- 1Department of Clinical Pharmacy, School of Pharmacy, College of Medicine and Health Sciences, Wollo University, Dessie, Ethiopia
- 2Department of Statistics, College of Natural Sciences, Wollo University, Dessie, Ethiopia
- 3Department of Clinical Pharmacy, College of Health Sciences, Mekelle University, Mekelle, Ethiopia
- 4Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health, College of Medicine and Health Sciences, Wollo University, Dessie, Ethiopia
- 5Public Health & Economics Modeling Group, School of Medicine & Dentistry, Griffith University, Gold Coast, QLD, Australia
Background: Optimal medication adherence is vital for the successful implementation of highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) in managing HIV infection. Global efforts aim to minimize the burden of antimicrobial resistance (AMR), including HIV-associated drug resistance.
Methods: This systematic review and meta-analysis followed PRISMA guidelines and searched multiple databases for eligible studies published until July 10, 2023. Eligible studies focused on Ethiopians receiving HAART, reported the prevalence of optimal adherence, and used appropriate assessment tools. Quality of included studies was assessed using JBI checklists A weighted inverse variance random-effects model was applied to calculate the pooled prevalence.
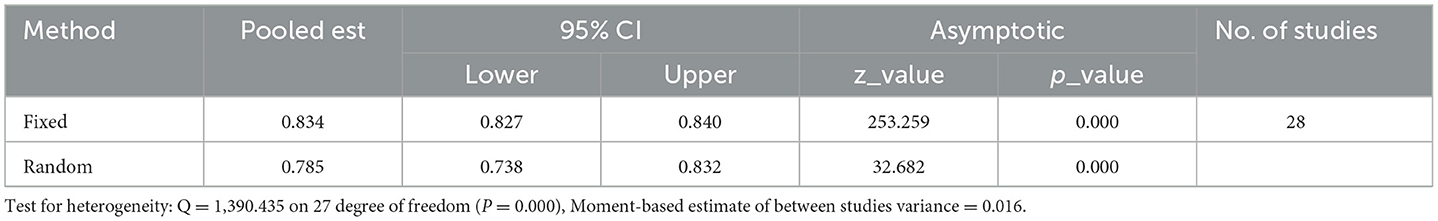
Results: Our meta-analysis aimed to determine the pooled prevalence of optimum Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy (HAART) adherence among HIV-positive adults in Ethiopia and explore variations based on assessment methods, recall periods, and regional factors. The estimated national pooled prevalence of optimal HAART adherence was 79% (95% CI: 74–83, I2 = 98.1%; p-value < 0.001). Assessment methods revealed a prevalence of 64% (95% CI: 54–73) using structured assessment and 82% (95% CI: 78–86) with self-reporting. Optimum adherence varied based on recall periods, ranging from 78 to 85% with self-reporting. Heterogeneity analysis indicated substantial variation (I2 = 98.1%; p-value < 0.001), addressed through subgroup analysis, sensitivity analysis, and univariate meta-regression. Subgroup analysis based on region identified varying prevalence: SNNPR (83%), Oromia (81%), Amhara (79%), and Addis Ababa (74%). Considering the 2018 guideline revision, year-based subgroup analysis showed a prevalence of 78% and 78% before and after 2018, respectively. Sensitivity analysis demonstrated the stability of results, with excluded studies having a minimal impact. Publication bias analysis indicated an absence of bias, as evidenced by a non-significant Egger's regression test (p-value = 0.002) and no adjustment in trim and fill analysis.
Conclusions: The estimated overall prevalence of optimal adherence was 79%, indicating a substantial level of adherence to HAART in the Ethiopian context. The study identified variations in adherence levels based on assessment methods and recall periods, highlighting the importance of considering these factors in evaluating adherence rates. These insights contribute valuable information for policymakers, healthcare practitioners, and researchers working toward enhancing HAART adherence in Ethiopia.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/display_record.php?RecordID=459679
Introduction
Globally, according to a recent World Health Organization (WHO) report, 39 million people were living with HIV, 1.3 million had new HIV infections, and 630,000 faced AIDS-related deaths in 2022. Out of these, 37.5 million people living with HIV and 540,000 HIV/AIDS deaths were exhibited among the adult population (≥15 years of age) (1). Continent-wise, the African Region appears to be most gravely impacted, with roughly 1 in every 25 adults (3.2%) living with HIV and constituting more than two-thirds of the people living with HIV (2). Ethiopia being one of the erstwhile countries in sub-Saharan Africa massively shares the burden. Roughly, 11,000 Ethiopian adults aged 15 and above died because of AIDS-related illnesses in 2020 (3).
Following the issuance of the 2002 National Antiretroviral Drugs Supply (ARVS) and use policy, Ethiopia was among the first African countries to acquaint antiretroviral therapy (ART) in selected health facilities in 2003 (1). ART is a combination of different types of antiretroviral medications used for lifetime treatment of HIV to boost the quality of life of patients by increasing levels of CD4 cells and minimizing viral load (4). Sustainable and optimum adherence to therapy is a major factor that determines the success of HAART (5, 6). This is mainly because poor adherence has a significant impact on the emergence of virologic failure, viral resistance, and grievous adverse health outcomes such as substance abuse, depression, and the spread of infections (7–9).
Although HAART plays a paramount role in improving the lives of HIV-positive patients, HIV-related morbidity and mortality occurred substantially even in the presence of HAART regimens (10, 11). One of the decisive factors that determines the efficacy and enduringness of HAART regimens is medication adherence (12). Though the minimum value for optimum HAART adherence is not well-delineated, at least ≥ 95% adherence is indicated for optimal therapeutic effect (13, 14). The most frequently reported barriers to optimum HAART adherence are attributed to socio-demographic, behavioral, clinical, and health-system related factors (4, 15, 16).
Apparently, both national and international systematic review and meta-analysis studies (17–20) have been conducted among the children population. In Ethiopia, numerous observational studies (3, 16, 21) have been conducted related to the prevalence of adherence to HAART and its associated factors among HIV-infected adults. However, massive discrepancies were reported amidst these studies even within the same geographical setting, across regions, at similar and different time intervals. For instance, the magnitude of optimum adherence to HAART among HIV-infected adults varied from 72.4 to 94.3% in Ethiopia (3). Consequently, the pooled prevalence of optimum HAART adherence among HIV-infected adults remains ill-defined. Hence, this systematic review and meta-analysis study aimed to determine the national pooled prevalence of optimum adherence to HAART among adult HIV patients in Ethiopia.
Methods
Study protocol
Records identification, titles, and abstract screening along with full-text eligibility evaluation for the final analysis was done in accordance with The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analysis (PRISMA) algorithm (22). The study protocol was successfully registered at PROSPERO with a reference number: CRD 42023459679.
Databases and search strategy
A stringent inclusive literature search was performed to retrieve studies reporting the prevalence of optimum HAART adherence and associated predictors of HIV-positive adults in Ethiopia. Both electronic and gray literature searches were conducted in a systematic manner. A comprehensive search was carried out in PubMed, Google Scholar, Hinari, SCOPUS, and EMBASE electronic databases up to 10 July 2023. The search was centered on studies/articles published in the English language with a reported prevalence of optimal HAART adherence among Ethiopians living with HIV. The following terms and/or phrases were employed: “Adherence*,” “Nonadherence*,” “Noncompliance*,” “Non-Adherence*,” “Non Adherence*,” “poor adherence,” “good adherence,” “Persistence*,” Compliance*,” “Non-Compliance*,” “Non Compliance*,” “ART,” “Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy,” “HAART,” “Combination Antiretroviral Therapy,” “Antiretroviral Therapies.” “Antiretroviral Therapy” AND “Ethiopia”. Search strings were employed using “AND” and “OR” Boolean operators. Moreover, the proceedings of professional associations and university repositories were filtered. Furthermore, a direct Google search and reference tracing were also executed by deploying the bibliographies of the identified studies to incorporate further relevant studies missed while digging into the electronic databases.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
The studies were incorporated if they met the following inclusion criteria: studies conducted on adult Ethiopians who are on HAART; observational studies, including cross-sectional, cohort, and case-control studies; studies that reported prevalence of optimum adherence; studies which clearly delineate the measurement tool used for assessment of adherence and operationally defined optimum adherence as patients who took 95% or more of the recommended dose during the specified recall period; studies conducted in Ethiopia; studies published only in the English language. Included studies in this meta-analysis used two types of adherence measurement tools to examine optimum HAART adherence: the self-report method and the structured assessment method. Qualitative studies and citations without full text and studies on the sphere of adherence to HAART prophylaxis were precluded.
Study selection and quality assessment
Endnote version 20 reference manager (23) was deployed to remove duplicated studies. Two independent reviewers (MY and TD) autonomously screened the titles and abstracts to consider the articles in the full-text review. Two investigators (MH and TS) assessed the quality of the studies by using Joanna Briggs Institute's (JBI) critical appraisal checklist for studies reporting prevalence data (24). The following items were used to appraise the selected studies: (1) appropriateness of the sampling frame to address the target population, (2) appropriateness of participants sampling technique and adequacy of sample size, (3) detailed description of study subjects and setting, (4) sufficient analysis of the data and validity and reliability of HAART adherence assessment methods, (5) appropriateness of statistical analysis used and adequacy of response rate. The disagreements were resolved by mutual consensus via blunt joint discussion with a third reviewer. Studies scored five and above out of nine were considered low risk.
Data extraction
A Microsoft Excel format was synthesized for data abstraction. Two independent reviewers (MY and MH) extracted the data. The procedure was repeated whenever a discrepancy appeared. Data pertaining to the first author and year of publication, regions where studies were conducted, study design, study setting, sample size, total number of adherents, assessment tools used, number of days used as a recall period for calculation of adherence level, and the thresholds used for definition of optimum adherence were extracted. In all included studies, structured questionnaires, and self-report techniques were used as assessment methods for measuring adherence levels. Accordingly, we have thematized studies based on their assessment tools as self-report and structured questionnaire methods. Furthermore, studies that use self-report as a measuring tool used different recall time periods prior to the interviews and thus were further classified based on their duration of recall period as 7, 15, and 30 days. Hence, data regarding the level of adherence was collected in four groups in this meta-analysis.
Data analysis
A weighted inverse variance random-effects model (25) was employed to estimate the pooled prevalence of optimal HAART adherence. Subgroup analysis was conducted to adjust for variation in the pooled estimates based on the specific region where the studies were conducted and the year of publication. Due to the inherent variability in the accuracy of adherence measurements, which can be affected by both the assessment methods and the recall periods used, a subgroup analysis was conducted, this allowed us to account for potential differences in adherence estimates based on how the data was collected and the length of the recall period.
Heterogeneity among the included studies was examined using I2 statistic by considering 25, 50, and 75% as low, moderate, and high heterogeneity (26). To ascertain the risk of publication bias, a Funnel plot and Egger's regression test were performed (27). A sensitivity analysis was conducted to ascertain the stability of the summary estimate after the omission of individual studies. STATA version 17 statistical software (28) was used to carry out this meta-analysis.
Outcome of interest
In this meta-analysis, our main objective is to assess the prevalence of optimal adherence to Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy (HAART) among Ethiopian adults living with HIV. For this review, optimal adherence is operationally defined as consuming 100% of the recommended dose for recall periods of 15 days or less. For recall periods of 30 days and above, optimal adherence was defined as patients taking 95% or more of the recommended dose during this timeframe. The population of interest includes HIV-positive adults undergoing highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) in Ethiopia. Our primary outcome is the determination of optimal adherence to HAART. The study designs considered encompass observational studies that detail adherence to ART among HIV-positive individuals in Ethiopia, utilizing a variety of adherence assessment methods. In this study, we categorized adherence assessment methods into structured assessment and self-report methods.
Result
Characteristics of included studies
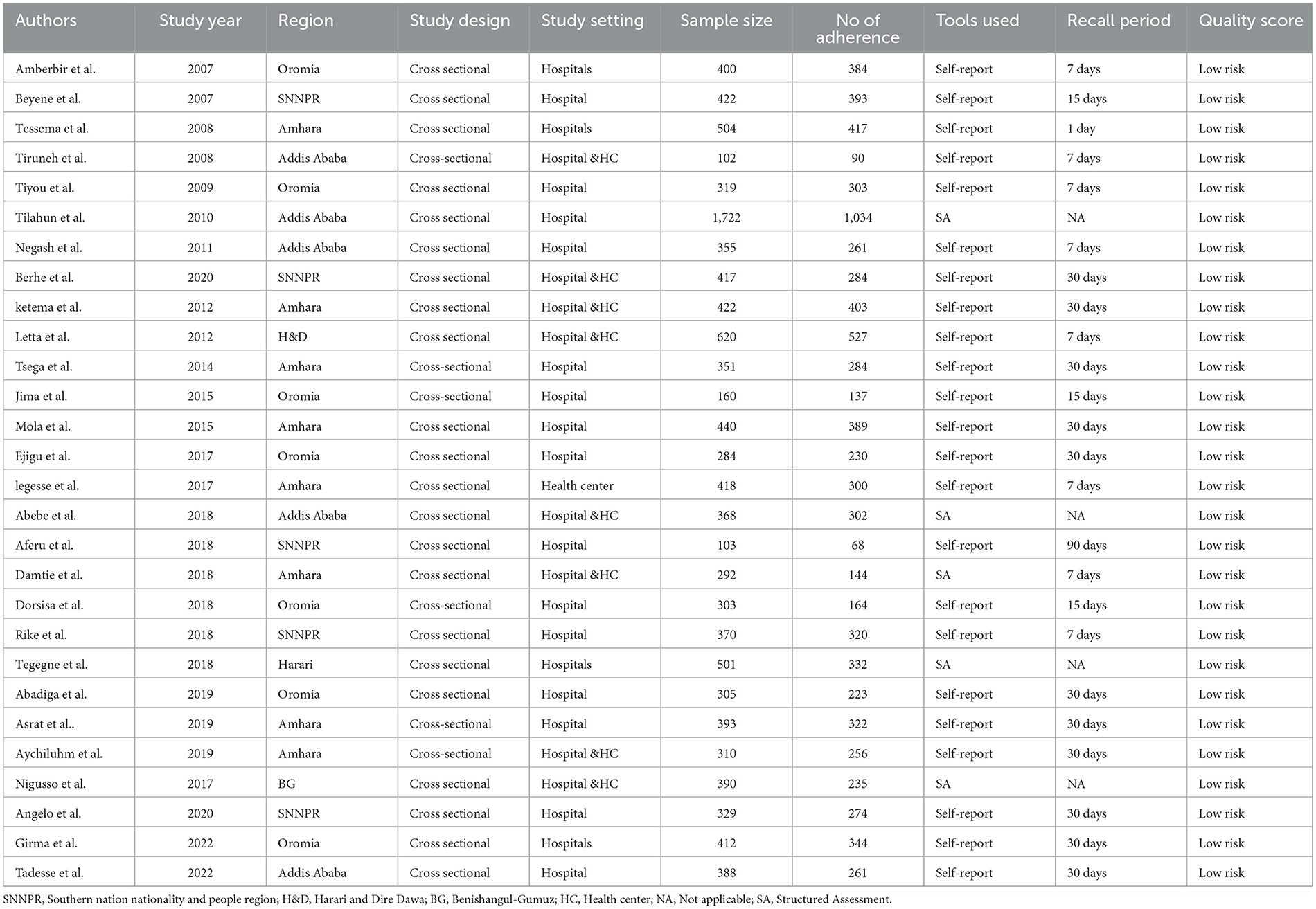
A total of 2,189 potential studies were identified; 976 articles from PubMed, 317 articles from Hinari (research4life), 370 from EMBASE, 476 articles from Scopus, and 350 articles from other sources. Figure 1 shows the results of the search and reasons of exclusion during the study selection process. A total of 28 articles were included to assess the prevalence of optimal adherence to HAART in Ethiopia. The included studies were published between the years 2007 and 2022. Of the included studies, 7 of them were published after 2018, a year in which the national ART guideline was updated. A cross-sectional study design was used for all included studies.
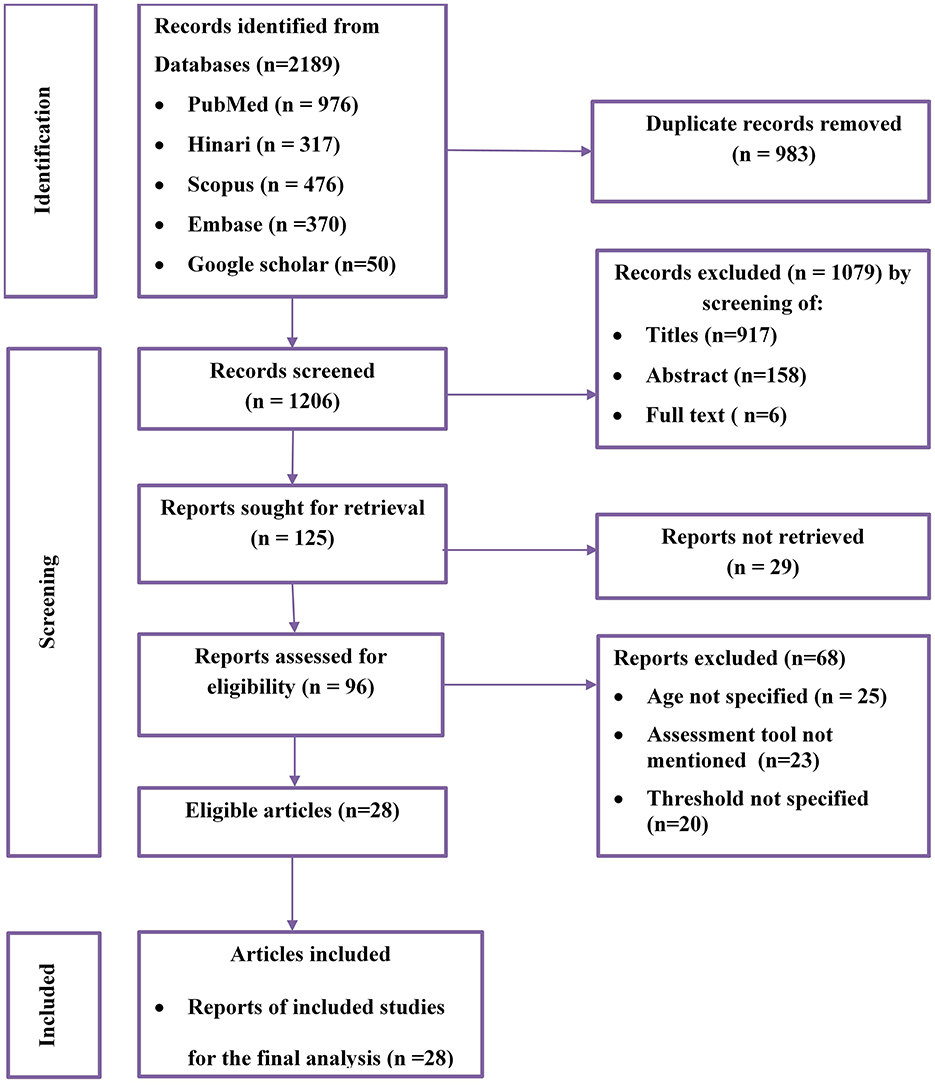
Figure 1. Flow diagram of the included studies for the systematic review and meta-analysis of optimum adherence to HAART in Ethiopia.
Eight studies were conducted in the Amhara region (29–36), seven in Oromia (37–44), five in SNNPR (21, 45–48), five in Addis Ababa (49–53), one in Harare (3), one in Harari and Dire Dawa city (54) and one in Benishangul Gumuz (55). Twenty-three studies reported the prevalence of optimal adherence based on self-report method (21, 29, 30, 32–42, 44–48, 50, 51, 53, 54, 56) while six studies (3, 31, 43, 49, 52, 55) reported via structured adherence assessment method. Among 23 studies that assessed optimal adherence based on the self-report method: seven studies used 7 days (33, 38, 44, 48, 50, 53, 54), three studies used 15 days (39, 42, 47), and eleven studies used 30 days (21, 29, 30, 32, 34, 36, 37, 40, 41, 46, 51, 56) recall period. A total of 11,388 adults living with HIV and on HAART participated in the included studies. Table 1 depicts the characteristics of the included studies.
Quality of the included studies
All of the included studies reporting prevalence data were assessed using the JBI critical appraisal checklist (24). The JBI quality appraisal checklist assessment indicated that none of the incorporated studies were pitiful in quality and precluded from the meta-analysis (Table 1).
Meta-analysis
Pooled prevalence of optimum HAART adherence in Ethiopia
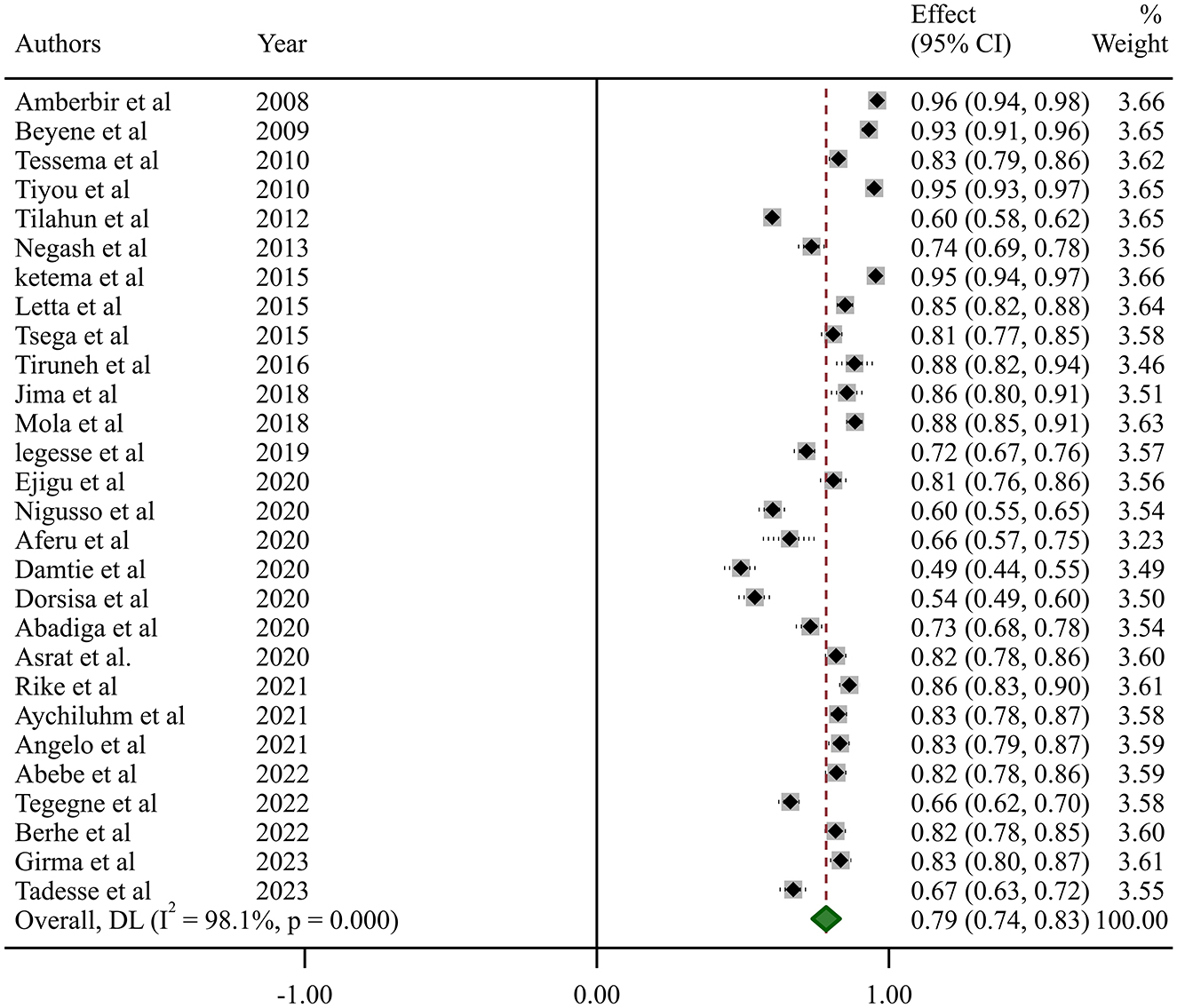
In this systematic review and meta-analysis, the estimated national pooled prevalence of optimal HAART adherence among HIV-positive adults in Ethiopia was 79% (95% CI: 74–83, I2 = 98.1%; p-value < 0.001) (Figure 2).
Heterogeneity analysis
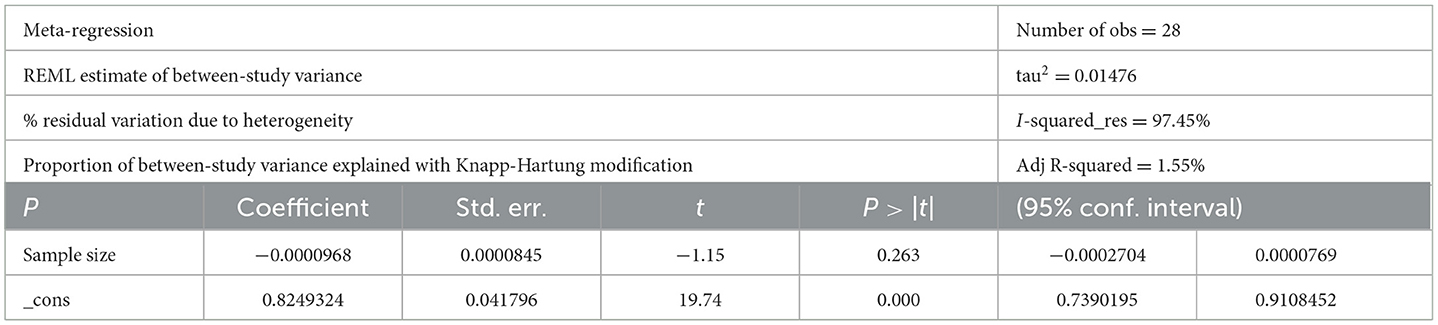
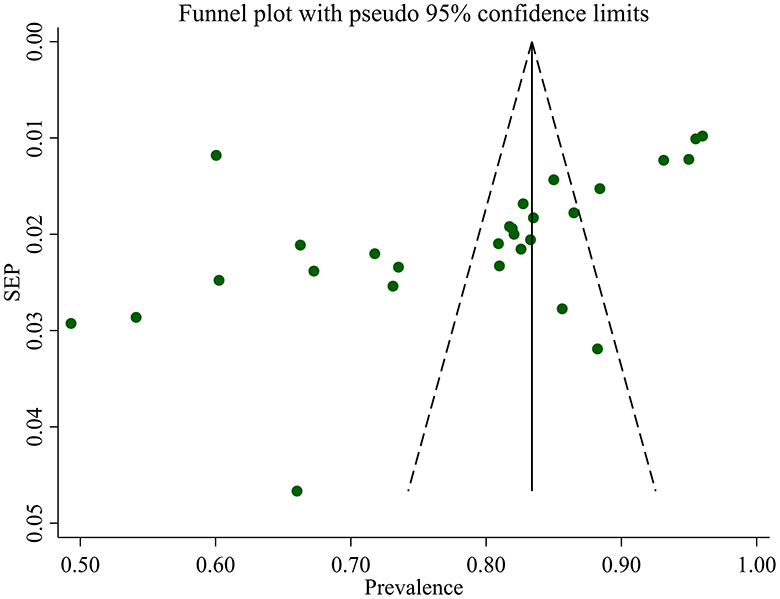
Studies incorporated for the analysis demonstrated massive heterogeneity (I2 = 98.1%; p-value < 0.001), which was not adequately addressed with a weighted inverse variance random-effects model. For further analysis of this heterogeneity, we used a funnel plot as a subjective assessment and conducted subgroup analysis, sensitivity analysis, and univariate meta-regression for objective assessment of the etiologies of heterogeneity (Figure 3; Table 2).
Subgroup analysis
Subgroup analysis based on the region where studies were conducted revealed that the highest prevalence of optimum HAART adherence was in SNNPR at 83% (95% CI: 77–90, I2 = 92.8%; p < 0.001), while the lowest was in Addis Ababa at 74% (95% CI: 63–85, I2 = 97.2%; p < 0.001). Additionally, subgroup analysis based on the study years was conducted using 2018 as a dichotomization point, given that it marked the revision of the Ethiopian ART guideline and the full implementation of the test-and-treat approach (57). The prevalence of optimum HAART adherence among adults before 2018 was 78% (95% CI: 72–84, I2 = 98.5%; p < 0.001) and 79% (95% CI: 75–83, I2 = 86.6%; p < 0.001) after 2018.
Subgroup analysis based on study methods revealed that the prevalence of optimum HAART adherence was 64% (95% CI: 54–73, I2 = 96.7%; p < 0.001) when assessed with structured assessment methods, and 82% (95% CI: 78–86, I2 = 96.4%; p < 0.001) when examined with the self-report method To further address the impact of recall periods on adherence levels, we analyzed optimal HAART adherence within subgroups categorized by different recall periods. The national pooled prevalence of optimum HAART adherence at 7, 15, and 30 days prior to an interview was 85% (95% CI: 79–92, I2 = 96.8%; p < 0.001), 78% (95% CI: 55–100, I2 = 98.7%; p < 0.001), and 82% (95% CI: 77–87, I2 = 95.1%; p < 0.001), respectively (Table 3).
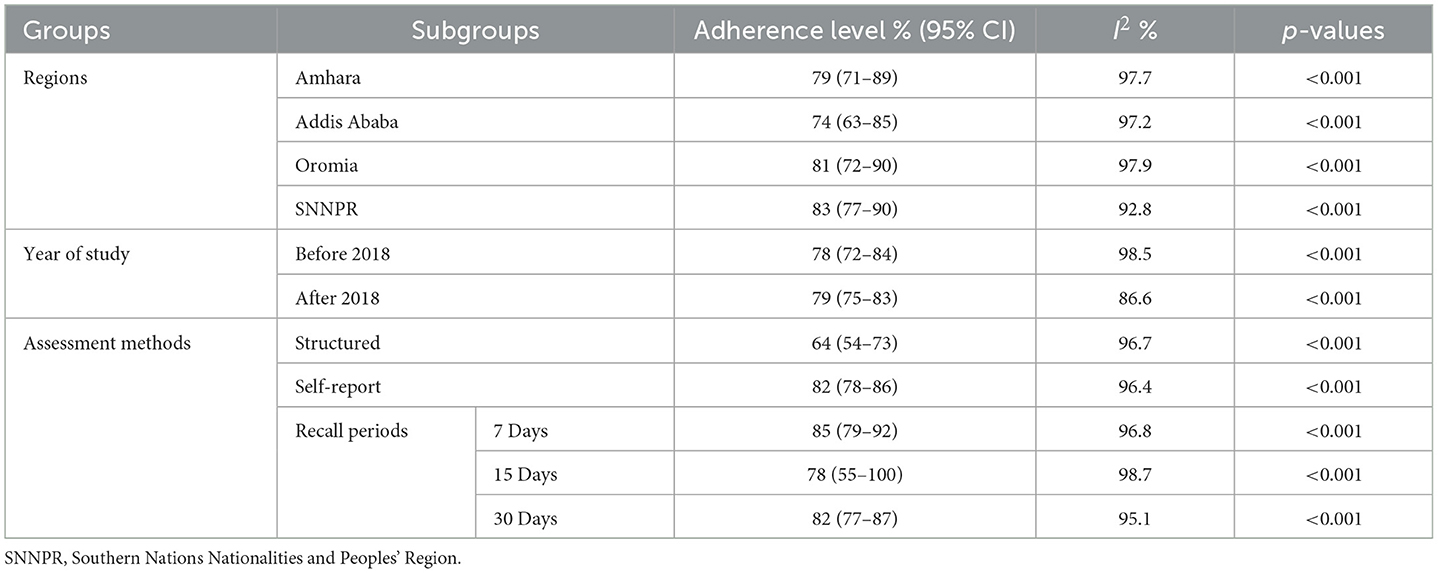
Table 3. Subgroup analysis of the prevalence of optimum HAART adherence based on different variables.
Sensitivity analysis
We did the sensitivity analysis of adherence to HAART by applying a random effects model (Table 4). Excluded studies with a smaller sample size resulted in a slight difference in the pooled prevalence of optimal HAART adherence, which did not significantly affect the stability of the summary result.
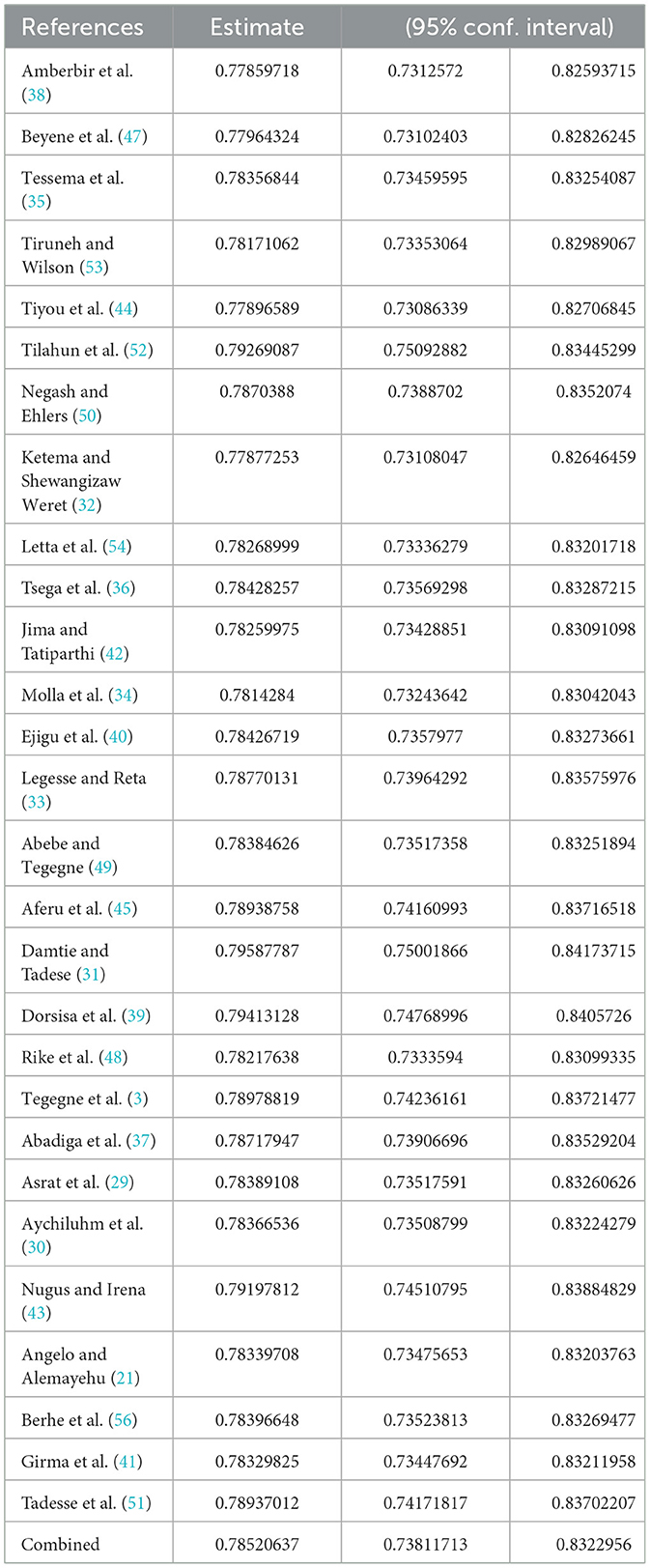
Table 4. Sensitivity analysis of studies included for estimation of optimum adherence to HAART in Ethiopia.
Publication bias
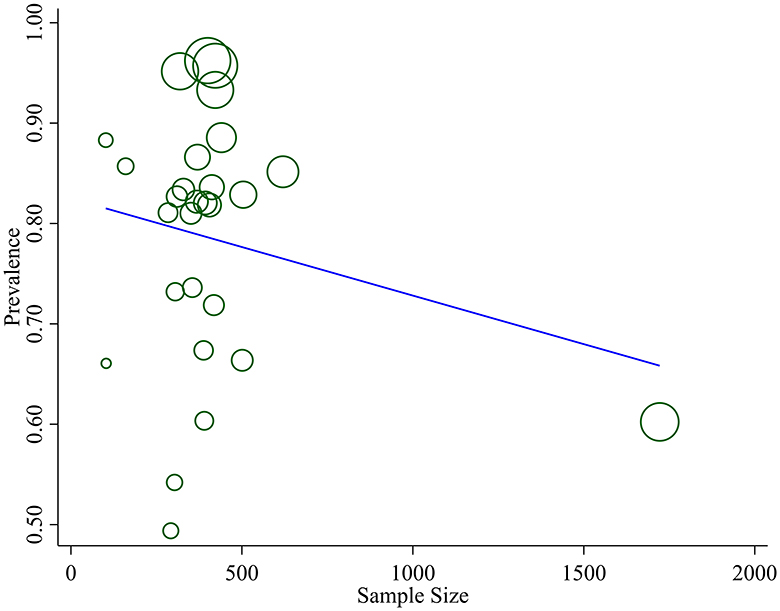
We assessed publication bias both subjectively and objectively. Subjectively, we observed the funnel plot (Figure 4), and objectively, we conducted Egger's regression test, which resulted in a p-value of 0.002. Additionally, we performed a trim and fill analysis (Table 5), which neither added nor removed studies, indicating the absence of missed small studies and, ultimately, the absence of publication bias.
Discussion
The present systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted to estimate the national pooled prevalence of optimal HAART adherence among HIV-infected adults in Ethiopia. The finding of this study is indispensable to crafting policies and contriving public health interventions to trim HIV-associated mortality and morbidity. Accordingly, the pooled prevalence of optimal HAART adherence among HIV-positive adults in Ethiopia was 79% (95% CI 74–83%; I2 = 98.1%). The finding of this meta-analysis was comparable to a study conducted in China (77.6%) (58), Africa (77%) (2), and Latin American, and Caribbean countries (70%) (59) and recently reported finding in Ethiopia (60). However, it was higher than a globally meta-analyzed report (62%) (61), studies done in India (70%) (19), and West Africa (42%) (62) as well as recently published single studies in Ethiopia (63, 64), but lower compared to studies done in South India (90.9%) (18), and US (86%) (65). The discrepancies amidst these studies might be ascribed to the variations in socio-demographic characteristics, study population, study design, healthcare systems, recall period, and the adherence report method. Perhaps, the figure is indicative of promising progress which is not consonant with the developed nation's misconception that sub-optimal therapy is apparent in the African regions.
The optimum HAART adherence prevalence via structured assessment method and self-report method were 64 and 82%, respectively. Although there is no masterpiece assessment tool for determining HAART adherence, studies (66, 67) spotlighted that the self-report method may lead to an overestimation of the pooled prevalence of true adherence owing to its subjective nature as compared to the more objective tools. This might be a possible concern engrossed to our study too. A precisely 18% difference is noted in terms of the proportion of HAART adherence between these adherence measurement tools.
In this meta-analysis, a lower pooled prevalence of HAART adherence in Ethiopia was reported among the studies published before 2018 (78%), as compared to those published after 2018 (79%). The possible reason for this could be better provision of targeted adherence measures, improved ART medication availability and accessibility, and implementation of the updated guideline treatment recommendation in the actual clinical setting. It is apparent that medical science is dynamic in its nature necessitating updated knowledge, skills, and attitudes.
The subgroup analysis showed that HAART adherence among adults was highest in the SNNPR region (83%) compared to other regions, with the lowest adherence observed in Addis Ababa (74%). This incongruity might be owing to the difference in the health care system and clinical setting, socio-economic assets, attitude, and awareness of caregivers about HAART regimens. Moreover, it could also be attributed to the regions' varied beliefs about the merit of HAART, religious practices, political affiliations, and traditional medicine usage practice. This finding is different from a similar study (17) in Ethiopia done on children which exhibited the highest prevalence in the Amhara region (93.4%), Addis Ababa (90.1%), Oromia region (73.04%), and Tigray region (87.3%), respectively.
The findings in this study reveal variations in adherence prevalence based on assessment methods, recall periods, and regional factors, shedding light on the multifaceted nature of adherence evaluation.
Assessment methods play a crucial role in determining reported adherence rates. Our study indicates that when assessed using structured adherence assessment questionnaires, the optimum HAART adherence prevalence was lower at 64%. In contrast, self-reporting yielded a higher prevalence of 82%. This discrepancy emphasizes the impact of the chosen assessment tool on reported adherence rates, suggesting that the methodological approach can influence the interpretation of adherence levels.
Furthermore, the influence of recall periods on reported adherence rates is evident in our study. The prevalence of optimum adherence assessed by the self-report method varied from 78 to 85%, depending on the recall period used (07, 15, or 30 days prior to an interview). This finding highlights the importance of considering the timeframe for assessing adherence, as it can significantly impact the reported prevalence.
The observed massive heterogeneity (I2 = 98.1%; p-value <0.001) among the studies necessitated additional analyses. While a weighted inverse variance random-effects model was insufficient to address the heterogeneity, subjective assessments through funnel plots and objective analyses such as subgroup analysis, sensitivity analysis, and univariate meta-regression were conducted. These approaches aimed to explore potential sources of heterogeneity, providing a more nuanced understanding of the variability in reported adherence rates.
Subgroup analysis based on regional factors identified variations in adherence prevalence among different regions of Ethiopia. Higher adherence rates were observed in SNNPR, Oromia, and Amhara compared to Addis Ababa, suggesting potential regional disparities in healthcare infrastructure and support systems. Additionally, the year-based subgroup analysis, considering the implementation of the test and treat approach in 2018, showed a slight increase in adherence prevalence after this pivotal year.
Sensitivity analysis, which involved excluding studies with smaller sample sizes, demonstrated the stability of the overall results, with minimal impact on the pooled prevalence of optimal HAART adherence. Publication bias analysis, conducted through Egger's regression test and trim and fill analysis, indicated the absence of bias, reinforcing the reliability of our findings.
Strength and limitation
The study employed a comprehensive and rigorous search strategy to identify all possibly available eligible primary studies. This approach enhances the inclusivity of the analysis, ensuring that a wide range of relevant studies was considered and it also comprehensively assessed optimal adherence to HAART based on various methods, including both self-reporting and structured adherence assessment questionnaires. This approach allows for a more nuanced exploration of adherence levels, capturing the diverse ways in which adherence is measured in the included studies. The study addressed various factors that may affect the prevalence of optimal adherence to HAART through extensive sub-group analysis. This approach enables the exploration of heterogeneity among studies, allowing for a more detailed examination of regional and temporal variations. However, it is not devoid of limitations, the primary limitation of this study is the absence of more reliable biological methods for assessing adherence in the included primary studies. The reliance on self-reporting and structured assessments, with varying recall periods across the included primary studies, may impact the homogeneity of the studies. While this is common in adherence research and introduces a subjective element along with the potential for recall bias, we attempted to address this by providing operational definitions. Additionally, several studies in our review employed non-probability sampling methods, which could introduce selection bias and ultimately affect the accuracy of the pooled estimate.
Conclusion
This systematic review and meta-analysis revealed that overall HAART adherence in Ethiopian adults appears in good progress and is consistent with findings noted from other developing countries. However, it still requires a lot of work to bring the adherence level to its theoretically presumed value (100%). The lowest prevalence of optimum HAART adherence is observed in Addis Ababa, the capital city of Ethiopia. Patient-specific interventional measures should be rigorously performed by underpinning potential predictors of HAART adherence to make it more promising.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
MG: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. NT: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. TS: Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MD: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. TF: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. GT: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. TK: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. FB: Formal analysis, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MH: Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the College of Medicine and Health Science Wollo University who technically provided us a capacity building training on systematic review and meta-analysis.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Author disclaimer
This study is based on data from primary studies. The analysis, discussions, conclusions, opinions, and statements expressed in this text are those of the authors.
References
1. WHO. National Guidelines for Comprehensive HIV Prevention, Care and Treatment. Addis Ababa Ministry of Health (2017).
2. Mills EJ, Nachega JB, Buchan I, Orbinski J, Attaran A, Singh S, et al. Adherence to antiretroviral therapy in sub-Saharan Africa and North America: a meta-analysis. JAMA. (2006) 296:679–90. doi: 10.1001/jama.296.6.679
3. Tegegne D, Mamo G, Negash B, Habte S, Gobena T, Letta S. Poor adherence to highly active antiretroviral therapy and associated factors among people living with HIV in Eastern Ethiopia. SAGE Open Med. (2022) 10:20503121221104429. doi: 10.1177/20503121221104429
4. Shubber Z, Mills EJ, Nachega JB, Vreeman R, Freitas M, Bock P, et al. Patient-reported barriers to adherence to antiretroviral therapy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Med. (2016) 13:e1002183. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1002183
5. Nischal K, Khopkar U, Saple D. Improving adherence to antiretroviral therapy. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. (2005) 71:316. doi: 10.4103/0378-6323.16780
6. Starace F, Massa A, Amico KR, Fisher JD. Adherence to antiretroviral therapy: an empirical test of the information-motivation-behavioral skills model. Health Psychol. (2006) 25:153. doi: 10.1037/0278-6133.25.2.153
7. Abaasa AM, Todd J, Ekoru K, Kalyango JN, Levin J, Odeke E, et al. Good adherence to HAART and improved survival in a community HIV/AIDS treatment and care programme: the experience of The AIDS Support Organization (TASO), Kampala, Uganda. BMC Health Serv Res. (2008) 8:1–10. doi: 10.1186/1472-6963-8-241
8. Morowatisharifabad MA, Movahed E, Farokhzadian J, Nikooie R, Hosseinzadeh M, Askarishahi M, et al. Antiretroviral therapy adherence and its determinant factors among people living with HIV/AIDS: a case study in Iran. BMC Res Notes. (2019) 12:1–5. doi: 10.1186/s13104-019-4204-5
9. Zoufaly A, Fillekes Q, Hammerl R, Nassimi N, Jochum J, Drexler JF, et al. Prevalence and determinants of virological failure in HIV-infected children on antiretroviral therapy in rural Cameroon: a cross-sectional study. Antivir Ther. (2013) 18:681–90. doi: 10.3851/IMP2562
10. B-Lajoie M-R, Drouin O, Bartlett G, Nguyen Q, Low A, Gavriilidis G, Easterbrook P, Muhe L. Incidence and prevalence of opportunistic and other infections and the impact of antiretroviral therapy among HIV-infected children in low-and middle-income countries: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Infect Dis. (2016) 62:1586–94. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciw139
11. Moges N, Kassa G. Prevalence of opportunistic infections and associated factors among HIV positive patients taking anti-retroviral therapy in DebreMarkos Referral Hospital, Northwest Ethiopia. J AIDs Clin Res. (2014) 5:1–300. doi: 10.4172/2155-6113.1000301
12. Harries AD, Gomani P, Teck R, de Teck OA, Bakali E, Zachariah R, et al. Monitoring the response to antiretroviral therapy in resource-poor settings: the Malawi model. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. (2004) 98:695–701. doi: 10.1016/j.trstmh.2004.05.002
13. Ayalew MB, Kumilachew D, Belay A, Getu S, Teju D, Endale D, et al. First-line antiretroviral treatment failure and associated factors in HIV patients at the University of Gondar Teaching Hospital, Gondar, Northwest Ethiopia. HIV/AIDS Res Palliat Care. (2016) 8:141–6. doi: 10.2147/HIV.S112048
14. Bangsberg DR. Less than 95% adherence to nonnucleoside reverse-transcriptase inhibitor therapy can lead to viral suppression. Clin Infect Dis. (2006) 43:939–41. doi: 10.1086/507526
15. Coetzee B, Kagee A, Bland R. Barriers and facilitators to paediatric adherence to antiretroviral therapy in rural South Africa: a multi-stakeholder perspective. AIDS Care. (2015) 27:315–21. doi: 10.1080/09540121.2014.967658
16. Reda AA, Biadgilign S. Determinants of adherence to antiretroviral therapy among HIV-infected patients in Africa. AIDS Res Treat. (2012) 2012:574656. doi: 10.1155/2012/574656
17. Endalamaw A, Tezera N, Eshetie S, Ambachew S, Habtewold TD. Adherence to highly active antiretroviral therapy among children in ethiopia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. AIDS Behav. (2018) 22:2513–23. doi: 10.1007/s10461-018-2152-z
18. Mehta K, Ekstrand M, Heylen E, Sanjeeva G, Shet A. Adherence to antiretroviral therapy among children living with HIV in South India. AIDS Behav. (2016) 20:1076–83. doi: 10.1007/s10461-015-1207-7
19. Mhaskar R, Alandikar V, Emmanuel P, Djulbegovic B, Patel S, Patel A, et al. Adherence to antiretroviral therapy in India: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Indian J Commun Med. (2013) 38:74. doi: 10.4103/0970-0218.112435
20. Newell M-L, Brahmbhatt H, Ghys PD. Child mortality and HIV infection in Africa: a review. Aids. (2004) 18:S27–34. doi: 10.1097/00002030-200406002-00004
21. Angelo AT, Alemayehu DS. Adherence and its associated factors among adult HIV-infected patients on antiretroviral therapy in South Western Ethiopia, 2020. Patient Prefer Adher. (2021) 15:299–308. doi: 10.2147/PPA.S298594
22. Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Int J Surg. (2021) 88:105906. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2021.105906
23. Gotschall T. EndNote 20 desktop version. J Med Libr Assoc. (2021) 109:520. doi: 10.5195/jmla.2021.1260
24. JB Institute. JBI Critical Appraisal Checklist for Studies Reporting Prevalence Data. Adelaide, SA: University of Adelaide (2017).
25. DerSimonian R, Kacker R. Random-effects model for meta-analysis of clinical trials: an update. Contemp Clin Trials. (2007) 28:105–14. doi: 10.1016/j.cct.2006.04.004
26. Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. Bmj. (2003) 327:557–60. doi: 10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557
27. Peters JL, Sutton AJ, Jones DR, Abrams KR, Rushton L. Comparison of two methods to detect publication bias in meta-analysis. JAMA. (2006) 295:676–80. doi: 10.1001/jama.295.6.676
29. Asrat B, Lund C, Ambaw F, Garman EC, Schneider M. Major depressive disorder and its association with adherence to antiretroviral therapy and quality of life: cross-sectional survey of people living with HIV/AIDS in Northwest Ethiopia. BMC Psychiatry. (2020) 20:462. doi: 10.1186/s12888-020-02865-w
30. Aychiluhm SB, Tadesse AW, Mare KU, Melaku MS, Ibrahim IM, Ahmed O, et al. Level of non-adherence and its associated factors among adults on first-line antiretroviral therapy in Amhara Regional State, Ethiopia. PLoS ONE. (2021) 16:e0255912. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0255912
31. Damtie Y, Tadese F. Antiretroviral therapy adherence among patients enrolled after the initiation of the Universal Test and Treat strategy in Dessie town: a cross-sectional study. Int J Std AIDS. (2020) 31:886–93. doi: 10.1177/0956462420927205
32. Ketema AK, Shewangizaw Weret Z. Assessment of adherence to highly active antiretroviral therapy and associated factors among people living with HIV at Debrebrihan Referral Hospital and Health Center, Northeast Ethiopia: a cross-sectional study. HIV AIDS. (2015) 7:75–81. doi: 10.2147/HIV.S79328
33. Legesse TA, Reta MA. Adherence to antiretroviral therapy and associated factors among people living with HIV/AIDS in Hara Town and its surroundings, North-Eastern Ethiopia: a cross-sectional study. Ethiop J Health Sci. (2019) 29:299–308. doi: 10.4314/ejhs.v29i3.2
34. Molla AA, Gelagay AA, Mekonnen HS, Teshome DF. Adherence to antiretroviral therapy and associated factors among HIV positive adults attending care and treatment in University of Gondar Referral Hospital, Northwest Ethiopia. BMC Infect Dis. (2018) 18:266. doi: 10.1186/s12879-018-3176-8
35. Tessema B, Biadglegne F, Mulu A, Getachew A, Emmrich F, Sack U. Magnitude and determinants of nonadherence and nonreadiness to highly active antiretroviral therapy among people living with HIV/AIDS in Northwest Ethiopia: a cross-sectional study. AIDS Res Ther. (2010) 7:2. doi: 10.1186/1742-6405-7-2
36. Tsega B, Srikanth BA, Shewamene Z. Determinants of non-adherence to antiretroviral therapy in adult hospitalized patients, Northwest Ethiopia. Patient Prefer Adher. (2015) 9:373–80. doi: 10.2147/PPA.S75876
37. Abadiga M, Hasen T, Mosisa G, Abdisa E. Adherence to antiretroviral therapy and associated factors among Human immunodeficiency virus positive patients accessing treatment at Nekemte referral hospital, west Ethiopia, 2019. PLoS ONE. (2020) 15:e0232703. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0232703
38. Amberbir A, Woldemichael K, Getachew S, Girma B, Deribe K. Predictors of adherence to antiretroviral therapy among HIV-infected persons: a prospective study in Southwest Ethiopia. BMC Public Health. (2008) 8:265. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-8-265
39. Dorsisa B, Ahimed G, Anand S, Bekela T. Prevalence and factors associated with depression among HIV/AIDS-infected patients attending ART clinic at Jimma University Medical Center, Jimma, Southwest Ethiopia. Psychiatry J. (2020) 2020:5414072. doi: 10.1155/2020/5414072
40. Ejigu M, Desalegn Z, Mulatu B, Mosisa G. Adherence to combined antiretroviral therapy and associated factors among people living with HIV Attending Nekemte Specialized Hospital, Oromia, Ethiopia: A Cross-Sectional Study. HIV AIDS. (2020) 12:97–106. doi: 10.2147/HIV.S239995
41. Girma D, Dejene H, Geleta LA, Tesema M, Legesse E, Nigussie T, et al. Health related quality of life of HIV-positive women on ART follow-up in north Shewa zone public hospitals, central Ethiopia: evidence from a cross-sectional study. Heliyon. (2023) 9:e13318. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e13318
42. Jima F, Tatiparthi R. Prevalence of nonadherence and its associated factors affecting on HIV adults follow-up at antiretroviral therapy clinic in Batu Hospital, Eastern Ethiopia. Indian J Sex Transm Dis AIDS. (2018) 39:91–7. doi: 10.4103/ijstd.IJSTD_37_17
43. Nugus GG, Irena ME. Determinants of active tuberculosis occurrences after ART initiation among adult HIV-positive clients in West Showa Zone Public Hospitals, Ethiopia: a case-control study. Adv Public Health. (2020) 2020:1–8. doi: 10.1155/2020/8237928
44. Tiyou A, Belachew T, Alemseged F, Biadgilign S. Predictors of adherence to antiretroviral therapy among people living with HIV/AIDS in resource-limited setting of southwest ethiopia. AIDS Res Ther. (2010) 7:39. doi: 10.1186/1742-6405-7-39
45. Aferu T, Doang G, Zewudie A, Nigussie T. Adherence to antiretroviral therapy among HIV-positive pregnant women on followup at Mizan Tepi University Teaching and Tepi General Hospitals, Southwest Ethiopia. J Prim Care Community Health. (2020) 11:2150132720902561. doi: 10.1177/2150132720902561
46. Berhe H, Godana W, Sidamo NB, Birgoda GT, Gebresillasie L, Hussen S, et al. Perceived social support and associated factors among adults living with HIV/AIDS attending ART Clinic at Public Hospitals in Gamo Zone, Southern Ethiopia 2021. HIV/AIDS Res Palliat Care. (2022) 14:103–17. doi: 10.2147/HIV.S351324
47. Beyene KA, Gedif T, Gebre-Mariam T, Engidawork E. Highly active antiretroviral therapy adherence and its determinants in selected hospitals from south and central Ethiopia. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. (2009) 18:1007–15. doi: 10.1002/pds.1814
48. Rike M, Loha E, Kassa A. Adherence to antiretroviral treatment among adult people living with HIV/AIDS attending highly active antiretroviral therapy at Adare Hospital, Southern Ethiopia. Ethiop J Health Dev. (2021) 35:1–11.
49. Abebe KB, Tegegne AS. Predictors of non-adherence to medication and time to default from treatment on HIV infected patients under HAART: a comparison of joint and separate models. Afr Health Sci. (2022) 22:443–55. doi: 10.4314/ahs.v22i1.53
50. Negash T, Ehlers V. Personal factors influencing patients' adherence to ART in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. J Assoc Nurses AIDS Care. (2013) 24:530–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jana.2012.11.004
51. Tadesse A, Badasso K, Edmealem A. Poor sleep quality and associated factors among people living with HIV/AIDS attending ART clinic at Tirunesh Beijing Hospital, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. AIDS Res Treat. (2023) 2023:6381885. doi: 10.1155/2023/6381885
52. Tilahun HA, Mariam DH, Tsui AO. Effect of perceived stigma on adherence to highly active antiretroviral therapy and self-confidence to take medication correctly in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. J HIV AIDS Soc Serv. (2012) 11:346–62. doi: 10.1080/15381501.2012.735169
53. Tiruneh YM, Wilson IB. What time is it? Adherence to Antiretroviral Therapy in Ethiopia. AIDS Behav. (2016) 20:2662–73. doi: 10.1007/s10461-016-1322-0
54. Letta S, Demissie A, Oljira L, Dessie Y. Factors associated with adherence to Antiretroviral Therapy (ART) among adult people living with HIV and attending their clinical care, Eastern Ethiopia. BMC Int Health Hum Rights. (2015) 15:33. doi: 10.1186/s12914-015-0071-x
55. Nigusso FT, Mavhandu-Mudzusi AH. Magnitude of non-adherence to antiretroviral therapy and associated factors among adult people living with HIV/AIDS in Benishangul-Gumuz Regional State, Ethiopia. PeerJ. (2020) 8:e8558. doi: 10.7717/peerj.8558
56. Berhe N, Tegabu D, Alemayehu M. Effect of nutritional factors on adherence to antiretroviral therapy among HIV-infected adults: a case control study in Northern Ethiopia. BMC Infect Dis. (2013) 13:233. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-13-233
57. Federal Ministry of Health. National Consolidated Guidelines for Comprehensive HIV Prevention, Care and Treatment. Addis Ababa (2018).
58. Huan Z, Fuzhi W, Lu L, Min Z, Xingzhi C, Shiyang J. Comparisons of adherence to antiretroviral therapy in a high-risk population in China: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE. (2016) 11:e0146659. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0146659
59. de Mattos Costa J, Torres TS, Coelho LE, Luz PM. Adherence to antiretroviral therapy for HIV/AIDS in Latin America and the Caribbean: systematic review and meta-analysis. Afr J Reprod Gynaecol Endosc. (2018) 21:25066. doi: 10.1002/jia2.25066
60. Aytenew TM, Demis S, Birhane BM, Asferie WN, Simegn A, Nibret G, et al. Non-adherence to anti-retroviral therapy among adult people living with HIV in Ethiopia: systematic review and meta-analysis. AIDS Behav. (2024) 28:609–24. doi: 10.1007/s10461-023-04252-4
61. Ortego C, Huedo-Medina TB, Llorca J, Sevilla L, Santos P, Rodríguez E, et al. Adherence to highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART): a meta-analysis. AIDS Behav. (2011) 15:1381–96. doi: 10.1007/s10461-011-9942-x
62. Polisset J, Ametonou F, Arrive E, Aho A, Perez F. Correlates of adherence to antiretroviral therapy in HIV-infected children in Lome, Togo, West Africa. AIDS Behav. (2009) 13:23–32. doi: 10.1007/s10461-008-9437-6
63. Gela CD, Tsegaye GW, Shibesh BF. Adherence to antiretroviral therapy and determining factors in adults living with HIV receiving services at public health facilities amidst the COVID-19 crisis in Bahir Dar city, Northwest Ethiopia. Front Public Health. (2024) 12:1380055. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1380055
64. Tekle A, Tsegaye A, Ketema T. Adherence to anti-retroviral therapy (ART) and its determinants among people living with HIV/AIDS at Bonga, Kaffa, South-West Ethiopia. Patient Prefer Adher. (2024) 18:543–54. doi: 10.2147/PPA.S445164
65. Beer L, Skarbinski J. Adherence to antiretroviral therapy among HIV-infected adults in the United States. AIDS Educ Prev. (2014) 26:521–37. doi: 10.1521/aeap.2014.26.6.521
66. Arnsten JH, Demas PA, Farzadegan H, Grant RW, Gourevitch MN, Chang C-J, et al. Antiretroviral therapy adherence and viral suppression in HIV-infected drug users: comparison of self-report and electronic monitoring. Clin Infect Dis. (2001) 33:1417–23. doi: 10.1086/323201
Keywords: adherence, antiretroviral therapy, adult, HIV medication, meta-analysis, Ethiopia
Citation: Gobezie MY, Tesfaye NA, Solomon T, Demessie MB, Fentie Wendie T, Tadesse G, Kassa TD, Berhe FT and Hassen M (2024) Exploring optimal HAART adherence rates in Ethiopian adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Public Health 12:1390901. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1390901
Received: 24 February 2024; Accepted: 27 September 2024;
Published: 14 October 2024.
Edited by:
Miguel Angel Sanchez-Aleman, National Institute of Public Health, MexicoReviewed by:
Nilesh Chandrakant Gawde, Tata Institute of Social Sciences, IndiaManoj Kumar Gupta, Hannover Medical School, Germany
Copyright © 2024 Gobezie, Tesfaye, Solomon, Demessie, Fentie Wendie, Tadesse, Kassa, Berhe and Hassen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Mengistie Yirsaw Gobezie, emVtZW4uZ2lydW1AZ21haWwuY29t
†ORCID: Fentaw Tadese Berhe orcid.org/0000-0001-9058-1854
 Mengistie Yirsaw Gobezie
Mengistie Yirsaw Gobezie Nuhamin Alemayehu Tesfaye
Nuhamin Alemayehu Tesfaye Tewodros Solomon
Tewodros Solomon Mulat Belete Demessie1
Mulat Belete Demessie1 Teklehaimanot Fentie Wendie
Teklehaimanot Fentie Wendie Fentaw Tadese Berhe
Fentaw Tadese Berhe Minimize Hassen
Minimize Hassen