- Department of Critical Medicine, Ningbo Medical Center Lihuili Hospital, Ningbo, China
Background: Aromatic amines (AAs) are a group of compounds widely found in chemical industry, tobacco smoke, and during food processing, with established carcinogenic properties. To date, there have been no reports on the potential neurotoxic effects of adult exposure to AAs. Serum neurofilament light chain (sNfL) is a protein released into the bloodstream following nerve axon injury and has been validated as a reliable biomarker for various neurological diseases. However, there has been no research to investigate the relationship between AAs exposure and sNfL.
Methods: In this study, we selected adults (aged ≥20 years) with data on both AAs and sNfL from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) conducted in 2013–2014. We used multivariable linear regression models to explore the correlation between urinary AAs and sNfL.
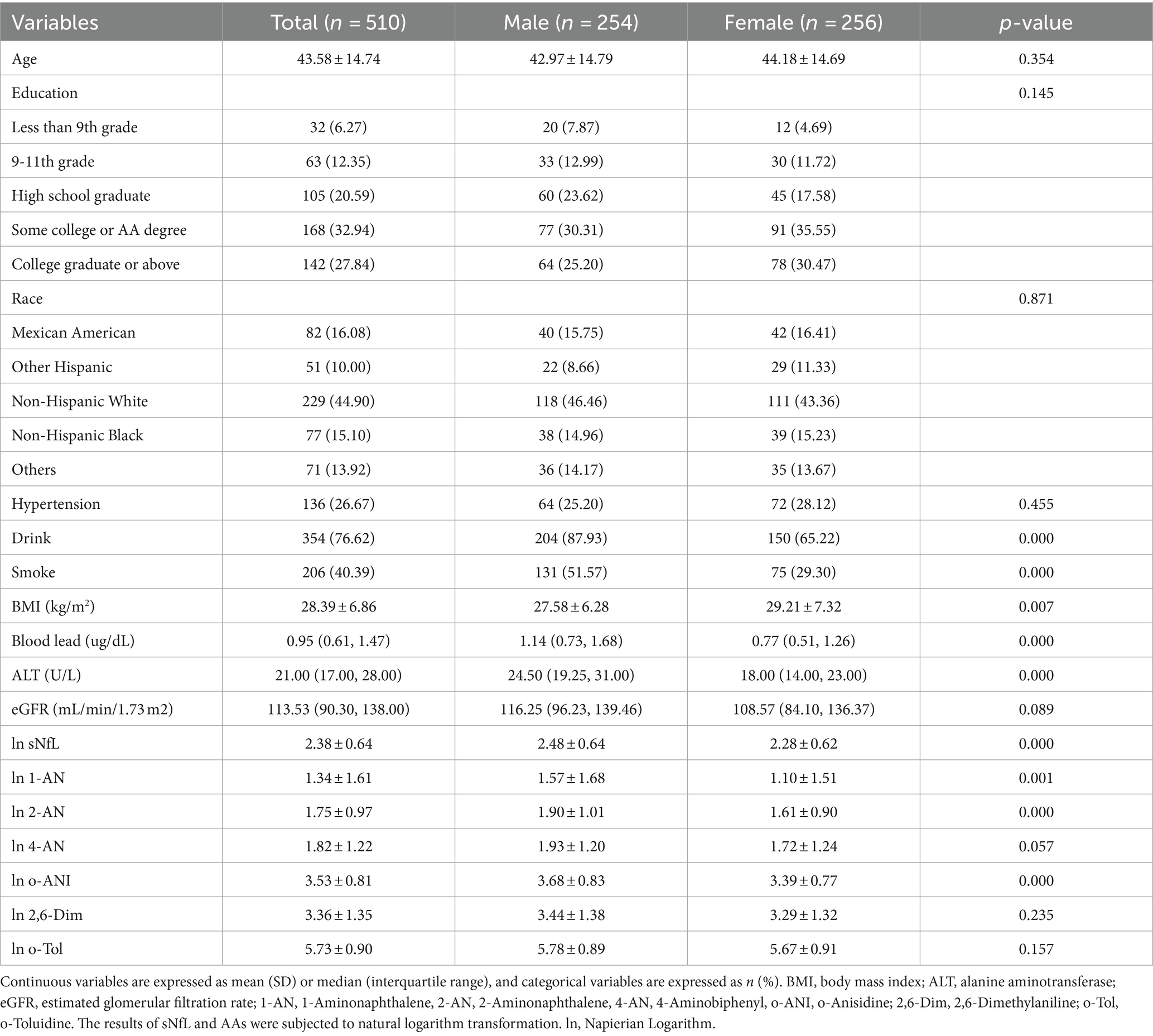
Results: In total, 510 adult participants with an average age of 43.58 ± 14.74 years were included in the study. Our findings indicate that, based on univariate linear regression and between-group comparative analyses, 1-Aminonaphthalene (1-AN), 2-Aminonaphthalene (2-AN), 4-Aminobiphenyl (4-AN) and o-Anisidine (o-ANI) showed a positive correlation with serum neurofilament light chain (P < 0.05). However, multiple linear regression analysis revealed that only 2-AN exhibited a positive correlation with serum neurofilament light chain (P < 0.05), while the correlations of other compounds with serum neurofilament light chain became non-significant.
Conclusion: Although our cross-sectional study fails to establish causal relationships or determine clinical significance, the findings indicate a potential association between adult exposure to AAs, notably 2-AN, and nerve damage. Consequently, further research is needed to explore the connection between AAs exposure, sNfL, and neurological conditions in adults.
Background
Aromatic amines (AAs) are a category of organic compounds characterized by the presence of a benzene ring and amino functional groups. These compounds are widely found in various industrial products, including dyes and pigments (such as azo dyes and indigo dyes), pharmaceuticals, pesticides, herbicides, synthetic rubber, plastics (1) and even be released during the cooking process of edible oils (2). Aromatic amines can enter the human body through inhalation, skin contact, or ingestion.
However, a significant concern associated with aromatic amines is their presence in tobacco smoke. Tobacco smoke is a complex mixture containing thousands of compounds, including over 60 known carcinogens, some of which are aromatic amines (3). People can be exposed to aromatic amines by inhaling tobacco smoke, using tobacco-related products (such as smoking or chewing tobacco), or being exposed to secondhand smoke (the smoke released by others who are smoking) (4). The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has established a roster of harmful and potentially harmful constituents (HPHCs) found in tobacco products and tobacco smoke. Among these, aromatic amines, including 1-aminonaphthalene (1-AN), 2-aminonaphthalene (2-AN), and 4-aminobiphenyl (4-AN), have been included on the FDA’s HPHC list (5). Moreover, the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) has categorized 2-aminonaphthalene, 4-aminobiphenyl, and o-toluidine (o-TOL) as Group 1 carcinogens due to their association with the development of various malignant tumors (6). Aromatic amines are primarily metabolized in the liver, subsequently entering the bladder and ultimately being excreted through urine. Extensive research has established the genotoxic mechanisms of aromatic amines, particularly in relation to DNA adduct formation and mutagenesis (7). Occupational exposure to aromatic amines has been demonstrated to significantly elevate the risk of bladder cancer (8, 9). Furthermore, certain animal experiments have suggested that 2-acetylaminofluorene, a constituent of aromatic amines, can instigate hepatocarcinogenesis in mice (10).
Serum neurofilament light chain (sNfL) is a major cytoskeletal protein of neuronal axons, often referred to as one of the subunits of neuronal neurofilaments (NF), which are structural proteins in neurons playing a crucial role in maintaining the morphology and function of neurons; sNfL, being a constituent of NFs, is typically released into the bloodstream in only minimal amounts under normal physiological conditions (11). However, when neurons are subjected to damage or in cases of neurodegenerative diseases that result in neuronal injury, there is a significant increase in the release of sNfL. Therefore, measuring sNfL levels in serum can serve as a non-specific biomarker for neuronal injury. This has significant value in the diagnosis, disease progression monitoring, and prognosis assessment of neurological conditions such as neurodegenerative diseases [e.g., Alzheimer’s disease (12), Parkinson’s disease (13), multiple sclerosis (14), ischemic stroke (15)]. Elevated serum sNfL levels can reflect the extent and progression of neuronal damage, making it useful for assessing disease severity, predicting the trajectory of the disease, and monitoring treatment efficacy (16).
Regrettably, there is currently no existing research examining the connection between AAs levels and adult neurological function. To address this gap, we have obtained accessible data on urinary AAs metabolites and serum sNfL from the 2013–2014 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). The primary objective of this study is to investigate the potential relationship between AAs exposure and serum sNfL levels within a demographically representative sample of the U.S. population.
Materials and methods
Ethical statement
The NHANES protocol received authorization from the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), US and written informed consent was obtained from all participants upon admission. The Ethics Review Committee of Ningbo Medical Center Lihuil Hospital concluded that the study was exempt from ethical review since it utilized de-identified data that was publicly accessible.
Study population
The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) in the United States is a nationwide survey that recruits a representative sample of citizens every 2 years. Detailed survey methods and participant consent forms can be found on the NHANES website (https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/). In NHANES 2013–2014, a total of 10,175 participants were involved. Urinary AAs metabolites were measured in participants aged 6 years and older. sNfL were assessed in participants aged 20 to 75 years, with a total of 2,071 valid samples. Data is available for 510 study subjects for variables common to both datasets, excluding those with diseases known to cause elevated sNfL levels, such as depression (17), dementia (18), stroke (19), and diabetes (20), which were identified through the NHANES questionnaire. Depressive symptoms were measured using the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9), with a score of ≥10 indicating depression. Dementia was identified through cognitive function tests, and stroke was determined via a questionnaire. The workflow is illustrated in Figure 1.
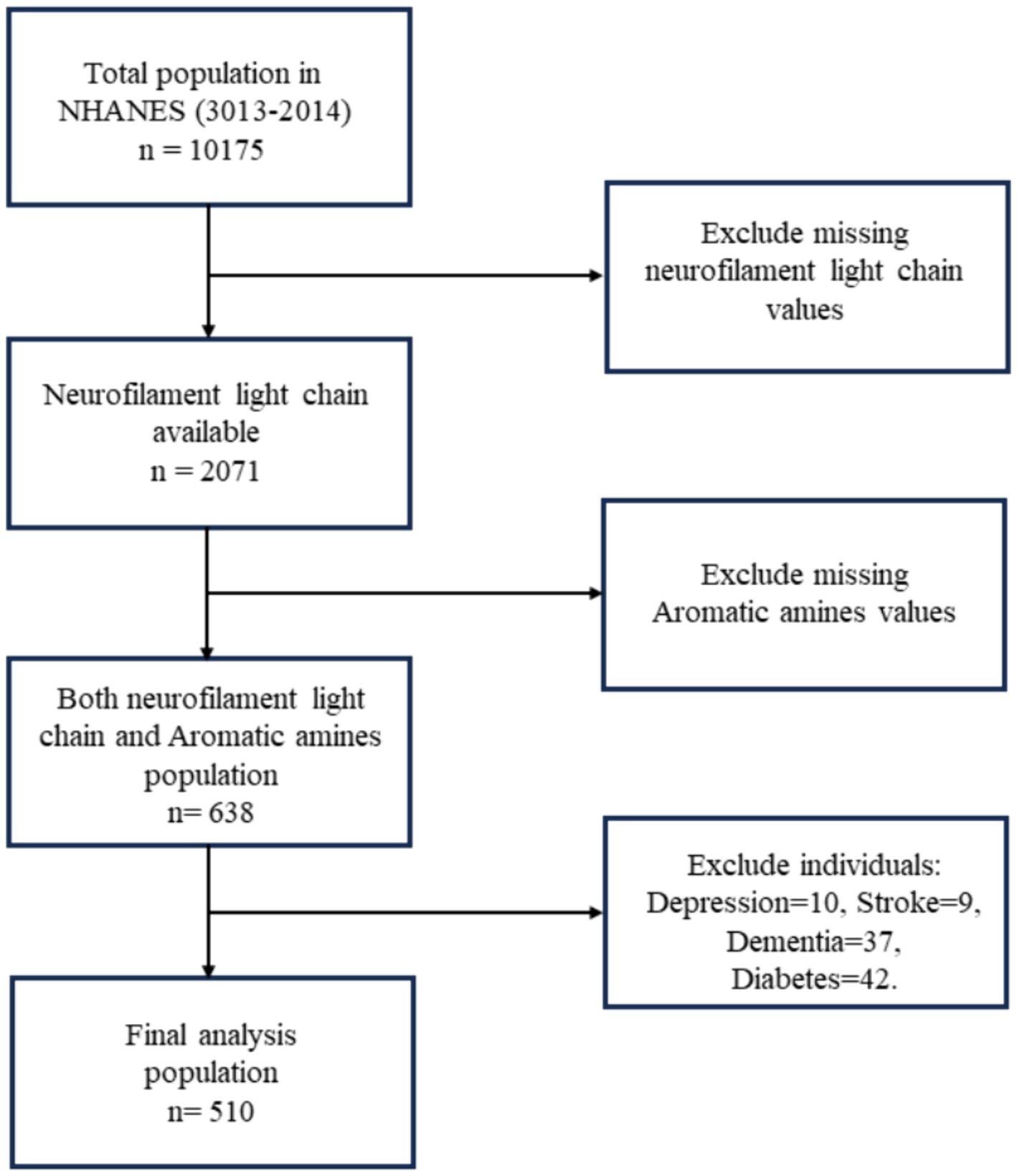
Figure 1. Flowchart algorithm for study population inclusion (National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, NHANES).
Measurement of urine aromatic amines metabolites
NHANES 2013–2014 database contains six urinary aromatic amines metabolites: 1-Aminonaphthalene (1-AN), 2-Aminonaphthalene (2-AN), 4-Aminobiphenyl (4-AN), o-Anisidine (o-ANI), 2,6-Dimethylaniline (2,6-Dim), and o-Toluidine (o-Tol). Aromatic amines are quantified using a precise method involving isotope-dilution gas chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry (ID GC–MS/MS). Urine samples are collected and stored at approximately −70°C. Internal standards are added, and the samples undergo hydrolysis, cleanup, and extraction. Analytes are then derivatized and analyzed by GC/MS/MS with multiple reaction monitoring (MRM). Details regarding the urinary aromatic amines metabolites detection method can be accessed on the homepage (https://wwwn.cdc.gov/Nchs/Nhanes/2013-2014/AA_H.htm).
Measurement of sNfL
In NHANES 2013–2014, serum sNfL levels were measured using a highly sensitive immunoassay system developed by Siemens Healthineers. The analytical method utilizes acridinium ester (AE) chemiluminescence and paramagnetic particles on the Attelica platform. This involves incubating the sample with AE-labeled antibodies that bind to the sNfL antigen. Paramagnetic particles coated with capture antibodies are then added to form antigen–antibody complexes. After removing unbound AE-labeled antibodies, chemiluminescence is initiated with acid and base, and light emission is measured. This process is fully automated on the Attelica immunoassay system. Details regarding the urinary aromatic amines metabolites detection method can be accessed on the homepage (https://wwwn.cdc.gov/Nchs/Nhanes/2013-2014/SSSNFL_H.htm).
Covariates
We systematically examined a wide array of demographic attributes, encompassing age, gender, race/ethnicity, educational level, smoking habits, alcohol consumption, and a medical history encompassing hypertension. These extensive data points were collected through structured family interviews utilizing standardized questionnaires. In terms of race/ethnicity, participants were categorized into groups recommended by NHANES, which included Mexican American, other Hispanic, non-Hispanic white, non-Hispanic black, and other races (including multi-racial). Educational attainment was classified into three levels: below high school, high school, and above high school. Smoking status was defined as having smoked at least 100 cigarettes during one’s lifetime. Alcohol consumption was determined by a positive response to the question, “In any 1 year, have you had at least 12 drinks of any type of alcoholic beverage?” Body mass index (BMI) was calculated as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared (kg/m2) during the physical examination. Biochemical measures, including alanine aminotransferase (ALT), blood lead levels in the blood sample, were quantified through laboratory analysis and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) (21) calculated from serum creatinine.
Statistical analysis
Due to the non-normal distribution of aromatic amine metabolites and sNfL levels, natural logarithms of these two variables were employed in our analyses. Sampling weights were used based on the methods recommended on the NHANES website. Continuous variables are presented as means [standard deviation (SD)] or medians (interquartile range, IQR), while categorical variables are presented as frequencies or percentages (n, %). Chi-squared tests were used to analyze categorical variables, and Student’s two-tailed t test or Mann–Whitney U tests were used to assess descriptive variable differences between different genders. In the general linear model for our sample (model 1), sNfL was considered the dependent variable, and aromatic amine metabolites were treated as independent variables, categorized into three groups for inter-group comparisons. In multivariate linear regression models, an extended model approach was employed for covariate adjustments. Model 2 included age, gender, ethnicity, BMI, smoking, and drinking status. Model 3 further adjusted for the presence of chronic conditions such as hypertension. Model 4, built on model 3, additionally incorporated biochemical indicators. Subsequent to the statistical significance observed in models 2 and 3 for the metabolite 2-AN, subgroup analyses and discussions were conducted.
All analyses were conducted using R 4.0.5 statistical software (The R Foundation) and GraphPad Prism 8.0. A two-sided value of p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Participant characteristics
A total of 510 adults were included (mean age 43.58 ± 14.74 years), with 256 (50.20%) being female. Participant characteristics are summarized by gender in Table 1. The average ages of males and females were 42.97 ± 14.79 years and 44.18 ± 14.69 years, respectively. In comparison to the male group, there were no significant differences in education level, ethnicity, or the presence of chronic conditions hypertension in the female group (p > 0.05). Notably, the female group had a higher BMI (29.21 ± 7.32) compared to the male group (27.58 ± 6.28), and the proportion of alcohol intake and smoking was higher in males (87.93% vs. Sixty five.22 and 51.57% vs. 29.30%, respectively). Additionally, there were differences in blood lead and liver function between the male and female groups (p < 0.05). sNfL levels and urinary levels of 1-AN, 2-AN and o-ANI were higher in the male group (p < 0.05).
Univariate linear regression analyses
As shown in Table 2, model 1 indicates that in univariate linear regression analysis, there was a positive correlation between sNfL and urinary 1-AN, 2-AN, 4-AN, and o-ANI (β values of 0.055, 0.100, 0.052, and 0.147, respectively, p < 0.05). Furthermore, the trend analysis of three-class concentration gradients of aromatic amine compounds indicated that as the concentrations of 1-AN, 4-AN, and o-ANI increased, sNfL levels also increased correspondingly (p < 0.05, Figure 2).

Table 2. Linear regression coefficients (standard error) of ln-serum neurofilament light chain with a unit increase in ln-urine aromatic amine metabolites in multiple linear regression models, with results weighted for sampling strategy.
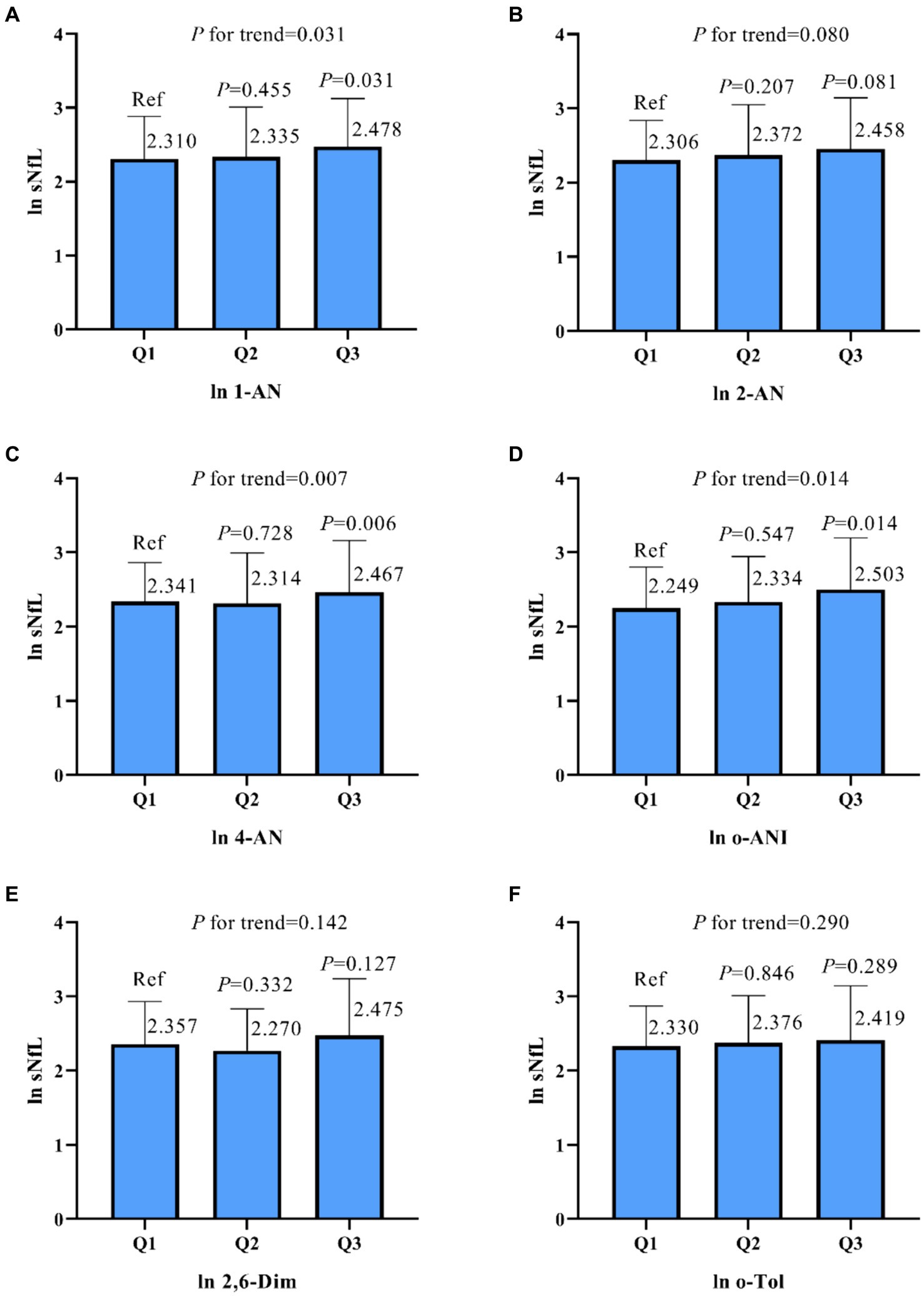
Figure 2. Based on the results of a univariate linear regression, urine samples were classified into three groups based on the concentration of aromatic amines (AAs), and the relationship between the concentration in these groups and the neurofilament light chain (sNfL) was compared. The results for sNfL and AAs were subjected to natural logarithm transformation, and the analysis was conducted using a weighted strategy. Panel (A) represents the association between 1-Aminonaphthalene (1-AN) and sNfL, (B) shows the relationship for 2-Aminonaphthalene (2-AN), (C) for 4-Aminobiphenyl (4-AN), (D) for o-Anisidine (o-ANI), (E) for 2,6-Dimethylaniline (2,6-Dim), and (F) for o-Toluidine (o-Tol). P-values and trends are indicated for each panel. ln, natural logarithm.
Multivariable linear regression analyses
In model 2, additional variables such as age, gender, ethnicity, BMI, smoking status, and drinking status were included, causing the previously observed correlations of 1-AN and 4-AN with sNfL to disappear. However, 2-AN and o-ANI still exhibited a positive correlation (p < 0.05, Table 2). In model 3, after further adjusting for covariate parameters and including the underlying condition of hypertension from model 2, the positive correlation between 2-AN, o-ANI, and sNfL persisted (p < 0.05, Table 2). In model 4, after additional adjustments for biochemical indicators (blood lead levels, ALT, and eGFR) based on model 3, 2-AN still showed a positive correlation with sNfL (p = 0.038, Table 2).
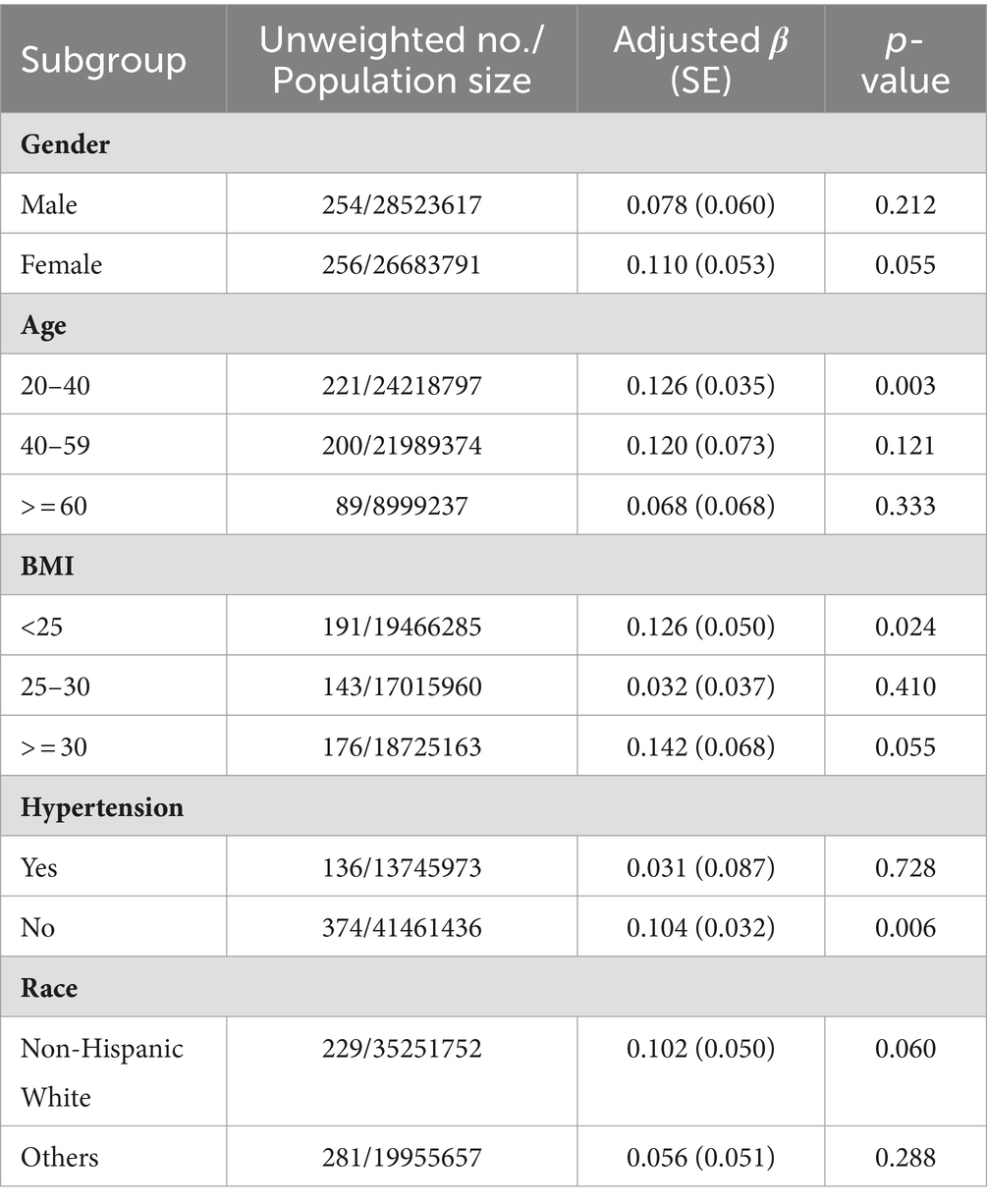
Subgroup analysis of 2-AN
Models 1, 2, 3 and 4 consistently showed a positive correlation between 2-AN and sNfL. Subgroup analysis was therefore conducted for 2-AN. The regression coefficient (S.E.) for sNfL per unit increase in ln 2-AN is presented in Table 3. The analysis revealed that as 2-AN level increased, average sNfL levels increased in subgroups of individuals aged 20–40, BMI <25 kg/m2, those without hypertension (Table 3).
Discussion
Serum neurofilament light chain (sNfL) is a structural protein of neuronal cells that is released into the bloodstream during neurological damage or disease (11). It is commonly regarded as a biomarker for neuronal injury, and current research indicates its abnormal increase in conditions such as depression (17), dementia (18), stroke (19). Studies have shown a positive correlation between sNfL levels in the general US population and mortality rates (22). Aromatic amine compounds, common in daily life and production, can enter the body through inhalation, skin contact, or ingestion, but their relationship with sNfL has not been reported.
Therefore, we investigated the relationship between aromatic amine compounds and sNfL using data from the NHANES database, excluding individuals with neurological diseases including depression, dementia, stroke to ensure the accuracy of our findings. Additionally, studies have demonstrated significantly elevated levels of serum neurofilament light chain in diabetic patients, a phenomenon relatively uncommon in non-diabetic populations (20). Considering diabetes itself as a potential confounding factor, we excluded diabetic patients from our study. Our research shows a significant correlation between the concentration of the urinary metabolite 2-aminonaphthalene (2-AN) and serum neurofilament light chain (sNfL) levels. While single-factor linear regression showed a positive correlation between several aromatic amine compounds, including 1-AN, 2-AN, 4-AN, and o-ANI, with sNfL, this association disappeared after conducting a multiple-factor linear regression. However, multiple models consistently indicated a statistically significant relationship between 2-AN and serum neurofilament light chain.
In subgroup analysis, the correlation between 2-AN and sNfL appears significant among individuals with hypertension. While direct research reports on the correlation between hypertension and sNfL are lacking, it is plausible that similar underlying factors May be involved. Hypertension could induce biochemical and metabolic alterations that might affect sNfL levels, potentially influencing the association between aromatic amines and sNfL. Nevertheless, further comprehensive research is needed to validate this relationship. Furthermore, in the age group of 20–40, specific factors May contribute to a more pronounced correlation between aromatic amine and neurofilament light chain. These factors include a lower incidence of chronic diseases, a higher risk of exposure to aromatic amines in the work environment, and a higher rate of smoking (23). These factors May lead to prolonged exposure to aromatic amines and consequently result in a significant correlation between 2-AN and sNfL.
This is the first study to establish a link between aromatic amine compounds and biomarkers of adult neurologic injury, suggesting a potential association between aromatic amine compounds and neurological health in adults. Nevertheless, it remains unclear whether elevated sNfL due to 2-AN is clinically significant in terms of neurological diseases. This linear relationship suggests a close connection between the elevation of the metabolic product of aromatic amine 2-AN and the increase in sNfL.
Serum neurofilament light chain is typically used as a biomarker for assessing neurological damage (16). Neurofilaments are the most abundant proteins in mature myelinated axons, comprising light, medium, and heavy chains. Following nerve axon injury, neurofilaments are released into the bloodstream and cerebrospinal fluid (11). Due to their high solubility, sNfL has been recognized as a novel biomarker for several neurologic disorders, including Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis and cerebrovascular events (12–15). The levels of sNfL are also associated with the severity of multiple sclerosis and Alzheimer’s disease (24, 25). It is worth noting that there is currently no established threshold level of sNfL that leads to adult neurological injury. Therefore, this elevation May reflect the impact of 2-AN on the nervous system, potentially causing stress or damage to the nervous system, resulting in an increased release of neurofilament light chains. Aromatic amines are substances released in tobacco smoke, and studies have shown that smoking or exposure to secondhand smoke increases the risk of stroke and dementia (26, 27). However, the specific pathogenic mechanism or the substance in tobacco responsible for these effects is not yet clear.
Regrettably, there has been a lack of reported findings regarding the impact or damage to the nervous system associated with aromatic amine compounds. However, we can propose some possible pathological mechanisms. Aromatic amine compounds are primarily metabolized in the liver and then excreted through urine. During the metabolism process, they May form some metabolic products, where the amine functional groups May undergo acetylation or glucuronidation, or they May oxidize into hydroxylamine forms, which can further transform into N-acetyloxy metabolites through acetylation. These N-acetyloxy metabolites May break down, generating highly reactive nitrogen ions, nitroso groups, or free radicals, which can react with large molecules (such as proteins) and DNA in tissues to form adducts (28, 29). These free radicals May play a crucial role in neurological damage and disease. Free radicals are highly reactive molecules that can be generated through various cellular pathways, including oxygen free radicals and nitrogen free radicals. When free radical production is excessive, it May lead to oxidative stress, triggering the pathogenesis of brain injury, ischemia, and other neurological disorders (30, 31).
Furthermore, the characteristics of aromatic amine compounds, such as molecular size, polarity, charge, and lipophilicity, May influence whether they can pass through the blood–brain barrier. Some small and lipophilic aromatic amines May more easily penetrate the blood–brain barrier, which May directly lead to damage to the nervous system (32, 33).
Regarding the metabolism of aromatic amine 2-AN, it is typically carried out by the cytochrome P450 enzyme family. Research has found that 2-aminonaphthalene May significantly reduce the cytochrome P-450 o-demethylation activity in liver microsomes (34). These CYP450 enzymes May have various functions in the nervous system, including influencing the synthesis and degradation of neurotransmitters, thereby affecting neural signal transmission (35). Additionally, CYP450 enzymes May also be involved in the synthesis of neuroprotective substances to combat neurodegenerative diseases (36). For example, the CYP46A1 enzyme (a type of CYP450) can catalyze the hydrolysis of cholesterol in the brain, generating a neuroprotective substance with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and apoptosis-regulating properties (37). However, 2-AN may reduce the activity of these enzymes, leading to a weakening of their bioactive functions, resulting in neural dysfunction. These factors May be related to neurological injury and diseases but require further research for clarification.
This study has several limitations. Firstly, the sample size is limited as only NfL data from NHANES 2013–2014 are available, which limits the ability to conduct a comprehensive analysis and increase the credibility of the research results. Secondly, this is a cross-sectional study, so we cannot infer causality. Thirdly, we did not include other pollutants that May co-expose with aromatic amines or potentially significant confounding factors. For instance, heterocyclic aromatic amines (HAAs) are compounds containing nitrogen atoms in a heterocyclic aromatic structure, where an amino group (-NH₂) or substituted amino groups (-NHR, -NR₂) are attached to the aromatic ring. HAAs differ significantly in structure and sources from aromatic amines. They are primarily formed during the high-temperature cooking of meat and can enter the body through ingestion, known for their carcinogenic and neurotoxic effects (38, 39). Although there is currently a lack of research linking HAAs to serum neurofilament light chain levels, their neurotoxicity has been established, which could potentially confound study outcomes. Fourthly, our study population consists of American adults, so we cannot assume that this finding applies to other age groups or other countries.
Conclusion
While this is a cross-sectional study and causal relationships cannot be inferred, and clinical significance remains uncertain, our study results suggest that exposure to AAs in adults, particularly 2-AN, May potentially lead to nerve damage. Thus, further research is warranted to investigate the relationship between AAs exposure, sNfL, and neurological diseases in adults.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
Ethics statement
Ethical approval was not required for the study involving humans in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent to participate in this study was not required from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and the institutional requirements.
Author contributions
TL: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. HM: Writing – review & editing. SH: Writing – review & editing, Formal analysis. JC: Writing – review & editing, Data curation.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Medical and Health Science and Technology Project of Zhejiang Province (2023KY242).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpubh.2024.1344087/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Pereira, L, Mondal, PK, and Alves, M. Aromatic amines sources, environmental impact and remediation In: E Lichtfouse, J Schwarzbauer, and D Robert, editors. Pollutants in buildings, water and living organisms. Environmental chemistry for a sustainable world. Cham: Springer International Publishing (2015). 297–346.
2. Tai-An chiang,, wu pei-fen,, Liao su ying,, Li-Fang Wang,, and chin ko,. Mutagenicity and aromatic amine content of fumes from heated cooking oils produced in Taiwan. Food Chem Toxicol. (1999) 37:125–34. doi: 10.1016/s0278-6915(98)00081-7
3. Ji, H, and Jin, Z. Analysis of six aromatic amines in the mainstream smoke of tobacco products. Anal Bioanal Chem. (2022) 414:4227–34. doi: 10.1007/s00216-022-04075-7
4. Stabbert, R, Schäfer, KH, Biefel, C, and Rustemeier, K. Analysis of aromatic amines in cigarette smoke. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrometry. (2003) 17:2125–32. doi: 10.1002/rcm.1161
5. Products C for T. Reporting harmful and potentially harmful constituents in tobacco products and tobacco smoke under section 904(a)(3) of the Federal Food, drug, and cosmetic act. (2020). Available at: https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/reporting-harmful-and-potentially-harmful-constituents-tobacco-products-and-tobacco-smoke-under (Accessed October 1, 2023).
6. Humans IWG on the E of CR to. IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risk to Humans. Some aromatic amines, organic dyes, and related exposures. IARC monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans. Volume 99. Lyon (2010). Available at: https://publications.iarc.fr/Book-And-Report-Series/Iarc-Monographs-On-The-Identification-Of-Carcinogenic-Hazards-To-Humans/Some-Aromatic-Amines-Organic-Dyes-And-Related-Exposures-(2010)
7. Bartsch, H, Malaveille, C, Friesen, M, Kadlubar, FF, and Vineis, P. Black (air-cured) and blond (flue-cured) tobacco cancer risk. IV: molecular dosimetry studies implicate aromatic amines as bladder carcinogens. Eur J Cancer. (1993) 29:1199–207. doi: 10.1016/s0959-8049(05)80315-6
8. Gawrych, KG, Pesch, R, Weiss, C, Rihs, A, and Bueno-de-Mesquita, R Kaaks, et al. 62 occupational exposure to aromatic amines and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and bladder cancer: results from the EPIC cohort. Occup Environ Med. (2013) 70:A21.1–A21. doi: 10.1136/oemed-2013-101717.62
9. Pira, E, Piolatto, G, Negri, E, Romano, C, Boffetta, P, Lipworth, L, et al. Bladder Cancer mortality of workers exposed to aromatic amines: a 58-year follow-up. JNCI J Natl Cancer Inst. (2010) 102:1096–9. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djq214
10. Neumann, H-G. Aromatic amines in experimental cancer research: tissue-specific effects, an old problem and new solutions. Crit Rev Toxicol. (2007) 37:211–36. doi: 10.1080/10408440601028603
11. Gaetani, L, Blennow, K, Calabresi, P, di Filippo, M, Parnetti, L, and Zetterberg, H. Neurofilament light chain as a biomarker in neurological disorders. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. (2019) 90:870–81. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2018-320106
12. Chatterjee, P, Pedrini, S, Ashton, NJ, Tegg, M, Goozee, K, Singh, AK, et al. Diagnostic and prognostic plasma biomarkers for preclinical Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. (2022) 18:1141–54. doi: 10.1002/alz.12447
13. Mollenhauer, B, Dakna, M, Kruse, N, Galasko, D, Foroud, T, Zetterberg, H, et al. Validation of serum Neurofilament light chain as a biomarker of Parkinson’s disease progression. Mov Disord. (2020) 35:1999–2008. doi: 10.1002/mds.28206
14. Benkert, P, Meier, S, Schaedelin, S, Manouchehrinia, A, Yaldizli, Ö, Maceski, A, et al. Serum neurofilament light chain for individual prognostication of disease activity in people with multiple sclerosis: a retrospective modelling and validation study. Lancet Neurol. (2022) 21:246–57. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(22)00009-6
15. Pekny, M, Wilhelmsson, U, Stokowska, A, Tatlisumak, T, Jood, K, and Pekna, M. Neurofilament light chain (NfL) in blood-a biomarker predicting Unfavourable outcome in the acute phase and improvement in the late phase after stroke. Cells. (2021) 10:1537. doi: 10.3390/cells10061537
16. Khalil, M, Teunissen, CE, Otto, M, Piehl, F, Sormani, MP, Gattringer, T, et al. Neurofilaments as biomarkers in neurological disorders. Nat Rev Neurol. (2018) 14:577–89. doi: 10.1038/s41582-018-0058-z
17. Bavato, F, Cathomas, F, Klaus, F, Gütter, K, Barro, C, Maceski, A, et al. Altered neuroaxonal integrity in schizophrenia and major depressive disorder assessed with neurofilament light chain in serum. J Psychiatr Res. (2021) 140:141–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2021.05.072
18. Gu, L, Shu, H, Wang, Y, and Wang, P. Blood Neurofilament light chain in different types of dementia. Curr Alzheimer Res. (2023) 20:149–60. doi: 10.2174/1567205020666230601123123
19. Dhana, A, DeCarli, C, Aggarwal, NT, Dhana, K, Desai, P, Evans, DA, et al. Serum neurofilament light chain, brain infarcts, and the risk of stroke: a prospective population-based cohort study. Eur J Epidemiol. (2023) 38:427–34. doi: 10.1007/s10654-023-00978-6
20. Ciardullo, S, Muraca, E, Bianconi, E, Cannistraci, R, Perra, S, Zerbini, F, et al. Diabetes mellitus is associated with higher serum Neurofilament light chain levels in the general US population. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2023) 108:361–7. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgac580
21. Cockcroft, DW, and Gault, MH. Prediction of creatinine clearance from serum creatinine. Nephron. (1976) 16:31–41. doi: 10.1159/000180580
22. Ciardullo, S, Muraca, E, Bianconi, E, Ronchetti, C, Cannistraci, R, Rossi, L, et al. Serum neurofilament light chain levels are associated with all-cause mortality in the general US population. J Neurol. (2023) 270:3830–8. doi: 10.1007/s00415-023-11739-6
23. Reitsma, MB, Flor, LS, Mullany, EC, Gupta, V, Hay, SI, and Gakidou, E. Spatial, temporal, and demographic patterns in prevalence of smoking tobacco use and initiation among young people in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019. Lancet Public Health. (2021) 6:e472–81. doi: 10.1016/S2468-2667(21)00102-X
24. Disanto, G, Barro, C, Benkert, P, Naegelin, Y, Schädelin, S, Giardiello, A, et al. Serum Neurofilament light: a biomarker of neuronal damage in multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol. (2017) 81:857–70. doi: 10.1002/ana.24954
25. Preische, O, Schultz, SA, Apel, A, Kuhle, J, Kaeser, SA, Barro, C, et al. Serum neurofilament dynamics predicts neurodegeneration and clinical progression in presymptomatic Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Med. (2019) 25:277–83. doi: 10.1038/s41591-018-0304-3
26. Zhou, S, and Wang, K. Childhood secondhand smoke exposure and risk of dementia, Alzheimer’s disease and stroke in adulthood: a prospective cohort study. J Prev Alzheimers Dis. (2021) 8:1–6. doi: 10.14283/jpad.2021.10
27. Markidan, J, Cole, JW, Cronin, CA, Merino, JG, Phipps, MS, Wozniak, MA, et al. Smoking and risk of ischemic stroke in young men. Stroke. (2018) 49:1276–8. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.117.018859
28. Riedel, K, Scherer, G, Engl, J, Hagedorn, H-W, and Tricker, AR. Determination of three carcinogenic aromatic amines in urine of smokers and nonsmokers. J Anal Toxicol. (2006) 30:187–95. doi: 10.1093/jat/30.3.187
29. Talaska, G, and Al-Zoughool, M. Aromatic amines and biomarkers of human exposure. J Environ Sci Health C Environ Carcinog Ecotoxicol Rev. (2003) 21:133–64. doi: 10.1081/GNC-120026234
30. Lewén, A, Matz, P, and Chan, PH. Free radical pathways in CNS injury. J Neurotrauma. (2000) 17:871–90. doi: 10.1089/neu.2000.17.871
31. Holecek, V, Racek, J, Trefil, L, and Rokyta, R. Free radicals and antioxidants in cerebrospinal fluid in central nervous system diseases. Cesk Fysiol. (2002) 51:129–32. doi: 10.1039/p19910002039
32. Vogt, PF, and Gerulis, JJ. Amines, aromatic. Ullmann’s Encycl Ind Chem. (2000). doi: 10.1002/14356007.a02_037
33. Tong, X, Wang, D, Ding, X, Tan, X, Ren, Q, Chen, G, et al. Blood-brain barrier penetration prediction enhanced by uncertainty estimation. J Cheminform. (2022) 14:44. doi: 10.1186/s13321-022-00619-2
34. Unger, M, Andersen, O, and Clausen, J. Effect of 2-aminonaphthalene on glutathione content and cytochrome P-450 p-nitroanisole O-demethylation activity in mouse liver. Cancer Res. (1977) 37:1264–5.
35. Dutheil, F, Beaune, P, and Loriot, M-A. Xenobiotic metabolizing enzymes in the central nervous system: contribution of cytochrome P450 enzymes in normal and pathological human brain. Biochimie. (2008) 90:426–36. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2007.10.007
36. Navarro-Mabarak, C, Camacho-Carranza, R, and Espinosa-Aguirre, JJ. Cytochrome P450 in the central nervous system as a therapeutic target in neurodegenerative diseases. Drug Metab Rev. (2018) 50:95–108. doi: 10.1080/03602532.2018.1439502
37. Petrov, AM, and Pikuleva, IA. Cholesterol 24-hydroxylation by CYP46A1: benefits of modulation for brain diseases. Neurotherapeutics. (2019) 16:635–48. doi: 10.1007/s13311-019-00731-6
38. Syeda, T, and Cannon, JR. Potential role of heterocyclic aromatic amines in neurodegeneration. Chem Res Toxicol. (2022) 35:59–72. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.1c00274
Keywords: aromatic amines, 2-Aminonaphthalene, serum neurofilament light chain, NHANES, nerve injury
Citation: Lin T, Mao H, Huang S and Chen J (2024) Association between aromatic amines and serum neurofilament light chain as a biomarker of neural damage: a cross-sectional study from NHANES. Front. Public Health. 12:1344087. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1344087
Edited by:
Mohiuddin Md. Taimur Khan, Washington State University Tri-Cities, United StatesReviewed by:
Marwa Kh. Mohammed, Assiut University, EgyptBang-Tun Zhao, Luoyang Normal University, China
Adil Dalaf, Tikrit University, Iraq
T. M. Rangarajan, University of Delhi, India
Copyright © 2024 Lin, Mao, Huang and Chen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Tong Lin, a2FpODkzQGZveG1haWwuY29t
 Tong Lin
Tong Lin Haiyan Mao
Haiyan Mao Shanshan Huang
Shanshan Huang