
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Psychiatry, 05 March 2025
Sec. Neurostimulation
Volume 16 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1545318
 Mohamed A. Abdelnaim1,2*
Mohamed A. Abdelnaim1,2* Tobias Hebel1
Tobias Hebel1 Verena Lang-Hambauer2,3
Verena Lang-Hambauer2,3 Juergen Schlaier2,4
Juergen Schlaier2,4 Berthold Langguth1,2
Berthold Langguth1,2 Andreas Reissmann1
Andreas Reissmann1Introduction: Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a common condition characterized by abdominal pain and altered bowel habits, affecting around 11% of individuals globally. It is linked to dysregulation of the brain-gut axis, with altered activity and connectivity in various brain regions. IBS patients often have psychiatric comorbidities like anxiety, or obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). Deep brain stimulation (DBS) is an established treatment option for severe, therapy-refractory OCD. It has been suggested that DBS for OCD could also have a beneficial effect on accompanying IBS-symptoms.
Methods and patients: Nine patients with treatment-refractory OCD who underwent DBS in the bed nucleus striae terminalis (BNST) have been included in this study (4 males, 5 females, mean age: 39.1 ± 11.5 years). Patients were examined with the Gastrointestinal Symptom Rating Scale for Irritable Bowel Syndrome (GSRS-IBS) as well as the Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale (Y-BOCS) both before the beginning of DBS as well as throughout several follow-up visits for 12 months following the start of DBS.
Results: Three patients displayed clinically relevant levels of IBS-symptoms at baseline (GSRS-IBS scores at or beyond 32). All of those three patients showed a reduction of the GSRS-IBS score at the last follow-up (12-40%). For the other 6 patients, 5 of them showed also a reduction of the GSRS-IBS compared to the score at baseline. The mean score for all patients showed a descriptive trend toward score reduction throughout the study period and until the last follow up visit after 12 months. The mean Y-BOCS decreased from 31.11 at baseline to 16.50 at the last follow-up. Out of the 9 patients, 7 (78%) were considered responders with Y-BOCS scores decreasing between 37% to 74%. Moderate-to-large correlations between both scales could be observed at both the 9-month and the 12-month follow-up visit. However, none of these associations was statistically significant.
Conclusion: In this study, we found alleviation of IBS symptoms after DBS of the BNST, along with improvement in OCD symptoms. Future research using larger sample sizes should address whether the reductions are tied to the improvement of OCD symptoms or if DBS exerts positive effects on IBS independently of OCD symptoms.
With a global prevalence of 11% (1), irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a very common condition. It is characterized by abdominal pain or discomfort with altered bowel habits such as constipation, diarrhea, or both. but without pathological alterations in bowel tissue (2, 3). Many affected individuals can control their symptoms by managing diet, lifestyle and stress, whereas others are substantially impaired in their quality of life (4, 5).
Despite being identified more than 150 years ago, IBS continues to pose a clinical challenge with only limited treatment options (6, 7). According to the biopsychosocial model, IBS symptoms arise from the interplay of psychological, behavioral, sociocultural, and environmental factors, but the exact pathophysiological mechanisms remain incompletely understood (8–12).
There is increasing evidence that IBS is related to abnormal processing of internal pain signals, leading to changes in visceral sensitivity (13). Both central and peripheral mechanisms have been proposed to play a role in the emergence of pain symptoms (14), with multiple studies linking IBS to a dysregulation of the brain-gut axis, in which an imbalance can manifest as either sensory changes in the peripheral nervous system or disruptions in central processing (15–18). The term “brain-gut axis” subsumes bidirectional communication between the gut and the brain, both at rest and during stimuli such as postprandial states or luminal distension, regulating motions, reflexes, and sensory perceptions in the gastrointestinal tract. These ongoing complex interactions between the gastrointestinal tract and the central nervous system are essential for maintaining homeostasis and regulating gastrointestinal physiology (16).
Neuroimaging studies of patients with IBS have shown increased activation in various brain regions including anterior cingulate cortex, mid cingulate cortex, amygdala, anterior insula, posterior insula and prefrontal cortex (19). In individuals with IBS, these brain regions are linked to aberrant emotional arousal, intrinsic pain regulation, gastrointestinal hyperactivity and regulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis (20–23).
According to recent studies, patients with IBS are frequently suffering from psychiatric comorbidities like anxiety, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) and depression (24–27). Among patients with functional bowel disorders, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) is the second most prevalent psychiatric comorbidity, occurring in approximately 20% of cases (28, 29). For patients with OCD, similarly, the prevalence of gastrointestinal disorders is notably high, ranging from 14,9% (30), 16% (31) up to about 35% (32). Furthermore, patients with OCD are nearly twice as likely to report constipation of medically unexplained or mental origins (33). The co-occurrence and high prevalence of gastrointestinal symptoms should be thus a significant therapeutic consideration in the treatment of OCD patients, and vice versa (34).
OCD is a very debilitating disease, with approximately 40–60% of patients achieving only partial recovery with standard therapies, while around 10% of patients with OCD exhibit chronic, severe, and refractory illness, resulting in considerable functional impairments (35–37). Deep brain stimulation (DBS) represents a treatment option for severe, therapy-refractory OCD. In DBS, electrodes are stereotactically implanted in designated brain regions. Electrical impulses generated by a battery-driven stimulator situated beneath the skin of the upper chest are transmitted through these electrodes in order to affect brain activity in the targeted area(s). This procedure has become an established treatment option for patients with Parkinson’s disease, dystonia, tremor and other movement disorders. DBS has also been explored for the treatment of various psychiatric disorders with best evidence being available for the treatment of OCD (38). In 2009, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved DBS for treatment-refractory OCD as a humanitarian device exemption (HDE H050003) (39). For the treatment of OCD, various targets were investigated including the anterior limb of internal capsule (ALIC) (40–42), the bed nucleus striae terminalis (BNST) (43), the ventral capsule/ventral striatum (VC/VS) (44–46), the nucleus accumbens (NA) (47–49), and the nucleus subthalamicus (STN) (50), with most of them reporting statistically significant effects (51, 52). This can be explained by the fact that many of the target areas are located in close proximity to each other or are functionally connected respectively. In a case report, it has been reported that DBS targeting the anterior limb of the internal capsule (ALIC) in a 55-year-old female patient with both OCD and IBS led to a substantial and reproducible reduction in IBS symptoms. This improvement was dependent on specific stimulation parameters and was not directly associated with changes in OCD symptoms (53).
Here we aimed to further explore effects of DBS in OCD patients on IBS symptoms. For this purpose, we analyzed IBS symptoms in our patients with treatment-refractory OCD who received DBS in the BNST (54). To do so, we investigated whether DBS in the BNST in patients suffering from OCD would lead to decreases both in measures of OCD as well as IBS symptom severity. Additionally, we looked at the correlation between the two symptom domains across the study period in order to get a deeper understanding of the potential temporal dynamics between symptom domains. Hence, we report of 9 patients, who underwent DBS in the BNST for their OCD between January 2021 and 2023 at the multidisciplinary center of deep brain stimulation at the University of Regensburg, Germany. Please note that the results of the same assessment instrument (e.g. Y-BOCS) may differ compared to the first study (54), as not all patients who were presented in the first study are also presented in the current one.
All patients have provided written informed consent to this study, which was approved by the ethic committee of the University of Regensburg (ethic vote: 21-2707-104). Potential candidates for DBS were screened for their eligibility first at the outpatient clinic of the department of psychiatry and psychotherapy and then at the outpatient clinic of the department of neurosurgery. The inclusion process consisted of multiple screening visits to confirm the OCD diagnosis, to check all available health records and to get a detailed summary of previous treatment trials, as well as to collect information on the patient’s psychosocial history and overall functioning.
The two main inclusion criteria were treatment resistance and disease severity. We defined treatment resistance as non-response to adequate trials with a maximum tolerated dose of at least two different serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRI) and one trial with clomipramine or augmentation with an antipsychotic (risperidone or aripiprazole) as well as non-response to cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) for at least one year (>50 sessions), including exposure therapy and non-response to an adequate multi-professional treatment procedure (e.g., inpatient clinic with different therapy modalities). Regarding severity, we considered overall impairment in social, occupational functioning and patient’s normal routine.
Patients who met the criteria for DBS during the psychiatric assessment were referred to the neurosurgery department for evaluation of their surgical eligibility. Patients were provided with comprehensive information regarding the surgical procedure. All patients provided informed written consent for the surgical procedure, and the operation was conducted only after a minimum deliberation period of 60 days.
Preoperative MR imaging was conducted two days before the procedure using a 3T SIEMENS Magnetom Skyra scanner, with patients under general anesthesia throughout the imaging to prevent movement artifacts in preparation for DBS surgery. Sagittal T1 and axial and sagittal T2 images aligned with the intercommisural plane were obtained for trajectory planning, along with T1 images enhanced with a double dose of Gadolinium to delineate essential blood arteries and minimize the risk of hemorrhage during the insertion of stylets and DBS electrodes. On the day of surgery, a preoperative CT scan, utilizing a stereotactic frame affixed to the patient’s head (CRW, Integra Radionics, Burlington, USA), was acquired from a SIEMENS Somatom Definition Flash scanner and served as the reference for surgical planning. Trajectories avoiding relevant blood vessels, sulci and crucial neurological structures were defined using iPlanNet 3.0 (BRAINLAB, Munich, Germany) with targets in the bed nucleus striae terminalis (BNST). The stereotactic implantation of the electrodes (3391, 3387 or B3301533; Medtronic plc, Dublin, Ireland) and the implantation of the internal pulse generator (IPG) (ActivaRC or PerceptPC; Medtronic plc, Dublin, Ireland) was performed in one setting with the patient under general anesthesia. Postoperatively, the position of the electrode was verified using CT scans with a slice thickness of 1mm, which were integrated with MR imaging.
Stimulation typically started 6-8 weeks post-surgery and was adjusted by a psychiatrist experienced in DBS. Bilateral stimulation of each of the four contacts was initially assessed for tolerability and efficacy. Subsequently, the optimal contact voltage was gradually increased to attain maximum therapeutic efficacy. Upon achieving optimal voltage, subsequent optimization of additional stimulation parameters, including frequency and pulse width, was conducted. If the target effectiveness was not achieved, the same procedure was conducted with the second-best contact.
Y-BOCS was used to evaluate the existence and severity of OCD symptoms (55), which measures the severity of symptoms of OCD based on scores of obsessions and compulsions. The Y-BOCS comprises ten items that assess the severity and influence of both obsessions and compulsions. Each of the ten items is evaluated on a five-point scale ranging from zero to four, as follows: No symptoms are indicated by a value of 0, while extreme symptoms are defined by a value of 4. The Y-BOCS has a maximal possible score of 40. It is divided into the following categories: Obsessions subscale (Items 1–5): Scores range from 0 to 20. Compulsions subscale (Items 6–10): Scores range from 0 to 20.
The scores are generally interpreted with the following criteria: 0–7: Subclinical or no symptoms, 8–15: Mild symptoms of OCD, 16–23: Moderate symptoms of OCD, 24–31: Symptoms of OCD that are severe, 32–40: Severe symptoms of OCD.
For IBS-symptoms, we used the Gastrointestinal Symptom Rating Scale for Irritable Bowel Syndrome (GSRS-IBS) (56), in its German version (Reizdarm-Fragebogen RDF), which proves to be an effective, reliable, and valid questionnaire for the assessment of symptom severity in IBS (57). The GSRS-IBS is a 13-item measure of gastrointestinal symptom severity for the last week. The items measure severity of abdominal pain (Item 1), pain relieved by a bowel action (Item 2), bloating (Item 3), passing gas (Item 4), constipation (Item 5), diarrhea (Item 6), loose stools (Item 7), hard stools (Item 8), urgent need for bowel movement (Item 9), incomplete bowel emptying (Item 10), fullness shortly after meal (Item 11), fullness long after eating (Item 12), and visible distension (Item 13). The items are scored between 1 and 7, where 1 corresponds to “no discomfort at all” and 7 to “very severe discomfort” from the symptom (58).
The GSRS-IBS is not designed to serve as a diagnostic instrument for IBS, but rather for evaluating the severity of symptoms over time. In general, a higher total score indicates more severe symptoms. In our analysis, we considered scores of 32 and above as an indicator of clinically relevant symptom severity, as this cut-off score has been shown good levels of sensitivity and acceptable levels of specificity (59).
All statistical analyses were performed using R (version 4.3.2) and R-Studio (2023.12.1 Build 402) with the nlme package (version 3.1-166 (60) Pinheiro et al., 2021).
To evaluate symptom changes in Y-BOCS and GSRS-IBS scores over study visits (baseline, before stimulation, optimized stimulation, 3 months follow-up, 6 months follow-up, 9 months follow-up, and 12 months follow-up), linear mixed effects models were applied. Models were estimated using restricted maximum likelihood estimation (REML) without specific imputation of missing values, assuming data were missing at random (MAR). In these analyses, study visit was treated as a fixed effect and the individual patient as a random effect. In case of a significant effect of study visit (tested using the expected mean squares approach), post-hoc pairwise comparisons of the fixed effects were performed. In case of the Y-BOCS scale, post hoc results were adjusted using the Tukey method. For the GSRS-IBS, post hoc testing of differences between time points was conducted irrespective of overall significance for the fixed effect and without adjustment of p-values for multiple comparisons, meaning each comparison was independently tested for significance without correction for cumulative error probability. The level for statistical significance was set at 5%. The liberal testing of significant differences between time points for the GSRS-IBS was chosen due to the exploratory nature of the study and the restricted sample size. The primary goal was to identify potential trends and relationships that warrant further investigation in future, more targeted studies. Adjusting the alpha level might increase the risk of Type II errors, potentially obscuring meaningful findings in this early phase of research. As such, we present the results without correction to avoid an overly conservative approach, but acknowledge that any significant findings should be interpreted with caution and confirmed in subsequent confirmatory analyses. Additionally, we performed a bivariate correlation analysis using Spearman’s rho in order to investigate the associations between the Y-BOCS scale scores and the GSRS-IBS for each of the study visits.
Since not all of our patients were investigated with GSRS-IBS, we are reporting in this study only the results of those 9 patients who completed the questionnaire (4 males, 5 females; age between 24 and 61 years, mean age: 39.1 ± 11.5 years).
The results are primarily presented in a descriptive manner due to the small sample size. For detailed scores over different timepoints, please see Supplementary Materials.
Only three patients scored more than 32 points at baseline. As shown in Table 1, the mean score did not differ substantially between baseline assessment (27.78) and the optimization of stimulation (24.71), however there was a descriptive trend toward score reduction throughout the study period and until the last follow up visit after 12 months (23.88). As can also be seen from the Table, there were slight fluctuations in the number of completed questionnaires across the study period (see Table 1).
Three patients were scoring 32 points or more at baseline, and all of them showed a reduction of the GSRS-IBS score at the last follow-up (12% (patient 1), 30% (patient 7), and 40% (patient 6)). Among the other 6 patients, five showed decreased scores at last follow-up.
The linear mixed effects model revealed no significant (fixed) effect of study visit (F(6, 43) = 1.90), p >.10). The (fixed) effect of study visit (marginal R2= .037) explained only 3.7% of variance, while the specified model explained a total of 82.4% of variance in the data (conditional R2 = .824), implying strong effects of the (random) effect of patient (i.e. large interindividual differences in the scale scores). However, exploratory post-hoc comparisons between study visits showed significant or near-significant differences between GSRS-IBS scores between study visits at baseline or before stimulation versus those conducted at the 9 or 12 month follow-ups (see Figure 1). Re-running the model in the subsample of three patients with clinical GSRS-IBS scores (≥ 32) at baseline yielded similar results: the fixed effect of study visit remained non-significant (F(6, 10) = 2.25, p >.12). However, in this subsample, marginal R2 increased to.214, indicating that study visit accounted for 21.4% of variance—a notable increase compared to the full sample. The conditional R2 = .719 showed that the full model still explained 71.9% of variance, reinforcing the strong interindividual differences in scale scores driven by the random effect of patient.
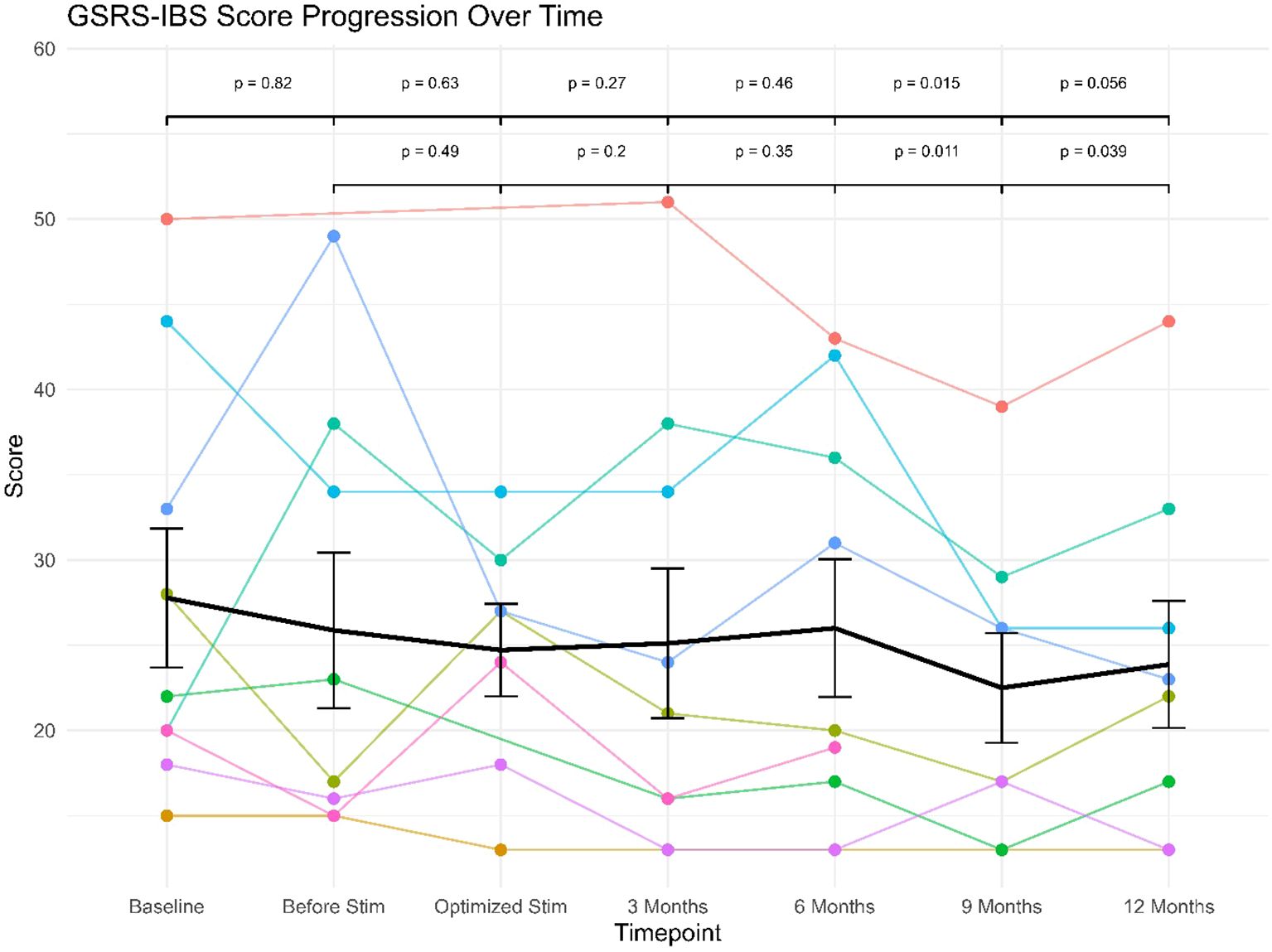
Figure 1. GSRS-IBS scores progression over follow-up for individual patients (star symbols mark patients displaying clinical levels of IBS).
The 9 patients had baseline scores ranging from 23 to 37 points. Regarding severity according to Y-BOCS, one patient of them was showing moderate symptoms, three patients were showing severe symptoms, while five patients were showing extreme symptoms. After optimizing the stimulation, the mean Y-BOCS score decreased from 31.11 at baseline to 16.89 after the optimization of stimulation. Furthermore, the reduction in Y-BOCS score remained stable through following visits to reach 16.50 at the last follow-up.
The treatment response was defined as a reduction in YBOCS of at least 35% compared to baseline, in accordance with established standards (61). Out of the 9 patients, 7 of them (78%) were responders with Y-BOCS score decreases ranging from 37% to 74%. All three patients displaying clinical levels of IBS were responders with Y-BOCS score decreases ranging from 45% to 62% (see Table 2).
The linear mixed effects model revealed a significant (fixed) effect of study visit (F(6, 43) = 27.54), p <.0001). The (fixed) effect of study visit explained 50.1% of variance (marginal R2= .501), while the specified model explained a total of 81.9% of variance in the data (conditional R2 = .819). The conducted post-hoc comparisons between study visits showed highly significant differences in Y-BOCS scores between study visits at baseline or before stimulation versus all subsequent study visits (see Figure 2), since Y-BOCS scores dropped considerably with optimization of the deep brain stimulation. As can also be seen from the Figure, this drop in Y-BOCS scores was stable at the level of the individual patients.
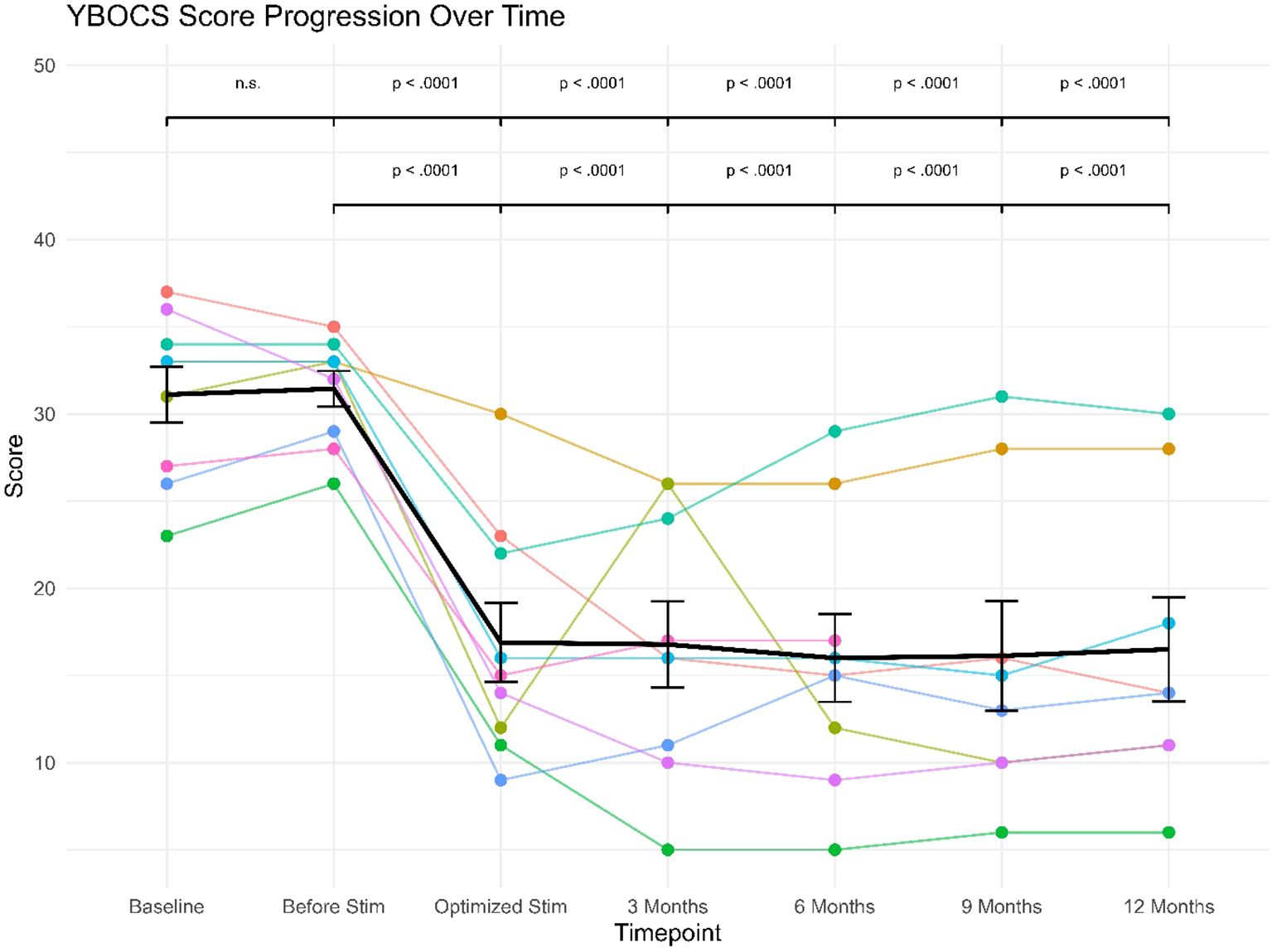
Figure 2. Y-BOCS’ scores progression over follow-up for individual patients (star symbols mark patients displaying clinical levels of IBS).
In order to test for potential associations between OCD and IBS symptoms, bivariate correlations between the GSRS-IBS and Y-BOCS scale scores were calculated for each of the study visit timepoints (see Table 3). As can be seen, there were negligible associations between scale scores both before the beginning of DBS treatment as well as throughout the first half of the follow-up period (i.e. until the 6-month follow-up visit). Following this, however, there was an increase in the strength of association and moderate-to-large correlations between scale scores could be observed at both the 9-month and the 12-month follow-up visit (.38 -.51, see Table 3). However, none of these associations was statistically significant (all p’s >.19).
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a chronic functional gastrointestinal disorder that affects 9%-23% of the population across the world. It can be both physically and emotionally debilitating, making it difficult for people to work, socialize, and even take care of daily activities (62).
While drug therapy has successfully induced remission in many cases of IBS, its effectiveness is limited and it may result in significant adverse effects (63).
Given the rising prevalence of psychological disorders in gastroenterology, innovative strategies are necessary to enhance the management of patients with IBS (27). Both patients and clinicians have actively sought alternate therapeutic options, which has led to an increasing interest in neuromodulative approaches within the IBS-research field (64, 65). For example, some studies have been conducted to assess the potential of vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) in this area depending on its anti-inflammatory effects, in both its invasive (66–69), or non-invasive variant (70, 71), yielding promising findings. Also, other neurostimulative methods like invasive sacral nerve stimulation (72, 73), non-invasive tibial nerve stimulation (74), auricular neurostimulation (75), transcutaneous electrical acustimulation (76), and transcranial magnetic stimulation (77) have been suggested.
Both OCD and IBS are diseases which often coexist together, and could also be exacerbated by increased stress and anxiety. The explanation of the pathogenesis of IBS has been often linked with chronic stress as a role factor (78, 79). The link between psychological disturbances and the digestive tract in the so called brain–gut axis appear to be primarily modulated by the autonomic nervous system (79, 80). Acute or chronic stress, even in healthy persons, causes the autonomic nervous system to release corticotrophin-releasing factor, which is known to disrupt gut function and may consequently result in gastrointestinal symptoms (81). In IBS, the HPA axis becomes dysregulated (79), leading the individual to be more susceptible to, and less able to recover from, stressful events (82). This dysregulation HPA axis is also known to have a role in many psychiatric disorders like OCD and depression (83, 84), which could explain the frequent co-existence of such disorders with IBS (27). Studies have shown that IBS patients have altered activity in brain regions associated with pain processing and emotion regulation (85, 86). It has been suggested that the parts of the brain that regulate visceral pain are located in the central amygdala, hippocampus, BNST and locus coeruleus, while the brain regions located in hypothalamus, amygdala, and dorsal raphe nucleus (DRN) affect psychological state (87).
For OCD, stress is also believed to play an important role. Research indicated that stress may serve as both a triggering and aggravating factor for OCD-symptoms (88), demonstrating that stress has obvious effects on brain regions or circuits that are involved in the pathogenesis of OCD, like corticostriatal and limbic circuitry. For instance, stress can lead to neuronal atrophy in frontal cortices, the dorsomedial striatum, and the hippocampus as well as neuronal hypertrophy in the dorsolateral striatum putamen and amygdala (89).
As mentioned before, deep brain stimulation for OCD has been studied in treatment-resistant patients targeting different brain regions. For DBS in OCD, the BNST is considered to be a reliable implanting target option, yielding satisfying results. Many studies have shown that BNST-DBS for OCD can be effective (54, 90–92), comparable to other brain targets (93) or even with better outcome (43, 94).
The BNST is considered as a part of the “extended amygdala” (95), and believed to be involved in striatal circuitry that integrates descending glutamatergic input with ascending modulatory inputs (96). The BNST plays a crucial role in linking limbic forebrain structures to hypothalamus and brainstem regions involved in autonomic and neuroendocrine functions, hence facilitating the integration of physiological and behavioral responses (97).
In this study we investigated treatment resistant patients with severe OCD, who underwent DBS treatment with respect to IBS symptoms.
In this group three patients (33%) had a GSRS-IBS score of at least 32 corresponding to a significant impairment by co-morbid IBS symptoms, which is in the expected range of IBS comorbidity among OCD patients (30–32). The other patients had GSRS-IBS baseline scores between 15 and 28. In the majority of patients IBS symptoms fluctuated over the course of treatment with a slight tendency toward improvement. In all but one patient the GSRS-IBS score at the end of follow-up was lower than at baseline. The patient whose IBS symptoms worsened did not respond to DBS regarding his OCD symptoms. Importantly, OCD symptoms decreased in all treated patients, with symptom decreases of at least 35% of Y-BOCS scores occurring in 7 out of 9 patients. We found moderate-to-large correlations between scores in the Y-BOCS and the GSRS-IBS at the 9 month and 12 month follow-up visits (see Table 3), albeit these associations did not reach statistical significance which may be due to the small sample size.
The lack of statistical significance has to be put into perspective of the small sample size in which only 3 patients exhibited clinically relevant IBS symptoms. The small sample size, particularly with only three patients meeting criteria for clinically relevant IBS symptoms, naturally limits the generalizability and robustness of our conclusions, necessitating cautious interpretation. Thus, with our data we can neither confirm nor exclude an effect of DBS on IBS symptoms. Whereas IBS symptoms showed relatively large fluctuations over time in most participants and were only very loosely correlated with OCD symptoms at the beginning, the correlation between the GSRS-IBS and the Y-BOCS scores tended to increase and were largest at the 9 months and 12 months follow-up visits. One may speculate that the tendency toward IBS symptom reduction and toward increased correlation between OCD and IBS symptoms over the course of treatment might reflect an effect of DBS on IBS symptoms. Whether this may be a direct effect of stimulation or whether the effects are mediated via OCD symptom improvement remains speculative as well. Furthermore, it is important to acknowledge the possibility that gastrointestinal symptom changes observed in some patients may not solely reflect therapeutic benefits but could also represent complications or side effects of the DBS treatment process. This perspective highlights the complexity of interpreting symptom changes and reinforces the need for future studies to carefully distinguish between potential therapeutic effects and side effects.
Notably, the observation of gastrointestinal side effects further underscores, that stimulation of the NAc-ALIC region can have an impact on gastrointestinal regulation. Whether stimulation results in beneficial effects or in adverse effects may depend on the individual’s symptomatology and related brain activity. One could imagine that IBS related increased connectivity can be disrupted by DBS, which then results in symptom reduction, whereas disruption of physiological brain activity in patients without IBS might cause gastrointestinal side effects.
Since the reported correlations were statistically insignificant (despite medium-to-large effect sizes, see Table 3), they should be considered as preliminary and clearly need to be replicated and extended in future, larger trials. Given the limited statistical power inherent in such a small cohort, even medium-to-large effect sizes may not have reached statistical significance. Therefore, these results should be regarded as exploratory and hypothesis-generating rather than conclusive.
Nevertheless, our findings support the notion that DBS exhibits an effect on comorbid IBS symptoms in OCD patients and warrants further investigations of this topic. It also has to be considered that the stimulation protocol was optimized in every individual patient in order to achieve maximal reduction of OCD symptoms (see Table 4). We cannot exclude that other stimulation parameters and especially other contacts at the stimulation electrode might have been more successful for reduction of IBS symptoms, as suggested in a previous case report (53). This raises the broader question of whether the BNST represents the “optimal” target for patients with co-occurring OCD and IBS symptoms. To investigate these possibilities more robustly, future studies with larger sample sizes are needed, ideally encompassing more patients with more severe IBS symptoms. Future studies could benefit from multi-center collaborations to recruit a larger, more representative cohort or by specifically targeting patients with both severe OCD and IBS symptoms to better assess the effects of DBS.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
The studies involving humans were approved by ethics committee of the University of Regensburg. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
MA: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. TH: Investigation, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization. VL-H: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. JS: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. BL: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. AR: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1545318/full#supplementary-material
1. Canavan C, West J, Card T. The epidemiology of irritable bowel syndrome. Clin Epidemiol. (2014) 6:71–80. doi: 10.2147/CLEP.S40245
2. Ringel Y, Sperber AD, Drossman DA. Irritable bowel syndrome. Annu Rev Med. (2001) 52:319–38. doi: 10.1146/annurev.med.52.1.319
3. Drossman DA, Camilleri M, Mayer EA, Whitehead WE. AGA technical review on irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology. (2002) 123:2108–31. doi: 10.1053/gast.2002.37095
4. Longstreth GF, Wilson A, Knight K, Wong J, Chiou CF, Barghout V, et al. Irritable bowel syndrome, health care use, and costs: a U.S. managed care perspective. Am J Gastroenterol. (2003) 98:600–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2003.07296.x
5. Occhipinti K, Smith JW. Irritable bowel syndrome: a review and update. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. (2012) 25:46–52. doi: 10.1055/s-0032-1301759
6. Horwitz BJ, Fisher RS. The irritable bowel syndrome. N Engl J Med. (2001) 344:1846–50. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200106143442407
7. Halmos EP, Power VA, Shepherd SJ, Gibson PR, Muir JG. A diet low in FODMAPs reduces symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology. (2014) 146:67–75.e5. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.09.046
8. Chang JY, Talley NJ. An update on irritable bowel syndrome: from diagnosis to emerging therapies. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. (2011) 27:72–8. doi: 10.1097/MOG.0b013e3283414065
9. Mayer EA, Naliboff BD, Chang L. Basic pathophysiologic mechanisms in irritable bowel syndrome. Dig Dis. (2001) 19:212–8. doi: 10.1159/000050682
10. Soares RL. Irritable bowel syndrome: a clinical review. World J Gastroenterol. (2014) 20:12144–60. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i34.12144
11. Tanaka Y, Kanazawa M, Fukudo S, Drossman DA. Biopsychosocial model of irritable bowel syndrome. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. (2011) 17:131–9. doi: 10.5056/jnm.2011.17.2.131
12. Drossman DA, Li Z, Andruzzi E, Temple RD, Talley NJ, Thompson WG, et al. U.S. householder survey of functional gastrointestinal disorders. Prevalence, sociodemography, and health impact. Dig Dis Sci. (1993) 38:1569–80. doi: 10.1007/BF01303162
13. Mertz H, Morgan V, Tian H, Nicolson M, Kufner K, Schwartz S, et al. Altered rectal perception is a biological marker of patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology. (1995) 109:40–52. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(95)90267-8
14. Keszthelyi D, Troost FJ, Simrén M, Ludidi S, Kruimel JW, Conchillo, et al. Revisiting concepts of visceral nociception in irritable bowel syndrome. Eur J Pain. (2012) 16:1444–54. doi: 10.1002/j.1532-2149.2012.00147.x
15. Azpiroz F, Bouin M, Camilleri M, Mayer EA, Poitras P, Serra J, et al. Mechanisms of hypersensitivity in IBS and functional disorders. Neurogastroenterol Motil. (2007) 19:62–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2982.2006.00875.x
16. Coss-Adame E, Rao SS. Brain and gut interactions in irritable bowel syndrome: new paradigms and new understandings. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. (2014) 16:379. doi: 10.1007/s11894-014-0379-z
17. Aziz Q, Thompson DG. Brain-gut axis in health and disease. Gastroenterology. (1998) 114:559–78. doi: 10.1016/S0016-5085(98)70540-2
18. Gaman A, Kuo B. Neuromodulatory processes of the brain-gut axis. Neuromodulation. (2008) 11:249–59. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1403.2008.00172.x
19. Weaver KR, Sherwin LB, Walitt B, Melkus GD, Henderson WA. Neuroimaging the brain-gut axis in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther. (2016) 7:320–33. doi: 10.4292/wjgpt.v7.i2.320
20. Berman SM, Naliboff BD, Suyenobu B, Labus JS, Stains J, Ohning G, et al. Reduced brainstem inhibition during anticipated pelvic visceral pain correlates with enhanced brain response to the visceral stimulus in women with irritable bowel syndrome. J Neurosci. (2008) 28:349–59. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2500-07.2008
21. Price JL. Comparative aspects of amygdala connectivity. Ann N Y Acad Sci. (2003) 985:50–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2003.tb07070.x
22. Wilder-Smith CH. The balancing act: endogenous modulation of pain in functional gastrointestinal disorders. Gut. (2011) 60:1589–99. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2011-300253
23. Tillisch K, Mayer EA, Labus JS. Quantitative meta-analysis identifies brain regions activated during rectal distension in irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology. (2011) 140:91–100. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2010.07.053
24. Pae CU, Masand PS, Ajwani N, Lee C, Patkar AA. Irritable bowel syndrome in psychiatric perspectives: a comprehensive review. Int J Clin Pract. (2007) 61:1708–18. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-1241.2007.01409.x
25. Zamani M, Alizadeh-Tabari S, Zamani V. Systematic review with meta-analysis: the prevalence of anxiety and depression in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. (2019) 50:132–43. doi: 10.1111/apt.2019.50.issue-2
26. Banerjee A, Sarkhel S, Dhali GK, Paul I, Das A. A follow-up study of anxiety and depressive symptoms in irritable bowel syndrome. Indian J Psychiatry. (2024) 66:142–7. doi: 10.4103/indianjpsychiatry.indianjpsychiatry_732_23
27. Staudacher HM, Black CJ, Teasdale SB, Mikocka-Walus A, Keefer L. Irritable bowel syndrome and mental health comorbidity - approach to multidisciplinary management. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2023) 20:582–96. doi: 10.1038/s41575-023-00794-z
28. Aguglia A, Signorelli MS, Albert U, Maina G. The impact of general medical conditions in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Psychiatry Investig. (2018) 15:246–53. doi: 10.30773/pi.2017.06.17.2
29. Fakhraei B, Firouzabadi A, Farjam M, Fattahi M, Kazemi M, Naini M, et al. Frequency of different psychiatric disorders in patients with functional bowel disorders: A short report. Ann Colorectal Res. (2015) 3. doi: 10.17795/acr-27621
30. Davarinejad O, RostamiParsa F, Radmehr F, Farnia V, Alikhani M. The prevalence of obsessive-compulsive disorder in patients with irritable bowel syndrome: A cross-sectional study. J Educ Health Promot. (2021) 10:50. doi: 10.4103/jehp.jehp_812_20
31. Gros DF, Antony MM, McCabe RE, Swinson RP. Frequency and severity of the symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome across the anxiety disorders and depression. J Anxiety Disord. (2009) 23:290–6. doi: 10.1016/j.janxdis.2008.08.004
32. Masand PS, Keuthen NJ, Gupta S, Virk S, Yu-Siao B, Kaplan D. Prevalence of irritable bowel syndrome in obsessive-compulsive disorder. CNS Spectr. (2006) 11:21–5. doi: 10.1017/S1092852900024123
33. North CS, Napier M, Alpers DH, Spitznagel EL. Complaints of constipation in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Ann Clin Psychiatry. (1995) 7:65–70. doi: 10.3109/10401239509149029
34. Turna J, Grosman Kaplan K, Patterson B, Bercik P, Anglin R, Soreni N, et al. Higher prevalence of irritable bowel syndrome and greater gastrointestinal symptoms in obsessive-compulsive disorder. J Psychiatr Res. (2019) 118:1–6. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2019.08.004
35. Denys D. Pharmacotherapy of obsessive-compulsive disorder and obsessive-compulsive spectrum disorders. Psychiatr Clin North Am. (2006) 29:553–84, xi. doi: 10.1016/j.psc.2006.02.013
36. Eddy KT, Dutra L, Bradley R, Westen D. A multidimensional meta-analysis of psychotherapy and pharmacotherapy for obsessive-compulsive disorder. Clin Psychol Rev. (2004) 24:1011–30. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2004.08.004
37. Fineberg NA, Brown A, Reghunandanan S, Pampaloni I. Evidence-based pharmacotherapy of obsessive-compulsive disorder. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. (2012) 15:1173–91. doi: 10.1017/S1461145711001829
38. Perlmutter JS, Mink JW. Deep brain stimulation. Annu Rev Neurosci. (2006) 29:229–57. doi: 10.1146/annurev.neuro.29.051605.112824
39. H.d.e. Available from: humanitarian device exemption (hde). fda.gov (2009). Available online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/psychiatry/articles/10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1242566/full.
40. Abelson JL, Curtis GC, Sagher O, Albucher RC, Harrigan M, Taylor SF, et al. Deep brain stimulation for refractory obsessive-compulsive disorder. Biol Psychiatry. (2005) 57:510–6. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2004.11.042
41. Menchón JM, Real E, Alonso P, Aparicio MA, Segalas C, Plans G, et al. A prospective international multi-center study on safety and efficacy of deep brain stimulation for resistant obsessive-compulsive disorder. Mol Psychiatry. (2021) 26:1234–47. doi: 10.1038/s41380-019-0562-6
42. Nuttin B, Cosyns P, Demeulemeester H, Gybels J, Meyerson B. Electrical stimulation in anterior limbs of internal capsules in patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder. Lancet. (1999) 354:1526. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(99)02376-4
43. Luyten L, Hendrickx S, Raymaekers S, Gabriëls L, Nuttin B, et al. Electrical stimulation in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis alleviates severe obsessive-compulsive disorder. Mol Psychiatry. (2016) 21:1272–80. doi: 10.1038/mp.2015.124
44. Goodman WK, Foote KD, Greenberg BD, Ricciuti N, Bauer R, Ward H, et al. Deep brain stimulation for intractable obsessive compulsive disorder: pilot study using a blinded, staggered-onset design. Biol Psychiatry. (2010) 67:535–42. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2009.11.028
45. Greenberg BD, Gabriels LA, Malone DA Jr, Rezai AR, Friehs GM, Okun MS, et al. Deep brain stimulation of the ventral internal capsule/ventral striatum for obsessive-compulsive disorder: worldwide experience. Mol Psychiatry. (2010) 15:64–79. doi: 10.1038/mp.2008.55
46. Tyagi H, Apergis-Schoute AM, Akram H, Foltynie T, Limousin P, Drummond LM, et al. A randomized trial directly comparing ventral capsule and anteromedial subthalamic nucleus stimulation in obsessive-compulsive disorder: clinical and imaging evidence for dissociable effects. Biol Psychiatry. (2019) 85:726–34. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2019.01.017
47. Barcia JA, Avecillas-Chasín JM, Nombela C, Arza R, García-Albea J, Pineda-Pardo JA, et al. Personalized striatal targets for deep brain stimulation in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Brain Stimul. (2019) 12:724–34. doi: 10.1016/j.brs.2018.12.226
48. Denys D, Mantione M, Figee M, van den Munckhof P, Koerselman F, Westenberg H, et al. Deep brain stimulation of the nucleus accumbens for treatment-refractory obsessive-compulsive disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry. (2010) 67:1061–8. doi: 10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2010.122
49. Huff W, Lenartz D, Schormann M, Lee SH, Kuhn J, Koulousakis A, et al. Unilateral deep brain stimulation of the nucleus accumbens in patients with treatment-resistant obsessive-compulsive disorder: Outcomes after one year. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. (2010) 112:137–43. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2009.11.006
50. Mallet L, Polosan M, Jaafari N, Baup N, Welter ML, Fontaine D, et al. Subthalamic nucleus stimulation in severe obsessive-compulsive disorder. N Engl J Med. (2008) 359:2121–34. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0708514
51. Cruz S, Gutiérrez-Rojas L, González-Domenech P, Díaz-Atienza F, Martínez-Ortega JM, Jiménez-Fernández S. Deep brain stimulation in obsessive-compulsive disorder: Results from meta-analysis. Psychiatry Res. (2022) 317:114869. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2022.114869
52. Hageman SB, van Rooijen G, Bergfeld IO, Schirmbeck F, de Koning P, Schuurman PR, et al. Deep brain stimulation versus ablative surgery for treatment-refractory obsessive-compulsive disorder: A meta-analysis. Acta Psychiatr Scand. (2021) 143:307–18. doi: 10.1111/acps.v143.4
53. Langguth B, Sturm K, Wetter TC, Lange M, Gabriels L, Mayer EA, et al. Deep brain stimulation for obsessive compulsive disorder reduces symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome in a single patient. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2015) 13:1371–1374.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2015.01.023
54. Abdelnaim MA, Lang-Hambauer V, Hebel T, Schoisswohl S, Schecklmann M, Deuter D, et al. Deep brain stimulation for treatment resistant obsessive compulsive disorder; an observational study with ten patients under real-life conditions. Front Psychiatry. (2023) 14:1242566. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1242566
55. Goodman WK, Price LH, Rasmussen SA, Mazure C, Fleischmann RL, Hill CL, et al. The Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale. I. Development, use, and reliability. Arch Gen Psychiatry. (1989) 46:1006–11. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1989.01810110048007
56. Wiklund IK, Fullerton S, Hawkey CJ, Jones RH, Longstreth GF, Mayer EA, et al. An irritable bowel syndrome-specific symptom questionnaire: development and validation. Scand J Gastroenterol. (2003) 38:947–54. doi: 10.1080/00365520310004209
57. Schäfer SK, Weidner KJ, Hoppner J, Becker N, Friedrich D, Stokes CS, et al. Design and validation of a German version of the GSRS-IBS - an analysis of its psychometric quality and factorial structure. BMC Gastroenterol. (2017) 17:139. doi: 10.1186/s12876-017-0684-8
58. Ljótsson B, Jones M, Talley NJ, Kjellström L, Agréus L, Andreasson A, et al. Discriminant and convergent validity of the GSRS-IBS symptom severity measure for irritable bowel syndrome: A population study. United Eur Gastroenterol J. (2020) 8:284–92. doi: 10.1177/2050640619900577
59. Schäfer SK, Weidner KJ, Becker N, Lass-Hennemann J, Stokes C, Lammert F, et al. Sensitivity and specificity of the reizdarm-fragebogen. Psychother Psychosom Med Psychol. (2019) 69:382–8. doi: 10.1055/a-0834-6207
60. Pinheiro J, Bates D, DebRoy S, Sarkar D, R Core Team. nlme: Linear and Nonlinear Mixed Effects Models (2021). Available online at: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=nlme (Accessed November 05, 2024).
61. Farris SG, McLean CP, Van Meter PE, Simpson HB, Foa EB. Treatment response, symptom remission, and wellness in obsessive-compulsive disorder. J Clin Psychiatry. (2013) 74:685–90. doi: 10.4088/JCP.12m07789
62. Saha L. Irritable bowel syndrome: pathogenesis, diagnosis, treatment, and evidence-based medicine. World J Gastroenterol. (2014) 20:6759–73. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i22.6759
63. Cheng J, Shen H, Chowdhury R, Abdi T, Selaru F, Chen JDZ. Potential of electrical neuromodulation for inflammatory bowel disease. Inflammation Bowel Dis. (2020) 26:1119–30. doi: 10.1093/ibd/izz289
64. Abell TL, Chen J, Emmanuel A, Jolley C, Sarela AI, Törnblom H. Neurostimulation of the gastrointestinal tract: review of recent developments. Neuromodulation. (2015) 18:221–7. doi: 10.1111/ner.12260
65. Alam MJ, Chen JDZ. Non-invasive neuromodulation: an emerging intervention for visceral pain in gastrointestinal disorders. Bioelectron Med. (2023) 9:27. doi: 10.1186/s42234-023-00130-5
66. Clarençon D, Pellissier S, Sinniger V, Kibleur A, Hoffman D, Vercueil L, et al. Long term effects of low frequency (10 hz) vagus nerve stimulation on EEG and heart rate variability in Crohn's disease: a case report. Brain Stimul. (2014) 7:914–6. doi: 10.1016/j.brs.2014.08.001
67. Bonaz B, Sinniger V, Hoffmann D, Clarençon D, Mathieu N, Dantzer C, et al. Chronic vagus nerve stimulation in Crohn's disease: a 6-month follow-up pilot study. Neurogastroenterol Motil. (2016) 28:948–53. doi: 10.1111/nmo.2016.28.issue-6
68. D’Haens G, Cabrijan Z, Eberhardson M, Berg R, Löwenberg M, Danese S, et al. 367 – vagus nerve stimulation reduces disease activity and modulates serum and autonomic biomarkers in biologicrefractory crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. (2019) 156:S–75. doi: 10.1016/S0016-5085(19)36973-2
69. Kibleur A, Pellissier S, Sinniger V, Robert J, Gronlier E, Clarençon D, et al. Electroencephalographic correlates of low-frequency vagus nerve stimulation therapy for Crohn's disease. Clin Neurophysiol. (2018) 129:1041–6. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2018.02.127
70. Mion F, Pellissier S, Garros A. Transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation for the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome: a pilot, open-label study. Bioelectronics Med. (2020) 3:5–12. doi: 10.2217/bem-2020-0004
71. Shi X, Hu Y, Zhang B, Li W, Chen JD, Liu F. Ameliorating effects and mechanisms of transcutaneous auricular vagal nerve stimulation on abdominal pain and constipation. JCI Insight. (2021) 6. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.150052
72. Krames E, Mousad DG. Spinal cord stimulation reverses pain and diarrheal episodes of irritable bowel syndrome: a case report. Neuromodulation. (2004) 7:82–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1094-7159.2004.04011.x
73. Lind G, Winter J, Linderoth B, Hellström PM. Therapeutic value of spinal cord stimulation in irritable bowel syndrome: a randomized crossover pilot study. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. (2015) 308:R887–94. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00022.2015
74. Vitton V, Damon H, Roman S, Nancey S, Flourié B, Mion F. Transcutaneous posterior tibial nerve stimulation for fecal incontinence in inflammatory bowel disease patients: a therapeutic option? Inflammation Bowel Dis. (2009) 15:402–5. doi: 10.1002/ibd.20774
75. Krasaelap A, Sood MR, Li BUK, Unteutsch R, Yan K, Nugent M, et al. Efficacy of auricular neurostimulation in adolescents with irritable bowel syndrome in a randomized, double-blind trial. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2020) 18:1987–1994.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.10.012
76. Hu P, Sun K, Li H, Qi X, Gong J, Zhang Y, et al. Transcutaneous electrical acustimulation improved the quality of life in patients with diarrhea-irritable bowel syndrome. Neuromodulation. (2022) 25:1165–72. doi: 10.1016/j.neurom.2021.10.009
77. Li G, Jin B, Fan Z. Clinical application of transcranial magnetic stimulation for functional bowel disease. Front Med (Lausanne). (2023) 10:1213067. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1213067
78. Pellissier S, Bonaz B. The place of stress and emotions in the irritable bowel syndrome. Vitam Horm. (2017) 103:327–54. doi: 10.1016/bs.vh.2016.09.005
79. Chang L. The role of stress on physiologic responses and clinical symptoms in irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology. (2011) 140:761–5. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.01.032
80. Spetalen S, Sandvik L, Blomhoff S, Jacobsen MB. Autonomic function at rest and in response to emotional and rectal stimuli in women with irritable bowel syndrome. Dig Dis Sci. (2008) 53:1652–9. doi: 10.1007/s10620-007-0066-0
81. Dinan TG, Quigley EM, Ahmed SM, Scully P, O'Brien S, O'Mahony L, et al. Hypothalamic-pituitary-gut axis dysregulation in irritable bowel syndrome: plasma cytokines as a potential biomarker? Gastroenterology. (2006) 130:304–11. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2005.11.033
82. Kennedy PJ, Clarke G, Quigley EM, Groeger JA, Dinan TG, Cryan JF. Gut memories: towards a cognitive neurobiology of irritable bowel syndrome. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. (2012) 36:310–40. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2011.07.001
83. Labad J, Soria V, Salvat-Pujol N, Segalàs C, Real E, Urretavizcaya M, et al. Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis activity in the comorbidity between obsessive-compulsive disorder and major depression. Psychoneuroendocrinology. (2018) 93:20–8. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2018.04.008
84. Waters RP, Rivalan M, Bangasser DA, Deussing JM, Ising M, Wood SK, et al. Evidence for the role of corticotropin-releasing factor in major depressive disorder. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. (2015) 58:63–78. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2015.07.011
85. Tache Y, Larauche M, Yuan PQ, Million M. Brain and gut CRF signaling: biological actions and role in the gastrointestinal tract. Curr Mol Pharmacol. (2018) 11:51–71. doi: 10.2174/1874467210666170224095741
86. Chen XF, Guo Y, Lu XQ, Qi L, Xu KH, Chen Y, et al. Aberrant intraregional brain activity and functional connectivity in patients with diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome. Front Neurosci. (2021) 15:721822. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.721822
87. Liang YF, Chen XQ, Zhang MT, Tang HY, Shen GM. Research progress of central and peripheral corticotropin-releasing hormone in irritable bowel syndrome with comorbid dysthymic disorders. Gut Liver. (2024) 18:391–403. doi: 10.5009/gnl220346
88. Raposo-Lima C, Morgado P. The role of stress in obsessive-compulsive disorder: A narrative review. Harv Rev Psychiatry. (2020) 28:356–70. doi: 10.1097/HRP.0000000000000274
89. Adams TG, Kelmendi B, Brake CA, Gruner P, Badour CL, Pittenger C. The role of stress in the pathogenesis and maintenance of obsessive-compulsive disorder. Chronic Stress (Thousand Oaks). (2018) 2:1–11. doi: 10.1177/2470547018758043
90. Mar-Barrutia L, Ibarrondo O, Mar J, Real E, Segalàs C, Bertolín S, et al. Long-term comparative effectiveness of deep brain stimulation in severe obsessive-compulsive disorder. Brain Stimul. (2022) 15:1128–38. doi: 10.1016/j.brs.2022.07.050
91. Naesström M, Hariz M, Strömsten L, Bodlund O, Blomstedt P. Deep brain stimulation in the bed nucleus of stria terminalis in obsessive-compulsive disorder-1-year follow-up. World Neurosurg. (2021) 149:e794–802. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2021.01.097
92. Nuttin B, Gielen F, van Kuyck K, Wu H, Luyten L, Welkenhuysen M, et al. Targeting bed nucleus of the stria terminalis for severe obsessive-compulsive disorder: more unexpected lead placement in obsessive-compulsive disorder than in surgery for movement disorders. World Neurosurg. (2013) 80:S30.e11–6. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2012.12.029
93. Farrand S, Evans AH, Mangelsdorf S, Loi SM, Mocellin R, Borham A, et al. Deep brain stimulation for severe treatment-resistant obsessive-compulsive disorder: An open-label case series. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. (2018) 52:699–708. doi: 10.1177/0004867417731819
94. Islam L, Franzini A, Messina G, Scarone S, Gambini O. Deep brain stimulation of the nucleus accumbens and bed nucleus of stria terminalis for obsessive-compulsive disorder: a case series. World Neurosurg. (2015) 83:657–63. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2014.12.024
95. Flavin SA, Winder DG. Noradrenergic control of the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis in stress and reward. Neuropharmacology. (2013) 70:324–30. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.02.013
96. Fudge JL, Haber SN. Bed nucleus of the stria terminalis and extended amygdala inputs to dopamine subpopulations in primates. Neuroscience. (2001) 104:807–27. doi: 10.1016/S0306-4522(01)00112-9
Keywords: DBS, IBS, deep brain stimulation, irritable bowel syndrome, OCD
Citation: Abdelnaim MA, Hebel T, Lang-Hambauer V, Schlaier J, Langguth B and Reissmann A (2025) Deep brain stimulation for obsessive compulsive disorder leads to symptom changes of comorbid irritable bowel syndrome. Front. Psychiatry 16:1545318. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1545318
Received: 14 December 2024; Accepted: 17 February 2025;
Published: 05 March 2025.
Edited by:
Ningfei Li, Charité University Medicine Berlin, GermanyReviewed by:
Rachel Anne Davis, University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, United StatesCopyright © 2025 Abdelnaim, Hebel, Lang-Hambauer, Schlaier, Langguth and Reissmann. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Mohamed A. Abdelnaim, bW9oYW1lZC5hYmRlbG5haW1AbWVkYm8uZGU=; ZHJtb2hhbWVkLmFiZGVsbmFpbUBnbWFpbC5jb20=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.