- 1Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Medical University, Zhanjiang, Guangdong, China
- 2First College for Clinical Medicine, Guangdong Medical University, Zhanjiang, Guangdong, China
- 3Department of Information Technology, Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Medical University, Zhanjiang, Guangdong, China
Background: Anxiety and depression are common in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), especially older adult patients. This can complicate the disease progression and lead to increased clinical and economic burden. We sought to investigate the clinical and economic burdens associated with the presence of anxious and/or depressive symptoms among older adult COPD patients.
Methods: We screened 579 patients aged over 60 years and diagnosed with COPD via a lung function test following the 2017 Global Initiative Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) guidelines. Anxiety and depression were measured using the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS) through face-to-face interviews at admission. Follow-up was conducted by telephone calls at 6, 12, 18, 24, and 36 months after discharge to assess clinical and economic burden. COPD-anxiety and/or depression patients were matched to patients without anxiety and depression (COPD-only) using propensity scores. Multivariate regression models were used to compare clinical and economic burden between COPD-anxiety and/or depression and COPD-only groups.
Results: Compared with COPD-only patients, COPD patients complicated with anxiety and/or depression had increased clinical burden, including higher COPD-related outpatient visits, COPD-related hospitalizations, and length of COPD-related hospitalizations (p < 0.001). Moreover, they also had an increased economic burden, including higher annual total healthcare costs, medical costs, and pharmacy costs (p < 0.001).
Conclusion: Older adult COPD patients with anxiety or depression had significantly higher clinical and economic burdens than patients without these comorbidities. These findings deserve further exploration and may be useful for the formulation of relevant healthcare policies.
1 Introduction
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a chronic disease characterized by persistent airflow restriction. With the rapidly aging population, high prevalence of smoking, and high levels of air pollution, the clinical burden of COPD in China is expected to continue to increase. Individuals with chronic conditions often experience poor mental health (1); older adult COPD patients are more likely to develop mental illnesses, specifically anxiety and depression (2, 3). In a previous study, we also found that 13.93% of patients with stable COPD reported anxious symptoms, and 23.37% experienced depression (4).
For COPD patients, there are many identified risk factors for suffering from anxiety or depression, such as continuous smoking, poor knowledge level, low acceptance of disease, and low socioeconomic status (5–8). More importantly, as COPD progresses, patients experience long-term use of systemic corticosteroids, poorer quality of life, increased breathing difficulties, and severe impairment of physical function, leading to more severe symptoms of anxiety and depression (9–11). The presence of anxiety or depression may impose substantial disease burden, and increases healthcare utilization among older adult COPD patients (12). Either can complicate the course of COPD by causing poor adherence to treatment, as well as increased risks of exacerbation and emergency care use (13–15). Furthermore, they can also affect various aspects of quality of life in older adult COPD patients, such as functional, cognitive, and emotional domains, resulting in more significant functional impairments, more severe disease outcomes, poorer quality of life, and higher risk of death (16–18). All of these conditions may result in additional costs for outpatient visits, emergency room visits, hospitalizations, and prescription expenses, which represent significant clinical and economic burdens for patients, their families, and the whole healthcare system (19–22). Thus, evaluating the burden of mental comorbidities plays an indispensable role in guiding policymakers in allocating resources to achieve optimal treatment goals.
Our previous research has shown that anxiety and depression symptoms are prevalent in COPD patients and are associated with more severe disease outcomes, suggesting that psychological distress may complicate the course of COPD (4). Therefore, we suspect that the combination of anxiety and/or depression symptoms may result in additional visits and medical costs for COPD patients. Although some studies have shown that anxiety and depression increase the clinical and economic burdens of COPD in Europe and America (23, 24), there is a paucity of similar data in China. Therefore, we conducted a study in older adult COPD patients in China to estimate differences in the clinical and economic burdens of patients with or without symptoms of anxiety and/or depression. It is hoped that our study will enable clinicians to pay more attention to anxiety and/or depression in patients with COPD, and to consider the impact of patients’ mental state when formulating relevant healthcare policies and the next version of COPD GOLD guidelines.
2 Methods
2.1 Data source
The data were sourced from the Registry for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease With Anxiety and Depression in China (the COPD-AD China Registry) study, a national clinical registration study initiated in June 2017, with a duration of 3.5 years (clinical trial ID: NCT03187236) (25). The study was approved by the institutional review boards of all participating hospitals and carried out in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. Written informed consent was obtained from all participating patients before data recording began.
2.2 Patient selection
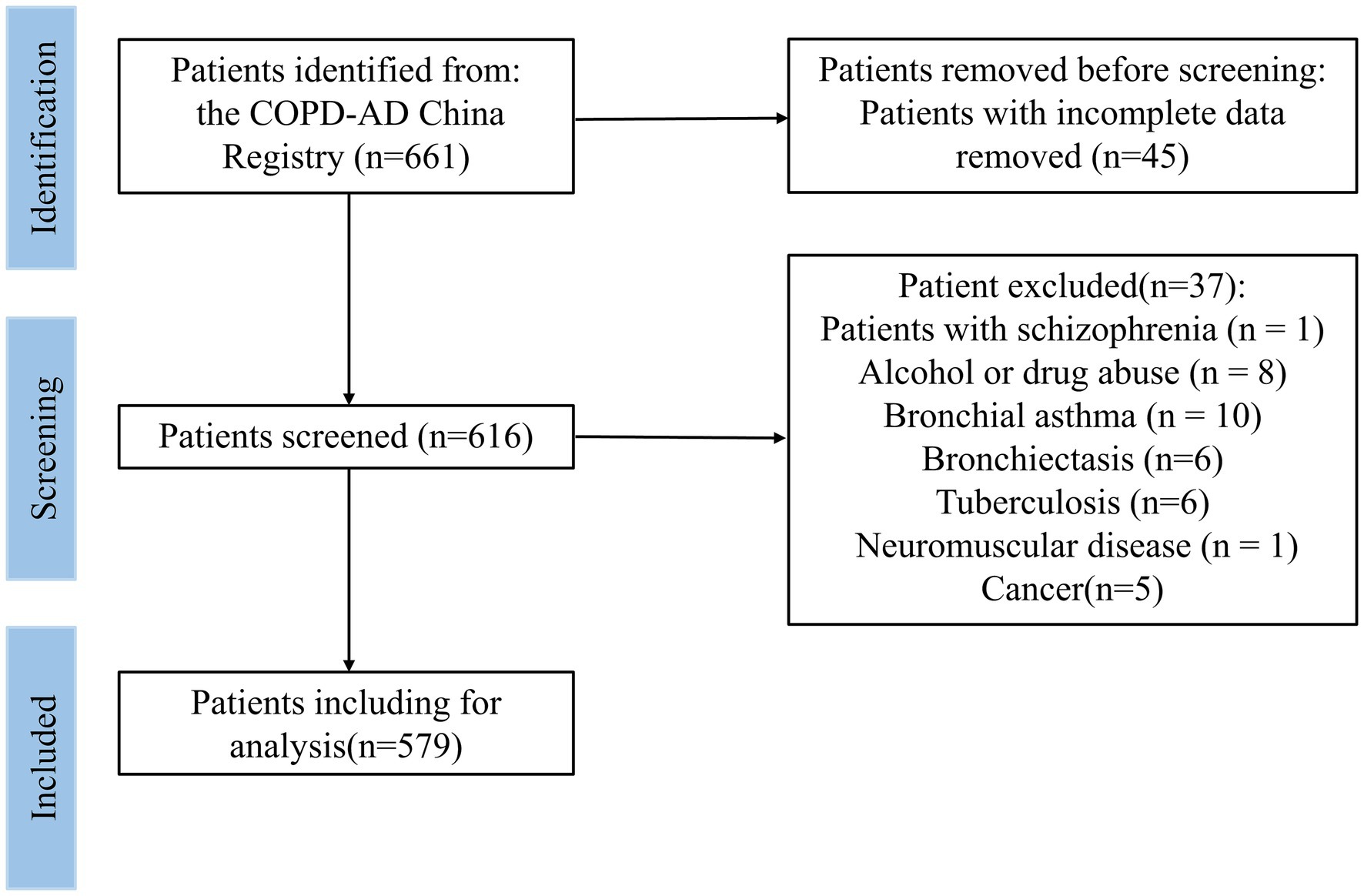
In this study, patients from the respiratory department of the Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Medical University were selected, and their 3-year follow-up information was collected. Face-to-face interviews were conducted at admission, and telephone follow-up was conducted at 6, 12, 18, 24, and 36 months after initial discharge. The interviewer set fixed questions before the interview to ensure that all interviews were similar. Between 2017 and 2021, 661 patients participated in this study. The inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) able to understand the research purpose and sign a consent form; (2) have a diagnosed COPD via a lung function test following the 2017 Global Initiative Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of COPD (26). (3) aged 60 and older. The exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) patients with incomplete data (n = 45); (2) pregnancy; (3) severe cognitive disorder; (4) suicide attempt or psychiatric hospitalization in the past year; (5) current suicidal ideation with plan or intent; (6) patients with mental illness, such as dementia, autism, schizophrenia (n = 1), or bipolar disorder; (7) patients with other chronic respiratory diseases, such as bronchial asthma (n = 10), bronchiectasis (n = 6), pulmonary fibrosis, or tuberculosis (n = 6); (8) neuromuscular disease (n = 1); (9) cancer (n = 5). After applying the exclusion criteria, 579 participants were included in the final baseline study sample (Figure 1).
2.3 Characteristics and spirometry
Demographic characteristics (age, sex, height, weight, body mass index [BMI], smoking history, education, and household income) and clinical characteristics, including number of acute exacerbations in the past year, COPD Assessment Test (CAT) score, and modified Medical Research Council (mMRC) score, were collected from the data management network.1 We performed spirometry according to the guidelines for lung function tests formulated by the Chinese Thoracic Society. We measured the percentage of predicted forced expiratory volume in 1 s (FEV1% predicted) for all participating patients (27).
2.4 Clinical and economic burden measurements
All COPD-related clinical and economic burdens were calculated after 3 years of follow-up. Specific clinical burden measures included the annual number of COPD-related outpatient visits, COPD-related hospitalizations, and length of COPD-related hospitalizations. Specific economic burden measures included annual COPD-related medical, pharmacy, and total healthcare costs. Costs were presented in Chinese Yuan (CNY). Outpatient visits related to COPD were defined by claims initially diagnosed with COPD. Similarly, hospitalization related to COPD was also defined by claims for initial discharge diagnosis of COPD.
2.5 Determination of anxiety and depression
Anxiety and depression were measured using the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS). HADS was developed specifically to detect anxiety and depression in patients with physical disorders (28). It is a proven symptom severity screening tool in cases of anxiety and depression in patients with chronic conditions, including COPD (29, 30). HADS includes 14 items for detecting anxious and depressive symptoms in patients with chronic diseases. There were seven programs each for anxiety and depression, and their total scores are calculated separately. Each item is rated on a Likert scale from 0 to 3. A score of 0–7 indicates no anxiety/depression, while a score greater than 7 indicates anxiety/depression. The higher the score, the greater the likelihood that the patient has anxiety or depression disorders (31).
2.6 Propensity score matching
Because this study evaluates the impact of anxiety and depression on clinical and economic burden based on the assumption that all other factors are the same, baseline differences between groups may have the potential to bias the results. Therefore, propensity scores were used to match patients in the COPD-anxiety and/or depression group and the COPD-only group in a 1:1 ratio, with each patient’s score defined as the probability of both anxiety and/or depression under the condition of a baseline variable, including demographic characteristics (i.e., age, sex, BMI, smoking status, number of comorbidities, education, and household monthly income) and clinical characteristics (CAT, mMRC, number of acute exacerbations in the past year, and FEV1% predicted). Matching proceeded using the closest available matching technique on the estimated propensity score, performed to 2 decimal places (0.02).
3 Statistical analysis
All statistical analyses were performed with IBM SPSS Statistics, Version 25.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA) with the statistical significance level set at p < 0.001. Categorical data are reported as numbers (percentages). Continuous variables are presented as means±standard deviation (SD) for normally distributed data or medians (interquartile range [IQR]) for non-normal distributions. The chi-square test was used for comparisons of categorical variables, and the independent t-test, Mann–Whitney U test, and Kruskal-Wallis test (ANOVA) were used for the comparison of continuous variables.
After propensity score matching, baseline characteristics were compared between groups using paired t-tests or Wilcoxon signed-rank tests (continuous variables) and McNemar’s tests (categorical variables). Adjusted clinical and economic burdens were assessed using multivariate analyses. Covariates with statistical differences were incorporated after matching into the statistical model. Generalized linear models using a gamma distribution with a log link were used to adjust for healthcare costs and medical visits.
4 Results
4.1 Demographic and clinical characteristics
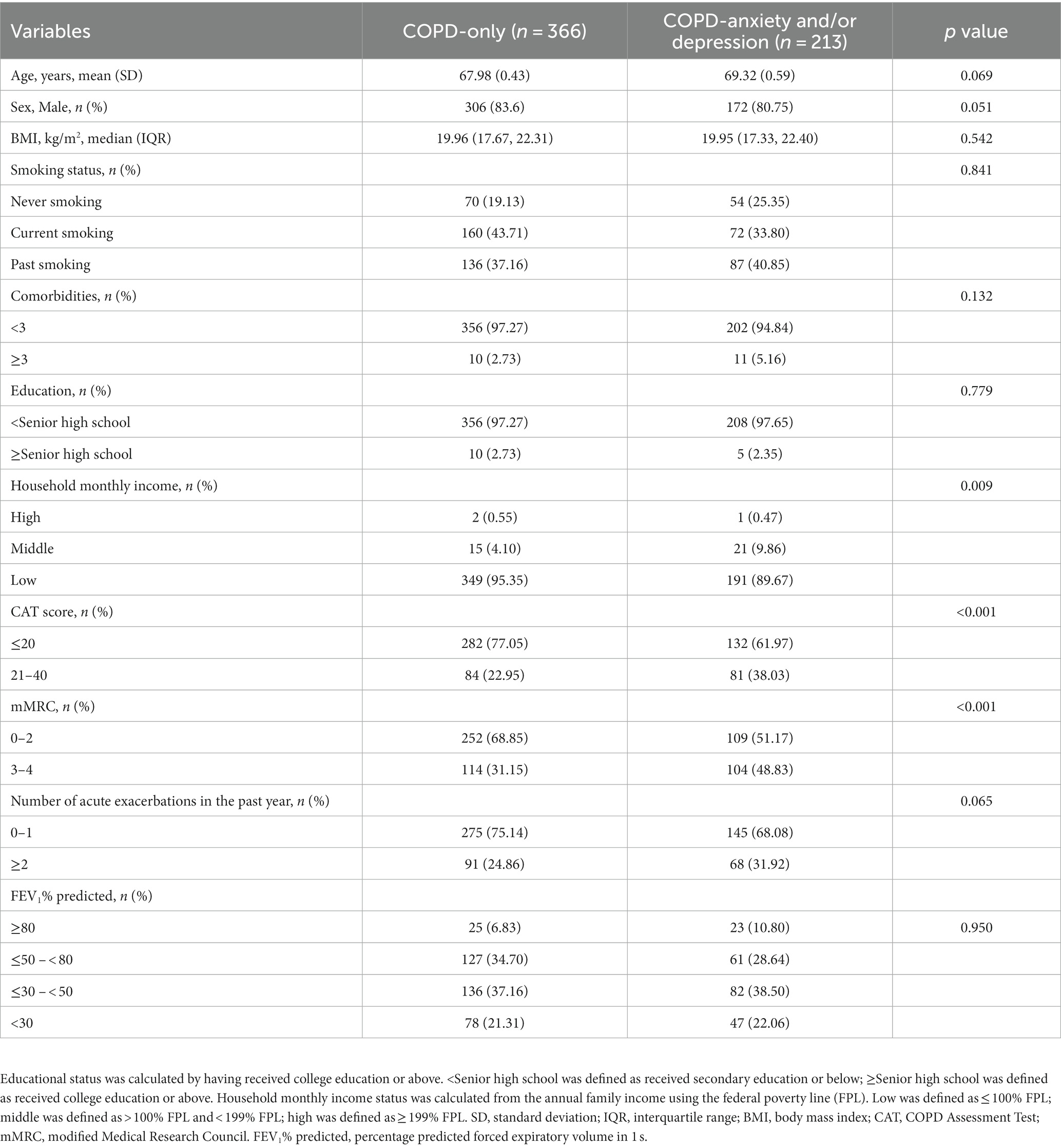
In total, 579 patients with COPD were included in our analyses; 213 (36.79%) were complicated with anxiety and/or depression. The mean age of the enrolled subjects was 68.75 ± 0.44 years, with men comprising 82.55% of the cohort. We divided all participants into two groups: those without anxiety or depression and those with anxiety and/or depression. At baseline, we observed that the two groups differed significantly in household monthly income, CAT score, and mMRC score among all participants (Table 1).
4.2 Clinical burden of anxiety and/or depression among COPD patients
The annual number of COPD-related outpatient visits in the COPD-anxiety and/or depression group was 33.33% higher than in the COPD-only group. Additionally, in this group, there were significant increases of 100.00% in the annual number of COPD-related hospitalizations and 50.00% in the length of hospitalizations (Table 2).
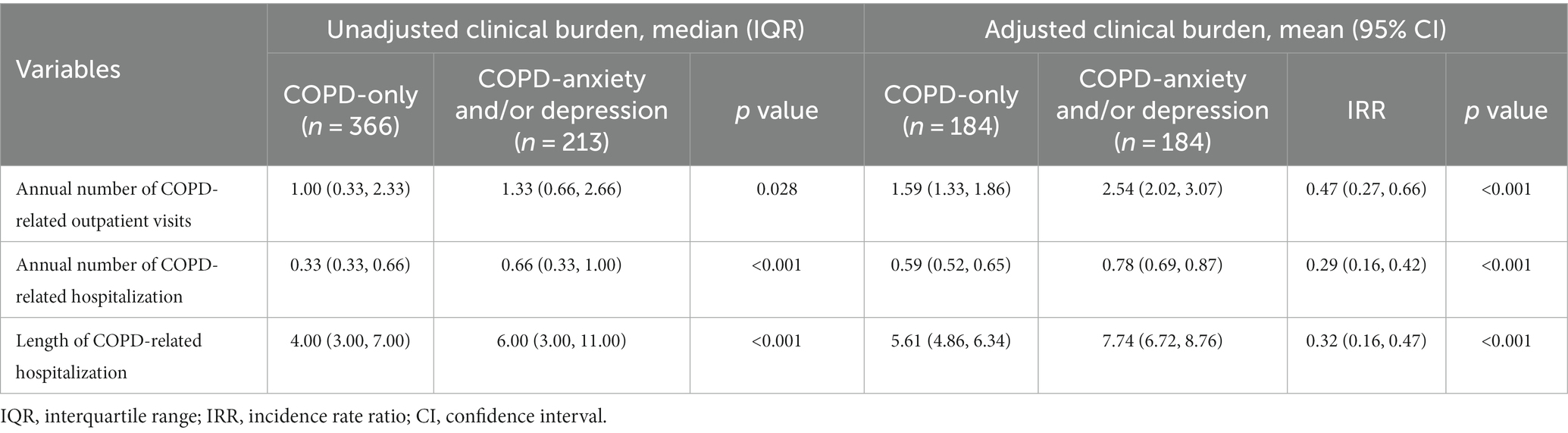
Table 2. Unadjusted and adjusted clinical burden of anxiety and depression among patients with COPD.
When clinical burden was adjusted for demographic and clinical characteristics, the annual number of COPD-related outpatient visits was 59.74% (incidence rate ratio [IRR] =0.47; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.27, 0.66) higher in the COPD-anxiety and/or depression group compared with the COPD-only group. At the same time, the annual number of COPD-related hospitalizations and the annual length of COPD-related hospitalizations were 32.20% (IRR = 0.29; 95% CI: 0.16–0.42) and 37.97% (IRR = 0.32; 95% CI: 0.16–0.48) higher, respectively, in the COPD-anxiety and/or depression group (Table 2).
4.3 Economic burden of anxiety and/or depression among COPD patients
The median annual total healthcare cost in the COPD-anxiety and/or depression group was CNY 7224.49 (quartile 2 to quartile 3: CNY 3771.36–4079.84), while in the COPD-only group it was CNY 5218.59 (quartile 2 to quartile 3: CNY 3097.75–9934.68), indicating that the annual COPD-related total healthcare costs were significantly higher in COPD-anxiety and/or depression group. Similarly, the COPD-related medical and pharmacy costs were also higher for the COPD-anxiety and/or depression group versus the COPD-only group, with the differences in the median value of annual COPD-related medical costs (CNY 4429.19 vs. CNY 3148.14) and the median value of annual COPD-related pharmacy costs (CNY 2467.45 vs. CNY 2014.53) (Table 3).
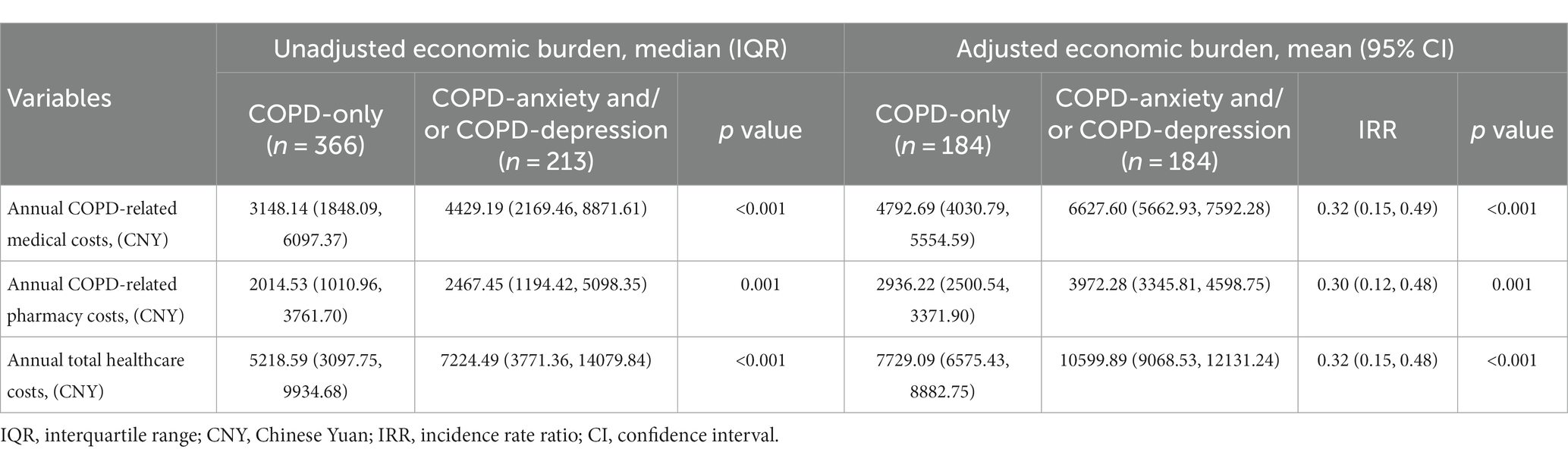
Table 3. Unadjusted and adjusted economic burden of anxiety and depression among patients with COPD.
After adjustment for all other factors that may influence healthcare expenditures, the COPD-anxiety and/or depression group was still associated with higher healthcare costs compared with the COPD-only group. The adjusted mean annual total healthcare cost in the COPD-anxiety and/or depression group was CNY 10599.89 (95% CI: 9068.53–12131.24), while in the COPD-only group, the mean cost was CNY 7729.09 (95% CI: 6575.43–8882.75). The total healthcare costs were 37.13% (IRR = 0.32; 95% CI: 0.15–0.48) higher in the COPD-anxiety and/or depression group. Furthermore, this group showed higher mean annual COPD-related medical costs (CNY 6627.60; 95% CI: 5662.93–7592.28) and mean annual COPD-related pharmacy costs (CNY 3972.28; 95% CI: 3345.81–4598.75) (Table 3).
5 Discussion
The COPD-AD China Registry is a nationwide registration study with a comprehensive database in China to track COPD patients with anxious and depressive symptoms. Its goal is to screen for anxiety and depression among COPD patients at an early stage, and to track how these conditions affect the overall progression and prognosis of COPD. In this study, we further analyzed this database and found that older adult COPD patients with anxious and depressive symptoms had an increased clinical burden, including higher COPD-related outpatient visits, more COPD-related hospitalizations, and longer COPD-related hospitalizations. Moreover, they also had higher healthcare costs, including medical and pharmacy costs.
Anxiety and depression are common comorbidities among older adult COPD patients. Our previous study showed that these significantly reduce quality of life and are associated with a greater burden of symptoms and exacerbations among COPD patients (4). However, studies on the clinical burden of COPD-related outpatient visits, COPD-related hospitalizations, and length of COPD-related hospitalizations caused by anxiety and depression remain very limited in China. Dalal et al. estimated the clinical burden of depression/anxiety in COPD patients using data from a comprehensive source of medical and pharmacy claims from the IMS LifeLink Database in the United States, and found that COPD patients with depression/anxiety have a significantly higher risk of acute exacerbations (23). Our study further confirms that anxiety and depression not only increase the risk of COPD exacerbations, but also increase the number of outpatient visits and extend the length of hospital stay, thereby increasing medical resource utilization in older adult COPD patients. Studies have shown that anxiety and depression can activate the sympathetic nervous system and the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis in COPD patients, causing a decrease in immunity, thus increasing the risk of respiratory infection and exacerbations (32, 33). Additionally, they are associated with disinterest in self-care, poorer adherence to treatment, and a higher probability of continuing to smoke, contributing to poor control and deterioration of COPD (34, 35). Moreover, they can result in cognitive function impairment, making patients more sensitive to or likely to report respiratory symptoms. This may lead to more frequent doctor visits and increased opportunities to be prescribed medication to manage their symptoms (13, 36). These findings suggest that anxiety and/or depression can increase the risk of outpatient visits, hospitalizations due to acute exacerbation of COPD, and length of hospitalizations in older adult COPD patients. Hence, we believe that anxiety and/or depression increase the clinical burden among older adult COPD patients.
In this study, we also examined the healthcare costs of older adult COPD patients caused by anxiety and depression. We found that co-anxiety or co-depression contributed to increased pharmacy costs among older adult COPD patients. COPD is a chronic disease that requires long-term treatment and management, including drug therapy, oxygen therapy, rehabilitation training, and other therapeutic means (37). The cost of these treatments can place a significant financial burden on patients and families. When COPD patients suffer from anxiety and/or depression, they can complicate the course of COPD. A causal relationship has been reported between anxiety or depression in COPD patients and changes in routine use of pharmacies, including bronchodilators and inhaled steroids (38). A Spanish cohort study also showed that the presence of anxious and depressive symptoms increased the use of antibiotics and systemic corticosteroids in COPD patients (39). These studies suggest that co-psychiatric symptoms are associated with increased pharmacy use in COPD patients. It may be that anxiety and depression can cause worsening symptoms and frequent acute exacerbations, resulting in increased use of pharmacies. In addition, our study also found that older adult COPD patients co-morbid with anxiety or depression had higher medical costs, including examination fees, nursing fees, and surgery fees.
On one hand, anxiety or depression can directly affect the health status of COPD patients. Symptoms of anxiety or depression in COPD patients are directly related to continued smoking, increased burden of symptoms, poorer physical and social functioning, and difficulty with daily activities (21, 40). Depressed states also damage the immune system, making them vulnerable to infections that increase the frequency of exacerbations (41). Hence, COPD patients with psychiatric symptoms had more severe clinical symptoms, poorer quality of life, and high risk of acute exacerbation, thus increasing the risk of complications that require more medical resources and time to treat (39, 42–44).
On the other hand, anxious and depressive symptoms can also negatively affect the mental state and behavior of COPD patients, leading to more unnecessary medical procedures (21, 45, 46). In general, patients with anxiety or depression rated their health as worse than that of the general population, including its impact on quality of life and functional status (47). This low confidence in their own health and the effectiveness of treatment can lead to a reduced ability to cope with chronic diseases (48). As a result, anxiety and/or depression may affect a patient’s ability to provide informed consent and understand whether to accept or reject a particular treatment, thus affecting their treatment compliance (49, 50). In addition, anxious and depressive symptoms have also been associated with an increased perception of breathing difficulties (51). This may result in unnecessary hospital visits and increased use of bronchodilators, inhaled and systemic corticosteroids, and antibiotics (49). All of these may result in more examinations or nursing interventions.
Our study provides a new direction on how to control healthcare costs for older adult COPD patients by focusing on the mental health of COPD patients and early intervention and treatment of psychiatric symptoms, which may be beneficial in reducing healthcare costs. Therefore, psychiatric symptoms should be included in routine screening in the health management of older adult COPD patients to provide appropriate psychiatric treatment or prompt referral to mental health services for this population.
Nonetheless, there are limitations to our study. First, as with any observational study, our results may not be applicable to older adult COPD patients in the general population or in other clinical environments. This study included only older adult COPD patients admitted to the Respiratory Department of the Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Medical University. Second, even though matching and multivariate adjustment were conducted, the possibility remains that the groups were not fully matched on all unobserved characteristics (i.e., residual confounding). Third, other comorbidities and severe symptoms of COPD may increase the risk of anxiety and depression, and their potential impact on the economic burden of COPD patients cannot be excluded. Finally, the healthcare costs may have been underestimated, as our study did not delve into indirect economic burdens, such as the loss of working time of caregivers and the heavy mental burdens caused by illness and disability to the patients and their families.
In summary, our study found that anxious and/or depressive symptoms were significantly associated with more severe clinical and economic burdens in older adult COPD patients. In the management of chronic diseases such as COPD, routine screening of psychiatric symptoms should be an integral part of clinical care to diagnose and treat anxious and depressive symptoms in a timely manner, and to provide mental health counseling services and prompt referrals for mental health services. Further understanding of the impact of comorbidities such as anxiety and depression on the assessment and management of COPD may be beneficial for controlling the healthcare costs of chronic diseases and guiding the formulation of health insurance policies.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving human participants were approved by Ethics Committee of Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Medical University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The patients/participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
DW: supervision. XZ: data curation, writing-original draft preparation. GL: writing-original draft preparation. DL: formal analysis, methodology. LZ: investigation. QH: data curation. MC: writing-reviewing and editing. DL: conceptualization and methodology. BW: conceptualization and methodology. DH: formal analysis and validation. HW: visualization, investigation, data curation. All authors agreed to be accountable for the content of the work, and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (grant no. 2016YFC1304404), the Guangdong Medical Science and Technology Research Fund Project (grant number: B2021294), the Discipline Construction Project of Guangdong Medical University (grant no. 4SG21231G), the Clinical Research Project of Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Medical University (grant nos. LCYT2017A003, LCYJ2020B008, LCYJ2021B007, and LCYJ2022DL01), and the Project of Zhanjiang City (grant nos. 2021A05052 and 2021A05077).
Acknowledgments
We thank all the patients participating in the study and all the staff involved at the participating hospitals. We also thank John Daniel from Liwen Bianji (Edanz) (www.liwenbianji.cn), for editing the English text of a draft of this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
BMI, body mass index; CAT, COPD Assessment Test; CI, confidence interval; CNY, Chinese Yuan; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; the COPD-AD China Registry study, the Registry for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease With Anxiety and Depression in China; FEV1% predicted, the percentage predicted forced expiratory volume in 1 s; GOLD, Global Initiative Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease; HADS, Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale; IQR, interquartile range; IRR, incidence rate ratio; mMRC, modified Medical Research Council dyspnea scale; SD, standard deviation.
Footnotes
References
1. Read, JR, Sharpe, L, Modini, M, and Dear, BF. Multimorbidity and depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Affect Disord. (2017) 221:36–46. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2017.06.009
2. Kunik, ME, Roundy, K, Veazey, C, Souchek, J, Richardson, P, Wray, NP, et al. Surprisingly high prevalence of anxiety and depression in chronic breathing disorders. Chest. (2005) 127:1205–11. doi: 10.1378/chest.127.4.1205
3. Mikkelsen, RL, Middelboe, T, Pisinger, C, and Stage, KB. Anxiety and depression in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). A review. Nord J Psychiatry. (2004) 58:65–70. doi: 10.1080/08039480310000824
4. Wu, D, Zhao, X, Huang, D, Dai, Z, Chen, M, Li, D, et al. Outcomes associated with comorbid anxiety and depression among patients with stable COPD: a patient registry study in China. J Affect Disord. (2022) 313:77–83. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2022.06.059
5. Uchmanowicz, I, Jankowska-Polanska, B, Motowidlo, U, Uchmanowicz, B, and Chabowski, M. Assessment of illness acceptance by patients with COPD and the prevalence of depression and anxiety in COPD. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. (2016) 11:963–70. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S102754
6. Zhang, Q, Liao, J, Liao, X, Wu, X, Wan, M, Wang, C, et al. Disease knowledge level is a noteworthy risk factor of anxiety and depression in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a cross-sectional study. BMC Pulm Med. (2014) 14:92. doi: 10.1186/1471-2466-14-92
7. Pumar, MI, Gray, CR, Walsh, JR, Yang, IA, Rolls, TA, and Ward, DL. Anxiety and depression-important psychological comorbidities of COPD. J Thorac Dis. (2014) 6:1615–31. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2014.09.28
8. Wagena, EJ, van Amelsvoort, LGPM, Kant, I, and Wouters, EFM. Chronic bronchitis, cigarette smoking, and the subsequent onset of depression and anxiety: results from a prospective population-based cohort study. Psychosom Med. (2005) 67:656–60. doi: 10.1097/01.psy.0000171197.29484.6b
9. Cleland, JA, Lee, AJ, and Hall, S. Associations of depression and anxiety with gender, age, health-related quality of life and symptoms in primary care COPD patients. Fam Pract. (2007) 24:217–23. doi: 10.1093/fampra/cmm009
10. Di Marco, F, Verga, M, Reggente, M, Maria Casanova, F, Santus, P, Blasi, F, et al. Anxiety and depression in COPD patients: the roles of gender and disease severity. Respir Med. (2006) 100:1767–74. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2006.01.026
11. Gift, AG, Wood, RM, and Cahill, CA. Depression, somatization and steroid use in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Int J Nurs Stud. (1989) 26:281–6. doi: 10.1016/0020-7489(89)90009-6
12. Yohannes, AM, Mülerová, H, Lavoie, K, Vestbo, J, Rennard, SI, Wouters, E, et al. The Association of Depressive Symptoms with Rates of acute exacerbations in patients with COPD: results from a 3-year longitudinal follow-up of the ECLIPSE cohort. J Am Med Dir Assoc. (2017) 18:955–959.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2017.05.024
13. Gudmundsson, G, Gislason, T, Janson, C, Lindberg, E, Hallin, R, Ulrik, CS, et al. Risk factors for rehospitalisation in COPD: role of health status, anxiety and depression. Eur Respir J. (2005) 26:414–9. doi: 10.1183/09031936.05.00078504
14. Gudmundsson, G, Gislason, T, Janson, C, Lindberg, E, Suppli Ulrik, C, Brøndum, E, et al. Depression, anxiety and health status after hospitalisation for COPD: a multicentre study in the Nordic countries. Respir Med. (2006) 100:87–93. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2005.04.003
15. Pooler, A, and Beech, R. Examining the relationship between anxiety and depression and exacerbations of COPD which result in hospital admission: a systematic review. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. (2014) 9:315–30. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S53255
16. Mendlowicz, MV, and Stein, MB. Quality of life in individuals with anxiety disorders. Am J Psychiatry. (2000) 157:669–82. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.157.5.669
17. Panagioti, M, Scott, C, Blakemore, A, and Coventry, PA. Overview of the prevalence, impact, and management of depression and anxiety in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. (2014) 9:1289–306. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S72073
18. Wells, KB, Stewart, A, Hays, RD, Burnam, MA, Rogers, W, Daniels, M, et al. The functioning and well-being of depressed patients. Results from the medical outcomes study. JAMA. (1989) 262:914–9. doi: 10.1001/jama.1989.03430070062031
19. Bilde, L, Rud Svenning, A, Dollerup, J, Baekke Borgeskov, H, and Lange, P. The cost of treating patients with COPD in Denmark--a population study of COPD patients compared with non-COPD controls. Respir Med. (2007) 101:539–46. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2006.06.020
20. Fan, VS, Ramsey, SD, Giardino, ND, Make, BJ, Emery, CF, Diaz, PT, et al. Sex, depression, and risk of hospitalization and mortality in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Arch Intern Med. (2007) 167:2345–53. doi: 10.1001/archinte.167.21.2345
21. Ng, T-P, Niti, M, Tan, W-C, Cao, Z, Ong, K-C, and Eng, P. Depressive symptoms and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: effect on mortality, hospital readmission, symptom burden, functional status, and quality of life. Arch Intern Med. (2007) 167:60–7. doi: 10.1001/archinte.167.1.60
22. Ramsey, SD, and Sullivan, SD. The burden of illness and economic evaluation for COPD. Eur Respir J Suppl. (2003) 21:29s–35s. doi: 10.1183/09031936.03.00078203
23. Dalal, AA, Shah, M, Lunacsek, O, and Hanania, NA. Clinical and economic burden of depression/anxiety in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients within a managed care population. COPD. (2011) 8:293–9. doi: 10.3109/15412555.2011.586659
24. Ställberg, B, Janson, C, Larsson, K, Johansson, G, Kostikas, K, Gruenberger, J-B, et al. Real-world retrospective cohort study ARCTIC shows burden of comorbidities in Swedish COPD versus non-COPD patients. NPJ Prim Care Respir Med. (2018) 28:33. doi: 10.1038/s41533-018-0101-y
25. He, J. Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Fuwai hospital. Registry for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease with anxiety and depression in China. ClinicalTrials.gov. Available at: https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03187236#wrapper
26. Vogelmeier, CF, Criner, GJ, Martinez, FJ, Anzueto, A, Barnes, PJ, Bourbeau, J, et al. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive lung disease 2017 report. GOLD executive summary. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2017) 195:557–82. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201701-0218PP
27. Singh, D, Agusti, A, Anzueto, A, Barnes, PJ, Bourbeau, J, Celli, BR, et al. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive lung disease: the GOLD science committee report 2019. Eur Respir J. (2019) 53:1900164. doi: 10.1183/13993003.00164-2019
28. Zigmond, AS, and Snaith, RP. The hospital anxiety and depression scale. Acta Psychiatr Scand. (1983) 67:361–70. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1983.tb09716.x
29. Dowson, C, Laing, R, Barraclough, R, Town, I, Mulder, R, Norris, K, et al. The use of the hospital anxiety and depression scale (HADS) in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a pilot study. N Z Med J. (2001) 114:447–9.
30. Bjelland, I, Dahl, AA, Haug, TT, and Neckelmann, D. The validity of the hospital anxiety and depression scale. An updated literature review. J Psychosom Res. (2002) 52:69–77. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3999(01)00296-3
31. Turon, H, Carey, M, Boyes, A, Hobden, B, Dilworth, S, and Sanson-Fisher, R. Agreement between a single-item measure of anxiety and depression and the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale: a cross-sectional study. PLoS One. (2019) 14:e0210111. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0210111
32. Barnes, PJ, and Celli, BR. Systemic manifestations and comorbidities of COPD. Eur Respir J. (2009) 33:1165–85. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00128008
33. Herbert, TB, and Cohen, S. Depression and immunity: a meta-analytic review. Psychol Bull. (1993) 113:472–86. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.113.3.472
34. Ouellette, DR, and Lavoie, KL. Recognition, diagnosis, and treatment of cognitive and psychiatric disorders in patients with COPD. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. (2017) 12:639–50. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S123994
35. Rábade Castedo, C, de Granda-Orive, JI, and González-Barcala, FJ. Increased prevalence of smoking: what is causing it and how should we intervene? Arch Bronconeumol (Engl Ed). (2019) 55:557–8. doi: 10.1016/j.arbres.2019.06.021
36. Graham, NM. The influence of psychological status on respiratory symptom reporting. Am Rev Respir Dis. (1989) 140:1498–9. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/140.5.1498
37. Zhang, J, Song, Y-L, and Bai, C-X. MIOTIC study: a prospective, multicenter, randomized study to evaluate the long-term efficacy of mobile phone-based internet of things in the management of patients with stable COPD. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. (2013) 8:433–8. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S50205
38. Xu, W, Collet, J-P, Shapiro, S, Lin, Y, Yang, T, Platt, RW, et al. Independent effect of depression and anxiety on chronic obstructive pulmonary disease exacerbations and hospitalizations. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2008) 178:913–20. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200804-619OC
39. Montserrat-Capdevila, J, Godoy, P, Marsal, JR, Barbé, F, Pifarré, J, Alsedà, M, et al. Overview of the impact of depression and anxiety in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Lung. (2017) 195:77–85. doi: 10.1007/s00408-016-9966-0
40. Regvat, J, Žmitek, A, Vegnuti, M, Košnik, M, and Šuškovič, S. Anxiety and depression during hospital treatment of exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Int Med Res. (2011) 39:1028–38. doi: 10.1177/147323001103900338
41. Cohen, S, Tyrrell, DA, and Smith, AP. Negative life events, perceived stress, negative affect, and susceptibility to the common cold. J Pers Soc Psychol. (1993) 64:131–40. doi: 10.1037//0022-3514.64.1.131
42. Huang, J, Bian, Y, Zhao, Y, Jin, Z, Liu, L, and Li, G. The impact of depression and anxiety on chronic obstructive pulmonary disease acute exacerbations: a prospective cohort study. J Affect Disord. (2021) 281:147–52. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2020.12.030
43. Mehta, JR, Ratnani, IJ, Dave, JD, Panchal, BN, Patel, AK, and Vala, AU. Association of psychiatric co-morbidities and quality of life with severity of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. East Asian Arch Psychiatr. (2014) 24:148–55.
44. Underner, M, Cuvelier, A, Peiffer, G, Perriot, J, and Jaafari, N. The influence of anxiety and depression on COPD exacerbations. Rev Mal Respir. (2018) 35:604–25. doi: 10.1016/j.rmr.2018.04.004
45. Eisner, MD, Blanc, PD, Yelin, EH, Katz, PP, Sanchez, G, Iribarren, C, et al. Influence of anxiety on health outcomes in COPD. Thorax. (2010) 65:229–34. doi: 10.1136/thx.2009.126201
46. Ståhl, E, Lindberg, A, Jansson, S-A, Rönmark, E, Svensson, K, Andersson, F, et al. Health-related quality of life is related to COPD disease severity. Health Qual Life Outcomes. (2005) 3:56. doi: 10.1186/1477-7525-3-56
47. Tsiligianni, I, Kocks, J, Tzanakis, N, Siafakas, N, and van der Molen, T. Factors that influence disease-specific quality of life or health status in patients with COPD: a review and meta-analysis of Pearson correlations. Prim Care Respir J. (2011) 20:257–68. doi: 10.4104/pcrj.2011.00029
48. Yohannes, AM, Willgoss, TG, Baldwin, RC, and Connolly, MJ. Depression and anxiety in chronic heart failure and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: prevalence, relevance, clinical implications and management principles. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. (2010) 25:1209–21. doi: 10.1002/gps.2463
49. Hill, K, Geist, R, Goldstein, RS, and Lacasse, Y. Anxiety and depression in end-stage COPD. Eur Respir J. (2008) 31:667–77. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00125707
50. DiMatteo, MR, Lepper, HS, and Croghan, TW. Depression is a risk factor for noncompliance with medical treatment: meta-analysis of the effects of anxiety and depression on patient adherence. Arch Intern Med. (2000) 160:2101–7. doi: 10.1001/archinte.160.14.2101
Keywords: anxiety, clinical burden, COPD, depression, economic burden
Citation: Zhao X, Liu G, Liu D, Zou L, Huang Q, Chen M, Li D, Wu B, Wu H, Huang D and Wu D (2024) Clinical and economic burden of anxiety/depression among older adult COPD patients: evidence from the COPD-AD China Registry study. Front. Psychiatry. 14:1221767. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1221767
Edited by:
Ashwani Kumar Mishra, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, IndiaReviewed by:
Zifeng Yang, Guangzhou Institute of Respiratory Health, ChinaŞenol Turan, Istanbul University Cerrahpasa, Türkiye
Copyright © 2024 Zhao, Liu, Liu, Zou, Huang, Chen, Li, Wu, Wu, Huang and Wu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Dong Wu, wudong98@126.com; Dan Huang, 287538250@qq.com
†These authors share first authorship
 Xuanna Zhao1†
Xuanna Zhao1† Gege Liu
Gege Liu