- 1Department of Intensive Care Unit, The Second Affiliated Hospital and Yuying Children's Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou, Zhejiang, China
- 2Department of Endocrinology, The Second Affiliated Hospital and Yuying Children's Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou, Zhejiang, China
- 3Department of Ultrasound, The Second Affiliated Hospital and Yuying Children's Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou, Zhejiang, China
- 4Department of Gastroenterology, Pingyang Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou, Zhejiang, China
Background: Recent studies have identified a correlation between inflammation and depression. This study aims to explore the correlation between the red blood cell distribution width (RDW) to albumin ratio (RAR), a practical measure for assessing inflammation, and depression in the general population.
Methods: In this population-based cross-sectional study, data from 28932 adults aged≥18 years old in the NHANES during the period of 1999–2018 were analyzed. To examine the correlation between RAR and depression, multivariate logistic regression analyses, subgroup analyses, restricted cubic spline analyses, and interaction tests were conducted. Furthermore, a mediation analysis was performed to elucidate the role of atherogenic index of plasma (AIP) in mediating the effect of RAR on depression.
Results: Multivariate logistic regression analyses and restricted cubic splines analysis indicated that RAR can exhibit a linearly correlation with depression (OR = 1.335; 95% CI: 1.222, 1.458). Subjects in RAR Q2, Q3, Q4 groups had an increased risk on depression as 22.8%, 22.9% and 51.9% than those in the Q1 group. This positive correlation was more pronounced in those with history of cancers. The ROC analysis indicated that the area under the curve (AUC) for RAR (AUC=0.593) was significantly greater than that for RDW and albumin individually. Mediation analysis indicated that AIP mediated 7.8% of the correlation of RAR with depression.
Conclusions: The findings of this study indicated a significant linear positive correlation between RAR and the prevalence of depression, with AIP serving as a mediator.
Introduction
Depression has been a widely acknowledged mental illness that has a substantial correlation with suicide. Approximately 40% of individuals died by suicide have been diagnosed as depression (1, 2). The World Health Organization (WHO) identified depression as the third largest contributor to the global disease burden as early as 2008 and predicted that it could become the leading cause of diseased burden by 2030 (3, 4). In the United States, it was estimated that 17.3 million adults, representing 6.7% of its population, experienced at least one major depressive episode in 2017, positioning it as the foremost cause of disability among individuals aged 15 to 44 (5, 6). Furthermore, depression is correlative with an increased risk of developing a range of physical illnesses, including cardiovascular disease, metabolic disorders, dementia, and cancers (7–10). Given the frequent comorbidity and high prevalence of depression with other diseases, preventing depression has become a critical public health concern.
A growing body of studies suggest that inflammation and nutrition state are considered as crucial mechanisms in depression (11, 12). RDW, a parameter derived from routine laboratory tests, serves as an indicator of the variability in erythrocyte volume. Increased RDW levels, which may arise from abnormal survival and impaired erythropoiesis of red blood cells, have been linked to a range of pathological conditions and increased chronic inflammation (13). Notably, the study revealed a correlation between increased RDW levels and depression. Serum albumin, the predominant circulating protein in the bloodstream, is a critical marker of both inflammatory response and nutritional status (14–17). The physiological functions of albumin encompass antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antiplatelet aggregation properties, and anticoagulant, in addition to its role in maintaining colloid osmotic pressure (18). The literature provided evidence of a correlation between serum albumin levels and depression among various cohorts, including HIV patients, stroke survivors, individuals with chronic liver disease, elderly females, and community-dwelling populations (19–23).
Given the critical roles in diseases, physiological functions, and inflammation assessment, the combined evaluation of albumin concentration and RDW may provide valuable information for assessing the risk of depression. RAR, a parameter derived from standard laboratory tests, may provide the substantial information beyond individual values themselves. Recently, RAR has been identified as a potential risk biomarker for adverse outcomes in various diseases, including atrial fibrillation (24), acute myocardial infarction (25), heart failure (26), diabetes (27), stroke (28), and chronic kidney disease (29). However, the correlation between RAR and depression remains to be elucidated.
Consequently, this study aims to investigate the correlation between RAR and depression within a large, nationally representative sample of adults residing in data of Americans were sourced from the NHANES during the period of 1999-2018.
Methods
Research subjects and design
National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), conducted by National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) (30), is a comprehensive study designed to assess the correlation between nutrition, health promotion, and disease prevention. The National Center for Health Statistics Ethics Review Board has approved the implementation of NHANES(NCHS ERB protocols #2011–17), and has obtained the written informed consent of all subjects following the Declaration of Helsinki. The survey shall be conducted every two years by taking physical examinations, interviews, and various sections covering dietary, demographic, examination, and laboratory data. Additional information regarding the NHANES database can be found at http://www.cdc.gov/nhanes.
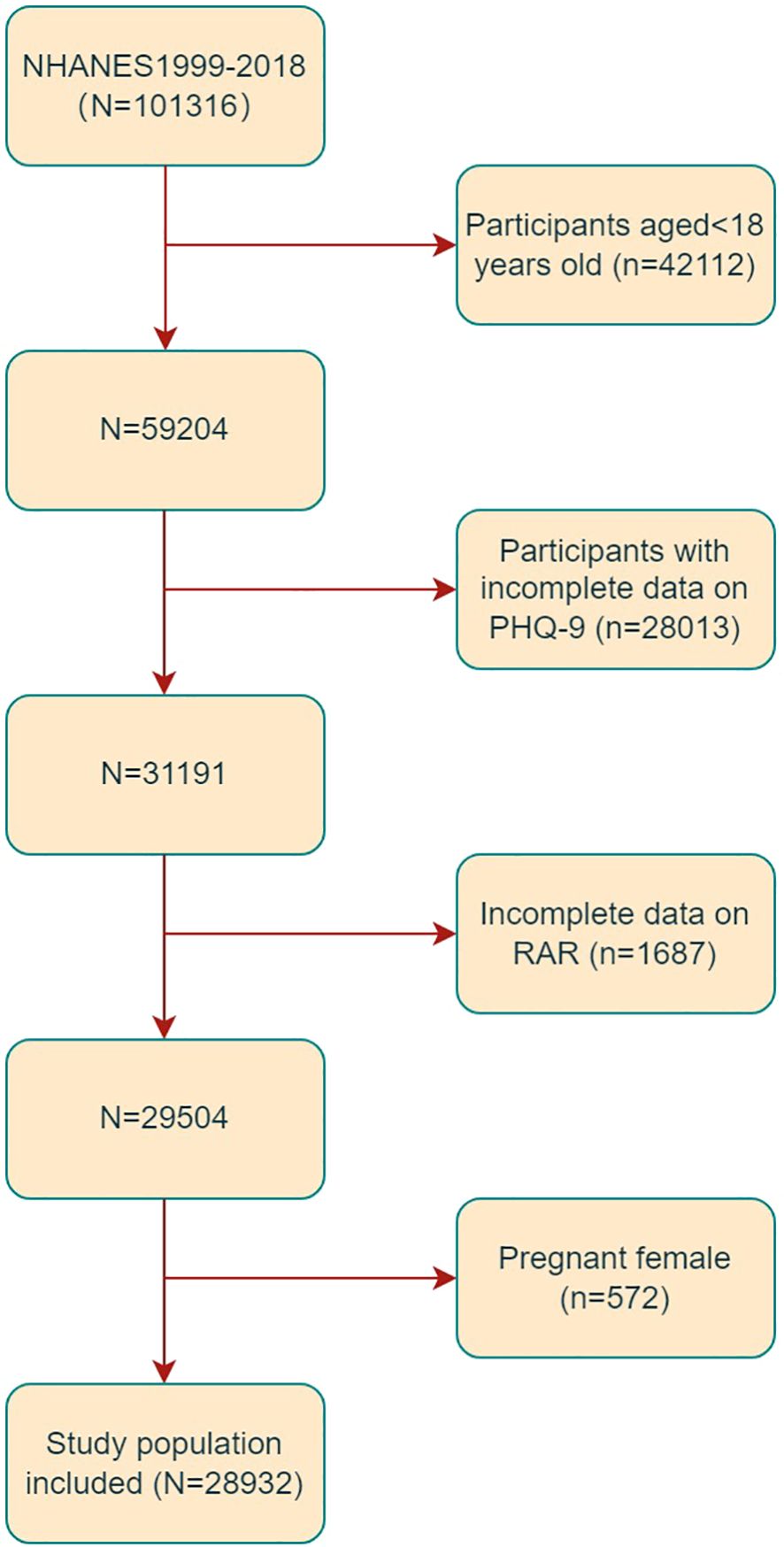
For the present study, data were collected from ten 2-year cycles of NHANES from 1999 to 2018. Subjects aged 18 years old or more were eligible for inclusion (n=59204). Subjects with incomplete Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9) (n=28013) and RAR (n=1687) data were excluded according to the exclusion criteria. Furthermore, 572 pregnant individuals were excluded (as shown in Figure 1). Ultimately, the study comprised a total of 28932 individuals.
Ascertainment of depression
PHQ-9 (31, 32) is a widely utilized instrument for screening depression, consisting of 9 items with a scale from 0 to 3, resulting in a total score ranging from 0 to 27. A cumulative score of 10 or higher indicates depression. This threshold is frequently employed in epidemiological studies to identify individuals with depression and has been validated through clinical evaluation (31).
Measurement of RAR
RAR was calculated as a previously established formula (33): RAR = RDW (%)/albumin (g/dL). Subjects were classified into four groups according to RAR quartiles as <2.82, 2.82–3.04, 3.04–3.31, and ≥3.31, with the lowest RAR category (<2.82) serving as the control group.
Ascertainment of AIP
The determination of AIP was predicated upon the measurement on concentrations of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) and triglycerides (TG) in the bloodstream. The precise mathematical formula utilized for calculating AIP was expressed as follows: log10 [TG (mmol/L)/HDL-C (mmol/L)] (34, 35).
Covariates
Demographic and lifestyle data were collected through household interview questionnaires administered by highly trained medical personnel. Anthropometric measurements and biochemical parameters were obtained during medical examinations and subsequent laboratory assessments conducted at the Mobile Examination Center (MEC). The demographic data encompassed age, poverty-income ratio (PIR), gender, marital status, race, and education level. Self-reported health information included participants past medical history, specifically coronary heart disease (CHD), stroke, diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and cancers, as well as details on physical activity, smoking, and alcohol consumption. Physical examination data, including body mass index (BMI), were recorded by trained health technicians at the MEC. Blood samples were collected at the MEC for the measurement of serum triglycerides (TG), urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio (UACR), total cholesterol (TC), red cell distribution width (RDW), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C). Less than 3% of values missed in total. Multiple imputation was performed for missing values. The definitions for alcohol intaking and smoking were consistent with previous reports (36). Estimated-glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) was calculated as the Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI) formula (37, 38). Chronic kidney disease (CKD) was defined in accordance with current clinical guidelines as UACR exceeding 30 mg/g, eGFR of less than 60 mL/min/1.73 m², or both conditions (39, 40).
Statistical analyses
In accordance with the PHQ-9 scores, subjects in this study were categorized into two distinct groups: depression and non-depression groups (31, 32). Normal distribution was evaluated by determining skewness with a Kolmogorov–Smirnov test. The normality of continuous variables was assessed and expressed as either median and interquartile range or mean ± SD. Between-group comparisons were made using Student’s t-test and the Kruskal–Wallis equality-of-populations rank test for normally distributed and skewed continuous variables, respectively, and using the χ2 test for categorical variables. To elucidate the correlation between RAR and depression, OR and 95% CI were estimated with logistic regression models. Variables demonstrating clinical and statistical significance in the univariate analyses (p<0.05) were incorporated into the multivariate analyses. Three models were employed in the analyses: Model 1 was unadjusted, and Model 2 was adjusted for gender and age. Model 3, the final multivariable model, included additional adjustments for race, hyperlipidemia, alcohol intaking, BMI, smoking, moderate physical activities, CHD, stroke, diabetes, CKD, PIR, education level, marital status, hypertension, HbA1c, and cancers. The dose–response correlation between depression and RAR was investigated through restricted cubic spline (RCS) curves, with a particular focus on potential non-linearity. Moreover, subgroup analyses were performed to ascertain whether the correlation between RAR and depression differed among subjects with varying characteristics. Subsequently, the mediation analyses were conducted with the mediation package, and the confidence interval of the mediation effect was evaluated with the Bootstrap method to quantify the proportion of AIP in the mediation effect. Data analyses were executed by using R software and Free Statistics software, with statistical significance established at a two-sided P value of less than 0.05.
Results
Baseline characteristics
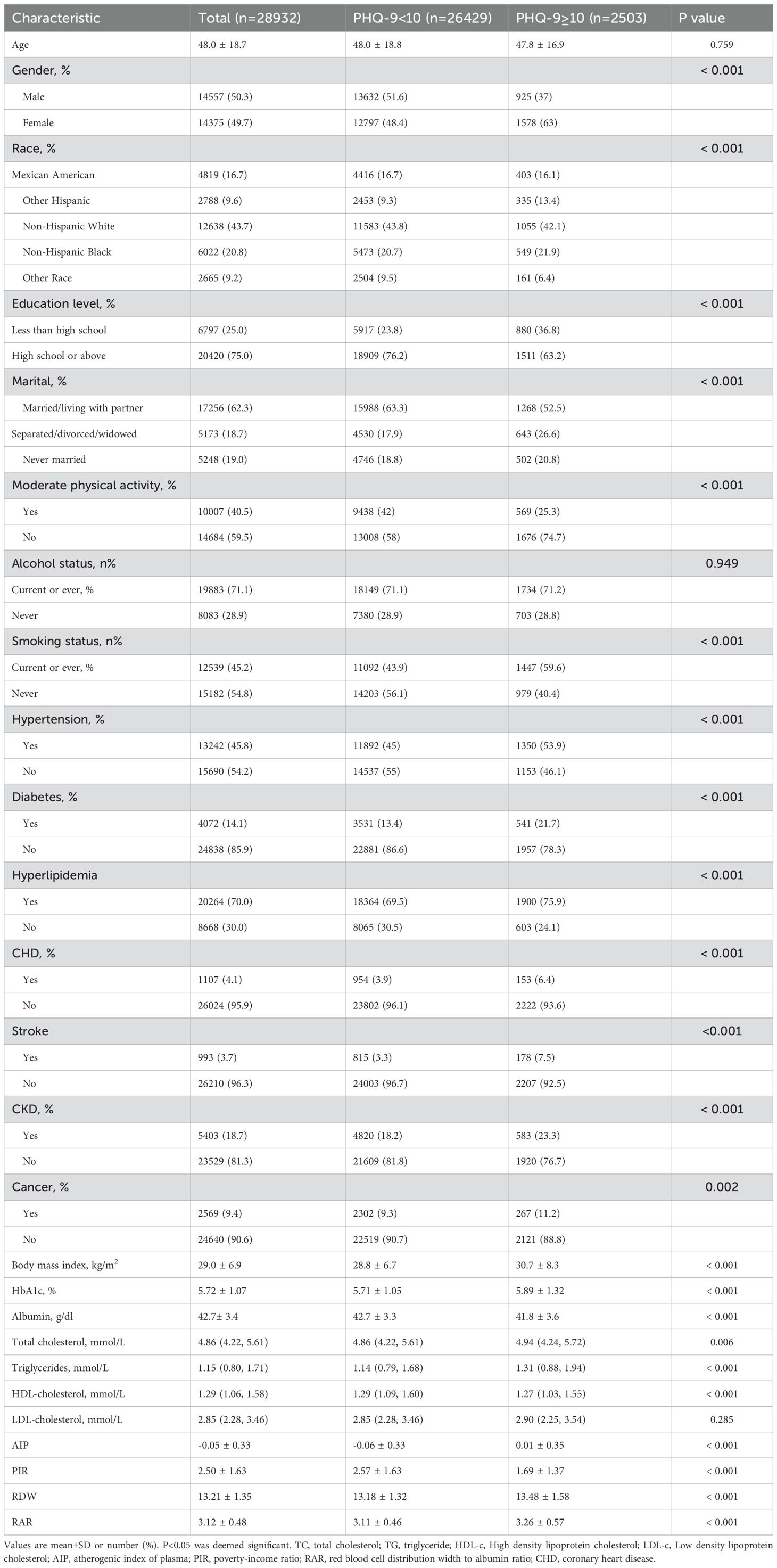
Table 1 shows a comprehensive summary of the subjects’ characteristics. Of the 28932 subjects included in the study, 14375 (49.7%) were females, with a mean age of 48.0 ± 18.7 years old. Among these subjects, 2503 (9.5%) presented with depression. The majority of individuals with depression were females, who had a higher prevalence of current or former smoking, lived alone, and had lower HDL-C and family PIR levels. Additionally, they were more likely to lack physical activities and had higher levels of BMI, RDW, HbA1c, TC, and TG. Furthermore, these individuals were more frequently correlative with underlying medical conditions such as hyperlipidemia, hypertension, CHD, diabetes, CKD, stroke, and cancers. RAR in the depression group was 3.26 ± 0.57, which was higher than 3.11 ± 0.46 observed in the non-depression group.
Correlation between RAR and depression
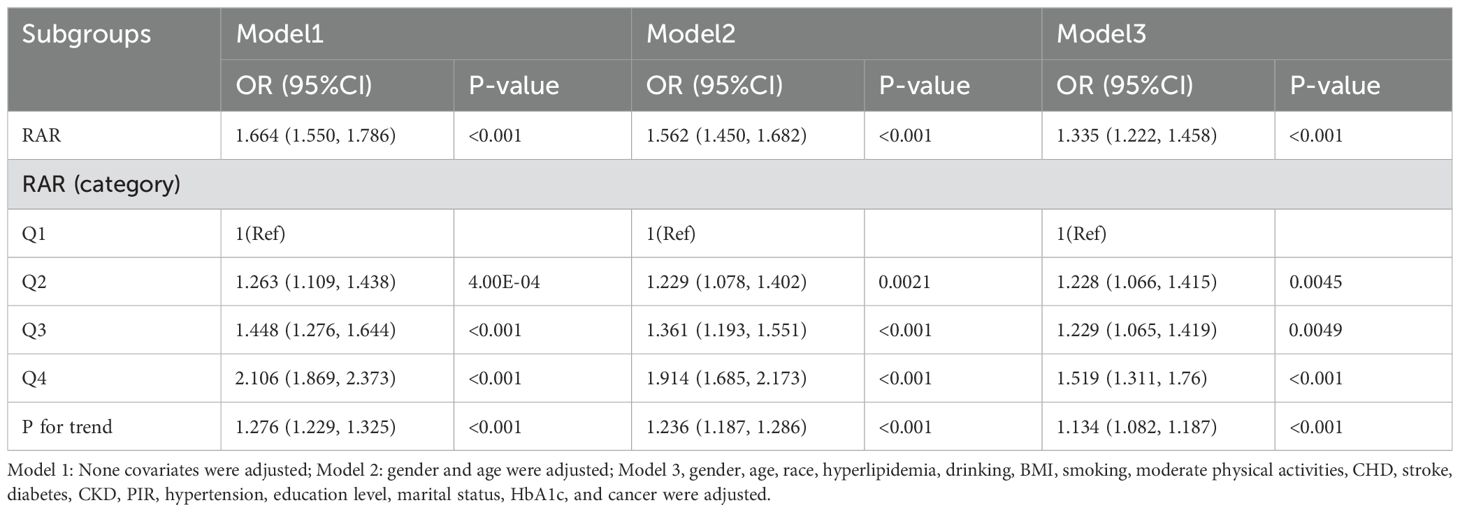
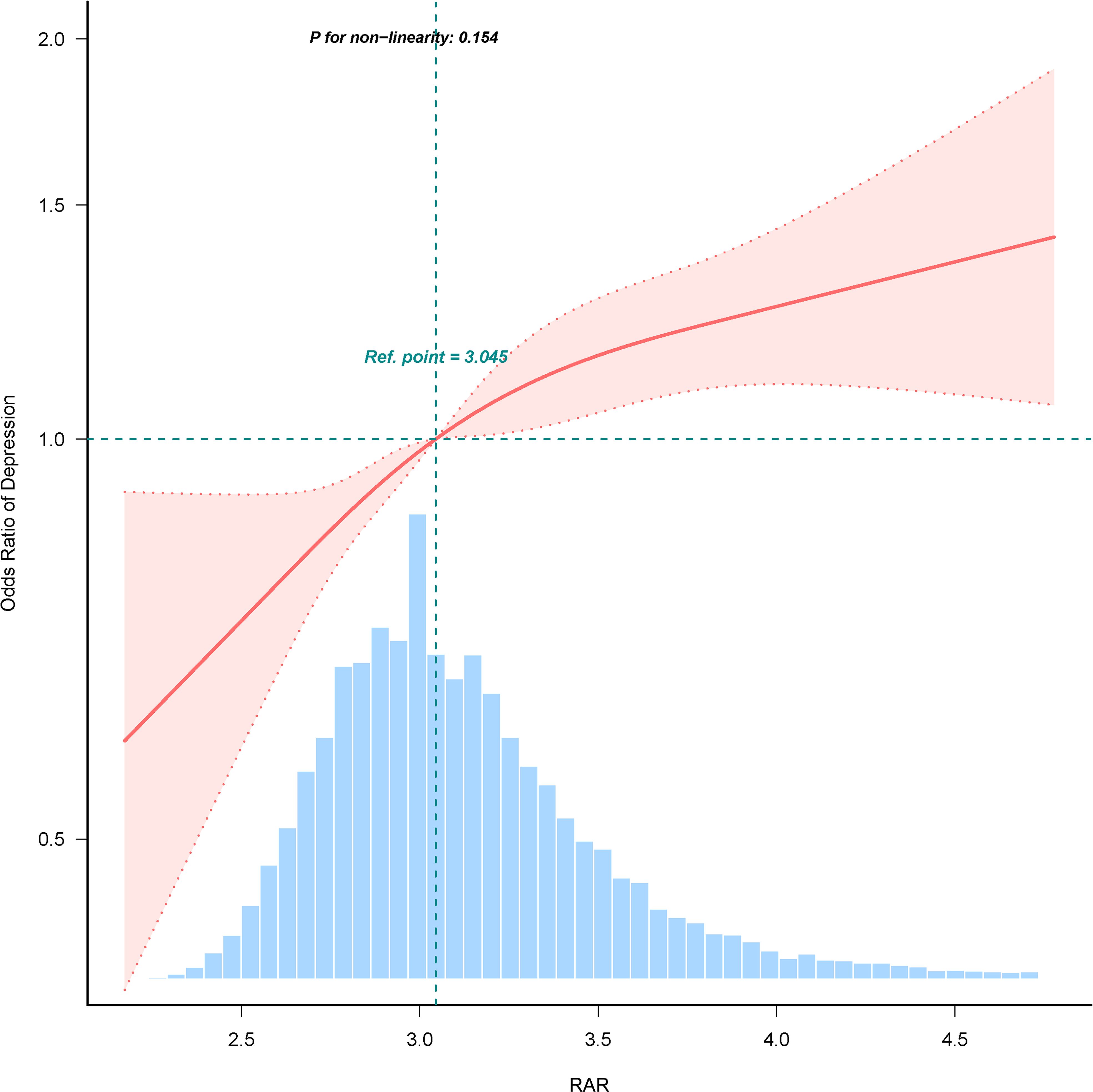
In multiple logistic regression analyses, a significant positive correlation between RAR and depression was identified after adjusting for confounders in Model 3 (OR=1.335, 95% CI: 1.222, 1.458). To further investigate RAR, these subjects were categorized into quartiles. In the totally adjusted Model 3, OR and 95% CI for subjects in RAR Q2, Q3, and Q4 groups were 1.228 (1.066, 1.415), 1.229 (1.065, 1.419), and 1.519 (1.311, 1.76), compared to the control group with Q1 group, respectively, for depression risk (p for trend <0.001), as detailed in Table 2. RCS analyses demonstrated a linear correlation between RAR and depression (as shown in Figure 2).
Subgroup analysis
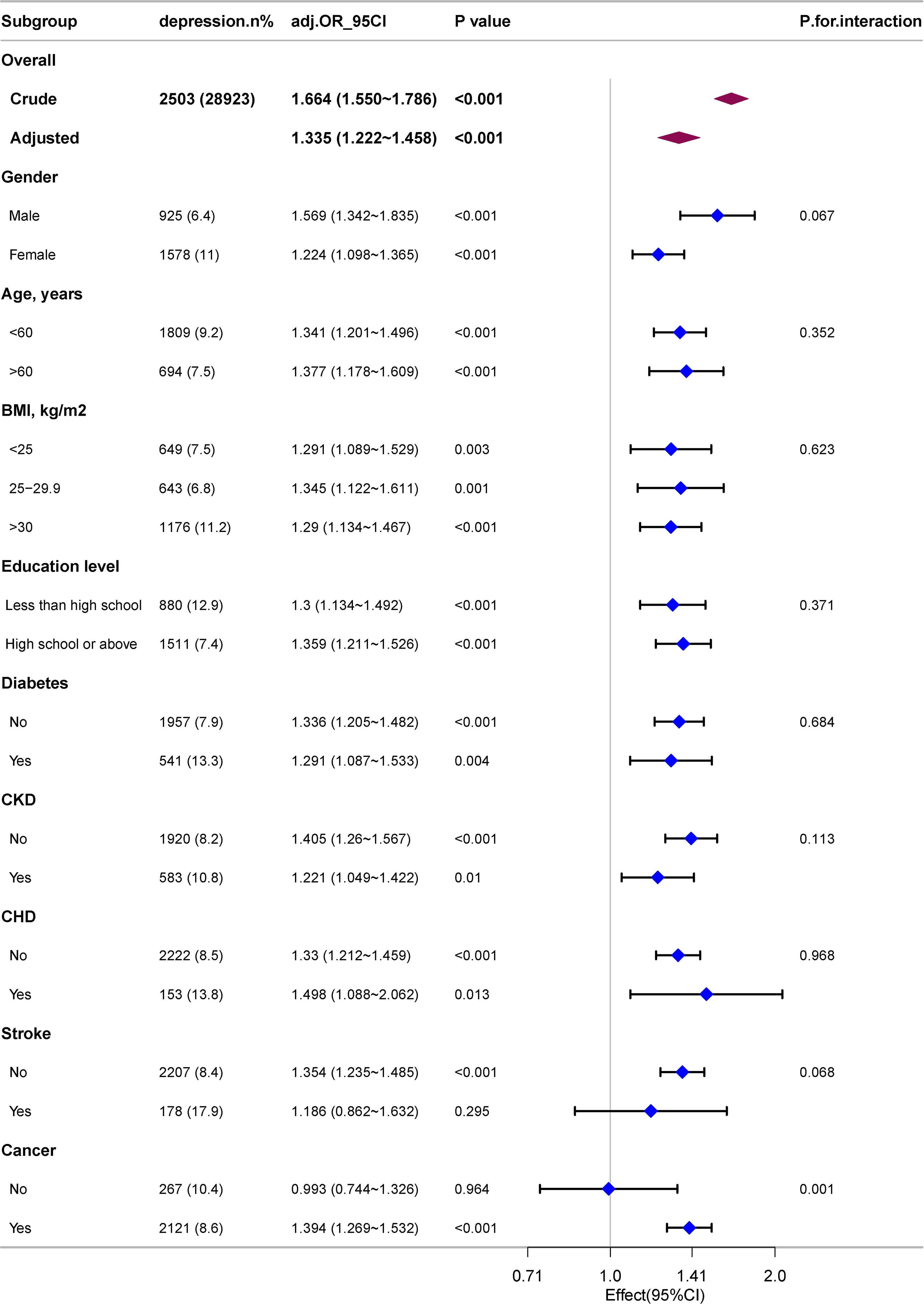
Through subgroup analyses on further exploration of the correlation between RAR and depression across various populations stratified by age, BMI, education level, gender, and disease status (including CHD, diabetes, cancers, CKD and stroke), a significant interaction effect of cancer status on the correlation between RAR and depression was identified, with an interaction p<0.001. Specifically, among individuals with cancers, each one-unit increase in RAR was correlative with a 39.4% increase in the incidence of depression (OR: 1.394; 95%CI: 1.269–1.532). Notably, other covariates, including age and gender, did not demonstrate interactive effects on the correlation between RAR and depression (as shown in Figure 3).
ROC analysis
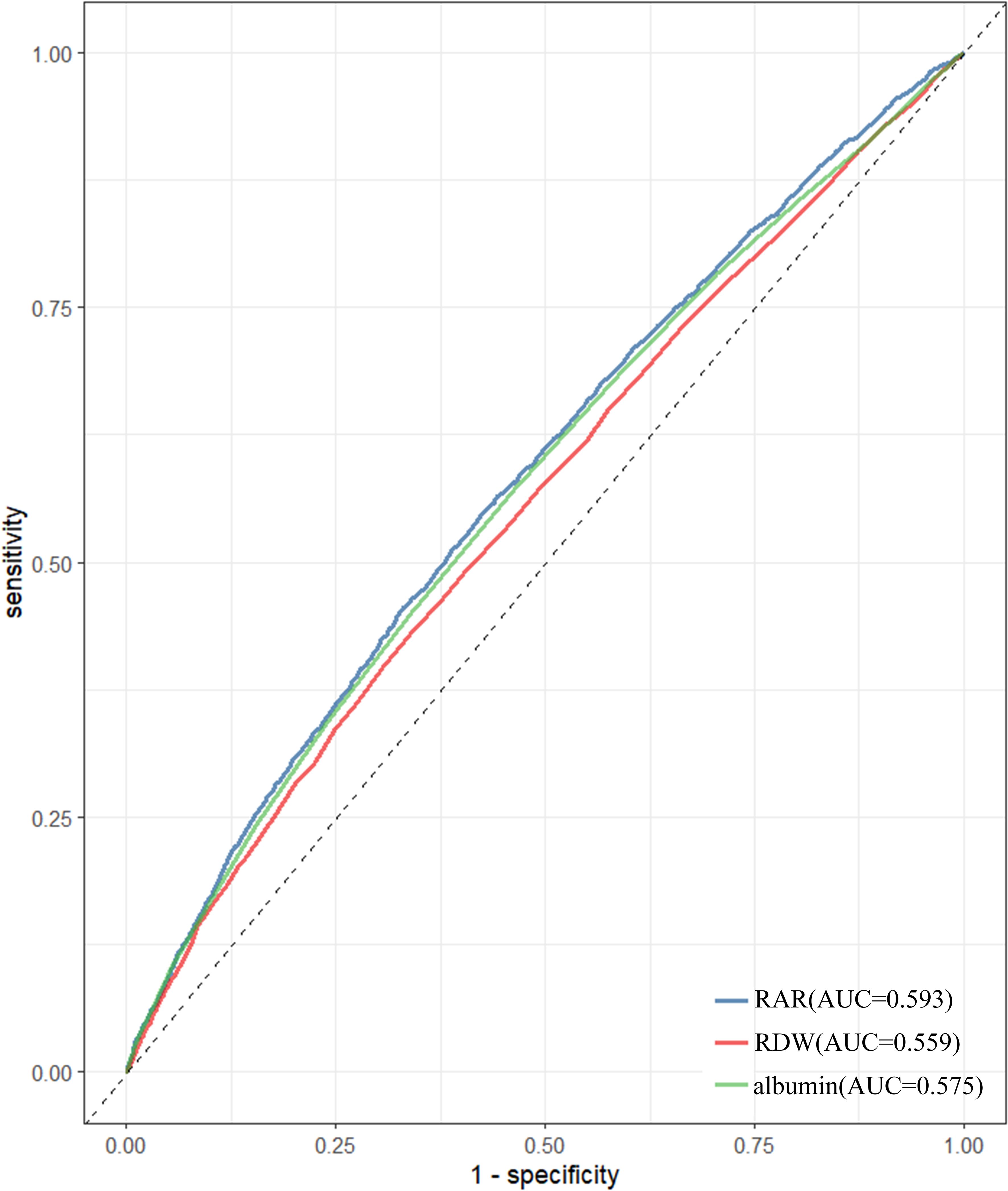
ROC analyses revealed that, in subjects with depression, AUC for RAR was 0.593, which exceeded AUC for RDW (ACU=0.559) and albumin (AUC=0.575). These results were statistically significant (P < 0.05), as detailed in Figure 4.
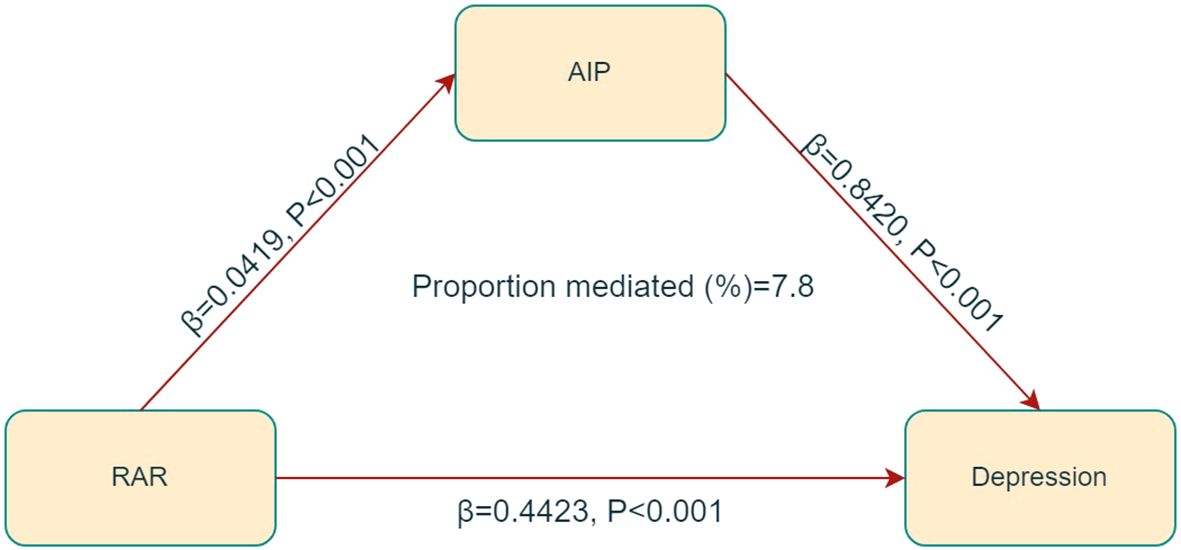
Figure 4. Mediated analysis model path diagram. RAR was defined as the independent variable; depression as the dependent variable; and AIP as the mediating variable.
Mediation analysis
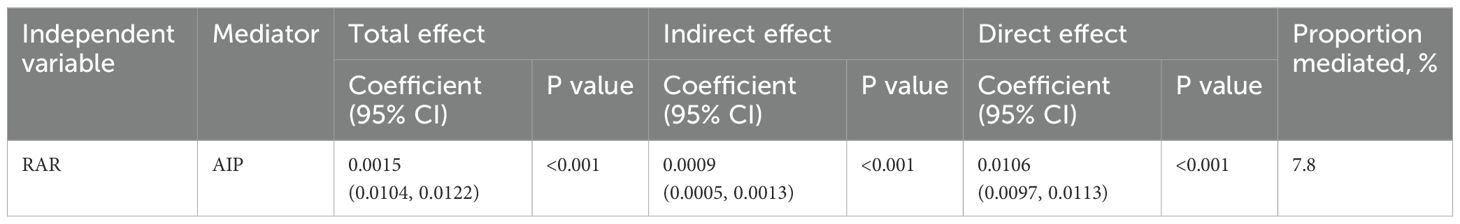
In the mediation analysis, RAR was treated as the independent variable, depression as the dependent variable, and AIP as the mediator. The mediation model and its correlative pathways have been depicted in Figure 5. The results indicate a significant correlation between RAR and AIP (β = 0.0419, p < 0.001), as well as that between AIP and depression (β = 0.8420, p < 0.001). Further analyses revealed a significant indirect effect of RAR on depression through AIP, with an effect size of 0.0009 (p < 0.001), suggesting that AIP partially mediates the correlation between RAR and depression, accounting for approximately 7.8% of the total effect, as detailed in Table 3.
Discussion
This study identified a positive correlation between RAR and depression, with a notably stronger correlation among individuals with a history of cancers. RAR demonstrated superior diagnostic accuracy for depression compared to RDW and albumin independently. In addition, mediation analysis revealed that AIP partially mediated the correlation between RAR and depression.
In previous studies, it has been established that RAR possesses predictive capabilities regarding the mortality and severity of various cardiovascular disease, including stroke, acute coronary syndrome, coronary heart disease, heart failure, and atrial fibrillation (24–26, 28). Furthermore, an increased RAR has been linked to increased mortality rates in various conditions, including cancers, kidney diseases, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and diabetes (29, 41–43). Given that many of these conditions involve arteriosclerosis and injury, which are important risk factors for depression (44, 45), a strong correlation between RAR and depression was hypothesized. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to investigate the correlation between RAR and depression.
Erythrocyte pathologies and inflammation are often correlative. Inflammatory mediators contribute to endothelial and erythrocyte injury, thereby facilitating the development of atherosclerosis (46, 47). Erythrocyte dysfunction, in turn, can initiate inflammatory responses (47, 48) and oxidative dysregulation. Notably, RDW has been recognized as a biomarker for erythrocyte injury, which has been utilized in assessing depression risk (49, 50). Similarly, serum albumin can be recognized as an inflammatory marker (51). Previous studies have indicated that serum albumin levels are significantly lower in individuals with depressive disorders compared to healthy controls (23), and these levels are correlative with the severity of diseases (52, 53). Given that RDW and serum albumin are used to calculate RAR, this composite measure may provide a more reliable assessment of inflammation than either parameter alone. The results obtained from the ROC analysis of this study further affirmed the diagnostic potential of RAR for depression (as shown in Figure 5).
A significant interaction effect was identified between RAR and the history of cancers, indicating that the correlation between RAR and depression is particularly pronounced among individuals with cancers. This finding may be related to higher rates of depression among individuals with caners than those without cancers (54). Cancers are usually accompanied by chronic inflammation and malnutrition (55). The presence of cancers may exacerbate the effects of chronic inflammation correlative with increased RAR levels, potentially playing a contributory role in the onset and progression of depressive symptoms. Consequently, it is imperative to consider patients with cancers exhibiting high RAR levels as a high-risk group for depression. Further longitudinal and clinical studies are warranted to validate these findings.
The findings suggest that AIP partially mediates the correlation between inflammation (as determined by RAR) and depression, which underscores the importance of monitoring AIP in patients with a high RAR. Previous studies have demonstrated a significant correlation between depression and lipid metabolism disorders (56–59). Therefore, regulating AIP, particularly by reducing TG levels and increasing HDL-C levels, may mitigate the risk of depression in individuals with a high RAR.
The precise mechanisms underlying the correlation between depression and RAR remain incompletely elucidated. However, several potential pathways have been proposed. Chronic stress has been shown to induce sustained activation of microglia, which subsequently leads to the production of various proinflammatory cytokines, thereby contributing to the pathogenesis of depression (60). Additionally, early life stress can activate the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, resulting in increased cortisol levels. This hormonal imbalance can disrupt the homeostasis of neurotransmitters and the synthesis of nerve growth factors, ultimately leading to a decrease in hippocampal volume and the onset of depressive symptoms (61, 62). Furthermore, inflammation influences the release and reuptake of glutamate by glial cells. This dysregulation enables glutamate to bind to extra synaptic N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors, thereby inhibiting growth factors and induces excitotoxicity, and contributing to the development of depression (63). Serum albumin serves as the primary extracellular molecule for maintaining plasma redox homeostasis. A decrease in albumin may result in the dysregulation of oxidative stress, with increased levels of free radicals and oxidative injury being observable in patients with depression (64). Furthermore, albumin can be adversely affected by inflammatory processes as the predominant protein synthesized in liver, thereby indicating immune dysfunction and systemic inflammatory (65).
A significant strength of this study lies in the utilization of a nationally representative sample from the NHANES, enabling a thorough evaluation of diverse characteristics in population. This methodological approach enhances the generalizability of findings to a broader spectrum of American adults. Furthermore, the study meticulously controlled for numerous confounding variables, yielding robust estimates of the independent correlation between RAR and the prevalence of depression. Finally, an intermediary analysis was performed in this study to explore the correlation between chronic inflammation, AIP, and depression.
It is essential to recognize several significant limitations inherent in this study. Firstly, the cross-sectional research design constrains the capacity to infer causality between RAR and depression. To address this limitation, future research should incorporate experimental methodologies and longitudinal surveys to elucidate temporal correlation and underlying mechanisms. Secondly, the diagnosis of depression by using the PHQ-9 scale relies on self-reported data and lacks validation by clinical practitioners. It is important to acknowledge that PHQ-9 is extensively employed in both epidemiological and clinical contexts, which has been rigorously validated, demonstrating the high specificity and the high sensitivity (66). Lastly, the findings are specific to Americans, thereby constraining the generalizability of the results to other demographic groups.
Conclusion
In summary, a significant correlation between RAR levels and depression after adjusting for multiple confounding variables was identified in this study. Increased RAR levels may have important implications for the treatment and diagnosis of depression. Nevertheless, this hypothesis necessitates further validation through prospective studies.
Data availability statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found here: NHANES, http://www.cdc.gov/nhanes.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by National Center for Health Statistics Ethics Review Board. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
TS: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing – original draft. JX: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing – original draft. XW: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing – original draft. HL: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the NHANES database for providing the data source for this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Nock MK, Green JG, Hwang I, McLaughlin KA, Sampson NA, Zaslavsky AM, et al. Prevalence, correlates, and treatment of lifetime suicidal behavior among adolescents: results from the National Comorbidity Survey Replication Adolescent Supplement. JAMA Psychiatry. (2013) 70:300–10. doi: 10.1001/2013.jamapsychiatry.55
2. Nock MK, Hwang I, Sampson NA, Kessler RC. Mental disorders, comorbidity and suicidal behavior: results from the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Mol Psychiatry. (2010) 15:868–76. doi: 10.1038/mp.2009.29
3. Liu J, Liu Y, Ma W, Tong Y, Zheng J. Temporal and spatial trend analysis of all-cause depression burden based on Global Burden of Disease (GBD) 2019 study. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:12346. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-62381-9
4. Mathers CD, Loncar D. Projections of global mortality and burden of disease from 2002 to 2030. PloS Med. (2006) 3:e442. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0030442
5. Collaborators GBDMD. Global, regional, and national burden of 12 mental disorders in 204 countries and territories, 1990-2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Psychiatry. (2022) 9:137–50. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(21)00395-3
6. Tiller JW. Depression and anxiety. Med J Aust. (2013) 199:S28–31. doi: 10.5694/mja2.2013.199.issue-S6
7. Byers AL, Yaffe K. Depression and risk of developing dementia. Nat Rev Neurol. (2011) 7:323–31. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2011.60
8. Carney RM, Freedland KE. Depression and coronary heart disease. Nat Rev Cardiol. (2017) 14:145–55. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2016.181
9. Hidese S, Asano S, Saito K, Sasayama D, Kunugi H. Association of depression with body mass index classification, metabolic disease, and lifestyle: A web-based survey involving 11,876 Japanese people. J Psychiatr Res. (2018) 102:23–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2018.02.009
10. Wakefield CE, Butow PN, Aaronson NA, Hack TF, Hulbert-Williams NJ, Jacobsen PB. International Psycho-Oncology Society Research C: Patient-reported depression measures in cancer: a meta-review. Lancet Psychiatry. (2015) 2:635–47. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(15)00168-6
11. Zheng Y, Yin K, Li L, Wang X, Li H, Li W, et al. Association between immune-inflammation-based prognostic index and depression: An exploratory cross-sectional analysis of NHANES data. J Affect Disord. (2024) 362:75–85. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2024.06.103
12. Li Z, Zhang L, Yang Q, Zhou X, Yang M, Zhang Y, et al. Association between geriatric nutritional risk index and depression prevalence in the elderly population in NHANES. BMC Public Health. (2024) 24:469. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-17925-z
13. Salvagno GL, Sanchis-Gomar F, Picanza A, Lippi G. Red blood cell distribution width: A simple parameter with multiple clinical applications. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. (2015) 52:86–105. doi: 10.3109/10408363.2014.992064
14. Hou C, Huang X, Wang J, Chen C, Liu C, Liu S, et al. Inflammation and nutritional status in relation to mortality risk from cardio-cerebrovascular events: evidence from NHANES. Front Nutr. (2024) 11:1504946. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1504946
15. Gradel KO. Interpretations of the role of plasma albumin in prognostic indices: A literature review. J Clin Med. (2023) 12(19):6132. doi: 10.3390/jcm12196132
16. Don BR, Kaysen G. Serum albumin: relationship to inflammation and nutrition. Semin Dial. (2004) 17:432–7. doi: 10.1111/j.0894-0959.2004.17603.x
17. Fanali G, di Masi A, Trezza V, Marino M, Fasano M, Ascenzi P. Human serum albumin: from bench to bedside. Mol Aspects Med. (2012) 33:209–90. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2011.12.002
18. Arques S. Human serum albumin in cardiovascular diseases. Eur J Intern Med. (2018) 52:8–12. doi: 10.1016/j.ejim.2018.04.014
19. Cao J, Qiu W, Yu Y, Li N, Wu H, Chen Z. The association between serum albumin and depression in chronic liver disease may differ by liver histology. BMC Psychiatry. (2022) 22:5. doi: 10.1186/s12888-021-03647-8
20. Gudmundsson P, Skoog I, Waern M, Blennow K, Palsson S, Rosengren L, et al. The relationship between cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers and depression in elderly women. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. (2007) 15:832–8. doi: 10.1097/JGP.0b013e3180547091
21. Pascoe MC, Skoog I, Blomstrand C, Linden T. Albumin and depression in elderly stroke survivors: An observational cohort study. Psychiatry Res. (2015) 230:658–63. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2015.10.023
22. Poudel-Tandukar K, Jacelon CS, Bertone-Johnson ER, Palmer PH, Poudel KC. Serum albumin levels and depression in people living with Human Immunodeficiency Virus infection: a cross-sectional study. J Psychosom Res. (2017) 101:38–43. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychores.2017.08.005
23. Al-Marwani S, Batieha A, Khader Y, El-Khateeb M, Jaddou H, Ajlouni K. Association between albumin and depression: a population-based study. BMC Psychiatry. (2023) 23:780. doi: 10.1186/s12888-023-05174-0
24. Chen C, Cai J, Song B, Zhang L, Wang W, Luo R, et al. Relationship between the Ratio of Red Cell Distribution Width to Albumin and 28-Day Mortality among Chinese Patients over 80 Years with Atrial Fibrillation. Gerontology. (2023) 69:1471–81. doi: 10.1159/000534259
25. Li D, Ruan Z, Wu B. Association of red blood cell distribution width-albumin ratio for acute myocardial infarction patients with mortality: A retrospective cohort study. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. (2022) 28:10760296221121286. doi: 10.1177/10760296221121286
26. Ni Q, Wang X, Wang J, Chen P. The red blood cell distribution width-albumin ratio: A promising predictor of mortality in heart failure patients - A cohort study. Clin Chim Acta. (2022) 527:38–46. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2021.12.027
27. Hong J, Hu X, Liu W, Qian X, Jiang F, Xu Z, et al. Impact of red cell distribution width and red cell distribution width/albumin ratio on all-cause mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes and foot ulcers: a retrospective cohort study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2022) 21:91. doi: 10.1186/s12933-022-01534-4
28. Zhao N, Hu W, Wu Z, Wu X, Li W, Wang Y, et al. The red blood cell distribution width-albumin ratio: A promising predictor of mortality in stroke patients. Int J Gen Med. (2021) 14:3737–47. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S322441
29. Kimura H, Tanaka K, Saito H, Iwasaki T, Kazama S, Shimabukuro M, et al. Impact of red blood cell distribution width-albumin ratio on prognosis of patients with CKD. Sci Rep. (2023) 13:15774. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-42986-2
30. Terry AL, Chiappa MM, McAllister J, Woodwell DA, Graber JE. Plan and operations of the national health and nutrition examination survey, august 2021-august 2023. Vital Health Stat 1. (2024) 66:1–21. doi: 10.15620/cdc/151927
31. Chen Y, Lin H, Xu J, Zhou X. Estimated glucose disposal rate is correlated with increased depression: a population-based study. BMC Psychiatry. (2024) 24:786. doi: 10.1186/s12888-024-06257-2
32. Kroenke K, Spitzer RL, Williams JB. The PHQ-9: validity of a brief depression severity measure. J Gen Intern Med. (2001) 16:606–13. doi: 10.1046/j.1525-1497.2001.016009606.x
33. Hao M, Jiang S, Tang J, Li X, Wang S, Li Y, et al. Ratio of red blood cell distribution width to albumin level and risk of mortality. JAMA Netw Open. (2024) 7:e2413213. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.13213
34. Huang J, Chen C, Jie C, Li R, Chen C. L-shaped relationship between atherogenic index of plasma with uric acid levels and hyperuricemia risk. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2024) 15:1461599. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1461599
35. Dobiasova M, Frohlich J. The plasma parameter log (TG/HDL-C) as an atherogenic index: correlation with lipoprotein particle size and esterification rate in apoB-lipoprotein-depleted plasma (FER(HDL)). Clin Biochem. (2001) 34:583–8. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9120(01)00263-6
36. Li C, Xu J. Negative correlation between metabolic score for insulin resistance index and testosterone in male adults. Diabetol Metab Syndr. (2024) 16:113. doi: 10.1186/s13098-024-01353-5
37. Peruzzo S, Ottaviani S, Tagliafico L, Muzyka M, Ponzano M, Marelli C, et al. Renal function assessment in older people: comparative analysis of estimation equation with serum creatinine. Front Med (Lausanne). (2024) 11:1477500. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1477500
38. Inker LA, Schmid CH, Tighiouart H, Eckfeldt JH, Feldman HI, Greene T, et al. Estimating glomerular filtration rate from serum creatinine and cystatin C. N Engl J Med. (2012) 367:20–9. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1114248
39. Chen TK, Knicely DH, Grams ME. Chronic kidney disease diagnosis and management: A review. JAMA. (2019) 322:1294–304. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.14745
40. Inker LA, Astor BC, Fox CH, Isakova T, Lash JP, Peralta CA, et al. KDOQI US commentary on the 2012 KDIGO clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of CKD. Am J Kidney Dis. (2014) 63:713–35. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2014.01.416
41. Liu J, Wang X, Gao TY, Zhang Q, Zhang SN, Xu YY, et al. Red blood cell distribution width to albumin ratio associates with prevalence and long-term diabetes mellitus prognosis: an overview of NHANES 1999-2020 data. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2024) 15:1362077. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1362077
42. Qiu Y, Wang Y, Shen N, Wang Q, Chai L, Liu J, et al. Association between red blood cell distribution width-albumin ratio and hospital mortality in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients admitted to the intensive care unit: A retrospective study. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. (2022) 17:1797–809. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S371765
43. Lu C, Long J, Liu H, Xie X, Xu D, Fang X, et al. Red blood cell distribution width-to-albumin ratio is associated with all-cause mortality in cancer patients. J Clin Lab Anal. (2022) 36:e24423. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24423
44. Shikimoto R, Sasaki T, Abe Y, Nishimoto Y, Hirata T, Mimura M, et al. Depressive symptoms and carotid arteriosclerosis in very old people aged 85 years and older: A cross-sectional study by the Kawasaki Aging and Wellbeing Project. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. (2024) 78:209–11. doi: 10.1111/pcn.13636
45. Teismann H, Wersching H, Nagel M, Arolt V, Heindel W, Baune BT, et al. Establishing the bidirectional relationship between depression and subclinical arteriosclerosis–rationale, design, and characteristics of the BiDirect Study. BMC Psychiatry. (2014) 14:174. doi: 10.1186/1471-244X-14-174
46. Wang JH, Pan GR, Jiang L. A bibliometric analysis of immunotherapy for atherosclerosis: trends and hotspots prediction. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1493250. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1493250
47. Robbie L, Libby P. Inflammation and atherothrombosis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. (2001) 947:167–179; discussion 179-180. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2001.tb03939.x
48. Toledo SLO, Guedes JVM, Alpoim PN, Rios DRA, Pinheiro MB. Sickle cell disease: Hemostatic and inflammatory changes, and their interrelation. Clin Chim Acta. (2019) 493:129–37. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2019.02.026
49. Said AS, Spinella PC, Hartman ME, Steffen KM, Jackups R, Holubkov R, et al. RBC distribution width: biomarker for red cell dysfunction and critical illness outcome? Pediatr Crit Care Med. (2017) 18:134–42. doi: 10.1097/PCC.0000000000001017
50. Dai M, Wei Q, Zhang Y, Fang C, Qu P, Cao L. Predictive value of red blood cell distribution width in poststroke depression. Comput Math Methods Med. (2021) 2021:8361504. doi: 10.1155/2021/8361504
51. Eckart A, Struja T, Kutz A, Baumgartner A, Baumgartner T, Zurfluh S, et al. Relationship of nutritional status, inflammation, and serum albumin levels during acute illness: A prospective study. Am J Med. (2020) 133:713–722 e717. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2019.10.031
52. Zhou D, Yu H, Yao H, Yuan S, Xia Y, Huang L, et al. A novel joint index based on peripheral blood CD4+/CD8+ T cell ratio, albumin level, and monocyte count to determine the severity of major depressive disorder. BMC Psychiatry. (2022) 22:248. doi: 10.1186/s12888-022-03911-5
53. Huang SY, Chiu CC, Shen WW, Chang HC, Wu PL, Su KP. Hypoalbuminemia in drug-free patients with major depressive disorder compared with a dietary matched control group: a clinical meaning beyond malnutrition. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. (2005) 15:227–30. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2004.10.003
54. Shalata W, Gothelf I, Bernstine T, Michlin R, Tourkey L, Shalata S, et al. Mental health challenges in cancer patients: A cross-sectional analysis of depression and anxiety. Cancers (Basel). (2024) 16(16):2827. doi: 10.3390/cancers16162827
55. Shen X, Xiang M, Tang J, Xiong G, Zhang K, Xia T, et al. Evaluation of peripheral blood inflammation indexes as prognostic markers for colorectal cancer metastasis. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:20489. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-68150-y
56. Wang Y, Shen R. Association of remnant cholesterol with depression among US adults. BMC Psychiatry. (2023) 23:259. doi: 10.1186/s12888-023-04770-4
57. Zhang G, Zhang H, Fu J, Zhao Y. Atherogenic Index of Plasma as a Mediator in the association between Body Roundness Index and Depression: insights from NHANES 2005-2018. Lipids Health Dis. (2024) 23:183. doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02177-y
58. Huang TL, Chen JF. Cholesterol and lipids in depression: stress, hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenocortical axis, and inflammation/immunity. Adv Clin Chem. (2005) 39:81–105. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2423(04)39003-7
59. Guillemot-Legris O, Muccioli GG. Obesity-induced neuroinflammation: beyond the hypothalamus. Trends Neurosci. (2017) 40:237–53. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2017.02.005
60. Fujigaki H, Saito K, Fujigaki S, Takemura M, Sudo K, Ishiguro H, et al. The signal transducer and activator of transcription 1alpha and interferon regulatory factor 1 are not essential for the induction of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase by lipopolysaccharide: involvement of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and nuclear factor-kappaB pathways, and synergistic effect of several proinflammatory cytokines. J Biochem. (2006) 139:655–62. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvj072
61. Rana T, Behl T, Sehgal A, Singh S, Sharma N, Abdeen A, et al. Exploring the role of neuropeptides in depression and anxiety. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. (2022) 114:110478. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2021.110478
62. Heim C, Nemeroff CB. The role of childhood trauma in the neurobiology of mood and anxiety disorders: preclinical and clinical studies. Biol Psychiatry. (2001) 49:1023–39. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3223(01)01157-X
63. Hardingham GE, Bading H. Synaptic versus extrasynaptic NMDA receptor signalling: implications for neurodegenerative disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci. (2010) 11:682–96. doi: 10.1038/nrn2911
64. Liu T, Zhong S, Liao X, Chen J, He T, Lai S, et al. A meta-analysis of oxidative stress markers in depression. PloS One. (2015) 10:e0138904. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0138904
65. Ishida S, Hashimoto I, Seike T, Abe Y, Nakaya Y, Nakanishi H. Serum albumin levels correlate with inflammation rather than nutrition supply in burns patients: a retrospective study. J Med Invest. (2014) 61:361–8. doi: 10.2152/jmi.61.361
Keywords: depression, albumin, red blood cell distribution width, cancer, inflammation
Citation: Shangguan T, Xu J, Weng X and Lin H (2025) Red blood cell distribution width to albumin ratio is associated with increased depression: the mediating role of atherogenic index of plasma. Front. Psychiatry 16:1504123. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1504123
Received: 04 October 2024; Accepted: 15 January 2025;
Published: 30 January 2025.
Edited by:
Lenin Pavón, National Institute of Psychiatry Ramon de la Fuente Muñiz (INPRFM), MexicoReviewed by:
Ying Xiong, Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, ChinaAzmi Eyiol, Konya Beyhekim State Hospital, Türkiye
Copyright © 2025 Shangguan, Xu, Weng and Lin. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hao Lin, NDkxMDM1NzUwQHFxLmNvbQ==
 Tingting Shangguan
Tingting Shangguan Jing Xu
Jing Xu Xiaochun Weng
Xiaochun Weng Hao Lin
Hao Lin