- 1Beijing Xiaotangshan Hospital, Beijing, China
- 2The First Affiliated Hospital of Hunan University of Medicine, Huaihua, China
- 3Hunan Primary Digital Engineering Technology Research Center for Medical Prevention and Treatment, Huaihua, China
- 4National Institute of Hospital Administration (NIHA), Beijing, China
Mobile collaborative intelligent nursing robots have gained significant attention in the healthcare sector as an innovative solution to address the challenges posed by the increasing aging population and limited medical resources. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the research advancements in this field, covering hospital care, home older adults care, and rehabilitation assistance. In hospital settings, these robots assist healthcare professionals in tasks such as patient monitoring, medication management, and bedside care. For home older adults care, they enhance the older adults sense of security and quality of life by offering daily life support and monitoring. In rehabilitation, these robots provide services such as physical rehabilitation training and social interaction to facilitate patient recovery. However, the development of intelligent nursing robots faces challenges in technology, ethics, law, and user acceptance. Future efforts should focus on improving robots’ perceptual and cognitive abilities, enhancing human-robot interaction, and conducting extensive clinical experiments for broader applications.
1 Introduction
With the rapid global aging population and increasing demand for patient care, healthcare resources are facing unprecedented challenges. For example, it is expected that from 2020 onwards, China will enter a serious aging stage, as the number of people over the age of 60 has reached 185 million, accounting for 13.9 percent of the total population according to China’s sixth national census. The United Nations has classified China as an “aging country,” and the rate of aging is accelerating. It is projected that the aging level will reach 17.17% by 2020. By 2050, China will become a super-aging country, with 30% of the population aged 60 and above (1), this indicates that China is facing a severe situation of population aging. Simultaneously, on a global scale, the trend toward an aging population is evident across all 195 regions (2). Japan is recognized as one of the world’s most rapidly aging societies and faces rising healthcare costs alongside a severe shortage of long-term care resources (3). Similarly, European countries such as Germany and Italy are experiencing significant increases in their older adults populations, which is placing pressure on their healthcare systems (4). Consequently, the escalating global demand for medical treatment, care, and rehabilitation, compounded by the relative shortage of medical personnel, is placing immense pressure on the capacity of health services (5).
With the rapid global aging population and increasing demand for patient care, healthcare resources are facing unprecedented challenges. Traditional nursing models are currently unable to meet the growing demand for care, indicating the need for innovative solutions. Various methods, such as telemedicine (6) and home-based care programs (7), have been proposed to address these challenges; however, these approaches often fall short due to issues such as limited accessibility and scalability, as well as concerns regarding privacy and security.
In this context, mobile nursing robots emerge as a promising solution. These robots aim to assist the older adults in independent living, mobility, risk monitoring, and dietary planning (8). Mobile collaborative nursing robots, as highly integrated artificial intelligence applications, primarily perform various specialized tasks in the nursing field, including vital sign monitoring, medication preparation, venous blood collection, suctioning, and throat swab sampling. In hospitals, their applications cover guiding, disinfection, patient transfer, and logistics. Additionally, in the field of home rehabilitation, mobile collaborative nursing robots are used for caring for older adults individuals at home, home hygiene care, health recovery, and psychological companionship, providing new impetus for the development of traditional nursing disciplines (9). The versatile nature of mobile collaborative nursing robots enables them to meet the nursing needs of different fields and populations, offering broader prospects for application in the medical care industry.
Given the advantages of mobile collaborative care robots in meeting diverse care needs, they represent a significant advance in the field and are gaining attention in many countries. At present, nursing robot technology in many developed countries has been at the forefront of world development. The development of China’s service robot industry has been listed as a key project of the “863” project and has attracted the attention of relevant departments and scientific research units (10). Although nursing robots are used in some medical institutions and scientific research experiments, there are still certain shortcomings in the popularization and widespread use of the entire field of nursing, mainly including technical limitations, high costs, stereotypes and social acceptance, legal and ethical issues (11). These problems largely interfere with the clinical application and efficiency release of nursing robots.
This paper primarily reviews the applications of different types of nursing robots in various contexts both domestically and internationally, including clinical professional nursing, auxiliary and support tasks, as well as the use of nursing robots in home-assisted care (see Tables 1, 2). Specifically, this study aims to address the following research question: ‘How can the integration of mobile collaborative nursing robots into clinical and home care environments improve the efficiency and quality of nursing services, and what are the major challenges and ethical considerations associated with their implementation?’ Through a comprehensive review of the literature, this study seeks to gain a deeper understanding of the current state of nursing robotics technology and identify potential strategies to optimize their application.
2 Research method
This study employs a systematic approach to conducting a literature review, aiming to provide a comprehensive examination of the research advancements in the field of mobile collaborative nursing robots. To ensure a thorough and systematic literature review, a rigorous search strategy was utilized to identify relevant studies. Our methodology encompasses the following key steps.
2.1 Literature search strategy
Databases: The search was conducted across several scientific literature databases, including PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, Association for Computing Machinery database, Electronics Engineers database, Google Scholar, and IEEE Xplore.
2.2 Keywords
We utilized a set of keywords such as “nursing robots,” “intelligent nursing robots,” “robotic nursing care,” “rehabilitation robots,” “mobile collaborative,” “clinical applications,” “healthcare assistance,” “home care,” “quality of care,” “challenges,” and “ethical considerations.” The search was performed using various combinations of these terms to maximize relevance and coverage.
2.3 Selection criteria
Inclusion Criteria: The studies were selected based on the following criteria: (1) Direct focus on research concerning mobile collaborative nursing robots. (2) Description of nursing robots’ applications in medical, home care, or rehabilitation settings. (3) Discussion on the impact of nursing robots on the efficiency and quality of care. (4) Provision of detailed information regarding technical aspects, clinical applications, or studies on user acceptance and ethical considerations.
Exclusion Criteria: The criteria for exclusion included: (1) Literature unrelated to the main theme. (2) Studies that only discuss theory without empirical validation. (3) Conference abstracts, editorials, or review articles.
2.4 Data analysis
The selected studies were critically analyzed to extract key findings relevant to the research question. The analysis focused on identifying common themes, assessing the quality of evidence, and synthesizing results to draw meaningful conclusions.
2.5 Structure of the paper
Introduction: Provides background information on the study and clarifies the questions and objectives the study aims to address. Research Method: Offers a detailed explanation of the literature search strategy, criteria for study selection, and the data analysis process. Literature Review: Gives an overview of current nursing robot applications, compares different types of nursing robots, and discusses challenges and ethical considerations. Discussion: Synthesizes the findings and their implications, suggesting potential strategies for optimizing the application of nursing robots. Conclusion: Summarizes the key findings and suggests directions for future research. References: lists the works cited in the paper.
The chosen structure ensures a logical progression from the introduction of the topic to the detailed analysis of the literature, culminating in a comprehensive discussion and conclusion. This ensures that the findings are presented in a clear manner and supports the overall aim of the study.
3 Definition, development process, and characteristics of mobile collaborative nursing robots
Robots are virtual or mechanical objects designed to assist in human daily activities. The United States has been utilizing robots in industrial settings since the 1960s, and their introduction to healthcare in the 1980s had a positive impact on nursing activities (12). Various types of robotic technologies contribute to patient care, including assisting with patient mobility, medication administration, health assessments, physiological parameter monitoring, and providing companionship (13).
A proposed classification based on the characteristics of human-computer interaction modalities is of high value. The Human-Robot Interaction (HRI) taxonomy that has been proposed is partitioned into three distinct clusters, each focusing on different aspects of HRI. This taxonomy offers a more universal approach in contrast to existing frameworks that often lack broad applicability (14). The first cluster of the taxonomy enables the categorization of the overarching context in which the interaction takes place, covering all domains extensively. It takes into account both the area of application and the nature of human exposure during human-robot interactions (15). Once this broader context is defined, robot attributes such as its function, physical characteristics, and level of independence can be specifically identified and categorized. The second cluster delves into team dynamics, further subdividing into the human role, team composition, communication pathway, and spatial proximity (16). This hierarchical arrangement of the taxonomy serves a dual purpose: it allows for a top-down examination of existing interactions, moving from general settings to individual team nuances, and it also serves as a guide for tailoring and enhancing HRI designs in a bottom-up manner (17). As shown in Table 3, to enhance usability, the taxonomy is supplemented with visual aids that underscore the three cluster domains and their associated sub-categories, offering a clear template for detailing specific HRI scenarios.
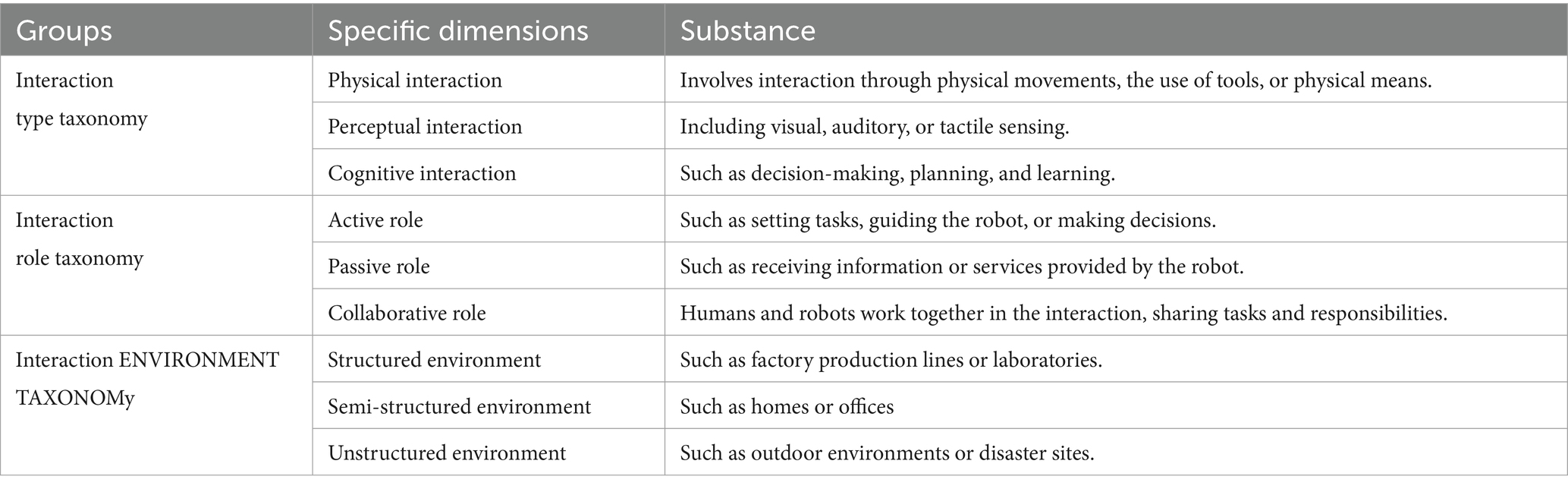
Table 3. The human-robot interaction (HRI) taxonomy can be divided into the following three distinct taxonomic groups (14–17).
Social Assistive Robots (SARs) aim to support independent living, primarily focusing on providing intelligent assistance. SARs can be categorized into service robots and assistive robots. Service robots play a crucial role in offering assistance in daily life, including aspects such as diet, health monitoring, reminders, and safety (18). Mobile service robots, with significant potential, can support various daily living capabilities such as object, person, or target detection, cognitive training, and entertainment.
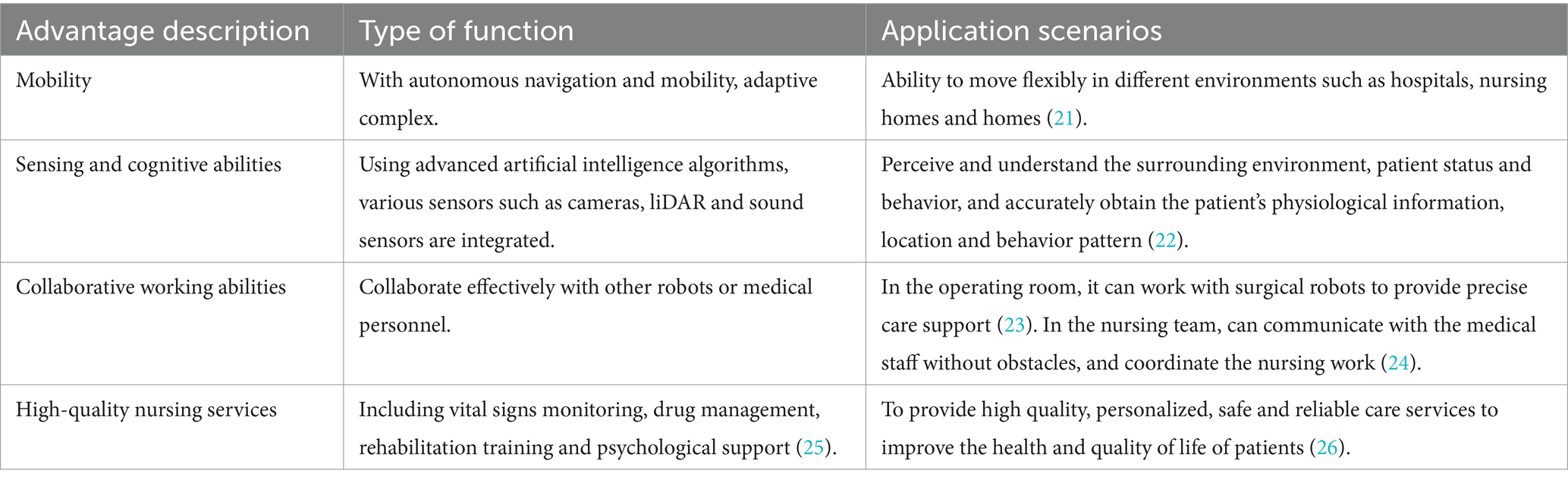
Mobile collaborative nursing robots refer to intelligent robots with mobility, sensing and cognitive capabilities, and collaborative working abilities (19). They are designed to provide high-quality nursing services in clinical and home environments, originating from the integration of intelligent service robot technology and the healthcare domain (20). As shown in Table 4, the advantages of mobile collaborative nursing robots over traditional nursing robots include:
Mobility: Mobile collaborative nursing robots possess autonomous navigation and mobility, allowing them to flexibly move in various environments such as hospitals, nursing homes, and homes, adapting to complex and dynamic scene requirements (21).
Sensing and Cognitive Abilities: These robots integrate various sensors (such as cameras, lidar, and sound sensors) and advanced artificial intelligence algorithms to perceive and understand the surrounding environment, patient status, and behaviors (22). This enables accurate acquisition of patient physiological information, location, and behavior patterns, facilitating personalized and precise nursing services.
Collaborative Working Abilities: Mobile collaborative nursing robots have the capability to collaborate with other robots or healthcare personnel effectively. For example, in the operating room, nursing robots can collaborate with surgical robots to provide precise nursing support (23). In nursing teams, these robots can communicate seamlessly with nurses and doctors, collectively completing nursing tasks (24).
High-Quality Nursing Services: Through interaction with patients and healthcare personnel, mobile collaborative nursing robots provide various nursing functions, including vital sign monitoring, medication management, rehabilitation training, and psychological support (25). Their goal is to deliver high-quality, personalized, safe, and reliable nursing services, improving patient health and quality of life (26).
Mobile collaborative nursing robots embody the integration of mobility, sensing, cognitive abilities, and collaborative functionalities. These intelligent systems are designed to deliver high-quality nursing services in both clinical and home settings, thereby addressing the continuously escalating demands of healthcare and promoting innovation within the medical field.
4 Application of mobile collaborative nursing robots in clinical settings
4.1 Overview
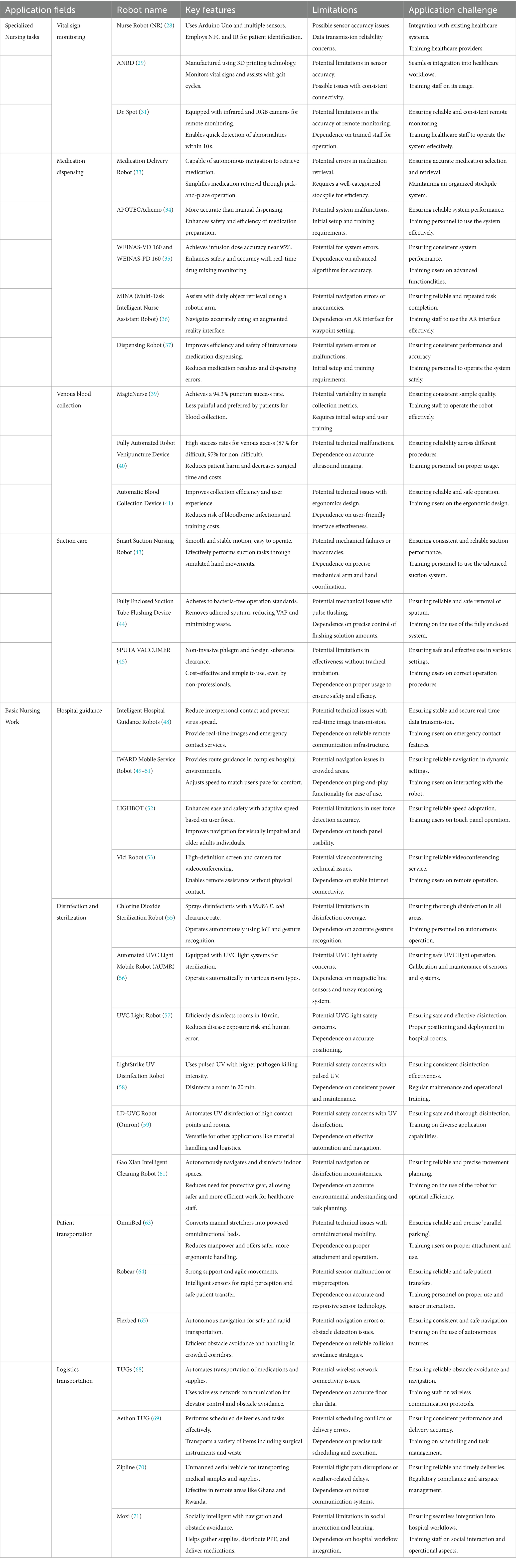
This section provides a comprehensive examination of the diverse roles played by mobile collaborative nursing robots within clinical settings. From specialized care tasks such as vital signs monitoring, medication dispensing, and venipuncture, to fundamental care duties like hospital navigation, disinfection, patient transport, and logistics management, advancements in dynamic mobile collaborative nursing robots offer innovative solutions aimed at enhancing patient care, boosting operational efficiency, and alleviating the workload on healthcare professionals. Each subsection delves into the specific applications and benefits of these robots, supported by examples drawn from current research and development in the field.
4.2 Purpose
The main purpose of this section is to illustrate how mobile collaborative nursing robots can contribute to modern healthcare practice. By detailing their capabilities and benefits, we aim to highlight the potential of these robots to transform care practice, improve patient outcomes, and address some of the pressing challenges facing the healthcare industry today, while also providing an analysis of the difficult challenges of mobile collaborative nursing robots in clinical practice.
4.3 Providing specialized nursing tasks
4.3.1 Vital sign monitoring
Mobile collaborative nursing robots offer unique advantages in clinical settings by reducing close contact, lowering cross-infection risk, and minimizing PPE use. They are reliable and adaptable, providing rapid and accurate vital sign monitoring (27), presenting an innovative healthcare solution. Specifically, the Nurse Robot (NR) (28), a multifunctional nursing robot developed by the Egyptian College of Computing and Artificial Intelligence, utilizes an Arduino Uno board and multiple sensors. The system uses NFC to read patient labels and IR sensors to detect patients. It measures vital signs like heart rate, blood pressure, pulse, and blood oxygen saturation, transmitting data to physicians.
Mireles et al. (29) developed a new nursing mobile robot, ANRD. The structure and mechanical components of this robot device are manufactured using 3D printing technology. The instrument includes embedded electronic devices and sensors to understand the relative position between the robot and the patient. ANRD monitors vital signs such as electrocardiogram, blood oxygen saturation, skin temperature, and non-invasive arterial pressure, and assists with gait cycles for mobility-challenged individuals. It facilitates interactions between nursing robots, patients, and physicians, providing effective primary healthcare support.
The widespread impact of the COVID-19 pandemic has prompted the development of non-contact assessment methods for patients in hospital environments (30). To minimize face-to-face contact with potentially COVID-19-infected patients and preserve personal protective equipment, the research team at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology’s Department of Mechanical Engineering has created a mobile quadruped nursing robot system named “Dr. Spot” (31). The ‘Dr. Spot’ nursing robot, equipped with infrared and RGB cameras, facilitates remote vital sign monitoring including skin temperature, respiratory rate, and heart rate, via a tablet interface. Operated by trained staff, it allows for contactless operation, maintaining social distancing without the need to remove masks. This system enables quick detection of abnormalities within the first 10 s of interaction, significantly reducing contact between healthcare providers and patients, preventing disease spread, and conserving PPE. Its application is especially beneficial during the COVID-19 pandemic.
4.3.2 Medication dispensing
With the rapid development of electronic information technology, increasingly intelligent software and devices are being applied to Pharmacy Intravenous Admixture Service (PIVAS). According to data released by the American College of Clinical Pharmacy (32), 0.3% of hospitals have introduced robotic systems for intravenous medication dispensing, leading to the avoidance of 5,420 medication errors, annual savings of $288,350, improved medication accuracy, enhanced safety, cost reduction, and time savings.
George and Megalingam (33) have designed and developed a prototype of a medication delivery robot capable of fetching the specified drug from a well-categorized stockpile through a straightforward pick-and-place operation. The process entails inputting the prescribed medication information, following which the robot autonomously navigates to the storage source and retrieves the required medicine.
A study by Iwamoto et al. (34) in Japan revealed that the robotic system APOTECAchemo for intravenous medication dispensing is more accurate and efficient than manual dispensing. This system significantly enhances the accuracy and safety of medication preparation. Wang et al. (35) utilizes the robotic systems WEINAS-VD 160 and WEINAS-PD 160 for medication dispensing. These robots integrate features like robotic vision, gravity sensing, advanced algorithms, and multi-axis arms, along with a comprehensive liquid transfer system. They achieve infusion dose accuracy near 95%, identify prescriptions, and monitor real-time drug mixing, enhancing safety and accuracy while reducing errors and occupational exposure risks.
Harish and Stephanie A. A. (36) have proposed a Multi-Task Intelligent Nurse Assistant Robot (MINA), designed to assist nurses with daily object retrieval, features a robotic arm on an omnidirectional mobile base. Using an augmented reality interface for setting waypoints, MINA can map and navigate to specified locations, such as supply cabinets, and complete grasp and retrieval tasks accurately and repeatedly.
Harbin Medical University Cancer Hospital utilizes the intelligent intravenous medication dispensing robot Dispensing Robot (37), improving the efficiency, convenience, and safety of intravenous infusion operations. This reduces the occurrence of medication residues and dispensing errors. During the medication dispensing process, the personnel are completely isolated from the medication, providing effective protection for operators and reducing injuries caused by medication preparation.
4.3.3 Venous blood collection
Automatic blood collection nursing robots provide a positive patient experience, especially for those prone to fainting due to needles and blood. Moreover, they reduce healthcare workers’ needle stick injuries and contact infection (38), offering an innovative solution to improve nursing processes and enhance medical efficiency.
Wang et al. (39) evaluated the performance of the intelligent venous blood collection robot MagicNurse, demonstrating that the automatic blood collection robot outperformed manual collection in terms of specimen collection volume and pain. The robot achieved a 94.3% puncture success rate. Although there were statistically significant differences in 11 indicators of anticoagulant blood samples collected by the robot versus manual collection, these did not impact clinical diagnosis or prognosis. The robot’s blood collection method is less painful, well-received by patients, and suitable for clinical anticoagulant sampling.
Leipheimer et al. (40) developed a fully automated robot venipuncture device. Combining ultrasound imaging and micro-robot technology, the success rates for difficult and non-difficult venous access blood collection were 87 and 97%, respectively. This device improves venous access success rates, reduces patient harm, and decreases surgical time and institutional costs. Its applications include venous catheter insertion, central venous access, dialysis, and arterial catheter placement.
Furthermore, Chen et al. (41) designed an automatic blood collection device based on ergonomics and user journeys. This device aims to improve collection efficiency, reduce the risk of bloodborne disease infections caused by needle injuries to medical personnel, alleviate the workload and training costs for healthcare workers, and enhance the user experience.
4.3.4 Suction care
Remote-controlled or automated robots can replace nursing staff, effectively reducing close contact between healthcare workers and infected patients, as well as minimizing exposure to high concentrations of droplets and aerosols in the air (42). This, in turn, lowers the risk of infection, alleviates the psychological burden and workload of healthcare workers, which is particularly crucial during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Tan et al. (43) developed a smart suction nursing robots that is stable in motion, easy to operate, and ensures a smooth process. By simulating the suction process with mechanical arms and hands, key parameters and procedural data were derived from clinical practices, informing the robot’s motion unit design. The robot replicates suction actions using thumb, index finger, and palm joints to grip the suction tube, mimicking wrist and elbow movements through servo and arm structures. Its feasibility was confirmed using an advanced suction training model. The robot performs smoothly, executing tasks like gripping, feeding, retracting, and rotating the tube effectively.
Peng et al. (44) designed a fully enclosed suction tube flushing device. This nursing robot features an integrated design with fully enclosed suction, humidification, and flushing materials, adhering to bacteria-free operation standards. The syringe’s pulse flushing removes adhered sputum, reducing ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP). Usage controls the flushing solution amount, ensuring patient safety and minimizing waste. Additionally, Ishikita (45) from Japan invented a 3D-printable device called SPUTA VACCUMER, which can clear phlegm and foreign substances non-invasively without tracheal intubation, it is characterized by minimal invasiveness, simplicity, and cost-effectiveness. Manufacturable via 3D printing, its plastic injection model gained Japanese drug approval in Amritha Ashok et al. (46) and is now used clinically. Operable by non-professionals, it is also suitable for use in space to enhance astronauts’ quality of life.
4.4 Basic nursing work in the hospital
4.4.1 Hospital guidance
Intelligent hospital guidance robots are poised to play a crucial role in the healthcare sector. They offer accurate navigation, enhance operational efficiency (47), reduce the risk of cross-infection, and provide personalized services for patients.
During the Global COVID-19 Pandemic, intelligent hospital guidance robots have been jointly developed by institutions such as Siao et al. (48) to reduce interpersonal contact during the pandemic, prevent the spread of the virus, and assist medical staff in patient guidance and communication services. These robots offer emergency contact information for users to seek assistance remotely, and provide real-time images and control permissions to security personnel for immediate situational awareness and response. Today, one common issue encountered in large hospital buildings is that patients struggle to navigate within the hospital. The IWARD project (49–51), funded by the European Union, investigates the utilization of mobile service robots to assist hospital staff in their daily tasks, offering route guidance services to patients and visitors within hospital facilities. This robot guides patients to the X-ray room or through complex, dynamic, and crowded hospital environments, adjusting its speed to match the user’s pace for comfort, and incorporates plug-and-play functionality.
Tobita et al. (52) have focused on providing efficient guidance support to visually impaired individuals and the older adults within large hospital environments, culminating in the successful development of a novel guidance robot, LIGHBOT. This robot uses a touch panel for destination setting and adapts its speed based on the user’s applied force, enhancing ease, safety, and user confidence. LIGHBOT, known for its applicability and practicality, significantly improves navigation for visually impaired and older adults individuals in healthcare facilities. The Vici robot (53), for example, developed by InTouch Health, has a high-definition screen and camera that enable doctors and nurses to assist patients via videoconferencing services, without physical contact.
4.4.2 Disinfection and sterilization
The high infectivity and severity of the novel coronavirus (COVID-19) in 2019 underscored the necessity of hospital space disinfection technology and preventing human exposure to pathogenic environments (54).
Robot disinfection generally falls into two categories: ultraviolet light irradiation and chemical disinfection. Zhao et al. (55) from the Department of Mechanical Engineering at National Taiwan University have researched and developed a novel chlorine dioxide (ClO2) sterilization technology robot to reduce bacteria and viruses in the air and on surfaces. An intelligent disinfection robot, designed based on experimental results and hospital needs, sprays disinfectants in operating rooms and wards. Using IoT and gesture recognition, it operates autonomously with a 99.8% E. coli clearance rate.
Rusdinar et al. (56) developed a mobile sterilization robot equipped with UVC light systems at the top and bottom to emit UVC light. The Automated UVC Light Mobile Robot (AUMR) operates automatically using magnetic line sensors and a fuzzy reasoning system. Experiments show excellent sterilization performance in various room types, including positive and negative pressure environments.
UVD Robotics (57), a company based in Denmark, has introduced clinically tested and verified mobile UVC light robots into hospitals to efficiently disinfect rooms. The robot positions itself in the hospital room and approaches critical objects during the 10-min disinfection process, eliminating disease exposure risk to staff and reducing human error. Xenex, a U.S. company, produces the LightStrike UV disinfection robot (58), which uses pulsed UV (200–315 nm) with 4,300 times greater pathogen killing intensity than traditional UVC (254 nm) sources, disinfecting a room in 20 min. Deployed in over 400 hospitals globally, these robots enhance environmental hygiene practices.
Omron introduced the LD-UVC robot specifically to fight the COVID-19 pandemic, automating the UV disinfection process safely and wisely (59). This robot is used for effective disinfection of high contact points and rooms and is suitable for healthcare, hospitality, assisted living and commercial buildings. Due to its OMRON LD base, it can be used for various other applications such as material handling, catering, and other logistical needs.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, many AI technology companies in China continue to develop and fine-tune disinfection robots (60), donating them to hospitals in Hubei Province and other severely affected regions nationwide. Examples include the Titanium Intelligent Sterilization Robot, “Chuang Chuang” Sterilization Robot, and the Gao Xian Intelligent Cleaning Robot (61). These intelligent sterilization robots autonomously navigate and disinfect indoor spaces, planning movements precisely. They understand their environment and tasks, reducing the need for protective gear and allowing healthcare workers to focus on high-value tasks more safely and efficiently.
4.4.3 Patient transportation
Patient transportation in hospitals faces numerous challenges, including limited manpower, work-related injuries, and inefficient traditional stretcher methods (62). Patient transportation nursing robots can autonomously perform patient transfer tasks, reducing the need for manual operations. They provide patients with safer, more comfortable, and efficient transfer experiences.
Guo et al. (63) have developed a novel electric robot bed mover called OmniBed, featuring omnidirectional mobility, this device attaches to a manual hospital stretcher, converting it into a powered omnidirectional bed (OmniBed) for single person uses. The OmniBed reduces manpower, decreases back muscle activity, and offers more ergonomic, efficient, and safer handling compared to traditional beds, with precise ‘parallel parking’ in small spaces.
To meet diverse nursing transportation requirements in various scenarios, Japan and the United States have jointly developed humanoid dual-arm patient transfer robots like Robear (64). These robots boast strong support and agile movements in addition to intelligent sensors for rapid perception of the external environment, assisting nurses in easily and safely transferring patients in different scenarios.
Wang et al. (65) have developed a new intelligent robot bed called Flexbed, equipped with autonomous navigation capabilities for rapid and safe transportation of critically ill neurosurgery patients without changing the bed. Compared to traditional hospital beds, the Flexbed is more efficient and safe during transportation. It avoids obstacles using collision avoidance strategies and moves at maximum speed when clear, navigating crowded corridors and overcoming mobility obstacles.
4.4.4 Logistics transportation
Logistics transportation nursing robots can execute the transportation tasks of supplies and medications within medical institutions, including logistics distribution from warehouses to wards, operating rooms, and other locations (66). They can quickly deliver urgently needed supplies in emergency situations. With features such as automated transportation, efficiency, reliability, reduced risk of cross-infection, and conservation of human resources, these robots provide medical institutions with safe, efficient, and reliable material transportation solutions (67).
At the University of California, San Francisco Medical Center, an introduction of 25 intelligent transport robots called TUGs (68) assists medical staff in transporting medications, goods, laboratory specimens, and food. These robots automatically navigate through the hospital’s stored floor plan, avoiding obstacles at all times. They utilize wireless network communication to control elevator door opening and closing applications. Currently, TUGs are in use in multiple hospitals, with excellent feedback on their effectiveness. Another example of a hospital service robot is the “Aethon TUG (69),” which transports surgical instruments, medications, food and beverages, linens, and waste. The robot can perform scheduled deliveries or required tasks with outstanding performance.
In Ghana and Rwanda, the “Zipline (70)” unmanned aerial vehicle is used to transport coronavirus samples, blood products, and medications. Moxi uses a freight mobile base for navigation and obstacle avoidance, with a compliant arm and hand for manipulation. It is socially intelligent, learns from humans, and adapts to hospital workflows. Moxi has been piloted to gather patient supplies, distribute PPE, and deliver medications, helping staff spend more time with patients and provide efficient care support (71).
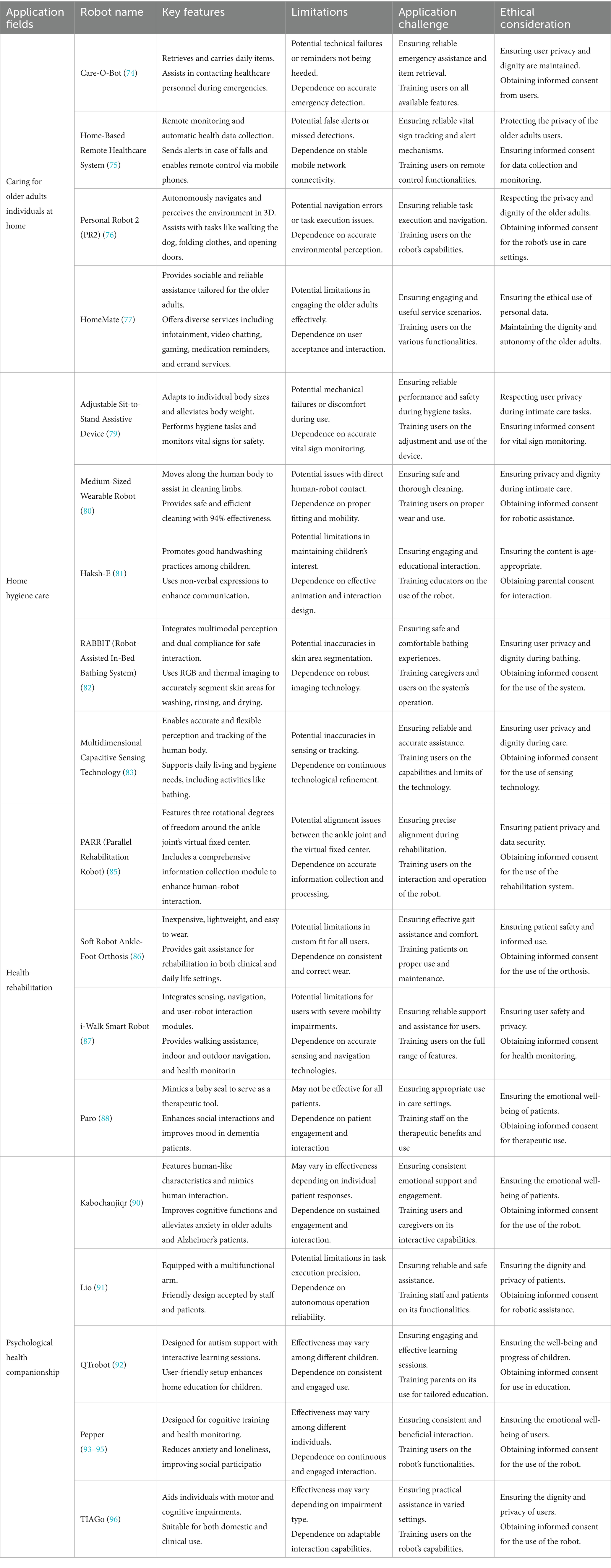
5 Application of nursing robot in home rehabilitation field
5.1 Overview
This section will discuss the application of mobile collaborative nursing robots in the field of home rehabilitation, including home care for the older adults, home health care, physical rehabilitation and psychological companionship. By introducing a variety of nursing robot systems and technologies developed in different countries and regions, we show how they support multiple aspects of patients’ daily life through intelligent functions, from providing social companionship to performing personal hygiene and care tasks to assisting in health rehabilitation training.
5.2 Purpose
This section aims to reveal how mobile collaborative nursing robots can improve the quality of care in home rehabilitation Settings and improve the lives of older people and those with special needs. Through the study of existing technologies and their practical application cases, it shows how these innovative solutions meet the growing needs of home care, and provides inspiration for future research and development directions.
5.3 Caring for older adults individuals at home
Homecare nursing robots possess intelligent technologies and features such as facial recognition, voice recognition, autonomous navigation, etc. (72). They offer advantages such as daily care provision, health condition monitoring, safety assurance, and social companionship (73).
Lorenz et al. (74) has developed a social companion robot for older adults care named Care-O-Bot. This robot can retrieve and carry common daily items, assist in contacting healthcare personnel during emergency situations (falls, etc.), provide support for daily care functions, remind older adults individuals to eat, and help them fetch items.
In China, Zhou et al. (75) has developed a new home-based remote healthcare system for the older adults based on mobile robots. This nursing system, with remote monitoring and automatic health data collection, constantly tracks the vital signs and activity of the older adults, sending alerts in case of falls. It also enables remote control of the robot via mobile phones.
Personal Robot 2 (PR2) (76) is a multifunctional artificial-assistance mobile nursing robot designed to provide independent living and interaction for humans, especially the older adults. PR2 autonomously navigates by perceiving the environment in 3D, assisting with tasks like walking the dog, folding clothes, and opening doors, providing home care for the older adults.
The robot “HomeMate” represents an innovative attempt based on its sociability and reliability (77), realized through extensive user studies. Older adults individuals cared for by senior welfare centers are chosen as the target group, for whom five service scenarios are designed: infotainment, video chatting, gaming, medication reminders, and, notably, errand services.
5.4 Home hygiene care
Hygiene care nursing robots typically have user-friendly designs, including soft materials, smooth movements, etc., to provide a comfortable experience (78). In China, Fu et al. (79) have designed an adjustable sit-to-stand assistive device for personal hygiene nursing robots. This device adapts to individual body sizes, alleviates body weight, and performs hygiene tasks like washing hair and drying the body. It includes vital sign monitoring for safety during bathing and features water and energy efficiency, compact design, and high comfort.
Liu et al. (80) have developed a medium-sized wearable robot that can move along the human body, assisting in cleaning the surface of limbs. This solution addresses direct human-robot contact challenges through wearable design and flexible mobility, providing a safe and efficient way to clean patients’ body surfaces with a 94% effectiveness, improving hygiene, comfort, and reducing caregiver workload.
The robot Haksh-E (81) is designed to promote good handwashing practices among children. It is engineered with two degrees of freedom and physically resembles an anthropomorphic soap dispenser. Its face features an animated mouth, human-like eyes with large irises, and eyebrows that enhance verbal communication through non-verbal expressions. This design is based on prior research in child-robot interaction scenarios.
RABBIT (82) is an innovative robot-assisted in-bed bathing system designed to meet the growing demand for assistive technology in personal hygiene tasks. It integrates multimodal perception and dual compliance for safe and comfortable physical human-robot interaction. RABBIT uses RGB and thermal imaging to accurately segment dry, soapy, and wet skin areas, performing washing, rinsing, and drying tasks according to professional nursing practices.
Erickson et al. (83) have developed a multidimensional capacitive sensing technology, offering a promising method for robots to perceive and track the human body in assistive tasks requiring human-robot interaction. This technology equips nursing robots with accurate and flexible capabilities to support the daily living and hygiene needs of disabled individuals, including activities like bathing. It shows promise and potential for future robot-assisted care.
5.5 Health rehabilitation
Health rehabilitation robots have achieved certain results in active training, flexible control, and rehabilitation assessment (84). Zhang et al. (85) has developed a parallel rehabilitation robot, PARR, based on end effector, featuring three rotational degrees of freedom around the virtual fixed center of the ankle joint. During rehabilitation, the ankle joint’s center should align with the virtual fixed center. The system includes a comprehensive information collection module to enhance human-robot interaction among the robot, patient, and doctor, making it widely applicable for ankle rehabilitation.
Kwon et al. (86) has proposed a soft robot ankle-foot orthosis for post-stroke patients. This orthosis is inexpensive, lightweight, easy to wear, and provides gait assistance for rehabilitation not only in clinics but also in daily life. It improves the walking propulsion force and prevents foot drop in patients, benefiting their gait and overall rehabilitation.
Moustris et al. (87) have developed the i-Walk smart robot, a comprehensive system integrating sensing, navigation, and user-robot interaction modules. It combines user-adaptive motion control, dynamic environment navigation, and cognitive assistance, suitable for individuals with mild to moderate mobility impairments. It provides stable body posture support, walking assistance, indoor and outdoor navigation, and health monitoring.
Paro, designed to mimic a baby seal, serves as a therapeutic tool to reduce anxiety and loneliness in dementia patients (88). Its interactive capabilities enhance social interactions and mood, improving patients’ behavioral outcomes. Used in care facilities and homes, Paro provides emotional support.
5.6 Psychological health companionship
Psychological companion nursing robots play an important role in providing emotional support and psychological counseling (89). Ke et al. (90) developed the humanoid social robot Kabochanjiqr, featuring human-like characteristics. Through interactive capabilities, mimics human interaction, meeting patients’ emotional needs. It improves cognitive functions in older adults women living alone and alleviates anxiety in Alzheimer’s patients.
Lio is a mobile robot platform equipped with a multifunctional arm, specifically designed for human-robot interaction and personal care assistant tasks. Its friendly appearance has led to widespread acceptance among healthcare staff and patients (91). This robot has already been deployed in several healthcare facilities, where it operates autonomously, assisting staff and patients on a daily basis.
QTrobot is an innovative social robot specifically designed to support the education and development of autistic children (92). QTrobot offers interactive and consistent learning sessions focused on speech, social–emotional skills, and cognitive development, making home education fun and effective. Its user-friendly setup empowers parents to provide tailored education, fostering children’s growth.
Pepper (93–95), the robot, is a long-term semi-humanoid autonomous synthetic aperture radar developed by Softbank Robotics, originating from Japan and France. This robot is designed for cognitive training, health monitoring, companionship, and more, this robot aids various groups including Alzheimer’s patients, older adults stroke survivors, those with depression, and healthy older adults. It effectively reduces anxiety, loneliness, and improves social participation. TIAGo robot can conveniently aid individuals with disabilities (96), including those with motor and cognitive impairments in both domestic and clinical settings.
6 Challenges and ethical issues in the application of nursing robots
With the significant growth of the world’s older adults population, the care of older adults and disabled individuals has become a focal point of societal and governmental concern. Mobile collaborative nursing robots play a crucial role in promoting social care services, contributing to the enhancement of patient and older adults care quality, and alleviating the burden on healthcare personnel (97). However, the development and application of nursing robots still face challenges and ethical issues. Based on our review, these issues are discussed in detail below.
The challenges are reviewed below: (1) Technological Challenges: Mobile collaborative nursing robots require high levels of intelligence and autonomous navigation capabilities to adapt to complex and dynamic clinical environments. This involves technical challenges such as perception and understanding of the environment, path planning, indoor navigation, maneuvering, telecommunications, and the integration of robots with existing hospital technology (98). (2) Safety Challenges: Nursing robots closely interact with patients and healthcare professionals, necessitating the assurance of their safety. Existing safety challenges include multiple personal safety risks such as uncontrolled systems, potentially harmful physical contact, falls and collisions (99), so robots need safety sensors and control systems to prevent harm to patients or others. (3) Human-Robot Interaction Challenges: Human-robot interaction is a critical aspect of nursing robot applications. Robots need to possess effective speech recognition, emotional understanding, and expressive capabilities (100) to facilitate communication and collaboration with patients and healthcare professionals.
Upon review, existing ethical issues include: (1) Privacy protection: providing nursing services may involve the acquisition and processing of patients’ personal privacy information. The uncertainty of data protection requirements creates privacy data security issues for users, especially for vulnerable robot users (101). Therefore, protecting patient privacy becomes a significant ethical issue, requiring the formulation of corresponding privacy protection policies and measures. (2) Ethical Decision-Making: In some cases, nursing robots may need to make decisions regarding patient care and treatment. This raises ethical decision-making issues (102), ensuring that robots adhere to ethical guidelines and make correct decisions in the best interest of the patient. (3) Responsibility and Accountability Issues: The interaction between nursing robots, patients, and healthcare professionals necessitates a clear delineation of responsibilities and accountabilities between robots and humans (103). This includes issues such as behavioral norms for robots, accountability, and legal responsibilities (104).
Based on a comprehensive review of the current challenges and ethical issues in the development and application of nursing robots, we believe that addressing the challenges and ethical issues in the application of nursing robots requires a multifaceted approach, including technological advances, legal regulations, and the establishment of ethical codes. To be specific: (1) Technological Innovation: Continuous technological innovation is essential to enhance the perception, cognition, and decision-making abilities of mobile collaborative nursing robots (105). Introducing advanced sensing technologies, artificial intelligence algorithms, and autonomous navigation systems can improve the adaptability and safety of robots in complex environments. (2) Legal Regulations: Establishing relevant laws and regulations to standardize the design, development, and use of nursing robots. This includes safety certifications for robots, privacy protection measures, and regulations on ethical decision-making (106). (3) Ethical Guidelines: Formulating ethical guidelines and moral principles to clarify the principles and ethical requirements of nursing robots. This involves provisions for protecting patient privacy, ethical decision-making principles, and regulations for accountability (107).
Mobile collaborative nursing robots have immense potential in application to enhance care efficiency, alleviate healthcare resource pressures, and improve patient care experiences. However, it is imperative to fully consider technological challenges and ethical issues, promoting the sustainable development of nursing robots through technological innovation and institutional development to achieve better care services and societal well-being.
7 Summary of the future development direction of nursing robots
Mobile collaborative nursing robots, as an innovative solution, have vast development prospects. With continuous technological advancements and increasing medical demands, the future development of mobile collaborative nursing robots will progress in the following directions:
(1) Enhancement of Intelligence and autonomy: future mobile collaborative nursing robots will become more intelligent, possessing advanced perception, cognition, and decision-making capabilities. Through cutting-edge artificial intelligence technology and machine learning algorithms, these robots can better understand and adapt to patients’ needs, providing personalized nursing services (46, 108). Additionally, robots will have enhanced autonomous navigation capabilities (109), enabling flexible movement in complex environments and rapid adaptation to changes.
(2) Multimodal interaction and emotional expression: to provide a better care experience, future nursing robots will have diverse interaction methods, including voice recognition, posture sensing, and touch feedback (100). This allows for more natural and seamless communication between patients and nursing robots. Furthermore, nursing robots will possess the ability to express emotions through speech (110), facial expressions, and gestures, fostering a stronger emotional connection with patients.
(3) Multitasking collaboration and teamwork: future nursing robots will be capable of multitasking and collaborating efficiently with other medical devices and robot teams (111). For example, in the operating room, nursing robots can collaborate with surgical robots to provide more precise care support. In nursing teams, nursing robots can seamlessly communicate and cooperate with nurses and doctors, facilitating efficient care processes.
(4) Data sharing and remote monitoring: future nursing robots will have the capability for data sharing and remote monitoring. By connecting to electronic health record systems, nursing robots can real-time record and transmit patients’ health data, allowing healthcare professionals to stay informed about patients’ conditions (112). Additionally, nursing robots can enable remote care and receive guidance from doctors through video monitoring and remote control (29), providing timely care services to patients in remote areas or those unable to be physically present.
(5) Resolution of safety and ethical issues: the future development of nursing robots also requires addressing safety and ethical issues. Technologically, nursing robots need to ensure high levels of safety through safety sensors and control systems, safeguarding both patients and the environment (113). Simultaneously, it is essential to establish relevant laws and regulations, along with ethical guidelines, to clarify the responsibilities and relationships between nursing robots and humans, protecting patient privacy and rights.
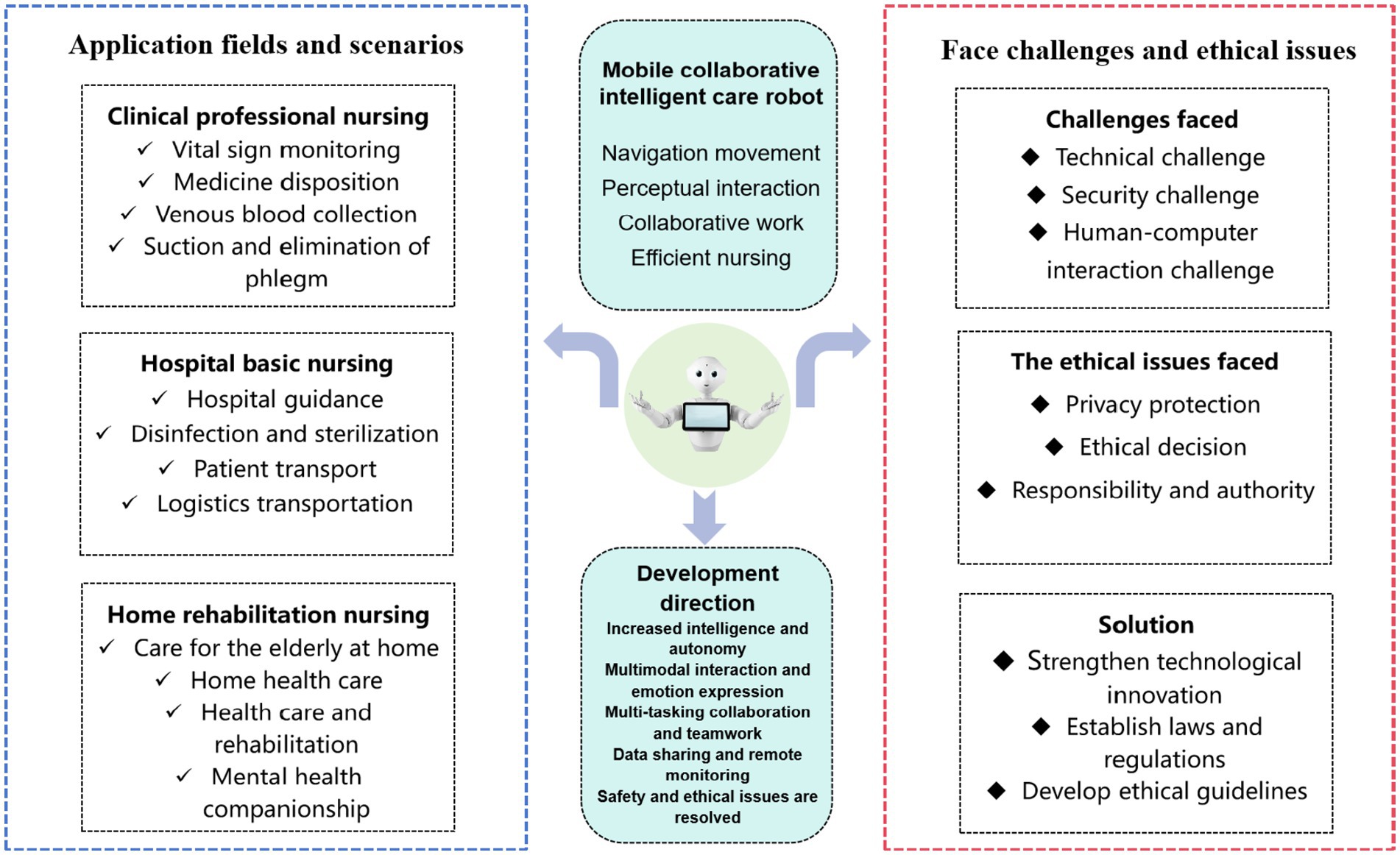
Finally, we summarize the whole review study It is vividly displayed in the form of graphic framework (as shown in Figure 1), which is convenient for readers to understand more intuitively.
8 Conclusion
In conclusion, the application of nursing robots spans both clinical settings within hospitals and home care environments outside of medical facilities. Given the distinct differences in application environments and user needs, we chose to discuss these applications in separate chapters. Specifically, clinical applications require robust technological capabilities and adhere to stringent regulatory standards, whereas home care robots focus more on user-friendliness and adaptability to diverse domestic settings. Additionally, there are variances in data management and privacy protection protocols between the two contexts. By delineating these differences through dedicated chapters, we aimed to provide a thorough exploration of the unique challenges and opportunities associated with each setting. However, it is crucial to recognize the interconnectedness of these applications, as advancements in one domain often inform innovations in the other. Both clinical and home care robots contribute to the broader goal of enhancing patient care and improving quality of life, thus forming an integral part of the evolving landscape of healthcare technology.
With the application of technologies such as intelligent enhancement, multimodal interaction, multitasking collaboration, and remote monitoring, the efficiency and convenience of nursing robots in the healthcare field will be further improved. Mobile collaborative nursing robots are expected to become key tools supporting the development of healthcare services. However, it is important to recognize that the development and application of nursing robots still face certain limitations. These include high costs, adaptability in complex environments, and a lack of emotional resonance. Therefore, governments and society need to establish relevant policies to support and regulate the application of nursing robots while protecting patients’ rights and privacy.
Future research on nursing robots should focus on enhancing their perception and cognition capabilities and strengthening their emotional interaction with humans. Additionally, exploring the application of nursing robots in specific areas such as operating rooms and rehabilitation centers, as well as studying their collaboration with other medical devices and personnel, will contribute to improving nursing efficiency. Continuous technological innovation and institutional development will drive the sustainable development of nursing robots and lead to transformative advancements in the healthcare field. Therefore, nursing robots are expected to be more widely applied in the future, leading to improved efficiency and quality of nursing work through close collaboration with doctors, nurses, and other healthcare professionals. This will help alleviate the burden on nursing staff, allowing them to have more time and energy to communicate with and care for patients, providing a more warm and personalized nursing service.
Author contributions
BW: Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization. SC: Writing – original draft. GX: Conceptualization, Methodology, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Resources, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (no. 2021YFC0122701) and National Institute of Hospital Administration (NIHA) “R&D of Intelligent Robot Systems for Critical Care” Project Collaboration Topic (no. HLJQRS_2023A15).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Liu, XZ. Research on social Care for the Elderly [J]. J Beijing Youth Univ Polit Sci. (2013) 22:51–6.
2. Li, J, Han, X, Zhang, X, and Wang, S. Spatiotemporal evolution of global population ageing from 1960 to 2017. BMC Public Health. (2019) 19:127. doi: 10.1186/s12889-019-6465-2
3. Haward, V. Impact of Japan’s aging population on healthcare costs and the Long-term care insurance system. Stud Soc Sci Hum. (2024) 3:39–44. doi: 10.56397/SSSH.2024.02.06
4. Tzouganatou, SG. The ageing population of the European Union: challenges and prospects. HAPSc Policy Briefs Series. (2022) 3:206–14. doi: 10.12681/hapscpbs.31010
5. Li, QL, Cao, Y, Mao, N, Yu, CT, and Liu, KL. Nursing robot technology development review. J Jiangsu Inst Technol. (2020) 26:62–70. doi: 10.19831/j.cnki.2095-7394.2020.04.010
6. Bujnowska-Fedak, M, and Grata-Borkowska, U. Use of telemedicine-based care for the aging and elderly: promises and pitfalls. Smart Homec Technol TeleHealth. (2015):91–105. doi: 10.2147/SHTT.S59498
7. Johannessen, T, Ree, E, Aase, I, Bal, R, and Wiig, S. Exploring challenges in quality and safety work in nursing homes and home care—a case study as basis for theory development. BMC Health Serv Res. (2020) 20:1–12. doi: 10.1186/s12913-020-05149-x
8. The White House. (2019). Emerging technologies to support an aging population. Available at: https://www.whitehouse.gov/wpcontent/uploads/2019/03/-Emerging-Tech-to-Support-Aging-2019.pdf
9. Maalouf, N, Sidaoui, A, Elhajj, IH, and Asmar, D. Robotics in nursing: a scoping review. J Nurs Scholarsh. (2018) 50:590–600. doi: 10.1111/jnu.12424
10. Li, Y, and Zhou, MF. Analysis on development characteristics of China’s medical robot industry. Robot Industry. (2018) 2:95–100. doi: 10.19609/j.cnki.cn10-1324/tp.2018.02.018
11. Johansson-Pajala, RM, and Gustafsson, C. Significant challenges when introducing care robots in Swedish elder care[J]. Disabil Rehabil Assist Technol. (2022) 17:166–76. doi: 10.1080/17483107.2020.1773549
12. Kutjat, L. How have robots impacted healthcare? The Review: A Journal of Undergraduate Student Research, (2010) 12:6–8. Available at: https://fisherpub.sjf.edu/ur/vol12/iss1/4 (Accessed October 22, 2024).
13. Francis, P, and Winfield, H. Medical robotics: the impact on perioperative nursing practice. Urol Nurs. (2006) 26:99–109.
14. Onnasch, L, and Roesler, E. A taxonomy to structure and analyze human–robot interaction. Int J Soc Robotics. (2021) 13:833–49. doi: 10.1007/s12369-020-00666-5
15. Lasota, PA, Fong, T, and Shah, JA. A survey of methods for safe human-robot interaction. Robotics. (2017) 5:261–349. doi: 10.1561/2300000052
16. Kim, Stephanie, Anthis, Jacy Reese, and Sebo, Sarah. “A taxonomy of robot autonomy for human-robot interaction.” Proceedings of the 2024 ACM/IEEE International Conference on Human-Robot Interaction. (2024).
17. Jiang, Shu, and Arkin, Ronald C. “Mixed-initiative human-robot interaction: definition, taxonomy, and survey.” 2015 IEEE international conference on systems, man, and cybernetics. IEEE, (2015).
18. Asgharian, P, Panchea, AM, and Ferland, F. A review on the use of mobile service robots in elderly care. Robotics. (2022) 11:127. doi: 10.3390/robotics11060127
19. Lanza, F, Seidita, V, and Chella, A. Agents and robots for collaborating and supporting physicians in healthcare scenarios. J Biomed Inform. (2020) 108:103483. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2020.103483
20. Lee, JY, Song, YA, Jung, JY, Kim, HJ, Kim, BR, do, HK, et al. Nurses’ needs for care robots in integrated nursing care services. J Adv Nurs. (2018) 74:2094–105. doi: 10.1111/jan.13711
21. Qiu, R, Ji, Z, Chivarov, N, Arbeiter, G, Weisshardt, F, Rooker, M, et al. The development of a semi-autonomous framework for personal assistant robots-SRS project. Int J Intel Mechatr Robot. (2013) 3:30–47. doi: 10.4018/ijimr.2013100102
22. Cai, X, Ning, H, Dhelim, S, Zhou, R, Zhang, T, Xu, Y, et al. Robot and its living space: a roadmap for robot development based on the view of living space. Digit Commun Netw. (2021) 7:505–17. doi: 10.1016/j.dcan.2020.12.001
23. Francis, P. The evolution of robotics in surgery and implementing a perioperative robotics nurse specialist role. AORN J. (2006) 83:629–50. doi: 10.1016/S0001-2092(06)60191-9
24. Tietze, M, and McBride, S. Robotics and the impact on nursing practice. Maryland: American Nurses Association (2020).
25. Jiang, JG, Huang, Z, Huo, B, Zhang, Y, and Song, S. Research progress of clinical application of nursing robots. J Nurs. (2023) 30:39–43. doi: 10.2174/2212797611666180306124236
26. Song, YA, Kim, HJ, and Lee, HK. Nursing, Robotics, technological revolution: Robotics to support nursing work. Nursing. (2018) 20:144–53. doi: 10.17079/jkgn.2018.20.s1.s144
27. Guo, Xuechen. “Development status of medical nursing robots: focused on Flexiblility, autonomous mobility, and non-contact physical signs monitoring.” Proceedings of the 2nd International Symposium on Artificial Intelligence for Medicine Sciences. (2021).
28. Mostafa, H. Development of a multi-functional nurse robot for enhanced patient care and vital sign monitoring in hospitals EasyChair (2023).
29. Mireles, C, Sanchez, M, Cruz-Ortiz, D, Salgado, I, and Chairez, I. Home-care nursing controlled mobile robot with vital signal monitoring. Med Biol Eng Comput. (2023) 61:399–420. doi: 10.1007/s11517-022-02712-y
30. Purnomo, AT, Lin, D-B, Adiprabowo, T, and Hendria, WF. Non-contact monitoring and classification of breathing pattern for the supervision of people infected by COVID-19. Sensors. (2021) 21:3172. doi: 10.3390/s21093172
31. Huang, HW, Chen, J, Chai, PR, Ehmke, C, Rupp, P, Dadabhoy, FZ, et al. Mobile robotic platform for contactless vital sign monitoring. Cyborg Bionic Syst. (2022) 2022:497. doi: 10.34133/2022/9780497
32. Yang, C, Ni, X, Zhang, L, and Peng, L. Intravenous compounding robots in pharmacy intravenous admixture services: a systematic review. Medicine. (2023) 102:e33476. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000033476
33. George, D. B., and Megalingam, R. K., “Autonomous pharmaceutical dispensing robot”, 2022 IEEE 3rd Global Conference for Advancement in Technology (GCAT), pp. 1–6, (2022).
34. Iwamoto, T, Morikawa, T, Hioki, M, Sudo, H, Paolucci, D, and Okuda, M. Performance evaluation of the compounding robot, APOTECAchemo, for injectable anticancer drugs in a Japanese hospital. J Pharma Health Care Sci. (2017) 3:1–8. doi: 10.1186/s40780-017-0081-z
35. Wang, X, Gu, M, Gao, X, Xiong, X, Wang, N, Li, Q, et al. Application of information-intelligence technologies in pharmacy intravenous admixture services in a Chinese third-class a hospital. BMC Health Serv Res. (2022) 22:1–14. doi: 10.1186/s12913-022-08580-4
36. Nambiappan, HR, Kodur, KC, Kyrarini, M, Makedon, F, and Gans, N. MINA: a multitasking intelligent nurse aid robot. The 14th PErvasive technologies related to assistive environments conference. (2021):266–7. doi: 10.1145/3453892.3461010
37. Zhang, L, Liu, W, and Zhang, Y. Application of intelligent intravenous drug dispensing robot in clinical nursing. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. (2022) 2022:4769883. doi: 10.1155/2022/4769883
38. Yang, Z, Wen, S, Qi, Q, Lv, Z, and Ji, A. A trocar puncture robot for assisting venipuncture blood collection. Robotica. (2024) 42:1597–613. doi: 10.1017/S0263574724000407
39. Wang, C, Gu, M, Zhu, J, Yang, S, Tang, W, Liu, Z, et al. Clinical application of a fully automated blood collection robot and its assessment of blood collection quality of anticoagulant specimens. Front Med. (2023) 10:1251963. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1251963
40. Leipheimer, JM, Balter, ML, Chen, AI, Pantin, EJ, Davidovich, AE, Labazzo, KS, et al. First-in-human evaluation of a hand-held automated venipuncture device for rapid venous blood draws. Technology. (2019) 7:98–107. doi: 10.1142/S2339547819500067
41. Chen, R., Luo, J., and Luximon, Y. (2021). A conceptual design and research of automatic blood sampling device. Human Aspects of IT for the Aged Population Supporting Everyday Life Activities: 7th International Conference, ITAP 2021, Held as Part of the 23rd HCI International Conference, HCII 2021, Virtual Event, July 24–29, 2021, Proceedings, Part II, 223–233.
42. di Lallo, A, Murphy, R, Krieger, A, Zhu, J, Taylor, RH, and Su, H. Medical robots for infectious diseases: lessons and challenges from the COVID-19 pandemic. IEEE Robot Autom Magaz. (2021) 28:18–27. doi: 10.1109/MRA.2020.3045671
43. Tan, W, Shen, C, Luo, Y, Zhu, H, Ma, T, Dong, D, et al. Development of motion unit of simulated intelligent endotracheal suctioning robot. Chin J Med Instrum. (2019) 43:17–20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7104.2019.01.0005
44. Peng, Q, Yang, X, and Zeng, X. Design and application of flushing device of a totally enclosed sputum suction tube for reducing the incidence of ventilator-associated pneumonia. Zhonghua wei Zhong Bing ji jiu yi xue. (2022) 34:871–2. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20220328-00302
45. Ishikita, N. Novel 3-D printable aspiration device “SPUTA VACUUMER” designed to minimize invasion. IEEE Open J Eng Med Biol. (2023) 4:180–3. doi: 10.1109/OJEMB.2023.3248875
46. Amritha Ashok, K, Savy, A, Shijoh, V, Shaw, RN, and Ghosh, A. Hospital assistance robots control strategy and machine learning technology. Mach Learn Robot Appl. (2021):35–46. doi: 10.1007/978-981-16-0598-7_3
47. Kodur, K, and Kyrarini, M. Patient–robot co-navigation of crowded hospital environments. Appl Sci. (2023) 13:4576. doi: 10.3390/app13074576
48. Siao, CY, Chien, TH, and Chang, RG. Robot scheduling for assistance and guidance in hospitals. Appl Sci. (2022) 12:337. doi: 10.3390/app12010337
49. Hasan, MK. Developing a person guidance module for hospital robots Dublin City University (2013).
50. Mamun, K A, Sharma, A, Hoque, A S M, et al. Remote patient physical condition monitoring service module for iWARD hospital robots[C]//Asia-Pacific world congress on computer science and engineering. IEEE, (2014): 1–8.
51. Baalbaki, H, Lamiri, M, and Xie, X. Joint location and configuration of mobile service robots for hospitals[C]//2008. IEEE Int Conf Autom Sci Eng IEEE. (2008):615–20. doi: 10.1109/COASE.2008.4626452
52. Tobita, K, Sagayama, K, Mori, M, and Tabuchi, A NSK Ltd. 1-5-50 Kugenuma-shinmei, Fujisawa-shi, Kanagawa 251-8501, Japan. Structure and examination of the guidance robot LIGHBOT for visually impaired and elderly people. J Robot Mech. (2018) 30:86–92. doi: 10.20965/jrm.2018.p0086
53. Matyus, A. “Meet the robot helping doctors treat coronavirus patients.” digital trends. Available at: https://www.digitaltrends.com/news/meet-the-robot-helping-doctors-treat-coronavirus-patients/ (Accessed Oct. 7, 2020).
54. Sharafi, SM, Ebrahimpour, K, and Nafez, A. Environmental disinfection against COVID-19 in different areas of health care facilities: a review. Rev Environ Health. (2021) 36:193–8. doi: 10.1515/reveh-2020-0075
55. Zhao, YL, Huang, HP, Chen, TL, Chiang, PC, Chen, YH, Yeh, JH, et al. A smart sterilization robot system with chlorine dioxide for spray disinfection. IEEE Sensors J. (2021) 21:22047–57. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3101593
56. Rusdinar, A, Purnama, I, Fuadi, AZ, Adiluhung, H, Wicaksono, M, Risnanda, R, et al. Automated ultraviolet C light Mobile robot for room sterilization and disinfection. Int J Technol. (2021) 12:854. doi: 10.14716/ijtech.v12i4.4817
57. Thomsen, K, Kyndi, L, Johansen, HK, and Knudsen, JD. P141 microbiological evaluation of an automated UV-disinfection robot on cystic fibrosis-related pathogens. J Cyst Fibros. (2023) 22:S107. doi: 10.1016/S1569-1993(23)00516-7
58. Holland, J, Kingston, L, McCarthy, C, Armstrong, E, O’Dwyer, P, Merz, F, et al. Service robots in the healthcare sector. Robotics. (2021) 10:47. doi: 10.3390/robotics10010047
59. OMRON. LD UVC: automating UV disinfection process safely and wisely. (2015). Available at: https://web.omron-ap.com/th/ld-uvc (Accessed on 15 January 2021).
60. Shen, D, Guo, F, Long, LA, Mateos, H, Ding, ZX, Xiu, Z, et al. Robots under COVID-19 pandemic: a comprehensive survey. Access. (2021) 9:1590–615. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3045792
61. Xiong, AD. (2020). Disinfection and delivery robot: blocking the virus transmission channel with the steel body. Beijing, China: Robot Industry, 31, 41–45.
62. Eiding, H, Kongsgaard, UE, and Braarud, A-C. Interhospital transport of critically ill patients: experiences and challenges, a qualitative study. Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med. (2019) 27:27–9. doi: 10.1186/s13049-019-0604-8
63. Guo, Z, Xiao, X, and Yu, H. Design and evaluation of a motorized robotic bed mover with omnidirectional mobility for patient transportation. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. (2018) 22:1775–85. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2018.2849344
64. Jiang, C., Ueno, S., and Hayakawa, Y. (2015). Optimal control of non-prehensile manipulation control by two cooperative arms. Proceedings of the 2015 international conference of advanced mechatronic systems.
65. Wang, C, Savkin, AV, Clout, R, and Nguyen, HT. An intelligent robotic hospital bed for safe transportation of critical neurosurgery patients along crowded hospital corridors. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng. (2015) 23:744–54. doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2014.2347377
66. Fragapane, G, Hvolby, H-H, Sgarbossa, F, and Strandhagen, JO. Autonomous mobile robots in hospital logistics In: Advances in production management systems. The path to digital transformation and innovation of production management systems: IFIP WG 5.7 international conference, APMS 2020, Novi Sad, Serbia, august 30 – September 3, 2020, proceedings, part I. Cham: Springer International Publishing (2020)
67. Cognominal, M, Patronymic, K, and Wańkowicz, A. Evolving field of autonomous Mobile Robotics: technological advances and applications. Fusion Multidiscipl Res Int J. (2021) 2:189–200.
68. Smart Hospital Robot Is an Autonomous, High Tech Courier. (2020). Available at: https://www.springwise.com/smarthospital-robot-autonomous-high-tech-courier (Accessed 12 May 2020).
69. Bloss, and Richard. (2021). “Mobile hospital robots cure numerous logistic needs.” Industrial Robot Emerald Publishing. 38:567–571. Available at: https://www.emeraldgrouppublishing.com/journal/ir
70. Ackerman, E, and Michael, K. (2019). “The blood is here: Zipline’s medical delivery drones are changing the game in Rwanda.” IEEE spectrum 56.5. 24–31. doi: 10.1109/MSPEC.2019.8701196
71. Robotics, Diligent. Care is a team effort. Available at: https://diligentrobots.com/moxi (Accessed January 18, 2021).
72. Yang, G, Pang, Z, Jamal Deen, M, Dong, M, Zhang, Y-T, Lovell, N, et al. Homecare robotic systems for healthcare 4.0: visions and enabling technologies. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. (2020) 24:2535–49. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2020.2990529
73. Abou Allaban, A, Wang, M, and Padır, T. A systematic review of robotics research in support of in-home care for older adults. Information. (2020) 11:75. doi: 10.3390/info11020075
74. Lorenz, T, Weiss, A, and Hirche, S. Synchrony and reciprocity: key mechanisms for social companion robots in therapy and care. Int J Soc Robot. (2016) 8:125–43. doi: 10.1007/s12369-015-0325-8
75. Zhou, B, Wu, K, Lv, P, Wang, J, Chen, G, Ji, B, et al. A new remote health-care system based on moving robot intended for the elderly at home. J Healthc Eng. (2018) 2018:1–11. doi: 10.1155/2018/4949863
76. Garber, L. Robot OS: a new day for robot design. Computer. (2013) 46:16–20. doi: 10.1109/MC.2013.434
77. Lee, S, and Naguib, AM. Toward a sociable and dependable elderly care robot: design, implementation and user study. J Intell Robot Syst. (2020) 98:5–17. doi: 10.1007/s10846-019-01028-8
79. Fu, D, Han, J, and Hu, Z. Design and research on standing-assist device for healthcare robots. Mech Trans. (2013) 37:43–6. doi: 10.16578/j.issn.1004-2539.2013.11.003
80. Liu, F, Patil, V, Erickson, Z, and Temel, Z. Characterization of a Meso-scale wearable robot for bathing assistance In: In 2022 IEEE international conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO). Jinghong, China: IEEE (2022). 2146–52.
81. Sasidharan, S, Pasupuleti, D, Das, AM, Kapoor, C, Manikutty, G, and Rao, RB. Haksh-e: an autonomous social robot for promoting good hand hygiene among children In: IROS 2021 Workshop on The Roles of Robotics in Achieving the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals. IEEE Robotics and Automation Society. (2021)
82. Madan, R, Valdez, S, Kim, D, Fang, S, Zhong, L, Virtue, D. T, et al. RABBIT: a robot-assisted bed bathing system with multimodal perception and integrated compliance. Proc ACM/IEEE Int Conf Hum-Robot Interaction. (2024):472–81. doi: 10.1145/3610977.3634989
83. Erickson, Z, Clever, HM, Gangaram, V, Turk, G, Liu, CK, and Kemp, CC. Multidimensional capacitive sensing for robot-assisted dressing and bathing. IEEE Int Conf Rehabil Robot. (2019) 2019:224–31. doi: 10.1109/ICORR.2019.8779542
84. Bessler, J, Prange-Lasonder, GB, Schaake, L, Saenz, JF, Bidard, C, Fassi, I, et al. Safety assessment of rehabilitation robots: a review identifying safety skills and current knowledge gaps. Front Robot AI. (2021) 8:602878. doi: 10.3389/frobt.2021.602878
85. Zhang, L, Li, J, Dong, M, Fang, B, Cui, Y, Zuo, S, et al. Design and workspace analysis of a parallel ankle rehabilitation robot (PARR). J Healthc Eng. (2019) 2019:1–10. doi: 10.1155/2019/4164790
86. Kwon, J, Park, JH, Ku, S, Jeong, YH, Paik, NJ, and Park, YL. A soft wearable robotic ankle-foot-orthosis for post-stroke patients. IEEE Robot Automat Lett. (2019) 4:2547–52. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2019.2908491
87. Moustris, G, Kardaris, N, Tsiami, A, Chalvatzaki, G, Koutras, P, Dometios, A, et al. The i-walk lightweight assistive rollator: first evaluation study. Front Robot AI. (2021) 8:677542. doi: 10.3389/frobt.2021.677542
88. Geva, N, Uzefovsky, F, and Levy-Tzedek, S. Touching the social robot paro reduces pain perception and salivary oxytocin levels. Sci Rep. (2020) 10:9814. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-66982-y
89. Park, Y, Chang, SJ, Kim, HJ, and Jeong, HN. Effectiveness of artificial intelligence robot interventions on psychological health in community-dwelling older adults: a systematic review. Nursing. (2024) 26:234–47. doi: 10.17079/jkgn.2024.00353
90. Ke, C, Lou, VW, Tan, KC, Wai, MY, and Chan, LL. Changes in technology acceptance among older people with dementia: the role of social robot engagement. Int J Med Inform. (2020) 141:104241. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2020.104241
91. Miseikis, J, Caroni, P, Duchamp, P, Gasser, A, Marko, R, Miseikiene, N, et al. Lio—a personal robot assistant for human–robot interaction and care applications. IEEE Robot Autom Lett. (2020) 5:5339–46. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2020.3007462
92. Vulpe, A, Crăciunescu, R, Drăgulinescu, A-M, Kyriazakos, S, Paikan, A, and Ziafati, P. Enabling security Services in Socially Assistive Robot Scenarios for healthcare applications. Sensors. (2021) 21:6912. doi: 10.3390/s21206912
93. Pandey, AK, and Gelin, R. A mass-produced sociable humanoid robot: pepper: the first machine of its kind. IEEE Robot Autom Mag. (2018) 25:40–8. doi: 10.1109/MRA.2018.2833157
94. Tanaka, F., Isshiki, K., Takahashi, F., Uekusa, M., Sei, R., and Hayashi, K. (2015). Pepper learns together with children: development of an educational application. In proceedings of the 2015 IEEE-RAS 15th international conference on humanoid robots (humanoids) (pp. 270–275). Seoul, Republic of Korea.
95. Martinez-Martin, E, Escalona, F, and Cazorla, M. Socially assistive robots for older adults and people with autism: an overview. Electronics. (2020) 9:367. doi: 10.3390/electronics9020367
96. Bajrami, A, Palpacelli, M-C, Carbonari, L, and Costa, D. Posture optimization of the TIAGo highly-redundant robot for grasping operation. Robotics. (2024) 13:56. doi: 10.3390/robotics13040056
97. Jiang, J, Huang, Z, Huo, B, Zhang, Y, and Song, S. Research progress and prospect of nursing robot. Recent Patents Mech Eng. (2018) 11:41–57.
98. Christoforou, EG, Avgousti, S, Ramdani, N, Novales, C, and Panayides, AS. The upcoming role for nursing and assistive Robotics: opportunities and challenges ahead. Front Digit Health. (2020) 2:585656. doi: 10.3389/fdgth.2020.585656
99. Miyagawa, M, Kai, Y, Yasuhara, Y, Ito, H, Betriana, F, Tanioka, T, et al. Consideration of safety management when using pepper, a humanoid robot for Care of Older Adults. Intell Control Autom. (2020) 11:15–24. doi: 10.4236/ica.2020.111002
100. Dino, MJS, Davidson, PM, Dion, KW, Szanton, SL, and Ong, IL. Nursing and human-computer interaction in healthcare robots for older people: an integrative review. Int J Nurs Stud Adv. (2022) 4:100072. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnsa.2022.100072
101. Fosch-Villaronga, E, Felzmann, H, Ramos-Montero, M, et al. Cloud services for robotic nurses? Assessing legal and ethical issues in the use of cloud services for healthcare robots[C]//2018 IEEE/RSJ international conference on intelligent robots and systems (IROS). IEEE. (2018):290–6. doi: 10.1109/IROS.2018.8593591
102. Laakasuo, M, Palomäki, J, Kunnari, A, Rauhala, S, Drosinou, M, Halonen, J, et al. Moral psychology of nursing robots: exploring the role of robots in dilemmas of patient autonomy. Eur J Soc Psychol. (2023) 53:108–28. doi: 10.1002/ejsp.2890
103. Tabudlo, J, Kuan, L, and Garma, PF. Can nurses in clinical practice ascribe responsibility to intelligent robots? Nurs Ethics. (2022) 29:1457–65. doi: 10.1177/09697330221090591
104. Rajamäki, J, and Helin, J. Ethics and accountability of care robots. Robotics. (2022) 4:72–7. doi: 10.34190/eciair.4.1.762
105. Vasquez, B, Moreno-Lacalle, R, Soriano, GP, Juntasoopeepun, P, Locsin, RC, and Evangelista, LS. Technological machines and artificial intelligence in nursing practice. Nurs Health Sci. (2023) 25:474–81. doi: 10.1111/nhs.13029
106. Pfeifer-Chomiczewska, K. Intelligent service robots for elderly or disabled people and human dignity: legal point of view. AI & Soc. (2023) 38:789–800. doi: 10.1007/s00146-022-01477-0
107. Stokes, F, and Palmer, A. Artificial intelligence and robotics in nursing: ethics of caring as a guide to dividing tasks between AI and humans. Nurs Philos. (2020) 21:e12306. doi: 10.1111/nup.12306
108. Chang, C-Y, Jen, H-J, and Su, WS. Trends in artificial intelligence in nursing: impacts on nursing management. J Nurs Manag. (2022) 30:3644–53. doi: 10.1111/jonm.13770
109. Narayanan, KL, Krishnan, RS, Son, LH, Tung, NT, Julie, EG, Robinson, YH, et al. Fuzzy guided autonomous nursing robot through wireless beacon network. Multimed Tools Appl. (2022) 89:1–29. doi: 10.1007/s11042-021-11264-6
110. Nimmagadda, R, Arora, K, and Martin, MV. Emotion recognition models for companion robots. J Supercomput. (2022) 78:13710–27. doi: 10.1007/s11227-022-04416-4
111. Brinkmann, A, Böhlen, C F-v, Kowalski, C, Lau, S, Meyer, O, Diekmann, R, et al. Providing physical relief for nurses by collaborative robotics. Sci Rep. (2022) 12:8644. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-12632-4
112. Zhao, D, Yang, C, Zhang, T, Yang, J, and Hiroshi, Y. A task allocation approach of multi-heterogeneous robot system for elderly care. Mach Des. (2022) 10:622. doi: 10.3390/machines10080622
Keywords: internet of things, mobile collaboration, nursing robots, artificial intelligence, clinical applications, review literature
Citation: Wang B, Chen S and Xiao G (2024) Advancing healthcare through mobile collaboration: a survey of intelligent nursing robots research. Front. Public Health. 12:1368805. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1368805
Edited by:
Marios Kyriazis, National Gerontology Centre, CyprusReviewed by:
Sotiria Moza, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, GreeceLuka Peternel, Delft University of Technology, Netherlands
Copyright © 2024 Wang, Chen and Xiao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Gexin Xiao, Z2V4aW5feGlhb0BzaW5hLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Boyuan Wang
Boyuan Wang Shanji Chen
Shanji Chen Gexin Xiao4*
Gexin Xiao4*