
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Plant Sci., 08 April 2025
Sec. Plant Systematics and Evolution
Volume 16 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2025.1558995
Astereae, the second-largest tribe within Asteraceae, includes numerous species of economic and medicinal importance. While comprehensive systematic studies have been conducted on Astereae classification, certain controversies remain unresolved. The taxonomic boundaries between alpine Aster and Erigeron are uncertain due to their morphological similarity, and the systematic placement of Formania mekongensis remains debated. To address these issues, we applied a combination of morphological and molecular phylogenetic approaches. 21 species from 12 genera within Astereae were selected based on a morphological and molecular phylogenetic framework. Sampling, experiments, photography, and measurements were conducted using standardized methods, resulting in 12 pollen trait parameters. These parameters were then used to construct a hierarchical dendrogram of pollen morphology. A molecular phylogeny was constructed based on ITS sequences to further elucidate the systematic relationships among these species. The results revealed that pollen morphology provides valuable insights into subtribal classifications. Significant differences in pollen size and spine morphology were observed between Aster and Erigeron, with the former exhibiting larger pollen grains with long, broad, and sparsely distributed spines. Clustering results also provided the first palynological evidence for placing F. mekongensis within Asterinae. This study underscores the importance of integrating pollen morphology and molecular evidence to refine the classification and phylogeny of Astereae.
Morphological and molecular data provide essential evidence for estimating evolutionary relationships in plants (Sattler and Rutishauser, 1997, 2022; Janaćković et al., 2019; Bog et al., 2020; Sattler, 2022; Zhang et al., 2024). While molecular techniques offer insights at the genetic level, morphological analysis remains fundamental for understanding phenotypic evolution (Wanninger, 2015). The combined use of these approaches has improved the resolution of classification and phylogenetic relationships (Wortley and Scotland, 2006; Huang et al., 2013; Bapst et al., 2018; Keating et al., 2023). Pollen morphology serves as a valuable tool for species identification and classification due to its conserved characteristics (Wang and Wang, 1983; Dajoz et al., 1991; Blackmore, 2007; Lin et al., 2023). These stable features make pollen morphology particularly useful in plant systematics (Hesse and Blackmore, 2013; Lacourse et al., 2016; Bahadur et al., 2018). Integrating morphological data with other approaches may further advance our understanding in this field.
Astereae is the second-largest tribe within Asteraceae, comprising approximately 222 genera and 3,100 species (Ling et al., 1985; Anderberg et al., 2007; Funk et al., 2009). Its classification remains challenging, partly due to the limited sampling (Brouillet et al., 2009; Li et al., 2012). The taxonomic framework of Astereae has undergone notable revisions since Bentham’s (1873) initial division into six subtribes: Solidagininae, Grangeinae, Bellidinae, Asterinae, Conyzinae, and Baccharidinae. Zhang and Bremer (1993) later redefined this classification, recognizing Grangeinae as basal and consolidating the remaining taxa into two primary subtribes: Solidagininae and Asterinae. Nesom (1994) further refined the classification system by establishing 14 subtribes based on morphological features. Despite these advances, several taxonomic uncertainties persist. Notably, the morphological convergence between alpine Aster and Erigeron has resulted in ambiguous generic boundaries (Cronquist, 1955; Nesom, 1994). The systematic position of the monophyletic F. mekongensis has puzzled taxonomists for a long time. While Shi and Fu (1983) classified it within Chrysantheminae (Anthemideae), Chen and Brouillet (2011b) regarded its taxonomic placement as unresolved. Molecular phylogenetic evidence later prompted Fu et al. (2016) to suggest its inclusion in Astereae, and more recently, Nesom (2020) assigned it to the newly established subtribe Formaniinae. These studies highlight the necessity for integrated systematic approaches in Astereae classification.
Pollen morphology has long been employed to address taxonomic questions within the Asteraceae (Tellería, 2017; Younis et al., 2021; Lu et al., 2022; Usma et al., 2022; Ali et al., 2023; Hayat et al., 2023). Key pollen characteristics, including size, shape, aperture type, and exine ornamentation, provide valuable insights for taxonomic classification (Ahmad et al., 2018; Reshmi and Rajalakshm, 2019). Wortley et al. (2007) demonstrated its importance in resolving the classification of problematic taxa. Peng et al. (2023) used pollen morphology to examine Blumea and Cyathocline, revealing discrepancies between palynological evidence and molecular phylogenetic analyses in certain groups. Nevertheless, research on the pollen morphology of Astereae remains limited (Zhang and Zhou, 2016). Few studies have explored the integration of pollen data with molecular evidence, and such combined approaches may help clarify taxonomic boundaries within the tribe.
This study aims to explore the role of pollen traits in the classification of Astereae by integrating pollen morphological data with molecular phylogenetic frameworks. Systematic sampling was conducted on 12 pollen traits across 21 representative species. The specific objectives are as follows: (1) to compare the clustering dendrogram of pollen traits with the molecular phylogenetic tree and evaluate the relevance of pollen traits in systematics; (2) to analyze the pollen morphological differences and phylogenetic relationships among subtribes and genera within Astereae; and (3) to provide foundational pollen data for the taxonomic study of Astereae. This work presents a new perspective on Astereae classification and contributes to the integration of morphological and molecular evidence.
To systematically analyze pollen morphological variation in Astereae, we conducted light microscopy (LM) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) examinations, following the phylogenetic frameworks for Asteraceae outlined by Li et al. (2012). The subtribal classification was based on Anderberg et al. (2007), which employed morphological diagnostic characters for systematic identification. A total of 21 taxonomically representative species spanning Aster, Erigeron, and related genera, were included in this study. Specimens were selected from voucher sheets in the PE herbarium at the Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences (Table 1). All pollen samples, along with the scientific names of genera and species, were verified against the Flora of China (Shi et al., 2011) and Plants of the World Online (POWO, https://powo.science.kew.org/, last access: 1 March 2025).
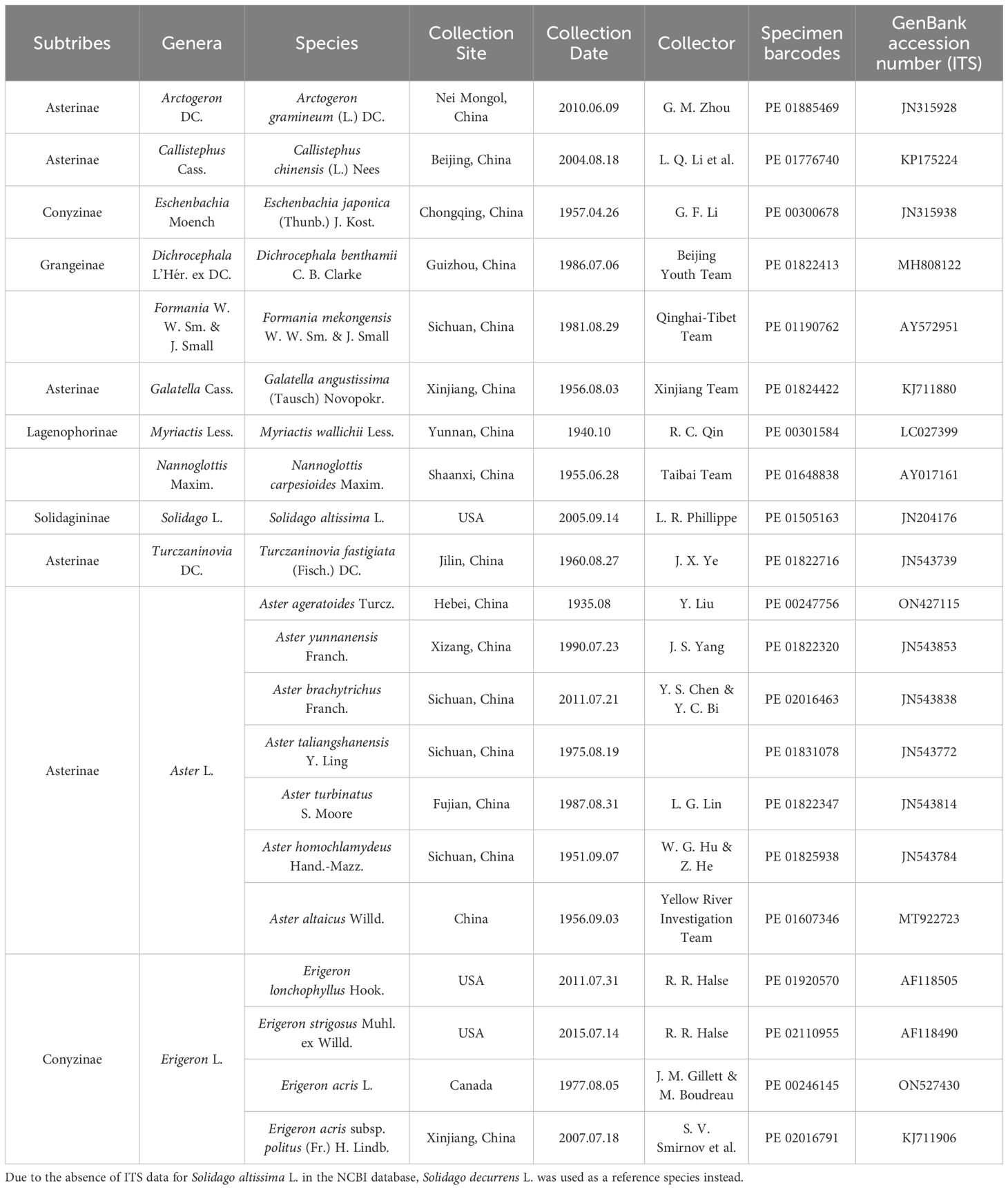
Table 1. List of the voucher specimens in PE Herbarium, Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences and the GenBank Numbers.
Pollen samples were acetolysed by the standard methods (Erdtman, 1960) and fixed in glycerine jelly. Processing and observation under LM and SEM followed standard procedures (Wang et al., 1995). The pollen grains were observed and photographed at a magnification of ×600 under LM (Leica DM 4000) and at an accelerating voltage of 30 kV under SEM (Hitachi S-4800). Descriptions of pollen morphology were based on the terminology systems proposed by Halbritter et al. (2018) and Hesse et al. (2009). As shown in Figure 1, the pollen morphological traits measured under LM included P: polar length in equatorial view; E: equatorial width in equatorial view; P/E; T: exine thickness in polar view; L: pollen length in polar view; T/L. Each trait was measured on 20 pollen grains per species. The exine ornamentation traits measured under SEM included D: diameter of spinule base; H: spinule height; D/H; Ss: spinule spacing. For these four traits, measurements were taken on five pollen grains per trait, with four randomly selected regions per pollen grain, yielding 20 measurements per trait (Lu et al., 2022). Given the sample sizes of Galatella angustissima (n=16) and Aster taliangshanensis (n=15), the mean values of the available data were used to supplement the missing samples, ensuring a complete and representative sample size of 20 for statistical analysis. The sexine/nexine (S/N) ratio was measured based on LM observations of the exine structure (Table 2; Supplementary Data).
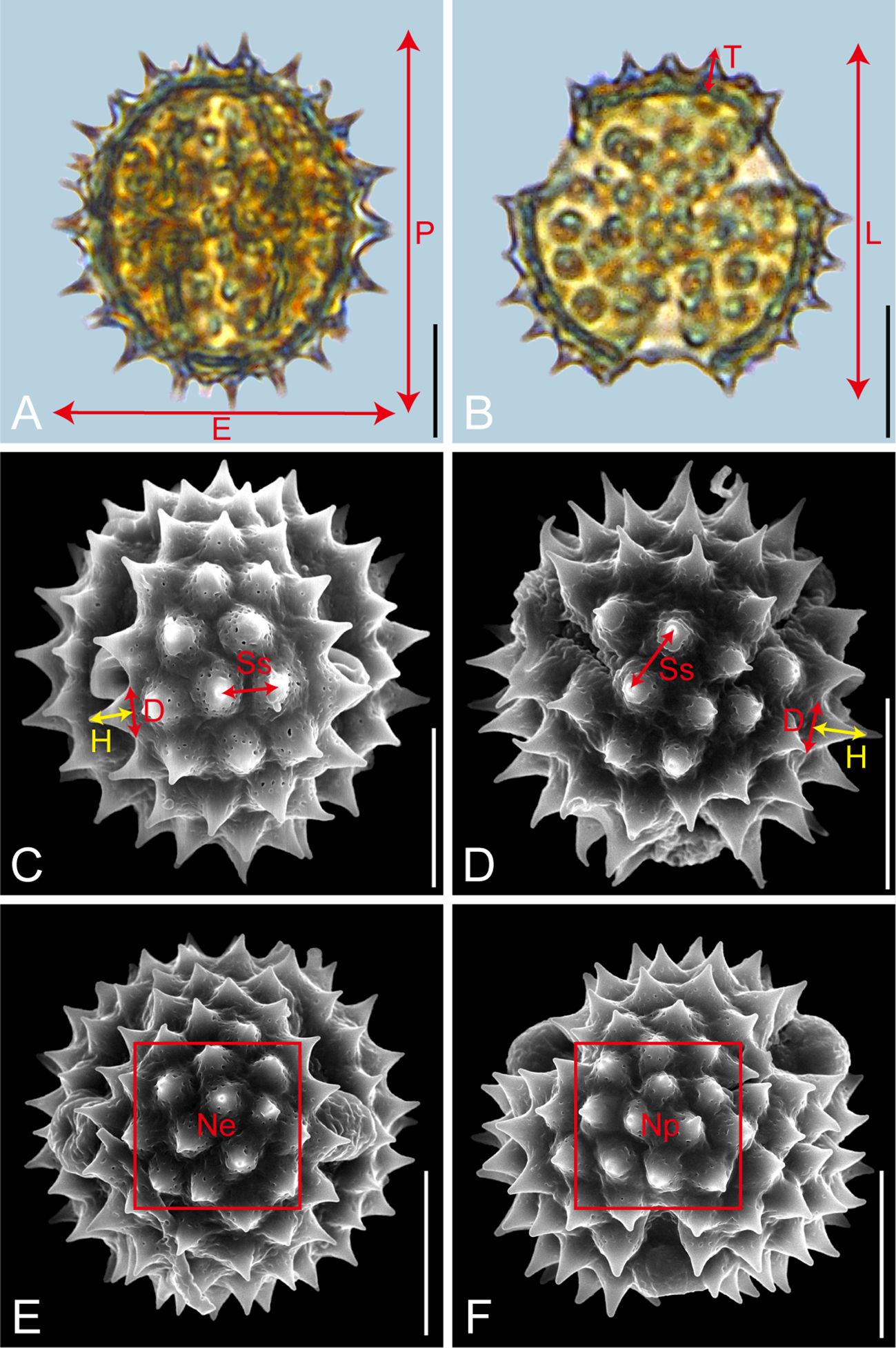
Figure 1. Graphical illustration of measured pollen morphological traits in Astereae (A, Myriactis wallichii; B, Erigeron lonchophyllus; C, Galatella angustissima; D, Arctogeron gramineum; E, F, Aster altaicus). Scale bar in LM and SEM overview 10µm, and in SEM close-up 1µm.
Furthermore, for SEM analysis, standard polar and equatorial views of each species were selected. A 10 µm × 10 µm square grid was used to count the spines within, and the resulting trait parameters, termed Np and Ne, were used to characterize the distribution and number of spines in the polar and equatorial views, respectively. The counting rule was: ‘‘count the top, but not the bottom; count the left, but not the right.’ For these views, the mean values (M) and standard deviations (SD) of 10 pollen traits (P, E, P/E, T, L, T/L, D, H, D/H, Ss) were measured and calculated across the 21 representative species. Unlike the other traits, Np and Ne are presented as individual counts rather than M ± SD (Table 2; Supplementary Data).
Pollen trait data were standardized using Z-scores (Andrade, 2021) to eliminate dimensional differences and ensure comparability. The data were then imported into IBM SPSS Statistics 26 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY) for clustering analysis using Ward’s method and squared Euclidean distance. The proximity matrix was converted to Newick format using the “ape” and “readxl” packages in R v4.3.3 (https://www.R-project.org/). Visualization and refinement of the dendrogram were performed in Figtree v1.4.4, generating the hierarchical dendrogram of pollen morphology.
This study constructed a molecular phylogenetic tree based on ITS sequences from 21 species. Initially, the ITS sequences of these species were downloaded from the NCBI database, followed by quality control measures to ensure completeness and accuracy. Due to the temporary unavailability of ITS data for Solidago altissima in the NCBI database, S. decurrens, a congeneric species, was selected as a substitute for subsequent analyses. The ITS sequences were then aligned using MAFFT v.7.520 (Katoh and Standley, 2013) with default parameters to optimize sequence alignment. The aligned sequences were uploaded to the CIPRES Science Gateway platform (https://www.phylo.org/), where a maximum likelihood (ML) method was employed to construct the phylogenetic tree in RAxML (Stamatakis et al., 2008) under the GTR + GAMMA model, with 1,000 bootstrap replicates to enhance reliability. The resulting tree was visualized and adjusted in Figtree v1.4.4 (http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree/), with branch modifications and annotations guided by the findings of Li et al. (2012) to produce the final phylogenetic tree. Throughout the adjustment process, clarity of the branches and integrity of the information were maintained to facilitate interpretation and presentation.
Box plots of the 10 morphological traits measured under LM and SEM were generated using Excel 2019 (Microsoft Corp., Redmond, WA, USA). To further analyze differences in these morphological traits, an analysis of variance (ANOVA) was conducted on pollen morphological traits for all species using SPSS. Additionally, an independent samples t-test was conducted on pollen morphological data from Aster and Erigeron to compare morphological differences between these two genera.
In this study, the Robinson-Foulds (RF) distance method (Briand et al., 2020) was employed to compare the topological structures of the two phylogenetic trees. Initially, both trees were manually imported using a file browser for analysis. The RF distance between the trees was then calculated to assess their topological differences quantitatively. To enhance the interpretability of the results, we normalized the RF distance to produce the Tree Congruence Index (TCI), which quantifies the topological similarity between the two trees. A TCI value closer to 1 indicates higher topological similarity between the trees (de Vienne et al., 2007; Mir et al., 2013).
Detailed pollen morphological data observed under LM and SEM, along with habitat information for the 21 sampled species, are presented in Figures 2–8. Table 2 summarizes the quantitative values of pollen morphological traits for these species. Except for Np and Ne traits, the remaining 10 morphological characteristics are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (M ± SD). Table 3 presents the qualitative morphological traits of pollen, providing an overview of its key characteristics. Box plots (Figure 9) depict the distribution patterns of these data, highlighting the interquartile range (25%-75%). The specific trait information for each species is detailed in the Supplementary Material.
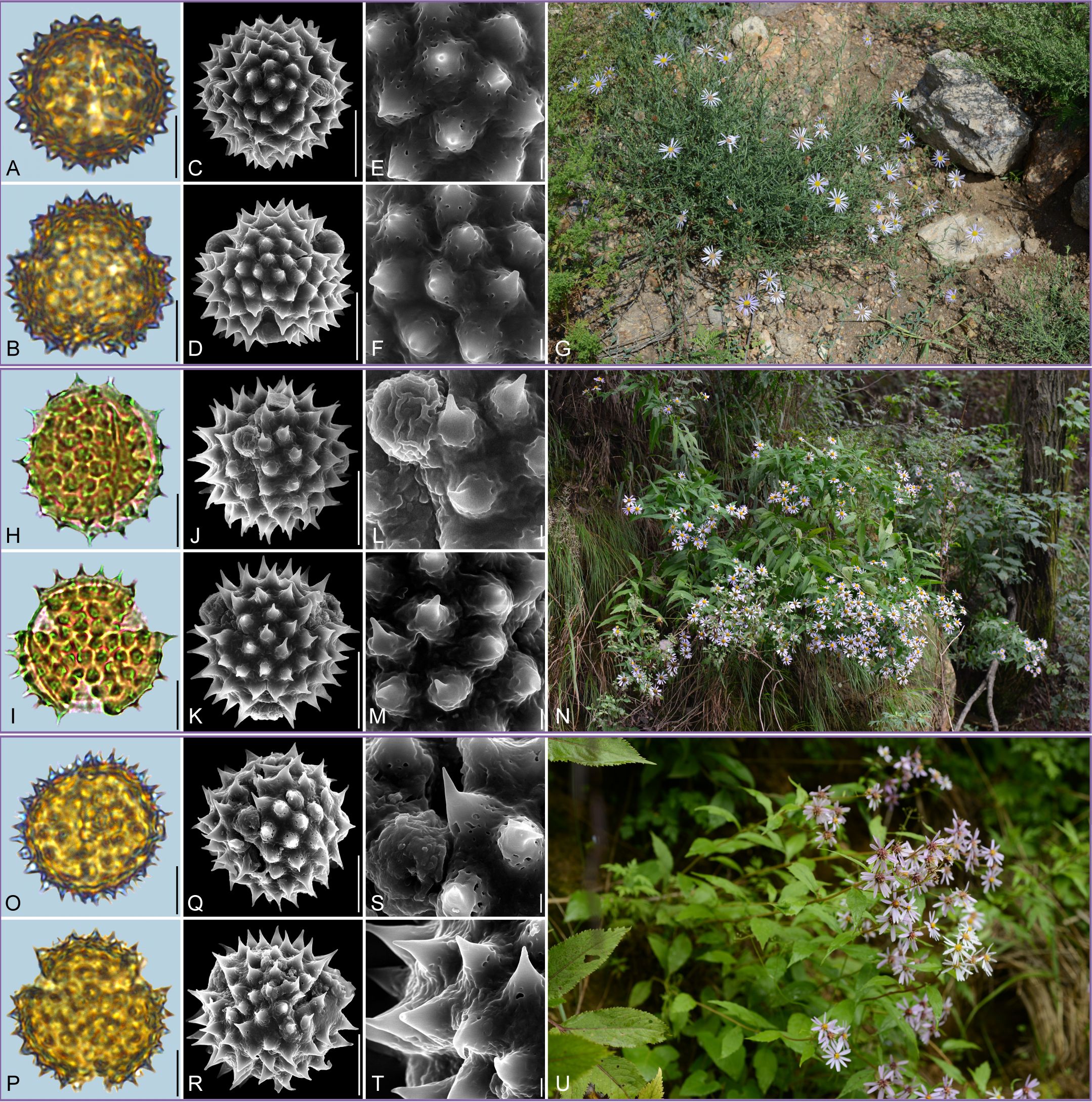
Figure 2. Pollen grains and the habitats of their source plants. (A-G) Aster altaicus; (H-N) Aster ageratoides; and (O-U) Aster homochlamydeus. Pollen grains in equatorial view under LM (A, H, O) and SEM (C, E, J, L, Q, S), in polar view under LM (B, I, P) and SEM (D, F, K, M, R, T), along with the habitats of their source plants (G cited from https://ppbc.iplant.cn/tu/10803110, last access: 6 November 2024, by © Y. S. Chen, N cited from https://ppbc.iplant.cn/tu/5937894, last access: 6 November 2024, by © R. (B) Zhu, U cited from https://ppbc.iplant.cn/tu/10697277, last access: 6 November 2024, by © Y. S. Chen). Scale bar in LM and SEM overview 10µm, and in SEM close-up 1µm.
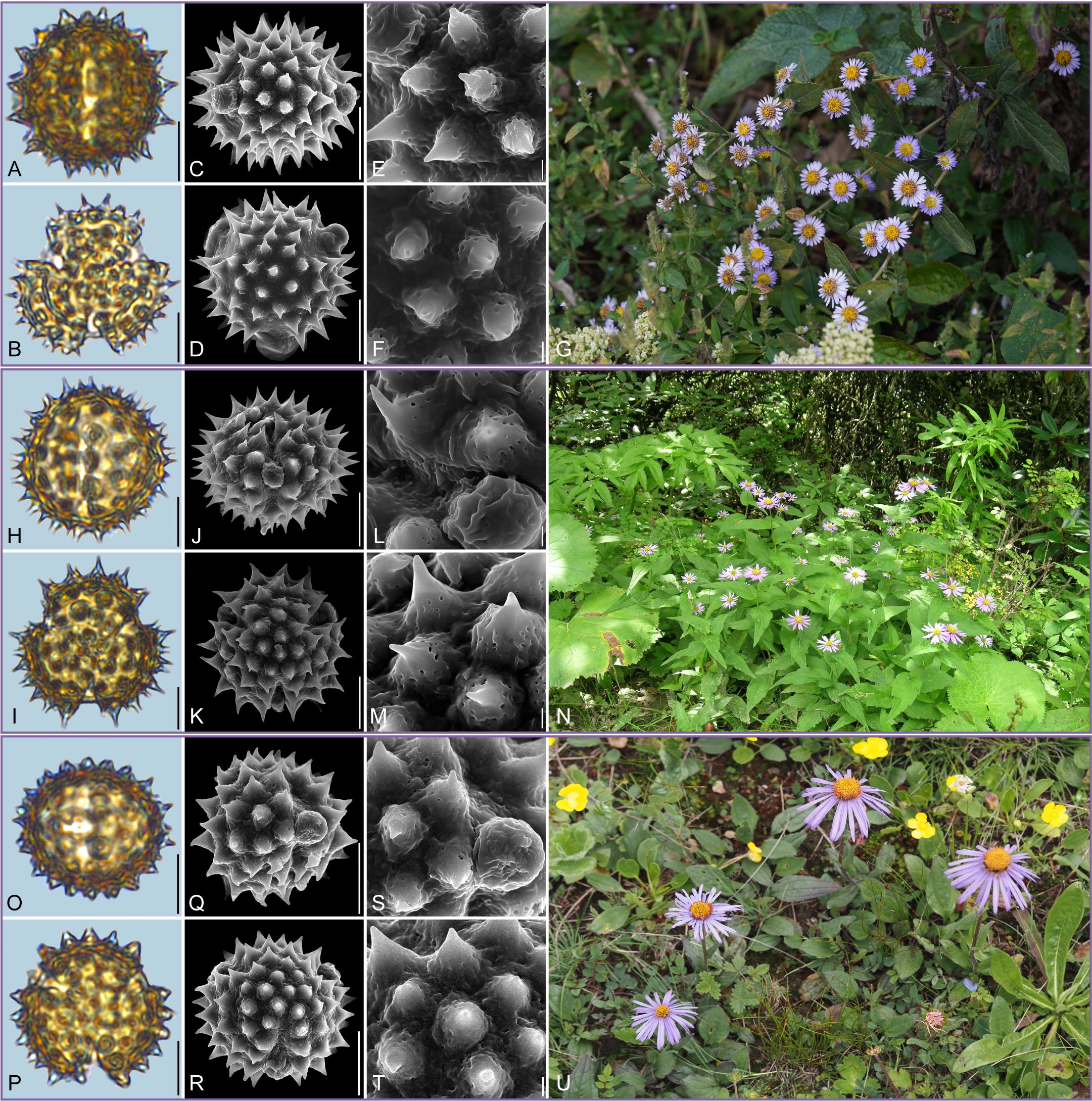

Figure 3. Pollen grains and the habitats of their source plants. (A-G) Aster turbinatus; (H-N) Aster taliangshanensis; and (O-U) Aster brachytrichus. Pollen grains in equatorial view under LM (A, H, O) and SEM (C, E, J, L, Q, S), in polar view under LM (B, I, P) and SEM (D, F, K, M, R, T), along with the habitats of their source plants (G cited from https://ppbc.iplant.cn/tu/15652366, last access: 6 November 2024, by © X. Y. Ye, N cited from https://ppbc.iplant.cn/tu/451749, last access: 6 November 2024, by © Y. S. Chen, U cited from https://ppbc.iplant.cn/tu/15002989, last access: 6 November 2024, by © Y. S. Chen). Scale bar in LM and SEM overview 10µm, and in SEM close-up 1µm.
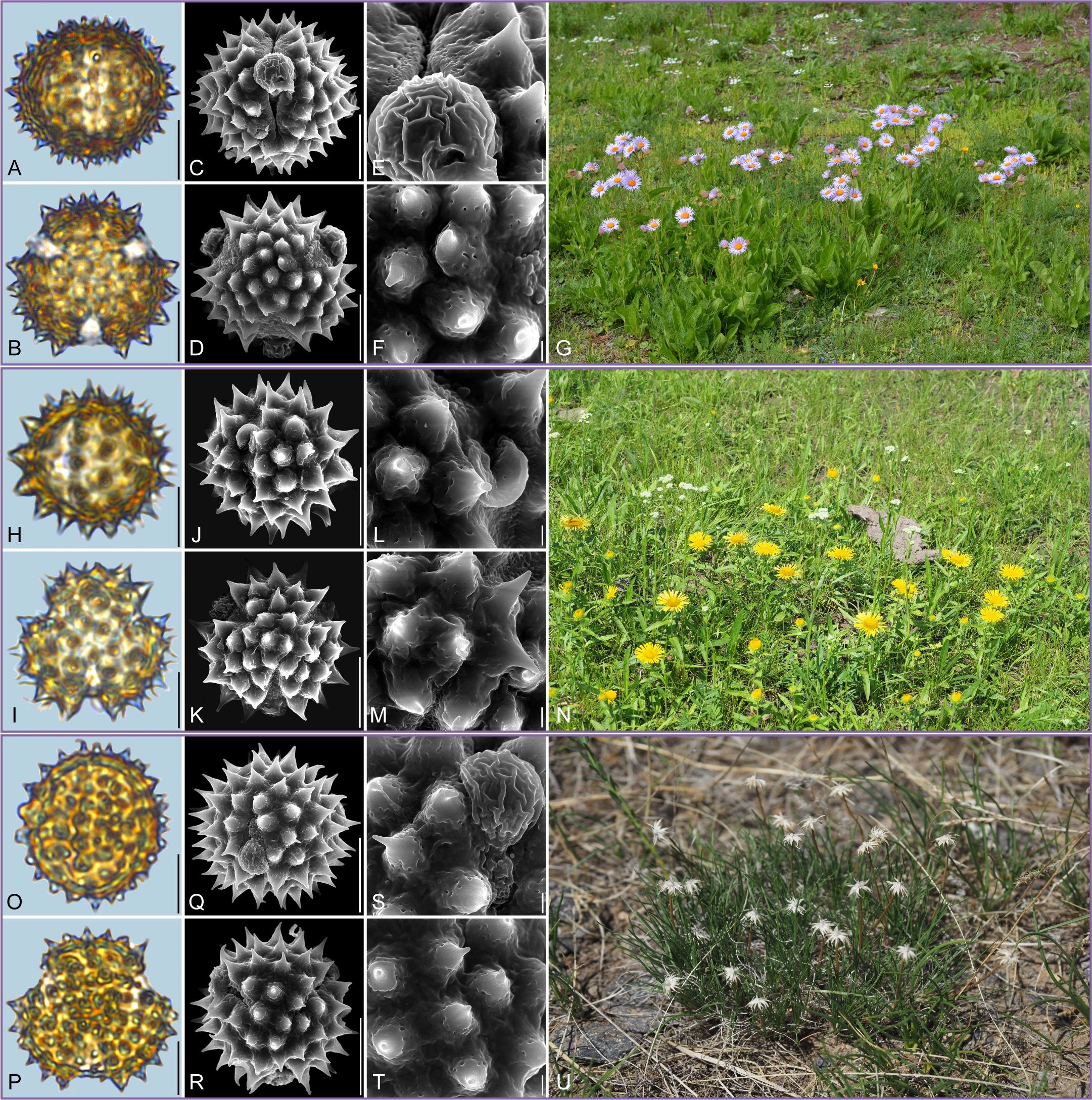

Figure 4. Pollen grains and the habitats of their source plants. (A-G) Aster yunnanensis; (H-N) Turczaninovia fastigiata; and (O-U) Arctogeron gramineum. Pollen grains in equatorial view under LM (A, H, O) and SEM (C, E, J, L, Q, S), in polar view under LM (B, I, P) and SEM (D, F, K, M, R, T), along with the habitats of their source plants (G cited from https://ppbc.iplant.cn/tu/11716277, last access: 6 November 2024, by © Y. P. Zeng, N cited from https://ppbc.iplant.cn/tu/8233925, last access: 6 November 2024, by © Q. W. Lin, U cited from https://ppbc.iplant.cn/tu/8258978, last access: 6 November 2024, by © Q. W. Lin). Scale bar in LM and SEM overview 10µm, and in SEM close-up 1µm.
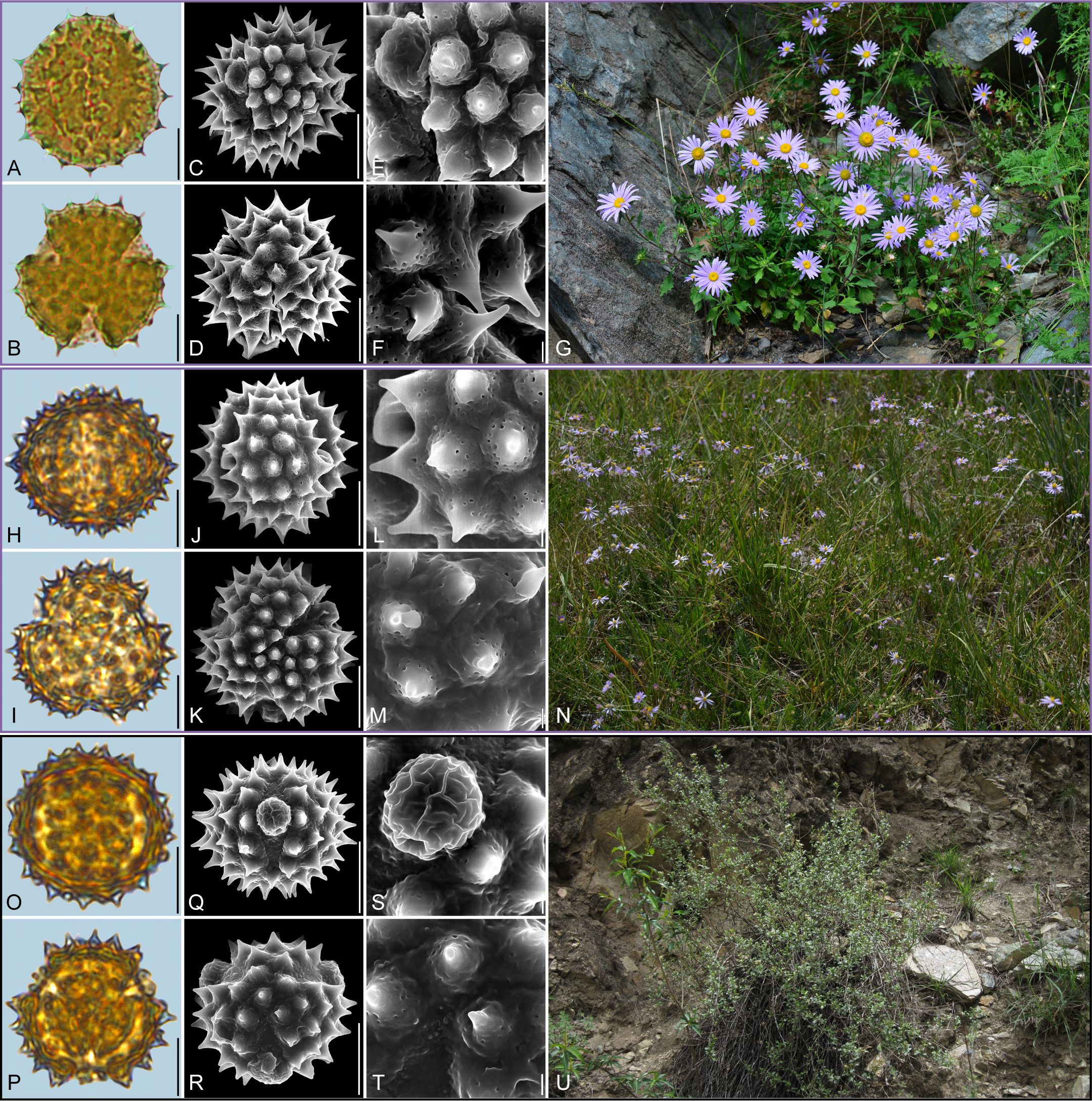
Figure 5. Pollen grains and the habitats of their source plants. (A-G) Callistephus chinensis; (H-N) Galatella angustissima; and (O-U) Formania mekongensis. Pollen grains in equatorial view under LM (A, H, O) and SEM (C, E, J, L, Q, S), in polar view under LM (B, I, P) and SEM (D, F, K, M, R, T), along with the habitats of their source plants (G cited from https://ppbc.iplant.cn/tu/2409876, last access: 6 November 2024, by © R. (B) Zhu, N cited from https://ppbc.iplant.cn/tu/10824525, last access: 6 November 2024, by © Y. S. Chen, U cited from https://ppbc.iplant.cn/tu/836417, last access: 6 November 2024, by © Y. S. Chen). Scale bar in LM and SEM overview 10µm, and in SEM close-up 1µm.
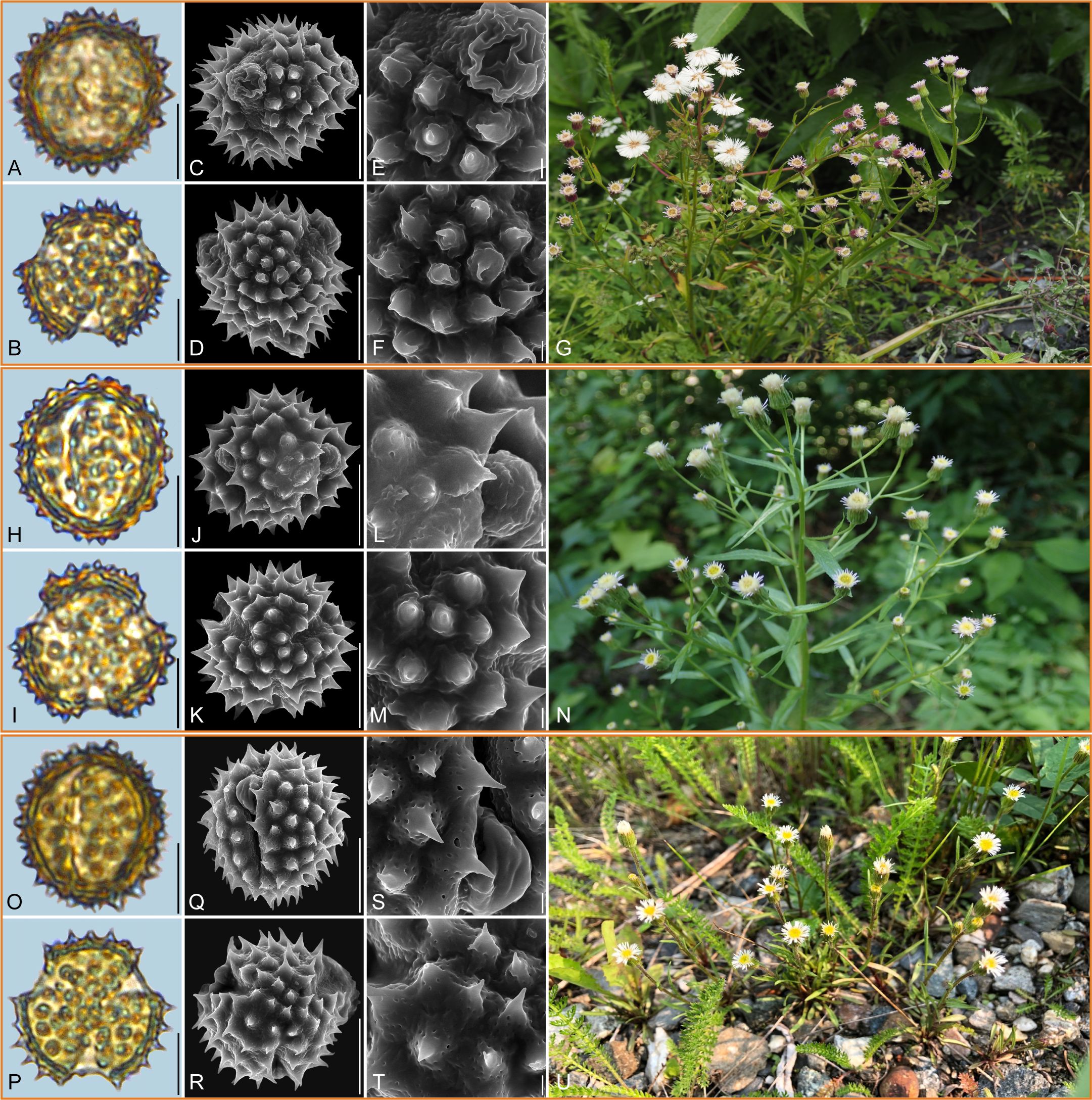

Figure 6. Pollen grains and the habitats of their source plants. (A-G) Erigeron acris; (H-N) Erigeron acris subsp. politus; and (O-U) Erigeron lonchophyllus. Pollen grains in equatorial view under LM (A, H, O) and SEM (C, E, J, L, Q, S), in polar view under LM (B, I, P) and SEM (D, F, K, M, R, T), along with the habitats of their source plants (G cited from https://ppbc.iplant.cn/tu/15006256, last access: 6 November 2024, by © Y. S. Chen, N cited from https://ppbc.iplant.cn/tu/8196316, last access: 6 November 2024, by © Q. W. Lin, U cited from https://www.inaturalist.org/observations/28542542, last access: 6 November 2024, by © J. Grant). Scale bar in LM and SEM overview 10µm, and in SEM close-up 1µm.
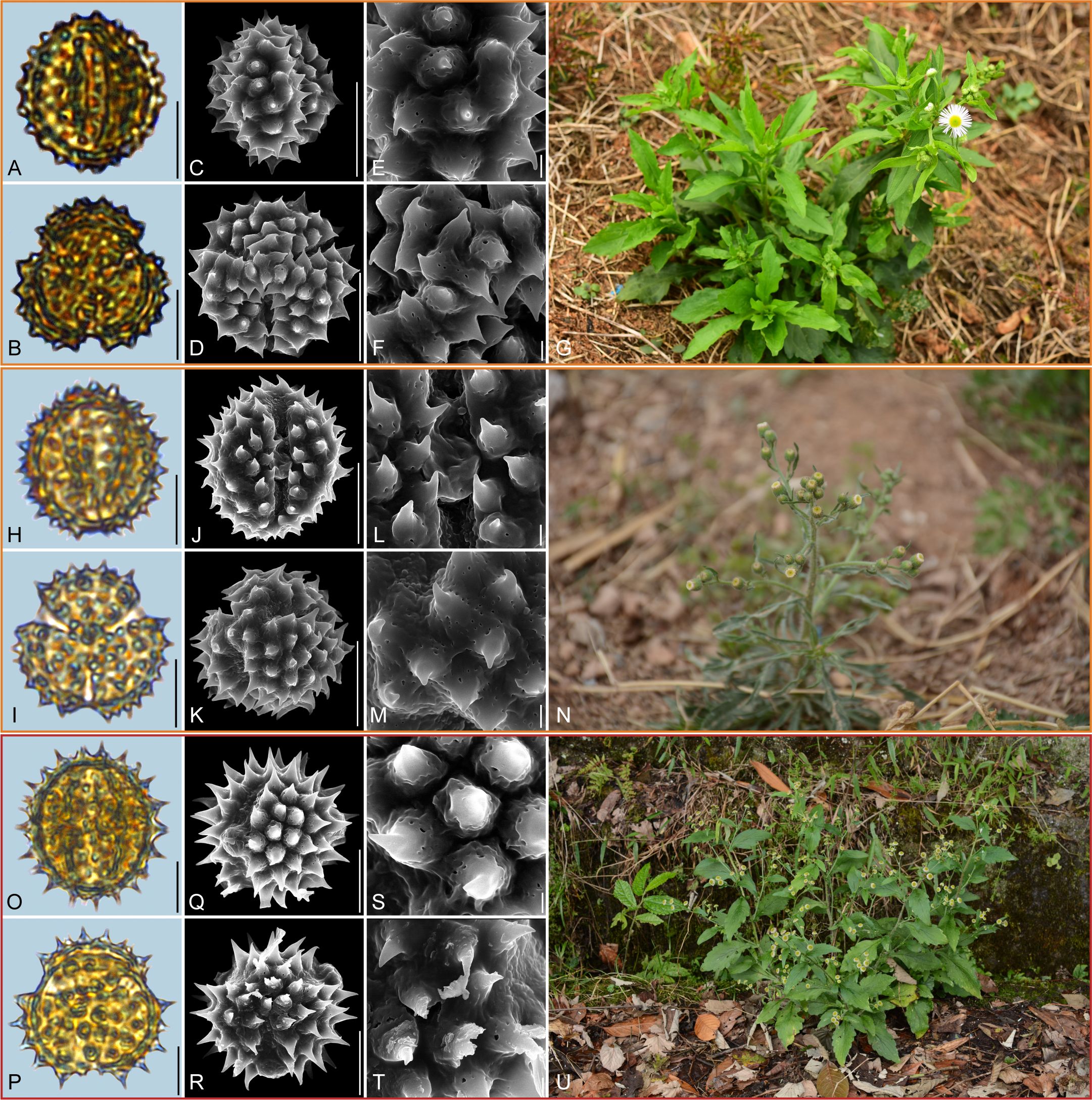

Figure 7. Pollen grains and the habitats of their source plants. (A-G) Erigeron strigosus; (H-N) Eschenbachia japonica; and (O-U) Myriactis wallichii. Pollen grains in equatorial view under LM (A, H, O) and SEM (C, E, J, L, Q, S), in polar view under LM (B, I, P) and SEM (D, F, K, M, R, T), along with the habitats of their source plants (G cited from https://ppbc.iplant.cn/tu/7206727, last access: 6 November 2024, by © A. Liu, N cited from https://ppbc.iplant.cn/tu/11445230, last access: 6 November 2024, by © Y. P. Zeng, U cited from https://ppbc.iplant.cn/tu/11461423, last access: 6 November 2024, by © Y. P. Zeng). Scale bar in LM and SEM overview 10µm, and in SEM close-up 1µm.
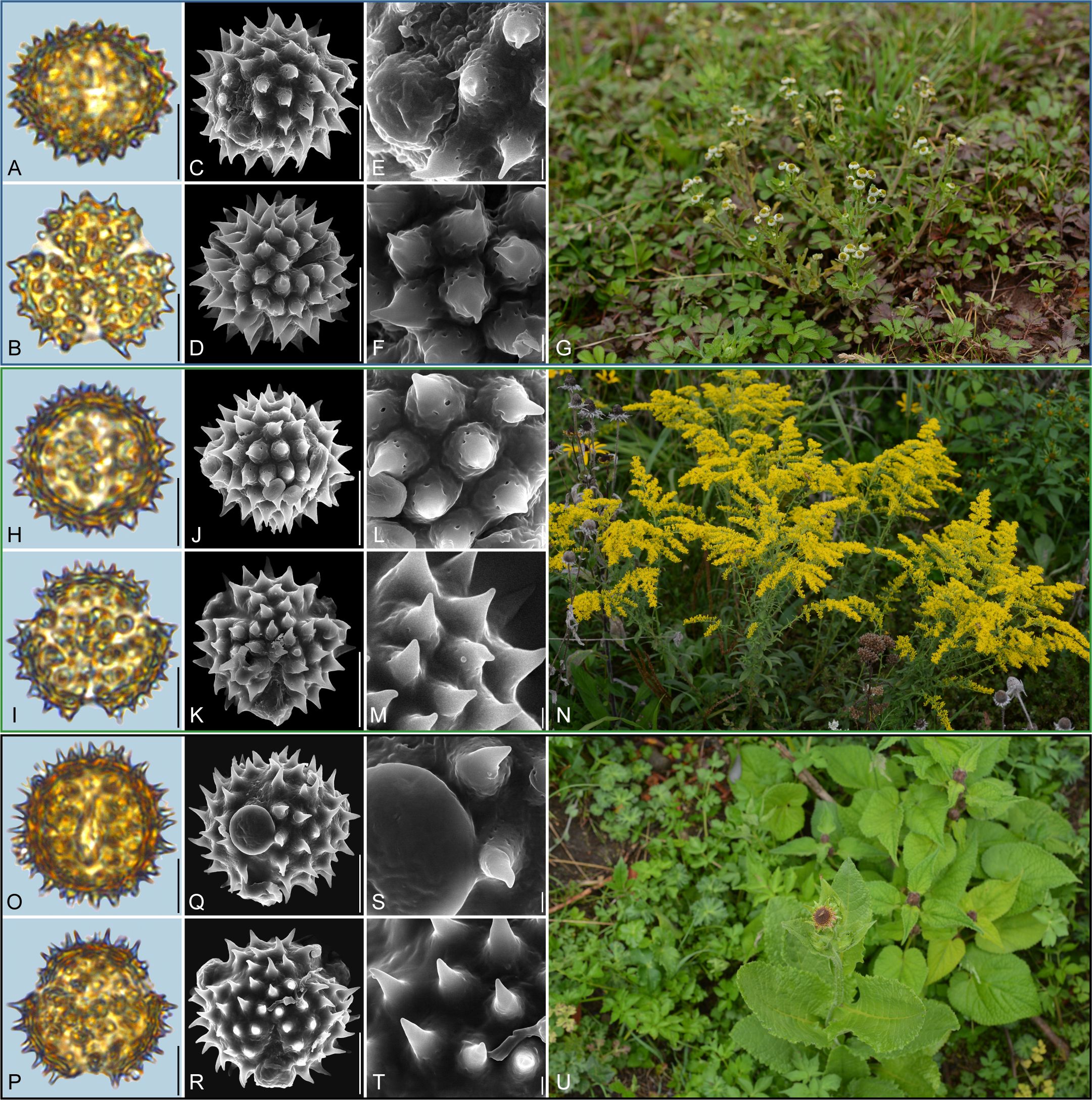
Figure 8. Pollen grains and the habitats of their source plants. (A-G) Dichrocephala benthamii; (H-N) Solidago altissima; and (O-U) Nannoglottis carpesioides. Pollen grains in equatorial view under LM (A, H, O) and SEM (C, E, J, L, Q, S), in polar view under LM (B, I, P) and SEM (D, F, K, M, R, T), along with the habitats of their source plants (G cited from https://ppbc.iplant.cn/tu/11457706, last access: 6 November 2024, by © Y. P. Zeng, N cited from https://ppbc.iplant.cn/tu/10518902, last access: 6 November 2024, by © Y. S. Chen, U cited from https://ppbc.iplant.cn/tu/11485800, last access: 6 November 2024, by © Y. P. Zeng). Scale bar in LM and SEM overview 10µm, and in SEM close-up 1µm.
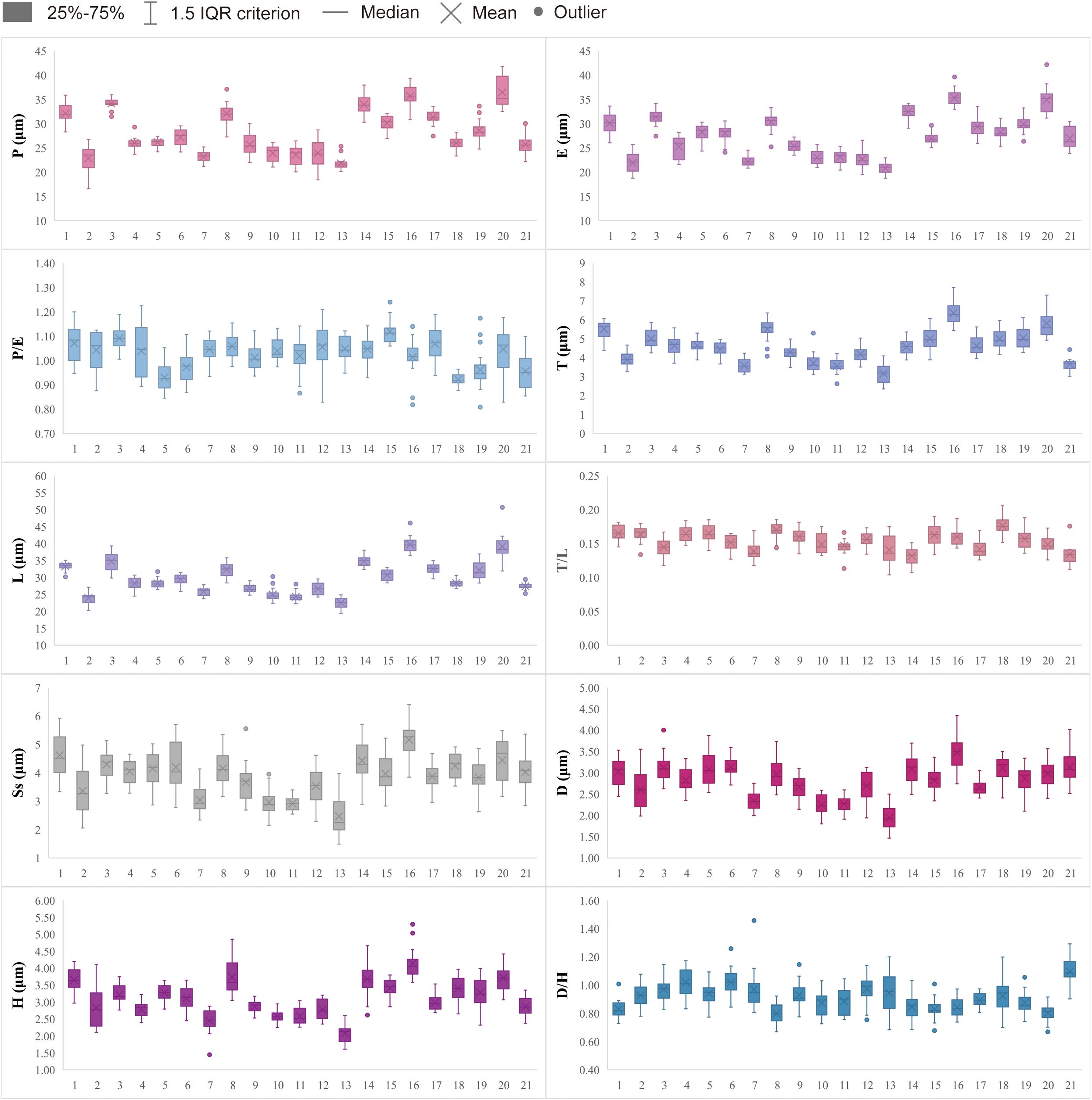
Figure 9. Boxplots of 21 sampled taxa showing the variations in pollen morphological traits. 1. Nannoglottis carpesioides; 2. Dichrocephala benthamii; 3. Galatella angustissima; 4. Formania mekongensis; 5. Aster yunnanensis; 6. Aster brachytrichus; 7. Eschenbachia japonica; 8. Myriactis wallichii; 9. Solidago altissima; 10. Erigeron acris; 11. Erigeron acris subsp. Politus; 12. Erigeron lonchophyllus; 13. Erigeron strigosus; 14. Callistephus chinensis; 15. Arctogeron gramineum; 16. Aster taliangshanensis; 17. Aster ageratoides; 18. Turczaninovia fastigiata; 19. Aster turbinatus; 20. Aster homochlamydeus; 21. Aster altaicus.
The results indicate that most pollen grains of the studied species are nearly spheroidal (0.90 < P/E < 1.10), with only Arctogeron gramineum exhibiting a subprolate shape (P/E = 1.12 > 1.10) (Figure 4). All species display three-colporate apertures, which are clearly observed as tricolporate structures under both LM and SEM. The P/E (the length of polar axis/the length of equatorial axis) ranges from 0.92 to 1.12. In equatorial view, P ranges from 21.80 to 36.46 µm, while E ranges from 20.81 to 35.32 µm. Significant interspecies differences were observed in P, E, and P/E (p < 0.01).
All pollen grains exhibit spines, which are prominently spinose under SEM. The spines gradually taper, typically conical in shape, or have a noticeably widened base. The D ranges from 1.94 to 3.48 µm, the H ranges from 2.08 to 4.14 µm, and the D/H (diameter of spinule base/spinule height) ranges from 0.80 to 1.10. Significant interspecies differences were observed in D and H (p < 0.01). Tiny pores are present at the spinule bases, with 1-3 layers that vary depending on species and individual differences.
Morphological traits, including pollen size, aperture type, and exine ornamentation, were measured for 21 species of Astereae. Based on these data, a hierarchical dendrogram of pollen morphology was constructed (Figure 10). Nannoglottis carpesioides was used as the outgroup, following the phylogenetic framework proposed by Li et al. (2012). The clustering results revealed that species within the same subtribe formed distinct, well-defined clusters, with clear separation between subtribes. At the genus level, Aster and Erigeron were grouped into well-separated branches, reflecting differentiation between the two genera.
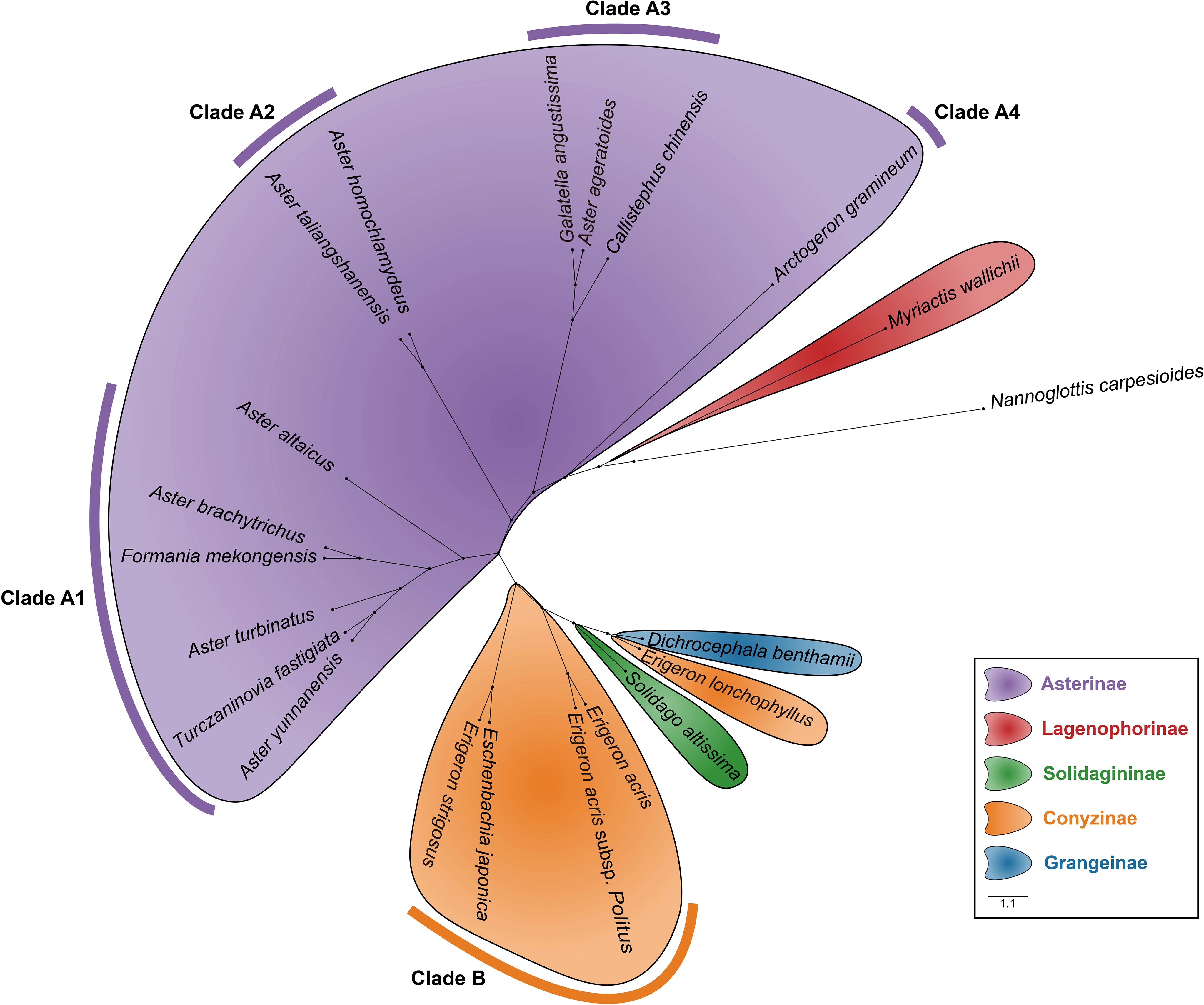
Figure 10. The hierarchical dendrogram of pollen morphology depicts the classification of pollen types within the Astereae based on morphological features.
Based on the clustering results, the branches corresponding to the Asterinae and Conyzinae were designated as Clade A and Clade B, respectively. Clade A was further subdivided into four branches: Clade A1, Clade A2, Clade A3, and Clade A4 (Figure 10). Principal component analysis (PCA) of the 21 Astereae species identified eight key pollen morphological traits—Ss, E, D, L, H, Np, P, and T — that distinguished these clusters. The results of the t-test for these traits are presented in Table 4.
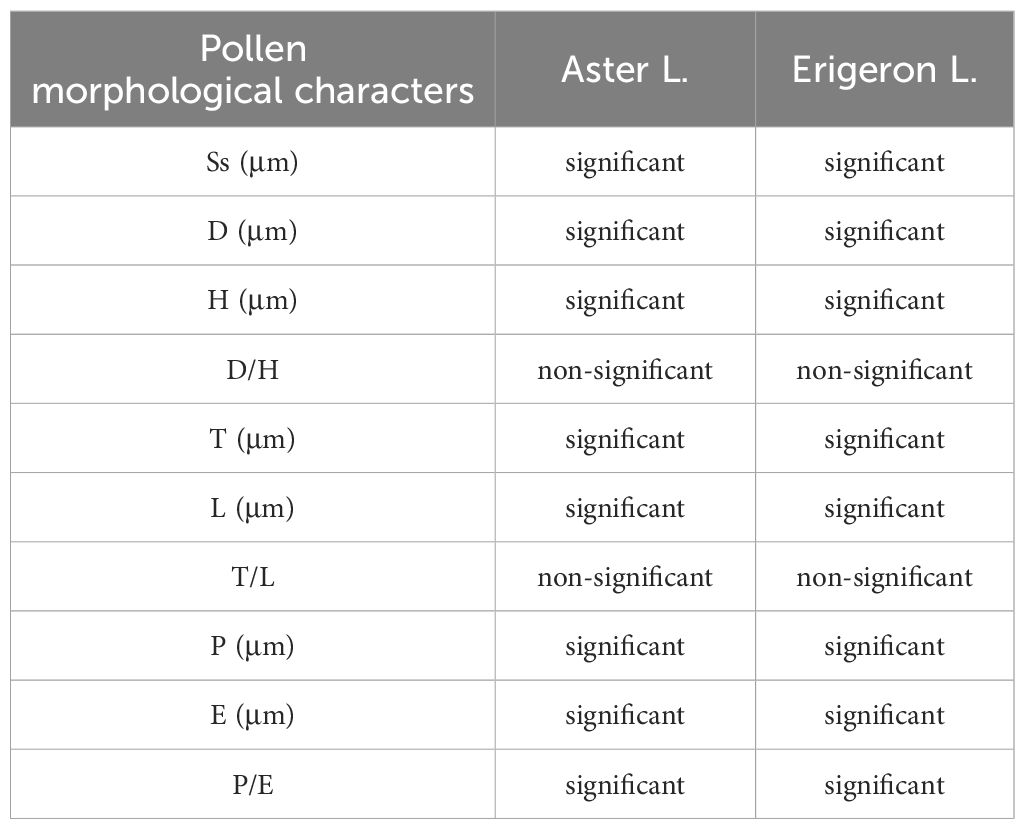
Table 4. The t-test analysis results for the pollen morphological characteristics of the Aster L. and the Erigeron L.
Several pollen traits partially explain the differences between the pollen types of Aster and Erigeron. The L values of Aster pollen (Clade A1 and Clade A2) range from 27.38 to 39.72 μm, significantly larger than those of Erigeron (Clade B), which range from 22.50 to 26.76 μm (t-test, p < 0.01). This trait serves as a reliable distinguishing feature for the latter. Within Aster, Clade A2 (A. taliangshanensis and A. homochlamydeus) exhibits higher L values (39.72 μm and 39.13 μm, respectively) compared to Clade A1 (27.38-32.17 μm). Similarly, The Ss shows significant differences between the two genera (Aster: 3.83-5.16 μm; Erigeron: 2.47-3.67 μm; t-test, p < 0.01), making it another critical parameter for differentiation. In contrast, the Np and Ne values are generally higher in Erigeron, reflecting a denser spine distribution compared to Aster. Regarding D and H, Erigeron exhibits smaller values (D: 1.94-2.70 μm; H: 2.08-2.88 μm) than Aster (D: 2.83-3.48 μm; H: 2.78-4.14 μm). These differences highlight the short and narrow spines in Erigeron, in contrast to the long and wide spines in Aster. Additionally, pollen grains of Erigeron observed in polar view under LM are significantly smaller than those of Aster.
Meanwhile, some species exhibit unique characteristics. For instance, A. ageratoides, grouped within Clade A3, shares most of its pollen traits with other Aster species. However, its D value (2.65 μm) is lower than the minimum observed in other Aster species, while its P/E (1.07) exceeds their maximum. Similarly, Arctogeron gramineum displays the highest P/E (1.12), indicating a pollen shape approaching subprolate. Additionally, Myriactis wallichii (Lagenophorinae), Solidago decurrens (Solidagininae), and Dichrocephala benthamii (Grangeinae), each cluster within distinct branches corresponding to their respective subtribes, reflecting clear subtribal-level separation.
A molecular phylogenetic tree was constructed based on ITS sequence data from 21 Astereae species (Figure 11), following the framework proposed by Li et al. (2012). N. carpesioides, identified as basal or near-basal within the Astereae (Liu et al., 2002), was selected as the outgroup. This tree illustrates the phylogenetic relationships among the studied species and serves as a basis for comparison with the pollen morphology dendrogram.
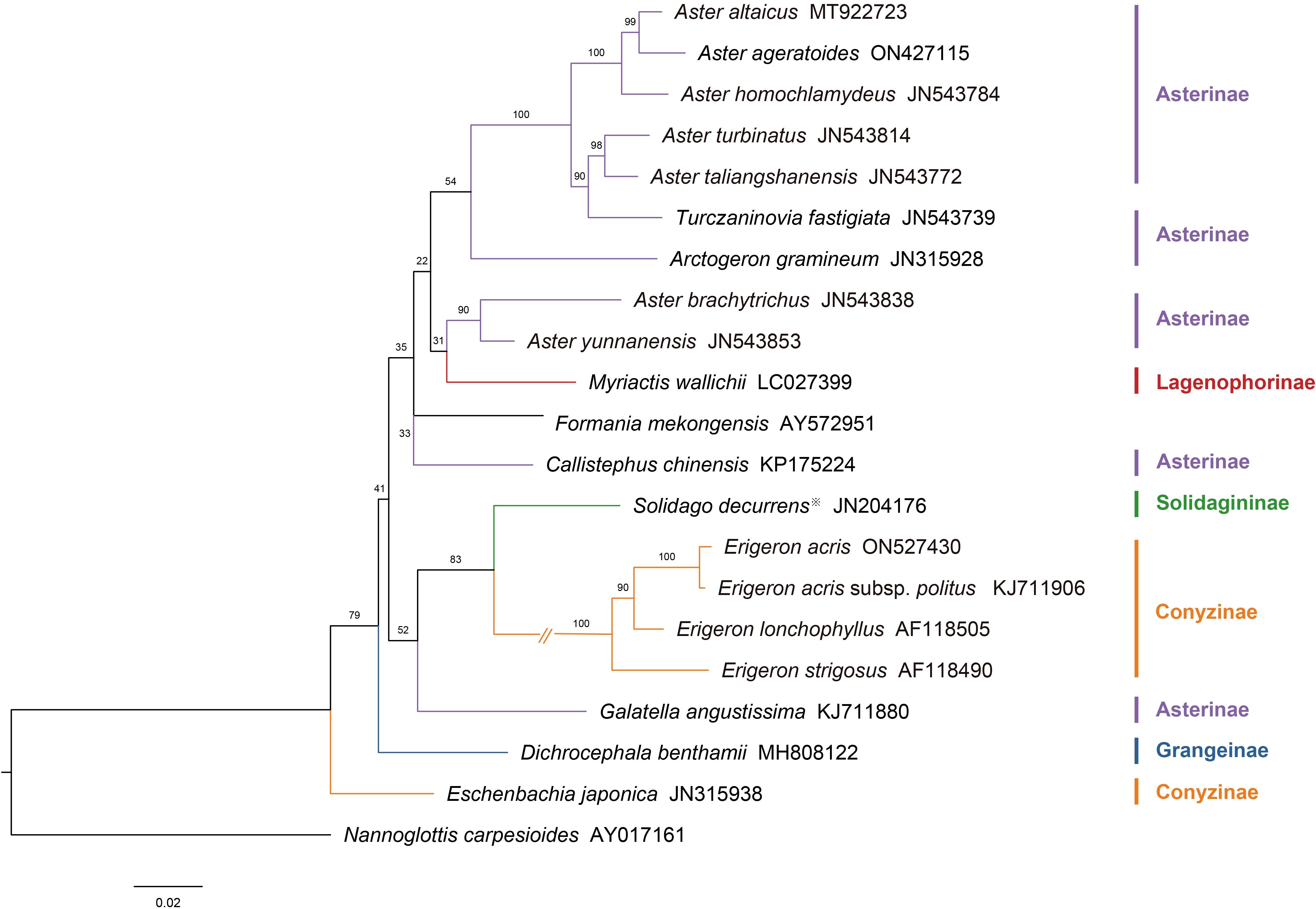
Figure 11. The molecular phylogeny tree of the Astereae is based on nuclear ribosomal DNA internal transcribed spacer sequences. Subtribus classification follows the framework of Anderberg et al. (2007) as outlined. (Note: ※Solidago decurrens replaces S. altissima).
The molecular phylogenetic tree reveals the evolutionary relationships within the Astereae. Asterinae species form a major branch, with closely clustered representatives such as A. taliangshanensis, A. homochlamydeus, and A. altaicus. Conyzinae is represented by Erigeron species (e.g., E. acris, E. lonchophyllus), forming a distinct lineage, while Eschenbachia japonica appears as a separate branch within the subtribe. Other subtribes, such as Lagenophorinae (M. wallichii), Solidagininae (S. decurrens), and Grangeinae (D. benthamii), each form independent branches, reflecting their phylogenetic distinctiveness.
The TCI value between the pollen morphology dendrogram and the molecular phylogenetic tree was 0.545.
At the subtribal level, the pollen morphology dendrogram revealed well-defined clustering patterns. Species of Asterinae were primarily grouped in Clade A (Figure 10), whereas their distribution in the molecular phylogenetic tree was more dispersed. Notably, although Erigeron species within Conyzinae clustered together in a single branch in the molecular tree, E. lonchophyllus was separated from the main cluster of Erigeron species in the pollen dendrogram. Other subtribes, including Lagenophorinae, Solidagininae, and Grangeinae, formed independent branches in both trees.
At the genus level, species of Aster and Erigeron showed consistent clustering patterns in both trees. Species of Aster (e.g., A. altaicus, A. turbinatus, A. homochlamydeus, and A. taliangshanensis) clustered within Clades A1 and A2 in the pollen dendrogram, closely matching their distribution in the molecular phylogenetic tree. Similarly, species of Erigeron (e.g., E. acris and E. strigosus) formed distinct major branches in both trees, reinforcing their phylogenetic independence. In contrast, genera such as Callistephus and Solidago showed lower congruence between the two trees. Notably, F. mekongensis clustered with Asterinae species in Clade A1 (Figure 10), but appeared on a neighboring branch in Figure 11.
The TCI value of 0.545 indicates a moderate topological similarity (de Vienne et al., 2007; Mir et al., 2013) between the molecular and morphological trees, which is expected given the different data types used. While some differences are inevitable, this cross-validation strongly supports the use of pollen morphology in classification (Keating et al., 2023). The pollen morphology clustering tree clearly shows species groupings within the same subtribe, highlighting its effectiveness. Lagenophorinae and Grangeinae form independent branches, distinct from Asterinae and Conyzinae. These findings underscore the significance of pollen traits in subtribal classifications and phylogenetic studies (Moon et al., 2008). Moreover, the high concordance with the macroscopic morphological classification framework (Anderberg et al., 2007) and the molecular phylogenetic tree (Li et al., 2012) reinforces the reliability of pollen morphology in subtribal-level classification. At the genus level, variations in pollen traits reflect phylogenetic relationships and distinctions among genera, highlighting their unique evolutionary trends and affinities with closely related taxa (Wodehouse, 1935; Zhang and Zhou, 2016).
N. carpesioides occupies the basal position of the pollen morphology dendrogram (Figure 10), showing a trend of decreasing pollen size as species radiate outward. Within Asterinae, species in Clades A2, A3, and A4 exhibit larger pollen parameters (P and E) compared to Clade A1. In contrast, Conyzinae species consistently display smaller P and E values. These findings provide important insights into the phylogenetic relationships within Astereae, particularly the separation of Erigeron from Asterinae, which aligns more closely with Conyzinae (Zhang and Zhou, 2016; Iamonico, 2018; Bhattacharjee et al., 2024; Chakraborty et al., 2024). Interestingly, Turczaninovia fastigiata (P/E = 0.92) and Arctogeron gramineum (P/E = 1.12) cluster closely in Figure 11, yet are positioned at opposite ends of Asterinae (Clade A) in Figure 10. This discrepancy may be attributed to their P/E values representing the minimum and maximum observed in this study, suggesting that the P/E may be an important factor influencing pollen morphology clustering (Wodehouse, 1928; Bahadur et al., 2022).
The taxonomic placement of F. mekongensis remains unresolved. Shi and Fu (1983) classified it within Chrysantheminae of Anthemideae, while Chen and Brouillet (2011b) considered its classification uncertain. Fu et al. (2016) placed it in Astereae based on molecular phylogenetic analysis, and Nesom (2020) later assigned it to the newly established subtribe Formaniinae within Astereae. In this study, pollen morphological clustering places F. mekongensis with Asterinae species in Clade A1 (Figure 10), providing the first palynological evidence supporting its placement in Asterinae. This finding builds on earlier studies that recognized F. mekongensis within Astereae (Fu et al., 2016).
In summary, pollen morphological analysis reveals significant phylogenetic patterns and evolutionary trends across taxonomic levels. Unlike molecular methods, it offers unique structural insights and visual evidence (Wodehouse, 1928, 1929; Keating et al., 2023). This study underscores the value of pollen morphology in subtribal classification within Astereae, helps distinguish between the Aster and Erigeron, and provides new insights into the taxonomic placement of F. mekongensis. Although focused on Astereae, the approach presented here has broader implications for using pollen traits in plant systematics. By integrating molecular and morphological data, this work paves the way for more comprehensive plant classification at various taxonomic levels and encourages future research into combining these data types.
Aster, the largest genus in Astereae, is of considerable economic importance. Its capitula are typically solitary or arranged in corymbiform or paniculiform synflorescences (Chen et al., 2011, 2024). Erigeron, the second-largest genus in the tribe, is characterized by radiate capitula (Chen and Brouillet, 2011a; Zhang and Zhou, 2016). Despite these differences, morphological similarities between certain species of Aster and Erigeron have complicated their classification (Nesom, 1994; Li et al., 2012; Fu et al., 2016). This study identifies significant differences in pollen size and exine ornamentation between the two genera, offering new insights into their taxonomic distinction.
SEM reveals differences in exine ornamentation, with Aster pollen exhibiting long, broad, and sparsely distributed spines, while Erigeron pollen features short, narrow, and more densely arranged spines. Under LM, the pollen grains of Aster are significantly larger than those of Erigeron, with nearly a twofold difference in size. Despite these morphological differences, both genera share a typical spinulose ornamentation pattern (Skvarla et al., 1977; Zhang and Zhou, 2016). Zhang and Zhou (2016) reported a close relationship between E. strigosus, A. batangensis, and T. fastigiata. Chen et al. (2024) further demonstrated that A. batangensis and A. yunnanensis cluster within the “Alpine Aster” group, supporting their recognition as a distinct taxonomic unit. In our phylogenetic analysis (Figure 10), A. yunnanensis and T. fastigiata closely cluster within Clade A1, showing a phylogenetic affinity with E. strigosus in Clade B. These findings corroborate previous studies and, coupled with the observed pollen morphological differences, highlight the complex evolutionary relationships among these taxa.
From a biogeographical perspective, Aster and Erigeron belong to the Eurasian (EA) and North American (NA) evolutionary lineages of the Astereae, respectively (Li et al., 2012). Molecular phylogenetic studies have revealed a significant genetic divergence between the EA and NA lineages (Noyes and Rieseberg, 1999; Selliah and Brouillet, 2008; Brouillet et al., 2009; Li et al., 2012; Jafari et al., 2015; Korolyuk et al., 2015). The observed differences in pollen morphology likely reflect divergent natural selection pressures as the two lineages adapted to distinct ecological environments (Wang and Wang, 1983). Aster has diversified in temperate climates, exhibiting high species diversity (Chen et al., 2011, 2024). In contrast, Erigeron has adapted to arid environments, where the role of insect pollination is reduced, leading to changes in pollen size and other traits, such as spine reduction, as part of the adaptation to these conditions (Zhang and Zhou, 2016; Zhang et al., 2019; Bhattacharya et al., 2022). These ecological adaptations, reflected in pollen morphology, are also supported by molecular phylogenetic evidence (Li et al., 2012; Jafari et al., 2015).
Pollen morphology, combining the strengths of both morphological and molecular analyses, provides an accurate and cost-effective tool for plant taxonomy (Kriebel et al., 2017; Keating et al., 2023). In the Astereae, pollen morphology analyses of Aster and Erigeron reveal significant differences in pollen grain size and exine spine morphology. These microstructural traits offer reliable evidence for taxonomic classification and are essential for elucidating the phylogenetic relationships within the Astereae. The application of pollen morphology is highly operable and reliable, overcoming the limitations of single-method morphological or molecular studies, and serves as a critical complement to systematic plant taxonomy (Kriebel et al., 2017; Wang et al., 2023).
Future research on pollen morphology in Asteraceae may focus on the following aspects: (1) employing high-resolution imaging techniques, such as SEM and transmission electron microscopy (TEM), to conduct detailed analyses of pollen microstructures, uncovering subtle interspecific differences and improving classification accuracy (Polevova et al., 2023; Gabarayeva et al., 2024); (2) integrating molecular markers, such as ribosomal DNA and chloroplast DNA, to further explore genetic diversity and phylogenetic relationships within the Asteraceae (Zhang et al., 2024); and (3) expanding sample sizes and ecological ranges, thereby deepening our understanding of the role of pollen in ecological adaptation and evolutionary processes (Martín-Hernanz et al., 2019; Cozzolino et al., 2021).
This study integrates molecular systematics and pollen morphology to examine phylogenetic relationships within Astereae. The alignment of pollen morphology with molecular phylogenetic trees demonstrates that palynology is a reliable tool for plant taxonomy at both the genus and subtribal levels. Significant morphological differences were observed between Aster and Erigeron, and the placement of F. mekongensis provides further evidence for its taxonomic position. These findings highlight the potential of pollen data to refine classification and clarify evolutionary relationships within Astereae. The integration of palynological and molecular data offers a comprehensive approach to plant systematics. Future studies incorporating broader taxon sampling, additional molecular markers, and more detailed morphological analyses will be essential for developing a robust phylogeny of Astereae.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
TQ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft. GX: Methodology, Resources, Writing – original draft. XZ: Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft. XC: Formal Analysis, Software, Writing – review & editing. YZ: Formal Analysis, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. LL: Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization. ZF: Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 32000158, No. T2192952), the National Science & Technology Fundamental Resources Investigation Program of China (No. 2021XJKK0702), the Foundation of Sustainable Development Research Center of Resources and Environment of Western Sichuan, Sichuan Normal University (No. 2020CXZYHJZX03), Key Laboratory of Chemistry in Ethnic Medicinal Resources (Yunnan Minzu University), State Ethnic Affairs Commission & Ministry of Education (No. MZY2301).
The authors are deeply grateful to Dr. Xiuping Xu (Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences) for her expert technical guidance in SEM. We sincerely thank Dr. Yousheng Chen and Dr. Youpai Zeng (South China Botanical Garden, Chinese Academy of Sciences), Dr. Ang Liu (Central South University of Forestry and Technology), Dr. Renbin Zhu (Xishuangbanna Tropical Botanical Garden, Chinese Academy of Sciences), Dr. Qinwen Lin (Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences), Dr. Xiyang Ye (Zhejiang A&F University), and Dr. Jason Grant (Université de Neuchâtel, Switzerland) for their enthusiastic assistance in providing habitat photographs, which greatly enriched our study. Their contributions were indispensable in preparing this manuscript and significantly enhanced the quality of our research.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpls.2025.1558995/full#supplementary-material
Ahmad, M., Zafar, M., Sultana, S., Ahmad, M., Abbas, Q., Ayoub, M., et al. (2018). Identification of green energy ranunculaceous flora of district Chitral, Northern Pakistan using pollen features through scanning electron microscopy. Microsc. Res. Tech. 81, 1004–1016. doi: 10.1002/jemt.23066
Ali, S., Zafar, M., Ahmad, M., Sultana, S., Khan, A., Majeed, S., et al. (2023). Palyno-taxonomic approach through light and scanning electron microscopy for the identification of herbaceous Asteraceae species from Sikaram Mountain Pak-Afghan border. Microsc. Res. Tech. 86, 1274–1297. doi: 10.1002/jemt.24311
Anderberg, A. A., Baldwin, B. G., Bayer, R. G., Breitwieser, J., Jeffrey, C., Dillon, M. O., et al. (2007). “Compositae,” in The Families and Genera of Vascular Plants VIII, Flowering Plants. Eudicots: Asterales. Eds. Kadereit, J. W., Jeffrey, C. (Springer, Germany, Berlin), 61–588.
Andrade, C. (2021). Z scores, standard scores, and composite test scores explained. Indian. J. Psychol. Med. 43, 555–557. doi: 10.1177/02537176211046525
Bahadur, S., Ahmad, M., Mir, S., Zafar, M., Sultana, S., Ashfaq, S., et al. (2018). Identification of monocot flora using pollen features through scanning electron microscopy. Microsc. Res. Techniq. 81, 599–613. doi: 10.1002/jemt.23015
Bahadur, S., Taj, S., Long, W. X., Ahmad, M. (2022). Pollen morphology and its implication in the taxonomy of some selected tribes of the Asteraceae of Hainan Island South China. Bot. Rev. 88, 271–298. doi: 10.1007/s12229-022-09277-3
Bapst, D. W., Schreiber, H. A., Carlson, S. J. (2018). Combined analysis of extant Rhynchonellida (Brachiopoda) using morphological and molecular data. Syst. Biol. 67, 32–48. doi: 10.1093/sysbio/syx049
Bentham, G. (1873). “Compositae,” in Genera plantarum, vol. 2 . Eds. Bentham, G., Hooker, H. D. (Reeve, London), 163–533.
Bhattacharjee, A., Bhattacharjee, B., Chakraborty, K., Banu, F., Sherpa, N., Layola, M. R. R. (2024). Resolving the ongoing confusion between Erigeron multiradiatus and Tibetiodes himalaica (Asteraceae). Phytotaxa 670, 133–147. doi: 10.11646/phytotaxa.670.2.6
Bhattacharya, S., Hernández, F., Alves, M. F., MaChado, R. M., Sun, Y. Y., Wang, M. R., et al. (2022). Genetic diversity and population structure of invasive and native populations of Erigeron canadensis L. J. Plant Ecol. 15, 864–876. doi: 10.1093/jpe/rtac016
Blackmore, S. (2007). Pollen and spores: Microscopic keys to understanding the earth’s biodiversity. Plant Syst. Evol. 263, 3–12. doi: 10.1007/s00606-006-0464-3
Bog, M., Appenroth, K. J., Sree, K. S. (2020). Duckweed (Lemnaceae): Its molecular taxonomy. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 3. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2019.00117
Briand, S., Dessimoz, C., El-Mabrouk, N., Lafond, M., Lobinska, G. (2020). A generalized Robinson-Foulds distance for labeled trees. BMC Genomics 21, 779. doi: 10.1186/s12864-020-07011-0
Brouillet, L., Lowrey, T. K., Urbatsch, L., Karaman-Castro, V., Sancho, G., Wagstaff, S., et al. (2009). “Astereae,” in Systematics, evolution and biogeography of the Compositae. Eds. Funk, V. A., Susanna, A., Stuessy, T., Bayer, R. (IAPT, Vienna), 449–490.
Chakraborty, K., Bhattacharjee, B., Ghosh, A., Bhattacharjee, A. (2024). Rediscovery of Erigeron jaeschkei (Asteraceae: Astereae: Conyzinae) and notes on its correct protologue and typification. Phytotaxa 674, 275–280. doi: 10.11646/phytotaxa.674.3.4
Chen, Y. L., Brouillet, L. (2011a). “Erigeron L,” in Flora of China, vol. 20-21 . Eds. Wu, Z. Y., Raven, P. H. (Science Press, Beijing), 634–650.
Chen, Y. L., Brouillet, L. (2011b). “Formania W. W. Sm. & J. Small,” in Flora of China, vol. 20-21 . Eds. Wu, Z. Y., Raven, P. H. (Science Press, Beijing), 569.
Chen, Y. L., Brouillet, L., Semple, J. C. (2011). “Aster L,” in Flora of China, vol. 20-21 . Eds. Wu, Z. Y., Raven, P. H., Hong, D. Y. (Science Press, Beijing), 574–632.
Chen, H., Li, T. Y., Chen, X. Y., Qu, T. M., Zheng, X. Y., Luo, J. J., et al. (2024). Insights into comparative genomics, structural features, and phylogenetic relationship of species from Eurasian Aster and its related genera (Asteraceae: Astereae) based on complete chloroplast genome. Front. Plant Sci. 15. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1367132
Cozzolino, S., Scopece, G., Lussu, M., Cortis, P., Schiestl, F. P. (2021). Do floral and ecogeographic isolation allow the co-occurrence of two ecotypes of Anacamptis papilionacea (Orchidaceae)? Ecol. Evol. 11, 9917–9931. doi: 10.1002/ece3.7432
Cronquist, A. (1955). “Compositae,” in Vascular Plants of the Pacific Northwest, vol. 5 . Eds. Hitchcock, C. L., Cronquist, A., Ownbey, M., Thompson, J. W. (University of Washington Press, Seattle), 1–343.
Dajoz, I., Till-Bottraud, I., Gouyon, P. H. (1991). Evolution of pollen morphology. Science 253, 66–68. doi: 10.1126/science.253.5015.66
de Vienne, D. M., Giraud, T., Martin, O. C. (2007). A congruence index for testing topological similarity between trees. Bioinformatics 23, 3119–3124. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btm500
Fu, Z. X., Jiao, B. H., Nie, B., Zhang, G. J., Gao, T. G. (2016). A comprehensive generic-level phylogeny of the sunflower family: implications for the systematics of Chinese Asteraceae. J. Syst. Evol. 54, 416–437. doi: 10.1111/jse.12216
Funk, V. A., Susanna, A., Stuessy, T. F., Robinson, H. (2009). “Classification of Compositae,” in Systematics, Evolution, and Biogeography of the Compositae. Eds. Funk, V. A., Susanna, A., Stuessy, T. F., Bayer, R. J. (IAPT, Vienna), 171–189.
Gabarayeva, N. I., Britski, D. A., Grigorjeva, V. V. (2024). Pollen wall development in Impatiens glandulifera: exine substructure and underlying mechanisms. Protoplasma 261, 111–124. doi: 10.1007/s00709-023-01887-x
Halbritter, H., Silvia, U., Grímsson, F., Weber, M., Zetter, R., Hesse, M., et al. (2018). Illustrated pollen terminology. 2nd ed (Berlin: Springer Press). doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-71365-6
Hayat, K., Khan, W. M., Khan, M. N., Shah, S. N. (2023). Pollen morphological investigation of selected species of family Asteraceae from Pakistan by using light and scanning electron microscopy. Microsc. Res. Tech. 86, 1258–1273. doi: 10.1002/jemt.24308
Hesse, M., Blackmore, S. (2013). Preface to the special focus manuscripts. Pl. Syst. Evol. 299, 1011–1012. doi: 10.1007/s00606-013-0811-0
Hesse, M., Halbritter, H., Zetter, R., Weber, M., Buchner, R., Frosch-Radivo, A. (2009). Pollen Terminology: An illustrated handbook. (New York: Springer) doi: 10.1093/aob/mcp289
Huang, J. F., Zhang, M. L., Cohen, J. I. (2013). Phylogenetic analysis of Lappula Moench (Boraginaceae) based on molecular and morphological data. Pl. Syst. Evol. 299, 913–926. doi: 10.1007/s00606-013-0772-3
Iamonico, D. (2018). Nomenclature of the Italian species of subtribe Conyzinae (Asteraceae: Astereae). Taxon 67, 798–800. doi: 10.12705/674.12
Jafari, F., Osaloo, S. K., Mozffarian, V. (2015). Molecular phylogeny of the tribe Astereae (Asteraceae) in SW Asia based on nrDNA ITS and cpDNA psbA-trnH sequences. Willdenowia 45, 77–92. doi: 10.3372/wi.45.45108
Janaćković, P., Susanna, A., Marin, P. D. (2019). Micromorphology and anatomy in systematics of Asteraceae. An old-fashioned approach? Biol. Nyssana 10, 77–85. doi: 10.5281/zenodo.3600177
Katoh, K., Standley, D. M. (2013). MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 30, 772–780. doi: 10.1093/molbev/mst010
Keating, J. N., Garwood, R. J., Sansom, R. S. (2023). Phylogenetic congruence, conflict and consilience between molecular and morphological data. BMC Ecol. Evol. 23, 30. doi: 10.1186/s12862-023-02131-z
Korolyuk, E., Makunin, A., Matveeva, T. (2015). Relationships and generic delimitation of Eurasian genera of the subtribe Asterinae (Astereae, Asteraceae) using molecular phylogeny of ITS. Turk. J. Bot. 39, 808–824. doi: 10.3906/bot-1410-12
Kriebel, R., Khabbazian, M., Sytsma, K. J. (2017). A continuous morphological approach to study the evolution of pollen in a phylogenetic context: An example with the order Myrtales. PloS One 12, e0187228. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0187228
Lacourse, T., Beer, K. W., Hoffman, E. H. (2016). Identification of conifer stomata in pollen samples from western North America. Rev. Palaeobot. Palyno. 232, 140–150. doi: 10.1016/j.revpalbo.2016.05.005
Li, W. P., Yang, F. S., Jivkova, T., Yin, G. S. (2012). Phylogenetic relationships and generic delimitation of Eurasian Aster (Asteraceae: Astereae) inferred from ITS, ETS and trnL-F sequence data. Ann. Bot. 109, 1341–1357. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcs054
Lin, M., Qiu, J., Xie, K. Q., Tan, D. Y. (2023). Palynological features and taxonomic significance for 16 species of Gagea (Liliaceae) from Xinjiang, China. PhytoKeys 225, 53–68. doi: 10.3897/phytokeys.225.101518
Ling, R., Chen, Y. L., Shi, Z. (1985). “Astereae,” in Flora Reipublicae Popularis Sinicae, vol. 74 . Eds. Ling, R., Chen, Y. L., Shi, Z. (Science Press, Beijing), 70–353.
Liu, J. Q., Gao, T. G., Chen, Z. D., Lu, A. M. (2002). Molecular phylogeny and biogeography of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau endemic Nannoglottis (Asteraceae). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 23, 307–325. doi: 10.1016/s1055-7903(02)00039-8
Lu, L. L., Jiao, B. H., Qin, F., Xie, G., Lu, K. Q., Li, J. F., et al. (2022). Artemisia pollen dataset for exploring the potential ecological indicators in deep time. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 14, 3961–3995. doi: 10.5194/essd-14-3961-2022
Martín-Hernanz, S., Martínez-Sánchez, S., Albaladejo, R. G., Lorite, J., Arroyo, J., Aparicio, A. (2019). Genetic diversity and differentiation in narrow versus widespread taxa of Helianthemum (Cistaceae) in a hotspot: The role of geographic range, habitat, and reproductive traits. Ecol. Evol. 9, 3016–3029. doi: 10.1002/ece3.4481
Mir, A., Rosselló, F., Rotger, L. A. (2013). A new balance index for phylogenetic trees. Math. Biosci. 241, 125–136. doi: 10.1016/j.mbs.2012.10.005
Moon, H. K., Vinckier, S., Smets, E., Huysmans, S. (2008). Palynological evolutionary trends within the tribe Mentheae with special emphasis on subtribe Menthinae (Nepetoideae: Lamiaceae). Plant Syst. Evol. 275, 93–108. doi: 10.1007/s00606-008-0042-y
Nesom, G. L. (1994). Review of the taxonomy of Aster sensu lato (Asteraceae: Astereae), emphasizing the New World species. Phytologia 77, 141–297.
Nesom, G. L. (2020). Revised subtribal classification of Astereae (Asteraceae). Phytoneuron 53, 1–39.
Noyes, R. D., Rieseberg, L. H. (1999). ITS sequence data support a single origin for North American Astereae (Asteraceae) and reflect deep geographic divisions in Aster s.l. Am. J. Bot. 86, 398–412. doi: 10.2307/2656761
Peng, Y. L., Pu, X. M., Yu, Q., Zhou, H. L., Huang, T. F., Xu, B., et al. (2023). Comparative pollen morphology of selected species of Blumea DC. and Cyathocline Cass. and its taxonomic significance. Plants (Basel) 12, 2909. doi: 10.3390/plants12162909
Polevova, S. V., Grigorjeva, V. V., Gabarayeva, N. I. (2023). Pollen wall and tapetal development in Cymbalaria muralis: the role of physical processes, evidenced by in vitro modelling. Protoplasma 260, 281–298. doi: 10.1007/s00709-022-01777-8
Reshmi, G. R., Rajalakshm, R. (2019). Systematic significance of pollen morphology of the genus Acmella Rich. (Heliantheae: Asteraceae). Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Sci. 43, 1469–1478. doi: 10.1007/s40995-018-0660-3
Sattler, R. (2022). Kaplan’s principles of plant morphology: A critical review. Bot. Rev. 88, 257–270. doi: 10.1007/s12229-022-09280-8
Sattler, R., Rutishauser, R. (1997). The fundamental relevance of morphology and morphogenesis to plant research. Ann. Bot. 80, 571–582. doi: 10.1006/anbo.1997.0474
Sattler, R., Rutishauser, R. (2022). Fundamentals of plant morphology and plant evo-devo (Evolutionary Developmental Morphology). Plants (Basel) 12, 118. doi: 10.3390/plants12010118
Selliah, S., Brouillet, L. (2008). Molecular phylogeny of the North American eurybioid Asters (Asteraceae, Astereae) based on the nuclear ribosomal internal and external transcribed spacers. Botany 86, 901–915. doi: 10.1139/B08-070
Shi, Z., Chen, Y. L., Chen, Y. S., Lin, Y. R., Liu, S. W., Ge, X. J., et al. (2011). “Asteraceae (Compositae),” in Flora of China, vol. 20-21 . Eds. Wu, Z. Y., Raven, P. H., Hong, D. Y. (Science Press, Beijing; Missouri Botanical Garden Press, St. Louis), 1–894.
Shi, Z., Fu, G. X. (1983). “Formania W. W. Sm. & J. Small,” in Flora Reipublicae Popularis Sinica, vol. 76, 81 . Eds. Chen, Y. L., Shi, Z. (Science Press, Beijing).
Skvarla, J. J., Turner, B. L., Patel, V. C., Tomb, A. S., Thanikaimoni, G. (1977). “Pollen morphology in the Compositae and in morphologically related families,” in The Biology and Chemistry of the Compositae. Eds. Heywood, V. H., Harborne, J. B., Turner, B. L. (Academic Press, London), 141–248.
Stamatakis, A., Hoover, P., Rougemont, J. (2008). A rapid bootstrap algorithm for the RAxML Web servers. Syst. Biol. 57, 758–771. doi: 10.1080/10635150802429642
Tellería, M. C. (2017). Spines vs. microspines: an overview of the sculpture exine in selected basal and derived Asteraceae with focus on Asteroideae. J. Plant Res. 130, 1023–1033. doi: 10.1007/s10265-017-0956-y
Usma, A., Ahmad, M., Ramadan, M. F., Khan, A. M., Zafar, M., Hamza, M., et al. (2022). Micro-morphological diversity of pollen among Asteraceous taxa from Potohar Plateau-Pakistan. Microsc. Res. Tech. 85, 2467–2485. doi: 10.1002/jemt.24102
Wang, Y. H., Huang, Z. Q., Ma, W. X., Liu, J. J., Tian, L., Zhou, Y. C., et al. (2023). Comparative pollen morphology of the genus Chaenomeles Lindl. (Rosaceae): Diagnostic features and implications for taxonomy. Diversity 15, 960. doi: 10.3390/d15090960
Wang, F. X., Qian, N. F., Zhang, Y. L., Yang, H. Q. (1995). Pollen morphology of Chinese plants. 2nd ed (Beijing: Science Press).
Wanninger, A. (2015). Morphology is dead long live morphology! Integrating MorphoEvoDevo into molecular EvoDevo and phylogenomics. Front. Ecol. Evol. 3. doi: 10.3389/fevo.2015.00054
Wodehouse, R. P. (1928). The phylogenetic of pollen grain characters. Ann. Bot. 42, 891–934. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aob.a090149
Wodehouse, R. P. (1929). Pollen grains in the identification and classification of plants. IV. The Mutisieae. Am. J. Bot. 16, 297–313. doi: 10.1002/j.1537-2197.1929.tb09484.x
Wortley, A. H., Funk, V. A., Robinson, H., Skvarla, J. J., Blackmore, S. (2007). A search for pollen morphological synapomorphies to classify rogue genera in Compositae (Asteraceae). Rev. Palaeobot. Palynol. 146, 169–181. doi: 10.1016/j.revpalbo.2007.03.003
Wortley, A. H., Scotland, R. W. (2006). The effect of combining molecular and morphological data in published phylogenetic analyses. Syst. Biol. 55, 677–685. doi: 10.1080/10635150600899798
Younis, S., Shaheen, S., Harun, N., Abbas, M., Ahmad, M., Hussain, K., et al. (2021). Application of multimicroscopic techniques (LM and SEM) in comparative palynological study of Asteroideae members, inhabited in Pakistan. Microsc. Res. Tech. 84, 1063–1077. doi: 10.1002/jemt.23667
Zhang, X. P., Bremer, K. (1993). A cladistic analysis of the tribe Astereae (Asteraceae) with notes on their evolution and subtribal classification. Plant Syst. Evol. 184, 259–283. doi: 10.1007/BF00937439
Zhang, G. J., Hu, H. H., Gao, T. G., Gilbert, M. G., Jin, X. F. (2019). Convergent origin of the narrowly lanceolate leaf in the genus Aster-with special reference to an unexpected discovery of a new Aster species from East China. PeerJ 7, e6288. doi: 10.7717/peerj.6288
Zhang, G. J., Yang, J. B., Zhang, C. F., Jiao, B. H., Panero, J. L., Cai, J., et al. (2024). Nuclear phylogenomics of Asteraceae with increased sampling provides new insights into convergent morphological and molecular evolution. Plant Commun. 5, 100851. doi: 10.1016/j.xplc.2024.100851
Keywords: taxonomy, Aster, Erigeron, SEM, phylogeny, cluster analysis
Citation: Qu T, Xie G, Zheng X, Chen X, Zhang Y, Lu L and Fu Z (2025) Systematic analysis of some Astereae (Asteraceae) species by Integrating pollen morphology and molecular evidence. Front. Plant Sci. 16:1558995. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1558995
Received: 11 January 2025; Accepted: 19 March 2025;
Published: 08 April 2025.
Edited by:
Saraj Bahadur, Hainan University, ChinaReviewed by:
Kaiqing Xie, Xinjiang Agricultural University, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Qu, Xie, Zheng, Chen, Zhang, Lu and Fu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Lili Lu, bHVsaWxpQGl2cHAuYWMuY24=; Zhixi Fu, ZnV6eDIwMTdAc2ljbnUuZWR1LmNu
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.