- 1Department of Psychiatry, The First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, China
- 2Psychiatric Center, The First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, China
- 3Department of Psychiatry, University of Alberta, Edmonton, AB, Canada
- 4Mental Health Center, University-Town Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, China
Background: The consumption of takeaways is becoming increasingly prevalent. Despite this, the relationship between takeaway food consumption and depressive symptoms in Chinese populations has not been clarified. Furthermore, the factors that mediate the association between takeaway frequency and depressive symptoms are unknown.
Methods: Questionnaires were employed to collect data from 6,417 new students at Chongqing Medical University in the autumn of 2023, including sociodemographic information, takeaway frequency, physical activity levels (measured by the International Physical Activity Questionnaire Short Form), and depressive symptoms (measured by the Patient Health Questionnaire-9). Multiple linear regression and mediation analysis were performed. Multiple imputations were used to fill in missing data through sensitivity analyses.
Results: Among 6417 participants, 2,606 (40.6%) students ordered takeaway at least once a week, with 235 (3.7%) of them ordering takeaway food every day. Takeaway frequency was significantly associated with depressive symptoms (β=0.034, P=0.006), and physical activity partially mediated this relationship (95% bootstrap confidence interval=0.0024, 0.0371).
Conclusions: The study highlights the negative relationship between takeaway frequency and emotional well-being, emphasizing the need to focus on the emotional health of frequent takeaway food consumers. Moreover, our study suggests that increased physical activity may alleviate takeaway-induced mood-related outcomes.
1 Introduction
The takeaway industry has witnessed significant growth in recent years owing to the rapid development of the social economy and online business (1). The popularity of takeaway food is due to its convenience and time-saving advantage (2, 3). Moreover, the Covid-19 pandemic further triggered in the creation of several takeaway platforms, driven by a substantial urban customer base (4). In 2022, the number of users on all takeaway platforms in China was about 520 million (5). Among the consumers who ordered takeaway during the same year, 50.38% indulged in takeaway at least once daily (6).
Chinese college students commonly reside in university dormitories (7). Despite the availability of dining facilities provided by universities, the variety of takeaway food and the convenience of takeaway food ordering has prompted a significant number of students to order takeaway food (8). A survey of Chinese young people revealed that 15.4% order takeaway at least once a week (9). This dietary pattern has often been regarded as unhealthy due to its high energy, fat, salt, and sugar content and low vitamin and mineral intake (10, 11). Moreover, the convenience of takeaway food being delivered directly to dormitory floors reduces the likelihood of students dining out. Research indicated a direct correlation between takeaway food consumption and sedentary behavior (8). It is therefore necessary to examine the potential health implications of consuming takeaway food.
However, few studies have explored the emotional health implications of takeaway transactions on customers. A Chinese college students survey conducted in 2018 found that those who ordered takeaway more frequently had higher depression scores (12), but the detailed results and methodology are not accessible. A cohort study conducted in Australia showed that Western dietary patterns at the age of 14, which included high consumption of red meat, takeaways, refined foods, and sweets, were linked to more severe depressive symptoms at the age of 17 (13). However, this study did not specifically focus on takeaway behaviors but rather considered them as part of Western dietary patterns. This highlights the need to explore the impact of takeaway habits on mood, especially among Chinese younger people (12).
Previous research indicated that takeaway consumption may reduce physical activity. An Australian study showed that individuals who ordered takeaway twice a week or more tend to spend more time sitting than those who order only once a week (14). Moreover, individuals who order takeaways may have a lower level of physical activity and tend to spend more time sitting compared to those who cook their meals or dine out.
A correlation between physical activity and depressed mood has been documented in several studies. The result of a meta-analysis, which included 15 longitudinal studies, indicated that compared to adults who did not engage in any physical activity, those who completed half of the recommended amount of physical activity per week (4.4 marginal metabolic equivalent task hours per week [mMET-h/wk]) had an 18% lower risk of depression. Moreover, adults who reached 8.8 mMET-h/wk experienced a 25% reduction in the risk of depression (15). Based on findings from prior research, we speculate that frequent consumption of takeaway meals might elevate the risk of depression, with physical activity potentially exerting a significant influence on this correlation. To the best of our knowledge, no study has investigated the relationship between the frequency of takeaway food consumption and the presence of depressive symptoms. Furthermore, no research has employed mediation analysis to examine the mediating of physical activity on the association between these two factors. Therefore, this study aimed to: (1) explore the relationship between takeaway frequency and depressive symptoms and (2), investigate the mediating role of physical activity in the relationship between takeaway frequency and depressive symptoms.
2 Methods
2.1 Data collection and subjects
In this cross-sectional study, freshmen of Chongqing Medical University were recruited in 2023 Fall. All participants provided written informed consent prior to their inclusion in the study. They were subsequently requested to complete a questionnaire. A total of 6,417 students completed the valid scale, with 260 students excluded due to illness, absence from school, refusal to complete, etc. The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the National Clinical Medical Research Center, Second Xiangya Hospital, Central South University (NO.2022S010).
2.2 Measures
2.2.1 Sociodemographic characteristics
The following sociodemographic characteristics were collected as control variables: age, gender (male or female), ethnicity (Han or other national minority), only child status (only child or non-only child), the condition of residence (rural or urban), religion(with or without), parental marriage status(single parent family or non-single parent family), family history of mental illness(with or without), physical disease(with or without any diabetes, cardiovascular, liver, kidney, or other physical disease), current smoking(yes or no), and current drinking(yes or no).
2.2.2 Depressive symptoms
Depressive symptoms were analyzed using the Chinese version of the Patient Health Questionnaire for depression (PHQ-9). The scale consists of nine items, with each item having four answer choices: “none at all,” “occasional days,” “more than half of the days,” and “almost every day.” Each choice corresponds to a score of 0, 1, 2, or 3, respectively. The total score ranges from 0 to 27 points, with higher scores indicating a greater likelihood of depression. In China, the scale has been widely employed, demonstrating both high reliability and validity (16, 17). The Cronbach’s alpha coefficient of the scale is 0.84 (18).
2.2.3 Takeaway frequency
The frequency of takeaway orders was assessed using a single question: “Do you usually order takeaway food for your meals?” The answer included the following five choices; “never,” “1-3 times/month,” “1-2 times/week,” “3-5 times/week,” “almost every day”.
2.2.4 Physical activity
Physical activity levels were explored using the Chinese version of the International Physical Activity Questionnaire Short Form (IPAQ-SF) (19, 20). The IPAQ-SF assesses physical activity levels based on seven items that evaluate four distinct types of activity conducted during the past week: vigorous-intensity activity, moderate-intensity activity, light-intensity activity, and sitting behavior. Physical activity was determined based on metabolic equivalents (MET). Previous studies have defined 1 MET as the amount of oxygen consumed at rest. Vigorous-intensity activity corresponds to 8 METs, whereas moderate-intensity activity is equivalent to 4 METs, and light-intensity activity corresponds to 3.3 METs (21). The total physical activity level was calculated by multiplying the MET assignment corresponding to a physical activity of a certain intensity by the weekly frequency of that physical activity and the time spent exercising per day following the scoring protocol (22). The reliability and validity of the Chinese version of the IPAQ-SF employed in this study have been confirmed in various studies (22–24). In this study, 2582 students completed the IPAQ-SF questionnaire. Compared to non-respondents, respondents were older, less likely to be female, had lower depression scores, and there was no difference in the frequency of takeaway ordering.
2.2.5 Statistical analysis
Data analysis was conducted using SPSS 27.0, including the PROCESS macro for mediation analysis. Categorical variables were presented using numerical values and percentages. Given that the PHQ-9 scores were not normally distributed, the data were expressed as medians (quartiles) and the PHQ-9 scores were compared between groups using the Mann-Whitney U test. To explore the relationship between takeaway frequency and depressive symptoms, we employed linear regression analysis.
Utilizing the PROCESS macro, mediation analyses were conducted to analyze whether the relationship between takeaway frequency and depressive symptoms was mediated by physical activity. To best test the mediation effect, the bootstrap method was used to estimate the indirect effect and calculate the 95% confidence interval (CI). The number of bootstrap samples was 5000. Previous literature indicates that a mediation effect is considered significant when the confidence interval (CI) does not include zero for both the lower limit (LLCI) and upper limit (ULCI) (25, 26). The mediation model included sociodemographic characteristics as covariates.
In the sensitivity analysis, missing values were imputed using multiple imputations to test the influence of the missing data. This method generates five imputed datasets, where missing values are replaced with plausible estimates based on the observed data. Multiple linear regression adjusted for model 3 and mediation analysis were then performed on the filled dataset to verify the robustness of the results. Two-tailed p-value <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3 Results
3.1 Demographic characteristics of participants
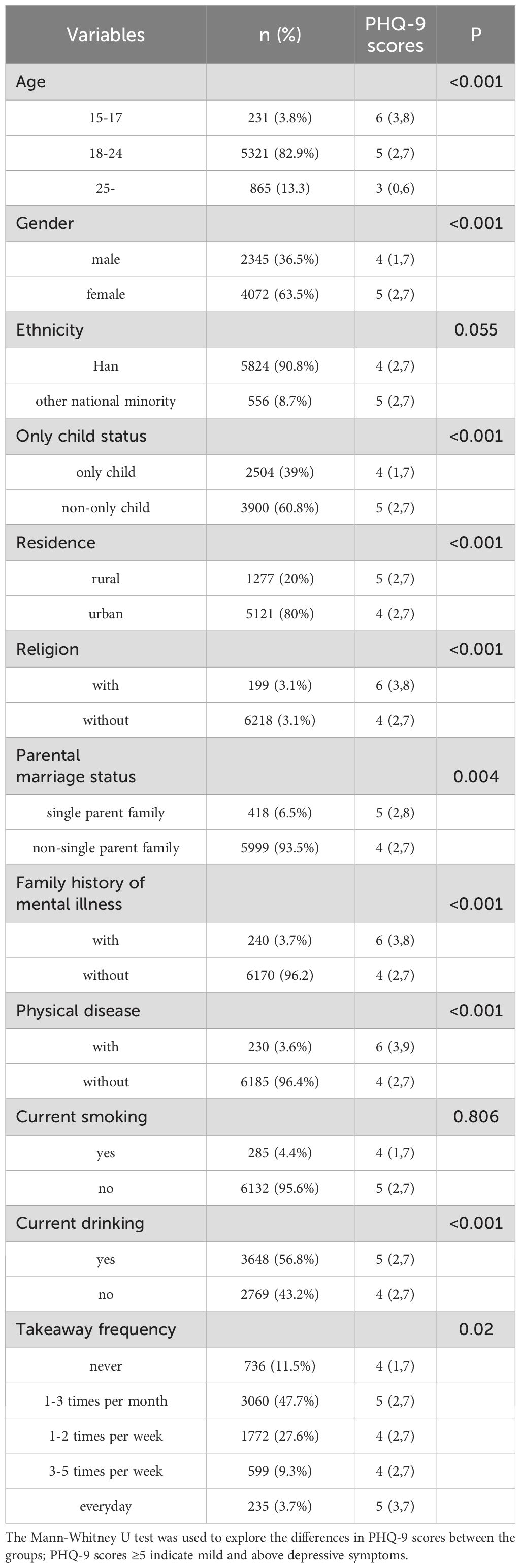
This survey enrolled 6,417 students, with a median age of 19 years (interquartile range: 18-23). Among them, there were 2345 (36.5%) males and 4072 (63.5%) females. Table 1 displays the demographic characteristics of the participants and the disparities in PHQ-9 scores between various groups. According to sociodemographic classification, individuals who are female, younger, non-only children, reside in rural areas, adhere to a religion, come from single-parent households, have a family history of mental illness, suffer from physical ailments, and are current drinkers were more likely to experience severe depressive symptoms.
3.2 Relationship between takeaway frequency and depressive symptoms
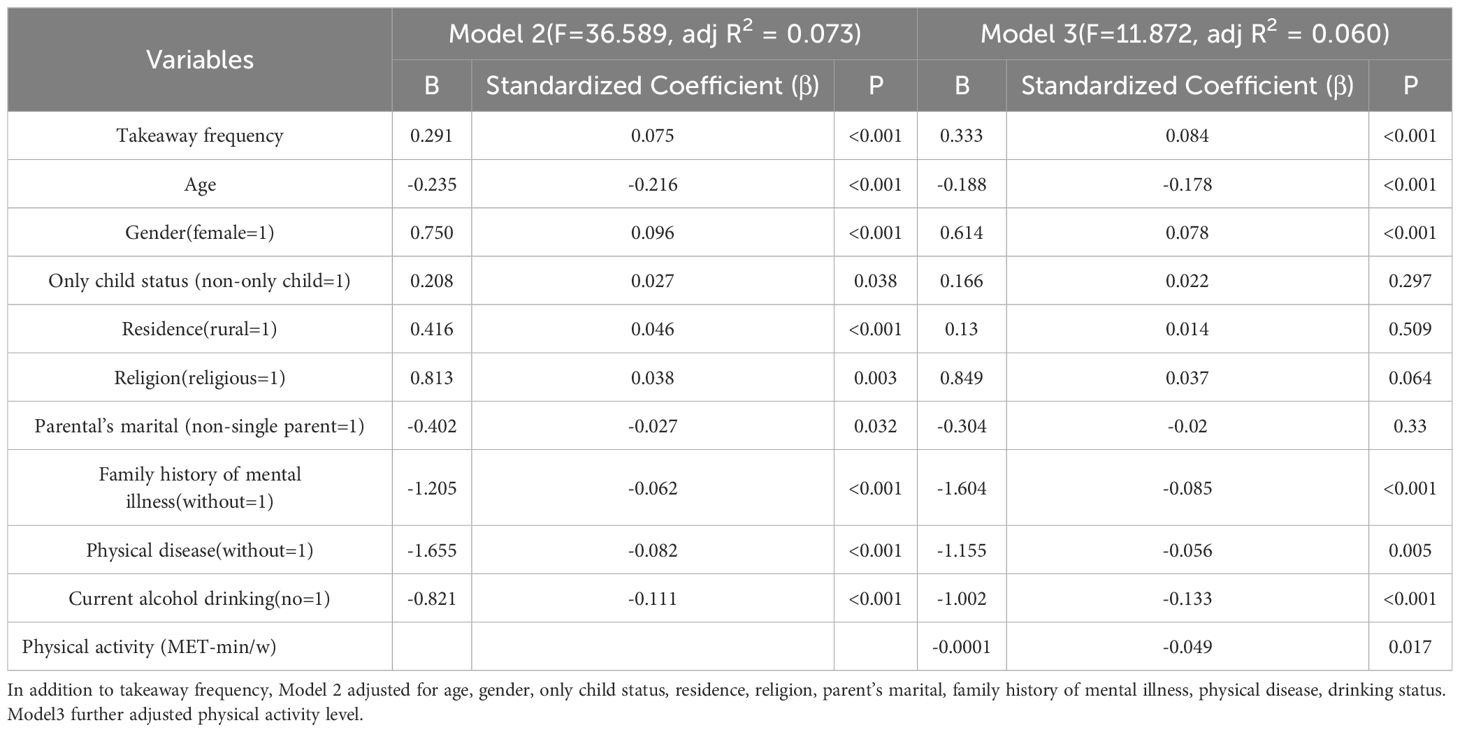
Among the respondents, 2,606 (40.6%) order takeaway at least once a week, with 235 (3.7%) of them ordering takeaway food every day. Through stepwise multiple linear regression analysis, we investigated the correlation between takeaway frequency and depressive symptoms. In Model 1, we considered takeaway frequency as the independent variable and depressive symptoms as the dependent variable. The analysis revealed a significant association between takeaway frequency and depressive symptoms (B=0.135, β=0.034, P=0.006). In Model 2, sociodemographic characteristics (age, gender, only child status, residence, religion, parent’s marital, family history of mental illness, physical disease, and drinking status) were selected as the independent variables (based on the one-way analyses, two factors were excluded: ethnicity and current smoking status). The relationship between takeaway frequency and depressive symptoms remained significant (β=0.075, P<0.001). Moreover, depressive symptoms were significantly correlated with age, gender, only child status, condition of residence, religion, parental marriage status, family history of mental illness, history of physical disease, smoking, and drinking status. In Model 3, physical activity level (expressed as MET) was included. The relationship between takeaway frequency and depressive symptoms remained significant (β=0.084, P<0.001, Table 2).
3.3 Mediating role of physical activity level in the relationship between takeaway frequency and depressive symptoms
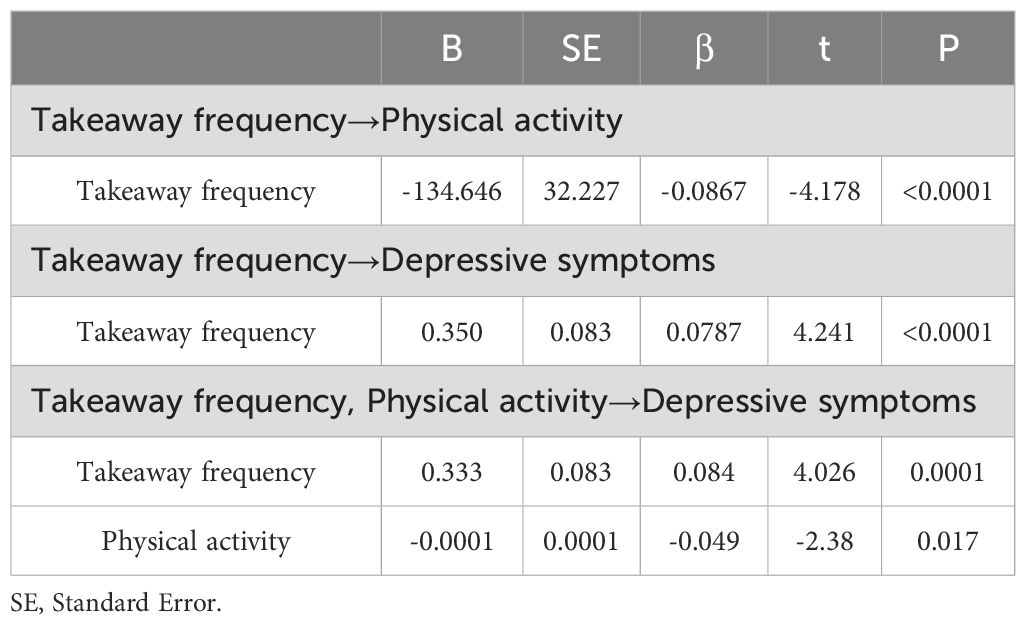
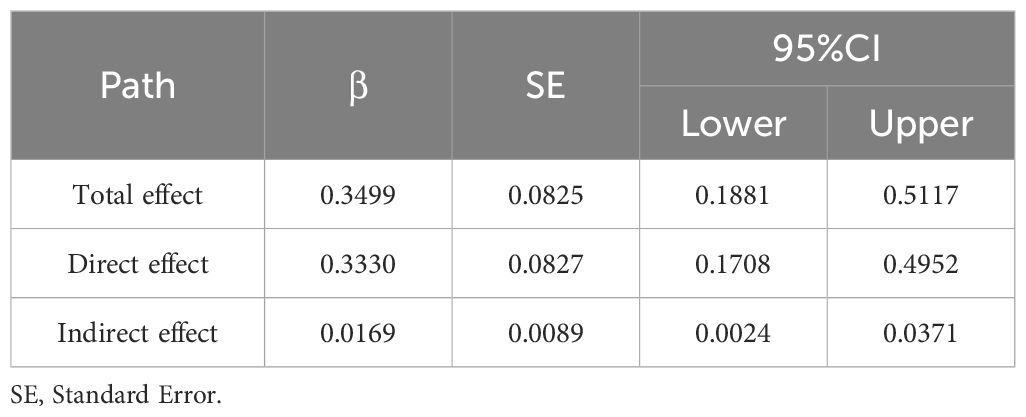
To examine the role of physical activity as a mediator in the relationship between takeaway frequency and depressive symptoms, we utilized a bootstrapping procedure. The mediation analysis results are presented in Table 3 after controlling for sociodemographic characteristics (age, gender, ethnicity, only child status, condition of residence, religion, parental marriage status, family history of mental illness, history of physical disease, smoking, and drinking status). A significant negative correlation was observed between takeaway frequency and the physical activity pathway (β=-0.0867, P<0.0001). The total effect of takeaway frequency on depressive symptoms was statistically significant (β=0.0787, P<0.0001). After including both takeaway frequency and physical activity in the model, a significant association was obtained between both takeaway frequency (β=0.084, P=0.0001) and physical activity (β=-0.049, P=0.017) with depressive symptoms. The bootstrap procedure results (Table 4) suggested that the association between takeaway frequency and depressive symptoms was partially mediated by physical activity level (indirect effect=0.0169, SE=0.0089, 95%CI [0.0024, 0.0371]). The mediating effect contributes to 4.83% of the total effect. To elucidate the relationship between takeaway frequency, physical activity level, and depressive symptoms further, we constructed a mediating effect model (Figure 1).
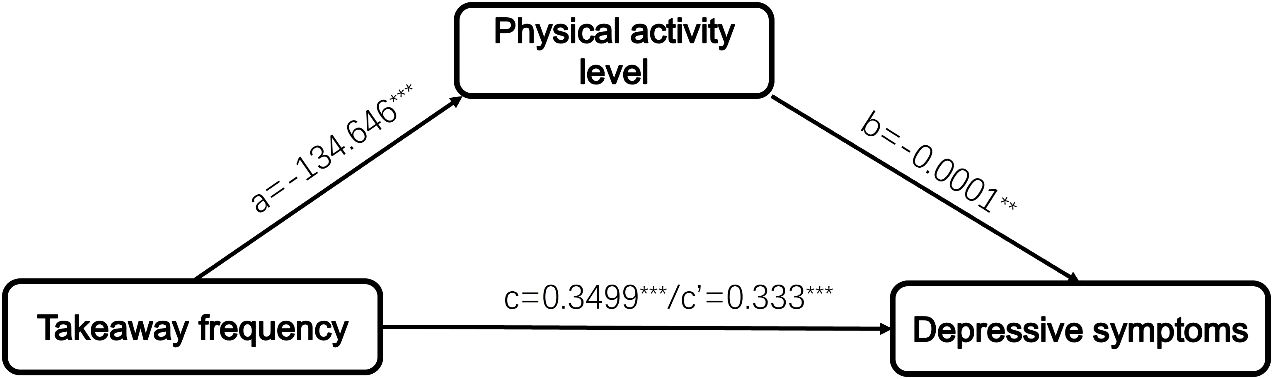
Figure 1. The framework for physical activity level mediating the relationship between takeaway frequency and depressive symptoms. ∗∗∗P < 0.001, ∗∗P < 0.01.
3.4 Sensitivity analysis
In sensitivity analysis, we performed multiple linear regression adjusted for Model 3. The results (in Supplementary Table 1) were consistent with the main results that takeaway frequency was also significantly associated with depressive symptoms (B=0.253, P<0.001). The mediation analysis results (Supplementary Table 2) were also consistent with previous finding (indirect effect=0.0105, SE=0.0041, 95%CI [0.0032, 0.0191]).
4 Discussion
In this cross-sectional study, we found that takeaway consumption frequency was significantly positively correlated with depressive symptoms after accounting for multiple sociodemographic characteristics. The relationship between takeaway frequency and depressive symptoms was significantly mediated by physical activity level.
The strong relationship between takeaway consumption frequency and depressive symptoms was also observed in a large survey involving Chinese college students. The survey, which was reported as news rather than a study, showed that approximately 43.2% of college students ordered takeout at least once a week, with around 6.4% ordering takeout nearly every day. Those with more frequent takeaway orders also exhibited higher depression scores (12). A limitation of this study is that its findings were published as news, with no access to detailed results or methodology, limiting its reliability assessment. However, it suggests a link between takeaway consumption and depressive symptoms, highlighting the need for further investigation in college students. Shakya et al. analyzed 1743 participants aged ≥ 24 years and also reported a significant association between takeaway food consumption and depressive symptoms (27).
The adverse effects of takeaway food consumption on mood may be attributed to a multitude of underlying mechanisms. The first possible reason is the nutritional and health issues of the takeaway food itself. In a recent study conducted across 10 major cities in China, researchers investigated the nutritional quality of takeaway food. They found that majority of the top 10 best-selling takeaway dishes have low nutrient quality (28). A study conducted in New Zealand analyzed takeaway food menus from popular online takeaway platforms and found that 90% of the options were unhealthy. These foods were rich in saturated fats, sugars, sodium, and/or alcohol, and deficient in dietary fiber (29). In 2018, a longitudinal study suggested that takeaway behaviors contributed to obesity and inflammation, which in turn caused depressive symptoms (13). The nutritional composition of the diet, encompassing vitamins, fiber, micronutrients, and unsaturated fatty acids, greatly influences emotional well-being (30, 31).
Secondly, takeaway food containers are often made of petroleum-based plastics. Evidence from prior studies indicated that microplastics can be released from carrier container into food, and pose a potential health threat due to polymer degradation (1, 32). In a study conducted by Zhou et al., it was observed that individuals who frequently order takeaway food (approximately 5-10 times per month) may inadvertently consume a range of 145 to 5520 microplastic particles originating from food containers (33). Microplastics, tiny particles originating from various sources, will accumulate in body organs, tissues, and cells. Their presence aggravates the toxicological and pathological reactions within organisms (34–36). Consequently, oxidative stress (37, 38), inflammation (39), and metabolic disturbances (40, 41) may intensify, damaging the emotional well-being (42–44).
Thirdly, frequent takeaway consumption may limit real-life social interactions. Individuals who regularly order takeaway food often exhibit tendencies toward staying indoors, self-isolation, and a reluctance to engage with others, thereby increasing the risk of depression (45–47).
Given the multifaceted nature of takeaway habits, identifying the exact mechanism linking takeaway to depression is difficult. This aspect may only be comprehensively investigated in future prospective studies that meticulously control for confounding factors. In this study, we tested the mediating role of physical activity on the relationship between the takeaway frequency and depressive symptoms. Results indicated that physical activity partially explains the relationship between them. In the mediation analysis, there was a significant negative association between takeaway frequency and physical activity (β=-0.0867, P<0.0001). Previous studies have documented a similar relationship. A study conducted in China analyzed the physical activity habits and takeaway frequency of 2,130 college students. It was found that students who had higher take-out consumption tended to be less physically active and more sedentary (8). In another study, people who order takeaway twice a week tend to spend more time sitting than those who order less frequently (48). Many previous studies have reported a negative relationship between physical activity and symptoms of depression (15, 49). Although the mediating effect of physical activity accounted for only 4.83% of the total effect, it highlights a potential mechanism through which takeaway frequency may influence depressive symptoms. This suggests that promoting physical activity could help mitigate the mental health impacts of frequent takeaway consumption. However, further research is needed to explore other potential mechanisms, such as dietary patterns, sleep quality, and social isolation.
This study has the following strengths. To our knowledge, this is the first study to investigate the relationship between takeaway frequency and depressive symptoms among Chinese college students, while considering several confounding factors. In addition, this is also the first study to explore the mediating role of physical activity on the relationship between takeaway frequency and depressive symptoms.
There were several limitations in this study. Firstly, the use of data from a cross-sectional study makes it impossible to establish causality. Secondly, the study was conducted at a single center, suggesting that the findings may not be universally applicable. Thirdly, a significant number of participants were excluded due to invalid IPAQ questionnaire responses. The excluded population was found to have higher PHQ-9 scores, potentially biasing the outcomes. In a sensitivity analysis, we repeated the main analysis after multiple imputations of missing values, yielding similar results and demonstrating the robustness of the findings. Fourthly, the study only captured data on the frequency of takeaway consumption, without collecting information on the reasons for ordering takeaways or the specific food choices made. This limitation prevented a comprehensive examination of the relationship between various aspects of takeaway behavior and mental health. Future research designs in this area could consider the collection of additional data for analysis.
In conclusion, a significant association was found between takeaway frequency and depressive symptoms. Physical activity partially mediated this relationship. Our results highlight the potential negative effect of takeaway consumption on emotional well-being and recommends that stakeholders should monitor the emotional health of frequent takeaway consumers. In addition, the results indicate that increasing physical activity may alleviate the negative impact of frequent takeaway consumption on mood.
Data availability statement
The datasets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Ethics Committee of the National Clinical Medical Research Center, Second Xiangya Hospital, Central South University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
JT: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. RW: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Software, Writing – review & editing. ZS: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. YK: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. PR: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. AG: Writing – review & editing. SH: Data curation, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. QZ: Data curation, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. WW: Data curation, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. MA: Data curation, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. LK: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the STI2030-Major Projects grant from the Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China (grant number: 2021ZD0200700), The Key Project of Technological Innovation and Application Development of Chongqing Science and Technology Bureau (grant number: CSTC2021 jscx-gksb-N0002), Chongqing Excellence Program (grant number: CQYC202101).
Acknowledgments
The authors of this paper would like to acknowledge all those who took part in this study, including the students, volunteers, and all the teachers who helped to collect the information.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1450718/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Du F, Cai H, Zhang Q, Chen Q, Shi H. Microplastics in take-out food containers. J Hazard Mater. (2020) 399:122969. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122969
2. Li C, Mirosa M, Bremer P. Review of online food delivery platforms and their impacts on sustainability. Sustainability. (2020) 12:5528. doi: 10.3390/su12145528
3. Li F, Zhang J. Current consumption and problems of online food delivery of university students-A case study on students of Jiujiang college. J Hubei Univ Econ(Humanit Soc Sci). (2018) 12:40–2. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0975.2018.12.012
4. Meituan Research Institute. Available online at: https://mri.meituan.com/research/home (Accessed 3.12.24).
5. Statistical report on Internet Development in China . Available online at: https://www.cnnic.net.cn/n4/2023/0303/c88-10757.html (Accessed 3.12.24).
6. Survey Data on Consumer Behavior of Online Delivery Platforms in China. Available online at: https://www.iimedia.cn/c1077/97809.html (Accessed 3.12.24).
7. Yuan C, Lv J, VanderWeele TJ. An assessment of health behavior peer effects in Peking University dormitories: a randomized cluster-assignment design for interference. PloS One. (2013) 8:e75009. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0075009
8. Qi Q, Sun Q, Yang L, Cui Y, Du J, Liu H. High nutrition literacy linked with low frequency of take-out food consumption in chinese college students. BMC Public Health. (2023) 23:1132. doi: 10.1186/s12889-023-16078-9
9. Luo M, Wang Q, Yang S, Jia P. Changes in patterns of take-away food ordering among youths before and after COVID-19 lockdown in China: the COVID-19 Impact on Lifestyle Change Survey (COINLICS). Eur J Nutr. (2022) 61:1121–31. doi: 10.1007/s00394-021-02622-z
10. Dai X, Wu L, Hu W. Nutritional quality and consumer health perception of online delivery food in the context of China. BMC Public Health. (2022) 22:2132. doi: 10.1186/s12889-022-14593-9
11. Kang M, Kim DW, Lee H, Lee YJ, Jung HJ, Paik HY, et al. The nutrition contribution of dietary supplements on total nutrient intake in children and adolescents. Eur J Clin Nutr. (2016) 70:257–61. doi: 10.1038/ejcn.2015.156
12. Panel study of Chinese university students . Available online at: http://www.pscus.cn/detail.jsp (Accessed 3.12.24).
13. Oddy WH, Allen KL, Trapp GSA, Ambrosini GL, Black LJ, Huang RC, et al. Dietary patterns, body mass index and inflammation: Pathways to depression and mental health problems in adolescents. Brain Behav Immun. (2018) 69:428–39. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2018.01.002
14. Smith KJ, McNaughton SA, Gall SL, Blizzard L, Dwyer T, Venn AJ. Takeaway food consumption and its associations with diet quality and abdominal obesity: a cross-sectional study of young adults. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. (2009) 6:29. doi: 10.1186/1479-5868-6-29
15. Pearce M, Garcia L, Abbas A, Strain T, Schuch FB, Golubic R, et al. Association between physical activity and risk of depression: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Psychiatry. (2022) 79:550–9. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2022.0609
16. Chen S, Chiu H, Xu B, Ma Y, Jin T, Wu M, et al. Reliability and validity of the PHQ-9 for screening late-life depression in Chinese primary care. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. (2010) 25:1127–33. doi: 10.1002/gps.v25:11
17. Liu ZW, Yu Y, Hu M, Liu HM, Zhou L, Xiao SY. PHQ-9 and PHQ-2 for screening depression in chinese rural elderly. PloS One. (2016) 11:e0151042. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0151042
18. Wang W, Bian Q, Zhao Y, Li X, Wang W, Du J, et al. Reliability and validity of the Chinese version of the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9) in the general population. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. (2014) 36:539–44. doi: 10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2014.05.021
19. Craig CL, Marshall AL, Sjöström M, Bauman AE, Booth ML, Ainsworth BE, et al. International physical activity questionnaire: 12-country reliability and validity. Med Sci Sports Exerc. (2003) 35:1381–95. doi: 10.1249/01.MSS.0000078924.61453.FB
20. Qu Nn, Li K. Study on the reliability and validity of international physical activity questionnaire (Chinese Vision, IPAQ). Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. (2004) 25:265–8. doi: 10.3760/j.issn:0254-6450.2004.03.021
21. Kim SY, Jeon SW, Shin DW, Oh KS, Shin YC, Lim SW. Association between physical activity and depressive symptoms in general adult populations: An analysis of the dose-response relationship. Psychiatry Res. (2018) 269:258–63. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2018.08.076
22. Macfarlane DJ, Lee CCY, Ho EYK, Chan KL, Chan DTS. Reliability and validity of the Chinese version of IPAQ (short, last 7 days). J Sci Med Sport. (2007) 10:45–51. doi: 10.1016/j.jsams.2006.05.003
23. Kamolthip R, Yang YN, Latner JD, O’Brien KS, Chang YL, Lin CC, et al. The effect of time spent sitting and excessive gaming on the weight status, and perceived weight stigma among Taiwanese young adults. Heliyon. (2023) 9:e14298. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e14298
24. Zhu L, Hou J, Zhou B, Xiao X, Wang J, Jia W. Physical activity, problematic smartphone use, and burnout among Chinese college students. PeerJ. (2023) 11:e16270. doi: 10.7717/peerj.16270
25. Hayes AF. Beyond baron and kenny: statistical mediation analysis in the new millennium. Commun Monogr. (2009) 76:408–20. doi: 10.1080/03637750903310360
26. Hayes AF, Rockwood NJ. Regression-based statistical mediation and moderation analysis in clinical research: Observations, recommendations, and implementation. Behav Res Ther. (2017) 98:39–57. doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2016.11.001
27. Shakya PR, Melaku YA, Page A, Gill TK. Association between dietary patterns and adult depression symptoms based on principal component analysis, reduced-rank regression and partial least-squares. Clin Nutr. (2020) 39:2811–23. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2019.12.011
28. Frederic MK, Guo X, Zhao X, Nzudie HLF, Tillotson MR, Zhou Y, et al. Evaluating the water footprint and nutritional quality of takeaway dishes for selected large cities in China. Sci Total Environ. (2024) 911:168632. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.168632
29. Mahawar N, Jia SS, Korai A, Wang C, Allman-Farinelli M, Chan V, et al. Unhealthy food at your fingertips: cross-sectional analysis of the nutritional quality of restaurants and takeaway outlets on an online food delivery platform in New Zealand. Nutrients. (2022) 14:4567. doi: 10.3390/nu14214567
30. Firth J, Gangwisch JE, Borisini A, Wootton RE, Mayer EA. Food and mood: how do diet and nutrition affect mental wellbeing? BMJ. (2020) 369:m2382. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m2382
31. Grajek M, Krupa-Kotara K, Białek-Dratwa A, Sobczyk K, Grot M, Kowalski O, et al. Nutrition and mental health: A review of current knowledge about the impact of diet on mental health. Front Nutr. (2022) 9:943998. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.943998
32. Hernandez LM, Xu EG, Larsson HCE, Tahara R, Maisuria VB, Tufenkji N. Plastic teabags release billions of microparticles and nanoparticles into tea. Environ Sci Technol. (2019) 53:12300–10. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.9b02540
33. Zhou X, Wang J, Ren J. Analysis of microplastics in takeaway food containers in China using FPA-FTIR whole filter analysis. Molecules. (2022) 27:2646. doi: 10.3390/molecules27092646
34. Garcia MA, Liu R, Nihart A, El Hayek E, Castillo E, Barrozo ER, et al. Quantitation and identification of microplastics accumulation in human placental specimens using pyrolysis gas chromatography mass spectrometry. Toxicol Sci. (2024) 199(1):kfae021. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfae021
35. Nel A, Xia T, Mädler L, Li N. Toxic potential of materials at the nanolevel. Science. (2006) 311:622–7. doi: 10.1126/science.1114397
36. van Raamsdonk LWD, van der Zande M, Koelmans AA, Hoogenboom RLAP, Peters RJB, Groot MJ, et al. Current insights into monitoring, bioaccumulation, and potential health effects of microplastics present in the food chain. Foods. (2020) 9:72. doi: 10.3390/foods9010072
37. Tang J, Ni X, Zhou Z, Wang L, Lin S. Acute microplastic exposure raises stress response and suppresses detoxification and immune capacities in the scleractinian coral Pocillopora damicornis. Environ pollut. (2018) 243:66–74. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.08.045
38. Wright SL, Kelly FJ. Plastic and human health: A micro issue? Environ Sci Technol. (2017) 51:6634–47. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.7b00423
39. Lu L, Luo T, Zhao Y, Cai C, Fu Z, Jin Y. Interaction between microplastics and microorganism as well as gut microbiota: A consideration on environmental animal and human health. Sci Total Environ. (2019) 667:94–100. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.380
40. Prata JC, da Costa JP, Lopes I, Duarte AC, Rocha-Santos T. Environmental exposure to microplastics: An overview on possible human health effects. Sci Total Environ. (2020) 702:134455. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134455
41. Shen M, Zhang Y, Zhu Y, Song B, Zeng G, Hu D, et al. Recent advances in toxicological research of nanoplastics in the environment: A review. Environ pollut. (2019) 252:511–21. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.05.102
42. Ait Tayeb AEK, Poinsignon V, Chappell K, Bouligand J, Becquemont L, Verstuyft C. Major depressive disorder and oxidative stress: A review of peripheral and genetic biomarkers according to clinical characteristics and disease stages. Antioxid (Basel). (2023) 12:942. doi: 10.3390/antiox12040942
43. Tickell AM, Rohleder C, Ho N, McHugh C, Jones G, Song YJC, et al. Identifying pathways to early-onset metabolic dysfunction, insulin resistance and inflammation in young adult inpatients with emerging affective and major mood disorders. Early Interv Psychiatry. (2022) 16:1121–9. doi: 10.1111/eip.v16.10
44. Ye Z, Kappelmann N, Moser S, Davey Smith G, Burgess S, Jones PB, et al. Role of inflammation in depression and anxiety: Tests for disorder specificity, linearity and potential causality of association in the UK Biobank. EClinicalMedicine. (2021) 38:100992. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100992
45. Gariépy G, Honkaniemi H, Quesnel-Vallée A. Social support and protection from depression: systematic review of current findings in Western countries. Br J Psychiatry. (2016) 209:284–93. doi: 10.1192/bjp.bp.115.169094
46. Li Y, Bai X, Chen H. Social isolation, cognitive function, and depression among chinese older adults: examining internet use as a predictor and a moderator. Front Public Health. (2022) 10:809713. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.809713
47. Sommerlad A, Marston L, Huntley J, Livingston G, Lewis G, Steptoe A, et al. Social relationships and depression during the COVID-19 lockdown: longitudinal analysis of the COVID-19 Social Study. Psychol Med. (2021) 52(15):1–10. doi: 10.1017/S0033291721000039
48. Smith KJ, Blizzard L, McNaughton SA, Gall SL, Dwyer T, Venn AJ. Takeaway food consumption and cardio-metabolic risk factors in young adults. Eur J Clin Nutr. (2012) 66:577–84. doi: 10.1038/ejcn.2011.202
Keywords: takeaway, mediation effect, depressive symptoms, physical activity, college students
Citation: Tan J, Wang R, Su Z, Kong Y, Ran P, Greenshaw A, Hong S, Zhang Q, Wang W, Ai M and Kuang L (2025) Takeaway food consumption and depressive symptoms in Chinese university students: mediating effects of physical activity. Front. Psychiatry 15:1450718. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1450718
Received: 18 June 2024; Accepted: 23 December 2024;
Published: 16 January 2025.
Edited by:
Wulf Rössler, Charité University Medicine Berlin, GermanyCopyright © 2025 Tan, Wang, Su, Kong, Ran, Greenshaw, Hong, Zhang, Wang, Ai and Kuang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Li Kuang, a3VhbmdsaTAzMDhAMTYzLmNvbQ==
 Jianyu Tan
Jianyu Tan Rui Wang1,2
Rui Wang1,2 Pan Ran
Pan Ran Andrew Greenshaw
Andrew Greenshaw Wo Wang
Wo Wang Ming Ai
Ming Ai Li Kuang
Li Kuang