- 1School of Sociology, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China
- 2Crown Family School of Social Work, Policy, and Practice, University of Chicago, Chicago, IL, United States
- 3School of Marxism, Zhongnan University of Economics and Law, Wuhan, China
Education holds significant implications for individual health. This work aims to examine the relationship between educational attainment, lifestyle, self-rated health, and depressive symptoms among Chinese adults. We used China Family Panel Studies data from 2012 to 2020. Multiple linear regression models were used to explore the relationship between educational attainment and self-rated health and depressive symptoms, where multidimensional lifestyle (sleep time, exercise time, overtime time, leisure time, housework time, and protein intake) was the mediator variable of the above relationship, and the causal step method was used to test the mediating effect. Our findings show that educational attainment is associated with higher levels of self-rated health and lower levels of depressive symptoms. More importantly, educational attainment also indirectly affects individuals’ self-rated health and depressive symptoms through lifestyle. These findings reveal health interventions to develop education further and improve its quality.
1 Introduction
Health is an essential concern for the world, as it constitutes a vital foundation for ensuring individuals’ quality of life and overall well-being (1, 2). Education plays a critical role in shaping health inequalities because it is a fundamental determinant of an individual’s occupation and income, which can have long-lasting impacts on health (3, 4).
However, research findings on the relationship between education and health have not yielded a consensus. Some studies indicate a positive correlation, thus establishing an educational gradient in health (5, 6). Conversely, others have discovered negative or non-significant associations (7, 8). Furthermore, although previous studies have examined the importance of health behaviors, such as smoking and alcohol consumption, in the education-health relationship (9, 10), the research on lifestyle as a mediating mechanism is less comprehensive. Most importantly, much research has been conducted in Western countries, with limited studies across social, political, and economic contexts, thus necessitating further in-depth exploration.
1.1 Educational attainment and health
Education plays a crucial role in health stratification (11). Researchers have shown the positive impact of education on physical and mental health (11). Individuals with higher levels of education exhibit significant health advantages compared to those with lower levels of education (12), such as lower mortality rates (13), reduced incidence of hypertension (14), higher self-rated health (15), and lower risk of depression (16).
Despite the widely established notion that higher education levels are a stable predictor of favorable health outcomes (12), some scholars have expressed skepticism regarding the positive relationship between educational attainment and health. Some studies show that individuals with higher education did not have a statistically significant advantage in self-rated health and reduced depression (17, 18). For instance, Bracke et al.’s research revealed that individuals with higher levels of education were more likely to experience mental health issues such as depression (7, 19).
While a strong correlation between educational attainment and health has been extensively established (6, 7, 11, 19), some scholars argue that the role of educational attainment in influencing individual health is limited. For example, Veenstra (20) found no significant causal relationship between educational attainment and health status among individuals under 39. The current study aims to harness longitudinal data across 10 years on Chinese adults to examine the associations between educational attainment and health.
1.2 Lifestyle as a mediator
1.2.1 Educational attainment and lifestyle
Similar to the educational gradient in health, there is also an educational gradient in health behaviors; well-educated individuals tend to develop healthier lifestyles (21, 22). There is also socioeconomic inequality in dietary habits (23). Individuals with higher levels of education tend to consume relatively more lean meat and low-fat dairy products (24). Another study suggested that people with higher educational attainment are more likely to follow the Nordic Nutrition Recommendations (NNR 2012), meaning they are more likely to consume protein as recommended (23). A systematic review shows that individuals with higher cultural capital are less likely to smoke and have a higher propensity to eat healthier and engage in physical activity (25).
However, as lifestyle is closely related to specific cultural norms (26), the strong positive correlations described above may show opposite trends in different cultural contexts. In contrast to Western societies, a comparative study of Chinese and American samples found that unhealthy behaviors (e.g., imbalanced diet, low physical activity, smoking, and alcohol consumption) are more prevalent among individuals with higher levels of education and income in China (27). Regarding working hours, a recent study indicates that upper-class women are less likely to spend time working during non-standard hours (e.g., weekends) (28). Another study found that people with lower levels of education spent more time watching television due to fewer opportunities to choose leisure activities (29). However, Farrell’s study suggested that there might not be a sustained causal link between educational attainment and health behaviors, such as smoking (30). The relationship between educational attainment and health behaviors has yet to reach a consensus.
1.2.2 Lifestyle and physical and mental health
A healthy lifestyle is a crucial pathway to achieving health, and extensive research has confirmed a positive correlation between health behaviors and health status (22, 31, 32). Empirical studies have shown that alcohol consumption (9), lack of exercise (9), sleep deprivation (9), prolonged overtime work (33), and extended housework (34) all have significant adverse effects on health. Among them, overtime work was considered an important risk factor for mental disorders. A comparative study found that anxiety and depression rates were significantly higher among overtime workers (35) compared to workers with normal working hours. Furthermore, inadequate sleep (<7 h) may be a risk factor for poorer self-rated health and depressive symptoms in Chinese older individuals (34, 36). Several studies supported a close relationship between leisure activity participation and health (37, 38). Research showed that participation in sedentary leisure activities, such as watching television and engaging in crafts, played a significant role in reducing depressive emotions and enhancing psychological well-being, but increased the risk of developing type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease (37). The relationship between housework time and health is complex, with some studies suggesting that prolonged housework implies a “burden” in an individual’s life, which may lead to a higher risk of physical symptoms, illness, self-rated poor health, and mental disorders (34, 39–41). Some researchers also suggest that housework is a form of physical activity, similar to sports and exercise, that has a positive role in maintaining health and is associated with reduced mortality and adverse mental health (42). In addition, protein intake is considered to contribute to the improvement of physical function (43), thereby promoting overall health and well-being. Empirical studies on the older adults found that higher levels of protein intake were associated with a greater likelihood of healthy aging, including a lower probability of chronic diseases and physical impairment, as well as an increased likelihood of better self-rated health and mental well-being (44, 45).
1.2.3 The mediating role of lifestyle
Education may help individuals adopt a healthy lifestyle, benefiting their overall well-being. According to the efficiency hypothesis of health production (3, 46, 47), well-educated individuals exhibit higher allocation efficiency in the health production function, enabling them to produce greater health. This efficiency may be realized through various aspects such as physical activity, diet, and smoking (3, 48). Based on previous findings (10, 25, 27), we further expand lifestyle to a multi-dimensional concept that includes six dimensions: overtime work, sleep, exercise, leisure, housework, and protein intake. The current study aims to examine whether different lifestyle dimensions mediate education attainment’s effects on health.
1.3 Objectives and hypotheses
This study has two aims: (1) to examine the relationship between educational attainment and self-rated health and depressive symptoms among Chinese adults and (2) to examine multi-dimensional lifestyles as mediators between educational attainment and self-rated health and depressive symptoms. We pose the following hypotheses: (H1) individuals with higher educational attainment are more likely to report higher levels of self-rated health and lower levels of depressive symptoms and (H2) multi-dimensional lifestyle factors, including exercise time, sleep time, overtime time, leisure time, housework time, and protein intake, mediate the association between educational attainment, self-rated health and depressive symptoms.
2 Methods
2.1 Study design and samples
The data were obtained from the first to the sixth wave of the China Family Panel Studies (CFPS) from 2012 to 2020. It was a nationwide longitudinal social survey that aimed to reflect the economic, demographic, educational, and health changes and their interactions among residents in China. The CFPS sample covered 31 provinces/municipalities/autonomous regions in mainland China. Because this study focused on the impact of educational attainment on the health status of Chinese adults, we excluded samples younger than 18 years of age. In addition, we also excluded samples of poor quality (e.g., missing information or anomalous values for critical variables, etc.). The analytic sample included 159,970 adults aged 18 years and older.
All participants provided written informed consent to participate in this study. The data used in this study were approved by the Biomedical Ethics Committee.
2.2 Measurements
2.2.1 Outcome variables
2.2.1.1 Self-rated health
Based on previous research (49), we used self-reported health (SRH) to measure people’s physical health. Self-reported health refers to people’s subjective assessment of their health, which was measured by asking respondents, “How would you rate your health?”; The responses to this question were “very poor,” “poor,” “fair,” “good,” and “very good,” which were assigned a score from 1 to 5, with larger scores indicating better health status. Self-rated health is a comprehensive assessment of an individual’s physical and psychological condition and has been widely used in health-related studies of Chinese adults (15).
2.2.1.2 Depressive symptoms
Depressive symptoms were assessed with the Center for Epidemiological Studies Depression scale (CES-D) (50), which consists of 20 items ranging from one (rarely or never; less than 1 day) to four (most or all of the time; 5–7 days). Respondents reported the frequency of each item according to their psychological state and then summed the items to obtain a score ranging from 20 to 80. The higher the score, the more severe the respondent’s depressive symptoms. The scale was applied to the Chinese sample, proving high reliability and validity (51). This study’s reliability coefficient (Cronbach’s alpha value) was 0.93.
2.2.2 Mediating variables
Lifestyle was measured by the amount of time a person spent working overtime, sleeping, exercising, leisure, doing housework each week/day, and protein intake, expanding previous research (10, 25, 27). Exercise time was the average weekly exercise frequency of the respondent. Housework time was measured by asking respondents, “Approximately how many hours do you spend doing housework at home every day?” Leisure time was measured by asking respondents how many hours they watched television, movies, and other video programs per week. Overtime was calculated by subtracting the regular scheduled working hours (usually 40 h per week in China) from the weekly total working hours. Sleep time was measured by asking respondents: “How many hours of sleep do you get each day?” Protein intake was measured by asking respondents: “In the past week, have you eaten meat (including pork, beef, lamb, chicken, duck, fish, shrimp, shellfish, etc.)?”
2.2.3 Independent variable
Following Lynch’s method (5), educational attainment was measured by the years an individual has received education. Respondents were asked to answer their highest level of education based on the number of years of study they had completed.
2.2.4 Confounding variables
Based on previous studies on education and physical and mental health (15, 52), we obtained the control variables for this study. They consisted of two main aspects: demographic characteristics and socioeconomic characteristics. The demographic characteristics variables mainly included gender (male, female), age (18–109), marital status (yes, no), members of the Communist Party of China (CPC) (yes, no), residence area (urban, rural), and geographic location (Western China, Central China, Eastern China). The socioeconomic variables comprised income level (low-income group, middle-income group, high-income group) and occupational types (professional technicians and managers, business service workers and office workers, production workers, farmers and the unemployed).
2.3 Statistical analysis
All data analysis was performed in Stata 15.1. Descriptive analysis was applied to present sample characteristics. In this case, mean and standard deviation were used to characterize continuous variables (e.g., age, educational attainment, depressive symptoms, and self-rated health), and frequency and percentage were used to characterize categorical variables (e.g., gender, marital status, CPC member, residence area, geographic location, income level, occupational types, and protein intake). The specific analytic process comprised three steps: first, we ran two multiple linear regression models to examine the relationship between educational attainment and self-rated health/depressive symptoms. Second, multiple linear regression models/binary logistic regression models were adopted to explore the association between educational attainment and lifestyle. Finally, based on the first step of the model, multidimensional lifestyle was further included in the model to test the mediating role of lifestyle in the associations between educational attainment and self-rated health, and educational attainment and depressive symptoms. The same covariates (age, gender, marital status, CPC member, residence area, geographic location, income level, occupational types) were incorporated into the model at each step.
3 Results
3.1 Descriptive analysis
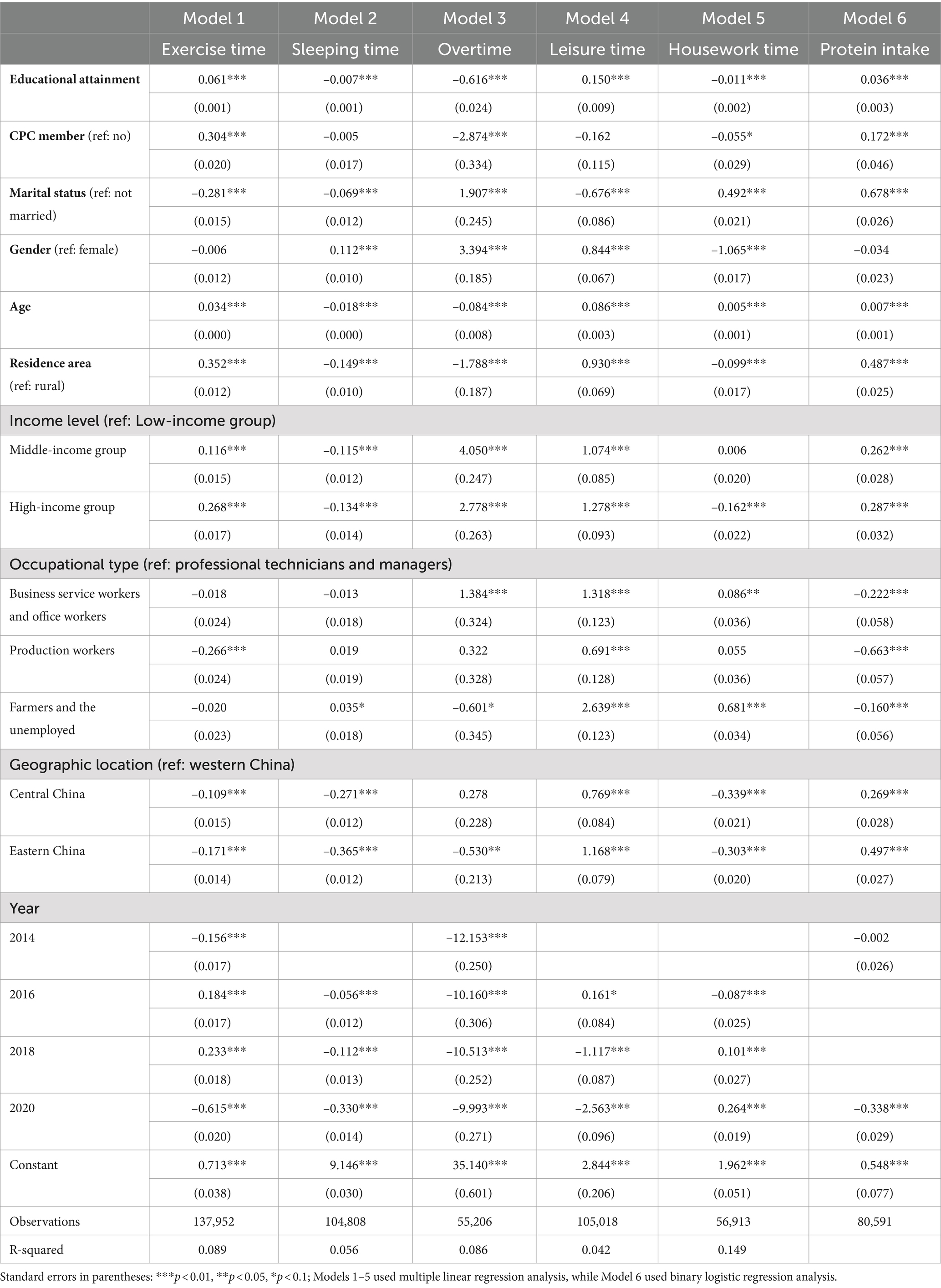
Among 159,970 participants, the proportion of men and women was relatively evenly distributed, with both men and women accounting for approximately 50%. Most participants were married, and only 8.86% were members of the CPC (n = 13,964). Roughly 47.56% (n = 72,686) lived in urban areas. The average number of years of education for all participants was 7.209 years (range 0–22, SD = 5.079). For lifestyle, the average weekly overtime hours of the respondents was 24.119 (SD = 20.677), the average sleep time was 7.752 (SD = 1.521), the average leisure time was 10.971 (SD = 10.399), and the average housework time was 2.196 (SD = 2.009). More than half (n = 85,373, 55.76%) of the respondents exercised less than once a month, compared to about 26.95% (n = 41,270) who exercised seven times a week. The respondents’ age were 47.628 (range 18–109, SD = 16.633). Additionally, 85.16% (n = 75,915) of respondents consumed protein in the past week. More than 40% of the respondents were from Eastern China, with equal proportions (29%) from Central China and Western China. Regarding socioeconomic status variables, the distribution of respondents’ income was relatively even, with approximately 32% in the low-income and middle-income, respectively. In terms of occupation, the majority (60.63%) of respondents were farmers or unemployed, while professionals and managers accounted for only 8.56%. Among all respondents, the mean scores for self-rated health and depressive symptoms were 2.921 (range 1–5, SD = 1.24) and 33.088 (range 20–77, SD = 8.105), respectively, indicating that the respondents’ physical health and mental health conditions were all at a moderate level (Table 1).
3.2 The association between educational attainment and health outcomes
Table 2 displays the results of multiple linear regression analysis of the relationship between educational attainment, self-rated health, and depressive symptoms. Model 1 indicated that educational attainment was significantly positively linked to higher levels of self-rated health after controlling for the relevant covariates (B = 0.006, p < 0.000). As for depressive symptoms, Model 2 revealed a significantly inverse association between educational attainment and depressive symptoms (B = −0.168, p < 0.000).
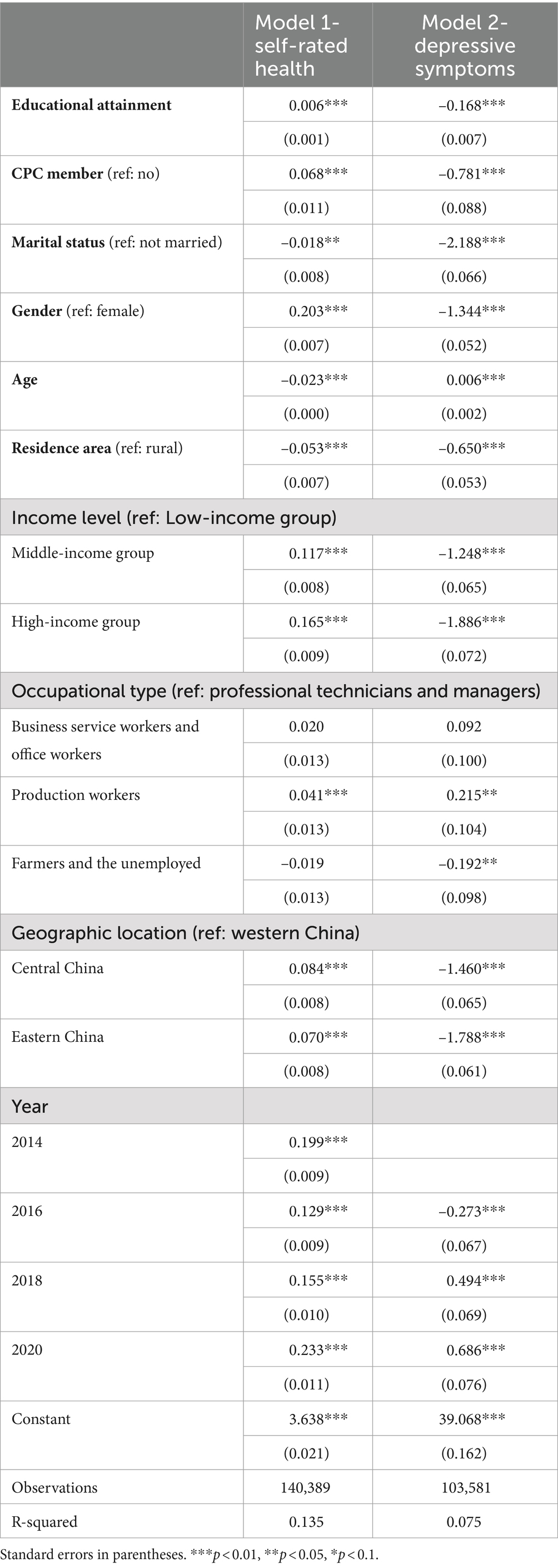
Table 2. Multiple linear regression analysis of the relationship between educational attainment, self-rated health, and depressive symptoms
3.3 Mediating effect of lifestyle on the association between educational attainment and health outcomes
Tables 3, 4 present the results of the causal steps approach (53) of the mediating effect of the lifestyle dimensions on the link between educational attainment and self-rated health, as well as educational attainment and depressive symptoms. Models 1–6 in Table 3 indicated that educational attainment showed a significant negative correlation with sleeping time (B = –0.007, p < 0.000), housework time (B = –0.011, p < 0.000), and overtime (B = –0.616, p < 0.000), as opposed to a significant positive correlation with exercise time (B = 0.061, p < 0.000), leisure time (B = 0.150, p < 0.000), and protein intake (B = 0.036, p < 0.000).
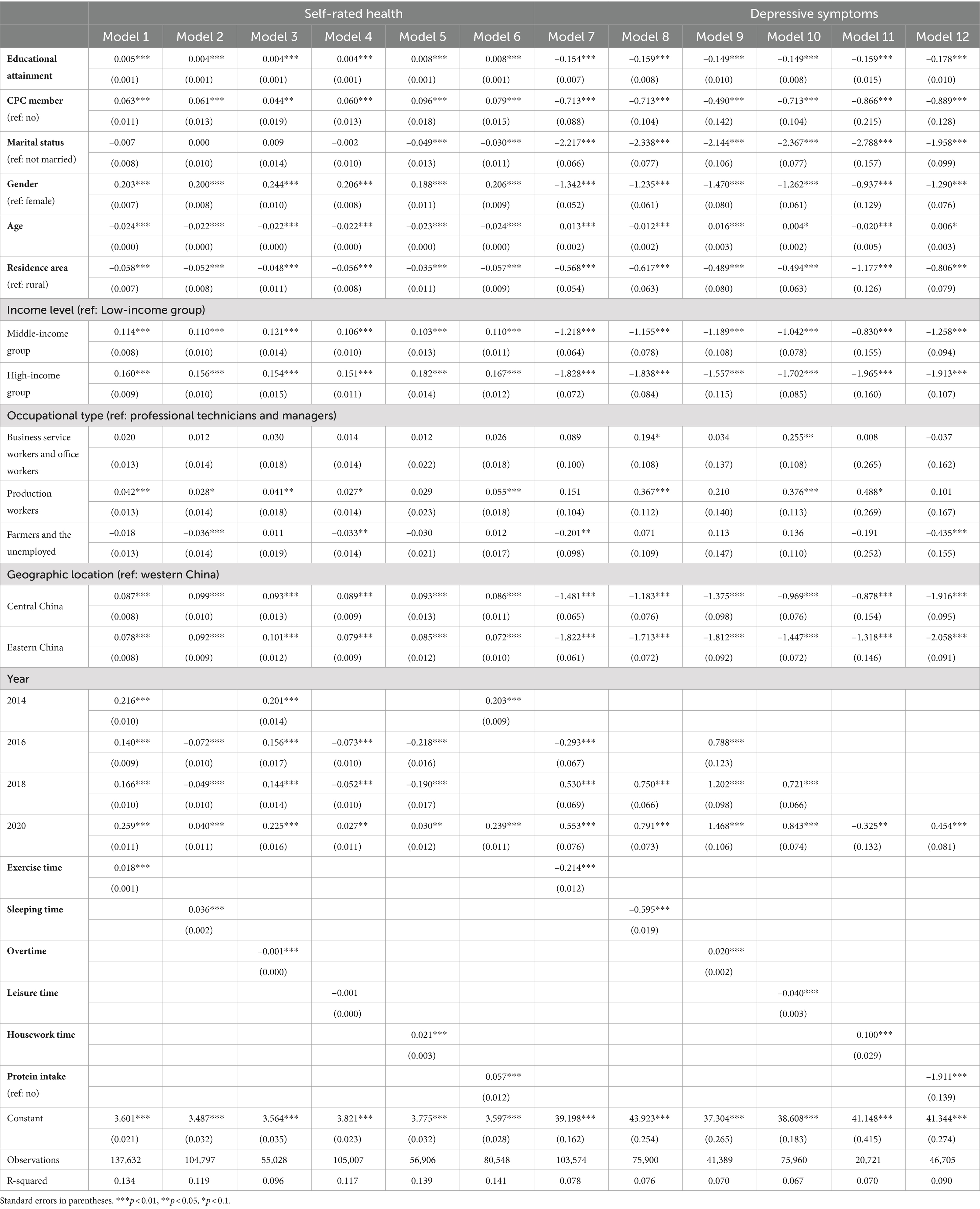
Table 4. Multiple linear regression analysis of the relationship between educational attainment, lifestyle, and health outcomes.
Model 3–4 in Table 4 showed that leisure time was not significantly related to self-rated health, and overtime work was negatively associated with self-rated health (B = –0.001, p < 0.000). In contrast, sleeping time, exercise time, housework time, and protein intake all indicated a significant positive relationship with self-rated health (B = 0.036, p < 0.000; B = 0.018, p < 0.000; B = 0.021, p < 0.000; B = 0.057, p < 0.000). In addition, the indirect effect values for time spent exercising (0.061*0.018), overtime (–0.616*–0.001), and protein intake (0.036*0.057) were in the same direction as the direct effect values for their respective educational attainment (B = 0.005; B = 0.004; B = 0.008; see model 1, model 3, and model 6 in Table 4). That means that exercise time, overtime, and protein intake mediated the relationship between educational attainment and self-rated health. However, the indirect effect value for sleeping time (–0.007*0.036) was in the opposite direction to the direct effect value for educational attainment (B = 0.004, see model 2), as was the indirect effect value for housework time (–0.011*0.021) and the corresponding direct effect value for educational attainment (B = 0.008, see model 5 in Table 4).
The results of Models 7–12 in Table 4 demonstrated that exercise time, sleeping time, leisure time, and protein intake all exhibited an important adverse correlation with depressive symptoms (B = −0.214, p < 0.000; B = −0.595, p < 0.000; B = −0.040, p < 0.000; B = −1.911, p < 0.000), while overtime and housework time were both exhibited a significant positive correlation with depressive symptoms (B = 0.020, p < 0.000; B = 0.100, p < 0.000). Moreover, the indirect effect values for exercise time (0.061*–0.214), leisure time (0.150*–0.040), housework time (–0.011*0.1), overtime (–0.616*0.020), and protein intake (0.036*–1.911) were in the same direction as the respective direct effect values for educational attainment (B = –0.154; B = –0.149; B = –0.159; B = –0.149; B = –0.178; see models 7–12 in Table 4), while the direction of the indirect effect for sleeping time (–0.007*–0.595) and the direction of the direct effect of educational attainment were reversed (B = –0.159, see model 8 in Table 4). That is, exercise time, leisure time, housework time, overtime time, and protein intake all normally mediated the relationship between educational attainment and depressive symptoms, while sleep time acted as a suppressive effect (54) in the above relationship.
4 Discussion
This study examined the relationship between educational attainment and health outcomes, with multidimensional lifestyle factors as mediators. Our empirical results showed that individuals with higher educational attainment had better physical and mental health, supporting H1. In line with hypothesis 2, we found that various lifestyle dimensions (exercise time, sleep time, overtime, housework time, and protein intake) mediated the relationship between educational attainment and self-rated health, as well as educational attainment and depressive symptoms. Also, leisure time mediated the association between educational attainment and depressive symptoms but not the association between educational attainment and self-rated health, which partially supported H2. Specifically, educational attainment improved individuals’ self-rated health and reduced depressive symptoms by reducing overtime work hours, increasing exercise time, and enhancing protein intake. Meanwhile, elevated educational attainment reduced individuals’ sleep time, leading to lower self-rated health and higher levels of depressive symptoms. Additionally, the reduced housework time and more leisure time mediate higher educational attainment’s associations with lower depressive symptoms, but not with better self-rated health.
Consistent with previous research (5, 6, 13), higher educational attainment significantly promoted individuals’ self-rated health and reduced depressive symptoms, and these findings hold true across most income groups. The link between educational attainment and physical and mental health could be attributed to several aspects. According to the human capital theory of education (55), receiving an education is the process of stockpiling human capital and developing productive capacity. Thus, the longer an individual gets an education, the more human capital is gained, i.e., more knowledge, skills, and competencies are possessed, which can promote health. Hummer et al.’s study showed that those with 12 years of education had a 21% lower mortality rate than those with eight or fewer years but a 33% higher mortality rate than those with 17 or more years (6). From the perspective of the fundamental cause theory in sociology, SES is considered a fundamental determinant of health (56). Education is the primary and core dimension of SES (55) and may have become a reproducer of inequality. Higher education reflects an individual’s socioeconomic resource advantage within the social structure. The upper social classes can translate the socioeconomic resource advantage they possess into a health advantage, which creates a health gradient between the upper and lower social classes (those with lower SES) due to differences in the resources they have access to (57). Numerous studies demonstrated the education-health gradient, whereby higher levels of education are associated with better physical health (e.g., lower mortality, etc.) and better psychological states (e.g., less depressive emotion, etc.) (13, 58).
Moreover, increased exercise time, higher protein intake, and reduced overtime work were critical ways that educational attainment improved self-rated health and decreased depressive symptoms, which could be understood in the following ways. According to the human capital perspective of learned effectiveness (10), greater problem-solving abilities enable education to guide individuals to become active and effective agents in their own lives and cultivate beliefs in control over their lives. This motivation encourages people to integrate health-promoting behaviors into a coherent lifestyle (10), which becomes an effective means for highly educated individuals to achieve their health. Higher levels of education contribute to improving individuals’ health literacy, enhancing their ability to comprehend health information, and consequently encouraging individuals to adopt more proactive health behaviors (59). A previous study found that participants with higher education exhibited significantly greater adherence to dietary guidelines than those with primary education (23). Besides, well-educated individuals are more likely to allocate more leisure time to physical activity on weekends/holidays (25, 60). These activities are particularly beneficial in reducing diseases and alleviating emotional distress, such as depression and anxiety (61).
Furthermore, working hours may contribute to health inequalities due to class differences in non-standard working hours. A recent study showed that individuals with lower levels of education are more likely to work outside of standard working hours due to their lower autonomy in time control (28). It is worth noting that long working hours (e.g., more than 69 h per week) have been established as predictors of diabetes, musculoskeletal disorders, and severe depression (33, 62). The perspective of class distinction (63–65) also helps to understand this mechanism. Class status and its associated resources lead to health inequality through the habitus mechanism (66). Lifestyle is a habitual tendency formed through the interaction of capital and field, reflecting the behavioral patterns of specific social classes (65). Higher social classes have more time and resources to adopt the healthiest lifestyles (65). For instance, Bourdieu observed that class-oriented consumption habits shape the differentiated dietary practices and exercise preferences across social classes: the middle and upper classes preferred less fatty, light, low-calorie, and high-protein foods (e.g., beef and lamb, fresh fruits and vegetables) to shape their bodies, while the working class favored cheaper, calorie-dense, nutritious foods (e.g., potatoes, cabbage, and pork) to maintain a sense of strength in the male body (63). Moreover, activities that represented the refined cultural tastes of higher cultural capital classes, such as moderate weight training, intense aerobic exercise, and avoiding physically dominating competitive sports, were more commonly found among the upper classes (67). All these factors directly or indirectly contributed to improved health outcomes (10, 33). Hence, it is not difficult to understand the gradient between exercise time and overtime hours in health in cultural capital (education). Moreover, the longevity benefits perspective based on cost–benefit principles (13, 68) also provides a valuable explanation: education can offer individuals a better future, such as higher income and increased happiness. Therefore, highly educated individuals are more willing to invest in health (e.g., engaging in health behaviors) to protect these future gains. In contrast, individuals with lower levels of education have a lower future value of living to old age (i.e., less benefit from longevity) and may be more likely to focus on the present, engaging in health-risk behaviors. For low-educated individuals, the rewards of healthy behaviors are limited (because of shorter life expectancy), and instead, indulging in unhealthy but enjoyable behaviors may be more meaningful (64).
Also, decreased sleeping time resulting from higher educational attainment suppressed the positive effects of educational attainment in improving self-rated health and reducing depressive symptoms, contrary to the role of sleep in previous studies (69). Concerning the first pathway - the negative correlation between higher educational attainment and sleep hours - could be explained by the substitution effect at work (60). From an economic perspective of opportunity cost, in situations where the total available time is limited, individuals with higher levels of education are more productive. Their value in the labor market (wage rate) is higher, which may lead to higher opportunity costs for individuals with higher educational levels in allocating sleep time (64). An earlier study found that both more educated men and women allocated less time to certain health-promoting activities such as sleep and that this was worse at work than on weekends (60). The second pathway pertains to the relationship between sleeping time, self-rated health, and depressive symptoms. Several systematic reviews suggest that sleep deprivation (e.g., less than 7 h of sleep per day) may affect health-related quality of life, such as an increased risk of cardiovascular and Alzheimer’s disease, cognitive decline, and may lead to depression and phobias (36, 70).
More interestingly, increases in leisure time and reductions in housework time resulting from higher educational attainment hold different effects on self-rated health and depressive symptoms. Firstly, for the first path - the positive effects of higher educational attainment on increased personal leisure time and reduced housework time - the previously mentioned theories of learned effectiveness (10) and class distinction (63–65) still contribute to the understanding of this issue and will not be repeated and expanded upon here. A cross-sectional study focusing on respondents aged 25–64 in the United States concluded that those with higher levels of education spent less time on personal/family activities during the workday due to the work substitution effect (60). Another study illustrated that certain leisure activities (e.g., going to the movies or watching a play) were perceived as expressions of high culture tastes and were more likely to be part of the daily leisure activities of those with higher cultural capital (71). Secondly, one of the dimensions of the second pathway—the association between housework time/leisure time and self-rated health/depressive symptoms—will be discussed separately.
Concerning the role of housework time in self-rated health, a large number of studies have confirmed the critical role of housework participation in improving individuals’ self-rated health and decreasing the risk of disease (34, 39, 40), and our study further supports these viewpoints. Household labor participation may have beneficial effects similar to physical activity, thus compensating for the drawbacks of insufficient exercise on physical health, and by participating in housework, individuals can succeed in their family roles and enhance their sense of self-worth (42), which may be beneficial to individual health. The cognitive benefits of housework may also contribute to an individual’s quality of life (e.g., brain health) (72). Thus, while higher educational attainment assists individuals in getting rid of burdensome housework, it concurrently suppresses their physical well-being. However, regarding the role of housework in mental health, as in previous studies (41), less housework is associated with fewer depressive symptoms. According to the Work–Family Conflict Model and Role Conflict Theory (73, 74), when individuals simultaneously experience multiple role pressures in the domains of work and family and lack the (temporal or psychological) resources to fulfill these roles, this situation may result in individuals experiencing role overload and role conflict, potentially leading to various physical and psychological symptoms. Thus, the reduced housework resulting from higher educational attainment may contribute to alleviating the “burden” in family life, reducing the stress of daily life, and avoiding role overload, thus aiding in reducing depressive symptoms.
As for the other dimension of the second pathway—the link between leisure time and self-rated health and depressive symptoms—the following study may help to understand it. For depressive symptoms, consistent with previous research (75), more leisure time may help to reduce individuals’ depressive symptoms. Individuals may resort to watching television to escape or alleviate real-life stress or problems (75). Short-term avoidance behavior may be adaptive as an avoidance coping strategy in a given situation, as it helps to divert attention from excessive personal stress, thereby reducing psychological distress (76). Regarding self-rated health, the association between leisure time and self-rated health was insignificant, implying that leisure time did not mediate the relationship between educational attainment and self-rated health. This may be because, recreational leisure activities, such as watching TV, imply prolonged sedentary behavior and reduced physical activity (77), which may lead to health risks such as obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease (77). Besides, sedentary leisure activities like watching TV may involve an increased high-density energy intake (38), and these unhealthy diets may increase the potential risk of future disease.
4.1 Limitations and implications
There are limitations in our study. On the one hand, the measurement of educational attainment was limited to years of formal schooling and did not include other types of education such as vocational schools. On the other hand, our assessment of lifestyle factors was not sufficiently comprehensive due to inconsistent measurement across waves, particularly as it did not consider health risk behaviors such as smoking and drinking. This limited a deeper exploration of the role of lifestyle factors in the health returns to education.
Despite these limitations, our study provides valuable insights. First, we find that educational attainment can promote individuals’ physical and mental well-being. Therefore, the government should guarantee its citizens fair access to education, continuously increase its investment in public education, and improve the quality of education to enhance their human capital. Second, lifestyle is a significant mediating mechanism. Therefore, schools should incorporate health education into their regular curriculum, disseminating and broadening students’ health knowledge and assisting them in developing healthy lifestyle habits.
5 Conclusion
This study demonstrates that educational attainment is associated with elevated self-rated health and decreased depressive symptoms among Chinese adults. Educational attainment promoted physical and mental health by increasing exercise time, reducing overtime, and improving protein intake. Our findings also indicate that the adverse consequence associated with educational attainments, such as reduced sleeping time, might suppress the positive effects of higher educational attainment on better health outcomes. Moreover, our research reveals that other dimensions of lifestyle—leisure time and housework time—might mediate differently between educational attainment and self-rated health, as well as educational attainment and depressive symptoms, respectively. These findings provide crucial insights for the government to reduce health inequalities in the future.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Biomedical Ethics Committee of Peking University (No. IRB00001052-14010). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
XX: Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. RH: Visualization, Writing – review & editing. WN: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Visualization.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Karimi, M, and Brazier, J. Health, health-related quality of life, and quality of life: what is the difference? PharmacoEconomics. (2016) 34:645–9. doi: 10.1007/s40273-016-0389-9
2. World Health Organization. Ment Health. (2022). Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/mental-health-strengthening-our-response/?gclid=CjwKCAjws9ipBhB1EiwAccEi1HV858kd5k22E9HSP5phjiUPIACRQcGtuuOKXCZUtBKXXipxuyahwxoCMzwQAvD_BwE.
3. Grossman, M. Effect of education on health. In: Behrman JR and Stacey N, editors. The Social Benefits of Education. Ann Arbor, MI: University of Michigan Press (1997). p. 69–124.
4. Ross, CE, and Wu, C-L. Education, age, and the cumulative advantage in health. J Health Soc Behav. (1996) 37:104. doi: 10.2307/2137234
5. Lynch, SM. Explaining life course and cohort variation in the relationship between education and health: the role of income. J Health Soc Behav. (2006) 47:324–38. doi: 10.1177/002214650604700402
6. Hummer, RA, and Lariscy, JT. Educational attainment and adult mortality. In: Rogers RG and Crimmins EM, editors. International Handbook of Adult Mortality. Vol. 2. Dordrecht: Springer (2011). p. 241–261.
7. Bracke, P, Pattyn, E, and Von dem Knesebeck, O. Overeducation and depressive symptoms: diminishing mental health returns to education. Sociol Health Illn. (2013) 35:1242–59. doi: 10.1111/1467-9566.12039
8. Khawaja, M, and Mowafi, M. Types of cultural capital and self-rated health among disadvantaged women in outer Beirut, Lebanon. Scand J Public Health. (2007) 35:475–80. doi: 10.1080/14034940701256958
9. Kenkel, DS. Should you eat breakfast? Estimates from health production functions. Health Econ. (1995) 4:15–29. doi: 10.1002/hec.4730040103
10. Mirowsky, J, and Ross, CE. Education, personal control, lifestyle and health: a human capital hypothesis. Res Aging. (1998) 20:415–49. doi: 10.1177/0164027598204003
11. Reynolds, JR, and Ross, CE. Social stratification and health: Education's benefit beyond economic status and social origins. Soc Probl. (1998) 45:221–47. doi: 10.2307/3097245
12. Winkleby, MA, Jatulis, DE, Frank, E, and Fortmann, SP. Socioeconomic status and health: how education, income, and occupation contribute to risk factors for cardiovascular disease. Am J Public Health. (1992) 82:816–20. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.82.6.816
13. Cutler, DM, and Lleras-Muney, A. Education and Health: Evaluating Theories and Evidence. Cambridge, MA: National Bureau of Economic Research (2006).
14. Winkleby, MA, Fortmann, SP, and Barrett, DC. Social class disparities in risk factors for disease: eight-year prevalence patterns by level of education. Prev Med. (1990) 19:1–12. doi: 10.1016/0091-7435(90)90001-Z
15. Chen, F, Yang, Y, and Liu, G. Social change and socioeconomic disparities in health over the life course in China: a cohort analysis. Am Sociol Rev. (2010) 75:126–50. doi: 10.1177/0003122409359165
16. Chang-Quan, H, Zheng-Rong, W, Yong-Hong, L, Yi-Zhou, X, and Qing-Xiu, L. Education and risk for late life depression: a meta-analysis of published literature. Int J Psychiatry Med. (2010) 40:109–24. doi: 10.2190/PM.40.1.i
17. Wang, F. Does social mobility contribute to reduce the inequality of health? Soc Stud. (2011) 25:78–101. doi: 10.19934/j.cnki.shxyj.2011.02.004
18. Chevalier, A, and Feinstein, L. Sheepskin or Prozac: The Causal Effect of Education on Mental Health. Bonn: IZA (2006).
19. Bracke, P, van de Straat, V, and Missinne, S. Education, mental health, and education-labor market misfit. J Health Soc Behav. (2014) 55:442–59. doi: 10.1177/0022146514557332
20. Veenstra, G. Social capital, SES and health: an individual-level analysis. Soc Sci Med. (2000) 50:619–29. doi: 10.1016/S0277-9536(99)00307-X
21. Kenkel, DS. Health behavior, health knowledge, and schooling. J Polit Econ. (1991) 99:287–305. doi: 10.1086/261751
22. Mechanic, D, and Cleary, PD. Factors associated with the maintenance of positive health behavior. Prev Med. (1980) 9:805–14. doi: 10.1016/0091-7435(80)90023-7
23. Nilsen, L, Hopstock, LA, Skeie, G, Grimsgaard, S, and Lundblad, MW. The educational gradient in intake of energy and macronutrients in the general adult and elderly population: the Tromsø study 2015–2016. Nutrients. (2021) 13:405. doi: 10.3390/nu13020405
24. Van Rossum, C, Van de Mheen, H, Witteman, J, Grobbee, E, and Mackenbach, J. Education and nutrient intake in Dutch elderly people. The Rotterdam study. Eur J Clin Nutr. (2000) 54:159–65. doi: 10.1038/sj.ejcn.1600914
25. Hashemi, N, Sebar, B, and Harris, N. The relationship between cultural capital and lifestyle health behaviours in young people: a systematic review. Public Health. (2018) 164:57–67. doi: 10.1016/j.puhe.2018.07.020
26. Abel, T. Measuring health lifestyles in a comparative analysis: theoretical issues and empirical findings. Soc Sci Med. (1991) 32:899–908. doi: 10.1016/0277-9536(91)90245-8
27. Kim, S, Symons, M, and Popkin, BM. Contrasting socioeconomic profiles related to healthier lifestyles in China and the United States. Am J Epidemiol. (2004) 159:184–91. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwh006
28. Vagni, G. The social stratification of time use patterns. Br J Sociol. (2020) 71:658–79. doi: 10.1111/1468-4446.12759
29. Clark, BK, Sugiyama, T, Healy, GN, Salmon, J, Dunstan, DW, Shaw, JE, et al. Socio-demographic correlates of prolonged television viewing time in Australian men and women: the AusDiab study. J Phys Act Health. (2010) 7:595–601. doi: 10.1123/jpah.7.5.595
30. Farrell, P, Fuchs, VR, and Fuchs, VR. Schooling and health: the cigarette connection. J Health Econ. (1982) 1:217–30. doi: 10.1016/0167-6296(82)90001-7
31. Lahelma, E, Rahkonen, O, Berg, M-A, Helakorpi, S, Prättälä, R, Puska, P, et al. Changes in health status and health behavior among Finnish adults 1978-1993. Scand J Work Environ Health. (1997) 23:85–90.
32. Anderson, AR, Kurz, AS, Szabo, YZ, McGuire, AP, and Frankfurt, SB. Exploring the longitudinal clustering of lifestyle behaviors, social determinants of health, and depression. J Health Psychol. (2022) 27:2922–35. doi: 10.1177/13591053211072685
33. Choi, E, Choi, KW, Jeong, H-G, Lee, M-S, Ko, Y-H, Han, C, et al. Long working hours and depressive symptoms: moderation by gender, income, and job status. J Affect Disord. (2021) 286:99–107. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2021.03.001
34. Adjei, NK, and Brand, T. Investigating the associations between productive housework activities, sleep hours and self-reported health among elderly men and women in western industrialised countries. BMC Public Health (2018) 18:10. doi: 10.1186/s12889-017-4979-z
35. Kleppa, E, Sanne, B, and Tell, GS. Working overtime is associated with anxiety and depression: the Hordaland health study. J Occup Environ Med. (2008) 50:658–66. doi: 10.1097/JOM.0b013e3181734330
36. Al-Abri, MA. Sleep deprivation and depression: a bidirectional association. Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J. (2015). 15:e4-6.
37. Dupuis, SL, and Smale, BJA. An examination of relationship between psychological well-being and depression and leisure activity participation among older adults. Loisir et Société / Society and Leisure. (1995) 18:67–92. doi: 10.1080/07053436.1995.10715491
38. Grøntved, A, and Hu, FB. Television viewing and risk of type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and all-cause mortality: a meta-analysis. JAMA. (2011) 305:2448–55. doi: 10.1001/jama.2011.812
39. Artazcoz, L, Cortès, I, Moncada, S, Rolhlfs, I, and Borrell, C. Gender differences in the influence of housework on health. Gac Sanit. (1999) 13:201–7. doi: 10.1016/S0213-9111(99)71351-8
40. Landstedt, E, Harryson, L, and Hammarström, A. Changing housework, changing health? A longitudinal analysis of how changes in housework are associated with functional somatic symptoms. Int J Circumpolar Health. (2016) 75:31781. doi: 10.3402/ijch.v75.31781
41. Pinho, PS, and Araújo, TM. Association between housework overload and common mental disorders in women. Rev Bras Epidemiol. (2012) 15:560–72. doi: 10.1590/S1415-790X2012000300010
42. Chu, L, Gong, X, Lay, JC, Zhang, F, Fung, HH, and Kwok, T. The perks of doing housework: longitudinal associations with survival and underlying mechanisms. BMC Geriatr. (2023) 23:355. doi: 10.1186/s12877-023-04039-1
43. Hruby, A, Sahni, S, Bolster, D, and Jacques, PF. Protein intake and functional integrity in aging: the Framingham heart study offspring. J Gerontol: Series A. (2020) 75:123–30. doi: 10.1093/gerona/gly201
44. An, R, Xiang, X, Liu, J, and Guan, C. Diet and self-rated health among oldest-old Chinese. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. (2018) 76:125–32. doi: 10.1016/j.archger.2018.02.011
45. Korat, AVA, Shea, MK, Jacques, PF, Sebastiani, P, Wang, M, Eliassen, AH, et al. Dietary protein intake in midlife in relation to healthy aging–results from the prospective nurses’ health study cohort. Am J Clin Nutr. (2024) 119:271–82. doi: 10.1016/j.ajcnut.2023.11.010
46. Rosenzweig, MR, and Schultz, TP. Education and the household production of child health. In: Proceedings of the American Statistical Association, Social Statistics Section. Washington, DC: American Statistical Association (1981).
47. Cowell, AJ. The relationship between education and health behavior: some empirical evidence. Health Econ. (2006) 15:125–46. doi: 10.1002/hec.1019
48. Fuchs, VR. Time preference and health: An exploratory study. In: Fuchs VR, editor. Economic Aspects of Health. Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press (1982). p. 93–120.
49. Cwikel, JMG, Dielman, TE, Kirscht, JP, and Israel, BA. Mechanisms of psychosocial effects on health: the role of social integration, coping style and health behavior. Health Educ Q. (1988) 15:151–73. doi: 10.1177/109019818801500202
50. Radloff, LS. The CES-D scale: a self-report depression scale for research in the general population. Appl Psychol Meas. (1977) 1:385–401. doi: 10.1177/014662167700100306
51. Yang, L, Jia, CX, and Qin, P. Reliability and validity of the Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale (CES-D) among suicide attempters and comparison residents in rural China. BMC Psychiatry. (2015) 15:15. doi: 10.1186/s12888-015-0458-1
52. Li, C, Ning, G, Wang, L, and Chen, F. More income, less depression? Revisiting the nonlinear and heterogeneous relationship between income and mental health. Front Psychol. (2022) 13:1016286. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.1016286
53. Baron, RM, and Kenny, DA. The moderator–mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. J Pers Soc Psychol. (1986) 51:1173–82. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.51.6.1173
54. MacKinnon, DP, Krull, JL, and Lockwood, CM. Equivalence of the mediation, confounding and suppression effect. Prev Sci. (2000) 1:173–81. doi: 10.1023/A:1026595011371
55. Mirowsky, J, Ross, CE, and Ross, C. Education, social status, and health. Somerset, United States: Taylor & Francis Group (2003).
56. Link, BG, and Phelan, J. Social conditions as fundamental causes of disease. J Health Soc Behav. (1995) 35:80. doi: 10.2307/2626958
57. Adler, NE, and Ostrove, JM. Socioeconomic status and health: what we know and what we don't. Ann N Y Acad Sci. (1999) 896:3–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1999.tb08101.x
58. Lee, J. Pathways from education to depression. J Cross Cult Gerontol. (2011) 26:121–35. doi: 10.1007/s10823-011-9142-1
59. Sørensen, K, Van den Broucke, S, Fullam, J, Doyle, G, Pelikan, J, Slonska, Z, et al. Health literacy and public health: a systematic review and integration of definitions and models. BMC Public Health. (2012) 12:1–13. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-12-80
60. Mullahy, J, and Robert, SA. No time to lose: time constraints and physical activity in the production of health. Rev Econ Househ. (2010) 8:409–32. doi: 10.1007/s11150-010-9091-4
61. Saxena, S, Van Ommeren, M, Tang, KC, and Armstrong, TP. Mental health benefits of physical activity. J Ment Health. (2005) 14:445–51. doi: 10.1080/09638230500270776
62. Ervasti, J, Pentti, J, Nyberg, ST, Shipley, MJ, Leineweber, C, Sørensen, JK, et al. Long working hours and risk of 50 health conditions and mortality outcomes: a multicohort study in four European countries. Lancet Reg Health Eur. (2021) 11:100212. doi: 10.1016/j.lanepe.2021.100212
63. Bourdieu, P. Distinction a social critique of the judgement of taste. In: Grusky D and Szelényi S, editors. Inequality: Classic Readings in Race, Class, and Gender. New York, NY: Routledge (2018). p. 287–318.
64. Pampel, FC, Krueger, PM, and Denney, JT. Socioeconomic disparities in health behaviors. Annu Rev Sociol. (2010) 36:349–70. doi: 10.1146/annurev.soc.012809.102529
65. Cockerham, WC. Bourdieu and an update of health lifestyle theory. In: Cockerham WC, editor. Medical sociology on the move: New directions in theory. Dordrecht: Springer (2013).
66. Freese, J, and Lutfey, K. Fundamental causality: Challenges of an animating concept for medical sociology. In: Pescosolido BA, Martin JK, and Rogers A, editors. Handbook of the Sociology of Health, Illness, and Healing: A Blueprint for the 21st Century. New York, NY: Springer (2011). p. 67–81.
67. Stempel, C. Adult participation sports as cultural capital: a test of Bourdieu’s theory of the field of sports. Int Rev Sociol Sport. (2005) 40:411–32. doi: 10.1177/1012690206066170
68. Murphy, KM, and Topel, RH. Black-white differences in the economic value of improving health. Perspect Biol Med. (2005) 48:176–S194. doi: 10.1353/pbm.2005.0026
69. Moore, PJ, Adler, NE, Williams, DR, and Jackson, JS. Socioeconomic status and health: the role of sleep. Psychosom Med. (2002) 64:337–44. doi: 10.1097/00006842-200203000-00018
70. Liew, SC, and Aung, T. Sleep deprivation and its association with diseases-a review. Sleep Med. (2021) 77:192–204. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2020.07.048
71. Gershuny, J. Changing times: Work and leisure in postindustrial society. USA: Oxford University Press (2003).
72. Koblinsky, ND, Meusel, L-AC, Greenwood, CE, and Anderson, ND. Household physical activity is positively associated with gray matter volume in older adults. BMC Geriatr. (2021) 21:1–10. doi: 10.1186/s12877-021-02054-8
73. Michel, JS, Kotrba, LM, Mitchelson, JK, Clark, MA, and Baltes, BB. Antecedents of work-family conflict: a meta-analytic review. J Organ Behav. (2011) 32:689–725. doi: 10.1002/job.695
74. Creary, SJ, and Gordon, JR. Role conflict, role overload, and role strain. In: Shehan CL, editor. The Wiley Blackwell Encyclopedia of Family Studies. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons (2016). p. 1–6.
75. Potts, R, and Sanchez, D. Television viewing and depression: no news is good news. J Broadcast Electron Media. (1994) 38:79–90. doi: 10.1080/08838159409364247
76. Vagni, M, Maiorano, T, Giostra, V, and Pajardi, D. Coping with COVID-19: emergency stress, secondary trauma and self-efficacy in healthcare and emergency workers in Italy. Front Psychol. (2020) 11:566912. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.566912
Keywords: educational attainment, sleep time, exercise time, overtime, leisure time, housework time, self-rated health, depressive symptoms
Citation: Xiong X, Hu RX and Ning W (2024) The relationship between educational attainment, lifestyle, self-rated health, and depressive symptoms among Chinese adults: a longitudinal survey from 2012 to 2020. Front. Public Health. 12:1480050. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1480050
Edited by:
Evasio Pasini, University of Brescia, ItalyReviewed by:
Michael Wiblishauser, University of Houston Victoria, United StatesPaolo Barabanti, Istituto nazionale per la valutazione del sistema educativo di istruzione e di formazione (INVALSI), Italy
Copyright © 2024 Xiong, Hu and Ning. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Wenyuan Ning, bnd5ODAwOEAxNjMuY29t
 Xinyan Xiong
Xinyan Xiong Rita Xiaochen Hu
Rita Xiaochen Hu Wenyuan Ning
Wenyuan Ning