- 1Crop Research Institute, National Engineering Laboratory for Wheat and Maize, National Key Laboratory of Wheat Improvement, Key Laboratory of Wheat Biology and Genetic Improvement in the Northern Yellow-Huai Rivers Valley of Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, Shandong Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Jinan, China
- 2Shangqiu Academy of Agriculture and Forestry Sciences, Shangqiu, China
- 3Collage of Life Science, Yantai University, Yantai, China
- 4Department of Cell Biology, Zunyi Medical University, Guizhou, Zunyi, China
- 5Institute of Crop Sciences, National Wheat Improvement Center, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS), Beijing, China
A Corrigendum on
Genome-wide linkage mapping of Fusarium crown rot in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)
By Li F, Guo C, Zhao Q, Wen W, Zhai S, Cao X, Liu C, Cheng D, Guo J, Zi Y, Liu A, Song J, Liu J, Liu J and Li H (2024) Front. Plant Sci. 15:1457437. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1457437
In the published article, there was an error. A correction has been made to the Abstract.
This paragraph previously stated:
“Introduction: Powdery mildew (PM) poses an extreme threat to wheat yields and quality z. [Methods] In this study, 262 recombinant inbred lines (RILs) of Doumai and Shi 4185 cross were used to map PM resistance genes across four environments. A high-density genetic linkage map of the Doumai/Shi 4185 RIL population was constructed using the wheat Illumina iSelect 90K single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) array.
Results: In total, four stable quantitative trait loci (QTLs) for PM resistance, QPm.caas-2AS, QPm.caas-4AS, QPm.caas-4BL, and QPm.caas-6BS, were detected and explained 5.6%–15.6% of the phenotypic variances. Doumai contributed all the resistance alleles of QPm.caas-2AS, QPm.caas-4AS, QPm.caas-4BL, and QPm.caas-6BS. Among these, QPm.caas-4AS and QPm.caas-6BS overlapped with the previously reported loci, whereas QPm.caas-2AS and QPm.caas-4BL are potentially novel. Additionally, six high-confidence genes encoding the NBS-LRR-like resistance protein, disease resistance protein family, and calcium/calmodulin-dependent serine/threonine-kinase were selected as the candidate genes for PM resistance. Three kompetitive allele-specific PCR (KASP) markers, Kasp_PMR_2AS for QPm.caas-2AS, Kasp_PMR_4BL for QPm.caas-4BL, and Kasp_PMR_6BS for QPm.caas-6BS, were developed, and their genetic effects were validated in a natural population including 100 cultivars.
Discussion: These findings will offer valuable QTLs and available KASP markers to enhance wheat marker-assisted breeding for PM resistance.”
The corrected paragraph appears below:
“Introduction: Fusarium crown rot (FCR) is a severe soil-borne disease that affects wheat globally and leads to significant yield reductions. Identifying the loci associated with resistance to FCR and developing corresponding markers are essential for the breeding of resistant wheat varieties.
Methods: In this study, we evaluated the resistance to FCR in a recombinant inbred line (RIL) population originating from Gaocheng 8901 and Zhoumai 16 across four environments. The RILs and their parents were genotyped using a wheat 90K single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) array.
Results: We identified a total of five quantitative trait loci (QTLs) related to FCR resistance: QFCR.caas-3AL, QFCR.caas-3DL, QFCR.caas-5BL, QFCR.caas-6BS, and QFCR.caas-7DS. These QTLs accounted for 4.6% to 12.8% of the phenotypic variance. Notably, QFCR.caas-5BL and QFCR.caas-6BS had been previously detected, whereas QFCR.caas-3AL, QFCR.caas-3DL, and QFCR.caas-7DS are novel loci. The favorable alleles of QFCR.caas-3DL and QFCR.caas-5BL were contributed by Zhoumai 16, while the favorable alleles for QFCR.caas-3AL, QFCR.caas-6BS, and QFCR.caas-7DS originated from Gaocheng 8901. Additionally, this study identified seven candidate genes that encode disease resistance proteins, the BTB/POZ domains, peroxidase activity, and leucine-rich repeat receptor-like protein kinase. Furthermore, we developed and validated two kompetitive allele-specific PCR (KASP) markers, Kasp_3AL_FCR (QFCR.caas-3AL) and Kasp_5BL_FCR (QFCR.caas-5BL), in a natural population of 202 wheat varieties.
Discussion: This study contributes new genetic insights and provides new stable loci and available KASP markers for breeding to enhance FCR resistance in common wheat.”
In the published article, there was an error in Figure 3 as published. The leftmost box plot did not include the different letters to mark significant differences. The corrected Figure 3 appears below.
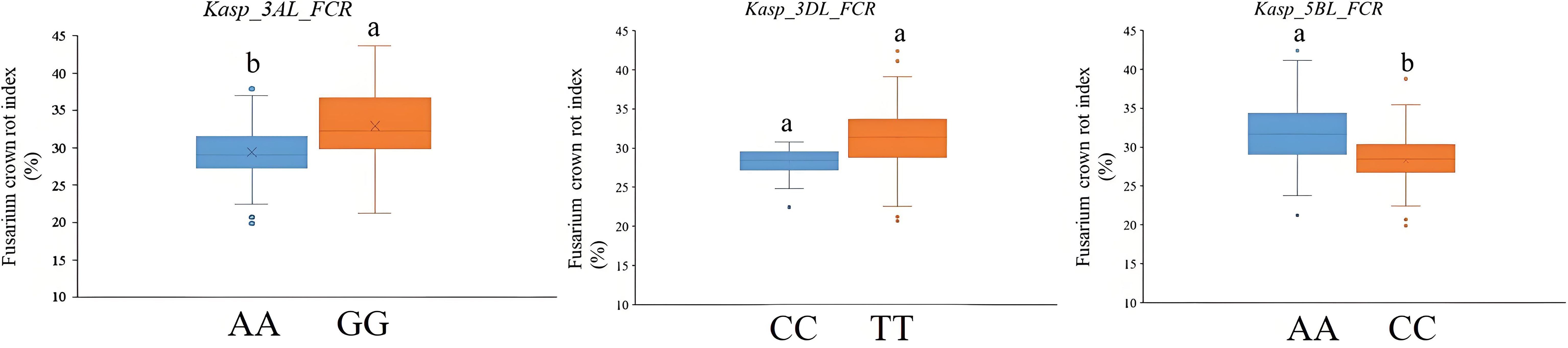
Figure 3. Validation of Kasp_3AL_FCR, Kasp_3DL_FCR, and Kasp_5BL_FCR in the panel of 202 wheat cultivars from the Huang-Huai River Valleys region. Different letters indicate significant differences at the P <0.05 level.
The authors apologize for these errors and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: common wheat, Fusarium crown rot (FCR), molecular marker-assisted selection, quantitative trait Loci (QTL), kompetitive allele-specific PCR (KASP)
Citation: Li F, Guo C, Zhao Q, Wen W, Zhai S, Cao X, Liu C, Cheng D, Guo J, Zi Y, Liu A, Song J, Liu J, Liu J and Li H (2025) Corrigendum: Genome-wide linkage mapping of Fusarium crown rot in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Front. Plant Sci. 16:1563575. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1563575
Received: 20 January 2025; Accepted: 21 January 2025;
Published: 06 February 2025.
Approved by:
Frontiers Editorial Office, Frontiers Media SA, SwitzerlandCopyright © 2025 Li, Guo, Zhao, Wen, Zhai, Cao, Liu, Cheng, Guo, Zi, Liu, Song, Liu, Liu and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Haosheng Li, bGloYW9zaGVuZzgxMEAxNjMuY29t
 Faji Li
Faji Li Can Guo2
Can Guo2 Weie Wen
Weie Wen Shengnan Zhai
Shengnan Zhai Xinyou Cao
Xinyou Cao Cheng Liu
Cheng Liu Jun Guo
Jun Guo Aifeng Liu
Aifeng Liu Jindong Liu
Jindong Liu Haosheng Li
Haosheng Li