- 1Department of Psychiatry, Dokkyo Medical University School of Medicine, Tochigi, Japan
- 2The Japanese Association of Neuro-Psychiatric Clinics, Tokyo, Japan
- 3The Japanese Society of Clinical Neuropsychopharmacology, Tokyo, Japan
- 4Department of Neuropsychiatry, Kansai Medical University, Osaka, Japan
- 5Department of Psychiatry, University of Occupational and Environmental Health, Fukuoka, Japan
- 6Department of Neuropsychiatry, St. Marianna University School of Medicine, Kanagawa, Japan
- 7Department of Neuropsychiatry, Keio University School of Medicine, Tokyo, Japan
- 8Department of Neuropsychiatry, Kyorin University School of Medicine, Tokyo, Japan
Background: Bipolar disorder is a psychiatric disorder characterized by mood swings between manic and depressed states that causes psychosocial problems. Cognitive function deteriorates with each recurrence, making it important to maintain remission through continued treatment. Bipolar disorder often co-occurs with alcohol dependence, which is known to lead to decreased treatment adherence and increased suicide risk. However, the real-world clinical determinants of alcohol dependence in outpatients with bipolar disorder in Japan remain unclear.
Methods: We conducted an observational study targeting 2392 patients with bipolar disorder using data from the MUSUBI study, a joint project of the Japanese Association of Neuro-Psychiatric Clinics and the Japanese Society of Clinical Neuropsychopharmacology. After determining the prevalence of alcohol dependence and the sociodemographic characteristics of patients with bipolar disorder, multivariate analysis was performed to identify risk factors for alcohol comorbidity.
Results: The prevalence of alcohol dependence among outpatients with bipolar disorder in this study was 5.7%. The prevalence was 7.6% for males and 3.1% for females. The results of the binomial logistic regression analysis revealed that bipolar I disorder, manic state, comorbidities with other psychiatric disorders, male sex, and suicidal ideation were significantly associated with alcohol dependence. Stratified analysis by gender showed that alcohol dependence was more strongly associated with the presence of suicidal ideation in women than in men.
Limitation: First, because this was an observational study with a cross-sectional design, causal relationships between factors cannot be determined. In addition, this study included outpatients in Japan but lacked information on inpatients. Therefore, it was considered necessary to conduct the study on a larger population in order to generate more robust evidence.
Conclusions: We found that outpatients with bipolar disorder, especially men, had higher rates of alcohol dependence overall than the general population in Japan. In addition, the relationship between alcohol dependence and suicidal ideation was stronger in women than in men with bipolar disorder. There was a strong association between manic states and alcohol dependence in outpatients with bipolar disorder. These results are useful to clinicians because they reinforce real-world clinical evidence for the treatment of bipolar disorder and co-occurring alcohol dependence.
Introduction
Bipolar disorder is a psychiatric disorder characterized by mood swings between manic and depressed states that significantly negatively impact cognitive and social functioning (1). The estimated lifetime incidence is 0.6% for bipolar I disorder and 0.4% for bipolar II disorder (2). The average age of onset is 18 years for bipolar I disorder and 20 years for bipolar II disorder, with nearly equal prevalence among males and females (2). Notably, relatives of adults with bipolar I disorder have a tenfold risk of onset, indicating a genetic influence on the disorder (3). Furthermore, individuals with bipolar disorder have a 20-30 times greater risk of suicide than the general population (4). Additionally, the co-occurrence of alcohol problems in outpatients with bipolar disorder has been noted to increase suicidal behavior (5). Therefore, it is crucial to provide support for alcohol dependence for outpatients with bipolar disorder while paying attention to suicidal ideation. Given that functional impairment worsens with each recurrence of bipolar disorder, maintaining remission of mood swings through appropriate psychotherapy and pharmacotherapy to achieve functional recovery is important (6). However, previous studies have reported that comorbid substance use disorders reduce treatment adherence in patients with bipolar disorder and adversely affect patients’ prognosis (7). According to the latest WHO report released on June 25, 2024, approximately 400 million people, or about 7% of the global population aged 15 and over, suffer from alcohol use disorders, with an estimated 209 million people being alcohol dependent (8). The disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) due to alcohol use are estimated to be 2.3% for women and 8.9% for men, making it the 7th leading risk factor globally (9).
Alcohol is a frequent cause of substance abuse also in Japan, with an estimated 12-month incidence of alcohol dependence reaching 0.9% (10). Furthermore, women are thought to exhibit more severe adverse effects (e.g., cognitive and motor function) with relatively low doses of alcohol than men (11). Despite efforts such as the Healthy Japan 21 project, which aims to improve lifestyles and reduce alcohol consumption, the percentage of women who are habitual drinkers has increased significantly (12). Thus, the relationship between alcohol problems and bipolar disorder has significant public health implications in Japan. However, the factors associated with bipolar disorder and alcohol dependence in Japan, including sex differences, remain unclear.
A previous study reported that the risk factors for the comorbidity of bipolar disorder and alcohol use disorder in Australia included male sex, youth, and the presence of self-harming behavior (13). Nevertheless, there were several limitations to that study, such as data robustness issues due to small sample sizes, selection bias from a single-center study, and the lack of comparisons of bipolar subtypes (13). Therefore, we attempted to update the existing evidence on factors associated with the comorbidity of bipolar disorder and alcohol dependence with a particular focus on suicidal ideation and gender differences by performing multivariate analyses using a large-scale multicenter dataset.
In Japan, more than 90% of individuals diagnosed with mood disorders receive treatment as outpatients, and approximately half of them is treated at clinics affiliated with the Japanese Association of Neuro-Psychiatric Clinics (JAPC) (14). In this context, collaborative research, known as the MUlticenter treatment SUrvey on BIpolar disorder in Japanese psychiatric clinics (MUSUBI), was conducted by the JAPC and the Japanese Society of Clinical Neuropsychopharmacology (14–18). The aim of the project was to gather evidence for the real-world practical treatment of bipolar disorder in Japan. In this study, we aimed to investigate the prevalence of alcohol dependence among outpatients with bipolar disorder and identify risk factors for alcohol dependence in patients with bipolar disorder using data from the MUSUBI study.
Subjects and methods
Study design and subjects
In the MUSUBI study, a questionnaire was administered at 176 outpatient clinics belonging to the JAPC from September to October 2016. We collected data on outpatients with bipolar disorder who visited each psychiatric clinic from October 1, 2016, to December 31, 2016. The analysis included the baseline data for each patient at the time of the first visit during the study period. The classification of the bipolar subtype was determined one year after the observation baseline to September-October 2017. At each clinic, data were collected for up to 20 patients with bipolar disorder in the order that they visited the clinic (17). Participants were diagnosed with bipolar disorder and alcohol dependence based on the ICD-10 criteria (19). In addition, we classified bipolar I disorder and bipolar II disorder according to the DSM-5 criteria (20).
Study procedures
Clinical psychiatrists were requested to participate in a retrospective medical record survey by filling out a questionnaire on outpatients with bipolar disorder. The questionnaire included the following participant characteristics: age at study entry, age at onset, sex, body mass index (BMI), bipolar subtypes, work status, educational background, mood status, intelligence quotient (IQ), Global Assessment of Functioning (GAF) score, mood stabilizer prescriptions, antidepressant prescriptions, antipsychotic prescriptions, anxiolytic prescriptions, hypnotic prescriptions, rapid cycling, other psychiatric comorbidities, physical comorbidities, psychotic symptoms, suicidal ideation and alcohol dependence.
Statistical analysis
We conducted all statistical analyses using EZR (Saitama Medical Center, Jichi Medical University, Saitama, Japan) (21), which is a user-friendly interface for R (The R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria, version 4.3.0). EZR is a customized version of R Commander (version 2.7-1) that integrates commonly used statistical functions in biostatistics.
We set the two-sided significance level for all statistical tests at 0.05 utilizing the chi-square test and the Mann−Whitney U test to examine differences in demographic and clinical characteristics between patients with and without alcohol dependence. Univariate analyses were conducted to identify demographic and clinical features. To thoroughly explore factors associated with alcohol dependence among patients with bipolar disorder, we employed binomial logistic regression with forced entry to ensure that no potential associations were overlooked. The independent variables included age at study entry, age at onset, sex, BMI, bipolar subtypes, work status, educational background, mood status, IQ, GAF score, mood stabilizer prescription, antidepressant prescriptions, antipsychotic prescriptions, anxiolytic prescriptions, hypnotic prescriptions, rapid cycling, other psychiatric comorbidities, physical comorbidities, psychotic symptoms and suicidal ideation.
Ethics
This research was conducted following the Declaration of Helsinki and the Japanese Ethical Guidelines for Medical and Health Research Involving Human Subjects. Approval for the study protocol was obtained from the institutional review board of the ethics committee of the JAPC and Dokkyo Medical University School of Medicine before the research began. Because this study involved a retrospective examination of medical records, informed consent was waived. Nevertheless, we provided information about the research to allow patients the option to opt out when they wished (17). Our team obtained the necessary administrative permissions and licenses to access the data utilized in this study. The ethics committee of the Japanese Association of Neuro-Psychiatric Clinics set restrictions on data sharing because of potentially identifying or sensitive patient information. Please contact the institutional review board of the ethics committee when requesting data. Contact information for our ethics committee is as follows: The Institutional Review Board of the Ethics Committee of the Japanese Association of Neuro-Psychiatric Clinics; Shibuya-ku, Yoyogi 1-38-2, Tokyo Metropolis, Japan, Postal Code 151–0053, Phone +81-3-3320-1423.
Results
We obtained questionnaire data for 2392 outpatients with bipolar disorder from 176 psychiatric clinics affiliated with the JAPC. The proportion of study participants with alcohol dependence was 5.2% (125/2392). Of these, 7.6% (85/1096) were male and 3.1% (40/1296) were female. The results of the univariate analysis are shown in Table 1. Because of multiple 20 comparisons, a Bonferroni correction was applied that yielded a corrected significance criterion of p <0.0025. According to the univariate analysis of alcohol dependence in bipolar patients, the bipolar subtypes, GAF score, mood status, physical comorbidities, psychotic symptoms, other psychiatric comorbidities, sex and the presence of suicidal ideation were significantly associated with alcohol dependence.
The results of the binomial logistic regression analysis for all participants are shown in Table 2. Our study revealed that outpatients with alcohol dependence and bipolar disorder had a significantly greater proportion of bipolar I disorder (odds ratio [OR] [95% CI] = 1.98 [1.31-2.98], p=0.001; reference factor = bipolar II disorder), manic/hypomanic state (OR = 3.06 [1.52-6.15], p=0.002; reference factor = remission), mixed feature state (OR = 3.46 [1.74-6.89], p<0.001; reference factor = remission), male sex (OR=3.40 [2.20-5.24], p<0.001), other psychiatric comorbidities (OR = 1.89 [1.20-2.98], p=0.006) and suicidal ideation (OR=2.65 [1.59-4.40], p<0.001).
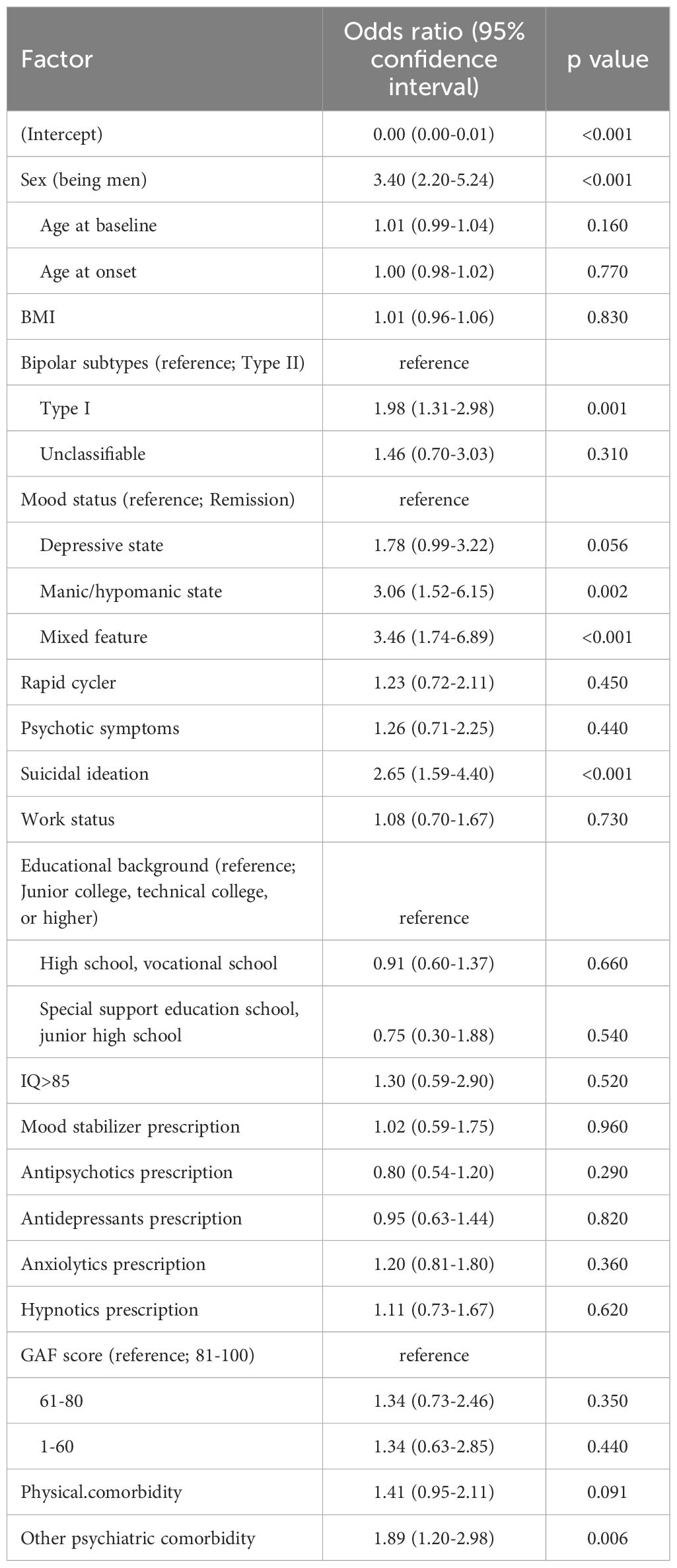
Table 2. Binomial logistic regression analysis of factors associated alcohol dependence among all participants.
Next, we present the results of the multivariate analysis stratified by sex. The results of the binomial logistic regression analysis of factors associated with alcohol dependence among male participants are shown in Table 3. Male patients with alcohol dependence were significantly older at baseline, had a greater proportion of bipolar I disorder (OR= 2.25 [1.35-3.75], p=0.002; reference factor = bipolar II disorder), were in a depressive state (OR= 2.29 [1.13-4.64], p=0.021; reference factor = remission), were in a manic/hypomanic state (OR= 2.71 [1.14-6.43], p=0.023; reference factor = remission), were in a mixed feature state (OR= 2.78 [1.11-6.95], p=0.028; reference factor = remission), had other psychiatric comorbidities (OR = 1.95 [1.08-3.52], p=0.027) and had suicidal ideation (OR=2.13 [1.07-4.24], p=0.030).
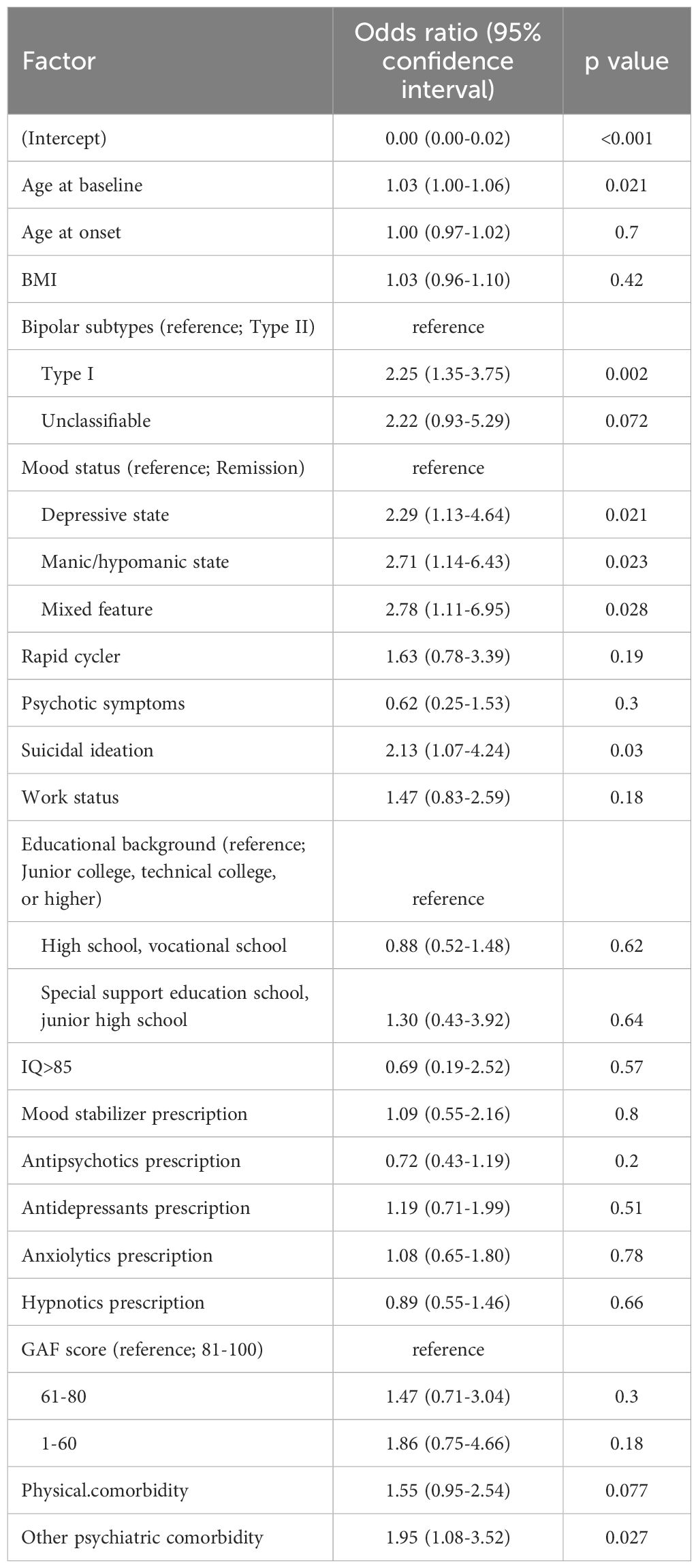
Table 3. Binomial logistic regression analysis of factors associated alcohol dependence among male participants.
The results of the binomial logistic regression analysis of factors associated with alcohol dependence among female participants are shown in Table 4. Female patients with alcohol dependence had significant psychotic symptoms (OR=3.33 [1.45-7.64], p=0.005) and suicidal ideation (OR=2.93 [1.27-6.77], p=0.012). Suicidal ideation was found to be a factor associated with alcohol dependence in both genders, with a stronger correlation observed in women than in men. (odds ratio: 2.13 for men and 2.93 for women).
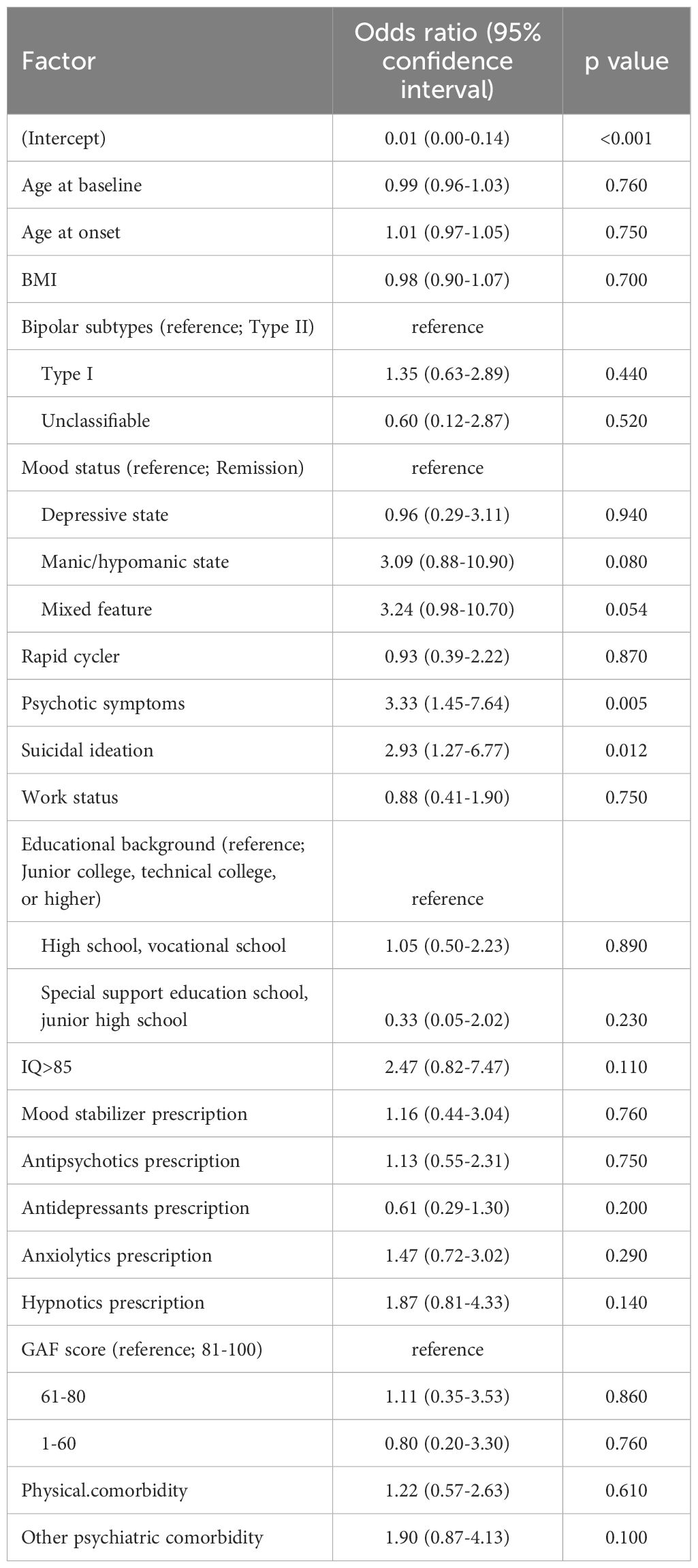
Table 4. Binomial logistic regression analysis of factors associated alcohol dependence among female participants.
Discussion
In this study, we found that the prevalence of alcohol dependence among patients with bipolar disorder was 5.2%. This is notably higher than the prevalence of alcohol dependence in the general population (22). A significant result of this study was the identification of suicidal ideation as an important factor associated with alcohol dependence in outpatients with bipolar disorder. This finding remained consistent even when stratified by sex. Previous research has shown that the co-occurrence of alcohol use disorders in individuals with bipolar disorder increases the rate of suicide attempts (23). The lifetime suicide attempt rate in bipolar disorder patients with comorbid substance use disorders is reported to be 39.5%, compared to 23.8% in those without comorbidities (24). Furthermore, bipolar disorder patients with comorbid substance use disorders have a higher mortality rate, with alcohol problems particularly affecting this increase in the mortality rate (25). In fact, 16.5% of men and 14.4% of women with bipolar disorder and comorbid alcohol substance use disorders have been reported to have completed suicide (26). Regarding the prevalence of suicide, the presence of alcohol use disorder in individuals with bipolar disorder increases the suicide completion rate by 1.46 times in men and 3.11 times in women; this is a particularly noticeable effect on the increase in suicide completion among women (26). Our study revealed that women with comorbid alcohol dependence and bipolar disorder had greater odds ratios for suicidal ideation than men did (suicidal ideation associated with alcohol dependence; male participants OR = 2.13, female participants OR = 2.93). Targeted interventions that address gender differences in alcohol dependence could prevent suicide in patients with bipolar disorder.
The association between sex differences and alcohol dependence is an important issue not only in bipolar patients but also in the general population. Previous research has shown that in Asian countries, the co-occurrence of substance use disorders is more common in men (27). However, the proportion of young women with drinking habits in Japan is increasing annually (12). The Japanese government has explicitly addressed alcohol issues and emphasized the health risks associated with drinking as part of its social policy called “Health Japan 21” (12). Therefore, it is important to raise awareness of these issues throughout society. Previous studies have reported that the prevalence of current alcohol dependence in Japan is 1.0% in men and 0.1% in women, indicating a gender difference of approximately tenfold (28). However, we found that the prevalence of alcohol dependence in individuals with bipolar disorder was 7.6% in men and 3.1% in women, showing an overall increase in the prevalence of alcohol dependence and a reduction in the gender gap. It appears that being affected by bipolar disorder increases the risk of alcohol dependence in women more than men compared to the general population. Given the increasing prevalence of drinking habits among women in the general population in Japan, the need for continued appropriate education and support for alcohol issues has become evident.
Interestingly, the bipolar subtype was also significantly associated with alcohol dependence. Compared to bipolar II disorder, bipolar I disorder has a greater prevalence of alcohol dependence. Bipolar I disorder is defined as more severe manic episodes than bipolar II disorder based on diagnostic criteria (20). Additionally, alcohol consumption by patients with bipolar disorder can increase the risk of manic episodes (29). In our study, mood status was also found to be associated with alcohol dependence. Specifically, a statistically significant association was observed between a manic/hypomanic state or mixed features and alcohol dependence compared to remission overall. However, no significant association was observed for depressive state. According to treatment guidelines, pharmacotherapy for acute mania includes lithium and valproate as first-line mood stabilizers (30). Quetiapine, asenapine, and paliperidone have also been reported to be effective for treating and preventing acute mania (30). For this reason, it appears that individualized pharmacotherapy strategies based on the guidelines with a focus on manic states might reduce the risk of alcohol dependence in patients with bipolar disorder.
As an explanation for the relationship between alcohol dependence and mood disorders, the “self-medication hypothesis” has garnered increasing attention (31). Alcohol, a substance that temporarily relieves anxiety or induces euphoria, is often used as a means of coping with stress for escape purposes (32). It is also suggested that alcohol, due to its sedative effects, may be consumed in an attempt to alleviate mood disturbances caused by excessive euphoria (33). However, alcohol has both physical and psychological dependence effects, which can worsen the prognosis of patients with bipolar disorder. Therefore, evidence suggests that it is essential to maintain remission of bipolar disorder through appropriate pharmacotherapy, which primarily consists of mood stabilizers and antipsychotics (30). It is also important to not overlook alcohol dependence in the treatment of bipolar disorder because social problems may manifest in the context of alcohol problems, leading to secondary mood declines (34). Thus, it is crucial to address alcohol issues from a psychosocial perspective in the treatment of outpatients with bipolar disorder.
The key point is that integrated treatment of alcohol dependence and bipolar disorder contributes to maintaining remission of psychiatric symptoms in patients (35). This is because alcohol dependence is one of the factors that worsens the symptoms of bipolar disorder and leads to poor treatment outcomes (36). Similar to our research findings, alcohol dependence is also known to increase the risk of mood episodes (especially mania and mixed states) in patients with bipolar disorder (37). Interestingly, it has been reported that not only medications specifically for alcohol dependence, such as naltrexone and acamprosate, but also medications for bipolar disorder, such as lithium carbonate and valproic acid, can help improve alcohol-related issues in patients with both conditions (37, 38). Successful treatment of alcohol dependence may reduce the risk of relapse and suicide in patients with bipolar disorder, and an approach combining individualized pharmacotherapy and psychosocial support is considered particularly effective (36).
Previous studies have emphasized that the treatment setting for comorbid cases of bipolar disorder and alcohol dependence primarily focuses on outpatient care (22). However, patients with comorbid bipolar disorder and alcohol dependence are more likely to miss outpatient appointments and have poor medication adherence. Even with treatment, patients with alcohol dependence are reported to have short-term remission rates limited to 20-50% (39, 40). Those who do not receive support have even higher rates of relapse (41). Due to the strong association of alcohol dependence with social isolation (42), achieving recovery requires not only pharmacotherapy and individual psychotherapy but also group psychotherapy facilitated by self-help groups and collaboration involving social workers. Furthermore, since comorbid substance use disorders have been reported to increase the risk of hospitalization for patients with bipolar disorder (43), collaborative care between medical facilities with inpatient capabilities and psychiatric clinics is essential to avoid crisis.
This study revealed a significant association between the presence of psychotic symptoms and alcohol dependence in women with bipolar disorder. Alcohol use disorder has been identified as a vulnerability factor for psychotic symptoms, particularly hallucinations, in individuals with bipolar disorder (44). The comorbidity of psychotic symptoms is associated with greater severity and affects subsequent functional outcomes. Compared with men, women are reported to develop alcohol problems when they consume even small amounts of alcohol, and they are at greater risk for binge drinking, suggesting the need for gender-specific interventions for alcohol dependence (45). Additionally, women have a higher incidence of bipolar disorder during the perinatal period (46). During this time, the comorbidity of alcohol dependence may increase the risk of fetal alcohol spectrum disorder (47) and child abuse (48), potentially causing adverse effects not only for the individual but also for children. Therefore, gender-specific approaches to addressing bipolar disorder and alcohol dependence are important.
This study has several limitations. First, because this was an observational study with a cross-sectional design, causal relationships between factors cannot be determined. In addition, this study included outpatients in Japan but lacked information on inpatients. Thus, excluding inpatient populations who may have more severe comorbidities, limiting the generalizability to all individuals with bipolar disorder. Moreover, this study included only clinics affiliated with the JAPC, which may have introduced selection bias. Patient selection was not random but rather retrospective, which may also have introduced selection bias. The reliance on retrospective data from medical records may introduce bias, as the study lacks control over data accuracy and completeness. Additionally, the tendency toward alcohol dependence in this study was not quantitatively assessed for severity. To establish more robust evidence in the future, it is necessary to stratify the level of alcohol dependence using assessment criteria such as the Addiction Severity Index (49) and to more accurately assess risk factors for comorbid alcohol dependence and bipolar disorder. The study uses binomial logistic regression on a large sample size of participants, but the absence of a validation cohort to cross-check findings could raise concerns about model overfitting. The study also found that other psychiatric comorbidities were significantly associated with alcohol dependency, but the sample size was insufficient for stratified analysis of each psychiatric comorbidities (e.g., attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, panic disorder, personality disorder). Therefore, it was considered necessary to conduct the study on a larger population in order to generate more robust evidence.
Conclusions
We found that outpatients with bipolar disorder had higher rates of alcohol dependence overall than the general population in Japan, especially among males. In addition, the relationship between substance use disorder and suicidal ideation was stronger in women than in men with bipolar disorder. There was also a strong association between manic states and alcohol dependence in outpatients with bipolar disorder. These results are useful to clinicians because they reinforce real-world clinical evidence for the treatment of bipolar disorder and co-occurring alcohol dependence.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the institutional review board of the ethics committee of the Japanese Association of Neuro-Psychiatric Clinics and Dokkyo Medical University School of Medicine. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The ethics committee/institutional review board waived the requirement of written informed consent for participation from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin because this study involved a retrospective examination of medical records. Nevertheless, we provided information about the research to allow patients the option to opt out when they wished.
Author contributions
KT: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. NS: Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. NA: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. YK: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. YW: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. KM: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. TA: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. KE: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. EK: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. SH: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. EG: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. HU: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. MK: Writing – review & editing. RY: Writing – review & editing. AN: Writing – review & editing. TK: Writing – review & editing. TT: Writing – review & editing. KW: Writing – review & editing. NY: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by a Ken Tanaka Memorial Research Grant (grant numbers: 2016–2, 2017–4). The funder had no role in the study design, the data collection and analysis, the decision to publish, or the preparation of the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the following psychiatrists belonging to the Japanese Association of Neuro-Psychiatric Clinics: Dr. Kazunori Otaka, Dr. Satoshi Terada, Dr. Tadashi Ito, Dr. Munehide Tani, Dr. Atsushi Satomura, Dr. Hiroshi Sato, Dr. Hideki Nakano, Dr. Yoichi Nakaniwa, Dr. Eiichi Hirayama, Dr. Keiichi Kobatake, Dr. Koji Tanaka, Dr. Mariko Watanabe, Dr. Shiguyuki Uehata, Dr. Asana Yuki, Dr. Nobuko Akagaki, Dr. Michie Sakano, Dr. Akira Matsukubo, Dr. Yukihisa Kibota, Dr. Yasuyuki Inada, Dr. Hiroshi Oyu, Dr. Tsuneo Tsubaki, Dr. Tatsuji Tamura, Dr. Shigeki Akiu, Dr. Atsuhiro Kikuchi, Dr. Keiji Sato, Dr. Toshihiko Lee, Dr. Kazuyuki Fujita, Dr. Fumio Handa, Dr. Hiroyuki Karasawa, Dr. Kazuhiro Nakano, Dr. Kazuhiro Omori, Dr. Seiji Tagawa, Dr. Daisuke Maruno, Dr. Hiroaki Furui, Dr. You Suzuki, Dr. Takeshi Fujita, Dr. Yukimitsu Hoshino, Dr. Kikuko Ota, Dr. Akira Itami, Dr. Kenichi Goto, Dr. Norio Okamoto, Dr. Yoshiaki Yamano, Dr. Kiichiro Koshimune, Dr. Junko Matsushita, Dr. Takatsugu Nakayama, Dr. Kazuyoshi Takamuki, Dr. Nobumichi Sakamoto, Dr. Miho Shimizu, Dr. Muneo Shimura, Dr. Norio Kawase, Dr. Ryouhei Takeda, Dr. Takuya Hirota, Dr. Hideko Fujii, Dr. Riichiro Narabayashi, Dr. Yutaka Fujiwara, Dr. Junkou Sato, Dr. Kazu Kobayashi, Dr. Yuko Urabe, Dr. Miyako Oguru, Dr. Osamu Miura, Dr. Yoshio Ikeda, Dr. Hidemi Sakamoto, Dr. Yosuke Yonezawa, Dr. Makoto Nakamura, Dr. Yoichi Takei, Dr. Toshimasa Sakane, Dr. Kiyoshi Oka, Dr. Kyoko Tsuda, Dr. Yasushi Furuta, Dr. Yoshio Miyauchi, Dr. Keizo Hara, Dr. Misako Sakamoto, Dr. Shigeki Masumoto, Dr. Yasuhiro Kaneda, Dr. Yoshiko Kanbe, Dr. Masayuki Iwai, Dr. Naohisa Waseda, Dr. Nobuhiko Ota, Dr. Takahiro Hiroe, Dr. Ippei Ishii, Dr. Hideki Koyama, Dr. Terunobu Otani, Dr. Osamu Takatsu, Dr. Takashi Ito, Dr. Norihiro Marui, Dr. Toru Takahashi, Dr. Tetsuro Oomori, Dr. Toshihiko Fukuchi, Dr. Kazumichi Egashira, Dr. Shigemitsu Hayashi, Dr. Kiyoshi Kaminishi, Dr. Ryuichi Iwata, Dr. Satoshi Kawaguchi, Dr. Kazuko Miyauchi, Dr. Yoshinori Morimoto, Dr. Kunihiko Kawamura, Dr. Hirohisa Endo, Dr. Yasuo Imai, Dr. Eri Kohno, Dr. Aki Yamamoto, Dr. Naomi Hasegawa, Dr. Sadamu Toki, Dr. Hideyo Yamada, Dr. Hiroyuki Taguchi, Dr. Hiroshi Yamaguchi, Dr. Hiroki Ishikawa, Dr. Sakura Abe, Dr. Kazuhiro Uenoyama, Dr. Kazunori Koike, Dr. Mikako Oyama, Dr. Yoshiko Kamekawa, Dr. Michihito Matsushima, Dr. Ken Ueki, Dr. Sintaro Watanabe, Dr. Tomohide Igata, Dr. Yoshiaki Higashitani, Dr. Eiichi Kitamura, Dr. Junko Sanada, Dr. Takanobu Sasaki, Dr. Kazuko Eto, Dr. Ichiro Nasu, Dr. Kenichiro Sinkawa, Dr. Yukio Oga, Dr. Michio Tabuchi, Dr. Daisuke Tsujimura, Dr. Tokunai Kataoka, Dr. Kyohei Noda, Dr. Nobuhiko Imato, Dr. Ikuko Nitta, Dr. Yoshihiro Maruta, Dr. Satoshi Seura, Dr. Toru Okumura, Dr. Osamu Kino, Dr. Tomoko Ito, Dr. Ryuichi Iwata, Dr. Wataru Konno, Dr. Toshio Nakahara, Dr. Masao Nakahara, Dr. Hiroshi Yamamura, Dr. Masatoshi Teraoka, EG, Dr. Masato Nishio, Dr. Miwa Mochizuki, Dr. Tsuneo Saitoh, Dr. Tetsuharu Kikuchi, Dr. Chika Higa, Dr. Hiroshi Sasa, Dr. Yuichi Inoue, Dr. Muneyoshi Yamada, Dr. Yoko Fujioka, Dr. Kuniaki Maekubo, Dr. Hiroaki Jitsuiki, Dr. Toshihito Tsutsumi, Dr. Yasumasa Asanobu, Dr. Seiji Inomata, Dr. Kazuhiro Kodama, Dr. Aikihiro Takai, Dr. Asako Sanae, Dr. Shinichiro Sakurai, Dr. Kazuhide Tanaka, Dr. Masahiko Shido, Dr. Haruhisa Ono, Dr. Wataru Miura, Dr. Yukari Horie, Dr. Tetso Tashiro, Dr. Tomohide Mizuno, Dr. Naohiro Fujikawa, Dr. Hiroshi Terada, Dr. Kenji Taki, Dr. Kyoko Kyotani, Dr. Masataka Hatakoshi, Dr. Katsumi Ikeshita, Dr. Keiji Kaneta, Dr. Ritsu Shikiba, Dr. Tsuyoshi Iijima, Dr. Masaru Yoshimura, NA, Dr. Masumi Ito, Dr. Shunsuke Murata, Dr. Mio Mori, and Dr. Toshio Yokouchi.
Conflict of interest
YK has received consultant fees from Pfizer and Meiji-Seika Pharma and speaker’s honoraria from Meiji-Seika Pharma, MSD, Eli Lilly, Janssen Pharmaceutical, Dainippon Sumitomo Pharma, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, Yoshitomi Yakuhin, Otsuka Pharmaceutical, Takeda Pharmaceutical, Lundbeck Japan, and Eisai. TA has received speaker’s honoraria from Eli Lilly, Otsuka Pharmaceutical, Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma and Eisai. HU has received manuscript fees or speaker’s honoraria from Eli Lilly, Janssen Pharmaceutical, Meiji Seika Pharma, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, MSD, Otsuka Pharmaceutical, Pfizer, Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma, Takeda Pharmaceutical, and Yoshitomi Yakuhin. KE has received speaker’s honoraria from Eli Lilly, Meiji Seika Pharma, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, MSD, Otsuka Pharmaceutical, Pfizer, Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma, Kyowa, Yoshitomi Yakuhin, and Takeda Pharmaceutical. EK has received speaker’s honoraria from Daiichi Sankyo, Eisai, Eli Lilly, Janssen Pharmaceutical, Kyowa Pharmaceutical, Meiji Seika Pharma, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, MSD, Otsuka Pharmaceutical, Pfizer, Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma, UCB, and Viatris. SH has received manuscript fees or speaker’s honoraria from Eli Lilly, Janssen Pharmaceutical, Kyowa Pharmaceutical, Meiji Seika Pharma, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, Mochida Pharmaceutical, Ono Pharmaceutical, Otsuka Pharmaceutical, Pfizer, Shionogi, Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma, Takeda Pharmaceutical, and Yoshitomi Yakuhin. EG has received manuscript fees or speaker’s honoraria from Eli Lilly, Janssen Pharmaceutical, Meiji Seika Pharma, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, MSD, Otsuka Pharmaceutical, Takeda Pharmaceutical, Eisai, Ono Pharmaceutical, Kyowa Pharmaceutical Industry and Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma. HU has received manuscript fees or speaker’s honoraria from Eli Lilly, Janssen Pharmaceutical, Kyowa Pharmaceutical, Meiji Seika Pharma, Otsuka Pharmaceutical, Pfizer, Shionogi, Dainippon Sumitomo Pharma, Takeda Pharmaceutical, Lundbeck Japan and Yoshitomi Yakuhin. MK has received grant funding from the Japanese Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare, the Japan Society for the Pro- motion of Science, SENSHIN Medical Research Foundation, the Japan Research Foundation for Clinical Pharmacology and the Japanese Society of Clinical Neuropsychopharmacology and speaker’s honoraria from Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma, Otsuka, Meiji-Seika Pharma, Eli Lilly, MSD K.K., Pfizer, Janssen Pharmaceutical, Shionogi, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, Takeda Pharmaceutical, Lundbeck and Ono Pharmaceutical and participated in an advisory/review board for Otsuka, Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma, Shionogi and Boehringer Ingelheim. RY has received speaker’s honoraria from Eli Lilly, Dainippon Sumitomo, Otsuka, and Esai. AN has received speaker’s honoraria from Pfizer, Eli Lilly, Otsuka, Janssen Pharmaceutical, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, Mochida, Dainippon Sumitomo and NTT Docomo, and participated in an advisory board for Takeda, Meiji Seika, Tsumura and Yoshitomi Yakuhin. TK has received consultant fees from Takeda Pharmaceutical and the Center for Cognitive Behavioral Therapy and Training. TT has received consultant fees from Pfizer and speaker’s honoraria from Eli Lilly, Meiji- Seika Pharma, MSD, Janssen Pharmaceutical, Dainippon Sumitomo Pharma, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, Yoshitomi Yakuhin, Mochida Pharmaceutical, Otsuka Pharmaceutical, Kyowa Pharmaceutical, and Takeda Pharmaceutical. KW has received manuscript fees or speaker’s honoraria from Daiichi Sankyo, Eisai, Eli Lilly, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen Pharmaceutical, Kyowa Pharmaceutical, Meiji Seika Pharma, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, MSD, Otsuka Pharmaceutical, Pfizer, Shionogi, Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma, Takeda Pharmaceutical, and Yoshitomi Yakuhin, has received research/grant support from Daiichi Sankyo, Eisai, MSD, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, Meiji Seika Pharma, Otsuka Pharmaceutical, Pfizer, Shionogi, Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma, Takeda Pharmaceutical, and is a consultant for Boehringer Ingelheim, Daiichi Sankyo, Eisai, Eli Lilly, Kyowa Pharmaceutical, Lundbeck Japan, Otsuka Pharmaceutical, Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma, Taisho Toyama Pharmaceutical, Takeda Pharmaceutical, and Viatris. NY-F has received grant/research support or honoraria from, and received speaker’s honoraria of Dainippon-Sumitomo Pharma, Mochida Pharmaceutical, MSD, and Otsuka Pharmaceutical.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. McIntyre RS, Berk M, Brietzke E, Goldstein BI, López-Jaramillo C, Kessing LV, et al. Bipolar disorders. Lancet. (2020) 396:1841–56. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31544-0
2. Merikangas KR, Jin R, He JP, Kessler RC, Lee S, Sampson NA, et al. Prevalence and correlates of bipolar spectrum disorder in the world mental health survey initiative. Arch Gen Psychiatry. (2011) 68:241–51. doi: 10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2011.12
3. Barnett JH, Smoller JW. The genetics of bipolar disorder. Neuroscience. (2009) 164:331–43. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.03.080
4. Miller JN, Black DW. Bipolar disorder and suicide: a review. Curr Psychiatry Rep. (2020) 22:1–10. doi: 10.1007/s11920-020-1130-0
5. Oquendo MA, Currier D, Liu S-M, Hasin DS, Grant BF, Blanco C. Increased risk for suicidal behavior in comorbid bipolar disorder and alcohol use disorders: results from the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions (NESARC). J Clin Psychiatry. (2010) 71:902. doi: 10.4088/JCP.09m05198gry
6. Lewandowski KE, Cohen BM, Ongur D. Evolution of neuropsychological dysfunction during the course of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Psychol Med. (2011) 41:225–41. doi: 10.1017/S0033291710001042
7. Jónsdóttir H, Opjordsmoen S, Birkenaes AB, Simonsen C, Engh JA, Ringen PA, et al. Predictors of medication adherence in patients with schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica. (2013) 127:23–33. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.2012.01911.x
8. World Health Organization. Global status report on alcohol and health and treatment of substance use disorders. Geneva: World Health Organization (2024).
9. GBD 2016 Alcohol Collaborators. Alcohol use and burden for 195 countries and territories, 1990-2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet. (2018) 392:1015–35. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31310-2
10. Ishikawa H, Kawakami N, Kessler RC, World Mental Health Japan Survey C. Lifetime and 12-month prevalence, severity and unmet need for treatment of common mental disorders in Japan: results from the final dataset of World Mental Health Japan Survey. Epidemiology and psychiatric sciences. Epidemiol Psychiatr Sci (2016) 25(3):217–29. doi: 10.1017/S2045796015000566
11. Nolen-Hoeksema S. Gender differences in risk factors and consequences for alcohol use and problems. Clin Psychol Review. (2004) 24:981–1010. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2004.08.003
12. Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. The second term of Health Japan 21: final evaluation (2022). Available online at: https://www.mhlw.go.jp/content/10904750/000998787.pdf (Accessed April 11 2024).
13. Xia Y, Ma D, Perich T, Hu J, Mitchell PB. Demographic and clinical differences between bipolar disorder patients with and without alcohol use disorders. Front Psychiatry. (2020) 11:570574. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2020.570574
14. Tokumitsu K, Yasui-Furukori N, Adachi N, Kubota Y, Watanabe Y, Miki K, et al. Real-world clinical features of and antidepressant prescribing patterns for outpatients with bipolar disorder. BMC Psychiatry. (2020) 20:555. doi: 10.1186/s12888-020-02967-5
15. Kato M, Adachi N, Kubota Y, Azekawa T, Ueda H, Edagawa K, et al. Clinical features related to rapid cycling and one-year euthymia in bipolar disorder patients: A multicenter treatment survey for bipolar disorder in psychiatric clinics (MUSUBI). J Psychiatr Res. (2020) 131:228–34. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2020.09.030
16. Yasui-Furukori N, Adachi N, Kubota Y, Azekawa T, Goto E, Edagawa K, et al. Factors associated with doses of mood stabilizers in real-world outpatients with bipolar disorder. Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci. (2020) 18:599–606. doi: 10.9758/cpn.2020.18.4.599
17. Tsuboi T, Suzuki T, Azekawa T, Adachi N, Ueda H, Edagawa K, et al. Factors associated with non-remission in bipolar disorder: the multicenter treatment survey for bipolar disorder in psychiatric outpatient clinics (MUSUBI). Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. (2020) 16:881–90. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S246136
18. Adachi N, Azekawa T, Edagawa K, Goto E, Hongo S, Kato M, et al. Estimated model of psychotropic polypharmacy for bipolar disorder: Analysis using patients’ and practitioners’ parameters in the MUSUBI study. Hum Psychopharmacol. (2021) 36:e2764. doi: 10.1002/hup.v36.2
19. World Health Organization. International classification of diseases and related health problems, 10th revision. Geneva: World Health Organization (1992).
20. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders: DSM-5. Arlington VA: American Psychiatric Publising (2013).
21. Kanda Y. Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software ‘EZR’ for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transplant. (2013) 48:452–8. doi: 10.1038/bmt.2012.244
22. Grunze H, Schaefer M, Scherk H, Born C, Preuss UW. Comorbid bipolar and alcohol use disorder-A therapeutic challenge. Front Psychiatry. (2021) 12:660432. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.660432
23. Cardoso BM, Sant’Anna MK, Dias VV, Andreazza AC, Ceresér KM, Kapczinski F. The impact of co-morbid alcohol use disorder in bipolar patients. Alcohol. (2008) 42:451–7. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2008.05.003
24. Dalton EJ, Cate-Carter TD, Mundo E, Parikh SV, Kennedy JL. Suicide risk in bipolar patients: the role of co-morbid substance use disorders. Bipolar Disord. (2003) 5:58–61. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-5618.2003.00017.x
25. Hjorthøj C, Østergaard MLD, Benros ME, Toftdahl NG, Erlangsen A, Andersen JT, et al. Association between alcohol and substance use disorders and all-cause and cause-specific mortality in schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and unipolar depression: a nationwide, prospective, register-based study. Lancet Psychiatry. (2015) 2:801–8. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(15)00207-2
26. Yoon Y-H, Chen CM, H-y Yi, Moss HB. Effect of comorbid alcohol and drug use disorders on premature death among unipolar and bipolar disorder decedents in the United States, 1999 to 2006. Compr Psychiatry. (2011) 52:453–64. doi: 10.1016/j.comppsych.2010.10.005
27. Subramanian K, Sarkar S, Kattimani S. Bipolar disorder in Asia: Illness course and contributing factors. Asian J Psychiatry. (2017) 29:16–29. doi: 10.1016/j.ajp.2017.04.009
28. Osaki Y, Kinjo A, Higuchi S, Matsumoto H, Yuzuriha T, Horie Y, et al. Prevalence and trends in alcohol dependence and alcohol use disorders in Japanese adults; results from periodical nationwide surveys. Alcohol Alcoholism. (2016) 51:465–73. doi: 10.1093/alcalc/agw002
29. Gordon-Smith K, Lewis KJS, Vallejo Auñón FM, Di Florio A, Perry A, Craddock N, et al. Patterns and clinical correlates of lifetime alcohol consumption in women and men with bipolar disorder: Findings from the UK Bipolar Disorder Research Network. Bipolar Disord. (2020) 22:731–8. doi: 10.1111/bdi.12905
30. Yatham LN, Kennedy SH, Parikh SV, Schaffer A, Bond DJ, Frey BN, et al. Canadian Network for Mood and Anxiety Treatments (CANMAT) and International Society for Bipolar Disorders (ISBD) 2018 guidelines for the management of patients with bipolar disorder. Bipolar Disord. (2018) 20:97–170. doi: 10.1111/bdi.2018.20.issue-2
31. Khantzian EJ, Albanese MJ. Understanding addiction as self medication. In: Finding hope behind the pain. New York: Rowman & Littlefield Publishers (2008).
32. Tokumitsu K, Sugawara N, Okayasu H, Kawamata Y, Shinozaki M, Sato Y, et al. The relationship of stress coping styles on substance use, depressive symptoms, and personality traits of nurses in higher education institution. Neuropsychopharmacol Rep. (2023) 43:482–95. doi: 10.1002/npr2.12324
33. Azorin J-M, Perret LC, Fakra E, Tassy S, Simon N, Adida M, et al. Alcohol use and bipolar disorders: Risk factors associated with their co-occurrence and sequence of onsets. Drug Alcohol dependence. (2017) 179:205–12. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2017.07.005
34. Boden JM, Fergusson DM. Alcohol and depression. Addiction. (2011) 106:906–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.2010.03351.x
35. Farren CK, Hill KP, Weiss RD. Bipolar disorder and alcohol use disorder: a review. Curr Psychiatry Rep. (2012) 14:659–66. doi: 10.1007/s11920-012-0320-9
36. Salloum IM, Thase ME. Impact of substance abuse on the course and treatment of bipolar disorder. Bipolar Disord. (2000) 2:269–80. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-5618.2000.20308.x
37. Frye MA, Salloum IM. Bipolar disorder and comorbid alcoholism: prevalence rate and treatment considerations. Bipolar Disord. (2006) 8:677–85. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-5618.2006.00370.x
38. Salloum IM, Cornelius JR, Daley DC, Kirisci L, Himmelhoch JM, Thase ME. Efficacy of valproate maintenance in patients with bipolar disorder and alcoholism: a double-blind placebo-controlled study. Arch Gen Psychiatry. (2005) 62:37–45. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.62.1.37
39. Miller WR, Walters ST, Bennett ME. How effective is alcoholism treatment in the United States? J Stud Alcohol. (2001) 62:211–20. doi: 10.15288/jsa.2001.62.211
40. Monahan SC, Finney JW. Explaining abstinence rates following treatment for alcohol abuse: a quantitative synthesis of patient, research design and treatment effects. Addiction. (1996) 91:787–805. doi: 10.1046/j.1360-0443.1996.9167876.x
41. Moos RH, Moos BS. Rates and predictors of relapse after natural and treated remission from alcohol use disorders. Addiction. (2006) 101:212–22. doi: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.2006.01310.x
42. Le TM, Wang W, Zhornitsky S, Dhingra I, Chen Y, Zhang S, et al. The neural processes interlinking social isolation, social support, and problem alcohol use. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. (2021) 24:333–43. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyaa086
43. Hoblyn JC, Balt SL, Woodard SA, Brooks JO 3rd. Substance use disorders as risk factors for psychiatric hospitalization in bipolar disorder. Psychiatr Serv. (2009) 60:50–5. doi: 10.1176/ps.2009.60.1.50
44. Pignon B, Sescousse G, Amad A, Benradia I, Vaiva G, Thomas P, et al. Alcohol use disorder is differently associated with psychotic symptoms according to underlying psychiatric disorders: A general population study. Alcohol Alcohol. (2020) 55:112–20. doi: 10.1093/alcalc/agaa026
45. Erol A, Karpyak VM. Sex and gender-related differences in alcohol use and its consequences: Contemporary knowledge and future research considerations. Drug Alcohol Depend. (2015) 156:1–13. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2015.08.023
46. Masters GA, Hugunin J, Xu L, Ulbricht CM, Moore Simas TA, Ko JY, et al. Prevalence of bipolar disorder in perinatal women: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Psychiatry. (2022) 83:1–23. doi: 10.4088/JCP.21r14045
47. Popova S, Charness ME, Burd L, Crawford A, Hoyme HE, Mukherjee RAS, et al. Fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Nat Rev Dis primers. (2023) 9:11. doi: 10.1038/s41572-023-00420-x
48. Widom CS, Hiller-Sturmhöfel S. Alcohol abuse as a risk factor for and consequence of child abuse. Alcohol Res Health. (2001) 25:52–7.
Keywords: alcohol dependence, bipolar disorder, suicidal ideation, real-world, Japanese
Citation: Tokumitsu K, Sugawara N, Adachi N, Kubota Y, Watanabe Y, Miki K, Azekawa T, Edagawa K, Katsumoto E, Hongo S, Goto E, Ueda H, Kato M, Yoshimura R, Nakagawa A, Kikuchi T, Tsuboi T, Watanabe K and Yasui-Furukori N (2024) Real-world clinical determinants of alcohol dependence in outpatients with bipolar disorder: a multicenter treatment survey for bipolar disorder in psychiatric outpatient clinics with 2,392 participants. Front. Psychiatry 15:1434810. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1434810
Received: 18 May 2024; Accepted: 21 October 2024;
Published: 07 November 2024.
Edited by:
Alfredo B. Cuellar-Barboza, Autonomous University of Nuevo León, MexicoReviewed by:
Ulrich W. Preuss, Martin Luther University of Halle-Wittenberg, GermanyTetsu Tomita, Hirosaki University, Japan
Copyright © 2024 Tokumitsu, Sugawara, Adachi, Kubota, Watanabe, Miki, Azekawa, Edagawa, Katsumoto, Hongo, Goto, Ueda, Kato, Yoshimura, Nakagawa, Kikuchi, Tsuboi, Watanabe and Yasui-Furukori. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Norio Sugawara, bnN1Z2EzQGRva2t5b21lZC5hYy5qcA==
 Keita Tokumitsu
Keita Tokumitsu Norio Sugawara
Norio Sugawara Naoto Adachi
Naoto Adachi Yukihisa Kubota2
Yukihisa Kubota2 Eiichi Katsumoto
Eiichi Katsumoto Masaki Kato
Masaki Kato Reiji Yoshimura
Reiji Yoshimura Atsuo Nakagawa
Atsuo Nakagawa Takashi Tsuboi
Takashi Tsuboi Koichiro Watanabe
Koichiro Watanabe Norio Yasui-Furukori
Norio Yasui-Furukori