
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Plant Sci. , 18 February 2025
Sec. Plant Abiotic Stress
Volume 16 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2025.1549506
This article is part of the Research Topic Plant Ecophysiology: Responses to Climate Changes and Stress Conditions View all 31 articles
Micro-sprinkler irrigation has been a promising irrigation method to promote Panax notoginseng (Burk) F. H. Chen production but their scientific irrigation frequency in improving yield and water use efficiency of P. notoginseng remains contradictory and inconclusive. The objective of this study was therefore to examine and propose a scientific irrigation frequency in water management of P. notoginseng cultivation considering their impact on soil water, soil available nutrients, root growth, yield, and water use efficiency (WUE). The micro-sprinkler irrigation experiment under shading and rain-shelter conditions was carried out in the growing season of P. notoginseng from 2017 to 2018.The treatments included four micro-sprinkler irrigation frequencies, such as IF1 (irrigation once every three days), IF2 (irrigation once every five days), IF3 (irrigation once every seven days), and IF4 (irrigation once every nine days) in 2017-2018. The results indicated that the IF3 treatment significantly increased the nitrogen accumulation of P. notoginseng (271.98 mg plant-1). In addition, the IF2 treatment enhanced the phosphorus accumulation (27.82 mg plant-1), potassium accumulation (408.38 mg plant-1), total root surface area (67.49 cm2 plant-1), total root volume (3.79 cm3 plant-1) and yield (702 kg ha-1). The IF2 treatment significantly increased WUE by 29.2%, 28.1%, and 37.7% compared with the IF1, IF3, and IF4 treatments, respectively. Our findings suggested that IF2 treatment increased the soil water content, reduced the soil nutrient content, increased the accumulation of phosphorus and potassium in P. notoginseng, promoted the root growth of P. notoginseng, and improved the quality and yield of P. notoginseng, providing a scientific theoretical basis for reasonable water control and green quality production in the cultivation of P. notoginseng under shade and rain shelter cultivation.
P. notoginseng (Burk. F. H. Chen) was a traditional perennial precious herb with an artificially cultivated history of more than 400 years (Armstrong, 2005; Bengough et al., 2011). It was widely distributed in the world, especially in southwest China (Wang et al., 2006). The roots, stems and leaves of P. notoginseng contain saponins, salicylidine, GABA (γ-aminobutyric acid), and other components, which had extremely high pharmacological effects (Li et al., 2022; Zhou et al., 2020). Modern studies confirmed that P. notoginseng has multiple pharmacological functions on antihypertensive, antithrombotic, antioxidation and neuroprotective actions, regulating the immune system and promoting metabolism and so on (Yang et al., 2015). P. notoginseng was also the main component of Yunnan Baiyao, Compound Danshen Dripping Pills, Pien Tze Huang and many other traditional Chinese medicine preparations, which had important economic value (Ji et al., 2022). Due to its unique medicinal and edible value, the market demand of P. notoginseng was growing rapidly (Chen et al., 2023). To improve the yield of P. notoginseng and pursue the maximization of economic benefits, growers often use excessive water and fertilizer applications (Xia et al., 2016). However, adequate irrigation was not sustainable for the semiarid areas of Yunnan Province. Excessive irrigation may lead to soil salinization and water resource depletion, which would have a negative impact on the ecological environment and the sustainable development of agricultural management. Therefore, it was urgent to balance the relationship between agricultural production demand and ecological protection in irrigation management, explore the demand of P. notoginseng for nutrients and water, and propose appropriate irrigation strategies.
Water and fertilizer regulation was crucial to the physiological growth and nutrient absorption of P. notoginseng (Shen, 2024). Irrigation mechanisms could regulate soil water and temperature, and soil water content directly affects plants’ water regimes and is closely related to plants’ healthy growth (Man, 2014). Excessive or low soil water content could significantly affect the growth, water absorption, and yield of P. notoginseng, thus reducing water use efficiency (Li et al., 2019). Irrigation requirements vary according to location, soil type and crop growth characteristics, involving the form of irrigation water entering the soil in the root zone of the crops (Lebourgeois et al., 2010; Ravikumar et al., 2011; Rodrigues et al., 2013). Micro-sprinkler irrigation was an effective water-saving irrigation technology, that was widely used in crop precision irrigation and could achieve sustainable economic benefits of crops. Compared with drip irrigation, micro-sprinkler irrigation significantly increased crop yield by 7.3% (Majumder et al., 2008). Appropriate micro-sprinkler irrigation could improve water use efficiency, enhance soil permeability, reduce soil water loss, and effectively increase the yield of P. notoginseng (Kumar et al., 2014; Xu et al., 2022; Zheng et al., 2021). Previous studies have found that different irrigation frequencies have significant effects on crop growth and yield (Liu H. et al., 2019; Souza and Vieira, 2020). At the same time, no irrigation frequency will also change the root water absorption capacity of crops (Brighenti, 2024). Adopting scientific and reasonable irrigation methods was of great significance for improving the growth environment of P. notoginseng and promoting the sustainable development of P. notoginseng cultivation (Yang et al., 2023).
Suitable irrigation enhanced plant immunity and promotes growth by affecting plant nutrient accumulation and soil physical properties, which was beneficial for higher yields (Chai et al., 2016). The water-demand characteristics of many crops have been studied in conventional agricultural cultivation (Kresović et al., 2016; Chai et al., 2016), however, there were few research reports on the effects of irrigation frequencies on P. notoginseng. This experiment investigated the effects of micro-sprinkler irrigation combined with organic fertilizer on the growth, root hydraulic conductivity, nutrient accumulation, yield, and water use efficiency of 2-year-old P. notoginseng. Therefore, this experiment studied the effect of irrigation frequency of micro-sprinkler irrigation on P. notoginseng under the condition of shading and rain avoidance, aiming at (1) exploring the effects of irrigation frequencies on soil water content and soil nutrients in the soil layer of 0~40 cm; (2) analyzing the effects of irrigation frequencies on the morphological characteristics of P. notoginseng roots, root hydraulic conductivity, nutrient accumulation, yield and water use efficiency; and (3) determining effective irrigation management strategies for P. notoginseng cultivation.
The experiment was conducted in the shade and rain shelter cultivation greenhouse (102°52′13″E, 24°50′57″N) at the experimental base of Kunming University of Science and Technology (KUST) Chenggong Campus from March 2017 to November 2018. The specific geographic location was shown in Figure 1. The top of the greenhouse was covered with three layers of shading net, and the light transmittance was 8.3%. The climate was subtropical plateau monsoon. The water used for irrigation was tap water for domestic use, containing trace amounts of sodium chloride and sub-sodium chloride, as well as calcium, magnesium, potassium and sulfate. pH was 6.87, showing weak acidity. Soil properties, both physical and chemical, at the experimental site are shown in Table 1.
Figure 1. (A) The location of Yunnan Province in China. (B) the location of Kunming in Yunnan Province. (C) The location of the experimental site.
The experiment included four irrigation frequency levels (IF1:3 d time-1, IF2:5d time-1, IF3:7 d time-1, IF4: 9 d time-1). Each treatment was repeated 2 times, a total of 8 experimental cells. In the shade and rain shelter cultivation greenhouse, there were 8 ridges of P. notoginseng test field, the ridge length was 4.4 m, the width was 1.2 m, the height was 0.3 m, and the ridge distance was 0.5 m. The experiment used micro-sprinkler fertilization (water and fertilizer integration fertilization technology). The soluble fertilizer (Sichuan Shifang DEMEI company. China) dissolved in water through a proportional fertilization device (Jinhua Yurun Fountain Drip Irrigation Co., Ltd.). China) at a ratio of 1:800. During irrigation, fertilizer is applied simultaneously through a micro-sprinkler irrigation device. Fertilization frequency is 15 days a time. Irrigation and fertilization were conducted from 17:00 to 19:00. During the test, keep the greenhouse ventilated and remove the diseased plants in time.
According to previous studies, the root growth of P. notoginseng was mainly distributed in the 0-40 cm soil layer (Yue et al., 2023; Zang, 2022), so the soil indexes in this study were sampled and analyzed in 0-40 cm soil layer.
During the experiment, soil samples at depths of 10, 20, 30, and 40 cm were collected by artificial spiral drills at 1 h before irrigation, 1 day after irrigation, and in the middle of irrigation (IF1 at 1.5 days after irrigation, IF2 at 2.5 days after irrigation, IF3 at 3.5 days after irrigation and IF4 at 4.5 days after irrigation) at the seedling stage, flowering stage, fruiting stage, and root growth stage, respectively. Determine the soil water content. Each plot was repeated three times to calculate the average soil water content. The soil moisture content of soil samples was determined by the drying method. All soil samples were dried at 105°C for 6-8h to constant weight, and then the soil water content was determined by weighing method. The volumetric soil water content was calculated by multiplying the mass soil water content by the soil bulk density (Liang et al., 2021).
According to the characteristics of the growth stage of P. notoginseng, soil samples were collected at seedling, flowering, fruiting, and root growth stages. The sampling depths were 10, 20, 30, and 40 cm, respectively, and each plot was repeated three times. Soil alkali hydrolyzed nitrogen content was determined by the standard method of the Agricultural industry of the People’s Republic of China (LY/T 1229-1999). Soil available phosphorus content was determined by the agricultural industry-standard method of the People’s Republic of China (NY/T 1121.7-2014) and was extracted by ammonium fluorine-hydrochloric acid solution. Soil available potassium content was determined via the flame photometer specified in the agricultural industry-standard method (NY/T 889-2004) (Cheng et al., 2023). The average soil alkali hydrolyzed nitrogen content, available phosphorus, and available potassium were calculated respectively.
The dried samples of the aboveground and underground parts of P. notoginseng were crushed in a grinder and filtered with a 0.5 mm sieve. The total nitrogen content was determined by an automatic Kjeldahl nitrogen analyzer (Haineng Company, China). The content of total phosphorus was determined by the molybdenum antimony anti-colorimetric method. The total potassium content was determined by a flame photometer (Fuentes-Soriano et al., 2019).
Three representative healthy plants were randomly selected from each plot, and the hydraulic conductivity of P. notoginseng at seedling, flowering, fruiting, and root growth stages was measured by HPFM-Gen3 high pressure flow meter (Dynamax Company, USA).
The aboveground and underground parts of P. notoginseng were collected during the root growth stage, each test plot was repeated three times. After the roots were cleaned, the STD4800 root scanner (EPSON, Japan) was used to scan the whole roots. Then the total root length, total root surface area, and total root volume were analyzed and output by the WINRHIZOPRO2007 root analysis system. The aboveground and underground parts of P. notoginseng were put into file bags and then dried at 60 °C for 48 hours in the oven (Donnelly et al., 2016). Then the samples were weighed to obtain the dry matter mass of the aboveground and underground parts of P. notoginseng.
The yield was calculated by multiplying the average yield per plant by the planting density (number of plants per hectare) and then by the planting area (Xia et al., 2016).
Soil water storage (SWS) in the root zone (0-40 cm) of P. notoginseng was calculated by the following equation (Liang et al., 2019):
Where SWS is soil water storage in the root zone (0-40 cm) of P. notoginseng, mm; is the average soil water content in 0-10 cm soil layer (cm3 cm-3); is the average soil water content in 10-20 cm soil layer (cm3 cm-3); is the average soil water content in 20-30 cm soil layer (cm3 cm-3); is the average soil water content in 30-40 cm soil layer (cm3 cm-3).
Soil water content (SWC) in the root zone (0-40 cm) of P. notoginseng was calculated by the following equation (Liang et al., 2021):
Evapotranspiration (ET) in the root zone (0-40 cm) of P. notoginseng was calculated by the following equation (Liang et al., 2019):
Where ET was soil water consumption in the root zone of P. notoginseng, mm; P was the precipitation, mm; I was water consumption in each plot, mm; G is groundwater recharge, mm; D was runoff, mm; R represented the amount of deep leakage, mm. This experiment was carried out in a rain shelter unaffected by precipitation, groundwater recharge, runoff, and deep leakage. In this experiment, micro-sprinkler irrigation was used for irrigation, timing irrigation. Therefore, the P, G, D, and R were neglected. ΔSWS is the difference between SWS before and 1 day after irrigation in 0-40 cm soil layer at seedling, flowering, fruiting, and root growth stage.
Water use efficiency (WUE) was calculated by the following equation (Liang et al., 2019):
Where Y was crop yield, kg ha−1; ET was evapotranspiration, mm.
Material input mainly includes land leasing costs, labor expenditure, sunshade materials, micro-sprinkler irrigation systems, water and fertilizer integration machinery, P. notoginseng seedlings, microbial fertilizers, sunshade nets, plastic tarpaulin renewal and installation, and infrastructure strengthening. The production value was the yield of P. notoginseng with a selling price of 96.23 $ kg-1 (no pesticides are used in cultivation due to the high saponin content in P. notoginseng). Expenditure on land rent, labor, sunshade materials, irrigation, and machinery in 2017 and 2018 were assessed: 1215.25 $ ha-1, 50,219.18 $ ha-1, 47281.35 $ ha-1, 49251.54 $ ha-1and 61.52 $,151.21 $, 1126.53 $ and 185.21 $. Inputs of fertilizers were 0.54 $ kg-1. Infrastructure development of P. notoginseng seedlings and fertilizers, updating and installing shade nets, and installing plastic tarpaulins were 312.42 $ and 1073.42 $. The exchange rate is 1 USD ≈ 6.98 RMB.
Microsoft Excel 2018 software was used to sort out the data. SPSS 27.0 was used for the analysis of variance. The analysis of variance was one-way analysis of variance, and the Duncan (P< 0.05) method was used to test the difference significance. ArcMap 10.2 was used to map the latitude and longitude profile of the study area, Origin 2022 was used to produce bar charts. Data in the histograms were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (NS not significant, *P< 0.05, **P< 0.01, ***P< 0.001). The Mantel test was run using R software to correlate irrigation frequencies with soil environmental factors, P. notoginseng physiological indicators, and yield. Constructing structural equation model (SEM). The Mantel test was used to explore potential associations between irrigation frequencies, soil environmental factors, physiological indicators, and yield of P. notoginseng. Pearson’s correlation analysis determined the correlation between soil physicochemical properties and P. notoginseng growth parameters. The analysis of these processes was completed through the ggcor package in R. Partial Least Squares Path Modelling (PLS-PM) was used to investigate the direct or indirect effects of irrigation frequencies, soil water content, and soil nutrients on P. notoginseng growth indicators and yield.
The soil water content (SWC) and soil water storage (SWS) in the root zone (0 - 40 cm) of the P. notoginseng plant before irrigation and first, second days after irrigation during the seedling stage, flowering stage, and fruiting stage were showed in Figure 2 and Table 2. Soil water content (SWC) decreased with increasing time after irrigation events due to soil evaporation and root water accumulation. According to Figure 2 and Table 3, there were significant (P< 0.05) differences in soil water content (SWC) and soil water storage (SWS) at the root zone (0-40 cm soil depth) of P. notoginseng among different irrigation frequency treatments. Before irrigation, the order of soil water content (SWC) and soil water storage (SWS) from high to low was IF1 > IF3 > IF2 > IF4 at the seeding stage and IF2 > IF1 > IF4 >IF3 at other growth stages. Compared with other treatments, the IF2 treatment significantly (P< 0.05) increased SWC and SWS by 2.4%-6.4% at the flowering stage, 3.0%-17.3% at the fruiting stage, and 0.6%-7.3% at the root growth stage before irrigation. After irrigation, the first and second days SWC and SWS had no significant (P< 0.05) regularity in each growth stage. The ΔSWS increased with decreasing irrigation frequencies in the seedling stage, flowering stage, and root growth stage of P. notoginseng.
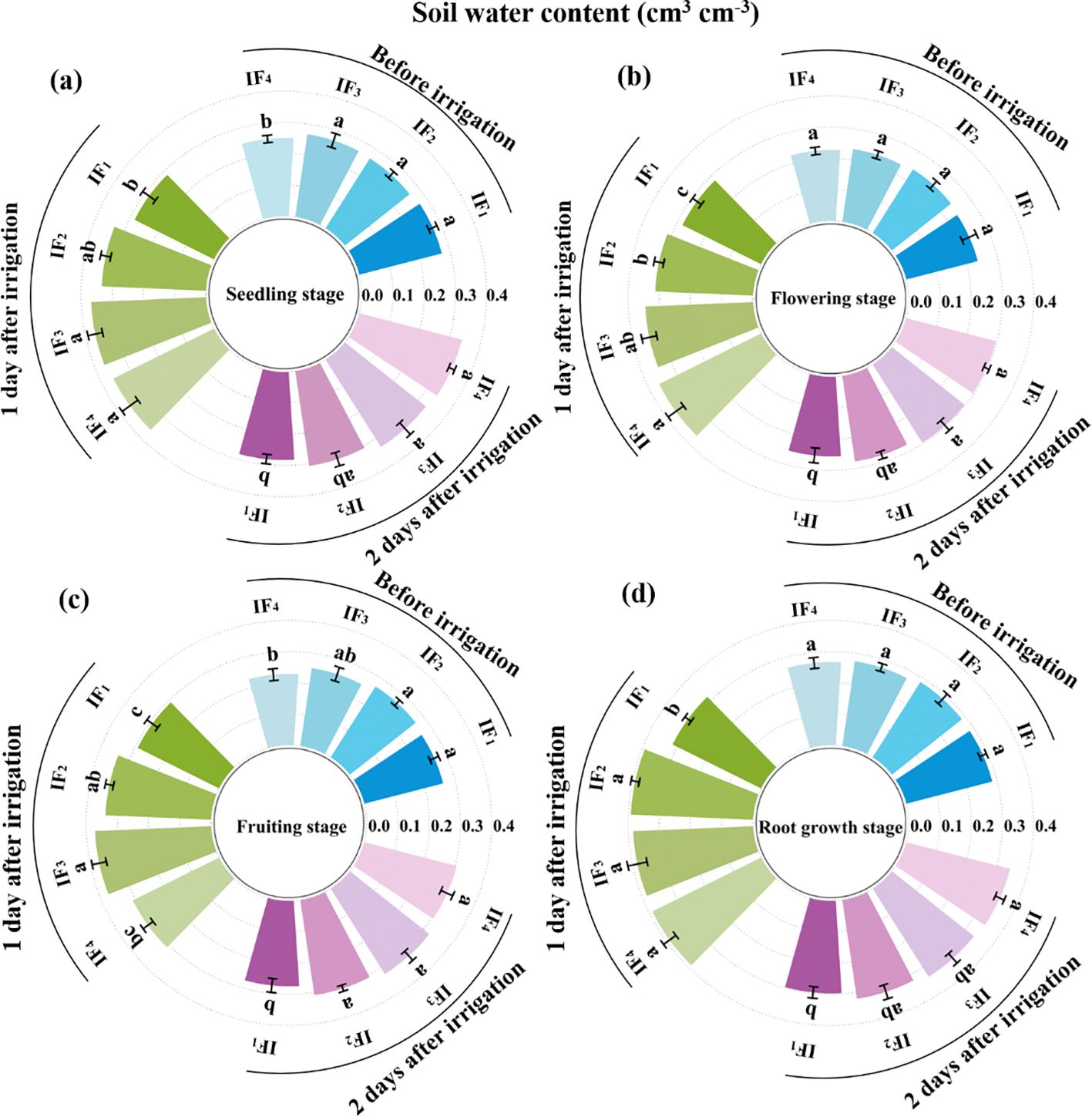
Figure 2. Effects of different irrigation frequencies on soil water content (SWC) in P. notoginseng root zone (0-40 cm). (A) Soil moisture content at seedling stage. (B) Soil water content at flowering stage. (C) Soil water content at fruiting stage. (D) Soil water content at root growth stage.
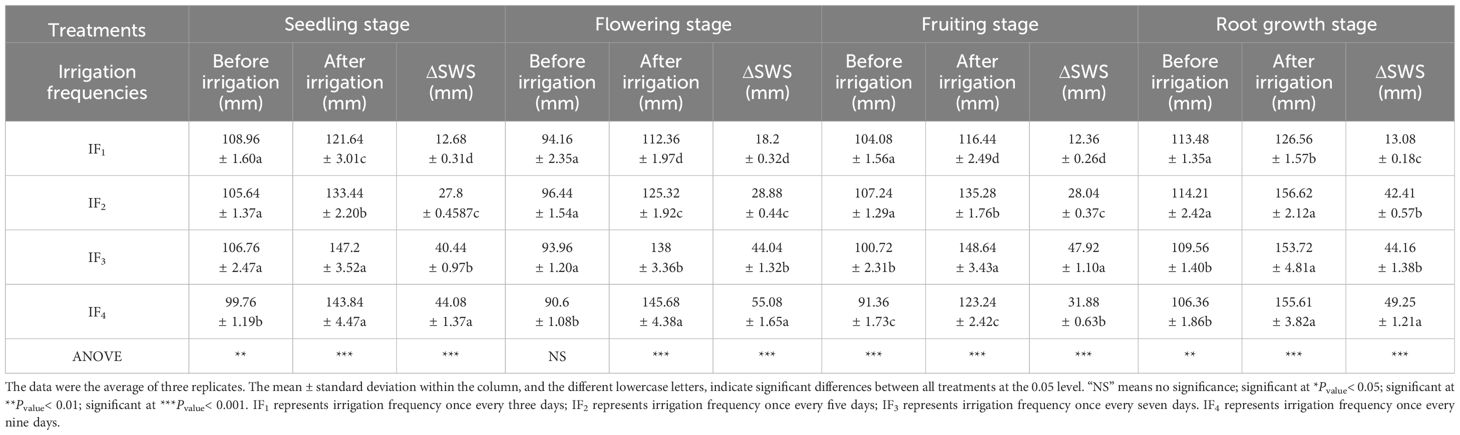
Table 2. Effects of different irrigation frequencies on soil water storage (SWS) in the root zone (0-40 cm soil layer) of P. notoginseng.
Irrigation frequency significantly affected (P< 0.05) the contents of soil alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen, soil-available phosphorus, and soil-available potassium in the root zone (0-40 cm) of P. notoginseng (Table 4). The contents of soil alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen and soil-available potassium in the root zone of P. notoginseng decreased first and then increased with the increase of irrigation frequency. The content of soil available phosphorus was IF4 > IF3 > IF1 >IF2 at the seedling stage, and IF3 > IF1 > IF4 > IF2 at the flowering and fruit stage and root weight gain stage. Under IF2 treatment the contents of soil alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen, available phosphorus, and available potassium were the lowest. Compared with IF1, IF3, and IF4, the IF2 treatment significantly (P< 0.05) decreased the soil alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen content by 1.0-9.3%, the soil available phosphorus content by 3.4-11.1%, and the soil available potassium content by 2.1-20.6% at each growth stages. The contents of soil available nitrogen and available potassium in the root zone of P.notoginseng under IF4 treatment were the highest in each growth stage. Compared with other treatments, the contents of soil available nitrogen and available potassium in IF4 treatment were significantly (P< 0.05) increased by 0.2-10% and 9.8-23.2%, respectively. Therefore, IF4 (9 d time-1) treatment was the best irrigation frequency to increase soil available nitrogen content and soil available potassium content.
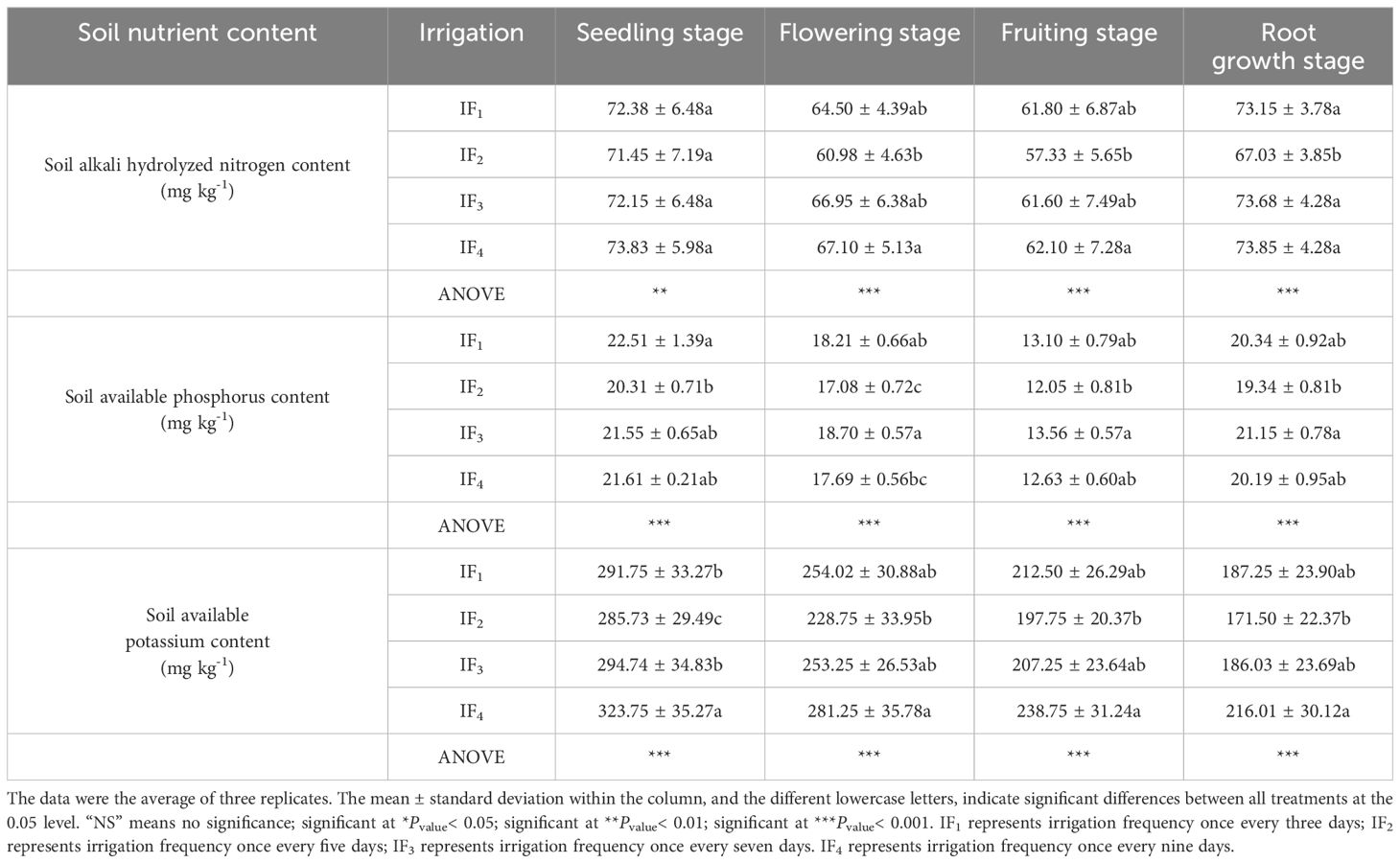
Table 4. Effects of different irrigation frequencies on soil alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen content, soil available phosphorus content, and soil available potassium content in P. notoginseng root zone.
The effects of different irrigation frequencies on the accumulation of nitrogen accumulation, phosphorus accumulation, and potassium accumulation, in the aboveground part (stem + leaf) and underground part (root) for P. notoginseng were significant (P< 0.05) (Table 5). The accumulation of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium in the aboveground part and underground part of P. notoginseng increased first and then decreased with the increase of irrigation frequency. The accumulation of nitrogen in the aboveground part and underground part of P. notoginseng under the IF3 treatment was the largest. The IF3 treatment significantly (P< 0.05) increased nitrogen accumulation by 3.18% -141.55% compared with IF1, IF2, and IF4. The accumulation of phosphorus and potassium in the aboveground and underground parts of P.notoginseng was the largest under IF2 treatment. Compared with IF1, IF3, and IF4, the IF2 treatment significant (P< 0.05) increased phosphorus accumulation by 17.44% -172.86%, and potassium accumulation by 27.57%-171.68%. The results showed that IF3 treatment helped increase the accumulation of nitrogen in P.notoginseng, and IF2 treatment helped increase the accumulation of phosphorus and potassium in P.notoginseng.
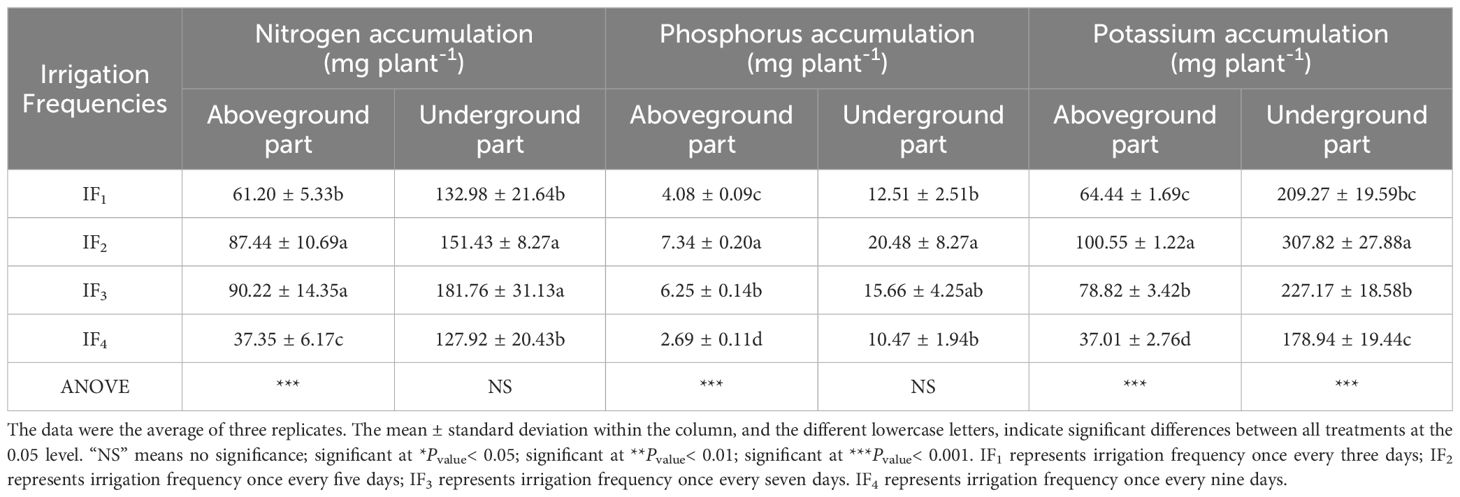
Table 5. Effects of different irrigation frequencies on the accumulation of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium in P. notoginseng.
The root hydraulic conductivity (kr) of P. notoginseng was significantly (P< 0.05) different under different irrigation frequency treatments (Table 6). The root hydraulic conductivity (kr) of P. notoginseng increased first and then decreased with the increase of irrigation frequency and the root hydraulic conductivity of P. notoginseng treated with IF2 was the highest in the seedling stage, fruiting stage, and root growth stage. Affected by different irrigation frequencies, the root hydraulic conductivity (kr) of P. notoginseng under IF2 treatment was significantly (P< 0.05) increased by 6.69% -19.62% compared with IF1, IF3, and IF4 treatments. However, the root hydraulic conductivity (kr) of P. notoginseng decreased with the increase in irrigation frequency and the root hydraulic conductivity of P. notoginseng treated with IF4 was the highest in the flowering stage. The results showed that IF2 treatment was the most suitable irrigation frequency to increase the root hydraulic conductivity of P. notoginseng during the seedling stage, fruiting stage, and root growth stage of P. notoginseng.
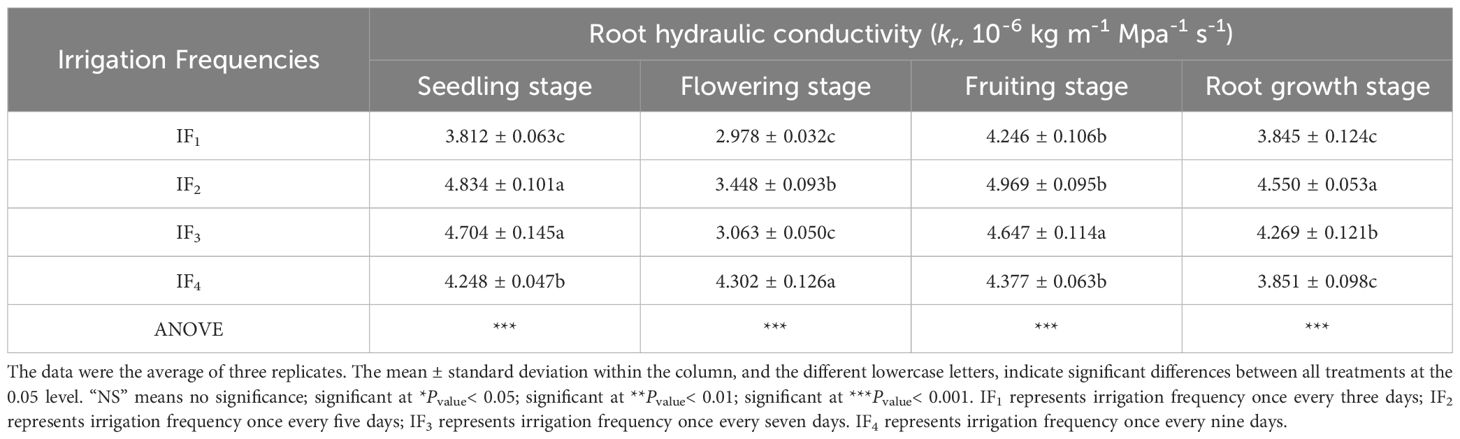
Table 6. Effects of different irrigation frequency on root hydraulic conductivity of P. notoginseng.
The root mean diameter, root total length, root total surface area, and root total volume of P. notoginseng were significantly (P< 0.05) affected by different irrigation frequencies (Figure 3). The average diameter of P. notoginseng from high to low was IF3 > IF2 > IF1 > IF4, the root total length of P. notoginseng from high to low was IF4 > IF2 > IF1 > IF3, the root total surface area, and root total volume of P. notoginseng from high to low were IF2 > IF3 > IF1 > IF4. The highest average root diameter was 2.04 mm under the IF3 treatment. Compared with other treatments, IF3 significantly (P< 0.05) increased the average root diameter by 1.89%-56.67%(Figure 3A). The maximum root total length of P. notoginseng was 217.65 cm under the IF4 treatment (Figure 3B). Compared with other treatments, IF4 treatment significantly (P< 0.05) increased the root total length by 1.89% -56.67%. Under the IF2 treatment, the total root surface area and total root volume of P. notoginseng reached the maximum values of 67.49 cm2 and 3.79 cm3 (Figures 3C, D) and the IF2 significantly (P< 0.05) increased root surface area by 2.76%-11.86% and root volume by 45.77%-99.47% compared with other treatments.
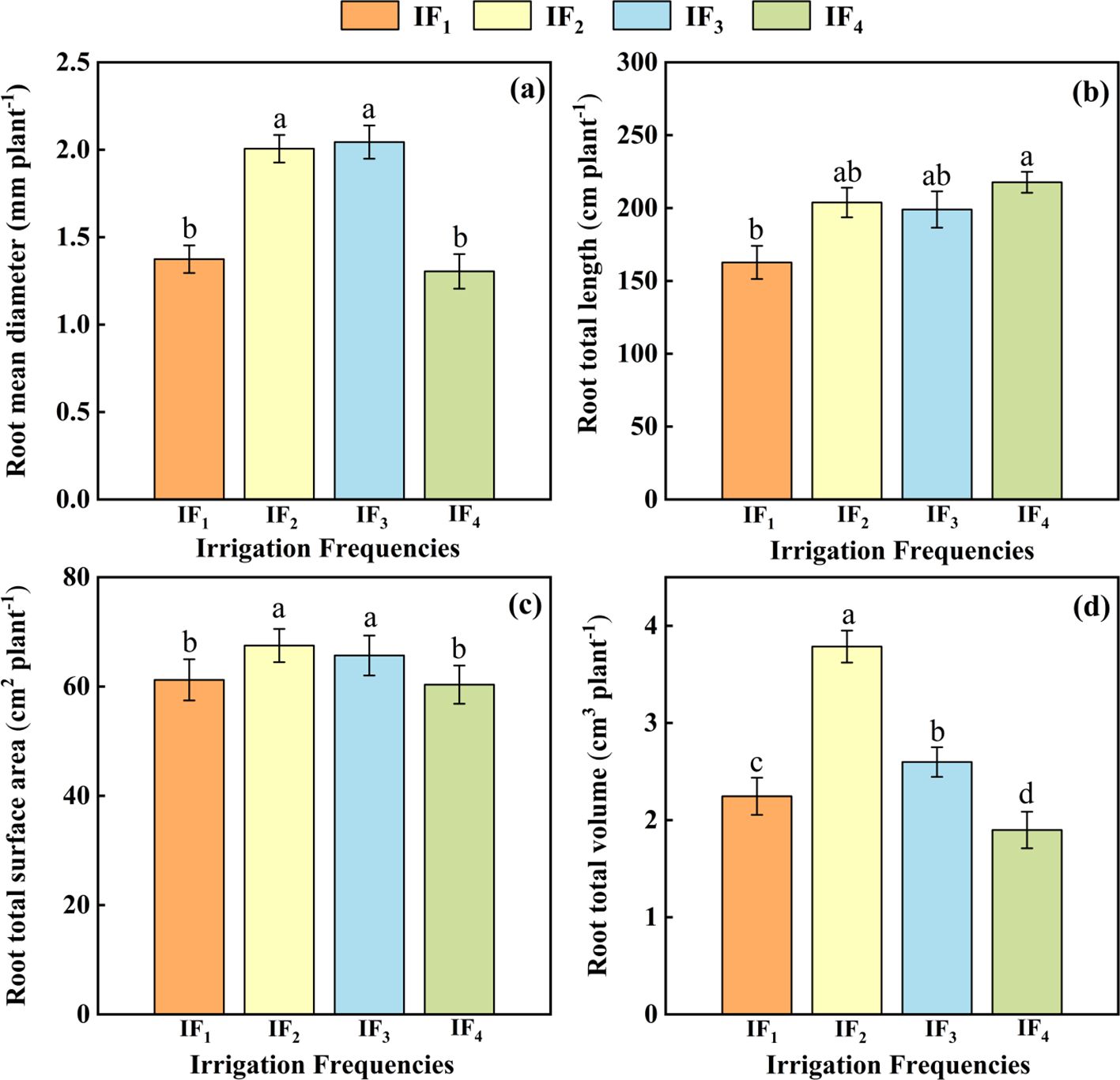
Figure 3. (A) Effects of different irrigation frequencies on the root mean diameter of P. notoginseng. (B) Effects of different irrigation frequencies on the root total length of P. notoginseng. (C) Effects of different irrigation frequencies on the root total surface area of P. notoginseng. (D) Effects of different irrigation frequencies on the root total volume of P. notoginseng.
The effect of different irrigation frequencies on the yield of P. notoginseng was significant (P< 0.05) (Figure 4). With the increase of irrigation frequency, the yield increased first and then decreased, and reached the highest point under IF2 treatment. The yield of P. notoginseng was 702 kg ha-1 under IF2 treatment. Compared with IF1, IF3, and IF4 treatments, IF2 treatment significantly (P< 0.05) increased by 25.13%-41.82%. The above results showed that the IF2 treatment (5 d time-1) had the most significant (P< 0.05) effect on increasing the yield of P. notoginseng. In order to determine the most suitable irrigation frequency for P. notoginseng production, the economic benefits of each treatment were evaluated. Although there was no significant (P< 0.05) difference in cost under different irrigation frequency treatments, there were significant (P< 0.05) differences in income and economic benefits among treatments. Under the IF2 treatment, the income and economic benefits of Panax notoginseng were the highest. Compared with other treatments, the economic benefits of the IF2 treatment increased by 41.66-75.96% in 2018. This showed that the IF2 treatment effectively improves the economic benefits. Therefore, it was recommended that local farmers adopt IF2 treatment to improve the yield and economic benefits of P. notoginseng.
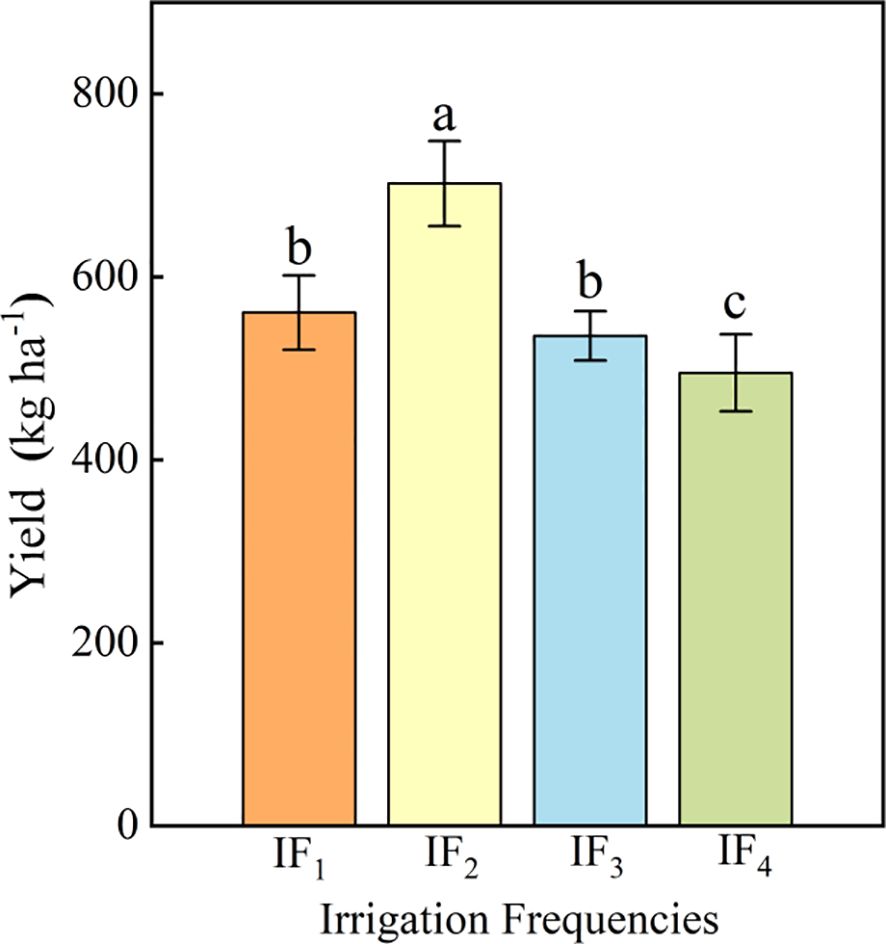
Figure 4. Effects of different irrigation frequencies on the yield of P. notoginseng. The data were the average of three replicates. The mean ± standard deviation within the column, and the different lowercase letters, indicate significant differences between all treatments at the 0.05 level. IF1 represents irrigation frequency once every three days; IF2 represents irrigation frequency once every five days; IF3 represents irrigation frequency once every seven days. IF4 represents irrigation frequency once every nine days.
Different irrigation frequency treatments significantly affected the water use efficiency (WUE) of P. notoginseng (Table 7). The water use efficiency of the four treatments from high to low was IF2>IF3>IF1>IF4. Among them, the WUE under IF2 treatment was significantly increased by 29.2%, 28.1%, and 37.7%, respectively, compared with IF1, IF3, and IF4 treatments. These results indicated that IF2 treatment (5 d time-1) could improve the water use efficiency of P. notoginseng.
The relationship between irrigation frequency and soil environmental factors and physiological indexes and yield of P. notoginseng was investigated by Mantel test and Spearman correlation analysis (Figure 5). Irrigation frequency showed significant positive correlations with soil moisture content SMC, alkaline dissolved nitrogen content AN, effective phosphorus AP, effective potassium AK, total surface area of P. notoginseng root system R-SA, root hydraulic conductivity kr, and dry matter mass, and irrigation frequency showed significant positive correlations with soil environmental factors and physiological indicators of P. notoginseng yield (Figure 5). N-accumulation, P-accumulation, K-accumulation, R-D, R-L, and R-V. The frequency of irrigation showed a significant negative correlation with N-accumulation, P-accumulation, K-accumulation, R-D, R-L, and R-V of P. notoginseng.
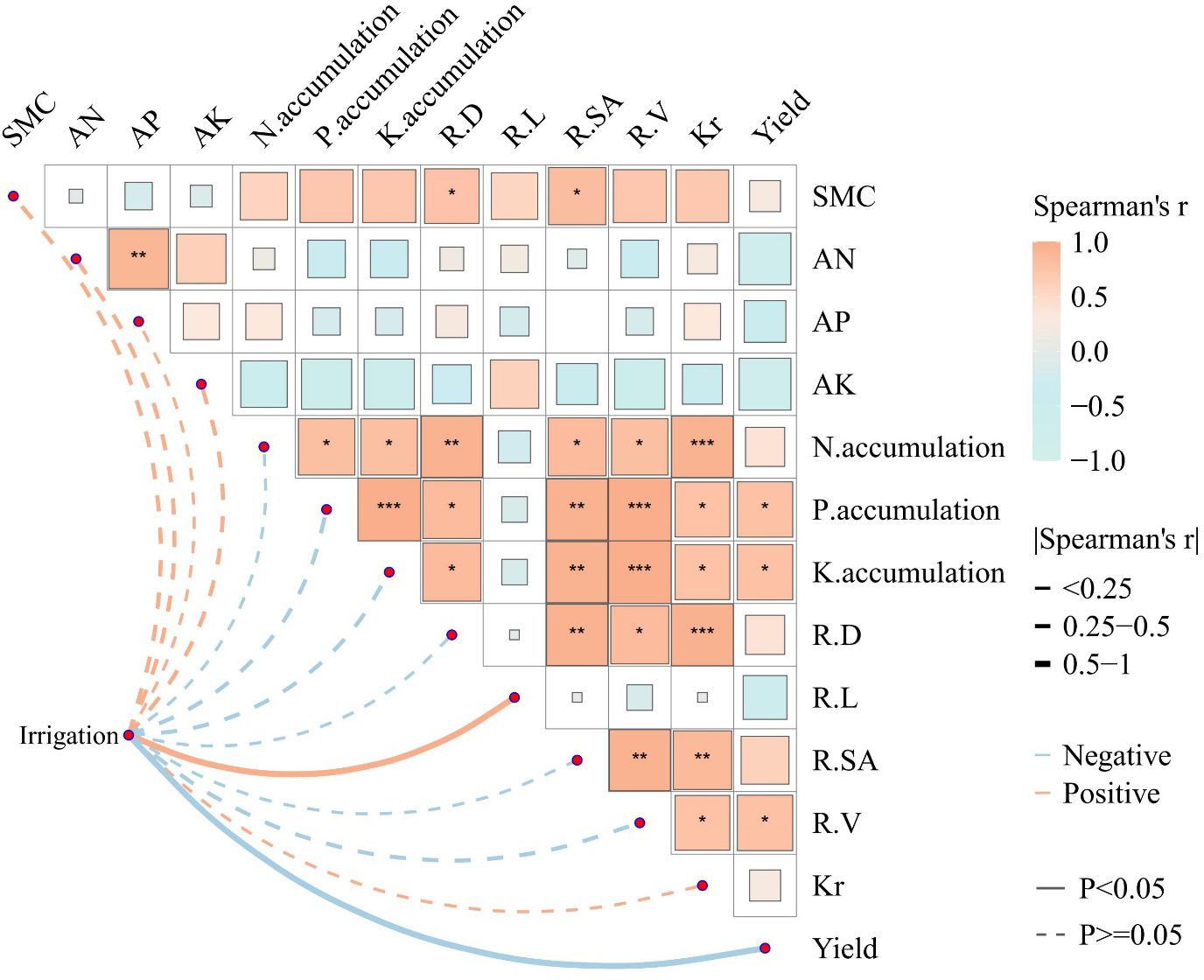
Figure 5. Analysis of the correlation analysis between soil physicochemical properties and the P. notoginseng growth indexes under different irrigation frequencies. Pairwise comparisons of the analyzed factors are displayed with a color gradient denoting Spearman’s correlation coefficients. Irrigation frequencies was related to most variables by Mantel test. SMC, soil moisture content; AN, soil alkali hydrolyzale nitrogen content; AP, soil available phosphorus content; AK, soil available potassium content; N-accumulation, P. notoginseng nitrogen accumulation; P-accumulation, P. notoginseng phosphorus accumulation; K-accumulation, P. notoginseng potassium accumulation; R-D, root mean diameter of P. notoginseng; R-L, root total length of P. notoginseng; R-SA, root total surface area of P. notoginseng; R-V, root total volume of P. notoginseng; kr, root hydraulic conductivity of P. notoginseng; Yield, yield of P. notoginseng. The mean ± standard deviation within the column, and the different lowercase letters, indicate significant differences between all treatments at the 0.05 level. “NS” means no significance; significant at *Pvalue< 0.05; significant at **Pvalue< 0.01; significant at ***Pvalue< 0.001.
In this study, irrigation frequency, soil moisture content, and soil nutrients were taken as influencing factors, and a structural equation model was established for their effects on root characteristics, root water conductivity, nutrient accumulation, and yield of P. notoginseng (Figure 6). Irrigation frequency, soil moisture content, soil nutrients, root characteristics, root water conductivity and nutrient accumulation of P. notoginseng. directly or indirectly affected the yield. Among them, root characteristics (0.49, contribution rate: 24.01%) and nutrient accumulation (0.30, contribution rate: 9.0%) had significant positive effects on the yield of P. notoginseng (P< 0.05), and soil water content (0.9, contribution rate: 81.0%) had a more significant positive effect on the yield of P. notoginseng (P< 0.01). Root hydraulic conductivity (kr) had a significant negative effect on the yield of P. notoginseng (P< 0.05), irrigation frequency (-0.6, contribution rate: 36%), and soil nutrient (-0.2, contribution rate: 4.0%) had a more significant negative effect on the yield of P. notoginseng (P< 0.01). Meanwhile, according to SEM, it could be found that irrigation frequency, soil moisture content, and soil nutrients significantly increase the yield of P. notoginseng by mediating the improvement of root characteristics.
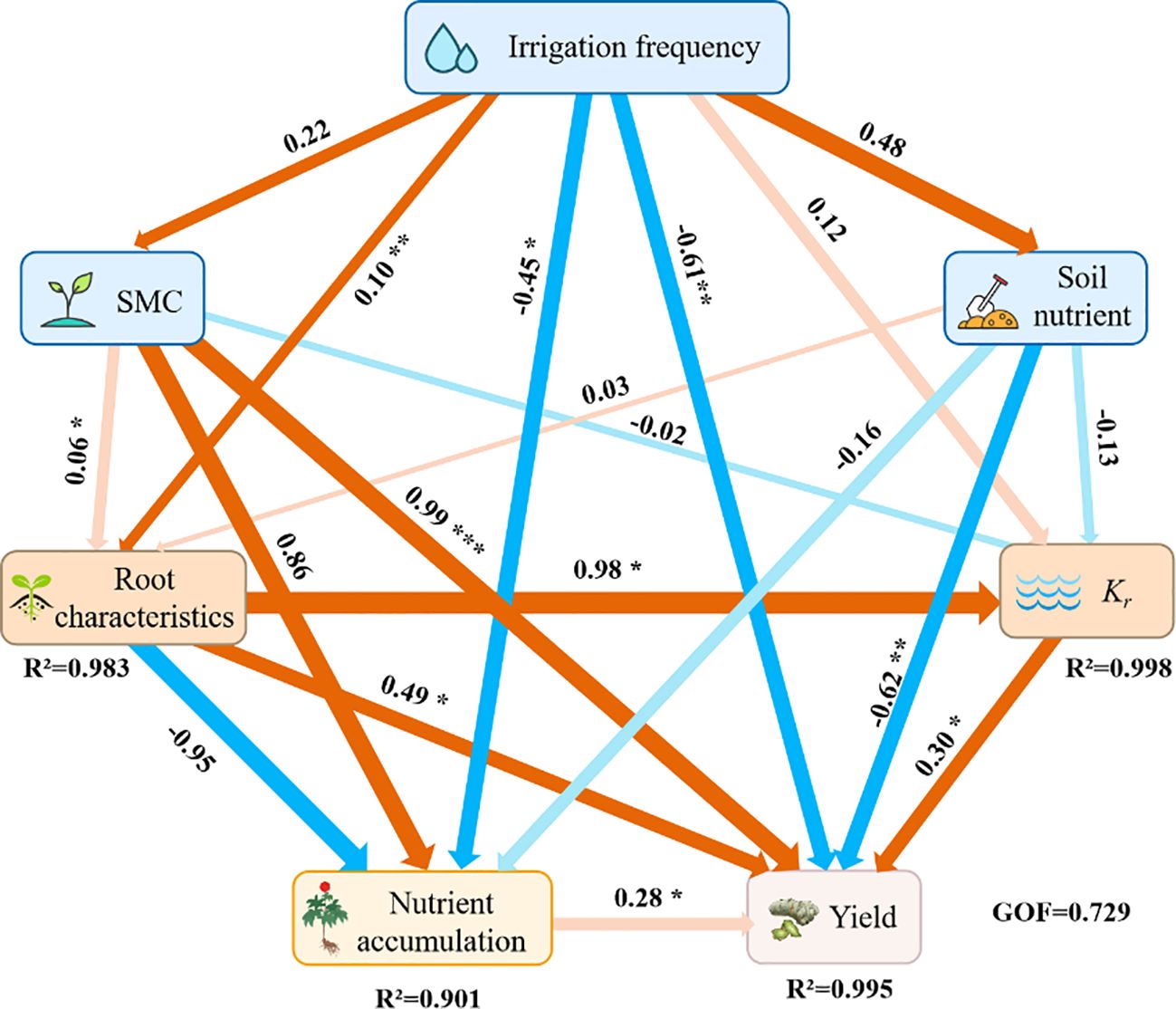
Figure 6. Partial least squares path modeling (PLS-PM) shows the direct and indirect effects of irrigation frequency, SMC, and soil nutrients on physiological indicators and yield of P. notoginseng. Each box represents a set of variables. Orange and blue arrows indicate positive and negative flows of causality, respectively. The higher path coefficients are shown as bold arrows. ‘*’, ‘**’ and ‘***’ denote significant differences at P< 0.05, P<0.01, P<0.001, respectively.
Under the current situation of uneven temporal and spatial distribution of water resources and low utilization efficiency of water resources in Yunnan Province, China, it was of great economic value to research the influence of irrigation frequency on the cultivation of P. notoginseng, which provided a sustainable development way to improve the utilization efficiency of water resources and alleviate the uneven distribution of water resources. This study suggested that the appropriate irrigation frequency has the potential to promote the growth and development of P. notoginseng, improve the water use efficiency of P. notoginseng, and increase the yield and economic benefits of P. notoginseng. The findings presented in Tables 4–8, and Figures 2–6 corroborated these hypotheses.
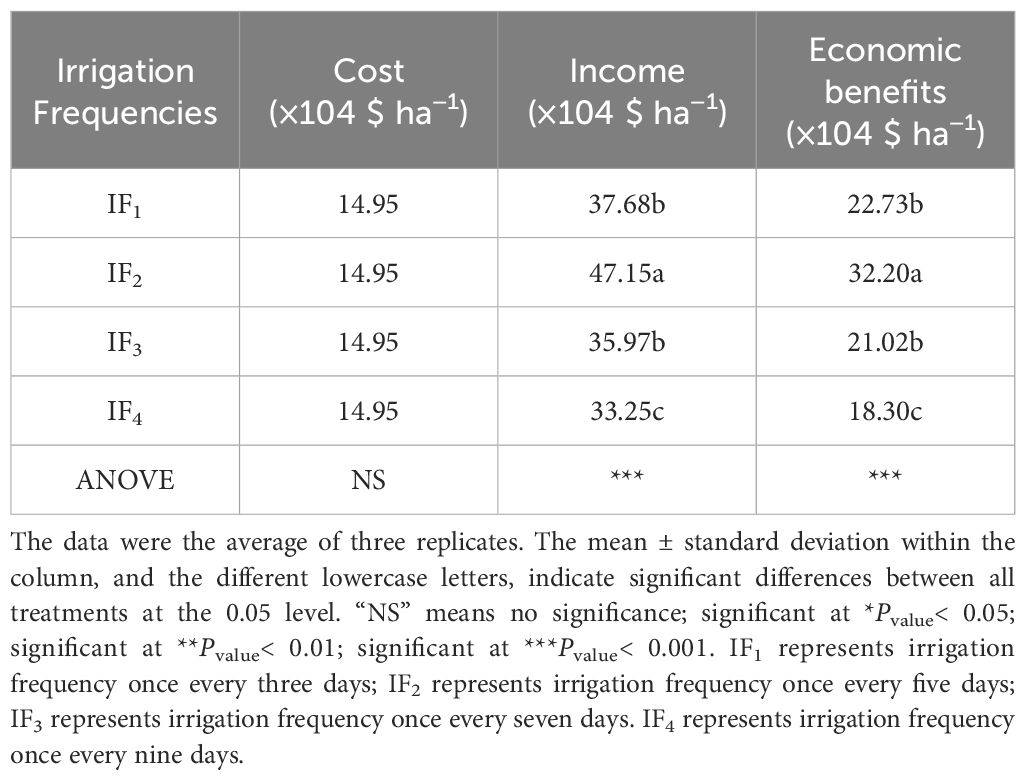
Table 8. Effects of different irrigation frequency treatments on economic benefits of P. notoginseng.
The root system was the foundation of plant growth, which was not only involved in regulating water balance, nutrient absorption, and growth of plants but also the key organ for plant growth and survival. It is the most direct and earliest part of the plant to feel stress stimulus signals (Li et al., 2021). Root morphological characteristics directly affect plant growth and development, material metabolism, yield, and quality (Lynch, 1995). This study indicated that the root volume and root surface area of P. notoginseng root system under medium-frequency irrigation IF2 showed a significant increase, but the average diameter of the root system was the largest in the IF3 treatment and the maximum total length of the root system under the IF4 treatment was largest (Figure 4). With this phenomenon, we speculated that the main reason may be that the shallow P. notoginseng root system was in a low-oxygen or anaerobic state under IF1(high-frequency irrigation) treatment. The morphological characteristics and physiological functions of its root system were greatly affected, and the root growth of P. notoginseng was inhibited, which was consistent with the results of previous studies on rice (Bengough et al., 2011; Armstrong, 2005). Under IF4 (low-frequency irrigation) treatment, the water content of the surface soil decreased, which stimulated the root system of P. notoginseng to penetrate deeper into the soil, and the root length of P. notoginseng increased. However, the root diameter did not increase with the growth of the root system. This may be due to the decrease of the turgor pressure of the root cells of P. notoginseng caused by the low soil moisture content, and the root growth was blocked (Ahluwalia et al., 2021). At the same time, the cell wall at the distal end of the root was extended, which was a growth strategy adopted by plants to adapt to insufficient water. This helped the roots to continue to grow deeper under drought conditions to obtain more water and nutrients, thereby maximum guaranteeing the water and nutrients required for the healthy growth of P. notoginseng. At the same time, this correlation has also been verified in the correlation analysis of each index (Figure 5) and the structural equation model (Figure 6). Therefore, compared with other treatments, the most suitable treatment for root growth of P. notoginseng was IF2 treatment.
Soil nutrient transport and utilization of soil nutrients by plants were affected by various factors (Wang et al., 2023), including water, root absorption capacity, soil physicochemical properties, and soil microorganisms (Briat et al., 2020). Among them, water was the most active and significant factor in soil, and it is an important factor affecting the effective absorption and utilization of nutrients (Wang et al., 2023; Fischer et al., 2019). Inappropriate soil water content could destroy plants’ absorption of water and nutrients, which was not conducive to the normal growth and metabolism of plants (Lyzenga et al., 2023; Xu et al., 2022; Liu L. et al., 2019). In this study, irrigation frequencies significantly affected the distribution of soil water as well as the accumulation and utilization of soil alkali hydrolyzed nitrogen, available phosphorus, and available potassium by P. notoginseng roots. The soil water content in the root zone of P. notoginseng was the highest under IF2 treatment during the fruiting stage and root growth stage. When the irrigation frequency was IF1 (3 d time-1), soil water was mainly concentrated in the 10 cm-20 cm soil layer due to the low volume but high frequency of irrigation. At the moment, the soil surface water content was too high, which led to poor soil permeability. Soil CO2 concentration in the root zone increased and O2 content decreased, which was unfavorable for nutrient absorption and utilization by the root system. The low number of irrigations IF4 (9 d time-1) resulted in mild drought stress, which affected the growth of plant stems, leaves, and roots (Sun et al., 2017; Liu M. et al., 2016). It was detrimental to the accumulation and utilization of soil nutrients by the P. notoginseng root system. These results were consistent with Miao and Li’s study (Li et al., 2021; Miao et al., 2015), which found that too high or too low irrigation amount was not conducive to the accumulation of nutrients by P. notoginseng.
Soil moisture, soil alkali hydrolyzed nitrogen, available phosphorus, and available potassium content in P. notoginseng root zone showed seasonal changes. The trends of soil alkali hydrolyzed nitrogen and available phosphorus were both ‘S’ shaped, with an increasing trend from March 2017 to the seedling stage, a decreasing trend from the seedling stage to the fruiting stage, and an increasing trend from the fruiting stage to the period of the root growth stage. The difference was that the soil alkali hydrolyzed nitrogen decreased the most at the flowering stage, and the soil effective phosphorus content decreased the most at the fruiting stage. It indicated that the peak nitrogen requirement of 2-year-old P. notoginseng occurred at the flowering stage and the peak phosphorus requirement occurred at the fruiting stage. These results were similar to those reported by Cui Xiuming (Cui et al., 1994). P. notoginseng was a plant with a high demand for potassium, and the soil available potassium content showed a decreasing trend during the whole growth stage. The absorption of K played a key role in the growth of P. notoginseng taproots (Wei et al., 2020). The results indicated that the critical nitrogen requirement period of 2-year-old P. notoginseng was the flowering stage, the critical phosphorus requirement stage was the fruiting stage, and the critical potassium requirement was the root growth stage. The N, P, and K accumulations under IF2 (5 d time-1) and IF3 (7 d time-1) treatments were significantly higher than those under IF1 and IF4 treatments. Previous studies have shown that appropriate soil water content is more conducive to the propagation of soil microorganisms, enhances the activity of beneficial microorganisms in the soil, accelerates the decomposition of organic matter and nutrient cycling, and promotes the respiration of crop roots, thus facilitating the accumulation of nutrients by the roots of P. notoginseng (Zhu et al., 2019). In this study, the IF2 treatment had a better effect on the nutrient absorption of P. notoginseng.
Plant hydraulic conductivity (kr), also known as plant water conduction, indicates the water flux of plants under a unit pressure gradient and reflects the ability of roots to absorb and conduct water. It was one of the important water physiological indexes to evaluate the suitability of plant growth (Martre et al., 2001). Plant water conduction was related to soil water content, nutrients, and plant growth stage (Cai et al., 2022). The results of this experiment showed that compared with other treatments, IF2 treatment was the most suitable irrigation frequency to improve the root hydraulic conductivity of P. notoginseng at the seedling stage, fruiting stage, and root growth stage (Figure 4). This result may be due to the following aspects: (1) The roots of P. notoginseng are mainly distributed in the range of 0-20 cm soil layer. When the irrigation frequency was too high (the IF1 treatment), the soil surface water content was too high, and then the soil permeability became worse, the root respiration was weakened, the soil CO2 concentration in the root zone increased, and the O2 content decreased, which led to the change of root morphology and structure, accelerates the senescence and death of root cells, and reduces the water absorption and water conductivity of P. notoginseng roots (Vandeleur et al., 2005). (2) When under low-frequency irrigation (IF4 treatment), due to the long irrigation cycle, the temperature in the greenhouse is higher, the humidity is lower, and the root system is subjected to water stress for a long time, which leads to the lower root hydraulic conductivity of P. notoginseng (Comas et al., 2010). Irrigation was an important factor affecting crop WUE and yield. A meta-analysis found that too high or too low irrigation frequency would lead to a decrease in crop WUE and yield (Cavero et al., 2018). In this study, the WUE (Table 7) and yield (Figure 4) of P. notoginseng under the IF2 treatment were the highest, but too-low irrigation frequency (IF1) and too-high irrigation frequency (IF4) would lead to a decrease in WUE and yield, confirming the above view. This was because the appropriate irrigation frequency could provide a suitable soil environment for crop roots, improve the root hydraulic conductivity of crops, increase WUE, and thus increase crop yield (Zhang et al., 2019). However, too high and too low irrigation frequency would put the soil moisture content in an extreme state, resulting in water stress on crops, thereby affecting the WUE of crops, and resulting in a decrease in crop dry matter accumulation and yield (Liu et al., 2016). At the same time, some researchers found that there was a positive correlation between crop yield and kr (Du et al., 2024), which was consistent with the fact that the kr (Table 6) and yield (Figure 4) of the IF2 treatment were higher than the other treatments in this study. From the perspective of economic benefits, the cost of water resources consumed by IF2 treatment was 66.6% lower than that of IF1 treatment, but the WUE of P. notoginseng increased by 29.2% and the yield increased by 42.21%. Therefore, the IF2 treatment was more suitable as the best irrigation system for water saving and yield increase of P. notoginseng. Crop development and production are restricted by water and fertilizer. In this study, only the single variable of irrigation frequency is considered. In the future research, multivariate experiments should be carried out in combination with different fertilizers to achieve a more perfect water and fertilizer management system.
It was of great significance to research the effects of irrigation frequency on P. notoginseng root growth, nutrient absorption, and yield. According to the current study, compared with other irrigation strategies, the IF2 treatment significantly increased the hydraulic conductivity of the P. notoginseng root system, promoted the growth of the P. notoginseng root system, nutrient absorption as well as yield, and significantly improved WUE and yield. Therefore, the IF2 (irrigation once every five days) treatment was recommended as a suitable management strategy to improve the physiological growth of P. notoginseng, enhance yield and quality, promote efficient and refined cultivation, and improve farmers’ economic benefits.
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
HH: Writing – original draft. YS: Writing – review & editing. AL: Writing – review & editing. YX: Writing – original draft. JL: Writing – original draft. ZH: Writing – original draft.
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the Open Fund of the National Engineering and Technology Research Center for Development &Utilization of Phosphate Resources (NECP2023-09).
Authors AL and YX were employed by the company Yunnan Phosphate Chemical Group Co., Ltd.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Ahluwalia, O., Singh, P. C., Bhatia, R. (2021). A review on drought stress in plants: Implications, mitigation and the role of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria. Resources Environ. Sustainability 5, 100032. doi: 10.1016/j.resenv.2021.100032
Armstrong, J., Armstrong, W. (2005). Rice: sulfide-induced barriers to root radial oxygen loss, fe2+ and water accumulation, and lateral root emergence. Ann. Bot-London 96, 625–638. doi: 10.1093/aob/mci215
Bengough, A. G., McKenzie, B. M., Hallett, P. D., Valentine, T. A. (2011). Root elongation, water stress, and mechanical impedance: a review of limiting stresses and beneficial root tip traits. J. Exp. Bot. 62, 59–68. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erq350
Briat, J. F., Gojon, A., Plassard, C., Rouached, H., Lemaire, G. (2020). Reappraisal of the central role of soil nutrient availability in nutrient management in light of recent advances in plant nutrition at crop and molecular levels. Eur. J. Agron. 116, 126069. doi: 10.1016/j.eja.2020.126069
Brighenti, S. (2024). Drip irrigation frequency leads to plasticity in root water uptake by apple trees. Agric. Water Manag. doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2024.108870
Cai, G., Ahmed, M. A., Abdalla, M., Carminati, A. (2022). Root hydraulic phenotypes impacting water accumulation in drying soils. Plant Cell Environ. 45, 650–663. doi: 10.1111/pce.14259
Cavero, J., Medina, E. T., Montoya, F. (2018). Sprinkler irrigation frequency affects maize yield depending on irrigation time. Agron. J. 110, 1862–1873. doi: 10.2134/agronj2018.05.0315
Chai, Q., Gan, Y., Zhao, C., Xu, H.-L., Waskom, R. M., Niu, Y., et al. (2016). Regulated deficit irrigation for crop production under drought stress. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 36, 3. doi: 10.1007/s13593-015-0338-6
Chen, H., Ding, Z., Dai, T., Lin, J., Xu, D., Xia, F., et al. (2023). Quantitative comparison and rapid discrimination of Panax notoginseng powder and Caulis clematidis armandii using NMR combined with pattern recognition. J. Sci. Food Agr. 103, 3766–3775. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.12264
Cheng, C., Zhang, Y., Liu, H., Ren, Z., Liu, J., Xiang, B., et al. (2023). Effect of continuous application of bioorganic fertilizer on tobacco rhizosphere microecosystems. J. Biotech. Res. 14, 67–77.
Comas, L. H., Bauerle, T. L., Eissenstat, D. M. (2010). Biological and environmental factors controlling root dynamics and function: effects of root ageing and soil moisture. Aust. J. Grape Wine R 16, 131–137. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-0238.2009.00078.x
Cui, X., Wang, C., Li, W., Li, Z. (1994). Dynamic analysis of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium absorption in Panax Notoginseng (In Chinese). Yunnan Agric. Sci. Tech. 2, 9–10. doi: CNKI:SUN:YNKJ.0.1994-02-004
Donnelly, D. M., Yang, H., Combs, D. K. (2016). Comparison of dry matter measurements between three hand-held near-infrared units with oven drying at sixty degrees Celsius for forty-eight hours. J. Anim. Sci. 94, 311–312. doi: 10.2527/jam2016-0652
Du, P., Lynch, J. P., Sun, Z., Li, F.-M. (2024). Does root respiration and root anatomical traits affect crop yield under stress? A meta-analysis and experimental study. Plant Soil. 1–15. doi: 10.1007/s11104-024-06892-4
Fischer, S., Hilger, T., Piepho, H. P., Jordan, I., Cadisch, G. (2019). Do we need more drought for better nutrition? The effect of precipitation on nutrient concentration in East African food crops. Sci. Total Environ. 658, 405–415. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.12.181
Fuentes-Soriano, P., Bellido-Milla, D., García-Guzmán, J. J., Hernández-Artiga, M. P., Gallardo-Bernal, J. J., Palacios-Santander, J. M., et al. (2019). A simple phosphorus determination in walnuts and assessment of the assimilable fraction. Talanta 204, 57–62. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2019.05.097
Ji, C., Zhang, Q., Shi, R., Li, J., Wang, X., Wu, Z., et al. (2022). Determination of the authenticity and origin of Panax Notoginseng : A Review. J. AOAC Int. 105, 1708–1718. doi: 10.1093/jaoacint/qsac081
Kresović, B., Tapanarova, A., Tomić, Z., Životić, L., Vujović, D., Sredojević, Z., et al (2016). Grain yield and water use efficiency of maize as influenced by different irrigation regimes through sprinkler irrigation under temperate climate. Agricultural Water Management. 169, 34–43.
Kumar, G., Kurothe, R. S., Brajendra, B., Vishwakarma, A. K., Rao, B. K., Pande, V. C. (2014). Effect of farmyard manure and fertilizer application on crop yield, runoff and soil erosion and soil organic carbon under rainfed pearl millet (Pennisetum glaucum). Indian J. Agr Sci. 84, 816–823. doi: 10.56093/ijas.v84i7.41986
Lebourgeois, V., Chopart, J. L., Bégué, A., Le Mézo, L. (2010). Towards using a thermal infrared index combined with water balance modelling to monitor sugarcane irrigation in a tropical environment. Agric. Water Manage. 97, 75–82. doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2009.08.013
Li, J., Bao, Y., Wang, Z., Yang, Q., Cui, X. (2022). Research progress in diseases of Panax notoginseng. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 121, 101878. doi: 10.1016/j.pmpp.2022.101878
Li, J., Yang, Q., Shi, Z., Zang, Z., Liu, X. (2021). Effects of deficit irrigation and organic fertilizer on yield, saponin and disease incidence in Panax notoginseng under shaded conditions. Agr Water Manage. 256, 107056. doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2021.107056
Li, J., Zhang, Z., Liu, Y., Yao, C. (2019). Effects of micro-sprinkling with different irrigation amount on grain yield and water use efficiency of winter wheat in the North China Plain. Agric. Water Manage. 224, 105736. doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2019.105736
Liang, J., Li, Y., Si, B., Wang, Y., Chen, X., Wang, X., et al. (2021). Optimizing biochar application to improve soil physical and hydraulic properties in saline-alkali soils. Sci. Total Environ. 771, 144802. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144802
Liang, J., Shi, W., He, Z., Pang, L., Zhang, Y. (2019). Effects of poly-γ-glutamic acid on water use efficiency, cotton yield, and fiber quality in the sandy soil of southern Xinjiang, China. Agr Water Manage. 218, 48–59. doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2019.03.009
Liu, E. K., Mei, X. R., Yan, C. R., Gong, D. Z., Zhang, Y. Q. (2016). Effects of water stress on photosynthetic characteristics, dry matter translocation and WUE in two winter wheat genotypes. Agric. Water Manage. 167, 75–85. doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2015.12.026
Liu, H., Li, H., Ning, H., Zhang, X., Li, S., Pang, J., et al. (2019). Optimizing irrigation frequency and amount to balance yield, fruit quality T and water use efficiency of greenhouse tomato (Agricultural Water Management).
Liu, L., Tan, Z., Gong, H., Huang, Q. (2019). Migration and transformation mechanisms of nutrient elements (N, P, K) within biochar in straw–biochar–soil–plant systems: A review. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 7, 22–32. doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b04253
Liu, M., Li, J., Niu, J., Wang, R., Song, J., Lv, J., et al. (2016). Interaction of drought and 5-aminolevulinic acid on growth and drought resistance of Leymus chinensis seedlings. Acta Ecologica Sin. 36, 180–188. doi: 10.1016/j.chnaes.2016.04.004
Lynch, J. (1995). Root architecture and plant productivity. Plant Physiol. 109, 7–13. doi: 10.1104/pp.109.1.7
Lyzenga, W. J., Liu, Z., Olukayode, T., Zhao, Y., Kochian, L. V., Ham, B. K. (2023). Getting to the roots of N, P, and K accumulation. J. Exp. Bot. 74, 1784–1805. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erad035
Majumder, B., Mandal, B., Bandyopadhyay, P. K., Gangopadhyay, A., Mani, P. K., Kundu, A. L., et al. (2008). Organic amendments influence soil organic carbon pools and rice–wheat productivity. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 72, 775–785. doi: 10.2136/sssaj2006.0378
Man, J. (2014). Effects of supplemental irrigation with micro-sprinkling hoses on water distribution in soil and grain yield of winter wheat. Field Crop Res. 161, 26–37. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2014.02.001
Martre, P., North, G. B., Nobel, P. S. (2001). Hydraulic conductance and mercury-sensitive water transport for roots of opuntia acanthocarpa in relation to soil drying and rewetting. Plant Physiol. 126, 352–362. doi: 10.1104/pp.126.1.352
Miao, Y., Zhu, Z., Guo, Q., Ma, H., Zhu, L. (2015). Alternate wetting and drying irrigation-mediated changes in the growth, photosynthesis and yield of the medicinal plant Tulipa edulis. Ind. Crop Prod. 66, 81–88. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2014.12.002
Ravikumar, V., Vijayakumar, G., Šimůnek, J., Chellamuthu, S., Santhi, R., Appavu, K. (2011). Evaluation of fertigation scheduling for sugarcane using a vadose zone flow and transport model. Agr Water Manage. 98, 1431–1440. doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2011.04.012
Rodrigues, G. C., Paredes, P., Gonçalves, J. M., Alves, I., Pereira, L. S. (2013). Comparing sprinkler and drip irrigation systems for full and deficit irrigated maize using multicriteria analysis and simulation modelling: Ranking for water saving vs. farm economic returns. Agr Water Manage. 126, 85–96. doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2013.05.005
Shen, F. (2024). Effects of water and fertilizer regulation on soil physicochemical properties, bacterial diversity and community structure of Panax notoginseng. Sci. Hortic-amsterdam. 326, 112777. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2023.112777
Souza, S. A., Vieira, J. H. (2020). Impact of Irrigation Frequency and Planting Density on Bean’s Morpho-Physiological and Productive Traits. Using irrigation intervals to optimize water-use efficiency and maize yield in Xinjiang, northwest Chin. Crop J. 7, 322–334. doi: 10.1016/j.cj.2018.10.008
Sun, X., Shi, J., Ding, G. (2017). Combined effects of arbuscular mycorrhiza and drought stress on plant growth and mortality of forage sorghum. Appl. Soil Ecol. 119, 384–391. doi: 10.1016/j.apsoil.2017.07.030
Vandeleur, R., Niemietz, C., Tilbrook, J., Tyerman, S. D. (2005). Roles of aquaporins in root responses to irrigation. Plant Soil. 274, 141–161. doi: 10.007/s11104-004-8070-z
Wang, J., Chen, J., Cai, Q., Huang, J., Zhou, L. (2023). Knowledge map of soil nutrient migration analysis based on WOS (Web of science) database. Agric. Sci. 14, 398–421. doi: 10.4236/as.2023.143026
Wang, C. Z., McEntee, E., Wicks, S., Wu, J. A., Yuan, C. S. (2006). Phytochemical and analytical studies of Panax notoginseng (Burk.) F.H. Chen. J. Nat. Med-tokyo. 60, 97–106. doi: 10.1007/s11418-005-0027-x
Wei, W., Ye, C., Huang, H. C., Yang, M., Mei, X. Y., Du, F., et al. (2020). Appropriate nitrogen application enhances saponin synthesis and growth mediated by optimizing root nutrient accumulation ability. J. Ginseng Res. 44, 627–636. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2019.04.003
Xia, P., Guo, H., Zhao, H., Jiao, J., Deyholos, M. K., Yan, X., et al. (2016). Optimal fertilizer application for Panax notoginseng and effect of soil water on root rot disease and saponin contents. J. Ginseng Res. 40, 38–46. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2015.04.003
Xu, J., Gao, Z., Liu, S., Abou Elwafa, S. F., Tian, H. (2022). A multienvironmental evaluation of the N, P and K use efficiency of a large wheat diversity panel. Field Crop Res. 286, 108634. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2022.108634
Xu, T., Zhi, S., Zhao, S., Yang, Q. (2022). Effects of regulated deficit irrigation on soil nutrients, growth and morbidity of Panax notoginseng in Yunnan high altitude areas, China. Nat. Environ. pollut. Technol. 21, 581–588. doi: 10.46488/NEPT.2022.v21i02.016
Yang, K., Wang, H., Luo, L., Zhu, S., Huang, H., Wei, Z., et al. (2023). Effects of different soil moisture on the growth, quality, and root rot disease of organic Panax notoginseng cultivated under pine forests. J. Environ. Manage. 329, 117069. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.117069
Yang, M., Zhang, X., Xu, Y., Mei, X., Jiang, B., Liao, J., et al. (2015). Autotoxic ginsenosides in the rhizosphere contribute to the replant failure of Panax notoginseng. PloS One 10, e0118555. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0118555
Yue, X., Yang, Q., Liang, J., Tang, J., Yang, Y. (2023). Alternate micro-sprinkler irrigation synergized with organic fertilizer: A sustainable water-fertilizer management technology of improving quality and increasing efficiency in Panax notoginseng production. Ind. Crops Products 194, 116335. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2023.116335
Zang, Z. (2022). An adaptive abiotic stresses strategy to improve water use efficiency, quality, and economic benefits of Panax notoginseng : Deficit irrigation combined with sodium chloride. Agric. Water Manage. doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2022.107923
Zhang, G., Shen, D., Ming, B., Xie, R., Jin, X., Liu, C., et al. (2019). Using irrigation intervals to optimize water-use efficiency and maize yield in Xinjiang, northwest China. Crop J. 7, 322–334. doi: 10.1016/j.cj.2018.10.008
Zheng, Y., Xia, P., Zhao, H., Zheng, J., Chai, W., Liang, Z., et al. (2021). Suitable soil moisture contents for water use efficiency and saponins accumulation in Panax notoginseng. Chin. Herbal Medicines 13, 267–273. doi: 10.1016/j.chmed.2020.10.002
Zhou, Y., Zuo, Z., Xu, F., Wang, Y. (2020). Origin identification of Panax notoginseng by multi-sensor information fusion strategy of infrared spectra combined with random forest. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Mol. Biomolecular Spectrosc. 226, 117619. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2019.117619
Keywords: irrigation frequencies, nutrient accumulation, P. notoginseng, yield, water use efficiency
Citation: Huang H, Shi Y, Luo A, Xiao Y, Liang J and He Z (2025) Effects of irrigation frequency on root growth, nutrients accumulation, yield, and water use efficiency of Panax notoginseng under micro-sprinkler irrigation. Front. Plant Sci. 16:1549506. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1549506
Received: 21 December 2024; Accepted: 21 January 2025;
Published: 18 February 2025.
Edited by:
Raul Antonio Sperotto, Federal University of Pelotas, BrazilReviewed by:
Engin Gönen, Oil Seeds Research Institution, TürkiyeCopyright © 2025 Huang, Shi, Luo, Xiao, Liang and He. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yuzhe Shi, ODQ3NjY5NTY5QHFxLmNvbQ==; Anrong Luo, eXVuaHVpMDIyNEAxNjMuY29t
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.