
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
SYSTEMATIC REVIEW article
Front. Psychiatry , 02 December 2024
Sec. Anxiety and Stress Disorders
Volume 15 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1495418
 Sidan Huang1†
Sidan Huang1† Danni Zhang1†
Danni Zhang1† Xuliang Shi1,2*
Xuliang Shi1,2* Yi Zhang1
Yi Zhang1 Xuesong Wang1
Xuesong Wang1 Yanfen She1,2*
Yanfen She1,2* Ce Liang3
Ce Liang3 Xinyue Li1
Xinyue Li1 Christopher Zaslawski4
Christopher Zaslawski4Background: The decreased ovarian function has a negative impact on the mental health of women and increases the risk of anxiety and depression. A growing number of clinical studies have demonstrated that acupuncture-related therapies can effectively and safely restore hormone levels and improve ovarian reserve function. However, the effectiveness of acupuncture-related therapies in alleviating anxiety and depression symptoms in patients with ovarian hypofunction has not been thoroughly evaluated. Therefore, this study conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to assess the impact of the different acupuncture-related therapies on the mental health of patients with ovarian hypofunction.
Methods: We comprehensively searched eight famous databases for randomized controlled trials up to October 30, 2024. Databases include PubMed, Web of Science, EMBASE and Cochrane Library, China Biomedical (CBM), China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), Wanfang Database and VIP Database.
Results: The study included 12 RCTs, involving 780 patients with ovarian hypofunction, including 403 patients with POI, 297 patients with DOR, and 80 patients with POF. Acupuncture-related therapy was obviously superior to hormone therapy in relieving anxiety symptoms (SMD: -0.90; 95%CI: -1.28, -0.53; P<0.000 01) and depressive symptoms (SMD: -0.82; 95% CI: -1.25, -0.40; P=0.0001).
Conclusions: Acupuncture-related therapy was more effective than hormone therapy in improving anxiety and depression symptoms in patients with ovarian hypofunction. This study supports the use of acupuncture-related therapies for women experiencing decreased ovarian function associated with mental health issues.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/, identifier CRD42023488015.
Ovarian function is a reflection of the quantity and quality of follicles in the ovary, serving as an indicator of women’s reproductive capacity. Ovarian aging is a persistent physiological process, with the gradual decrease in follicle numbers from birth to menopause (1). Menopause marks a natural stage in women’s lives, signifying follicular failure and the cessation of ovarian function (2). Epidemiological studies have reported that the average age for natural menopause in women is 51 years and 5 months (3). At present, the risk of premature ovarian function decline and early menopause in women around the world is gradually increasing. Premature ovarian insufficiency (POI) is defined as the onset of amenorrhea for more than 4 months before the age of 40 years, accompanied by elevated follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) levels (4). Premature ovarian failure (POF) is considered as the terminal stage of POI (5). Although POF was reclassified as POI by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine (ASRM) in 2008, some studies still use the term POF (6). The prevalence rate of POI globally stands at 3.5%, particularly high in countries with low human development index (7, 8). Diminished ovarian reserve (DOR) is mainly manifested as the decline in the quality and quantity of oocytes and the decline in fertility but it is not postmenopausal, while there is no diagnostic criteria for DOR (9). Among various parameters used to diagnose DOR, FSH, antral follicle counting (AFC) and anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) are widely recognized and commonly utilized standards at present (10). There is a clinical overlap between DOR and POI. Although the clinical manifestations of the two diseases are different, they have some common genetic mutations related to ovarian aging (1, 11, 12).
Decreased ovarian function occurs in both POI and DOR and causes short-term complications associated with menopausal symptoms, including hot flashes, night sweats, sleep disturbances, vaginal dryness, and fatigue, which have an impact on skeletal and cardiovascular health as well as decreased fertility and sexual function (13, 14). Evidence suggests that patients with POI and DOR are at higher risk for cardiovascular disease and osteoporosis compared to normal menopausal women (15–18). In addition to physiological effects, the loss of ovarian function also negatively impacts the mental health of patients, greatly reducing their productivity and quality of life, while increasing the risk of anxiety and depression (19, 20). Compared with the general population, women diagnosed with POI had higher levels of depression, perceived stress, and lower self-ratings (21). The anxiety and depression risks of POI patients in China are 4.62 times and 3.14 times higher than those of healthy women, while that of American patients is 6.67 times and 3.07 times higher than that of healthy women (22). Unfortunately, there is often neglect in clinical settings regarding the presence of these negative emotions in patients with ovarian hypofunction. Problems related to infertility and irregular menstruation are often prioritized in patients, while mental health is inadvertently ignored (23). Therefore, it is crucial to focus on providing comprehensive physiological and psychological treatment as well as preventive strategies for women with ovarian hypofunction (24).
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is the most commonly utilized treatment for POI and DOR, with potential benefits in alleviating sleep disorders but controversial effects on anxiety and depression (25, 26). Some studies suggest that HRT may not significantly improve negative emotions in patients (21, 27, 28). Furthermore, this treatment is associated with multiple side effects, an increased risk of heart disease, breast cancer, endometrial hyperplasia, and the formation of venous thromboembolism, and is not recommended for long-term use (29). In this context, acupuncture stand out from the numerous non-drug treatment (30). A substantial body of clinical studies has demonstrated the efficacy and safety of acupuncture in managing POI and DOR (31–33). Additionally, evidence-based research has also confirmed this view (34, 35). Acupuncture not only effectively enhances ovarian reserve function, promotes pregnancy, and restores hormone levels but also demonstrates positive effects in relieving anxiety and depression symptoms (36–39). However, most clinical studies have not observed the changes of patients’ mental health symptoms. Effectiveness of acupuncture in improving anxiety and depression symptoms of patients with ovarian dysfunction has not been evaluated. Therefore, in order to gain a better understanding of the impact of the different acupuncture-related therapies on the mental health and quality of life associated with ovarian hypofunction, we conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of evidence from randomized controlled trials (RCTs) to assess the effectiveness of acupuncture-related therapies in alleviating anxiety and depression symptoms in patients with ovarian hypofunction.
This study was conducted in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) (40) and PRISMA for acupuncture checklist (41). It was registered in PROSPERO, with the registration number CRD42023488015.
Two researchers (DN Z and XY L) comprehensively searched eight famous databases. It included four English databases: PubMed, Web of Science, EMBASE and Cochrane Library, and four Chinese databases: China Biomedical (CBM), China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), Wanfang Database and VIP Database. We retrieved articles before October 30, 2024, without language and regional restrictions. The complete search strategy for each database can be found in the Supplementary Appendix.
The included studies met the following criteria:
1. The study type is randomized controlled trial (RCT), which is not limited by region or language.
2. Diagnosed as POI, POF or DOR. The diagnosis of POI meets the criteria for POI in the 2016 guidelines of the European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology (4). Diagnostic criteria of DOR: ① FSH ≥ 10 mIU/mL after two examinations or FSH/LH > 2 mIU/mL;
②AMH < 1.1 ng/mL; ③ AFC < 7, and any two of the above three items can be diagnosed as DOR (42). The diagnostic criteria of POF refer to the POF guidelines stipulated by Gynecology Branch of Chinese Medical Association (43).
3. The subjects in the study scored the anxiety and/or depression scale before and after the intervention.
4. The intervention measures in the treatment group are acupuncture (ACU), electroacupuncture (EA), warming acupuncture (WA), moxibustion (MOX), acupoint catgut embedding (ACE) and the combination of various methods (such as ACU combined with EA, ACU combined with MOX, etc.). The intervention measures of the control group were estradiol hormone therapy.
1. The course of treatment is less than one month.
2. No clear original data has been reported, or data cannot be extracted.
3. Duplicated published literature, or reported the same results.
We divided the result indicators into primary outcomes and secondary outcomes. At least one primary outcome indicator has been reported including: Self-rating Anxiety Scale (SAS) (44), Self-rating Depression Scale (SDS) (45), Hamilton Anxiety Scale (HAMA) (46) and Hamilton Depression Scale (HAMD) (47). Secondary outcomes were Kupperman index (KI), Integrals of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) syndromes score and adverse events.
Two researchers (SD H and DN Z) independently conducted literature screening and extract pertinent data. The screening process involved careful evaluation of titles, abstracts, and full texts to exclude articles that do not meet the predetermined inclusion and exclusion criteria. Consensus on the extracted data was reached through cross-checking. The following data were extracted from each study: first author’s name, publication year, age range of participants, sample size, diagnostic criteria, intervention measures for treatment and control groups, treatment duration, outcome indicators, and adverse events. Any discrepancies in this process were resolved through discussion and consultation with a third-party researcher (YZ).
Two researchers (SD H and DN Z) independently used the bias risk tool RoB2.0 recommended by Cochrane Manual to evaluate the bias risk of the included literature (48). The evaluation content includes the following six areas: bias caused by randomization process; Bias caused by deviation from intervention measures; Bias caused by lack of final data and bias of measurement results; Bias caused by choosing to report the results. Answer according to different questions set in each field (yes, probably yes, probably no, no, no information), and the evaluation results of each field are divided into low risk, some concerns and high risk. The differences in the evaluation process were solved by the third researcher (YZ).
We used RevMan 5.4 for meta-analysis. Each score is a numerical variable, and there may be different measurement methods and scoring standards. Therefore, we extracted the score difference before and after treatment, selected the standardized mean difference (SMD) as the effect index, and used the 95% confidence interval (95%CI) as the effect statistical test interval. Chi-square test and I-square test (I2) were used to evaluate the degree of heterogeneity. If I2>50%, P<0.10, the random-effect model is used for analysis; If I2 ≤ 50% and P≥0.10, the fixed-effect model is adopted. According to different disease diagnosis and different intervention measures, subgroup analysis was carried out to explore the potential sources of heterogeneity. We employed Stata 17.0 to conduct sensitivity analysis for exploring the robustness of the results. For a result indicator of more than 10 research reports, we conducted Egger test to evaluate the publication bias of the results.
In the initial search, a total of 342 studies were retrieved. Subsequently, 49 duplicate studies were excluded, with 45 removed by software and 4 through manual review. After screening the titles and abstracts, an additional 200 studies were excluded. After thorough examination of the full texts by the researchers, a final count of 12 studies met our inclusion criteria, and the selection process is shown in Figure 1.
Among these 12 RCTs, one study was a three-arm trial, while the remaining studies were all two-arm trials. All the studies were published in Chinese and conducted within China. A total of 780 participants were enrolled, including 403 POI participants, 297 DOR participants and 80 POF participants. 375 participants were treated in the control group, taking estradiol; 405 cases received the intervention of the treatment group, including ACU, MOX, EA, ACE, as well as combinations of these methods. As for the primary outcome indicators, all 12 studies reported anxiety scores utilizing scales such as SAS scale in eleven trials and HAMA scale in one trial. Six studies reported the results of depression score, all of which used SDS scale. Eight studies documented adverse events occurring during their respective trials. The baseline characteristics and detailed acupuncture methodologies employed across these studies are presented in Tables 1, 2.
All the studies mentioned the methods used in the process of random grouping, but ten studies did not describe whether the allocation sequence was hidden, so they were assessed as unclear. Because of the particularity of acupuncture operation (59), it is impossible to adopt blind method for both practitioners and subjects, so all the studies are assessed as some concerns. All included studies reported complete outcome data and were assessed as low risk. In two studies, it was found that there was a risk of bias in the measurement results, and the scoring standard and grade division were not clearly described. All the studies reported their predetermined results, and there was no selective reporting of results. The overall quality of the trial was assessed as moderate bias risk. The results of the risk evaluation are shown in Figure 2.
Eleven studies reported SAS score before and after treatment, while one study reported HAMA score. We extracted the difference in score values before and after treatment in these twelve studies for analysis, revealing a high level of heterogeneity (P<0.000 01, I2 = 83%). Consequently, we employed a random-effects model. The results indicated that acupuncture-related therapy was significantly more effective than hormone therapy in alleviating anxiety symptoms (SMD: -0.90; 95%CI: -1.28, -0.53; P<0.000 01).
In order to further explore the reasons for the high heterogeneity, we performed a subgroup analysis based on different diseases and various intervention measures. The results indicated that acupuncture-related therapies were more effective than hormone therapy in alleviating anxiety symptoms among patients with POI (SMD: -0.53; 95% CI: -1.04, -0.02; P=0.04), DOR (SMD: -1.32; 95% CI: -2.01, -0.64; P=0.0002), and POF (SMD: -0.86; 95% CI: -1.32, -0.40; P=0.0002) (Figure 3A). When comparing different interventions to hormone therapy, no statistically significant differences were found in improving anxiety symptoms among acupuncture (SMD: -0.24; 95% CI: -0.64, -0.15; P=0.23), acupuncture combined with electroacupuncture (SMD: -0.80; 95% CI: -2.18, -0.59; P=0.26), acupoint catgut embedding therapy (SMD: -0.99; 95%CI: -2.17, -0.19; P=0.10), and electroacupuncture (SMD: -0.37; 95% CI: -0.88, -0.14; P=0.15). However, in effecting relief of anxiety symptoms, acupuncture combined with moxibustion (SMD: -0.51; 95% CI: -0.90, -0.11; P=0.01) showed advantages over hormone therapy, as do acupuncture, electroacupuncture and moxibustion combined method (SMD: -1.38; 95% CI: -2.09, -0.67; P=0.0001) and moxibustion (SMD: -2.25; 95% CI: -2.91, -0.60; P<0.000 01) (Figure 3B). The results of sensitivity analysis were stable (Figure 4A).
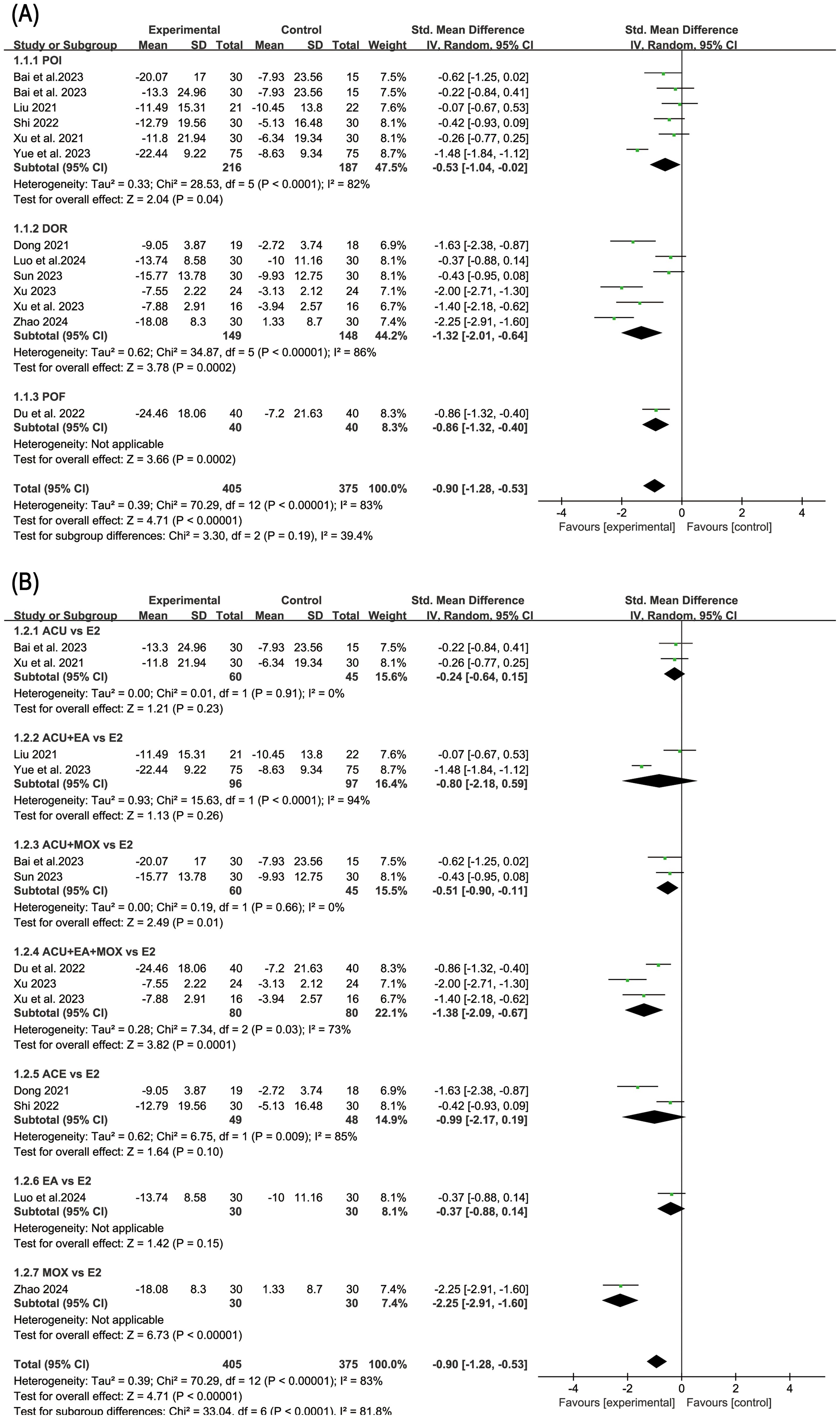
Figure 3. Forest plot of anxiety score in subgroup analyses. (A) Results of different disease subgroups; (B) Results of different intervention methods subgroups.
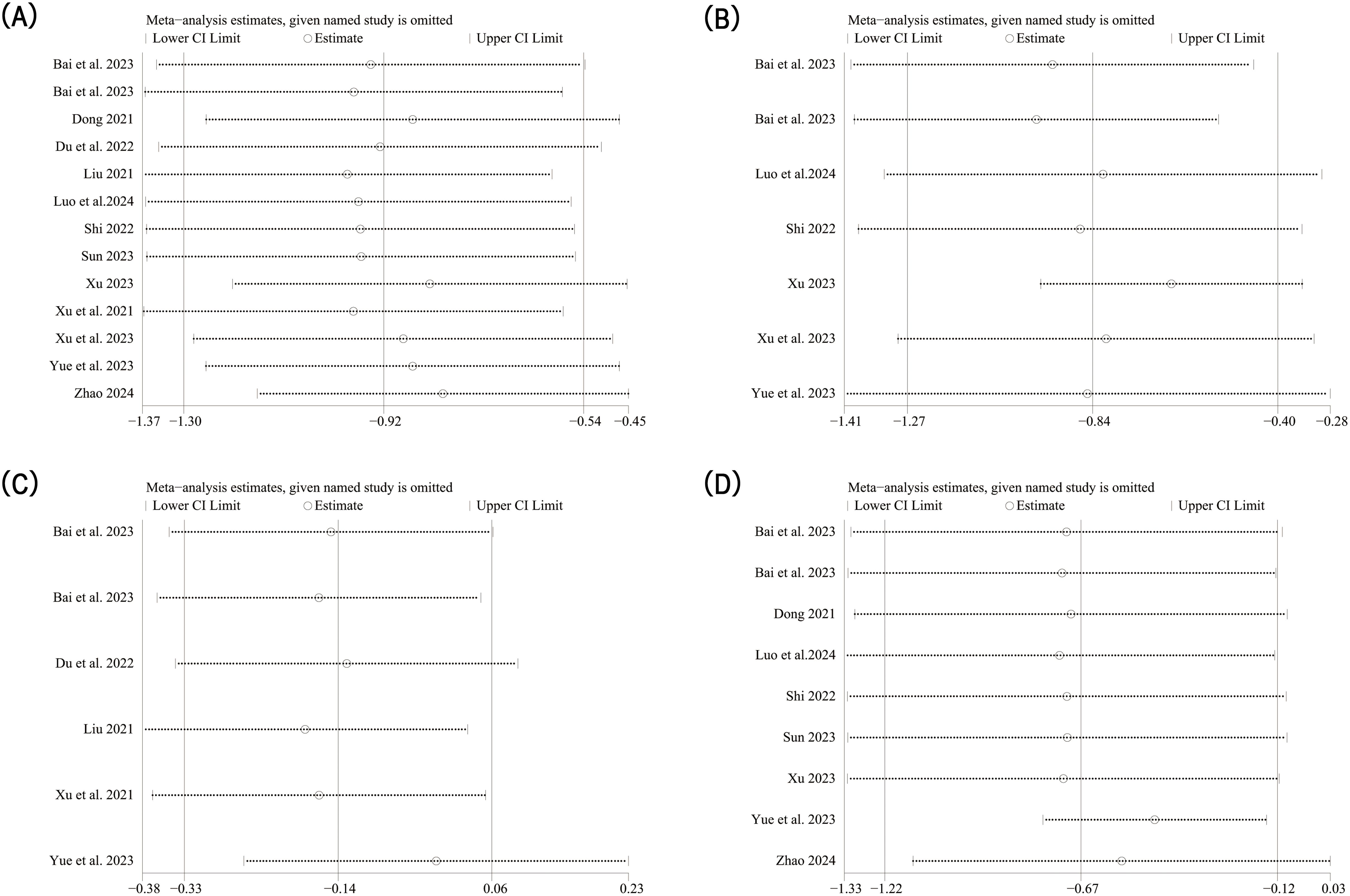
Figure 4. Sensitivity analysis results. (A) Sensitivity analysis of anxiety score; (B) Sensitivity analysis of depression score; (C) Sensitivity analysis of Kupperman index; (D) Sensitivity analysis of traditional Chinese medical syndrome integral.
Six studies reported SDS score. The random-effect model analysis (P=0.0001, I2 = 75%) showed that acupuncture-related therapy was significantly more effective than hormone therapy in alleviating depressive symptoms (SMD: -0.82; 95% CI: -1.25, -0.40; P=0.0001). Subgroup analysis of different diseases showed that acupuncture-related therapy was better than hormone therapy in improving depressive symptoms in both POI (SMD: -0.49; 95% CI: -0.87, -0.12; P=0.01) and DOR (SMD: -1.37; 95% CI: -2.10, -0.65; P=0.0002) (Figure 5). The results of sensitivity analysis were stable (Figure 4B).
Five studies reported the KI score. The fixed-effect model analysis (P=0.55, I2 = 0%) showed that there was no statistical difference between acupuncture-related therapy and hormone therapy (SMD: -0.13; 95% CI: -0.33, -0.06; P=0.17) (Figure 6). The results of sensitivity analysis were stable (Figure 4C).
Eight studies reported the TCM syndrome scores. The random-effect model analysis (P<0.000 01, I2 = 89%) showed that acupuncture-related therapy was significantly more effective than hormone therapy in improving TCM syndromes (SMD: -0.66; 95% CI: -1.21, -0.12; P=0.02). Subgroup analyses of different diseases revealed that, in terms of enhancing TCM syndrome outcomes, acupuncture-related therapy outperformed hormone therapy for POI patients (SMD: -0.49; 95% CI: -0.87, -0.12; P=0.01). However, no significant difference was observed between the two therapies for DOR patients (SMD: -1.37; 95% CI: -2.10, -0.65; P=0.0002) (Figure 7). The results of sensitivity analysis were stable (Figure 4D).

Figure 7. Forest plot of traditional Chinese medicine syndrome scores in analysis of different disease subgroups.
There are twelve studies that assessed participants’ anxiety scores, so evaluate this index with publication bias. First, we made a funnel chart with RevMan 5.4, but we couldn’t determine whether the funnel chart was symmetrical (Figure 8). Because the anxiety score is a continuous variable, we used the Egger test of Stata 17.0 to detect the publication bias (60). The results showed that P=0.734 > 0.05, which indicated that there was no publication bias.
Eight studies reported adverse events. Among these, two studies indicated that patients did not experience any adverse events during the intervention. The adverse events observed in the remaining six studies are summarized in Table 3. According to the findings from these six studies, acupuncture-related therapies were associated with several adverse events, including needle sensation, subcutaneous congestion, allergic reactions, burns from moxibustion, and residual sensations. The adverse effects of hormone therapy primarily encompass nausea and vomiting, irregular vaginal bleeding, and slight palpitations.
This is the first systematic review and meta-analysis of acupuncture-related therapy in treating emotional disorders in patients with ovarian hypofunction. This meta-analysis included 780 participants with ovarian hypofunction from 12 RCTs. Our study compared the efficacy of acupuncture-related therapy and hormone therapy in alleviating symptoms of anxiety and depression symptoms in patients with ovarian hypofunction. The comprehensive findings indicate that acupuncture-related therapy outperforms hormone therapy in improving emotional disorders associated with this condition.
Anxiety and depression are prevalent emotional disorders that often co-occur (61). Women are at a higher risk of experiencing depression compared to men (62). The quality of life for infertile women is lower, accompanied by heightened levels of anxiety and depression (63). This situation is particularly pronounced among patients with ovarian hypofunction, who typically experience varying degrees of emotional disorders. Factors such as the patient’s desire for normal ovarian function and feelings of inadequacy stemming from unmet external expectations contribute significantly to their anxiety and depressive symptoms (64). Additionally, the decreased ability of the ovaries to work and hormone levels not only cause physical discomfort but also lead to anxiety and depression. These negative emotions interact with ovarian function in a mutually causal manner. Study have shown a positive correlation between the psychological state of POI patients and their ovarian function (65). Hence, it is imperative to prioritize the psychological well-being of these female patients. In today’s society, an increasing number of individuals seek professional treatment to alleviate symptoms related to anxiety and depression. To assist patients in accurately assessing the severity of their conditions, non-psychiatric physicians commonly employ tools such as the Depression Anxiety Rating Scale within clinical settings (66). In this study, Hamilton Anxiety Scale (HAMA), Hamilton Depression Scale (HAMD), Self-rated Anxiety Scale (SAS) and Self-rated Depression Scale (SDS) were selected as the primary outcome measures. These scales are currently recognized as valid instruments for assessing the severity of emotional disorders related to anxiety and depression (67, 68). Unfortunately, out of 12 RCTs included in this study, only one utilized the HAMA scale for assessing anxiety scores; there were no reports on results using the HAMD scale for measuring depression scores.
Acupuncture is a traditional Chinese medical method and a popular complementary alternative therapy. In China, it is commonly used to treat mental diseases such as anxiety, stress, depression, and insomnia (69). There is increasing evidence that acupuncture related-therapy is effective for anxiety and depression (70–73). Maunder found that more than 50 percent of patients with DOR needed to address mental health issues, and these patients said that acupuncture was a very beneficial form of treatment (74). According to traditional Chinese medicine, the pathogenesis of ovarian hypofunction combined with anxiety and depression mainly involves liver depression (energy imbalance). The therapies included in this study comprise acupuncture, electroacupuncture, moxibustion, and acupoint catgut embedding. These therapies stimulate specific acupoints and interact with the corresponding internal organs to facilitate the dredging of meridians, nourish the kidneys, strengthen the spleen, and harmonize liver function (thereby coordinating energy flow throughout the body). This approach aims to restore ovarian function and alleviate emotional distress (75–77). Western medicine believes that acupuncture-related therapy approaches may enhance the vitality of cranial nerves, alter the functional connectivity and structure of the brain, and thereby influence emotional regulation (78). The prefrontal cortex is a critical region of the brain involved in the regulation of anxiety and depressive emotions. Chen’s research has demonstrated that acupuncture therapy can enhance synaptic function and plasticity in neurons within the prefrontal cortex, promote neuronal signal transduction, modulate immune inflammatory responses, and consequently alleviate emotional disorders (79). Similarly, another research also indicates that the antidepressant effects of electroacupuncture are associated with an enhancement of synaptic transmission in the ventromedial prefrontal cortex (80). Previous research has shown that ovarian hormones have beneficial effects on neurobehavior, with increased estradiol levels alleviating anxiety in ovariectomized model (OVA) rats (81–83). Watcharin N’s research shows that progesterone inhibits depression and anxiety-like behavior by increasing lactobacillus flora in the intestinal flora of OVA mouse (84). Furthermore, the regulation of intestinal flora has been demonstrated by several studies to be a promising new intervention strategy for emotional disorders (85–87). It is worth noting that acupuncture-related therapy has a significant effect on improving the level of estradiol in patients with ovarian hypofunction (88–90). At the same time, these therapies have the potential to restore ovarian function by modulating intestinal flora (91, 92). Therefore, it is hypothesized that the mechanism of acupuncture improving emotional disorders in patients with ovarian hypofunction may be closely related to ovarian hormones and intestinal flora.
Our research results demonstrate that acupuncture-related therapy is beneficial for improving the emotional disorders of patients with ovarian hypofunction, with a low incidence of adverse effects. In combination with previous research evidence (34, 35, 93), acupuncture-related therapy shows advantages in restoring ovarian function without obvious adverse effects. We advocate for the consideration of acupuncture as an alternative treatment for ovarian hypofunction. However, there are some limitations to this study. Firstly, all included studies are from China, which may restrict the generalizability of our results due to the absence of patient data from other countries. Secondly, owing to the unique nature of acupuncture therapy, blinding methods cannot be implemented for subjects and intervention providers as they can be in pharmacological research. Additionally, most studies do not describe whether group concealment was carried out in the random assignment process, which leads to the risk of bias in these studies. Furthermore, our study selected acupuncture-related therapy as the intervention measure and included patients with various types of ovarian hypofunction diseases which may introduce heterogeneity into the analysis. To address these limitations and their potential impact on our findings, we conducted subgroup analyses based on different interventions and disease types within the experimental group. The results of subgroup analysis unfortunately do not indicate that the aforementioned factors are responsible for the high heterogeneity. Moreover, one study in the assessment of anxiety scores utilized the HAMA scale, which differed from the SAS scale used in other studies. While this discrepancy was initially suspected to be a contributing factor to the high heterogeneity, subsequent exclusion of the article did not result in any change in overall heterogeneity, leading us to dismiss this conjecture. However, the results of the scoring scale are derived from the subjective feelings of patients. Given the cognitive variations among individual patients and the potential adoption of different methodologies and scoring standards in result measurement, these factors may significantly influence the scoring outcomes. Therefore, we have extracted the difference in score values before and after treatment as our data and employ SMD for evaluating each result, facilitating synthesis and comparison of data. Lastly, due to a limited number of included studies, it is not feasible to further explore heterogeneity despite variations in acupuncture related-therapy such as acupoint selection, duration and course of treatment.
These limitations somewhat undermine the reliability of the evidence presented in the current study, so further verification is necessary to draw conclusive findings. We recommend designing more rigorous large-scale multi-center RCTs with pre-registration of clinical trial protocols to prevent duplication or selective reporting of anticipated research outcomes. Additionally, adherence to STRICTA guidelines (94) for reporting clinical trials on acupuncture treatment will contribute towards providing more dependable evidence-based medical information. Moreover, we encourage clinical therapists to prioritize not only addressing disease symptoms but also paying greater attention towards patients’ mental health.
The findings of this study indicate that acupuncture-related therapy has more advantages in improving anxiety and depression symptoms of patients with ovarian hypofunction than hormone therapy. However, our proposal is constrained by the limited number of randomized controlled trials included, which are also of low quality. We anticipate further multi-center and high-quality randomized controlled trials, to make up for the study to further prove the conclusion.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
SH: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. DZ: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing – original draft. XS: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. YZ: Software, Supervision, Writing – original draft. XW: Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. YS: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. CL: Supervision, Writing – original draft. XL: Investigation, Writing – original draft. CZ: Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by Hebei Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine (No. 2022093); Hebei Natural Science Foundation (No. H2022423371); and Chinese National Natural Science Foundation (No. 81973755).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1495418/full#supplementary-material
1. Park SU, Walsh L, Berkowitz KM. Mechanisms of ovarian aging. Reproduction. (2021) 162:R19–33. doi: 10.1530/REP-21-0022
2. Cavalcante MB, Sampaio OGM, Camara FEA, Schneider A, de Avila BM, Prosczek J, et al. Ovarian aging in humans: potential strategies for extending reproductive lifespan. Geroscience. (2023) 45:2121–33. doi: 10.1007/s11357-023-00768-8
3. Inayat K, Danish N, Hassan L. Symptoms of menopause in peri and postmenopausal women and their attitude towards them. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad. (2017) 29:477–80.
4. European Society for Human R, Embryology Guideline Group on POI, Webber L, Davies M, Anderson R, Bartlett J, et al. Eshre guideline: management of women with premature ovarian insufficiency. Hum Reprod. (2016) 31:926–37. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dew027
5. Torrealday S, Kodaman P, Pal L. Premature ovarian insufficiency - an update on recent advances in understanding and management. F1000Research. (2017) 6:2069. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.11948.1
6. Welt CK. Primary ovarian insufficiency: A more accurate term for premature ovarian failure. Clin Endocrinol. (2008) 68:499–509. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.2007.03073.x
7. Li M, Zhu Y, Wei J, Chen L, Chen S, Lai D. The global prevalence of premature ovarian insufficiency: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Climacteric. (2023) 26:95–102. doi: 10.1080/13697137.2022.2153033
8. Golezar S, Ramezani TF, Khazaei S, Ebadi A, Keshavarz Z. The global prevalence of primary ovarian insufficiency and early menopause: A meta-analysis. Climacteric. (2019) 22:403–11. doi: 10.1080/13697137.2019.1574738
9. Diagnosis EGoCoC, Reserve MoDO, Association REFPSoCSoFPuCPM. Consensus on clinical diagnosis and management of diminished ovarian reserve. J Reprod Med. (2022) 31:425–34.
10. Cohen J, Chabbert-Buffet N, Darai E. Diminished ovarian reserve, premature ovarian failure, poor ovarian responder—a plea for universal definitions. J Assist Reprod Genet. (2015) 32:1709–12. doi: 10.1007/s10815-015-0595-y
11. Practice Committee of the American Society for Reproductive Medicine. Electronic address aao, Practice Committee of the American Society for Reproductive M. Testing and Interpreting Measures of Ovarian Reserve: A Committee Opinion. Fertil Steril. (2020) 114:1151–7. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2020.09.134
12. Ruth KS, Day FR, Hussain J, Martinez-Marchal A, Aiken CE, Azad A, et al. Genetic insights into biological mechanisms governing human ovarian ageing. Nature. (2021) 596:393–7. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03779-7
13. The L. Time for a balanced conversation about menopause. Lancet. (2024) 403:877. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(24)00462-8
14. Mendoza N, Julia MD, Galliano D, Coronado P, Diaz B, Fontes J, et al. Spanish consensus on premature menopause. Maturitas. (2015) 80:220–5. doi: 10.1016/j.maturitas.2014.11.007
15. Anagnostis P, Paschou SA, Katsiki N, Krikidis D, Lambrinoudaki I, Goulis DG. Menopausal hormone therapy and cardiovascular risk: where are we now? Curr Vasc Pharmacol. (2019) 17:564–72. doi: 10.2174/1570161116666180709095348
16. Quinn MM, Cedars MI. Cardiovascular health and ovarian aging. Fertil Steril. (2018) 110:790–3. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2018.07.1152
17. Qiu C, Chen H, Wen J, Zhu P, Lin F, Huang B, et al. Associations between age at menarche and menopause with cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and osteoporosis in Chinese women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2013) 98:1612–21. doi: 10.1210/jc.2012-2919
18. de Kat AC, Broekmans FJ, Laven JS, van der Schouw YT. Anti-mullerian hormone as a marker of ovarian reserve in relation to cardio-metabolic health: A narrative review. Maturitas. (2015) 80:251–7. doi: 10.1016/j.maturitas.2014.12.010
19. Li XT, Li PY, Liu Y, Yang HS, He LY, Fang YG, et al. Health-related quality-of-life among patients with premature ovarian insufficiency: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Qual Life Res: Int J Qual Life Aspects Treat Care Rehabil. (2020) 29:19–36. doi: 10.1007/s11136-019-02326-2
20. Schmidt PJ, Cardoso GM, Ross JL, Haq N, Rubinow DR, Bondy CA. Shyness, social anxiety, and impaired self-esteem in turner syndrome and premature ovarian failure. JAMA. (2006) 295:1374–6. doi: 10.1001/jama.295.12.1374
21. Ates S, Aydın S, Ozcan P, Bakar RZ, Cetin C. Sleep, depression, anxiety and fatigue in women with premature ovarian insufficiency. J Psychosom Obstet Gynaecol. (2022) 43:482–7. doi: 10.1080/0167482X.2022.2069008
22. Xi D, Chen B, Tao H, Xu Y, Chen G. The risk of depressive and anxiety symptoms in women with premature ovarian insufficiency: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Women’s Ment Health. (2023) 26:1–10. doi: 10.1007/s00737-022-01289-7
23. Liu YX, Lang JW, Chen MX, Fu SJ, Fu RJ, Xian RX, et al. Analysis and evaluation of menopause symptoms and mental status of anxiety and depression in patients with premature ovarian insufficiency. Chin J Reprod Contraception. (2019) 39:880–5. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2096-2916.2019.11.003
24. Cooper AR, Baker VL, Sterling EW, Ryan ME, Woodruff TK, Nelson LM. The time is now for a new approach to primary ovarian insufficiency. Fertil Steril. (2011) 95:1890–7. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2010.01.016
25. Ishizuka B. Current understanding of the etiology, symptomatology, and treatment options in premature ovarian insufficiency (Poi). Front Endocrinol. (2021) 12. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.626924
26. Zhang Q-l, Lei Y-l, Deng Y, Ma R-l, Ding X-s, Xue W, et al. Treatment progress in diminished ovarian reserve: western and Chinese medicine. Chin J Integr Med. (2023) 29:361–7. doi: 10.1007/s11655-021-3353-2
27. Guerrieri GM, Martinez PE, Klug SP, Haq NA, Vanderhoof VH, Koziol DE, et al. Effects of physiologic testosterone therapy on quality of life, self-esteem, and mood in women with primary ovarian insufficiency. Menopause. (2014) 21:952–61. doi: 10.1097/GME.0000000000000195
28. Sullivan SD, Sarrel PM, Nelson LM. Hormone replacement therapy in young women with primary ovarian insufficiency and early menopause. Fertil Steril. (2016) 106:1588–99. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2016.09.046
29. Harper-Harrison G, Shanahan MM. Hormone replacement therapy. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls. (2023).
30. Li Y, Yan MY, Chen QC, Xie YY, Li CY, Han FJ. Current research on complementary and alternative medicine in the treatment of premature ovarian failure: an update review. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2022) 2022:2574438. doi: 10.1155/2022/2574438
31. Tang WL, Hu YH, He XH. Acupuncture stimulation of acupoints of multiple meridians for patients with diminished ovarian reserve of both yin and yang deficiency. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. (2015) 40:479–83, 88. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.2015.06.010
32. Yang FX, Yang ZX. Thirteen acupoints for regulating menstruation and promoting pregnancy” for diminished ovarian reserve: A prospective cohort study. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. (2020) 40:619–22. doi: 10.13703/j.0255-2930.20190925-k0001
33. Wang LL, Xiang YG, Tan L, Zhu JY, Ren ZX, Ma XY, et al. Acupuncture-moxibustion treatment by stages based on the theory of “Transformation of yin and yang” for premature ovarian insufficiency. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. (2021) 41:742–6. doi: 10.13703/j.0255-2930.20200627-k0001
34. Lin G, Liu X, Cong C, Chen S, Xu L. Clinical efficacy of acupuncture for diminished ovarian reserve: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front Endocrinol. (2023) 14:1136121. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1136121
35. Zhang J, Huang X, Liu Y, He Y, Yu H. A comparison of the effects of chinese non-pharmaceutical therapies for premature ovarian failure: A prisma-compliant systematic review and network meta-analysis. Med (Baltimore). (2020) 99:e20958. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000020958
36. Zhou ZQ, Du XL, Huang JM, Ling SY, Zheng YH. Clinical effect of soothing liver and tonifying kidney method combined with acupuncture for regulating menstruation and promoting pregnancy on premature ovarian failure. Chin Arch Tradit Chin Med. (2023) 41:63–6. doi: 10.13193/j.issn.1673-7717.2023.09.012
37. Chen Y, Fang Y, Yang J, Wang F, Wang Y, Yang L. Effect of acupuncture on premature ovarian failure: A pilot study. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2014) 2014:718675. doi: 10.1155/ecam.v2014.1
38. Yang XY, Yang NB, Huang FF, Ren S, Li ZJ. Effectiveness of acupuncture on anxiety disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Ann Gen Psychiatry. (2021) 20:9. doi: 10.1186/s12991-021-00327-5
39. Yang L, Xu HF, Gou MH, Yang HS, Feng YX, Liu SY, et al. Application of Tiaojing Cuyun acupuncture in treatment of diseases with ovarian function decline. Chin Acupunct Moxibustion. (2022) 42:1200–4. doi: 10.13703/j.0255-2930.20220505-k0002
40. Shamseer L, Moher D, Clarke M, Ghersi D, Liberati A, Petticrew M, et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (Prisma-P) 2015: elaboration and explanation. BMJ (Clinical Res ed). (2015) 350:g7647. doi: 10.1136/bmj.g7647
41. Wang X, Chen Y, Liu Y, Yao L, Estill J, Bian Z, et al. Reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses of acupuncture: the prisma for acupuncture checklist. BMC Complement Altern Med. (2019) 19:208. doi: 10.1186/s12906-019-2624-3
42. Li J, Zhang Z, Wei Y, Zhu P, Yin T, Wan Q. Metabonomic analysis of follicular fluid in patients with diminished ovarian reserve. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2023) 14:1132621. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1132621
43. Dongzhimen Hospital of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Oriental Hospital of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Hebei medical university, Chinese Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guang ‘anmen Hospital of Chinese Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine, China-Japan Friendship Hospital of Ministry of Health, et al. Premature ovarian failure. China Press of Chinese Medicine. (2012).
44. Zung WW. A rating instrument for anxiety disorders. Psychosomatics. (1971) 12:371–9. doi: 10.1016/S0033-3182(71)71479-0
45. Zung WW. A self-rating depression scale. Arch Gen Psychiatry. (1965) 12:63–70. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1965.01720310065008
46. Hamilton M. The assessment of anxiety states by rating. Br J Med Psychol. (1959) 32:50–5. doi: 10.1111/j.2044-8341.1959.tb00467.x
47. Hamilton M. A rating scale for depression. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. (1960) 23:56–62. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.23.1.56
48. Sterne JAC, Savovic J, Page MJ, Elbers RG, Blencowe NS, Boutron I, et al. Rob 2: A revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. (2019) 366:l4898. doi: 10.1136/bmj.l4898
49. Bai TY, Li H. Efficacy of medical moxibustion at baliao points combined with regulating menstruation to promote pregnancy acupuncture on premature ovarian insufficiency of spleen and kidney yang deficiency type. Shandong J Tradit Chin Med. (2023) 42:1074–9. doi: 10.16295/j.cnki.0257-358x.2023.10.010
50. Dong WB. Clinical Study on Acupoint Catgut Embedding Therapy for Diminished Ovarian Reserve of Liver-kidney Yin Deficiency Type. master’s thesis. Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing (2021).
51. Du XN, Guan Y, Meng X, Wang CX. Clinical study on Peiyuan Tiaoshen acupuncture in the treatment of premature ovarian failure with syndrome of kidney deficiency and liver depression. Modern J Integrated Tradit Chin Western Med. (2022) 31:1502–7.
52. Liu XJ. Effects of acupuncture combined with HRT on sex hormone-related metabolites and metabolic pathways in POI patients based on metabonomics. Dissertation. Hunan university of traditional Chinese medicine, Hunan (2021).
53. Shi JX. Clinical Observation on Acupoint Catgut Embedding in Treating Premature Ovarian Insufficiency of Kidney Deficiency Type. master’s thesis. Shandong university of traditional Chinese medicine, Shandong (2022).
54. Sun YC. Clinical observation on the treatment of diminished ovarian reserve due to kidney deficiency and liver depression by acupuncture and moxibustion combined with regulating chong and ren and regulating mind. master’s thesis. Shandong university of traditional Chinese medicine, Shandong (2023).
55. Xu CC, Li H, Fang YG, Bai TY, Yu XH. Effect of regulating menstruation and promoting pregnancy acupuncture therapy on negative emotion in patients with premature ovarian insufficiency. Chin Acupunct Moxibustion. (2021) 41:279–82. doi: 10.13703/j.0255-2930.20200307-0004
56. Xu ZJ. Effect of “Biao-Ben Acupoint” acupuncture therapy combined with western medicine on patients decreasing ovarian reserve with repeated implantation failure. master’s thesis. Hubei University of Chinese Medicine, Hubei (2023).
57. Xu ZJ, Kong LH, Zhao Q. Effect of “Biao-Ben Acupoint” acupuncture therapy combined with western medicine on patients decreasing ovarian reserve with repeated implantation failure. Asia Pacif Tradit Med. (2023) 19:63–67.
58. Yue CH, Niu XX, Wang XM, Liu S, Luo XM, Zheng QC. Effect of staging acupuncture on ovarian function in patients with premature ovarian insufficiency based on the theory of transformation of waxing and waning of yinyang. J Changchun Univ Chin Med. (2024) 40:184–8. doi: 10.13463/j.cnki.cczyy.2024.02.014
59. Vase L, Baram S, Takakura N, Takayama M, Yajima H, Kawase A, et al. Can acupuncture treatment be double-blinded? An evaluation of double-blind acupuncture treatment of postoperative pain. PloS One. (2015) 10:e0119612. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119612
60. Sterne JA, Sutton AJ, Ioannidis JP, Terrin N, Jones DR, Lau J, et al. Recommendations for examining and interpreting funnel plot asymmetry in meta-analyses of randomised controlled trials. BMJ. (2011) 343:d4002. doi: 10.1136/bmj.d4002
61. Errington-Evans N. Acupuncture for anxiety. CNS Neurosci Ther. (2012) 18:277–84. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-5949.2011.00254.x
62. Lu J, Xu X, Huang Y, Li T, Ma C, Xu G, et al. Prevalence of depressive disorders and treatment in China: A cross-sectional epidemiological study. Lancet Psychiatry. (2021) 8:981–90. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(21)00251-0
63. Chachamovich JR, Chachamovich E, Ezer H, Fleck MP, Knauth D, Passos EP. Investigating quality of life and health-related quality of life in infertility: A systematic review. J Psychosom Obstet Gynaecol. (2010) 31:101–10. doi: 10.3109/0167482X.2010.481337
64. Massarotti C, Gentile G, Ferreccio C, Scaruffi P, Remorgida V, Anserini P. Impact of infertility and infertility treatments on quality of life and levels of anxiety and depression in women undergoing in vitro fertilization. Gynecol Endocrinol. (2019) 35:485–9. doi: 10.1080/09513590.2018.1540575
65. Ventura JL, Fitzgerald OR, Koziol DE, Covington SN, Vanderhoof VH, Calis KA, et al. Functional well-being is positively correlated with spiritual well-being in women who have spontaneous premature ovarian failure. Fertil Steril. (2007) 87:584–90. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2006.07.1523
66. Cepoiu M, McCusker J, Cole MG, Sewitch M, Belzile E, Ciampi A. Recognition of depression by non-psychiatric physicians–a systematic literature review and meta-analysis. J Gen Intern Med. (2008) 23:25–36. doi: 10.1007/s11606-007-0428-5
67. Dunstan DA, Scott N, Todd AK. Screening for anxiety and depression: reassessing the utility of the zung scales. BMC Psychiatry. (2017) 17:329. doi: 10.1186/s12888-017-1489-6
68. Zimmerman M, Martin J, Clark H, McGonigal P, Harris L, Holst CG. Measuring anxiety in depressed patients: A comparison of the Hamilton anxiety rating scale and the Dsm-5 anxious distress specifier interview. J Psychiatr Res. (2017) 93:59–63. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2017.05.014
69. Mukaino Y, Park J, White A, Ernst E. The effectiveness of acupuncture for depression–a systematic review of randomised controlled trials. Acupunct Med. (2005) 23:70–6. doi: 10.1136/aim.23.2.70
70. Chan YY, Lo WY, Yang SN, Chen YH, Lin JG. The benefit of combined acupuncture and antidepressant medication for depression: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Affect Disord. (2015) 176:106–17. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2015.01.048
71. Amorim D, Amado J, Brito I, Fiuza SM, Amorim N, Costeira C, et al. Acupuncture and electroacupuncture for anxiety disorders: A systematic review of the clinical research. Complement Therapies Clin Pract. (2018) 31:31–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ctcp.2018.01.008
72. Sang N, Chen C. Effect of moxibustion at Baihui (GV20) on emotion and sleep quality in anxiety patients. Hebei J Tradit Chin Med. (2023) 45:2075–8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2619.2023.12.031
73. Luo Z, Hu X, Chen C, Zhu L, Zhang W, Shen Y, et al. Effect of catgut embedment in du meridian acupoint on mental and psychological conditions of patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease. Evidence-Based Complement Altern Med. (2020) 22:5415813. doi: 10.1155/2020/5415813
74. Maunder A, Arentz S, Armour M, Costello MF, Ee C. Health needs, treatment decisions and experience of traditional complementary and integrative medicine use by women with diminished ovarian reserve: A cross-sectional survey. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. (2024) 64:390–8. doi: 10.1111/ajo.13805
75. Zhou XF, Li Y, Zhu H, Chen L. Impact of Acupuncture at twelve meridians Acupoint on Brain Wave of Patients with General Anxiety Disorder. Chin Acupunct Moxibustion. (2013) 33:395–8. doi: 10.13703/j.0255-2930.2013.05.008
76. Yang FZ, Lu ZZ, Yan JH. Pathogenesis and treatment of anxiety and depression in traditional Chinese medicine. China J Tradit Chin Med Pharm. (2012) 27:2338–40.
77. Samuels N, Gropp C, Singer SR, Oberbaum M. Acupuncture for psychiatric illness: A literature review. Behav Med (Washington DC). (2008) 34:55–64. doi: 10.3200/BMED.34.2.55-64
78. Tu C-H, MacDonald I, Chen Y-H. The effects of acupuncture on glutamatergic neurotransmission in depression, anxiety, schizophrenia, and Alzheimer’s disease: A review of the literature. Front Psychiatry. (2019) 10:14. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2019.00014
79. Chen S, Wang J, Xiaofang C, Zhang Y, Hong Y, Zhuang W, et al. Chinese acupuncture: A potential treatment for autism rat model via improving synaptic function. Heliyon. (2024) 10:e37130. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37130
80. Cai X, Wu M, Zhang Z, Liu H, Huang S, Song J, et al. Electroacupuncture alleviated depression-like behaviors in ventromedial prefrontal cortex of chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced rats: increasing synaptic transmission and phosphorylating dopamine transporter. CNS Neurosci Ther. (2023) 29:2608–20. doi: 10.1111/cns.14200
81. Nomikos GG, Spyraki C. Influence of oestrogen on spontaneous and diazepam-induced exploration of rats in an elevated plus maze. Neuropharmacology. (1988) 27:691–6. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(88)90077-9
82. Walf AA, Paris JJ, Frye CA. Chronic estradiol replacement to aged female rats reduces anxiety-like and depression-like behavior and enhances cognitive performance. Psychoneuroendocrinology. (2009) 34:909–16. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2009.01.004
83. Lu H, Ma K, Jin L, Zhu H, Cao R. 17beta-estradiol rescues damages following traumatic brain injury from molecule to behavior in mice. J Cell Physiol. (2018) 233:1712–22. doi: 10.1002/jcp.v233.2
84. Sovijit WN, Sovijit WE, Pu S, Usuda K, Inoue R, Watanabe G, et al. Ovarian progesterone suppresses depression and anxiety-like behaviors by increasing the lactobacillus population of gut microbiota in ovariectomized mice. Neurosci Res. (2021) 168:76–82. doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2019.04.005
85. Zheng P, Zeng B, Zhou C, Liu M, Fang Z, Xu X, et al. Gut microbiome remodeling induces depressive-like behaviors through a pathway mediated by the host’s metabolism. Mol Psychiatry. (2016) 21:786–96. doi: 10.1038/mp.2016.44
86. Marin IA, Goertz JE, Ren T, Rich SS, Onengut-Gumuscu S, Farber E, et al. Microbiota alteration is associated with the development of stress-induced despair behavior. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:43859. doi: 10.1038/srep43859
87. Valles-Colomer M, Falony G, Darzi Y, Tigchelaar EF, Wang J, Tito RY, et al. The neuroactive potential of the human gut microbiota in quality of life and depression. Nat Microbiol. (2019) 4:623–32. doi: 10.1038/s41564-018-0337-x
88. Wu S, Yan J. Clinical observation on premature ovarian failure by warming acupuncture at Zusanli (St 36) and Guanyuan (Cv 4) combined with ginger moxibustion at Baliao Points. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. (2018) 38:1267–71. doi: 10.13703/j.0255-2930.2018.12.004
89. Wang Y, Li Y, Chen R, Cui X, Yu J, Liu Z. Electroacupuncture for reproductive hormone levels in patients with diminished ovarian reserve: A prospective observational study. Acupunct Med. (2016) 34:386–91. doi: 10.1136/acupmed-2015-011014
90. Li X, Xu H, Fang Y, Shang J, Yang H, Zhou X, et al. Acupuncture with regulating menstruation to promote pregnancy for diminished ovarian reverse: A prospective case series study. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. (2017) 37:1061–5. doi: 10.13703/j.0255-2930.2017.10.009
91. Geng Z, Nie X, Ling L, Li B, Liu P, Yuan L, et al. Electroacupuncture may inhibit oxidative stress of premature ovarian failure mice by regulating intestinal microbiota. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2022) 2022:4362317. doi: 10.1155/2022/4362317
92. Zhang F, Ma T, Tong X, Liu Y, Cui P, Xu X, et al. Electroacupuncture improves metabolic and ovarian function in a rat model of polycystic ovary syndrome by decreasing white adipose tissue, increasing brown adipose tissue, and modulating the gut microbiota. Acupunct Med. (2022) 40:347–59. doi: 10.1177/09645284211056663
93. Li Y, Xia G, Tan Y, Shuai J. Acupoint stimulation and chinese herbal medicines for the treatment of premature ovarian insufficiency: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Complement Ther Clin Pract. (2020) 41:101244. doi: 10.1016/j.ctcp.2020.101244
94. MacPherson H, Altman DG, Hammerschlag R, Youping L, Taixiang W, White A, et al. Revised standards for reporting interventions in clinical trials of acupuncture (Stricta): extending the consort statement. J Altern Complement Med. (2010) 16:ST1–14. doi: 10.1089/acm.2010.1610
95. Luo QP, Yang ZH, Jin LM, Chen PB, Jiang Y, Li QK, et al. Electro-acupuncture at acupoints of liver meridian for the treatment of ovarian reserve dysfunction due to liver depression: a randomized controlled trial. Chin Acupunct Moxibustion. (2024) 44:1261–6. doi: 10.13703/j.0255-2930.20230905-k0005
Keywords: acupuncture, premature ovarian insufficiency, diminished ovarian reserve, anxiety, depression, meta-analysis
Citation: Huang S, Zhang D, Shi X, Zhang Y, Wang X, She Y, Liang C, Li X and Zaslawski C (2024) Acupuncture and related therapies for anxiety and depression in patients with premature ovarian insufficiency and diminished ovarian reserve: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Psychiatry 15:1495418. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1495418
Received: 12 September 2024; Accepted: 06 November 2024;
Published: 02 December 2024.
Edited by:
Yong Huang, Southern Medical University, ChinaReviewed by:
Xiaolan Su, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, ChinaCopyright © 2024 Huang, Zhang, Shi, Zhang, Wang, She, Liang, Li and Zaslawski. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xuliang Shi, c2hpLXh1LWxpYW5nQDE2My5jb20=; Yanfen She, c2hleWFuZmVuQDE2My5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.