
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
SYSTEMATIC REVIEW article
Front. Psychiatry , 24 March 2025
Sec. Mood Disorders
Volume 16 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1558505
Background: Xiaoyao Powder/Pill, as a classical Chinese herbal formula, has been widely used for treating depression. This meta-analysis aims to evaluate the effectiveness of Xiaoyao formula (XYF) as an adjuvant therapy for treating postpartum depression.
Methods: We searched studies indexed in international databases (Cochrane Library, Embase, and PubMed) and Chinese databases (SinoMed, CNKI, and Wanfang). Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) assessing the efficacy of XYF in combination with Western therapy compared to Western therapy alone for treating postpartum depression were eligible. The total response rate was defined as a reduction of more than 25% in depression scores, while clinical recovery was defined as a reduction of more than 75% in depression scores.
Results: Our analysis included ten RCTs comprising 810 women. The combination of XYF and Western therapy led to a significant improvement in the total response rate (risk ratios [RR] 1.17; confidence intervals [CI] 1.08-1.26) and the clinical recovery rate (RR 1.56; 95% CI 1.27-1.91) compared to Western therapy alone. Additionally, XYF as an adjuvant therapy also significantly decreased Hamilton Depression Scale scores (standard mean difference [SMD] -1.69; 95% CI -2.37 to -1.01).
Conclusions: Adjuvant treatment with XYF can effectively alleviate depression in postpartum women. However, further well-designed RCTs are necessary to validate these findings, as the current evidence remains uncertain.
Postpartum depression are serious mental illnesses that can affect women after giving birth. Around 17% of healthy delivery women who have no history of depression experience postpartum depression (1). If left untreated, this condition can disrupt the bonding between mother and child and create difficulties within the family. While psychotherapy and antidepressant medication are commonly recommended as initial treatments, some women with severe postpartum depression do not respond well to these approaches (2). Additionally, antidepressant medication can lead to unnecessary adverse reactions. Given the harmful consequences associated with postpartum depression (3), there is a clear need to develop additional therapies to better manage this condition.
Xiaoyao powder/pill, also known as Free and Easy Wanderer Powder, is a well-known Chinese herbal remedy that has gained attention for its potential to alleviate mood disorders, including postpartum depression (4). This prescription is composed of a combination of herbal ingredients, including Radix Paeoniae Alba, Radix Angelicae Sinensis, Herba Menthae, Radix Bupleuri, White Poria, Rhizoma Atractylodis Macrocephalae, Radix Glycyrrhizae Praeparata, and Rhizoma Zingiberis Recens. According to Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), this combination of herbs is believed to regulate the liver, soothe emotional distress, and harmonize the balance of Qi and blood, which are central concepts in treating mood disorders. Emerging research suggests that Xiaoyao formula (XYF) may help alleviate depressive symptoms by regulating neurotransmitters (such as serotonin, dopamine, and gamma-aminobutyric acid), the HPA axis, synaptic plasticity, inflammation, brain-derived neurotrophic factor, and the brain-gut axis (5). While several randomized clinical trials (RCTs) (6–11) have shown promising results when XYF was used in conjunction with Western therapy to alleviate depressive symptoms in postpartum women. However, there remains a lack of robust evidence due to the small sample sizes in these studies.
A recently published systematic review with meta-analysis has demonstrated that modified Xiaoyao powder, when used alone or in conjunction with Western therapy, could effectively reduce depressive symptoms in postpartum depression (12). However, this well-designed study did not differentiate between the original and modified Xiaoyao powder. Notably, the application of modified Xiaoyao powder poses significant challenges for non-TCM practitioners. This meta-analysis aims to synthesize the available evidence from RCTs to evaluate the effectiveness of XYF as an adjuvant therapy for treating postpartum depression.
We followed the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses guideline (13) to report the current study. The study analyzed data from individual studies and did not require ethical approval. We searched for articles indexed in international databases (Cochrane Library, Embase, and PubMed) and Chinese databases (SinoMed, CNKI, and Wanfang) from their inception to August 12, 2024, using the following terms (Supplementary Text S1): (“xiao yao” OR “Xiaoyao” OR “Shiau-Yau San”) AND (“postpartum depression” OR “postnatal depression”) AND (“controlled”) AND (“random”). We also manually reviewed the reference lists of the eligible RCTs for any potentially missing trials.
Eligible studies met the following criteria: 1) Participants: women diagnosed with postpartum depression (based on the Hamilton Depression Scale [HAMD] or other valid international depression scales); 2) Intervention: XYF in combination with Western therapy; 3) Comparison: Western therapy alone; 4) Outcomes: total response rate, clinical recovery rate, and changes in postpartum depression scores; and 5) Study design: RCTs. The total response rate was defined as a reduction of more than 25% in depression scores, while a clinical recovery rate was defined as a reduction of more than 75% in depression scores. The exclusion criteria were as follows: 1) modified XYF or XYF combined with other complementary therapies as an intervention; 2) response rate defined by reducing depressive symptoms rather than a quantitative reduction in depression score; and 3) retrospective studies or self-controlled trials. Two independent reviewers (Liu J and Rong AN) screened all relevant studies based on predefined inclusion criteria. Disagreements between reviewers were resolved through discussion or consultation with a third reviewer (Wang F).
Two authors independently extracted the following information from the included studies: first author’s name, publication year, number of delivery women, age, criteria for diagnosis of postpartum depression, preparations and dosages of XYF used, types of antidepressants, length of treatment, and endpoints. The Cochrane risk of bias tool for RCTs was employed to assess the study quality. This tool evaluated the generation of random sequences, allocation concealment, blinding method, selective reporting of outcomes, and other sources of bias (such as selection of delivery women based on TCM syndrome). For data extraction and risk of bias assessment, the same set of reviewers followed a pre-designed, standardized data extraction form. Any discrepancies were identified by cross-checking and resolved through group discussion.
All meta-analyses were conducted using STATA version 12.0 (Stata Corp LP, College Station) and Review Manager version 5.1. The risk ratio (RR) with a 95% confidence interval (CI) was used to combine dichotomous data, while the standard mean difference (SMD) with a 95% CI was used for continuous data. Significant heterogeneity among the included trials was defined as a p-value of ≤ 0.05 for the Cochrane Q test and an I2 statistic >50%. A random-effects or fixed-effects model was chosen based on the presence or absence of significant heterogeneity. A leave-one-out sensitivity analysis was performed to recalculate the pooled effect sizes. Subgroup analyses were conducted based on sample sizes, preparations of XYF, length of therapy, type of Western therapy, and whether patients were selected based on TCM syndrome differentiation. To determine publication bias, we used the Begg’s test and Egger’s test. If publication bias was detected, a trim-and-fill analysis was employed to adjust the pooled effect size.
Initially, we obtained 335 publications using the search strategy. Of these, 82 duplicate records were excluded, leaving 253 articles for evaluation of the titles and abstracts. After scanning the titles and abstracts, we retrieved 36 articles for full-text evaluation. Based on the criteria for inclusion and exclusion, 10 RCTs (6–11, 14–17) were ultimately included in this meta-analysis (Figure 1)
Table 1 presents the main features of the included RCTs. All the RCTs were carried out in China and were published between 2008 and 2021. The sample sizes of the individual trials ranged from 64 to 120, with a total of 810 delivery women. Most of the RCTs used the Chinese Classification and Diagnostic Criteria of Mental Disorders-3 and the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders to diagnose depression. The XYF preparation included pills, powders, and decoctions. The included RCTs used various antidepressant medications, such as paroxetine, fluoxetine, sertraline, venlafaxine, escitalopram, amitriptyline, and deanxit. The study quality was summarized in Supplementary Figures S1, S2. Overall, all eligible RCTs were of suboptimal methodological quality with an unclear risk of bias.
Five trials (6, 7, 9, 11, 16) examined the effect of XYF on the total response rate, defined as a reduction of more than 25% in depression scores. As shown in Figure 2, a fixed-effect model was used due to the lack of significant heterogeneity (I² = 0.0%; p = 0.750). The pooled RR for the total response rate was 1.17 (95% CI 1.08-1.26) for the combination of XYF and Western therapy compared to Western therapy alone. A sensitivity analysis, in which one trial was removed at a time, confirmed that no individual trial significantly influenced the overall risk estimate.
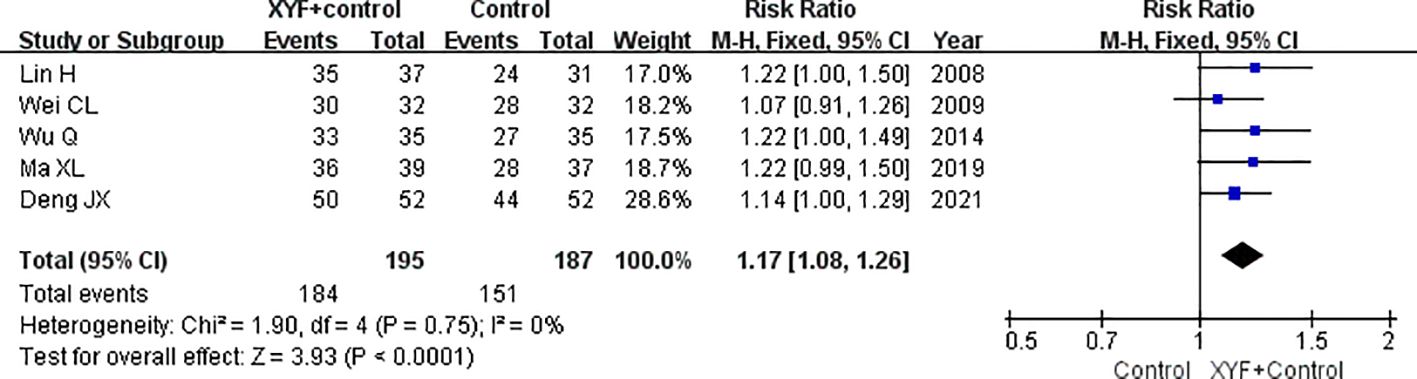
Figure 2. The pooled RR with a 95% CI for the total response rate of the XYF combined with Western therapy compared to Western therapy alone. XYF =Xiaoyao formula.
Six trials (6, 7, 9–11, 16) examined the effect of XYF on the total response rate, defined as a reduction of more than 75% in depression scores. As shown in Figure 3, a fixed-effect model was used due to the lack of significant heterogeneity (I2 = 0.0%; p=0.890). The combined RR for the clinical recovery rate was 1.56 (95% CI 1.27-1.91) for the combination of XYF and Western therapy compared to Western therapy alone. None of the individual trials had a significant impact on the overall risk estimate in the sensitivity analysis.
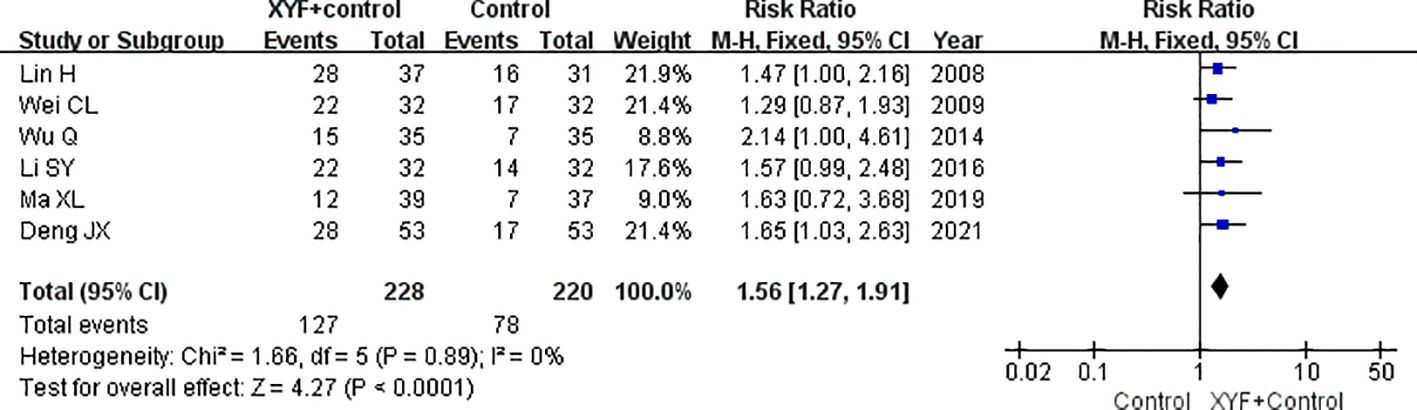
Figure 3. The pooled RR with a 95% CI for the clinical recovery rate of the XYF combined with Western therapy compared to Western therapy alone. XYF =Xiaoyao formula.
All the trials included provided data on changes in depression scores following treatment. Figure 4 shows significant heterogeneity among the trials (I2 = 94.0%; p<0.001). A meta-analysis utilizing a random effects model found that the combination of XYF and Western therapy significantly reduced depression scores (SMD -1.69; 95% CI -2.37 to -1.01) compared to Western therapy alone. A leave-one-out sensitivity analysis further confirmed the reliability of the original pooled effect sizes (Supplementary Figure S3). Subgroup analyses consistently revealed significant effects of XYF on improving depression scores across each predefined subgroup (Table 2). Begg’s test (p = 0.004) and Egger’s test (p = 0.012) suggested a likelihood of publication bias. However, the “trim-and-fill” analysis indicated that the corrected effect size was only slightly underestimated (SMD -1.85; 95% CI -2.57 to -1.13).
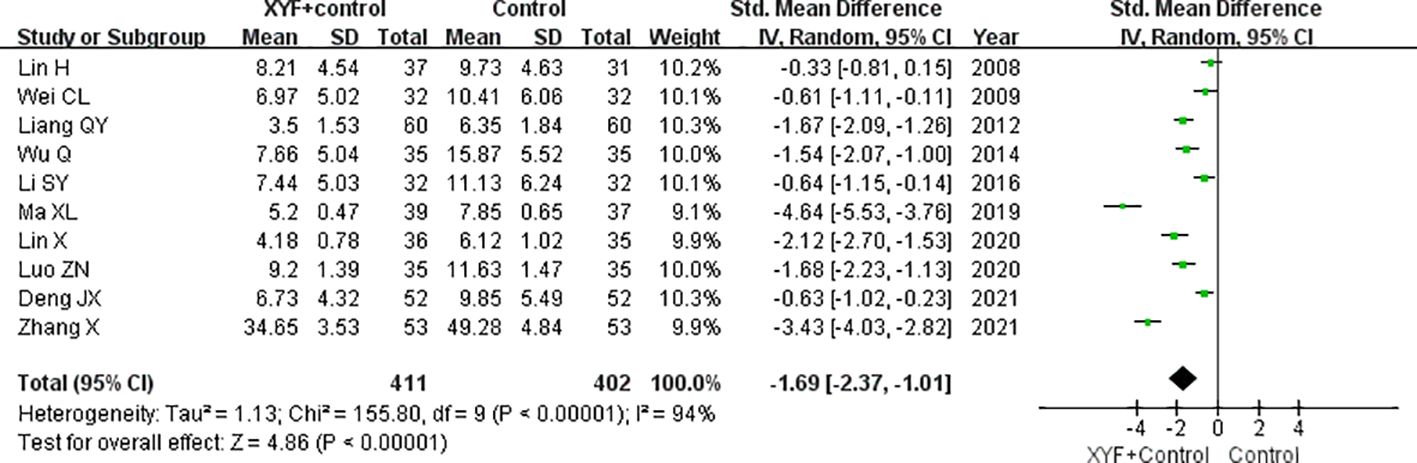
Figure 4. The pooled SMD with a 95% CI for the improvement in depression scores of the XYF combined with Western therapy compared to Western therapy alone. XYF =Xiaoyao formula.
This study represents the first meta-analysis to evaluate the effectiveness of XYF as an adjunctive therapy for postpartum depression. Our primary findings show that using XYF in addition to Western therapy leads to a significant improvement in both the total response rate (17%) and clinical recovery rate (56%) compared to using Western therapy alone. Furthermore, the adjuvant treatment with XYF led to a substantial reduction in depression (SMD -1.69) scores. This large effect size indicates that XYF has a clinically meaningful impact on reducing depressive symptoms. These findings suggest that combining XYF with Western therapy can greatly enhance its anti-depressive effectiveness.
There is a growing body of evidence supporting the beneficial effects of Xiaoyao powder/pill in treating depression. Previous meta-analyses (18–20) have demonstrate that XYF can effectively alleviate depressive symptoms in patients with depressive disorder. Furthermore, a recent meta-analysis (21) concluded that XYF, when used as an adjuvant therapy, provided further benefits by reducing HAMD scores in patients with post-stroke depression. However, these previous meta-analyses did not include patients with postpartum depression. Therefore, the current meta-analysis specifically evaluated the XYF as an adjunctive therapy in recently delivery women diagnosed with depression.
The precise mechanisms underlying the beneficial effects of XYS in the treatment of postpartum depression remain largely unclear. However, research has shown that changes in the levels of estradiol and monoamine neurotransmitters may play a role in the onset of postpartum depression (22). For example, a study has found that women with postpartum depression have lower levels of estradiol and 5-hydroxytryptamine in their blood compared to healthy women (23). Furthermore, adjuvant treatment with XYF has been shown to increase levels of estradiol, noradrenaline, dopamine, and 5-hydroxytryptamine in the blood (11, 14).
XYF, when used as an adjuvant therapy, demonstrated additional beneficial effects in postpartum depression. Syndrome differentiation is a crucial aspect of TCM; however, only five RCTs (7–9, 11, 16) considered this during the patient selection process. XYF is particularly suitable for treating depressive symptoms induced by liver–stomach disharmony syndrome. Our subgroup analysis further supports the superiority of RCTs that incorporate syndrome differentiation, as evidenced by a greater reduction in depression scale scores (SMD 1.76) compared to those that do not (SMD 1.63).
However, there was significant heterogeneity in the pooled depression scores when treated as continuous variables. This indicates considerable variation among the studies, which weakened the strength of our overall conclusion. To address this issue, we conducted a leave-one-out sensitivity analysis. This analysis demonstrated that our overall conclusion remained stable, suggesting that no single study was responsible for the observed heterogeneity. When categorizing the studies based on the type of antidepressant, we found that heterogeneity was reduced within the subgroups of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. This implies that the type of antidepressant may be a partial contributor to the heterogeneity. However, the method used to assess depression is a significant factor contributing to this variability. Additionally, the severity of depression among participants and variations in treatment regimens may also play a role in the observed heterogeneity.
Our meta-analysis results indicate that XYF is a promising adjunctive therapy for postpartum depression, demonstrating significant improvements in response rates, recovery rates, and depression scores. Sertraline belongs to a class of drugs known as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, which has been recommended as one of the safest antidepressants during breastfeeding in the context of balancing risks and benefits (24). Healthcare providers should consider incorporating XYF into treatment plans for postpartum depression, especially for patients who show inadequate response to Western therapy alone. As an adjunctive therapy, XYF can enhance the overall efficacy of conventional treatments, potentially reducing the need for higher doses of antidepressants or other medications that may carry side effects. Furthermore, patient selection based on TCM syndrome differentiation may further optimize the therapeutic benefits of XYF.
The current meta-analysis shows that XYF has short-term benefits for depression, but long-term RCTs are necessary to assess its sustained effects and safety during extended use. Future research should focus on incorporating pharmacogenetic testing to tailor treatment plans more effectively, taking into account the unique genetic profiles of individuals. Additionally, studies should compare XYF with other complementary and alternative therapies to determine its relative efficacy. Head-to-head trials comparing XYF with conventional antidepressants could also provide valuable insights into its potential as a first-line or adjunctive treatment. Further preclinical and clinical studies are needed to fully understand the mechanisms by which XYF alleviates depression.
We must acknowledge several limitations in our meta-analysis. Firstly, the lack of detailed descriptions of allocation concealment and blinding methods makes it difficult to assess the quality of the studies and the potential for bias. Secondly, the lack of clarity in the patient selection process could result in the inclusion of patients who do not have the specific TCM syndrome that XYF is intended to treat, potentially skewing the results. Thirdly, the sample sizes and the number of included trials were relatively small, necessitating caution when interpreting the results of subgroup analyses. Fourthly, the long-term efficacy of XYF for postpartum depression remains uncertain due to a lack of follow-up information. Finally, we did not conduct a quantitative analysis of adverse events associated with XYF, as the indices of adverse events were reported in various formats. However, no severe adverse events were documented in any of the included trials.
XYF as an adjunctive therapy offers additional benefits in alleviating depression in postpartum women. However, the current evidence remains uncertain due to the methodological flaw of the analyzed trials. Future research should focus on large, multi-center RCTs, dose-response studies, head-to-head comparisons with Western therapy, and investigations into XYF's mechanisms of action.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
FW: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. JL: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Resources, Validation, Writing – original draft. AR: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Resources, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1558505/full#supplementary-material
1. Shorey S, Chee CYI, Ng ED, Chan YH, Tam WWS, Chong YS. Prevalence and incidence of postpartum depression among healthy mothers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Psychiatr Res. (2018) 104:235–48. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2018.08.001
2. Brummelte S, Galea LA. Postpartum depression: Etiology, treatment and consequences for maternal care. Horm Behav. (2016) 77:153–66. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2015.08.008
3. Netsi E, Pearson RM, Murray L, Cooper P, Craske MG, Stein A. Association of persistent and severe postnatal depression with child outcomes. JAMA Psychiatry. (2018) 75:247–53. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2017.4363
4. Yeung WF, Chung KF, Ng KY, Yu YM, Zhang SP, Ng BF, et al. Prescription of chinese herbal medicine in pattern-based traditional chinese medicine treatment for depression: A systematic review. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2015) 2015:160189. doi: 10.1155/2015/160189
5. Wang YT, Wang XL, Wang ZZ, Lei L, Hu D, Zhang Y. Antidepressant effects of the traditional Chinese herbal formula Xiao-Yao-San and its bioactive ingredients. Phytomedicine. (2023) 109:154558. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154558
6. Lin H, Ye X, Guo ZP, Liao YL. Combination of paroxetine and Xiaoyao san for postpartum depression. Appl J Gen Practice. (2008) 6:476–7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-4152.2008.05.022
7. Wei CL, Ma YY, Hong GZ, Wang GP, Fei GX, Guan RC, et al. A clinical contrast Study of combination of sertraline and Xiaoyao pill on postpartum depression. MedicM J Chin People's Health. (2009) 21:1317–8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0369.2009.11.065
8. Liang QY, Xie YH, Wu XR, Chen LR, Wu LW. Evaluation on clinical efficacy and safety of Xiaoyao Pills combined with fluoxetine in treating postpartum depression. J Mod Med Health. (2012) 28:1972–3.
9. Wu Q, Wu Q, Li J, Luo YC, Huang LJ. Sertraline joint at large clinical observation on treatment of postpartum depression. Jilin J Traditional Chin Med. (2014) 34:469–71. doi: 10.13463/j.cnki.jlzyy.2014.05.013
10. Li SY, Li CY. Escitalopram combined with Xiaoyao Pill in the treatment of postpartum depression: A randomized controlled trial. Qinghai Med J. (2016) 46:71–3. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2016.01.028
11. Ma XL, Li LY. Clinical effect of Xiaoyao Pill combined with venlafaxine on postpartum depression induced by Qi and blood deficiency. Chin Traditional Patent Med. (2019) 41:2261–3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2019.09.052
12. Hu MY, Zhang XW, Zhang XY, Cheng D, Zhang YL, Zhang XY, et al. Modified Xiaoyao powder for postpartum depression: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Traditional Chin Med Sci. (2024) 11:120–30. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcms.2023.12.002
13. Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gotzsche PC, Ioannidis JP, et al. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration. J Clin Epidemiol. (2009) 62:e1–34. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000100
14. Lin X, Bai FX. Effects of Xiaoyao Pill Combined with paroxetine on estrogen, norepinephrine, serotonin and dopamine levels in patients with postpartum depression. Maternal Child Health Care China. (2020) 35:4229–31. doi: 10.19829/j.zgfybj.issn.1001-4411.2020.22.024
15. Luo ZN. Clinical effect of traditional Chinese medicine on postpartum depression. Chin Baby. (2020) 20:82.
16. Deng JX, Gou ZY, Ye SM, Wei CL. Clinical observation of Deanxit combined with Xiaoyao Pill in the treatment of postpartum depression. J Friontiers Med. (2021) 11:28–9.
17. Zhang X. Efficacy of Amitriptyline combined with Xiaoyao San on the psychological status of patients with postpartum depression. PSY. (2021) 16:75–6. doi: 10.19738/j.cnki.psy.2021.04.034
18. Man C, Li C, Gong D, Xu J, Fan Y. Meta-analysis of Chinese herbal Xiaoyao formula as an adjuvant treatment in relieving depression in Chinese patients. Complement Ther Med. (2014) 22:362–70. doi: 10.1016/j.ctim.2014.02.001
19. Zhang Y, Han M, Liu Z, Wang J, He Q, Liu J. Chinese herbal formula xiao yao san for treatment of depression: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Evidence-Based complementary Altern medicine: eCAM. (2012) 2012:931636. doi: 10.1155/2012/931636
20. Qin F, Wu XA, Tang Y, Huang Q, Zhang ZJ, Yuan JH. Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials to assess the effectiveness and safety of Free and Easy Wanderer Plus, a polyherbal preparation for depressive disorders. J Psychiatr Res. (2011) 45:1518–24. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2011.06.018
21. Jin X, Jiang M, Gong D, Chen Y, Fan Y. Efficacy and safety of xiaoyao formula as an adjuvant treatment for post-stroke depression: A meta-analysis. Explore (NY). (2018) 14:224–9. doi: 10.1016/j.explore.2017.12.007
22. Skalkidou A, Hellgren C, Comasco E, Sylven S, Sundstrom Poromaa I. Biological aspects of postpartum depression. Womens Health (Lond). (2012) 8:659–72. doi: 10.2217/WHE.12.55
23. Luo Y, Zheng LZ, Zhou JW, Pi PX. Relationship between the levels of estradiol and monoamine neurotransmitters and postpartum depression. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. (2007) 42:745–8. doi: 10.3760/j.issn:0529-567x.2007.11.008
Keywords: traditional Chinese medicine, Xiaoyao powder, Xiaoyao pill, postpartum depression, randomized controlled trials, meta-analysis
Citation: Liu J, Rong A and Wang F (2025) Meta-analysis of Xiaoyao formula as an adjuvant therapy for treating postpartum depression. Front. Psychiatry 16:1558505. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1558505
Received: 10 January 2025; Accepted: 03 March 2025;
Published: 24 March 2025.
Edited by:
Anna Brancato, University of Palermo, ItalyReviewed by:
Alessandro Cuomo, University of Siena, ItalyCopyright © 2025 Liu, Rong and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Fei Wang, V2YxMzg0NzEyNTg5NUAxNjMuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.