
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Plant Sci., 31 March 2025
Sec. Plant Abiotic Stress
Volume 16 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2025.1561280
This article is part of the Research TopicAdvanced Breeding for Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Crops, Volume IIView all 18 articles
 Obed Kweku Sackey1,2
Obed Kweku Sackey1,2 Naijie Feng1,2
Naijie Feng1,2 Yushawu Zakaria Mohammed1
Yushawu Zakaria Mohammed1 Chrystella Fernanda Dzou3
Chrystella Fernanda Dzou3 Dianfeng Zheng1,2
Dianfeng Zheng1,2 Liming Zhao1,2
Liming Zhao1,2 Xuefeng Shen1,2*
Xuefeng Shen1,2*The challenge of salinity stress significantly impacts global rice production, especially in coastal and arid regions where the salinization of agricultural soils is on the rise. This review explores the complex physiological, biochemical, and genetic mechanisms contributing to salinity tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.) while examining agronomic and multidisciplinary strategies to bolster resilience. Essential adaptations encompass the regulation of ionic balance, the management of antioxidants, and the adjustments to osmotic pressure, all driven by genes such as OsHKT1;5 and transcription factors like OsbZIP73. The evolution of breeding strategies, encompassing traditional methods and cutting-edge innovations, has produced remarkable salt-tolerant varieties such as FL478 and BRRI dhan47. The advancements in this field are enhanced by agronomic innovations, including integrated soil management, crop rotation, and chemical treatments like spermidine, which bolster stress tolerance through antioxidant activity and transcriptional regulation mechanisms. Case studies from South Asia, Sub-Saharan Africa, the Middle East and, Australia demonstrate the transformative potential of utilizing salt-tolerant rice varieties; however, challenges persist, such as the polygenic nature of salinity tolerance, environmental variability, and socioeconomic barriers. The review highlights the importance of collaborative efforts across various disciplines, merging genomic technologies, sophisticated phenotyping, and inclusive breeding practices to foster climate-resilient and sustainable rice cultivation. This work seeks to navigate the complexities of salinity stress and its implications for global food security, employing inventive and cohesive strategies to confront the challenges posed by climate change.
Rice (Oryza sativa L.) is a cornerstone of global food security, acting as the essential dietary staple for more than half of the world’s populace, particularly in regions such as Asia, Africa, and Latin America. This crop plays a crucial role in the caloric and protein consumption of billions, as nations in Asia account for more than 90% of the worldwide rice production and consumption (Dutta et al., 2019). The versatility of rice in thriving under various environmental conditions has facilitated its growth in a range of ecosystems, spanning from lowland paddies to upland rain-fed systems (Neupane et al., 2020; Gairola et al., 2024). Beyond its nutritional significance, rice cultivation serves as a foundation for the livelihoods of countless smallholder farmers, especially in developing nations where it represents an essential source of income and employment (Asma et al., 2023; Singh et al., 2024). The influence of the crop permeates various dimensions, shaping cultural practices, traditions, and the economic landscapes of numerous nations. In areas such as Sub-Saharan Africa, the growth of rice farming responds to the interrelated issues of food security and rural development (Saito et al., 2023). However, addressing the increasing demand for rice presents significant challenges. The surge in population and the expansion of urban areas are propelling a significant escalation in the necessity for rice production, anticipated to increase by 25% by the year 2030 to satisfy worldwide demand. The sustainability of rice production systems is further jeopardized by environmental challenges, including salinity, water scarcity, and the impacts of climate change (Ansari et al., 2023). In light of these challenges, advancements in breeding, biotechnology, and crop management, exemplified by the creation of climate-resilient rice varieties, provide a promising avenue for maintaining production levels and safeguarding global food security.
Salinity stress is a major abiotic challenge that profoundly influences rice production worldwide, especially in coastal and irrigated lowland regions where soil salinization is widespread. Approximately 20% of the world’s irrigated land experiences the detrimental effects of salinity, which leads to a decrease in rice yield as a result of ionic toxicity, osmotic stress, nutrient imbalance, and oxidative damage, as illustrated in Figure 1. O. sativa L. demonstrates a significant vulnerability to salinity, leading to pronounced growth inhibition and a decline in productivity when subjected to salt-affected soils, particularly during its early developmental phases (Abbas et al., 2024). Salinity causes an excessive buildup of sodium (Na+) and chloride (Cl−) ions in plant tissues, which disrupts ionic homeostasis and reduces the absorption of vital nutrients such as potassium (K+) and calcium (Ca²+). The ionic imbalance disrupts enzymatic activities, cellular functions, and the process of photosynthesis. Osmotic stress resulting from salinity diminishes water availability, reducing cell turgor and inhibiting growth. Excessive reactive oxygen species (ROS) lead to oxidative stress, which results in additional damage to cellular structures (Gupta et al., 2024; Požgajová et al., 2024; Ruksaar, 2024).
Recent advancements in breeding, including the incorporation of salt-tolerant genes and quantitative trait loci (QTLs) such as Saltol, have facilitated the creation of resilient rice varieties, exemplified by FL478. These varieties demonstrate improved ionic regulation and osmotic adjustment. Molecular tools, including CRISPR/Cas9, are being utilized to target and enhance stress-responsive genes, such as OsHKT1;5 and OsbHLH024, to improve salinity tolerance (Akhlasur Rahman et al., 2024). Salinity stress is expected to intensify due to climate change and the rising scarcity of water resources. Implementing effective strategies such as enhanced irrigation practices, soil management, and genetic improvement is crucial for sustaining rice production in saline-prone regions (Irin et al., 2024; Sikder and Khan, 2024). Integrating traditional breeding methods with contemporary biotechnological techniques is essential for maintaining productivity and tackling global food security issues (Zhang et al., 2024a).
This review aims to thoroughly examine the effects of salinity stress on rice (Oryza sativa L.) production, emphasizing the physiological, biochemical, and molecular pathways that contribute to salt tolerance in rice. It explores advancements in breeding strategies, genetic modifications, and agronomic interventions designed to mitigate the detrimental effects of high salinity and sustain yield stability in affected regions. Given the escalating challenges posed by climate change, irrigation practices, and soil deterioration, this study also assesses the global implications of salt-induced stress and evaluates region-specific adaptation strategies, particularly in vulnerable agricultural areas.
The soil microbiome is essential for plant growth and resistance, especially under abiotic stressors such as salinity (Chen et al., 2024; Etesami, 2024). Soil microbes, such as rhizobacteria, mycorrhizal fungi, and other beneficial microorganisms, interact with plant roots and affect essential physiological processes that alleviate the impacts of salinity stress (El-Aal et al., 2024; Yahyaoui et al., 2024; Zhang et al., 2024b). Microbial communities are widely acknowledged for their capacity to improve plant resilience to diverse stresses, such as drought, nitrogen shortage, and salinity, via numerous pathways (Ali et al., 2024; Muhammad et al., 2024).
Rhizobacteria and mycorrhizal fungi are two of the many types of soil microbes that play a crucial role in improving plant health and resilience to stress. Plants benefit from rhizobacteria, which reside in close proximity to their roots, since these microbes increase nutrient intake, produce chemicals that stimulate plant growth, and cause a defense mechanism against diseases (Chaudhary et al., 2024; Hiremath et al., 2024). Improving water intake or changing the ionic balance within plant tissues are two ways in which some rhizobacteria might reduce salinity stress (Basu et al., 2023; Acharya et al., 2024). For instance, Bacillus and Pseudomonas species enhance salt tolerance by producing exopolysaccharides, which help maintain cell turgidity under saline conditions (N et al., 2024). Similarly, mycorrhizal fungi, which create symbiotic associations with plant roots, are essential for alleviating salinity stress. These fungi enhance the root system via their hyphal networks, improving water and nutrient absorption, particularly in saline soils where nutrient availability is frequently restricted. Recent research indicate that mycorrhizal inoculation can markedly enhance the salt tolerance of crops like wheat and rice by improving the plant’s capacity to sustain osmotic equilibrium and mitigate ion toxicity (Basit et al., 2024; Chaudhary et al., 2024). Mycorrhizal fungi can boost the synthesis of stress hormones such as abscisic acid, enhancing the plant’s response to salt stress (Aizaz et al., 2024).
Soil microbes assist plants in managing salt stress via many methods, such as osmotic adjustment, ion homeostasis, and the control of plant hormones. Certain beneficial microorganisms synthesize suitable solutes (e.g., trehalose, proline) that assist plants in conserving water and sustaining cellular function in saline environments (Hmidi et al., 2018; Shafi et al., 2019; Imhoff et al., 2020; Gil et al., 2023). These solutes can concentrate in plant cells, preserving turgor pressure and stabilizing proteins and membranes, which is essential for survival in saline soils. Additionally, microbial communities play a key role in ion homeostasis by the regulation of sodium (Na+) and potassium (K+) ions in plant tissues, inhibiting the harmful buildup of Na+ and enhancing the absorption of K+ (Liu et al., 2023; Dong et al., 2024; Dreyer et al., 2024). Rhizobacteria can modulate the expression of salt-excluding or salt-tolerant genes in plants, hence assisting in the maintenance of ion equilibrium in the root zone (Guo et al., 2024). Specific bacterial strains, including Bacillus subtilis, have demonstrated the ability to augment the function of Na+/H+ antiporters in plant roots, hence mitigating salt absorption (Pabuayon et al., 2021; Song et al., 2023). Furthermore, beneficial microorganisms can stimulate the expression of plant stress-responsive genes, enhancing the plant’s capacity to endure oxidative damage caused by salt.
Recent research efforts provide insight into the intricate relationships between plants and their corresponding soil microbiomes under saline stress. A significant discovery is the influence of plant-associated microbiomes on the plant’s transcriptional response to salinity. Research indicate that beneficial bacteria can modify the expression of essential genes associated with stress signaling pathways, including those linked to abscisic acid (ABA) production, osmotic control, and ion transport (Davis et al., 2024; Wang et al., 2025). For instance, Salt-tolerant rhizobacteria, such as Microbacterium ginsengiterrae S4, enhance rice resilience by increasing antioxidant enzyme activity and regulating osmotic substances under saline stress (Ji et al., 2024).
Another notable discovery is the influence of microbial metabolites on enhancing plant health. Certain microbial species generate volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that improve plant salinity tolerance by regulating the plant’s hormonal equilibrium, namely by elevating auxin and cytokinin levels, which facilitate root development and salt resistance (Barghi and Jung, 2023; Mahadik and Kumudini, 2024). Current research on plant-microbe interactions underscores the potential for microbiome-based strategies to enhance conventional breeding methods in the creation of salinity-tolerant crops. Microbial inoculants, comprising consortia of beneficial bacteria and fungi, are being studied as economical and sustainable solutions for improving crop performance in salt conditions. Microbiome-based techniques may be incorporated into precision agriculture operations, facilitating more effective management of salt-affected soils. The soil microbiome’s function in facilitating salinity tolerance is an increasing area with significant potential for sustainable agriculture. Further studies into plant-microbe interactions and their utilization in saline agriculture may substantially improve crop resilience to salinity, hence aiding food security in salinity-affected areas.
The interaction between abiotic and biotic stressors in plants is a difficult challenge that profoundly affects worldwide agricultural growth and yield. Abiotic factors, like drought, salinity, and heat, frequently coincide with biotic pressures such as pests and diseases, resulting in complex interactions that may be either synergistic or antagonistic. Understanding these relationships is essential for creating resilient crop kinds and guaranteeing food security throughout climate change. Plants have developed intricate molecular defense mechanisms to withstand concurrent abiotic and biotic stressors. These encompass transcription factors and kinases that govern integrative plant responses (Menéndez and Tundo, 2024). Drought stress, for instance, induces morphophysiological changes such as reduced leaf area and enhanced root growth, which can prime plants for future stress events. Biochemical responses include the production of secondary metabolites and volatile organic compounds, which play roles in signaling and defense against herbivores (Shafi et al., 2024). Genome editing technologies offer precise tools for enhancing plant resilience to both abiotic and biotic stresses by enabling targeted alterations in plant genomes (Mann et al., 2024). Integrating bioinformatics and AI applications can enhance the identification and analysis of stress-responsive genes and regulatory networks, providing deeper insights into stress response pathways (Zhang et al., 2024). However, multi-omics approaches, including genomics, transcriptomics, and metabolomics, are crucial for understanding the complex regulatory networks involved in stress adaptation. Combining these approaches with eco-physiological assessments can provide a comprehensive understanding of how plants adapt to changing environments (Shafi et al., 2024). Comprehending the impact of these cumulative stresses on plants at physiological, molecular, and ecological levels is crucial for cultivating crops capable of sustaining output under realistic growing conditions, where numerous stresses frequently occur.
Abiotic stresses such as salinity, drought, and heat frequently intensify the effects of biotic pressures by modifying plant physiology, hence increasing their vulnerability to pests and diseases. Salt stress can diminish plant vigor and trigger water stress, hence impairing the plant’s innate defense mechanisms against diseases such as fungi or bacteria (Shafi et al., 2024). Drought and heat can also hinder a plant’s capacity to synthesize secondary compounds, essential for protection against insect pests (Shafi et al., 2024). Elevated temperatures can compromise disease resistance, making plants more susceptible to infections from fungi and bacteria (Shelake et al., 2024).
Conversely, the existence of pests might affect a plant’s resilience to abiotic pressures. Herbivore-induced stress can alter plant metabolism, thereby augmenting or impairing the plant’s resilience to other stressors. Research indicates that plants subjected to simultaneous drought and insect herbivory stress demonstrate modified hormonal responses, including heightened production of jasmonic acid, which is crucial to both drought resistance and pest defense (Khan et al., 2024; Margay et al., 2024). As illustrated in Figure 2, the combined stresses frequently have a synergistic or additive effect, whereby one stress amplifies the adverse impact of another, resulting in a more significant decline in growth, yield, and salt tolerance (Khalid et al., 2024; Li et al., 2024). In order to ensure the stability of salt tolerance characteristics under varying environmental conditions, breeding programs must integrate multi-stress tolerance. Multi-environment trials (METs) are crucial for evaluating salt-tolerant rice cultivars under diverse climatic circumstances and across several growth seasons. Such trials assist in identifying cultivars that sustain constant performance despite varying environmental conditions (Balasubramanian). Moreover, multi-stress breeding is essential to guarantee that rice varieties exhibit tolerance not only to salt but also to combined stresses such as drought and heat. This underscores the necessity for a comprehensive strategy in breeding for multi-stress tolerance, wherein the interconnections between abiotic and biotic stressors are concurrently addressed.
When plants suffer combined abiotic and biotic challenges, their physiological responses become more intricate than those experienced under singular stress conditions. The initial line of defense often entails a series of signaling pathways triggered by the perception of stress. In response to abiotic conditions including salt and drought, plants initiate osmotic regulation and antioxidant defense mechanisms to mitigate damage from reactive oxygen species (Liu et al., 2024; Rafique et al., 2024). Simultaneously, when plants encounter biotic stress, such as pathogen invasion, they activate defense mechanisms, including the synthesis of pathogenesis-related proteins and the initiation of systemic acquired resistance (SAR) pathways (Bandyopadhyay et al., 2024). Under conditions of combined salinity and pathogen stress, plants may prioritize their response to salinity by activating ion transporters such as NHX (Na+/H+ antiporters) and SOS (salt excessively sensitive) pathways, which facilitate the maintenance of ionic equilibrium (Maach et al., 2024). This may restrict the energy allocated for activating defense mechanisms against pathogens, leading to heightened disease vulnerability (Majidian and Ghorbani, 2024). In contrast, other plant species, such as those in the Brassica genus, exhibit cross-tolerance mechanisms that boost their response to abiotic challenges, including drought or heat, when subjected to biotic pressures like herbivore attacks (Cantila et al., 2024; Yoo et al., 2024). The interaction among various stress responses frequently entails communication between plant hormones at the molecular level. The hormone abscisic acid (ABA) is essential for drought tolerance and pathogen defense; however, the precise regulation of ABA signaling is vital in deciding whether a plant will initiate an effective defense response or prioritize survival during drought or heat stress (Rizhsky et al., 2004; Bharath et al., 2021; Lim et al., 2022). This crosstalk engenders a complex environment for breeding strategies, as selecting for tolerance to one stress may unintentionally diminish the plant’s capacity to withstand another.
Considering the intricate nature of combined stress reactions, breeding for multi-stress tolerance necessitates a more comprehensive strategy than conventional single-stress breeding. A variety of breeding strategies have developed to tackle the challenges posed by coupled stressors. These include Quantitative Trait Locus (QTL) Mapping and Marker-Assisted Selection (MAS), which have emerged as viable methods in recent years. For instance, QTLs linked to simultaneous drought and heat tolerance in Oryza sativa have been identified and utilized in marker-assisted selection to create varieties with improved resilience to both extremes concurrently (Hassan et al., 2023; Mohanavel et al., 2024). Transgenic and genome-editing approaches also play a significant role. Editing genes associated with ion transport, hormone control, and reactive oxygen species scavenging can result in the creation of plants that demonstrate improved tolerance to both abiotic conditions (e.g., salt, drought) and biotic challenges (e.g., diseases, pests) (Li et al., 2022; Yadav et al., 2023). The CRISPR/Cas9 technology has been employed to modify the OsERF48 gene in rice, which is involved in the regulation of drought tolerance and resistance to the rice blast fungus (Shim et al., 2018; Jung et al., 2021). Recent breakthroughs in functional genomics and systems biology have enabled researchers to examine the integrated responses of plants to various stimuli at the transcriptomic and proteomic levels. By comprehending the systemic coordination of stress responses in plants, breeders might formulate ways to augment the overall resistance of crops against various combined stressors. The utilization of transcriptome data has facilitated the identification of genes associated with heat and pest resistance in maize, potentially aiding in the breeding of maize varieties capable of enduring both stressors (Xue et al., 2024; Zhao et al., 2024).
Traditional breeding techniques remain essential in the creation of multi-stress tolerant cultivars. These programs must prioritize the assessment of stress tolerance under various environmental settings, mimicking the impacts of mixed abiotic and biotic stressors. Breeding projects for wheat have aimed to create varieties that exhibit tolerance to both drought and pest infestations, seeing some success in areas susceptible to these challenges (Tadesse, 2021; Bapela et al., 2022). Addressing combined abiotic and biotic stresses is crucial for crop resilience in the face of climate change and insect challenges. These stresses cause complicated physiological and molecular responses, typically requiring cross-talk between stress signaling pathways. Breeding efforts must use QTL mapping, transgenic methods, and functional genomics to create stress-resistant crops. Successful multi-stress tolerance breeding requires a profound understanding of plant stress physiology and a dedication to establishing breeding programs that analyze numerous stress combinations to create resilient, high-yielding crops.
A key mechanism enabling rice to withstand salinity is ionic homeostasis, which maintains the delicate ion balance within plant cells under saline conditions. Plant growth and productivity are significantly hampered by ionic toxicity, osmotic stress, and nutritional imbalance caused by high concentrations of sodium (Na+) and chloride (Cl-) ions in saline soils. As summarized in Figure 3, rice plants have developed several adaptive methods to lessen these negative effects and guarantee survival in the face of saline stress. A fundamental mechanism includes the management of sodium and potassium concentrations, in which effective ion transport networks uphold Na+/K+ balance, essential for enzyme functions and cellular integrity. The high-affinity potassium transporter (HKT) gene family, especially OsHKT1;5, is crucial for selectively extracting Na+ from the xylem, thus mitigating harmful buildup in the shoots while maintaining sufficient potassium levels in the cytoplasm (Shohan et al., 2019; Hussain et al., 2022). The sequestration of sodium ions into vacuoles is mediated by vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporters such as NHX1, which mitigate cytosolic toxicity and assist in maintaining osmotic equilibrium. The sequestration process is facilitated by proton pumps such as H+-ATPase and H+-PPase, which sustain the electrochemical gradient essential for Na+ transport (Patel and Mishra, 2021; Mansour, 2023). These physiological responses are molecular mechanisms like the salt overly sensitive (SOS) pathway, involving key components such as SOS1, SOS2, and SOS3. This pathway modulates Na+ efflux and facilitates K+ retention, hence maintaining ion homeostasis during salt stress. Transcriptomic analyses reveal the overexpression of these transporters in salt-tolerant rice cultivars, emphasizing their significance in salinity resilience (Hussain et al., 2022). These interconnected methods and mechanisms illustrate rice plants’ complex approach to sustaining ionic equilibrium and flourish in saline conditions.
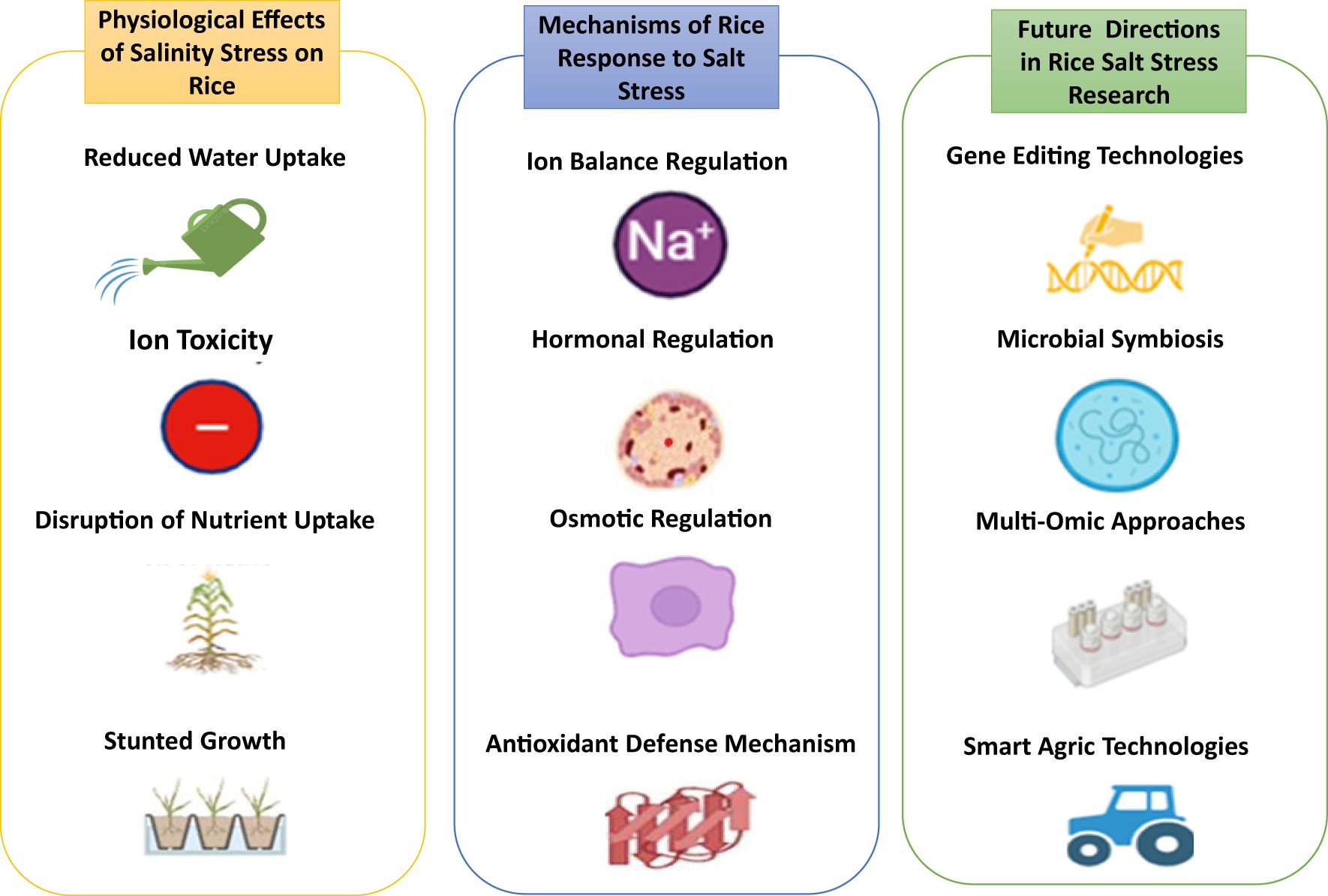
Figure 3. Overview of the physiological response of rice to salinity and drought stress: effects, mechanisms and future research directions.
Although sodium toxicity frequently generates greater focus, the management of chloride ions is of equal significance. Rice plants efficiently regulate Cl− absorption and translocation to prevent excessive buildup in sensitive tissues, with stronger discrimination mechanisms facilitating improved salinity tolerance (Sarangi et al., 2024; Gupta and Shaw, 2021; Guo et al., 2024). Alongside these intrinsic tactics, the utilization of biostimulants has surfaced as a promising method. Exogenous compounds like gallic acid and humic acid improve ionic homeostasis by decreasing Na+ buildup and optimizing the Na+/K+ ratio. These biostimulants also stimulate antioxidant defense mechanisms, alleviating oxidative damage caused by saline environments (Rahman et al., 2022; Abu-Ria et al., 2023; Zhang et al., 2024a).
Osmotic adjustment is essential for rice plants to adapt to salinity stress, as it helps maintain cellular turgor and water uptake, both of which are crucial for survival in salt-affected environments. This adaptive mechanism relies on the active accumulation of osmolytes, including proline, glycine betaine, and trehalose, as well as inorganic ions such as potassium (K+). These molecules reduce cellular osmotic potential, facilitating water retention in the presence of external osmotic imbalances due to elevated salinity (Suprasanna et al., 2016; Zouari et al., 2019; Mohammadi Alagoz et al., 2023). In addition to water regulation, these osmolytes play a role in stabilizing cellular proteins and membranes, reducing ionic toxicity from Na+ and Cl- accumulation, and enhancing antioxidant defenses. Proline serves as a molecular chaperone and a scavenger of reactive oxygen species (ROS), protecting cellular structures during stress conditions (Rehman et al., 2021; Liu et al., 2022; Ulrich, 2023). The importance of osmotic adjustment is further highlighted by research on salinity-tolerant rice lines, in which certain quantitative trait loci (QTLs) augment osmolyte synthesis and transport. These genetic modifications highlight the relevance of essential genes, especially those associated with tetrapyrrole production, which enhance osmotic balance and photosynthetic efficiency in saline environments (Nounjan et al., 2020). These findings highlight the interaction between metabolic pathways and stress resilience in rice. Advancements in biotechnology, have transformed approaches to improve osmotic adjustment. Researchers have engineered genes involved in osmolyte production to develop transgenic rice types with enhanced salt tolerance. The overexpression of glycine betaine biosynthetic genes has resulted in rice plants exhibiting enhanced growth and productivity in saline soils (Liu et al., 2022; Mandal et al., 2022; Yu et al., 2022). These insights and improvements collectively underscore the complex mechanisms of osmotic adjustment and its significant promise in developing salt-tolerant rice cultivars (Nurbekova et al., 2024).
Salinity stress in rice plants induces the excessive generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), such as superoxide anions, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), and hydroxyl radicals, leading to oxidative damage to critical cellular components, including lipids, proteins, and DNA. Rice plants employ a comprehensive antioxidant defense system consisting of enzymatic and non-enzymatic components to preserve cellular integrity during stress. Enzymatic antioxidants, including superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), ascorbate peroxidase (APX), and glutathione reductase (GR), are upregulated in response to salinity stress. This increased expression establishes a defense network that transforms harmful reactive oxygen species (ROS) into less reactive molecules, such as water and oxygen. Enhanced activities of APX and CAT have been observed in salt-tolerant rice varieties, such as CSR36, leading to reduced ROS levels and improved ionic homeostasis (Li et al., 2023; Kumar et al., 2024). Non-enzymatic antioxidants such as ascorbate (AsA), glutathione (GSH), proline, and phenolic compounds serve to enhance enzymatic defenses. Proline facilitates osmotic adjustment, stabilizes proteins, and scavenges free radicals, enhancing stress tolerance (Hadid et al., 2023; Renzetti et al., 2024). SOD serves as the initial line of defense, facilitating the conversion of superoxide radicals into oxygen and hydrogen peroxide through the process of dismutation. In rice, various isoforms of superoxide dismutase (SOD), such as Cu/Zn-SOD, Mn-SOD, and Fe-SOD, are distributed across distinct cellular compartments, including chloroplasts, mitochondria, and the cytosol, to offer protection that is specific to each compartment (Sanyal et al., 2022; Zhou et al., 2022). CAT is essential for the detoxification of hydrogen peroxide, facilitating its conversion into water and oxygen. Rice cultivars demonstrating elevated CAT activity in response to salinity stress show increased tolerance, as indicated by diminished oxidative damage and enhanced growth (Jiang et al., 2023). POD and APX play crucial role in the ascorbate-glutathione cycle, facilitating the detoxification of hydrogen peroxide within the cytosol and chloroplasts. APX specifically employs ascorbate as a reducing agent to transform H2O2 into water, whereas POD plays a crucial role in lignin biosynthesis and the fortification of cell walls during stress conditions (Foyer and Kunert, 2024; Yoshimura and Ishikawa, 2024).
The application of exogenous antioxidants, including gallic acid, significantly bolsters this defense mechanism by augmenting the enzymatic activity within the AsA-GSH cycle, which in turn mitigates oxidative damage in rice seedlings subjected to salinity stress (Rahman et al., 2020). In the realm of genetics, genes like OsAPX1 and OsCATC frequently exhibit upregulation in rice varieties that demonstrate salt tolerance. Furthermore, genetic modifications, particularly the overexpression of genes responsible for scavenging reactive oxygen species, have proven effective in enhancing salinity tolerance (Chen and Qiu, 2023; Song et al., 2024; Zhao et al., 2024). Breeding programs incorporating molecular tools to enhance antioxidant pathways are essential for developing rice varieties with improved salinity tolerance. This highlights the variability of antioxidant responses among different genotypes and their significance for sustainable agriculture.
Rice plants have developed a range of morphological and anatomical adaptations that enable them to cope with the detrimental impacts of salinity stress, such as decreased water availability, ionic toxicity, and oxidative stress. The adaptations are crucial for fostering growth and ensuring productivity in saline environments. A significant approach involves altering root morphology and architecture, which improves the absorption of water and nutrients while minimizing sodium buildup. Salt-tolerant rice varieties generally exhibit deeper and more expansive root systems, allowing them to reach less saline water located at greater depths.
Alterations in the density of root hairs and heightened root exudation play a significant role in enhancing ionic balance (Oburger et al., 2014; Holz et al., 2018). In light of the diminished water availability linked to salinity, rice plants demonstrate reduced leaf areas and heightened leaf rolling, adaptations that serve to conserve water effectively. The regulation of stomata is essential in this context, as the closure of these structures reduces water loss and inhibits the absorption of harmful ions through evapotranspiration (Raeisi Vanani et al., 2024). Salt-tolerant varieties exhibit anatomical adaptations such as thicker cuticles and reinforced epidermal layers. These features minimize water loss and serve as barriers to ion entry, thereby improving the plant’s capacity to sustain internal water potential and ionic balance. Moreover, vascular adaptations, including decreased xylem vessel diameters and a heightened number of xylem vessels, play a crucial role in regulating ion transport and mitigating sodium translocation to the shoots. Improved vascular compartmentalization isolates toxic ions, thus safeguarding metabolic processes (Pouzoulet et al., 2020). Furthermore, forming aerenchyma tissue in the roots enhances oxygen transport in saline, waterlogged soils, offering significant advantages for lowland rice varieties. Ultimately, the buildup of osmolytes such as proline and glycine betaine within the leaves and stems of rice plants plays a crucial role in sustaining cell turgor and osmotic potential. This adaptation allows the plants to persist in growth and photosynthesis, even when faced with salinity stress. The various adaptations contribute significantly to the resilience of salt-tolerant rice varieties, offering important insights for breeding programs and agricultural practices focused on enhancing rice production in areas susceptible to salinity.
Salinity tolerance in rice is modulated by complex genetic systems, with many Quantitative Trait Loci (QTLs) essential for sustaining ionic homeostasis, osmotic equilibrium, and stress signaling pathways. Recent advances in genomic technologies have facilitated the precise identification of key QTLs associated with salinity tolerance, especially during crucial growth phases. The genetic complexity of these features renders them difficult to identify and enhance via conventional breeding techniques. Modern methodologies such as Quantitative Trait Locus (QTL) mapping and Genome-Wide Association Studies (GWAS) have facilitated the identification of loci linked to salinity tolerance. Mapping these loci enhances the understanding of the genetic variation that contributes to salt tolerance in rice, hence informing breeding initiatives (Yin et al., 2023; Sugasi et al., 2024). One of the most thoroughly investigated QTLs is Saltol, situated on chromosome 1, which is significantly linked to the regulation of sodium-potassium homeostasis during salt stress (Marè et al., 2023). Saltol accounts for 62–80% of phenotypic variation under salinity stress (Nutan et al., 2019; Marè et al., 2023). The Saltol region, especially the SKC1 gene responsible for encoding a sodium-potassium transporter, has played a crucial role in marker-assisted selection (MAS) initiatives aimed at creating salt-tolerant rice varieties, exemplified by FL478. Research on haplotypes has demonstrated that various alleles in this region play a significant role in salinity tolerance, observed in elite lines and various landraces (Marè et al., 2023; Thippani et al., 2023). A comprehensive meta-analysis focusing on salinity tolerance QTLs has successfully identified 65 meta-QTLs (mQTLs) derived from an initial pool of 768 QTLs across 35 studies. This extensive research has effectively refined the confidence intervals for various traits, encompassing root architecture, osmotic adjustment, and ionic transport. Identifying these mQTLs has emerged as a critical focus for breeding initiatives designed to enhance salt tolerance (Satasiya et al., 2024). Recent sequencing studies have brought to light the significance of qCMS1 and qTN1 located on chromosome 1, which are linked to important traits such as cell membrane stability and tiller number in the context of salt stress. The identified loci exhibit notable phenotypic variance ranging from 16% to 20%, positioning them as strong candidates for the pyramiding of multiple QTLs aimed at improving salt tolerance (Songtoasesakul et al., 2023; Khunsanit et al., 2024).
Moreover, genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have identified new quantitative trait loci (QTLs), such as qGPR2 and qSLR9, which regulate seedling development and germination capacity in saline environments, providing new avenues for genetic enhancement in breeding programs employing SNP markers and marker-assisted selection (MAS) (Sayed et al., 2022; Baştaş, 2023; Maniruzzaman et al., 2023). The genes associated with these QTLs encompass transcription factors (e.g., MADS-box, calmodulin-binding proteins) and ion transporters (e.g., OsHKT1;5, OsSOS1), which are pivotal in ion transport, signaling, and stress responses, elucidating the molecular mechanisms of salinity tolerance (Leawtrakun et al., 2024a). Incorporating these quantitative trait loci into superior rice varieties, along with marker-assisted selection and advanced gene-editing technologies, are facilitating the creation of rice cultivars that exhibit improved tolerance to salinity. The recent advancements hold considerable importance for global food security, facilitating more sustainable rice production in areas susceptible to salinity, thus contributing to the stabilization of yields in the face of escalating environmental challenges.
In recent years, molecular markers and marker-assisted breeding (MAB) have become essential instruments for improving the salinity stress tolerance of rice varieties. Aside the Saltol QTL on chromosome 1, recent investigations have revealed additional QTLs, including qSES1, qK8, and qRL1, which exhibit distinct placements and notable stability across various genetic backgrounds, offering new opportunities for developing salt-tolerant rice varieties (Maniruzzaman et al., 2023). Molecular markers, such as single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) markers, have greatly enhanced the high-resolution mapping of salt-tolerant traits. SNP markers are crucial for accurately identifying traits in salt-tolerant rice, whereas RAPD markers are effective for screening aromatic rice varieties (Cuthbertson, 2022; Geng et al., 2023; Maniruzzaman et al., 2023). Marker-assisted backcrossing (MABC) effectively transfers salinity tolerance traits into elite varieties. Examples of success include the introgression of the Saltol locus into temperate japonica rice varieties such as Vialone Nano and Onice, which improves salinity tolerance while maintaining yield potential (Marè et al., 2023). In addition to Saltol, loci including SKC1 and new QTLs derived from landraces, such as Akundi, provide supplementary mechanisms for salinity tolerance, thereby expanding the genetic resources accessible for breeding purposes (Soda et al., 2013; Le et al., 2021). The variety CSR43, produced using MABC, has exhibited high yields under saline environments in India (Singh et al., 2016). Likewise, BRRI dhan67, introduced in Bangladesh, has demonstrated exceptional adaptation to coastal areas characterized by elevated soil salinity (Shamsuddin et al., 2022). These achievements underscore the promise of molecular markers in the creation of climate-resilient rice cultivars.
Omics technologies, including as transcriptomics and proteomics, have detailed the molecular pathways that govern salinity tolerance. Transcriptomic analyses have demonstrated the overexpression of genes like OsDREB2A and WRKY53, which are pivotal in stress response pathways. Proteomic investigations have discovered stress-protective proteins that facilitate osmotic adjustment and mitigate oxidative stress, thereby deepening the understanding of salt tolerance processes (Reddy et al., 2023). These developments have facilitated the precise modification of genes such as OsHKT1;5 and OsNHX1, which govern Na+ transport and vacuolar sequestration, respectively, enhancing salinity tolerance without diminishing yield (Rasheed et al., 2022). Modern breeding approaches, notably CRISPR/Cas9-mediated genome editing, genomic selection, and high-throughput phenotyping, have enhanced traditional and marker-assisted breeding procedures. For instance, CRISPR/Cas9 has been employed to delete the OsERF922 gene, thereby augmenting blast resistance in rice while preserving other agronomic characteristics (Liang et al., 2021). Similarly, genomic selection (GS) has been utilized to enhance complex traits, including grain quality and nitrogen use efficiency (NUE), in rice (Yu et al., 2022). High-throughput phenotyping platforms, coupled with advanced imaging technologies, have enabled the rapid screening of large breeding populations for traits such as canopy architecture, root morphology, and stress responses (Yang et al., 2014; Tanger et al., 2017). The combined use of genetic approaches (e.g., GWAS, GS) with high-throughput phenotyping has enabled the creation of salinity-tolerant rice cultivars with unparalleled precision and efficiency (Akhlasur Rahman et al., 2024).
The utilization of genomic technologies has significantly enhanced the study of salt tolerance in rice, uncovering complicated biochemical and genetic pathways that regulate this feature. Candidate genes such as MIKC-type MADS domain proteins and calmodulin-binding transcription factors have been emphasized for their involvement in salt stress signaling (Leawtrakun et al., 2024a). Further insight from transcriptomics and eQTL analyses reveals that salinity induces significant changes in gene expression in rice. The studies indicate that trans-eQTLs have a greater impact compared to cis-eQTLs, implying the importance of master regulatory genes in the adaptation to salinity stress (Gupta et al., 2024). Moreover, transcriptomic analysis highlights the potential of spermidine treatment in mitigating salinity-induced transcriptional disruptions, upregulating genes related to stress-alleviation pathways such as MAPK signaling and phenylalanine metabolism, thus complementing genomic strategies for enhanced salinity tolerance (Shen et al., 2024). Simultaneously, advanced genotyping technologies such as SNP chips and next-generation sequencing (NGS) have significantly propelled genome-wide association studies (GWAS) and marker-assisted selection (MAS) aimed at enhancing salinity tolerance. These instruments facilitate the recognition of markers associated with salinity, thus empowering more accurate breeding initiatives aimed at multi-trait tolerance (Singh and Devi, 2023). The exploration of functional genomics, especially regarding genes like OsHKT1;5 and OsNHX1, has deepened our understanding of the intricate mechanisms involved in ion transport and compartmentalization when faced with salinity stress.
Wild rice germplasm has become crucial for improving salinity tolerance in cultivated rice cultivars, tackling a significant agricultural concern. The genetic variety in wild rice species offers unique alleles and features that markedly enhance tolerance to salt stress, exceeding the constraints observed in domesticated varieties such as Oryza sativa (Shahzad et al., 2022). Species such as Oryza rufipogon, Oryza coarctata, Oryza latifolia, and Oryza alta are naturally adapted to saline environments, equipped with mechanisms including effective Na+ exclusion, K+ retention, and osmotic adjustment. These wild cousins offer distinct genes responsible for activities such as vacuolar sequestration of sodium, regulated xylem loading, and activation of stress-responsive antioxidant pathways, all contributing to salt tolerance (Solis et al., 2020). Furthermore, metabolomic analysis of Dongxiang wild rice has shown the important function of amino acids such as L-Asparagine in reducing salt stress and offering biochemical markers for tolerance building. Crucially for preserving cellular homeostasis under salt stress conditions, these metabolic changes include the activation of antioxidant pathways and the buildup of osmolytes (Chen et al., 2021a). Moreover, the identification of new Quantitative Trait Loci (QTLs) and candidate genes such as AGO2 and WRKY53, which improve salt tolerance at crucial phases like germination and early development, has been much aided by the establishment of Chromosome Segment Substitution Lines (CSSLs). The key to stress adaption is that these genes control fundamental processes, including reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenging and ion transport (Xing et al., 2024). A number of studies have effectively pinpointed and described salt-tolerant genes in wild rice species, while current endeavors focus on incorporating these traits into superior rice cultivars, thereby enhancing the genetic diversity accessible for salinity tolerance (Samy et al., 2024).
Salinity stress significantly impairs essential processes of photosynthesis and chlorophyll concentration in O. sativa, which are vital for plant growth and yield. Sodium ions (Na+) interfere with cellular ionic equilibrium and osmotic potential, causing structural and functional damage to the photosynthetic system. This disturbance results in diminished photosynthetic efficiency, decreased chlorophyll levels, and impaired light absorption. Salinity inhibits chlorophyll biosynthesis and hastens its breakdown, reducing light absorption and electron transport. A study on rice cultivars subjected to 80 mM NaCl demonstrated considerable chlorophyll decline, chiefly attributable to oxidative damage and the suppression of enzyme pathways essential for chlorophyll biosynthesis (da Silva et al., 2023). Rice genotypes possessing salt-tolerant QTLs, exemplified by the Pokkali variety, exhibited improved chlorophyll retention and superior photosynthetic efficiency in saline conditions, highlighting the significance of genetic diversity in stress adaptation (Nounjan et al., 2020). Furthermore, salt stress affects chloroplast thylakoid membranes, limiting Photosystem II (PSII) activity. This leads to reduced quantum efficiency (Fv/Fm) and poorer photochemical quenching, both of which are important for effective energy conversion during photosynthesis (Tabassam et al., 2016). Salt-tolerant genotypes, however, preserve higher PSII efficiency, ensuring better utilization of light energy. As a result, the overall photosynthetic rate (Pn) drops during salinity stress, mostly due to stomatal closure and lower CO2 absorption. Improvements in water use efficiency (WUE) and osmotic adaptations in salt-tolerant cultivars alleviate these impacts, as demonstrated by Pokkali rice, which showed a 19% rise in Pn under high salinity, indicating its superior physiological resilience (Santanoo et al., 2023).
Figure 4 illustrates that physiological alterations under salinity stress encompass various plant responses that result in diminished growth (Riaz et al., 2019). These changes include alterations in the Na+/K+ ratio, decreased stomatal conductance (gs), reduced photosynthetic rates, and heightened production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) to mitigate the detrimental effects of salinity on photosynthesis and to stimulate the synthesis of antioxidant enzymes. Moreover, antioxidant enzymes and osmoprotectants, like glutathione and proline, are crucial in safeguarding the photosynthetic apparatus from oxidative damage caused by salinity. These chemicals neutralize reactive oxygen species (ROS), mitigating cellular damage and preserving chloroplast integrity. Genetic findings regarding salt adaptation emphasize the significance of chlorophyll biosynthesis genes, particularly Os08g41990, which have demonstrated the ability to sustain chlorophyll levels under stress conditions. Studies employing chromosomal segment substitution lines (CSSLs) have demonstrated the significance of these genes in improving the rate of photosynthesis and strengthening salt tolerance (Nounjan et al., 2020). Thus, physiological and genetic techniques are required to minimize salinity’s deleterious effects on rice’s photosynthesis.
By mainly disrupting ionic equilibrium and nutritional shortages, salinity stress greatly hinders nutrient uptake and transport in rice. Key macronutrients like potassium (K+), calcium (Ca+), and magnesium (Mg2+), and micronutrients like manganese (Mn) and zinc (Zn) are hindered in their uptake by salty environments’ high sodium (Na+) and chloride (Cl−) concentrations. Ionic imbalances hinder plant development and productivity by interfering with essential physiological processes, including photosynthesis and enzymatic activities. Salinity significantly disturbs sodium-potassium homeostasis by elevating the Na+/K+ ratio, hence impairing metabolic processes and enzymatic functioning. Nevertheless, several salt-tolerant rice cultivars, including Pokkali, alleviate these impacts by effectively regulating Na+ and K+ transporters, such as OsHKT1;5 and OsNHX1, which decrease Na+ buildup in the shoots while preserving sufficient K+ levels for cellular activities (Nampei et al., 2021). Wild rice species, including O. coarctata, demonstrate mechanisms that improve K+ retention and mitigate Na+ toxicity through effective xylem unloading and vacuolar sequestration (Sarkar and Roy, 2020). Moreover, salt stress impedes the absorption of micronutrients, especially manganese and zinc, which are crucial for photosynthesis and enzymatic activities. Supplementing manganese under salty conditions aids in restoring nutritional equilibrium and promotes stress tolerance, presenting a viable technique for increasing rice development under salinity (Tabassam et al., 2022).
Calcium (Ca2+) is essential in decreasing Na+ toxicity by restricting Na+ transport to aerial parts and enhancing Cl− exclusion. In salt-tolerant cultivars like Nona Bokra, appropriate calcium levels considerably boost survival rates under salinity by reducing Na+ and Cl− translocation (Abouzied and Abd El-latif, 2017). Furthermore, elevated rhizospheric pH in saline environments restricts iron accessibility (Fe), an essential nutrient for plant development. Salinity-tolerant genotypes mitigate this issue by enhancing the expression of Fe transporters, including OsIRT1 and OsYSL15, so securing sufficient Fe availability in saline-alkaline environments (Nampei et al., 2021). The symbiosis between arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) fungus and rice is another molecular process that contributes to salt tolerance. By controlling the genes for cation transporters, AM fungi improve root potassium absorption and root sodium compartmentalization, which in turn reduces root-to-shoot Na+ transit. Another way to increase rice’s tolerance to salt is through this interaction, which upregulates genes such as OsSOS1 and OsNHX3 that help maintain ionic balance when the plant is exposed to salt (Porcel et al., 2016).
Salinity stress in O. sativa produces complicated hormonal changes that play a critical role in minimizing the detrimental consequences of excessive salt concentrations. Hormonal signaling serves as a conduit, merging environmental stimuli with growth and stress response pathways, allowing rice plants to acclimate to salinity stress via processes such as stomatal control, ionic homeostasis, and mitigation of oxidative damage (Xiao and Zhou, 2023). Elevated salt concentrations stimulate the excessive generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), resulting in oxidative damage to plant tissues, including lipid peroxidation, protein breakdown, and DNA damage. Malondialdehyde (MDA), a byproduct of lipid peroxidation, functions as a measure for oxidative stress levels in plants (Zhao et al., 2021; Zhao et al., 2024). Spermidine (Spd) treatment enhances the activity of antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT), significantly reducing reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels and boosting oxidative stress tolerance, especially in rice roots (Shen et al., 2024).
Central to the salinity stress response is abscisic acid (ABA), frequently referred to as the “stress hormone.” ABA concentrations increase significantly during salt stress, inducing stomatal closure to diminish transpiration and avert excessive water loss (Xiao and Zhou, 2023). Additionally, ABA stimulates downstream signaling pathways that engage ABA-responsive element-binding factors (ABFs), which modulate stress-protective genes and enhance water uptake efficiency by improving root hydraulic conductivity (Formentin et al., 2018). Salinity stress inhibits the manufacture of auxins (IAA) and gibberellins (GA), hormones essential for cell elongation and shoot development. In salt-tolerant rice varieties, an accelerated recovery of IAA and GA levels facilitates root and shoot regrowth following initial stress (Riaz et al., 2019; Liu et al., 2022). Cytokinin levels, which decline under salinity stress, also limit cell division and shoot growth. However, higher cytokinin levels in salt-tolerant varieties, particularly in the roots, enhance nutrient translocation and stimulate shoot development (Mandal et al., 2022; Li et al., 2023). They also interact with other hormones, such as abscisic acid (ABA), to modulate stress responses and delay senescence, thereby enhancing crop yields (Yu et al., 2022). Ethylene, a hormone increased by salinity, has a dual role. It induces stress-adaptive responses like leaf senescence and aerenchyma formation, but excessive ethylene can hinder growth. Rice varieties that regulate ethylene biosynthesis and signaling enhance growth in saline conditions (Ji et al., 2020). Salicylic acid (SA) and jasmonic acid (JA) also regulate defense responses to oxidative stress and ionic imbalance. SA boosts antioxidant enzyme activity to reduce ROS damage and promotes gene expression related to programmed cell death and autophagy, facilitating stress recovery (Khan et al., 2019). These hormones interact intricately, with ABA synergistically engaging with ethylene, SA, and cytokinins to coordinate adaptive responses. For example, the ABA-ethylene synergy helps regulate stomatal dynamics, while the interplay between ABA and SA enhances ROS scavenging mechanisms (Formentin et al., 2018). These hormonal responses create a network allowing rice plants to effectively manage salinity stress.
Traditional breeding has been essential in creating salinity-resistant rice varieties, especially in areas with restricted access to sophisticated molecular methods. Traditional breeding techniques have effectively utilized the inherent genetic variety in rice germplasm to identify and integrate features that improve salinity tolerance, providing sustainable methods to address soil salinization in prominent rice cultivation regions (Figure 5) (Mheni et al., 2024). Traditional salt-tolerant landraces, such as Pokkali and Nona Bokra, are among the principal contributions to these breeding initiatives and have demonstrated significant value. These kinds exhibit sodium exclusion, potassium retention, and improved osmotic adjustment, rendering them suitable donors for salinity tolerance to elite, high-yield rice cultivars (Chen et al., 2021b).
Recurrent selection, a cross-breeding approach, has been extensively utilized to impart saline tolerance to vulnerable types. By consistently selecting progeny exhibiting enhanced tolerance qualities, breeders have achieved gradual genetic improvements across generations. Crosses between Pokkali and the sensitive variety IR29 have created recombinant inbred lines (RILs) like FL478, which demonstrate enhanced salinity tolerance (Reddy et al., 2023). Phenotypic screening under controlled saline conditions has been essential for discovering salt-tolerant lineages. Parameters like seedling vigor, shoot biomass, and Na+/K+ ratios are employed to evaluate the lines’ resistance, while field testing in saline regions further corroborates the performance of these lines under natural settings (Aggarwal et al., 2024; Kumawat et al., 2024). Concerning notable accomplishments, including the creation and extensive utilization of salt-tolerant varieties such as BRRI dhan47 in Bangladesh and CSR10 in India, conventional breeding continues to encounter obstacles (Shamsuddin et al., 2022; Saminadane et al., 2024). The polygenic nature of salinity tolerance indicates that the integration of various traits into a single variety necessitates careful selection and assessment across multiple generations (Qin et al., 2020). The detailed nature of this issue restricts the pace at which salinity-tolerant varieties can be cultivated and introduced, posing a significant challenge for breeding initiatives (Akhlasur Rahman et al., 2024). Nonetheless, traditional breeding continues to serve as a fundamental strategy in tackling salinity stress in rice, providing practical and effective solutions, particularly in resource-constrained areas. Efforts to incorporate marker-assisted selection (MAS) with traditional breeding methods can speed up the process of developing better cultivars. To tackle salinity issues, it is possible to use a wider genetic base by incorporating novel donors, like wild rice species (Singh and Devi, 2023).
Transgenic methods have greatly progressed the creation of salinity-resistant rice cultivars by facilitating exact genetic alterations that improve stress tolerance. These strategies aim to introduce and express particular genes from various sources to enhance rice’s ionic control, osmotic equilibrium, and antioxidative responses. For instance, the overexpression of stress-responsive genes such as OsHKT1;5 and OsNHX1 improves sodium exclusion and compartmentalization, which are essential for sustaining Na+/K+ equilibrium in saline environments (Kobayashi et al., 2017; Prusty et al., 2018). Moreover, transgenic rice, including SaPMP3 from Spartina alterniflora has demonstrated enhanced ion homeostasis and plant vitality under saline stress (Biradar, 2012). The functional integration of halophyte-derived genes, such as SaVHAc1 (vacuolar H+-ATPase subunit) from S. alterniflora, enhances this methodology. Transgenic rice, including SaVHAc1 and SaPMP3 exhibits enhanced chlorophyll retention, decreased ion toxicity, and improved grain production under high-salinity conditions (Baisakh et al., 2012; Biradar et al., 2018). Moreover, the inhibition of stress-sensitive genes via RNA interference, specifically the silencing of OsDSR2, augments antioxidant activity, diminishes oxidative damage, and elevates proline accumulation, resulting in enhanced survival rates (Mamta and Rajam, 2018; Gahlaut et al., 2021). The regulation of antioxidant enzymes, including superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase, enhances resilience by reducing reactive oxygen species (ROS) damage, hence maintaining cellular integrity during oxidative stress (Reddy et al., 2023).
The CRISPR-Cas9 technique has transformed the emergence of salinity-tolerant rice by facilitating accurate genome editing to target genes essential for stress response pathways, improving ionic homeostasis, antioxidant capacity, and osmotic regulation. The downregulation of OsAKT1, a gene involved in potassium and sodium transport, in the salt-sensitive IR29 rice cultivar has been accomplished via CRISPR-Cas9, resulting in diminished sodium leakage and enhanced potassium retention, thus markedly improving survival in saline environments (Khan et al., 2023). In a similar vein, the elimination of negative regulators such as OsPUB7, which inhibits salinity tolerance, has demonstrated significant promise; rice lines with null mutations in OsPUB7 displayed elevated proline levels, less ion leakage, and improved survival rates under salt stress (Kim et al., 2023). This method has been successfully utilized in hybrid rice systems, where CRISPR-Cas9 editing of OsRR22, a crucial regulator of salinity responses, produced transgene-free third-generation hybrid rice exhibiting improved salt tolerance and consistent agronomic performance (Sheng et al., 2023). Another innovative application focuses on targeting the promoter regions of salinity-associated genes, such as OsSRFP1, inside the ubiquitination pathway; altering its promoter area has refined stress control mechanisms, enhancing the rice plant’s resilience to salt stress (Linh Khanh et al., 2024). Although CRISPR-Cas9 has significant potential, its integration with other genomic technologies, such as transcriptomics and phenomics, could further improve salt-tolerance characteristics. However, problems like legislative limitations and the establishment of effective delivery methods must be confronted, with the generation of transgene-free edited lines being crucial for broad acceptability and implementation.
The emergence of CRISPR/Cas9 technology has transformed plant breeding by facilitating precise genetic modifications with remarkable accuracy. Nonetheless, its use in agriculture presents significant regulatory, ethical, and biosafety issues that require meticulous consideration to guarantee its safe and equitable deployment. As CRISPR-edited crops approach commercialization, it is imperative to navigate the regulatory framework and address ethical considerations for their effective incorporation into global agriculture. The regulatory framework for genetically modified crops differs greatly among countries, illustrating diverse strategies for reconciling innovation with safety. In contrast to conventional genetically modified organisms (GMOs), which often entail the introduction of exogenous genes, CRISPR/Cas9 facilitates the precise alteration of an organism’s existing DNA. This differentiation has prompted continuous discussions on whether CRISPR-edited crops have to adhere to the same rigorous rules as GMOs or be classified as a unique category entirely (Prusty et al., 2018). In some countries, such as the United States, regulatory authorities like the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) have embraced a more adaptable approach, proposing that CRISPR-edited crops be regulated according to their characteristics rather than the technology employed in their creation, or whether they could have been produced through conventional breeding techniques (Ahmad et al., 2023). This method facilitates expedited approval procedures for crops that do not incorporate foreign DNA. In contrast, the European Union (EU) has adopted a more prudent stance, imposing identical stringent rules on CRISPR-edited crops as those applied to conventional GMOs. This regulatory disparity presents obstacles for global markets and trade. Crops sanctioned in one jurisdiction may encounter regulatory obstacles or complete prohibitions in others. Moreover, conflicting rules may induce confusion and impede the advancement of CRISPR-edited crops, thereby postponing their advantages for farmers and consumers.
In addition to regulatory difficulties, CRISPR/Cas9 presents other ethical and biosafety concerns. A significant ethical problem pertains to the possibility of unexpected outcomes, such as off-target mutations or the introduction of characteristics that may yield unknown ecological effects. For instance, research shows that off-target changes may occur, where the CRISPR-Cas9 system unintentionally alters non-target genomic regions, resulting in minor insertions, deletions, or nucleotide swaps (Sturme et al., 2022). The enduring impacts of CRISPR-modified crops on biodiversity, soil integrity, and non-target species remain inadequately comprehended, necessitating comprehensive biosafety evaluations to guarantee that these crops do not inflict ecological damage. Also, there are concerns regarding the equity and accessibility of CRISPR technology persist. The capacity to patent gene-edited crops may result in monopolies over essential agricultural features, thereby centralizing the advantages of CRISPR technology within a select number of multinational firms and restricting access for smallholder farmers in underdeveloped nations (Dace and Tony Blair Institute for Global Change, 2021). This may intensify pre-existing disparities in global food systems, especially if the technology is predominantly motivated by profit rather than the public interest. Guaranteeing fair access to CRISPR technology, particularly in resource-limited environments, necessitates international collaboration and open policies.
Another ethical problem is the possibility of “designer crops” customized to particular consumer tastes. Although CRISPR has the potential to create crops with superior nutritional profiles or enhanced disease resistance, there are concerns regarding the commercialization of traits aimed at affluent consumers, potentially overlooking the requirements of deprived communities who may derive greater benefit from traits like drought resistance or disease tolerance (Adane and Alamnie, 2024; Chen et al., 2024). The public’s view and acceptability of CRISPR-edited crops significantly influence their uptake, underscoring the necessity for clear communication and public engagement in the regulatory process (Food Standards Agency, 2021). This underscores the necessity for ethical considerations in prioritizing CRISPR research and development, ensuring that the technology serves all societal sectors, especially those most susceptible to climate change and food shortages.
Considering the global scope of food production and trade, international cooperation is essential for creating a unified regulatory framework for CRISPR-edited crops. Harmonized international standards would ease trade obstacles, eliminate regulatory fragmentation, and promote the global use of CRISPR technology (Gan and Ling, 2022). Entities like the World Health Organization (WHO), the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), and the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) are crucial in facilitating discourse and establishing guidelines for the secure application of CRISPR in agriculture. Moreover, international collaboration might mitigate ethical problems by fostering common values and principles in the production and dissemination of CRISPR-edited crops. This entails guaranteeing an even distribution of CRISPR technology benefits and the management of any dangers through comprehensive safety evaluations and oversight. A worldwide approach would enhance the dissemination of knowledge and resources, guaranteeing that developing nations are not overlooked in the biotechnology revolution. Although CRISPR/Cas9 presents significant potential for revolutionizing agriculture, its application requires careful regulation, ethical deliberation, and global collaboration. Addressing these difficulties is essential for unlocking the complete potential of CRISPR technology while ensuring human health, environmental sustainability, and social equality.
Agronomic approaches are essential for alleviating salt stress in rice agriculture by optimizing water, soil, and nutrient management, therefore improving productivity and maintaining soil health in saline-prone areas. Efficient irrigation management is essential for regulating salt levels in the root zone. Methods like alternating wetting and drying (AWD) and integrated irrigation-drainage systems have effectively diminished salt accumulation while preserving water use efficiency. Replacing saline water every three days in fields with a ponding depth of 2-5 cm markedly enhanced the production of salt-tolerant rice varieties such as Binadhan-10 and BRRI dhan-47 (Rahman et al., 2020). Conservation agriculture approaches, such as zero tillage, crop residue recycling, and crop rotations, mitigate soil salinity, enhance organic carbon levels, and augment soil water retention capacity. Research in the Ganges Delta has shown that these methods reduce water footprints and increase profitability relative to traditional tillage systems (Sarangi et al). Effective nutrient management is essential for minimizing salinity stress. Utilizing essential nutrients like zinc and potassium via foliar sprays mitigates ionic toxicity and enhances plant vitality. Moreover, the integration of continuous saturation irrigation with organic amendments like farmyard manure and vermicompost has demonstrated a 19% increase in rice yields compared to traditional methods in the saline soils of Bangladesh (Ali et al., 2024). Soil reclamation methods improve the management of salinity. Integrating organic amendments such as green manure and gypsum diminishes soil salinity, boosting microbial activity and improving soil structure. Utilizing raised-bed cultivation with these amendments effectively reduces salt intrusion in coastal agro-ecosystems (Mitran et al., 2021). Farmer-led approaches integrating salt-tolerant varieties (STVs) with modified agronomic practices, including nutrient management specific to sodic soils, have demonstrated significant outcomes. Participatory techniques enhanced rice yields by 35% in reclaimed saline areas, highlighting the significance of farmer involvement in adopting sustainable and localized practices (Singh and Singh, 2022).
Sustainable soil improvement, reduced salinity accumulation, and optimal resource use efficiency can be achieved by crop rotation and intercropping agronomic procedures, which are essential for salinity management in rice agriculture. These approaches promote long-term agricultural resilience in saline-prone regions by utilizing the complimentary features of multiple crops, which mitigates salt stress. Crop rotation is essential for salinity control, as it involves using salt-tolerant species like barley or mustard, which improve water infiltration and reduce salt buildup in the root zone. This method also promotes the drainage of surplus salts, establishing a conducive soil condition for future crops. Legume rotations, including pigeon pea, augment soil organic matter and nitrogen levels, so mitigating saline effects on rice. Research on saline soils in India indicates that rice-mustard and rice-sunflower rotations enhance soil permeability, decrease salinity levels, and sustain elevated rice-equivalent yields (Mitran et al., 2021).
Intercropping enhances crop rotation by improving soil health and production. The integration of rice with salt-tolerant legumes such as mung bean or cowpea enhances soil fertility and microbial activity, alleviating the detrimental impacts of salinity. Strategic intercropping methods, such as ridge-planted pigeon peas alongside furrow-planted rice, optimize water and nutrient utilization, promote soil aeration, and enhance yield stability under saline stress (Kumar et al., 2012). Furthermore, biodiversity-based intercropping of traditional and hybrid rice varieties, as evidenced in Yunnan Province, China, enhances system resilience and stabilizes yields under saline conditions. This method reintroduces historic rice varieties and enhances genetic variety, hence establishing resilient cropping systems (http://bioscience.oxfordjournals.org/). The incorporation of these approaches with organic amendments, such as farmyard manure and green leaf manure, enhances their synergistic advantages. Improving soil organic carbon, microbial biomass, and overall productivity highlights the efficacy of integrating crop rotation, intercropping, and organic inputs for successful salt management in rice cultivation (Raeisi Vanani et al., 2024).
Soil reclamation in minimizing salinity stress in rice farming aims to restore the productivity of salt-affected soils by enhancing soil structure, decreasing salinity, and improving crop performance. This is accomplished by a comprehensive approach integrating physical, chemical, and biological approaches. Gypsum and phosphogypsum are efficient chemical additions for displacing sodium ions from soil exchange sites, thus mitigating sodicity and enhancing soil permeability. Studies in coastal Bangladesh indicated that the synergistic application of phospho-gypsum and cyanobacteria markedly diminished soil electrical conductivity (EC) and enhanced rice yields by 15.3% during wet seasons (Ali et al., 2023). Likewise, incorporating organic materials, including farmyard manure, compost, and biochar, enhances soil carbon levels and microbial activity. In Nigeria’s saline-sodic soils, biochar derived from rice straw and Typha grass significantly diminished salinity, enhanced water retention, and augmented rice biomass (Adam et al., 2022).
Physical reclamation approaches, such as deep plowing, field leveling, and subsurface drainage, enhance water infiltration and salt leaching. Longitudinal data from Russian rice fields demonstrate that regulating groundwater tables and implementing appropriate irrigation-drainage systems regularly lowers salinity levels (Malysheva et al., 2020). Biological methods such as phytoremediation utilizing halophytes salt-tolerant plants like barley during off-seasons facilitate the biological extraction of salts while enhancing soil organic matter and microbial activity, hence conditioning soils for future rice growth (Singh and Singh, 2022). Moreover, integrated nutrient management, which integrates gypsum application with foliar sprays of urea, zinc sulfate, and potassium sulfate, enhances nutrient availability while minimizing salt effects. Field trials in Bangladesh exhibited a 19% enhancement in rice yield and an improved benefit-cost ratio through the implementation of these strategies (Akhlasur Rahman et al., 2024). These diverse strategies offer an extensive framework for addressing salinity in rice cultivation areas.
While research on salinity tolerance has progressed considerably, the majority of studies and breeding initiatives have concentrated on areas with particular environmental circumstances or geographical limitations. Consequently, remedies to salt stress have frequently been proposed within restricted geographic boundaries, limiting their relevance to wider, varied areas impacted by soil salinity.
Soil salinity is a prevalent issue in South Asia, notably in India and Pakistan, particularly in the Indo-Gangetic Plain and coastal regions. Both nations possess extensive areas of saline-sodic soils, where elevated concentrations of sodium chloride (NaCl) and sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) diminish agricultural output. Approximately 6.73 million hectares of agricultural land in India are impacted by salinity (Sarkar et al., 2024; Singh et al., 2024). The significant variability in soil salinity, coupled with unpredictable monsoons, inadequate irrigation techniques and poor drainage systems, complicates the management of salt stress, leading to the gradual accumulation of salts in the root zone (Verma et al., 2012). Furthermore, indigenous rice and wheat types demonstrate limited resistance to elevated saline, hence constraining yield (Shrivastava and Kumar, 2015). In response, breeding projects in South Asia have concentrated on creating salt-tolerant rice cultivars, exemplified by the ‘FL478’ cultivar, which exhibits tolerance to salinity stress and is being utilized in regions of Pakistan and India (Wu et al., 2024), and the wheat cultivar ‘KRL-19’, which has been effectively cultivated in saline-prone regions (Sheoran et al., 2021). Additionally, advanced irrigation methods, such as the implementation of drip irrigation and improved salinity management techniques, have contributed to alleviating the detrimental impacts of soil salinity (Wang et al., 2023).
Sub-Saharan Africa, especially coastal areas like Senegal and Egypt, is experiencing rising salinity in soil and water. Saltwater intrusion into the Senegal River Basin has emerged as a critical problem in Senegal, particularly in the lower delta regions (Kabir et al., 2024; Omuto et al., 2024). The implementation of flood irrigation in Egypt, along with increasing sea levels, has led to salt accumulation, threatening essential crops such as rice and wheat (Saqr and Abd-Elmaboud, 2024). These issues are exacerbated by inadequate freshwater supplies and inappropriate irrigation methods, which worsen the salinization of cultivable land. Furthermore, the agricultural industry in numerous African nations is deprived of access to contemporary salinity-tolerant cultivars and sophisticated irrigation technologies that could mitigate salt accumulation in soils (Stein et al., 2023; Ghiardelli et al., 2025; Tarolli et al., 2025). To address these challenges, Senegal has promoted the use of salt-tolerant crops, such as salt-resistant sorghum and millet, to improve agricultural resilience (Guden et al., 2024; Pankaj et al., 2024). In Egypt, investigations into the development of salt-tolerant rice cultivars, including those from the Agricultural Genetic Engineering Research Institute (AGERI), have demonstrated potential in mitigating issues associated with saline water sources (Leawtrakun et al., 2024b). Furthermore, enhanced water management strategies, including subirrigation systems and brackish water treatment technologies, are progressively being implemented to mitigate soil salinization.
The Middle East suffers significant issues associated with soil salinity, attributable to the region’s extreme temperature, scarce freshwater resources, and heavy dependence on irrigation (Al-Tardeh et al., 2023; Makttoof and Nafawa, 2024). In nations like Iraq and Saudi Arabia, elevated evaporation rates, along with inadequate water quality, result in considerable salinization of both surface and groundwater resources. In Iraq, salinity has made more than 20% of agricultural land unfit for crop cultivation (Benaafi et al., 2024; Makttoof and Nafawa, 2024). The interplay of increasing groundwater salinity and declining irrigation infrastructure in numerous Middle Eastern nations has hindered the maintenance of crop yields (Sameer et al., 2024). Climate change worsens the issues, as elevated temperatures result in heightened evaporation and increased soil salinity (Keutgen, 2023; Hakami-Kermani et al., 2024). To address these challenges, Saudi Arabia has invested in novel solutions, such as utilizing saline groundwater for agricultural purposes. The King Abdullah Initiative for Saudi Agricultural Investment Abroad seeks to research sustainable agricultural methodologies in saline conditions, emphasizing drip irrigation and greenhouse cultivation (Hemdan et al., 2024; Nurbekova et al., 2024; Wang et al., 2024). Similarly, Iraq has implemented salinity management strategies, such as developing salt-tolerant crop varieties, including drought- and salinity-resistant wheat cultivars through conventional breeding and biotechnological approaches (Al-Saadi et al., 2024; Tahir et al., 2024). Moreso, soil reclamation methods, including gypsum application and bio-amendment use, are being tested to alleviate salinity in certain regions (Ali et al., 2024).
Australia, especially the Murray-Darling Basin in the southeast, is facing salinity issues due to its dependence on irrigation for agricultural output. Salinity levels in the region have markedly risen over the past few decades, impacting both agricultural productivity and ecosystem health (Walker and Hart, 2024; Nelson et al., 2024). The primary concern in Australia is the extensive salinization of soils resulting from the excessive extraction of groundwater for irrigation purposes (Sanga et al., 2024). This has resulted in elevated salt concentrations in surface water and soils, making extensive regions of farming unproductive (Chanu, 2023). Ineffective land management techniques, such as monocropping and insufficient crop rotation, have further intensified the issue (Hannam, 2024). To address these challenges, Australia has led the advancement of salinity-resistant crop types, including wheat, barley, and cotton, utilizing both traditional breeding and genetic modification techniques (Sharma et al., 2024). Additionally, the Australian government has enacted rules to regulate groundwater extraction and encourage sustainable water management techniques (Abu Romman and Al Kuisi, 2023; Williams et al., 2023). Employing salt-tolerant plants and enhanced irrigation techniques, such as precision agriculture, has alleviated the impacts of salinity in certain areas of the region (Nurbekova et al., 2024).
The case studies from South Asia, Sub-Saharan Africa, the Middle East, and Australia demonstrate the necessity of region-specific techniques for addressing salinity stress in agriculture. Although salt-tolerant varieties and enhanced irrigation techniques have demonstrated efficacy in numerous regions, solutions must be tailored to local conditions, taking into account the distinct problems presented by each region’s soil, water resources, and climate. Along with that, the transfer of information and technology among places impacted by salinity is crucial for formulating global solutions to this escalating problem. With the acceleration of climate change leading to the salinization of agricultural lands globally, it is important to enhance research on salt tolerance, particularly across varied geographic settings, and to execute region-specific solutions that may be adapted and expanded internationally.
The introduction of salt-tolerant rice varieties has greatly enhanced agricultural production in saline-affected areas, providing sustainable solutions to food security issues. A prominent instance is the creation of the ‘Ezhome Rice’ varieties ‘Ezhome-1’ and ‘Ezhome-2’ in Kerala, India. These high-yielding, non-lodging organic red rice cultivars were specifically developed for the saline-prone Kaipad farms. Participatory plant breeding with local farmers resulted in these types yielding 3.5 and 3.2 tons per hectare, representing a 60-70% increase compared to standard cultivars (Vanaja et al., 2017). Similarly, the Qingdao Saline-Alkali Tolerant Rice Research and Development Center in China has developed ‘seawater rice’ types that can flourish in salty soils with up to 4 grams of salt per kilogram. By 2021, these types were farmed on 400,000 hectares, yielding an average of 8.8 tons per hectare, thus converting barren saline soils into arable regions (Micu, 2022). The International Rice Research Institute (IRRI) developed salt-tolerant rice strains by hybridizing commercial types with wild species such as O. coarctata. These hybrids feature specialized leaf glands that excrete excess salt, facilitating agriculture in high-salinity settings and increasing arable land availability (Barona-Edna, 2013). Additionally, the traditional ‘Pokkali’ rice type from Kerala, famous for its exceptional salt resistance, grows to a height of 140 cm and is farmed organically together with prawn culture in coastal areas that experience floods (Wikimedia, 2013).
The use of salt-tolerant rice varieties (STRVs), as listed in Table 1, has transformed agriculture in saline-affected areas of South Asia and Sub-Saharan Africa, providing sustainable solutions to food security issues and enhancing agricultural production (Radha et al., 2024; Sellathdurai et al., 2024; Sikder and Khan, 2024; Zayed et al., 2024). In the Mekong River Delta (MRD) of Vietnam, STRVs have significantly minimized the detrimental effects of sea-level rise and salinity intrusion. Advocated by the Consortium for Unfavorable Rice Environments (CURE), these types were implemented in 47% of salinity-affected rice fields during at least one of the two primary growth seasons. Their adoption was significantly elevated in non-irrigated regions and places lacking saline barrier gates, underscoring their effective focus on sensitive ecosystems. Although these varieties reduced production losses under salinity stress, they did not surpass traditional varieties in low-salinity years and frequently garnered lower market prices, indicating a trade-off between stress tolerance and marketability (Paik et al., 2020). In India, the Central Soil Salinity Research Institute (CSSRI) has pioneered the creation of salt-tolerant rice varieties like CSR10 and CSR36, tailored for saline and sodic soils (Kumar et al., 2024; Zayed et al., 2024). These innovations have restored about 1.5 million hectares of salt-affected land, enhancing food grain production by roughly 15 million tons each year (Okur et al., 2023; Farooqi et al., 2024; Nurbekova et al., 2024). CSSRI’s unified strategy merges genetic innovations with smart soil and water management, turning barren lands into thriving agricultural areas and showcasing an integrative approach to tackle salinity (Mishra et al., 2023; Shakar et al., 2024).
Table 1. A table listing salt-tolerant rice varieties, their genetic traits, and the regions of adoption.
The Stress-Tolerant Rice for Africa and South Asia (STRASA) initiative, led by the International Rice Research Institute (IRRI), has enabled the introduction of more than 150 stress-tolerant rice varieties throughout Sub-Saharan Africa. These initiatives have enabled millions of farmers to augment yields and improve resilience to salinity, drought, and flooding. The joint introduction of the salt-tolerant variety ‘KARANADA’ by the Kenya Agricultural and Livestock Research Organization (KALRO) and IRRI has enhanced productivity and income stability in saline-prone regions of Kenya, demonstrating the global efficacy of salt-tolerant rice varieties (STRVs) in mitigating environmental and economic challenges (IRRI, 2023).
Despite advancements in breeding and genetic research, severe impediments in saline-affected regions significantly hinder the deployment of salinity-tolerant rice varieties. These problems must be addressed for productivity and global food security. Rice salt tolerance is polygenic, governed by a complex interplay of genes and quantitative trait loci (QTLs) that influence sodium exclusion, potassium retention, and osmotic adjustment. This complexity hinders the identification, mapping, and integration of beneficial genes into breeding programs, hence impeding progress. The dynamic nature of salinity stress, together with waterlogging, temperature changes, and microclimatic variations, influences the expression of stress-responsive genes, resulting in significant variability in the performance of salt-tolerant rice varieties across different settings and seasons. The dependence on a limited genetic basis, primarily consisting of conventional salt-tolerant donors such as Pokkali, exacerbates these issues by constraining the investigation of innovative tolerance mechanisms and diminishing the adaptability of new types to changing stress conditions.
Phenotyping for salinity tolerance has historically posed a significant challenge in plant breeding, especially for high-throughput screening of extensive populations. Conventional phenotyping techniques, such as manual assessments of plant height, leaf area, and visual evaluations of salt damage, are laborious, time-consuming, and frequently susceptible to subjectivity (Chawade et al., 2019; Gill et al., 2022). Moreover, these approaches fail to comprehensively represent the extensive physiological responses of plants to salinity stress, which encompass complex alterations in ion balance, osmoregulation, and gene expression. A notable limitation is the incapacity of traditional phenotyping methods to deliver real-time, high-resolution data on physiological processes, including transpiration, root development, and ion buildup in reaction to differing salt levels. The magnitude and complexity of contemporary breeding programs require sophisticated and automated phenotyping tools capable of effectively assessing these qualities in both controlled and field environments (Gill et al., 2022). Furthermore, several modern phenotyping methodologies are inadequately equipped to manage the extensive datasets produced by high-throughput screening. This data frequently necessitates comprehensive processing and integration from various sources, potentially creating barriers in breeding processes. Moreover, conventional phenotyping techniques are inadequate for quantifying small differences in salinity tolerance, especially in field situations where environmental variability may hide genotype performance.
Recently, the combined use of remote sensing technologies and machine learning algorithms has surfaced as a potent method to address the constraints of conventional phenotyping. Remote sensing technologies, including drones and satellites, can acquire high-resolution imagery of plant canopies and root systems under salt stress, offering insights on phenotypic characteristics that are challenging to assess manually. Hyperspectral imaging, which captures a wide range of light wavelengths, can identify alterations in leaf pigment composition, water content, and stress-induced biochemical indicators at an early stage (Stutsel et al., 2021; Del Cioppo et al., 2024). This non-invasive method facilitates continuous assessment of plant health over extensive regions, rendering it suitable for field-based phenotyping of salinity tolerance. Furthermore, remote sensing technologies can be integrated with machine learning (ML) models to automate trait extraction and analysis. Training machine learning algorithms on datasets derived from hyperspectral imaging or other remote sensing technologies enables the prediction of essential physiological features associated with salinity tolerance, including leaf area, chlorophyll content, and stomatal conductance. These predictive models may efficiently screen huge populations and find potential genotypes with minimal human interaction (Haq et al., 2023; Mourched et al., 2023). Machine learning enables the amalgamation of diverse data sources, including environmental variables, soil salt levels, and genomic data, to improve the precision of predictions in apropos of plant performance in saline environments. By utilizing features acquired from drone-based imaging data, researchers were able to effectively apply ML algorithms to genotype classification according to salt tolerance (El-Hendawy et al., 2024a; El-Hendawy et al., 2024b). Machine learning can improve the efficiency of salt-tolerant variety production by integrating phenotypic and genotypic data for more informed breeding decisions.
There are still issues with scalability and cost-effectiveness, but there is great promise for enhancing phenotyping efficiency with remote sensing and machine learning. For smaller research projects or environments with limited resources, the expensive acquisition and maintenance of remote sensing equipment, along with the specialized knowledge needed to operate and analyze the data, can be a significant barrier. Many breeding projects in underdeveloped nations or areas with inadequate technological infrastructure also lack access to advanced phenotyping technologies because these tools are often reserved for well-funded institutions. Addressing these challenges necessitates the development of scalable and cost-effective phenotyping solutions. A promising approach involves the integration of low-cost sensors and imaging systems into current breeding facilities. Small-scale, high-throughput phenotyping platforms utilizing low-cost sensors to measure parameters like leaf temperature, soil moisture, and chlorophyll fluorescence are being developed. These platforms aim to deliver real-time, actionable data at a significantly lower cost compared to more complex remote sensing technologies (Wu et al., 2022; Yassue et al., 2022). These platforms are applicable in both controlled environments and field conditions, providing a more accessible alternative to costly drone or satellite-based systems. In addition, open-source software and cloud-based platforms can play a key role in making phenotyping technologies more accessible. By providing free access to data analysis tools and integrating them with cloud computing infrastructure, it becomes easier for researchers from diverse institutions to collaborate and share phenotypic data. Additionally, community-driven initiatives to develop open-source phenotyping solutions may foster innovation and lower the overall costs associated with technology adoption in breeding programs. To fully harness the potential of these new technologies, there is an urgent requirement for scalable, cost-efficient solutions that can be implemented by breeding programs globally. By addressing these issues, the domain of phenotyping can significantly aid in the advancement of salinity-resistant crops, thereby securing food availability in areas impacted by soil salinization.
To ensure that salt-tolerant rice varieties exhibit reliable performance in various environments, it is essential that they undergo thorough field-based evaluation. The evaluation of the stability of salinity tolerance traits is most effectively conducted through multi-environment trials (METs), which examine the performance of varieties across diverse climatic and soil conditions. For instance, the Saltol QTL, which has been integrated into widely cultivated varieties such as IR64 and BRRI dhan47, has undergone thorough evaluation in multi-location trials throughout South and Southeast Asia. The trials demonstrated that the Saltol QTL markedly enhances salinity tolerance during the seedling stage; however, its efficacy is influenced by the type of soil and the levels of salinity present (Ho et al., 2016; Yadav et al., 2020). In a similar vein, the FL478 variety, which originates from the salt-tolerant landrace Pokkali, has shown reliable performance in saline-affected areas of India, Bangladesh, and Vietnam, underscoring the significance of field validation. These trials enable researchers to discern varieties that exhibit both salt tolerance and adaptability to various environmental stresses, thereby securing sustained productivity over time (Debsharma et al., 2024; Krishnamurthy et al., 2024). Additionally, field testing can be enhanced through the integration of high-throughput phenotyping technologies, including UAV-based imaging and remote sensing, which facilitate precise monitoring of rice performance in natural field environments. These technologies offer accurate, non-invasive assessments of plant stress responses, enhancing the understanding of salt tolerance mechanisms in practical environments. The integration of METs with modern phenotyping techniques has the potential to connect the insights gained from controlled experiments to the real-world implementation of salt-tolerant rice varieties in the context of agriculture (Del Cioppo et al., 2024; Fu et al., 2024).
Salinity stress in cultivation of rice is complex and varying, requiring a multidisciplinary strategy that integrates genetics, soil science, agronomy, climate modelling, and socioeconomics to provide sustainable solutions. Integrating advancements in genetics, such as the identification of salt-tolerant QTLs and the application of transgenic technologies, with agronomic strategies is essential for achieving success in the field. The implementation of salt-tolerant rice cultivars, such as FL478, alongside efficient irrigation techniques like alternate wetting and drying, significantly improves productivity and resource utilization efficiency. Soil salinity arises from irrigation methods, variations in the water table, and climatic changes, highlighting the necessity for comprehensive soil science strategies. The use of soil additives, such as gypsum and charcoal, alongside breeding programs targeting features like root architecture and ionic exclusion, improves soil fertility and crop resilience.
Predictive climate modelling and stress forecasting improve interventions through the application of remote sensing and GIS technologies. These technologies offer accurate identification of salt-affected regions, guiding breeding and agronomic practices customized to particular geographies. Nevertheless, constrained landholdings and limited access to salt-tolerant seedlings impede technological utilization. Involving politicians, extension agencies, and agricultural communities in participatory breeding efforts fosters equitable transmission of innovation, including farmer preferences and local knowledge to improve uptake and efficacy. Biotechnological innovations and omics technologies have the potential to revolutionize breeding methodologies. However, they must be combined with bioinformatics and high-throughput phenotyping technologies to swiftly uncover context-relevant traits. These solutions synchronize productivity goals with sustainability objectives when incorporated into comprehensive frameworks. Integrating salinity-resistant rice farming with agroforestry in coastal areas improves productivity, increases biodiversity, and strengthens ecosystem resilience. Multidisciplinary approaches create a strong basis for mitigating salt stress and promoting sustainable agriculture and resilient livelihoods in saline-affected areas.
Salinity tolerance in rice presents a complex challenge, necessitating a collaborative strategy that combines genetics, agronomy, and sustainable practices. Significant breakthroughs encompass finding critical QTLs such as Saltol, creating salt-tolerant cultivars such as FL478 and BRRI dhan47, and advancements in gene-editing technologies. Agronomic techniques, such as enhanced irrigation, crop rotation, and organic amendments, augment these genetic remedies, improving soil health and production in saline areas. Case studies from South Asia, Sub-Saharan Africa, the Middle East and Australia, illustrate the effective implementation of salt-tolerant cultivars, showcasing their capacity to convert unproductive regions. Nonetheless, obstacles, including the polygenic characteristics of salt tolerance, restricted genetic diversity, and environmental unpredictability, persist as substantial issues. Future perspectives highlight the necessity for interdisciplinary cooperation, utilizing improved phenotyping, digital agriculture, and participatory breeding to guarantee climate-resilient and sustainable rice-producing systems. These initiatives facilitate the establishment of a more secure and resilient global food system.
Addressing salinity stress in rice farming requires coordinated global initiatives that combine scientific research, policy formulation, and community involvement. The complexity of salinity tolerance encompassing genetic, physiological, and environmental factors highlights the necessity for cooperative, interdisciplinary approaches. Breeding efforts must integrate advanced genomic techniques with traditional expertise to create hardy varieties suited to various agro-climatic settings. Simultaneously, agronomic advancements, like sustainable irrigation methods, crop diversity, and soil reclamation, must be expanded through inclusive policies and effective extension services. Global research consortia and platforms, including the International Rice Research Institute (IRRI) and Stress-Tolerant Rice for Africa and South Asia (STRASA), have exemplified the transformative potential of collaboration. Expanding these programs will facilitate resource-sharing, capacity building, and equitable access to innovations, especially in vulnerable areas such as South Asia and Sub-Saharan Africa. Policymakers must prioritize financing for climate-smart agriculture and endorse farmer-led participatory initiatives to guarantee the uptake and sustainability of solutions. Furthermore, the use of digital technology, like remote sensing and precision agriculture, in salinity management has the potential to transform the approach to addressing difficulties in the field. This necessitates collaborations across sectors connecting researchers, agribusinesses, and local communities to expedite the shift to resilient rice systems. Global collaboration is essential to confront the escalating issue of salinity. By cultivating partnerships, augmenting knowledge exchange, and investing in scalable innovations, we can ensure sustainable rice production systems and safeguard global food security for future generations.
OS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Visualization, Writing – original draft. NF: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. YM: Data curation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. CD: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. DZ: Formal Analysis, Writing – review & editing. LZ: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. XS: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was funded by Guangdong Ocean University Introduced Talents Scientific Research Start-up Project (grant number: R20062). This project was also supported by the Zhanjiang Science and Technology Plan Project (grant number: 2022A01044). The funding institutions did not play a role in study design, data collection or analysis, or manuscript writing.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbas, A., Rashad, A., Rehman, A., Bukhari, M. (2024). Exploring the response mechanisms of rice to salinity stress. Bull. Biol. Allied Sci. Res. 2024, 58. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-40277-8_7
Abouzied, S., Abd El-latif, A. (2017). Effect of different calcium concentrations in soil on survival percent and uptake of Na+ and Cl- ions by rice plant. Arab Univ J. Agric. Sci. 25, 289–297. doi: 10.21608/ajs.2017.13596
Abu-Ria, M., Shukry, W., Abo-Hamed, S., Albaqami, M., Almuqadam, L., Ibraheem, F. (2023). Humic acid modulates ionic homeostasis, osmolytes content, and antioxidant defense to improve salt tolerance in rice. Plants. 12, 1834. doi: 10.3390/plants12091834
Abu Romman, Z., Al Kuisi, M. (2023). The impact of water legislation on groundwater sustainability in an arid region: Spatial statistical approach. Environ. Dev. 46, 100852. doi: 10.1016/j.envdev.2023.100852
Acharya, B. R., Gill, S. P., Kaundal, A., Sandhu, D. (2024). Strategies for combating plant salinity stress: the potential of plant growth-promoting microorganisms. Front. Plant Sci. 15. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1406913
Adam, A. M., Bashir, M., Shehu, B. M., Hussain, I. Y. (2022). Effects of biochar amendments on rice growth and metabolic response to salinity stress in salt-affected soils. Dutse J. Pure Appl. Sci. 7. doi: 10.4314/dujopas.v7i4b.9
Adane, M., Alamnie, G. (2024). CRISPR/Cas9 mediated genome editing for crop improvement against Abiotic stresses: current trends and prospects. Funct. Integr. Genomics 24, 199. doi: 10.1007/s10142-024-01480-2
Aggarwal, G., Edhigalla, P., Walia, P., Jindal, S., Sandal, S. S. (2024). A method for screening salt stress tolerance in Indian mustard (Brassica juncea) (L.) Czern & Coss at seedling stage. Sci. Rep. 14, 12705. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-63693-6
Ahmad, A., Jamil, A., Munawar, N. (2023). GMOs or non-GMOs? The CRISPR conundrum. Front. Plant Sci. 14. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1232938
Aizaz, M., Lubna, Jan, R., Asaf, S., Bilal, S., Kim, K. M., et al. (2024). Regulatory dynamics of plant hormones and transcription factors under salt stress. Biol. (Basel) 13, 673. doi: 10.3390/biology13090673
Akhlasur Rahman, M., Khatun, H., Hossain, H., Iftekharuddaula, K. M., Singh, R. K. (2024). “Recent approaches in breeding for salt tolerance in rice in Bangladesh,” in Genetic Improvement of Rice for Salt Tolerance (Springer Nature Singapore, Singapore), 59–76.
Ali, S., Akhtar, M. S., Siraj, M., Zaman, W. (2024). Molecular communication of microbial plant biostimulants in the rhizosphere under abiotic stress conditions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25, 12424. doi: 10.3390/ijms252212424
Ali, M. H., Biswas, P., Islam, M. A., Azad, A. K. (2024). Effects of irrigation and nutrients managements with plant intensification on rice under saline soil. Bangladesh J. Nucl. Agric. 38, 53–64. doi: 10.3329/bjnag.v38i1.76565
Ali, M. A., Khan, M. A. I., Baten, M. A., Hiya, H. J., Farukh, M. A., Sarkar, S. K. (2023). Reclamation of coastal soil salinity towards sustainable rice production and mitigating global warming potentials in the changing climate. Am. J. Clim Change 12, 100–115. doi: 10.4236/ajcc.2023.121006
Ali, O. A. M., Zayed, B. A., Abou El-Enin, M. M. M., El Sheikha, A. F., Kheir, A. M. S., El-Tahlawy, Y. A., et al. (2024). Fusing genotype and soil organic/inorganic amendment to improve saline-sodic properties and rice productivity. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 24, 2413–2436. doi: 10.1007/s42729-024-01661-9
Al-Saadi, W. K., Hamdalla, M. S., Aljuaifari, W. (2024). Morphological, biochemical and proline-related genes analyses in resistant and susceptible wheat cultivars in Iraq. Basrah J. Agric. Sci. 37, 119–133. doi: 10.37077/25200860.2024.37.1.10
Al-Tardeh, S. M., Alqam, H. N., Kuhn, A. J., Kuchendorf, C. M. (2023). In vitro assessment of salinity stress impact on early growth in ten certified palestinian barley cultivars (Hordeum vulgare L.) potentially suitable for cultivation on former quarry substrates. Water. 15, 1065. doi: 10.3390/w15061065
Ansari, A., Pranesti, A., Telaumbanua, M., Alam, T., Taryono, Wulandari, R. A., et al. (2023). Evaluating the effect of climate change on rice production in Indonesia using multimodelling approach. Heliyon. 9, e19639. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e19639
Asma, J., Subrahmanyam, D., Krishnaveni, D. (2023). The global lifeline: A staple crop sustaining two-thirds of the world’s population. Agric. Arch. 2, 15–18. doi: 10.51470/AGRI.2023.2.3.15
Baisakh, N., RamanaRao, M. V., Rajasekaran, K., Subudhi, P., Janda, J., Galbraith, D., et al. (2012). Enhanced salt stress tolerance of rice plants expressing a vacuolar H + -ATPase subunit c1 (SaVHAc1) gene from the halophyte grass Spartina alterniflora Löisel. Plant Biotechnol. J. 10, 453–464. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-7652.2012.00678.x
Bandyopadhyay, S., Saha, P., Hooi, A., Mondal, A., Atta, K. (2024). “Prospective role of brassinosteroids in tolerance to biotic stress and plant defence,” in Plant Growth Regulators to Manage Biotic and Abiotic Stress in Agroecosystems (CRC Press, Boca Raton), 125–149.
Bapela, T., Shimelis, H., Tsilo, T. J., Mathew, I. (2022). Genetic improvement of wheat for drought tolerance: progress, challenges and opportunities. Plants. 11, 1331. doi: 10.3390/plants11101331
Barghi, A., Jung, H. W. (2023). Bacterial volatile organic compounds from Bacillus zanthoxyli HS-1 enhance tolerance responses against salt and high temperature in cucumber and cabbage. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3399549/v1
Barona-Edna (2013). Wild parent spawns super salt tolerant rice (Philippines: Rice Today). Available online at: https://ricetoday.irri.org/wild-parent-spawns-super-salt-tolerant-rice/ (Accessed December 28, 2024).
Baştaş, M. (2023). Genetic Dissection and QTL Pyramiding to Enhance Salinity Tolerance in Rice (Oryza sativa L.) (Louisiana, USA: Louisiana State University and Agricultural and Mechanical College).
Basit, A., Bano, Z., Nafees, M., Khan, M. J., Younas, M., Zulfiqar, S., et al. (2024). Morphological and physiological features of genotypes of Zea mays towards salt tolerance influenced by mycorrhizal fungi. Haya Saudi J. Life Sci. 9, 238–244. doi: 10.36348/sjls.2024.v09i06.005
Basu, S., Kumari, S., Subhadarshini, P., Rishu, A. K., Shekhar, S., Kumar, G. (2023). Plant growth promoting rhizobacterium Bacillus sp. BSE01 alleviates salt toxicity in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) by conserving ionic, osmotic, redox and hormonal homeostasis. Physiol. Plant 175. doi: 10.1111/ppl.14076
Benaafi, M., Pradipta, A., Tawabini, B., Al-Areeq, A. M., Bafaqeer, A., Humphrey, J. D., et al. (2024). Suitability of treated wastewater for irrigation and its impact on groundwater resources in arid coastal regions: Insights for water resources sustainability. Heliyon. 10, e29320. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29320
Bharath, P., Gahir, S., Raghavendra, A. S. (2021). Abscisic acid-induced stomatal closure: an important component of plant defense against abiotic and biotic stress. Front. Plant Sci. 12. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.615114
Biradar, H. (2012). Overexpression of a Plasma Membrane Protein Gene, SaPMP3, from Spartina alterniflora L. Enhances Salinity Tolerance in Rice (Oryza sativa L.) (Switzerland: Louisiana State University and Agricultural and Mechanical College).
Biradar, H., Karan, R., Subudhi, P. K. (2018). Transgene pyramiding of salt responsive protein 3-1 (SaSRP3-1) and SaVHAc1 from spartina alterniflora L. Enhances salt tolerance in rice. Front. Plant Sci. 9. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.01304
Cantila, A. Y., Chen, S., Siddique, K. H. M., Cowling, W. A. (2024). Heat shock responsive genes in Brassicaceae: genome-wide identification, phylogeny, and evolutionary associations within and between genera. Genome. 67, 464–481. doi: 10.1139/gen-2024-0061
Chanu, P. H. (2023). “Management of salt-affected soils for increasing crop productivity,” in Enhancing Resilience of Dryland Agriculture Under Changing Climate (Springer Nature Singapore, Singapore), 113–121.
Chaudhary, A., Poudyal, S., Kaundal, A. (2024). Role of mycorrhizal fungi in maintaining sustainable agroecosystem. doi: 10.20944/preprints202410.1820.v1
Chawade, A., van Ham, J., Blomquist, H., Bagge, O., Alexandersson, E., Ortiz, R. (2019). High-throughput field-phenotyping tools for plant breeding and precision agriculture. Agronomy. 9, 258. doi: 10.3390/agronomy9050258
Chen, F., Chen, L., Yan, Z., Xu, J., Feng, L., He, N., et al. (2024). Recent advances of CRISPR-based genome editing for enhancing staple crops. Front. Plant Sci. 15. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1478398
Chen, Y., Huang, W., Zhang, F., Luo, X., Hu, B., Xie, J. (2021a). Metabolomic profiling of dongxiang wild rice under salinity demonstrates the significant role of amino acids in rice salt stress. Front. Plant Sci. 12. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.729004
Chen, Y., Huang, W., Zhang, F., Luo, X., Hu, B., Xie, J. (2021b). Metabolomic profiling of dongxiang wild rice under salinity demonstrates the significant role of amino acids in rice salt stress. Front. Plant Sci. 12. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.729004/full
Chen, S., Qiu, G. (2023). Enhancement of salt tolerance of transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana by Zostera japonica DnaJ gene. Isr. J. Plant Sci. 70, 244–252. doi: 10.1163/22238980-bja10086
Chen, Z., Zhou, T., Huang, G., Xiong, Y. (2024). Soil microbial community and associated functions response to salt stresses: Resistance and resilience. Sci. Total Environ. 954, 176475. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.176475
Cuthbertson (2022). Molecular Genetics of Salinity Tolerance in Rice (Oryza sativa L.) (Louisiana, USA: Louisiana State University and Agricultural and Mechanical College).
Dace, H., Tony Blair Institute for Global Change (2021). Gene Editing in Food Production: Charting a Way Forward. Available online at: https://institute.global/insights/tech-and-digitalisation/gene-editing-food-production-charting-way-forward (Accessed February 19, 2025).
da Silva, V. J., de Sousa Lopes, L., de Carvalho, H. H., Cavalcante, F. L. P., Oliveira, A. R. F., da Silva, S. J., et al. (2023). Differential modulation of metabolites induced by salt stress in rice plants. South Afr. J. Bot. 162, 245–258. doi: 10.1016/j.sajb.2023.09.013
Davis, K. A., McKinney, M. M. S., Gittman, R. K., Peralta, A. L. (2024). Evaluating plant-microbe associations in response to environmental stressors to enhance salt marsh restoration. doi: 10.1101/2024.10.14.618360
Debsharma, S. K., Rahman, M. A., Khatun, M., Disha, R. F., Jahan, N., Quddus, M. R., et al. (2024). Developing climate-resilient rice varieties (BRRI dhan97 and BRRI dhan99) suitable for salt-stress environments in Bangladesh. PloS One 19, e0294573. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0294573
Del Cioppo, G., Scalabrino, S., Scippa, G. S., Trupiano, D. (2024). Opportunities and limits of image-based plant stress phenotyping: detecting plant salt stress status using machine learning techniques. Bot. J. Linn Soc. 207, 253–265. doi: 10.1093/botlinnean/boae069
Dong, H., Wang, Y., Di, Y., Qiu, Y., Ji, Z., Zhou, T., et al. (2024). Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria Pseudomonas aeruginosa HG28-5 improves salt tolerance by regulating Na+/K+ homeostasis and ABA signaling pathway in tomato. Microbiol. Res. 283, 127707. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2024.127707
Dreyer, I., Hernández-Rojas, N., Bolua-Hernández, Y., Tapia-Castillo, VDLA., Astola-Mariscal, S. Z., Díaz-Pico, E., et al. (2024). Homeostats: The hidden rulers of ion homeostasis in plants. Quant Plant Biol. 5, e8. doi: 10.1017/qpb.2024.8
Dutta, S., Bandyopadhyay, S., Jha, S. (2019). Cultural and morphological characterization of pyricularia grisea causing blast disease of rice. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 8, 514–522. doi: 10.20546/ijcmas.2019.809.062
El-Aal, M. S. A., Farag, H. R. M., Elbar, O. H. A., Zayed, M. S., Khalifa, G. S., Abdellatif, Y. M. R. (2024). Synergistic effect of Pseudomonas putida and endomycorrhizal inoculation on the physiological response of onion (Allium cepa L.) to saline conditions. Sci. Rep. 14, 21373. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-71165-0
El-Hendawy, S., Junaid, M. B., Al-Suhaibani, N., Al-Ashkar, I., Al-Doss, A. (2024a). Integrating hyperspectral reflectance-based phenotyping and SSR marker-based genotyping for assessing the salt tolerance of wheat genotypes under real field conditions. Plants. 13, 2610. doi: 10.3390/plants13182610
El-Hendawy, S., Tahir, M. U., Al-Suhaibani, N., Elsayed, S., Elsherbiny, O., Elsharawy, H. (2024b). Potential of thermal and RGB imaging combined with artificial neural networks for assessing salt tolerance of wheat genotypes grown in real-field conditions. Agronomy. 14, 1390. doi: 10.3390/agronomy14071390
Etesami, H. (2024). Enhancing soil microbiome resilience: the mitigating role of silicon against environmental stresses. Front. Agron. 6. doi: 10.3389/fagro.2024.1465165
Farooqi, Z., Sabir, M., Abdul Qadir, A., Mohy Ud Din, W., Zulfiqar, U. (2024). Assessment of the change in soil properties and aggregates formation of freshly restored texturally different marginally salt-affected soils under various soil amelioration strategies. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 55, 1714–1732. doi: 10.1080/00103624.2024.2325482
Food Standards Agency (2021). Consumer perceptions of genome edited food. doi: 10.46756/sci.fsa.aya629
Formentin, E., Barizza, E., Stevanato, P., Falda, M., Massa, F., Tarkowskà, D., et al. (2018). Fast Regulation of Hormone Metabolism Contributes to Salt Tolerance in Rice (Oryza sativa spp. Japonica, L.) by Inducing Specific Morpho-Physiological Responses. Plants 7, 75. doi: 10.3390/plants7030075
Foyer, C. H., Kunert, K. (2024). The ascorbate–glutathione cycle coming of age. J. Exp. Bot. 75, 2682–2699. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erae023
Fu, H., Lu, J., Cui, G., Nie, J., Wang, W., She, W., et al. (2024). Advanced plant phenotyping: unmanned aerial vehicle remote sensing and cimageA software technology for precision crop growth monitoring. Agronomy. 14, 2534. doi: 10.3390/agronomy14112534
Gahlaut, V., Jaiswal, V., Kumar, S. (2021). “Role of small RNA and RNAi technology toward improvement of abiotic stress tolerance in plants,” in CRISPR and RNAi systems (Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier), 491–507.
Gairola, A., Kumar, V., Kumar, S., Kumar, S., Patel, A., Singh, S. (2024). Upland rice: A water-efficient rice production system in India. Biot Res. Today 6, 46–50. doi: 10.54083/BioResToday/6.1.2024/46-50
Gan, W.C., Ling, A. P. K. (2022). CRISPR/Cas9 in plant biotechnology: applications and challenges. BioTechnologia. 103, 81–93. doi: 10.5114/bta.2022.113919
Geng, L., Zhang, W., Zou, T., Du, Q., Ma, X., Cui, D., et al. (2023). Integrating linkage mapping and comparative transcriptome analysis for discovering candidate genes associated with salt tolerance in rice. Front. Plant Sci. 14. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1065334
Ghiardelli, A., Straffelini, E., Park, E., D’Agostino, V., Masin, R., Tarolli, P. (2025). Seawater intrusion in coastal agricultural regions: a global review. doi: 10.5194/egusphere-egu24-6453
Gil, T., Teixeira, R., Sousa, A., d’Oliveira Palmeiro, M. A., Cruz Coimbra de Matos, A., Niza Costa, M., et al. (2023). Isolation and characterization of culturable osmotolerant microbiota in hypersaline and hypergypsic soils as new treatment for osmotic stress in plants. Soil Syst. 7, 86. doi: 10.3390/soilsystems7040086
Gill, T., Gill, S. K., Saini, D. K., Chopra, Y., de Koff, J. P., Sandhu, K. S. (2022). A comprehensive review of high throughput phenotyping and machine learning for plant stress phenotyping. Phenomics. 2, 156–183. doi: 10.1007/s43657-022-00048-z
Guden, B., Kiemde, O., Çelebi Akşahin, M., Uzun, B. (2024). Effects of salt stress on germination, seedling growth, and ion content of sweet sorghum. Mediterr Agric. Sci. 37, 91–98. doi: 10.29136/mediterranean.1473692
Guo, J., Ge, C., Wang, G., Zhou, D. (2024). Mechanisms of chloride to promote the uptake and accumulation of cadmium in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Sci. Total Environ. 926, 172046. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.172046
Guo, L., Han, C., Liu, T., Wang, Y., Sun, P., Pang, Q., et al. (2024). Integrated physiological, biochemical and transcriptomic analyses reveal the mechanism of salt tolerance induced by a halotolerant Serratia sp. NTN6 in maize. Environ. Exp. Bot. 221, 105724. doi: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2024.105724
Gupta, S., Groen, S. C., Zaidem, M. L., Sajise, A. G. C., Calic, I., Natividad, M. A., et al. (2024). Systems genomics of salinity stress response in rice. doi: 10.1101/2024.05.31.596807
Gupta, A., Shaw, B. P. (2021). Augmenting salt tolerance in rice by regulating uptake and tissue specific accumulation of Na + - through Ca 2+ -induced alteration of biochemical events. Plant Biol. 23, 122–130. doi: 10.1111/plb.v23.s1
Hadid, M. L., Ramadan, K. M. A., El-Beltagi, H. S., Ramadan, A. A., El-Metwally, I. M., Shalaby, T. A., et al. (2023). Modulating the antioxidant defense systems and nutrients content by proline for higher yielding of wheat under water deficit. Not Bot. Horti Agrobot Cluj-Napoca 51, 13291. doi: 10.15835/nbha51313291
Hakami-Kermani, A., Babazadeh, H., Kisseka, I., AlDughaishi, U. (2024). Climate change impacts on evapotranspiration, crop yield, and green and blue water footprints of main crops in a semi-arid region. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-4251417/v1
Hannam, I. D. (2024). “Soil conservation policies in Australia: successes, failures, and requirements for ecologically sustainable policy,” in Soil and Water Conservation Policies and Programs (CRC Press, Boca Raton), 493–514.
Haq, Y., Shahbaz, M., Asif, H. M. S., Al-Laith, A., Alsabban, W. H. (2023). Spatial mapping of soil salinity using machine learning and remote sensing in kot addu, Pakistan. Sustainability. 15, 12943. doi: 10.3390/su151712943
Hassan, M. A., Dahu, N., Hongning, T., Qian, Z., Yueming, Y., Yiru, L., et al. (2023). Drought stress in rice: morpho-physiological and molecular responses and marker-assisted breeding. Front. Plant Sci. 14. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1215371
Hemdan, N. A., El-Ashry, S. M., Abd-Elmabod, S. K., Zhang, Z., Mansour, H. A., Attia, M. (2024). Reclamation and improvement of saline soils using organo–mineral–natural resources, treated saline water, and drip irrigation technology. Water. 16, 3234. doi: 10.3390/w16223234
Hiremath, S. S., Prasanna, N. L., Sudhakar, S., Mohanan, A., C.K., A., Nigam, R., et al. (2024). A review on role of root exudates in shaping plant-microbe-pathogen interactions. J. Adv. Microbiol. 24, 1–17. doi: 10.9734/jamb/2024/v24i12868
Hmidi, D., Abdelly, C., Athar, H.U.R., Ashraf, M., Messedi, D. (2018). Effect of salinity on osmotic adjustment, proline accumulation and possible role of ornithine-δ-aminotransferase in proline biosynthesis in Cakile maritima. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 24, 1017–1033. doi: 10.1007/s12298-018-0601-9
Ho, V. T., Thomson, M. J., Ismail, A. M. (2016). Development of salt tolerant IR64 near isogenic lines through marker-assisted breeding. Journal of Crop Science and Biotechnology 19(5), 373–381. doi: 10.1007/s12892-016-0049-9
Holz, M., Zarebanadkouki, M., Kuzyakov, Y., Pausch, J., Carminati, A. (2018). Root hairs increase rhizosphere extension and carbon input to soil. Ann. Bot. 121, 61–69. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcx127
http://bioscience.oxfordjournals.org/. Available online at: http://bioscience.oxfordjournals.org/.
Hussain, S., Zhang, R., Liu, S., Li, R., Zhou, Y., Chen, Y., et al. (2022). Transcriptome-wide analysis revealed the potential of the high-affinity potassium transporter (HKT) gene family in rice salinity tolerance via ion homeostasis. Bioengineering. 9, 410. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering9090410
Imhoff, J. F., Rahn, T., Künzel, S., Keller, A., Neulinger, S. C. (2020). Osmotic adaptation and compatible solute biosynthesis of phototrophic bacteria as revealed from genome analyses. Microorganisms. 9, 46. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9010046
Irin, I. J., Akter, K., Rasul, S., Biswas, T., Alam, M. M. (2024). Mitigation of salinity stress on morpho-physiological and yield related parameters of rice using different organic amendments. Plant Sci. Today. 11, 604–611. doi: 10.14719/pst.3040
IRRI (2023). Salinity-tolerant rice variety set to boost rice yield in stress-prone areas in Kenya. Available online at: https://www.irri.org/news-and-events/news/salinity-tolerant-rice-variety-set-boost-rice-yield-stress-prone-areas-Kenya (Accessed December 23, 2024).
Ji, H., Qi, Y., Zhang, X., Yang, G. (2024). Transcriptomics and Metabolomics Analysis Revealed the Ability of Microbacterium ginsengiterrae S4 to Enhance the Saline-Alkali Tolerance of Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Seedlings. Agronomy. 14, 649. doi: 10.3390/agronomy14040649
Ji, J., Yuan, D., Jin, C., Wang, G., Li, X., Guan, C. (2020). Enhancement of growth and salt tolerance of rice seedlings (Oryza sativa L.) by regulating ethylene production with a novel halotolerant PGPR strain Glutamicibacter sp. YD01 containing ACC deaminase activity. Acta Physiol. Plant 42, 42. doi: 10.1007/s11738-020-3034-3
Jiang, W., Ye, Q., Wu, Z., Zhang, Q., Wang, L., Liu, J., et al. (2023). Analysis of CAT gene family and functional identification of OsCAT3 in rice. Genes (Basel) 14, 138. doi: 10.3390/genes14010138
Jung, S. E., Bang, S. W., Kim, S. H., Seo, J. S., Yoon, H. B., Kim, Y. S., et al. (2021). Overexpression of osERF83, a vascular tissue-specific transcription factor gene, confers drought tolerance in rice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 7656. doi: 10.3390/ijms22147656
Kabir, M. A., Hossain, M. K., Hossain, M. A., Molla, M. O. F., Khatun, M. S., Mostofa Jamal, M. A. H. (2024). Impact of water and soil salinity on coastal agriculture in Bangladesh: insights and mitigation strategies. Am. J. Multidiscip Res. Innov. 3, 36–48. doi: 10.54536/ajmri.v3i4.2927
Keutgen, A. J. (2023). Climate change: challenges and limitations in agriculture. IOP Conf Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 1183, 012069. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/1183/1/012069
Khalid, S., Chaudhary, N., Irum, A., Aas, M., Noor, S., Munsha, A., et al. (2024). Impact of salt stress on plant growth and approaches for enhanced tolerance. Biol. Clin. Sci. Res. J. 2024, 1356. doi: 10.54112/bcsrj.v2024i1.1356
Khan, M. S., Akther, T., Mubarak Ali, D., Hemalatha, S. (2019). An investigation on the role of salicylic acid alleviate the saline stress in rice crop (Oryza sativa (L)). Biocatal Agric. Biotechnol. 18, 101027. doi: 10.1016/j.bcab.2019.101027
Khan, T. A., Hassan, H., Wang, H., Inzamamulhaq, M., Ashraf, I., Luo, F., et al. (2024). How does jasmonic acid improve drought tolerance? Mechanisms and future prospects. Not Bot. Horti Agrobot Cluj-Napoca 52, 13604. doi: 10.15835/nbha52213604
Khan, I., Laboni, A. A., Azim, T., Elias, S. M., Seraj, Z. I. (2023). Downregulation of the OsAKT1 K+/Na+ Transporter gene by CRISPR-Cas9 mediated transformation in sensitive rice IR29 makes it tolerant to salt stress. Plant Tissue Cult Biotechnol. 33, 71–84. doi: 10.3329/ptcb.v33i1.66868
Khunsanit, P., Jitsamai, N., Thongsima, N., Chadchawan, S., Pongpanich, M., Henry, I. M., et al. (2024). QTL-Seq identified a genomic region on chromosome 1 for soil-salinity tolerance in F2 progeny of Thai salt-tolerant rice donor line “Jao Khao. Front. Plant Sci. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1424689
Kim, M. S., Ko, S. R., Jung, Y. J., Kang, K. K., Lee, Y. J., Cho, Y. G. (2023). Knockout mutants of OsPUB7 generated using CRISPR/Cas9 revealed abiotic stress tolerance in rice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 5338. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065338
Kobayashi, N. I., Yamaji, N., Yamamoto, H., Okubo, K., Ueno, H., Costa, A., et al. (2017). OsHKT1;5 mediates Na + exclusion in the vasculature to protect leaf blades and reproductive tissues from salt toxicity in rice. Plant J. 91, 657–670. doi: 10.1111/tpj.2017.91.issue-4
Krishnamurthy, S. L., Rathor, S., Lokeshkumar, L. B. M., Warriach, A. S. (2024). Genetic improvement of rice for inland saline and alkaline areas of North-Western India. In: Genetic Improvement of Rice for Salt Tolerance. pp. 77–100. doi: 10.1007/978-981-99-3830-8_5
Kumar, D., Singh, P., Jatav, A., Verma, V., Kumar, A., Singh, M., et al. (2024). Impact of saline water irrigation on growth, yield and quality of rice (Oryza sativa L.) varieties. Int. J. Res. Agron. 7, 117–122. doi: 10.33545/2618060X.2024.v7.i10b.1709
Kumar, M., Singh, R. S., Mahajan, G., Babu, S., Kumar, S., Kumar, R., et al. (2012). “Ridge planted pigeonpea and furrow planted rice in an intercropping system as affected by nitrogen and weed management,” in Weed Control (Rijeka, Croatia: InTech).
Kumar, V., Srivastava, A. K., Sharma, D., Pandey, S. P., Pandey, M., Dudwadkar, A., et al. (2024). Antioxidant defense and ionic homeostasis govern stage-specific response of salinity stress in contrasting rice varieties. Plants. 13, 778. doi: 10.3390/plants13060778
Kumawat, G., Jakhar, M. L., Singh, V., Singh, J., Gothwal, D. K., Yadava, D. K. (2024). High throughput phenotyping of functional traits and key indices for selection of salt tolerant Mustard [Brassica juncea (L.) Czern & Coss] genotypes. Physiol. Plant 176. doi: 10.1111/ppl.v176.1
Le, T. D., Gathignol, F., Vu, H. T., Nguyen, K., Tran, L. H., Vu, H. T. T., et al. (2021). Genome-wide association mapping of salinity tolerance at the seedling stage in a panel of Vietnamese landraces reveals new valuable QTLs for salinity stress tolerance breeding in rice. Plants. 10, 1088. doi: 10.3390/plants10061088
Leawtrakun, J., Aesomnuk, W., Khanthong, S., Dumhai, R., Songtoasesakul, D., Phosuwan, S., et al. (2024a). Identification of Candidate Genes for Salt Tolerance at Seedling Stage in Rice Using QTL-Seq and Chromosome Segment Substitution Line-Derived Population. Agron. 14, 929. doi: 10.3390/agronomy14050929
Leawtrakun, J., Aesomnuk, W., Khanthong, S., Dumhai, R., Songtoasesakul, D., Phosuwan, S., et al. (2024b). Identification of candidate genes for salt tolerance at seedling stage in rice using QTL-Seq and chromosome segment substitution line-derived population. Agronomy. 14, 929. doi: 10.3390/agronomy14050929
Li, Y., Wu, X., Zhang, Y., Zhang, Q. (2022). CRISPR/Cas genome editing improves abiotic and biotic stress tolerance of crops. Front. Genome Ed. 4. doi: 10.3389/fgeed.2022.987817
Li, L., Zheng, Q., Jiang, W., Xiao, N., Zeng, F., Chen, G., et al. (2023). Molecular regulation and evolution of cytokinin signaling in plant abiotic stresses. Plant Cell Physiol. 63, 1787–1805. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcac071
Li, Q., Zhu, P., Yu, X., Xu, J., Liu, G. (2024). Physiological and molecular mechanisms of rice tolerance to salt and drought stress: advances and future directions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25, 9404. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179404
Liang, T., Duan, B., Luo, X., Ma, Y., Yuan, Z., Zhu, R., et al. (2021). Identification of high nitrogen use efficiency phenotype in rice (Oryza sativa L.) through entire growth duration by unmanned aerial vehicle multispectral imagery. Front. Plant Sci. 12. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.740414
Lim, J., Lim, C. W., Lee, S. C. (2022). Core components of abscisic acid signaling and their post-translational modification. Front. Plant Sci. 13. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.895698
Linh Khanh, L., Van Doai, N., Thi Linh, N., Quyen, P., Hoang Ha, C., Bich Ngoc, P., et al. (2024). Development of CRISPR/Cas9 systems to induce targeted mutations in the promoter region of the OsSRFP1 gene in rice. Vietnam J. Biotechnol. 21, 463–475. doi: 10.1007/s10142-024-01347-6
Liu, C., Jiang, X., Yuan, Z. (2024). Plant responses and adaptations to salt stress: A review. Horticulturae. 10, 1221. doi: 10.3390/horticulturae10111221
Liu, C., Mao, B., Yuan, D., Chu, C., Duan, M. (2022). Salt tolerance in rice: Physiological responses and molecular mechanisms. Crop J. 10, 13–25. doi: 10.1016/j.cj.2021.02.010
Liu, X., Yao, T., Chai, J., Han, J. (2023). Adsorption of Sodium Ions by Exopolysaccharides from Pseudomonas simiae MHR6 and Its Improvement of Na +/K + Homeostasis in Maize under Salt Stress. J. Agric. Food Chem. 71, 19949–19957. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c05002
Maach, M., Akodad, M., Pilar Rodríguez-Rosal, M., Venema, K., Skalli, A., Ait Hmeid, H., et al. (2024). Strategies of NHX antiporters to deal with salt stress. Plant Sci. Today. 10, 2. doi: 10.14719/pst.2442
Mahadik, S. P., Kumudini, B. S. (2024). Halotolerant fungi secreting phytohormones and volatile organic compounds enhance growth and mineral content in finger millet under salinity stress. Plant Stress 11, 100426. doi: 10.1016/j.stress.2024.100426
Majidian, P., Ghorbani, H. (2024). “Salinity stress in plants: challenges in view of physiological aspects,” in Abiotic Stress in Crop Plants - Ecophysiological Responses and Molecular Approaches (London, United Kingdom: IntechOpen).
Makttoof, E. A., Nafawa, S. M. (2024). Study of salt phases and groundwater chemically in some Iraqi soils. IOP Conf Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 1371, 082004. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/1371/8/082004
Malysheva, N., Kizinek, S., Khadzhidi, A., Kravchenko, L., Chegge, V., Sarkisian, D., et al. (2020). “Studying soil-reclamation state of rice agricultural landscapes,” in E3S Web Conf. Eds. Rudoy, D., Olshevskaya, A., Kankhva, V.. (France: E3S Web of Conferences). doi: 10.1051/e3sconf/202021004006
Mamta, B., Rajam, M. V. (2018). “RNA interference: A promising approach for crop improvement,” in Biotechnologies of Crop Improvement, vol. 2. (Springer International Publishing, Cham), 41–65.
Mandal, S., Ghorai, M., Anand, U., Samanta, D., Kant, N., Mishra, T., et al. (2022). RETRACTED: Cytokinin and abiotic stress tolerance -What has been accomplished and the way forward? Front. Genet. 13. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.943025
Maniruzzaman, S., Rahman, M. A., Hasan, M., Rasul, M. G., Molla, A. H., Khatun, H., et al. (2023). Molecular mapping to discover reliable salinity-resilient QTLs from the novel landrace akundi in two bi-parental populations using SNP-based genome-wide analysis in rice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 11141. doi: 10.3390/ijms241311141
Mann, A., Ranga, P., Choudhary, P., Yadav, S., Kaul, N., Dahiya, A., et al. (2024). Genome editing technologies for enhancing plant resilience to biotic and abiotic stresses - brief review. J. Soil Salin Water Qual 16, 180–193. doi: 10.56093/jsswq.v16i2.156291
Mansour, M. M. F. (2023). Role of vacuolar membrane transport systems in plant salinity tolerance. J. Plant Growth Regul. 42, 1364–1401. doi: 10.1007/s00344-022-10655-9
Marè, C., Zampieri, E., Cavallaro, V., Frouin, J., Grenier, C., Courtois, B., et al. (2023). Marker-assisted introgression of the salinity tolerance locus saltol in temperate japonica rice. Rice. 16, 2. doi: 10.1186/s12284-023-00619-2
Margay, A. R., Mehmood, A., Bashir, L. (2024). Review on hormonal regulation of drought stress response in plants. Int. J. Plant Soil Sci. 36, 902–916. doi: 10.9734/ijpss/2024/v36i84921
Menéndez, E., Tundo, S. (2024). Editorial: The interplay of plant biotic and abiotic stresses: mechanisms and management. Front. Plant Sci. 15. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1518678
Mheni, N. T., Kilasi, N., Quiloy, F. A., Heredia, M. C., Bilaro, A., Meliyo, J., et al. (2024). Breeding rice for salinity tolerance and salt-affected soils in Africa: a review. Cogent Food Agric. 10. doi: 10.1080/23311932.2024.2327666
Micu, A. (2022). A significant rice in productivity: China’s output of GMO “seawater rice” doubled over the last 2 years (California, USA: ZME Science). Available online at: https://www.zmescience.com/science/rice-hybrid-China-seawater-4637363/ (Accessed December 28, 2024).
Mishra, A. K., Das, R., George Kerry, R., Biswal, B., Sinha, T., Sharma, S., et al. (2023). Promising management strategies to improve crop sustainability and to amend soil salinity. Front. Environ. Sci. 10. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2022.962581
Mitran, T., Basak, N., Mani, P. K., Tamang, A., Singh, D. K., Biswas, S., et al. (2021). Improving crop productivity and soil quality through soil management practices in coastal saline agro-ecosystem. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 21, 3514–3529. doi: 10.1007/s42729-021-00624-8
Mohammadi Alagoz, S., Asgari Lajayer, B., Ghorbanpour, M. (2023). “Proline and soluble carbohydrates biosynthesis and their roles in plants under abiotic stresses,” in Plant Stress Mitigators (Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier), 169–185.
Mohanavel, V., Muthu, V., Kambale, R., Palaniswamy, R., Seeli, P., Ayyenar, B., et al. (2024). Marker-assisted breeding accelerates the development of multiple-stress-tolerant rice genotypes adapted to wider environments. Front. Plant Sci. 15. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1402368
Mourched, B., Abdallah, M., Hoxha, M., Vrtagic, S. (2023). Machine-learning-based sensor design for water salinity prediction: A conceptual approach. Sustainability. 15, 11468. doi: 10.3390/su151411468
Muhammad, A., Kong, X., Zheng, S., Bai, N., Li, L., Khan, M. H. U., et al. (2024). Exploring plant-microbe interactions in adapting to abiotic stress under climate change: a review. Front. Plant Sci. 15. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1482739
N, L. K., Arati, M, A., S, S., Swati, Y.V, S., et al. (2024). The Plant Growth Promoting Potential of Saline Tolerant Rhizobacteria under In vitro Saline Stressed Conditions. J. Adv. Biol. Biotechnol. 27, 1003–1010. doi: 10.9734/jabb/2024/v27i71061
Nampei, M., Jiadkong, K., Chuamnakthong, S., Wangsawang, T., Sreewongchai, T., Ueda, A. (2021). Different Rhizospheric pH Conditions Affect Nutrient Accumulations in Rice under Salinity Stress. Plants 10, 1295. doi: 10.3390/plants10071295
Nelson, T., Hose, G. C., Dabovic, J., Korbel, K. L. (2024). Salinity as a major influence on groundwater microbial communities in agricultural landscapes. Mar. Freshw. Res. 75. doi: 10.1071/MF23014
Neupane, G., Dhakal, A., Bhattarai, K., Teli, P. K. (2020). Management options for drought prone rainfed lowland rice in asia: A review. Rev. Food Agric. 1, 82–84. doi: 10.26480/rfna.02.2020.82.84
Nounjan, N., Mahakham, W., Siangliw, J. L., Toojinda, T., Theerakulpisut, P. (2020). Chlorophyll retention and high photosynthetic performance contribute to salinity tolerance in rice carrying drought tolerance quantitative trait loci (QTLs). Agriculture 10, 620. doi: 10.3390/agriculture10120620
Nurbekova, Z., Satkanov, M., Beisekova, M., Akbassova, A., Ualiyeva, R., Cui, J., et al. (2024). Strategies for achieving high and sustainable plant productivity in saline soil conditions. Horticulturae. 10, 878. doi: 10.3390/horticulturae10080878
Nutan, K. K., Singla-Pareek, S. L., Pareek, A. (2019). The Saltol QTL-localized transcription factor OsGATA8 plays an important role in stress tolerance and seed development in Arabidopsis and rice. J. Exp. Bot. 71, 684–698. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erz368
Oburger, E., Gruber, B., Schindlegger, Y., Schenkeveld, W. D. C., Hann, S., Kraemer, S. M., et al. (2014). Root exudation of phytosiderophores from soil-grown wheat. New Phytol. 203, 1161–1174. doi: 10.1111/nph.2014.203.issue-4
Okur, B., Örçen, N., Okur, N. (2023). “Restoration of saline soils for sustainable crop production,” in Agroecological Approaches for Sustainable Soil Management (New Jersey, USA: Wiley), 319–337.
Omuto, C. T., Kome, G. K., Ramakhanna, S. J., Muzira, N. M., Ruley, J. A., Jayeoba, O. J., et al. (2024). Trend of soil salinization in Africa and implications for agro-chemical use in semi-arid croplands. Sci. Total Environ. 951, 175503. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.175503
Pabuayon, I. C. M., Jiang, J., Qian, H., Chung, J. S., Shi, H. (2021). Gain-of-function mutations of AtNHX1 suppress sos1 salt sensitivity and improve salt tolerance in Arabidopsis. Stress Biol. 1, 14. doi: 10.1007/s44154-021-00014-1
Paik, S., Le, D. T. P., Nhu, L. T., Mills, B. F. (2020). Salt-tolerant rice variety adoption in the Mekong River Delta: Farmer adaptation to sea-level rise. PloS One 15, e0229464. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0229464
Pankaj, Devi, S., Dhaka, P., Kumari, G., Satpal, Lakra, N., et al. (2024). Enhancing salt stress tolerance of forage sorghum by foliar application of ortho-silicic acid. Grass Res. 4. doi: 10.48130/grares-0024-0014
Patel, J., Mishra, A. (2021). “Role of sodium proton antiporters in cellular homeostasis of plants under abiotic stress conditions,” in Transporters and Plant Osmotic Stress (Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier), 273–290.
Porcel, R., Aroca, R., Azcon, R., Ruiz-Lozano, J. M. (2016). Regulation of cation transporter genes by the arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis in rice plants subjected to salinity suggests improved salt tolerance due to reduced Na+ root-to-shoot distribution. Mycorrhiza 26, 673–684. doi: 10.1007/s00572-016-0704-5
Pouzoulet, J., Rolshausen, P. E., Charbois, R., Chen, J., Guillaumie, S., Ollat, N., et al. (2020). Behind the curtain of the compartmentalization process: Exploring how xylem vessel diameter impacts vascular pathogen resistance. Plant Cell Environ. 43, 2782–2796. doi: 10.1111/pce.v43.11
Požgajová, M., Klongová, L., Kovár, M., Navrátilová, A. (2024). “Cell protection by oxidative stress mitigation using substances with bioactive properties,” in The Power of Antioxidants - Unleashing Nature’s Defense Against Oxidative Stress (London, United Kingdom: IntechOpen).
Prusty, M. R., Kim, S. R., Vinarao, R., Entila, F., Egdane, J., Diaz, M. G. Q., et al. (2018). Newly identified wild rice accessions conferring high salt tolerance might use a tissue tolerance mechanism in leaf. Front. Plant Sci. 9. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.00417
Qin, H., Li, Y., Huang, R. (2020). Advances and challenges in the breeding of salt-tolerant rice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21, 8385. doi: 10.3390/ijms21218385
Radha, J., Yaligar, R., Korabu, F., G, N., R, J., Madli, M., et al. (2024). Demonstration of salt tolerant paddy variety GNV-1109 for enhancing productivity in saline soils. Int. J. Agric. Ext Soc. Dev. 7, 38–40. doi: 10.33545/26180723.2024.v7.i6a.693
Raeisi Vanani, A., Sheikhi Shahrivar, F., Nouri, A., Sepehri, M. (2024). Exploring rice tolerance to salinity and drought stresses through Piriformospora indica inoculation: understanding physiological and metabolic adaptations. Front. Plant Sci., 15. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1428631
Rafique, S., Quadri, S. N., Abdin, M. Z. (2024). Plant defense mechanism in combined stresses - cellular and molecular perspective. J. Plant Stress Physiol., 33–42. doi: 10.25081/jpsp.2024.v10.8790
Rahman, M. A., Ahmed, T., Mojid, M. A. (2020). Coupled irrigation–drainage management practice for HYV rice cultivation with saline-irrigation water: evidence from lysimeter experiment. Agric. Sci. 2, p95. doi: 10.30560/as.v2n1p95
Rahman, A., Alam, M. U., Hossain, M. S., Mahmud, J., Nahar, K., Fujita, M., et al. (2022). Exogenous gallic acid confers salt tolerance in rice seedlings: modulation of ion homeostasis, osmoregulation, antioxidant defense, and methylglyoxal detoxification systems. Agronomy. 13, 16. doi: 10.3390/agronomy13010016
Rasheed, A., Li, H., Nawaz, M., Mahmood, A., Hassan, M. U., Shah, A. N., et al. (2022). Molecular tools, potential frontiers for enhancing salinity tolerance in rice: A critical review and future prospective. Front. Plant Sci. 13. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.966749
Reddy, M. P. K., Talekar, N., Kumar, A., Janeja, H. S., Krishna, B., Kumar, D. M. (2023). A review on understanding the effects and mechanisms of salinity tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Int. J. Plant Soil Sci. 35, 209–219. doi: 10.9734/ijpss/2023/v35i173201
Rehman, A. U., Bashir, F., Ayaydin, F., Kóta, Z., Páli, T., Vass, I. (2021). Proline is a quencher of singlet oxygen and superoxide both in in vitro systems and isolated thylakoids. Physiol. Plant 172, 7–18. doi: 10.1111/ppl.v172.1
Renzetti, M., Bertolini, E., Trovato, M. (2024). Proline metabolism genes in transgenic plants: meta-analysis under drought and salt stress. Plants. 13, 1913. doi: 10.3390/plants13141913
Riaz, M., Arif, M. S., Ashraf, M. A., Mahmood, R., Yasmeen, T., Shakoor, M. B., et al. (2019). “A comprehensive review on rice responses and tolerance to salt stress,” in Advances in Rice Research for Abiotic Stress Tolerance (Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier), 133–158.
Rizhsky, L., Liang, H., Shuman, J., Shulaev, V., Davletova, S., Mittler, R. (2004). When defense pathways collide. The response of arabidopsis to a combination of drought and heat stress. Plant Physiol. 134, 1683–1696. doi: 10.1104/pp.103.033431
Ruksaar, M. S. (2024). “Introduction to free radicals,” in Edited Book of Dietary Supplements and Nutraceuticals [According to latest syllabus of B Pharm-VIII Semester of Pharmacy Council of India] (India: Iterative International Publishers, Selfypage Developers Pvt Ltd), 93–111.
Saito, K., Senthilkumar, K., Dossou-Yovo, E. R., Ali, I., Johnson, J. M., Mujawamariya, G., et al. (2023). Status quo and challenges of rice production in sub-Saharan Africa. Plant Prod Sci. 26, 320–333. doi: 10.1080/1343943X.2023.2241712
Sameer, M., Hamza, I. K., Abdulhameed, I. M. (2024). Crop factor of maize (Zea mays L.) and its relationship to the salinity of irrigation water. IOP Conf Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 1371, 082016. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/1371/8/082016
Saminadane, T., Geddam, S., Krishnaswamy, P., Jothiganapathy, K., Tamilselvan, A., Ramadoss, B. R., et al. (2024). Development of early maturing salt-tolerant rice variety KKL(R) 3 using a combination of conventional and molecular breeding approaches. Front. Genet. 14. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1332691
Samy, P. M. A., Singh, R. K., Gregorio, G. B., Gautam, R. K., Krishnamurthy, S. L., Thirumeni, S. (2024). “Genetic improvement of rice for salt tolerance,” in Genetic Improvement of Rice for Salt Tolerance (Springer Nature Singapore, Singapore), 1–8.
Sanga, D. L., Mwamahonje, A. S., Mahinda, A. J., Kipanga, E. A. (2024). Soil salinization under irrigated farming: A threat to sustainable food security and environment in semi-arid tropics. J. Agric. Sci. Pract. 9, 32–47. doi: 10.31248/JASP2024.468
Santanoo, S., Lontom, W., Dongsansuk, A., Vongcharoen, K., Theerakulpisut, P. (2023). Photosynthesis performance at different growth stages, growth, and yield of rice in saline fields. Plants. 12, 1903. doi: 10.3390/plants12091903
Sanyal, R. P., Prashar, V., Jawali, N., Sunkar, R., Misra, H. S., Saini, A. (2022). Molecular and biochemical analysis of duplicated cytosolic CuZn superoxide dismutases of rice and in silico analysis in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 13. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.864330
Saqr, A. M., Abd-Elmaboud, M. E. (2024). Saltwater intrusion in coastal aquifers: A comprehensive review and case studies from Egypt. doi: 10.31586/ojes.2024.982
Sarangi, S. K., Mainuddin, M., Raut, S., Mandal, U. K., Mahanta, K. K. (2024). Coastal salinity management and cropping system intensification through conservation agriculture in the ganges delta. Soil Syst. 8, 80. doi: 10.3390/soilsystems8030080
Sarkar, S., Dutta, T., Hoda, M. N., Roy, T., Bhattacharya, P. (2024). Sodic soil in India: Concept, status and management. Int. J. Agric. Ext Soc. Dev. 7, 54–57. doi: 10.33545/26180723.2024.v7.i4Sa.531
Sarkar, B., Roy, S. (2020). “Ion transporter genes from wild relatives of cereals hold the key for the development of salinity tolerance,” in Sustainable Agriculture in the Era of Climate Change (Springer International Publishing, Cham), 187–209.
Satasiya, P., Patel, S., Patel, R., Raigar, O. P., Modha, K., Parekh, V., et al. (2024). Meta-analysis of identified genomic regions and candidate genes underlying salinity tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Sci. Rep. 14, 5730. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-54764-9
Sayed, M. A., Maurer, A., Schmutzer, T., Schnurbusch, T., Börner, A., Hansson, M., et al. (2022). Genome-wide association study of salt tolerance-related traits during germination and seedling development in an intermedium-spike barley collection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 11060. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911060
Sellathdurai, D., Burman, D., Mandal, U. K., Lama, T. D., Prakash, N. R., Lokeshkumar, B. M., et al. (2024). Crop improvement strategies for addressing waterlogging and salinity in coastal ecosystems. J. Soil Salin Water Qual 16, 207–218. doi: 10.56093/jsswq.v16i2.157117
Shafi, I., Gautam, M., Kariyat, R. (2024). Integrating ecophysiology and omics to unlock crop response to drought and herbivory stress. Front. Plant Sci. 15. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1500773
Shafi, A., Zahoor, I., Mushtaq, U. (2019). “Proline accumulation and oxidative stress: diverse roles and mechanism of tolerance and adaptation under salinity stress,” in Salt Stress, Microbes, and Plant Interactions: Mechanisms and Molecular Approaches (Springer Singapore, Singapore), 269–300.
Shahzad, B., Yun, P., Shabala, L., Zhou, M., Sellamuthu, G., Venkataraman, G., et al. (2022). Unravelling the physiological basis of salinity stress tolerance in cultivated and wild rice species. Funct. Plant Biol. 49, 351–364. doi: 10.1071/FP21336
Shakar, M., Sarfaraz, M., Ashfaq Anjum, M., Amjad Qureshi, M., Ali, A., Akhtar, N., et al. (2024). Integrated use of organic manures and chemical fertilizers on yield, nutrient contents of rice and wheat crops in recently reclaimed saline sodic soil. J. Agric. Vet. Sci. 3, 487–495. doi: 10.55627/agrivet.003.03.0587
Shamsuddin, I., Azad, A., The Business Standard (2022). Salt tolerant rice varieties bring hope to Bangladesh farmers.
Sharma, M., Sidhu, A. K., Samota, M. K., Shah, P., Pandey, M. K., Gangurde, S. S. (2024). Technological advancements in the CRISPR toolbox for improving plant salt tolerance. Discovery Agric. 2, 102. doi: 10.1007/s44279-024-00105-3
Shelake, R. M., Wagh, S. G., Patil, A. M., Červený, J., Waghunde, R. R., Kim, J. Y. (2024). Heat stress and plant–biotic interactions: advances and perspectives. Plants. 13, 2022. doi: 10.3390/plants13152022
Shen, X., Dai, S., Chen, M., Huang, Y. (2024). Spermidine augments salt stress resilience in rice roots potentially by enhancing OsbZIP73’s RNA binding capacity. BMC Plant Biol. 24. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-05492-9
Sheng, X., Ai, Z., Tan, Y., Hu, Y., Guo, X., Liu, X., et al. (2023). Novel salinity-tolerant third-generation hybrid rice developed via CRISPR/Cas9-mediated gene editing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 8025. doi: 10.3390/ijms24098025
Sheoran, P., Kumar, A., Sharma, R., Prajapat, K., Kumar, A., Barman, A., et al. (2021). Quantitative dissection of salt tolerance for sustainable wheat production in sodic agro-ecosystems through farmers’ Participatory approach: an Indian experience. Sustainability. 13, 3378. doi: 10.3390/su13063378
Shim, J. S., Oh, N., Chung, P. J., Kim, Y. S., Choi, Y., Kim, J. K. (2018). Overexpression of OsNAC14 improves drought tolerance in rice. Front. Plant Sci. 9. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.00310
Shohan, M. U. S., Sinha, S., Nabila, F. H., Dastidar, S. G., Seraj, Z. I. (2019). HKT1;5 transporter gene expression and association of amino acid substitutions with salt tolerance across rice genotypes. Front. Plant Sci. 10. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.01420
Shrivastava, P., Kumar, R. (2015). Soil salinity: A serious environmental issue and plant growth promoting bacteria as one of the tools for its alleviation. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 22, 123–131. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2014.12.001
Sikder, M. R., Khan, M. H. R. (2024). mitigation of salt stress in rice (oryza sativa l.) growth and yield in coastal saline soil using crop residue-driven organic amendments under varying moisture conditions. Dhaka Univ J. Biol. Sci. 33, 1–13. doi: 10.3329/dujbs.v33i2.75812
Singh, R.B., Devi, R. (2023). “Achieving salinity-tolerance in cereal crops: major insights into genomics-assisted breeding (GAB),” in Making Plant Life Easier and Productive Under Salinity - Updates and Prospects (London, United Kingdom: IntechOpen).
Singh, C., Kumari, G., Lalita, Gandhi, V., Jain, A., Madaan, S., et al. (2024). Remediation of saline soils using halo-tolerant plant growth promoting rhizobacteria. Int. J. Environ. Clim Change 14, 24–35. doi: 10.9734/ijecc/2024/v14i64208
Singh, Y. P., Mishra, V. K., Singh, S., Sharma, D. K., Singh, D., Singh, U. S., et al. (2016). Productivity of sodic soils can be enhanced through the use of salt tolerant rice varieties and proper agronomic practices. F Crop Res. 190, 82–90. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2016.02.007
Singh, A. K., Pathak, M., Joshi, M. D., Kumar, S., Kashyap, S., Hasan, W. (2024). The role of agriculture in poverty alleviation and rural development. J. Sci. Res. Rep. 30, 529–549. doi: 10.9734/jsrr/2024/v30i82276
Singh, Y. P., Singh, R. K. (2022). “Farmer’s participatory genetic and agronomic approaches for higher rice productivity in sodicity stress,” in The 2nd International Laayoune Forum on Biosaline Agriculture (MDPI, Basel Switzerland), 52.
Soda, N., Kushwaha, H. R., Soni, P., Singla-Pareek, S. L., Pareek, A. (2013). A suite of new genes defining salinity stress tolerance in seedlings of contrasting rice genotypes. Funct. Integr. Genomics 13, 351–365. doi: 10.1007/s10142-013-0328-1
Solis, C. A., Yong, M. T., Vinarao, R., Jena, K., Holford, P., Shabala, L., et al. (2020). Back to the wild: on a quest for donors toward salinity tolerant rice. Front. Plant Sci. 11. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.00323
Song, Y., Yu, K., Zhang, S., Li, Y., Xu, C., Qian, H., et al. (2024). Poplar glutathione S-transferase PtrGSTF8 contributes to reactive oxygen species scavenging and salt tolerance. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 212, 108766. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2024.108766
Song, P., Zhao, B., Sun, X., Li, L., Wang, Z., Ma, C., et al. (2023). Effects of Bacillus subtilis HS5B5 on Maize Seed Germination and Seedling Growth under NaCl Stress Conditions. Agronomy. 13, 1874. doi: 10.3390/agronomy13071874
Songtoasesakul, D., Aesomnuk, W., Pannak, S., Siangliw, J. L., Siangliw, M., Toojinda, T., et al. (2023). QTL-seq Identifies Pokkali-Derived QTLs and Candidate Genes for Salt Tolerance at Seedling Stage in Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Agriculture. 13, 1596. doi: 10.3390/agriculture13081596
Stein, S., Shalev, E., Sivan, O., Yechieli, Y. (2023). Challenges and approaches for management of seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers. Hydrogeol J. 31, 19–22. doi: 10.1007/s10040-022-02575-5
Sturme, M. H. J., van der Berg, J. P., Bouwman, L. M. S., De Schrijver, A., de Maagd, R. A., Kleter, G. A., et al. (2022). Occurrence and nature of off-target modifications by CRISPR-cas genome editing in plants. ACS Agric. Sci. Technol. 2, 192–201. doi: 10.1021/acsagscitech.1c00270
Stutsel, B., Johansen, K., Malbéteau, Y. M., McCabe, M. F. (2021). Detecting plant stress using thermal and optical imagery from an unoccupied aerial vehicle. Front. Plant Sci. 12. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.734944
Sugasi, Y. D., Srivastava, A., Badri, J., Pandey, M., Parmar, B., Singh, A. K., et al. (2024). Mapping quantitative trait loci (QTLs) for reproductive stage salinity tolerance in rice. Crops. 4, 684–700. doi: 10.3390/crops4040047
Suprasanna, P., Nikalje, G. C., Rai, A. N. (2016). “Osmolyte accumulation and implications in plant abiotic stress tolerance,” in Osmolytes and Plants Acclimation to Changing Environment: Emerging Omics Technologies (Springer India, New Delhi), 1–12.
Tabassam, T., Hyder, S. I., Manzoor, R., Suthar, V., Arshad, N. (2022). Influence of manganese on nutrient uptake in rice plants under saline conditions. Asian Res. J. Agric., 36–46. doi: 10.9734/arja/2022/v15i130149
Tabassam, T., Kanwal, S., Saqlan Naqvi, S. M., Ali, A., Zaman, B., Akhtar, M. E. (2016). Effect of manganese application on PS-II activity in rice under saline conditions. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 18, 837–843. doi: 10.17957/IJAB/15.0180
Tadesse, W. (2021). Wheat breeding for resistance to major insect pests. Agric. Res. Technol. Open Access J. 25. doi: 10.19080/ARTOAJ.2021.25.556321
Tahir, M. U., El-Hendawy, S., Al-Suhaibani, N. (2024). Comparative performance of ionic and agro-physiological traits for detecting salt tolerance in wheat genotypes grown in real field conditions. Life. 14, 1487. doi: 10.3390/life14111487
Tanger, P., Klassen, S., Mojica, J. P., Lovell, J. T., Moyers, B. T., Baraoidan, M., et al. (2017). Field-based high throughput phenotyping rapidly identifies genomic regions controlling yield components in rice. Sci. Rep. 7, 42839. doi: 10.1038/srep42839
Tarolli, P., Park, E., Luo, J., Masin, R. (2025). Preserving coastal agriculture: Nature-based solutions for the mitigation of soil salinization. doi: 10.5194/egusphere-egu24-4213
Thippani, S., Kumar, S. S., Senguttuvel, P., Madhav, M. S., Reddy, S. N. (2023). Marker Assisted Introgression of Saltol QTL into “APMS 6B” to Enhance Salt Tolerance at Seedling Stage of Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Int. J. Plant Soil Sci. 35, 1074–1082. doi: 10.9734/ijpss/2023/v35i193645
Ulrich, K. (2023). Redox-regulated chaperones in cell stress responses. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 51, 1169–1177. doi: 10.1042/BST20221304
Vanaja, T., Mammootty, K. P., Balakrishnan, P. C., Jayaprakash, N. B. (2017). A high yielding organic rice variety suited for coastal saline and non-saline fields:’Ezhome-2.’ J. Trop. Agric. 4, 21–28.
Verma, A. K., Gupta, S. K., Isaac, R. K. (2012). Use of saline water for irrigation in monsoon climate and deep water table regions: Simulation modeling with SWAP. Agric. Water Manage. 115, 186–193. doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2012.09.005
Walker, G., Hart, B. (2024). Comment on sustainable salinity management in ‘the three-infrastructures framework and water risks in the Murray-Darling Basin, Australia’ by Williams et al. (2022). Australas. J. Water Resour 28, 136–145. doi: 10.1080/13241583.2023.2261162
Wang, Y., Gao, M., Chen, H., Fu, X., Wang, L., Wang, R. (2023). Soil moisture and salinity dynamics of drip irrigation in saline-alkali soil of Yellow River basin. Front. Environ. Sci. 11. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2023.1130455
Wang, C., Tai, H., Chen, Y., Zhai, Z., Zhang, L., Pu, Z., et al. (2025). Soil microbiota modulates root transcriptome with divergent effect on maize growth under low and high phosphorus inputs. Plant Cell Environ. 48, 2132–2144. doi: 10.1111/pce.15281
Wang, M., Wang, R., Sun, Q., Li, Y., Xu, L., Wang, Y. (2024). Integrated drip irrigation regulates soil water–salt movement to improve water use efficiency and maize yield in saline–alkali soil. Water. 16, 2509. doi: 10.3390/w16172509
Wikimedia (2013). Pokkali Rice (Wikipedia). Available online at: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pokkali_Rice.
Williams, J., Colloff, M. J., Grafton, R. Q., Khan, S., Paydar, Z., Wyrwoll, P. (2023). The three-infrastructures framework and water risks in the Murray-Darling Basin, Australia. Australas. J. Water Resour. 27, 47–67. doi: 10.1080/13241583.2022.2151106
Wu, S., Wen, W., Gou, W., Lu, X., Zhang, W., Zheng, C., et al. (2022). A miniaturized phenotyping platform for individual plants using multi-view stereo 3D reconstruction. Front. Plant Sci. 13. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.897746
Wu, Y., Zhang, G., Zhang, C., Tang, W., Wang, T., Zhang, H., et al. (2024). Pooled mapping of QTLs associated with salt tolerance traits at seedling stage in rice. Bangladesh J. Bot. 53, 405–410. doi: 10.3329/bjb.v53i2.74431
Xiao, F., Zhou, H. (2023). Plant salt response: Perception, signaling, and tolerance. Front. Plant Sci. 13. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1053699
Xing, M., Nie, Y., Huang, J., Li, Y., Zhao, M., Wang, S., et al. (2024). A wild rice CSSL population facilitated identification of salt tolerance genes and rice germplasm innovation. Physiol. Plant 176. doi: 10.1111/ppl.v176.2
Xue, M., Han, X., Zhang, L., Chen, S. (2024). Heat-resistant inbred lines coordinate the heat response gene expression remarkably in maize (Zea mays L.). Genes (Basel) 15, 289. doi: 10.3390/genes15030289
Yadav, A. K., Kumar, A., Grover, N., Ellur, R. K., Krishnan, S. G., Bollinedi, H., et al. (2020). Marker aided introgression of ‘Saltol’, a major QTL for seedling stage salinity tolerance into an elite Basmati rice variety ‘Pusa Basmati 1509’. Scientific Reports 10, 13877. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-70664-0
Yadav, R. K., Tripathi, M. K., Tiwari, S., Tripathi, N., Asati, R., Chauhan, S., et al. (2023). Genome editing and improvement of abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Life. 13, 1456. doi: 10.3390/life13071456
Yahyaoui, H., El Allaoui, N., Aziz, A., Hafidi, M., Habbadi, K. (2024). Minimizing the adverse impacts of soil salinity on maize and tomato growth and productivity through the application of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Crops. 4, 463–479. doi: 10.3390/crops4040033
Yang, W., Guo, Z., Huang, C., Duan, L., Chen, G., Jiang, N., et al. (2014). Combining high-throughput phenotyping and genome-wide association studies to reveal natural genetic variation in rice. Nat. Commun. 5, 5087. doi: 10.1038/ncomms6087
Yassue, R. M., Galli, G., Borsato, R., Cheng, H., Morota, G., Fritsche-Neto, R. (2022). A low-cost greenhouse-based high-throughput phenotyping platform for genetic studies: A case study in maize under inoculation with plant growth-promoting bacteria. Plant Phenome J. 5. doi: 10.1002/ppj2.20043
Yin, W., Lu, T., Chen, Z., Lu, T., Ye, H., Mao, Y., et al. (2023). Quantitative trait locus mapping and candidate gene analysis for salt tolerance at bud stage in rice. Front. Plant Sci. 13. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1041081
Yoo, M. J., Hwang, Y., Koh, Y. M., Zhu, F., Deshpande, A. S., Bechard, T., et al. (2024). Physiological and molecular modulations to drought stress in the brassica species. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25, 3306. doi: 10.3390/ijms25063306
Yoshimura, K., Ishikawa, T. (2024). Physiological function and regulation of ascorbate peroxidase isoforms. J. Exp. Bot. 75, 2700–2715. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erae061
Yu, Y., Li, Y., Yan, Z., Duan, X. (2022). The role of cytokinins in plant under salt stress. J. Plant Growth Regul. 41, 2279–2291. doi: 10.1007/s00344-021-10441-z
Yu, P., Ye, C., Li, L., Yin, H., Zhao, J., Wang, Y., et al. (2022). Genome-wide association study and genomic prediction for yield and grain quality traits of hybrid rice. Mol. Breed. 42, 16. doi: 10.1007/s11032-022-01289-6
Zayed, B. A., El-Hendawy, S., Hu, Y., Okasha, A. M., Abdelhamed, M. M., Ghazy, H. A., et al. (2024). Enhancing the photosynthetic and yield performance of rice in saline soil by foliar-applying cost-effective compounds as sources of carbon dioxide and potassium. Agronomy. 14, 2850. doi: 10.3390/agronomy14122850
Zhang, Y., Guo, Z., Chen, X., Li, X., Shi, Y., Xu, L., et al. (2024a). Identification candidate genes for salt resistance through quantitative trait loci-sequencing in Brassica napus L. J. Plant Physiol. 294, 154187. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2024.154187
Zhang, X., Ibrahim, Z., Khaskheli, M. B., Raza, H., Zhou, F., Shamsi, I. H. (2024). Integrative approaches to abiotic stress management in crops: combining bioinformatics educational tools and artificial intelligence applications. Sustainability. 16, 7651. doi: 10.3390/su16177651
Zhang, Y., Wang, H., Zhang, X., Feng, Z., Liu, J., Wang, Y., et al. (2024b). Effects of salt stress on the rhizosphere soil microbial communities of Suaeda salsa (L.) Pall. in the Yellow River Delta. Ecol. Evol. 14. doi: 10.1002/ece3.70315
Zhao, K., Fan, G., Yao, W., Cheng, Z., Zhou, B., Jiang, T. (2024). PagMYB73 enhances salt stress tolerance by regulating reactive oxygen species scavenging and osmotic maintenance in poplar. Ind. Crops Prod. 208, 117893. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2023.117893
Zhao, P., Sun, L., Zhang, S., Jiao, B., Wang, J., Ma, C. (2024). Integrated Transcriptomics and Metabolomics Analysis of Two Maize Hybrids (ZD309 and XY335) under Heat Stress at the Flowering Stage. Genes (Basel) 15, 189. doi: 10.3390/genes15020189
Zhao, S., Zhang, Q., Liu, M., Zhou, H., Ma, C., Wang, P. (2021). Regulation of plant responses to salt stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 4609. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094609
Zhou, G., Liu, C., Cheng, Y., Ruan, M., Ye, Q., Wang, R., et al. (2022). Molecular evolution and functional divergence of stress-responsive Cu/Zn superoxide dismutases in plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 7082. doi: 10.3390/ijms23137082
Keywords: salt tolerance, spermidine treatments, quantitative trait loci (QTLs), global food security, CRISPR-Cas9 applications, oryza sativa
Citation: Sackey OK, Feng N, Mohammed YZ, Dzou CF, Zheng D, Zhao L and Shen X (2025) A comprehensive review on rice responses and tolerance to salt stress. Front. Plant Sci. 16:1561280. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1561280
Received: 15 January 2025; Accepted: 10 March 2025;
Published: 31 March 2025.
Edited by:
Meng Jiang, Zhejiang University, ChinaReviewed by:
Masood Jan, University of Florida, Gainesville, United StatesCopyright © 2025 Sackey, Feng, Mohammed, Dzou, Zheng, Zhao and Shen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xuefeng Shen, c2hlbnh1ZWZlbmdAZ2RvdS5lZHUuY24=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.