- 1Yulin City Veterans' Hospital, Yulin, Guangxi, China
- 2School of Mental Health, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan, Shanxi, China
- 3Psychological Counseling Center of the Second People's Hospital of Suzhou City, Suzhou, Anhui, China
- 4School of Humanities and Social Sciences, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan, Shanxi, China
- 5Taiyuan Psychiatric Hospital, Taiyuan, Shanxi, China
Background: Current research on aripiprazole adjunct therapy suggests potential benefits in improving psychiatric symptoms and metabolic disorders in patients with schizophrenia. However, the evidence remains limited due to the scarcity of research and a lack of detailed analysis on glucose and lipid metabolism indicators. This study aims to systematically review and analyze randomized controlled trials (RCTs) to evaluate the effects of aripiprazole combination therapy on both psychiatric symptoms and glycolipid metabolism.
Materials and methods: A systematic search of PubMed, EMBASE, and Web of Science databases was conducted to identify randomized controlled trials (RCTs) investigating the impact of aripiprazole combination therapy on glycolipid metabolism and clinical symptoms.
Results: Adjuvant treatment with aripiprazole reduced blood glucose, triglycerides, total cholesterol, and LDL levels in patients with schizophrenia, but had no significant effect on HDL levels. In addition, the study results showed a significant improvement in metabolic parameters at short-term (≤ 8 weeks) and dosing doses >15 mg. However, aripiprazole adjuvant therapy may lead to worsening of clinical symptoms, so caution is required when using it clinically.
Conclusions: Aripiprazole adjunct therapy shows potential benefits in improving both psychiatric symptoms and metabolic parameters, but more comprehensive research is needed to solidify these findings, particularly regarding glycolipid metabolism indicators.
Highlights
● The combined dose of aripiprazole >15 mg for less than 8 weeks can significantly improve metabolism.
● Metabolic improvement was more pronounced in the olanzapine group with combined aripiprazole therapy.
● The metabolic parameters included in some studies are not comprehensive, resulting in insufficient information of some indicators, which may lead to inaccurate outcomes.
1 Introduction
Schizophrenia is a serious mental condition that causes considerable impairment in everyday functioning due to irregularities in thinking, cognition, behavior, and emotions (1). In addition, the life expectancy of people with schizophrenia is reduced by 20 years (2).
Antipsychotic medications are an effective treatment for schizophrenia, but sadly, they can cause about 30% of patients to experience weight gain and disorders of glucolipid metabolism (3, 4), as abnormalities in metabolism usually manifest themselves within the first three months of therapy. The order of antipsychotic medications related to metabolic abnormalities is as follows: Clozapine > Olanzapine > Risperidone = Quetiapine > Ziprasidone = Aripiprazole (5). The biggest factor that affects the metabolism of antipsychotic medications may be the H1 receptor (6). Of course, some other receptors cannot be ignored (7). Although the degree of negative effects of different antipsychotic medications varies, almost all antipsychotic medications can cause weight gain (8). These medications bind to G-protein receptors on the postsynaptic membrane, activate D2 receptors, 5-HT receptors, M-cholinergic receptors, and H receptors that are coupled to them, and these receptors are distributed in the hypothalamus, liver, pancreatic β-cells, adipose tissue, and skeletal muscle. By affecting neuropeptides and 5′-AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activity, which in turn leads to a series of metabolic abnormalities through signal transduction (9). Abnormalities in glycolipid metabolism may lead to adverse consequences (10, 11) and may reduce patients’ compliance with the medication, accompanied by cognitive function impairment (12). Therefore, it is very important to intervene in the metabolic disorders of patients with schizophrenia.
On the other hand, antipsychotic medications are not effective for all patients with schizophrenia, with at least 30% of patients not responding well to the medications. These patients show no clinical improvement after treatment with a sufficient amount and duration of a medication, and even after switching to another medication. This condition is called refractory schizophrenia, and clozapine is usually chosen as the last option for treatment (13). Nevertheless, 40–70% of those with refractory schizophrenia are unresponsive to clozapine, even though the serum concentration of clozapine has reached therapeutic levels (14).
Monotherapy with antipsychotic medications is an evidence-based treatment plan, suitable for both acute and maintenance treatment. If monotherapy fails after two adequate doses and courses, and there are no absolute contraindications, a trial of clozapine should be considered. If treatment with adequate dose and duration has not resulted in significant clinical improvement, it is necessary to rule out other possible reasons for reduced treatment effectiveness. At this point, consider using long-acting injectables or measuring serum drug concentrations to confirm whether there is poor medication adherence or if the drug has reached an effective therapeutic concentration. In the final resort, consider using combination therapy with antipsychotic medications (15). Of course, during treatment, it is also important not to overlook the option of modified electroconvulsive therapy (MECT) (16).
In clinical practice, the combination of antipsychotic medications is inevitable, as drug switching strategies may not always lead to the expected therapeutic effects. An open-label short-term study of 33 schizophrenic patients switching from other antipsychotic medications to aripiprazole showed that all patients successfully switched (17). However, another 6-month follow-up study of schizophrenic patients (n=127) switching from combined treatment to single treatment found that only two-thirds of patients successfully switched to a monotherapy regimen, while the remaining one-third had to resume combined treatment. Furthermore, there are other studies that oppose drug switching strategies (18–20). These findings suggest that for some patients, the combination of antipsychotic medications may be necessary, as monotherapy may not achieve the expected therapeutic effects (21).
It is typical for clinicians to prescribe several antipsychotic drugs at once, a practice known as antipsychotic polypharmacy (APP) (22). Studies have shown that the incidence of combined treatment is 23.1% (23). Previous research has found that combined antipsychotic medication therapy has more side effects than monotherapy (24). A study of 364 patients who received second-generation antipsychotic combination therapy and monotherapy found that combination therapy was associated with a higher prevalence of metabolic syndrome (50.0% vs. 34.3%, p=0.015) and TG/HDL (50.7% vs. 35.0%, p=0.016) (25). Most treatment recommendations discourage the use of many medicines at once because of the complications that arise as a result of taking multiple drugs for the same condition, alongside higher incidence, greater intensity of side effects, reduced adherence, higher drug interaction ricks, and erratic medications (26). In addition, combined medications might increase the total dose of medication, raise the receptor occupancy threshold, but lack additional efficacy, and might increase the incidence of side effects at high doses (27).
Several meta-analyses of RCTs on the combination therapy of antipsychotic drugs evaluated the feasibility of APP, but the results were conflicting. Some of the studies supporting combination medication were usually short-term, open-label studies, whereas some high-quality studies tend not to support the idea of combination medication. Interestingly, these meta-analyses usually reserved their opinions on the combination treatment of aripiprazole, believing that the combination treatment regimen of aripiprazole may have a facilitating effect (15, 28–35). Nevertheless, there were studies that said it was too soon to draw the conclusion that aripiprazole was more successful than other medicines in terms of weight reduction, lowering the burden of severe side events, and improving clinical outcomes, instead using a small number of experimental results to compare (34). In addition, a random controlled trial exploring the efficacy and safety of aripiprazole combination therapy for schizophrenia (n=4457) found that combination aripiprazole had a significant advantage in weight gain, but did not explore its effects on glycolipid metabolism (36).
Thus, aripiprazole has attracted the attention of scholars. The scope of this study goes beyond that of just examining a potential strategy for metabolic regulation, but also to focus on improving metabolic problems while effectively controlling psychiatric symptoms, which will be more beneficial for clinical decisions. Previous studies on aripiprazole adjunct therapy mainly focused on weight research, with limited attention to glycolipid metabolism. The evidence for aripiprazole-assisted therapy is limited, and there is no clear clinical guideline. Thus, we did a comprehensive review and meta-analysis of RCTs to synthesize the current information and give a foundation for treatment choices about the impact of combination aripiprazole on glycolipid metabolism in patients with schizophrenia.
2 Methods
2.1 Search strategy
The review protocol has already been registered in PROSPERP (PROSPERO 2023 CRD42023447923). This study was reported according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines (37).
We conducted literature searches in three electronic databases, PubMed, Embase, and Web of Science(from the date of creation to 24 August 2023), with the following search strategy: (schizophrenia) AND (((Aripiprazole) AND ((((adjunctive) OR (additional)) OR (combine)) OR (coadministration))) AND ((((((((metabolic) OR (body mass index)) OR (Weight)) OR (fasting glucose)) OR (fasting triglycerides)) OR (total cholesterol)) OR (high-density lipoprotein)) OR (low-density lipoprotein)))(with no filters).
2.2 Study selection
Trials, specifically randomized controlled ones or RCTs, using adjunctive atypical antipsychotic medication in individuals with schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorders and indicators of glycolipid metabolism were included in this analysis. All studies did not restrict language. Primary outcomes included fasting glucose, fasting triglycerides, total cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein, and low-density lipoprotein. Psychological symptoms were assessed using the Positive and Negative Symptom Scale (PANSS), or CGI-S scale. As well as drug-related adverse effects were assessed. Studies were excluded if they used non-pharmacological treatments, if they used second-hand data, if the study procedures or results were unclear, and if the subjects had comorbidities or if the subjects were children or adolescents.
Two researchers (WTB and JLM) performed literature searches independently according to the selection criteria, screened all titles and abstracts, and after discussing eligible articles, compiled a list and obtained the full text of each article. Any subsequent exclusions were discussed case by case.
2.3 Quality assessment
The Cochrane bias risk assessment tool was used to assess all included studies for random sequence generation, allocation concealment, blinding of participants and personnel, incomplete outcome data, blinding of outcome assessment, selective reporting, and other potential biases (38). We rated the studies’ potential for bias as either low, high, or unclear based on the evaluation findings.
2.4 Data extraction
Standardized data and characteristics extracted from eligible studies, including authors of the literature, year of publication, source, sample size, intervention, primary outcome indicators (serum glucose, HDL, cholesterol, triglycerides, and LDL), secondary indicators (body mass index, body weight), results of psychiatric symptom assessment, and results of medication-related adverse effects.
2.5 Statistical analyses
For analyses of continuous outcomes, where positive psychiatric symptoms, negative symptoms, and total CGI-S scores were reported, values for metabolic indicators were reported as weighted mean differences (WMD) with 95% confidence interval (CI), whereas those for metabolic indicator values were reported as WMD with 95% CI. For analyses of dichotomous outcomes, summary statistics were expressed as odds ratios (OR) with 95%CI. When combining continuous results, we weighted each study using the inverse variance method. We utilized the I2 statistic to gauge the degree of dissimilarity across the studies, with values over 50% suggesting substantial variation. To further explore potential causes of variation, we also conducted sensitivity analyses, meta-regression with continuous variables, and subgroup analyses. For all analyses, we employed two-sided tests, with P<0.05 signifying statistical significance.
The meta-analyses were conducted using the free software RevMan version 5.4 from the Cochrane Collaboration database. Data from the graphs were extracted using GetData Graph Digitizer 2.2.6 (http://www.getdata-graph-digitizer.com).
3 Results
3.1 Literature search and characteristics
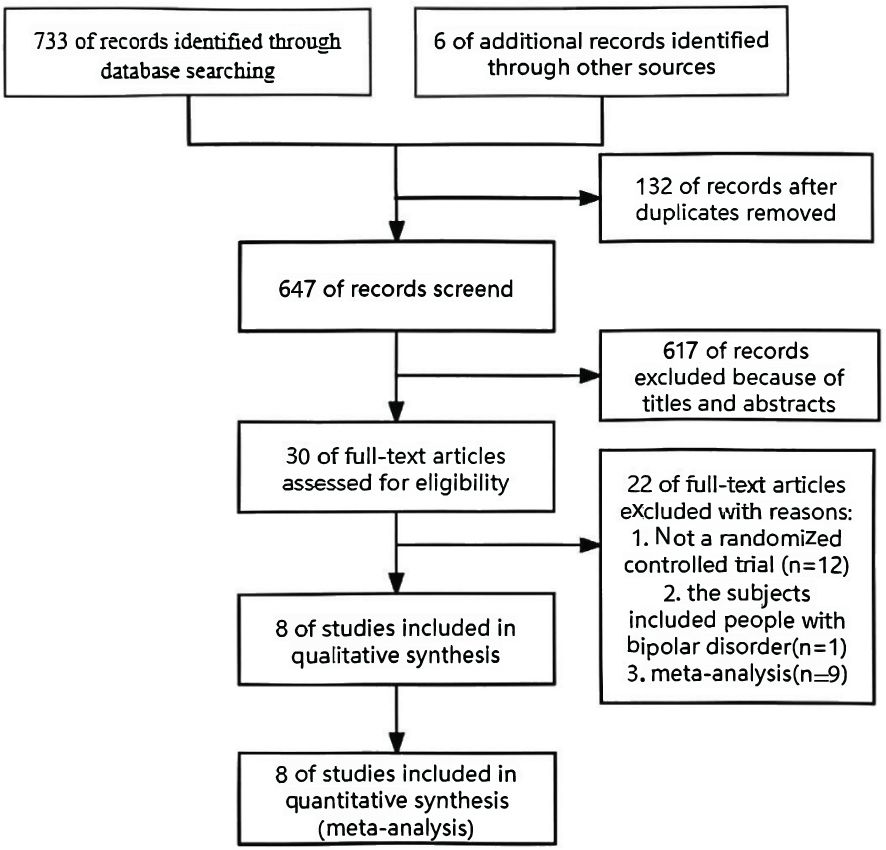
Seven hundred seventy-three trials were collected from the database for this meta-analysis, and an additional six publications were added after manual searches of their references. 749 trials were excluded after abstract evaluation. After reviewing the entire texts of 30 possible trials, 22 were deemed ineligible, leaving just eight publications that fulfilled the inclusion requirements. Figure 1 provides the steps involved in the screening procedure.
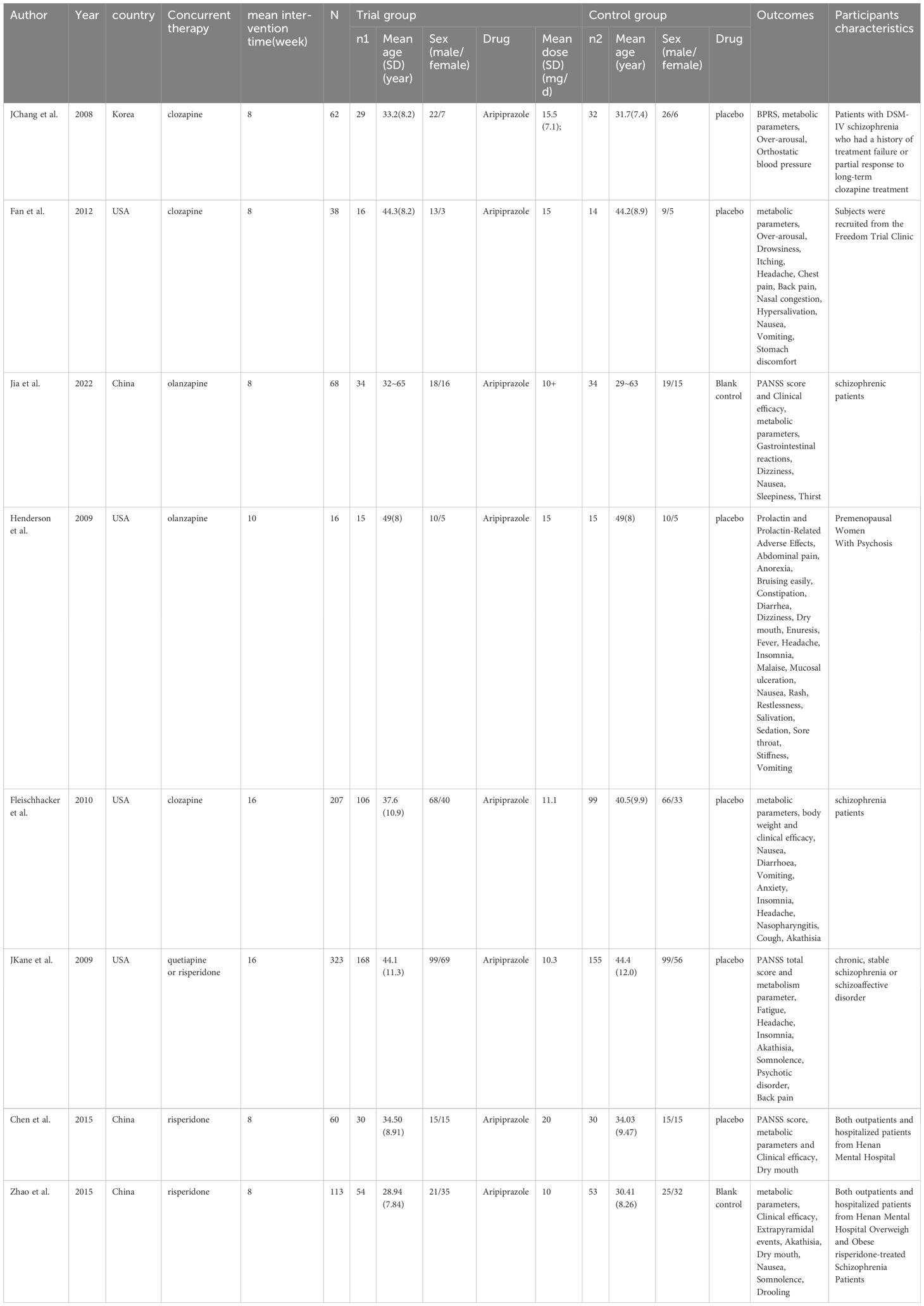
The primary features of these research are summarized in Table 1. The eight RCT-based studies examining the use of aripiprazole as an additional medication for schizophrenia patients also looked into its impact on glycolipid metabolism. Of the eight RCTs, five studies lasted 8 weeks of treatment, one study lasted 10 weeks and two studies lasted 16 weeks. Patients were randomly allocated to receive either an active antipsychotic drug (n=2) or a placebo (n=6). Primary outcomes differed between RCTs: 8 RCTs included reported blood glucose, triglycerides and cholesterol, 7 RCTs reported HDL, and 6 RCTs reported LDL, but one randomized controlled trial reported metabolic parameters using a median that could not be extracted, and therefore metabolic parameters were excluded from this literature. Five RCTs reported PANSS total scores and 3 RCTs reported CGI total scores. Adverse reactions such as inability to sit still, back pain, gastrointestinal reactions, dizziness, salivation, dry mouth, malaise, headache, insomnia, somnolence, vomiting, restlessness and nausea-induced vomiting, and extrapyramidal reactions were reported in the included literature, but the same adverse reaction was reported by up to four studies. Regarding the loss to follow-up in various studies, among which 3 studies have 0 participants lost to follow-up (39–41), 2 studies have 1 participant lost to follow-up (41, 42), 1 study has 2 participants lost to follow-up (43), 1 study has 6 participants lost to follow-up (44), and 1 study has 8 participants lost to follow-up (45).
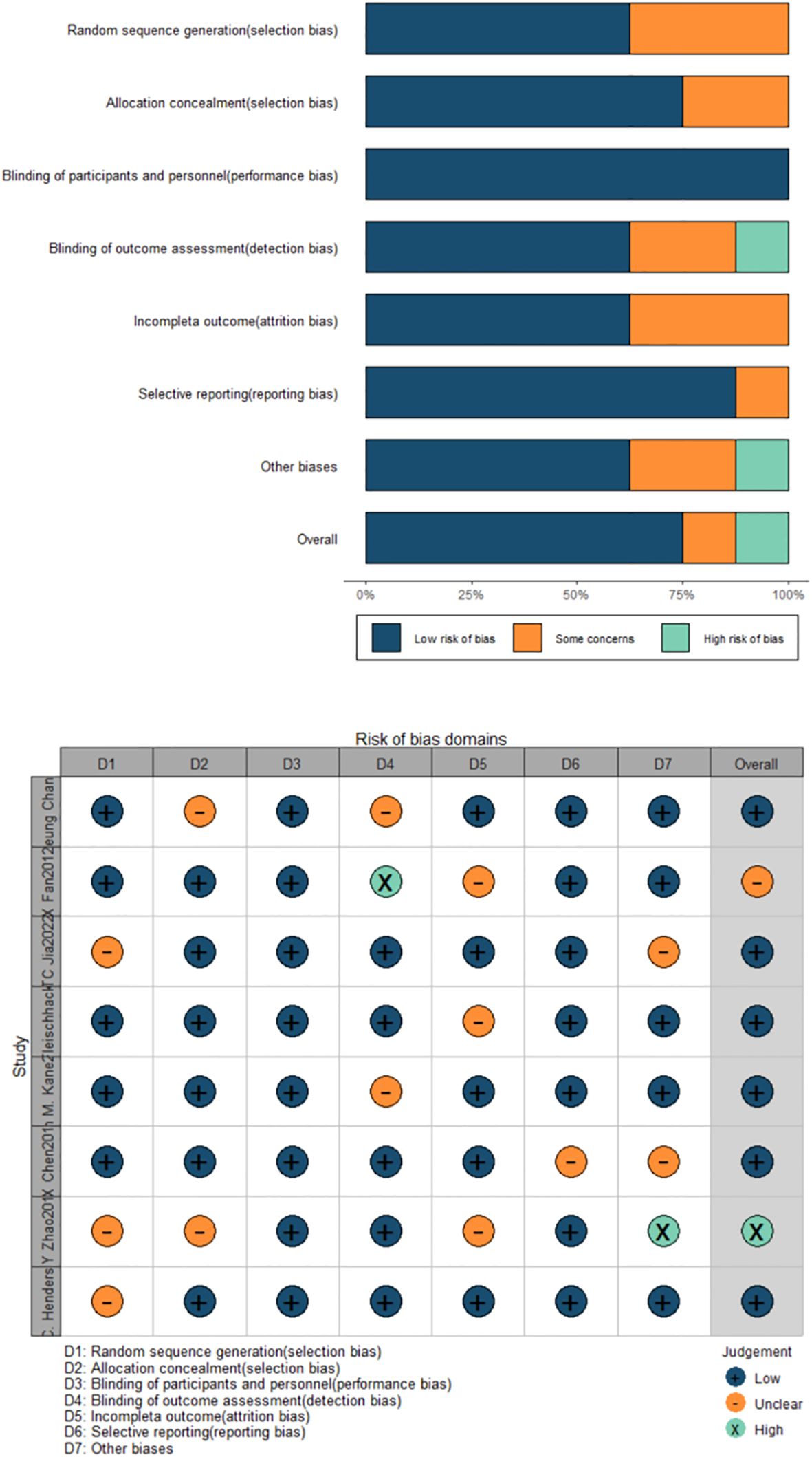
The Cochrane bias risk assessment result (Figure 2) showed that of the total 8 studies, 5 were classified as low risk of randomization, 3 were unclear; 6 RCTs clearly described allocation concealment, but 2 were unclear; all studies used blinded methods; 3 RCTs had unclear bias risks in incomplete outcome data. Eventually, 6 RCTs were judged as low risk, 1 as high risk, and 1 was unclear. Among them, 5 studies were supported by pharmaceutical companies.
3.2 Effect on blood glucose levels
The impact of aripiprazole adjunctive treatment on glycolipid metabolism in individuals with schizophrenia was evaluated using GLU as the outcome indicator, and seven studies satisfied the inclusion criteria (Figure 3A). Due to statistically insignificant heterogeneity (I2 = 0%, P=0.51), the fixed effect model was employed for the meta-analysis. Taking into account the sum of the effects, we found a statistically significant reduction [MD=-3.52, 95% CI (-5.82, -1.21)]. On the null line’s left side is a diamond-shaped square, which did not cross the line, indicating that adjuvant treatment with aripiprazole compared to the control group can effectively reduce blood glucose levels.
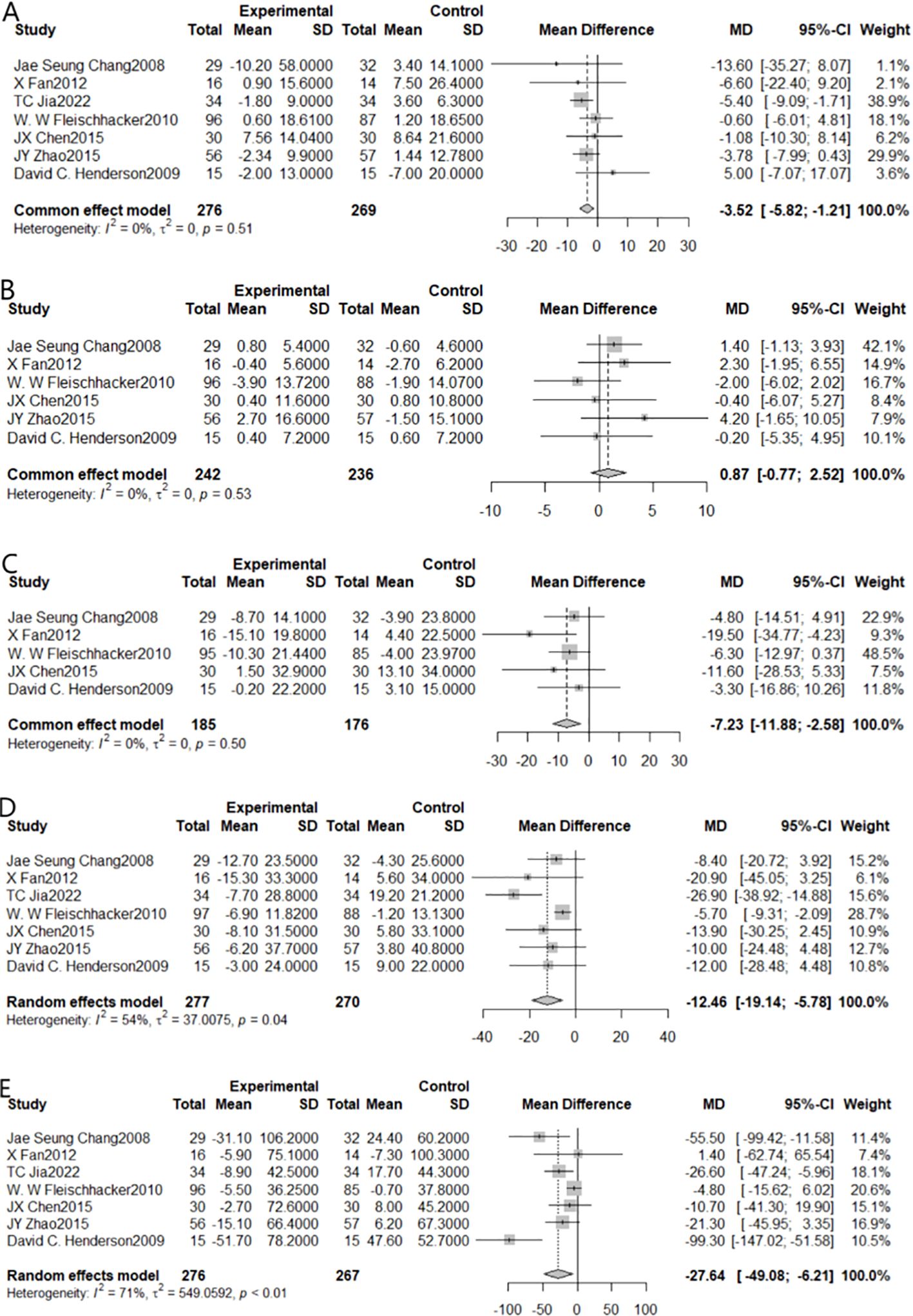
Figure 3. Forest plot of the results of all metabolic indicators in patients after combining aripiprazole [(A) for GLU, (B) for HDL, (C) for LDL, (D) for TC, (E) for TG].
3.3 Effect on high-density lipoprotein levels
When HDL was chosen as the outcome indicator, 6 studies could be included (Figure 3B). Due to statistically insignificant heterogeneity (I2 = 0%, P=0.53), for the meta-analysis, we employed the fixed effect model. The results showed that the synergistic impact was not statistically significant [MD=0.87, 95% CI (-0.77,2.54)]. Adjuvant treatment with aripiprazole was not more effective than monotherapy in lowering HDL levels, as shown by the fact that the diamond-shaped squares and the null line crossed.
3.4 Effect on low-density lipoprotein levels
When LDL was chosen as the outcome indicator, 5 studies could be included (Figure 3C). Due to negligible heterogeneity, the meta-analysis used a fixed-effects model (I²=0%, P<0.01). The results showed a statistically significant combined effect [MD=-7.23, 95% CI (-11.88, -2.58)]. The square with the diamond form was positioned to the left of the null line, non-intersecting, indicating that adjuvant treatment with aripiprazole was effective in reducing LDL levels compared to the control group.
3.5 Effect on total cholesterol levels
When TC was chosen as the outcome indicator, 7 studies could be included (Figure 3D). Due to statistically significant heterogeneity (I2 = 54%, P=0.04), we performed Meta-analysis using a random effects model. The results showed a statistically significant combined effect [MD=-12.46, 95% CI (-19.14, -5.78)]. Since the diamond-shaped square did not cross the null line (just on the line’s left side), indicating that adjuvant treatment with aripiprazole was effective in reducing total cholesterol levels compared to the control group.
3.6 Effect on triglyceride levels
When TG was chosen as the outcome indicator, 7 studies could be included (Figure 3E). Due to statistically significant heterogeneity (I2 = 71%, P < 0.01), we used a random effects model for our meta-analysis. The results indicated the statistical significance of the summative impact [MD=-27.64, 95% CI (-49.08, -6.21)]. The square with the diamond form was positioned to the left of the zero-line, non-intersecting, indicating that adjuvant treatment with aripiprazole was effective in reducing triglyceride levels compared to the control group.
3.7 Effects on psychiatric symptoms
Statistically significant variations in PANSS scale total scores were seen between the treatment and placebo groups in psychiatric examinations using the PANSS and the CGI. Positive and negative PANSS scale ratings were not different between the treatment and placebo groups. Of these, a total of 5 studies pinned to the PANSS scale total score were included, and Meta-analysis was performed using a fixed-effects model due to statistically non-significant heterogeneity (I2 = 6%, P=0.37). There was a statistically significant combined impact [MD=0.45, 95% CI (0.01,0.89)], with the diamond-shaped square to the right of the null line, i.e., in favor of the placebo-treated side, and not intersecting the null line. This means that adjuvant treatment with aripiprazole leads to an increase in PANSS scores compared to control and a worsening of clinical symptoms compared to placebo. There was no statistically significant change in the CGI scale total score between the treatment and placebo groups, while the overall impact from the three trials using the CGI scale was not statistically significant [MD=-0.16, 95% CI (-0.44,0.12)]. Details are shown in Figure 4.
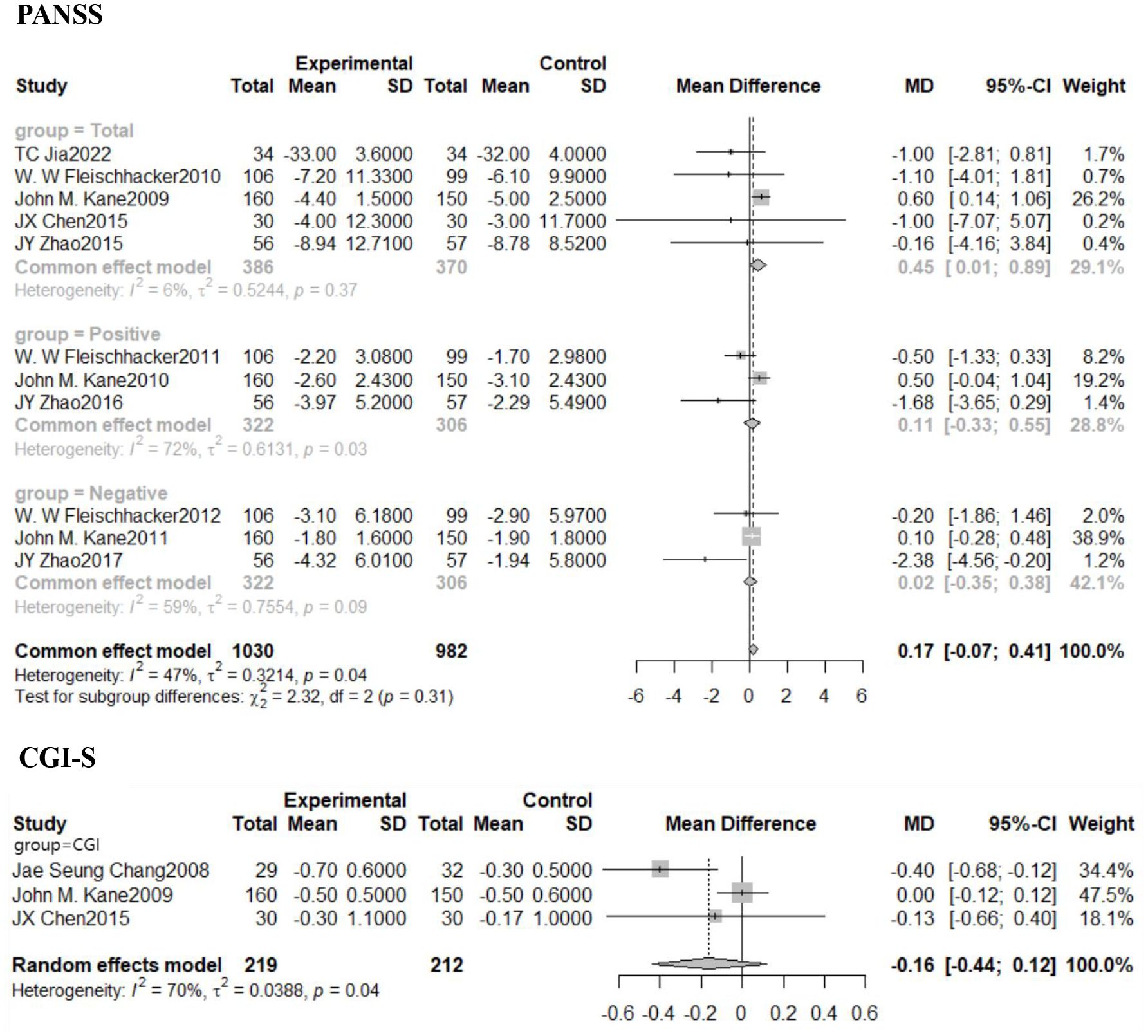
Figure 4. Forest plot of PANSS and CGI scores in patients after combination aripiprazole. PNASS, Positive and Negative Symptom Scale; CGI-S, Clinical Global Impressions-Severity of Illness Scale.
3.8 Effects on adverse reactions
Aripiprazole-assisted therapy did not significantly improve difficulties to sit still compared to placebo treatment (Supplementary Figure S1), along with back pain, gastrointestinal reactions, salivation, dizziness, dry mouth, insomnia, somnolence, and vomiting reactions.
Combination aripiprazole therapy was associated with a higher risk of nausea and vomiting than monotherapy, as evidenced by four RCTs reporting a statistically significant difference between the aripiprazole-adjuvant group and the control group (OR = 4.15, 95% CI: 1.93-8.91).
At least one extrapyramidal adverse event was documented in four RCTs. They discovered a statistically significant difference between the aripiprazole-adjuvant treatment group and the control group (OR = 1.83, 95% CI:1.18-2.84), with the combination treatment group having a greater risk of extrapyramidal adverse events than the monotherapy group.
In conclusion, combined aripiprazole therapy was generally well tolerated and safe, except for manifestations such as nausea and vomiting and extrapyramidal reactions.
3.9 Subgroup analyses, sensitivity analyses, and publication bias
We performed subgroup analyses of the main outcome indicators, including blood glucose, triglycerides, total cholesterol, HDL and LDL. The results of the subgroup analyses were shown in Supplementary Figures S2–S6. The effect of dose on metabolic indicators is often not negligible, but relevant studies are few and unclear (46). This is because the experimental group with combined aripiprazole treatment had a higher total dose, and it would be unfair not to increase the total dose in the control group (47). Therefore, we wanted to compare whether combined aripiprazole treatment with different doses would affect metabolic indices differently by subgroup analyses. In this study, the dose of combined aripiprazole therapy showed a significant difference after grouping the doses according to ≥15 mg and <15 mg, proving that aripiprazole greater than 15 mg improved the metabolic indexes more significantly.
A previous meta-analysis reported an effect of time of adjunctive aripiprazole therapy on outcome indicators (48), In our study the duration of treatment was grouped by ≤ 8 weeks and >8 weeks, and all metabolic indicators showed significant differences except for HDL. Metabolic improvement was more pronounced with combined treatment for ≤ 8 weeks than for >8 weeks, which showed significant differences except in terms of high-density lipoproteins, and metabolic improvement was more pronounced with combined treatment for ≤8 weeks than for >8 weeks, which may be due to the fact that long term use of aripiprazole tends to share the metabolic profile of other antipsychotic medications (49), and therefore combined aripiprazole should be used in short- to medium-term.
Meanwhile, metabolic indicators improved in the clozapine and olanzapine groups with aripiprazole-assisted medication, but there was no any significant improvement in the risperidone group (50). Aripiprazole may share the same metabolic profile as risperidone, which triggered a thought as to whether the difference in the type of the other drug may also have an effect on the effectiveness of aripiprazole-assisted therapy. Therefore, in this study, the included literatures were divided into clozapine, olanzapine and risperidone groups, indicating a statistically significant difference between the olanzapine and clozapine and risperidone groups. In addition, the metabolic improvement shown with combination aripiprazole treatment was more evident in the olanzapine group.
4 Discussion
The FDA has authorized the third-generation antipsychotic drug aripiprazole for the treatment of schizophrenia. In addition to its agonistic and antagonistic actions on certain D2 and 5-HT1A receptors, aripiprazole was available in both oral and long-acting injectable (LAI) stockpiling forms (51). As aripiprazole has a greater affinity for dopamine receptors (52) and has agonistic actions on D2 receptors (53), it may be reasonable to conduct the aforementioned combination experiments while some metabolic issues may be countered by partial agonist activity on 5-HT receptors (35). Most antipsychotics are clinically active when D2 receptor occupancy is about 65%, and when D2 receptor occupancy is over 80%, extrapyramidal side effects may occur; on the other hand, at 6-9mg/d, a peak is reached in dopamine D2 receptor accuracy (54), positron emission tomography (PET) studies have found that at a dose of 10mg/day, aripiprazole exhibits high occupancy rates at the D2 receptors in the striatum (caudate nucleus: 87%; putamen: 93%; ventral striatum: 91%), and the average occupancy rate at the 5-HT2 receptors is approximately 54%-60%, while the average occupancy rate at the 5-HT1A receptors is relatively low, around 16% (55). The pharmacological effects of aripiprazole on D2 receptors are unique, including not only partial agonism but also functionally selective effects on intracellular signaling pathways, which means that a D2 receptor occupancy rate of over 90% is required for aripiprazole to be clinically active, but relatively few side effects. Aripiprazole has bidirectional activity, serving as both an agonist and antagonist (postsynaptic) of D2 receptors, which can explain the fact that aripiprazole does not cause significant side effects despite high D2 receptor occupancy rates (56). Several long-term, follow-up studies have confirmed that aripiprazole is negative or non-significant for body weight when used as monotherapy, but may be protective for lipid metabolism (57, 58).
A previous meta-analysis found that switching to antipsychotic medications with lower metabolic risks or using combination therapies can improve lipid parameters in patients with schizophrenia. Nevertheless, it should be highlighted that meta-analysis focused on switching to drugs with reduced risk of metabolism, and as mentioned earlier, this strategy carries the risk of worsening clinical symptoms in some patients. Additionally, the data extraction in that meta-analysis had flaws, and the conclusion drawn by the authors that aripiprazole is superior to other lipid-lowering medications was overly hasty (59). In a comprehensive meta-analysis of 55 RCTs (n=4457) (36), it was found that combined aripiprazole significantly improved clinical symptoms, but did not involve data related to glycolipid metabolism. This finding contradicts the conclusion of our study that combined aripiprazole worsens clinical symptoms. This discrepancy may be due to the fact that this review primarily focused on metabolic parameters as outcome indicators and had insufficient inclusion of studies related to clinical symptoms. Many of the excluded studies only examined clinical symptoms without considering metabolic parameters. Therefore, the conclusions of this review regarding clinical symptoms may be inaccurate. However, a meta-analysis (Henderson Ferker Foundation 2013) explained the pharmacological strategies of antipsychotic drugs on weight gain and metabolic adverse effects, which also supported our research findings (60).
Currently, some clinical guidelines have now changed from their previous view of monotherapy. The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) guideline “Adult psychosis and schizophrenia: Prevention and management,” issued in 2014 and reviewed five years after, argues against using combination of antipsychotics on a daily basis unless it is for a temporary measure like drug switching. However, if clozapine monotherapy proves to be ineffective, the guideline allows for the addition of additional antipsychotics to augment the therapeutic effect of the patient. Both the study by Pilinger et al. (61). and our study emphasize that monotherapy does not show significant clinical improvement for positive symptoms; antipsychotics exhibit a restricted effectiveness in enhancing adverse symptoms among schizophrenia patients (30); by using a combination of antipsychotics, it may allow a decrease in the dosage of another drug (62), save medication expenses, lessen the severity of extrapyramidal side effects (26). This development is encouraging, and as more researches are reported, combination therapy is becoming more widely accepted. More consideration should be given to the possibilities of combination medication in the development of guidelines, and biases against combination therapy should be discarded to better serve clinical practice.
In addition, our study is subject to other shortcomings. The lack of comprehensive coverage of metabolic parameters in the included studies may result in an inadequate representation of the data, which could potentially impact the accuracy of the results. The brief follow-up period of the included study precludes insight into the long-term safety and efficacy of the treatment regimen. The lack of diversity in age, gender, and comorbidities among the included patients prevented an adequate validation of differences in the impact of metabolic parameters of aripiprazole in different populations. It is recommended that subsequent studies should assess the frequency and severity of adverse effects in adjuvant therapy with aripiprazole, in order to provide clinicians with clearer guidance on risks.
Author contributions
TW: Software, Writing – original draft. LJ: Data curation, Writing – original draft. RZ: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. HS: Data curation, Writing – original draft. ZS: Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. JS: Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
Thanks to Junwei Sun, MD for some helpful advice in the initial stages of preparing this work.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1496986/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Tandon R, Keshavan MS, Nasrallah HA. Schizophrenia, "Just the Facts": what we know in 2008 part 1: overview. Schizophr Res. (2008) 100:4–19. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2008.01.022
2. Frank E, Maier D, Pajula J, Suvitaival T, Borgan F, Butz-Ostendorf M, et al. Platform for systems medicine research and diagnostic applications in psychotic disorders-The METSY project. Eur Psychiatry. (2018) 50:40–6. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpsy.2017.12.001
3. Baptista T, Zárate J, Joober R, Colasante C, Beaulieu S, Páez X, et al. Drug induced weight gain, an impediment to successful pharmacotherapy:focus on antipsychotics. Curr Drug Targets. (2004) 5(3):279–99. doi: 10.2174/1389450043490514
4. Penninx B, Lange S. Metabolic syndrome in psychiatric patients: overview, mechanisms, and implications. Dialogues Clin Neurosci. (2018) 20:63–73. doi: 10.31887/DCNS.2018.20.1/bpenninx
5. Chen MH, Korenic SA, Wickwire EM, Wijtenburg SA, Hong LE, Rowland LM. Sex differences in subjective sleep quality patterns in schizophrenia. Behav Sleep Med. (2020) 18(5):668–79. doi: 10.1080/15402002.2019.1660168
6. Bosia M, Spangaro M, Sapienza J, Martini F, Civardi S, Buonocore M, et al. Cognition in schizophrenia: Modeling the interplay between interleukin-1β c-511T polymorphism, metabolic syndrome, and sex. Neuropsychobiology. (2021) 80(4):321–32. doi: 10.1159/000512082
7. Cernea S, Dima L, Correll CU, Manu P. Pharmacological management of glucose dysregulation in patients treated with second-generation antipsychotics. Drugs. (2020) 80(17):1763–81. doi: 10.1007/s40265-020-01393-x
8. Goh KK, Chen CY, Wu TH, Chen CH, Lu ML. Crosstalk between schizophrenia and metabolic syndrome: The role of oxytocinergic dysfunction. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23(13):7092. doi: 10.3390/ijms23137092
9. Carli M, Kolachalam S, Longoni B, Pintaudi A, Baldini M, Aringhieri S, et al. Atypical antipsychotics and metabolic syndrome: From molecular mechanisms to clinical differences. Pharm (Basel). (2021) 14(3):238. doi: 10.3390/ph14030238
10. Bora E, Akdede BB, Alptekin K. The relationship between cognitive impairment in schizophrenia and metabolic syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis - CORRIGENDUM. Psychol Med. (2018) 48:1224. doi: 10.1017/S0033291717003932
11. Vancampfort D, Wampers M, Mitchell AJ, Correll CU, De Herdt A, Probst M, et al. A meta-analysis of cardio-metabolic abnormalities in drug naïve, first-episode and multi-episode patients with schizophrenia versus general population controls. World Psychiatry. (2013) 12(3):240–50. doi: 10.1002/wps.20069
12. Kritharides L, Chow V, Lambert TJ. Cardiovascular disease in patients with schizophrenia. Med J Aust. (2017) 206:91–5. doi: 10.5694/mja2.2017.206.issue-2
13. Bioque M, Parellada E, García-Rizo C, Amoretti S, Fortea A, Oriolo G, et al. Clozapine and paliperidone palmitate antipsychotic combination in treatment-resistant schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders: A retrospective 6-month mirror-image study. Eur Psychiatry. (2020) 63(1):e71. doi: 10.1192/j.eurpsy.2020.72
14. Barber S, Olotu U, Corsi M, Cipriani A. Clozapine combined with different antipsychotic drugs for treatment-resistant schizophrenia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (2017) 3(3):CD006324. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006324.pub3
15. Baandrup L. Polypharmacy in schizophrenia. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. (2020) 126(3):183–92. doi: 10.1111/bcpt.13384
16. Lévy-Rueff M, Jurgens A, Lôo H, Olié JP, Amado I. Maintenance electroconvulsive therapy and treatment of refractory schizophrenia. Encephale. (2008) 34(5):526–33. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2007.08.008
17. Ganguli R, Brar JS, Garbut R, Chang CC, Basu R. Changes in weight and other metabolic indicators in persons with schizophrenia following a switch to aripiprazole. Clin Schizophr Relat Psychoses. (2011) 5(2):75–9. doi: 10.3371/CSRP.5.2.3
18. Cai J, Li L, Shao T, Sun M, Wang W, Xie P, et al. Relapse in patients with schizophrenia and amisulpride-induced hyperprolactinemia or olanzapine-induced metabolic disturbance after switching to other antipsychotics. Psychiatry Res. (2023) 322:115138. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2023.115138
19. Stroup TS, McEvoy JP, Ring KD, Hamer RH, LaVange LM, Swartz MS, et al. A randomized trial examining the effectiveness of switching from olanzapine, quetiapine, or risperidone to aripiprazole to reduce metabolic risk: comparison of antipsychotics for metabolic problems (CAMP). Am J Psychiatry. (2011) 168(9):947–56. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2011.10111609
20. Faries D, Ascher-Svanum H, Zhu B, Correll C, Kane J. Antipsychotic monotherapy and polypharmacy in the naturalistic treatment of schizophrenia with atypical antipsychotics. BMC Psychiatry. (2005) 5:26. doi: 10.1186/1471-244X-5-26
21. Essock SM, Schooler NR, Stroup TS, McEvoy JP, Rojas I, Jackson C, et al. Effectiveness of switching from antipsychotic polypharmacy to monotherapy. Am J Psychiatry. (2011) 168(7):702–8. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2011.10060908
22. Gallego JA, Nielsen J, De Hert M, Kane JM, Correll CU. Safety and tolerability of antipsychotic polypharmacy. Expert Opin Drug Saf. (2012) 11(4):527–42. doi: 10.1517/14740338.2012.683523
23. Zhang J, Cheng X, Zhang H, Xu P, Jin P, Ke X. Analysis of the status of drug treatment in 746 inpatients with early-onset schizophrenia in china: a retrospective study. BMC Psychiatry. (2021) 21(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s12888-020-02962-w
24. Correll CU, Frederickson AM, Kane JM, Manu P. Does antipsychotic polypharmacy increase the risk for metabolic syndrome? Schizophr Res. (2007) 89(1-3):91–100. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2006.08.017
25. Vancampfort D, Stubbs B, Mitchell AJ, De Hert M, Wampers M, Ward PBJ, et al. Risk of metabolic syndrome and its components in people with schizophrenia and related psychotic disorders, bipolar disorder and major depressive disorder: a systematic review and meta-analysis. World Psychiatry. (2015) 14(3):339–47. doi: 10.1002/wps.20252
26. Lähteenvuo M, Tiihonen J. Antipsychotic polypharmacy for the management of schizophrenia: Evidence and recommendations. Drugs. (2021) 81(11):1273–84. doi: 10.1007/s40265-021-01556-4
27. Reynolds GP. High dose antipsychotic polypharmacy and dopamine partial agonists - time to rethink guidelines? J Psychopharmacol. (2021) 35(9):1030–6. doi: 10.1177/02698811211026456
28. Tiihonen J, Taipale H, Mehtälä J, Vattulainen P, Correll CU, Tanskanen A. Association of antipsychotic polypharmacy vs monotherapy with psychiatric rehospitalization among adults with schizophrenia. JAMA Psychiatry. (2019) 76(5):499–507. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2018.4320
29. Galling B, Roldán A, Rietschel L, Hagi K, Walyzada F, Zheng W, et al. Safety and tolerability of antipsychotic co-treatment in patients with schizophrenia: results from a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Expert Opin Drug Saf. (2016) 15(5):591–612. doi: 10.1517/14740338.2016.1165668
30. Kamei H. Polypharmacy management of antipsychotics in patients with schizophrenia. Medicina (Kaunas). (2022) 58(11):1584. doi: 10.3390/medicina58111584
31. Galling B, Roldán A, Hagi K, Rietschel L, Walyzada F, Zheng W, et al. Antipsychotic augmentation vs. monotherapy in schizophrenia: systematic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression analysis. World Psychiatry. (2017) 16(1):77–89. doi: 10.1002/wps.20387
32. Ortiz-Orendain J, Castiello-de Obeso S, Colunga-Lozano LE, Hu Y, Maayan N, Adams CE. Antipsychotic combinations for schizophrenia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (2017) 6(6):CD009005. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009005.pub2
33. Ijaz S, Bolea B, Davies S, Savović J, Richards A, Sullivan S, et al. Antipsychotic polypharmacy and metabolic syndrome in schizophrenia: a review of systematic reviews. BMC Psychiatry. (2018) 18(1):275. doi: 10.1186/s12888-018-1848-y
34. Choi YJ. Efficacy of adjunctive treatments added to olanzapine or clozapine for weight control in patients with schizophrenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. ScientificWorld J. (2015) 2015:970730. doi: 10.1155/2015/970730
35. Zimbron J, Khandaker GM, Toschi C, Jones PB, Fernandez-Egea E. A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials of treatments for clozapine-induced obesity and metabolic syndrome. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. (2016) 26(9):1353–65. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2016.07.010
36. Zheng W, Zheng YJ, Li XB, Tang YL, Wang CY, Xiang YQ, et al. Efficacy and safety of adjunctive aripiprazole in schizophrenia: Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Clin Psychopharmacol. (2016) 36(6):628–36. doi: 10.1097/JCP.0000000000000579
37. Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Ann Intern Med. (2009) 151(4):264–W64. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-151-4-200908180-00135
38. Higgins JP, Altman DG, Gøtzsche PC, Jüni P, Moher D, Oxman AD, et al. The cochrane collaboration's tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. (2011) 343:d5928. doi: 10.1136/bmj.d5928
39. JJia T, Len X, Zhilian PI, Hong Z, Feng J, Chunhe MA. Effect of aripiprazole combined with olanzapine on the clinical efficacy of schizophrenia. Farmacia. (2022) 70(3):p550. doi: 10.31925/farmacia.2022.3.23
40. Chen JX, Su YA, Bian QT, Wei LH, Zhang RZ, Liu YH, et al. Adjunctive aripiprazole in the treatment of risperidone-induced hyperprolactinemia: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-response study. Psychoneuroendocrinology. (2015) 58:130–40. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2015.04.011
41. Chang JS, Ahn YM, Park HJ, Lee KY, Kim SH, Kang UG, et al. Aripiprazole augmentation in clozapine-treated patients with refractory schizophrenia: an 8-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Clin Psychiatry. (2008) 69(5):720–31. doi: 10.4088/jcp.v69n0505
42. Henderson DC, Fan X, Copeland PM, Sharma B, Borba CP, Boxill R, et al. Aripiprazole added to overweight and obese olanzapine-treated schizophrenia patients. J Clin Psychopharmacol. (2009) 29(2):165–9. doi: 10.1097/JCP.0b013e31819a8dbe
43. Fleischhacker WW, Heikkinen ME, Olié JP, Landsberg W, Dewaele P, McQuade RD, et al. Effects of adjunctive treatment with aripiprazole on body weight and clinical efficacy in schizophrenia patients treated with clozapine: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. (2010) 13(8):1115–25. doi: 10.1017/S1461145710000490
44. Zhao J, Song X, Ai X, Gu X, Huang G, Li X, et al. Adjunctive aripiprazole treatment for risperidone-induced hyperprolactinemia: An 8-week randomized, open-label, comparative clinical trial. PloS One. (2015) 10(10):e0139717. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0139717
45. Fan X, Borba CP, Copeland P, Hayden D, Freudenreich O, Goff DC, et al. Metabolic effects of adjunctive aripiprazole in clozapine-treated patients with schizophrenia. Acta Psychiatr Scand. (2013) 127(3):217–26. doi: 10.1111/acps.12009
46. Ventriglio A, Baldessarini RJ, Vitrani G, Bonfitto I, Cecere AC, Rinaldi A, et al. Metabolic syndrome in psychotic disorder patients treated with oral and long-acting injected antipsychotics. Front Psychiatry. (2019) 9:744. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00744
47. Baandrup L. How dosing might influence the conclusion in an antipsychotic polypharmacy effectiveness trial. Am J Psychiatry. (2011) 168(10):1117. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2011.11050751
48. Lippi M, Fanelli G, Fabbri C, De Ronchi D, Serretti A. The dilemma of polypharmacy in psychosis: is it worth combining partial and full dopamine modulation? Int Clin Psychopharmacol. (2022) 37(6):263–75. doi: 10.1097/YIC.0000000000000417
49. Vázquez-Bourgon J, Ortiz-García de la Foz V, Gómez-Revuelta M, Mayoral-van Son J, Juncal-Ruiz M, Garrido-Torres N, et al. Aripiprazole and risperidone present comparable long-term metabolic profiles: Data from a pragmatic randomized controlled trial in drug-naïve first-episode psychosis. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. (2022) 25(10):795–806. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyac033
50. Zheng W, Cai DB, Yang XH, Ungvari GS, Ng CH, Shi ZM, et al. Adjunctive aripiprazole for antipsychotic-related hyperprolactinaemia in patients with first-episode schizophrenia: a meta-analysis. Gen Psychiatr. (2019) 32(5):e100091. doi: 10.1136/gpsych-2019-100091
51. Preda A, Shapiro BB. A safety evaluation of aripiprazole in the treatment of schizophrenia. Expert Opin Drug Saf. (2020) 19(12):1529–38. doi: 10.1080/14740338.2020.1832990
52. Qiao Y, Yang F, Li C, Guo Q, Wen H, Zhu S, et al. Add-on effects of a low-dose aripiprazole in resolving hyperprolactinemia induced by risperidone or paliperidone. Psychiatry Res. (2016) 237:83–9. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2015.12.033
53. Zocchi A, Fabbri D, Heidbreder CA. Aripiprazole increases dopamine but not noradrenaline and serotonin levels in the mouse prefrontal cortex. Neurosci Lett. (2005) 387(3):157–61. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2005.06.035
54. Yasui-Furukori N, Furukori H, Sugawara N, Fujii A, Kaneko S. Dose-dependent effects of adjunctive treatment with aripiprazole on hyperprolactinemia induced by risperidone in female patients with schizophrenia. J Clin Psychopharmacol. (2010) 30(5):596–9. doi: 10.1097/JCP.0b013e3181ee832d
55. Stip E, Tourjman V. Aripiprazole in schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder: A review. Clin Ther. (2010) 32 Suppl 1:S3–S20. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2010.01.021
56. Tuplin EW, Aripiprazole HMR. A drug that displays partial agonism and functional selectivity. Curr Neuropharmacol. (2017) 15(8):1192–207. doi: 10.2174/1570159X15666170413115754#x3002
57. McQuade RD, Stock E, Marcus R, Jody D, Gharbia NA, Vanveggel S, et al. A comparison of weight change during treatment with olanzapine or aripiprazole: results from a randomized, double-blind study. J Clin Psychiatry. (2004) 65 Suppl 18:47–56. doi: 10.16306/j.1008-861x.2022.S1.002
58. Zhang Y, Dai G. Efficacy and metabolic influence of paliperidone ER, aripiprazole and ziprasidone to patients with first-episode schizophrenia through 52 weeks follow-up in china. Hum Psychopharmacol. (2012) 27(6):605–14. doi: 10.1002/hup.2270
59. Kanagasundaram P, Lee J, Prasad F, Costa-Dookhan KA, Hamel L, Gordon M, et al. Pharmacological interventions to treat antipsychotic-induced dyslipidemia in schizophrenia patients: A systematic review and meta analysis. Front Psychiatry. (2021) 12:642403. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.642403
60. Mizuno Y, Suzuki T, Nakagawa A, Yoshida K, Mimura M, Fleischhacker WW, et al. Pharmacological strategies to counteract antipsychotic-induced weight gain and metabolic adverse effects in schizophrenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Schizophr Bull. (2014) 40(6):1385–403. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbu030
61. Kuipers E, Yesufu-Udechuku A, Taylor C, Kendall T. Management of psychosis and schizophrenia in adults: summary of updated NICE guidance. BMJ. (2014) 348:g1173. doi: 10.1136/bmj.g1173
Keywords: schizophrenia, aripiprazole, combination therapy, glucolipid metabolism, review
Citation: Wei T, Jiang L, Zhang R, Su H, Sun Z and Sun J (2025) A systematic review and meta-analysis of the effects of combined aripiprazole on glycolipid metabolism in schizophrenia. Front. Psychiatry 15:1496986. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1496986
Received: 16 September 2024; Accepted: 11 December 2024;
Published: 10 January 2025.
Edited by:
Mirko Manchia, University of Cagliari, ItalyReviewed by:
Francesco Monaco, Azienda Sanitaria Locale Salerno, ItalyTakahiko Nagamine, Sunlight Brain Research Center, Japan
Copyright © 2025 Wei, Jiang, Zhang, Su, Sun and Sun. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Junwei Sun, SldTMDcyN0AxNjMuY29t
 Tianbao Wei1,2
Tianbao Wei1,2 Junwei Sun
Junwei Sun