
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Psychiatry , 13 February 2025
Sec. Psychological Therapy and Psychosomatics
Volume 16 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1490585
This article is part of the Research Topic Community Series in Psychocardiology: Exploring the Brain-Heart Interface, volume III View all 3 articles
Sleep disorders are highly prevalent in the general population and are considered a major public health issue. Insomnia constitutes the most frequent sleep disorder in healthy individuals and has been shown to be even more frequent in patients with physical illnesses including cardiovascular diseases. Inadequate sleep quality and short sleep duration, independent of underlying causes, have been linked to the development and progression of cardiometabolic disorders. Additionally, insomnia has been found to be associated with adverse outcome measures, including daytime sleepiness, fatigue, decreased self-reported physical functioning, lower exercise capacity, poor health related quality of life, depressive symptoms, higher rates of hospitalization and increased mortality in patients with cardiovascular diseases. Against this background, comparatively little information is available in the literature regarding the treatment of chronic insomnia in cardiac patient populations. While guidelines for the general population suggest cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia as a first-line treatment option and preliminary evidence suggests this treatment to be beneficial in cardiac patients with insomnia symptoms, it is often limited by availability and possibly the clinician’s poor understanding of sleep issues in cardiac patients. Therefore, pharmacologic treatment remains an important option indicated by the high number of hypnotic drug prescriptions in the general population and in patients with cardiovascular disorders. In this narrative review of the literature, we summarize treatment options for chronic insomnia based on clinical guidelines for the general population and highlight necessary considerations for the treatment of patients with cardiovascular diseases.
In the past decades, sleep and its impact on physical and mental health has increasingly become a research focus. It is now consensus that sleep disturbances negatively impact the quality of life, mood, and cognitive function and are associated with a heightened risk for somatic diseases (1). An expert panel convened by the United States-based National Sleep Foundation has suggested an appropriate sleep duration of 7-9 h/night for adults between the ages of 25 and 65 years (2). Contrarily, data indicate that sleep duration in the general population is comparably shorter, with 35% of adults reporting to sleep less than 6 h/night, and an additional 30% indicating a sleep duration of just 7 h/night (3). On the one hand, lifestyle habits associated with modern day society, including work schedules, unhealthy diet, smoking, lack of physical exercise, increasing use of electronic devices, and excessive psychosocial stress, are known to negatively impact sleep duration in adults (4). On the other hand, sleep disorders are highly prevalent in the general population and are therefore considered a major public health issue (5). Insomnia constitutes the most frequent sleep disorder (6). Based on the revised 5th edition of the Diagnostic Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5-TR) and the 3rd edition of the International Classification of Sleep Disorders (ICSD-3) diagnosis of insomnia requires the presence of at least one of the following criteria: difficulty initiation sleep, maintaining sleep, or early awakening. Additionally, at least one associated impairment in daytime functioning, for example a reduction in cognitive performance, fatigue, or disturbances in mood, have to be present (7, 8). The diagnosis of chronic insomnia requires the presence of dissatisfying sleep quality or sleep quantity for at least three nights a week over a time period of at least three months when adequate opportunity for sleep is given (7, 8). Finally, with the introduction of DSM-5 and based on a National Health Institute (NIH) conference on insomnia in 2005, the previous distinction between primary and secondary insomnia (referring to insomnia related to another somatic or mental disorder) was removed (9). Acute insomnia as a reaction to acute stressors is common, affecting 30-50% of the population in industrialized countries, and mostly resolves after cessation of the stressor (10). While acute insomnia does not require specific treatment, chronic insomnia necessitates clinical attention regardless of potential underlying causes.
The prevalence of chronic insomnia in the general population is estimated to be at least 5-10% in industrialized countries (11, 12), it has been found to be twice as common in women compared to men, and prevalence has been shown to increase with age (13). Compared to the general population, higher prevalence rates have been reported in the context of psychiatric and somatic illnesses. In this regard, data from general practice in Germany and Norway showed a prevalence of 20% and 50%, respectively (14, 15).
Chronic insomnia places a significant financial burden on healthcare systems in developed countries. It is associated with a marked impairment in functional status (16, 17), with increased absences from work (18), and with heightened occurrence of workplace and motor vehicle accidents (19, 20). Additionally, insomnia significantly increases the risk for psychiatric disorders (21, 22). According to data from the World Health Organization (WHO), insomnia ranked 11th on the list of brain disorders in terms of global burden and 9th among neuropsychiatric disorders in terms of disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) (23). In Europe, sleep disorders ranked 9th among brain disorders in 2010 regarding direct and indirect costs (24).
Inadequate sleep and sleep deprivation, independent of underlying causes, have been linked to the development and progression of cardiometabolic disorders. Several meta-analyses have confirmed that insomnia is associated with an increased cardiovascular disease risk (25–27). In particular, insomnia has been found to be a risk factor for arterial hypertension, myocardial infarction, and heart failure (28–30). Furthermore, insomnia has been associated with an increased risk for type 2 diabetes (31). Next to insomnia, short sleep duration defined as less than 6 h of sleep per night has been indicated as a risk factor for cardiometabolic conditions and health behaviors that predispose to cardiovascular disease, including increased calorie intake, obesity, type 2 diabetes, and hypertension (32–37). Finally, short sleep duration was found to increase the risk for cardiovascular disease (36). Based on the mounting evidence that indicates a significant connection between sleep and cardiovascular disease, sleep disturbances have been proposed as the 10th modifiable cardiovascular risk factor (38).
Similar to other mental disorders, including major depressive disorder and symptoms of depression, the association between insomnia and cardiometabolic diseases appears to be bidirectional, i.e. while individuals that suffer from insomnia and insomnia symptoms are more likely to develop cardiometabolic disorders, cardiac patient populations also have been shown to present with insomnia at higher prevalence rates than observed in the general population (39–41). Mechanisms and biological pathways involved in the bidirectional relationship have been extensively reviewed before (42, 43) and are summarized in Figure 1.
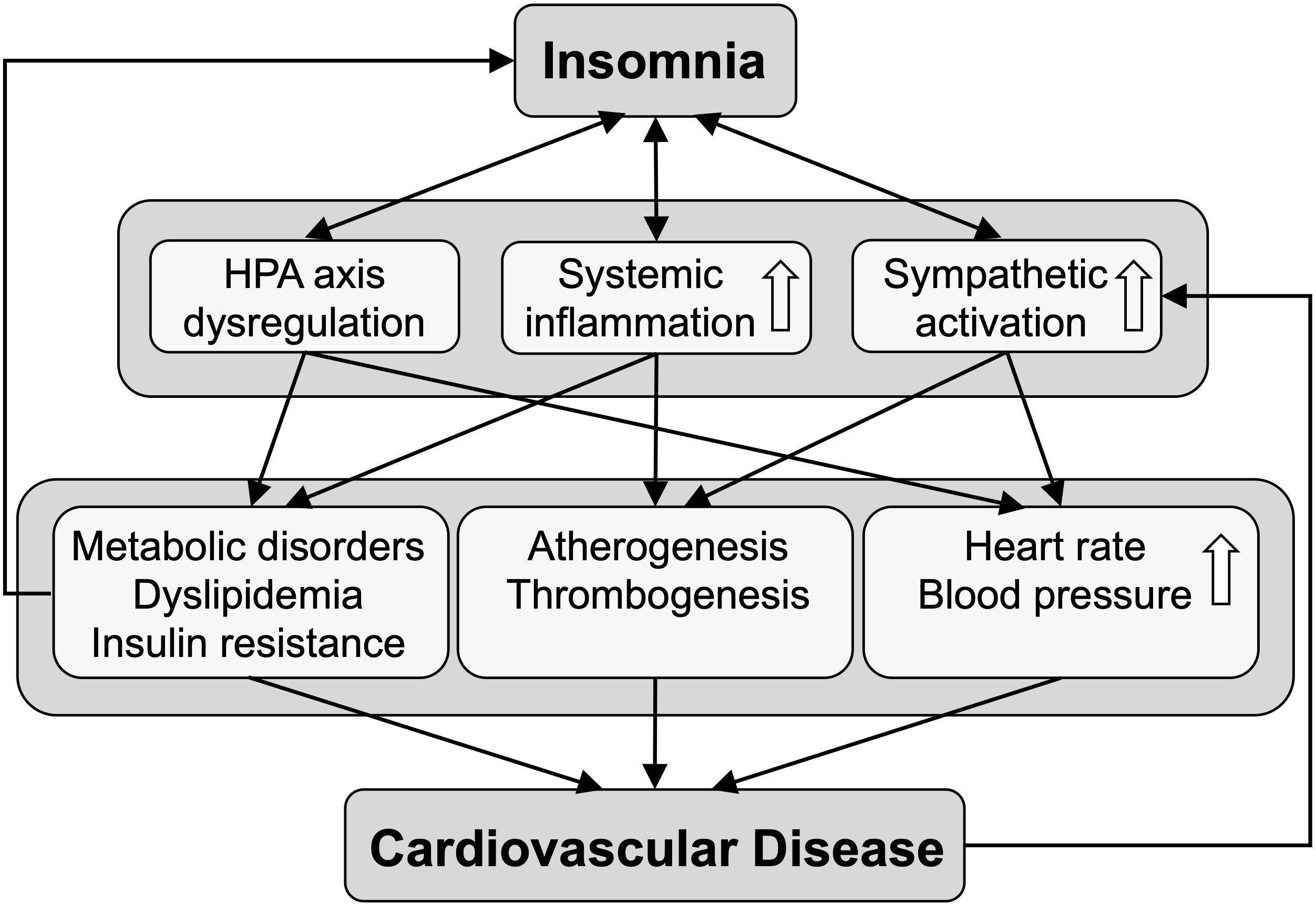
Figure 1. The scheme depicts biological pathways linking insomnia to cardiovascular disease. Insomnia is bidirectionally associated with dysregulation of the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, and with increased systemic inflammation and sympathetic activation, leading to various cardiometabolic conditions that predispose to cardiovascular disease.
In this regard, it is estimated that nearly 45% of patients that are diagnosed with cardiovascular disease have insomnia (44). Importantly, the presence of sleep disturbances and insomnia has been found to be associated with adverse outcome measures, including higher rates of hospitalization and increased mortality in patients with coronary heart disease (45, 46).
In the context of cardiovascular diseases, the impact of insomnia and insomnia symptoms on outcome measures has been most extensively studied in patients with heart failure. In this regard, a current integrative review suggests that insomnia and insomnia symptoms are associated with daytime sleepiness, fatigue, decreased self-reported physical functioning, lower exercise capacity, poor health related quality of life, depressive symptoms, and cardiac events (40).
Taking into account the high prevalence of insomnia and the associated adverse outcome measures, comparatively little information is available in the literature regarding treatment of chronic insomnia in cardiac patient populations.
Importantly, next to insomnia, sleep-related breathing disorders are common in patients with cardiovascular diseases and can be associated with sleep disruption due to repeated arousals during the night (47). Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) constitutes the most frequent form of sleep disordered breathing in patients with cardiovascular disorders and occurs in over 40% of patients (48). It is caused by repetitive closure of the upper airways during sleep. On the one hand this results in episodes of obstructive apneas, hypoapneas, or respiratory effort-related arousal. On the other hand, OSA constitutes the main cause of chronic intermittent hypoxia, which has been linked to the pathology of several cardiovascular conditions, including atherosclerosis, endothelial dysfunction, hypertension, insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, carotid intima-media thickness, and inflammation (49). Underlying mechanisms and pathways are reviewed in a recent dedicated publication by Assallum and colleagues (49). Accordingly, OSA has been found to be associated with heightened mortality and overall cardiovascular disease risk (50). Furthermore, an increased risk for hypertension, arrhythmias, coronary events and adverse outcome measures following myocardial infarction have been reported (50). Therefore, particularly in individuals that present with cardiovascular disease, diagnosis of sleep disorder breathing and OSA need to be considered, when excessive daytime sleepiness, fatigue, or snoring are present. Treatment options, including weight loss and continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy, have been found to likely improve parameters of quality of life and daytime sleepiness in patients with OSA and may benefit control of hypertension and paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Contrarily, in the absence of daytime sleepiness or nocturnal hypoxemia studies failed to demonstrate positive effects of OSA treatment on cardiovascular endpoints (50).
Position papers and recommendations on the treatment of sleep disorders in cardiac patients mainly focus on the diagnosis and treatment of sleep-related breathing disorders (51, 52), owing to the well-established association of sleep-disordered breathing and cardiovascular morbidity (53). However, a study by Redeker and colleagues that reported an association of insomnia symptoms and quality of life parameters in patients with stable heart failure, concluded that these relationships could not be explained by sleep-disordered breathing (54). Additionally, the study highlights that in patients receiving guideline-based therapies for heart failure, insomnia symptoms often persist, and that therefore therapeutic management of heart failure alone is insufficient to diminish insomnia symptomology (54). Accordingly, current data suggest that between 10% and 20% of heart failure patients take hypnotic medications at least three times per week (55–57).
Next to underlying somatic causes of sleep disturbances, a potential association of cardiovascular drugs and insomnia symptoms might be considered. While there is comparatively little literature available, it has been shown that beta-blockers, which constitute indispensable drugs in the treatment of patients with cardiovascular disease, can be attributed to psychiatric adverse events. In fact, early studies found a decrease in nighttime melatonin release in healthy volunteers in response to beta-blocker administration, caused by direct inhibition of the beta1-adrenoreceptor (58). Accordingly, a recent meta-analysis found that beta-blocker treatment could possibly be associated with an increased risk for sleep disturbances and sleep disorders, including insomnia (59).
Additionally, diuretics could be discussed as drugs that may potentially increase the likelihood of insomnia via nocturia. The cause of nocturia is often multifactorial, and includes age-related changes in the genitourinary system (such as benign prostate hypertrophy), uncontrolled diabetes mellitus, vasopressin deficiency, fluid redistribution associated with edematous states such as congestive heart failure, chronic kidney disease, as well as sleep disorders itself. In a prospective study by Endeshaw and colleagues, nocturia due to several reasons was examined concerning sleep problems and mortality. In total, 1,478 patients aged 73.8 ± 2.9 years were included and followed prospectively over 10 years in average (60). During the follow-up period, 760 deaths occurred. The results of the study indicate that the association between three or more nycturia episodes and mortality is independent of insomnia symptoms and can be better explained by prevalent diabetes mellitus and pre-existing cardiovascular morbidity. Although it cannot be ruled out that use of diuretics could lead to sleep problems via nycturia, it seems unlikely that this may influence long-term prognosis of cardiovascular diseases (60). Furthermore, diuretics are commonly given during the day, to prevent/minimize the risk of nocturia.
Of note, a recent qualitative descriptive study that assessed self-reported factors influencing the sleep situation and management of sleep problems of 20 patients (mean age 73 years) with cardiovascular disease and insomnia found four underlying categories of sleep disruptors, i.e. cognitive, social, physical, and behavioral. While direct side effects of cardiovascular drugs were not specifically named, the wondering whether drug-related adverse effects might cause sleep problems was found as one cognitive event that triggered sleep disruptions. Furthermore, while nocturia was cited as a trigger for the behavioral category, this was attributed to fluid intake in the late afternoon or evening rather than to drug side-effects (61).
Against this background, recommendations regarding the treatment of chronic insomnia in patients with cardiovascular disorders, especially in those with heart failure, are missing.
This narrative review was conducted to explore the pharmacologic and psychologic approaches for insomnia treatment in cardiac patients. A systematic search of the literature was performed across three major databases: PubMed, Google Scholar, and the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. Articles published up to July 31, 2023, were included.
The search strategy employed a combination of Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) terms and free-text keywords tailored to each database. Supplementary Table 1 provides an overview regarding the keywords utilized for each of the three relevant elements, i.e. insomnia, cardiovascular disease, and treatment approach, which were used either singly or in combination. Titles and abstracts of identified articles were screened and full-text articles were retrieved for potentially eligible studies. To refine the search and to ensure comprehensive coverage of the topic, Boolean operators (AND, OR) were used.
The present narrative review is limited to articles written in English and it does not encompass a systemic or quantitative meta-analysis. Rather, this article aims to provide a broad and integrative perspective on current evidence.
Insomnia is a key symptom of psychological distress. Fernandez-Mendoza and Vgontzas proposed a connection between insomnia and the activation of stress responses (62). This link is particularly evident in individuals experiencing chronic hyperarousal and depression, leading to persistent difficulties with sleeplessness (63, 64). Clinical practice guidelines in the United States, Canada, and Europe recommend non-drug interventions, in particular cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I), as the first-line treatment of chronic insomnia in adults of any age (65, 66). CBT-I can be applied either as face-to-face or as e-mental health intervention.
CBT-I is a relatively short-term (6-8 sessions), structured evidence-based, multi-component treatment approach to insomnia (67). CBT-I typically involves several techniques to target perpetuating factors and bring about a change in the behaviors and thoughts contributing to insomnia (68). These techniques include psychoeducation, stimulus control, sleep restriction, cognitive restructuring, and relaxation training (69). Stimulus control and sleep restriction are administered as synergistic therapeutic approaches. Stimulus control primarily focuses on effectively managing episodes of nocturnal wakefulness through behavioral modifications. On the other hand, sleep restriction aims to enhance the inclination to initiate sleep while facilitating the establishment of uninterrupted and consolidated periods of sleep (68).
The efficacy of CBT-I as a first-line treatment is well established in clinical guidelines (70). Numerous studies have demonstrated the efficacy of CBT-I in improving sleep outcomes. A recent meta-analysis by Feng and colleagues found that CBT-I demonstrated superiority over no treatment in addressing insomnia, although its relative efficacy compared to no treatment for depression remained uncertain (71). Moreover, the effectiveness of CBT-I appeared to be on par with hypnotics for managing both insomnia and depression (71). Notably, the authors highlighted that the noninvasive nature of CBT-I suggested the intervention is likely safe. However, the trials exhibited variability in methodological quality. Older adults often report trouble sleeping. Vgontzas and colleagues found that middle-aged men showed higher sensitivity to the arousing effects of corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) than younger men, which may explain physiologically the increased prevalence of insomnia in older subjects (72). A systematic review and meta-analysis examining the efficacy of CBT-I in older adults found that CBT-I was safe and effective in improving sleep outcomes for this population (73). This is an important consideration given that cardiovascular diseases tend to affect mostly people over 65 years of age (74). Offering CBT-I instead of prescribing medication for individuals experiencing insomnia has several advantages. While sleep medications can provide effective short-term relief for insomnia, certain patients encounter adverse effects such as amnestic episodes, cognitive decline, and residual drowsiness upon awakening (75). Moreover, a subset of individuals continues to grapple with sleep disturbances despite medication usage, often necessitating escalating doses and ultimately leading to dependency, overuse from increased tolerance and accidents caused by taking these drugs (76). In addition to improving insomnia symptoms, CBT-I has also been found to be effective in reducing depression, anxiety, chronic pain, and enhancing sleep-related quality of life (77–79).
CBT-I has also been found to be effective in treating insomnia in various populations, including individuals with chronic pain, comorbid psychiatric disorders such as depression and anxiety, and those with insomnia related to shift work or jet lag (80). This is important in the context of heart disease, as around one in five cardiac patients suffer from depression and anxiety (81) and shift workers tend to experience higher rates of heart disease and depression (82). Social determinants of health (i.e. housing, employment, social isolation) are also linked to sleep quality (83). Heenan and colleagues found that cardiac patients undergoing a CBT-I program reported improved sleep and significantly lower levels of anxiety and depression, indicating that this intervention is successful both for insomnia and overall emotional wellbeing (84). In addition, CBT-I has been found to be effective when delivered via telemedicine, making it more accessible to those who may have difficulty accessing in-person treatment (85). However, the findings of Kallestad et al. yielded inconclusive results in terms of the efficacy comparison between face-to-face delivery and telehealth-based administration of CBT-I (86).
According to Thomas et al. there is limited access to CBT-I providers (87). The authors estimated that in 2016 there were under one thousand CBT-I specialists worldwide, with the majority unequally distributed in the USA (87). Adequate training in CBT-I is important as although CBT-I is a relatively brief form of therapy based on principles of CBT, competence with the delivery of CBT-I in a cardiac population would be associated with better clinical outcomes (88).
While guidelines for the treatment of insomnia explicitly recommend CBT-I as the first-line treatment option for adults with insomnia, other psychotherapeutic approaches have been assessed for insomnia treatment. In this regard, mindfulness-based interventions (MBIs) have been suggested in insomnia treatment. Although mindfulness is most often defined as paying attention, on purpose, in the present moment without judgement, there appears to be little consensus on what constitutes mindfulness and what mechanisms underlie its effectiveness or how the construct is measured. Accordingly, a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials that investigated the effect of MBIs on sleep among adults with insomnia or sleep problems found considerable conceptual and methodological heterogeneity among 13 included studies, which included diverse MBIs (i.e. mindfulness stress reduction, mindful bridging, mindfulness based cognitive behavioral therapy, mindfulness based therapy for insomnia, and acceptance and commitment therapy) in diverse patient populations with insomnia (89). Additionally, none of the included trials was designed to compare effects of MBIs to another active treatment of insomnia. However, MBIs appeared to be significantly more effective in improving insomnia symptoms compared to attention/education and waitlist controls (89). Another meta-analysis that assessed the effect of MBIs as a component of the CBT-I therapeutic system and that included randomized controlled trials as well as non-randomized studies, identified nine studies that were included in subsequent analyses. The meta-analysis revealed small to medium effect sizes on ISI scores that failed to reach significance and although several studies combined MBIs with CBT-I components, no positive effect on chronic insomnia was found compared to the respective control conditions (90).
Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) constitutes another form of third wave behavioral therapy discussed as a treatment option for insomnia, that however is also not currently recommended in the guidelines. ACT is based on a comprehensive scientific philosophy called functional contextualism, and includes six treatment processes, i.e. acceptance, defusion, self, now, values, and action, with the overall goal to improve psychological flexibility (91). A limited number of studies have assessed the effectiveness of ACT in the context of insomnia and insomnia symptoms. A recent systematic review that assessed the efficacy of ACT for insomnia treatment identified 11 studies of which seven combined ACT with behavioral and/or cognitive elements, while four applied ACT only. The authors conclude that ACT as monotherapy constitutes a ‘possibly efficacious’ treatment for insomnia, while the combination of ACT with behavioral components, including sleep restriction and stimulus control, constitutes a ‘probably efficacious’ treatment for insomnia (92).
While Paulos-Guarnieri and colleagues included randomized and non-randomized trials as well as case series and case reports, a meta-analysis by Ruan et al. limited included studies to randomized trials and identified 18 studies (93). The authors found that ACT was better for insomnia relieve compared to waitlist control, while no significant improvement of subjective sleep parameter were found. Furthermore, ACT was more beneficial than psychoeducation in improving insomnia and had similar effects compared to CBT. The effects of ACT and CBT on subjective sleep parameters did also not significantly differ. In patients with other illnesses, the effect of ACT on sleep quality was similar to findings in insomnia patients. However, while ACT and CBT had comparable impact on sleep quality at early follow-ups, after 12 months ACT was found to be less effective than CBT (93).
Overall, recent systematic reviews and meta-analyses suggest that ACT might be beneficial in the short-term treatment of insomnia, while its long-term effectiveness remains uncertain. Additionally, ACT does not appear to be more effective than CBT in insomnia treatment and particularly studies comparing ACT to CBT-I, which is considered the state-of-the-art intervention concerning psychotherapeutic treatment of insomnia are currently limited. In this regard, a recent randomized control trial compared an ACT-based protocol to waitlist controls as well as to CBT-I treatment (94). The authors describe a beneficial effect of ACT compared to waitlist controls. However, CBT-I remained superior to ACT regarding ISI scores at post-treatment as well as at six months follow-up. Therefore, ACT might constitute an effective treatment option for insomnia patients, particularly in those, who struggle to adhere to behavioral techniques such as sleep restriction and stimulus control (94).
Short-term pharmacologic treatment of chronic insomnia, defined as a treatment duration of 4 to 5 weeks or less, might be considered if CBT-I is not applicable due to cost restrains or unavailability, reservations or inability of the patient to participate in the therapy, or in the case of non-response (65, 66, 95). Albeit the favorable benefit-to-risk ratio of CBT-I, pharmacologic treatment remains the most common approach to therapy (95). In this regard, an international survey found that a drug prescription was given to approximately 50% of patients in the US and Western Europe and to up to 90% of patients in Japan that consulted a physician regarding their sleep complaints (96). Accordingly, prescriptions of hypnotic medication and use of over-the-counter agents for treatment of insomnia have seen significant increases over the past two decades (5). Indeed, it is estimated that between 1999 and 2010 the number of prescriptions for any sleep medication increased by approximately 290% (97), thereby outpacing the increase in sleeplessness complaints and insomnia diagnoses (5). Finally, while a recent study from the US suggests a decline in the use of medications for sleep disturbances in recent years, especially in Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved drugs and particularly in older individuals aged 80+ years, pharmacologic treatment appears to remain the most frequent treatment approach for insomnia (98).
Against this background, a new, evidence-based Clinical Practice Guideline for the Pharmacologic Treatment of Chronic Insomnia in Adults (hereinafter referred to as Clinical Practice Guideline) was published in 2017 by the American Academy of Sleep Medicine (95). The guidelines are based on the GRADE methodology (Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluation) that takes into account quality of evidence, benefit versus harm of a given treatment, and patient values and preferences (99, 100), and represent a comprehensive and systematic analysis of single agents used for the treatment of chronic insomnia.
A variety of drugs are available for insomnia treatment. Those include prescription hypnotic drugs indicated for the treatment of insomnia, including benzodiazepine receptor agonists (BZRAs), chronobiotic drugs, and low-dose doxepin, as wells as prescription drugs with off-label usage for the treatment of insomnia, including antidepressants, antipsychotics, and anticonvulsants. Additionally, over-the-counter medications, including melatonin and antihistamines are commonly used (13).
The following section will discuss prescription medications approved by the FDA for the treatment of insomnia, as well as off-label treatments and over-the-counter options, and the according recommendations given in the Clinical Practice Guideline will be highlighted (95). Of note, all studies included in the guideline assessed the efficacy and/or safety of the respective medications as a short-term treatment (i.e. from one day to five weeks). The authors suggest that long-term use of newer generation BZRAs should be limited to individuals that have no access to or did not benefit from CBT-I treatment. For these cases a screening for potential contraindications has been performed and regular follow-ups are required (95). Finally, it has to be considered that the Clinical Practice Guideline is based on trials that assessed the respective medications for the treatment of primary chronic insomnia and did not include studies with patients that had significant comorbidities (95).
Benzodiazepine receptor agonists (BZRAs) constitute the most commonly prescribed, FDA-approved drugs for the treatment of insomnia and are among the most prescribed medications amongst older adults (101). BZRAs are hypnotic drugs that comprise benzodiazepines (BZs), characterized by a defining fused benzene and diazepine ring, and so-called Z-drugs that were introduced later and lack the classical BDZ structure. All BZRAs target the benzodiazepine-γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA)A receptor and elicit their hypnotic effect by enhancing the sleep-promoting action of GABA (102).
BZs are allosteric modulations of (GABA)A receptors. They act via the benzodiazepine side of the receptor (BZR) and are characterized by their sedative-hypnotic properties (103). The first classical BZs were introduced in the late 1950s and rapidly replaced barbiturates and related drugs as a safer option for anxiolytic and hypnotic treatment (104, 105). In the late 1970s, BZs constituted the most prescribed medications worldwide for treatment of anxiety, agitation, seizures muscle spasm, anesthesia premedication, and insomnia (106). Subsequently, with the more widespread use, reports regarding potential adverse effect of BZs, including addiction and misuse, became more frequent, which led to a significant decrease in prescriptions (107). However, recent research suggests that BZs constitute important and safe treatment options when prescribed to patients without substance use disorders and for appropriate indications (107, 108). More recent data from the US showed that BZs with FDA approval for insomnia treatment ranked third amongst insomnia prescriptions in 2009/2010. In this study, 0.4% of the sample population reported to have used a BZ at least once in the past month (101).
Six drugs belonging to the class of BZs were included in the Clinical Practice Guideline (95). All included BZs are FDA-approved, with indication for treatment of insomnia. Only temazepam was recommended for the treatment of sleep onset insomnia as well as sleep maintenance insomnia in adults (Table 1). Additionally, triazolam was recommended for the treatment of sleep onset insomnia. No recommendations were made for estazolam, flurazepam, oxazepam, and quazepam due to insufficient evidence regarding efficacy and/or safety (95).
Z-drugs owe their name to the fact that two of the three FDA-approved drugs of the class, i.e. zolpidem and zaleplon, begin with the letter Z, while eszopiclone constitutes the active stereoisomer of zopiclone (142). Z-drugs, while chemically heterogenous, constitute non-benzodiazepine BZRAs that were developed to improve pharmacokinetics of classical BZs and entered the market in the 1990s (143). Z-drugs are characterized by a rapid onset within 30 min and a short half-life from one to 7 hours (144). Compared to BZs that are approved for various condition, including anxiety, epilepsy, and insomnia, Z-drugs have only been approved for insomnia treatment.
Three medications belonging to the class of nonbenzodiazepine BZRAs were included in the Clinical Practice Guideline. All three drugs are FDA-approved for the treatment of insomnia. Zolpidem constitutes the most frequently described hypnotic medication in recent years worldwide (145). Zolpidem as well as eszopiclone were recommended for the treatment of sleep onset insomnia as well as sleep maintenance insomnia, while zaleplon, which has the shortest half-life of Z-drugs, was recommended for treatment of sleep onset insomnia only (95, 144) (Table 1).
Soporific effects associated with melatonin, a hormone secreted by the pineal gland, has been well established since the 1960s and clinical trials conducted in the 1970s implied sleep-promoting effects of melatonin (146). While melatonin exhibits both hypnotic and chronobiotic actions, it has some properties that limit its suitability as an oral agent for insomnia treatment, i.e. short half-life of (< 30 min) high first-pass metabolism, and binding to multiple melatonin receptors (147). With the characterization and cloning of the human melatonin receptors, MT1 and MT2 (148, 149), melatonin agonists were developed and entered the market in the mid 2000s.
Melatonin is marketed as a nutritional supplement. However, compared to other over-the-counter remedies, it has undergone more extensive evaluation regarding its effects as a hypnotic and chronobiotic agent (150). Melatonin as an over-the-counter treatment option was not recommended for sleep onset insomnia or sleep maintenance insomnia in the Clinical Practice Guideline (95) (Table 2). The recommendation was derived from studies in older adults (< 55 years) based on a lack of evidence for the efficacy of treatment compared to placebo and insufficient data concerning potential side effects.
Ramelteon is a selective MT1 and MT2 receptor agonist with a considerably higher receptor affinity compared to melatonin. Ramelteon was approved by the FDA and indicated for the treatment of insomnia in 2005. It was recommended for the treatment of sleep onset insomnia but not for sleep maintenance insomnia in the Clinical Practice Guideline (95) (Table 1). The melatonin receptor agonists agomelatine that is approved for treatment of major depression in Europe, and tasimelteon that is FDA-approved and indicated for non-24-hour sleep-wake disorder, were not discussed as insomnia treatment options (95).
Prescriptions of antidepressants for insomnia treatment increased substantially over the 1980s and 1990s (159). By the beginning of the 2000s off-label prescriptions of antidepressants for insomnia treatment was about 1.5 times higher than prescriptions of hypnotic medications with FDA-approved indication for insomnia treatment (160). This steep increase that occurred albeit scientific evidence of efficacy was lacking at the time (161), might be attributed to the perception of clinicians that antidepressants constitute a safer option to BZRAs owing to the negative image regarding tolerance and withdrawal effects of the latter (161). Antidepressant drugs assessed in the Clinical Practice Guidelines include the tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) doxepin and trimipramine, the serotonin antagonist trazodone, and the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) paroxetine. Dosages of antidepressants for insomnia treatment are lower than those used for treatment of depression and can be considered sub-therapeutic for depression treatment.
Of the discussed antidepressants, only doxepin has been approved for the treatment of insomnia, while trazodone, paroxetine, and trimipramine constitute common off-label choices.
The TCA doxepin is highly selectivity for the histamine H1 receptor at very low doses. As histamine is considered one of the key neurotransmitters that mediate wakefulness (162), the hypnotic actions of doxepin can be attributed to its inhibitory effect on the H1 receptor (102). Very low-dose doxepin was the only antidepressant recommended for the treatment of sleep maintenance insomnia in the Clinical Practice Guideline (95) (Table 1).
Trazodone constitutes a serotonin antagonist and reuptake inhibitor. Its hypnotic effect at low doses has been attributed to the blocking of the 5-HT2A, histamine H1, and alpha receptors (163). While trazodone received FDA-approval for treatment of depression in 1982, the off-label use of the medication for insomnia treatment has since surpassed its prescription as an antidepressant in the US (164). Trazodone was not recommended for the treatment of sleep onset insomnia or for sleep maintenance insomnia in the Clinical Practice Guideline due to absence of clinically significant improvement regarding all assessed sleep outcomes (95) (Table 2).
Trimipramine as well as paroxetine were both reviewed in the Clinical Practice Guideline, but no recommendation regarding either drug was made due to insufficient evidence regarding safety and efficacy (95).
The orexin system, comprising the two peptides orexin A and orexin B, and their target receptors orexin-1 and orexin-2, were first described by two independent working groups in 1998 (165, 166). The orexin system was originally described to be involved in feeding behavior and regulation of central energy expenditure, before first publications linked it to the sleep-wake cycle and established it as a potential target for treatment of sleep disorders (167–170). Similar to drugs that target the histamine H1 receptor, blocking of the orexin receptor system is based on the perspective of insomnia as a disorder of inappropriate wakefulness rather than a sleep disorder (171).
To date five dual and one selective orexin receptor antagonist (ORA) have been utilized in clinical practice or were included in clinical trials. Three of these compounds, i.e. suvorexant, lemborexant, and daridorexant, which all constitute dual ORAs, have been approved by the FDA and indicated for the treatment of chronic insomnia (172).
Only suvorexant that was the first dual ORA to receive approval for clinical use in 2014, was included in the Clinical Practice Guideline. Suvorexant was recommended for treatment of sleep maintenance insomnia but not for sleep onset insomnia (100). However, it is suggested that suvorexant might have beneficial effects on sleep latency at the higher dose of 20 mg (95).
Lemborexant and daridorexant entered the marked in the US after the Clinical Practice Guideline was published (Lemborexant in 2019 and daridorexant in 2022) (172). Additionally, daridorexant will constitute the first dual ORA to be approved for treatment of insomnia in the European Union. A systemic review and network meta-analyses published in 2022 by Xue and colleagues that assessed the efficacy and safety of dual ORAs in the treatment of primary insomnia found no significant differences between any of the ORAs with regard to subjective or objective parameters of sleep quality (173).
Two anticonvulsants were included in the Clinical Practice Guideline.
Tiagabine constitutes a selective GABA reuptake inhibitor that, by inhibiting the GAT-1 GABA transporter, increases synaptic availability of the neurotransmitter. Tiagabine is characterized by fast absorbance and has a half-life of 7 to 9 h (151). It has FDA-approval for adjunctive treatment of partial seizures, and has been proposed as an off-label treatment option for insomnia in older individuals (151). Tiagabine was not recommended for sleep onset insomnia or sleep maintenance insomnia in the Clinical Practice Guideline due to clinically insignificant effects on its efficacy (95) Table 2.
Gabapentin is a GABA analogue. It is not indicated for treatment of insomnia by the FDA and has been used off-label oftentimes in patients in whom other pharmacologic treatment options might be contraindicated (i.e. in the context of alcohol dependency) (174, 175). No recommendation was made regarding the use of gabapentin for insomnia treatment due to insufficient data (95).
Quetiapine is the only antipsychotic included in the Clinical Practice Guideline. It belongs to the class of atypical antipsychotics and exhibits a high affinity for 5-HT2A receptor as well as weak affinities for dopamine, muscarinic, and adrenergic receptors. No recommendation for quetiapine was made due to insufficient evidence regarding efficacy and safety (95).
Next to melatonin that was discussed in the according section above, non-prescription agents for the treatment of insomnia include sedating antihistamines as well as nutritional supplements and herbal remedies. Over-the-counter (OTC) sleeping aids are popular first-line treatment option for individuals with acute insomnia (176). However, studies suggest that especially older patients use OTC medication for longer than indicated (176). Albeit, the widespread use of OTC and nutritional supplements, including L-tryptophan and valerian, there are questions regarding their respective efficacy for insomnia treatment and their safety especially when used chronically (176).
Diphenhydramine (DPH) is an antihistamine with antimuscarinic properties. The sedative effect of DPH is brought forward by antagonism of the histamine H1 receptor. The Clinical Practice Guideline does not recommend use of diphenhydramine for treatment of sleep onset insomnia or sleep maintenance insomnia due to the absence of clear benefits (95) (Table 2).
The melatonin precursor tryptophan crosses the blood-brain barrier before being converted to serotonin and subsequently to melatonin. Similar to DPH no clinically significant effect on parameters of sleep quality or quantity was evident and therefore L-tryptophan was not recommended for treatment of sleep onset insomnia and sleep maintenance insomnia (95) (Table 2).
The sedating properties of valerian has been recognized since the 18th century and its sedating effects have been attributed to inhibitory effects on the sympathetic nervous system via modification of the GABA system (177). While patients might prefer a natural remedy for treatment of insomnia, valerian and valerian-hops preparation in variable doses were not recommended for sleep onset insomnia and sleep maintenance insomnia due to the absence of demonstrated efficacy (95) (Table 2).
A systematic review and network meta-analysis was published in 2022 that assessed to comparative effectiveness of pharmacologic treatment options of insomnia (178). Similarly, to the Clinical Practice Guideline, patients with physical comorbidities were not included in the respective analyses. Therefore, it remains unclear whether the results can be also attributed to patients with cardiovascular diseases. Nevertheless, this study provides a comprehensive overview regarding the comparative efficacy, tolerability, and safety of relevant pharmacologic treatment options for short- and long-term treatment of insomnia based on currently available literature, which is summarized in the following paragraph (178).
The respective meta-analysis included 154 studies that investigated the effect of 36 active pharmacological treatments or placebo in adults. The meta-analyses included a total 12,670 participants in the placebo groups and 35,280 participants in the respective treatment groups and effects of acute and long-term treatment were assessed. Clinical outcomes included parameters of efficacy, acceptability, tolerability, and safety. Importantly, attributable to the age of the included studies objective measures of sleep were often not available. Consequently, efficacy as primary outcome was evaluated based on subjective sleep quality. Overall, results suggested a favorable profile for the Z-drug eszopiclone that however might be associated with considerable adverse effects and for the dual ORA lemborexant albeit safety data were inconclusive. Several pharmacologic options were found to have positive data regarding tolerance, including doxepin, seltorexant, and zaleplon. However, respective results concerning efficacy were inconclusive due to a lack of data. While several prescription medications were found to be effective in short-term treatment, including BZs, daridorexant, suvorexant, and trazodone, these, however, were often associated with poor tolerability and data regarding long-term effects are missing. Similar as the Clinical Practice Guideline, melatonin, ramelteon, and over-the-counter medication overall failed to show beneficial effects in the treatment of insomnia. Overall, it needs to be considered that several limiting factors are highlighted by the authors. In this regard, only five of the included studies provided long-term data for more than four weeks and most comparisons were based on indirect evidence from a respective small subset of studies.
Given the adverse outcome measures associated with insufficient sleep quality and duration, adequate treatment of chronic insomnia in patients with cardiovascular diseases is of importance (40, 45, 46). In this regard, it is noteworthy that the efficacy and safety of available treatment options for chronic insomnia have not been widely explored in patients with heart conditions and treatment recommendation for this clinical population are currently missing. The authors are unaware of according literature regarding pharmacologic interventions. Consequently, the Clinical Practice Guideline for the Pharmacological Treatment of Chronic Insomnia in Adults highlighted in this article are based on studies conducted with patients with primary chronic insomnia without any significant physical or mental comorbidities (95). Therefore, additional factors need to be considered when deciding on treatment options in cardiac patients. As recommended for the general population, before deciding on a specific treatment option for a patient, a comprehensive assessment of previous sleep complains, medical and psychiatric history, and information on medication and substance use should be performed (70, 95, 179). Additionally, the patient’s preferences as well as treatment availability should be taken into account. As in somatically healthy individuals, nonpharmacologic approaches, especially CBT-I, should be implemented as first line of treatment.
When deciding on pharmacologic therapies, which become clinically important in cases where CBT-I is unavailable, not tolerated by the patient, or ineffective, potential interactions with drugs utilized for the treatment of the cardiac condition have to be taken into account. Especially in patients with heart failure, treatment regimens are oftentimes complex and may lead to prolonged drug-elimination times. Consequently, particularly drugs with a longer half-life might be associated with an increased risk for daytime sleepiness.
Regarding pharmacologic options recommended by the Clinical Practice Guideline for treatment of sleep onset insomnia or sleep maintenance insomnia, little evidence regarding their efficacy and safety in cardiovascular patient populations exist. The following section summarizes limited data regarding pharmacologic treatment options and potential effects on the cardiovascular system and an according overview is given in Table 3. In this regard, while drug-drug interactions (DDI) between pharmacologic insomnia treatment approaches and cardiovascular medications are seldomly described, many psychopharmacologic drugs are metabolized via the cytochrome (CYP) P-450 pathway, and potential DDIs should be considered, i.e. by use of interaction databases.
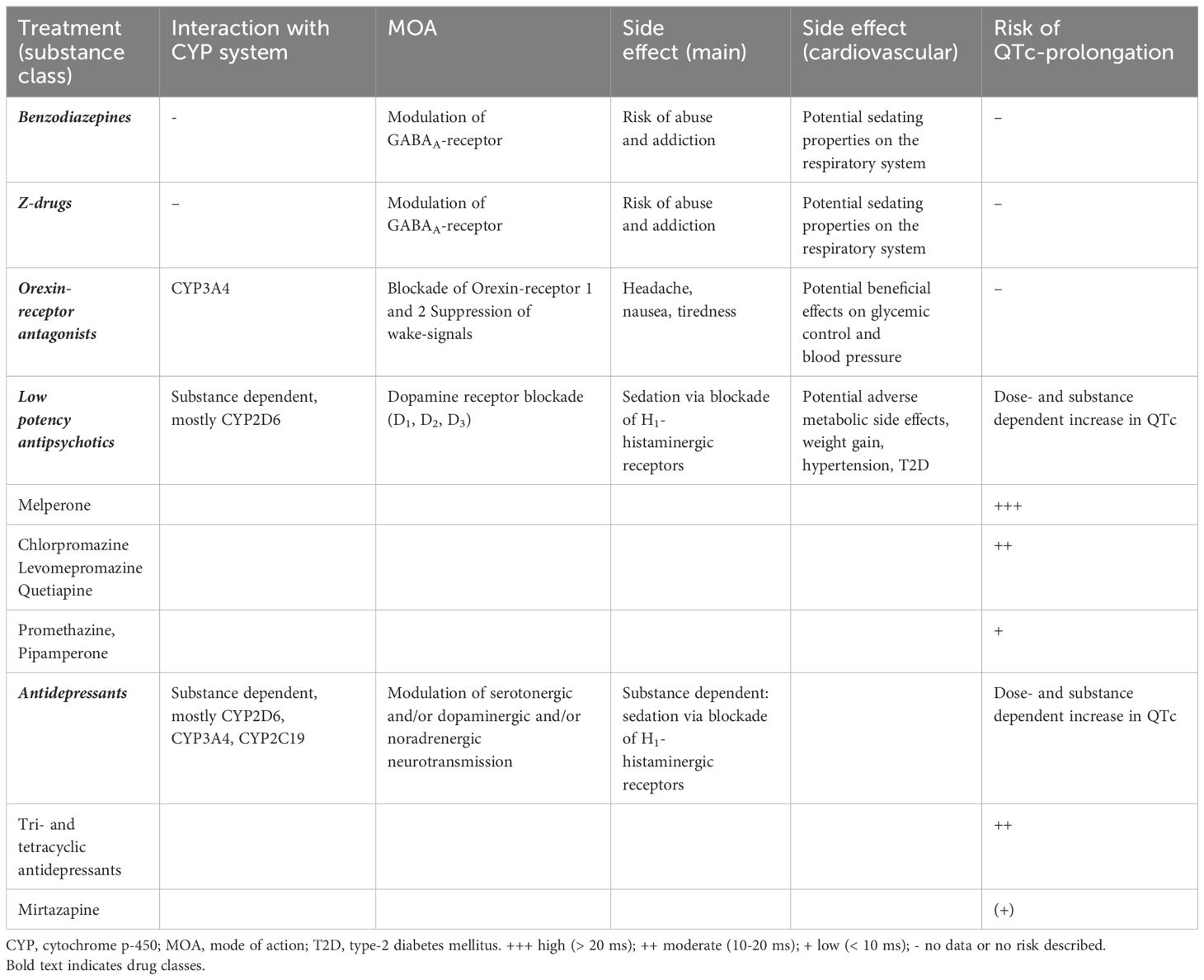
Table 3. Relative risk of QTc prolongation associated with drugs frequently used for treatment of insomnia [adapted from (180)].
In a publication from 2008, while highlighting the lack of according data, treatment with ramelteon is suggested as a safe treatment for sleep disturbances in patients with systolic heart failure (181). This recommendation was based on the selectivity of ramelteon for the melatonin (MT)1 and MT2 receptor and the hypothesis that beta-blocker treatment that is common in this patient group, might be associated with impaired melatonin synthesis and secretion (182). While ramelteon is recommended for use in cases of sleep onset insomnia in the Clinical Practice Guideline, no recommendation was made for the treatment of sleep maintenance insomnia, due to clinically insignificant improvement in sleep quality and efficiency compared to placebo (95).
BZs have been attributed with sedating properties on the respiratory center. Therefore, their use for insomnia treatment in patients with cardiovascular disorders that often present with comorbidities regarding sleep-disordered breathing (183). This is substantiated by a recent study that compared the prognostic impact of BZs and Z-drugs in patients with heart failure and insomnia (184). Sato and colleagues report increased rehospitalization of patients that received a BZ for treatment of insomnia compared to those that received a Z-drug at discharge. However, it should be taken into account that patients were assigned to the respective study groups based on the prescription of hypnotic drug class at the time of discharge, and potential changes in medication or discontinuation were not assessed in the follow-up (184). Additionally, it might be considered that adverse impact on cognitive function that has been described for both, BZs and Z-drugs, particularly when prescribed long-term, might negatively influence adherence to cardiovascular drug treatment (185).
ORAs constitute relatively new pharmacologic options in the treatment of chronic insomnia and studies regarding their respective efficacy and safety in patients with cardiovascular diseases are currently limited. A multicenter study that included 82 patients with insomnia and treated hypertension assessed the effect of a two-week treatment with 20 mg/d suvorexant. While the study reported a significant improvement in self-reported total sleep time (TST) and time to sleep onset (TSO) as well as a significant decline in night time blood pressure, no significant differences compared to the placebo group were found (186). This is in contrast to previous studies with estazolam and zolpidem, respectively, that reported a significant decrease in blood pressure associated with a significant improvement in sleep quality (187, 188). Potential blood pressure lowering properties of orexin receptor antagonist are supported by pre-clinical studies in mice and rats that commonly reported hypertensive effects of orexin (189–191).
In a study that included 18 individuals with insomnia and type-2 diabetes, three-day treatment with suvorexant was associated with significant improved total sleep time and sleep efficacy, while change in sleep latency was not significant. Suvorexant treatment was associated with improvement in glycemic control (192). A recent study assessed the efficacy and safety of the dual ORA daridorexant in patients with mild to moderate obstructive sleep apnoea. The study that included 28 patients concluded that single, as well as repeated doses of 50 mg daridorexant did not negatively impact night time respiratory function and improved sleep parameters (193). Additionally, daridorexant was not associated with changes in cardiac repolarization in healthy volunteers (194).
Among the sedating antidepressant, only doxepin received a weak recommendation for the treatment of sleep maintenance insomnia at very-low dosage (95). Nevertheless, other sedating antidepressants are commonly prescribed as off-label treatment options as clinicians often perceive them as the safer pharmacologic treatment option compared to BZ and Z-drugs, especially in older individuals and as long-term treatment, i.e. 5 weeks or longer (195, 196). However, studies that assessed the safety and efficacy of these drugs in the context of depression and accordingly studies in the context of insomnia treatment are scarce and data regarding their efficacy as long-term treatment option are currently missing (195). As dosages for off-label insomnia treatment are commonly lower than those used for indicated treatments, reported cardiovascular side-effects might be less of a concern. However, clinicians should be aware of common cardiovascular and cardiometabolic side-effects attributed to antidepressants when deciding on insomnia treatments for patients with cardiovascular diseases. Potential adverse effects of antidepressants in the context of cardiovascular disease have been discussed in several dedicated review articles (180, 197, 198). Owing to the wide-spread use of antidepressants for insomnia treatment, a short overview regarding potential interactions of antidepressants with the cardiovascular system is provided in the following paragraph.
TCAs that are frequently used for insomnia treatment albeit in sub-therapeutic doses for treatment of depression (195, 199). Among TCAs, doxepin, trimipramine, and amitriptyline appear to be the most commonly prescribed for insomnia treatment (66, 195, 200). TCAs have been associated with strong cardiovascular side-effects attributable to their anticholinergic and chinidine-like properties. Described abnormalities in cardiac conduction in the context of TCA treatment include QTc prolongation, atrioventricular block, atrial fibrillation, and ventricular tachycardia (180, 197, 198). Additionally, a higher risk of stroke and myocardial infarction have been attributed to TCAs when compared to SSRIs (180, 197, 198).
Trazodone is a heterocyclic antidepressant that is used frequently as an anti-insomnia drug, especially in the US (101). Trazodone has been associated with comparable cardiovascular side-effects to TCAs, including the induction of atrial and ventricular arrythmias especially in individuals that present with pre-existing cardiovascular disease (201). As trazodone has been reported to introduce polymorphous ventricular tachycardia and QT prolongation in the context of simultaneous amiodarone treatment, trazodone should not be given in combination with QT interval-prolonging drugs (201).
Mirtazapine constitutes a heterocyclic antidepressant with specific serotonergic and noradrenergic properties. It has been attributed with a comparatively favorable profile regarding cardiovascular side-effects that might include weight gain and orthostatic hypotension (180).
Agomelatine is considered in insomnia treatment due to its melatonergic properties and no evidence regarding cardiovascular side-effects have been published to our knowledge (180).
SSRIs appear to disrupt sleep in the early phases of treatment (202). Additionally, although generally considered safe for patients with cardiovascular disease, SSRIs have been associated with the potential to increase QTc intervals, which necessitates regular ECG monitoring (180).
Antipsychotics are divided into high potency and low potency drugs. Low potency antipsychotics are characterized by a low affinity for the dopamine receptor, but due to their high potency for histaminergic receptors, exhibit sedative properties. Although not approved for insomnia treatment, low potency antipsychotics, including melperone, promethazine, pipamperone, prothendyle, chlorprothixene, and levomepromazine, are frequently prescribed. Low potency antipsychotics, including quetiapine, which constitutes the most commonly used antipsychotic for insomnia treatment, have been shown to be associated with a moderate risk for QTc prolongation (180). In general, low potency antipsychotics should be avoided, if no primary indication for its use is present, as these drugs can be associated with metabolic side-effects including weight gain, hypertension and type-2 diabetes (203). Furthermore, antipsychotics have been reported to be associated with impaired cardiac function, myocardial fibrosis and inflammation in patients with schizophrenia (204).
Insomnia is more frequent in patients with cardiovascular disease when compared to the general population. Although insomnia and short sleep duration have been shown to negatively impact outcome parameters in the context of cardiovascular disease, treatment guidelines regarding the treatment of chronic insomnia in this patient population are currently missing. Based on studies and guidelines for insomnia treatment in individuals without additional somatic diseases, non-pharmacologic treatment options, especially CBT-I, should also be first-line treatment choices in patients with cardiovascular diseases. Pharmacotherapy should only be considered when other options are not available or failed to improve the condition. Available pharmacologic treatment options are mostly licensed for short-term treatment up to four weeks. Importantly, the type of sleep complaint, i.e. sleep onset insomnia versus sleep maintenance insomnia, or both, needs to be considered when choosing a hypnotic drug for a patient. Among the drugs with indication for insomnia treatment, Z-drugs should be preferred over BZs for treatment of patients with cardiovascular disorders, based on their sedating effects on the respiratory center and on recent research indicating adverse outcomes among BZ-treated patients with heart failure. Additionally, BZs are often associated with safety concerns, due to their longer half-life and higher risk of dependence and habituation compared to Z-drugs. Off-label treatment of insomnia with sedating antidepressant is common, especially when long-term treatment is considered. However, evidence regarding efficacy is scarce. When considering antidepressant treatment for insomnia in cardiac patient populations, clinicians should be aware of the potential side-effects on the cardiovascular system and respective safety measures, i.e. ECG monitoring, should be considered. Finally, ORAs constitute a newer drug class for insomnia treatment that is licensed also for long-term treatment. However, studies regarding their safety in patients with cardiovascular disease are currently missing.
Overall, studies regarding insomnia treatment of patients with cardiovascular disease, regarding efficacy and safety of commonly prescribed drugs are missing. Given the high frequency of insomnia in this patient population and the adverse outcomes associated with insomnia, studies regarding treatment efficacy and safety of insomnia medications as well as clinical treatment guidelines concerning insomnia treatment in cardiac patients are urgently needed.
BS: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing – original draft. MA: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing – original draft. KK: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
The authors declare the following potential conflicts of interest: KK received speaker honoraria and travel grants from EliLilly, Janssen, Takeda, Medice, Servier, Dr. Schwabe, and Idorsia.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decisio.n
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1490585/full#supplementary-material
1. Medic G, Wille M, Hemels ME. Short- and long-term health consequences of sleep disruption. Nat Sci Sleep. (2017) 9:151–61. doi: 10.2147/NSS.S134864
2. Hirshkowitz M, Whiton K, Albert SM, Alessi C, Bruni O, DonCarlos L, et al. National sleep foundation’s updated sleep duration recommendations: final report. Sleep Health. (2015) 1:233–43. doi: 10.1016/j.sleh.2015.10.004
3. Liu Y, Wheaton AG, Chapman DP, Cunningham TJ, Lu H, Croft JB. Prevalence of healthy sleep duration among adults–United States, 2014. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. (2016) 65:137–41. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6506a1
4. Hafner M, Stepanek M, Taylor J, Troxel WM, van Stolk C. Why sleep matters-the economic costs of insufficient sleep: A cross-country comparative analysis. Rand Health Q. (2017) 6:11.
5. Moloney ME, Konrad TR, Zimmer CR. The medicalization of sleeplessness: A public health concern. Am J Public Health. (2011) 101:1429–33. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2010.300014
6. Ohayon MM. Epidemiological overview of sleep disorders in the general population. Sleep Med Res. (2011) 2:1–9. doi: 10.17241/smr.2011.2.1.1
7. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: Dsm-5-Tr, Fifth Edition, Text Revision. Arlington, VA, US: American Psychiatric Publishing, Inc (2022).
8. Sateia MJ. International classification of sleep disorders-third edition: highlights and modifications. Chest. (2014) 146:1387–94. doi: 10.1378/chest.14-0970
9. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th ed. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Publishing, Inc. (2013).
10. Ellis JG, Perlis ML, Neale LF, Espie CA, Bastien CH. The natural history of insomnia: focus on prevalence and incidence of acute insomnia. J Psychiatr Res. (2012) 46:1278–85. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2012.07.001
11. Ohayon MM. Epidemiology of insomnia: what we know and what we still need to learn. Sleep Med Rev. (2002) 6:97–111. doi: 10.1053/smrv.2002.0186
12. Ohayon MM. Observation of the natural evolution of insomnia in the American general population cohort. Sleep Med Clin. (2009) 4:87–92. doi: 10.1016/j.jsmc.2008.12.002
13. Morin CM, Benca R. Chronic insomnia. Lancet. (2012) 379:1129–41. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60750-2
14. Bjorvatn B, Meland E, Flo E, Mildestvedt T. High prevalence of insomnia and hypnotic use in patients visiting their general practitioner. Fam Pract. (2017) 34:20–4. doi: 10.1093/fampra/cmw107
15. Wittchen HU, Krause P, Hofler M, Pittrow D, Winter S, Spiegel B, et al. Nisas-2000: the “Nationwide insomnia screening and awareness study”. Prevalence and interventions in primary care. Fortschr Med Orig. (2001) 119:9–19.
16. DiBonaventura M, Richard L, Kumar M, Forsythe A, Flores NM, Moline M. The association between insomnia and insomnia treatment side effects on health status, work productivity, and healthcare resource use. PloS One. (2015) 10:e0137117. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0137117
17. Spira AP, Kaufmann CN, Kasper JD, Ohayon MM, Rebok GW, Skidmore E, et al. Association between insomnia symptoms and functional status in U.S. older adults. J Gerontol B Psychol Sci Soc Sci. (2014) 69 Suppl 1:S35–41. doi: 10.1093/geronb/gbu116
18. Leigh JP. Employee and job attributes as predictors of absenteeism in a national sample of workers: the importance of health and dangerous working conditions. Soc Sci Med. (1991) 33:127–37. doi: 10.1016/0277-9536(91)90173-a
19. Laugsand LE, Strand LB, Vatten LJ, Janszky I, Bjorngaard JH. Insomnia symptoms and risk for unintentional fatal injuries–the hunt study. Sleep. (2014) 37:1777–86. doi: 10.5665/sleep.4170
20. Hagg SA, Toren K, Lindberg E. Role of sleep disturbances in occupational accidents among women. Scand J Work Environ Health. (2015) 41:368–76. doi: 10.5271/sjweh.3495
21. Breslau N, Roth T, Rosenthal L, Andreski P. Sleep disturbance and psychiatric disorders: A longitudinal epidemiological study of young adults. Biol Psychiatry. (1996) 39:411–8. doi: 10.1016/0006-3223(95)00188-3
22. Baglioni C, Battagliese G, Feige B, Spiegelhalder K, Nissen C, Voderholzer U, et al. Insomnia as a predictor of depression: A meta-analytic evaluation of longitudinal epidemiological studies. J Affect Disord. (2011) 135:10–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2011.01.011
23. Collins PY, Patel V, Joestl SS, March D, Insel TR, Daar AS, et al. Grand challenges in global mental health. Nature. (2011) 475:27–30. doi: 10.1038/475027a
24. Gustavsson A, Svensson M, Jacobi F, Allgulander C, Alonso J, Beghi E, et al. Cost of disorders of the brain in Europe 2010. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. (2011) 21:718–79. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2011.08.008
25. Li M, Zhang XW, Hou WS, Tang ZY. Insomnia and risk of cardiovascular disease: A meta-analysis of cohort studies. Int J Cardiol. (2014) 176:1044–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2014.07.284
26. Sofi F, Cesari F, Casini A, Macchi C, Abbate R, Gensini GF. Insomnia and risk of cardiovascular disease: A meta-analysis. Eur J Prev Cardiol. (2014) 21:57–64. doi: 10.1177/2047487312460020
27. Meng L, Zheng Y, Hui R. The relationship of sleep duration and insomnia to risk of hypertension incidence: A meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Hypertens Res. (2013) 36:985–95. doi: 10.1038/hr.2013.70
28. Palagini L, Bruno RM, Gemignani A, Baglioni C, Ghiadoni L, Riemann D. Sleep loss and hypertension: A systematic review. Curr Pharm Des. (2013) 19:2409–19. doi: 10.2174/1381612811319130009
29. Laugsand LE, Strand LB, Platou C, Vatten LJ, Janszky I. Insomnia and the risk of incident heart failure: A population study. Eur Heart J. (2014) 35:1382–93. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/eht019
30. Laugsand LE, Vatten LJ, Platou C, Janszky I. Insomnia and the risk of acute myocardial infarction: A population study. Circulation. (2011) 124:2073–81. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.025858
31. Anothaisintawee T, Reutrakul S, Van Cauter E, Thakkinstian A. Sleep disturbances compared to traditional risk factors for diabetes development: systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Med Rev. (2016) 30:11–24. doi: 10.1016/j.smrv.2015.10.002
32. Nedeltcheva AV, Kilkus JM, Imperial J, Kasza K, Schoeller DA, Penev PD. Sleep curtailment is accompanied by increased intake of calories from snacks. Am J Clin Nutr. (2009) 89:126–33. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.2008.26574
33. Patel SR, Hu FB. Short sleep duration and weight gain: A systematic review. Obes (Silver Spring). (2008) 16:643–53. doi: 10.1038/oby.2007.118
34. Cappuccio FP, D’Elia L, Strazzullo P, Miller MA. Quantity and quality of sleep and incidence of type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Care. (2010) 33:414–20. doi: 10.2337/dc09-1124
35. Faraut B, Touchette E, Gamble H, Royant-Parola S, Safar ME, Varsat B, et al. Short sleep duration and increased risk of hypertension: A primary care medicine investigation. J Hypertens. (2012) 30:1354–63. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0b013e32835465e5
36. Buxton OM, Marcelli E. Short and long sleep are positively associated with obesity, diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease among adults in the United States. Soc Sci Med. (2010) 71:1027–36. doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2010.05.041
37. Bayon V, Leger D, Gomez-Merino D, Vecchierini MF, Chennaoui M. Sleep debt and obesity. Ann Med. (2014) 46:264–72. doi: 10.3109/07853890.2014.931103
38. Redline S, Foody J. Sleep disturbances: time to join the top 10 potentially modifiable cardiovascular risk factors? Circulation. (2011) 124:2049–51. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.062190
39. Frojd LA, Munkhaugen J, Moum T, Sverre E, Nordhus IH, Papageorgiou C, et al. Insomnia in patients with coronary heart disease: prevalence and correlates. J Clin Sleep Med. (2021) 17:931–8. doi: 10.5664/jcsm.9082
40. Gharzeddine R, McCarthy MM, Yu G, Dickson VV. Insomnia and insomnia symptoms in persons with heart failure: an integrative review. J Cardiovasc Nurs. (2021) 36:374–84. doi: 10.1097/JCN.0000000000000719
41. Hayes D Jr., Anstead MI, Ho J, Phillips BA. Insomnia and chronic heart failure. Heart Fail Rev. (2009) 14:171–82. doi: 10.1007/s10741-008-9102-1
42. Wang Q, Wang X, Yang C, Wang L. The role of sleep disorders in cardiovascular diseases: culprit or accomplice? Life Sci. (2021) 283:119851. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119851
43. Javaheri S, Redline S. Insomnia and risk of cardiovascular disease. Chest. (2017) 152:435–44. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2017.01.026
44. Taylor DJ, Mallory LJ, Lichstein KL, Durrence HH, Riedel BW, Bush AJ. Comorbidity of chronic insomnia with medical problems. Sleep. (2007) 30:213–8. doi: 10.1093/sleep/30.2.213
45. Leineweber C, Kecklund G, Janszky I, Akerstedt T, Orth-Gomer K. Poor sleep increases the prospective risk for recurrent events in middle-aged women with coronary disease. The Stockholm female coronary risk study. J Psychosom Res. (2003) 54:121–7. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3999(02)00475-0
46. Clark A, Lange T, Hallqvist J, Jennum P, Rod NH. Sleep impairment and prognosis of acute myocardial infarction: A prospective cohort study. Sleep. (2014) 37:851–8. doi: 10.5665/sleep.3646
47. Cowie MR, Linz D, Redline S, Somers VK, Simonds AK. Sleep disordered breathing and cardiovascular disease: jacc state-of-the-art review. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2021) 78:608–24. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2021.05.048
48. Javaheri S, Barbe F, Campos-Rodriguez F, Dempsey JA, Khayat R, Javaheri S, et al. Sleep apnea. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2017) 69:841–58. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2016.11.069
49. Assallum H, Song TY, Aronow WS, Chandy D. Obstructive sleep apnoea and cardiovascular disease: A literature review. Arch Med Sci. (2021) 17:1200–12. doi: 10.5114/aoms.2019.88558
50. Cowie MR, Linz D, Redline S, Somers VK, Simonds AK. Sleep disordered breathing and cardiovascular disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2021) 78:608–24. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2021.05.048
51. Parati G, Lombardi C, Castagna F, Mattaliano P, Filardi PP, Agostoni P, et al. Heart failure and sleep disorders. Nat Rev Cardiol. (2016) 13:389–403. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2016.71
52. Fox H, Arzt M, Bergmann MW, Bitter T, Linz D, Oldenburg O, et al. Positionspapier “Schlafmedizin in der Kardiologie “, update 2021. Der Kardiologe. (2021) 15:429–61. doi: 10.1007/s12181-021-00506-4
53. Madsen MT, Huang C, Zangger G, Zwisler ADO, Gogenur I. Sleep disturbances in patients with coronary heart disease: A systematic review. J Clin Sleep Med. (2019) 15:489–504. doi: 10.5664/jcsm.7684
54. Redeker NS, Jeon S, Muench U, Campbell D, Walsleben J, Rapoport DM. Insomnia symptoms and daytime function in stable heart failure. Sleep. (2010) 33:1210–6. doi: 10.1093/sleep/33.9.1210
55. Chen HM, Clark AP, Tsai LM, Chao YF. Self-reported sleep disturbance of patients with heart failure in Taiwan. Nurs Res. (2009) 58:63–71. doi: 10.1097/NNR.0b013e31818c3ea0
56. Moradi M, Mehrdad N, Nikpour S, Haghani H, Aalaa M, Sanjari M, et al. Sleep quality and associated factors among patients with chronic heart failure in Iran. Med J Islam Repub Iran. (2014) 28:149.
57. Lee KS, Lennie TA, Heo S, Song EK, Moser DK. Prognostic importance of sleep quality in patients with heart failure. Am J Crit Care. (2016) 25:516–25. doi: 10.4037/ajcc2016219
58. Stoschitzky K, Sakotnik A, Lercher P, Zweiker R, Maier R, Liebmann P, et al. Influence of beta-blockers on melatonin release. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. (1999) 55:111–5. doi: 10.1007/s002280050604
59. Riemer TG, Villagomez Fuentes LE, Algharably EAE, Schafer MS, Mangelsen E, Furtig MA, et al. Do beta-blockers cause depression?: systematic review and meta-analysis of psychiatric adverse events during beta-blocker therapy. Hypertension. (2021) 77:1539–48. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.120.16590
60. Endeshaw YW, Schwartz AV, Stone K, Caserotti P, Harris T, Smagula S, et al. Nocturia, insomnia symptoms and mortality among older men: the health, aging and body composition study. J Clin Sleep Med. (2016) 12:789–96. doi: 10.5664/jcsm.5870
61. Siebmanns S, Johansson L, Sandberg J, Johansson P, Brostrom A. Experiences and management of incidents that influence sleep in patients with cardiovascular disease and insomnia. J Cardiovasc Nurs. (2020) 35:364–74. doi: 10.1097/JCN.0000000000000626
62. Fernandez-Mendoza J, Vgontzas AN. Insomnia and its impact on physical and mental health. Curr Psychiatry Rep. (2013) 15:418. doi: 10.1007/s11920-013-0418-8
63. Kalmbach DA, Cuamatzi-Castelan AS, Tonnu CV, Tran KM, Anderson JR, Roth T, et al. Hyperarousal and sleep reactivity in insomnia: current insights. Nat Sci Sleep. (2018) 10:193–201. doi: 10.2147/NSS.S138823
64. Nutt D, Wilson S, Paterson L. Sleep disorders as core symptoms of depression. Dialogues Clin Neurosci. (2008) 10:329–36. doi: 10.31887/DCNS.2008.10.3/dnutt
65. Qaseem A, Kansagara D, Forciea MA, Cooke M, Denberg TD. Clinical guidelines committee of the American College of P. Management of chronic insomnia disorder in adults: A clinical practice guideline from the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. (2016) 165:125–33. doi: 10.7326/M15-2175
66. Riemann D, Baglioni C, Bassetti C, Bjorvatn B, Dolenc Groselj L, Ellis JG, et al. European guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of insomnia. J Sleep Res. (2017) 26:675–700. doi: 10.1111/jsr.12594
67. Alimoradi Z, Jafari E, Brostrom A, Ohayon MM, Lin CY, Griffiths MD, et al. Effects of cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (Cbt-I) on quality of life: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Med Rev. (2022) 64:101646. doi: 10.1016/j.smrv.2022.101646
68. Walker J, Muench A, Perlis ML, Vargas I. Cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (Cbt-I): A primer. Klin Spec Psihol. (2022) 11:123–37. doi: 10.17759/cpse.2022110208
69. Pigeon WR. Treatment of adult insomnia with cognitive-behavioral therapy. J Clin Psychol. (2010) 66:1148–60. doi: 10.1002/jclp.20737
70. Schutte-Rodin S, Broch L, Buysse D, Dorsey C, Sateia M. Clinical guideline for the evaluation and management of chronic insomnia in adults. J Clin Sleep Med. (2008) 4:487–504. doi: 10.5664/jcsm.27286
71. Feng G, Han M, Li X, Geng L, Miao Y. The clinical effectiveness of cognitive behavioral therapy for patients with insomnia and depression: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2020) 2020:8071821. doi: 10.1155/2020/8071821
72. Vgontzas AN, Bixler EO, Wittman AM, Zachman K, Lin HM, Vela-Bueno A, et al. Middle-aged men show higher sensitivity of sleep to the arousing effects of corticotropin-releasing hormone than young men: clinical implications. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2001) 86:1489–95. doi: 10.1210/jcem.86.4.7370
73. Huang K, Li S, He R, Zhong T, Yang H, Chen L, et al. Efficacy of cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (Cbt-I) in older adults with insomnia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Australas Psychiatry. (2022) 30:592–7. doi: 10.1177/10398562221118516
74. Rodgers JL, Jones J, Bolleddu SI, Vanthenapalli S, Rodgers LE, Shah K, et al. Cardiovascular risks associated with gender and aging. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. (2019) 6(2):19. doi: 10.3390/jcdd6020019
75. Rossman J. Cognitive-behavioral therapy for insomnia: an effective and underutilized treatment for insomnia. Am J Lifestyle Med. (2019) 13:544–7. doi: 10.1177/1559827619867677
76. Gordon HW. Differential effects of addictive drugs on sleep and sleep stages. J Addict Res (OPAST Group). (2019) 3. doi: 10.33140/JAR.03.02.01
77. Blom K, Jernelov S, Kraepelien M, Bergdahl MO, Jungmarker K, Ankartjarn L, et al. Internet treatment addressing either insomnia or depression, for patients with both diagnoses: A randomized trial. Sleep. (2015) 38:267–77. doi: 10.5665/sleep.4412
78. Koffel E, Branson M, Amundson E, Wisdom JP. Sign me up, I’m ready!”: helping patients prescribed sleeping medication engage with cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (Cbt-I). Behav Sleep Med. (2021) 19:629–39. doi: 10.1080/15402002.2020.1828085
79. Kyle SD, Morgan K, Spiegelhalder K, Espie CA. No pain, no gain: an exploratory within-subjects mixed-methods evaluation of the patient experience of sleep restriction therapy (Srt) for insomnia. Sleep Med. (2011) 12:735–47. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2011.03.016
80. Peter L, Reindl R, Zauter S, Hillemacher T, Richter K. Effectiveness of an online Cbt-I intervention and a face-to-face treatment for shift work sleep disorder: A comparison of sleep diary data. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2019) 16(17):3081. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16173081
81. Henao Perez M, Lopez Medina DC, Lemos Hoyos M, Rios Zapata P. Depression and the risk of adverse outcomes at 5 years in patients with coronary heart disease. Heliyon. (2020) 6:e05425. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e05425
82. Mosendane T, Mosendane T, Raal FJ. Shift work and its effects on the cardiovascular system. Cardiovasc J Afr. (2008) 19:210–5.
83. Blanc J, Barr P, Seixas A, Chery M, Bernard M, Rogers A, et al. 0823 Social determinants of sleep disorders among multiethnic Americans in the Nih all of us research program. Sleep. (2023) 46:A362–A. doi: 10.1093/sleep/zsad077.0823
84. Heenan A, Pipe A, Lemay K, Davidson JR, Tulloch H. Cognitive-behavioral therapy for insomnia tailored to patients with cardiovascular disease: A pre-post study. Behav Sleep Med. (2020) 18:372–85. doi: 10.1080/15402002.2019.1594815
85. Arnedt JT, Conroy DA, Mooney A, Furgal A, Sen A, Eisenberg D. Telemedicine versus face-to-face delivery of cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia: A randomized controlled noninferiority trial. Sleep. (2021) 44. doi: 10.1093/sleep/zsaa136
86. Kallestad H, Scott J, Vedaa Ø, Lydersen S, Vethe D, Morken G, et al. Mode of delivery of cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia: A randomized controlled non-inferiority trial of digital and face-to-face therapy. Sleep. (2021) 44. doi: 10.1093/sleep/zsab185
87. Thomas A, Grandner M, Nowakowski S, Nesom G, Corbitt C, Perlis ML. Where are the behavioral sleep medicine providers and where are they needed? A geographic assessment. Behav Sleep Med. (2016) 14:687–98. doi: 10.1080/15402002.2016.1173551
88. Brown LA, Craske MG, Glenn DE, Stein MB, Sullivan G, Sherbourne C, et al. Cbt competence in novice therapists improves anxiety outcomes. Depress Anxiety. (2013) 30:97–115. doi: 10.1002/da.22027
89. Rash JA, Kavanagh VAJ, Garland SN. A meta-analysis of mindfulness-based therapies for insomnia and sleep disturbance: moving towards processes of change. Sleep Med Clinics. (2019) 14:209–33. doi: 10.1016/j.jsmc.2019.01.004
90. de Entrambasaguas M, Diaz-Silveira C, Burgos-Julian FA, Santed MA. Can mindfulness-based interventions improve outcomes in cognitive-behavioural therapy for chronic insomnia disorder in the general population? Systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Psychol Psychother. (2023) 30:965–78. doi: 10.1002/cpp.2874
91. Hayes SC, Pistorello J, Levin ME. Acceptance and commitment therapy as a unified model of behavior change. Couns Psychol. (2012) 40:976–1002. doi: 10.1177/0011000012460836
92. Paulos-Guarnieri L, Linares IMP, El-Rafihi-Ferreira R. Evidence and characteristics of acceptance and commitment therapy (Act)-based interventions for insomnia: A systematic review of randomized and non-randomized trials. J Contextual Behav Sci. (2022) 23:1–14. doi: 10.1016/j.jcbs.2021.11.001
93. Ruan J, Chen S, Liang J, Mak YW, Yee Ho FY, Chung KF, et al. Acceptance and commitment therapy for insomnia and sleep quality: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Contextual Behav Sci. (2022) 26:139–55. doi: 10.1016/j.jcbs.2022.09.002
94. El-Rafihi-Ferreira R, Hasan R, Toscanini AC, Linares IMP, Suzuki Borges D, Brasil IP, et al. Acceptance and commitment therapy versus cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia: A randomized controlled trial. J Consulting Clin Psychol. (2024) 92:330–43. doi: 10.1037/ccp0000881
95. Sateia MJ, Buysse DJ, Krystal AD, Neubauer DN, Heald JL. Clinical practice guideline for the pharmacologic treatment of chronic insomnia in adults: an American academy of sleep medicine clinical practice guideline. J Clin Sleep Med. (2017) 13:307–49. doi: 10.5664/jcsm.6470
96. Leger D, Poursain B, Neubauer D, Uchiyama M. An international survey of sleeping problems in the general population. Curr Med Res Opin. (2008) 24:307–17. doi: 10.1185/030079907x253771
97. Ford ES, Wheaton AG, Cunningham TJ, Giles WH, Chapman DP, Croft JB. Trends in outpatient visits for insomnia, sleep apnea, and prescriptions for sleep medications among us adults: findings from the national ambulatory medical care survey 1999-2010. Sleep. (2014) 37:1283–93. doi: 10.5665/sleep.3914
98. Kaufmann CN, Spira AP, Wickwire EM, Mojtabai R, Ancoli-Israel S, Fung CH, et al. Declining trend in use of medications for sleep disturbance in the United States from 2013 to 2018. J Clin Sleep Med. (2022) 18:2459–65. doi: 10.5664/jcsm.10132
99. Morgenthaler TI, Deriy L, Heald JL, Thomas SM. The evolution of the Aasm clinical practice guidelines: another step forward. J Clin Sleep Med. (2016) 12:129–35. doi: 10.5664/jcsm.5412
100. Sateia MJ, Sherrill WC Jr., Winter-Rosenberg C, Heald JL. Payer perspective of the American academy of sleep medicine clinical practice guideline for the pharmacologic treatment of chronic insomnia. J Clin Sleep Med. (2017) 13:155–7. doi: 10.5664/jcsm.6428
101. Bertisch SM, Herzig SJ, Winkelman JW, Buettner C. National use of prescription medications for insomnia: Nhanes 1999-2010. Sleep. (2014) 37:343–9. doi: 10.5665/sleep.3410
102. Stahl SM. Selective histamine H1 antagonism: novel hypnotic and pharmacologic actions challenge classical notions of antihistamines. CNS Spectrums. (2008) 13:1027–38. doi: 10.1017/S1092852900017089
103. Baldwin DS, Aitchison K, Bateson A, Curran HV, Davies S, Leonard B, et al. Benzodiazepines: risks and benefits. A reconsideration. J Psychopharmacol. (2013) 27:967–71. doi: 10.1177/0269881113503509
104. Greenblatt DJ, Shader RI. Drug therapy. Benzodiazepines (First of two parts). N Engl J Med. (1974) 291:1011–5. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197411072911906
105. Greenblatt DJ, Shader RI. Drug therapy. Benzodiazepines (Second of two parts). N Engl J Med. (1974) 291:1239–43. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197412052912308
106. Balon R, Starcevic V, Silberman E, Cosci F, Dubovsky S, Fava GA, et al. The rise and fall and rise of benzodiazepines: A return of the stigmatized and repressed. Braz J Psychiatry. (2020) 42:243–4. doi: 10.1590/1516-4446-2019-0773
107. Silberman E, Balon R, Starcevic V, Shader R, Cosci F, Fava GA, et al. Benzodiazepines: it’s time to return to the evidence. Br J Psychiatry. (2021) 218:125–7. doi: 10.1192/bjp.2020.164
108. Dubovsky SL, Marshall D. Benzodiazepines remain important therapeutic options in psychiatric practice. Psychother Psychosom. (2022) 91:307–34. doi: 10.1159/000524400
109. Wu R, Bao J, Zhang C, Deng J, Long C. Comparison of sleep condition and sleep-related psychological activity after cognitive-behavior and pharmacological therapy for chronic insomnia. Psychother Psychosom. (2006) 75:220–8. doi: 10.1159/000092892
110. Hindmarch I. Effects of hypnotic and sleep-inducing drugs on objective assessments of human psychomotor performance and subjective appraisals of sleep and early morning behaviour. Br J Clin Pharmacol. (1979) 8:43S–6S. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1979.tb00455.x
111. Glass JR, Sproule BA, Herrmann N, Busto UE. Effects of 2-week treatment with temazepam and diphenhydramine in elderly insomniacs: A randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J Clin Psychopharmacol. (2008) 28:182–8. doi: 10.1097/JCP.0b013e31816a9e4f
112. Roehrs T, Bonahoom A, Pedrosi B, Rosenthal L, Roth T. Treatment regimen and hypnotic self-administration. Psychopharmacol (Berl). (2001) 155:11–7. doi: 10.1007/s002130000661
113. Zammit GK, McNabb LJ, Caron J, Amato DA, Roth T. Efficacy and safety of eszopiclone across 6-weeks of treatment for primary insomnia. Curr Med Res Opin. (2004) 20:1979–91. doi: 10.1185/174234304x15174
114. Uchimura N, Kamijo A, Kuwahara H, Uchiyama M, Shimizu T, Chiba S, et al. A randomized placebo-controlled polysomnographic study of eszopiclone in Japanese patients with primary insomnia. Sleep Med. (2012) 13:1247–53. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2012.08.015
115. Scharf M, Erman M, Rosenberg R, Seiden D, McCall WV, Amato D, et al. A 2-week efficacy and safety study of eszopiclone in elderly patients with primary insomnia. Sleep. (2005) 28:720–7. doi: 10.1093/sleep/28.6.720
116. McCall WV, Erman M, Krystal AD, Rosenberg R, Scharf M, Zammit GK, et al. A polysomnography study of eszopiclone in elderly patients with insomnia. Curr Med Res Opin. (2006) 22:1633–42. doi: 10.1185/030079906X112741
117. Erman MK, Zammit G, Rubens R, Schaefer K, Wessel T, Amato D, et al. A polysomnographic placebo-controlled evaluation of the efficacy and safety of eszopiclone relative to placebo and zolpidem in the treatment of primary insomnia. J Clin Sleep Med. (2008) 4:229–34. doi: 10.5664/jcsm.27185
118. Ancoli-Israel S, Krystal AD, McCall WV, Schaefer K, Wilson A, Claus R, et al. A 12-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study evaluating the effect of eszopiclone 2 mg on sleep/wake function in older adults with primary and comorbid insomnia. Sleep. (2010) 33:225–34. doi: 10.1093/sleep/33.2.225
119. Walsh JK, Vogel GW, Scharf M, Erman M, William Erwin C, Schweitzer PK, et al. A five week, polysomnographic assessment of zaleplon 10 mg for the treatment of primary insomnia. Sleep Med. (2000) 1:41–9. doi: 10.1016/s1389-9457(99)00006-4
120. Hedner J, Yaeche R, Emilien G, Farr I, Salinas E. Zaleplon shortens subjective sleep latency and improves subjective sleep quality in elderly patients with insomnia. The zaleplon clinical investigator study group. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. (2000) 15:704–12. doi: 10.1002/1099-1166(200008)15:8<704::aid-gps183>3.0.co;2-s
121. Elie R, Ruther E, Farr I, Emilien G, Salinas E. Sleep latency is shortened during 4 weeks of treatment with zaleplon, a novel nonbenzodiazepine hypnotic. Zaleplon clinical study group. J Clin Psychiatry. (1999) 60:536–44. doi: 10.4088/jcp.v60n0806
122. Scharf MB, Roth T, Vogel GW, Walsh JK. A multicenter, placebo-controlled study evaluating zolpidem in the treatment of chronic insomnia. J Clin Psychiatry. (1994) 55:192–9.
123. Staner L, Ertle S, Boeijinga P, Rinaudo G, Arnal MA, Muzet A, et al. Next-day residual effects of hypnotics in Dsm-Iv primary insomnia: A driving simulator study with simultaneous electroencephalogram monitoring. Psychopharmacol (Berl). (2005) 181:790–8. doi: 10.1007/s00213-005-0082-8
124. Walsh JK, Erman M, Erwin C, Jamieson A, Mahowald M, Regestein Q, et al. Subjective hypnotic efficacy of trazodone and zolpidem in dsmiii–R primary insomnia. Hum Psychopharmacol: Clin Exp. (1998) 13:191–8. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1099-1077(199804)13:3<191::AID-HUP972>3.0.CO;2-X
125. Ware JC, Walsh JK, Scharf MB, Roehrs T, Roth T, Vogel GW. Minimal rebound insomnia after treatment with 10-mg zolpidem. Clin Neuropharmacol. (1997) 20:116–25. doi: 10.1097/00002826-199704000-00002
126. Randall S, Roehrs TA, Roth T. Efficacy of eight months of nightly zolpidem: A prospective placebo-controlled study. Sleep. (2012) 35:1551–7. doi: 10.5665/sleep.2208
127. Perlis ML, McCall WV, Krystal AD, Walsh JK. Long-term, non-nightly administration of zolpidem in the treatment of patients with primary insomnia. J Clin Psychiatry. (2004) 65:1128–37. doi: 10.4088/jcp.v65n0816
128. Jacobs GD, Pace-Schott EF, Stickgold R, Otto MW. Cognitive behavior therapy and pharmacotherapy for insomnia: A randomized controlled trial and direct comparison. Arch Intern Med. (2004) 164:1888–96. doi: 10.1001/archinte.164.17.1888
129. Herrmann WM, Kubicki ST, Boden S, Eich FX, Attali P, Coquelin JP. Pilot controlled double-blind study of the hypnotic effects of zolpidem in patients with chronic ‘Learned’ Insomnia: psychometric and polysomnographic evaluation. J Int Med Res. (1993) 21:306–22. doi: 10.1177/030006059302100602
130. Dorsey CM, Lee KA, Scharf MB. Effect of zolpidem on sleep in women with perimenopausal and postmenopausal insomnia: A 4-week, randomized, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Clin Ther. (2004) 26:1578–86. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2004.10.003
131. Zammit G, Erman M, Wang-Weigand S, Sainati S, Zhang J, Roth T. Evaluation of the efficacy and safety of ramelteon in subjects with chronic insomnia. J Clin Sleep Med. (2007) 3:495–504. doi: 10.5664/jcsm.26914
132. Roth T, Seiden D, Wang-Weigand S, Zhang J. A 2-night, 3-period, crossover study of Ramelteon’s efficacy and safety in older adults with chronic insomnia. Curr Med Res Opin. (2007) 23:1005–14. doi: 10.1185/030079907x178874
133. Mayer G, Wang-Weigand S, Roth-Schechter B, Lehmann R, Staner C, Partinen M. Efficacy and safety of 6-month nightly Ramelteon administration in adults with chronic primary insomnia. Sleep. (2009) 32:351–60. doi: 10.1093/sleep/32.3.351
134. Kohsaka M, Kanemura T, Taniguchi M, Kuwahara H, Mikami A, Kamikawa K, et al. Efficacy and tolerability of Ramelteon in a double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover study in Japanese patients with chronic primary insomnia. Expert Rev Neurother. (2011) 11:1389–97. doi: 10.1586/ern.11.128
135. Lankford A, Rogowski R, Essink B, Ludington E, Heith Durrence H, Roth T. Efficacy and safety of doxepin 6 mg in a four-week outpatient trial of elderly adults with chronic primary insomnia. Sleep Med. (2012) 13:133–8. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2011.09.006
136. Scharf M, Rogowski R, Hull S, Cohn M, Mayleben D, Feldman N, et al. Efficacy and safety of doxepin 1 mg, 3 mg, and 6 mg in elderly patients with primary insomnia: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover study. J Clin Psychiatry. (2008) 69:1557–64. doi: 10.4088/jcp.v69n1005
137. Roth T, Rogowski R, Hull S, Schwartz H, Koshorek G, Corser B, et al. Efficacy and safety of doxepin 1 mg, 3 mg, and 6 mg in adults with primary insomnia. Sleep. (2007) 30:1555–61. doi: 10.1093/sleep/30.11.1555
138. Krystal AD, Lankford A, Durrence HH, Ludington E, Jochelson P, Rogowski R, et al. Efficacy and safety of doxepin 3 and 6 mg in a 35-day sleep laboratory trial in adults with chronic primary insomnia. Sleep. (2011) 34:1433–42. doi: 10.5665/SLEEP.1294
139. Krystal AD, Durrence HH, Scharf M, Jochelson P, Rogowski R, Ludington E, et al. Efficacy and safety of doxepin 1 mg and 3 mg in a 12-week sleep laboratory and outpatient trial of elderly subjects with chronic primary insomnia. Sleep. (2010) 33:1553–61. doi: 10.1093/sleep/33.11.1553
140. Herring WJ, Connor KM, Ivgy-May N, Snyder E, Liu K, Snavely DB, et al. Suvorexant in patients with insomnia: results from two 3-month randomized controlled clinical trials. Biol Psychiatry. (2016) 79:136–48. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2014.10.003
141. Herring WJ, Snyder E, Budd K, Hutzelmann J, Snavely D, Liu K, et al. Orexin receptor antagonism for treatment of insomnia: A randomized clinical trial of suvorexant. Neurology. (2012) 79:2265–74. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e31827688ee
142. Dang A, Garg A, Rataboli PV. Role of zolpidem in the management of insomnia. CNS Neurosci Ther. (2011) 17:387–97. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-5949.2010.00158.x
143. Drover DR. Comparative pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of short-acting hypnosedatives: zaleplon, zolpidem and zopiclone. Clin Pharmacokinet. (2004) 43:227–38. doi: 10.2165/00003088-200443040-00002
144. Gunja N. The clinical and forensic toxicology of Z-drugs. J Med Toxicol. (2013) 9:155–62. doi: 10.1007/s13181-013-0292-0
145. MaChado FV, Louzada LL, Cross NE, Camargos EF, Dang-Vu TT, Nobrega OT. More than a quarter century of the most prescribed sleeping pill: systematic review of zolpidem use by older adults. Exp Gerontol. (2020) 136:110962. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2020.110962
146. Lynch HJ, Wurtman RJ, Moskowitz MA, Archer MC, Ho MH. Daily rhythm in human urinary melatonin. Science. (1975) 187:169–71. doi: 10.1126/science.1167425
147. Turek FW, Gillette MU. Melatonin, sleep, and circadian rhythms: rationale for development of specific melatonin agonists. Sleep Med. (2004) 5:523–32. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2004.07.009
148. Reppert SM, Weaver DR, Ebisawa T. Cloning and characterization of a mammalian melatonin receptor that mediates reproductive and circadian responses. Neuron. (1994) 13:1177–85. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90055-8
149. Reppert SM, Weaver DR, Godson C. Melatonin receptors step into the light: cloning and classification of subtypes. Trends Pharmacol Sci. (1996) 17:100–2. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(96)10005-5
150. Meoli AL, Rosen C, Kristo D, Kohrman M, Gooneratne N, Aguillard RN, et al. Oral nonprescription treatment for insomnia: an evaluation of products with limited evidence. J Clin Sleep Med. (2005) 01:173–87. doi: 10.5664/jcsm.26314
151. Roth T, Wright KP Jr., Walsh J. Effect of tiagabine on sleep in elderly subjects with primary insomnia: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Sleep. (2006) 29:335–41. doi: 10.1093/sleep/29.3.335
152. Walsh JK, Zammit G, Schweitzer PK, Ondrasik J, Roth T. Tiagabine enhances slow wave sleep and sleep maintenance in primary insomnia. Sleep Med. (2006) 7:155–61. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2005.05.004
153. Walsh JK, Perlis M, Rosenthal M, Krystal A, Jiang J, Roth T. Tiagabine increases slow-wave sleep in a dose-dependent fashion without affecting traditional efficacy measures in adults with primary insomnia. J Clin Sleep Med. (2006) 2:35–41. doi: 10.5664/jcsm.26433
154. Morin CM, Koetter U, Bastien C, Ware JC, Wooten V. Valerian-hops combination and diphenhydramine for treating insomnia: A randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial. Sleep. (2005) 28:1465–71. doi: 10.1093/sleep/28.11.1465
155. Wade AG, Ford I, Crawford G, McMahon AD, Nir T, Laudon M, et al. Efficacy of prolonged release melatonin in insomnia patients aged 55-80 years: quality of sleep and next-day alertness outcomes. Curr Med Res Opin. (2007) 23:2597–605. doi: 10.1185/030079907X233098
156. Luthringer R, Muzet M, Zisapel N, Staner L. The effect of prolonged-release melatonin on sleep measures and psychomotor performance in elderly patients with insomnia. Int Clin Psychopharmacol. (2009) 24:239–49. doi: 10.1097/YIC.0b013e32832e9b08
157. Lemoine P, Nir T, Laudon M, Zisapel N. Prolonged-release melatonin improves sleep quality and morning alertness in insomnia patients aged 55 years and older and has no withdrawal effects. J Sleep Res. (2007) 16:372–80. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2869.2007.00613.x
158. Hudson C, Hudson SP, Hecht T, MacKenzie J. Protein source tryptophan versus pharmaceutical grade tryptophan as an efficacious treatment for chronic insomnia. Nutr Neurosci. (2005) 8:121–7. doi: 10.1080/10284150500069561
159. Walsh JK, Schweitzer PK. Ten-year trends in the pharmacological treatment of insomnia. Sleep. (1999) 22:371–5. doi: 10.1093/sleep/22.3.371
160. Walsh JK. Drugs used to treat insomnia in 2002: regulatory-based rather than evidence-based medicine. Sleep. (2004) 27(8:)1441–2. doi: 10.1093/sleep/27.8.1441
161. Winkelman J, Pies R. Current patterns and future directions in the treatment of insomnia. Ann Clin Psychiatry. (2005) 17:31–40. doi: 10.1080/10401230590905344
162. Tasaka K, Chung YH, Sawada K, Mio M. Excitatory effect of histamine on the arousal system and its inhibition by H1 blockers. Brain Res Bull. (1989) 22:271–5. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(89)90053-1
163. Stahl SM. Mechanism of action of trazodone: A multifunctional drug. CNS Spectrums. (2009) 14:536–46. doi: 10.1017/S1092852900024020
164. Jaffer KY, Chang T, Vanle B, Dang J, Steiner AJ, Loera N, et al. Trazodone for insomnia: A systematic review. Innov Clin Neurosci. (2017) 14:24–34.
165. de Lecea L, Kilduff TS, Peyron C, Gao X, Foye PE, Danielson PE, et al. The hypocretins: hypothalamus-specific peptides with neuroexcitatory activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (1998) 95:322–7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.1.322
166. Sakurai T, Amemiya A, Ishii M, Matsuzaki I, Chemelli RM, Tanaka H, et al. Orexins and orexin receptors: A family of hypothalamic neuropeptides and G protein-coupled receptors that regulate feeding behavior. Cell. (1998) 92:573–85. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80949-6
167. Lin L, Faraco J, Li R, Kadotani H, Rogers W, Lin X, et al. The sleep disorder canine narcolepsy is caused by a mutation in the hypocretin (Orexin) receptor 2 gene. Cell. (1999) 98:365–76. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81965-0
168. Chemelli RM, Willie JT, Sinton CM, Elmquist JK, Scammell T, Lee C, et al. Narcolepsy in orexin knockout mice: molecular genetics of sleep regulation. Cell. (1999) 98:437–51. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81973-x
169. Thannickal TC, Moore RY, Nienhuis R, Ramanathan L, Gulyani S, Aldrich M, et al. Reduced number of hypocretin neurons in human narcolepsy. Neuron. (2000) 27:469–74. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)00058-1
170. Nishino S, Ripley B, Overeem S, Lammers GJ, Mignot E. Hypocretin (Orexin) deficiency in human narcolepsy. Lancet. (2000) 355:39–40. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(99)05582-8
171. Riemann D, Spiegelhalder K, Feige B, Voderholzer U, Berger M, Perlis M, et al. The hyperarousal model of insomnia: A review of the concept and its evidence. Sleep Med Rev. (2010) 14:19–31. doi: 10.1016/j.smrv.2009.04.002
172. Wu X, Xue T, Chen Z, Wang Z, Chen G. Orexin receptor antagonists and insomnia. Curr Psychiatry Rep. (2022) 24:509–21. doi: 10.1007/s11920-022-01357-w
173. Xue T, Wu X, Chen S, Yang Y, Yan Z, Song Z, et al. The efficacy and safety of dual orexin receptor antagonists in primary insomnia: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Sleep Med Rev. (2022) 61:101573. doi: 10.1016/j.smrv.2021.101573
174. Karam-Hage M, Brower KJ. Open pilot study of gabapentin versus trazodone to treat insomnia in alcoholic outpatients. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. (2003) 57:542–4. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1819.2003.01161.x
175. Furieri FA, Nakamura-Palacios EM. Gabapentin reduces alcohol consumption and craving: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Clin Psychiatry. (2007) 68:1691–700. doi: 10.4088/jcp.v68n1108
176. Albert SM, Roth T, Toscani M, Vitiello MV, Zee P. Sleep health and appropriate use of Otc sleep aids in older adults-recommendations of a gerontological society of America workgroup. Gerontologist. (2017) 57:163–70. doi: 10.1093/geront/gnv139
177. Ortiz JG, Nieves-Natal J, Chavez P. Effects of Valeriana officinalis extracts on [3h]Flunitrazepam binding, synaptosomal [3h]Gaba uptake, and hippocampal [3h]Gaba release. Neurochem Res. (1999) 24:1373–8. doi: 10.1023/a:1022576405534
178. De Crescenzo F, D’Alo GL, Ostinelli EG, Ciabattini M, Di Franco V, Watanabe N, et al. Comparative effects of pharmacological interventions for the acute and long-term management of insomnia disorder in adults: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Lancet. (2022) 400:170–84. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00878-9
179. Chesson A Jr., Hartse K, Anderson WM, Davila D, Johnson S, Littner M, et al. Practice parameters for the evaluation of chronic insomnia. An American academy of sleep medicine report. Standards of practice committee of the American academy of sleep medicine. Sleep. (2000) 23:237–41. doi: 10.1093/sleep/23.2.1k
180. Kahl KG, Stapel B, Correll CU. Psychological and psychopharmacological interventions in psychocardiology. Front Psychiatry. (2022) 13:831359. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.831359
181. Javaheri S. Sleep dysfunction in heart failure. Curr Treat Options Neurol. (2008) 10:323–35. doi: 10.1007/s11940-008-0035-8
182. Brismar K, Mogensen L, Wetterberg L. Depressed melatonin secretion in patients with nightmares due to beta-adrenoceptor blocking drugs. Acta Med Scand. (1987) 221:155–8. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1987.tb01260.x
184. Sato Y, Yoshihisa A, Hotsuki Y, Watanabe K, Kimishima Y, Kiko T, et al. Associations of benzodiazepine with adverse prognosis in heart failure patients with insomnia. J Am Heart Assoc. (2020) 9:e013982. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.119.013982
185. Zetsen SPG, Schellekens AFA, Paling EP, Kan CC, Kessels RPC. Cognitive functioning in long-term benzodiazepine users. Eur Addict Res. (2022) 28:377–81. doi: 10.1159/000525988
186. Kario K, Yamasaki K, Yagi K, Tsukamoto M, Yamazaki S, Okawara Y, et al. Effect of suvorexant on nighttime blood pressure in hypertensive patients with insomnia: the super-1 study. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). (2019) 21:896–903. doi: 10.1111/jch.13505
187. Huang Y, Mai W, Cai X, Hu Y, Song Y, Qiu R, et al. The effect of zolpidem on sleep quality, stress status, and nondipping hypertension. Sleep Med. (2012) 13:263–8. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2011.07.016
188. Li Y, Yang Y, Li Q, Yang X, Wang Y, Ku WL, et al. The impact of the improvement of insomnia on blood pressure in hypertensive patients. J Sleep Res. (2017) 26:105–14. doi: 10.1111/jsr.12411
189. Li A, Roy SH, Nattie EE. An augmented Co2 chemoreflex and overactive orexin system are linked with hypertension in young and adult spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Physiol. (2016) 594:4967–80. doi: 10.1113/JP272199
190. Jackson KL, Dampney BW, Moretti JL, Stevenson ER, Davern PJ, Carrive P, et al. Contribution of orexin to the neurogenic hypertension in Bph/2j mice. Hypertension. (2016) 67:959–69. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.115.07053
191. Xiao F, Jiang M, Du D, Xia C, Wang J, Cao Y, et al. Orexin a regulates cardiovascular responses in stress-induced hypertensive rats. Neuropharmacology. (2013) 67:16–24. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2012.10.021
192. Toi N, Inaba M, Kurajoh M, Morioka T, Hayashi N, Hirota T, et al. Improvement of glycemic control by treatment for insomnia with suvorexant in type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Clin Transl Endocrinol. (2019) 15:37–44. doi: 10.1016/j.jcte.2018.12.006
193. Boof ML, Ufer M, Fietze I, Pepin JL, Guern AS, Lemoine V, et al. Assessment of the effect of the dual orexin receptor antagonist daridorexant on various indices of disease severity in patients with mild to moderate obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Med. (2022) 92:4–11. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2021.11.015
194. Schilling U, Henrich A, Muehlan C, Krause A, Dingemanse J, Ufer M. Impact of daridorexant, a dual orexin receptor antagonist, on cardiac repolarization following bedtime dosing: results from a thorough Qt study using concentration-Qt analysis. Clin Drug Investig. (2021) 41:711–21. doi: 10.1007/s40261-021-01062-1
195. Everitt H, Baldwin DS, Stuart B, Lipinska G, Mayers A, Malizia AL, et al. Antidepressants for insomnia in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (2018) 5:CD010753. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010753.pub2
196. Sivertsen B, Nordhus IH, Bjorvatn B, Pallesen S. Sleep problems in general practice: A national survey of assessment and treatment routines of general practitioners in Norway. J Sleep Res. (2010) 19:36–41. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2869.2009.00769.x
197. Kahl KG, Westhoff-Bleck M, Kruger THC. Effects of psychopharmacological treatment with antidepressants on the vascular system. Vascul Pharmacol. (2017) 96-98:11–8. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2017.07.004
198. Kahl KG. Direct and indirect effects of psychopharmacological treatment on the cardiovascular system. Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig. (2018) 36(1):20180054. doi: 10.1515/hmbci-2018-0054
199. Everitt H, McDermott L, Leydon G, Yules H, Baldwin D, Little P. Gps’ Management strategies for patients with insomnia: A survey and qualitative interview study. Br J Gen Pract. (2014) 64:e112–9. doi: 10.3399/bjgp14X677176
200. Lai LL, Tan MH, Lai YC. Prevalence and factors associated with off-label antidepressant prescriptions for insomnia. Drug Healthc Patient Saf. (2011) 3:27–36. doi: 10.2147/DHPS.S21079
201. James SP, Mendelson WB. The use of trazodone as a hypnotic: A critical review. J Clin Psychiatry. (2004) 65:752–5. doi: 10.4088/jcp.v65n0605
202. Mayers AG, Baldwin DS. Antidepressants and their effect on sleep. Hum Psychopharmacol. (2005) 20:533–59. doi: 10.1002/hup.726
203. Hirsch L, Yang J, Bresee L, Jette N, Patten S, Pringsheim T. Second-generation antipsychotics and metabolic side effects: A systematic review of population-based studies. Drug Saf. (2017) 40:771–81. doi: 10.1007/s40264-017-0543-0
Keywords: insomnia, cardiovascular disease, pharmacological treatment, benzodiazepine, orexin receptor antagonist, antidepressant, Z-drug, melatonin
Citation: Stapel B, Alvarenga ME and Kahl KG (2025) Pharmacological and psychological approaches to insomnia treatment in cardiac patients: a narrative literature review. Front. Psychiatry 16:1490585. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1490585
Received: 03 September 2024; Accepted: 24 January 2025;
Published: 13 February 2025.
Edited by:
Domenico De Berardis, ASL 4, ItalyReviewed by:
Ibiyemi Arowolo, University of Winnipeg, CanadaCopyright © 2025 Stapel, Alvarenga and Kahl. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Britta Stapel, c3RhcGVsLmJyaXR0YUBtaC1oYW5ub3Zlci5kZQ==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.