- Department of Child and Adolescent Psychology Division I, The Affiliated Encephalopathy Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhumadian, China
Introduction: This study aimed to investigate the influence of negative emotions on adjustment disorder (AjD) in young adults, focusing on the mediating role of rumination and insomnia.
Methods: The study recruited 2015 young patients (aged 18–35) receiving treatment at the Psychosomatic Medicine Department of the Affiliated Encephalopathy Hospital of Zhengzhou University from February 2023 to March 2024. Participants completed the Depression Anxiety and Stress Scale (DASS), Ruminative Responses Scale (RRS), Insomnia Severity Scale (ISI), and Adjustment Disorder – New Module 20(ADNM-20) to assess negative emotions, rumination thinking, sleep status, and AjD. Data were analyzed utilizing descriptive statistics, correlation, hierarchical linear regression, and mediation analyses.
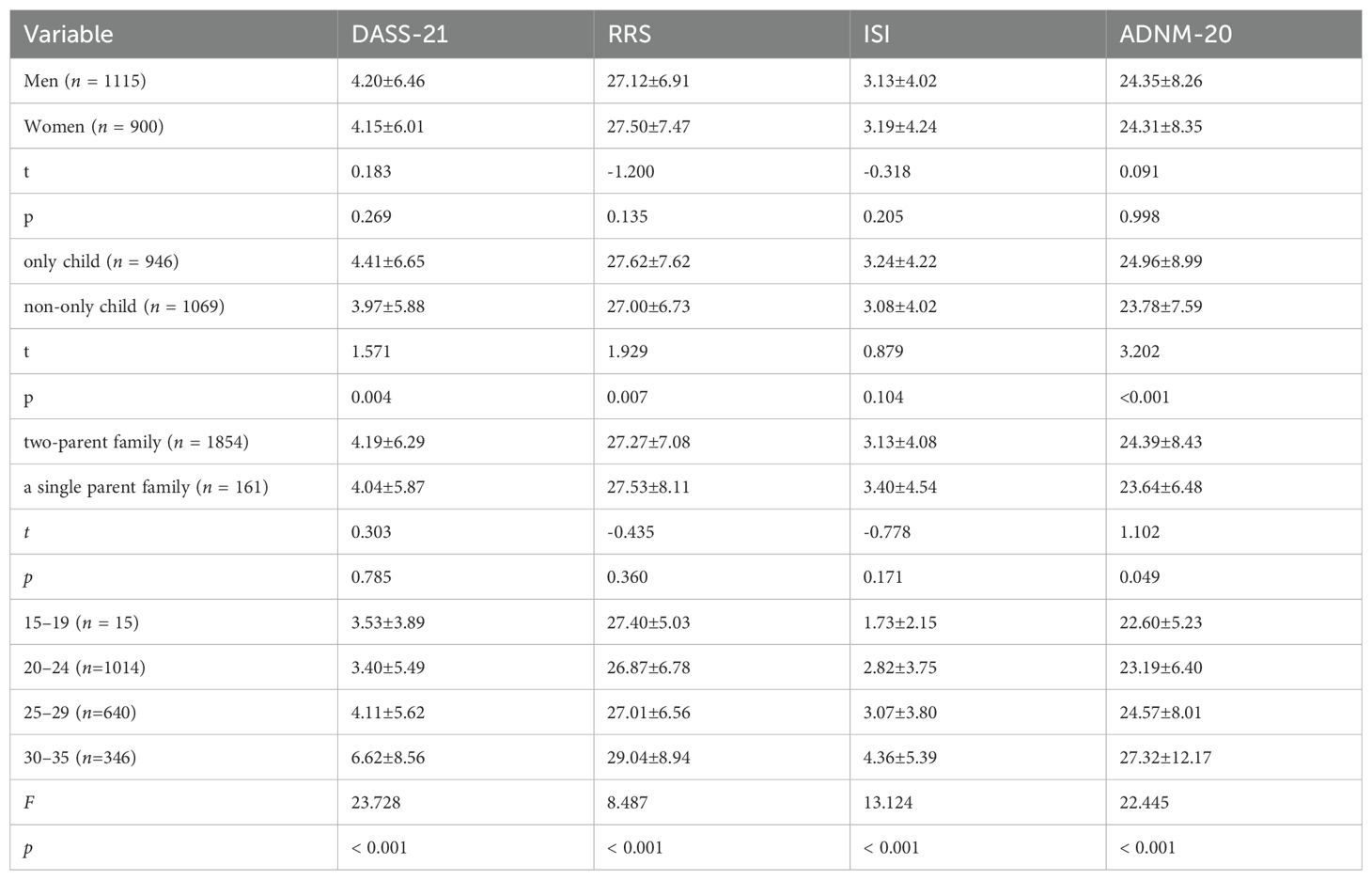
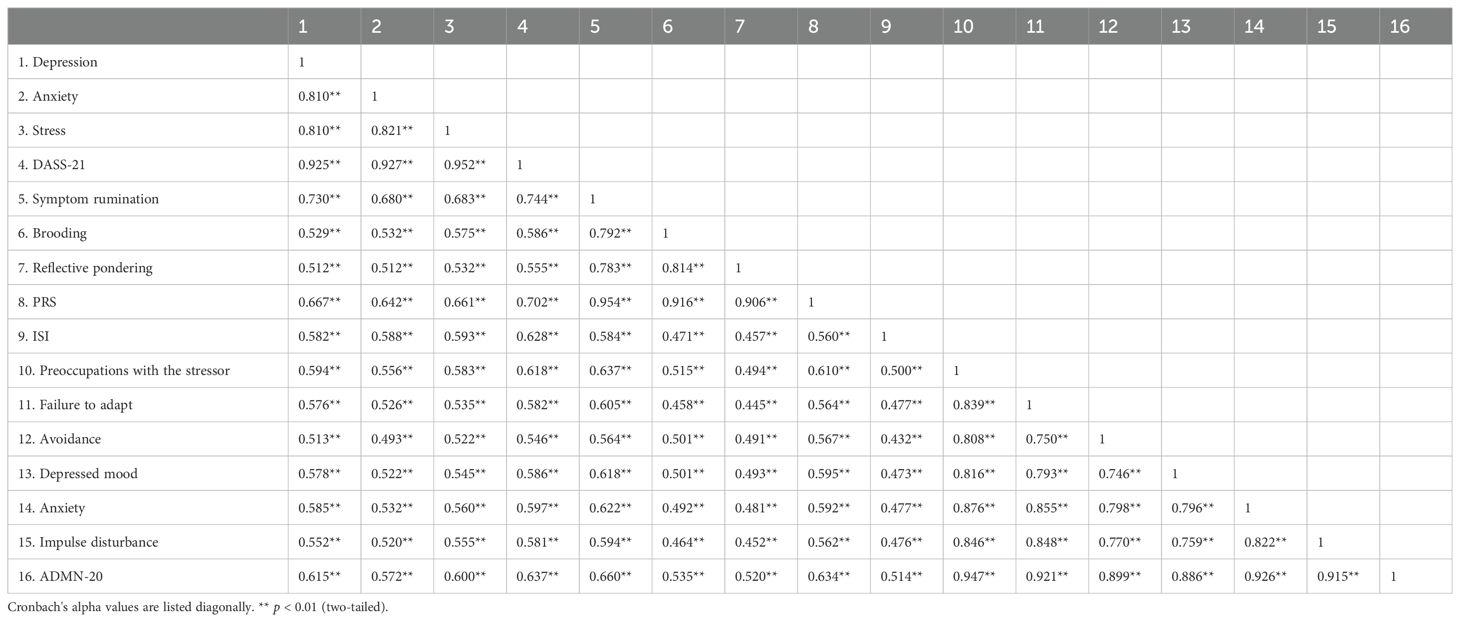
Results: 1) AjD was significantly influenced by being an only child and family composition, but there was no significant gender difference. Scores for negative emotions, rumination, insomnia, and AjD varied significantly different among different age groups, with the 30–35 age group scoring significantly higher than others. 2) Total scores for the DASS-21and its subscales, the RRS and its subscales, insomnia, and AjD were significantly correlated (p < 0.01). Negative emotions and ruminative thoughts predicted AjD, accounting for 47.8% of the total variation in AjD. 3) Negative emotions positively predicted AjD (β = 0.37, p < 0.001). Negative emotions affect AjD in young adults through rumination and insomnia alone and together, and the mediating effect accounts for 34%, 7.9%, and 20% of the total effect.
Discussion: The study’s findings suggest that rumination and insomnia play significant mediating roles in the relationship between negative emotions and AjD in young adults. Negative emotions directly affect AjD and have indirect effects through rumination and insomnia.
1 Introduction
Adjustment disorder (AjD) is a reaction caused by important life changes or stressful events, characterized primarily by emotional disorders accompanied by maladaptive behaviors or physiological dysfunction, considerably affecting social functioning (1, 2). According to the World Health Organization (WHO) International Classification of Diseases 11th version, AjD is defined as the development of emotional and behavioral symptoms in response to external life stressors (3). AjD is one of the mental disorders most commonly diagnosed in clinical practice that includes major emotional or behavioral symptoms that generally result from major life events or other stressors, such as serious illness (4). Epidemiological studies have demonstrated that the prevalence of AjD is 2% in the general population (5), 27% among individuals who have recently experienced involuntary job loss (6), and 18% among widowed individuals (7). AjD is particularly prevalent in counseling and liaison settings (8). In psychiatric consultations, 12% of cases involve patients diagnosed with AjD, with an additional 11% considered probable cases (9). According to statistics, the population of young adults aged 14-35 in China is about 400 million, accounting for 28.4% of the total population of the country. In a cross-sectional study (10), Yousif and colleagues found that the prevalence of AjD in the younger age group (15-33 years old) was significantly higher than that in other age groups. Some studies have also found that AjD with depressed mood are the most common diagnoses of suicide attempts in young people (11, 12). Given the high incidence and suicide rates of AjD in young adults, there is a need for greater understanding and awareness of the pathophysiological and psychological processes involved, which are essential for the prevention and treatment of AjD in young adults.
AjD is primarily associated with susceptibility and maladjustment. For related and risk factors, it has been reported that the likelihood of AjD varies according to the type and impact of stressors, including personal factors such as sex (13), age (14), self-efficacy, and coping, as well as interpersonal factors such as economic status (10) and social support (15). The core symptoms—adaptive disorder focus, rumination, and worry—can be classified as factual thinking related to stressors that are often associated with negative emotions (16). Negative emotions are a crucial component of subjective perspectives and reflect personal experiences of subjective tension and unpleasant involvement. Depression and anxiety are common negative emotions experienced by young adults. Long-term immersion in depression, anxiety, pressure, and other negative emotions will not only reduce general enthusiasm and initiative but also have a negative impact on individuals, resulting in social dysfunction such as AjD, as well as self-harm and suicide in severe cases (17, 18). It has been found that negative emotion is one of the risk factors for adverse reactions to AjD, and thus the pathopsychological process from negative emotion to AjD is worth investigating.
Prior studies have found that rumination is related to the occurrence, development, and persistence of negative emotions (19–21); it has been defined as “after encountering negative life events, the individual’s thinking stays under the influence of life events and repeatedly thinks about the causes, consequences and feelings of the events” (20). Ruminative thinking is a maladaptive cognitive style that causes individuals to fall into a vicious cycle of negative emotions and cognition under external pressures and cognitive dissonance. Individuals who frequently experience stressful events are more inclined to have more serious and long-term negative emotions post-event and are therefore more likely to engage in ruminative thinking (22, 23). Numerous studies have demonstrated that rumination is an important factor that influences negative emotions and that there is a significant positive correlation between rumination and negative emotions. According to the reaction style theory, rumination not only triggers and prolongs negative emotions, such as depression and anxiety (24), but also aggravates negative emotions and negative cognition (25). More recently, evidence from an empirical sampling study suggested that rumination engagement partially mediates the link between negative events and negative emotions (26). Emotional regulation of cognitive dissonance has been emphasized as a key factor in the occurrence and maintenance of negative emotions.
Insomnia refers to the continuous struggle to fall asleep, destruction of sleep integrity, and a decline in sleep quality, often accompanied by daytime dysfunction despite adequate sleep opportunities and a conducive sleeping environment (27). Insomnia is a disease (primary insomnia) and a symptom of other diseases (comorbid insomnia) (28). Maladjustment is one of the three core symptom factors of the negative event stress response, and its symptoms often interfere with daily functioning, such as difficulty concentrating or sleep disturbance (2). Studies have found a close relationship between negative emotions and insomnia, whereby insomnia plays a causal role in the development of negative emotions such as depression and anxiety (29). Sleep disorders are common among patients with depression (30); the higher the depressive mood, the worse the sleep quality (31, 32). It is often associated with anxiety disorders (29, 33). Sleep quality often interacts with emotional disorders, and sleep-wake regulation disorders aggravate negative emotions, forming a vicious cycle that may lead to inevitable negative thoughts and behaviors (34). Additionally, the influence of rumination on insomnia has been confirmed (35–37). The cognitive model of sleep posits that rumination, a relatively common intrusive thought, can prevent individuals from entering and maintaining sleep activities (28). Studies have found that the higher the level of rumination thinking, the worse the quality of sleep (35–37). As an important indicator of mental health, sleep is closely related to the mental state of the individual (38) and has a substantial impact on the occurrence, development, and maintenance of emotional problems in young individuals (39). In summary, there is a paired correlation between negative emotions, rumination, and insomnia. However, research on the internal relationship between rumination and insomnia in young individuals with AjD needs to be enhanced, and that between rumination, insomnia, negative emotions, and AjD warrants further research.
Based on the findings of prior studies and the theory of response styles, this study developed a mediation model to explore the relationships and combined effects among negative emotions, rumination, and insomnia in young patients with AjD. The study considered negative emotions, rumination, and insomnia as independent variables, with rumination and insomnia as mediating variables and AjD as the dependent variable. Additionally, the study sought to determine whether rumination can induce, prolong, or exacerbate negative emotions, leading to insomnia and ultimately resulting in AjD. This research aimed to reveal the mechanisms by which negative emotions contribute to AjD and to elucidate the mediating roles of rumination and insomnia.
2 Methods
2.1 Participants
Baseline assessment was conducted from February 2023 to March 2024. Participants with negative emotional problems, whose ages ranged from 18 to 44 years old and were treated in the psychosomatic outpatient department, were recruited consecutively through the Affiliated Encephalopathy Hospital of Zhengzhou University (Zhumadian Second People’s Hospital), most of whom came from Zhumadian and the surrounding areas. Participants were excluded if they were below 18 years of age; were not able to participate as a result of severe physical diseases, severe mental disorders, serious disabilities; or if the basic information was incomplete and could not be verified and supplemented by other means.
A total of 2176 questionnaires were collected, of which 161 were excluded for not meeting the inclusion criteria and for providing answers that were too short, a response rate of 92.60%. Among the 2015 participants, 55.3% (n =1115) were male and 44.7% (n = 900) female. The mean age of the sample was 25.41 years (SD = 3.91, range 18–78 years). Among the participants, 92.0% (n =1856) of participants reported living in two-parent family, while 46.9% (n =946) were only child. The study was approved by the Affiliated Encephalopathy Hospital of Zhengzhou University (ethics approval number: KS-2023-005-01).
2.2 Measures
2.2.1 General information questionnaire
The initial part of the survey was a self-developed general information questionnaire that included the measurement of sociodemographic variables such as gender, age, being an only child, and family composition.
2.2.2 Depression anxiety and stress scale
The Depression Anxiety and Stress Scale (DASS) was originally compiled by Lovibond in 1995 (40). This study adopted a simplified version of the DASS (DASS-21) revised by Chinese scholar Gong Xiang (41). The full scale contains 21 items, and the three subscales (depression, anxiety, and stress) each contain seven items. All subscales are scored from 0 (“inconsistent”) to 3 (“always consistent”); in the dimensions of depression, anxiety, and stress, higher scores on the survey indicate a more severe level of these negative emotions.The internal consistency coefficient of the scale in this study exhibited a Cronbach’s α of 0.940, and the Cronbach’s a coefficients for the depression, anxiety, and stress subscales are 0.794, 0.746, and 0.752 respectively, indicating good reliability and validity of the scale.
2.2.3 Ruminative Responses Scale
The Ruminative Responses Scale (RRS) was compiled by Nolen-Hoeksema and is used to assess individual differences in the tendency to ruminate. It has high internal consistency as well as acceptable convergent validity (19), and its Chinese version was revised by Han and Yang (2009) (42). The scale consists of 22 items divided into three categories: rumination, brooding, and reflective pondering. It is scored from 1 “never” to 4 “always,” and the higher the score, the more severe the rumination.
2.2.4 Insomnia Severity Index
The Insomnia Severity Index (ISI) was compiled by Morin (43) to assess the nature, severity, and impact of insomnia., with seven items and a 5-level score ranging from 0 to 4 points. The dimensions evaluated are the severity of sleep onset, sleep maintenance, early morning awakening issues, sleep dissatisfaction, interference of sleep difficulties with daytime functioning, noticeability of sleep issues by others, and distress caused by sleep challenges. The higher the total score on the scale, the more severe the insomnia. Cronbach’s a for the total score in this study was 0.84, indicating good reliability and validity.
2.2.5 Adjustment disorder – New module 20
The Adjustment Disorder – New Module 20 (ADNM-20) is a self-report measurement developed by Glaesmer to assess whether individuals have AjD and to measure the symptoms of AjD (5). The scale has 20 items, including six factors. Pre-occupation (entries 2, 4, 13, 15) and failure to adapt (entries 10, 17, 19, 20) were the two core symptom clusters. Additionally, four accessory symptom factors were included: anxiety (item 6, 16), depressive mood (item 1, 5, 18), impulsivity (item 8, 9, 12), and avoidance (item 3, 7, 11, 14). Item 20 was a functional impairment item. Participants indicated the frequency of all symptoms assessed utilizing these items on a 4-point Likert scale (1 = “never” to 4 = “often”); a sum score over all items measures the severity of AjD symptoms. In this study, ADNM- 20 scores had an excellent internal consistency of α = 0.91.
2.3 Procedure
The survey was conducted in The Affiliated Encephalopathy Hospital of Zhengzhou University, and the electronic questionnaire link was distributed through the questionnaire star platform. All participants were presented with an informed consent sheet, the contents of which were explained by a trained research assistant. The participants were assured of the confidentiality of their responses and the voluntary nature of their participation.
An anonymous assessment was adopted, and the purpose of the study and relevant requirements for the answers were clarified to participants utilizing standardized guidelines; the entire process took approximately 20 to 30 minutes. After all participants completed the questionnaire, they were validated by two trained psychologists. Questionnaires were regarded as invalid and were excluded if they had missing items, unusually short response times, or irregularities in the response options.
The collected data included sociodemographic characteristics, emotional states (such as anxiety, depression, and stress symptoms), sleep patterns, and AjD.
2.4 Statistical analysis
Descriptive statistics were calculated from basic demographic data. Statistical analysis was conducted with IBM SPSS Statistics 28. Pearson’s correlation analysis was utilized to examine the correlation between the scores of each scale and the scores of its sub-dimensions. A univariate test was conducted utilizing the t-test, ANOVA and post hoc test with a statistical significance of p < 0.05. Multiple regression was utilized to identify risk factors for the multivariate analysis. The regression model uses adjustment R² to explains the variance. Amos 7.0 statistical software was used to conduct a path analysis of potential variables in the structural model to determine the mediating effect of rumination and insomnia on negative emotions and AjD. The significance of the mediating effect was tested utilizing a bias-corrected bootstrap method.
3 Results
3.1 Demographics of participants
An independent samples t-test, ANOVA and post hoc test were conducted to assess demographic differences in negative emotions, rumination, insomnia, and AjD among young individuals. Descriptive statistics for all sociodemographic variables included in the study are presented in Table 1. There were no significant differences in the total mean scores of negative emotions, rumination, and insomnia based on demographic variables such as gender and family completeness (p > 0.05). However, regarding AjD, the scores for only child were significantly higher than those for non-only child, and those for individuals from two-parent family were significantly higher than those from a single parent family, with no significant difference between genders. Scores of negative emotions, rumination, insomnia, and AjD varied significantly across different age groups. Post-test results showed that the score of AjD in the age group of 30 to 35-year-olds was significantly higher than that in other age groups(LSD-t=2.189-8.119,P< 0.05).
3.2 Correlation analysis of negative emotions, rumination, insomnia, and AjD
As shown in Table 2, the Pearson product-difference correlation analysis demonstrated all factors in the model were significantly and positively correlated, ranging from 0.445 to 0.952. (p < 0.01). The correlation coefficients between AjD symptoms and depression, anxiety, as well as stress, were r = 0.615 (p < 0.001), r = 0.572 (p < 0.001), and r = 0.600 (p < 0.001), respectively.
3.3 Structural model analyses
The relationship between negative emotions, rumination, insomnia, and AjD was explored. To exclude the interaction between variables and test the predictive effect of each variable on adaptation disorders, a multilevel regression analysis was utilized. The regression analysis comprised three models. Model 1 included anxiety, stress, and depression on the DASS-21. Model 2 included anxiety, stress, depression, and rumination. Model 3 included anxiety, stress, depression, rumination, and insomnia. The dependent variable was adjustment barrier.
As exhibited in Table 3, the adjusted R² value of Model 1 was 0.410, indicating that negative emotions could explain 41.0% of the variance in adjusted disorders. When rumination was included in Model 1, adjusted R2 changed from 0.410 to 0.477, indicating that negative emotions and rumination explained 47.7% of the AjD. The coefficient of ruminative thought was 0.422, which was significant (t = 16.065, p < 0.001) and had a positive effect on AjD. When insomnia was included to Model 3, adjusted R2 increased from 0.477 to 0.486, indicating that insomnia could explain 0.9% of AjD based on Model 2. The regression coefficient of insomnia was 0.249, which was significant (p < 0.001), indicating that rumination had a significant positive effect on insomnia. In Model 1, anxiety, stress, and depression made independent positive contributions to AjD. Furthermore, when rumination and insomnia were included in Model 3, the contributions of depression, anxiety, and stress changed. However, anxiety was not significant.
This study found that increased rumination and insomnia significantly predicted AjD. This model accounted for half of the variance in the changes in AjD (F (5,2009) = 381.203, p < 0.001; adjusted R2 = 0.486). Regression models identified depression, stress, rumination, and insomnia as important predictors of AjD.
These results provide preliminary support for the proposed structural equation model exhibited in Figure 1. Maximum likelihood estimation was employed to calculate the goodness-of-fit indices (χ2/df = 25.597/6 = 4.266, GFI = 0.996, AGFI = 0.985, CFI =0.998, TLI = 0.994, NFI = 0.994, RMSEA =0.040).
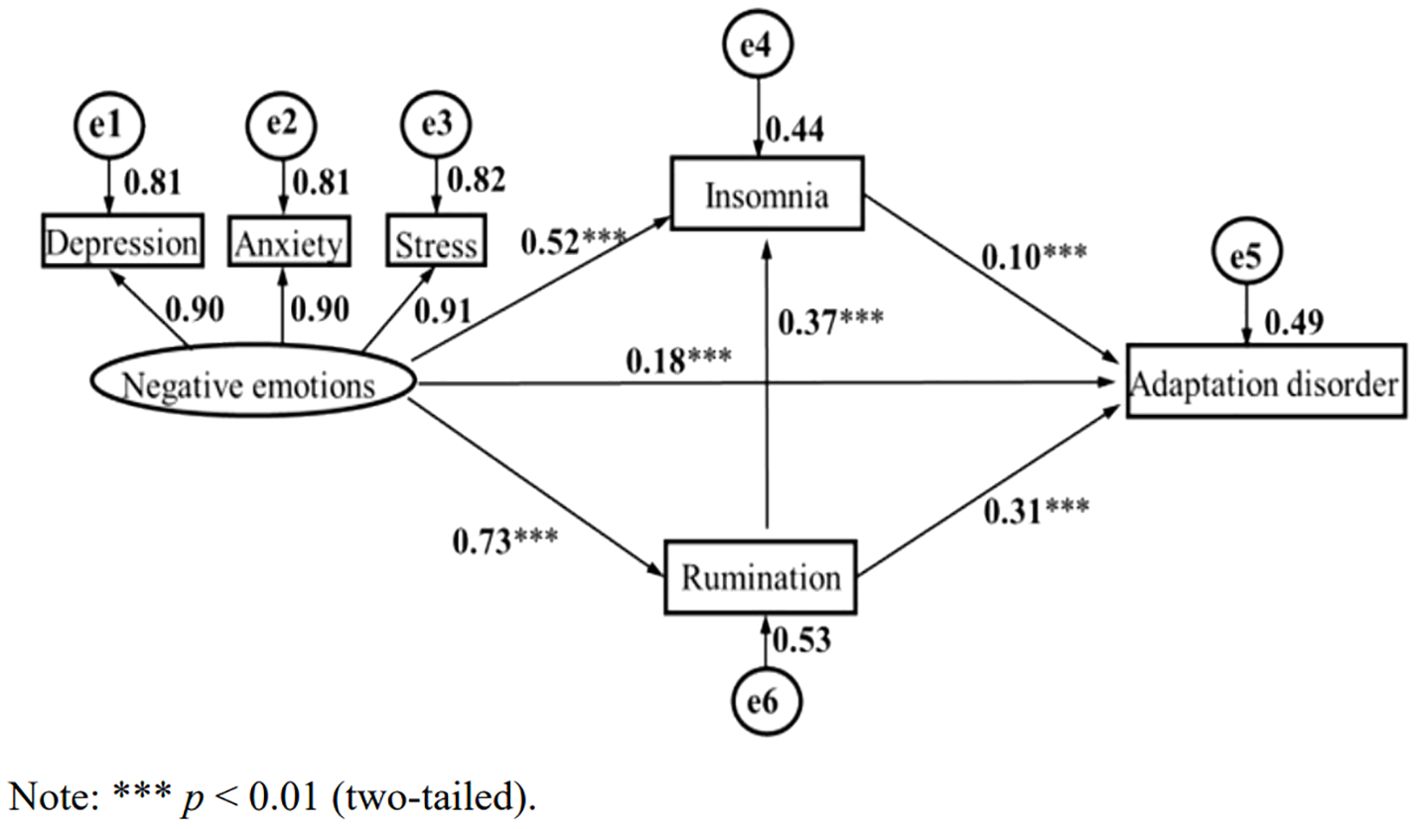
Figure 1. Negative emotion, rumination, insomnia, and adaptation disorder chain mediation effect. ***p<0.01 (two-tailed).
According to existing studies and the above findings, to further explore the specific role of ruminative thinking and insomnia in negative emotions and AjD, a structural equation model was utilized to analyze the influence of negative emotions on AjD and to assess the mediating effect of ruminative thinking and insomnia. The structural equation model was constructed with negative emotions as an exogenous variable, rumination and insomnia as endogenous latent variables, adaptation disorder as the dependent variable, and depression, anxiety, and stress as negative emotion control variables. As shown in Figure 1, in the measurement model, the standardized load of negative emotions on the latent variable was above 0.90, which indicates that the measurement of the latent variable by the observed variable was sufficient and effective.
Figure 1 demonstrates that negative emotion can significantly and positively predict AjD (β = 0.37, p < 0.001), insomnia (β = 0.52, p < 0.001), as well as rumination (β = 0.73, p < 0.001). Rumination was a significant positive predictor of adaptation disorder (β = 0.31, p < 0.001) and insomnia (β = 0.18, p < 0.001). Insomnia was a positive predictor of AjD (β = 0.10, p < 0.001).
Bootstrapping techniques were utilized to evaluate multiple mediations. As exhibited in Table 4, all paths were explicitly significant (zero was not included in the 95% CI), indicating that ruminative thinking and insomnia had mediating effects on negative emotions and AjD.
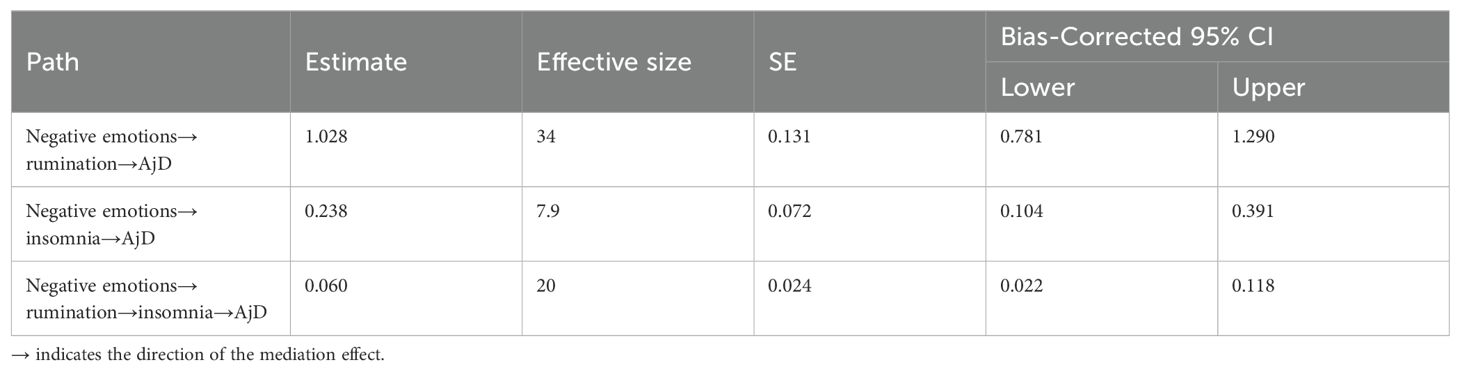
Table 4. Bootstrap test of the mediating effect of rumination and insomnia on negative emotion and AjD.
In this model, the direct effect of negative emotions on AjD was 0.37, and the total mediation effect was 1.326 (1.028 + 0.238 + 0.060). The results indicate that negative emotions can not only directly predict suicidal ideation but can also predict AjD through the chain-mediating effect of rumination and insomnia, that is, rumination and insomnia play a chain-mediating role between negative emotion and AjD in young individuals. Integrating Figure 1 with Table 5, a clearer association can be observed where rumination and insomnia exert multiple mediation effects on the relationship between negative emotions and AjD.
4 Discussion
This study found that, in terms of AjD, the scores of only child were significantly higher than those of non-only child and the scores of individuals from two-parent family were significantly higher than those of a single parent family. However, there was no significant difference between genders, consistent with prior studies (44, 45). This finding may be because family relationships influence a child’s personality traits and cognitive style, with only children often being overcontrolled and protected by their parents (13, 46, 47). This overprotection can have a lasting impact on cognition and increase the risk of disorders through mechanisms, such as heightened susceptibility to stress, which raises the possibility of AjD. Prior research has found similar findings, indicating that overprotective parenting can increase the risk of mental disorders such as depression and stress (47, 48).
The scores of negative emotions, rumination, insomnia, and AjD were significantly different among various age groups, and the score of AjD in the age group of 30 to 35-year-olds was significantly higher than that in other age groups. Prior studies have found that the relationship between age and the prevalence of AjD is controversial (5). The current study found that age is an influencing factor for AjD, and the core symptom pattern of AjD is related to various sociodemographic factors such as a lower family budget (6). Among the interviewed young adults, the 31-35 age group felt more competitive pressure. Behind this, the young people in the 31-35 age group bear the responsibility of taking care of the elderly and children in life. Moreover, they have to face the challenge of “35-year-old crisis” in the workplace. With the increase of various pressures from society, family and work, the probability of AjD also increases. Notably, the AjD score exhibited no gender differences, even though there is substantial evidence that women are at a higher risk for mental disorders (49), possibly as a result of differences in study assessment tools and sample sizes. This suggests more attention should be given to the mental health of young individuals aged over 30 or being the only child in family.
Additionally, the current study found that among the factors related to AjD, including anxiety, depression, stress, rumination, and insomnia, the correlations between each factor were very high (0.445–0.954), consistent with the results of other studies (50). Negative life events, as psychological and social stressors, are significant causes of psychological problems that can easily induce anxiety, depression, and other negative emotional issues. Stress-induced rumination exacerbates anxiety and depression (51). Prior studies have demonstrated a vicious cycle between ruminative thinking and negative emotions; persistent rumination leads to negative emotional outcomes, while negative emotions trigger negative cognition and intensify rumination, resulting in AjD (52–55). Empirical research has also shown that the role of rumination plays in the maintenance of depression, anxiety, and other negative emotions for those with a propensity for rumination (21, 56). Negative emotions can cause sleep disorders, such as short sleep latency, reduced deep sleep, early waking, and difficulty falling asleep after waking (29, 57). As individual levels of negative emotions increase, engaging in ruminative thinking is more likely, creating a vicious cycle between rumination and negative emotions. Higher levels of negative emotions result in poorer sleep quality. Thus, rumination and insomnia act as bridges between negative emotions and AjD.
Negative emotions, rumination, and adjustment disorders are important mediating factors of psychological stress. The findings of the regression analysis indicated that both negative emotions and rumination had predictive effects on AjD and could explain 47.7% of the variance in AjD. Negative emotions have a significant predictive effect on AjD, which has been supported by numerous studies (16) The stress-response syndrome model (58) posits that disorders caused by psychosocial stressors follow a specific developmental pattern, with generally stressful events eliciting intense emotional responses (58), followed by denial of the new reality and a period of re-experience and invasion as the individual recognizes the stressor and all its consequences. Rumination partially mediates the relationship between negative emotions and AjD (59); that is, the more severe the rumination, the more likely it is to produce AjD, which is consistent with prior studies (51). According to Nolen-Hoeksema’s reaction style theory (20), individuals with a ruminative response style tend to repeatedly focus on their negative emotions following a stressful event, engaging in habitual overthinking and introspection, becoming immersed in feelings of sadness and feeling unable to disengage, thereby intensifying the negative emotions triggered by the stressor and exacerbating AjD. This underscores that negative emotions and rumination are significant risk factors for AjD. Interestingly, the results of the regression analysis indicated that depression, anxiety, and stress positively predicted AjD within the dimension of negative emotions in Model 1, whereas the relationship between anxiety and AjD was not significant in Model 3. This suggests that compared to anxiety, depression and stress are more internally focused dimensions whose negative impacts are more pronounced.
Sleep is an indispensable physiological process in humans. Good sleep has beneficial effects, such as eliminating fatigue, storing energy, enhancing immunity, and preventing diseases (60). According to the cognitive model of insomnia, rumination often induces cognitive impairment in patients. Rumination not only makes it difficult for individuals to conduct rational analysis in the face of stressors but also consumes cognitive resources and increases negative self-concern, which is prone to negative bias, distorted cognition, and unconstructive consequences (54). Prior studies have shown that an increase in rumination is associated with longer sleep onset latency and lower sleep quality and efficiency (37). According to the micro-analysis theory of insomnia, the primary mechanism causing insomnia is the excessive activation of physiology, cognition, and emotional systems; ruminative thinking, as an invasive thought, can over-activate the sympathetic nervous system (29), resulting in excessive physiological awakening. Patients with insomnia repeatedly consider their sleep conditions and possible adverse consequences, further causing excessive awakening at the cognitive level (61). The more individuals utilize ruminative thinking, the more their negative emotion level increases; the higher the level of negative emotion, the worse the quality of sleep. Thus, rumination acts as a bridge between negative emotions and insomnia.
According to Morin ‘s comprehensive model (17), insomnia is the result of a dynamic interaction between cognitive dysfunction, maladaptive behaviors (or habits), concerns about the consequences of sleep deprivation (mood, fatigue, and performance), and arousal (mood, cognition, and physiology). Cognitive models (62) provide strong predictions for the development of mental disorders based on the concept of cognitive, emotional, and behavioral interactions, in which maladaptive thoughts lead to negative emotions that produce behavioral changes. Several studies support the role of cognitive dysfunction in insomnia (32, 38). Specifically, individuals with rumination tendencies tend to worry too much about sleep quality, triggering autonomic arousal and emotional distress or anxiety, which leads to distorted perceptions of insomnia, producing maladaptive behaviors such as adaptation disorders.
Additionally, the structural equation model of multiple mediating effects indicated that negative emotions not only directly affected the AjD of young individuals but also indirectly impacted their AjD through rumination and insomnia. In this study, negative emotion could positively predict AjD (β = 0.328, p < 0.01), with a direct effect of 0.37. The mediating effects test showed that rumination and insomnia explained 61.9% of the total effect and played a partial mediating role in the relationship between negative emotions and AjD. Rumination can not only exacerbate the vicious circle between negative emotions and negative cognition, resulting in reduced problem-solving ability (63), but it also weakens the emotional regulation ability of young individuals (64), therefore increasing susceptibility to AjD. Despite emerging evidence that AjD is a gateway to more serious mental illnesses, it is important to emphasize that AjD itself is associated with significantly negative outcomes. When young individuals encounter life stress events, they produce negative emotions, which make it relatively easier to generate ruminative thinking, resulting in insomnia and other problems, in addition to eventually leading to adaptation disorders. Specifically, the greater the stress intensity of young individuals, the more likely they are to be immersed in depression, anxiety, pressure, and other negative emotions, thereby inducing ruminative thinking, compulsive thinking, and reflection on negative moods and emotions brought about by life events (65). This negative way of thinking results in insomnia, an incapacity to adapt to changes in the life environment, cognitive distortion, and an inability to deal with problems rationally and calmly, all of which ultimately lead to adaptation disorders (66).
Therefore, alleviating the rumination of young individuals and enhancing their ability to face negative emotions caused by stressful events can improve mental health and reduce the possibility of AjD. This has positive implications for the prevention and intervention of adaptation disorders in young individuals. For those experiencing negative emotions, active intervention should be carried out as soon as possible, focusing on promoting positive and optimistic cognitive tendencies while preventing ruminative thinking and depression; such interventions can also enhance sleep quality and thereby mental health, reducing the possibility of adaptation disorders. This study’s findings can guide effective interventions for adaptation disorders and have positive implications for enhancing young adults’ mental health.
This study has several important limitations. First, it utilized a self-rating scale, which may introduce self-report bias. Future research could enhance assessment accuracy by incorporating structured interview questionnaires or a combination of both methods. Second, this study examined the development of AjD from a cross-sectional perspective. Longitudinal tracking would be beneficial to explore the causal relationships between various variables of AjD and other influencing factors. Additionally, the explanatory power of rumination and insomnia is limited, as negative emotions can lead to diverse reactions that impact social functioning. Future studies should comprehensively consider multiple factors influencing AjD and the interrelationships among these factors.
5 Conclusion
In summary, negative emotions, rumination, insomnia, and AjD are interrelated. Rumination and insomnia partially mediate the relationship between negative emotions and AjD. Negative emotions not only directly impact AjD in young adults but also indirectly influence them through rumination and insomnia.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
XS: Methodology, Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. ZD: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Formal analysis, Software. SZ: Validation, Writing – review & editing. YQ: Validation, Writing – review & editing. HZ: Supervision, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. HG: Conceptualization, Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by 2023 Henan Province medical science and technology research plan joint construction project (LHGJ20231005).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank all the participants of the study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Strain JJ, Friedman MJ. Considering adjustment disorders as stress response syndromes for DSM-5. Depress Anxiet. (2011) 28:818–23. doi: 10.1002/da.20782
2. Maercker A, Brewin CR, Bryant RA, Cloitre M, van Ommeren M, Jones LM, et al. Diagnosis and classification of disorders specifically associated with stress: proposals for ICD-11. World Psychiatry. (2013) 12:198–206. doi: 10.1002/wps.20057
3. Sachser C, Goldbeck L. Consequences of the diagnostic criteria proposed for the ICD-11 on the prevalence of PTSD in children and adolescents. J Trauma Stress. (2016) 29:120–3. doi: 10.1002/jts.2016.29.issue-2
4. Bachem R, Casey P. Adjustment disorder: a diagnosis whose time has come. J Affect Disord. (2018) 227:243–53. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2017.10.034
5. Glaesmer H, Romppel M, Brähler E, Hinz A, Maercker A. Adjustment disorder as proposed for ICD-11: dimensionality and symptom differentiation. Psychiatry Res. (2015) 229:940–8. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2015.07.010
6. Perkonigg A, Lorenz L, Maercker A. Prevalence and correlates of ICD-11 adjustment disorder: findings from the Zurich Adjustment Disorder Study. Int J Clin Health Psychol. (2018) 18:209–17. doi: 10.1016/j.ijchp.2018.05.001
7. Killikelly C, Lorenz L, Bauer S, Mahat-Shamir M, Ben-Ezra M, Maercker A. Prolonged grief disorder: its co-occurrence with adjustment disorder and post-traumatic stress disorder in a bereaved Israeli general-population sample. J Affect Disord. (2019) 249:307–14. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2019.02.014
8. Foster P, Oxman T. A descriptive study of adjustment disorder diagnoses in general hospital patients. Irish J Psychol Med. (1994) 11:153–7. doi: 10.1017/S0790966700001683
9. Strain J. Adjustment disorder: a multisite study of its utilization and interventions in the consultation-liaison psychiatry setting. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. (1998) 20:139–49. doi: 10.1016/S0163-8343(98)00020-6
10. Carta M, Balestrieri M, Murru A, Hardoy MC. Adjustment disorder: epidemiology, diagnosis and treatment. Clin Pract Epidemiol Ment Health. (2009) 5:15. doi: 10.1186/1745-0179-5-15
11. Portzky G, Audenaert K, van Heeringen K. Adjustment disorder and the course of the suicidal process in adolescents. J Affect Disord. (2005) 87:265–70. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2005.04.009
12. Bhatia MS, Aggarwal NK, Aggarwal BB. Psychosocial profile of suicide ideators, attempters and completers in India. Int J Soc Psychiatry. (2000) 46:155–63. doi: 10.1177/002076400004600301
13. Hund B, Reuter K, Härter M, Brähler E, Faller H, Keller M, et al. Stressors, symptom profile, and predictors of adjustment disorder in cancer patients. Depress Anxiety. (2016) 33:153–61. doi: 10.1002/da.2016.33.issue-2
14. Chen PF, Chen CS, Chen CC, Lung FW. Alexithymia as a screening index for male conscripts with adjustment disorder. Psychiatr Q. (2011) 82:139–50. doi: 10.1007/s11126-010-9156-9
15. Schwarzbach M, Luppa M, Forstmeier S, König HH, Riedel-Heller SG. Social relations and depression in late life-a systematic review. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. (2014) 29:1–21. doi: 10.1002/gps.v29.1
16. Eberle DJ, Maercker A. Preoccupation as psychopathological process and symptom in adjustment disorder: a scoping review. Clin Psychol Psychother. (2022) 29:455–68. doi: 10.1002/cpp.v29.2
17. Carrigan N, Barkus E. A systematic review of cognitive failures in daily life: healthy populations. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. (2016) 63:29–42. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2016.01.010
18. Barley EA, Murray J, Walters P, Tylee A. Managing depression in primary care: a meta-synthesis of qualitative and quantitative research from the UK to identify barriers and facilitators. BMC Fam Pract. (2011) 12:47. doi: 10.1186/1471-2296-12-47
19. Nolen-Hoeksema S, Morrow J. Effects of rumination and distraction on naturally occurring depressed mood. Cognit Emot. (1993) 7:561–70. doi: 10.1080/02699939308409206
20. Nolen-Hoeksema S. Responses to depression and their effects on the duration of depressive episodes. J Abnorm Psychol. (1991) 100:569–82. doi: 10.1037/0021-843X.100.4.569
21. Grassia M, Gibb BE. Rumination and prospective changes in depressive symptoms. J Soc Clin Psychol. (2008) 27:931–48. doi: 10.1521/jscp.2008.27.9.931
22. Nolen-Hoeksema S, Parker LE, Larson J. Ruminative coping with depressed mood following loss. J Pers Soc Psychol. (1994) 67:92–104. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.67.1.92
23. Michl LC, McLaughlin KA, Shepherd K, Nolen-Hoeksema S. Rumination as a mechanism linking stressful life events to symptoms of depression and anxiety: longitudinal evidence in early adolescents and adults. J Abnorm Psychol. (2013) 122:339–52. doi: 10.1037/a0031994
24. Abela JRZ, Hankin BL. Rumination as a vulnerability factor to depression during the transition from early to middle adolescence: a multiwave longitudinal study. J Abnorm Psychol. (2011) 120:259–71. doi: 10.1037/a0022796
25. Slavish DC, Graham-Engeland JE. Rumination mediates the relationships between depressed mood and both sleep quality and self-reported health in young adults. J Behav Med. (2015) 38:204–13. doi: 10.1007/s10865-014-9595-0
26. Moberly NJ, Watkins ER. Ruminative self-focus, negative life events, and negative affect. Behav Res Ther. (2008) 46:1034–9. doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2008.06.004
27. Sateia MJ. International classification of sleep disorders-third edition: highlights and modifications. Chest. (2014) 146:1387–94. doi: 10.1378/chest.14-0970
28. Espie CA. Understanding insomnia through cognitive modelling. Sleep Med. (2007) 8:S3–8. doi: 10.1016/S1389-9457(08)70002-9
29. Johnson EO, Roth T, Breslau N. The association of insomnia with anxiety disorders and depression: exploration of the direction of risk. J Psychiatr Res. (2006) 40:700–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2006.07.008
30. Steer RA, Rissmiller DJ, Beck AT. Use of the Beck Depression Inventory-II with depressed geriatric inpatients. Behav Res Ther. (2000) 38:311–8. doi: 10.1016/S0005-7967(99)00068-6
31. Palesh OG, Collie K, Batiuchok D, Tilston J, Koopman C, Perlis ML, et al. A longitudinal study of depression, pain, and stress as predictors of sleep disturbance among women with metastatic breast cancer. Biol Psychol. (2007) 75:37–44. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2006.11.002
32. Gregory AM, Buysse DJ, Willis TA, Rijsdijk FV, Maughan B, Rowe R, et al. Associations between sleep quality and anxiety and depression symptoms in a sample of young adult twins and siblings. J Psychosom Res. (2011) 71:250–5. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychores.2011.03.011
33. Jansson-Fröjmark M, Lindblom K. A bidirectional relationship between anxiety and depression, and insomnia? A prospective study in the general population. J Psychosom Res. (2008) 64:443–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychores.2007.10.016
34. Li G, Zhang X, Zhang J, Wang E, Zhang H, Li Y. Magnetic resonance study on the brain structure and resting-state brain functional connectivity in primary insomnia patients. Medicine. (2018) 97:e11944. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000011944
35. Carney CE, Edinger JD, Meyer B, Lindman L, Istre T. Symptom-focused rumination and sleep disturbance. Behav Sleep Med. (2006) 4:228–41. doi: 10.1207/s15402010bsm0404_3
36. Guastella AJ, Moulds ML. The impact of rumination on sleep quality following a stressful life event. Pers Individ Dif. (2007) 42:1151–62. doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2006.04.028
37. Zoccola PM, Dickerson SS, Lam S. Rumination predicts longer sleep onset latency after an acute psychosocial stressor. Psychosom Med. (2009) 71:771–5. doi: 10.1097/PSY.0b013e3181ae58e8
38. Neylan TC, Metzler TJ, Best SR, Weiss DS, Fagan JA, Liberman A, et al. critical incident exposure and sleep quality in police officers. Psychosom Med. (2002) 64:345–52. doi: 10.1097/00006842-200203000-00019
39. Sivertsen B, Harvey AG, Reichborn-Kjennerud T, Torgersen L, Ystrom E, Hysing M. Later emotional and behavioral problems associated with sleep problems in toddlers: a longitudinal study. JAMA Pediatr. (2015) 169:575–82. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2015.0187
40. Lovibond PF, Lovibond SH. The structure of negative emotional states: comparison of the Depression Anxiety Stress Scales (DASS) with the Beck Depression and Anxiety Inventories. Behav Res Ther. (1995) 33:335–43. doi: 10.1016/0005-7967(94)00075-U
41. Gong X, Xie XY, Xu R, Luo YJ. Psychometric properties of the Chinese versions of DASS-21 in Chinese college students. Chin J Clin Psychol. (2010) 18:443–6. doi: 10.16128/j.cnki.1005-3611.2010.04.020
42. Han X, Yang HF. Chinese version of Nolen-Hoeksema Ruminative Responses Scale(RRS) used in 912 college students:reliability and validity. Chin J Clin Psychol. (2009) 17:550–1.
43. Morin CM, Belleville G, Bélanger L, Ivers H. The Insomnia Severity Index: psychometric indicators to detect insomnia cases and evaluate treatment response. Sleep. (2011) 34:601–8. doi: 10.1093/sleep/34.5.601
44. For-Wey L, Fei-Yin L, Bih-Ching S. The relationship between life adjustment and parental bonding in military personnel with adjustment disorder in Taiwan. Mil Med. (2002) 167:678–82. doi: 10.1093/milmed/167.8.678
45. Yaseen YA. Adjustment disorder: prevalence, sociodemographic risk factors, and its subtypes in outpatient psychiatric clinic. Asian J Psychiatr. (2017) 28:82–5. doi: 10.1016/j.ajp.2017.03.012
46. Shu BC, Chang YY, Lee FY, Tzeng DS, Lin HY, Lung FW. Parental attachment, premorbid personality, and mental health in young males with hyperventilation syndrome. Psychiatr Res. (2007) 153:163–70. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2006.05.006
47. Kakihara F, Tilton-Weaver L, Kerr M. The relationship of parental control to youth adjustment: do youths’ feelings about their parents play a role? J Youth Adolesc. (2010) 39:1442–56. doi: 10.1007/s10964-009-9479-8
48. Roca M, Vilaregut A, Palma C, Barón FJ, Campreciós M, Mercadal L. Basic family relations, parental bonding, and dyadic adjustment in families with a member with psychosis. Community Ment Health J. (2020) 56:1262–8. doi: 10.1007/s10597-020-00581-z
49. Vikas M, Chandrasekaran R. A case of obsessive-compulsive disorder by proxy. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. (2011) 33:303. doi: 10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2011.02.011
50. Thomsen DK, Yung Mehlsen M, Christensen S, Zachariae R. Rumination—relationship with negative mood and sleep quality. Pers Individ Dif. (2003) 34:1293–301. doi: 10.1016/S0191-8869(02)00120-4
51. McLaughlin KA, Nolen-Hoeksema S. Rumination as a transdiagnostic factor in depression and anxiety. Behav Res Ther. (2011) 49:186–93. doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2010.12.006
52. Koster EHW, De Lissnyder E, Derakshan N, De Raedt R. Understanding depressive rumination from a cognitive science perspective: the impaired disengagement hypothesis. Clin Psychol Rev. (2011) 31:138–45. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2010.08.005
53. Selby EA, Connell LD, Joiner TE. The pernicious blend of rumination and fearlessness in non-suicidal self-injury. Cognit Ther Res. (2010) 34:421–8. doi: 10.1007/s10608-009-9260-z
54. Watkins ER. Constructive and unconstructive repetitive thought. Psychol Bull. (2008) 134:163–206. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.134.2.163
55. Selby EA, Anestis MD, Joiner TE. Understanding the relationship between emotional and behavioral dysregulation: emotional cascades. Behav Res Ther. (2008) 46:593–611. doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2008.02.002
56. Harrington JA, Blankenship V. Ruminative thoughts and their relation to depression and anxiety. J Appl Soc Psychol. (2002) 32:465–85. doi: 10.1111/j.1559-1816.2002.tb00225.x
57. McCann SJH, Stewin LL. Worry, anxiety, and preferred length of sleep. J Genet Psychol. (1988) 149:413–8. doi: 10.1080/00221325.1988.10532169
58. Horowitz MJ. Stress-response syndromes: a review of posttraumatic and adjustment disorders. Hosp Community Psychiatry. (1986) 37:241–9. doi: 10.1176/ps.37.3.241
59. Smith JM, Alloy LB. A roadmap to rumination: a review of the definition, assessment, and conceptualization of this multifaceted construct. Clin Psychol Rev. (2009) 29:116–28. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2008.10.003
60. Shiraishi N, Yasuda K, Kitano S. Laparoscopic gastrectomy with lymph node dissection for gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. (2006) 9:167–76. doi: 10.1007/s10120-006-0380-9
61. Ballesio A, Ottaviani C, Lombardo C. Poor cognitive inhibition predicts rumination about insomnia in a clinical sample. Behav Sleep Med. (2019) 17:672–81. doi: 10.1080/15402002.2018.1461103
62. Ehring T, Ehlers A, Glucksman E. Do cognitive models help in predicting the severity of posttraumatic stress disorder, phobia, and depression after motor vehicle accidents? A prospective longitudinal study. J Consult Clin Psychol. (2008) 76:219–30. doi: 10.1037/0022-006X.76.2.219
63. Watkins E, Moulds M, Mackintosh B. Comparisons between rumination and worry in a non-clinical population. Behav Res Ther. (2005) 43:1577–85. doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2004.11.008
64. Joormann J, Dkane M, Gotlib IH. Adaptive and maladaptive components of rumination? Diagnostic specificity and relation to depressive biases. Behav Ther. (2006) 37:269–80. doi: 10.1016/j.beth.2006.01.002
65. Gao Y, Wang H, Liu X, Xiong Y, Wei M. Associations between stressful life events, non-suicidal self-injury, and depressive symptoms among Chinese rural-to-urban children: a three-wave longitudinal study. Stress Health. (2020) 36:522–32. doi: 10.1002/smi.v36.4
Keywords: negative emotions, adjustment disorder, rumination, insomnia, multiple mediating role, young adults
Citation: Shao X, Dong Z, Zhang S, Qiao Y, Zhang H and Guo H (2025) The relationship between negative emotions and adjustment disorder in young adults: the mediating role of rumination and insomnia. Front. Psychiatry 16:1474108. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1474108
Received: 01 August 2024; Accepted: 04 February 2025;
Published: 24 February 2025.
Edited by:
Takahiro Nemoto, Toho University, JapanReviewed by:
Savita G Bhakta, University of California, San Diego, United StatesSeungwon Shin, Sangji University, Republic of Korea
Copyright © 2025 Shao, Dong, Zhang, Qiao, Zhang and Guo. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hua Guo, Z3VvaHVhMTY2OTlAMTYzLmNvbS5jb20=
 Xinyue Shao
Xinyue Shao Hua Guo
Hua Guo