- 1Psychological Clinic, Guangxi Chest Hospital, Liuzhou, Guangxi, China
- 2Medical Department, Huizhou Central People’s Hospital, Huizhou, Guangdong, China
- 3Department of Pulmonary Medicine, Guangxi Chest Hospital, Liuzhou, Guangxi, China
- 4Department of Psychiatry & Medical Psychology, The First Affiliated Hospital, College of Clinical Medicine, Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China
Introduction: This study aims to evaluate the effects of group computer magnanimous therapy (GCMT) on magnanimous-enterprising levels and brain metabolic changes in patients with advanced lung cancer.
Methods: In this multicenter, randomized controlled trial, 47 participants diagnosed with advanced stage (III or IV) lung cancer were randomly assigned to either the GCMT group (GCMTG, n = 31) or the control group (CTRLG, n = 16). The GCMTG received routine oncotherapy and care along with eight sessions of GCMT over 2 weeks, while the CTRLG received only oncotherapy and routine care. Psychological and brain metabolic changes were assessed using the Enterprising and Magnanimous Questionnaire (EMQ) and proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H-MRS).
Results: After 2 weeks, the GCMTG showed significant improvements in the EMQ “total score” and “enterprising” dimensions compared to baseline (p < 0.05), while the CTRLG showed no significant changes. Significant increases in NAA/Cr levels were observed in the right amygdala, and significant decreases in mI/Cr levels were observed in the right cingulate gyrus in the GCMTG. Pearson correlation analysis indicated that changes in Cho/Cr levels in the left amygdala and Glx/Cr levels in the left hippocampus were significantly correlated with improvements in the enterprising dimension.
Conclusions: GCMT significantly enhanced enterprising attitudes and induced beneficial changes in brain metabolites among patients with advanced lung cancer. Further research with larger sample sizes is warranted to confirm these results and explore the long-term effects of GCMT.
Clinical trial registration: https://www.chictr.org.cn/showproj.html?proj=129557, identifier ChiCTR2100053015.
Introduction
Lung cancer is a malignant tumor with the highest mortality throughout the world (1, 2). According to the World Health Organization (WHO), lung cancer has surpassed gastric cancer as the main cause of cancer death, accounting for 27.3% of all cancer deaths in China (3). The onset of lung cancer is hidden, and the early symptoms are easy to be ignored (4–6). When diagnosed, it is often in the advanced stage of the disease, which brings huge psychological and physiological changes to patients (7). This not only increases the complexity of treatment but also profoundly impacts the psychological health of patients.
Research indicates that patients with advanced lung cancer frequently face severe psychological issues, including depression, anxiety, despair, and social withdrawal (8, 9). These psychological problems may lead to decreased treatment compliance, significantly impair quality of life, and even affect survival rates (10). For instance, a study by Smith et al. found a significant correlation between depressive symptoms and high mortality rates among lung cancer patients (11). Additionally, psychological issues may exacerbate physical symptoms such as pain and fatigue, creating a vicious cycle.
Magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) is a non-invasive examination method used to analyze the neurobiochemical metabolism and pathophysiology of human organs and tissues. ¹H-MRS is the most widely used in studying changes in biochemistry and metabolites in the brain (12). In recent years, a growing number of researchers (13–16) have conducted MRS research on psychiatric mental illness. Huang BJ and Yang Y conducted a 2-month group cognitive behavior therapy on patients with Internet addiction. The results showed that after the intervention, the Cho/Cr ratio of the medial prefrontal lobe was significantly higher than that before treatment, and the behavior of Internet addiction was improved (17, 18). The study of Streeter CC et al. (19) showed that after a 3-month period of exercise therapy, the level of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in the thalamus increased significantly, while the level of anxiety was lower than before. It has been shown that the concentration of Glx in the right caudate nucleus decreased and the compulsive behavior gradually decreased in obsessive–compulsive disorder patients after 4 months of behavioral therapy (20). However, few empirical studies exist on cerebral metabolic mechanisms in advanced lung cancer patients with psychotherapy. Therefore, it is urgent to collect additional evidence on brain metabolic transformations in patients with advanced lung cancer.
Magnanimous therapy (MT) is a brand-new psychotherapy method proposed by Huang X (21), based on over 20 years of clinical treatment experience of research groups and research on cancer psychotherapy at home and abroad. It combines the cultural and psychological habits of Chinese people and integrates the essence of Chinese civilization, Zen, and Taoism. The purpose of treatment is to present the magnanimous and open-minded, enterprising and positive, and optimistic attitude toward life to individuals in a simple, interesting, and vivid way. In a 2021 study, we assessed the psychological status of lung cancer patients using the Psychosomatic Status Scale for Cancer Patients (PSSCP) and the Hospital Anxiety Depression Scale (HADS); additionally, we evaluated immune function by measuring plasma levels of immunoglobulins IgA, IgG, and IgM, as well as natural killer (NK) cell activity; our findings indicate that MT contributed to improvements in depression, anxiety, psychosomatic status, and immune function in patients with advanced lung cancer (22). Our early studies (23–28) found that patients with breast cancer and lung cancer had positive improvements in physical symptoms, behavior patterns, social functions, and emotional status, through therapeutic intervention of MT. GCMT was an improved psychotherapy based on the technology and theory of MT, which combines MT, group psychotherapy, and game psychotherapy, so that more patients can participate in the treatment under the guidance of therapists.
GCMT has been applied to different kinds of diseases. However, the therapeutic role and mechanism of GCMT in lung cancer are largely unknown. The effects of psychotherapy on the magnanimous-enterprising level and cerebral metabolic mechanism of advanced lung cancer patients have not yet been tested. In order to fill the current research gap, this study aims to 1) evaluate the magnanimous-enterprising levels and brain metabolic levels of GCMT in advanced lung cancer patients, 2) reveal the relationship between the effects of GCMT on magnanimous-enterprising and brain metabolites, and 3) explore the possible mechanism of GCMT in lung cancer patients (2). To our knowledge, this study is the first of its kind to explore the cerebral metabolic mechanism of GCMT in patients with lung cancer.
Methods
Study design
This two‐arm, parallel, blocked, multicenter, randomized controlled trial (RCT) study was approved by the Clinical Medical Ethics Committee [Approval No. 2013 Clinical Medicine (06)] and performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. This study aimed to investigate the effects of GCMT on magnanimous-enterprising and brain metabolite levels in patients with advanced lung cancer. Participants were randomly assigned to the group computer magnanimous therapy group (GCMTG) or the control group (CTRLG). The control group only received routine oncotherapy and nursing, while the GCMT group received eight times GCMT on this basis. Patients were assessed at baseline and 2 weeks later using the Enterprising and Magnanimous Questionnaire (EMQ) and MRS brain metabolic indexes [the peak heights of N-acetylaspartate (NAA), choline (Cho), myo-inositol (mI), glutamate, and glutamine complex (Glx) in the bilateral anterior cingulate gyrus, hippocampus, and amygdala were collected by 1H-MRS, and the spectrum was analyzed relatively quantitatively with reference to creatine (CR) peak, and the values of NAA/Cr, Cho/Cr, mI/Cr, and Glx/Cr were recorded]. The relationship between the changes in magnanimous-enterprising levels and brain biochemical metabolism was analyzed to explore the possible mechanism.
Participants
Consecutive eligible patients were recruited at the oncology inpatient department of three teaching hospitals in Guangdong, China, from 2014 to 2021. Relevant study information was provided through prospective contact by doctors or nurses during routine visits or through online recruitment (WeChat, Moments, Public Accounts). For interested patients, after an interview by the researchers, an eligibility assessment was conducted through paper-based screening questionnaires; eligible patients signed a written informed consent. A cohort comprising 84 individuals diagnosed with advanced stage (III or IV) lung carcinoma was initially enrolled in the study. Due to dropouts during the course of therapy and subsequent follow-up, the dataset was reduced to 47 subjects for the final statistical analysis (Figure 1).
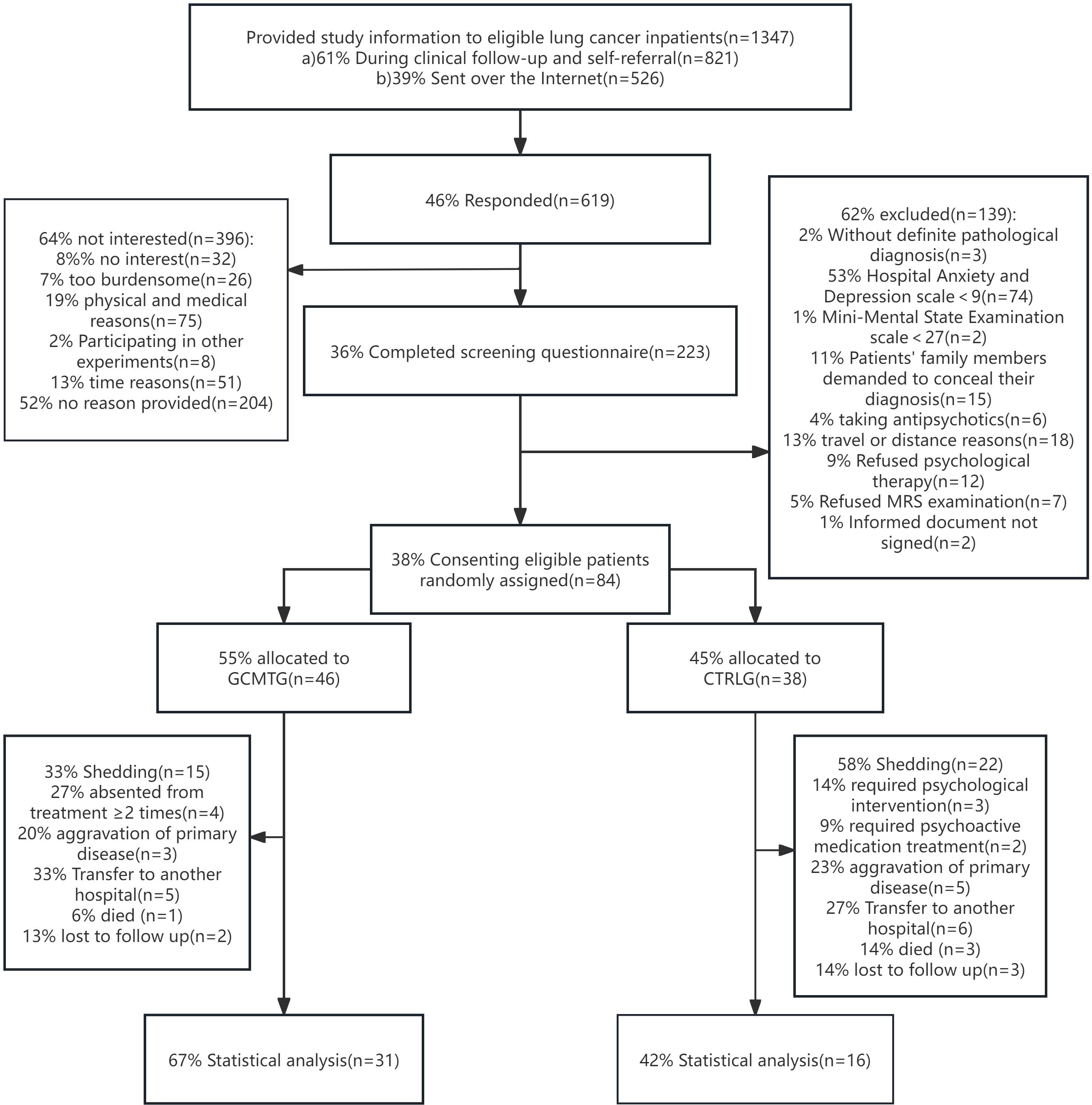
Figure 1. The CONSORT flow chart shows the recruitment and enrollment of 47 participants for final statistical analysis.
The inclusion criteria were as follows: 1) age range: 25–85 years old, primary education or above; 2) have a definite pathological diagnosis; 3) Hospital Anxiety and Depression (HAD) scale ≥9, Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) scale ≥27; 4) patients with stable condition after clinical oncology therapy; 5) no obvious intellectual disability or psychiatric disorders; and 6) patients voluntarily participated and signed informed documents.
The exclusion criteria were 1) without a definite pathological diagnosis, 2) patients’ family members demanded to conceal their diagnosis, 3) with cognitive impairment (MMSE < 27), 4) taking antipsychotics or receiving other psychotherapy, 5) a history of psychoactive drug abuse, 6) pregnant or lactating women, and 7) other reasons for being unable to accept psychological intervention.
The shedding criteria were as follows: 1) absent from treatment on two or more occasions, 2) could not continue to receive psychotherapy because of the aggravation of the primary disease and unstable vital signs, 3) with cognitive impairment due to brain metastasis during the experiment, and 4) participants in the control group who needed other psychological intervention or psychotropic drug therapy due to their condition.
Randomization and masking
This blocked RCT involved participants who, subsequent to baseline assessments, were stratified by gender (male or female), educational level, cancer diagnosis (pathological classification and clinical stage), and therapeutic approaches. Eligible subjects were randomly assigned in a 1:1 ratio to either the GCMTG or the CTRLG using block randomization with varying block sizes of two to four participants. The randomization was facilitated by an online program developed in-house by the hospital’s Information Technology Department, which ensured immediate allocation. Participants allocated to the GCMTG received an invitation to book a session with a psychologist. Neither the participants nor the research staff were blinded to the intervention status, which is common in psychological intervention trials and is understood as part of the intervention, akin to clinical practice. The statistician entrusted with data analysis remained blinded to the intervention allocation.
Intervention
Before the intervention, the patients in the experimental group were randomly divided into treatment groups of three to four people. Through careful observation and patient communication, the therapist initially understood the psychosomatic state of the group members, introduced the treatment-related situation to the patients, and initially established a treatment relationship with the group members. GCMT was implemented with computer games as the carrier (play therapy games, the games focused on inspiring a positive interaction effect in a group). After each game, the therapist guided the patients to comprehend, share, and communicate; made the patients resonate and introspect; and required each of them to spend 30 min every day recalling the treatment content and apply what they have learned to their daily lives. At the beginning of the next session, the therapist led the members to review the last learning content and check the completion of the homework, so that they could share their feelings on the application. Participants in the GCMT group received an eight-time course of GCMT (4 times per week for 2 weeks). (The length of hospital stay of Chinese lung cancer patients is usually 2 weeks.) Through a 2-week continuous learning and daily consolidation, the participants could discuss, support, and encourage each other; gradually experience and understand the beliefs and essence of a magnanimous, enterprising, and optimistic attitude; and achieve a relaxing, harmonious, and peaceful state.
Outcome measurements
Magnanimous-enterprising levels were assessed using the 23-item EMQ self-rating scale, prepared by Yang R et al. in 2014 (29). This scale consists of 2 dimensions and 23 questions; the lower the score of each dimension, the less aggressive or open-minded the patient is. On the other hand, they have corresponding magnanimous or enterprising psychological and behavioral characteristics. This scale has good reliability and validity; the test–retest coefficients for the two dimensions and the total scores were from 0.710 to 0.825. The split-half reliability for the scale was 0.861. The calibration validity of the 16PF Personality Questionnaire on the boldness factor and stability factor was 0.623 and 0.728. Given our previous report on the effects of MT on emotional outcomes (22), this study focuses on exploring the impact on magnanimous-enterprising levels, thus omitting the repeated use of the PSSCP and HADS scales.
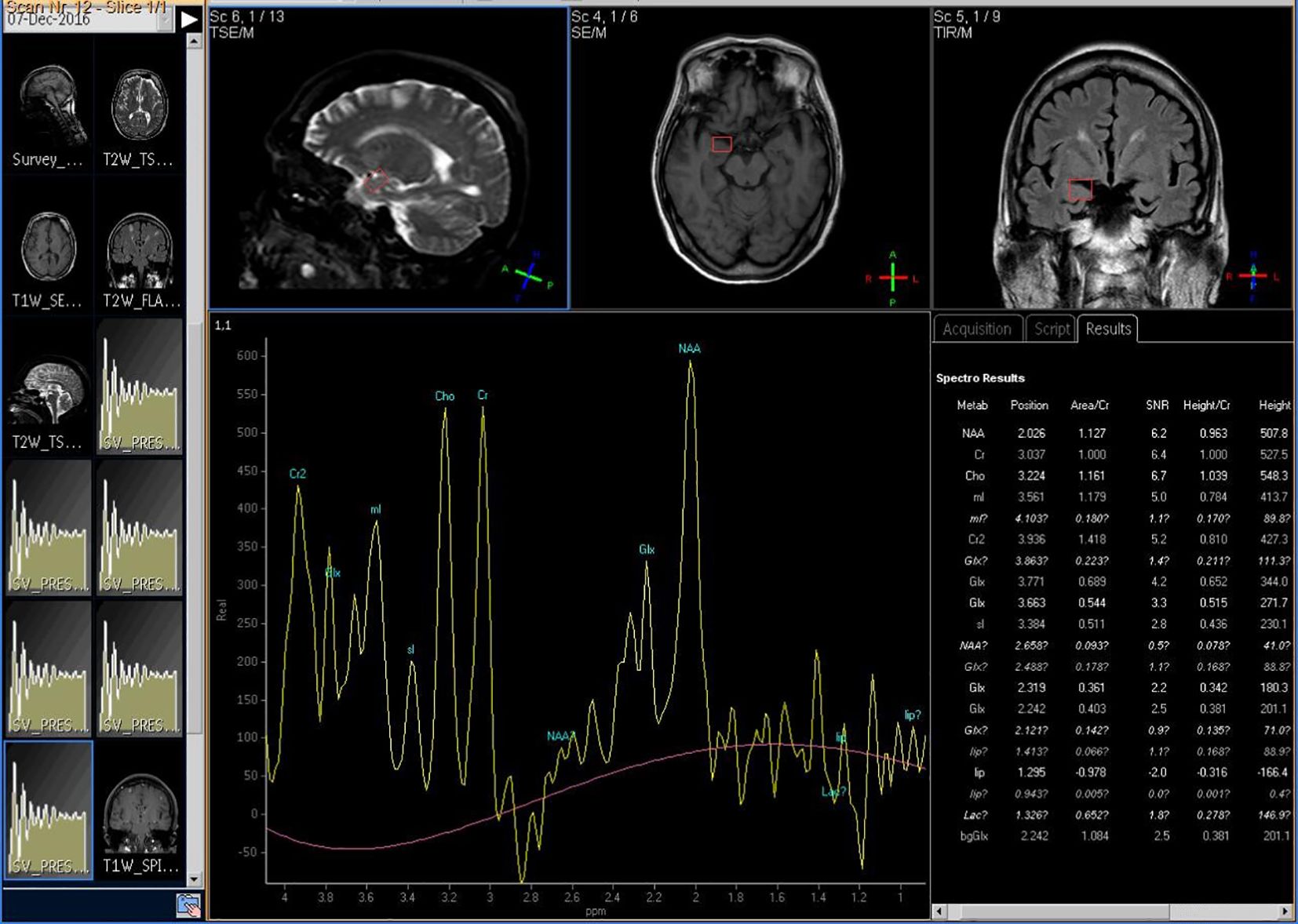
The Siemens 3.0T superconducting magnetic resonance imaging system (Magnetom Trio Tim, Siemens, Erlangen, Germany) was used to measure brain metabolic indices. Firstly, routine MRI scanning was performed with SE sequence to exclude brain lesions and locate 1H-MRS. Triaxial localization was used in this study. Multi-voxel imaging (MVS) 3D-CSI (chemical shift image) sequence was used for 1H-MRS scanning. The repetition time was 1,700 ms and the recovery time was 135 ms. The signal was processed by Philips random software (Achieva 3.0TTx) and converted into data and spectrogram to reflect the relative levels of NAA, Cho, Cr, mI, and Glx (because the absolute quantitative difference of a single metabolite was too large, it was represented by international relative quantitative NAA/Cr, Cho/Cr, mI/Cr, and Glx/Cr). As shown in Figure 2, taking Cr as the reference, NAA/Cr, Cho/Cr, mI/Cr, and Glx/Cr were calculated.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using the IBM SPSS application (version 25.0: IBM, Armonk, NY, USA). Classified data were recorded by absolute frequency and percentage, and quantitative data were recorded by mean and standard deviation.
To assess comparability between the two groups, baseline sociodemographic and clinical characteristics were tested by the χ² test and t-test. The differences in the outcome variables between the GCMT group and the control group were compared by independent samples t-test, and the differences of the outcome variable between baseline and 2 weeks later within the two groups were analyzed using paired samples t-test. Pearson correlation was employed to probe the impact factors on the changes in brain metabolic levels. The level of statistical significance was set at p <0.05, and the statistical analyses were considered two-tailed.
Results
Baseline characteristics of the study groups
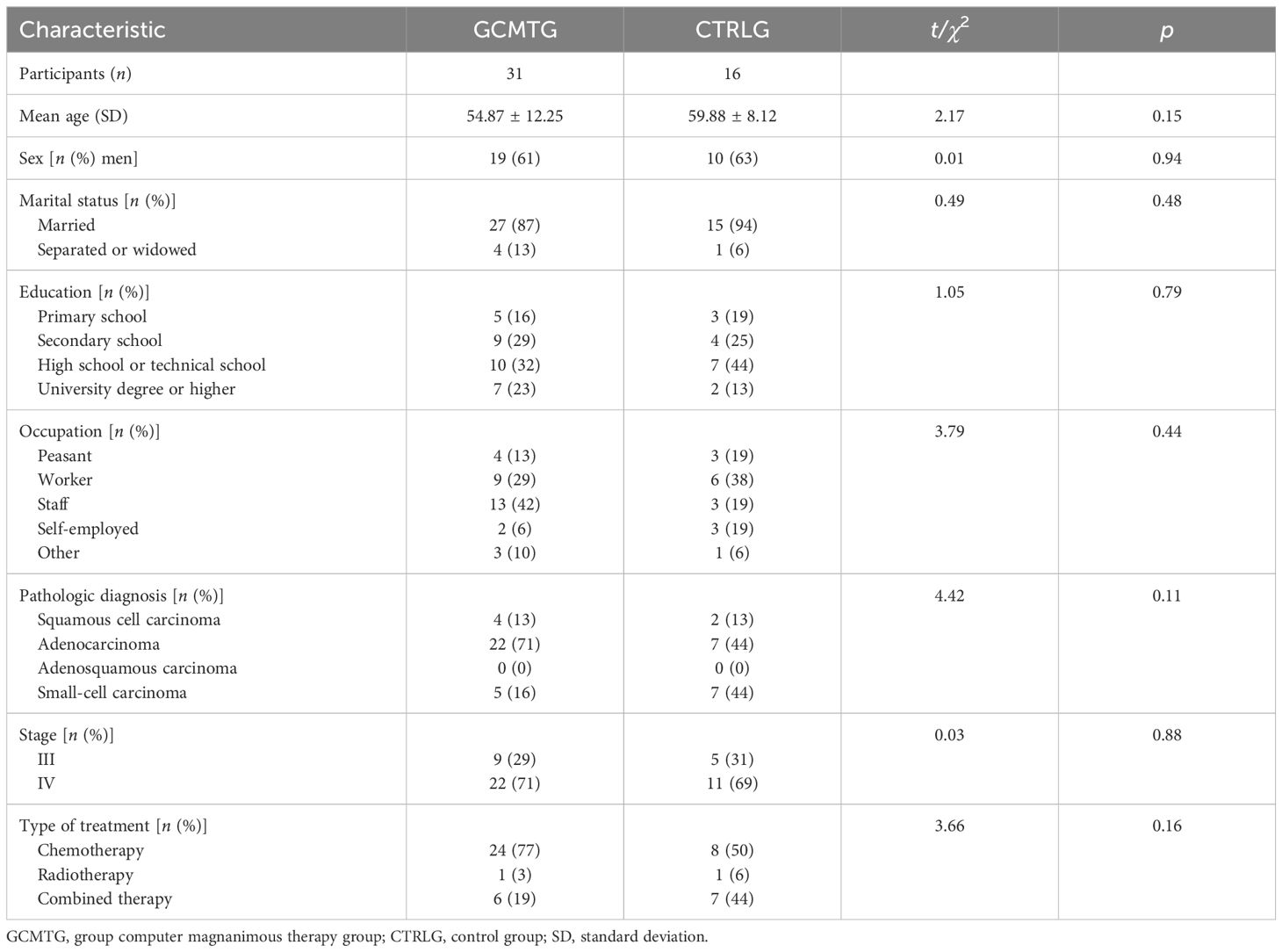
A total of 47 participants were included in this study: 31 patients in the GCMTG and 16 patients in the CTRLG. There were 19 men in the GCMTG, with a mean age of 54.87 ± 12.25; 27 were married and 4 separated or widowed; 5 had primary school education, 9 secondary school education, 10 high school or technical school education, and 7 university education or above; 4 were farmers, 9 workers, 13 staff, 2 self-employed individuals, and 3 others; 4 had squamous cell carcinoma, 22 adenocarcinoma, 5 small-cell carcinoma, and 0 adenosquamous carcinoma; 9 were in stage III and 22 in stage IV; 24 patients received chemotherapy, 1 received radiotherapy, and 6 received combined therapy. There were 10 men in the control group, with a mean age of 59.88 ± 8.12; 15 were married and 1 separated or widowed; 3 had primary school education, 4 secondary school education, 7 high school or technical school education, and 2 university education or above; 3 were farmers, 6 workers, 3 staffs, 3 self-employers, and 1 others; 2 had squamous cell carcinoma, 7 adenocarcinoma, 7 small-cell carcinoma, and 0 adenosquamous carcinoma; 5 were in stage III and 11 in stage IV; 8 patients received chemotherapy, 1 received radiotherapy, and 7 received combined therapy. As shown in Table 1, there were no significant differences between the two groups on baseline demographics. Within patients with the same cancer stage, there were also no differences between conditions on medical variables.
Magnanimous-enterprising level
After 2 weeks of GCMT, the dimensions of “total score,” “enterprising,” and “magnanimous” (4.87 ± 6.18, 17.06 ± 3.49, and −12.31 ± 4.88) of the GCMTG were higher than baseline (1.77 ± 5.91, 14.94 ± 3.68, and −13.16 ± 4.27). There were significant differences in the dimensions of “total score” and “enterprising” (p < 0.05). However, no significant difference was found in the dimension of “magnanimous” (p > 0.05).
The “total score,” “enterprising,” and “magnanimous” dimensions in the CTRLG (3.38 ± 5.94, 16.25 ± 2.72, and −12.88 ± 4.52) decreased compared with baseline (4.68 ± 7.68, 17.31 ± 3.63, and −12.63 ± 5.40). There was no significant difference in each of the three dimensions (p > 0.05).
Compared with the CTRLG (17.31 ± 3.63), the GCMTG (17.06 ± 3.49) scored significantly lower on the “enterprising” dimension at baseline (p < 0.05). However, there were no significant differences between the two groups 2 weeks later. The average difference between baseline and 2 weeks later in the dimension of “enterprising” for the GCMTG was significantly different from the CTRLG (p < 0.05). No statistically significant difference between the two groups was evident on the “magnanimous” dimension whether at baseline or after treatment. The difference between baseline and 2 weeks later on “magnanimous” of the two groups was not significant (p > 0.05) (Table 2).
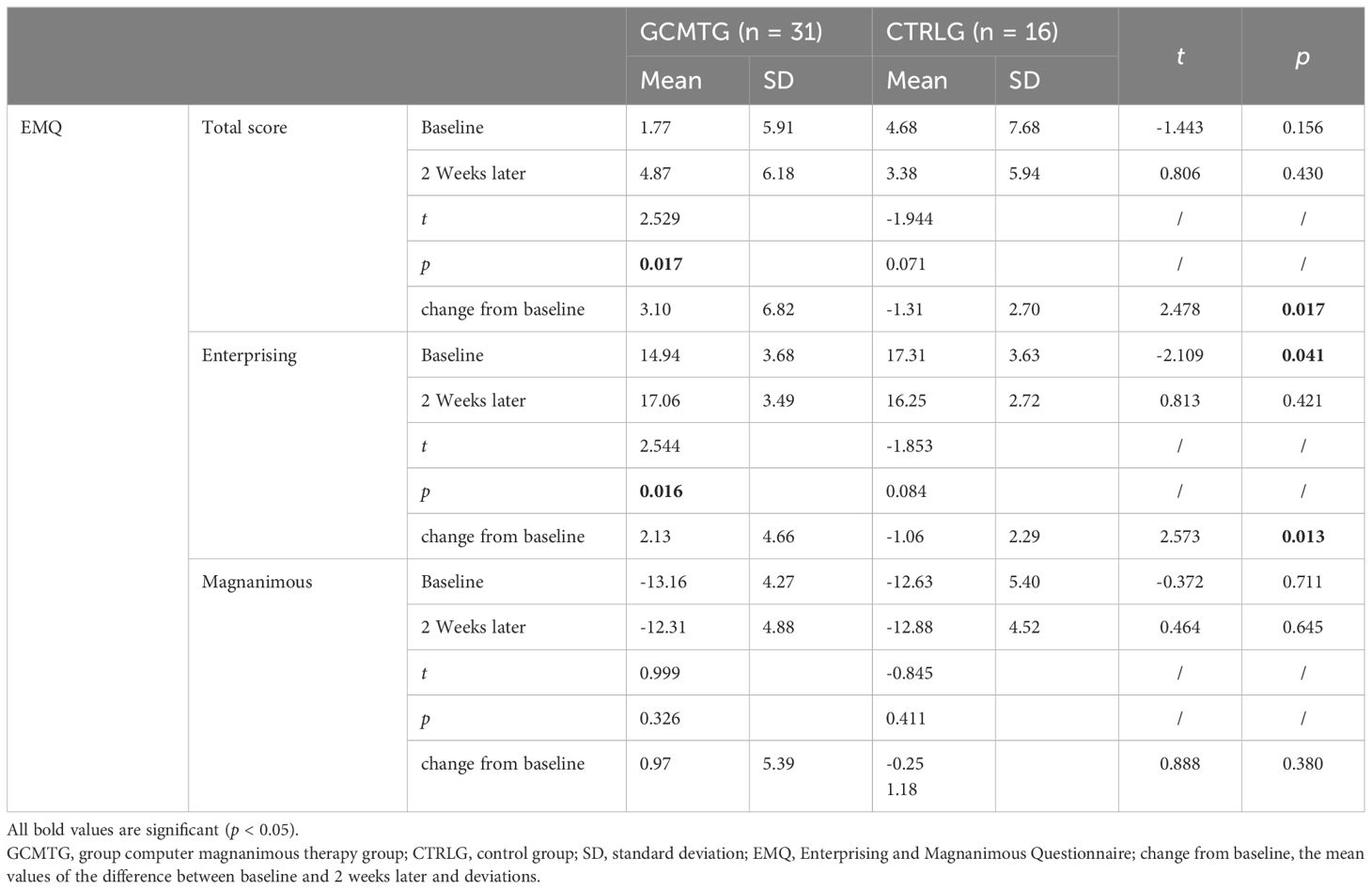
Table 2. Mean values and standard deviations of EMQ at baseline and post-intervention compared with the two groups.
The evaluation results of brain metabolites
The baseline brain metabolite variables did not have a statistically significant difference between the two groups. The mean level in the NAA/Cr of the right amygdala was significantly increased in the GCMTG, whereas there was no significant difference between the two groups (Table 3). The Cho/Cr levels of the left cingulate gyrus and right hippocampus of the control group were significantly higher than 2 weeks ago. However, there were no significant differences between the two groups. The average difference between baseline and 2 weeks later of the mean level of Cho/Cr of the right cingulate gyrus and left amygdala in the intervention group was significantly different from the control group (Table 4). The GCMTG had a significantly lower mean level of mI/Cr in the right cingulate gyrus than the CTRLG after 2 weeks. The average difference between baseline and 2 weeks later of the mean level of mI/Cr in the right cingulate gyrus of the GCMTG was clearly distinct from the CTRLG (Table 5). There was no significant difference in the ratios of Glx/Cr in the bilateral cingulate gyrus, hippocampus, and amygdala (Table 6).
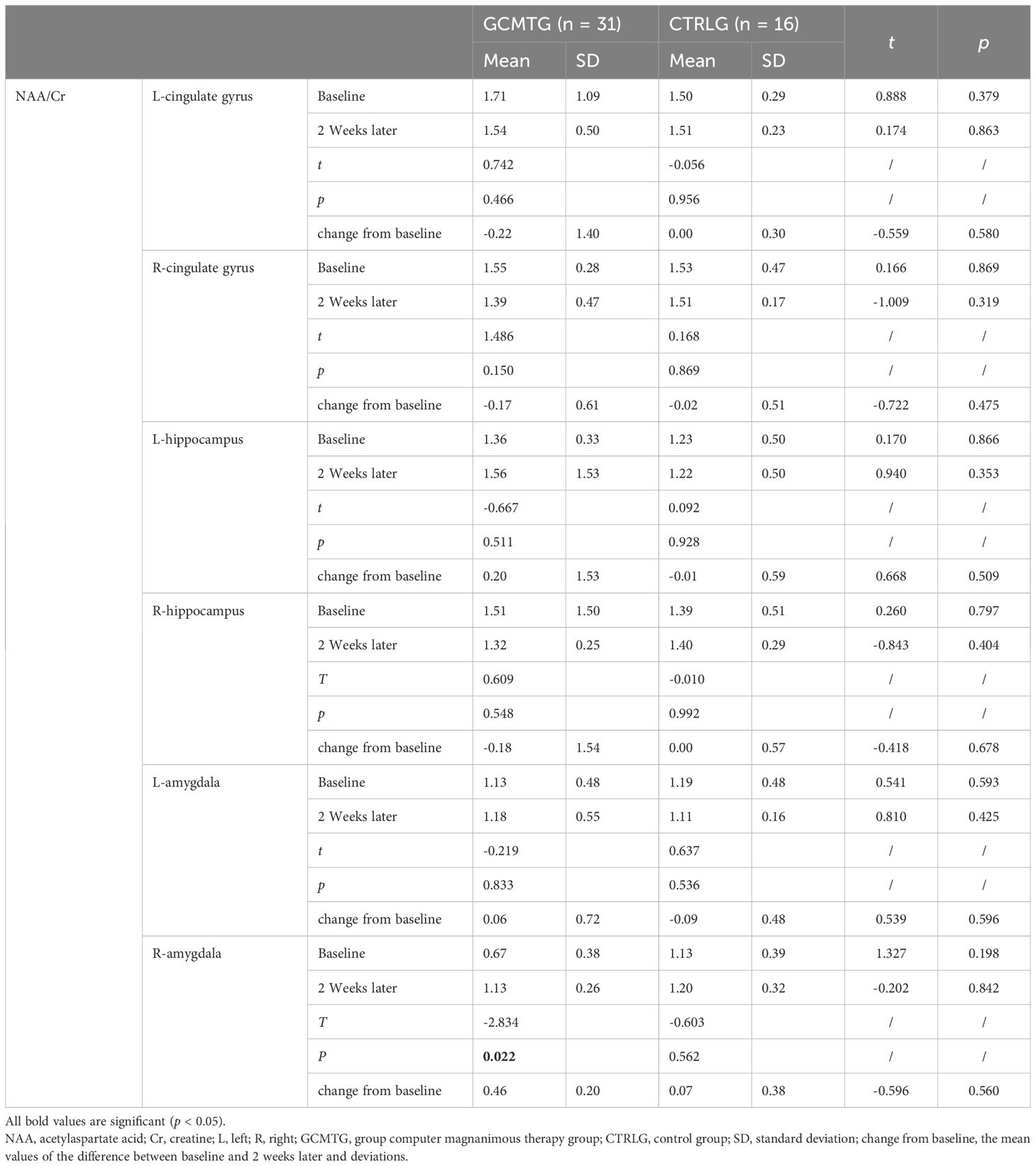
Table 3. Mean values and standard deviations of NAA/Cr at baseline and post-intervention compared with the two groups.
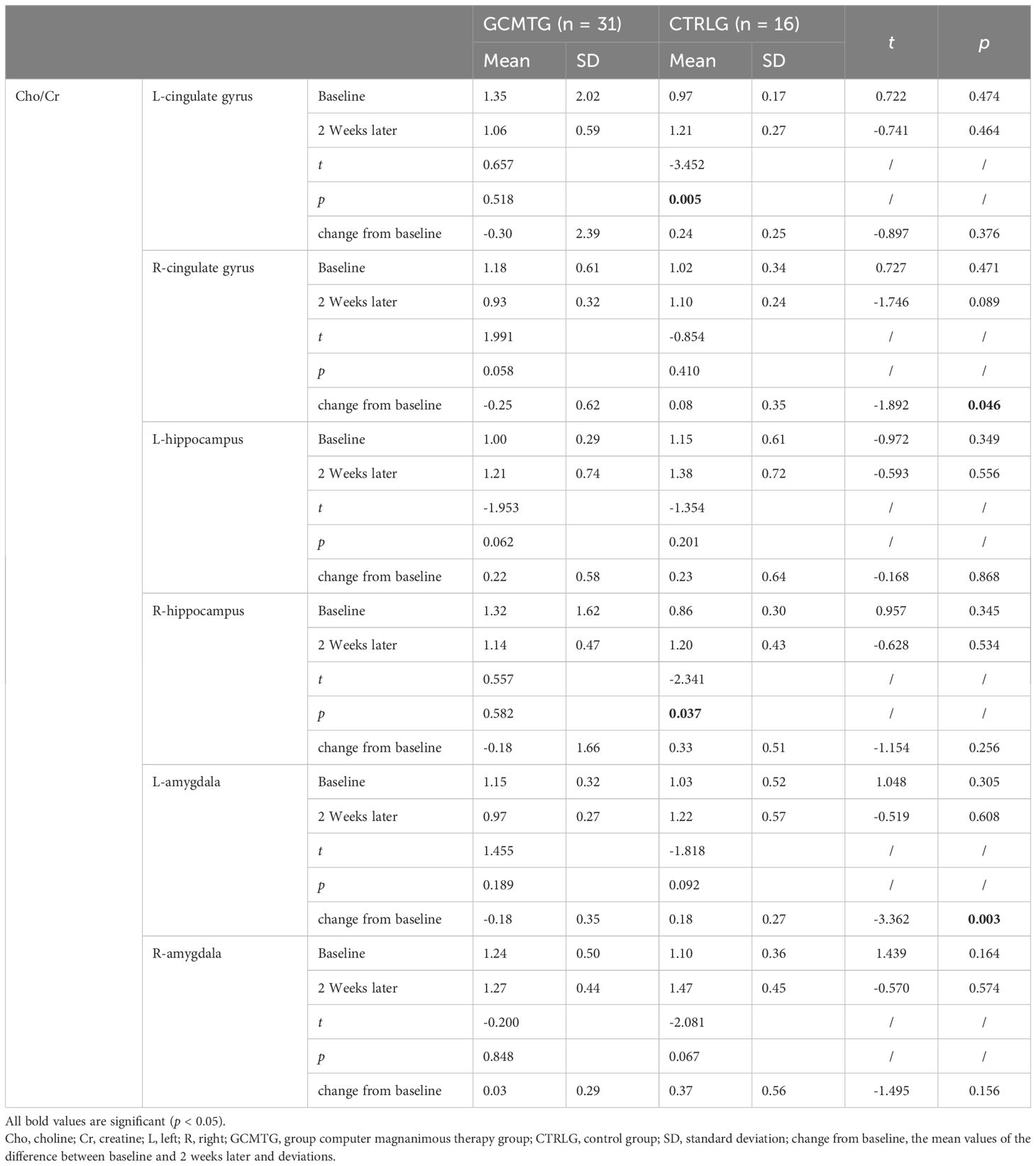
Table 4. Mean values and standard deviations of Cho/Cr at baseline and post-intervention compared with the two groups.
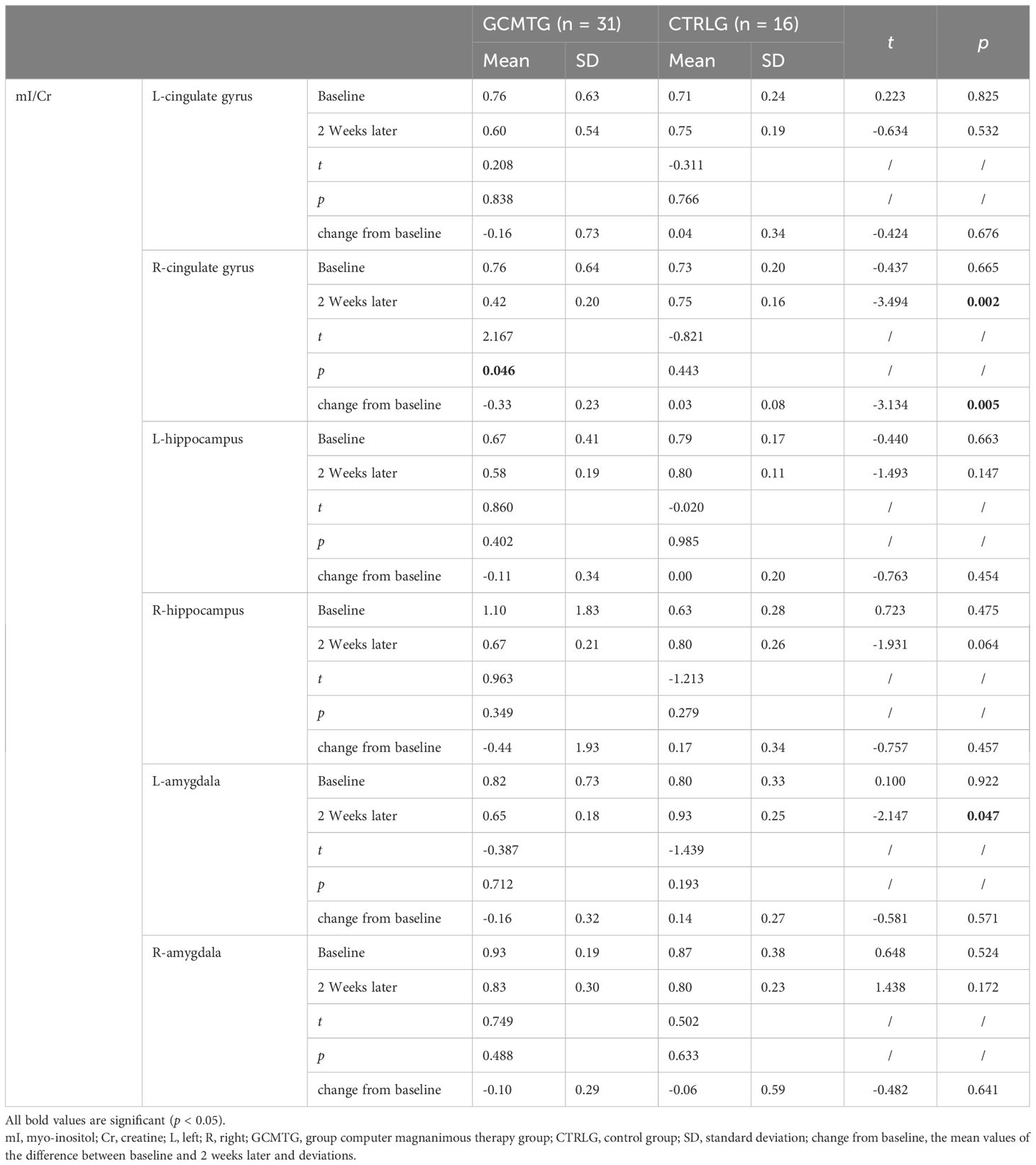
Table 5. Mean values and standard deviations of mI/Cr at baseline and post-intervention compared with the two groups.

Table 6. Mean values and standard deviations of Glx/Cr at baseline and post-intervention compared with the two groups.
The relationship between the changes of magnanimous-enterprising level and brain biochemical metabolism
A Pearson correlation analysis of the changes from baseline between the biochemical metabolism of the brain regions and EMQ scores was conducted to investigate the possible neuroanatomical mechanism. The results showed that changes in the mean level of Cho/Cr in the left amygdala and Glx/Cr in the left hippocampus were significantly correlated to the changes in enterprising level (Figures 3–5). The changes in individual magnanimous level had a significant correlation with the changes of mI/Cr level and Glx/Cr in the left cingulate gyrus (Figures 3, 5, 6).

Figure 3. Pearson correlation radar chart of changes in magnanimous-enterprising level and NAA/Cr metabolism in various brain regions.
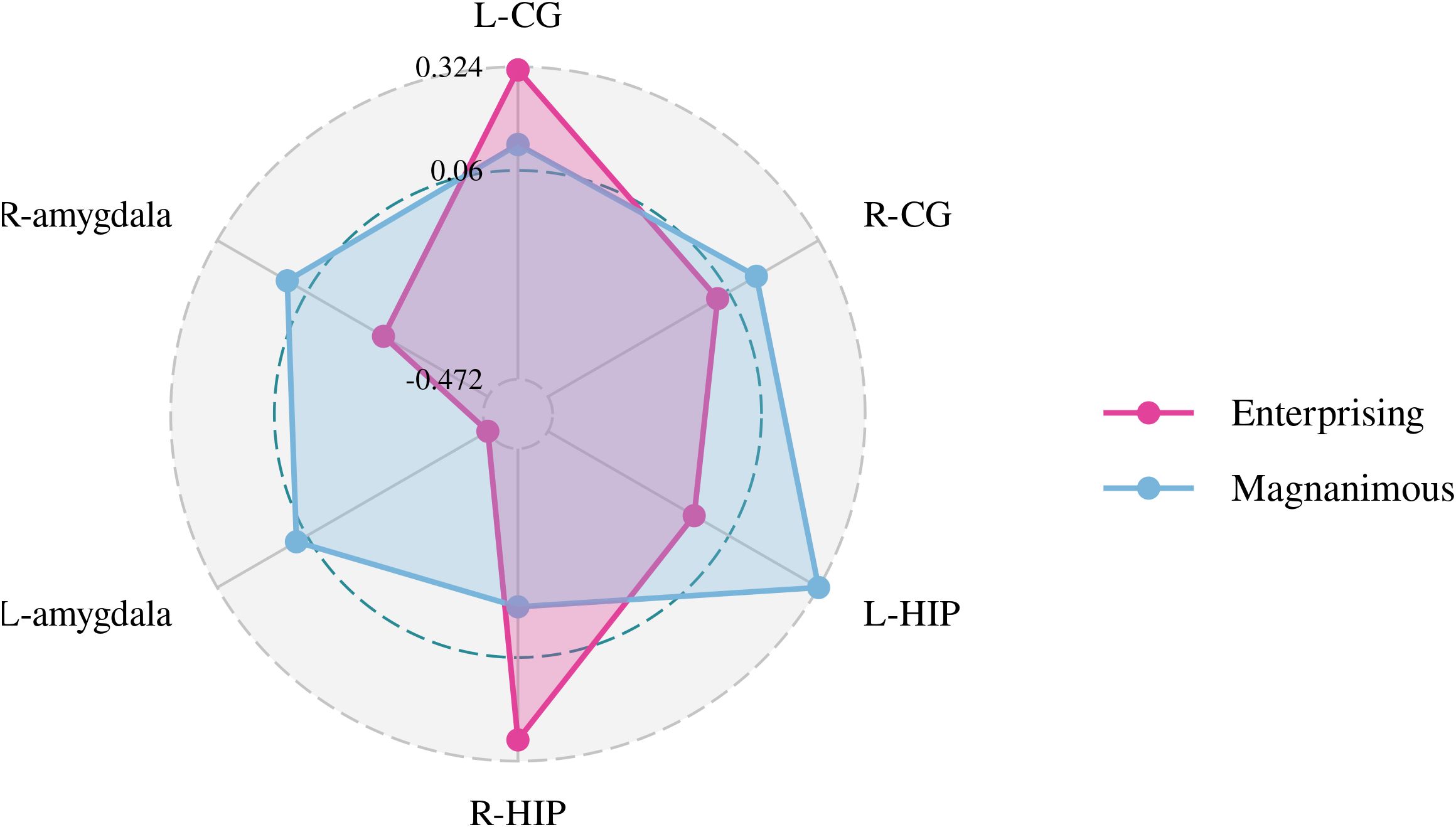
Figure 4. Pearson correlation radar chart of changes in magnanimous-enterprising level and Cho/Cr metabolism in various brain regions.
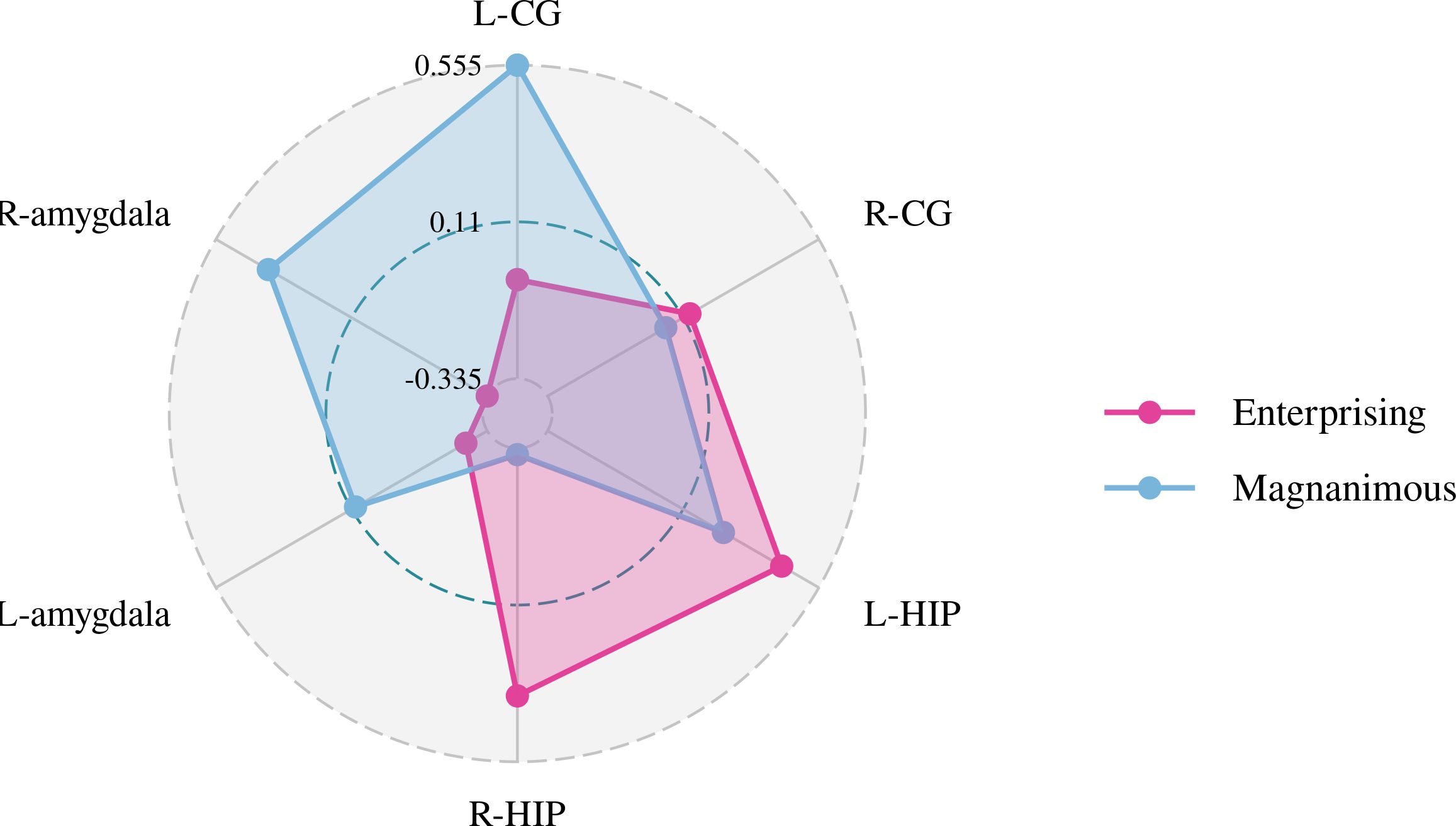
Figure 5. Pearson correlation radar chart of changes in magnanimous-enterprising level and Glx/Cr metabolism in various brain regions.
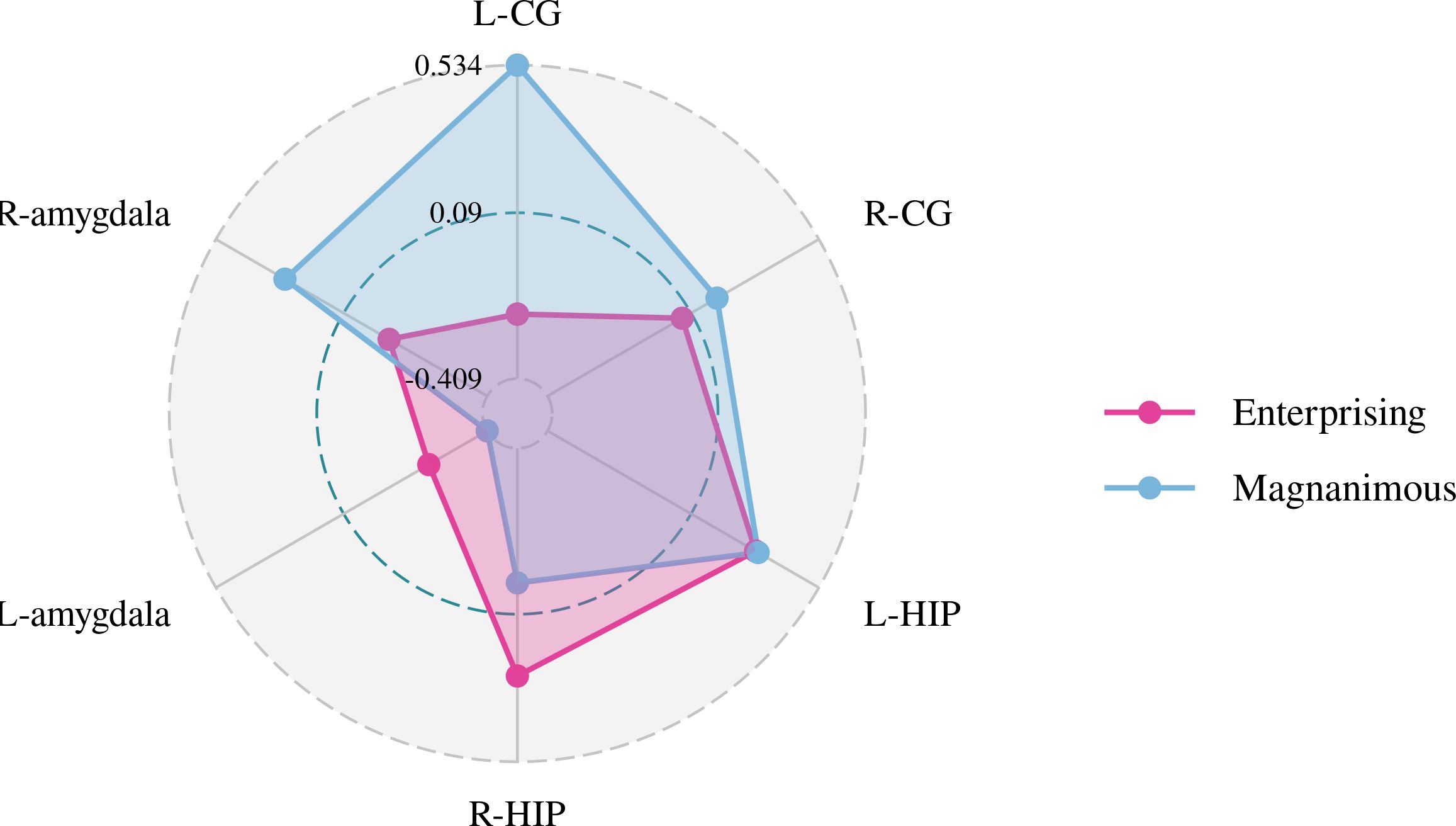
Figure 6. Pearson correlation radar chart of changes in magnanimous-enterprising level and mI/Cr metabolism in various brain regions.
Discussion
In China, previous studies have reported that per capita medical resources are relatively scarce, and the population’s health awareness of cancer prevention is comparatively poor. A total of 75% of lung cancer patients were diagnosed at the advanced stage and missed the best treatment period (30). Although tumor diagnosis and treatment technology have made great progress, we are still helpless in the face of the most advanced tumors. Therefore, it is particularly important to use psychotherapy to intervene with the psychosomatic status of cancer patients, assist in clinical treatment, and improve the long-term quality of life of cancer patients.
As a new psychotherapy for patients with advanced lung cancer, GCMT significantly improved the levels of enterprising and brain metabolism in our study. After the intervention, the “total score” and “enterprising” dimensions of EMQ revealed a significant improvement in the GCMTG, and the magnitude of the changes from baseline was significantly different from the control group. After 2 weeks, NAA/Cr of the right amygdala and mI/Cr of the right cingulate gyrus showed significant (p < 0.05) changes in the GCMTG. Although there was no difference between baseline and 2 weeks later of Cho/Cr in the left amygdala and right cingulate gyrus in either the GCMTG or the CTRLG, there was a statistically significant difference when comparing the changes over 2 weeks between the two groups.
It has been found that the mental health status of cancer patients corresponds to their personality traits (introversion, loneliness, stubbornness, emotional imbalance, obsessive–compulsive symptoms and thinking, maladjustment, interpersonal sensitivity) (31, 32). At the same time, studies have shown that the occurrence, development, and prognosis of tumors are closely related to the psychological personality factors of patients (33). Cancer patients with long-term survival and quality of life generally have common psychological characteristics of positive optimism, balanced understanding, open-minded tolerance, and good fortune (34). Therefore, a positive and open-minded attitude can delay the occurrence and development of cancer and affect its prognosis, which is the key factor to improve the quality of life and extend the lifespan of cancer patients (35–37). Our study showed that GCMT was helpful in cultivating a positive and enterprising belief in hospitalized patients with lung cancer, which showed that GCMT has a positive significance for clinical rehabilitation and long-term survival of patients with advanced lung cancer.
In the treatment stage, through the guidance and inspiration of the therapist, the patients experienced gradual realization or epiphany; through interaction and communication among group members, GCMT aroused resonance and reflection, promoted the growth of members, deepened their understanding of life, improved the curative effect, enabled patients to cooperate with the clinical treatment of lung cancer with a positive attitude, established effective social support, and helped patients reduce loneliness caused by cancer; these are made possible through repeated learning, remembering, and perceiving the enterprising and magnanimous information and applying to solve the problems in daily life, leading to an enterprising and magnanimous state of mind. Through mutual encouragement among group members and the sharing of successful cases, the levels of the “enterprising” dimension have changed significantly.
Aside from the observation of the psychological advantages of GCMT, we were especially encouraged by the observed improvement in brain metabolism. Although no significant changes in brain metabolism were observed in most brain regions in the GCMTG before and after the intervention, which was consistent with the research results of Yang R (38) and Bao H (39), the results suggest that the NAA/Cr level in the right amygdala in the intervention group increased significantly, while the NAA/Cr level in the left hippocampus and left amygdala tended to increase, which was similar to other studies (40). NAA widely exists in the neurons and is responsible for the integrity of neurons. Many studies have shown that the NAA/Cr ratio of the prefrontal cortex and anterior cingulate cortex was significantly associated with neuronal damage, cognitive decline, and unhealthy emotions (41–43). Therefore, it can be inferred that GCMT can improve patients’ negative emotions and functional abilities, which also confirms the results of our previous psychological measurements (27, 28) from the perspective of neuroimaging.
There was a significant difference in Cho/Cr in the right cingulate gyrus and left amygdala between the GCMTG and the CTRLG before and after treatment (p < 0.05). The Pearson correlation analysis of the changes from baseline and 2 weeks later of the indicators for the study groups showed that the changes of Cho/Cr in the left amygdala and Glx/Cr in the left hippocampus may be the factors that drive the improvements of enterprising mentality. Therefore, it can be inferred that the impact of GCMT on enterprising attitude may be related to the reduction of Cho/Cr in the left amygdala. Studies showed that the left amygdala may be related to negative emotions such as anger, fear, sadness, and continuous daily painful emotional experiences (44, 45). It was speculated that the decreased level of Cho/Cr in the amygdala leads to improvement of negative emotional experiences. In other words, GCMT was probable to make patients more confident in the treatment and lead to positive changes by improving patients’ daily negative emotional experiences. A meta-analysis of proton magnetic resonance (1H-MRS) spectroscopy studies (11) showed that reduced levels of Glx metabolites in the medial prefrontal cortex may be associated with the pathophysiology of depression (SMD = −0.38; 95% CI, −0.69 to −0.07). However, due to technical localization reasons, we were unable to measure the Glx/Cr in the medial prefrontal cortex of lung cancer patients. We will supplement the brain metabolism studies of the medial prefrontal cortex in subsequent experiments and further explore the intrinsic relationship between emotions such as depression or anxiety and magnanimous-enterprising levels.
Based on Moher D and Newell’s recommendations and revised CONSORT statement (46), we clearly and in detail explained the procedure of this study in the “study design” section, taking full account of the sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of all patients to control bias. In addition, each volunteer was followed up. The manner and process of intervention have been described above. The study design has been examined by oncologists, statisticians, other psychologists, and psychiatrists, which was considered scientific and strict.
There are several limitations in the present study. First, we failed to observe significant changes in the “magnanimous” dimension, which was probably due to the limitation of intervention time and the stability of psychological and behavioral habits. Further research is warranted to assess the long-term effects. Secondly, our strict inclusion and exclusion criteria lowered our sample size, which made the statistical results prone to deviation. Further research with larger sample sizes is needed to confirm our results. Third, with the limitation of experimental conditions, we were unable to collect data from other brain regions like the striatum and thalamus, which are closely related to the generation and regulation of emotion. Further studies to investigate the mechanism of the improvements of cerebral metabolic functions for GCMT are needed.
Conclusion
We demonstrated that GCMT has positive short-term effects on the enterprising levels and brain metabolic functions of patients with advanced lung cancer. Patients who received GCMT intervention exhibited a significant increase in their scores on the “enterprising” dimension and a notable decrease in the Cho/Cr ratio in the left amygdala. This suggests that GCMT may improve patients’ psychological states by influencing the metabolic activity of emotion-related brain regions.
These results provide empirical support for the application of GCMT in patients with advanced lung cancer, expanding the potential of psychological interventions in cancer treatment. Future studies should further validate these findings and explore the long-term effects and underlying mechanisms of GCMT.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the clinical medical ethics committee of Guangdong Pharmaceutical University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
QL: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. QM: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. QS: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Resources, Validation, Writing – review & editing. XH: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was supported by grants from the Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC): grant no. 81372488.
Acknowledgments
We thank the contribution of the patients, statisticians, doctors, nurses, and the hospital’s information technology department from the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, Guangzhou Cancer Hospital, and the Oncology Department of Dongguan Donghua Hospital.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1397375/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. (2021) 71:209–49. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660
2. Global Burden of Disease 2019 Cancer Collaboration, Kocarnik JM, Compton K, Dean FE, Fu W, Gaw BL, et al. Cancer incidence, mortality, years of life lost, years lived with disability, and disability–adjusted life years for 29 cancer groups from 2010 to 2019: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2019. JAMA Oncol. (2022) 8:420–44. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2021.6987
3. World Health Organization (WHO). World cancer report: Cancer research for cancer prevention. In: Wild CP, Weiderpass E, Stewart BW (Eds.), World Cancer Reports. (2021)
4. Rajapakse P. An update on survivorship issues in lung cancer patients. World J Oncol. (2021) 12:45–9. doi: 10.14740/wjon1368
5. Arbyn M, Weiderpass E, Bruni L, de Sanjosé S, Saraiya M, Ferlay J, et al. Estimates of incidence and mortality of cervical cancer in 2018: a worldwide analysis. Lancet Glob Health. (2020) 8:e191–203. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(19)30482-6
6. Cao M, Chen W. Epidemiology of lung cancer in China. Thorac Cancer. (2019) 10:3–7. doi: 10.1111/tca.2019.10.issue-1
7. Carlson LE, Zelinski EL, Toivonen KI, Sundstrom L, Jobin CT, Damaskos P, et al. Prevalence of psychosocial distress in cancer patients across 55 North American cancer centers. J Psychosoc Oncol. (2019) 37:5–21. doi: 10.1080/07347332.2018.1521490
8. de Mol M, Visser S, Aerts J, Lodder P, van Walree N, Belderbos H, et al. The association of depressive symptoms, personality traits, and sociodemographic factors with health–related quality of life and quality of life in patients with advanced–stage lung cancer: an observational multi–center cohort study. BMC Cancer. (2020) 20:431. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-06823-3
9. Niedzwiedz CL, Knifton L, Robb KA, Katikireddi SV, Smith DJ. Depression and anxiety among people living with and beyond cancer: a growing clinical and research priority. BMC Cancer. (2019) 19:943. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-6181-4
10. Andersen BL, McElroy JP, Carbone DP, Presley CJ, Smith RM, Shields PG, et al. Psychological symptom trajectories and non–small cell lung cancer survival: A joint model analysis. Psychosom Med. (2022) 84:215–23. doi: 10.1097/PSY.0000000000001027
11. Moriguchi S, Takamiya A, Noda Y, Horita N, Wada M, Tsugawa S, et al. Glutamatergic neurometabolite levels in major depressive disorder: a systematic review and meta–analysis of proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy studies. Mol Psychiatry. (2019) 24:952–64. doi: 10.1038/s41380-018-0252-9
12. Igarashi H, Takeda M, Natsumeda M, Fujii Y. (Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H–MRS)). No Shinkei Geka. (2021) 49:438–44. doi: 10.11477/mf.1436204411
13. Knudsen MK, Near J, Blicher AB, Videbech P, Blicher JU. Magnetic resonance (MR) spectroscopic measurement of γ–aminobutyric acid (GABA) in major depression before and after electroconvulsive therapy. Acta Neuropsychiatr. (2019) 31:17–26. doi: 10.1017/neu.2018.22
14. Reddy S, Goyal N, Shreekantiah U. Adjunctive deep transcranial magnetic stimulation (dTMS) in obsessive compulsive disorder: Findings from 1H–magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Asian J Psychiatr. (2021) 62:102721. doi: 10.1016/j.ajp.2021.102721
15. Park SE, Choi NG, Jeong GW. Metabolic abnormality in the right dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in patients with obsessive–compulsive disorder: proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Acta Neuropsychiatr. (2017) 29:164–9. doi: 10.1017/neu.2016.48
16. Benson KL, Bottary R, Schoerning L, Baer L, Gonenc A, Eric Jensen J, et al. 1H MRS measurement of cortical GABA and glutamate in primary insomnia and major depressive disorder: relationship to sleep quality and depression severity. JAffect Disord. (2020) 274:624–31. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2020.05.026
17. Huang BJ. The impact of electro–acupuncture therapy on the cerebral executive function of the patients with IAD based on the application of MRS. Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu, China (2014).
18. Yang Y. The impact of electro–acupuncture on the impulsive behaviour and the change of magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) in patients with internet addiction disorder. Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu, China (2013).
19. Streeter CC, Whitfield TH, Owen L, Rein T, Karri SK, Yakhkind A, et al. Effects of yoga versus walking on mood, anxiety, and brain GABA levels: a randomized controlled MRS study. J Altern Complement Med. (2010) 16:1145–52. doi: 10.1089/acm.2010.0007
20. Whiteside SP, Abramowitz JS, Port JD. Decreased caudate N–acetyl–l–aspartic acid in pediatric obsessive–compulsive disorder and the effects of behaviour therapy. Psychiatry Res. (2012) 202:53–9. doi: 10.1016/j.pscychresns.2011.11.010
22. Huang X, Liu Q, Li WW, Wu L, Yan A. Effects of magnanimous therapy on emotional, psychosomatic and immune functions of lung cancer patients. J Health Psychol. (2021) 26:1096–108. doi: 10.1177/1359105319901312
23. Lu H. Individual gaming edition enterprising–magnanimous– relaxed therapy and effect of its use in depression. Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, Guangzhou, China (2013).
24. Qian L. Individual computer magnanimous–relaxed therapy and effect of its use in breast cancer. Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, Guangzhou, China (2011).
25. Huang X, Guo B, Wang X, Zhang Y, Lv B. Development and evaluation of the Cancer Coping Modes Questionnaire. Chin Ment Health J. (2007) 121:517–20,525. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6729.2007.08.002
26. Huang X, Wang X, Zhang Y, Lv B, Guo B. Development and evaluation of the Psychological Adjustment Scale for cancer patients. Chin Ment Health J. (2007) 121:521–5. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6729.2007.08.003
27. Huang X, Yan A, Liu Q, Wu L. Effects of magnanimous therapy on coping, adjustment, and living function in advanced lung cancer. Curr Oncol. (2019) 26:e48–e56. doi: 10.3747/co.26.4126
28. Li R, Huang X, Li Y, Wang X. Effect of group computer magnanimous–relaxed therapy in coping and adjustment in breast cancer. Chin J Clin Res. (2017) 30:1718–20, 1723. doi: 10.13429/j.cnki.cjcr.2017.12.041
29. Yang R, Huang X, Pang R, Lin D, Qiu H, Chen S, et al. Development and evaluation of enterprising and magnanimous questionnaire. Chin J Behavi– Oral Med Brain Sci. (2014) 23:175–7. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-6554.2014.02.024
30. Xiao J, Zheng Y. The global prevalence and prevention progress of lung cancer. China Oncol. (2020) 30:721–5. doi: 10.19401/j.cnki.1007-3639.2020.10.001
31. Wang YH, Li JQ, Shi JF, Que JY, Liu JJ, Lappin JM, et al. Depression and anxiety in relation to cancer incidence and mortality: a systematic review and meta– analysis of cohort studies. Mol Psychiatry. (2020) 25:1487–99. doi: 10.1038/s41380-019-0595-x
32. Ota A, Li Y, Yatsuya H, Tanno K, Sakata K, Yamagishi K, et al. Working cancer survivors' physical and mental characteristics compared to cancer–free workers in Japan: a nationwide general population–based study. J Cancer Surviv. (2021) 15:912–21. doi: 10.1007/s11764-020-00984-7
33. Zhao X, Tong S, Yang Y. The correlation between quality of life and positive psychological resources in cancer patients: A meta–analysis. Front Psychol. (2022) 13:883157. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.883157
34. Firkins J, Hansen L, Driessnack M, Dieckmann N. Quality of life in "chronic" cancer survivors: a meta–analysis. J Cancer Surviv. (2020) 14:504–17. doi: 10.1007/s11764-020-00869-9
35. Tian X, Yi LJ, Liang CS, Gu L, Peng C, Chen GH, et al. The impact of mindfulness–based stress reduction (MBSR) on psychological outcomes and quality of life in patients with lung cancer: A meta–analysis. Front Psychol. (2022) 13:901247. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.901247
36. Hulbert–Williams NJ, Storey L, Wilson KG. Psychological interventions for patients with cancer: psychological flexibility and the potential utility of Acceptance and Commitment Therapy. Eur J Cancer Care (Engl). (2015) 24:15–27. doi: 10.1111/ecc.12223
37. Khosravi N, Stoner L, Farajivafa V, Hanson ED. Exercise training, circulating cytokine levels and immune function in cancer survivors: A meta–analysis. Brain Behav Immun. (2019) 81:92–104. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2019.08.187
38. Yang R, Gou R, Yan H, Wang P, Yuan Y, Huo Z, et al. Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy of the thalamus and hypothalamus in patients with depressive disorder before and after treatment. J Pract Radiol. (2014) 2014(10):1610–3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1671.2014.10.002
39. Li Y, Wang C, Teng C, Jiao K, Song X, Tan Y, et al. Hippocampus–driving progressive structural alterations in medication–naïve major depressive disorder. J Affect Disord. (2019), 256:148–155. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2019.05.053
40. Erbay MF, Zayman EP, Erbay LG, Ünal S. Evaluation of transcranial magnetic stimulation efficiency in major depressive disorder patients: A magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. Psychiatry Investig. (2019) 16:745–50. doi: 10.30773/pi.2019.07.17.3
41. He C, Rong S, Zhang P, Li R, Li X, Li Y, et al. Metabolite changes in prefrontal lobes and the anterior cingulate cortex correlate with processing speed and executive function in Parkinson disease patients. Quant Imaging Med Surg. (2022) 12:4226–38. doi: 10.21037/qims-21-1126
42. Chen LP, Dai HY, Dai ZZ, Xu CT. Wu RH.Anterior cingulate cortex and cerebellar hemisphere neurometabolite changes in depression treatment: A 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. (2014) 68:357–64. doi: 10.1111/pcn.2014.68.issue-5
43. Bonnekoh LM, Seidenbecher S, Knigge K, Hünecke AK, Metzger CD, Tempelmann C, et al. Long–term cortisol stress response in depression and comorbid anxiety is linked with reduced N–acetylaspartate in the anterior cingulate cortex. World J Biol Psychiatry. (2023) 24:34–45. doi: 10.1080/15622975.2022.2058084
44. Roseman L, Demetriou L, MB W, DJ N, Carhart–Harris RL. Increased amygdala responses to emotional faces after psilocybin for treatment–resistant depression. Neuropharmacology. (2018) 142:263–9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.12.041
45. Puccetti NA, Schaefer SM, van Reekum CM, Ong AD, Almeida DM, Ryff CD, et al. Linking amygdala persistence to real–world emotional experience and psychological well–being. J Neurosci. (2021) 41:3721–30. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1637-20.2021
Keywords: group computer magnanimous therapy, magnanimous-enterprising level, brain metabolism, lung cancer, psychosomatic effects
Citation: Liu Q, Ma Q, Sun Q and Huang X (2024) The cerebral metabolic mechanism of group computer magnanimous therapy based on magnetic resonance spectroscopy: effects on improving magnanimous-enterprising levels of lung cancer patients. Front. Psychiatry 15:1397375. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1397375
Received: 07 March 2024; Accepted: 18 November 2024;
Published: 10 December 2024.
Edited by:
Samuel Ridout, Kaiser Permanente, United StatesReviewed by:
Khaldoon Dhou, Texas A&M University Central Texas, United StatesKathryn Ridout, Kaiser Permanente, United States
Copyright © 2024 Liu, Ma, Sun and Huang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xuewei Huang, c25vd3lfaHVhbmdAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†ORCID: Xuewei Huang, orcid.org/0000-0003-0552-8034
 Qianyu Liu
Qianyu Liu Qihui Ma2
Qihui Ma2 Qingfeng Sun
Qingfeng Sun