- 1Department of Psychosomatic Medicine, People’s Hospital of Deyang City, Deyang, Sichuan, China
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, The First Affiliated Hospital, Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou, China
- 3Department of Psychiatry, Affiliated Brain Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China
- 4Institute of Mental Health, Tianjin Anding Hospital, Mental Health Center of Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin, China
- 5Department of Psychiatry, Fujian Medical University Affiliated Fuzhou Neuropsychiatric Hospital, Fuzhou, Fujian, China
- 6Department of Neurology, Shanghai Renji Hospital, Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China
- 7Department of Biobehavioral Health and Nursing Science, College of Nursing, University of South Carolina, Columbia, SC, United States
- 8Precision Regenerative Medicine Research Centre, Medical Science Division, and State Key Laboratory of Quality Research in Chinese Medicine, Macau University of Science and Technology, Macau, Macao SAR, China
- 9Beijing Huilongguan Hospital, Peking University Huilongguan School of Clinical Medicine, Beijing, China
- 10Department of Psychiatry, Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT, United States
- 11Shanghai Mental Health Center, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China
Objectives: SERINC2 has been associated with alcoholism, bipolar disorder and autism, but the comparability and specificity issues of the findings remain unaddressed. The present study aimed to comprehensively analyze various neuropsychiatric disorders pinpoint the most reliable conditions predisposed by SERINC2.
Methods: A total of 2,187 imputed SNPs across SERINC2 were examined in 1,167,439 subjects from 72 independent cohorts with 18 different neuropsychiatric disorders. SNP-disease associations were tested and then meta-analyzed, followed by FDR correction, to identify significant disease-risk SNPs. Finally, functional studies on the differential SERINC2 mRNA expression in brains and the potential regulatory effects of disease-risk alleles on SERINC2 mRNA expression, gray matter volumes (GMVs) of subcortical structures, cortical surface area (SA) and average thickness (TH) were conducted.
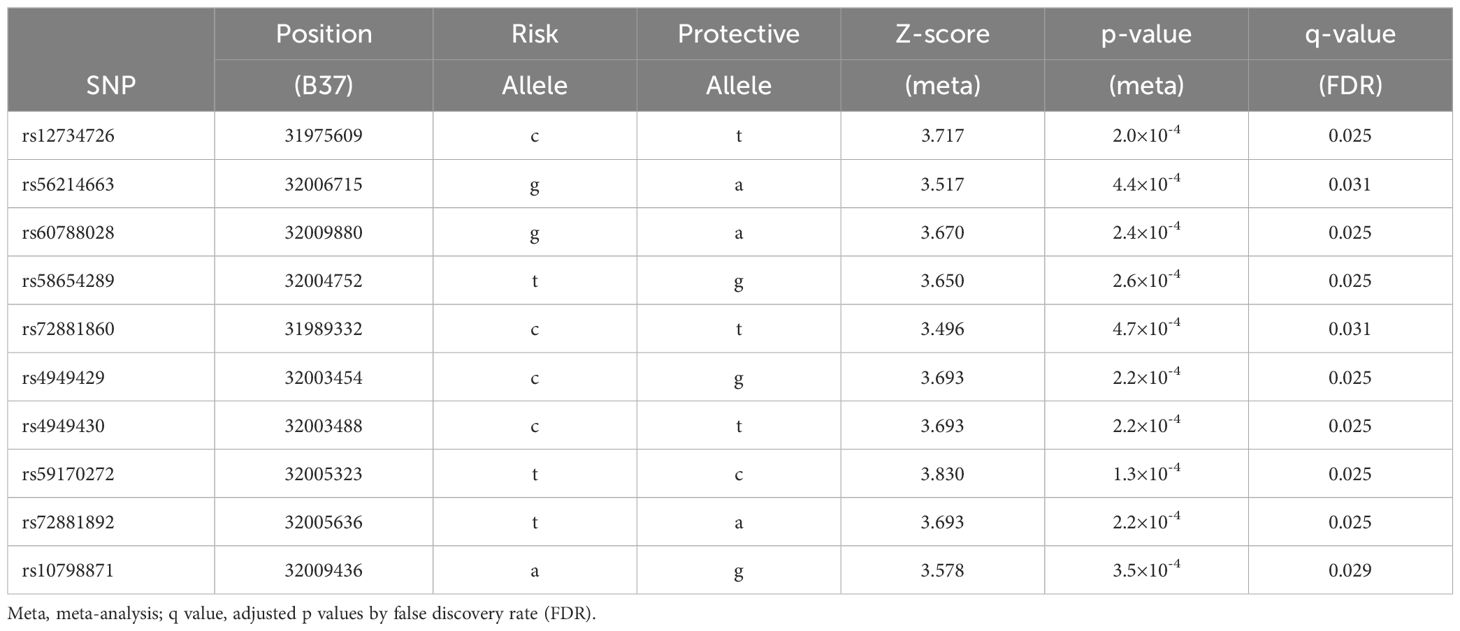
Results: In European descent, alcoholism was most significantly associated with SERINC2 variants (245 SNPs with 5.5×10-8≤p ≤ 0.049 and 4.9×10-5≤q ≤ 0.034) that were largely shared across cocaine dependence, marijuana dependence, nicotine dependence, polysubstance dependence, schizophrenia, OCD, and autism (8.2×10-8≤p ≤ 0.050 and 1.9×10-5≤q ≤ 0.049); in Chinese population, bipolar disorder was also significantly associated with SERINC2 variants (10 SNPs: 1.3×10-4≤p ≤ 4.7×10-4 and 0.025≤q ≤ 0.031). Furthermore, the disease-risk alleles had highly similar regulatory effects on mRNA expression (8.1×10-7≤p ≤ 0.046), subcortical GMVs (7.0×10-4≤p ≤ 0.048) and cortical TH and SA (1.3×10-3≤p ≤ 0.050) in brains across alcoholism, schizophrenia, OCD and autism. The bipolar disorder-risk alleles had these regulatory effects but with different effect patterns. Finally, SERINC2 mRNA was differentially expressed in several brain regions between alcoholism or schizophrenia and controls.
Conclusion: SERINC2 is primarily linked to substance use disorders, schizophrenia, OCD, autism and bipolar disorder, not only statistically but also biologically.
1 Introduction
Several genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have identified serine incorporator 2 gene (SERINC2) as a genome-wide significant risk gene for alcohol dependence in European descent (1–3). Further, the common SERINC2 variants and rare SERINC2 variant constellations have both been reported to be “specific” to risk for alcohol dependence in European descent among 12 diverse neuropsychiatric disorders (1, 4). Following these studies, SERINC2 variants have also been associated to bipolar disorder (BP) in a Chinese population (5) and autism spectrum disorder (ASD) in a Thai population (6). In a family-based sample with multiple BP-affected Chinese pedigrees, whole-exome sequencing identified several rare SERINC2 variants significantly associated with BP, which was confirmed by a larger population-based Chinese cohort (5). In a Thai sample with ASD, microarray experiment identified a rare de novo duplication of a pathogenic copy number variation (CNV) in SERINC2 predisposing risk for ASD (6).
SERINC2 encodes a transmembrane protein that facilitates incorporation of serine into phosphatidylserine and sphingolipids (7). The concentration of sphingolipids is highest in the brain; they play important roles in neural plasticity, signaling and axonal guidance (8). MRI image results show that SERINC2 variants affect the brain structures such as white matter volume of cerebellum (5). These physiological functions support a potential role of SERINC2 in multiple neuropsychiatric, neurodegenerative and neurodevelopmental diseases such as alcoholism, bipolar disorder and autism.
However, whether SERINC2 is most significantly associated with alcoholism, whether SERINC2 is also associated with alcoholism-comorbid disorders, whether SERINC2 is associated with more other neuropsychiatric disorders than alcoholism, BP and ASD, and how to make the findings from different studies with diverse study design, genetic marker sets, and analytic methodologies comparable remains to be answered. To answer these questions, here, we proposed a single study to comprehensively analyze a huge dataset harboring a total of 1,167,439 subjects from 72 independent cohorts with 18 different neuropsychiatric disorders, by standardizing study design, genetic marker sets, and analytic methodologies across phenome.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Subjects
We conducted a comprehensive analysis involving 1,167,439 participants from 72 independent cohorts, each representing one of 18 distinct neuropsychiatric disorders. These disorders spanned a broad spectrum, including schizophrenia (12 cohorts), bipolar disorder (BP; 10 cohorts), major depression (7 cohorts), autism (1 cohort), alcoholism (4 cohorts), nicotine dependence (7 cohorts), cocaine dependence (2 cohorts), marijuana dependence (2 cohorts), opioid dependence (3 cohorts), ADHD (7 cohorts), Alzheimer’s disease (2 cohorts), Parkinson’s disease (4 cohorts), multiple sclerosis (4 cohorts), amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (1 cohort), and stroke (3 cohorts). In particular, in European populations, there were nine separate cohorts dedicated to the study of substance dependence, including two cohorts for alcoholism, one cohort for cocaine dependence, one cohort for marijuana dependence, four cohorts for nicotine dependence, and one cohort for multi-substance dependence; and there were eight separate cohorts for schizophrenia, one for OCD, and one for autism. In Chinese populations, there were two separate cohorts for bipolar disorder. All participants provided written informed consent or assent, and all study procedures were rigorously reviewed and approved by the Human Investigation Committee of the respective institutions.
Supplementary Table S1 provides comprehensive information for each cohort, including sample types, microarray platforms, cohort numbers, dataset names, diagnoses, ethnicities, study designs, sample sizes, grant support numbers, principal investigators, references, and dbGaP accession numbers. Detailed demographic data for these cohorts have been previously published and can be accessed via the PMID# listed in Supplementary Table S1.
2.2 Genotyping and imputation
All study participants underwent genotyping using microarray technologies; however, different cohorts were genotyped using distinct array panels. To ensure consistency in the genetic marker sets across all cohorts, we performed imputation for untyped SNPs across the entire SERINC2 (5’, ORF, and 3’) separately for each ethnicity, utilizing reference panels from the 1000 Genomes Project and HapMap3 Project. The imputation was conducted using the IMPUTE2 program (9), following a well-established protocol from previous literature (10). This rigorous approach ensured the accuracy and quality of the imputed genotype data. For internal cross-validation, each cohort was divided into case and control groups, and imputation was performed separately for cases, controls, and the total group. Only imputed SNPs with high imputation accuracy (INFO > 0.8) across all three groups were included in the following SNP-disease association analysis. After the association analysis, the phase of each imputed risk SNP was re-checked across the groups to further confirm the accuracy of imputation.
2.3 Summary of analytic strategy
Before conducting the association analysis, we thoroughly cleaned the phenotype and genotype data, as previously described (10, 11). The SNP-disease associations within each cohort were analyzed using the PLINK software (12), incorporating appropriate analytical approaches. To account for population stratification and admixture (11), the first 10 principal components (PCs) of ancestry were included as covariates. The p-values from these associations were then combined through meta-analysis to generate combined p-values for each of the 18 disorders across three distinct ethnic groups: Chinese, Europeans, and African Americans. To further ensure the robustness of our findings, we calculated q-values, adjusting the combined p-values using an optimized false discovery rate (FDR) approach (13) to identify significant disease-risk alleles.
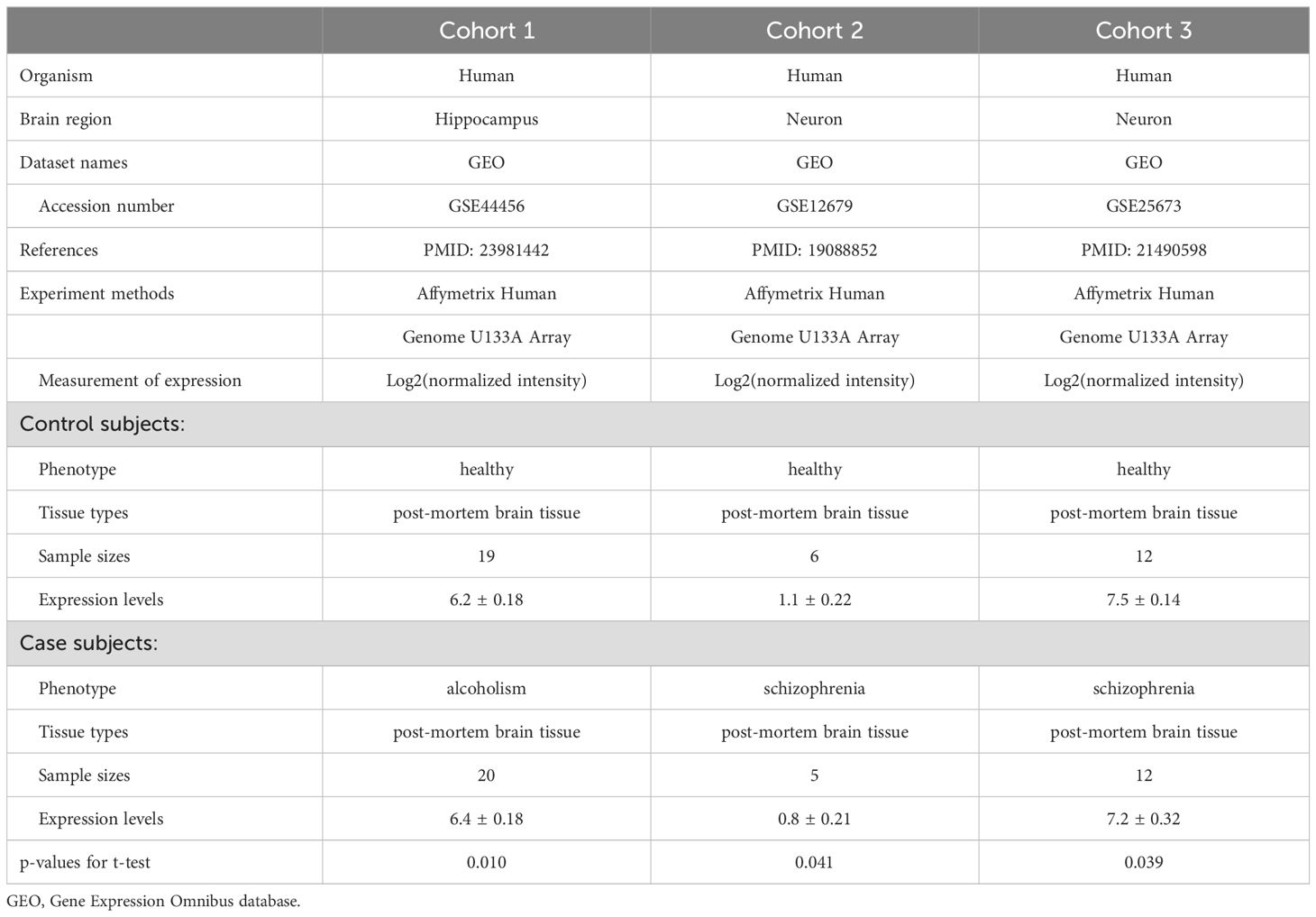
We also examined SERINC2 mRNA expression in postmortem human brains using the GTEx dataset (14) and performed a cis-eQTL analysis to explore the regulatory effects of disease-risk variants on SERINC2 expression. To support the potential functional significance of the SERINC2 risk SNPs, we conducted differential expression analysis of SERINC2 mRNA across 10 independent cohorts of postmortem brain tissues. These cohorts included one for alcoholism (15), one for cocaine dependence (16), one for nicotine dependence (17), two for bipolar disorder (18, 19), and five for schizophrenia (19–22), along with respective controls. Detailed information on these cohorts is available in the published literature (15–22).
Finally, we assessed the regulatory effects of disease-risk alleles on intracranial volume (ICV), subcortical grey matter volumes (GMVs), cortical surface area (SA), and cortical thickness (TH) to explore their potential biological functions. Comprehensive details on the data cleaning procedures, SNP-disease association analysis, differential expression of SERINC2 mRNA, cis-eQTL analysis, and the analysis of regulatory effects on ICV, GMVs, cortical SA, and average TH can be found in the Supplementary Materials and Methods of the study by Guo et al. (2024) (23).
3 Results
3.1 SNP-disease association
3.1.1 SNP-disease association in each cohort
A total of 2,187 imputed SNPs across 5’, open reading frame and 3’ of SERINC2 were examined in all 72 cohorts. Variants numbered from 1 to 313 were found to be nominally associated with a disease in each of the 72 cohorts (8.0×10-11≤p<0.05), except for cohorts #53, #57, and #58 (ADHD) and #71 (Stroke), where no significant associations were observed (Supplementary Table S1).
3.1.2 SNP-disease association for each disease
After meta-analysis of 2,187 SNP-disease associations for each of all 18 neuropsychiatric disorders within the same ethnicity, variants ranging from 2 to 251 remained nominally associated with their respective diseases (meta: 5.9×10-9≤p ≤ 0.028; some data are provided in Table 1), except for Stroke in Europeans (p>0.05; data not shown).
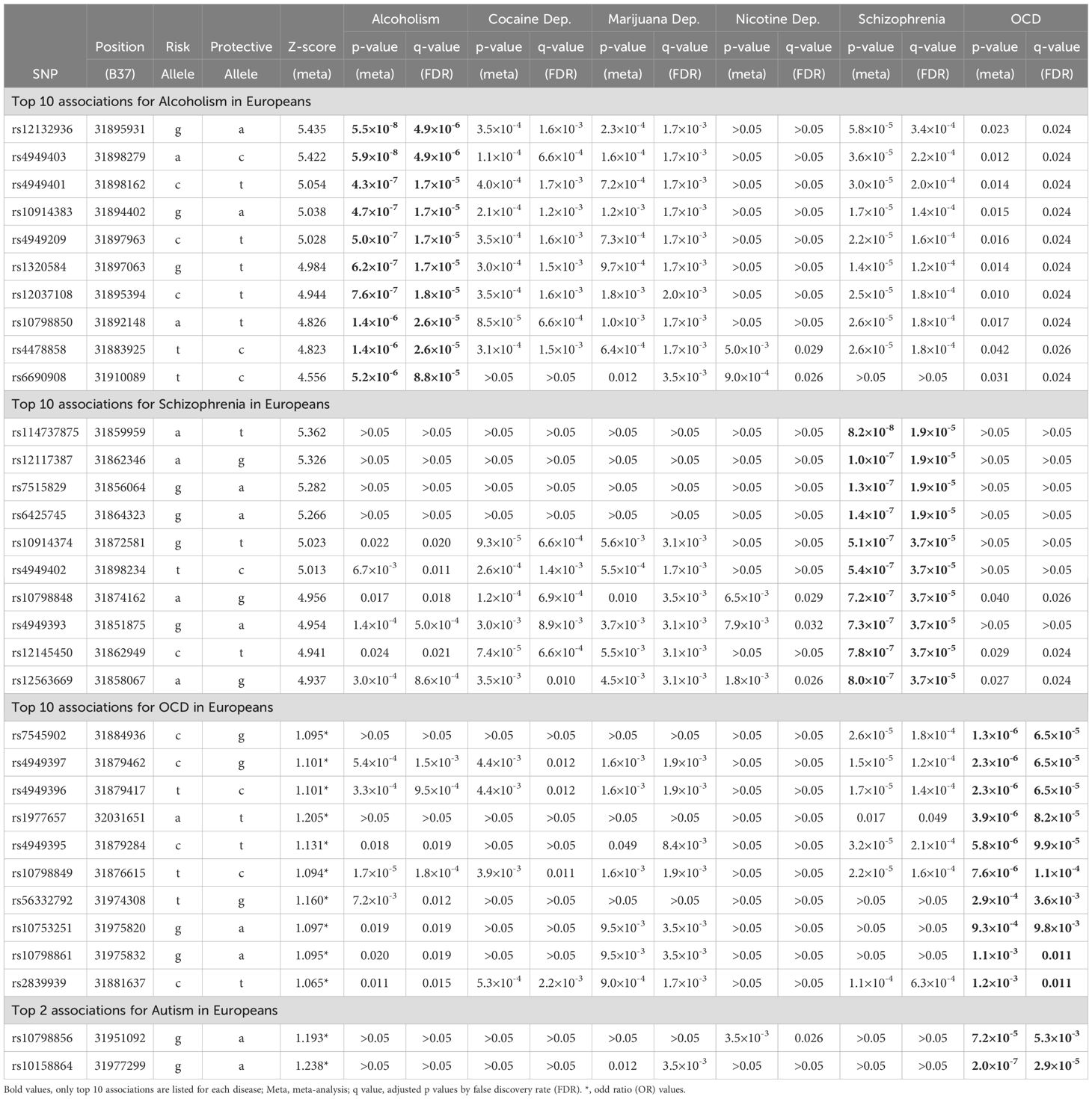
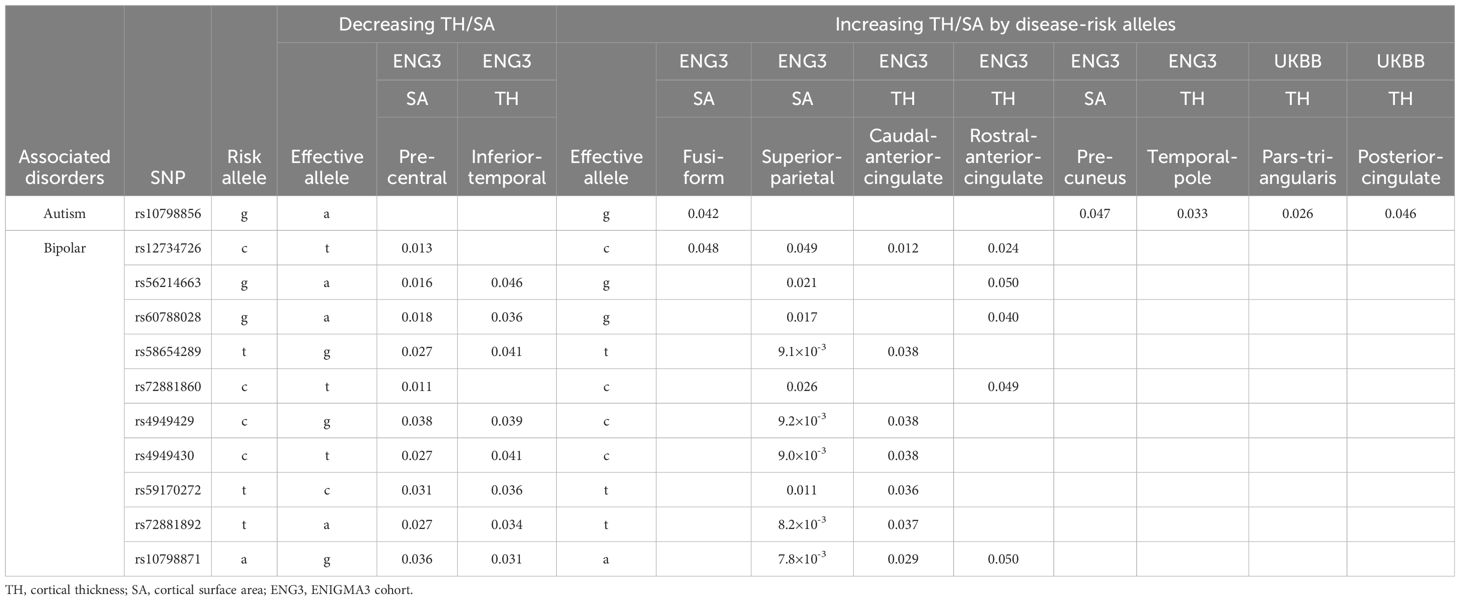
Table 1A. Significant associations between SERINC2 variants and neuropsychiatric disorders in European descent.
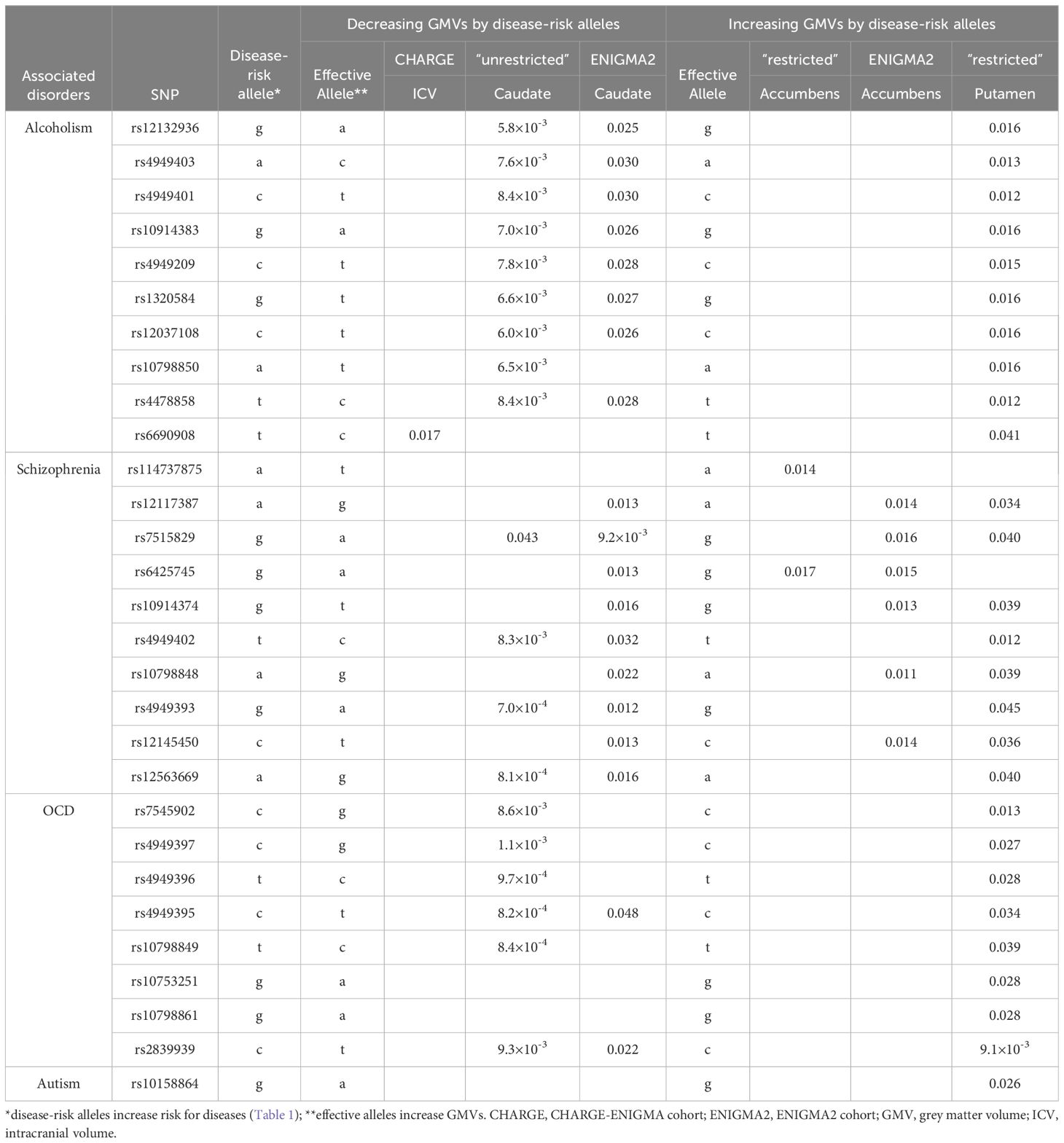
Followed by FDR correction, alcoholism was most significantly associated with SERINC2 variants in EAs (245 SNPs with 5.5×10-8≤p ≤ 0.049 and 4.9×10-5≤q ≤ 0.034; Table 1A). Interestingly, multiple other substance dependence in EAs was significantly associated with SERINC2 variants too, including cocaine dependence (107 SNPs with 2.6×10-5≤p ≤ 0.020 and 6.6×10-4≤q ≤ 0.046; Table 1A), marijuana dependence (213 SNPs with 1.6×10-4≤p ≤ 0.049 and 1.7×10-3≤q ≤ 8.5×10-3; Table 1A), nicotine dependence (85 SNPs with 6.9×10-4≤p ≤ 0.016 and 0.026≤q ≤ 0.049; Table 1A), and multi-substance dependence (rs28742121 and rs28759069: p=1.7×10-3 and q=0.033; data not shown).
The second most significant disease associated with SERINC2 variants was schizophrenia in EAs (187 SNPs with 8.2×10-8≤p ≤ 0.018 and 1.9×10-5≤q ≤ 0.049; Table 1A), followed by OCD in EAs (150 SNPs with 1.3×10-6≤p ≤ 0.050 and 6.5×10-5≤q ≤ 0.028; Table 1A). Additionally, a much smaller number of SERINC2 variants was significantly associated with autism in EAs (rs10798856 and rs10158864: 2.0×10-7≤p ≤ 7.2×10-5 and 2.9×10-5≤q ≤ 5.3×10-3; Table 1A) and bipolar disorder in Chinese population (10 SNPs with 1.3×10-4≤p ≤ 4.7×10-4 and 0.025≤q ≤ 0.031; Table 1B). Notably, these risk variants were largely shared across various substance dependence, schizophrenia, OCD and autism (Table 1A), but not bipolar disorder (Table 1B).
Finally, the phase of each imputed risk SNP listed in Table 1 is the same across cases, controls, and total group, confirming the accuracy of imputation.
3.2 Differential expression of SERINC2 mRNA in brains
In GTEx cohort, SERINC2 mRNA is significantly expressed in two brain regions, including substantia nigra (median TPM = 1.8) and cerebellum (1.4) (Figure 1).
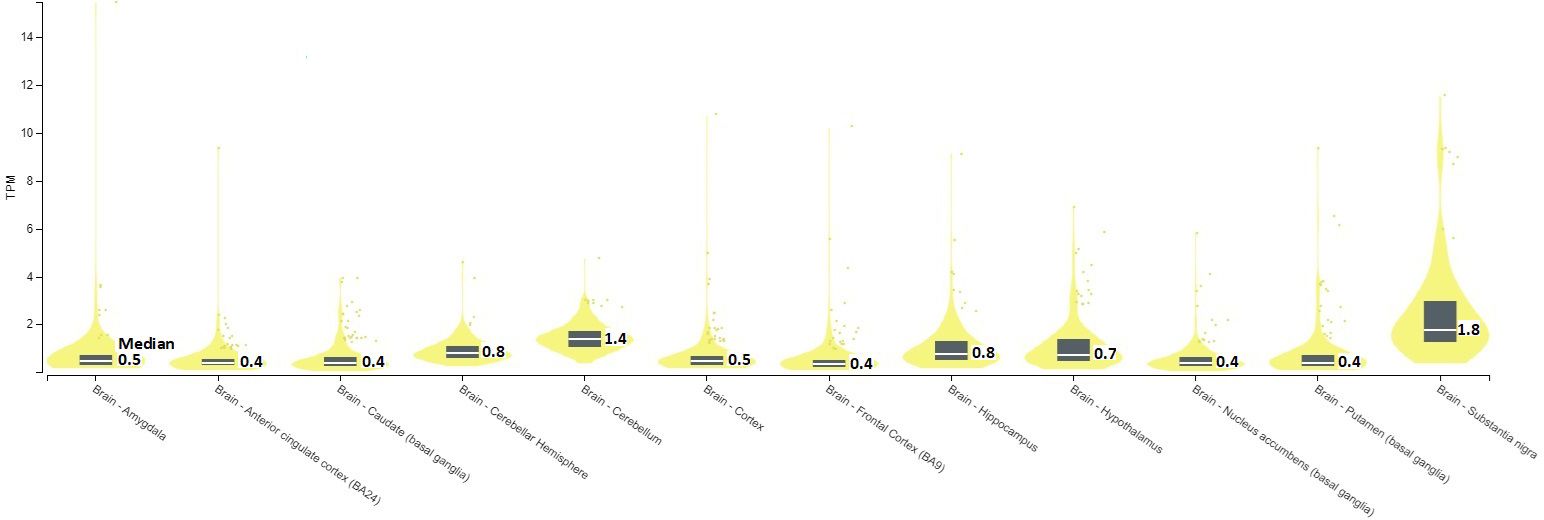
Figure 1. SERINC2 mRNA expression in brains [TPM, Transcripts Per Million; Median, median TPM value; TPM>1 indicates the presence of mRNA expression].
Three independent cohorts showed SERINC2 mRNA was differentially expressed in several other brains between alcoholism or schizophrenia and controls. The expression in hippocampus was increased in alcoholism (p=0.010), but the expression in neurons was decreased in schizophrenia in two cohorts (p=0.041 and 0.039, respectively), when compared to controls (Table 2). No differential expression was detected in other 7 cohorts (data not shown).
3.3 SNP-mRNA associations: cis-eQTL analysis
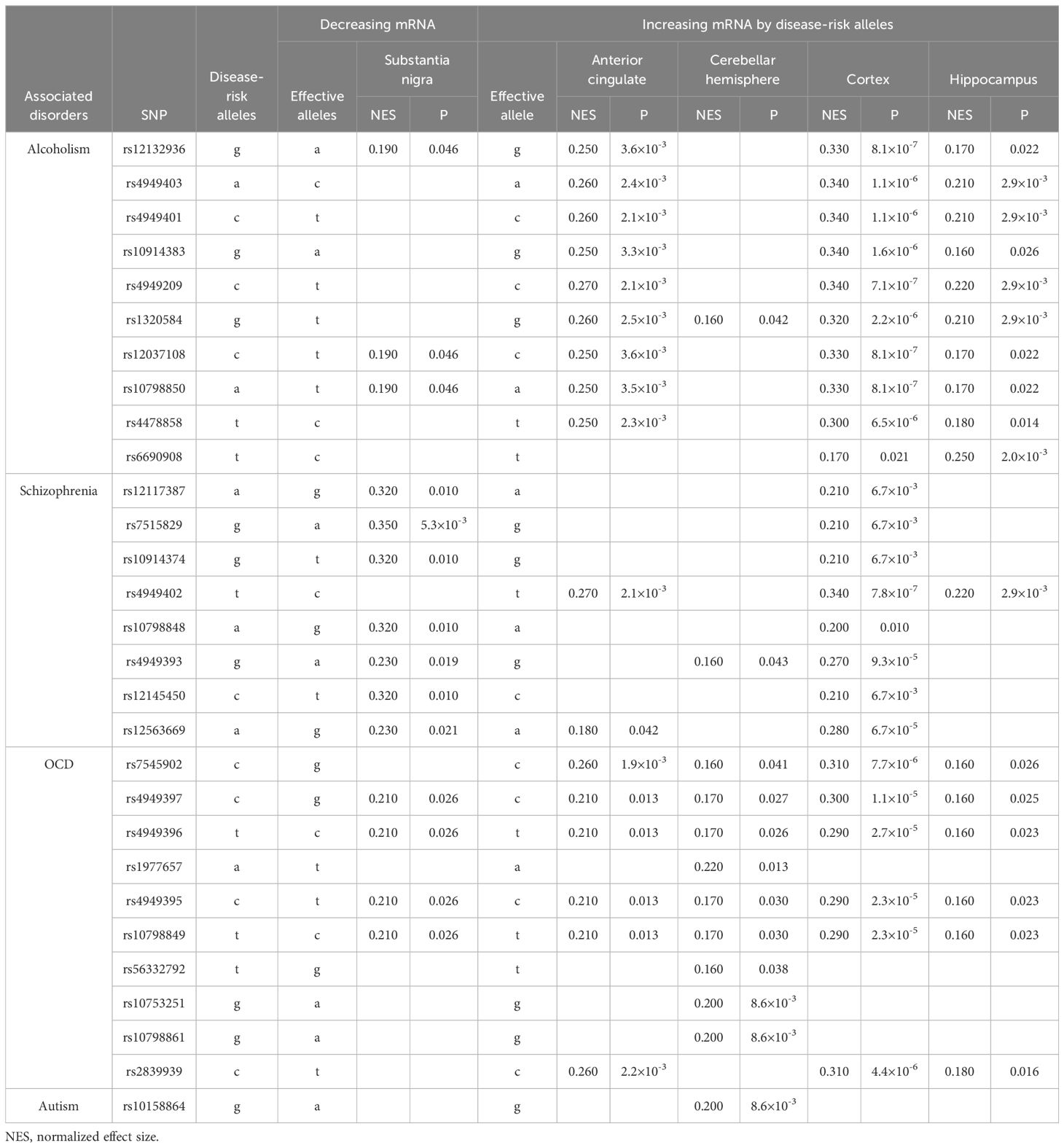
The disease-risk alleles had highly similar association patterns with mRNA expression in brain regions and effect directions across alcoholism, schizophrenia, OCD and autism (Table 3A). In substantia nigra, the disease-risk alleles decreased SERINC2 mRNA expression (5.3×10-3≤p ≤ 0.046), but in other brain regions, including anterior cingulate cortex, cerebellar hemisphere, cortex and hippocampus, they increased mRNA expression (8.1×10-7≤p ≤ 0.042; Table 3A).
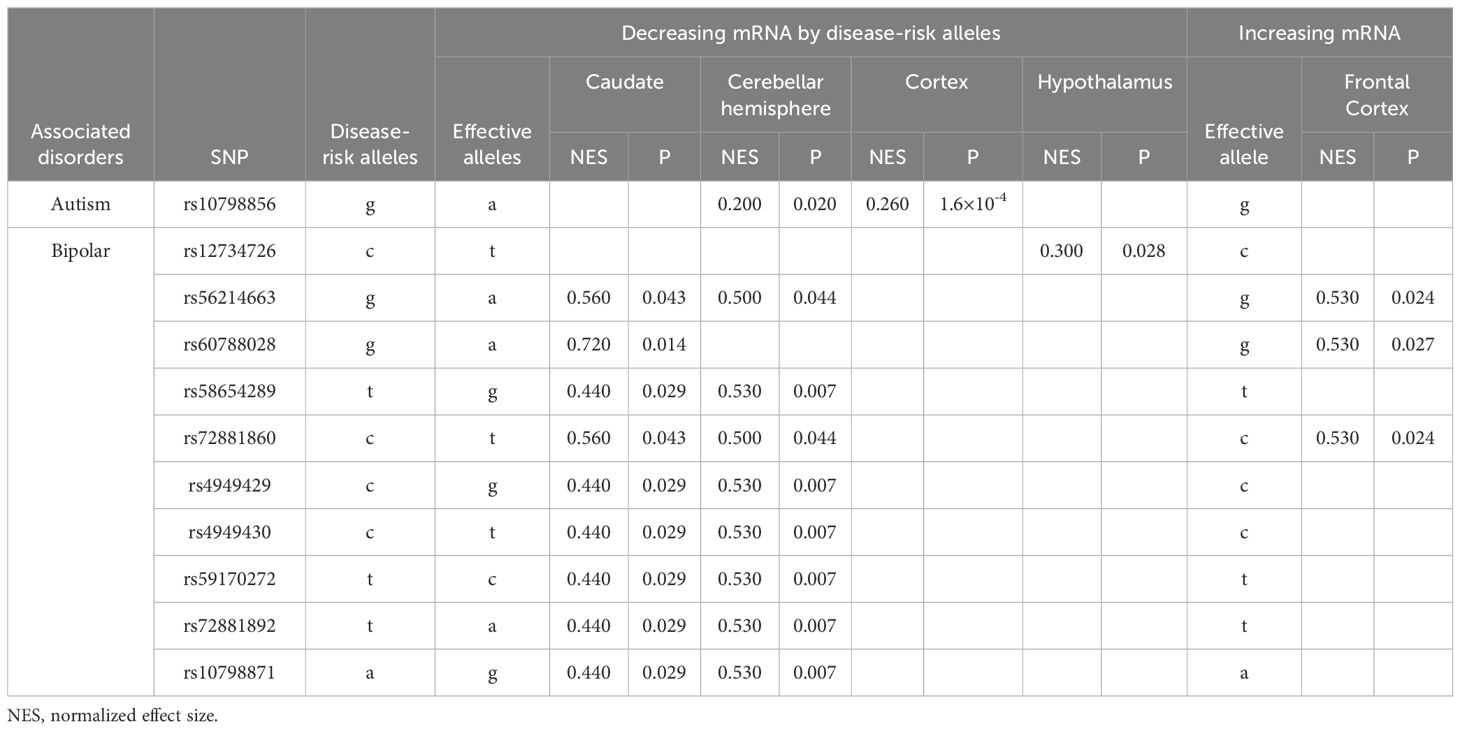
The bipolar disorder-risk alleles decreased SERINC2 mRNA expression in caudate, cerebellar hemisphere and hypothalamus (0.007≤p ≤ 0.044) but increased it in frontal cortex (0.024≤p ≤ 0.027; Table 3B). Additionally, one autism-risk allele decreased SERINC2 mRNA expression in cerebellar hemisphere and cortex (1.6×10-4≤p ≤ 0.020; Table 3B).
3.4 The disease-risk alleles decreased the ICV and the GMV of caudate and pallidum but increased the GMVs of accumbens and putamen
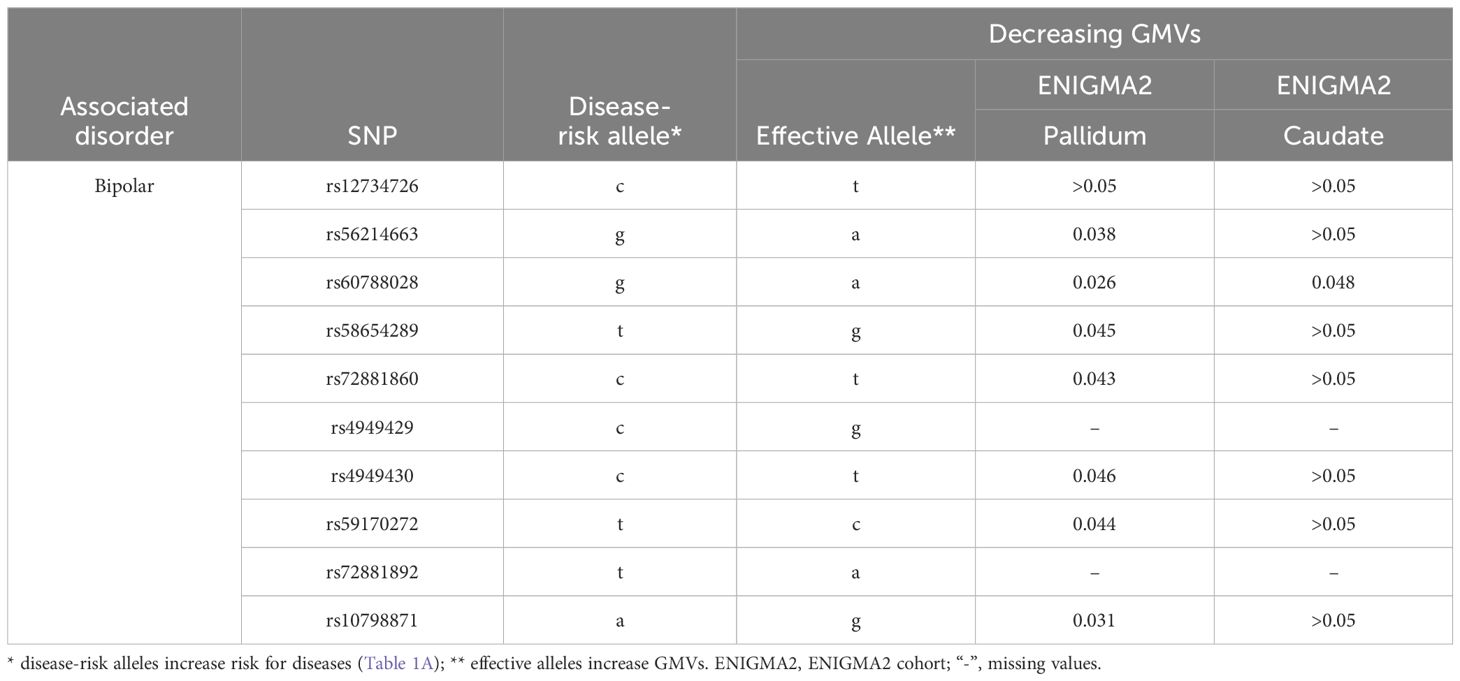
The disease-risk alleles had highly similar association patterns with GMVs of caudate and putamen across alcoholism, schizophrenia, OCD and autism (Table 4A). These alleles decreased caudate GMVs across two independent cohorts (7.0×10-4≤p ≤ 0.048) and increased putamen GMV in one cohort (9.1×10-3≤p ≤ 0.041; Table 4A). Furthermore, the alcoholism-risk allele T of rs6690908 decreased ICV in one cohort (p=0.017) but the schizophrenia-risk alleles increased accumbens GMVs across two independent cohorts (0.011≤p ≤ 0.017; Table 4A). Additionally, the bipolar-risk alleles decreased caudate and pallidum GMVs (0.026≤p ≤ 0.048; Table 4B).
3.5 The disease-risk alleles regulated the cortical SA and TH of multiple brain regions
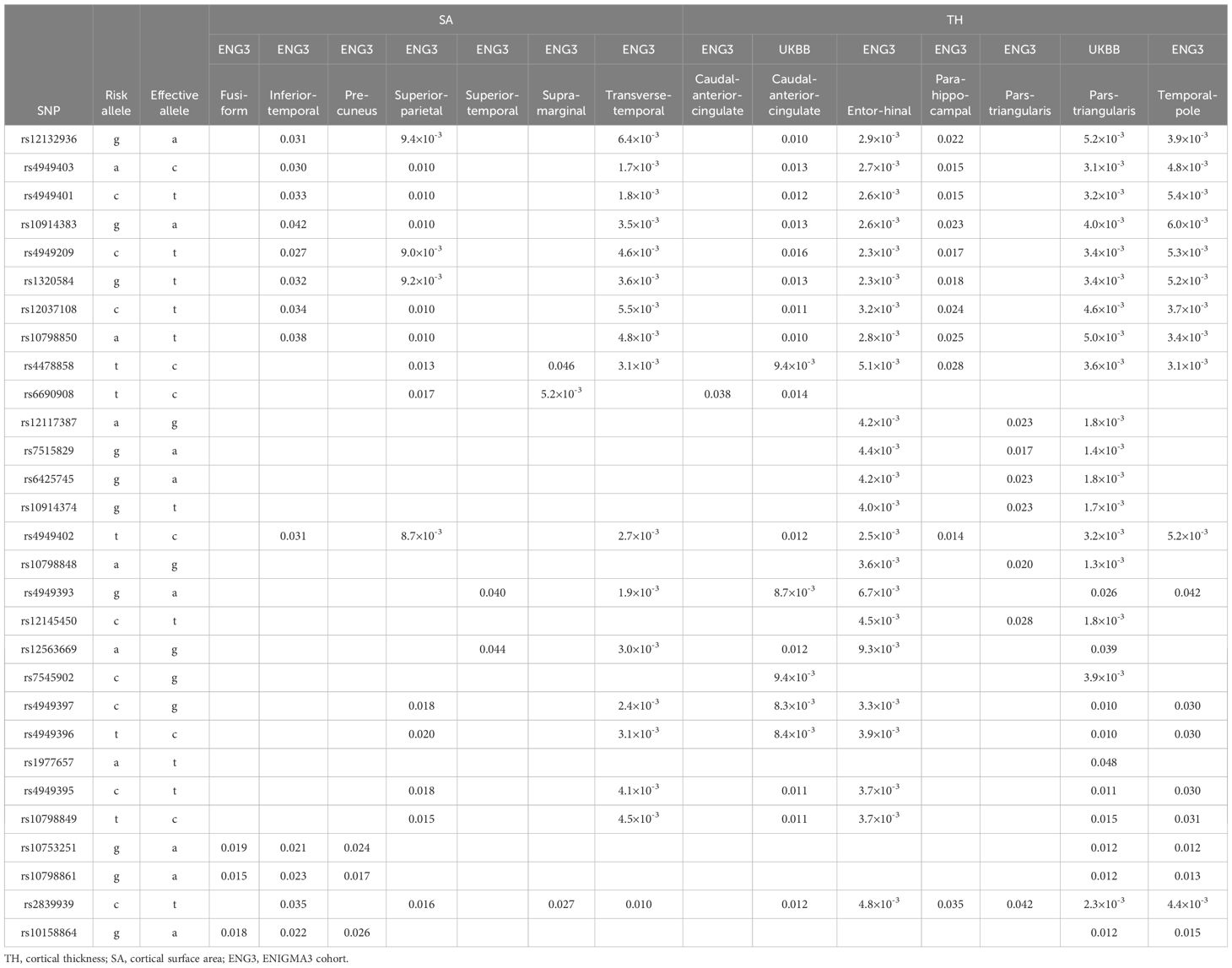
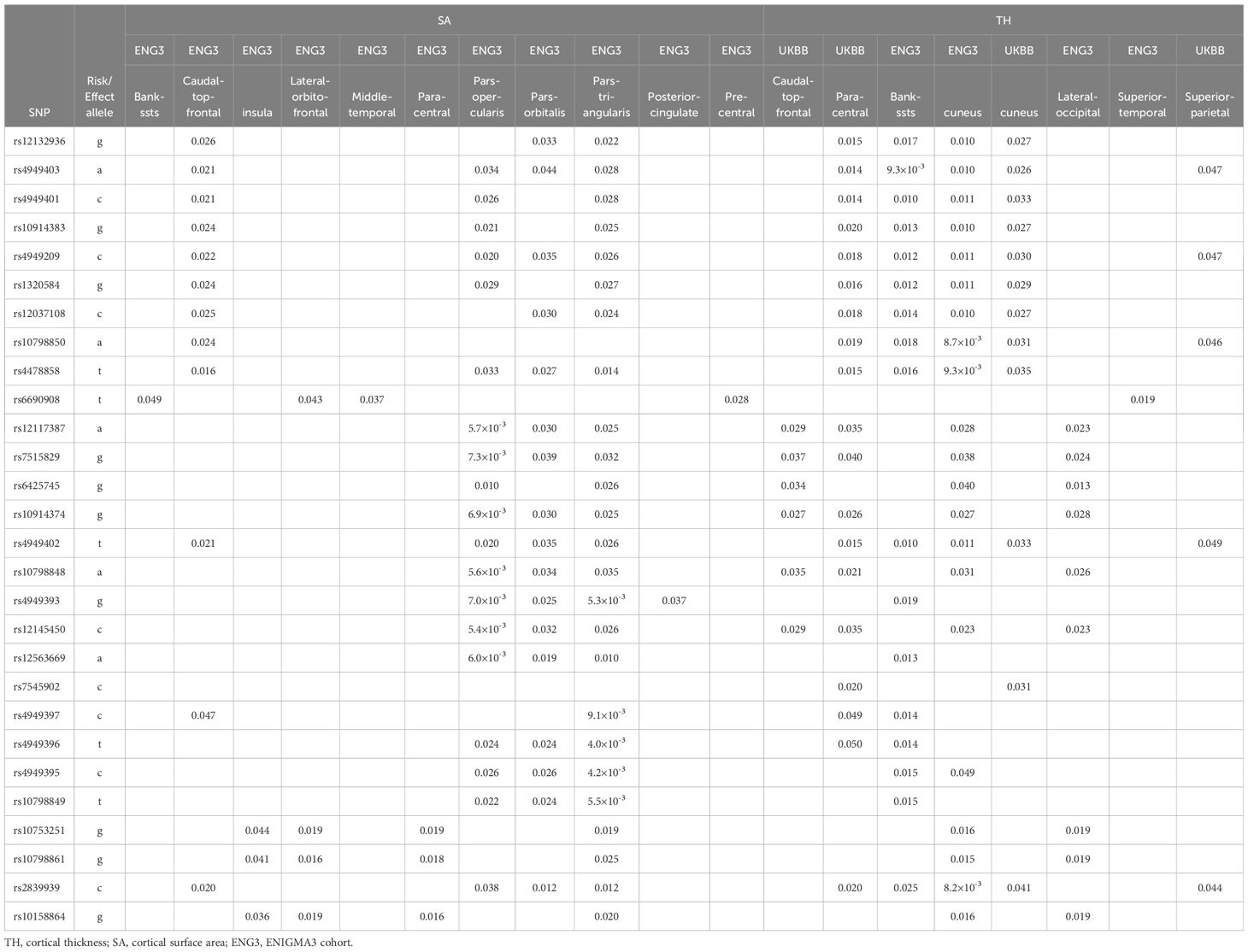
The disease-risk alleles had highly similar association patterns with cortical SA/TH across alcoholism, schizophrenia, OCD and autism (Table 5). These alleles decreased SA/TH of fusiform, inferior temporal, precuneus, superior parietal, superior temporal, supramarginal, transverse temporal, caudal anterior cingulate, entorhinal, parahippocampal, parstriangularis and temporal pole cortices (1.3×10-3≤p ≤ 0.048; Table 5A) and increased SA/TH of bankssts, caudal middle frontal, insula, lateralorbitofrontal, middle temporal, paracentral, parsopercularis, parsorbitalis, parstriangularis, posterior cingulate, precentral, caudal middle frontal, cuneus, lateral occipital, superior temporal and superior parietal cortices (5.4×10-3≤p ≤ 0.050; Table 5B).
The bipolar-risk alleles decreased TH/SA of precentral and inferior temporal cortices, and increased TH/SA of fusiform, superior parietal, caudal anterior cingulate, rostral anterior cingulate, precuneus, temporal pole, parstriangularis and posterior cingulate cortices (7.8×10-3≤p ≤ 0.050; Table 5C). Additionally, one autism-risk allele increased TH/SA of fusiform, precuneus, temporal pole, parstriangularis and posteriorcingulate cortices (0.026≤p ≤ 0.047; Table 5C).
4 Discussion
As introduced above, we ever phenome-wide scanned a total of 49,268 subjects of European or African descent with 12 different neuropsychiatric disorders and reported that the common SERINC2 variants and the rare SERINC2 variant constellations were “specific” to alcoholism in European descent (1, 4). In this study with an expanded sample size of a total of 1,167,439 participants of European, African or Asian descent with 18 diverse neuropsychiatric disorders, and harmonized genetic marker sets, analytical methods, meta-analysis and FDR correction, we confirmed that alcoholism was still the most significant disease associated with SERINC2 variants in European descent among all neuropsychiatric disorders. Meanwhile, more other substance use disorders that usually are comorbid and share common pathogenesis with alcoholism were also significantly associated with SERINC2 variants in European descent, including cocaine dependence, marijuana dependence, nicotine dependence, and polysubstance dependence. Additionally, we found that schizophrenia, OCD, and autism in European descent and bipolar disorder in Chinese were also significantly associated with SERINC2 variants, supporting the findings in literatures. Interestingly, substance use disorders, schizophrenia, OCD and autism but not bipolar disorder had highly similar patterns in association with SERINC2 variants and regulation by risk SERINC2 alleles, suggesting potential common mechanism related to SERINC2 underlying the former four diseases and distinct mechanism from bipolar disorder.
A series of functional studies substantiated the above disease-SERINC2 associations, which included (i) the significant expression of SERINC2 mRNA in brain regions, (ii) differential expression of SERINC2 mRNA in the brains of individuals with alcoholism and schizophrenia compared to controls, and (iii) the regulation of SERINC2 mRNA expression in the brain, intracranial volume (ICV), subcortical grey matter volumes (GMVs), and cortical surface area (SA) and thickness (TH) by disease-risk alleles. Although much of this nominal functional evidence became only suggestive after correction for multiple testing, a group of suggestive evidence still retains clinical significance. Literature has extensively reported the significant alteration of GMVs in alcoholism, schizophrenia, OCD, autism, and bipolar disorder (24–32). SERINC2 alleles may play critical roles in the pathogenesis of these diseases via altering the GMVs. Therefore, our conclusion is that SERINC2 predominantly predisposes individuals to substance dependence, schizophrenia, OCD, autism and bipolar disorder, a conclusion supported not only by statistical evidence but also by biological findings.
Specifically, SERINC2 mRNA exhibited its highest expression levels in the substantia nigra, followed by the cerebellum (Figure 1), and the expression in the substantia nigra and cerebellar hemisphere was down-regulated and up-regulated, respectively, by risk alleles for substance dependence, schizophrenia, OCD, and autism (Table 3A). These disease-risk alleles also up-regulated expression in the anterior cingulate, hippocampus, and other cortical regions (Table 3A). Additionally, these disease-risk alleles decreased caudate GMV but increased putamen GMV (Table 4A). Enlarged putamen GMV has been frequently observed in dopamine-related phenotypes associated with impulsive behaviors, such as substance use disorders (24), schizophrenia (25, 26), autism (27, 28), and OCD (28–31). This supports our hypothesis that SERINC2 alleles may increase the risk for these disorders by enlarging putamen GMV.
In contrast, bipolar disorder-risk alleles down-regulated SERINC2 mRNA expression in the caudate, hypothalamus, and cerebellar hemisphere, while up-regulating it in the frontal cortex (Table 3B). These bipolar-risk alleles also decreased caudate and pallidum GMVs (Table 4B), consistent with reports of reduced GMVs in these regions in bipolar disorder (33–36). This supports the hypothesis that SERINC2 alleles may increase the risk for bipolar disorder by reducing caudate and pallidum GMVs. Additionally, one autism-risk allele down-regulated mRNA expression in both the cerebellar hemisphere and cortex (Table 3B).
An alcoholism-risk allele was also found to decrease ICV (Table 4A), aligning with evidence of widespread brain shrinkage in alcoholism (37–41), supporting the hypothesis that this SERINC2 allele may increase the risk for alcoholism by reducing brain volume. Furthermore, several schizophrenia-risk alleles were associated with increased accumbens GMVs (Table 4A), consistent with prior findings of enlarged nucleus accumbens GMV in schizophrenia (42). This suggests that SERINC2 alleles may contribute to schizophrenia risk through accumbens GMV enlargement. Lastly, the disease-risk SERINC2 alleles were found to regulate the SA/TH of various cortical regions (Table 5), consistent with previous reports of cortical alterations in psychiatric disorders, such as schizophrenia (43, 44). This supports the idea that SERINC2 alleles may play key roles in the pathogenesis of these psychiatric diseases by altering cortical SA/TH too.
The sharing of risk SERINC2 variants and their functional patterns among alcoholism, cocaine dependence, marijuana dependence, nicotine dependence, polysubstance dependence, schizophrenia, OCD, and autism may be interpreted by the high comorbidity rates among these diseases. For example, there is a higher incidence of alcoholism in the family members of ASD patients compared with the general population; also, there is a link between the autism susceptibility candidate 2 gene (AUTS2) in the regulation of alcohol consumption (45–47).
In summary, these findings indicate that SERINC2 is primarily linked to substance dependence, schizophrenia, OCD, autism and bipolar disorder, a conclusion that is supported by both statistical and biological evidence and published literatures.
Data availability statement
The datasets used for the analyses described in this manuscript were obtained from dbGaP. The dbGaP accession numbers, PIs’ names, grant numbers and references are listed in Supplementary Table S1.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Yale University institutional review board. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation was not required from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
PL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. XGL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. XG: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Validation, Writing – original draft. XQL: Investigation, Validation, Writing – original draft. YZ: Conceptualization, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. JJ: Conceptualization, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. XW: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. XP: Formal analysis, Software, Validation, Writing – review & editing. KW: Formal analysis, Software, Validation, Writing – review & editing. ZW: Funding acquisition, Investigation, Resources, Writing – review & editing. RY: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. TZ: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. LC: Conceptualization, Investigation, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. YT: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. C-sL: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by China National Nature and Science Foundation (NSF) (81771452), Capital’s Funds for Health Improvement and Research (CFH2020-2-2134; 2022-2-2133; 2024-1-2131), Beijing Hospitals Authority Clinical Medicine Development of Special Funding (XMLX202130), Beijing Municipal Science and Technology Project (Z171100001017021 and Z171100001017022), Beijing municipal hospital scientific research and Cultivation Program (PX2021072), Shanghai Municipal Health Bureau Project (20124109), National Key Research and Development Program of China (2023YFC2506202), and Three-year action plan for Shanghai public health system construction (GWVI-2.1.4).
Acknowledgments
We thank NIH GWAS Data Repository, the investigator(s) who contributed the phenotype and genotype data in the original studies, and the funding organizations that supported the those studies.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1420395/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Zuo LJ, Wang KS, Zhang XY, Krystal JH, Li CSR, Zhang FY, et al. NKAIN1-SERINC2 is a functional, replicable and genome-wide significant risk gene region specific for alcohol dependence in subjects of European descent. Drug Alcohol Depend. (2013) 129:254–64. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2013.02.006
2. Zuo L, Tan Y, Zhang X, Wang X, Krystal J, Tabakoff B, et al. A new genomewide association meta-analysis of alcohol dependence. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. (2015) 39:1388–95. doi: 10.1111/acer.12786
3. Zuo L, Lu L, Tan Y, Pan X, Cai Y, Wang X, et al. Genome-wide association discoveries of alcohol dependence. Am J Addict. (2014) 23:526–39. doi: 10.1111/j.1521-0391.2014.12147.x
4. Zuo L, Wang KS, Zhang XY, Li CS, Zhang F, Wang X, et al. Rare SERINC2 variants are specific for alcohol dependence in individuals of European descent. Pharmacogenet Genomics. (2013) 23:395–402. doi: 10.1097/FPC.0b013e328362f9f2
5. Yang D, Chen J, Cheng X, Cao B, Chang H, Li X, et al. SERINC2 increases the risk of bipolar disorder in the Chinese population. Depress Anxiety. (2021) 38:985–95. doi: 10.1002/da.23186
6. Hnoonual A, Thammachote W, Tim-Aroon T, Rojnueangnit K, Hansakunachai T, Sombuntham T, et al. Chromosomal microarray analysis in a cohort of underrepresented population identifies SERINC2 as a novel candidate gene for autism spectrum disorder. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:12096. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-12317-3
7. Inuzuka M, Hayakawa M, Ingi T. Serinc, an activity-regulated protein family, incorporates serine into membrane lipid synthesis. J Biol Chem. (2005) 280:35776–83. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M505712200
8. Guirland C, Suzuki S, Kojima M, Lu B, Zheng JQ. Lipid rafts mediate chemotropic guidance of nerve growth cones. Neuron. (2004) 42:51–62. doi: 10.1016/S0896-6273(04)00157-6
9. Howie BN, Donnelly P, Marchini J. A flexible and accurate genotype imputation method for the next generation of genome-wide association studies. PloS Genet. (2009) 5:e1000529. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000529
10. Zuo L, Wang K, Zhang XY, Pan X, Wang G, Tan Y, et al. Association between common alcohol dehydrogenase gene (ADH) variants and schizophrenia and autism. Hum Genet. (2013) 132:735–43. doi: 10.1007/s00439-013-1277-4
11. Zuo L, Gelernter J, Zhang CK, Zhao H, Lu L, Kranzler HR, et al. Genome-wide association study of alcohol dependence implicates KIAA0040 on chromosome 1q. Neuropsychopharmacology. (2012) 37:557–66. doi: 10.1038/npp.2011.229
12. Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K, Thomas L, Ferreira MA, Bender D, et al. PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet. (2007) 81:559–75. doi: 10.1086/519795
13. Storey J, Bass A, Dabney A, Robinson D. qvalue: Q-value estimation for false discovery rate control. R package version 2.32.0. (2023). Available online at: http://github.com/jdstorey/qvalue (Accessed December 9, 2024).
14. GTEx Consortium. The genotype-tissue expression (GTEx) project. Nat Genet. (2013) 45:580–5. doi: 10.1038/ng.2653
15. McClintick JN, Xuei X, Tischfield JA, Goate A, Foroud T, Wetherill L, et al. Stress-response pathways are altered in the hippocampus of chronic alcoholics. Alcohol. (2013) 47:505–15. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2013.07.002
16. Bannon MJ, Johnson MM, Michelhaugh SK, Hartley ZJ, Halter SD, David JA, et al. A molecular profile of cocaine abuse includes the differential expression of genes that regulate transcription, chromatin, and dopamine cell phenotype. Neuropsychopharmacology. (2014) 39:2191–9. doi: 10.1038/npp.2014.70
17. Philibert RA, Ryu GY, Yoon JG, Sandhu H, Hollenbeck N, Gunter T, et al. Transcriptional profiling of subjects from the Iowa adoption studies. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. (2007) 144B:683–90. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.30512
18. Ryan MM, Lockstone HE, Huffaker SJ, Wayland MT, Webster MJ, Bahn S. Gene expression analysis of bipolar disorder reveals downregulation of the ubiquitin cycle and alterations in synaptic genes. Mol Psychiatry. (2006) 11:965–78. doi: 10.1038/sj.mp.4001875
19. Brennand KJ, Simone A, Jou J, Gelboin-Burkhart C, Tran N, Sangar S, et al. Modelling schizophrenia using human induced pluripotent stem cells. Nature. (2011) 473:221–5. doi: 10.1038/nature09915
20. Barnes MR, Huxley-Jones J, Maycox PR, Lennon M, Thornber A, Kelly F, et al. Transcription and pathway analysis of the superior temporal cortex and anterior prefrontal cortex in schizophrenia. J Neurosci Res. (2011) 89:1218–27. doi: 10.1002/jnr.22647
21. Maycox PR, Kelly F, Taylor A, Bates S, Reid J, Logendra R, et al. Analysis of gene expression in two large schizophrenia cohorts identifies multiple changes associated with nerve terminal function. Mol Psychiatry. (2009) 14:1083–94. doi: 10.1038/mp.2009.18
22. Harris LW, Wayland M, Lan M, Ryan M, Giger T, Lockstone H, et al. The cerebral microvasculature in schizophrenia: a laser capture microdissection study. PloS One. (2008) 3:e3964. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0003964
23. Guo X, Luo X, Zhang Y, Yu Z, Tan Z, Cao L, et al. Phenome-wide association studies of TXNRD2-COMT-ARVCF cluster pinpoint schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Asian J Psychiatr. (2024) 98:104145. doi: 10.1016/j.ajp.2024.104145
24. Ersche KD, Jones PS, Williams GB, Turton AJ, Robbins TW, Bullmore ET. Abnormal brain structure implicated in stimulant drug addiction. Science. (2012) 335:601–4. doi: 10.1126/science.1214463
25. Buchsbaum MS, Shihabuddin L, Brickman AM, Miozzo R, Prikryl R, Shaw R, et al. Caudate and putamen volumes in good and poor outcome patients with schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. (2003) 64:53–62. doi: 10.1016/S0920-9964(02)00526-1
26. Hokama H, Shenton ME, Nestor PG, Kikinis R, Levitt JJ, Metcalf D, et al. Caudate, putamen, and globus pallidus volume in schizophrenia: a quantitative MRI study. Psychiatry Res. (1995) 61:209–29. doi: 10.1016/0925-4927(95)02729-H
27. Sato W, Kubota Y, Kochiyama T, Uono S, Yoshimura S, Sawada R, et al. Increased putamen volume in adults with autism spectrum disorder. Front Hum Neurosci. (2014) 8:957. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2014.00957
28. Hollander E, Anagnostou E, Chaplin W, Esposito K, Haznedar MM, Licalzi E, et al. Striatal volume on magnetic resonance imaging and repetitive behaviors in autism. Biol Psychiatry. (2005) 58:226–32. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2005.03.040
29. Radua J, van den Heuvel OA, Surguladze S, Mataix-Cols D. Meta-analytical comparison of voxel-based morphometry studies in obsessive-compulsive disorder vs other anxiety disorders. Arch Gen Psychiatry. (2010) 67:701–11. doi: 10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2010.70
30. Radua J, Mataix-Cols D. Voxel-wise meta-analysis of grey matter changes in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Br J Psychiatry. (2009) 195:393–402. doi: 10.1192/bjp.bp.108.055046
31. Hibar DP, Cheung JW, Medland SE, Mufford MS, Jahanshad N, Dalvie S, et al. Significant concordance of genetic variation that increases both the risk for obsessive-compulsive disorder and the volumes of the nucleus accumbens and putamen. Br J Psychiatry. (2018) 213:430–6. doi: 10.1192/bjp.2018.62
32. Luo X, Mao Q, Shi J, Wang X, Li CR. Putamen gray matter volumes in neuropsychiatric and neurodegenerative disorders. World J Psychiatry Ment Health Res. (2019) 3:pii:1020.
33. Beyer JL, Kuchibhatla M, Payne M, Moo-Young M, Cassidy F, MacFall J, et al. Caudate volume measurement in older adults with bipolar disorder. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. (2004) 19:109–14. doi: 10.1002/gps.1030
34. Janiri D, Sani G, Rossi P, Piras F, Iorio M, Banaj N, et al. Amygdala and hippocampus volumes are differently affected by childhood trauma in patients with bipolar disorders and healthy controls. Bipolar Disord. (2017) 19:353–62. doi: 10.1111/bdi.12516
35. McWhinney SR, Abe C, Alda M, Benedetti F, Boen E, Del Mar Bonnin C, et al. Association between body mass index and subcortical brain volumes in bipolar disorders-ENIGMA study in 2735 individuals. Mol Psychiatry. (2021) 26:6806–19. doi: 10.1038/s41380-021-01098-x
36. Zhang X, Gao W, Cao W, Kuang L, Niu J, Guo Y, et al. Pallidal volume reduction and prefrontal-striatal-thalamic functional connectivity disruption in pediatric bipolar disorders. J Affect Disord. (2022) 301:281–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2022.01.049
37. Chandrasekar R. Alcohol and NMDA receptor: current research and future direction. Front Mol Neurosci. (2013) 6:14. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2013.00014
38. Dager AD, McKay DR, Kent JW Jr., Curran JE, Knowles E, Sprooten E, et al. Shared genetic factors influence amygdala volumes and risk for alcoholism. Neuropsychopharmacology. (2015) 40:412–20. doi: 10.1038/npp.2014.187
39. Le Berre AP, Rauchs G, La Joie R, Mezenge F, Boudehent C, Vabret F, et al. Impaired decision-making and brain shrinkage in alcoholism. Eur Psychiatry. (2014) 29:125–33. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpsy.2012.10.002
40. Tongsong T, Puntachai P, Mekjarasnapha M, Traisrisilp K. Severe fetal brain shrinkage following heavy maternal alcohol consumption. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. (2014) 44:245–7. doi: 10.1002/uog.13396
41. Zhang K, Luo J. Role of MCP-1 and CCR2 in alcohol neurotoxicity. Pharmacol Res. (2019) 139:360–6. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2018.11.030
42. Lauer M, Senitz D, Beckmann H. Increased volume of the nucleus accumbens in schizophrenia. J Neural Transm (Vienna). (2001) 108:645–60. doi: 10.1007/s007020170042
43. Mao Q, Lin X, Yin Q, Liu P, Zhang Y, Qu S, et al. A significant, functional and replicable risk KTN1 variant block for schizophrenia. Sci Rep. (2023) 13:3890. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-27448-z
44. Guo X, Luo X, Huang X, Zhang Y, Ji J, Wang X, et al. The role of 3' Regulatory region flanking kinectin 1 gene in schizophrenia. Alpha Psychiatry. (2024) 25:413–20. doi: 10.5152/alphapsychiatry.2024.241616
45. Miles JH, Takahashi TN, Haber A, Hadden L. Autism families with a high incidence of alcoholism. J Autism Dev Disord. (2003) 33:403–15. doi: 10.1023/a:1025010828304
46. Regier DA, Farmer ME, Rae DS, Locke BZ, Keith SJ, Judd LL, et al. Comorbidity of mental disorders with alcohol and other drug abuse. Results from the Epidemiologic Catchment Area (ECA) Study. Jama. (1990) 264:2511–8. doi: 10.1001/jama.1990.03450190043026
Keywords: SERINC2, phenome, alcoholism, schizophrenia, OCD, autism, bipolar disorder, mRNA expression
Citation: Liu P, Luo X, Cao L, Zhang Y, Ji J, Wang X, Wang K, Pan X, Yang R, Tan Z, Tan Y, Li C-s, Guo X, Wang Z and Luo X (2025) Phenome-wide association studies between SERINC2 and neuropsychiatric disorders. Front. Psychiatry 15:1420395. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1420395
Received: 20 April 2024; Accepted: 29 November 2024;
Published: 20 January 2025.
Edited by:
Konstantinos Poulas, University of Patras, GreeceReviewed by:
Jie Zhang, Third People’s Hospital of Zhongshan City, ChinaCho-Yi Chen, National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University, Taiwan
Copyright © 2025 Liu, Luo, Cao, Zhang, Ji, Wang, Wang, Pan, Yang, Tan, Tan, Li, Guo, Wang and Luo. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiaoyun Guo, eGlhb3l1bmd1b0AxNjMuY29t; Zhiren Wang, emhpcmVuNzVAZ21haWwuY29t; Xingguang Luo, WGluZ2d1YW5nLkx1b0B5YWxlLmVkdQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Ping Liu1†
Ping Liu1† Liping Cao
Liping Cao Yong Zhang
Yong Zhang Jiawu Ji
Jiawu Ji Xiaoping Wang
Xiaoping Wang Zewen Tan
Zewen Tan Yunlong Tan
Yunlong Tan Xiaoyun Guo
Xiaoyun Guo Zhiren Wang
Zhiren Wang Xingguang Luo
Xingguang Luo