
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Public Health, 19 March 2025
Sec. Injury Prevention and Control
Volume 13 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2025.1488923
This article is part of the Research TopicGender Differences in Falls and Mobility Patterns of Older AdultsView all 7 articles
Background: This study aims to examine the combined effects of depressive symptoms (DS) and cardiovascular disease (CVD) on fall risk in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), as well as evaluating the potential moderating effects of sleep status and gender.
Methods: This study analyzed 941 participants from the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study (CHARLS). Participants were divided into four groups: those with both depressive symptoms and CVD (DS+/CVD+), those with only depressive symptoms (DS+/CVD−), those with only CVD (DS−/CVD+), and those with neither depressive symptoms nor CVD (DS−/CVD−). Additionally, stratified analyses were conducted to differentiate participants based on sleep statuses and gender.
Results: In the absence of potential confounding variables, the phenotypes DS+/CVD+, DS+/CVD−, and DS−/CVD+ were each independently linked to a higher fall risk relative to the reference category DS−/CVD− (RR = 1.96, 95% CI: 1.25–3.07; RR = 1.92, 95% CI: 1.29–2.87; RR = 1.58, 95% CI: 1.03–2.42, respectively). Specifically, within the sleep sufficiency group, the DS+/CVD+, DS+/CVD−, and DS−/CVD+ phenotypes exhibited a significantly elevated risk of falls relative to the DS−/CVD− phenotype (RR = 2.23, 95% CI: 1.22–4.05; RR = 2.02, 95% CI: 1.19–3.43; RR = 1.73, 95% CI: 1.02–2.93, respectively). After adjusting for confounding variables, Males with DS−/CVD+ phenotypes are significantly more likely to fall (RR = 2.04, 95% CI: 1.04–3.98). In contrast, the DS+/CVD+ and DS+/CVD− phenotypes are linked to a heightened risk of falls in females, with relative risk of 1.79 (95% CI: 1.04–3.09) and 1.82 (95% CI: 1.11–2.98), respectively. Furthermore, there was no evidence of an additive interaction between depression and CVD in relation to fall risk among patients with T2DM (p > 0.05).
Conclusion: The co-occurrence of depression and CVD significantly elevates the risk of falls in diabetic patients. It is recommended that female patients prioritize the prevention and management of depression, whereas male patients should focus on the prevention and management of cardiovascular diseases. Additionally, ensuring adequate sleep is essential for all patients.
Diabetes encompasses a heterogeneous group of disorders marked by abnormalities in glucose regulation (1). T2DM is most prevalent among diabetics. The prevalence of diabetes in China is approximately 12.8%, with T2DM comprising 95% of the diabetic population (2). T2DM can result in numerous severe complications, including diabetic foot, cardiovascular disease, cerebrovascular disease, and blindness, all of which impose significant social and economic burdens. T2DM patients are more likely to fall compared to healthy individuals, according to an increasing body of research (3–5). Consequently, an effective intervention needs to be developed based on empirical evidence to address the risk factors associated with falls in diabetics.
Depression, a prevalent mental disorder globally, has a reported prevalence of 16.8% in China (6). The relationship between depression and the onset of T2DM has been studied in several studies (7–9). It is unequivocally established that depression increases the risk of T2DM (10). According to research, depression is twice as common among women as it is among men (11). Depression is linked to circadian rhythms and sleep disturbances, with women exhibiting more severe depressive symptoms also demonstrating poorer sleep continuity (12). Globally, CVD—a chronic and multifaceted condition resulting from heart and vascular disorders—remains the foremost cause of premature mortality and chronic disability (13). Atherosclerosis-related vascular disorders are also associated with diabetes, according to studies (14). Numerous studies have demonstrated an association between both the quantity and quality of sleep and the risk of CVD (15, 16). The incidence of falls escalates with advancing age, particularly among middle-aged and older adults individuals with T2DM.
The China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study (CHARLS) is a comprehensive national panel survey targeting China’s middle-aged and older adults population, encompassing over 337 million individuals (17). While some researchers have leveraged the CHARLS datasets to explore the effects of body mass index (BMI) and grip strength on fall risk among older adults, there is a notable scarcity of research focusing specifically on the susceptibility of individuals with diabetes to falls. A cross-sectional study utilizing the CHARLS dataset examined the association between frailty and fall risk in diabetic patients but did not establish a conclusive link between frailty and falls. Although depression and cardiovascular disease are acknowledged as independent risk factors for the onset of T2DM, physiological and behavioral variations, such as sleep patterns and physical activity levels, among middle-aged and older adults may contribute to differing fall rates and outcomes.
Consequently, this study aims to investigate the combined effects of depression and CVD on fall risk in patients with T2DM, utilizing data from the CHARLS. Additionally, the study seeks to evaluate the potential moderating effects of different sleep statuses and gender on this association.
We utilized data from two waves of CHARLS database. The CHARLS study is a nationally representative, population-based longitudinal health survey conducted by the National School of Development at Peking University. It targets individuals aged 45 and older in China. In 2011, a baseline survey was conducted, followed by follow-up surveys in 2013, 2015, 2018, 2020 (18). Respondents were selected by means of a multistage probability sampling strategy. Data collection for the CHARLS database was ethically approved by the Biomedical Ethics Review Committee of Peking University (approval no. IRB00001052-11015). All participants in the CHARLS database provided informed consent.
A longitudinal cohort study was undertaken utilizing baseline data from the 2015 CHARLS and follow-up data from 2018. Initially, a preliminary screening of the general demographics of 21,038 participants was conducted, resulting in 1,670 individuals meeting the inclusion criteria. Participants lacking either a BMI measurement or a depression scale score (n = 497) were subsequently excluded. Consequently, 1,173 participants were monitored over a three-year period, with further exclusions applied to those who were lost to follow-up (n = 232). Ultimately, the final sample for the longitudinal cohort study comprised 941 participants.
Baseline data encompassing individual characteristics, sociodemographic information, physical measurements, and both physical and mental health status were collected through a structured questionnaire. The outcome measures for falls were derived from summary data collected during the follow-up period in 2018. The exposure measures, including depressive symptoms and CVD, along with covariates such as age, BMI, sex, sleep duration, marital status, residence, education, smoking status, alcohol consumption, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and disability, were obtained from baseline data collected in 2015. In order to perform subsequent bioassays, trained nurses collected venous blood samples from fasting participants.
A self-reported questionnaire item asked: “Have you been diagnosed by your physician with dyslipidemia, hypertension, or T2DM?” evaluated hypertension, dyslipidemia, and T2DM. Participants who responded affirmatively to this question were classified as having dyslipidemia, hypertension, or T2DM (19).
CVD was assessed through self-reported diagnoses provided by participants. Specifically, participants were queried with the following questions: “Have you been diagnosed with coronary heart disease, heart attack, congestive heart failure, angina, or other heart problems by a physician?” and “Have you been diagnosed with a stroke?” Individuals who answered affirmatively to either question were classified as having CVD (20).
Sleep duration was evaluated through a self-reported questionnaire in which respondents were asked, “What is the average number of hours of sleep you got during the past month? This may be less than the number of hours you spend in bed.” Sleep insufficiency and sufficiency were operationally defined as less than 6 h and 6 h or more, respectively.
The Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale (CES-D) was employed to assess the severity of depressive symptoms in CHARLS (21). This instrument has been validated for evaluating depression within the Chinese population. There are 10 items on the CES-D, each rated on a 4-point Likert scale, asking respondents to indicate how frequently they have experienced depressive symptoms during the past week. Depression is indicated by a score of 10 or higher on the total score, which ranges from 0 to 30 (22).
Using the question “Have you fallen down in the last two years?” as the primary outcome, this study assessed whether diabetic patients fall. Participants who responded affirmatively to the question regarding falls were categorized as having experienced falls.
Categorical variables were expressed as percentages, and the Chi-square test was employed for group comparisons of categorical variables. Continuous variables were presented as mean ± standard deviation, and comparisons were conducted using either the ANOVA or the Mann–Whitney U test.
Multivariate logistic regression analysis was employed to examine the impact of depressive symptoms and CVD on the risk of falls among diabetic patients, with the calculation of relative risk (RR) both unadjusted and adjusted. Drawing from existing literature (2), variables that demonstrated statistical significance in the univariate analysis were included as covariates in the logistic regression model. The study constructed three distinct models: Model 1 was unadjusted; Model 2 was adjusted for age, BMI, sex, sleep duration, marital status, residence, education, smoking status, and alcohol consumption; and Model 3 was further adjusted for age, BMI, sex, sleep duration, marital status, residence, education, smoking status, alcohol consumption, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and disability.
To enhance the precision of our evaluation regarding the combined association of depressive symptoms and CVD with the incidence of falls among diabetic patients, an analysis of additive interactions was conducted using the relative excess risk due to interaction (RERI), attributable proportion due to interaction (AP), and synergy index (SI) (23). In the absence of biological interaction, both RERI and AP would equal 0, while SI would equal 1.
In this study, SPSS (version 26) software was used for the statistical analysis, and R software was used for the statistical analysis (version 3.5.1 from the Vienna, Austria-based R Foundation for Statistical Computing), and GraphPad Prism software (version 8.0.2), all p-values are two-sided and p = 0.05 is considered statistically significant.
The sample selection process is illustrated in Figure 1. A total of 941 eligible participants took part in this cohort study. Follow-up took place over a period of time, 254 new cases of falls were documented, accounting for 26.99% of the study population. Table 1 presents the baseline characteristics of the participants. The mean age of the participants was 62.27 ± 8.56 years. Additionally, 375 participants (39.85%) were identified as having depression, while 357 participants (37.94%) were diagnosed with CVD. Depressive symptoms were observed among participants in the same CVD categories (DS+/CVD+ vs. DS−/CVD+ and DS+/CVD− vs. DS−/CVD−) were significantly more likely to experience sleep insufficiency (50.00% vs. 31.47%, p < 0.001, and 44.65% vs. 22.22%, p < 0.001, respectively), be female (71.87% vs. 52.79%, p < 0.001, and 66.51% vs. 54.47%, p < 0.01), reside in rural areas (61.25% vs. 39.59%, p < 0.001, and 61.86% vs. 46.61%, p < 0.001), have a history of hypertension (53.13% vs. 42.64%, p < 0.05, and 39.07% vs. 34.96%, p < 0.05), and report disability (63.12% vs. 43.65%, p < 0.001, and 50.70% vs. 29.27%, p < 0.001) compared to those without depressive symptoms. Within the same categories of depressive symptoms, participants with CVD (DS+/CVD+ vs. DS+/CVD−, DS−/CVD+ vs. DS−/CVD−) were more likely to exhibit a higher body mass index (BMI) (25.98 ± 3.96 vs. 24.87 ± 3.68, p < 0.01; 26.15 ± 3.79 vs. 25.31 ± 3.40, p < 0.01), a history of dyslipidemia (60.63% vs. 45.12%, p < 0.01; 43.65% vs. 29.27%, p < 0.01), and disability (63.12% vs. 50.70%, p < 0.05; 50.70% vs. 29.27%, p < 0.001) compared to those without CVD. Based on the detailed baseline information provided in Table 1 and Supplementary Tables 1, 2, no significant differences were observed between these groups when it comes to marital status or smoking status.
During the follow-up period, a total of 254 individuals with T2DM reported a history of falls, yielding a cumulative incidence of 26.99%. We employed the Chi-square test to compare the incidence of falls across different depressive symptomatology and CVD phenotypes within the two groups (Figure 2). A significant increase in falls was observed among participants with depressive symptoms (DS+/CVD+ and DS+/CVD−) compared to participants without depressive symptoms (DS−/CVD+ and DS−/CVD−). Additionally, among individuals with depression, those with concurrent CVD demonstrated a significantly higher incidence of falls than those without CVD.
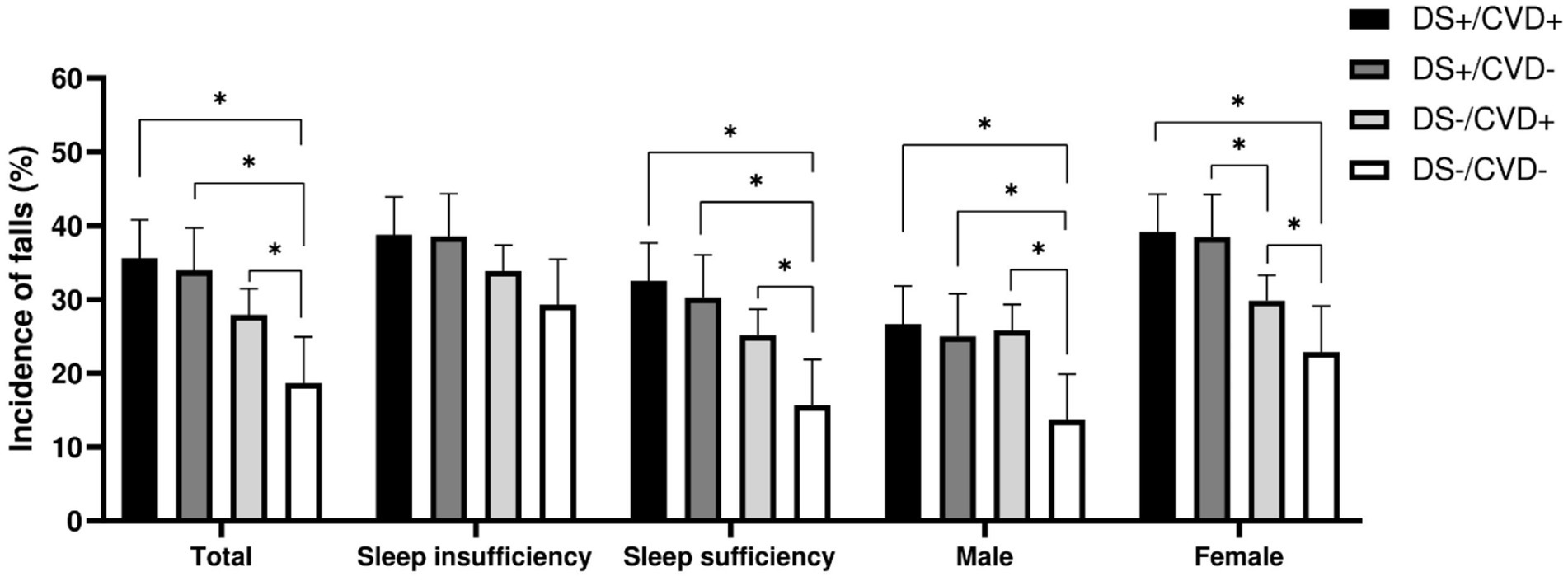
Figure 2. Incidence of falls across different depressive symptoms and CVD phenotypes within the two groups. *: p < 0.05, DS, depressive symptoms; CVD, cardiovascular disease.
Logistic regression was used to investigate the independent effects of various phenotypes on falls. Taking into account potential confounding factors, the phenotypes DS+/CVD+, DS+/CVD−, and DS−/CVD+ were found to be independently associated with an increased risk of falls compared to the reference category DS−/CVD− (RR = 1.96, 95% CI: 1.25–3.07; RR = 1.92, 95% CI: 1.29–2.87; RR = 1.58, 95% CI: 1.03–2.42, respectively) (Figure 3; Table 2).
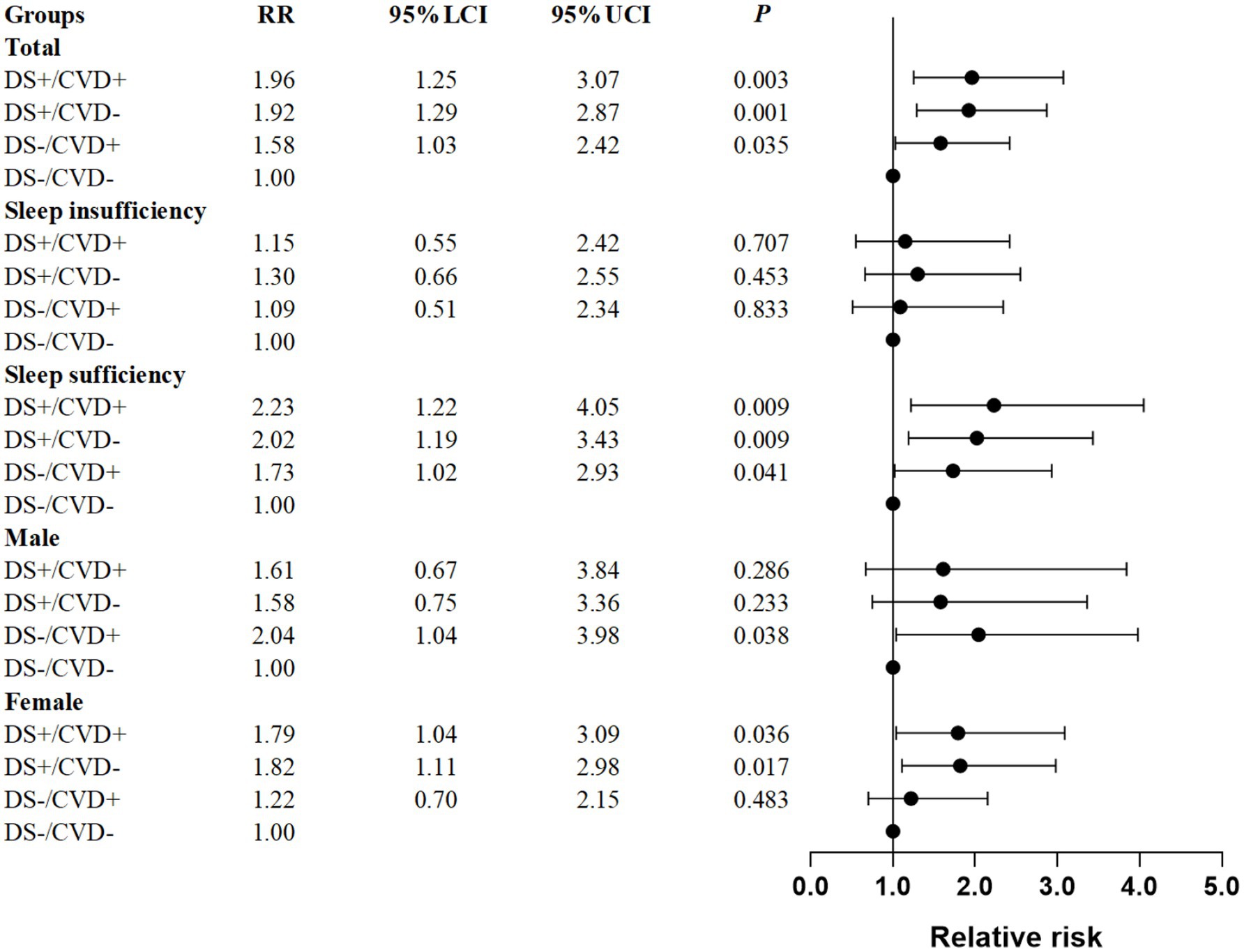
Figure 3. Forest plot for the relative risk of the combined association of depressive symptoms and CVD on fall risk in patients with T2DM. Relative risk are after adjustment for age, BMI, sex, sleep duration, marital status, residence, education, smoking status, alcohol consumption, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and disability. DS, depressive symptoms; CVD, cardiovascular disease.
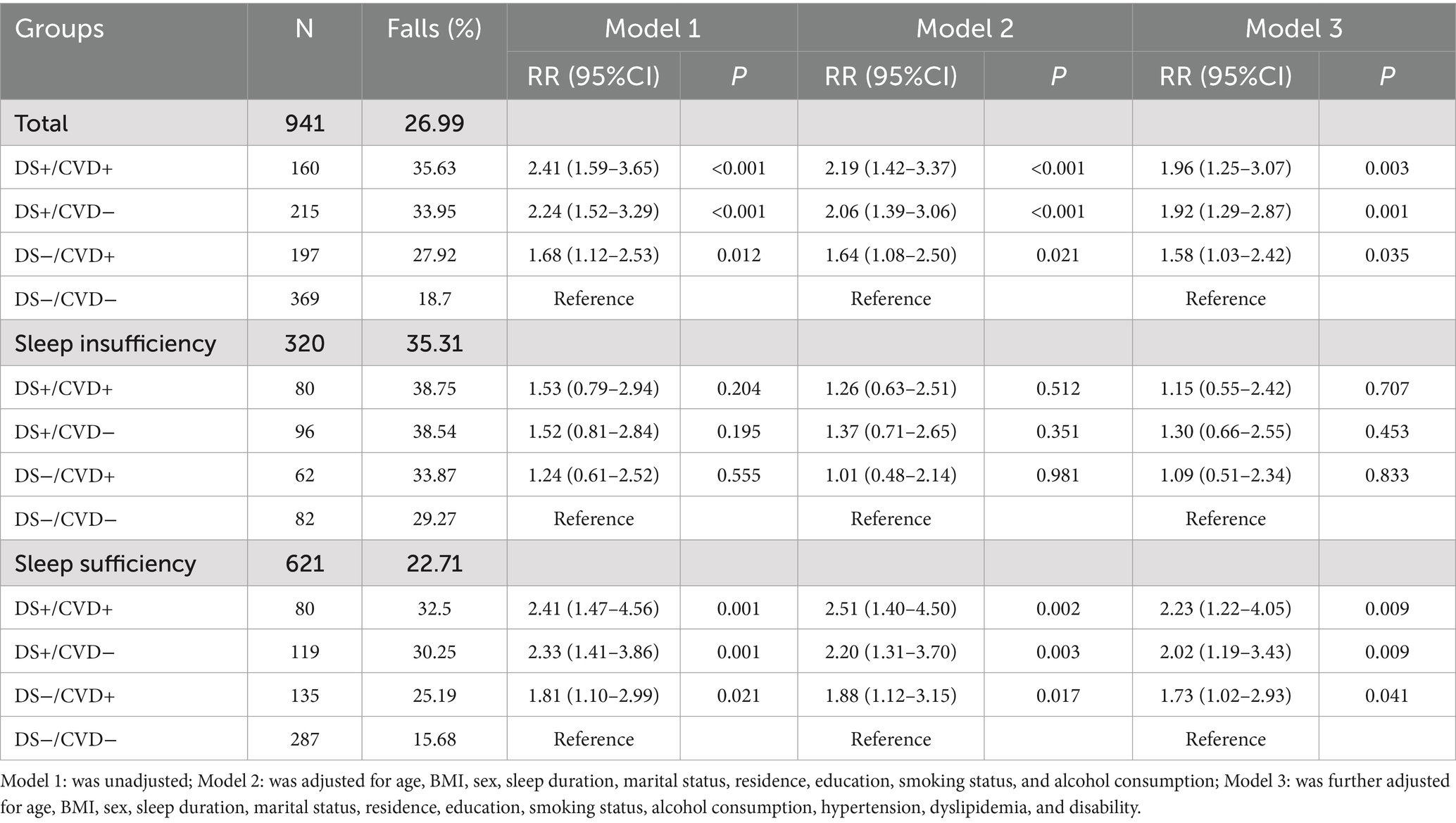
Table 2. Results of logistic regression analysis for combined association of depressive symptoms and CVD on fall risk in patients with T2DM.
For patients with sufficient sleep, the DS+/CVD+, DS+/CVD−, and DS−/CVD+ phenotypes demonstrated a higher incidence of falls compared to the DS−/CVD− phenotype (32.50, 30.25, 25.19% vs. 15.68%, p < 0.05). Contrary to what was observed in patients with inadequate sleep, there was no significant difference between these phenotypes (Table 2; Figure 2). Furthermore, logistic regression analysis was conducted to adjust for potential confounders. Within the sleep sufficiency group, the DS+/CVD+, DS+/CVD−, and DS−/CVD+ phenotypes were associated with a significantly increased risk of falls compared to the DS−/CVD− phenotype (RR = 2.23, 95% CI: 1.22–4.05; RR = 2.02, 95% CI: 1.19–3.43; RR = 1.73, 95% CI: 1.02–2.93, respectively) (Table 2; Figure 3).
Given the sex-specific differences in both CVD and depressive symptoms, we performed a sex-stratified analysis. Among males, the incidence of falls was significantly higher in the DS+/CVD+, DS+/CVD−, and DS−/CVD+ phenotypes compared to the DS−/CVD− phenotype (26.67, 25.00, 25.81% vs. 13.69%, p < 0.05). Similarly, among females, those with depressive symptoms (DS+/CVD+ and DS+/CVD−) exhibited a higher incidence of falls compared to the DS−/CVD− phenotype (39.13, 38.46% vs. 22.89%, p < 0.05) (refer to Table 3 and Figure 2). Notably, after adjusting for confounding variables, it was found that the DS−/CVD+ phenotype is associated with an increased risk of falls exclusively in males (RR = 2.04, 95% CI: 1.04–3.98). Conversely, the DS+/CVD+ and DS+/CVD− phenotypes are associated with a heightened risk of falls exclusively in females (RR = 1.79, 95% CI: 1.04–3.09 and RR = 1.82, 95% CI: 1.11–2.98, respectively) (refer to Table 3 and Figure 2).

Table 3. Results of logistic regression analysis for combined association of depressive symptoms and CVD on fall risk in patients with T2DM stratified by sex.
To evaluate the influence of depressive symptoms and CVD on the risk of falling, we calculated the Relative Excess Risk due to Interaction (RERI), Attributable Proportion (AP), and Synergy Index (SI) (Table 4). The results indicated no evidence of additive interaction (RERI = −0.534, 95% CI: −1.740 to 0.672; AP = −0.221, 95% CI: −0.755 to 0.313; SI = 0.726, 95% CI: 0.360 to 1.464). Additionally, no multiplicative interaction was observed (p > 0.05, Supplementary Table 3). Stratified analyses by different sleep durations and sex yielded consistent results.
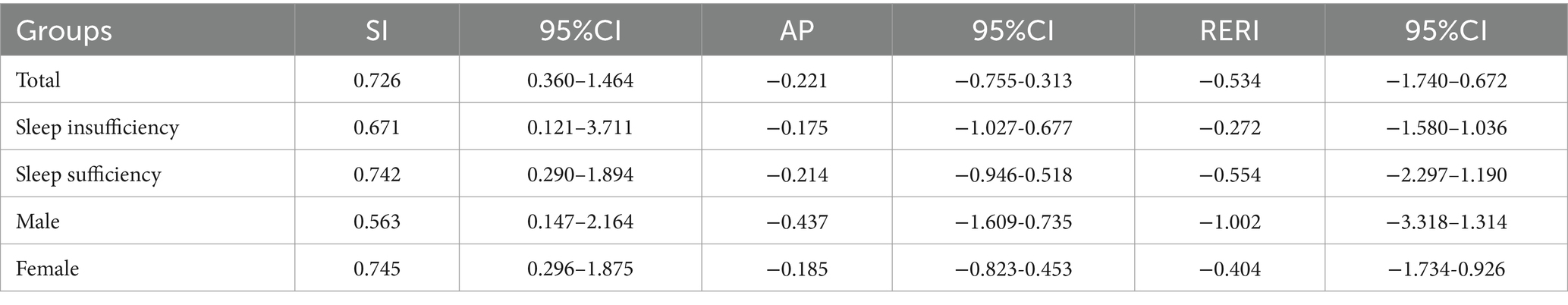
Table 4. Quantitative analysis of additive interaction between depressive symptoms and CVD on fall risk in patients with T2DM.
Globally, 463 million people live with the disease in 2019 (24). Projections indicate that this figure will escalate to 700 million by 2045 (25). T2DM represents a substantial global health burden, significantly impacting individuals’ quality of life. Our study revealed that 26.99% of diabetic patients experienced falls during the follow-up period, with 51.15% of these patients also suffering from depression and 44.09% from CVD. In middle-aged and older adults Chinese patients with T2DM with depression and CVD, this study represents the first attempt to analyze their combined effect on fall risk, with analyses stratified by sleep status and gender. It appears that both depression and CVD increase the risk of falls in diabetics, which is consistent with previous studies (26). Notably, the concomitance of depression and CVD may exacerbate fall risk in diabetic patients more than the presence of either condition alone, particularly among women. Further analysis of the individual and combined effects of depression and CVD on fall risk revealed no evidence of additive or multiplicative interactions between these conditions. Compared to the DS−/CVD− phenotype, the DS+/CVD+, DS+/CVD−, and DS−/CVD+ phenotypes were generally identified as risk factors for T2DM. Notably, the risk of falls in the DS+/CVD+ group was approximately 1.96 times higher than that in the DS−/CVD− group. There was no significant association between depression and falls in the meta-analysis (27). In order to better understand depression’s impact on fall risk among diabetics, further research is needed.
Our findings indicate that CVD can elevate the risk of diabetes, corroborating previous studies (28). CVD complications, such as sarcopenia, are significant risk factors for falls (29). Additionally, Aged individuals with elevated levels of cardiac troponin T and N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-pro BNP) are more likely to fall (30). Our findings indicate that CVD can elevate the risk of diabetes, corroborating previous research (30). Additionally, Depression and falls seem to be bidirectionally correlated, according to studies. Depressive disorders are frequently associated with excessive fear of falling, which further increases the likelihood of falling. Cognitive, sensory, and motor pathways all play a role in the association between depression and fear of falling and disturbances in gait and balance (31). Furthermore, the use of antidepressants has been shown to elevate the risk of falls (32). Depressive symptoms can hinder patients’ adherence to medical recommendations, such as timely medication intake, weight management, and increased physical activity, potentially leading to falls in individuals with diabetes (33). However, Depression and falls continue to be a controversial topic.
The concomitance of depressive symptoms and CVD may elevate the incidence of falls among patients with T2DM. Previous studies have demonstrated that both depressive symptoms and CVD can serve as independent risk factors for falls (34–37). Furthermore, the coexistence of depression and CVD can directly or indirectly influence the onset and progression of diabetes, thereby augmenting the risk of falls. However, our study revealed that depressive symptoms did not exhibit any additive interaction with CVD in relation to falls in patients with T2DM. Limited research has explored this interaction among middle-aged and older adults Chinese populations, highlighting the need for further investigation. It is noteworthy that individuals with diabetes are particularly susceptible to other chronic systemic diseases. In this study, we observed that the coexistence of one or more chronic diseases with depression or cardiovascular disease heightened the risk of falls in diabetic patients. This suggests that these factors play a significant role, which is not only associated with the clinical manifestations of the diseases but may also be linked to the chronic stress resulting from the prolonged duration of depression and cardiovascular disease, as well as the potential exacerbation of these conditions. Such chronic stress may be intricately connected to the combined effects of economic pressure, mental strain, physical health, psychological state, and the disease burden experienced by diabetic patients. Therefore, the management of chronic disease comorbidities in diabetic patients should be prioritized in future research and healthcare strategies.
Given that depressive symptoms and CVD typically exhibit gender-specific variations, Analyses were conducted based on gender. Among men, the DS−/CVD+ phenotype emerged as a significant risk factor for falls in diabetic patients when compared to the DS−/CVD− phenotype, whereas neither the DS+/CVD+ nor the DS+/CVD− phenotypes demonstrated a similar association. In female patients, a comparison of the DS+/CVD+ and DS+/CVD− phenotypes and DS−/CVD− phenotype revealed that both were significantly associated with falls, whereas the DS−/CVD+ phenotype was not. Patients with female diagnoses had a higher rate of falls than patients with male diagnoses. Women with diabetes are at greater risk of falling than men with diabetes due to depression, while men with diabetes are at greater risk of falling due to CVD. This study primarily included women who were either perimenopausal or postmenopausal. During this stage, women experience substantial physical and psychological changes due to the decline in ovarian function (38). These women are more likely to suffer from depressive symptoms than their older counterparts, potentially attributable to an elevated risk of metabolic disorders stemming from age-related alterations in steroidogenesis, which may contribute to the incidence of falls (39). In addition to influencing glucose and lipid metabolism, sex hormones and sex-specific molecular mechanisms have also been found to affect cardiac energy metabolism, the prevalence of CVD in men is higher than that in women (40). This disparity may account for the higher incidence of falls in male patients.
The analysis based on sleep duration indicated that the incidence of falls in the sleep insufficiency group was 35.31%, suggesting that sleep insufficiency constitutes a risk factor for falls among diabetic patients. In the sleep insufficiency cohort, the DS+/CVD+, DS+/CVD−, and DS−/CVD+ phenotypes did not emerge as significant risk factors for falls among diabetic individuals when compared to the DS−/CVD− phenotype. Conversely, within the cohort receiving adequate sleep, these three phenotypes were significantly associated with an increased risk of falls relative to the DS−/CVD− phenotype. Consequently, it can be inferred that sleep deprivation markedly elevates the incidence of falls in diabetic patients, surpassing the impact of DS and CVD factors. Previous research has established that poor sleep quality heightens fall risk (41, 42), and insufficient sleep has been linked to an increased incidence of sarcopenia, thereby further elevating fall risk (43).
This study constitutes the inaugural examination of the synergistic impact of depression and CVD on fall risk in patients with T2DM within this specific demographic in China. Additionally, it evaluates the interplay between various sleep statuses and gender on this combined effect. The strengths of our investigation include a substantial sample size sourced from a national cohort study, which significantly bolsters the robustness and generalizability of our findings. The findings of this study may serve as a valuable reference for the prevention of falls among diabetic patients in China. Implementing targeted interventions to enhance the quality of life and alleviate physical symptoms in middle-aged and older diabetic individuals of varying genders could potentially mitigate the risk of falls. Despite existing research, substantial gaps remain, requiring further studies to clarify the mechanisms behind falls in diabetic patients.
Diabetes patients with falls are at high risk for falls, and this study holds significant potential as a reference for preventing and treating falls. It is crucial for patients with T2DM to prioritize the management of depression and CVD in order to mitigate the associated risk of falls. However, our study is subject to several limitations. Firstly, the data on T2DM, depression, and other medical conditions were obtained through self-reported questionnaires, which may introduce biases in the assessment of these conditions. Secondly, we did not consider the potential effects of medication and the length of illness in our analysis. Lastly, the study was unable to incorporate critical factors contributing to falls in diabetic patients, such as peripheral neuropathy. Consequently, future research should aim to undertake more extensive and comprehensive prospective cohort studies with extended follow-up durations to substantiate our findings.
In summary, our study determined that the concurrent presence of depression and CVD substantially elevates the risk of falls among diabetic patients, a finding that is particularly relevant to middle-aged and older adults populations. However, no significant interaction between depression and CVD on fall risk was observed in this cohort. The prevention and management of depression should be emphasized for female patients, whereas for male patients, priority should be given to the prevention and management of CVD. Patients should ensure adequate sleep and maintain a healthy lifestyle.
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found below: https://charls.charlsdata.com/.
The studies involving humans were approved by Peking University’s Biomedical Ethics Review Committee. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
KL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. XC: Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. LC: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. DL: Conceptualization, Investigation, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was supported by Youth Science Foundation of Guangxi Medical University (GXMUYSF202332).
We would like to acknowledge the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study (CHARLS) research team and all the participants.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpubh.2025.1488923/full#supplementary-material
1. Semenkovich, K, Brown, ME, Svrakic, DM, and Lustman, PJ. Depression in type 2 diabetes mellitus: prevalence, impact, and treatment. Drugs. (2015) 75:577–87. doi: 10.1007/s40265-015-0347-4
2. Chen, P, Song, Q, Wang, X, Li, M, Liu, L, Ning, J, et al. Combined association of abdominal obesity and depressive symptoms with risk of type 2 diabetes: a cohort study. J Psychosom Res. (2024) 179:111627. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychores.2024.111627
3. Lisco, G, Disoteo, OE, De Tullio, A, De Geronimo, V, Giagulli, VA, Monzani, F, et al. Sarcopenia and diabetes: a detrimental liaison of advancing age. Nutrients. (2023) 16:63. doi: 10.3390/nu16010063
4. Rasmussen, NH-H, Dal, J, Jensen, MH, Kvist, AV, van den Bergh, J, Hirata, RP, et al. Impaired postural control in diabetes-a predictor of falls? Arch Osteoporos. (2022) 18:6. doi: 10.1007/s11657-022-01188-5
5. Freire, LB, Brasil-Neto, JP, da Silva, ML, Miranda, MGC, de Mattos, CL, Martins, WR, et al. Risk factors for falls in older adults with diabetes mellitus: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Geriatr. (2024) 24:201. doi: 10.1186/s12877-024-04668-0
6. Gu, Y, Li, X, Zhang, Q, Liu, L, Meng, G, Wu, H, et al. Grip strength and depressive symptoms in a large-scale adult populatio n: the TCLSIH cohort study. J Affect Disord. (2021) 279:222–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2020.08.023
7. Fiore, V, Marci, M, Poggi, A, Giagulli, VA, Licchelli, B, Iacoviello, M, et al. The association between diabetes and depression: a very disabling cond ition. Endocrine. (2015) 48:14–24. doi: 10.1007/s12020-014-0323-x
8. Maina, JG, Balkhiyarova, Z, Nouwen, A, Pupko, I, Ulrich, A, Boissel, M, et al. Bidirectional Mendelian randomization and multiphenotype GWAS show causality and shared pathophysiology between depression and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. (2023) 46:1707–14. doi: 10.2337/dc22-2373
9. Roy, T, and Lloyd, CE. Epidemiology of depression and diabetes: a systematic review. J Affect Disord. (2012) 142:S8–S21. doi: 10.1016/S0165-0327(12)70004-6
10. Renn, BN, Feliciano, L, and Segal, DL. The bidirectional relationship of depression and diabetes: a systemati c review. Clin Psychol Rev. (2011) 31:1239–46. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2011.08.001
11. Seney, ML, Glausier, J, and Sibille, E. Large-scale transcriptomics studies provide insight into sex differences in depression. Biol Psychiatry. (2022) 91:14–24. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2020.12.025
12. White, KH, Rumble, ME, and Benca, RM. Sex differences in the relationship between depressive symptoms and Actigraphic assessments of sleep and rest-activity rhythms in a population-based sample. Psychosom Med. (2017) 79:479–84. doi: 10.1097/psy.0000000000000434
13. Qian, X, Li, Y, Zhang, X, Guo, H, He, J, Wang, X, et al. A cardiovascular disease prediction model based on routine physical examination indicators using machine learning methods: a cohort study. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2022) 9:9. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.854287
14. Regitz-Zagrosek, V, and Kararigas, G. Mechanistic pathways of sex differences in cardiovascular disease. Physiol Rev. (2017) 97:1–37. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00021.2015
15. Chen, J, Patel, SR, Redline, S, Durazo-Arvizu, R, Garside, DB, Reid, KJ, et al. Weekly sleep trajectories and their associations with obesity and hypertension in the Hispanic/Latino population. Sleep. (2018) 41:zsy150. doi: 10.1093/sleep/zsy150
16. Miller, MA, and Howarth, NE. Sleep and cardiovascular disease. Emerg Topics Life Sci. (2023) 7:457–66. doi: 10.1042/etls20230111
17. Zhao, Y, Atun, R, Oldenburg, B, McPake, B, Tang, S, Mercer, SW, et al. Physical multimorbidity, health service use, and catastrophic health expenditure by socioeconomic groups in China: an analysis of population-based panel data. Lancet Glob Health. (2020) 8:e840–9. doi: 10.1016/s2214-109x(20)30127-3
18. Zhao, Y, Hu, Y, Smith, JP, Strauss, J, and Yang, G. Cohort profile: the China health and retirement longitudinal study (CH ARLS). Int J Epidemiol. (2014) 43:61–8. doi: 10.1093/ije/dys203
19. Fan, Z-Y, Yang, Y, Zhang, C-H, Yin, R-Y, Tang, L, and Zhang, F. Prevalence and patterns of comorbidity among middle-aged and elderly people in China: a cross-sectional study based on CHARLS data. Int J Gen Med. (2021) 14:1449–55. doi: 10.2147/ijgm.S309783
20. Shi, Z, Tuomilehto, J, Kronfeld-Schor, N, Alberti, GK, Stern, N, El-Osta, A, et al. The circadian syndrome predicts cardiovascular disease better than metabolic syndrome in Chinese adults. J Intern Med. (2020) 289:851–60. doi: 10.1111/joim.13204
21. Jin, B, Zhang, H, Song, F, Wu, G, and Yang, H. Interaction of sleep duration and depression on cardiovascular disease: a retrospective cohort study. BMC Public Health. (2022) 22:1752. doi: 10.1186/s12889-022-14143-3
22. Luo, H, Li, J, Zhang, Q, Cao, P, Ren, X, Fang, A, et al. Obesity and the onset of depressive symptoms among middle-aged and older adults in China: evidence from the CHARLS. BMC Public Health. (2018) 18:909. doi: 10.1186/s12889-018-5834-6
23. Wu, P-H, Ocak, G, Khairoun, M, Khairoun, O, Bos, WJW, Fu, EL, et al. Chronic kidney disease and atrial fibrillation: a dangerous combination. PLoS One. (2022) 17:e0266046. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0266046
24. Saeedi, P, Petersohn, I, Salpea, P, Malanda, B, Karuranga, S, Unwin, N, et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 157: results from the international diabetes federation diabetes atlas. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. (2019) 157:107843. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107843
25. Zhang, Y, Meng, F, Fei, X, Wang, K, Wu, Y, and Wang, X. Association between physical activity level and diabetes incidence among Chinese middle-aged and older adults: a cross-sectional study from the China health and retirement longitudinal study. Front Public Health. (2024) 12:12. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1430229
26. Nie, X-Y, Dong, X-X, Lu, H, Li, D-L, Zhao, C-H, Huang, Y, et al. Multimorbidity patterns and the risk of falls among older adults: a community-based study in China. BMC Geriatr. (2024) 24:660. doi: 10.1186/s12877-024-05245-1
27. Gambaro, E, Gramaglia, C, Azzolina, D, Campani, D, Molin, AD, and Zeppegno, P. The complex associations between late life depression, fear of falling and risk of falls. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ageing Res Rev. (2022) 73:101532. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2021.101532
28. Gebre, AK, Sim, M, Dalla Via, J, Rodríguez, AJ, Zhu, K, Schousboe, JT, et al. Cardiovascular disease, muscle function, and long-term falls risk: the Perth longitudinal study of ageing women. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. (2023) 107:104911. doi: 10.1016/j.archger.2022.104911
29. Sasaki, K-i, and Fukumoto, Y. Sarcopenia as a comorbidity of cardiovascular disease. J Cardiol. (2022) 79:596–604. doi: 10.1016/j.jjcc.2021.10.013
30. Juraschek, SP, Daya, N, Appel, LJ, Miller, ER, Matsushita, K, Michos, ED, et al. Subclinical cardiovascular disease and fall risk in older adults: results from the atherosclerosis risk in communities study. J Am Geriatr Soc. (2019) 67:1795–802. doi: 10.1111/jgs.16041
31. Iaboni, A, and Flint, AJ. The complex interplay of depression and falls in older adults: a clinical review. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. (2013) 21:484–92. doi: 10.1016/j.jagp.2013.01.008
32. Wabe, N, Huang, G, Silva, SM, Nguyen, AD, Seaman, K, Raban, MZ, et al. A longitudinal study of the use and effects of fall-risk-increasing Dr ugs in residential aged care. J Am Med Dir Assoc. (2024) 25:105074. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2024.105074
33. Lin, EHB, Katon, W, Von Korff, M, Rutter, C, Simon, GE, Oliver, M, et al. Relationship of depression and diabetes self-care, medication adherence, and preventive care. Diabetes Care. (2004) 27:2154–60. doi: 10.2337/diacare.27.9.2154
34. Briggs, R, Kennelly, SP, and Kenny, RA. Does baseline depression increase the risk of unexplained and accident al falls in a cohort of community-dwelling older people? Data from the Irish longitudinal study on ageing (TILDA). Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. (2018) 33:e205–11. doi: 10.1002/gps.4770
35. Lohman, MC, Fairchild, AJ, and Merchant, AT. Antidepressant use partially mediates the association between Depressi on and risk of falls and fall injuries among older adults. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. (2021) 76:e171–8. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glaa253
36. O'Halloran, AM, Cremers, J, Vrangbæk, K, Roe, L, Bourke, R, Mortensen, LH, et al. Cardiovascular disease and the risk of incident falls and mortality am ong adults aged ≥ 65 years presenting to the emergency department: a c ohort study from national registry data in Denmark. BMC Geriatr. (2024) 24:93. doi: 10.1186/s12877-023-04618-2
37. Silveira, H, Lima, J, Plácido, J, Ferreira, JV, Ferreira, R, Laks, J, et al. Dual-task performance, balance and aerobic capacity as predictors of falls in older adults with cardiovascular disease: a comparative study. Behav Sci. (2023) 13:488. doi: 10.3390/bs13060488
38. Jeong, HG, and Park, H. Metabolic disorders in menopause. Meta. (2022) 12:954. doi: 10.3390/metabo12100954
39. Kautzky-Willer, A, Harreiter, J, and Pacini, G. Sex and gender differences in risk, pathophysiology and complications of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Endocr Rev. (2016) 37:278–316. doi: 10.1210/er.2015-1137
40. Colafella, KMM, and Denton, KM. Sex-specific differences in hypertension and associated cardiovascular disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. (2018) 14:185–201. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2017.189
41. Stevens, D, Jackson, B, Carberry, J, McLoughlin, J, Barr, C, Mukherjee, S, et al. The impact of obstructive sleep apnea on balance, gait, and falls risk: a narrative review of the literature. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. (2020) 75:2450–60. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glaa014
42. Kim, SY, Kim, S-G, Sim, S, Park, B, and Choi, HG. Excessive sleep and lack of sleep are associated with slips and falls in the adult Korean population: a population-based cross-sectional Stu dy. Medicine (Baltimore). (2016) 95:e2397. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000002397
Keywords: depression, cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, falls, additive interaction
Citation: Li K, Chen X, Chen L and Liang D (2025) The impact of depression and cardiovascular disease on fall risk in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a gender and sleep status analysis. Front. Public Health. 13:1488923. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1488923
Received: 30 August 2024; Accepted: 26 February 2025;
Published: 19 March 2025.
Edited by:
Yijian Yang, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, ChinaReviewed by:
Ryuichi Saura, Osaka Medical and Pharmaceutical University, JapanCopyright © 2025 Li, Chen, Chen and Liang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Dianyin Liang, NzI3NjI1NDQxQHFxLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
‡ORCID: Kehua Li, orcid.org/0009-0002-5416-0213
Dianyin Liang, orcid.org/0000-0003-1354-2581
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.