- 1College of Clinical Medicine, Hebei University of Engineering, Handan, China
- 2Department of Oncology, Affiliated Hospital of Hebei University of Engineering, Handan, China
- 3Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, Affiliated Hospital of Hebei University of Engineering, Handan, China
- 4First Department of Head and Neck Surgery, Yunnan Cancer Hospital, Kunming, China
- 5Department of Medical Oncology, The People's Hospital of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, Nanning, China
Background: Advancements in radiotherapy (RT) technology have led to the prominence of precision RT in head and neck cancer (HNC) treatment. The new progress in precision RT offers more efficient therapy, potentially improving outcomes for HNC patients.
Objective: The present cross-sectional study aimed to assess the knowledge, attitude, and practice (KAP) of patients in advanced precision RT for HNC treatment.
Methods: This study enrolled HNC patients at the Affiliated Hospital of Hebei University of Engineering between October 2023 and May 2024. Then, the demographic data and KAP scores were collected using an investigator-designed questionnaire. Afterwards, descriptive statistics were provided for all study variables, and the relationship among KAP was analyzed using appropriate statistical tests, including Spearman correlation, logistic regression, and path analysis.
Results: A total of 436 participants with a mean age of 52.03 ± 12.19 years old were included. The mean knowledge score, attitude score, and practice score were 18.33 ± 4.21, 36.14 ± 1.71, and 26.26 ± 1.83, respectively. Although most of the participants were unfamiliar with advanced precision RT, they expressed a high willingness to follow their doctor's recommendation for this treatment. The multivariable analysis revealed a positive association between attitude score and proactive practice. The path analysis revealed that knowledge directly influenced attitude and practice, while attitude directly impacted practice.
Conclusion: HNC participants had poor knowledge of advanced precision RT techniques, but had a positive attitude and the willingness to undergo treatment when recommended by their physicians. These results suggest that improving patients' awareness for advanced precision RT can help to promote better attitude and advanced precision RT practice.
1 Introduction
Head and neck cancer (HNC) encompasses malignancies of the oral cavity, lips, pharynx (nasopharynx, oropharynx, and hypopharynx), larynx (glottic, supraglottic and subglottic larynx), ethmoid sinus, maxillary sinus, and salivary glands, mucosal melanoma, and other rare cancers (1). In 2022, approximately 946,477 new cases of the lip, oral, laryngeal, nasopharyngeal, oropharyngeal, hypopharyngeal, and salivary gland cancers (4.7% of all cancers) were diagnosed, with 481,941 deaths (4.9% of all cancer-related deaths) attributed to the disease (2). Globally, the incidence of HNC is increasing, posing a significant public health burden (3, 4).
Management of HNC typically involves a multidisciplinary approach and includes surgery, systemic therapies, radiotherapy (RT), and other interventions. However, these treatments are frequently associated to adverse effects, particularly impacting nutrition and causing oral mucositis (5–7). Surgery may lead to swallowing difficulties, while RT and chemotherapy would commonly cause oral mucositis, taste alterations, decreased appetite, and other nutritional challenges, all of which disrupt the patients' normal eating patterns and nutritional intake (8, 9). Given these treatment-related adverse effects, improving interventions to enhance the patients' quality of life and treatment outcomes has become critical (10, 11). Traditional precision RT regimens, such as three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy (3D-CRT) or intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT), often yield variable responses and severe adverse effects in the treatment of HNC, highlighting the limitations of these approaches.
In recent years, the continuous development of medical science and technology has led to the emergence of advanced precision RTs that utilize sophisticated imaging technology and computer technologies. These methods, such as TomoTherapy (TOMO therapy), CyberKnife, and proton therapy (PT), have become efficient, individualized, and accurate cancer treatment options, ushering in a new era of HNC treatment. Precision TOMO therapy, which is a spiral computed tomography (CT) radiation therapy system, offers significant advantages over traditional 3D-CRT and IMRT by delivering more accurate and effective treatment through rotating CT scans and multi-directional beams (12, 13). In addition, CyberKnife, a type of stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT), minimizes damage to normal tissue through highly precise dose delivery (14, 15). PT, which is another advanced precision particle RT, features beams that exponentially decline with increasing tissue depth, depositing most of the energy deep in the tumor tissue while causing minimal damage to surrounding normal tissues (16, 17). Advanced precision RT represents a crucial step toward achieving optimal outcomes (18). These approaches, which are grounded in scientific evidence, can help prevent or minimize adverse effects on function, maintaining the nutritional status, enhancing immune function, shortening hospital stays, and ultimately improving quality of life.
Proper knowledge of the treatment options and expectations for efficacy and side effects may help patients make informed decisions (19, 20). Knowledge, attitude and practice (KAP) studies provide quantitative and qualitative data by identifying misconceptions and misunderstandings that can act as barriers to the optimal treatment implementation within a specific population (21). These studies can inform discussions between patients and physicians, by highlighting areas where patients may require additional knowledge or clarification. Previous KAP studies on RT of HNC mainly focus on complications and dental care (22, 23). Although, studies have shown positive perceptions of TOMO therapy in breast cancer patients (24), the KAP of HNC patients on advanced precision RT remains unclear.
The present study aims to bridge the present gap by preliminarily investigating KAP for advanced precision RT in patients with HNC. The present findings suggest a relatively low level of patient knowledge on advanced precision RT. These study results may inform the introduction of new advanced precision RT technologies into clinical practice, potentially benefiting a greater number of patients with HNC.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Study design and participants
This cross-sectional study enrolled HNC patients at the Affiliated Hospital of Hebei University of Engineering from October 2023 to May 2024. The inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) ≥ 18 years old, (2) diagnosis of malignant HNC confirmed by histology or cytology, and (3) Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status ≤ 2. The exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) diagnosis of other malignant tumors within the past 5 years, except for cured cases of basal cell carcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma of the skin, superficial bladder cancer, cervical intraepithelial neoplasia, or ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast treated with local treatment, (2) patients with communication disorders, and (3) patients with psychiatric disorders. This study was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of the Affiliated Hospital of Hebei University of Engineering (Approval No: 2023[K]103, Date: October 18, 2023). All the participants signed the written informed consent after fully understanding the study's objectives, who were voluntary to take part in the study.
2.2 Questionnaire
The questionnaire design was based on NCCN Guidelines Insights: Head and Neck Cancers (Version 1.2022) (1); Radiation-induced oral mucositis: A review of current literature on prevention and management (25); Advancements of RT for recurrent head and neck cancer in the modern era (26). After the first draft was completed, a panel of four oncology specialists was consulted. Each expert, with over 10 years of experience, rigorously reviewed the questionnaire items to ensure their accuracy and relevance, leading to the removal of any items deemed incorrect or inappropriate, thereby enhancing the content validity. The questionnaire was revised based on their feedback. A preliminary survey of 25 participants was conducted, yielding a Cronbach's α value of 0.820, which indicated good internal consistency. Therefore, after the pilot study, the questionnaire was improved and all the questions were made more clearly.
The final questionnaire was in Chinese and comprised four sections:
• Demographics: age, gender, education level, weight, height, lifestyle habits, dietary status, body mass index (BMI) and present treatment plans. BMI was calculated as BMI=weight (kg)/height (m)2.
• Knowledge: this consisted of 20 items. The responses were scored using a three-point scale: 2-point for “very familiar,” 1-point for “heard of,” and 0-point for “unclear.” The total scores ranged within 0-40 points.
• Attitude: this consisted of eight questions. A 5-point Likert scale was used, which ranged from “strongly agree” to “strongly disagree”. The score ranged from 8 to 40 points.
• Practice: this consisted of seven items. The responses for items P1-P6 responses ranged from “never” to “always”, and were scored from 1 to 5. The total score ranged within 6–30 points. Since item P7 did not show positive or negative attitude tendencies, this was descriptively analyzed. Scores that exceeded 70% of the maximum possible mark in each section were considered indicative of good knowledge, a positive attitude, and proactive practice (27).
2.3 Questionnaire distribution and quality control
The questionnaires were distributed to the study participants offline in the hospital wards and collected on the spot. All questionnaires were collected anonymously. Research assistants received thorough training on the entire process, such as elucidating the questionnaire's contents to participants, managing the distribution and collection of questionnaires, rules for filling questionnaires, and procedures for data input. In the knowledge section, the participants should answer the knowledge questions directly and avoided other factors influencing their genuine responses. In the attitude and practice section, our research assistants distributed an educational brochure introducing advanced precision RT, and clarified any doubts or questions the participants had. This approach helped them gain a basic understanding of advanced precision RT and maintained the integrity of the data collection process. One member of the research team was responsible for the distribution and collection of questionnaires, and then another researcher input the data into the database and verified the results for accuracy.
2.4 Statistical analysis
The study sample size was determined according to a previous study (28) using the following formula:
Where “n” refers to the number of participants, “z” equals to 1.96 (which corresponds to a 95% confidence interval), “p” refers to the anticipated proportion, “q” equals to 1-p, and “e” refers to the margin of error (which is fixed at 5%). A conservative approach was adopted, and 50% was selected as the expected proportion to optimize the sample size. This calculation yielded a required sample size of 384. In order to account for potential participant loss, a theoretical sample size of 422 was targeted (including a 10% buffer).
The data analysis was performed using SPSS 26.0 and AMOS 24.0 (IBM, Armonk, NY, USA). The normality of continuous data was assessed using the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. The continuous variables that conformed to the normal distribution were presented in means ± standard deviations (SD) and analyzed using Student's t-test (two groups) or ANOVA (more than two groups). Data with a skewed distribution were presented in medians (range) and analyzed by the Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney U-test (two groups) or the Kruskal-Wallis analysis of variance (more than two groups). Categorical variables were presented in n (%) and analyzed by the chi-squared test. Spearman correlation coefficients were used to analyze the correlations among the KAP dimensions. Univariable and multivariable logistic regression were conducted to identify the independent factors associated to proactive practice [defined as a score that exceeded 70% of the maximum possible score (27)]. Variables with p < 0.05 in the univariable analyses were included in the multivariable analysis. Path analysis was employed to test the following hypotheses: (H1) knowledge directly affects attitude; (H2) knowledge directly affects practice; (H3) knowledge indirectly affects practice through attitude. Two-sided p < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
3 Results
3.1 Characteristics of the participants
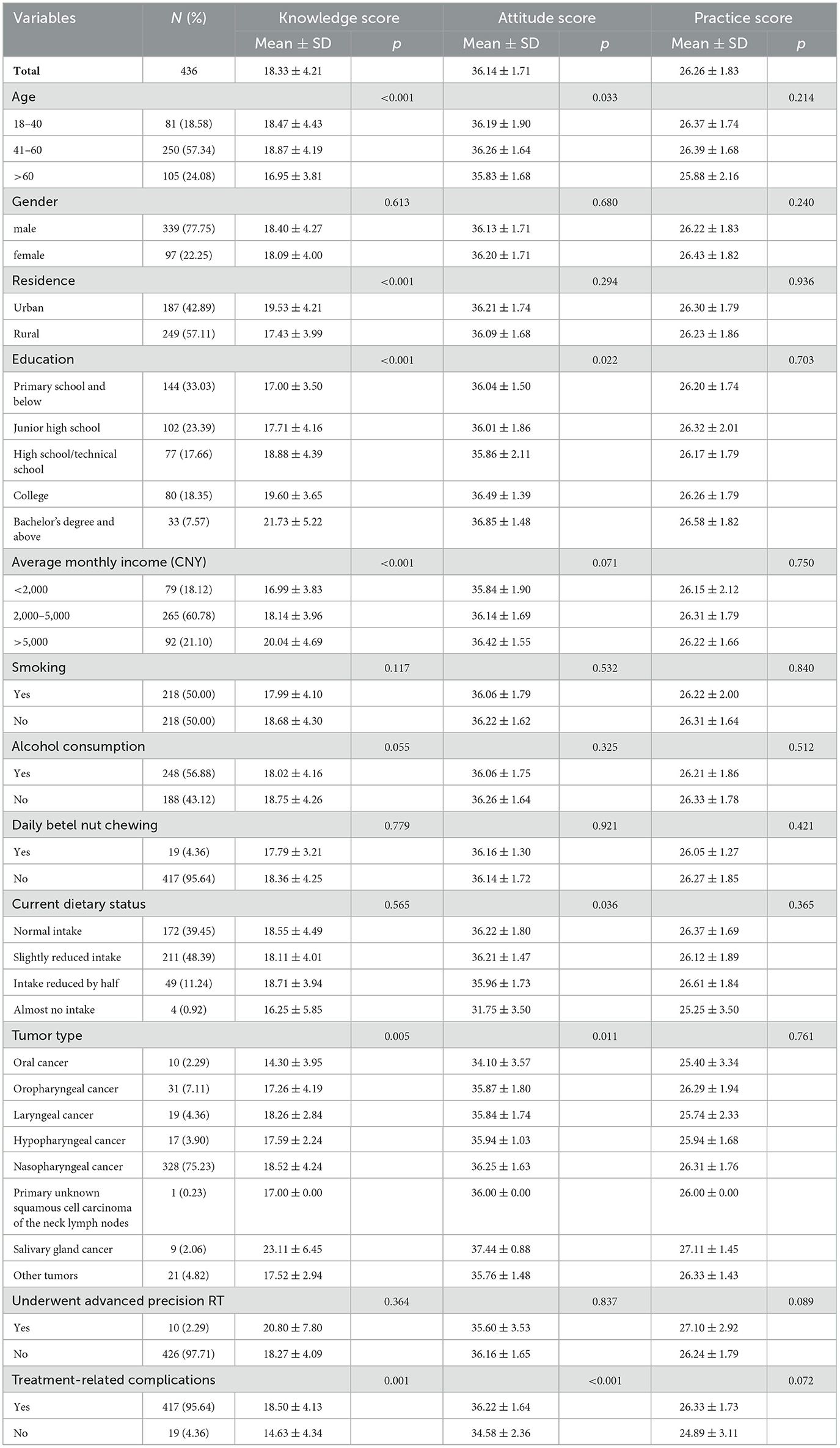
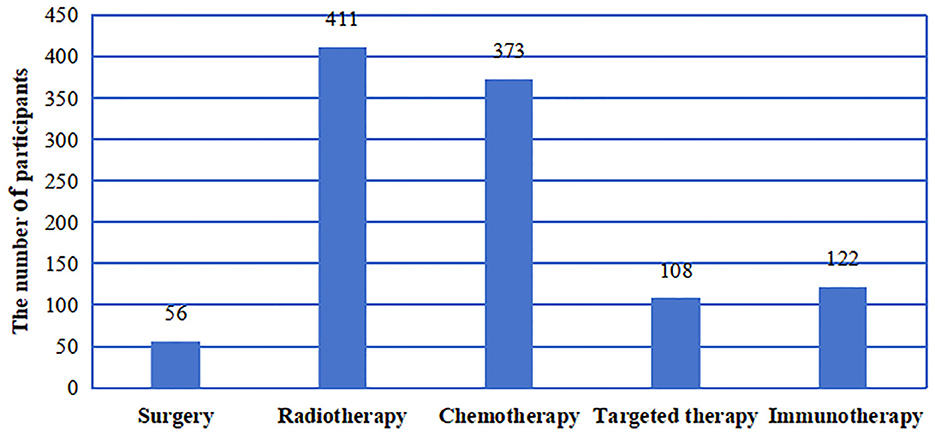
A total of 440 questionnaires were collected. Among these questionnaires, one questionnaire had abnormal data, and three were incomplete. Thus, a total of 436 valid questionnaires were analyzed. Among all the participants, 339 (77.75%) were male, and 97 (22.25%) were female. The average participant age was 52.03 (± 12.19) years old with a mean BMI of 22.84 (± 2.88) kg/m2. Half of the participants reported smoking (50.00%). The characteristics of the participants were as follow (Table 1): rural residence (57.11%), primary school education or below (33.03%), monthly income of 2,000–5,000 CNY (60.78%), drinking (56.88%), not using betel nut (95.64%), reducing dietary intake (60.55%), diagnosed with nasopharyngeal cancer (75.23%), not undergoing advanced precision RT (97.71%), and experiencing treatment-related complications (95.64%). The other detail information was shown in the Table 1. Among the 436 participants, 12.84% of the participants underwent surgery, 94.27% of the participants received RT, 85.55% received chemotherapy, 24.77% received targeted therapy, and 27.98% received immunotherapy (Figure 1).
3.2 Knowledge of precision RT in HNC patients
The average knowledge score for precision RT in HNC (Table 1) was 18.33 ± 4.21 (range: 0–40). The average knowledge score per age group was shown as follows: 18–40 years old had an average knowledge score 18.47 ± 4.43, 41–60 years old had an average knowledge score 18.87 ± 4.19, and >60 years old had an average knowledge score 16.95 ± 3.81. Specifically, the results indicated significant differences in knowledge (p < 0.001) and attitude (p = 0.033) across age groups, though no significant difference was observed in practice scores (p = 0.214). Regarding gender, there were no significant differences in knowledge (p = 0.613), attitude (p = 0.680), or practice (p = 0.240) scores between male and female participants (Table 1). Residence, education, income, HNC type, using advanced new techniques for precision RT and treatment complications were significantly associated with knowledge scores. Knowledge dimension distribution was as follows (Table 2): The knowledge item with the highest score was K19 (99.77%; “During treatment, one should consume foods rich in minerals and vitamins, such as leafy vegetables and fruits”). Conversely, the lowest score was K10 (5.73%; “PT, CyberKnife, and other advanced radiotherapies are presently the best radiotherapy technologies, which can strictly limit the radiation dose strictly to the lesion area, reducing radiation exposure to adjacent organs and normal tissues”). Most of the participants had a general lack of awareness on specific technologies, such as helical TOMO therapy (item K9; 93.12%) or CyberKnife, PT and other new precision RT technologies (item K10; 94.27%).
3.3 Attitude toward precision RT in HNC
The average attitude score (Table 1) was 36.14 ± 1.71 (range: 8–40). Differences in attitude scores were identified based on education, dietary status, HNC type, us of advanced and new techniques for precision RT, and complications. The attitude dimension distribution was as follows (Supplementary Table S1): The attitude item with the highest score was A6 (99.54%; “I believe that strict maintenance of oral hygiene is crucial and can effectively prevent the occurrence of treatment-related oral complications”), while the item with the lowest score was A2 (86.69%; “If recommended by my doctor, I am willing to undergo genetic sequencing tests”). Most of the participants expressed their willingness to undergo RT (item A3, 97.25%).
3.4 Practices toward precision RT of HNC
The average practice score (Table 1) was 26.26 ± 1.83 (range: 6–30). No significant differences in practice scores was observed across the participant characteristics. The practice dimension distribution was as follow (Supplementary Table S2): The practice item with the highest score was P5 (99.31%; “I strictly abstain from smoking and alcohol consumption during treatment.”), while the item with the lowest score was P3 (49.31%; “I actively consult with doctors on dietary nutrition and scientific nutrition.”).
3.5 The main means for participants to obtain information on precision RT
The primary sources of information on cancer treatment and complications contained hospital education (92.66%), followed by social media (51.15%), relatives and friends (13.99%), medical books or materials (2.98%), and traditional media (1.61%) (Figure 2). This highlights the diverse avenues through which individuals access medical information in the digital age, suggesting that medical professionals can leverage new media to disseminate knowledge on precision RT technology to the public.
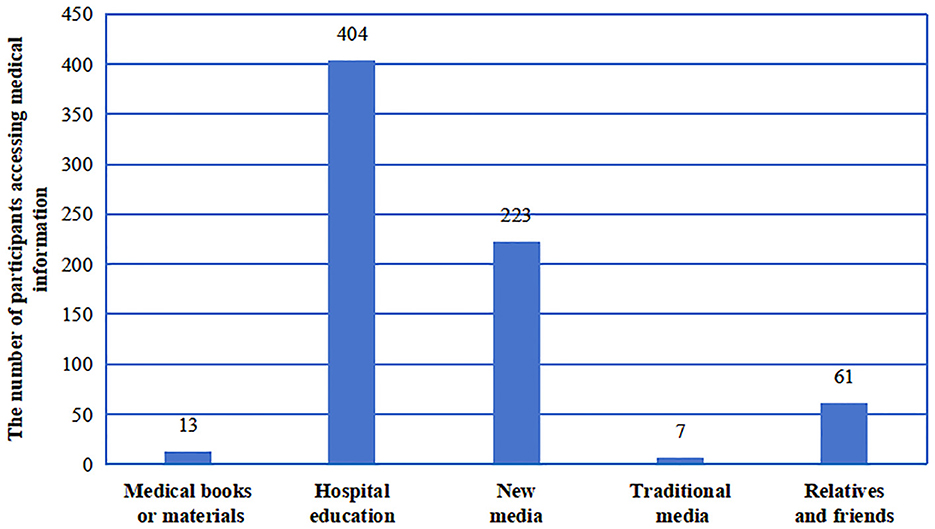
Figure 2. The different sources of knowledge about advanced precision radiotherapy were obtained by HNC patients.
3.6 Correlation analysis of knowledge, attitude, and practice
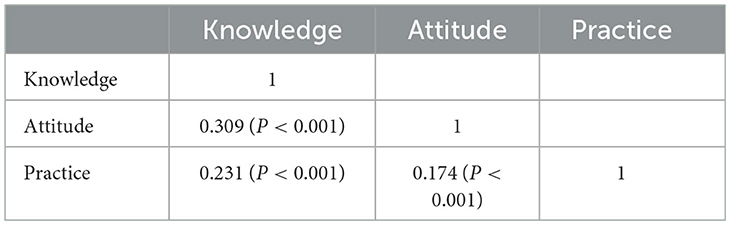
The correlation analysis (Table 3) revealed significant positive correlations between knowledge scores and attitude scores (r = 0.309, p < 0.001), and between knowledge scores and practice scores (r = 0.231, p < 0.001). In addition, there was a significant positive correlation between the attitude scores and practice scores (r = 0.174, p < 0.001). These results indicated that higher levels of knowledge on precision RT are associated to more positive attitudes, and these positive attitudes further enhance proactive practices among patients.
3.7 Univariable and multivariable logistics regression analysis for practice
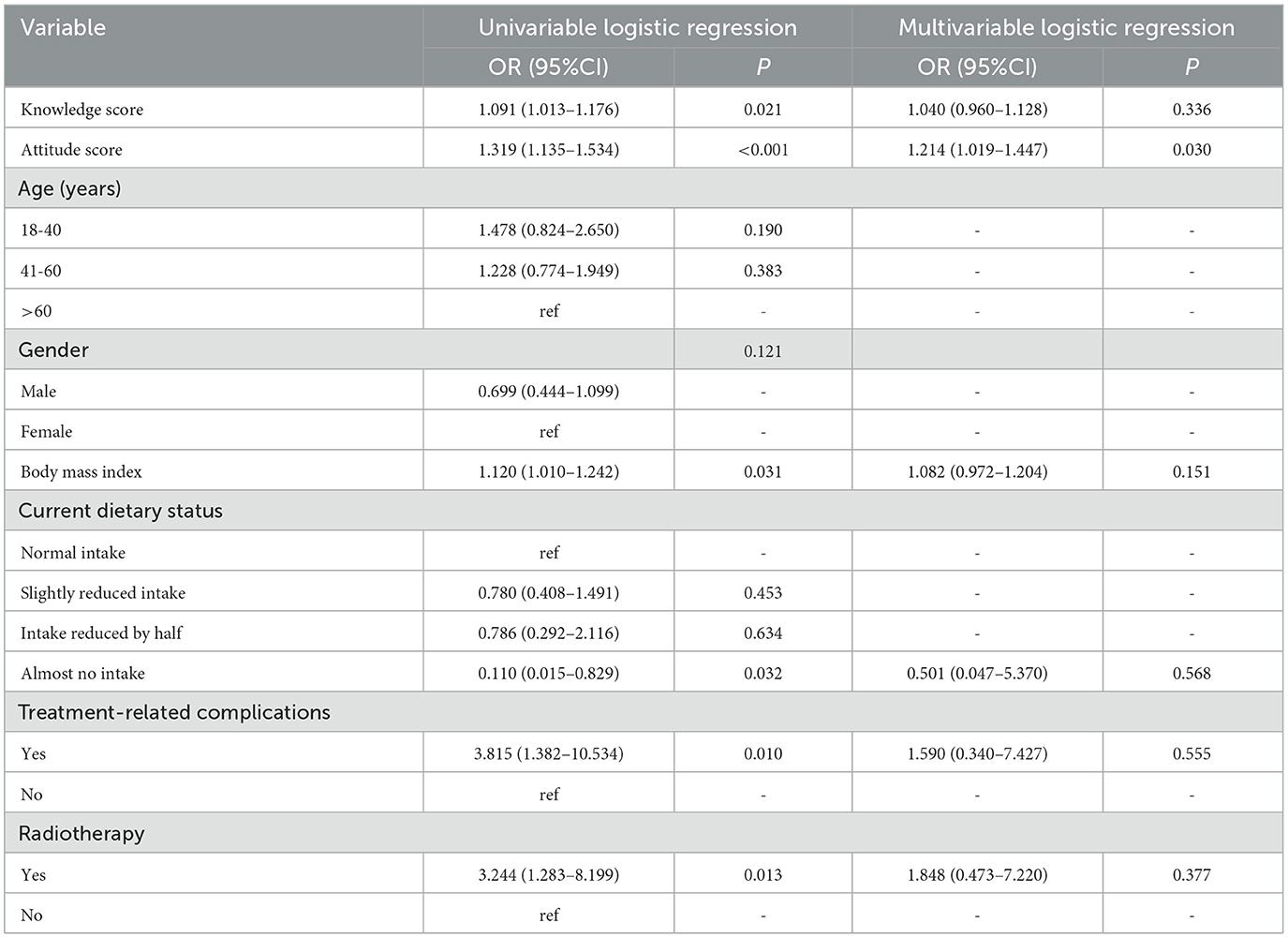
The factors that influenced practice were evaluated by univariable and multivariable logistics regression analysis, in order to identify the possible predictors that affect practice toward advanced precision RT (Table 4). Univariate analysis revealed that knowledge score (OR = 1.091, 95% CI: 1.013–1.176, p = 0.021), attitude score (OR = 1.319, 95%CI: 1.135–1.534, p < 0.001), BMI (OR = 1.120, 95% CI: 1.010-1.242, p = 0.031), almost no intake (OR = 0.110, 95% CI: 0.015–0.829, p = 0.032), with treatment-related complications (OR = 3.815, 95% CI: 1.382–10.534, p = 0.010), and RT experience (OR = 3.244, 95% CI: 1.283–8.199, p = 0.013) were significantly associated to practice scores. Multivariate analysis was performed when the p-value was < 0.05 in univariate analysis. However, in the multivariable analysis, merely the only attitude scores (OR = 1.214, 95%CI: 1.019–1.447, p = 0.030) remained as the an independent influence factor. These findings suggested that although knowledge levels and certain clinical factors influence practice to some extent, attitudes plays a more substantial role in determining a patient' proactive behavior.
3.8 Path analysis
The path analysis (Table 5, Figure 3) further revealed the complex relationships among KAP. The results revealed that knowledge directly influenced both attitude (β = 0.131, p < 0.001) and practice (β = 0.087, p < 0.001), and that attitudes directly influenced practice (β = 0.121, p = 0.021). This finding indicates that knowledge impacts practice not only directly but also indirectly by improving attitude. These findings highlight the importance of enhancing both knowledge and attitudes through patient education, in order to foster proactive practice in precision RT.
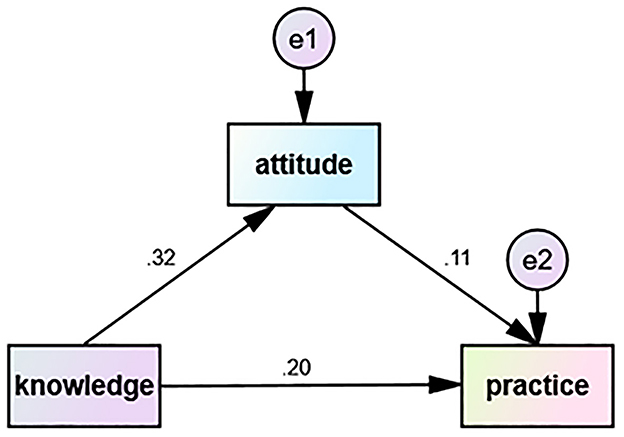
Figure 3. The correlation between knowledge, attitude, and practice scores for advanced precision radiotherapy in HNC was analyzed using path analysis. The direction of causality is displayed by a single-headed arrow.
4 Discussion
Advancements in RT technology have introduced innovative approaches. The present study contributes to the growing body of evidence supporting the clinical adoption of advanced precision RT technologies (TOMO therapy, CyberKnife, PT, etc.), which outperform traditional precision RT. The present datas suggest that although HNC patients generally lacked knowledge on advanced precision RT, they demonstrated a positive attitude and a willingness to participate in the treatment. In addition, significant positive correlations were observed the KAP scores. These findings underscored the critical role of patient education and communication in optimizing HNC treatment.
The knowledge of new advanced precision RT technologies is very important for HNC patients, which help the patients to make a better treatment option. Possessing a strong foundation of knowledge on available treatment options can help patients make the choice when discussing with their oncologists, and develop realistic expectations for treatment outcomes (19, 20). The results of this study revealed poor knowledge of advanced precision RT technologies among patients. Most of studies are consistent with our findings. For example, a survey on patients' knowledge of PT among oncology patients reported a mean knowledge score of 3.4 ± 3.6 (range: 0–12), indicating insufficient knowledge (29). Another study investigating KAP in rectal cancer patients regarding chemoradiotherapy similarly found limited knowledge (30). In addition, a study conducted in Tanzania revealed that the public had poor knowledge of RT, with an average correct response rate of 35.6% across 13 awareness items (31). Thus, the participants always had low level of knowledge score in the KAP studies, which indicated that there was a need to improve the knowledge.
The study also found that rural residents, participants with lower educational levels, and those with lower incomes had lower knowledge scores. Rural populations often have limited access to healthcare resources and educational materials, which restricts their health literacy. Studies have consistently reported that geographic disparities, particularly between rural and urban areas, affect the availability and quality of healthcare information, leading to poorer health outcomes in rural communities (32). Lower educational attainment has also been strongly correlated with reduced health literacy, as individuals with less education may struggle to comprehend complex medical information and treatment options, resulting in a lower understanding of advanced medical technologies like RT (33, 34). Similarly, low-income individuals face additional barriers such as limited access to healthcare services, financial constraints, and less frequent interactions with healthcare providers, which contribute to a gap in knowledge (35). These findings emphasize the need for tailored educational interventions that address the specific challenges of rural, low-income, and less-educated populations, which are essential for improving health outcomes and ensuring equitable access to information on advanced treatments.
The findings showed that participants exhibited low knowledge but maintained a positive attitude toward advanced precision RT, and the similar results were also seen in other studies (36, 37). A study on rectal cancer patients undergoing chemoradiotherapy is consistent with our research, they also found that limited knowledge was coexisted with favorable attitude (30). Another study found that patients often showed positive attitude after consulting the suggestions of healthcare providers, although they did not know much about the new knowledge or technology (38). When faced with complex medical decisions, such as the use of advanced precision RT, patients may rely on the expertise of their doctors rather than seeking to fully understand the intricacies of the treatment (39). Additionally, patients' positive attitude could be driven by the perception that advanced technologies are superior and offer better outcomes, despite their limited knowledge of the specific techniques. Another possible reason might be the lower incidence of HNC compared to common conditions like hypertension or diabetes, which leads to less public propaganda and lower awareness (40). However, given the severe impact of HNC on longevity and quality of life, participants may have stronger expectations for better treatments, fostering a positive attitude despite limited knowledge.
Studies have reported that a higher socioeconomic status is generally associated to better health literacy (41), which translates into more active engagement in medical consultations (42). However, in the present study, the knowledge scores or the socioeconomic characteristics were not independently associated to the practice scores. However, attitude scores had an independent association to the practice. A similar finding was reported by a study in Sweden (43). Nonetheless, the path analysis indicated that knowledge positively influenced attitude and practice, and that attitude positively influenced practice. Therefore, improving knowledge should also improve attitude and practice. The present study revealed that knowledge of novel technologies (such as TOMO therapy, CyberKnife, and PT) was dismal and needed improvement. However, participants' attitudes toward accepting advanced precision RT were high. Knowledge gaps exist regarding HNC, the risk of related malnutrition, gene mutations in HNC, the role of gene mutations in treatments, HNC treatment options, and immunotherapy for HNC. The present study unveiled healthcare providers as the primary source of information for participants, aligning with findings from prior research (44, 45). These results underscore the crucial role of healthcare providers in maintaining present knowledge about HNC and treatment options to educate patients adequately. Therefore, healthcare providers were also a focus of this study; a research from America revealed that non-oncologist physicians at a community hospital exhibited poor knowledge of RT (46). Despite participants reporting limited access to medical information through interactions with relatives and friends, potentially due to feelings of embarrassment when discussing their illness, the role of social support shouldn't be underestimated. Stickel et al. (47) found in a survey of participants' knowledge and attitudes toward cancer peer support programs that approximately half of the participants expressed interest in such programs. They sought to gain insights from peer patients' experiences, practical assistance, and emotional support, bolstering their confidence in treatment.
The present findings have significant implications for clinical practice, particularly in terms of participants education and communication strategies. Despite low knowledge of advanced precision RT, participants exhibited a positive attitude, indicating that the suggestion of healthcare providers is a key factor in treatment acceptance (38, 39). This highlights the importance of clear, effective communication from healthcare providers, especially when explaining complex, novel treatments such as TOMO therapy, CyberKnife, and PT. Incorporating more interactive education sessions and utilizing visual aids or simplified explanations can enhance participants' understanding. Moreover, healthcare providers need to maintain up-to-date knowledge to effectively improve the level of patient's understanding. In China, disparities in healthcare infrastructure and resource distribution are evident. The findings also showed significant differences in knowledge between rural and urban populations, underscoring the necessity of tailored educational interventions (32). For participants with lower incomes, lower education levels, or rural residences, simple, easy-to-understand short videos could be used to convey information about advanced precision RT, as videos have proven effective in improving cancer patients' understanding of best practices (48). For participants with higher incomes, higher education levels, or urban residence, advanced precision RT information can be provided by printing information brochures (49) or developing Internet platforms (50) or mobile apps (51).
This study had several limitations. The results of this study represented the present situation of KAP in advanced precision RT for participants with HNC in one research center. Similar situations may exist in most underdeveloped cities in China, which is a relatively common phenomenon, and should be given attention. To address this, future investigations should include participants from multiple research centers to ensure a more representative opinion reflecting varied cognitive levels, attitudes, and practices toward advanced precision RT. The use of self-reported data also presented limitations, including recall and social desirability biases, which may lead to inaccurate reporting, compounded by the lack of objective verification. The lack of objective verification makes it difficult to confirm the accuracy of the responses, thus requiring careful interpretation of the findings. Moreover, while we collected some socioeconomic indicators, such as residence, education level, and income, these do not fully capture the broader socioeconomic context. Therefore, future studies should address these gaps by incorporating more detailed demographic and socioeconomic data.
In conclusion, participants with HNC have a common lack of knowledge on advanced precision RT, but they have a positive attitude and a proactive practice. Therefore, there is a pressing need for tailored educational and communication initiatives, in order to enhance the development of advanced precision RT in HNC. Furthermore, wider adoption of advanced precision RT technology would improve the efficacy and quality of life for patients with HNC.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of the Affiliated Hospital of Hebei University of Engineering. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation in this study was provided by the participants' legal guardians/next of kin.
Author contributions
ZG: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing – original draft. QC: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing – original draft. BL: Writing – review & editing, Formal analysis. LZ: Supervision, Data curation, Writing – review & editing. YX: Supervision, Data curation, Writing – review & editing. ZL: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. RL: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. YW: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. XC: Project administration, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Resources. ZZ: Project administration, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Resources.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Science and Technology Research Project of Colleges and Universities of Hebei Province (QN2020234), the Precision Medicine Joint Cultivation Fund Project of the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (H2021402007), and the Handan Key Laboratory Project of Precision Diagnosis and Treatment of Digestive Tract Cancer (23313014021).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to honestly thank all the participants who volunteered to participate in the questionnaire survey.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpubh.2024.1461808/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Caudell JJ, Gillison ML, Maghami E, Spencer S, Pfister DG, Adkins D, et al. NCCN Guidelines® insights: head and neck cancers, version 1.2022. J Nat Compreh Cancer Netw. (2022) 20:224–34. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2022.0016
2. Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. (2024) 74:229–63. doi: 10.3322/caac.21834
3. Gormley M, Creaney G, Schache A, Ingarfield K, Conway DI. Reviewing the epidemiology of head and neck cancer: definitions, trends and risk factors. Br Dent J. (2022) 233:780–6. doi: 10.1038/s41415-022-5166-x
4. Marur S, Forastiere AA. Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: update on epidemiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Mayo Clin Proc. (2016) 91:386–96. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2015.12.017
5. Crowder SL, Douglas KG, Yanina Pepino M, Sarma KP, Arthur AE. Nutrition impact symptoms and associated outcomes in post-chemoradiotherapy head and neck cancer survivors: a systematic review. J Cancer Surviv. (2018) 12:479–94. doi: 10.1007/s11764-018-0687-7
6. Pulito C, Cristaudo A, Porta CL, Zapperi S, Blandino G, Morrone A, Strano S. Oral mucositis: the hidden side of cancer therapy. J Exp Clini Canc Res. (2020) 39:1. doi: 10.1186/s13046-020-01715-7
7. Rocha PHP, Reali RM, Decnop M, Souza SA, Teixeira LAB, Júnior AL, et al. Adverse radiation therapy effects in the treatment of head and neck tumors. RadioGraphics. (2022) 42:806–21. doi: 10.1148/rg.210150
8. Arribas L, Hurtós L, Taberna M, Peiró I, Vilajosana E, Lozano A, et al. Nutritional changes in patients with locally advanced head and neck cancer during treatment. Oral Oncol. (2017) 71:67–74. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2017.06.003
9. Epstein JB, Huhmann MB. Dietary and nutritional needs of patients undergoing therapy for head and neck cancer. J Am Dent Assoc. (2011) 142:1163–7. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.2011.0085
10. Machiels JP, René Leemans C, Golusinski W, Grau C, Licitra L, Gregoire V. Squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity, larynx, oropharynx and hypopharynx: EHNS–ESMO–ESTRO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. (2020) 31:1462–75. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2020.07.011
11. Johnson DE, Burtness B, Leemans CR, Lui VWY, Bauman JE, Grandis JR. Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. (2020) 6:92. doi: 10.1038/s41572-020-00224-3
12. Van Gestel D, Van den Weyngaert D, De Kerf G, De Ost B, Vanderveken O, Van Laer C, et al. Helical tomotherapy in head and neck cancer: a european single-center experience. Oncologist. (2015) 20:279–90. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2014-0337
13. Zhang X, Wang T, Xiao X, Li X, Wang CY, Huang B, et al. Radiotherapy for head and neck tumours using an oral fixation and parameter acquisition device and TOMO technology: a randomised controlled study. BMJ Open. (2021) 11:11. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-052542
14. Soman C, Alghamdi SRM, Alazemi FNM, Alghamdi AAA. Cyberknife radiosurgery for the treatment of head and neck cancer: a systematic review. Eur J Dent. (2021) 16:266–73. doi: 10.1055/s-0041-1736330
15. Lim CM, Clump DA, Heron DE, Ferris RL. Stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) for primary and recurrent head and neck tumors. Oral Oncol. (2013) 49:401–6. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2012.12.009
16. Zhou Z, Guan B, Xia H, Zheng R, Xu B. Particle radiotherapy in the era of radioimmunotherapy. Cancer Lett. (2023) 567:216268. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2023.216268
17. Blanchard P, Gunn GB, Lin A, Foote RL, Lee NY, Frank SJ. Proton therapy for head and neck cancers. Semin Radiat Oncol. (2018) 28:53–63. doi: 10.1016/j.semradonc.2017.08.004
18. Chandra RA, Keane FK, Voncken FEM, Thomas CR. Contemporary radiotherapy: present and future. Lancet. (2021) 398:171–84. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00233-6
19. Rocque GB, Rasool A, Williams BR, Wallace AS, Niranjan SJ, Halilova KI, et al. What is important when making treatment decisions in metastatic breast cancer? A qualitative analysis of decision-making in patients and oncologists. Oncologist. (2019) 24:1313–21. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2018-0711
20. Yennurajalingam S, Rodrigues LF, Shamieh O, Tricou C, Filbet M, Naing K, et al. Perception of curability among advanced cancer patients: an international collaborative study. Oncologist. (2018) 23:501–6. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2017-0264
21. Andrade C, Menon V, Ameen S, Kumar Praharaj S. Designing and conducting knowledge, attitude, and practice surveys in psychiatry: practical guidance. Indian J Psychol Med. (2020) 42:478–81. doi: 10.1177/0253717620946111
22. Alqahtani AS, Alshamrani Y, Alhazmi Y, Halboub E. Oral and dental complications of radiotherapy for head and neck cancer: knowledge of dental practitioners in Saudi Arabia. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. (2021) 22:2033–41. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2021.22.7.2033
23. Karimi Afshar M, Behniafar M, Abbaszadeh E, Parizi MT, Karimi Afshar M. Knowledge about dental care in patients with head and neck cancer among senior dental school students: a cross-sectional descriptive study. BMC Med Educ. (2024) 24:776. doi: 10.1186/s12909-024-05728-0
24. Shaverdian N, Wang X, Hegde JV, Aledia C, Weidhaas JB, Steinberg ML, et al. The patient's perspective on breast radiotherapy: Initial fears and expectations versus reality. Cancer. (2018) 124:1673–81. doi: 10.1002/cncr.31159
25. Mallick S, Benson R, Rath GK. Radiation induced oral mucositis: a review of current literature on prevention and management. Eur Arch Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. (2015) 273:2285–93. doi: 10.1007/s00405-015-3694-6
26. Zhang S, Zeng N, Yang J, He J, Zhu F, Liao W, et al. Advancements of radiotherapy for recurrent head and neck cancer in modern era. Radiat Oncol. (2023) 18:166. doi: 10.1186/s13014-023-02342-0
27. Kim D, Lee S, Choi JY, Lee J, Lee HJ, Min JY, et al. Association of α-klotho and lead and cadmium: a cross-sectional study. Sci Total Environ. (2022) 843:156938. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.156938
28. Chen Q, Zhang Y, Li H. Knowledge, attitude, and practice toward non-nutritive sweeteners among the population with reduced sugar intake requirement. Front Nutri. (2023) 10:1268599. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1268599
29. Xie W, Wang H, Sun Q, Wang Y, Wang Y, Chen H, Liu X. Knowledge and attitude toward proton radiotherapy among oncology patients: a multi-center, cross-sectional study. Future Oncol. (2024) 2004:1–7. doi: 10.1080/14796694.2024.2383169
30. Chen X, Lin R, Li H, Su M, Zhang W, Deng X, et al. Knowledge, attitudes, and practices related to preoperative chemoradiotherapy in rectal cancer patients. Gastroenterol Res Pract. (2016) 2016:1081374. doi: 10.1155/2016/1081374
31. Soko GF, Burambo AB, Mngoya MM, Abdul BA. Public awareness and perceptions of radiotherapy and their influence on the use of radiotherapy in Dar es Salaam, Tanzania. Journal of global oncology. (2019) 5:1–10. doi: 10.1200/JGO.19.00175
32. Wang H, Hua X, Yao N, Zhang N, Wang J, Anderson R, et al. The urban-rural disparities and associated factors of health care utilization among cancer patients in China. Frontiers in public health. (2022) 10:842837. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.842837
33. Sponselee HCS, Kroeze W, Poelman MP, Renders CM, Ball K, Steenhuis IHM. Food and health promotion literacy among employees with a low and medium level of education in the Netherlands. BMC Public Health. (2021) 21:1273. doi: 10.1186/s12889-021-11322-6
34. Estrela M, Semedo G, Roque F, Ferreira PL, Herdeiro MT. Sociodemographic determinants of digital health literacy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Med Inform. (2023) 177:105124. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2023.105124
35. Sriram V, Bennett S. Strengthening medical specialisation policy in low-income and middle-income countries. BMJ Global Health. (2020) 5:e002053. doi: 10.1136/bmjgh-2019-002053
36. Almutairi AN, Altuaysi AM, Alwhaid MS, Alhasson MA, Alharbi MA, Alsalam HA, et al. Knowledge and attitude of the general population regarding infant hearing loss in Saudi Arabia. J Family Med Primary Care. (2022) 11:644–52. doi: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_1399_21
37. Muhsin AA, Munyogwa MJ, Kibusi SM, Seif SA. Poor level of knowledge on elderly care despite positive attitude among nursing students in Zanzibar Island: findings from a cross-sectional study. BMC Nurs. (2020) 19:96. doi: 10.1186/s12912-020-00488-w
38. Zhang R, Lu X, Wu W, Shang X. Why do patients follow physicians' advice? The influence of patients' regulatory focus on adherence: an empirical study in China. BMC Health Serv Res. (2019) 19:301. doi: 10.1186/s12913-019-4127-9
39. Kreps GL. Promoting patient comprehension of relevant health information. Isr J Health Policy Res. (2018) 7:56. doi: 10.1186/s13584-018-0250-z
40. Abraham ZS, McHele K, Kahinga AA. Awareness of head and neck cancer among patients attended at a regional referral hospital in Tanzania. BMC Public Health. (2023) 23:1544. doi: 10.1186/s12889-023-16333-z
41. Svendsen MT, Bak CK, Sorensen K, Pelikan J, Riddersholm SJ, Skals RK, et al. Associations of health literacy with socioeconomic position, health risk behavior, and health status: a large national population-based survey among Danish adults. BMC Public Health. (2020) 20:565. doi: 10.1186/s12889-020-08498-8
42. Allen S, Rogers SN, Harris RV. Socio-economic differences in patient participation behaviours in doctor–patient interactions—a systematic mapping review of the literature. Health Expect. (2019) 22:1173–84. doi: 10.1111/hex.12956
43. Olsson LI, Granstrom F, Glimelius B. Socioeconomic inequalities in the use of radiotherapy for rectal cancer: a nationwide study. Eur J Cancer. (2011) 47:347–53. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2010.03.015
44. Swoboda CM, Van Hulle JM, McAlearney AS, Huerta TR. Odds of talking to healthcare providers as the initial source of healthcare information: updated cross-sectional results from the Health Information National Trends Survey (HINTS). BMC Fam Pract. (2018) 19:146. doi: 10.1186/s12875-018-0805-7
45. Alduraywish SA, Altamimi LA, Aldhuwayhi RA, AlZamil LR, Alzeghayer LY, Alsaleh FS, et al. Sources of health information and their impacts on medical knowledge perception among the saudi arabian population: cross-sectional study. J Med Internet Res. (2020) 22:e14414. doi: 10.2196/14414
46. Siau E, Salazar H, Livergant J, Klein J. Non-oncologist physician knowledge of radiation therapy at an urban community hospital. J Cancer Educ. (2021) 36:199–206. doi: 10.1007/s13187-019-01618-y
47. Stickel A, Gröpper S, Pallauf A, Goerling U. Patients' knowledge and attitudes towards cancer peer support programs. Oncology. (2015) 89:242–4. doi: 10.1159/000430918
48. Rachel Hirschey ALB, Walker JS, Nolan TS. Systematic review of video education in underrepresented minority cancer survivors. Cancer Nurs. (2020) 43:259–68. doi: 10.1097/NCC.0000000000000829
49. Martina E, Schmidt MM, Weiß C, Reinke P, Grapp M, Steindorf K. Cancer related fatigue benefits of information booklets to improve patients' knowledge and empowerment. Support Care Cancer. (2022) 30:4813–21. doi: 10.1007/s00520-022-06833-w
50. Emily Warren KF, Tinelli M, McKee M, Knai C. Do cancer-specific websites meet patient's information needs? Patient Educ Couns. (2014) 95:126–36. doi: 10.1016/j.pec.2013.12.013
Keywords: knowledge, attitude, practice, precision radiotherapy, head and neck cancer
Citation: Guo Z, Cai Q, Liu B, Zhao L, Xie Y, Li Z, Liu R, Wang Y, Chen X and Zhang Z (2024) Knowledge, attitude, and practice toward advanced precision radiotherapy among patients with head and neck cancer. Front. Public Health 12:1461808. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1461808
Received: 09 July 2024; Accepted: 27 September 2024;
Published: 17 October 2024.
Edited by:
Antoaneta Ene, Dunarea de Jos University, RomaniaReviewed by:
Huseyin Ozan Tekin, University of Sharjah, United Arab EmiratesHesham M. H. Zakaly, Ural Federal University, Russia
Copyright © 2024 Guo, Cai, Liu, Zhao, Xie, Li, Liu, Wang, Chen and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhiwei Zhang, emhhbmd6dzEyOEAxMjYuY29t; Xiaodan Chen, Y3hkaWJlc3RAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Zhanfei Guo
Zhanfei Guo Qingrui Cai3†
Qingrui Cai3† Liufang Zhao
Liufang Zhao Zhiwei Zhang
Zhiwei Zhang