
76. Lerner JE, Robles G. Perceived barriers and facilitators to health care utilization in the United States for transgender people: a review of recent literature. J Health Care Poor Unders. (2017) 28:127–52. doi: 10.1353/hpu.2017.0014
77. Huang I-C, Du P-L, Lin L-S, Liu T-Y, Lin T-F, Huang W-C. The effect of perceived value, trust, and commitment on patient loyalty in Taiwan. Inquiry. (2021) 58:7217. doi: 10.1177/00469580211007217
78. Vimla, Taneja U. Navigating from brand image to patient loyalty: mediating effect of service quality and patient satisfaction. J Health Manage. (2020) 22:430–445. doi: 10.1177/0972063420937940
79. Gérard L, François M, de Chefdebien M, Saint-Lary O, Jami A. The patient, the doctor, and the patient' s loyalty: a qualitative study in French general practice. Br J General Pract. (2016) 66:E810–E818. doi: 10.3399/bjgp16X687541
Keywords: medical services, Andersen Healthcare Utilization Model, national survey, influencing factors, structural equation model
Citation: Jia H, Miao C, Song X, Feng T and Zhao Y (2025) Factors influencing intentional non-utilization of healthcare: a study using the Andersen model. Front. Public Health 13:1503601. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1503601
Received: 29 September 2024; Accepted: 24 March 2025;
Published: 09 April 2025.
Edited by:
Chao Ma, Southeast University, ChinaReviewed by:
M. Alvi Syahrin, Immigration Polytechnic, IndonesiaAsbjørn Steiro, Norwegian Directorate of Health, Norway
Copyright © 2025 Jia, Miao, Song, Feng and Zhao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Huanhuan Jia, amhoXzE5OTRAMTYzLmNvbQ==
 Huanhuan Jia
Huanhuan Jia Chunxia Miao1
Chunxia Miao1