- 1Mental Health Center, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, Sichuan, China
- 2West China School of Nursing, Sichuan University, Chengdu, Sichuan, China
- 3Psychiatric Laboratory, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, Sichuan, China
- 4West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, Sichuan, China
- 5Department of Clinical Epidemiology and Evidence-Based Medicine, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, Sichuan, China
- 6Jingzhou Mental Health Center, Jingzhou, Hubei, China
- 7Wenjiang People’s Hospital, Chengdu, Sichuan, China
- 8Ya’an Fourth People’s Hospital, Ya’an, Sichuan, China
Background: Although the COVID-19 pandemic has greatly changed the way students studied, it is still unknown about the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on students’ academic performance and mental health.
Objective: To explore the academic performance and mental health status of middle and high school students after the lifting of COVID-19 restrictions in China.
Methods: An online survey was conducted in Sichuan province, China from Dec 14, 2022 to Feb 28, 2023. All participants were students in middle and high schools, recruited via their teachers. The general information, COVID-19-related information, and academic performance were collected. The Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9), Generalized Anxiety Disorder-7 (GAD-7), and Internet Addiction Test (IAT) were used to assess the mental health problems.
Results: Of 60,268 participants, 36,247 (60.2%) middle and high school students reported that their studies were affected by the COVID-19 pandemic, and 24,864 (41.2%) reported that their academic performance had worsened. The prevalence of depression and anxiety symptoms was 38.4 and 32.7%, respectively. There was a significant association between academic performance change and mental health problems. The logistic regression analysis showed that improved academic performance was a protective factor for depression, and declined academic performance was a risk factor for depression and anxiety. Being COVID-19 infected, family members being infected, with quarantine experience, and with COVID-19-related stigma were risk factors for depression and anxiety.
Conclusion: Academic studies and mental health status of middle and high school students in Sichuan, China have been negatively impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic, even after the lifting of COVID-19 restrictions. Students’ academic performance, academic concerns, and mental health status should be considered for educational policymakers and institutions to improve students’ academic studies and mental well-being.
1. Introduction
The COVID-19 pandemic had not only posed a great threat to human life and health, but also had an impact on almost all social fields, including students’ studies. In order to stop the spread of the virus, the Chinese government implemented many policies, including business cessation and school closures. To ensure not to interrupt students’ studies, online learning was adopted by educational institutions. Students had to change their way to study from traditional face-to-face learning at school to online learning at home. Previous studies indicated that the shift in learning style during the COVID-19 pandemic had a significant impact on students’ academic performance (1–3) and mental health status (4–7). However, it is still unclear how would academic performance changes affect mental health among Chinese students.
Evidence showed that most of previous studies on academic performance focused on students in colleges or universities, especially medical and nursing students (8–11). However, few studies have been conducted on academic performance in middle and high school students. The relationship between students’ academic performance and mental health should be explored further. China began to lift the COVID-19 restrictions on December 7, 2022. Then, in China, students, including those at middle and high schools, gradually returned back to normal campus life at schools. However, it is still unknown about the students’ academic performance and mental health status, especially after the lifting of COVID-19 restrictions in China.
This study aimed to explore the changes of academic performance and the association between academic performance and mental health among middle and high school students during and after the COVID-19 pandemic in Sichuan Province, China. We hypothesized that academic performance of students was impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic and students’ academic performance was significantly associated with their mental health problems.
2. Methods
2.1. Study design and participants
From December 14, 2022 to February 28, 2023, the cross-sectional mental health survey was conducted among middle and high school students in Sichuan Province, China. The online self-report questionnaires were sent firstly to school principals or teachers, then these principals and teachers sent the questionnaires directly to their students at schools. Adolescent students voluntarily participated in the online survey via platform of Wenjuanxing. Informed consent was obtained before participants began the survey. This study was approved by the Biomedical Research Ethics Committee of West China Hospital, Sichuan University (NO: 2022–1790).
2.2. Measurements
General information: The information included personal information (e.g., gender, age, grade, and ethnic minority, etc.) and family background (e.g., Household register, parents’ marital status, parents’ educational background, monthly family income, family economic level, one-child status, and parenting style, etc.).
COVID-19 related information: This part included whether individuals or family members were infected with COVID-19, quarantine experience, the levels of psychological stress in different stages, the impact of COVID-19 pandemic on daily life routine, and whether their study returned to normal status.
COVID-19 Stigma scale, with good reliability and validity (12), consists of 11 items including “I concern that people infected with novel coronavirus will cause harm to others,” “I will try to distance myself from those infected with novel coronavirus,” etc. Each item is scored from 1–4 (strongly disagree ~ strongly agree) with a total score of 11–44. The cut-off point of 2.5 was used for each item in this study.
Academic performance related information: The impact of COVID-19 on academic performance was assessed by the question “Has your study been affected during COVID-19 pandemic (e.g., worsened, no change, and improved).” This section also included concerns about the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on their studies, and whether their studies returned to normal status after the lifting of COVID-19 restrictions. The information of online learning was also collected.
The Internet Addiction Test (IAT), including 20 items, was used to assess whether participants were addicted to the internet and its extent (13). The total score ranged from 20 to 100. The cut-off point of 40 was used for internet addiction in this study. IAT is a commonly used test for internet addiction. IAT has good reliability and validity among Chinese populations and young people (14).
The Generalized Anxiety Scale (GAD-7), a commonly used scale, was used to evaluate students’ anxiety symptoms in the last 2 weeks (15). The scale consists of 7 items with a total score ranging from 0 to 21. The cut-off point of 5 was used for mild anxiety. GAD-7 has good reliability and validity among Chinese populations and young people (16–18)..
The Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9), a commonly used questionnaire, was used to measure depression symptoms in the last 2 weeks (19). The scale consists of 9 items with a total score range of 0–27. The cut-off point of 5 was used for mild depression. PHQ-9 has good reliability and validity among Chinese populations and young people (20, 21).
2.3. Statistical analysis
Participants who reported academic performance being affected by the COVID-19 pandemic and making progress were included in Group 1. Those who reported academic performance being same as before were included in Group 2. Those who reported academic performance being affected by the COVID-19 pandemic and being declined were included in Group 3. The SPSS 25.0 was applied to analyze the data. Descriptive statistics were used to analyze general information. Correlation analysis was used to explore the variables associated with academic performance. ANOVA and post-hoc test were used to analyze differences in mental health problems among the three groups. The logistic regression was used to explore both risk and protective factors for depression and anxiety. Factors that showed a significant level in univariate analysis were entered into the logistic regression analysis. As this study mainly focused on the relationship between risk factors and mental health problems rather than predicting individual mental health problems, therefore, the good fitness of the logistic regression model (e.g., R-squared and Hosmer-Lemeshow test) was not of significant concern. Statistical significance was taken as p < 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. General information
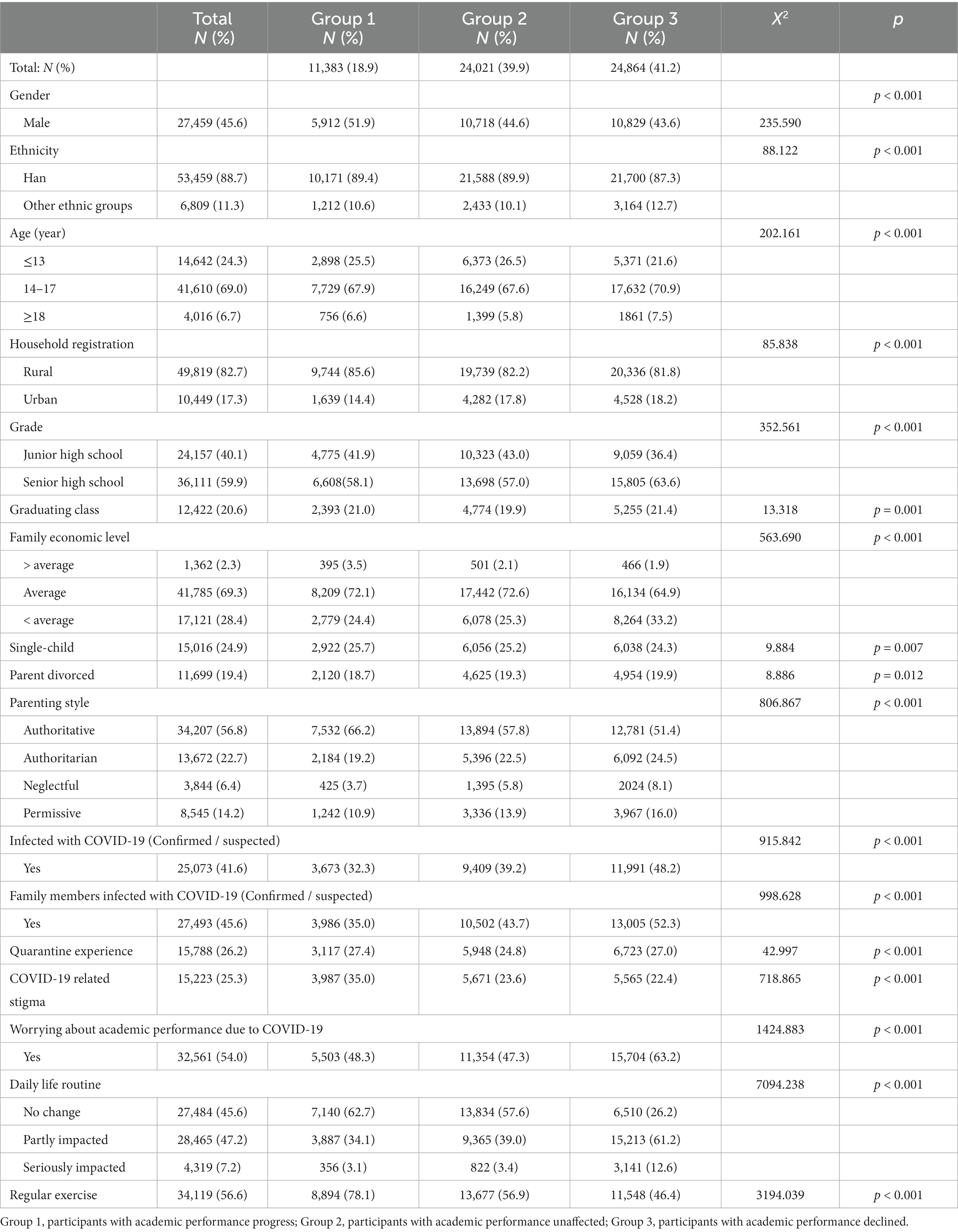
Table 1 shows the general information of the participants. A total of 60,268 participants voluntarily participated in this study and finished the questionnaires from middle and high schools in Sichuan, China. In total, all these middle and high school students aged from 11 to 19 (15.009 ± 1.813) years were included in the study. Among them, 27,459 (45.6%) participants were male, 53,459 (88.7%) were Han Chinese, 49,819 (82.7%) were resident in rural areas and 15,016 (24.9%) were from single-child family. There were 36,111 (59.9%) students from senior high schools, and 12,422 (20.6%) students were facing graduation. The proportion of students infected with COVID-19 was 41.6%.
3.2. Academic performance
For the academic performance, 11,383 (18.9%) participants reported that they had achieved academic progress, 24,021 (39.9%) had the same as before, and 24,864 (41.2%) were affected negatively by the COVID-19 pandemic and their academic performance declined. Participants in academic performance progress group (G1) had significantly higher rates of being male (51.9%), household registered in rural area (85.6%), with higher monthly family income (3.5%), authoritative parenting style (66.2%), and with regular exercise (78.1%) than those in G2 (44.6, 82.2, 2.1, 57.8, 56.9%) and G3 (43.6, 81.1, 1.9, 51.4, 46.4%) (p < 0.001). The rates of students with COVID-19-related stigma in participants with academic performance progress (G1) (35.0%) was significantly higher than that in G2 and G3 (23.6, 22.4%) (p < 0.001).
Compared with Group 1 and Group 3, participants in academic performance unaffected group (Group 2) had the lowest rates of being in graduating class (19.9% vs. 21.0, 21.4%), with quarantine experience (24.8% vs. 27.4, 27.0%) and worrying about the impact of COVID-19 pandemic on their studies (47.3% vs. 48.3, 63.2%) (p ≤ 0.001), and the highest rates of being Han Chinese (89.9% vs. 89.4, 87.3%), being in junior middle school (43.0% vs. 41.9, 36.4%) (p < 0.001). Participants’ worsen academic performance was significantly associated with household registered in urban area (18.2% vs. 14.4, 17.8%), in minority ethnic group (12.7% vs. 10.6, 10.1%), being senior high school students (63.6% vs. 58.1, 57.0%), lower family income (33.2% vs. 24.4, 25.3%), infected with COVID-19 (48.2% vs. 32.3, 39.2%), and family members infected (52.3% vs. 35.0, 43.7%) (p ≤ 0.001).
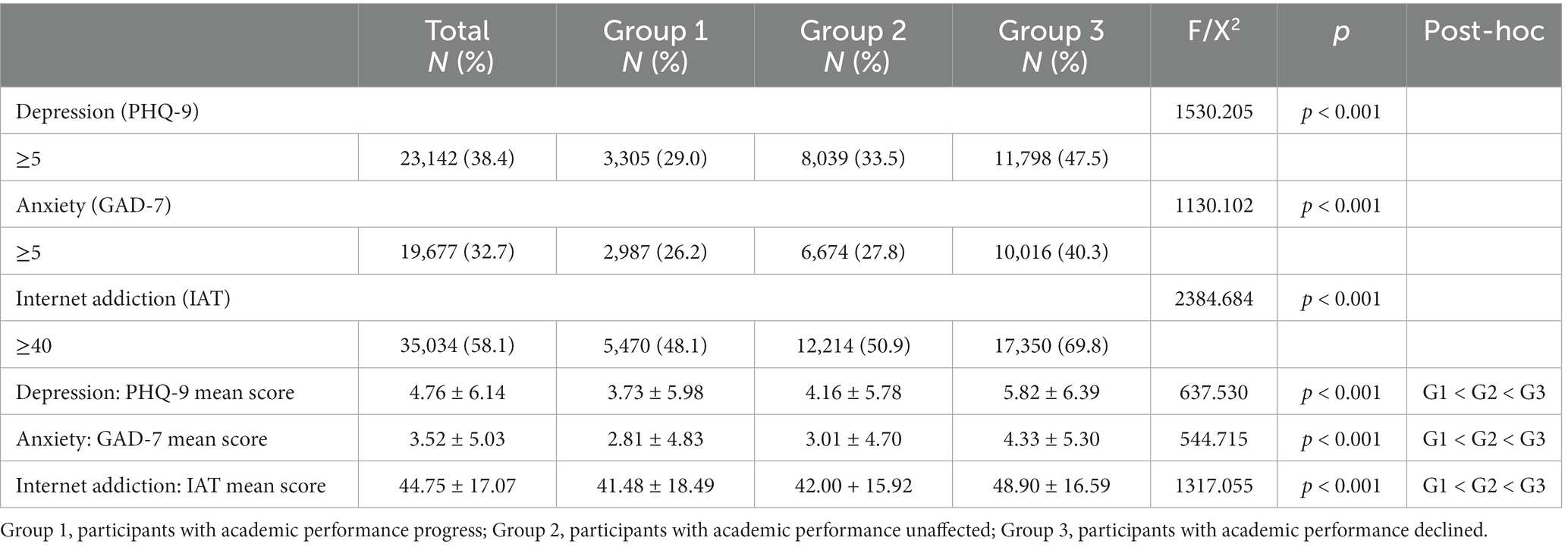
3.3. Academic performance and mental health
Table 2 shows the differences of mental health problems among three groups. The prevalence of depression symptoms, anxiety symptoms, and internet addiction among middle and high school students were 38.4, 32.7, and 58.1%, respectively. The rates of depression symptoms and anxiety symptoms were gradually increased from Group 1 to Group 3 (p < 0.001). The rates of internet addiction were 48.1, 50.9, and 69.8% in three groups, and were also gradually increased (p < 0.001). Participants with declined academic performance had the highest rates of mental health problems among the three groups (p < 0.001).
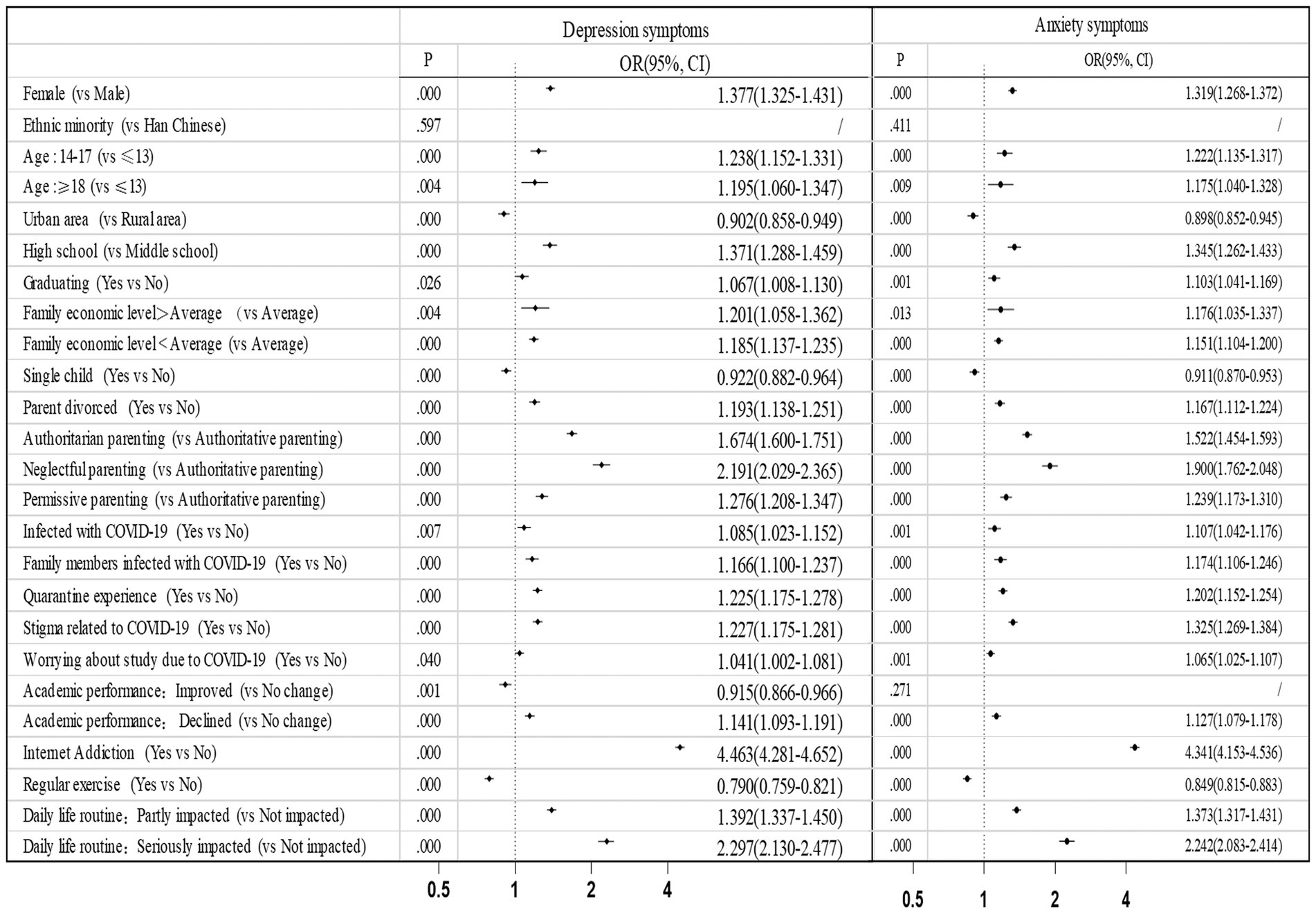
The results of logistic regression showed that being female, aged 14–17 and 18 years above, with parents divorced were risk factors for depression (OR = 1.377, 1.238, 1.195, 1.193) and anxiety (OR = 1.319, 1.222, 1.175, 1.167) (p < 0.05) (Figure 1). Participants being only child in one-child family, household registered in urban area, and with regular exercise had lower risk of depression (OR = 0.922, 0.902, 0.790) and anxiety (OR = 0.911, 0.898, 0.849) (p < 0.001). Participants in high-income and low-income families had a significantly higher risk of depression (OR = 1.201, 1.185) and anxiety (OR = 1.176, 1.151) than those from middle-income families (p < 0.05). Being infected of COVID-19, family members being infected, with quarantine experience, with COVID-19-related stigma were risk factors for depression (OR = 1.085, 1.166, 1.225, 1.227) and anxiety (OR = 1.107, 1.174, 1.202, 1.325) (p < 0.05).
In terms of academic-related factors, being high school students, facing graduation, concerns about the impact of COVID-19 on academic performance were risk factors for depression (OR = 1.371, 1.067, 1.041) and anxiety (OR = 1.345, 1.103, 1.065) (p < 0.05). Participants with declined academic performance had 1.141 and 1.127 times higher risk of depression and anxiety than those without change of academic performance, and improved academic performance was a protective factor for depression (p ≤ 0.001).
4. Discussion
This is the first study on the relationships between academic performance and mental health problems among middle and high school students after the lifting the COVID-19 restrictions in China. This study explored the characteristics of students’ learning style and academic performance, and the relationship between academic performance and mental health problems. The results of this study showed that 36,247 (60.2%) middle and high school students’ studies had been affected by the COVID-19 pandemic, and 24,864 (41.2%) students reported a declined academic performance. The rate of declined academic performance in this study is much higher than that in a previous study that 11.6% of high achieving students reported decline in academic performance after the COVID-19 outbreak (3). The shift in learning style (e.g., online learning and hybrid learning) may be one of the reasons (22–24). The results of this study showed that Han Chinese was associated with academic performance unaffected, and minority ethnical group was significantly related to academic performance declined. The possible reasons may be related to different social capital, vulnerability, and learning style (22, 25, 26).
The results of this study identified that the rates of depression and anxiety symptoms of middle and high school students were 38.4 and 32.7%, which is different with a previous study (27). The possible reason may be related to the different time of the investigations. The results of this study also showed that being female, household registered in rural area, studying at high school, and with siblings were risk factors for depression and anxiety symptoms, which is consistent with previous studies (27–32). This study indicates that the declined academic performance is a risk factor and the improved academic performance is a protective factor for depression and anxiety, which has tested the research hypothesis on the association between academic performance and mental health problems. The possible reasons maybe include the followings. First, lower grades and test may be associated with high levels of psychological distress (33), which may lead to mental health problem (34, 35). Second, students with high achievement might be more likely to adjust the environment and coping with negative emotion (36). Further studies should be conducted to explore the relationship betweem academic performance and mental health problems.
The results of this study showed that the prevalence of internet addiction was 58.3% among middle and high school students, which is higher than that in previous studies (37, 38). This study suggests that internet addiction is negatively associated with students’ academic performance, which is consistent with previous studies (39) and has tested the research hypothesis. Additionally, this study identified that students with internet addiction had a significantly higher risk of depression and anxiety symptoms, which is also consistent with previous studies (40). Therefore, it is crucial for education ministry to develop new policies and guidelines to prevent internet addiction for improving mental wellbeing among middle and high school students. Further studies should be conducted in this important area.
The results of this study showed that declined academic performance was significantly associated with being infected with COVID-19, family members infected with COVID-19, worrying about academic performance due to COVID-19, and daily lift routine disturbed by COVID-19. Previous studies showed that students with someone closed being infected of COVID-19 and with psychological distress had higher risks of poor academic performance (41, 42). The results of this study also showed that factors related to COVID-19 pandemic were also positively associated with depression and anxiety symptoms, which is consistent with previous studies (30, 32, 43–45). Moreover, COVID-19-related stigma was risk factors of mental health problems (e.g., depression and anxiety symptoms) (46). Education and health institutions should consider these potential factors for development of educational and health policies and psychosocial interventions for improving mental wellbeing of students.
The results of this study showed regular exercise was associated with academic performance progress, and was protective factor for depression and anxiety. Previous studies have suggested that sufficient physical activities could improve learning efficacy (47), reduce the risk of mental health problems, and improve academic performance (42, 48–50). Education institution should help students to establish regular exercise habits to improve students’ mental health status.
5. Strengths and limitations
This study had a few strengths. To our knowledge, this study should be the first study to explore the changes in academic performance and the association between academic performance and mental health problems among middle and high school students after the lifting of COVID-19 restrictions in China. It is possible for this study to explore the impact of home-based online learning on students’ academic performance. This study was conducted via school teachers (a questionnaire was distributed from school teachers to their students directly) in middle and high schools in Sichuan Province, China, and the quality of the results should be high.
This study had a few limitations. First, this study is a cross-sectional design, and no causal associations should be inferred. Further long-term follow-up studies should be conducted in this area to explore the causal relationship. Second, this study was conducted only in Sichuan province, China, and the results may not be generalized to other areas with different situations.
6. Conclusion
The objective of this study was to explore the changes of academic performance and associations between academic performance and mental health problems after the lifting of COVID-19 restrictions among middle and high school students in Sichuan, China. This study indicates a severe change of students’ academic performance as the impact of COVID-19 pandemic, and a significant association between students’ academic performance and mental health problems (e.g., symptoms of depression, anxiety, and internet addiction). Improved academic performance was a protective factor for depression, and declined academic performance, concerns about the COVID-19 impact and graduation were risk factors for both depression and anxiety. It is crucial for education and health institutions to consider these potential factors for development of educational and health policies and psychosocial interventions, and improve mental wellbeing of middle and high school students.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Biomedical Research Ethics Committee of West China Hospital, Sichuan University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation in this study was provided by the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin.
Author contributions
M-SR designed this study. M-SR, H-JS, Y-FM, JiaC, CW, Z-YD, A-PD, YH, WZ, W-WS, and JinC conducted this study. H-JS, Y-FM, and M-SR conducted data analysis and wrote the first draft of the paper. H-JS, Y-FM, CW, JiaC, Z-YD, A-PD, X-HH, X-DM, LZ, YH, WZ, W-WS, JinC, BL, RG, J-SZ, and M-SR participated in the data collection and made contributions to critical revision of the manuscript. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Funding
This work was funded by Initial Research Fund, West China Hospital (WCH, No: 136220012, PI: M-SR). The funder had no role in the design and conduct of the study, collection, management, analysis, and interpretation of the data; preparation, review, or approval of the manuscript; and decision to submit the manuscript for publication.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank all participants and their teachers and professors for their help and willingness to participate in the study and the time that they devoted to the study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Vargas-Ramos, JC, Lerma, C, Guzmán-Saldaña, RME, Lerma, A, Bosques-Brugada, LE, and González-Fragoso, CM. Academic performance during the COVID-19 pandemic and its relationship with demographic factors and alcohol consumption in college students. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2021) 19:365. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19010365
2. Mahdy, MAA. The impact of COVID-19 pandemic on the academic performance of veterinary medical students. Front Vet Sci. (2020) 7:594261. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2020.594261
3. Lee, J, Lim, H, Allen, J, and Choi, G. Effects of learning attitudes and COVID-19 risk perception on poor academic performance among middle school students. Sustainability. (2021) 13:5541. doi: 10.3390/su13105541
4. Brooks, SK, Smith, LE, Webster, RK, Weston, D, Woodland, L, Hall, I, et al. The impact of unplanned school closure on children's social contact: rapid evidence review. Euro Surveill. (2020) 25:2000188. doi: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.13.2000188
5. Barbosa-Camacho, FJ, Romero-Limón, OM, Ibarrola-Peña, JC, Almanza-Mena, YL, Pintor-Belmontes, KJ, Sánchez-López, VA, et al. Depression, anxiety, and academic performance in COVID-19: a cross-sectional study. BMC Psychiatry. (2022) 22:443. doi: 10.1186/s12888-022-04062-3
6. Guessoum, SB, Lachal, J, Radjack, R, Carretier, E, Minassian, S, Benoit, L, et al. Adolescent psychiatric disorders during the COVID-19 pandemic and lockdown. Psychiatry Res. (2020) 291:113264. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2020.113264
7. Gadermann, A, Thomson, K, Gill, R, Schonert-Reichl, KA, Gagné Petteni, M, Guhn, M, et al. Early Adolescents' experiences during the COVID-19 pandemic and changes in their well-being. Front Public Health. (2022) 10:823303. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.823303
8. Zeng, Q, Liang, Z, Zhang, M, Xia, Y, Li, J, Kang, D, et al. Impact of academic support on anxiety and depression of Chinese graduate students during the COVID-19 pandemic: mediating role of academic performance. Psychol Res Behav Manag. (2021) 14:2209–19. doi: 10.2147/PRBM.S345021
9. Xu, T, Zhu, P, Ji, Q, Wang, W, Qian, M, and Shi, G. Psychological distress and academic self-efficacy of nursing undergraduates under the normalization of COVID-19: multiple mediating roles of social support and mindfulness. BMC Med Educ. (2023) 23:348. doi: 10.1186/s12909-023-04288-z
10. Kim, DH, Lee, HJ, Lin, Y, and Kang, YJ. Changes in academic performance in the online, integrated system-based curriculum implemented due to the COVID-19 pandemic in a medical school in Korea. J Educ Eval Health Prof. (2021) 18:24. doi: 10.3352/jeehp.2021.18.24
11. Freitas, EO, Silva, NRD, Silva, RMD, Souto, VT, Pinno, C, and Siqueira, DF. Self-evaluation of nursing students about their academic performance during the COVID-19 pandemic. Rev Gaucha Enferm. (2022) 43:e20210088. doi: 10.1590/1983-1447.2022.20210088
12. Zhang, TM, Fang, Q, Yao, H, and Ran, MS. Public stigma of COVID-19 and its correlates in the general population of China. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2021) 18:11718. doi: 10.3390/ijerph182111718
13. Moon, SJ, Hwang, JS, Kim, JY, Shin, AL, Bae, SM, and Kim, JW. Psychometric properties of the internet addiction test: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cyberpsychol Behav Soc Netw. (2018) 21:473–84. doi: 10.1089/cyber.2018.0154
14. Lai, CM, Mak, KK, Watanabe, H, Ang, RP, Pang, JS, and Ho, RC. Psychometric properties of the internet addiction test in Chinese adolescents. J Pediatr Psychol. (2013) 38:794–807. doi: 10.1093/jpepsy/jst022
15. Spitzer, RL, Kroenke, K, Williams, JB, and Löwe, B. A brief measure for assessing generalized anxiety disorder: the GAD-7. Arch Intern Med. (2006) 166:1092–7. doi: 10.1001/archinte.166.10.1092
16. He, XY, Li, CB, Qian, J, Cui, HS, and Wu, WY. Reliability and validity of a generalized anxiety disorder scale in general hospital outpatients. Shanghai Jingshen Yixue. (2010) 22:200–3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0829.2010.04.002
17. Löwe, B, Decker, O, Müller, S, Brähler, E, Schellberg, D, Herzog, W, et al. Validation and standardization of the generalized anxiety disorder screener (GAD-7) in the general population. Med Care. (2008) 46:266–74. doi: 10.1097/MLR.0b013e318160d093
18. Tong, X, An, D, McGonigal, A, Park, SP, and Zhou, D. Validation of the generalized anxiety disorder-7 (GAD-7) among Chinese people with epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. (2016) 120:31–6. doi: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2015.11.019
19. Kroenke, K, Spitzer, RL, and Williams, JB. The PHQ-9: validity of a brief depression severity measure. J Gen Intern Med. (2001) 16:606–13. doi: 10.1046/j.1525-1497.2001.016009606.x
20. Leung, DYP, Mak, YW, Leung, SF, Chiang, VCL, and Loke, AY. Measurement invariances of the PHQ-9 across gender and age groups in Chinese adolescents. Asia Pac Psychiatry. (2020) 12:e12381. doi: 10.1111/appy.12381
21. Xia, NG, Lin, JH, Ding, SQ, Dong, FR, Shen, JZ, du, YR, et al. Reliability and validity of the Chinese version of the patient health questionnaire 9 (C-PHQ-9) in patients with epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. (2019) 95:65–9. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2019.03.049
22. Fisher, HH, Hawkins, GT, Hertz, M, Sliwa, S, and Beresovsky, V. Student and school characteristics associated with COVID-19-related learning decline among middle and high school students in K-12 schools. J Sch Health. (2022) 92:1027–39. doi: 10.1111/josh.13243
23. Balayar, BB, and Langlais, MR. Parental support, learning performance, and Socioemotional development of children and teenagers during the COVID-19 pandemic. Fam J. (2022) 30:174–83. doi: 10.1177/10664807211052496
24. Kyung, E, and Oh, M. Does COVID-19 pandemic bring the changes in academic achievement of middle and high school students? J Learn Cent Curric Instr. (2022) 22:531–45. doi: 10.22251/jlcci.2022.22.4.531
25. Woolley, ME, Grogan-Kaylor, A, Gilster, ME, Karb, RA, Gant, LM, Reischl, TM, et al. Neighborhood social capital, poor physical conditions, and school achievement. Child Sch. (2008) 30:133–45. doi: 10.1093/cs/30.3.133
26. Wodtke, GT, Harding, DJ, and Elwert, F. Neighborhood effects in temporal perspective: the impact of long-term exposure to concentrated disadvantage on high school graduation. Am Sociol Rev. (2011) 76:713–36. doi: 10.1177/0003122411420816
27. Zhou, S-J, Zhang, L-G, Wang, L-L, Guo, Z-C, Wang, J-Q, Chen, J-C, et al. Prevalence and socio-demographic correlates of psychological health problems in Chinese adolescents during the outbreak of COVID-19. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. (2020) 29:749–58. doi: 10.1007/s00787-020-01541-4
28. Lessard, LM, and Puhl, RM. Adolescent academic worries amid COVID-19 and perspectives on pandemic-related changes in teacher and peer relations. Sch Psychol. (2021) 36:285–92. doi: 10.1037/spq0000443
29. Chen, S, Cheng, Z, and Wu, J. Risk factors for adolescents' mental health during the COVID-19 pandemic: a comparison between Wuhan and other urban areas in China. Glob Health. (2020) 16:96. doi: 10.1186/s12992-020-00627-7
30. Jiang, Q, She, X, Dill, SE, Sylvia, S, Singh, MK, Wang, H, et al. Depressive and anxiety symptoms among children and adolescents in rural China: a large-scale epidemiological study. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2022) 19:5026. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19095026
31. Laursen, B, Coy, KC, and Collins, WA. Reconsidering changes in parent-child conflict across adolescence: a meta-analysis. Child Dev. (1998) 69:817–32. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-8624.1998.00817.x
32. Yang, B, Ollendick, TH, Dong, Q, Xia, Y, and Lin, L. Only children and children with siblings in the people’s republic of China: levels of fear, anxiety, and depression. Child Dev. (1995) 66:1301–11. doi: 10.2307/1131648
33. Moore, SA, Dowdy, E, Nylund-Gibson, K, and Furlong, MJ. An empirical approach to complete mental health classification in adolescents. School Ment Health. (2019) 11:438–53. doi: 10.1007/s12310-019-09311-7
34. Herselman, MF, Bailey, S, Deo, P, Zhou, XF, Gunn, KM, and Bobrovskaya, L. The effects of walnuts and academic stress on mental health, general well-being and the gut microbiota in a sample of university students: a randomised clinical trial. Nutrients. (2022) 14:4776. doi: 10.3390/nu14224776
35. Karjanto, N, and Yong, ST. Test anxiety in mathematics among early undergraduate students in a British university in Malaysia. Eur J Eng Educ. (2013) 38:11–37. doi: 10.1080/03043797.2012.742867
36. Yang, F, and Tu, M. Self-regulation of homework behaviour: relating grade, gender, and achievement to homework management. Educ Psychol. (2020) 40:392–408. doi: 10.1080/01443410.2019.1674784
37. Yi, X, and Li, G. The longitudinal relationship between internet addiction and depressive symptoms in adolescents: a random-intercept cross-lagged panel model. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2021) 18:12869. doi: 10.3390/ijerph182412869
38. Zhang, W, Pu, J, He, R, Yu, M, Xu, L, He, X, et al. Demographic characteristics, family environment and psychosocial factors affecting internet addiction in Chinese adolescents. J Affect Disord. (2022) 315:130–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2022.07.053
39. Sengupta, A, Broyles, I, Brako, L, and Raskin, G. Internet addiction: impact on academic performance of premedical post-baccalaureate students. Med Sci Educ. (2018) 28:23–6. doi: 10.1007/s40670-017-0510-5
40. Sayed, M, Naiim, CM, Aboelsaad, M, and Ibrahim, MK. Internet addiction and relationships with depression, anxiety, stress and academic performance among Egypt pharmacy students: a cross-sectional designed study. BMC Public Health. (2022) 22:1826. doi: 10.1186/s12889-022-14140-6
41. Kimaru, LJ, Habila, MA, Mantina, NM, Lopez, DN, and Melton, F. The impact of COVID-19 on academic performance among college-level students. J Am Coll Heal. (2023) 3:1–7. doi: 10.1080/07448481.2022.2155052
42. Cao, W, Fang, Z, Hou, G, Han, M, Xu, X, Dong, J, et al. The psychological impact of the COVID-19 epidemic on college students in China. Psychiatry Res. (2020) 287:112934. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2020.112934
43. Son, C, Hegde, S, Smith, A, Wang, X, and Sasangohar, F. Effects of COVID-19 on college students' mental health in the United States: interview survey study. J Med Internet Res. (2020) 22:e21279. doi: 10.2196/21279
44. Ahmed, GK, Khedr, EM, Hamad, DA, Meshref, TS, Hashem, MM, and Aly, MM. Long term impact of Covid-19 infection on sleep and mental health: a cross-sectional study. Psychiatry Res. (2021) 305:114243. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2021.114243
45. Fischer, LS, Mansergh, G, Lynch, J, and Santibanez, S. Addressing disease-related stigma during infectious disease outbreaks. Disaster Med Public Health Prep. (2019) 13:989–94. doi: 10.1017/dmp.2018.157
46. Li, H, Zheng, L, le, H, Zhuo, L, Wu, Q, Ma, G, et al. The mediating role of internalized stigma and shame on the relationship between COVID-19 related discrimination and mental health outcomes among back-to-school students in Wuhan. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2020) 17:9237. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17249237
47. Hamer, M, Patalay, P, Bell, S, and David, BG. Change indevice-measured physical activity assessed in childhood and adolescence in relation to depressive symptoms: a general population-based cohort study. J Epidemiol Community Health. (2020) 74:330–5. doi: 10.1136/jech-2019-213399
48. Mammen, G, and Faulkner, G. Physical activity and the prevention of depression: a systematic review of prospective studies. Am J Prev Med. (2013) 45:649–57. doi: 10.1016/j.amepre.2013.08.001
49. Schuch, FB, Vancampfort, D, Richards, J, Rosenbaum, S, Ward, PB, and Stubbs, B. Exercise as a treatment for depression: a meta-analysis adjusting for publication bias. J Psychiatr Res. (2016) 77:42–51. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2016.02.023
Keywords: academic performance, mental health, students, COVID-19, China
Citation: Song H-J, Mu Y-F, Wang C, Cai J, Deng Z-Y, Deng A-P, Huang X-H, Meng X-D, Zhang L, Huang Y, Zhang W, Shen W-W, Chen J, Liu B, Gao R, Zhao J-S and Ran M-S (2023) Academic performance and mental health among Chinese middle and high school students after the lifting of COVID-19 restrictions. Front. Psychiatry. 14:1248541. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1248541
Edited by:
Natanael Karjanto, Sungkyunkwan University, Republic of KoreaReviewed by:
Hendra Bunyamin, Maranatha Christian University, IndonesiaAigerim Bulambayeva, Boston University, United States
Copyright © 2023 Song, Mu, Wang, Cai, Deng, Deng, Huang, Meng, Zhang, Huang, Zhang, Shen, Chen, Liu, Gao, Zhao and Ran. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Mao-Sheng Ran, bXNyYW5jZEBvdXRsb29rLmNvbQ==
 Hong-Jun Song1,2
Hong-Jun Song1,2 Xue-Hua Huang
Xue-Hua Huang Xian-Dong Meng
Xian-Dong Meng Wei Zhang
Wei Zhang Jin Chen
Jin Chen Mao-Sheng Ran
Mao-Sheng Ran