- 1Institute of Public Health of Vojvodina, Novi Sad, Serbia
- 2University of Novi Sad, Faculty of Medicine, Novi Sad, Serbia
- 3Department of Traffic Engineering, Faculty of Economics and Engineering, Novi Sad, Serbia
- 4City Institute of Pubic Health of Belgrade, Belgrade, Serbia
- 5Institute of Public Health of Serbia “Dr Milan Jovanovic Batut”, Belgrade, Serbia
- 6University Clinical Center of Vojvodina, Novi Sad, Serbia
Introduction: Road traffic injuries (RTI) are the leading cause of death and severe disability among individuals under the age of 40, posing a significant public health challenge globally. This manuscript highlights key aspects of the epidemiology of injuries in road traffic crashes (RTC) in Serbia, based on hospitalization report data.
Objectives: The main aim of this study was to analyze the epidemiological characteristics of road traffic injuries (RTI) based on hospital data over a five-year period in Serbia.
Methods: The data for this study were obtained from the Hospitalization Report, which is part of the hospitalization database maintained by the Institute for Public Health of Serbia “Dr Milan Jovanović Batut,” covering the period from January 2015 to December 2019. The research included data from the Hospitalization Reports of 66 healthcare institutions across Serbia.
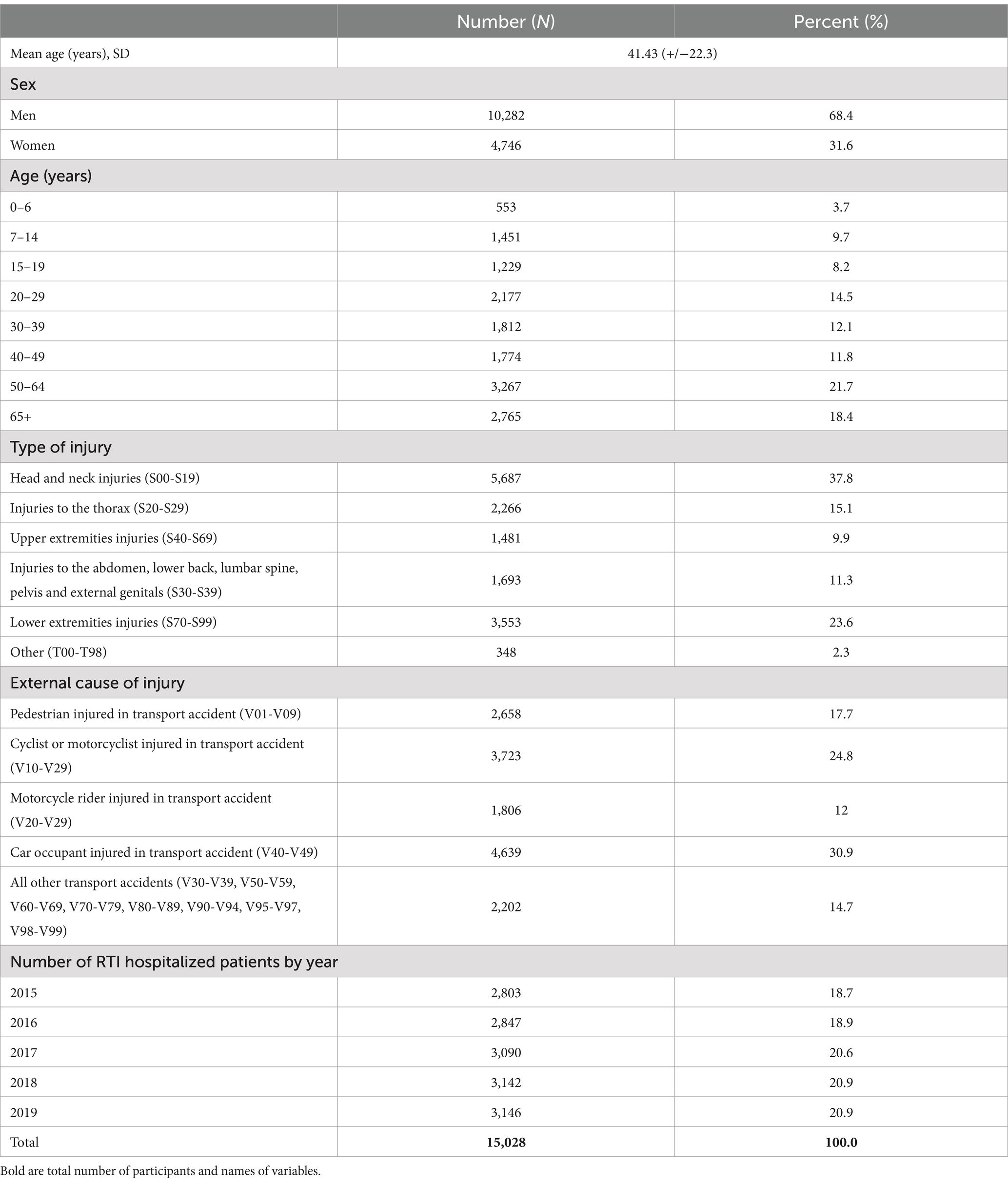
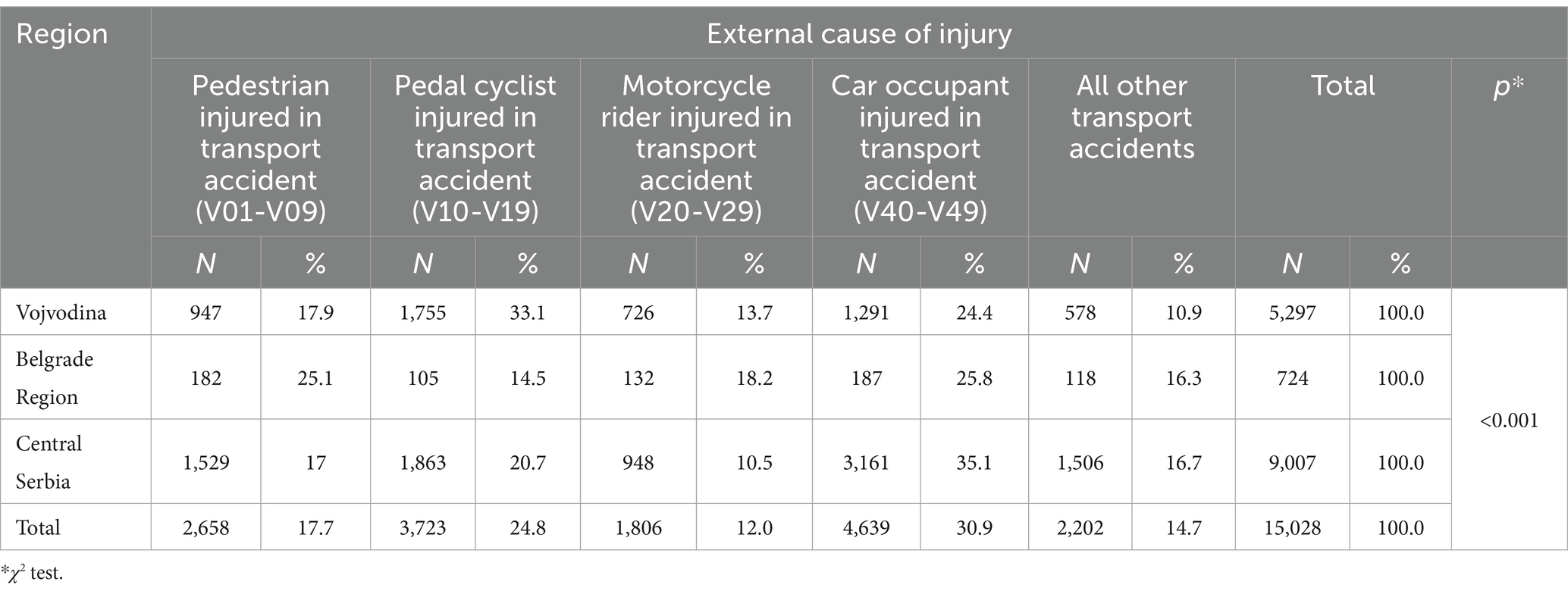
Results: During the study period, a total of 15,028 patients with road traffic injuries were admitted to healthcare institutions in Serbia. During the five-year period, the crude RTI incidence rate increased every year, from 39.0/100, 000 in 2015 to 43.7/100,000 in 2019. Older adult people aged 65 and over were particularly vulnerable as bicyclists and pedestrians (31.3, 27.7%, respectively). The Vojvodina region experienced a higher incidence of injuries among bicyclists compared and car accidents were most frequent in Central Serbia than in the other regions of Serbia. Craniocerebral injuries were the most common type of road traffic injury, accounting for 37.8% of cases. Significant differences in the types of injuries were observed based on age (χ2 = 649.859; p < 0.001) and gender (χ2 = 31.442; p < 0.001).
Conclusion: Understanding the epidemiological profile of road users involved in accidents is essential for monitoring and controlling specific risk factors. Our results highlight the need for enhanced traffic safety measures at the local level.
Introduction
RTI are a leading cause of death and disability worldwide, particularly in low-and middle-income countries. According to WHO, over 1.35 million people die in traffic accidents each year, equating to one death every 25 s. These accidents impose a global financial burden measured in billions of dollars (1, 2). In addition to the physical injuries, road traffic accidents also have profound psychological consequences for the victims and their families. A significant proportion of accident victims develop psychological disorders after a road accident traffic accidents such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), major depressive disorder, fear of driving, and other anxiety disorders (3, 4). Research shows that victims do not recover to their pre-accident condition for several years after a traffic accident (5, 6).
According to data from the Traffic Safety Agency of Serbia, between 2018 and 2022, a total of 2,648 people were killed in road traffic accidents (RTA) in the Republic of Serbia (RS), with 16,251 sustaining serious injuries and 81,158 experiencing minor injuries. During the period from 2010 to 2019, Serbia recorded a long-term decline in road traffic fatalities, decreasing from 13.9 deaths per 100,000 inhabitants in 2010 to 7.8 per 100,000 in 2019, representing a total reduction of 48%. Despite this progress, Serbia remains significantly above the EU average of 46 road traffic fatalities per million inhabitants in 2022 (7–9). Furthermore, road deaths increased in 19 PIN countries between 2021 and 2022, in Serbia increased from 75 to 83 road deaths per million inhabitants respectively, for the same period (9, 10). Serbia’s traffic environment presents several notable characteristics, particularly concerning infrastructure, the vehicle fleet, and mobility patterns. While Serbia has a well-developed road network, many local and regional roads remain in poor condition. The highway network is expanding, with recent investments focused on connecting major cities such as Belgrade, Novi Sad, and Niš, as well as key international borders. However, the infrastructure for cycling and pedestrian traffic, while improving, still lags behind European standards, with ongoing efforts to expand bike lanes and pedestrian-friendly zones. The average age of vehicles in Serbia is relatively high, at approximately 15 years, largely due to the prevalence of imported used cars, which are more affordable. Research has shown that older vehicles and poorly maintained roads are associated with higher accident severity and mortality rates. Serbia currently has over 2.5 million registered vehicles, the majority of which are passenger cars. Urbanization and economic growth have contributed to a steady rise in vehicle numbers, further straining the existing infrastructure. In larger cities like Belgrade, Novi Sad, and Niš, public transportation is primarily bus-based, with Belgrade also operating trams. However, the vehicle fleets are aging and in need of modernization. Increasing vehicle numbers, especially in urban areas, combined with insufficient infrastructure, have exacerbated congestion, raising the risk of accidents, particularly in cities like Belgrade where traffic jams are frequent during peak hours. Intercity bus services form the backbone of public transport, connecting cities and towns across Serbia, with additional routes to neighboring countries. In contrast, Serbia’s rail network is less developed, hampered by an aging fleet and underinvestment in infrastructure (11, 12).
The high rate of traffic-related injuries and fatalities in Serbia is recognized by the European Union (EU) as a significant public health concern. In response, the EU initiated a comprehensive five-year project (2019–2023) aimed at improving road safety in the country. By implementing targeted interventions and aligning road safety measures with EU standards, the project seeked to reduce traffic-related injuries and fatalities, promote safer driving behaviors, and foster a culture of safety among all road users in Serbia. This study was conducted as part of the EU-funded project “Improving Road Safety in Serbia (13). This is the first time that this problem is being approached in a multisectoral manner in our country, recognizing that RTA are not only a problem for the police and traffic experts but also require the involvement of healthcare in injury prevention.
In the past 10 years, the Republic of Serbia has significantly improved legal regulations related to traffic safety through the adoption of important legal and strategic documents, such as the Law on Road Traffic Safety. To improve traffic safety in the RS and achieve the goal of reducing the number of traffic accidents by 50%, the Government adopted the Traffic Safety Strategy of the Republic of Serbia for the period from 2023 to 2030, along with an action plan for 2023 to 2025 (14).
Studies around the world have shown that no single database on RTI, if used independently, without insight into other databases, provides enough information to obtain a complete picture of serious traffic injuries and to fully understand all injury mechanisms (15–17). Police databases are mainly based on the technical aspects of the traffic accident and do not contain a precise definition of the injury, and hospital databases that precisely define the type, degree, or severity of the injury do not contain details about the manner in which the traffic accident occurred. World experts agree that the best way to obtain quality data is to combine and combine data from different databases. Sweden or the Netherlands where combining police and healthcare data has led to significant improvements in road safety analysis (18, 19). Thus, the use of data from the health sector to classify and qualify injuries is necessary to complement police data and obtain an optimal data set for defining a serious injury and vice versa (8, 15, 16, 20).
Specific objectives and hypotheses of the study
The main aim of this study was to analyze the epidemiological characteristics of RTI based on hospital data over a five-year period in Serbia. The specific objectives were: (1) To analyze the incidence of RTIs across different regions of the Republic of Serbia from 2015 to 2019 using hospital data. (2) To examine the demographic characteristics of patients hospitalized due to RTIs and identify high-risk groups frequently affected by road traffic accidents (RTAs). (3) To analyze the external causes of injuries, categorized by gender and age. (4) To determine the most common types of injuries based on anatomical location, gender, and age.
Main research hypotheses
(1) There are regional differences in the incidence of road traffic injuries RTI across Serbia. (2) The frequency of RTI varies across age groups, with vulnerable road users including the older adult, children, and young drivers. (3) The proportion of male patients hospitalized after RTA is significantly higher than that of female patient. (4) The most common injuries among hospitalized traffic accident patients are head and limb injuries. (5) Car occupants constitute the majority of hospitalized patients when categorized by the external cause of injury.
These hypotheses and specific objectives provide a foundation for conducting a comprehensive epidemiological analysis of RTIs in Serbia.
Methods
This study is a retrospective analysis of data for patients hospitalized due to RTI in 66 hospitals in the Republic of Serbia from January 2015 to December 2019.
The data was obtained from the Hospitalization report, sourced from the hospitalization database of the Institute for Public Health of Serbia “Dr Milan Jovanović Butut,” initiated by the Ministry of Health.
The Hospitalization report is an individual statistical report, filled in when a patient is admitted for treatment in an inpatient health facility. The dataset obtained from these reports provides the necessary elements for relevant health-statistical analyses. Each hospitalization report is routinely filled out for every hospitalized patient with traffic accident injury information coded using the International Classification of Disease (ICD-10) with S or T codes from Chapter XIX (Injury, poisoning and certain consequences of external causes) for the type of injury and V01-V99 codes from Chapter XX (External causes of morbidity and mortality) for the external cause of injury. These reports are collected by district public health institutions and are primarily generated directly into the hospitalization database (World Health Organization).
For every person treated in hospitals Hospitalization Report is completed at the discharge of the patient. To determine how much hospitals are burdened with patients hospitalized after a traffic accident, the cumulative incidence was calculated, representing the number of hospitalized patients over a five-year period per 100,000 inhabitants.
In this study we collected data on the demographic characteristics of patient, type of injury, external cause of injury, an performed an analysis of injured patients according to districts. For the purpose of analysis, patients were divided into five groups based on the road-user category: pedestrian (V01-V09), bicyclist (V10-V19), motorcyclists (V20-V29), car occupants (V40-V49) and all other transport accidents (V30-V39, V50-V59, V60-V69, V70-V79, V80-V89, V90-V94, V95-V97, V98, V99). The car occupants and motorcyclists’ groups included both drivers and passengers.
The annual incidence rates of RTI were measured per 100,000 inhabitants. The numerator was the number of the reported injured cases, and the denominator was the total population of Serbia according to the 2011 census (21).
The statistical program SPSS (Statistical Package for Social Sciences), version 21.0, was used for statistical analysis. Descriptive statistics methods were used to describe the sample characteristics. Absolute values and percentages were used for the presentation of categorical variables. The χ2 test was used to test the differences in the frequencies of the type of injury and the external causes of injury between different genders and age groups. Values of p < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
Ethical considerations: Data used for this study are collected as part of a routine public health surveillance of hospital discharge reports. This surveillance is regulated by specific legislation of the Republic of Serbia (Law on health documentation and records in the field of health care) (22). All data are completely anonymized before being used for research purposes. To anonymize the data, direct identifiers were excluded from the database, and all unnecessary indirect data were also removed. All data are presented summarized and none of the data can be linked to specific individuals.
Results
A total of 15,028 road traffic injury (RTI) patients were admitted to healthcare institutions in Serbia during the study period (2015–2019). The findings revealed that men were more prone to injuries, with a male-to-female ratio of 2:1 (N = 10,282, 68.4%; N = 4,746, 31.6%). The mean age of the entire sample was 44.3 years, with a standard deviation of 22.3 years (±22.3). The youngest patient was less than 1 year old, and the oldest patient was 97 years old.
Car accidents were the most frequent type of incident, accounting for nearly one-third (30.9%) of hospitalized patients. The age groups 30–49 (24%) and young road users aged 15–29 years (22.7%) represented the majority of cases. The demographic and injury characteristics of the study sample are detailed in Table 1.
During the 5-year period, the crude RTI incidence rate increased every year, from 39.0/100, 000 in 2015 to 43.7/100,000 in 2019. The five-year mean RTI incidence was 41.8/100,000. The highest RTI incidence rates of hospitalized persons, with values over 500 per 100,000 inhabitants, were registered in three districts of Serbia (Raski, Macvanski, and West Backa districts). They were followed by the Moravian, South Backa, and North Backa districts that had incidence rates ranging from 400 to 500 per 100,000 inhabitants (Figure 1).
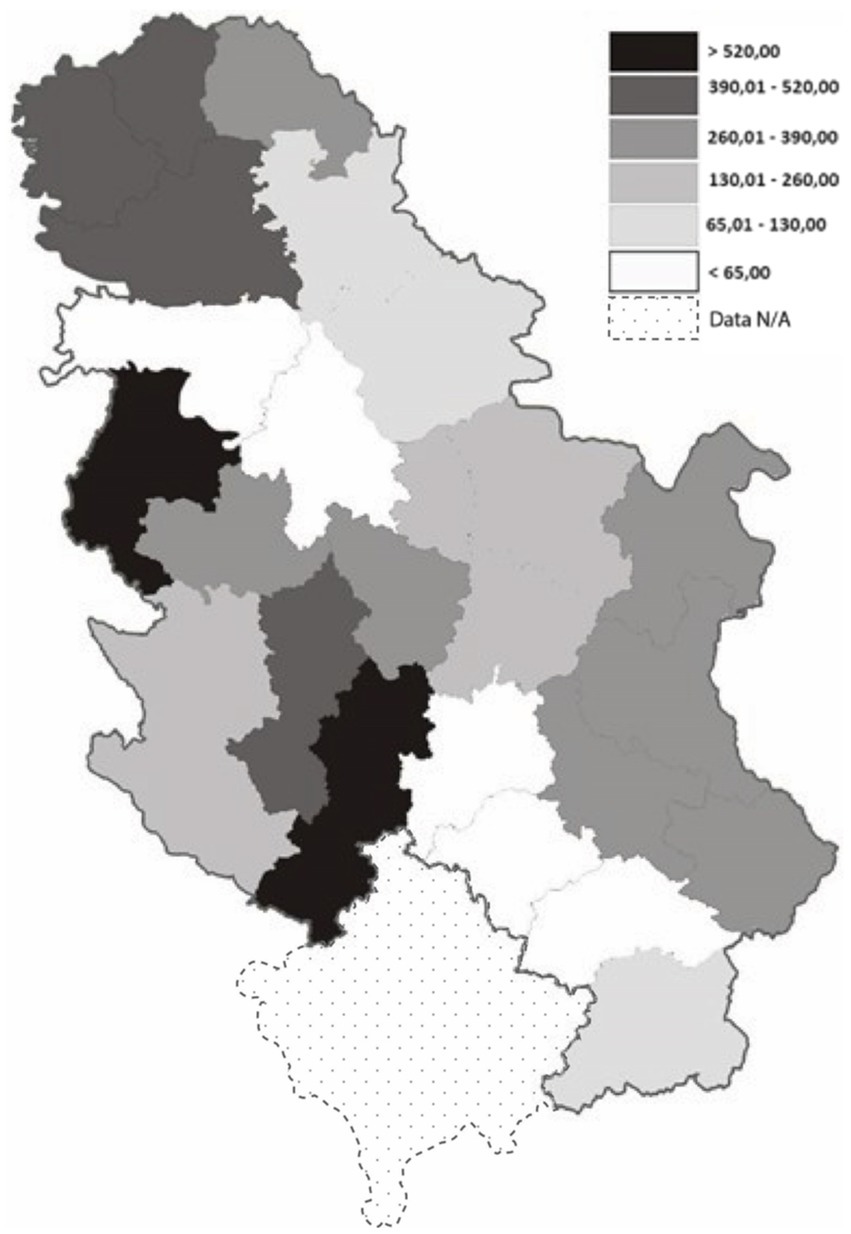
Figure 1. Road traffic injury incidence of hospitalized patients in Administrative districts in Serbia, period 2015–2019.
According to hospital data car occupants accounted the majority of hospitalized patients. Of the total number hospitalized due to RTI, 4,639 (30.9%) were car occupants, 3,723 (24.8%) were bicyclist, 2,658 (17.7%) were pedestrian and 1,806 (12%) were motorcyclists. Vulnerable road users (pedestrians, cyclists and motorcyclist) accounted half 8,187 (54.5%) of the injuries over the 5-year period. The results showed that car occupants, bicyclist as well as pedestrians, were the most affected road users in all three regions (30.9, 24.8, 17.7%). However, bicyclists were more affected in Vojvodina region than in the other two regions. Hospital data showed that every third patient (33.1%) in the Vojvodina region was injured as bicyclist at RTC, compared to Belgrade region and Central Serbia where patients were mostly affected as car passengers (25.8 and 35.1%, respectively). Generally, motorcyclists were the least affected road user (Table 2).
There were significant differences in types of injuries according to external cause of injury (χ2 = 1,208,054; p < 0.001). The most common injury among pedestrians injured in transport accidents and among motocyclists was lower extremities injuries. Among car occupants and cyclist, the most frequent injuries were head and neck injuries (Table 3).
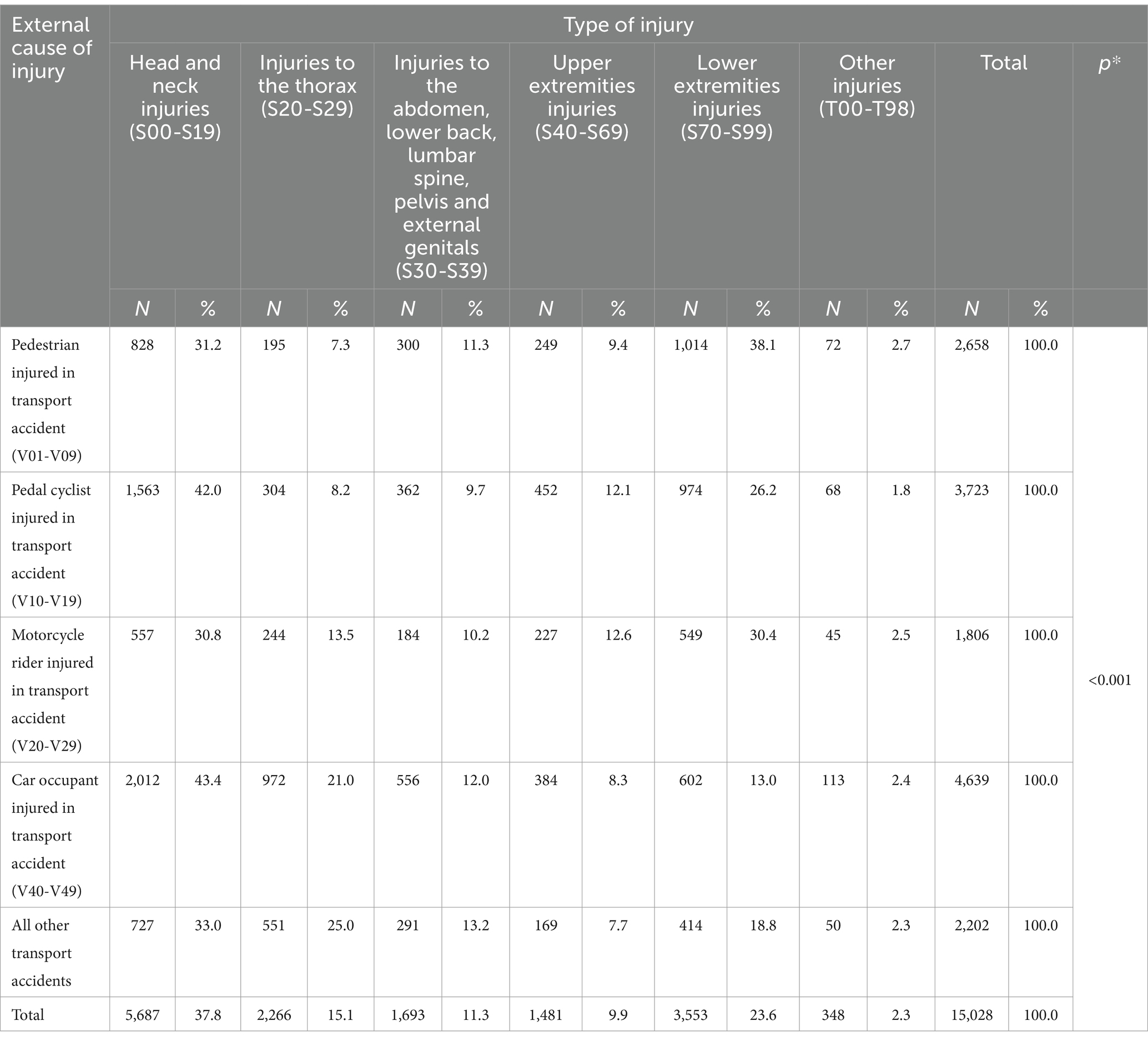
Table 3. Type of injury according to external cause of injury, hospitalized patients, Serbia, period 2015–2019.
Epidemiological characteristics of road users by age showed that children aged 7–14 were more affected as pedestrian or bicyclist compared to children younger than 7 years who were more often injured as car passenger and bicyclist. Among the age group 15–64 years old, car occupants were the most affected by RTC. Older adult people above 65 were particularly vulnerable as bicyclist and pedestrians (31.3, 27.7%, respectively) in RTC (Table 4).
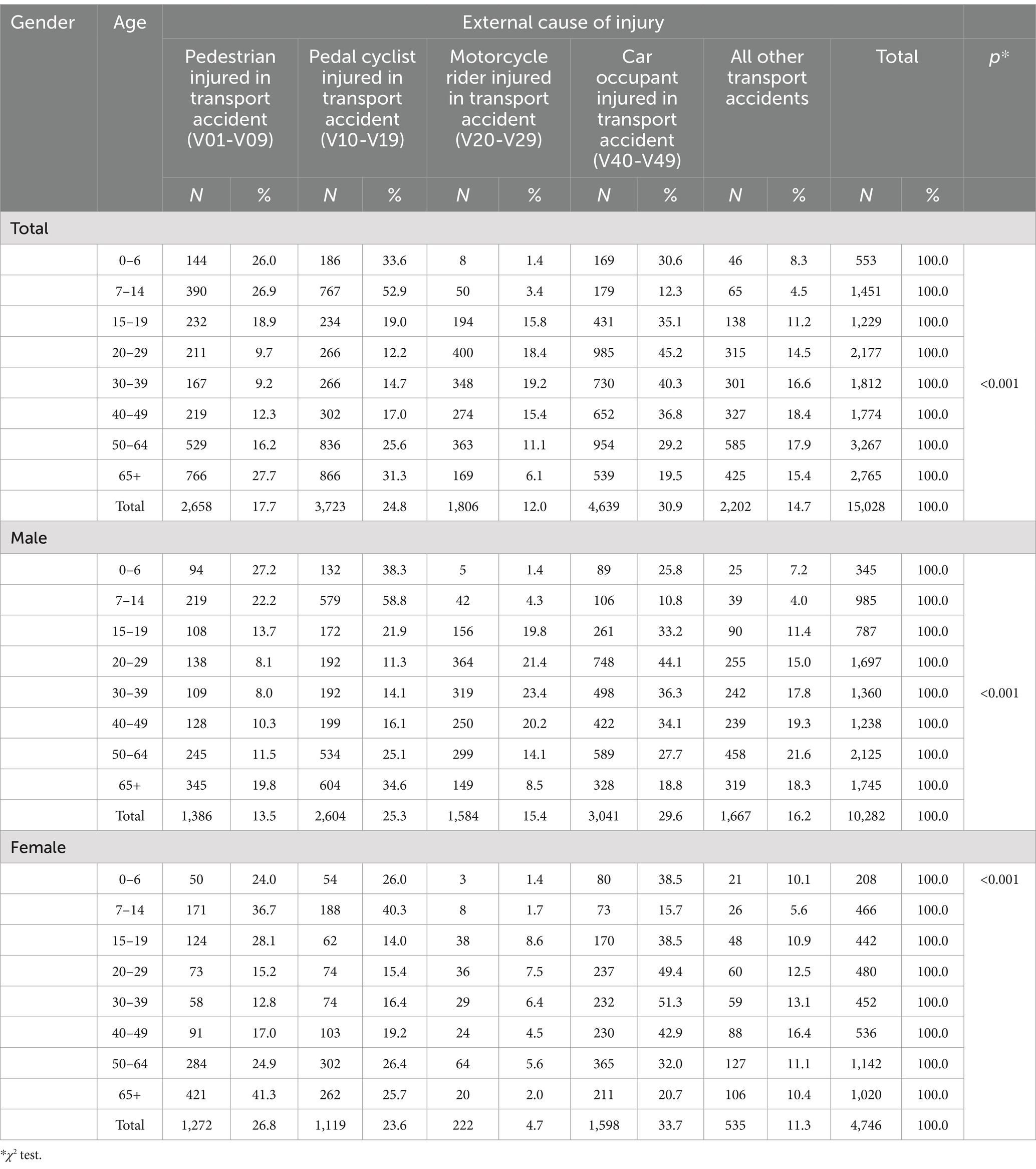
Table 4. Distribution of external causes of injury according to age and gender of the hospitalized patient, Serbia, period 2015–2019.
Regarding the spectrum of injuries among the study population, craniocerebral trauma was the most frequent RTI (37.8%), followed by upper and lower extremities injuries (33.5% in total) and thoracic injury (15.1%). The analysis of the structure of the type of injuries among different age categories showed that head injuries had a significantly higher participation in younger age categories than in older ones. Lower extremities injuries were more prevalent among older patients than in younger. Among children aged 0–6 every seventh injury was lower extremity injury (14.1%), while among persons aged 65 and over every third injury was lower extremities injury (33.6%) (Table 5).
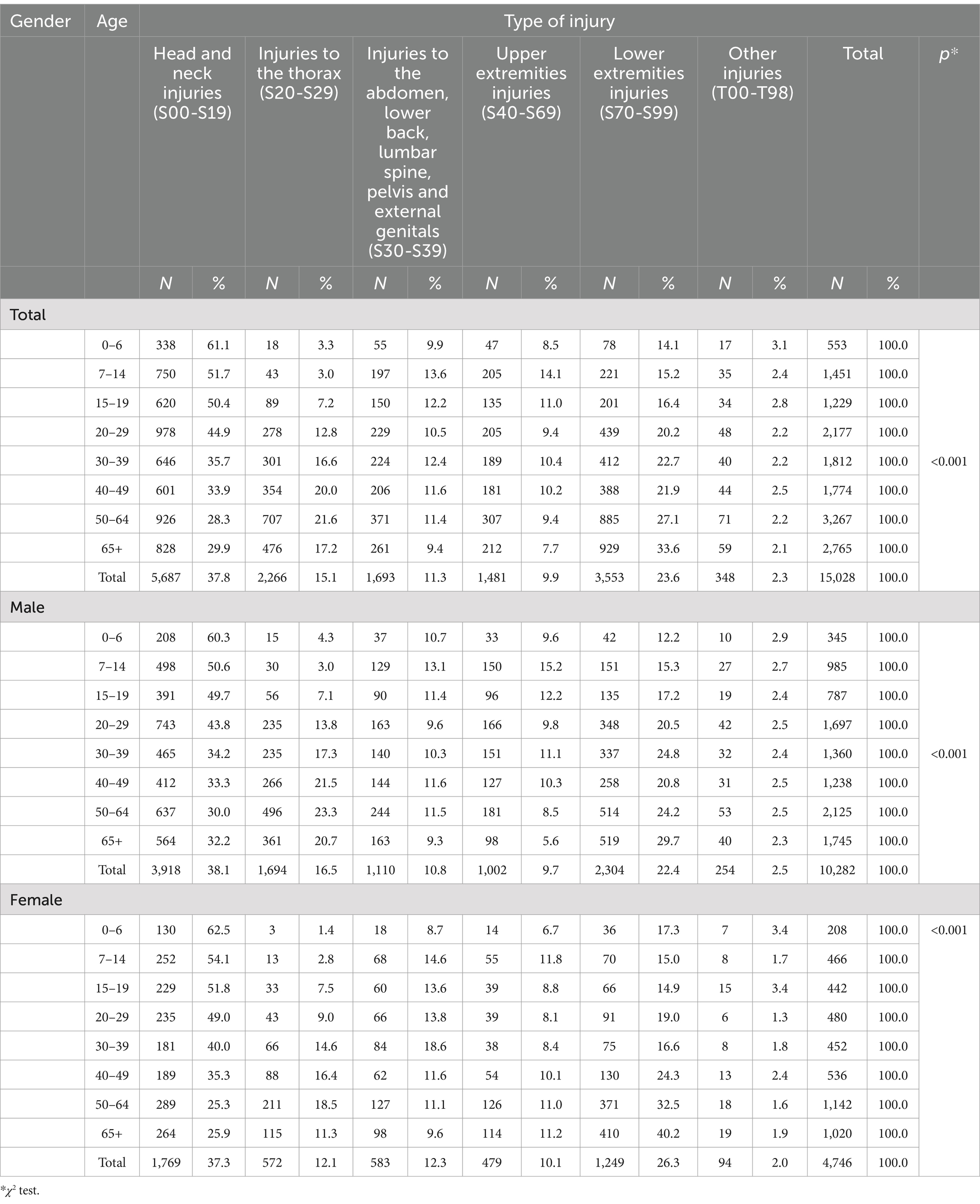
Table 5. Type of injury in hospitalized patients according after road traffic injuries, Serbia, period 2015–2019.
According to the obtained data, the highest age specific incidence of RTI was registered among young people aged 15–19 (Figure 2).
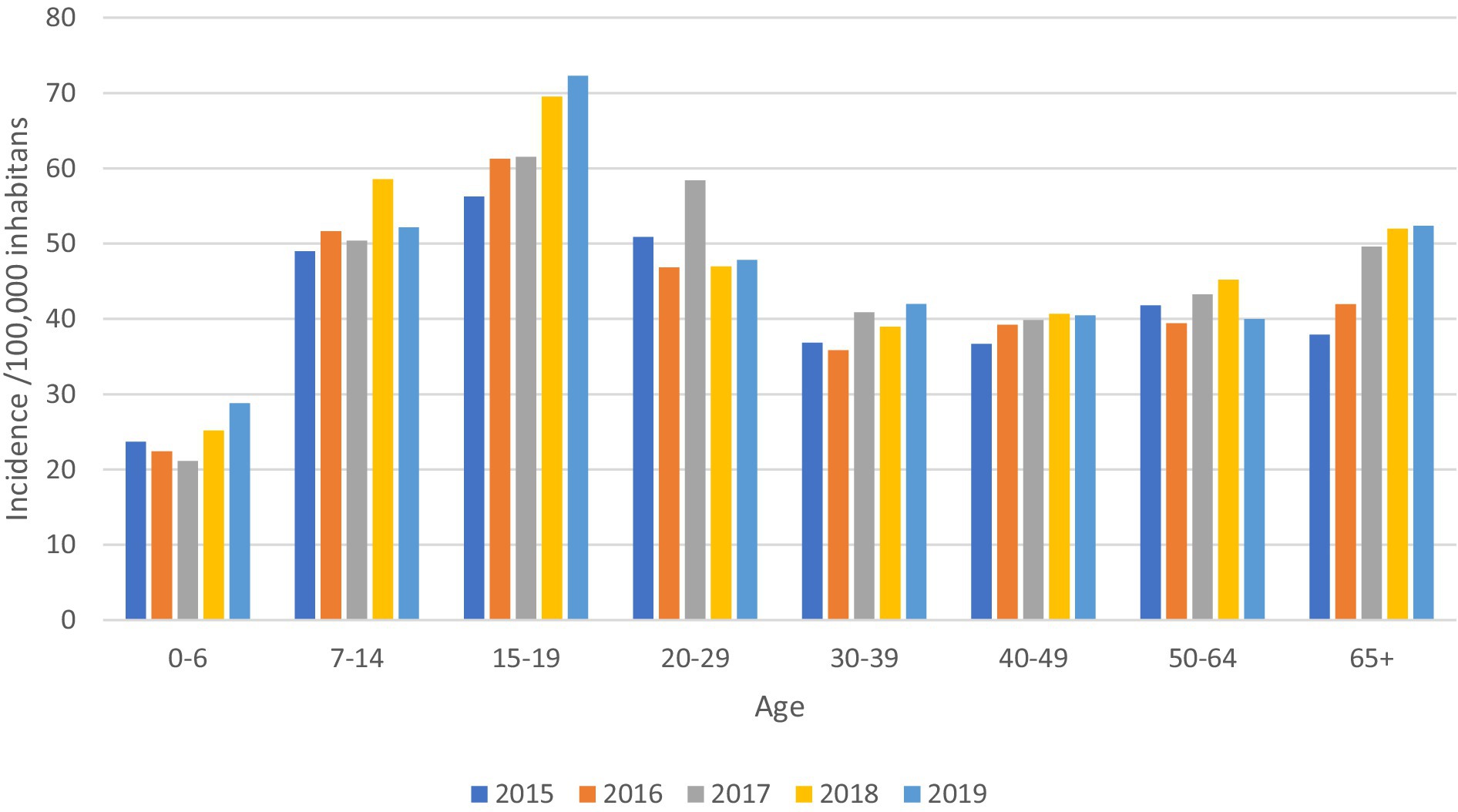
Figure 2. Age-specific incidence of RTI in hospitalized patients/100,000 inhabitants, Serbia, period 2015–2019.
Discussion
RTIs remained a significant public health issue, reflecting both global and regional trends in road safety. Understanding the epidemiology of injuries in RTC in Serbia is crucial for developing evidence-based interventions that can effectively reduce the burden of RTI. To our knowledge, this is the first study that analyzed the results on hospital data on RTI in Serbia. This manuscript highlights key aspects of the epidemiology of injuries in RTC in Serbia, based on hospitalization report data.
Serbia has experienced a concerning number of RTA with 170,090 recorded between 2018 and 2022, contributing to a high incidence of injuries. RTI remain a significant public health concern globally, and Serbia is no exception, with a five-year mean RTI incidence rate of 41.82 per 100,000 population. Our study revealed substantial disparities in RTI incidence across different regions of Serbia, confirming the hypothesis that regional differences exist and that the incidence fluctuated during the observed period without a significant reduction. The districts of Raški, Mačvanski, and West Bačka recorded the highest cumulative incidence rates based on hospitalized data. These geographical variations are likely influenced by factors such as road conditions, socioeconomic indicators, and geographical location, as these districts are border areas with frequent traffic and poor road infrastructure. In terms of road safety, Serbia’s roads are considered among the least safe in Europe. According to the World Economic Forum’s Global Competitiveness Report from 2019, Serbia ranked 33rd in road quality, with a score of 3.5. Countries with lower scores include Moldova (2.6), Bosnia and Herzegovina (2.8), Romania and Ukraine (3.0 each), and Bulgaria and North Macedonia (3.4 each) (23). During the study period (2015–2019), a total of 15,028 patients were admitted to healthcare institutions in Serbia for treatment following RTA. The number of RTI requiring hospitalization represents a substantial economic burden in Serbia, an upper-middle-income country (24). The total economic costs of road crashes in Serbia in 2017 amounted to EUR 272.1 million, or 0.7% of Serbia’s gross domestic product (GDP) (8). A study of RTI in Poland found that road traffic crashes equal 2.1% of (GDP) (25). Wachnicka et al. confirmed the impact of regional factors on road safety, identifying several statistically significant variables. These include gross domestic product per capita (GDPPC), the number of passenger cars per inhabitant (MRPC), the share of passenger vehicles (PPC), and life expectancy at birth (LIFE). Additionally, factors related to regional borders, such as inner-border (IB) and outer-border (OB) areas, were also found to be influential (26). Other researchers have also affirmed that road safety varies significantly between regions (27–30). Additionally, a study by Li et al. identified improper vehicle operation, speeding, loss of vehicle control, and inefficient driver management as the top four risk factors in the comprehensive evaluation of road safety risk. These findings align with other studies confirming the regional disparities in road safety outcomes (31).
The data indicate that the average age of hospitalized patients due to RTI in our sample was 41.4 years. This is higher than the average age reported in similar studies from Greece, Poland, Bangladesh, and Iran, where the average ages were 35.4, 36.2, 36.7, and 33.8 years, respectively (25, 32–34). In Serbia, the most frequently hospitalized individuals following road traffic collisions (RTCs) were those aged 50–64 (21.7%), followed by individuals aged 65 and older (18.4%), together comprising 40.1% of the total. The demographic aging of Serbia’s population is reflected in the lower proportion of younger people and the increasing share of older adult individuals. With 22.3% of the population aged 65 and older and an average age of 43.9, Serbia’s population is continually aging. This trend suggests that the burden of RTA on the healthcare system is likely to increase in the future (12). Similar findings, showing an increasing trend in the hospitalization of older adult drivers, were observed in studies by Goldman et al. and other researchers (35, 36).
The public health significance of RTA in Serbia is highlighted by the impact on children and young people, one of the most vulnerable groups. Data show that 36.1% of hospitalized RTA patients are children aged 0–14 and young people aged 15–29. The age distribution of those injured, along with findings from a study on non-fatal RTAs in Riyadh (37), emphasizes the urgent need for prevention programs. These programs should prioritize early awareness and education initiatives targeting both young drivers and passengers of all genders to improve road safety and reduce accident rates. A study conducted in India on the patterns of RTI and pre-hospitalization factors found that males and young adults aged 18–34 were the most affected in both urban and rural settings. In urban areas, most accident victims did not require hospitalization. However, in rural areas, a significant number of accidents occurred on national highways or rural roads, with most injuries resulting from routine, straight driving. Notably, 43.9% of these rural cases required hospitalization, indicating a higher injury severity in these areas (37–39). Conversely, a study in Isfahan Province found a higher number of fatal crashes in the provincial capital compared to other cities (40).
A review of the literature indicates that significantly more men than women are injured in RTA, with the exception of pedestrian groups aged 15–19 and over 65, where women constitute the majority. Similar studies have confirmed a higher incidence of injuries among women as pedestrians in RTA (34, 41). In our study, the male-to-female ratio was 2:1, confirming our hypothesis regarding gender differences among hospitalized patients following RTA. The data indicate that males are disproportionately represented among hospitalized RTI patients, which may be attributed to a higher likelihood of engaging in risky driving behaviors. Numerous studies have consistently shown that men face a greater risk of involvement in RTA (1, 42, 43).
Car occupants represented the majority of hospitalized patients, accounting for 30.9% of cases, while approximately one-fourth (24.8%) of hospitalized patients were injured in cycling accidents. Significant differences were observed in the age distribution concerning external causes of injuries. Children aged 0–14 and individuals aged 65 and older were primarily injured as pedal cyclists. In contrast, the most common external causes of injuries among the age categories 15–19, 20–29, 30–39, 40–49, and 50–64 were car accidents. Previous studies have demonstrated that vulnerable age groups, such as children and the older adult, are more susceptible to severe injuries, highlighting them as key focus groups for prevention efforts (44–46). Based on our study results, we confirmed the hypothesis that children, young drivers, and the older adult constitute a vulnerable category of road users. Similar findings were reported in studies conducted in Romania, which is the only country included in the Road Safety PIN report from 2012 that documented an increase in the number of young people killed on the roads (47). Young adults required emergency care for injuries, including road traffic injuries (RTIs), more frequently than for any other health condition (48, 49). Our data indicate that individuals aged 18 to 29 account for the highest proportion of emergency department visits due to RTIs, comprising 30.5% (n = 219) of cases. These findings are consistent with previous studies that support this trend (25, 50).
Certain demographic factors significantly influence the epidemiology of RTI in Serbia. Young adults, particularly males, are prone to engaging in risky behaviors, such as excessive speed, driving under the influence of alcohol or illicit drugs, and distractions from mobile phone use while driving. These behaviors are notably more prevalent in this age group, highlighting the urgent need for targeted interventions (8, 51). Multiple studies support the effectiveness of communication campaigns as a complement to road safety education and law enforcement, serving as a key element in reducing the severity of crash consequences. Such initiatives could have a positive impact on road safety prevention in the country (52–54). Additionally, Klinjun et al. identify several preventable risk factors associated with traffic injuries (55). Furthermore, bicyclists are particularly affected in the Vojvodina region, where bicycle usage is significantly higher than in other parts of Serbia. Understanding these demographic patterns can inform the development of public health campaigns and educational initiatives tailored to address specific high-risk groups (56). Our findings indicate that head and neck injuries (37.8%) and extremity injuries (33.5%) are the most prevalent among road traffic injuries (RTIs) in Serbia. The types of injuries observed in our study are consistent with those reported in another research (57, 58). Additionally, our data show that car occupants and cyclists face an increased risk of head and neck injuries compared to other groups of road users. The high percentage of head injuries among cyclists may be attributed to the low prevalence of protective equipment, such as helmets, in Serbia. Multiple studies have confirmed the effectiveness of helmet use in reducing mortality and injury severity following RTA (59–61). Baker et al. report that pedestrians and cyclists are at the greatest risk of severe injuries (62). In Europe, nearly 70% of all RTA fatalities involve a head injury, with 32% resulting from isolated head injuries (63). Furthermore, car occupants are at a higher risk of sustaining thoracic injuries, particularly in older age groups. The elevated frequency of thoracic injuries among car occupants may be attributed to the low percentage of seat belt usage, which aligns with findings from other reported studies (64, 65). In Benhamed et al.’s study, thoracic injuries were also identified as the most common type of injury among car occupants, accounting for 52.3% of cases (66). Lower extremity injuries were more prevalent among pedestrians, while cyclists and motorcyclists were more frequently exposed to upper extremity injuries. A previous study involving pedestrians and cyclists demonstrated that the lower extremities were the most commonly injured, followed by the upper extremities, which is consistent with our findings in this vulnerable road user group (67).
Understanding the epidemiological profile of road users involved in accidents is essential for monitoring and controlling specific risk factors. Analyzing hospital data on RTI enables the prioritization of preventive measures and the enhancement of emergency response protocols. These measures may include stricter law enforcement, public awareness campaigns promoting responsible driving behavior, improvements in road infrastructure, and the enhancement of emergency medical services. Through collaborative efforts between healthcare authorities, policymakers, and community stakeholders, targeted interventions can be implemented to reduce the incidence of RTIs and mitigate their adverse effects on public health and well-being. For future research on the epidemiological characteristics of traffic trauma in Serbia based on hospital data, we recommend the following key points:
• Data Collection and Standardization: Establish a national registry for injuries. Linking hospital data with emergency medical services, ambulance records, police reports, and insurance company databases can enhance the collection of accurate and comprehensive information.
• Analysis of Demographic Characteristics of the Injured: Investigate the demographic factors (such as gender, age, and socioeconomic status) associated with road traffic accidents (RTAs) in greater detail, focusing on variations among different groups, particularly vulnerable road users.
• Type and Severity of Injuries: Implement the Maximum Abbreviated Injury Scale (MAIS 3+) to assess the severity of injuries.
• Geographical Distribution of Traffic Accidents: Analyze the geographical distribution of traffic accidents and identify “black spots” (locations with a high risk of accidents) using hospital data.
• Research on Traffic Behavior of Participants: Conduct studies on the behaviors of road users, including driving speed, the use of safety systems, and compliance with regulations.
• Economic and Social Impact of Traffic Trauma: Investigate the economic costs associated with treating traffic injuries (both direct and indirect) as well as the long-term impact on families and communities.
This framework can serve as a base for the development of future research projects in Serbia, with the aim of improving traffic safety and reducing the rate of injuries and fatalities.
Limitations
There are several limitations to our study. First, hospitalization reports RTI patients provide minimal or no information on the circumstances or additional risk factors contributing to the severity of road traffic accidents, such as accident causes, participant behavior, or weather and road conditions. Second, data on final outcomes are incomplete. There is a lack of information regarding the severity of injuries and the long-term consequences for each patient, such as disability, quality of life, or the enduring economic impact on families. Third, the study did not include there data on fatalities, including the characteristics of those who died and cases where deaths occurred outside the hospital setting or did not require hospitalization. Fourth, the absence of data on hospital length of stay (number of days) limits insights into the healthcare system’s burden resulting from traffic injuries. Recommendations for further research include analyzing the duration of hospital treatment among RTI patients, associated hospital costs, and focusing on monitoring the long-term consequences of injuries, such as disability, quality of life, and the lasting economic costs for families.
Conclusion
Based on the results of our research, there is a clear disparity in the incidence rates of road traffic injuries (RTI) across various regions of Serbia, highlighting the need for enhanced traffic safety measures at the local level. Our findings indicate that men are a high-risk group, and there is a significant association between road user categories, age, and gender. These insights can inform the prioritization of targeted preventive measures. Implementing a multisectoral approach—integrating education, law enforcement, infrastructure improvements, and public health campaigns—can reduce the strain on healthcare systems and enhance overall road safety in Serbia.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
Ethical review and approval was not required for the study on human participants in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent from the [patients/participants OR patients/participants legal guardian/next of kin] was not required to participate in this study in accordance with the national legislation and the institutional requirements.
Author contributions
SR: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MŠ: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. DK: Writing – original draft. MM: Data curation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. II: Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. RP: Data curation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. IR: Formal analysis, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. WHO. (2022). Road traffic injuries. Available at: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/road-traffic-injuries.
2. World Health Organization. (2024). Global status report on road safety 2023. Available at: https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/375016/9789240086517-eng.pdf?sequence=1.
3. Fekadu, W, Mekonen, T, Belete, H, Belete, A, and Yohannes, K. Incidence of post-traumatic stress disorder after road traffic accident. Front Psychiatry. (2019) 10:10. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2019.00519
4. Bryant, RA, O’Donnell, ML, Creamer, M, McFarlane, AC, Clark, CR, and Silove, D. The psychiatric sequelae of traumatic injury. Am J Psychiatry. (2010) 167:312–20. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2009.09050617
5. Kenardy, J, Edmed, SL, Shourie, S, Warren, J, Crothers, A, Brown, EA, et al. Changing patterns in the prevalence of posttraumatic stress disorder, major depressive episode and generalized anxiety disorder over 24 months following a road traffic crash: results from the UQ SuPPORT study. J Affect Disord. (2018) 236:172–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2018.04.090
6. Kovacevic, J, Miskulin, M, Degmecic, D, Vcev, A, Leovic, D, Sisljagic, V, et al. Predictors of mental health outcomes in road traffic accident survivors. J Clin Med. (2020) 9:309. doi: 10.3390/jcm9020309
7. RTSA. RTSA. (2024). Road traffic safety agency, republic of Serbia. Available at: https://www.abs.gov.rs/en/about-rtsa.
8. International Transport Forum. Road safety annual report 2019 Serbia. (2019). Available at: https://www.itf-oecd.org/sites/default/files/serbia-road-safety.pdf.
9. Europian Transport safety Council. (2023). 17th annual road safety performance index (PIN report). Available at: www.etsc.eu/pin (Accessed March 16, 2023).
10. Road Traffic Safety Agency Serbia. (2021). statisticki-izvestaj-o-stanju-bezbednosti-saobracaja-u-republici-srbiji-za-2022.-godinu. Available at: https://www.abs.gov.rs
11. Road traffic safety agency, Republic of Serbia. (2023). Road traffic safety agency. Available at: https://www.abs.gov.rs/en/.
12. Statistical Office of the Republic of Serbia (2024). Statistical Office of the Republic of Serbia. Available at: https://www.stat.gov.rs/en-US/ (Accessed March 16, 2023).
13. Europian Transport Safety Council. (2018). Briefing: 5th EU road safety action Programme 2020–2030. Available at: https://goo.gl/BwTY9R (Accessed February 26, 2024).
14. Government of Republic of Serbia. (2023). 20231002113306-strategija-bezbednosti-saobracaja-2023-2030. Available at: https://abs.gov.rs/admin/upload/documents/20231002113306-strategija-bezbednosti-saobracaja-2023-2030.pdf (Accessed February 26, 2024).
15. World Road Association (PIARC). (2015). Crash data system | road safety manual - world road association (PIARC). Available at: https://roadsafety.piarc.org/en/road-safety-management-safety-data/crash-data-system.
16. Giummarra, MJ, Beck, B, and Gabbe, BJ. Classification of road traffic injury collision characteristics using text mining analysis: implications for road injury prevention. PLoS One. (2021) 16:e0245636. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0245636
17. Koppel, S, Bugeja, L, Smith, D, Lamb, A, Dwyer, J, Fitzharris, M, et al. Understanding fatal older road user crash circumstances and risk factors. Traffic Inj Prev. (2018) 19:S181–3. doi: 10.1080/15389588.2018.1426911
18. Elstad, M, Ahmed, S, Røislien, J, and Douiri, A. Evaluation of the reported data linkage process and associated quality issues for linked routinely collected healthcare data in multimorbidity research: a systematic methodology review. BMJ Open. (2023) 13:e069212. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-069212
19. Soltani, A, Edward Harrison, J, Ryder, C, Flavel, J, and Watson, A. Police and hospital data linkage for traffic injury surveillance: a systematic review. Accid Anal Prev. (2024) 197:107426. doi: 10.1016/j.aap.2023.107426
20. European Road Safety Observatory. (2022). European Road Safety Observatory Annual statistical report on road safety in the EU 2022 Data up to and including the year 2021. Available at: https://road-safety.transport.ec.europa.eu/document/download/287aa31e-48c2-4e04-a9cc-e2ca24d29cc2_en?filename=ERSO_annual_report_20220509.pdf.
21. Statistical Office of the Republic of Serbia. (2011). Census of population, households and dwellings in the republic of Serbia. Available at: http://pod2.stat.gov.rs/ObjavljenePublikacije/Popis2011/Nacionalna%20pripadnost-Ethnicity.pdf.
22. Paragraph Lex doo. Law on health documentation and records in the field of health. (2024). Available at: https://www.paragraf.rs/propisi/zakon-o-zdravstvenoj-dokumentaciji-i-evidencijama-u-oblasti-zdravstva.html.
23. Schwab, K. (2019). The global competitiveness report 2019. Available at: https://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_TheGlobalCompetitivenessReport2019.pdf.
24. Chen, S, Kuhn, M, Prettner, K, and Bloom, DE. The global macroeconomic burden of road injuries: estimates and projections for 166 countries. Lancet Planet Health. (2019) 3:e390–8. doi: 10.1016/S2542-5196(19)30170-6
25. Goniewicz, M, Nogalski, A, Khayesi, M, Lübek, T, Zuchora, B, Goniewicz, K, et al. Pattern of road traffic injuries in Lublin County, Poland. Cent Eur J Public Health. (2012) 20:116–20. doi: 10.21101/cejph.a3686
26. Wachnicka, J, Palikowska, K, Kustra, W, and Kiec, M. Spatial differentiation of road safety in Europe based on NUTS-2 regions. Accid Anal Prev. (2021) 150:105849. doi: 10.1016/j.aap.2020.105849
27. Gomes, MJTL, Cunto, F, and Silva, AR. Geographically weighted negative binomial regression applied to zonal level safety performance models. Accid Anal Prev. (2017) 106:254–61. doi: 10.1016/j.aap.2017.06.011
28. Chen, F, Wang, J, Wu, J, Chen, X, and Zegras, PC. Monitoring road safety development at regional level: a case study in the ASEAN region. Accid Anal Prev. (2017) 106:437–49. doi: 10.1016/j.aap.2017.07.016
29. Grisé, E, Buliung, R, Rothman, L, and Howard, A. A geography of child and elderly pedestrian injury in the City of Toronto, Canada. J Transp Geogr. (2018) 66:321–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jtrangeo.2017.10.003
30. Xu, Y, Chen, M, Yang, R, Wumaierjiang, M, and Huang, S. Global, Regional, and National Burden of Road Injuries from 1990 to 2019. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2022) 19:16479. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192416479
31. Li, F, Wang, X, Feng, Z, Wang, J, Li, M, Jiang, K, et al. Risk chain identification of single-vehicle accidents considering multi-risk factors coupling effect. PLoS One. (2024) 19:e0302216. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0302216
32. Roy, S, Delwer, M, Hawlader, H, Nabi, MH, Chakraborty, A, Zaman, S, et al. Patterns of injuries and injury severity among hospitalized road traffic injury (RTI) patients in Bangladesh. Heliyon. (2017) 7:e06440. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06440
33. Kashkooe, A, Yadollahi, M, and Pazhuheian, F. What factors affect length of hospital stay among trauma patients? A single-center study, southwestern Iran. Chin J Traumatol. (2020) 23:176–80. doi: 10.1016/j.cjtee.2020.01.002
34. Markogiannakis, H. Motor vehicle trauma: analysis of injury profiles by road-user category. Emerg Med J. (2006) 23:27–31. doi: 10.1136/emj.2004.022392
35. Goldman, S, Cohen-Manheim, I, Radomislensky, I, Savitsky, B, Bahouth, H, Bar, A, et al. Demographic and injury trends for car crash casualties hospitalized in level I trauma centers over two decades: data from the National Trauma Registry. Isr J Health Policy Res. (2024) 13:27. doi: 10.1186/s13584-024-00613-z
36. Lee, HH, Cho, JS, Lim, YS, Hyun, SY, Woo, JH, Jang, JH, et al. Relationship between age and injury severity in traffic accidents involving elderly pedestrians. Clin Exp Emerg Med. (2019) 6:235–41. doi: 10.15441/ceem.18.052
37. Gorge, J, Alsufyani, L, Almefreh, G, Aljuhani, S, Almutairi, L, Al Babtain, I, et al. The age and gender distribution of patients admitted following nonfatal road traffic accidents in Riyadh: a cross-sectional study. Int J Crit Illn Inj Sci. (2020) 10:76–80. doi: 10.4103/IJCIIS.IJCIIS_16_19
38. Bolandparvaz, S, Yadollahi, M, Abbasi, HR, and Anvar, M. Injury patterns among various age and gender groups of trauma patients in southern Iran: a cross-sectional study. Medicine. (2017) 96:e7812. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000007812
39. Sharma, N, Kumar, V, Mangal, DK, Sharma, Y, Bairwa, M, and Babu, BV. Pattern of road traffic injuries and their pre-hospitalization factors reported at a public tertiary healthcare facility and rural private healthcare Facility in Rajasthan India. Cureus. 15:e39390. doi: 10.7759/cureus.39390
40. Khorasgani, GA, Zeinab Almasi, S, Ahmadreza Almasi, S, Goli Khorasgani, A, Se, C, Goniewicz, K, et al. Computational engineering and physical modeling decoding the factors behind rising fatal roadway crashes in Iran: an in-depth analysis and predictive modelling study. Comput Eng Phys Model. (2024) 7:61–84. doi: 10.22115/cepm.2024.452006.1299
41. González-Sánchez, G, Olmo-Sánchez, MI, Maeso-González, E, Gutiérrez-Bedmar, M, and García-Rodríguez, A. Traffic injury risk based on mobility patterns by gender, age, mode of transport and type of road. Sustain For. (2021) 13:10112. doi: 10.3390/su131810112
42. Lastrucci, V, Innocenti, F, Lorini, C, Berti, A, Silvestri, C, Lazzeretti, M, et al. The prevalence of several risky driving behaviors and associated crash risk in adolescent: a population-based study of Tuscany region. Int J Public Health. (2022) 67:1604582. doi: 10.3389/ijph.2022.1604582
43. Mohamed, J, Mohamed, AI, Ali, DA, and Gebremariam, TT. Prevalence and factors associated with ever had road traffic accidents among drivers in Hargeisa city, Somaliland, 2022. Heliyon. (2023) 9:e18631. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e18631
45. Ranchet, M, Brémond, R, Pala, P, Colomb, M, and Cavallo, V. The detection of vulnerable road users by younger and older drivers. Transp Res F: Traffic Psychol. (2022) 91:357–67. doi: 10.1016/j.trf.2022.10.018
46. Ulak, MB, Ozguven, EE, Vanli, OA, Dulebenets, MA, and Spainhour, L. Multivariate random parameter Tobit modeling of crashes involving aging drivers, passengers, bicyclists, and pedestrians: spatiotemporal variations. Accid Anal Prev. (2018) 121:1–13. doi: 10.1016/j.aap.2018.08.031
47. Rus Ma, D, Peek-Asa, C, Baragan, EA, Chereches, RM, and Mocean, F. Epidemiology of road traffic injuries treated in a large Romanian emergency Department in Tîrgu-Mureş between 2009 and 2010. Traffic Inj Prev. (2015) 16:835–41. doi: 10.1080/15389588.2015.1030501
48. Ahmed, SK, Mohammed, MG, Abdulqadir, SO, El-Kader, RGA, El-Shall, NA, Chandran, D, et al. Road traffic accidental injuries and deaths: a neglected global health issue. Health Sci Rep. (2023) 6:e1240. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.1240
49. Canonica, AC, Alonso, AC, da Silva, VC, Bombana, HS, Muzaurieta, AA, Leyton, V, et al. Factors contributing to traffic accidents in hospitalized patients in terms of severity and functionality. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2023) 20:853. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20010853
50. Blaizot, S, Papon, F, Haddak, MM, and Amoros, E. Injury incidence rates of cyclists compared to pedestrians, car occupants and powered two-wheeler riders, using a medical registry and mobility data, Rhône County, France. Accid Anal Prev. (2013) 58:35–45. doi: 10.1016/j.aap.2013.04.018
51. Bumbasirevic, M, Lesic, A, Bumbasirevic, V, Zagorac, S, Milosevic, I, Simic, M, et al. Severe road traffic injuries and youth: a 4-year analysis for the city of Belgrade. Int J Inj Control Saf Promot. (2014) 21:313–7. doi: 10.1080/17457300.2013.823452
52. Faus, M, Alonso, F, Fernández, C, and Useche, SA. Are traffic announcements really effective? A systematic review of evaluations of crash-prevention communication campaigns. Safety. (2021) 7:66. doi: 10.3390/safety7040066
53. Dunn, HK, Pearlman, DN, Beatty, A, and Florin, P. Psychosocial determinants of teens’ online engagement in drug prevention social media campaigns: implications for public health organizations. J Prim Prev. (2018) 39:469–81. doi: 10.1007/s10935-018-0522-y
54. Pirkis, J, Rossetto, A, Nicholas, A, Ftanou, M, Robinson, J, and Reavley, N. Suicide prevention media campaigns: a systematic literature review. Health Commun. (2019) 34:402–14. doi: 10.1080/10410236.2017.1405484
55. Klinjun, N, Kelly, M, Praditsathaporn, C, and Petsirasan, R. Identification of factors affecting road traffic injuries incidence and severity in southern Thailand based on accident investigation reports. Sustain For. (2021) 13:12467. doi: 10.3390/su132212467
56. Statistical Office of the Republic of Serbia, Institute of Public Health of Serbia (2021). The 2019 Serbian National Health Survey. Available at: https://publikacije.stat.gov.rs/G2021/pdfE/G20216003.pdf.
57. Ghoubaira, J, Diab, M, Nassereldine, H, Tamim, H, Saadeh, S, Price, R, et al. Road traffic injury in Lebanon: a prospective study to assess injury characteristics and risk factors. Health Sci Rep. (2021) 4:e396. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.396
58. Herman, J, Ameratunga, S, and Jackson, R. Burden of road traffic injuries and related risk factors in low and middle-income Pacific Island countries and territories: a systematic review of the scientific literature (TRIP 5). BMC Public Health. (2012) 12:479. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-12-479
59. Choi, WS, Cho, JS, Jang, YS, Lim, YS, Yang, HJ, and Woo, JH. Can helmet decrease mortality of craniocerebral trauma patients in a motorcycle accident?: a propensity score matching. PLoS One. (2020) 15:e0227691. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0227691
60. Abdi, N, Robertson, T, Petrucka, P, and Crizzle, AM. Do motorcycle helmets reduce road traffic injuries, hospitalizations and mortalities in low and lower-middle income countries in Africa? A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Public Health. (2022) 22:824. doi: 10.1186/s12889-022-13138-4
61. Baker, CE, Yu, X, Patel, S, and Ghajari, M. A review of cyclist head injury, impact characteristics and the implications for helmet assessment methods. Ann Biomed Eng. (2023) 51:875–904. doi: 10.1007/s10439-023-03148-7
62. Baker, CE, Martin, P, Wilson, MH, Ghajari, M, and Sharp, DJ. The relationship between road traffic collision dynamics and traumatic brain injury pathology. Brain Commun. (2022) 4:fcac033. doi: 10.1093/braincomms/fcac033
63. Dewan, MC, Rattani, A, Gupta, S, Baticulon, RE, Hung, YC, Punchak, M, et al. Estimating the global incidence of traumatic brain injury. J Neurosurg. (2018) 130:1080–97. doi: 10.3171/2017.10.JNS17352
64. Choi, D, Lee, KH, Kim, OH, Kong, JS, Kang, CY, and Il, CY. Risk factors affecting severe thoracic injuries in motor vehicle collisions based on age group and collision directions. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. (2023) 49:2429–37. doi: 10.1007/s00068-023-02297-7
65. Schoell, SL, Weaver, AA, Talton, JW, Barnard, RT, Baker, G, Stitzel, JD, et al. Functional outcomes of motor vehicle crash thoracic injuries in pediatric and adult occupants. Traffic Inj Prev. (2018) 19:280–6. doi: 10.1080/15389588.2017.1409894
66. Benhamed, A, Ndiaye, A, Emond, M, Lieutaud, T, Boucher, V, Gossiome, A, et al. Road traffic accident-related thoracic trauma: epidemiology, injury pattern, outcome, and impact on mortality-a multicenter observational study. PLoS One. (2022) 17:e0268202. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0268202
Keywords: road traffic injuries, road traffic crash, hospitalization, hospital report, Serbia
Citation: Rajčević S, Štrbac M, Kukić D, Marković M, Ivanović I, Petrović R and Radić I (2024) The epidemiology of road traffic injuries in the republic of Serbia: a study based on hospital data, 2015-2019. Front. Public Health. 12:1468505. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1468505
Edited by:
Ayşe Ünal, Siirt University, TürkiyeReviewed by:
Mireia Faus, University of Valencia, SpainMaxim A. Dulebenets, Florida Agricultural and Mechanical University, United States
Copyright © 2024 Rajčević, Štrbac, Kukić, Marković, Ivanović, Petrović and Radić. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Smiljana Rajcevic, c21pbGphbmEucmFqY2V2aWNAbWYudW5zLmFjLnJz
 Smiljana Rajčević
Smiljana Rajčević Mirjana Štrbac1
Mirjana Štrbac1 Marija Marković
Marija Marković Ivana Radić
Ivana Radić