
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Plant Sci. , 06 March 2025
Sec. Plant Pathogen Interactions
Volume 16 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2025.1553348
Introduction: Fusarium oxysporum (FOX) causes severe Fusarium wilt in the potato (Solanum tuberosum group Phureja) annually around the world. As an Na+/H+ antiporter, SOS1, a member of the salt oversensitive (SOS) signaling pathway plays important role in salt tolerance, but its function in plant disease resistance has been less studied.
Methods: The function of the potato SOS1 gene (StSOS1-13) responding to the FOX infection was researched by gain- and loss-of-function assays.
Results: StSOS1-13-overexpressed Arabidopsis differed from WT plants in multiple aspects post-FOX infection. It exhibited less ROS accumulation and cell necrosis in leaves, higher SOD and CAT activities accompanied by reduced MDA content, enhanced root development, increased tolerance to FOX infection, and an accelerated leaf stomatal closure rate along with a reduced stomatal aperture area. Additionally, the ectopic overexpression of StSOS1-13 in Arabidopsis induced down-regulation of AtPR12. Conversely, silencing the ortholog gene NbSOS1-13 in Nicotiana benthamiana showed more accumulation of ROS, serious cell necrosis, reduced activities of SOD and CAT, significantly increased MDA level, obvious leaf wilting, decreased tolerance to infection, and reduced leaf stomatal closure rate and accelerated stomatal area. Furthermore, the expression of SA and JA response-related genes (NbPR5 and NbPR12) was up-regulated in NbSOS1-13-silenced plants.
Discussion: These findings suggest that StSOS1-13 may serve as a key hub in the immune response to FOX infection by enhancing the antioxidant defense system, promoting root development to improve water uptake, facilitating leaf stomatal closure to minimize water loss through evaporation, and associating with the SA and JA signaling pathways.
Plants have evolved several strategies to cope with salinity, in which the salt-overly-sensitive (SOS) pathway controls the net uptake of sodium by roots and the xylematic transfer to shoots in vascular plants (Gámez-Arjona et al., 2024; Villalta et al., 2021). SOS conduction pathway is consisted of three components: SOS1, SOS2 and SOS3 and, mediate salt stress signal transduction, transport excess Na+ out of the cell to maintain the relative balance of ion in the cell (Cheng et al., 2019; Jiang et al., 2019; Yang and Guo, 2017). The SOS1s of glycophytes and halophytes, located in the plasma membrane and expressed in the wood parenchyma and root epidermal cells, are primarily involved in the efflux of Na+ from the cytoplasm to the soil and the transport of Na+ to the leaves via transpiration (Ali et al., 2021).
At present, the involvement of SOS1 in plant salt tolerance has been demonstrated in a variety of plants, such as Arabidopsis (Shi et al., 2003), tomato (Olias et al., 2009), sweetpotato (Gao et al., 2012), cotton (Chen et al., 2017), soybean (Zhang M, et al., 2022; Zhao et al., 2016), maize (Zhou et al., 2022), potato (Liang et al., 2023). However, the involvement of SOS1 in plant disease resistance was only found in the immunity of Brassica juncea var. tumida SOS1 (BjSOS1) to Plasmodiophora Brassicae (Cheng et al., 2019). Furthermore, NHX1 is involved in the resistance to Phytophthora parasitica nicotianae (Ppn) in Nicotiana benthamiana. NbNHX1 silencing led to the reduction of H+ efflux from vacuole to cytoplasts, a lower pH in vacuole, the NAD(P) (H) pool decreased, and a lower reactive oxidative species (ROS) level in cell, down-regulated of ROS-responsive genes, impaired ability to scavenge ROS induced by the pathogen, and decreased Ppn resistance in N. benthamiana (Chen et al., 2014). In contrast, transient overexpressed NbNHX1 led to the increase of vacuolar pH and cellular ROS level in the N. benthamiana, which was associated with an enlarged NAD(P) (H) pool and up-regulated ROS-responsive genes, and SeNHX1 (from Salicornia europaea) or AtNHX1 (from Arabidopsis) ectopic expression enhanced the resistance to Ppn with a lower H2O2 concentration and the reduced blight area in the leaves. It has been shown that NHX1 is involved in plant disease defense by regulating the pH of the vacuole, affecting the oxidation state of cells, and priming the antioxidant system associated with resistance to Ppn in N. benthamiana (Chen et al., 2015). Nevertheless, whether SOS1 is involved in disease resistance in other plants remains to be explored further.
Potato is a significant staple crop globally, serving as an essential food source (Munthali et al., 2022) and after maize (Zea mays), wheat (Triticum aestivum) and rice (Oryza sativa) (Qin et al., 2022). However, the ever-changing biotic stresses are causing widespread declines in potato yields and quality (Dahal et al., 2019), such as the late blight pathogen Phytophthora (Ali et al., 2014), bacterial wilt pathogen Ralstonia solanacearum (Wullings et al., 1998) and Fusarium wilt pathogen Fusarium oxysporum f. sp (Li L, et al., 2022). Fusarium wilt disease poses a serious threat to global potato yields during the potato growing season (Li M, et al., 2022). Therefore, it is of great importance to mine stress-resistant genes at the molecular genetic level for the utilization of potato germplasm resources and the improvement of potato varieties (He F, et al., 2022). We have shown previously that the potato SOS1 (StSOS1-13) gene would be potential candidate gene for potato salt-tolerant seeding (Liang et al., 2023). However, the role of SOS1 in plant disease resistance response conjugating with operation of the SOS pathway for salt tolerance has not been assessed.
In this work, we aimed to determine the precise role of StSOS1-13 in response to FOX using gain- and loss-of-function assays in Arabidopsis and N. benthamiana. This approach allows the quick and accurate dissection of the gene function and pathway constituents in simplified gene expression systems for a preliminary investigation into its molecular mechanism in FOX resistance through silencing orthologous gene in tobacco and heterologous overexpression in Arabidopsis. Our results demonstrate that StSOS1-13 plays a special comprehensive regulatory role in plant immunity against FOX infection, providing interesting insights into understanding SOS1-mediated plant disease resistance responses.
The potato (Solanum tuberosum Group phureja), Nicotiana benthamiana and Arabidopsis thaliana (Col-0) seeds used in this study were all provided by institute of vegetables and flowers, Chinese academy of agricultural sciences, the corresponding plants were grown in a growth chamber with a 16:8 light:dark cycle, and at a 26°C/18°C: 60-70% (Ali et al., 2014), 24°C/22°C: 40% (Murphy et al., 2018) and 22°C: 70-80% (Zhang L, et al., 2022) temperature(day/night): relative humidity correspondingly. The FOX strain used in this study was stored in our laboratory and cultured with PDA at 28°C, and then transferred to PDB liquid culture in a shaker for propagation culture (Li M. et al., 2022), the culture solution was filtered, conidia were collected, and diluted to 1×107/mL. Plant seedlings were inoculated with suspension of FOX with a concentration of 107 spores/mL for 30 min before being transplanted back into the soil for normal culture using root infection method according to previous descriptions (Qian et al., 2022). Samples for RNA extraction were collected from the whole leaves at 6, 12, 24, 36, 48, 60, and 72 h (0 h as a control) after inoculation (Wang X, et al., 2022).
The tobacco rattle virus (TRV) system was used for VIGS analysis. A 300 bp interference fragment from NbSOS1-13 (NCBI accession number: Niben101Scf00485g02023.1, the ortholog of StSOS1-13 in N. benthamiana) was inserted into the pTRV2 vector by double-enzyme digestion (XbaI/BamHI) to generate the pTRV2-NbSOS1-13 vector and verified by sequencing (Kang et al., 2021). NbPDS gene (Supplementary Note 1) was also inserted into the pTRV2 vector and used as the positive control. The pTRV2, pTRV2-PDS, and pTRV2-NbSOS1-13 vectors were transformed into Agrobacterium strain GV3101 for Agrobacterium-mediated transient transformation of plants via syringe infiltration (Li et al., 2021; Yin et al., 2022).
To investigate the role of StSOS1-13 in Arabidopsis against FOX infection, StSOS1-13 was overexpressed in Arabidopsis under the control of the CaMV35S. Firstly, full-length StSOS1-13 cDNA sequence (1734 bp) was amplified using gene-specific primers, and then inserted into the pCAMBIAsuper1300 vector containing the XbaI and SacI restriction site, and then the pCAMBIAsuper1300-StSOS1-13 vector generated were transformed into E.coli DH5α and verified by sequencing (Shi et al., 2022). Secondly, the pCAMBIAsuper1300-StSOS1-13 vectors were transformed into the A. tumefaciens strain GV3101 (re-suspended with a suspension containing 5% sucrose and 0.05% Silwet L-77 to OD630 = 0.8) using the freeze-thaw method, and then transferred into the Arabidopsis via the flower dipping method. Thirdly, the Arabidopsis plants were incubated in the dark for 24 h (Sakata et al., 2022) before being transferred to a culture chamber for normal culture. The primary seeds harvested were recorded as the T0 generation and sown on soil, the resulting plants (T1 generation) were used to screen for homozygous transgenic lines by MS medium containing hygromycin (25 mg/L). Subsequently, Hyg-resistant T2 generation Arabidopsis plants were used for further validation whether the positive plant material, including DNA extracting by a DNA Quick Plant System (TransGen Biotech, Beijing, China), and PCR analysis based on the 35S promoter using specific primers (Supplementary Table S1).
Total RNAs were extracted using TransZol Up Plus RNA Kit (Transgen, Beijing, China) and then employed as a template with TransScript® One-Step gDNA Removal and cDNA Synthesis Super Mix for qPCR (Transgen, China) for the first strand cDNA synthesis. The RT-qPCR was performed on the QuantStudio-3 system (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Shanghai, China). The reaction mix contained 2 µL template cDNA, 0.4 µL F primer (10 µM), 0.4 µL R primer (10 µM), 0.4 µL passive reference dye (50×), 10 µL 2×PerfectStart® Green Super Mix and 6.8 µL nuclease-free water. The RT-qPCR amplification parameters were as follows: predenaturation at 94°C for 30 s, followed by 35 cycles of denaturation at 94°C for 30 s and annealing at 60°C for 30 s. Finally, the relative gene expression level was calculated using the 2−ΔΔCT method (He J, et al., 2022). As a reference, the actin of N. benthamiana, Arabidopsis and other primers (Supplementary Table S1) used in this study were designed by Primer Blast website1 of NCBI. Three biological experiments with three technical replicates were performed for each reaction.
The accumulation of H2O2 in the tobacco and Arabidopsis leaf tissues was visualized by 3,3′-diaminobenzidine (DAB) staining. The leaves immersed in DAB were incubated for 6 h with gentle shaking in dark conditions and the ROS fluorescence intensity was measured using ImageJ software (Yin et al., 2022).
Tobacco and Arabidopsis leaf tissue were evaluated for cell death using trypan blue staining. The leaves immersed in 0.4% trypan blue were incubated for 6 h with gentle shaking and cell death was measured using ImageJ software (Wang W, et al., 2022).
The malondialdehyde (MDA) content, catalase (CAT) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) activities of tobacco and Arabidopsis tissue were determined separately using the corresponding kits, following the manufacturer’s instructions (Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute, China).
Evaluation of FOX colonization in the inoculated plant leaves was determined using plate counts at specified time points by the colony forming unit (CFU) per gram of leaf tissues according to previous descriptions (Qian et al., 2022).
The stomatal movement of WT, OE5 and OE6 Arabidopsis lines were observed under a microscope (40 ×) before and after infection with FOX. Ten random visual fields for each group of plant and three duplicates for each line were also observed. Stomatal apertures (Stomata aspect ratios) in the images were measured using the software ImageJ (Zhu et al., 2021). The length of a stoma is defined as the distance between the internal contact points of the two guard cells, while the width is the maximum distance between the two innermost guard cells.
The data were presented as means ± standard deviation (SD) of at least three independent experiments. All statistical analysis was carried out by GraphPad Prism 9 software, and the significance of differences between different groups was evaluated by Student t-test or ANOVA.
To investigate whether StSOS1 genes were involved in immune response to FOX (Supplementary Figure S1), the phenotypes and StSOS1-13 gene expression of the potato infected by root infection method was observed and analyzed. The results showed that the leaves of potato plants exhibited slight wilting symptoms at 24 hpi after inoculation with FOX, while exhibited severe disease symptom at 60 hpi (Figure 1A). The StSOS1-13 gene expression level showed a significant trend of first increasing and then decreasing (Figure 1B), and rose 184-fold at 36 h after inoculation with FOX, suggesting that the StSOS1-13 was involved in the resistance of potato to FOX and played an important role.
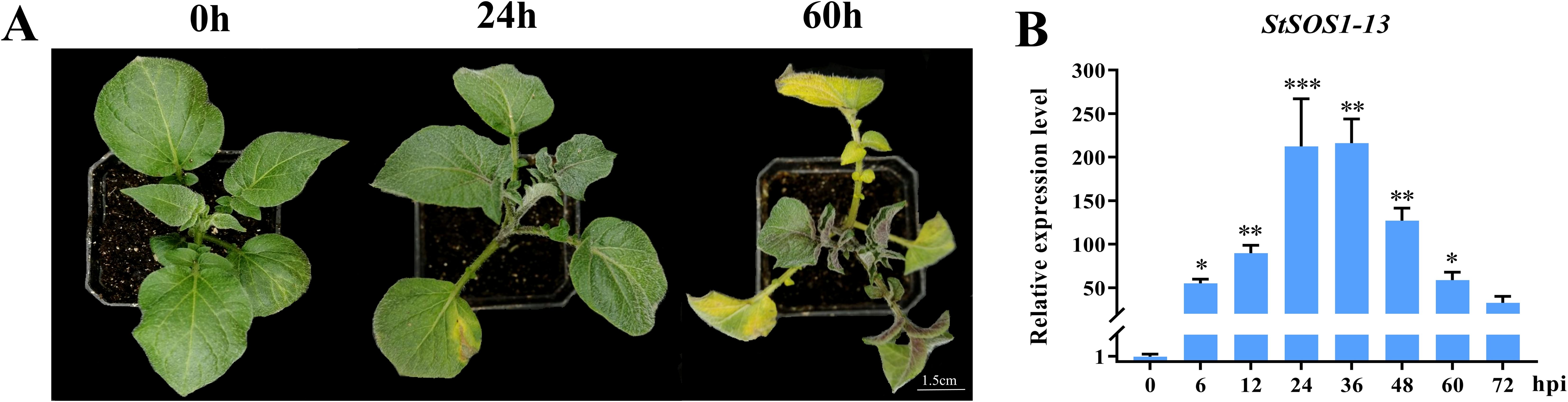

Figure 1. The expression analysis of StSOS1-13 gene under FOX infection. (A) The typical withering phenotype appeared at 60 hpi; (B) RT-qPCR level of StSOS1-13 gene expression under FOX infection. The expression level of StSOS1-13 (with control at 0 h) was normalized against StAct. The vertical bars indicate the standard error of the mean. Asterisks indicate a significant difference based on the T test. (*, p<0.05, **, p<0.01, ***, p<0.001).
To better understand the putative function of StSOS1-13 during the immune response against FOX, its ortholog gene (NbSOS1-13) was identified based on the highest sequence similarity for VIGS (Supplementary Figure S2) with the pTVR2-PDS as an inner reference. As shown in Supplementary Figure S3, compared to mock-treated wild type (WT), there was no obvious phenotypic change in the leaves of pTRV2 empty vector (EV) transformed plants. The leaves of pTRV2-NbSOS1-13 transformed strain showed yellow or even white pigmentation, and apparent shrinkage. The results of the RT-qPCR analysis indicated that the transcript level of NbSOS1-13 in pTRV2-NbSOS1-13 transformed plants was significantly reduced.
Within 60 hpi after infection, the vascular bundle browning and leaves wilting of NbSOS1-13 VIGSed plants were faster and more severe than those of WT plants (Figure 2A). The transcription level of NbSOS1-13 was significantly lower than that of WT leaves (Figure 2B) after continuous observation, especially at 24 h, it was only one fifth of that of WT. The staining degree of DAB and trypan blue in leaves was higher than that in WT plants, and the accumulation of ROS and the number of cell death were higher (Figures 2C, D). The activities of SOD and CAT decreased significantly, while the content of MDA increased significantly (Figure 2E). These results suggest that NbSOS1-13 may be involved in the early immune response of tobacco to FOX.
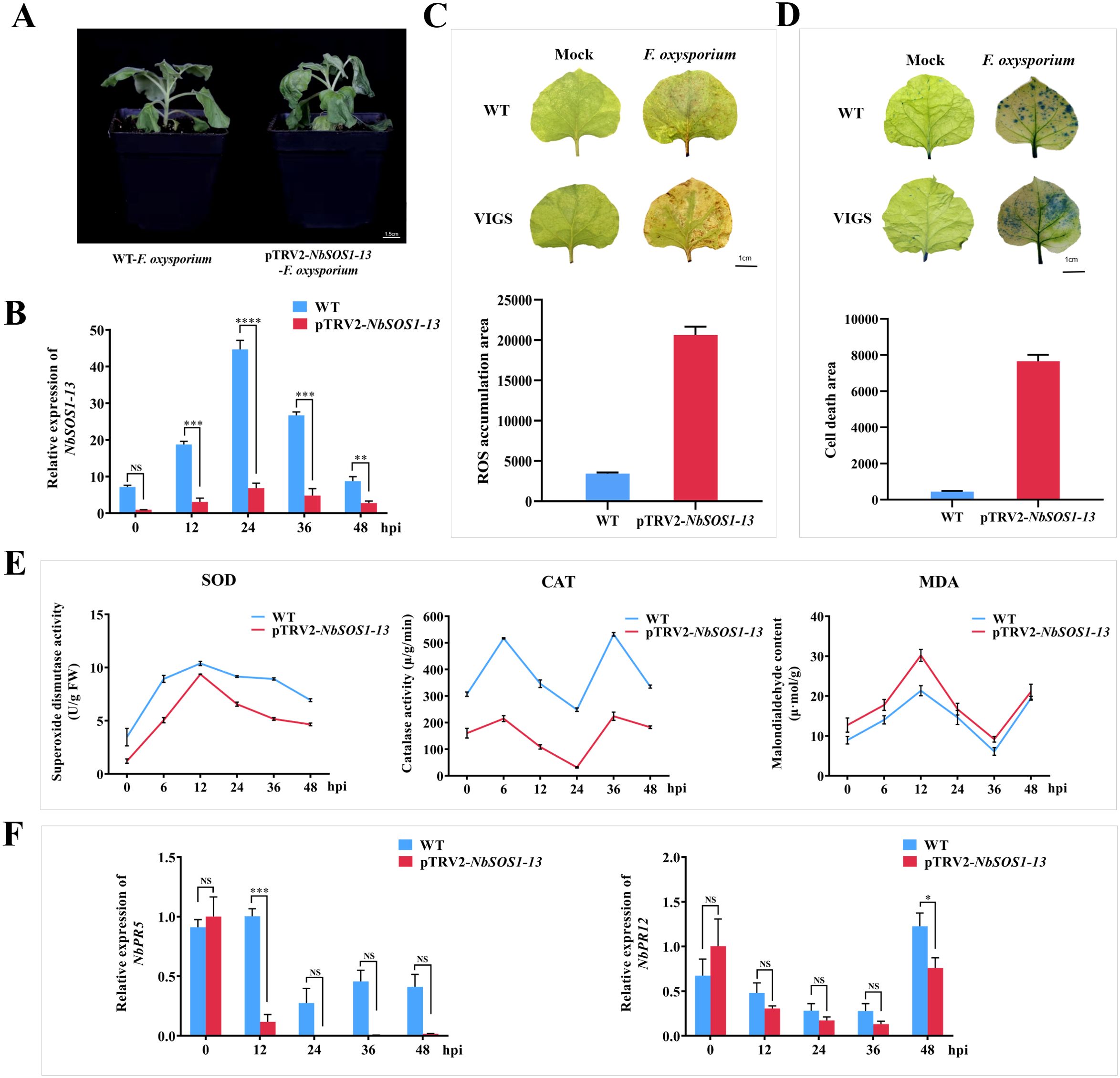
Figure 2. The resistance function analysis of the NbSOS1-13 gene using VIGS. (A) The phenotypic responses of WT and NbSOS1-13 VIGSed tobacco plants were observed following infection with FOX, with photographs captured five days post-inoculation; (B) The expression levels of WT and NbSOS1-13 VIGSed tobacco plants infected with FOX were quantified using RT-qPCR at various time points post-infiltration; (C) The ROS were detected through DAB staining, with the ROS-positive areas quantified using ImageJ software; WT plants served as the control group; (D) Cell death in 4-week-old WT and NbSOS1-13 VIGSed tobacco leaves was assessed two days post-inoculation with FOX. Trypan blue staining was employed to assess cell death, and ImageJ was utilized to quantify the regions of cell death, using WT as a control; (E) The activities of SOD and CAT, as well as the MDA content, were measured in WT and NbSOS1-13 VIGSed tobacco leaves subjected to varying hpi with FOX; (F) RT-qPCR was conducted to evaluate the transcription levels of NbPR5 and NbPR12, in WT and NbSOS1-13 VIGSed tobacco plants following FOX treatment. Asterisks indicate significant differences based on two-way ANOVA (NS, no significant difference, *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001), these experiments were performed with three independent biological replicates with similar results.
Furthermore, the expression of SA-responsible gene PR5 and JA-responsible gene PR12 related to the defense response (Anisimova et al., 2021) were compared between WT and NbSOS1-13 VIGSed plants infected by FOX. The results showed that the expression levels of NbPR5 and NbPR12 were significantly lower in NbSOS1-13 VIGSed plants than in WT plants at 12 h and 48 h, respectively (Figure 2F), suggesting that NbSOS1-13 is positively correlated with gene expression of NbPR5 and with NbPR12.
Based on the importance of stomatal movement in regulating transpiration in plants in response to adverse water conditions, the opening and closing of the leaf stomata pores of WT, NbSOS1-13 VIGSed plants before and after infected with FOX were observed microscopically. The results showed no significant difference in leaf stomatal aperture between the NbSOS1-13 VIGSed and WT plants before treated with FOX, but after treated with FOX for 48 hpi, compared with silenced plants, the leaf stomatal aperture of WT plants showed smaller (Figure 3A), the aspect ratio of stomatal aperture significantly greater (Figure 3B), and the stomata area significantly lesser (Figure 3C), respectively. It indicates that the WT plant shows a faster response to leaf stomatal movement under FOX treatment than the NbSOS1-13 VIGSed plant.
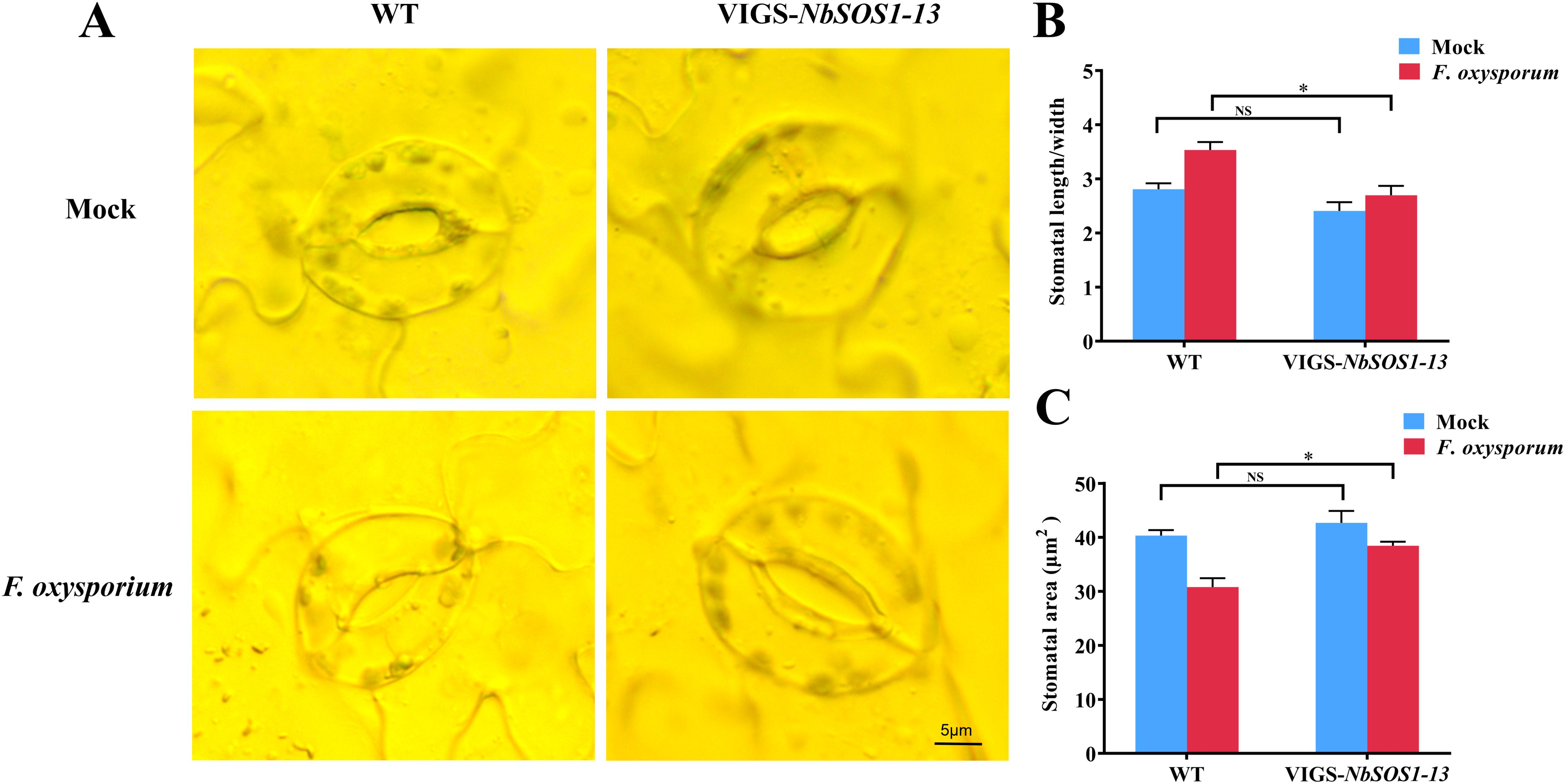
Figure 3. Stomata dynamics of tobacoo leaves under FOX treatment at 48 hpi. (A) Stomatal opening and closing of WT and NbSOS1-13 VIGSed leaves at seeding stage under FOX treatment; (B) Aspect ratio of stomatal aperture in WT and NbSOS1-13 VIGSed plants under FOX treatment 48 h calculated by ImageJ; (C) Leaf stomata area of WT and NbSOS1-13 VIGSed plants under FOX treatment 48 h calculated by ImageJ. Asterisks indicate significant differences based on two-way ANOVA (NS, no significant difference, *p<0.05).
To elucidate the role of StSOS1-13 gene in conferring resistance to FOX, StSOS1-13 was heterologously overexpressed in Arabidopsis (Supplementary Figure S4). In Appendix F, two overexpressing lines OE5 and OE6 were obtained and were employed for resistance analysis, the RT-PCR showed that StSOS1-13 was highly expressed compared with WT plants, and the root length was significantly increased at the seedling stage, but the plant height decreased significantly, and the florescence was delayed at the mature stage. These results indicated that the heterologous overexpression of StSOS1-13 inhibited the growth of the aboveground part of Arabidopsis, but promoted the root elongation.
Three days after inoculation of FOX at seedling stage, compared with the symptoms of yellowing and wilting of most leaves of WT plants and obvious damage to root growth, OE5 and OE6 lines only showed slight yellowing or even no symptoms of disease (Figure 4A). The root growth was weakened, but the damage was mild (Figure 4B). The expression of StSOS1-13 in WT, OE5 and OE6 lines increased after 24 h treatment, and the expression level of StSOS1-13 in OE5 and OE6 lines was 11 and 5 times higher than that in WT, respectively (Figure 4C). The content of FOX in the leaves of OE5 and OE6 strains was significantly lower than that of WT lines from 24 h to 48 h, and decreased by 1.64 and 1.25 times compared with WT plants at 48 h (Figure 4D), respectively. The ROS accumulation, cell death number and the content of MDA in the leaves of OE5 and OE6 lines were significantly lower than those of WT plants (Figures 4E–G), while the activities of SOD and CAT were significantly increased, which were 25.8 and 11.6 times higher than those of WT plants at 24 hpi (Figure 4G). In the above results, compared with WT, the change of OE5 was more obvious than that of OE6, which was consistent with the higher overexpression level of OE5 than OE6 (Supplementary Figure S5). The above results showed that the heterologous overexpression of StSOS1-13 could improve the disease resistance of Arabidopsis by promoting root growth and development, reducing the root damage caused by FOX, increasing the activity of antioxidant enzymes, eliminating ROS and reducing the damage caused by MDA production, and the level of heterologous overexpression was positively correlated with the disease resistance of Arabidopsis.
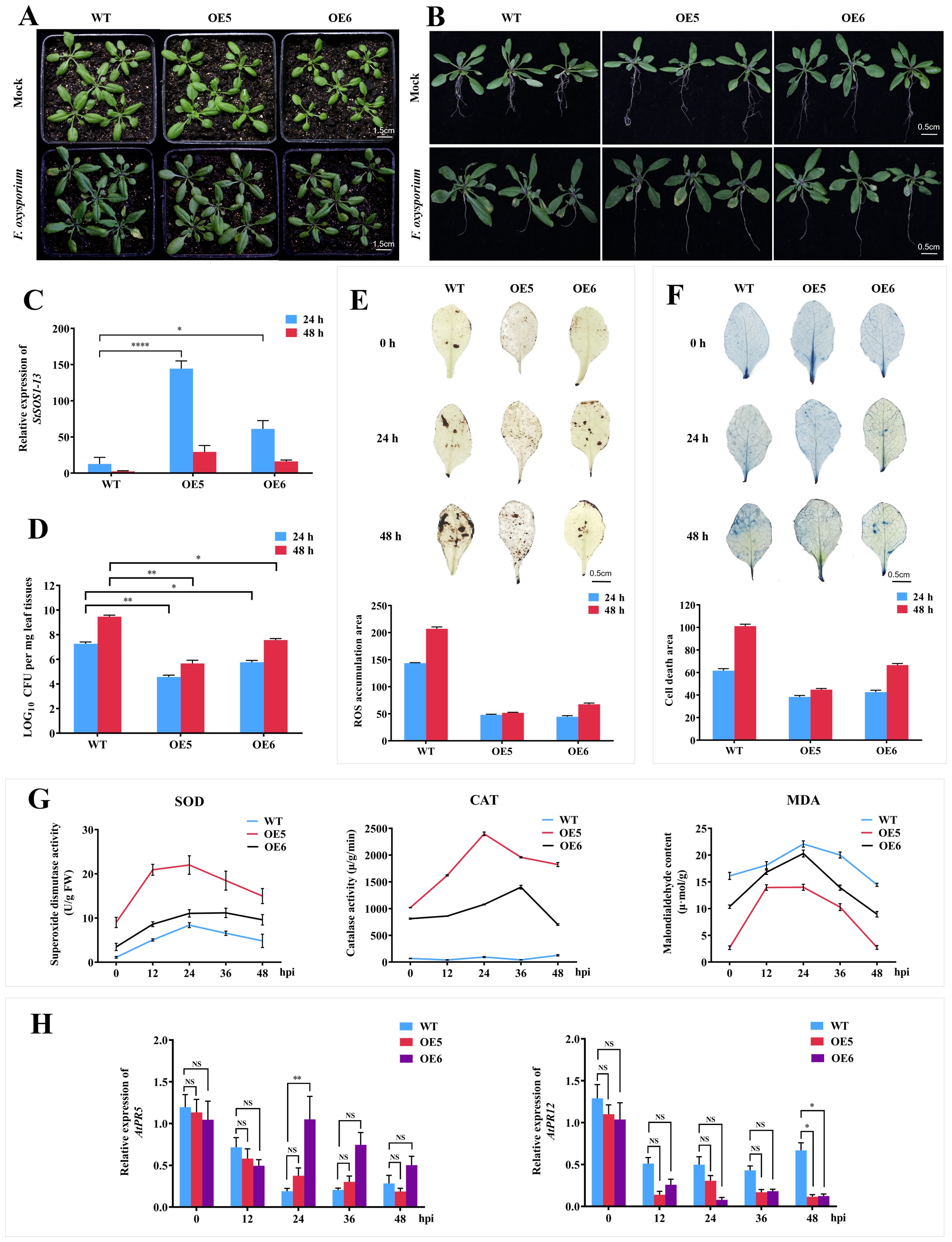
Figure 4. Heterologous overexpression of StSOS1-13 impacts the resistance to FOX in Arabidopsis. (A) Effect of FOX treatments on growth of WT, OE5 and OE6 in Arabidopsis; (B) Effect of FOX treatment on root growth of WT and transgenic lines (OE5 and OE6); (C) Relative expression levels of StSOS1-13 in WT, OE5 and OE6 inoculated with FOX; (D) Analysis of fungal biomass in the leaves of WT, OE5 and OE6 inoculated with FOX; (E) DAB staining of hydrogen peroxide (ROS) in the leaves of 2-week-old WT, OE5, and OE6 lines following inoculation with FOX; (F) Trypan blue staining indicates cell death in the leaves of 2-week-old WT, OE5, and OE6 lines post-inoculation with FOX; (G) Determination of SOD, CAT activities and MDA contents in leaves of WT, OE5 and OE6 inoculated with FOX for 0-48 hpi; (H) Transcription levels of AtPR5 and AtPR12. Asterisks indicate significant differences based on two-way ANOVA (*p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001), these experiments were performed with three independent biological replicates with similar results.
In contrast to the NbSOS1-13 VIGSed tobacco plants, infection with FOX resulted in elevated expression levels of AtPR5 in the OE5 and OE6 lines compared to WT plants at 24 hpi, with a particularly significant increase observed in the OE6 line. Unexpectedly, AtPR12 expression levels were significantly reduced in the OE5 and OE6 lines compared to WT plants at 48 hpi (Figure 4H). These findings suggest that StSOS1-13 may be positively correlated with the expression of the SA-responsible gene AtPR5, while exhibiting a negative correlation with JA-responsible gene AtPR12.
There was no significant difference in leaf stomatal aperture among the OE5, OE6 lines and WT before treated with FOX, but the difference was significant after FOX treatment for 48 hpi (Figure 5A), this was similar to NbSOS1-13 silence in tobacco. Specifically, the stomatal aspect ratios (length/width) of the OE5, OE6 lines and WT lines increased to 2.7, 1.63 and 1.58 times of that before treated with FOX, respectively (Figure 5B), and the stomata area decreased (Figure 5C), that was, stomata were partially closed. Compared to WT plants, the stomata of the OE5 and OE6 lines were significantly closed, and the closure of the OE5 line was even more significant. The above results indicate that the OE5 and OE6 lines show a faster response to leaf stomatal movement under FOX treatment than the WT, and further confirm the hypothesis of the silence experiment, that is, StSOS1-13 is involved in stomatal closure to maintain water and achieve disease resistance in Arabidopsis.
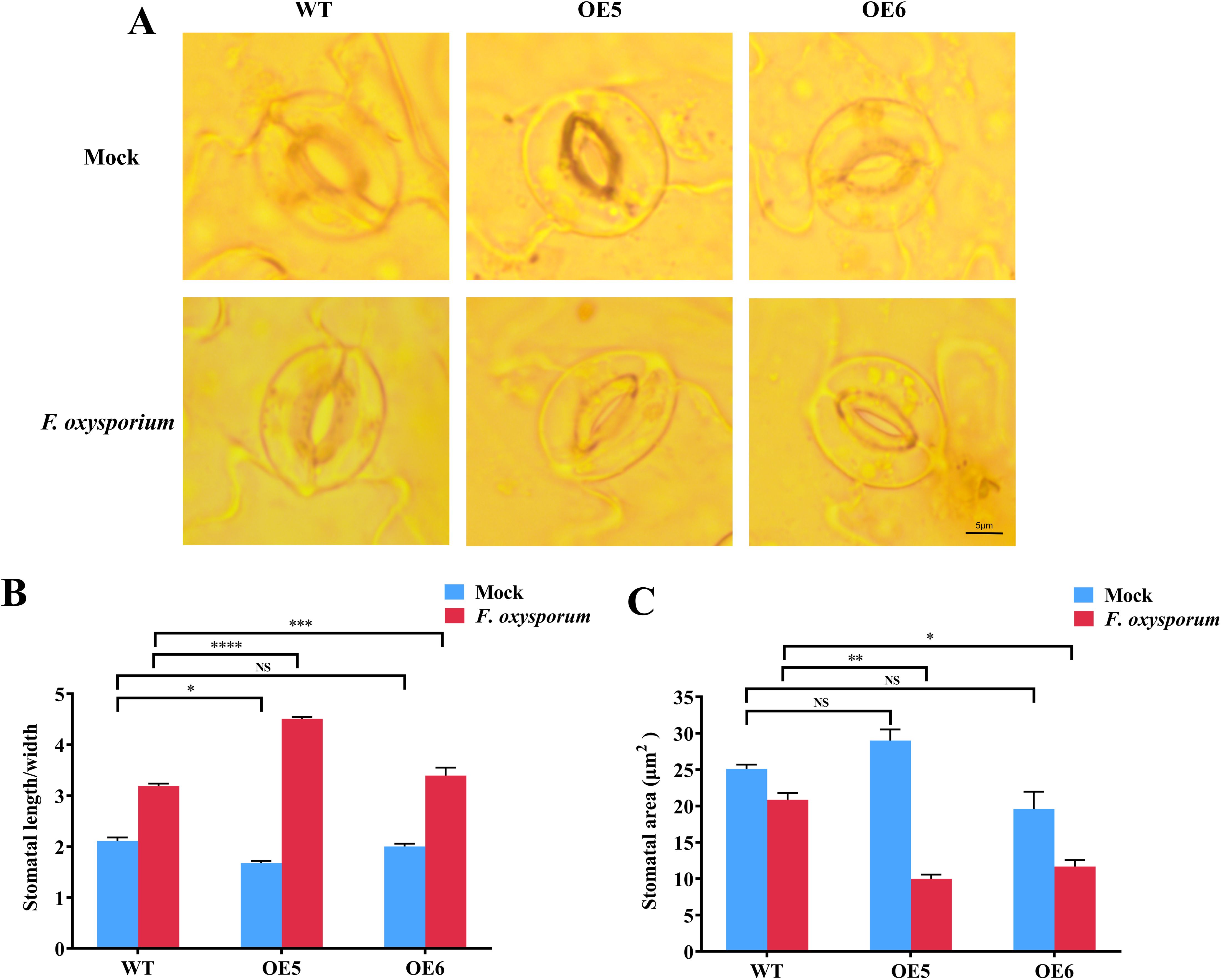
Figure 5. Stomata dynamics of Arabidopsis leaves under FOX treatment at 48 hpi. (A) Stomata aperture of WT and OE lines with mock (upper panel) and FOX (lower panel) treatment at 48 hpi; (B) Stomata aspect ratios (length/width) in WT, OE5 and OE6 lines before and after FOX treatment at 48 hpi calculated with ImageJ; (C) Leaf stomata area of WT, OE5 and OE6 lines before and after FOX treatment at 48 hpi calculated with ImageJ. Asterisks indicate significant differences based on two-way ANOVA (NS, no significant difference, *p<0.05, **p<0.01. ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001).
As an Na+/H+ antiporter, SOS1 has been confirmed playing an important role in salt tolerance in plants. There was evidence to suggest that BjSOS1 implicate in disease resistance to Plasmodiophora Brassicae (Cheng et al., 2019). In previous studies, we found that StSOS1 is involved in potato resistance to salt stress, but whether StSOS1 is involved in resistance to disease has not been reported. Therefore, this paper presents a preliminary study of whether and how StSOS1 is involved in resistance to FOX.
In this study, six StSOS1 genes were randomly selected for RT-qPCR analysis to assess their expression levels before and after infection with FOX. The results demonstrated that the expression levels of these genes initially increased and subsequently decreased, with StSOS1-13 exhibiting the most pronounced changes (Figure S1). To further investigate the role of StSOS1-13, we employed gene silencing of its ortholog, NbSOS1-13, in tobacco and heterologous overexpression of StSOS1-13 in Arabidopsis. The findings suggest that StSOS1-13 plays a significant role in mediating the immune response of both tobacco and Arabidopsis to FOX infection.
Under drought stress, stomata are closed which are regulated by ABA-mediated signal regulation mechanisms, thereby reducing transpiration, water loss and (Mega et al., 2015) photosynthesis (Gagné-Bourque et al., 2016). Under bacteria stress, plants also has evolved defense mechanisms for stomata closure, or inhibited pathogen-mediated stomata reopen upon sensing PAMPs to actively prevent bacteria from entering plant leaves (Melotto et al., 2006). Previous study has found that overexpression of AtGAP1 can reduce the size of the stomatal pore and thicken the mesophyll cell wall of Arabidopsis, forming a defense barrier that effectively limiting the entry of pathogens into the leaves (Cheng et al., 2022).
Research indicates that soybean chitinase enhances plant disease resistance and mitigates cell death by augmenting ROS accumulation and the activity of active oxygen scavenging enzymes (Zhang et al., 2016). Colletotrichum infection increased the accumulation of MDA, CAT, and SOD in cucumber resistant and susceptible lines. The resistant lines have lower MDA content and higher SOD and CAT activity compared to the sensitive lines (Yang et al., 2022). The resistance factor Pti4/5/6 may mediate the expression of PR genes regulated by SA- and ET/JA-, and Pti4 may play a role in the communication between these pathways. Over-expression of Pti4/5/6 in tomato plants increased CAT activity, decreased MDA content, and enhanced resistance to pathogens (Wang et al., 2021).
Our previous study found that StSOS1-13 was significantly up-regulated about 250 times at 1 d in leaves under ABA treatment (Liang et al., 2023), and in this study, compared with the wild type, over-expression of StSOS1-13 in Arabidopsis plants reduce the size of the stomatal pore (Figure 5A), increased SOD and CAT activity (Figure 4G), decreased ROS and MDA content (Figures 4E, G), and enhanced resistance to FOX (Figures 4D, F). However, NbSOS1-13 VIGSed tobacco lines demonstrated the contrary effect (Figures 2A, C, E). The findings suggest that StSOS1-13 plays a positive role in ABA-mediated signaling pathways during the initial immune responses of plants. This involvement is characterized by the closure of stomata, which serves to reduce transpiration and conserve water, thereby mitigating the effects of blocked xylem vessels and impaired water transport in roots induced by FOX elicitors. Additionally, StSOS1-13 contributes to the enhancement of the plant’s antioxidant capacity.
Overexpression of certain PR genes, including PR5 and PR12, greatly increased the level of plant defensive response to various pathogens (Liu et al., 2022), and overexpression of PR5 may active many defense genes in the SA or JA/ET signaling pathways (Liu et al., 2022; Yan et al., 2017). In A. sativum, expression of the PR1, PR3, and PR5 genes was thought to be a positive marker of plant resistance to FOX f. sp (Anisimova et al., 2021), and PR1, PR2, and PR5 were the marker genes induced by SA (Ali et al., 2022). In Arabidopsis, the cad-C/cad-D mutation negatively affected PR1 and PR5 expression after infection with P. syringae pv (Rong et al., 2016). Our prior study also corroborated these findings, and there was a significant upregulation of StSOS1-13 gene expression following 1 to 5 days of SA treatment, with a pronounced peak on day 3 (Liang et al., 2023). In the present study, the findings demonstrated that, compared to WT plants, the expression level of StSOS1-13 was significantly up-regulated in the OE5 and OE6 lines at 24 and 48 hpi with FOX (Figure 4C). Additionally, the expression level of AtPR5 at 12 hpi was significantly higher in the OE6 lines than in the WT plants (Figure 4H). Unexpectedly, the expression level of AtPR12 exhibited an opposite trend to that of AtPR5, being significantly lower at 48 hpi in the OE5 and OE6 lines compared to the WT (Figure 4H). The findings indicate that the overexpression of StSOS1-13 potentially enhances the expression of the SA-responsible gene AtPR5, while concurrently reduces the expression of the JA-responsible gene AtPR12. This divergent outcome may be attributed to the antagonistic effects of SA (is pivotal in early PTI) and JA (is essential in late ETI) signaling pathways during immune responses (Ali et al., 2018; Luo et al., 2020).
Conversely, in comparison to WT plants, the expression level of NbSOS1-13 was significantly downregulated in NbSOS1-13-silenced tobacco lines between 24 and 48 hpi (Figure 2B), particularly at 24 hpi. Furthermore, the expression levels of NbPR5 and NbPR12 in the NbSOS1-13-silenced tobacco lines were significantly lower than those in the WT at 12 and 48 hpi with FOX, respectively (Figure 2F). Compared with the OE5 and OE6 lines, the consistency of NbPR5 and NbPR12 gene expression trends in NBSOS1-13-silenced tobacco may be due to the fact that the silencing of NbSOS1-13 leads tobacco to enter the ETI stage from PTI more quickly, and there is a synergistic effect between SA and JA in this stage.
Based on the above analysis, it is speculated that StSOS1-13 plays a role in coordinating SA- and JA-mediated pathways, specifically, influencing PR5 and PR12 expression in response to FOX invasion during the early stages of immune events.
Gibberellic acid (GA), a phytohormone, plays a crucial role in regulating multiple facets of plant development and growth, including seed development and germination, stem and root growth, cell division, and the timing of flowering (Kwon and Paek, 2016). StSOS1-13 gene expression increased significantly within 1 to 2 days of GA treatment (Liang et al., 2023). Compared with WT, StSOS1-13 overexpression Arabidopsis (OE5 and OE6 lines) significantly increased root length (Figure 4B) and decreased sensitivity to FOX (Figures 4A, B), and during the mature stage, the OE5 and OE6 lines exhibited a significant decrease in plant height, a reduction in stem length, a delay in flowering (Supplementary Figure S5). These results indicated that the ectopic overexpression of StSOS1-13 may enhance resistance to FOX by inhibiting the growth of the aboveground part of Arabidopsis, but promoted the root elongation through positively participating in GA-mediated growth and development metabolic pathways. The results suggest that StSOS1-13 may enhance resistance to FOX by actively participating in GA-mediated growth and developmental metabolic pathways. This process promotes root development while inhibiting aerial growth in Arabidopsis.
Based on our findings and others existing studies (Dai et al., 2018; Feki et al., 2016; Guo et al., 2004; Kumari et al., 2017), a potential mechanism by which StSOS1-13 contributes to disease resistance in potato can be inferred as follows: upon infection by FOX, plants experience competition for essential nutrients and water with the pathogen, leading to water loss in plant tissues, elevated intracellular Na+ concentrations, Ca2+ influx, and the activation of downstream Ca2+ signal pathways. The proteins StSOS2 and StSOS3 interact to form a complex that activates StSOS1-13 (D et al., 2008; Yuan and Poovaiah, 2022), which plays a crucial role in pathogen immunity through signaling pathways mediated by ABA, GA, SA and JA. StSOS1-13 is actively involved in the early ABA-mediated PTI signaling pathway during the initial stages of FOX infection. This involvement includes enhancing the antioxidant capacity to mitigate damage caused by ROS accumulation, which further facilitates the binding of StSOS1-13 with the StSOS2-StSOS3 complex, and promoting stomatal closure to counteract the clogging of woody tubes and water loss (Gu et al., 2022) associated with the proliferation of FOX. In this study, plants overexpressing StSOS1-13 exhibited slower growth and delayed flowering in their above-ground parts (Supplementary Figure S5E), potentially due to excessive stomatal closure (Figure 5A). This condition likely resulted in reduced photosynthesis and a deceleration of anabolic metabolism. The involvement of StSOS1-13 in the ABA-mediated signaling pathway appears to inhibit growth and development in the aerial portions of the plants (Supplementary Figure S5E), and slowed down FOX reproduction (Figure 4D). Conversely, overexpression of StSOS1-13 is associated with increased GA-mediated root length (Figure 4B), which may enhance water absorption during stomatal closure (Gu et al., 2022) and provide resistance against FOX through root exudates (Lu et al., 2022; Zhang et al., 2020). Furthermore, the silencing or overexpression of SOS1-13 was found to respectively changed the expression of PR5 and PR12, suggesting that StSOS1-13 is involved in regulating SA and JA mediated immune responses. In general, StSOS1-13, as a regulate hub of the defense response to FOX, plays an indispensable role in multiple signaling pathways, thereby resisting the invasion of FOX. This study offers a novel perspective for further elucidating the mechanisms of StSOS1-13 mediated resistance to plant diseases.
However, The precise function of StSOS1-13 in the potato immune response requires more in-depth research, such as through genome editing techniques in potato to understand the function of this gene and its upstream and downstream regulatory relationships, and then use StSOS1-13 as a possible candidate gene for disease resistance breeding in the future.
In summary, this study shows that StSOS1 -13 can serve as a connection point for multiple signaling pathways, such as ABA, SA, JA, and GA, by improving the antioxidant defense system, promotes root development to enhance water uptake, and closes leaf stomata to conserve water from evaporation, in response to FOX stress in potatoes.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
LL: Writing – review & editing. XL: Writing – original draft. LG: Writing – original draft. LW: Software, Writing – original draft. YZ: Software, Writing – original draft. YW: Writing – original draft. YC: Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. WL: Writing – review & editing. GG: Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Fundamental Research Program of Shanxi Province (No.202203021211259), Fundamental Research Program of Shanxi Province (No.202203021211249), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.32472200), Postgraduate Innovation Project of Shanxi Province (No. 2023KY469), Postgraduate Education Reform Project of Shanxi Province (No. 2023JG096).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpls.2025.1553348/full#supplementary-material
Ali, M., Ahmad, H., Amin, B., Atif, M. J., Cheng, Z. (2022). Induce defense response of DADS in eggplants during the biotrophic phase of Verticillium dahliae. BMC Plant Biol. 22, 172. doi: 10.1186/s12870-022-03527-7
Ali, A., Alexandersson, E., Sandin, M., Resjö, S., Lenman, M., Hedley, P., et al. (2014). Quantitative proteomics and transcriptomics of potato in response to Phytophthora infestans in compatible and incompatible interactions. BMC Genomics 15, 497. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-497
Ali, S., Ganai, B. A., Kamili, A. N., Bhat, A. A., Mir, Z. A., Bhat, J. A., et al. (2018). Pathogenesis-related proteins and peptides as promising tools for engineering plants with multiple stress tolerance. Microbiological Res. 212-213, 29–37. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2018.04.008
Ali, A., Raddatz, N., Pardo, J. M., Yun, D. J. (2021). HKT sodium and potassium transporters in Arabidopsis thaliana and related halophyte species. Plant Physiol. 171, 546–558. doi: 10.1111/ppl.13166
Anisimova, O. K., Shchennikova, A. V., Kochieva, E. Z., Filyushin, M. A. (2021). Pathogenesis-related genes of PR1, PR2, PR4, and PR5 families are involved in the response to Fusarium infection in garlic (Allium sativum L.). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 6688. doi: 10.3390/ijms22136688
Chen, X., Bao, H., Guo, J., Jia, W., Li, Y. (2015). Overexpression ofSeNHX1improves both salt tolerance and disease resistance in tobacco. Plant Signaling Behavior 10, e993240. doi: 10.4161/15592324.2014.993240
Chen, X., Bao, H., Guo, J., Jia, W., Tai, F., Nie, L., et al. (2014). Na+/H+ exchanger 1 participates in tobacco disease defence against Phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae by affecting vacuolar pH and priming the antioxidative system. J. Exp. Botany 65, 6107–6122. doi: 10.1093/jxb/eru351
Chen, X., Lu, X., Shu, N., Wang, D., Wang, S., Wang, J., et al. (2017). GhSOS1, a plasma membrane Na+/H+ antiporter gene from upland cotton, enhances salt tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana. PloS One 12, e0181450. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0181450
Cheng, S.-S., Ku, Y.-S., Cheung, M.-Y., Lam, H.-M. (2022). AtGAP1 Promotes the Resistance to Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000 by Regulating Cell-Wall Thickness and Stomatal Aperture in Arabidopsis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 7540. doi: 10.3390/ijms23147540
Cheng, C., Zhong, Y., Wang, Q., Cai, Z., Wang, D., Li, C. (2019). Genome-wide identification and gene expression analysis of SOS family genes in tuber mustard (Brassica juncea var. tumida). PloS One 14, e0224672. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0224672
D, J. L., Boettcher, A., Little, A., Shirley, N., Able, A. J. (2008). Identification and characterisation of barley (Hordeum vulgare) respiratory burst oxidase homologue family members. Functioal Plant Biol. 35, 347–359. doi: 10.1071/fp08109
Dahal, K., Li, X. Q., Tai, H., Creelman, A., Bizimungu, B. (2019). Improving potato stress tolerance and tuber yield under a climate change scenario - A current overview. Front. Plant Sci. 10. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.00563
Dai, W., Wang, M., Gong, X., Liu, J. H. (2018). The transcription factor FcWRKY40 of Fortunella crassifolia functions positively in salt tolerance through modulation of ion homeostasis and proline biosynthesis by directly regulating SOS2 and P5CS1 homologs. New Phytologist. 219, 972–989. doi: 10.1111/nph.15240
Feki, K., Tounsi, S., Masmoudi, K., Brini, F. (2016). The durum wheat plasma membrane Na+/H+ antiporter SOS1 is involved in oxidative stress response. Protoplasma 254, 1725–1734. doi: 10.1007/s00709-016-1066-8
Gagné-Bourque, F., Bertrand, A., Claessens, A., Aliferis, K. A., Jabaji, S. (2016). Alleviation of drought stress and metabolic changes in timothy (Phleum pratense L.) Colonized with Bacillus subtilis B26. Front. Plant Sci. 7. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.00584
Gámez-Arjona, F., Park, H. J., García, E., Aman, R., Villalta, I., Raddatz, N., et al. (2024). Inverse regulation of SOS1 and HKT1 protein localization and stability by SOS3/CBL4 in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 121, e2320657121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2320657121
Gao, S., Yuan, L., Zhai, H., C.-l., L., He, S.-z., Liu, Q.-c. (2012). Overexpression of SOS genes enhanced salt tolerance in sweetpotato. J. Integr. Agric. 11, 378–386. doi: 10.1016/s2095-3119(12)60022-7
Gu, H., Zhang, K., Chen, J., Gull, S., Chen, C., Hou, Y., et al. (2022). OsFTL4, an FT-like gene, regulates flowering time and drought tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Rice 15, 47. doi: 10.1186/s12284-022-00593-1
Guo, Y., Qiu, Q.-S., Quintero, F. J., Pardo, J. M., Ohta, M., Zhang, C., et al. (2004). Transgenic evaluation of activated mutant alleles of SOS2 reveals a critical requirement for its kinase activity and C-terminal regulatory domain for salt tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell. 16, 435–449. doi: 10.1105/tpc.019174
He, F., Duan, S., Jian, Y., Xu, J., Hu, J., Zhang, Z., et al. (2022). Genome-wide identification and gene expression analysis of the 14-3-3 gene family in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). BMC Genomics 23, 811. doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-09037-y
He, J., Gu, L., Tan, Q., Wang, Y., Hui, F., He, X., et al. (2022). Genome-wide analysis and identification of the PEBP genes of Brassica juncea var. Tumida. BMC Genomics 23, 535. doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-08767-3
Jiang, Z., Zhou, X., Tao, M., Yuan, F., Liu, L., Wu, F., et al. (2019). Plant cell-surface GIPC sphingolipids sense salt to trigger Ca2+ influx. Nature 572, 341–346. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1449-z
Kang, W.-H., Park, B., Lee, J., Yeom, S.-I. (2021). Tissue-specific RNA-seq analysis and identification of receptor-like proteins related to plant growth in Capsicum annuum. Plants 10, 972. doi: 10.3390/plants10050972
Kumari, P. H., Kumar, S. A., Sivan, P., Katam, R., Suravajhala, P., Rao, K. S., et al. (2017). Overexpression of a plasma membrane bound Na+/H+ Antiporter-like protein (SbNHXLP) confers salt tolerance and improves fruit yield in tomato by maintaining ion homeostasis. Front. Plant Sci. 7. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.02027
Kwon, C. T., Paek, N. C. (2016). Gibberellic acid: A key phytohormone for spikelet fertility in rice grain production. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 17, 794. doi: 10.3390/ijms17050794
Li, M., Xie, L., Wang, M., Lin, Y., Zhong, J., Zhang, Y., et al. (2022). FoQDE2-dependent milRNA promotes Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense virulence by silencing a glycosyl hydrolase coding gene expression. PloS Pathogens 18, e1010157. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010157
Li, H., Zhang, D., Xie, K., Wang, Y., Liao, Q., Hong, Y., et al. (2021). Efficient and high-throughput pseudorecombinant-chimeric Cucumber mosaic virus-based VIGS in maize. Plant Physiol. 187, 2865–2876. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiab443
Li, L., Zhu, T., Song, Y., Feng, L., Kear, P. J., Riseh, R. S., et al. (2022). Salicylic acid fights against Fusarium wilt by inhibiting target of rapamycin signaling pathway in Fusarium oxysporum. J. Advanced Res. 39, 1–13. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2021.10.014
Liang, L., Guo, L., Zhai, Y., Hou, Z., Wu, W., Zhang, X., et al. (2023). Genome-wide characterization of SOS1 gene family in potato (Solanum tuberosum) and expression analyses under salt and hormone stress. Front. Plant Sci. 14. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1201730
Liu, Z., Sun, Z., Zeng, C., Dong, X., Li, M., Liu, Z., et al. (2022). The elemental defense effect of cadmium on Alternaria brassicicola in Brassica juncea. BMC Plant Biol. 22, 17. doi: 10.1186/s12870-021-03398-4
Lu, L., Liu, H., Wu, Y., Yan, G. (2022). Identification and validation of a chromosome 4D quantitative trait locus hotspot conferring heat tolerance in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Plants 11, 729. doi: 10.3390/plants11060729
Luo, Y., Wang, Q., Bai, R., Li, R., Chen, L., Xu, Y., et al. (2020). The effect of transcription factor MYB14 on defense mechanisms in Vitis quinquangularis-pingyi. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21, 706. doi: 10.3390/ijms21030706
Mega, R., Meguro-Maoka, A., Endo, A., Shimosaka, E., Murayama, S., Nambara, E., et al. (2015). Sustained low abscisic acid levels increase seedling vigor under cold stress in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Sci. Rep. 5, 13819. doi: 10.1038/srep13819
Melotto, M., Underwood, W., Koczan, J., Nomura, K., He, S. Y. (2006). Plant stomata function in innate immunity against bacterial invasion. Cell 126, 969–980. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.06.054
Munthali, C., Kinoshita, R., Onishi, K., Rakotondrafara, A., Mikami, K., Koike, M., et al. (2022). A model nutrition control system in potato tissue culture and its influence on plant elemental composition. Plants (Basel) 11, 2718. doi: 10.3390/plants11202718
Murphy, F., He, Q., Armstrong, M., Giuliani, L. M., Boevink, P. C., Zhang, W., et al. (2018). The potato MAP3K stVIK is required for the Phytophthora infestans RXLR effector pi17316 to promote disease. Plant Physiol. 177, 398–410. doi: 10.1104/pp.18.00028
Olias, R., Eljakaoui, Z., Li, J., De Morales, P. A., Marin-Manzano, M. C., Pardo, J. M., et al. (2009). The plasma membrane Na+/H+ antiporter SOS1 is essential for salt tolerance in tomato and affects the partitioning of Na+ between plant organs. Plant Cell Environ. 32, 904–916. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3040.2009.01971.x
Qian, H., Wang, L., Wang, B., Liang, W. (2022). The secreted ribonuclease T2 protein FoRnt2 contributes to Fusarium oxysporum virulence. Mol. Plant Pathol. 23, 1346–1360. doi: 10.1111/mpp.13237
Qin, J., Bian, C., Duan, S., Wang, W., Li, G., Jin, L. (2022). Effects of different rotation cropping systems on potato yield, rhizosphere microbial community and soil biochemical properties. Front. Plant Sci. 13. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.999730
Rong, W., Luo, M., Shan, T., Wei, X., Du, L., Xu, H., et al. (2016). A wheat cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase taCAD12 contributes to host resistance to the sharp eyespot disease. Front. Plant Sci. 7. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.01723
Sakata, N., Haraguchi, T., Masuo, S., Ishiga, T., Ishiga, Y. (2022). Pseudomonas cannabina pv. alisalensis Virulence Factors Are Involved in Resistance to Plant-Derived Antimicrobials during Infection. Plants 11, 1742. doi: 10.3390/plants11131742
Shi, Z., Chen, X., Xue, H., Jia, T., Meng, F., Liu, Y., et al. (2022). GhBZR3 suppresses cotton fiber elongation by inhibiting very-long-chain fatty acid biosynthesis. Plant J. 111, 785–799. doi: 10.1111/tpj.15852
Shi, H., Lee, B. H., Wu, S. J., Zhu, J. K. (2003). Overexpression of a plasma membrane Na+/H+ antiporter gene improves salt tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Natural Biotechnol. 21, 81–85. doi: 10.1038/nbt766
Villalta, I., García, E., Hornero-Mendez, D., Carranco, R., Tello, C., Mendoza, I., et al. (2021). Distinct roles of N-terminal fatty acid acylation of the salinity-sensor protein SOS3. Front. Plant Sci. 12. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.691124
Wang, Y., Feng, G., Zhang, Z., Liu, Y., Ma, Y., Wang, Y., et al. (2021). Overexpression of Pti4, Pti5, and Pti6 in tomato promote plant defense and fruit ripening. Plant Sci. 302, 110702. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2020.110702
Wang, W., Wang, S., Gong, W., Lv, L., Xu, L., Nie, J., et al. (2022). Valsa Mali secretes an effector protein VmEP1 to target a K homology domain-containing protein for virulence in apple. Mol. Plant Pathol. 23, 1577–1591. doi: 10.1111/mpp.13248
Wang, X., Yang, J., Mohamed, H., Shah, A. M., Li, S., Pang, S., et al. (2022). Simultaneous overexpression of Δ6-, Δ12- and Δ9-desaturases enhanced the production of γ-linolenic acid in Mucor circinelloides WJ11. Front. Microbiol. 13. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1078157
Wullings, B. A., Van Beuningen, A. R., Janse, J. D., Akkermans, A. D. L. (1998). Detection of Ralstonia solanacearum, which causes brown rot of potato, by fluorescent in situ hybridization with 23S rRNA-targeted probes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 64, 4546–4554. doi: 10.1128/aem.64.11.4546-4554.1998
Yan, X., Qiao, H., Zhang, X., Guo, C., Wang, M., Wang, Y., et al. (2017). Analysis of the grape (Vitis vinifera L.) thaumatin-like protein (TLP) gene family and demonstration that TLP29 contributes to disease resistance. Sci. Rep. 7, 4269. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-04105-w
Yang, Y., Guo, Y. (2017). Elucidating the molecular mechanisms mediating plant salt-stress responses. New Phytologist. 217, 523–539. doi: 10.1111/nph.14920
Yang, C., Wu, P., Cao, Y., Yang, B., Liu, L., Chen, J., et al. (2022). Overexpression of dihydroflavonol 4-reductase (CoDFR) boosts flavonoid production involved in the anthracnose resistance. Front. Plant Sci. 13. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1038467
Yin, C. M., Li, J. J., Wang, D., Zhang, D. D., Song, J., Kong, Z. Q., et al. (2022). A secreted ribonuclease effector from Verticillium dahliae localizes in the plant nucleus to modulate host immunity. Mol. Plant Pathol. 23, 1122–1140. doi: 10.1111/mpp.13213
Yuan, P., Poovaiah, B. W. (2022). Interplay between ca2+/calmodulin-mediated signaling and atSR1/CAMTA3 during increased temperature resulting in compromised immune response in plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 2175. doi: 10.3390/ijms23042175
Zhang, M., Cao, J., Zhang, T., Xu, T., Yang, L., Li, X., et al. (2022). A putative plasma membrane Na+/H+ Antiporter gmSOS1 is critical for salt stress tolerance in glycine max. Front. Plant Sci. 13. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.870695
Zhang, F., Ruan, X., Wang, X., Liu, Z., Hu, L., Li, C. (2016). Overexpression of a chitinase gene from Trichoderma asperellum increases disease resistance in transgenic soybean. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 180, 1542–1558. doi: 10.1007/s12010-016-2186-5
Zhang, L., Zhang, S., Dai, Y., Wang, S., Wang, C., Li, F., et al. (2022). Mapping and validation of BrGOLDEN: A dominant gene regulating carotenoid accumulation in Brassica rapa. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 12442. doi: 10.3390/ijms232012442
Zhang, C.-S., Zheng, Y., Peng, L., Cao, J. (2020). Rootstock-scion interaction affects the composition and pathogen inhibitory activity of tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.) root exudates. Plants 9, 1652. doi: 10.3390/plants9121652
Zhao, X., Wei, P., Liu, Z., Yu, B., Shi, H. (2016). Soybean Na+/H+ antiporter GmsSOS1 enhances antioxidant enzyme activity and reduces Na+ accumulation in Arabidopsis and yeast cells under salt stress. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum 39, 1–11. doi: 10.1007/s11738-016-2323-3
Zhou, X., Li, J., Wang, Y., Liang, X., Zhang, M., Lu, M., et al. (2022). The classical SOS pathway confers natural variation of salt tolerance in maize. New Phytologist. 236, 479–494. doi: 10.1111/nph.18278
Keywords: potato, SOS1, resistance, Fusarium oxysporum, stomata movement
Citation: Liang L, Liu X, Guo L, Wang L, Zhao Y, Wu Y, Chen Y, Liu W and Gao G (2025) Beyond salt tolerance: SOS1-13’s pivotal role in regulating the immune response to Fusarium oxysporum in Solanum phureja. Front. Plant Sci. 16:1553348. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1553348
Received: 30 December 2024; Accepted: 10 February 2025;
Published: 06 March 2025.
Edited by:
Jian Chen, Jiangsu University, ChinaReviewed by:
Feng-Zhu Wang, Sun Yat-sen University, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Liang, Liu, Guo, Wang, Zhao, Wu, Chen, Liu and Gao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Weizhong Liu, bGl1d3poQHN4bnUuZWR1LmNu; Gang Gao, Z2dzeG51QDEyNi5jb20=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.