
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Plant Sci. , 28 February 2025
Sec. Plant Pathogen Interactions
Volume 16 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2025.1547974
This article is part of the Research Topic Innovative Field Diagnostics for Real-Time Plant Pathogen Detection and Management View all articles
Diagnostic of plant bacterial pathogens underwent a leapfrog development from culture-based strategies to culture-free detection. Conventional diagnostics, such antibody- and PCR-based methods, are sensitive to identify pre-enriched pathogens in naturally infected crops at the late stage. However, they suffer from shortcomings relating to rapidity, signal strength, and a significant reduction in sensitivity in real plant extract. Progress has been made to address these challenges through development of labelled and non-labelled optical spectroscopy. Specifically, the micro-Raman spectroscopy enables fast, label-free, and non-invasive discrimination of viable but non-culturable pathogens at a single-cell level. A comprehensive spectroscopic database is always a prerequisite for identification, yet these spectroscopy-based methods are insufficient to detect previously unknown plant pathogens. The advance of single-cell sequencing and synthetic biology is beginning to address these crucial problems and is being used in related practical applications. Success will continue to be found at the interfaces between disciplines.
The world population is expected to rise from 7.2 billion to 9.7 billion by 2050 and 11 billion at the end of the century (Population Division of the Department of Economic and Social Affairs of the United Nations Secretaria, 2022). Global agricultural production must increase by 70% and 106% to satisfy a growing demand for food. However, the epidemic of crop pests and pathogens causes substantial economic losses and reduce food security at household, national, and global levels. Despite the difficulty in quantitative, standardized assessment of crop losses due to disease across crops, it was estimated to average 21.5% in wheat, 30.0% in rice, 22.6% in maize, 17.2% in potato, and 21.4% in soybean yield losses at a global level (Savary et al., 2019) while these crops account for half of the global human calorie intake (Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, 2024). The highest losses are associated with food-deficit regions with fast-growing populations (e.g., Indo-Gangetic Plain and Sub-Saharan Africa), and frequently with emerging or re-emerging diseases (Figure 1) (Savary et al., 2019). The situation is aggravated by global trade which intensifies the spread and distribution of quarantine pathogens (Elad and Pertot, 2014), many of which can spread or reemerge after having been under control (Bhattacharya, 2017). Secondary yield losses caused by the negative impacts of pests and diseases in the previous year was even worse (Cerda et al., 2017). Approximately 110 billion kilograms of food loss, 1.5 billion kilograms of cotton, 2.3 billion kilograms of oil, 50 billion kilograms of vegetables, and 6 billion kilograms of fruits could be saved by pest control each year, which is equivalent to an increase of 12% to 18% of the planting area. However, many countries, particularly low-income countries, are incompetent in monitoring and preventing disease spread. Therefore, to improve responses to unexpected crop disease spread and minimize the risk to food supplies, a global surveillance system for crop diseases is critical, which will extend and adapt established biosecurity practices and networking facilities (Carvajal-Yepes et al., 2019).
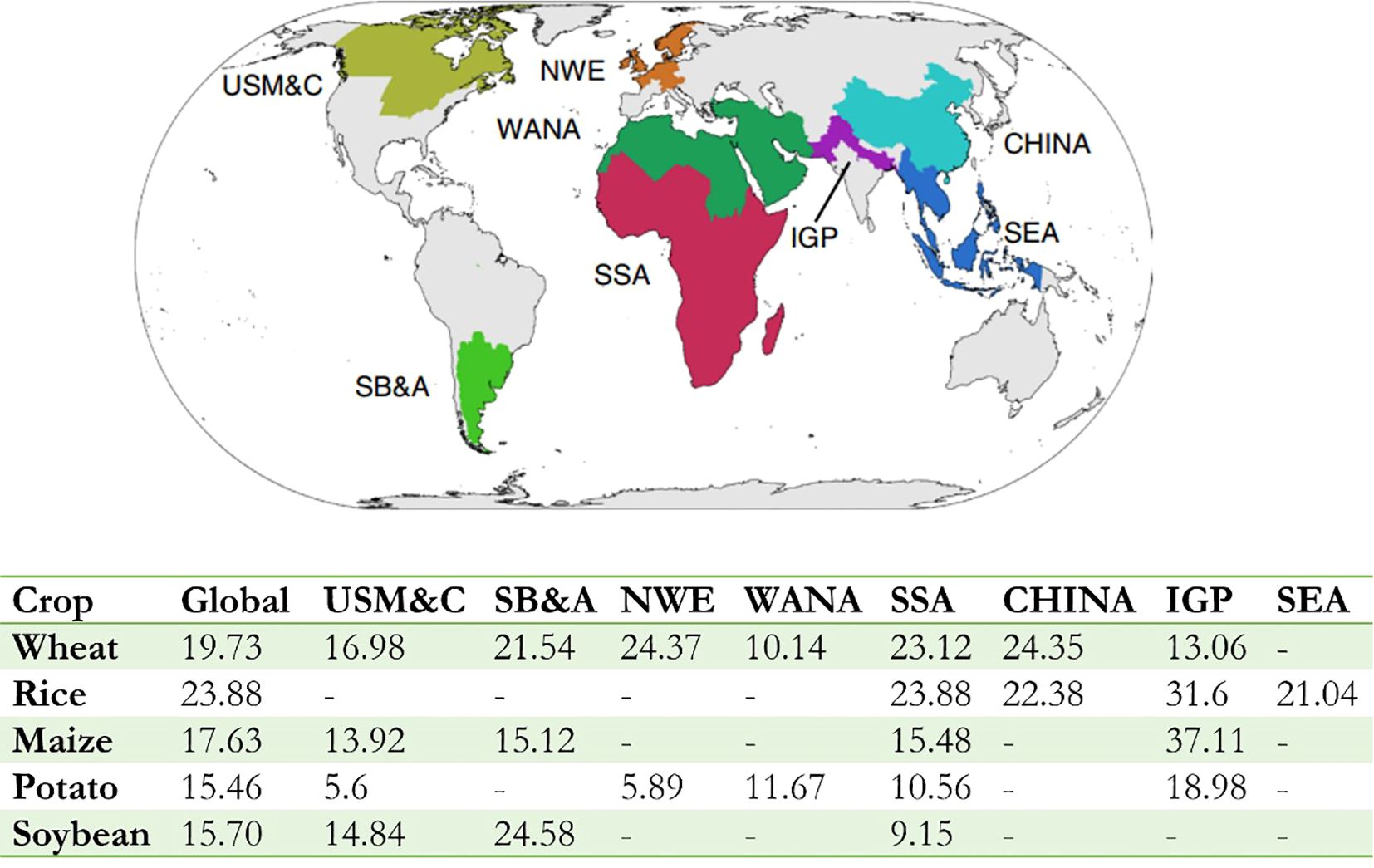
Figure 1. Global variations in crop losses and production. The global map shows the location of the eight food security hotspots where there were sufficient survey responses to estimate the loss (Hijmans et al., 2018). The bottom table shows losses for wheat, rice, maize, potato, and soybean globally or specifically to each food security hotspot. It can be see that crop losses are lower in hotspots generating food surpluses (USM&C, SB&A and NWE, except for soybean) and higher in hotspots located in food insecure regions (SSA and IGP) frequently. Food security hotspot: USM&C, US Midwest and Canada; SB&A, South Brazil, Paraguay, Uruguay and Argentina; NWE, Northwest Europe; WANA, West Asia and North Africa; SSA, Sub-Saharan Africa; CHINA, Mainland China; IGP, Indo-Gangetic Plain; SEA, Southeast Asia. [Adapted from previous study (Savary et al., 2019)].
The occurrence and prevalence of plant diseases vary from season to season, depending on the presence of the pathogen, environmental conditions, and the crops and varieties grown. Survival improves when pathogen is detected early. However, majority of plant diseases are at an advanced stage when diagnosed. Early detection of pathogen allows early intervention to try to slow or prevent disease development and lethality. To achieve early detection of all pathogen, numerous of methods have been developed. In this article, we review the development of the plant pathogen detection technology and briefly summarize the challenges and the future directions. We see how our existing knowledges about the pathogen biology and technology development promote the sensitivity, accuracy, and throughput of detection methods for plant pathogens. Interdisciplinary collaboration is key in transforming progress in technology and biology of plant pathogens to improve early detection and plant survival.
Conventional methods for the detection and identification of plant pathogens mainly rely on recognizing specific morphological features, which involves a time-consuming and labor-intensive process for pathogen cultivation (Camargo and Smith, 2009; Li et al., 2012; Li et al., 2014b; Li et al., 2014a) (Table 1). The period of time from the infection of pathogens to the observation of the syndromes of suspected infectious etiology is variable ranging from days for fast-growing bacteria to weeks for slower growing species (Qinhua et al., 2011). On the other hand, individual pathogens may cause a variety of plant diseases with a wide range of pathological phenotypes which are hard to standardize and have high false positive rates. Occasionally certain pathogens cause subtle symptoms in the tolerant crop cultivar but can have devastating effects in a susceptible one. The situation is among others further aggravated by the morphology similarity that may be caused by different pathogens. The diagnosis of pathogens from the plant host can be complicated by the fact that plants may be infected by multiple pathogens simultaneously or individually in nature or in a laboratory setting (Camargo and Smith, 2009). Considering the largely identical morphological symptoms, the identification of different pathogens from the same plant host can be difficult. Moreover, the morphology-based detection methods rely heavily upon cultivation methods. Although cultivation methods have been improved considerably over the past several decades with advances in the scope and diversity of media components, it still involves a time-consuming process of culture enrichment. Moreover, certain plant pathogens do not readily grow in a laboratory environment. We would thus observe strong bias toward bacteria that are amenable to cultivation. Therefore, morphology-based techniques have very low sensitivity and accuracy and are not suitable for detection of unculturable pathogens that are also not easily viewed by light microscopes such as viruses, viroids, and phytoplasmas.
The sensitivity for cultivation-amenable microorganisms have been dramatically improved with the development of immunological detection relying mainly on the specific binding of an antibody to an antigen. The immunogold staining (IGS) was begin to be applied in 1985 to identify the plant pathogenic bacterium Erwinia amylovora (Van Laere et al., 1985). It requires less primary antiserum and shows the advantage that the preparations can be conserved permanently and unchanged. An “indirect” immunohistological technique was developed by employing immunoglobulin adsorbed to colloidal gold as the secondary antiserum. The technique, the immunogold-silver staining (IGSS), is of much enhanced sensitivity (up to 200-fold) as compared with IGS (Holgate et al., 1983). To further improve the sensitivity, an enzyme‐linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was developed where the detection limit of Pseudomonas syringae pv. phaseolicola, the agent of halo blight disease of beans, was as high as 2 × 104 cells ml−1 (Wyatt et al., 1989; Gan et al., 2013). Indirect ELISA based on polyclonal antibodies was also developed to distinguish pathovars of Pseudomonas syringae from pea (Mazarei and Kerr, 1990). The suitability of the antigen-antibody complex depends mainly on the antibodies’ specificity. In order to ensure the reliable detection of pathogens, a variety of antibodies have been employed in different assay types. Most polyclonal antibodies, derived from either rabbit or goat serum, contain a collection of antibodies with different cellular origins and, therefore, somewhat different specificities. Monoclonal antibodies are often more useful than polyclonal ones for specific detection of a molecule, since they provide an indefinite supply of a single antibody. Lots of monoclonal antibodies have been commercialized. Specific polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies were developed for the identification of Xanthomonas campestris pv. Campestris and Pseudomonas syringae pv. pisi, with an enzyme immunoassay (EIA), immunofluorescence microscopy (IF), or a dot-blot immunoassay (DBI) (Franken et al., 1992).
With the development of monoclonal antibodies, immunological detection of microbial contamination has become more specific, sensitive, reproducible, and reliable (Table 1). When detecting Pseudomonas syringae, the immuno-assay method (competitive ELISA) is approximately 100 times more sensitive than the High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) method and requires no previous extraction (Gallo et al., 2000). On the other hand, the influence of sample preparation and antibody reactions should be thoroughly examined and understood first, as the detection sensitivity is often altered with the variability of these parameters. For example, comparison of dilution-plating by two different sample extraction methods revealed that, for samples of Pseudomonas syringae pv. Pisi in pea seed, methods involving longer time of soak in water for pea seeds were more sensitive (Gallo et al., 2000).
With the development of the immunological methods, reliable quantitative assessments detect plant pathogens were allowed to be managed in a high-throughput manner. Immune-dipstick and immune-lateral flow assays were developed and used in laboratories and then for field application. ELISA, immunofluorescence staining test (IFST), seed immunoblot binding assay (SIBA), dyed latex bead agglutination test, lateral-flow immunoassay, fluorescent silica nanoparticles (FSNP), and strip immunoassay have been successfully used to detect plant pathogens such as Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. vesicatoria (causing bacterial spot disease in tomatoes and peppers) (Yao et al., 2009) and E. amylovora (Braun-Kiewnick et al., 2011), with the detection limit equivalent to the typical of pathogen concentrations in symptomatic plant material (Anil et al., 2008).
To facilitate simultaneous detection of multiple pathogens, a multiplex dipstick immunoassay was developed by determining different major Fusarium toxins in wheat, oats, and maize (Lattanzio et al., 2012). An antibody for each plant pathogen was linked on a fluorescence-coded magnetic microsphere set which was used to capture corresponding pathogens (Lattanzio et al., 2012). The method was optimized by employing microsphere immunoassays where four important plant pathogens (i.e., fruit blotch bacterium Acidovorax avenae subsp. citrulli, chilli vein-banding mottle virus, watermelon silver mottle virus, and melon yellow spot virus) were simultaneously detected with substantially higher sensitivity and within much shorter assay time than ELISA (Charlermroj et al., 2013). The system was also shown to be capable of detecting pathogens in naturally infected plant samples. However, antibody-based detection is antigen-dependent and is still lacking the ability to detect plant pathogen in “real-time” for early infection detection and the timeline of disease progression.
Nucleic-acid-based approaches are rapid, specific, and highly sensitive and are among the most useful and efficient methods available for phytopathogen detection (Li et al., 2012; Gan et al., 2014a; Li et al., 2014b; Li et al., 2014a; Wang et al., 2015a) (Table 1). Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) has been demonstrated to be rapid and accurate to detect wide array of pathogens [e.g., E. amylovora (Bereswill et al., 1992), Agrobacterium tumefaciens (Pulawska, 1997), Pseudomonas marginalis (Qinhua et al., 2011), Xanthomonas campestris pv. Vesicatoria (Gan et al., 2014b) and different Pseudomonas syringae pathovars (Zaccardelli et al., 2003; Kong et al., 2004; Zaccardelli et al., 2005)], where detection limits ranging from 250 to 500 CFU mL-1 were obtained (De Boer, 1995). Since the invention of PCR, numerous of derivatives have been developed to improve the simplicity, sensitivity, accuracy of pathogen detection. Molecular methods, such as restriction enzyme digestion, have been employed to simplify the pathogen detection where PCR-RFLP (Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism) has been applied in detection of a numerous of phytopathogens from plant tissues, soil, and water extracts (Hélias et al., 1998; Shenge et al., 2008). Sample preparation, such as genomic DNA extraction, is time-consuming while automated DNA-extraction methods have been developed. Combined with the Real-time quantitative PCR (qPCR) assays, the detection method was able to discriminate E. amylovora (isolated from blighted woody plant material) from the other Erwinia strains (isolated from Hokkaido or necrotic pear blossoms) with a limit as low as 103 cells mL−l (i.e., four cells per reaction) (Pirc et al., 2009; Shao et al., 2009; Gan et al., 2013; Liu et al., 2013; Gan et al., 2014c). qPCR also showed high sensitivity when was used to differentiated Verticillium wilt on susceptible and resistant hop cultivars (Humulus lupulus L.) (Štajner et al., 2013), Saccharothrix yanglingensis Hhs.015 (a major apple Valsa canker pathogen) (Fan et al., 2016), and Pseudomonas syringae pv. lachrymans (in cucumber seeds) (Meng et al., 2016). TaqMan-PCR (Shao et al., 2011; Wang et al., 2015b) and loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) (Pang et al., 2009; Feng et al., 2013; Feng et al., 2015) have been developed to improve the sensitivity while a multiplex detection system could detect as low as 0.04 pg genomic DNA of fungal and oomycete pathogens of solanaceous crops (Ning et al., 2008). The sensitivity is able to be further enhanced by 1000-fold by employing nested PCR [is sufficient for single-cell detection in pure culture (Mcmanus and Jones, 1995)] or semi-selective medium prior to PCR [Bio-PCR, with a detection limit of five cells from pure culture (Manulis et al., 1998; Kumagai and Fabritius, 2008; Silva et al., 2015)]. Most recently, droplet digital PCR (ddPCR) began to be used for plant pathogen detection where ddPCR showed a significantly higher degree of sensitivity compared to the qPCR assay and the influence of PCR inhibitors can be reduced considerably in the ddPCR assay (Zhao et al., 2016). However, it is too instrument-dependent (Zhao et al., 2016) and technique-demanding.
PCR-based technology has been developed to detect multiple plant pathogens simultaneously. Primer design is very important, for it’s a component of the development of all nucleic acid-based methods. For example, repetitive sequences were used to distinguish different genetic profiles within P. syringae pathovars P. s. pvs. syringae, morsprunorum, and persicae (Gašić et al., 2012). The pathovar-specific primers based on rhs family gene sequences were also used to simultaneously identify the Xanthomonas species complex associated with tomato bacterial spot, including X. vesicatoria, X. perforans, and X. gardneri (Park et al., 2009; Araujo et al., 2012). To facilitate routine identification of Erwinia species, a PCR method based on species-specific sequences of the housekeeping genes recA and gpd was developed to differentiate E. amylovora, E. pyrifoliae, E. billingiae, E. persicina, E. rhapontici, and E. tasmaniensis. Moreover, differentiation using species-specific primers could be done via either conventional PCR (cPCR) or qPCR (Gehring and Geider, 2012). Moreover, multiplex qPCR with multiple fluorescent reporter dyes were developed to facilitate the simultaneous detection of different pathogenic species of genus Pseudomonas (Haan E.G.d and Bovenkamp G.W.v.d, 2009) and three important rice pathogens, Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae, X. oryzae pv. oryzicola, and Burkholderia glumae (Luqi et al., 2014). A combination of specific primers and multiplex-PCR could identify Pseudomonas syringae pv. morsprunorum, P. s. pv. lachrymans, and P. s. pv. syringae from different host plants, different cultivars of sweet cherry, and oil pumpkin grown in different locations (Ilicic et al., 2016). However, a significant reduction in sensitivity was observed for pathogens in the presence of plant extract (Mcmanus and Jones, 1995). In recent years, loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) is developed for pathogen detection and disease diagnosis (Yang et al., 2025).
Immunological and molecular techniques have advanced but have some issues related to rapidity, signal strength and instrumentation (Table 1). Nanoparticles are different from their bulk counterparts when reduced to nanosize (1-100 nm). In nanosize, they possess certain properties suitable for their development as diagnostic probes (Sharon et al., 2010). Nanofabrication techniques had been used in creating artificial plant parts such as stomata and xylem vessel which are then used to detect pathogens [e.g., Aspergillus niger (Etefagh et al., 2013), Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria (Yao et al., 2009), and Xylella fastidiosa (Meng et al., 2005)] and monitor the infection process and behavior of pathogens inside host plants (Meng et al., 2005). A conjugation with a secondary antibody improves the sensitivity when detecting pathogenic bacteria causing bacterial spot on solanaceous plants (Yao et al., 2009). The integration of immunological and molecular diagnostics with nanotechnology systems offers an option where all detection steps can be accommodated on a portable miniaturized device for rapid and accurate detection of plant pathogens. However, the nanotechnology-based diagnostics for plant pathogens is still developing and the cost is relatively high.
Fluorescent hybridization was first introduced to detect plant pathogens at the single-cell level. Pathogens [e.g., Pseudomonas cinnamomi (Li AY. et al., 2014) and Gamma proteobacteria (Li et al., 2017)] can be specifically detected and visualized directly using fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) via a species-specific fluorescently labelled DNA probe. The advantage of FISH is that the plant or pathogen could retain integrity without damage and there is no need for subculturing. In contrast, it is difficult to localize the hyphae and reproductive structures of pathogens within plant tissues, especially in woody tissues (Li AY. et al., 2014). An additional microscopic method is solid-phase cytometry (SPC) which allows rapid detecting plant pathogen bacteria at the single cell level, without the need for a growth phase. After filtration of the sample, the retained microorganisms are fluorescently labeled on the membrane filter and automatically counted and identified by an epifluorescence microscope (D’Haese and Nelis, 2002). SPC shows equally accurate for the quantification of bacteria compared culture-based method (Vanhee et al., 2009). It has considerable advantages compared to the culture-based method, including its low detection limit (4 cells/m3), rapid (within 24 h), and the straightforward microscopic identification (Vanhee et al., 2009) (Table 1). Moreover, SPC in conjunction with fluorescent viability staining is powerful to detect viable but non-culturable microbes (Cools et al., 2005). In parallel, flow cytometric analysis was developed. When combined with fluorescent labels (e.g., propidium iodide), flow cytometry could detect plant pathogens in crude seed extracts without further extraction (Tebaldi et al., 2010). However, the abovementioned methods are very device-dependent as high-resolution electron microscopies are indispensable to accurately determine the labeled single cells (Li et al., 2017). Moreover, the inherent disadvantage of these methods is the difficulty to find proper labels and determine the proper labelling conditions which is time-consuming and technique-demanding. Therefore, recent research has focused on finding alternative label-free approaches for super-sensitive pathogen identification at the single-cell level.
Comprehensive biochemical information can be provided by noninvasive optical spectroscopy techniques, e.g., infrared, hyperspectral imaging and Raman spectroscopy (Kubryk et al., 2015; Wang et al., 2016) (Table 1). With very low background noise of aqueous samples, Raman spectroscopy is especially well-suited for biological applications (Wang et al., 2016). A single-cell Raman spectrum of bacterium represents a sum of Raman spectra of all cell components. It provides comprehensive information about the cell (e.g., nucleic acids, proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids), and could enable the distinction of various strains at the unicellular level with appropriate chemometrical methods based on comprehensive reference databases (Kloss et al., 2013; Kloß et al., 2015; Kubryk et al., 2015). It has been applied to detect bacteria in plants by identifying different spectra that are unique to each bacterium, much like fingerprint analysis (Jarvis and Goodacre, 2008; Gan et al., 2017).
In particular, surface-enhanced Raman scattering spectroscopy (SERS) is able to enhance the signal by 11 orders of magnitude, which is sufficient for single-molecule detection (Blackie et al., 2009). SERS signal enhancement enables the detection of low concentrations of pathogenic bacteria in plant samples. Employing standardized protocol involving optimized parameters, such as mixing procedure of bacterial samples, concentrated colloidal suspension, and statistic analysis [e.g., principal component analysis (Guicheteau et al., 2008; Gan et al., 2017)], reproducible SERS spectra could be generated and numerous of plant pathogens have be identified from bacterial mixtures (Cam et al., 2010; Kang et al., 2010). Moreover, multiplex detection of agriculturally important plant pathogens (i.e., Botrytis cinerea, Pseudomonas syringae, and Fusarium oxysporum) was demonstrated by using SERS (Lau et al., 2016). Furthermore, micro-Raman spectroscopy-based bioassay could detect plant pathogens at single-bacterium level in plant tissue lesions without pre-enrichment (Gan et al., 2017a) which makes in-site identification of pathogens from real plants possible. Species-specific detection of either a single plant pathogen (Yüksel et al., 2015) or multiple pathogens (Lau et al., 2016) from infected plant materials was achieved via label-free SERS or the multiplex detection approach. In general, compared with conventional methods, with proper sample preparation, the single-cell technologies enable a highly sensitive, pre-enrichment-free, and real-time detection of plant pathogen at a single-cell level (Figure 2).
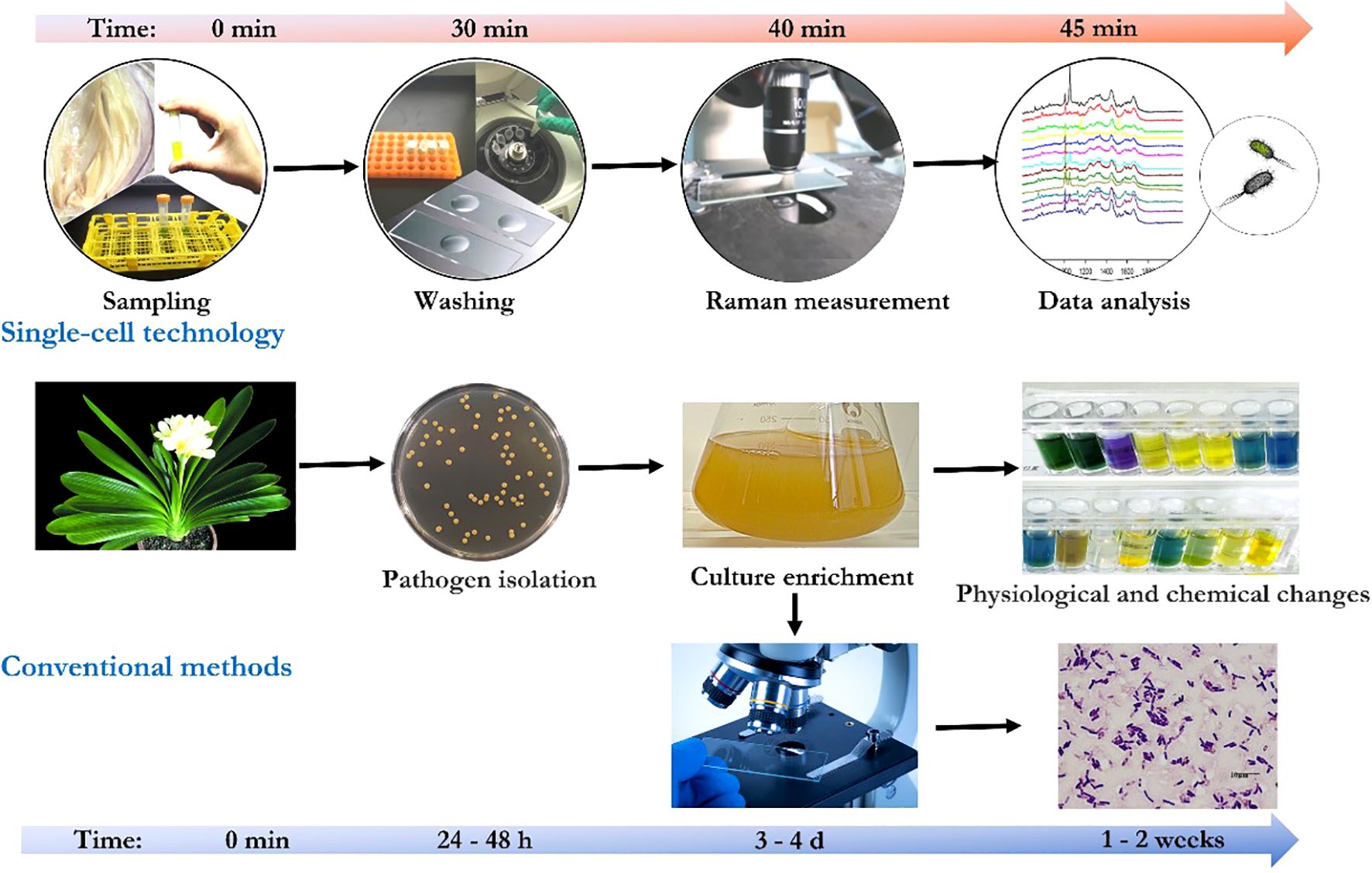
Figure 2. Comparison of conventional methods and the single-cell technologies for plant pathogen detection.
Although morphology-based diagnostics (e.g., morphology-, antibody-, nucleic-acid-based methods) and emerging single-cell technology (e.g., fluorescent hybridization, solid-phase cytometry, optical spectroscopy techniques) have, in many ways, met the growing need for in vitro diagnostic tools for pathogens, the advance of single-cell sequencing and synthetic biology promise a revolution toward the development of new diagnostic tests for a fraction of the cost and time (Gan et al., 2017; Marcolungo et al., 2022). The development and successful application of single-cell sequencing has greatly expanded our knowledge of the diversity and phylogeny of microorganisms. It provides an alternative to culturing organisms as a prerequisite for genomic sequencing and allows discrimination between subspecies when present either individually or in combination. Pathogen detection and typing could be achieved within approximately ten minutes of sequencing owing to the use of an internal control (Marcolungo et al., 2022). However, there are still challenges facing the field, such as an efficient method to obtain single cells. To address the challenge, microfluidic platforms have been developed that enable the isolation, enrichment, and biochemical or genetic analysis of individual cells with high spatiotemporal resolution (Li et al., 2019). The combination of microfluidics and single-cell sequencing has been applied for the whole-transcriptome sequencing of animal embryonic cells (Streets et al., 2014), the diagnosis of cancers and immune system diseases (Keller and Pantel, 2019). However, its application in plant pathogen detection is just emerging.
Synthetic biology was recognized early on as an opportunity to engineer organisms that could serve as whole-cell biosensors (Attaluri and Dharavath, 2023). As synthetic biology has matured, increasing gene circuit complexity has allowed for greater sensitivity and reporter tunability of the synthetic biosensors (Cubero et al., 2024). Bacterial viruses harbor natural specificity to a wide range of bacterial pathogens and can be explored for diagnostic applications of pathogens. The correct bacterial surface epitope or pathogen-derived peptides serves as a conditional input that regulates the output of signals generated by luciferase or other reporter genes of the engineered synthetic phage (Pardee et al., 2014). Low-cost microfluidics coupled with a pathogen capture technology could further improve the sensitivity of the phage-based detection (Kang et al., 2014). Although the application of single-cell sequencing and synthetic biology in plant pathogen detection is just emerging, new frontiers in the rational design principles of these technologies have been ushered with a direct impact on applied and foundational studies relating to pathogen biology and diagnostics (Mukherjee and Schroeder, 2016).
On-site diagnostic is a challenge for tangible application of plant quarantine. Progress is being made to address the challenge through transforming these diagnostic technologies into “outside-the-lab” application. For example, to identify pathogens in plant tissues (Llop et al., 2000) and soil (Puławska and Sobiczewski, 2005), a single-tube nested PCR was developed. It allowed reliable detection of pathogens with a number of as few as 100, and was unaffected by the presence of plant-tissue or soil-derived PCR inhibitors (Kositcharoenkul et al., 2011). More and more pathogens could be detected from real plant samples (Mirik and Aysan, 2009), even at the early stage of infection (Taylor et al., 2001) for different pathogens with similar symptoms (Umesha et al., 2015). PCR-based kits, such as Probelia™, for the detection of plant pathogens (e.g., Erwinia carotovora subsp. atroseptica in potatoes) have been evaluated at five laboratories in four countries. The kit was based on DNA-specific PCR amplification followed by detection of amplicons by hybridization to a peroxidase-labelled DNA probe in a microplate (Frechon et al., 1998). To increase the reproducibility, optimized protocol for DNA extraction from plants, specific primers, and procedure were used for pathogen detection in contaminated plants (Abd-Elsalam et al., 2011). Immunological assays have also been commercialized for the detection of a wide variety of pathogens due to that these methods are reliable and do not require highly trained personnel. The LAMP assay successfully detect American plum line pattern virus with crude flowering cherry extract (Garg et al., 2022). Nowadays, researchers achieved precise dual detection: One-tube reverse transcription-recombinase aided amplification (RT-RAA) combined with lateral flow strip (LFS) assay for RNA and DNA target genes from pepper mild mottle virus and Colletotrichum species in crude plant samples (Cao et al., 2025).
Synthetic phage can reproduce rapidly in fermenters (Schofield et al., 2012). Therefore, phage-based pathogen are now commercially approved products for microbial detection in industrial settings, and clinical applications have been demonstrated as well (Lu et al., 2013). An emerging trend for in-site diagnostic lies in in vitro synthetic biology where cellular context is completely removed and synthetic gene circuits are put on paper (Figure 3) (Pardee et al., 2014). The synthetic diagnostic systems are freeze-dried onto porous substrates to create poised genetic regulatory networks that are stable for long-term storage at room temperature and are activated by rehydration. The paper-based reactions could be merged with custom, low-cost electronics for quantification and automation of diagnostic reactions in the field. At the macroscopic scale, pathogen detection methods and plant disease forecasting in crop systems have been improved by using nanosensors which can be linked to a Global Positioning System for real-time monitoring of disease, soil conditions, and crop health (Abd-Elsalam, 2013). Despite these proof-of-concept demonstrations, several challenges remain for the practical implementation of these diagnostics, including meeting the detection thresholds required for field use.
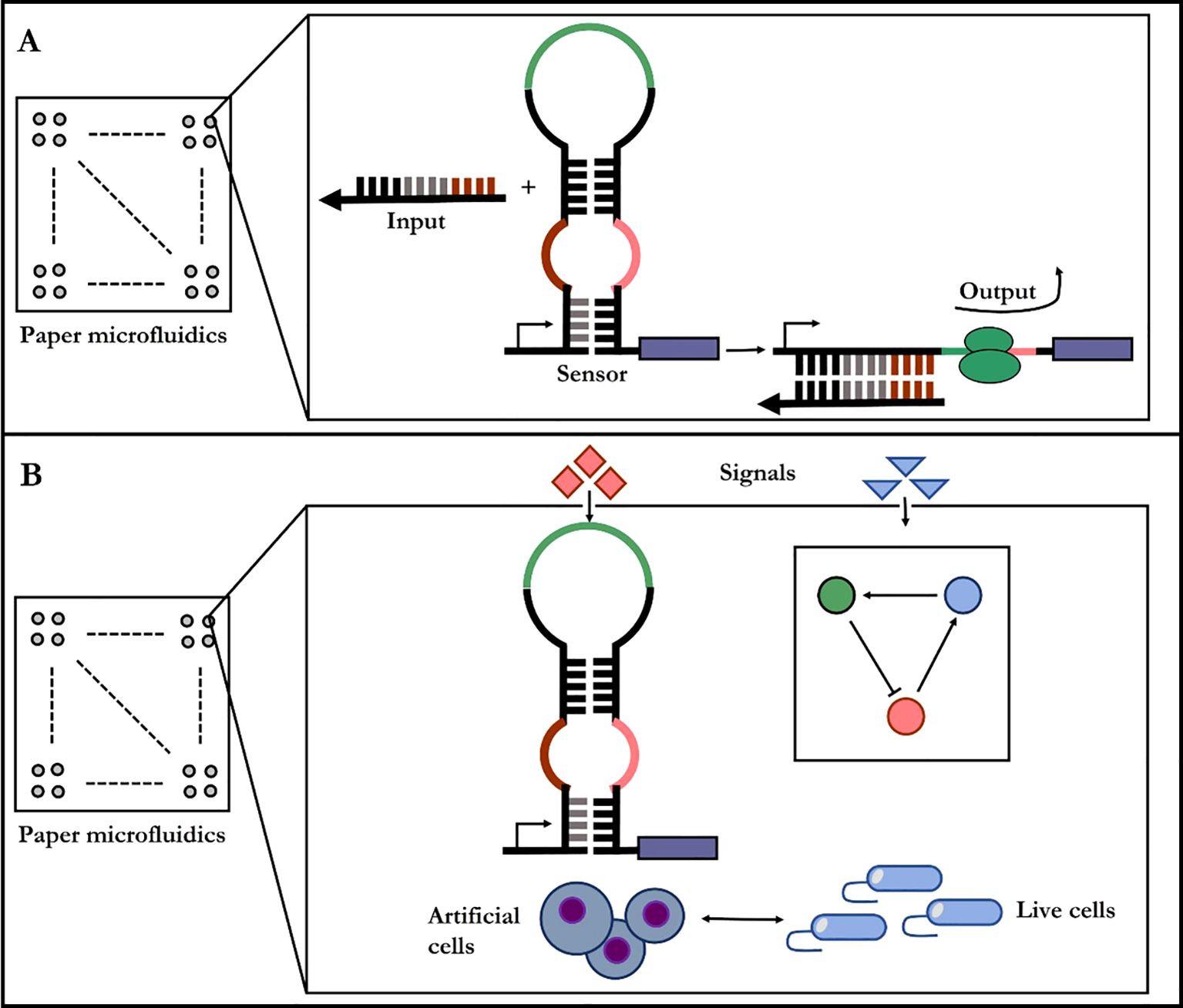
Figure 3. Paper-based diagnostic synthetic-biology designs. (A) The gene circuit becomes active when rehydrated with the test sample, containing target RNAs or small molecule. (B) Diagnostic gene networks and cell-free transcription/translation system are assembled into paper or other porous materials.
Detection of crop pathogens at the single-cell level is the latest goal of diagnostic technology at the present. Conventional diagnostics, such antibody- based techniques and PCR-based methods, are important and sensitive application methods. However, proper implementation of these techniques poses challenges, ranging from time-consuming bacteria enrichment to the significant cost of the technology. The most important is that these methods could not detect plant pathogenic bacteria at a single cell level.
We are witnessing a leapfrog development of pathogen detection from culture-based strategies to in-situ diagnostic when investigators begin to design FISH, SPC, and label-based optical spectroscopy experiments. These methods allow the detection of viable but non-culturable microbes in the field. However, the sensitivity and resolution needed for the experiments should be considered. The advent of microfluidic technologies, coupled with rapid advances in fluorescence-based molecular imaging, had spurred a revolution in biological analysis at the level of single cells (Khan, 2014). But these methods are label-dependent and technique-demanding.
The development of a micro-Raman spectroscopy-based bioassay enabled fast, label-free and non-invasive discrimination of plant pathogens, and accurate culture-free single-bacterium detection in plant tissue lesions with an identification ratio comparable to those of genetic molecular approaches (Gan et al., 2017). It signifies a trend towards the development of methods for in situ, real-time, and single-bacterium detection which offers exciting new opportunities in entry-exit quarantine, customs inspection, food-processing, medical diagnosis, and biological weapons inspections, crucial to national security. However, Raman spectroscopy requires capital funding for equipment. A systemic, standardized, and comprehensive spectroscopic database of cultured bacteria is always a precondition for measurements. The cultivation should include the respective environmental conditions and enough biological replicates to establish a classification model assessing the possibility to distinguish between taxa. Next generation sequencing also requires having a reference dataset of vouchered specimens for use in general diagnostics of unknown. Therefore, the capacity of Raman spectroscopy to detect unknown plant pathogens remains challenge.
As single-cell sequencing joins ranks with other diagnostics, its combination with microfluidic enables in situ, real-time, and single-cell detection of unknown microbes. On the other hand, synthetic biology provides low-cost, rapidly deployable diagnostics. The engineering approaches have the potential to significantly advance the translation of promising technologies into pragmatic tools suitable for real-world applications. The paper-based synthetic biosensor and portable hybrid devices incorporating synthetic sensors or single-cell sequencing fit the need for low-cost, practical, and simple diagnostic tools for use outside of the laboratory. It is also intriguing to imagine in vitro synthetic biology embedded into diagnostic wearables for crops, allowing for both in-site and real-time sensing. Success will continue to be found at the interfaces between disciplines.
QG: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Investigation. XW: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. SL: Writing – original draft. BC: Writing – review & editing. CL: Writing – original draft.
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported in part by grants from Hainan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (322QN250), the National Key R&D Program of China (2021YFA0909600), the Intergovernmental Project of National Key R&D Program of China (2021YFE0110100), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32060061), and the Key R&D Program of Hainan Province (ZDYF2022XDNY140).
The authors would like to acknowledge Prof Wenxu Zhou, State Key Laboratory of Marine Resource Utilization in South China Sea, Hainan University.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abd-Elsalam, K. A. (2013). Nano platforms for plant pathogenic fungi management. Fungal Enomics & Biology 2, e107. doi: 10.4172/2165-8056.1000e107
Abd-Elsalam, K., Bahkali, A., Moslem, M., Amin, O. E., Niessen, L. (2011). An optimized protocol for DNA extraction from wheat seeds and Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP) to detect Fusarium graminearum contamination of wheat grain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 12, 3459–3472. doi: 10.3390/ijms12063459
Anil, K., Singh, U. S., Kumar, J., Garg, G. K. (2008). Application of molecular and immuno-diagnostic tools for detection, surveillance and quarantine regulation of Karnal bunt (Tilletia indica) of wheat. Food Agric. Immunol. 19, 293–311. doi: 10.1080/09540100802478194
Araujo, E. R., Costa, J. R., Ferreira, M. A. S. V., Quezadoduval, A. M. (2012). Simultaneous detection and identification of the Xanthomonas species complex associated with tomato bacterial spot using species-specific primers and multiplex PCR. J. Appl. Microbiol. 113, 1479–1490. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2012.05431.x
Attaluri, S., Dharavath, R. (2023). Novel plant disease detection techniques-a brief review. Mol. Biol. Rep. 50, 9677–9690. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08838-y
Bereswill, S., Pahl, A., Bellemann, P., Zeller, W., Geider, K. (1992). Sensitive and species-specific detection of Erwinia amylovora by polymerase chain reaction analysis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 58, 3522–3526. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.11.3522-3526.1992
Bhattacharya, S. (2017). Deadly new wheat disease threatens Europe’s crops. Nature 542, 145–146. doi: 10.1038/nature.2017.21424
Blackie, E. J., Ru, E. C. L., Etchegoin, P. G. (2009). Single-molecule surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy of nonresonant molecules. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131, 14466–14472. doi: 10.1021/ja905319w
Braun-Kiewnick, A., Altenbach, D., Oberhänsli, T., Bitterlin, W., Duffy, B. (2011). A rapid lateral-flow immunoassay for phytosanitary detection of Erwinia amylovora and on-site fire blight diagnosis. J. Microbiological Methods 87, 1–9. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2011.06.015
Cam, D., Keseroglu, K., Kahraman, M., Sahin, F., Culha, M. (2010). Multiplex identification of bacteria in bacterial mixtures with surface-enhanced Raman scattering. J. Raman Spectrosc. 41, 484–489. doi: 10.1002/jrs.v41:5
Camargo, A., Smith, J. S. (2009). An image-processing based algorithm to automatically identify plant disease visual symptoms. Biosyst. Eng. 102, 9–21. doi: 10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2008.09.030
Cao, Y., Yan, D., Zhou, H., Han, K., Wan, Q., Peng, J., et al. (2025). Achieving precise dual detection: One-tube reverse transcription-recombinase aided amplification (RT-RAA) combined with lateral flow strip (LFS) assay for RNA and DNA target genes from pepper mild mottle virus and Colletotrichum species in crude plant samples. Talanta 281, 126908. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2024.126908
Carvajal-Yepes, M., Cardwell, K., Nelson, A., Garrett, K. A., Giovani, B., Saunders, D. G. O., et al. (2019). A global surveillance system for crop diseases. Science 364, 1237–1239. doi: 10.1126/science.aaw1572
Cerda, R., Avelino, J., Gary, C., Tixier, P., Lechevallier, E., Allinne, C. (2017). Primary and secondary yield losses caused by pests and diseases: assessment and modeling in coffee. PloS One 12, e0169133. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0169133
Charlermroj, R., Himananto, O., Seepiban, C., Kumpoosiri, M., Warin, N., Oplatowska, M., et al. (2013). Multiplex detection of plant pathogens using a microsphere immunoassay technology. PloS One 8, e62344. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062344
Cools, I., D'Haese, E., Uyttendaele, M., Storms, E., Nelis, H. J., Debevere, J. (2005). Solid phase cytometry as a tool to detect viable but non-culturable cells of Campylobacter jejuni. J. Microbiological Methods 63, 107–114. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2005.02.023
Cubero, J., Zarco-Tejada, P. J., Cuesta-Morrondo, S., Palacio-Bielsa, A., Navas-Cortés, J. A., Sabuquillo, P., et al. (2024). New approaches to plant pathogen detection and disease diagnosis. Phytopathology® 114, 1989–2006. doi: 10.1094/PHYTO-10-23-0366-IA
D’Haese, E., Nelis, H. J. (2002). Rapid detection of single cell bacteria as a novel approach in food microbiology. J. Aoac Int. 85, 979–983. doi: 10.1093/jaoac/85.4.979
De Boer, S. (1995). PCR Detection of Erwinia carotovora subsp. atroseptica Associated with Potato Tissue. Phytopathology 85, 854–858. doi: 10.1094/Phyto-85-854
Elad, Y., Pertot, I. (2014). Climate change impacts on plant pathogens and plant diseases. J. Crop Improvement 28, 99–139. doi: 10.1080/15427528.2014.865412
Etefagh, R., Azhir, E., Shahtahmasebi, N. (2013). Synthesis of CuO nanoparticles and fabrication of nanostructural layer biosensors for detecting Aspergillus Niger fungi. Scientia Iranica 20, 1055–1058. doi: 10.1016/j.scient.2013.05.015
Fan, D., Li, Y., Zhao, L., Li, Z., Huang, L., Yan, X. (2016). Study on Interactions between the Major Apple Valsa Canker PathogenValsa Maliand Its Biocontrol AgentSaccharothrix yanglingensisHhs.015 Using RT-qPCR. PloS One 11, e0162174. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0162174
Feng, L., Li, H., Ni, X., Wang, J., Ji, Y., Gan, Q. (2015). Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) for rapid detection of Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. manihotis. Plant Prot. (in Chinese) 41, 93–99.
Feng, L., Ni, X., Li, Y., Wu, X., Gan, Q. (2013). Detection of Pseudomonas syringae pv.pisi by LAMP (Loop-mediated isothermal amplification). Plant Quarantine (in Chinese) 27, 80–84.
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. (2024). Value of agricultural production (Statistics Database). Cham, Switzerland. Available online at: http://www.fao.org/faostat/en.
Franken, A. A. J. M., Zilverentant, J. F., Boonekamp, P. M., Schots, A. (1992). Specificity of polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies for the identification of Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris. Netherlands J. Plant Pathol. 98, 81–94. doi: 10.1007/BF01996321
Frechon, D., Exbrayat, P., Helias, V., Hyman, L., Jouan, B., Llop, P., et al. (1998). Evaluation of a PCR kit for the detection ofErwinia carotovora subsp.atroseptica on potato tubers. Potato Res. 41, 163–173. doi: 10.1007/BF02358439
Gallo, M., Fogliano, V., Ritieni, A., Peluso, L., Greco, M., Lops, R., et al. (2000). Immuno-assessment of Pseudomonas syringae lipodepsipeptides (syringomycins and syringopeptins). Phytopathol. Mediterr. 39, 410–416. doi: 10.1400/57873
Gan, Q., Chen, C., Wang, Y., Ji, Y., Wu, X., Shao, X. (2013). Detection and identification of Tomato black ring nepovirus from imported cucumber seeds. Food Res. Dev. (in Chinese) 34, 88–90.
Gan, Q., Wang, Y., Wei Shao, X. X., Liu, C., Li, Y. (2014a). Detection and sequence analysis of Hop stunt viroid in grapevine rootstock from France. Acta Phytophylacica Sin. (in Chinese) 41, 346–351.
Gan, Q., Lu, Y., Shao, X., Sun, T., Li, Y., Liu, C. (2014b). Rapid Detection and Typing of Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria by Pyrosequencing. J. Phytopathol. 162, 190–194. doi: 10.1111/jph.2014.162.issue-3
Gan, Q., Wang, X., Wang, Y., Xie, Z., Tian, Y., Lu, Y. (2017). Culture-free detection of crop pathogens at the single-cell level by micro-raman spectroscopy. Advanced Sci. 4, 1700127. doi: 10.1002/advs.201700127
Gan, Q., Wu, X., Feng, L. (2014c). Shandong Bureau intercepts and capture Hop dwarf virus like virus from grape rootstock imported from France. Plant Quarantine (in Chinese) 28, 92.
Garg, N., Ahmad, F. J., Kar, S. (2022). Recent advances in loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) for rapid and efficient detection of pathogens. Curr. Res. Microbial Sci. 3, 100120. doi: 10.1016/j.crmicr.2022.100120
Gašić, K., Prokić, A., Ivanović, M., Kuzmanović, N., Obradović, A. (2012). Differentiation of Pseudomonas syringae pathovars originating from stone fruits. Pesticidi I Fitomedicina 27, 219–229. doi: 10.2298/PIF1203219G
Gehring, I., Geider, K. (2012). Identification of Erwinia species isolated from apples and pears by differential PCR. J. Microbiological Methods 89, 57–62. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2012.01.018
Guicheteau, J., Argue, L., Emge, D., Hyre, A., Jacobson, M., Christesen, S. (2008). Bacillus spore classification via surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy and principal component analysis. Appl. Spectrosc. 62, 267–272. doi: 10.1366/000370208783759623
Haan E.G.d, Bovenkamp G.W.v.d (2009). Test development in Erwinia at the NAK: BioPlex real-time PCR. Gewasbescherming 40, 172–175.
Hélias, V., Le Roux, A., Bertheau, Y., Andrivon, D., Gauthier, J., Jouan, B. (1998). Characterisation of Erwinia carotovora subspecies and detection of Erwinia carotovora subsp. atroseptica in potato plants, soil and water extracts with PCR-based methods. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 104, 685–699. doi: 10.1023/A:1008666801839
Hijmans, R., Garcia, N., Wieczorek, J. (2018). Global administrative areas database (GADM) version 3.6 (New York, NY, USA: UN).
Holgate, C. S., Jackson, P., Cowen, P. N., Bird, C. C. (1983). Immunogold-silver staining: new method of immunostaining with enhanced sensitivity. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 31, 938–944. doi: 10.1177/31.7.6189883
Ilicic, R., Balaž, J., Stojšin, V., Bagi, F., Pivic, R., Stanojković-Sebić, A., et al. (2016). Molecular characterization of Pseudomonas syringae pvs. from different host plants by repetitive sequence-based PCR and multiplex-PCR@Įvairių augalų-šeimininkų Pseudomonas syringae pvs. molekulinis apibūdinimas taikant pasikartojančių sekų ir jungtinę PGR. Zemdirbyste-agriculture 103, 199–206. doi: 10.13080/z-a.2016.103.026
Jarvis, R. M., Goodacre, R. (2008). Characterisation and identification of bacteria using SERS. Chem. Soc. Rev. 37, 931–936. doi: 10.1039/b705973f
Kang, J. H., Super, M., Yung, C., Cooper, R., Domansky, K., Graveline, A., et al. (2014). An extracorporeal blood-cleansing device for sepsis therapy. Nat. Medcine 20, 1211–1216. doi: 10.1038/nm.3640
Kang, Y. P., Si, M. Z., Li, Q. Y., Huang, Q., Liu, R. M. (2010). SERS spectra of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. Oryzae (Xoo) on nano silver film prepared by electrolysis method. Spectrosc. Spectral Anal. 30, 372–375. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2010)02-0372-04
Keller, L., Pantel, K. (2019). Unravelling tumour heterogeneity by single-cell profiling of circulating tumour cells. Nat. Rev. Cancer 19, 553–567. doi: 10.1038/s41568-019-0180-2
Khan, A. S. (2014). Rapid advances in nucleic acid technologies for detection and diagnostics of pathogens. J. Microbiol. Experiment. 1, 1–7. doi: 10.15406/jmen.2014.01.00009
Kloß, S., Rösch, P., Pfister, W., Kiehntopf, M., Popp, J. (2015). Toward culture-free Raman spectroscopic identification of pathogens in ascitic fluid. Analytical Chem. 87, 937–943. doi: 10.1021/ac503373r
Kloss, S., Kampe, B., Sachse, S., Rösch, P., Straube, E., Pfister, W., et al. (2013). Culture independent Raman spectroscopic identification of urinary tract infection pathogens: a proof of principle study. Analytical Chem. 85, 9610–9616. doi: 10.1021/ac401806f
Kong, H., Patterson, C. D., Zhang, W., Takikawa, Y., Suzuki, A., Lydon, J. (2004). A PCR protocol for the identification of Pseudomonas syringae pv. tagetis based on genes required for tagetitoxin production. Biol. Control 30, 83–89. doi: 10.1016/j.biocontrol.2003.09.002
Kositcharoenkul, N., Chatchawankanphanich, O., Bhunchoth, A., Kositratana, W. (2011). Detection of Xanthomonas citri subsp. citri from field samples using single-tube nested PCR. Plant Pathol. 60, 436–442. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3059.2010.02390.x
Kubryk, P., Kölschbach, J., Marozava, S., Lueders, T., Meckenstock, R., Niessner, R., et al. (2015). Exploring the potential of stable isotope (Resonance) raman microspectroscopy and surface-enhanced raman scattering for the analysis of microorganisms at single cell level. Analytical Chem. 87, 6622–6630. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.5b00673
Kumagai, L., Fabritius, A.-L. (2008a). “Detection and Differentiation of Pathogenic Agrobacterium vitis and A. tumefaciens in Grapevine using Multiplex Bio-PCr,” in Proceedings of the 2nd Annual National Viticulture Research Conference. University of California, Davis, 42–43.
Lattanzio, V. M., Nivarlet, N., Lippolis, V., Gatta, S., Huet, A., Delahaut, P., et al. (2012). Multiplex dipstick immunoassay for semi-quantitative determination of Fusarium mycotoxins in cereals. Analytica Chimica Acta 718, 99–108. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2011.12.060
Lau, H. Y., Wang, Y., Wee, E. J. H., Botella, J. R., Trau, M. (2016). Field demonstration of a multiplexed point-of-care diagnostic platform for plant pathogens. Analytical Chem. 88, 8074–8081. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.6b01551
Li, Y., Wei, X., Gan, Q., Ji, Y., Shao, X., Wang, Y. (2014a). Isolation and identification of soft rot bacteria on imported Zantedeschia. J. Food Saf. Qual. (in Chinese) 5, 3944–3946.
Li, A. Y., Crone, M., Adams, P. J., Fenwick, S. G., Hardy, G. E. S. J., Williams, N. (2014). The microscopic examination of phytophthora cinnamomi in plant tissues using fluorescent in situ hybridization. J. Phytopathol. 162, 747–757. doi: 10.1111/jph.2014.162.issue-11-12
Li, J., Zhang, H., Menguy, N., Benzerara, K., Wang, F., Lin, X., et al. (2017). Single-cell resolution of uncultured magnetotactic bacteria via fluorescence-coupled electron microscopy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 83, e00409–e00417. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00409-17
Li, H., Torab, P., Mach, K. E., Surrette, C., England, M. R., Craft, D. W., et al. (2019). Adaptable microfluidic system for single-cell pathogen classification and antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 116, 10270–10279. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1819569116
Li, Y., Gan, Q., Feng, L., Shao, X. (2014b). Isolation, identification, and biological characterization of Burkholderia gladioli in Cymbidium imported from Korea. Acta Phytopathologica Sin. (in Chinese) 44, 313–317.
Li, Y., Wang, Y., Ni, X., Gan, Q., Feng, L. (2012). Isolation and identification of Erwinia cypripedii from imported Korea Cymbidium. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. (in Chinese) 31, 15243–15244.
Lin, C., Liang, C. Z., Xu, B., Sun, M., Liu, C. X., Gao, H. W., et al. (2009). Establishment of Loop-mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP) method for Campylobacter jejuni detection. Microbiol. China (in Chinese) 36, 923–928.
Liu, C., et al. (2013). Qualitative test of radish ingredients in food by Real-time PCR. Food Res. Dev. 34, 58–61.
Llop, P., Bonaterra, A., Penalver, J., Lopez, M. M. (2000). Development of a highly sensitive nested-PCR procedure using a single closed tube for detection of Erwinia amylovora in asymptomatic plant material. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 66, 2071–2078. doi: 10.1128/AEM.66.5.2071-2078.2000
Lu, T. K., Bowers, J., Koeris, M. S. (2013). Advancing bacteriophage-based microbial diagnostics with synthetic biology. Trends Biotechnol. 31, 325–327. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2013.03.009
Lu, W., Pan, L., Zhao, H., Jia, Y., Wang, Y., Yu, X., et al. (2014). Molecular detection of Xanthomonas oryzae pv.oryzae, Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola, and Burkholderia glumae in infected rice seeds and leaves. Crop J. 2, 398–406. doi: 10.1016/j.cj.2014.06.005
Manulis, S., Kogan, N., Valinsky, L., Dror, O., Kleitman, F. (1998). Detection of Erwinia herbicola pv. gypsophilae in gypsophila plants by PCR. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 104, 85–91. doi: 10.1023/A:1008659001313
Marcolungo, L., Passera, A., Maestri, S., Segala, E., Alfano, M., Gaffuri, F., et al. (2022). Real-time on-site diagnosis of quarantine pathogens in plant tissues by nanopore-based sequencing. Pathogens 11, 199. doi: 10.3390/pathogens11020199
Mazarei, M., Kerr, A. (1990). Distinguishing pathovars of Pseudomonas syringae on peas: nutritional, pathogenicity and serological tests. Plant Pathol. 39, 278–285. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3059.1990.tb02504.x
Mcmanus, P. S., Jones, A. L. (1995). Detection of Erwinia amylovora by nested PCR and PCR-dot-blot and reverse-blot hybridizations. Phytopathology 85, 618–623. doi: 10.1094/Phyto-85-618
Meng, Y., Li, Y., Galvani, C. D., Hao, G., Turner, J. N., Burr, T. J., et al. (2005). Upstream Migration of Xylella fastidiosa via Pilus-Driven Twitching Motility. J. Bacteriology 187, 5560–5567. doi: 10.1128/JB.187.16.5560-5567.2005
Meng, X., Chai, A. L., Chen, L., Shi, Y., Xie, X., Ma, Z., et al. (2016). Rapid detection and quantification of viable Pseudomonas syringae pv. lachrymans cells in contaminated cucumber seeds using propidium monoazide and a real-time PCR assay. Can. J. Plant Pathol. 38, 296–306. doi: 10.1080/07060661.2016.1216897
Mirik, M., Aysan, Y. (2009). Detection of Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. vesicatoria in naturally infected pepper seeds in Turkey. J. Plant Pathol. 91, 433–436. doi: 10.4454/JPP.V91I2.974
Mukherjee, A., Schroeder, C. M. (2016). Microfluidic methods in single cell biology. Ed. Lu, C., et al (Cham, Switzerland: Springer International Publishing).
Ning, Z., Meaghanl, M. C., Christined, S. (2008). A macroarray system for the detection of fungal and oomycete pathogens of solanaceous crops. Plant Dis. 92, 953–960. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-92-6-0953
Pardee, K., Green, A. A., Ferrante, T., Cameron, D. E., DaleyKeyser, A., Yin, P., et al. (2014). Paper-based synthetic gene networks. Cell 159, 940–954. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.10.004
Park, D., Shim, J. K., Kim, J. S., Lim, C. K., Shrestha, R., Hahn, J. H., et al. (2009). Sensitive and specific detection of Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria by PCR using pathovar-specific primers based on rhs family gene sequences. Microbiological Res. 164, 36–42. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2006.11.005
Pirc, M., Ravnikar, M., Tomlinson, J., Dreo, T. (2009). Improved fireblight diagnostics using quantitative real-time PCR detection of Erwinia amylovora chromosomal DNA. Plant Pathol. 58, 872–881. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3059.2009.02083.x
Population Division of the Department of Economic, Social Affairs of the United Nations Secretaria (2022). World population projected to reach 9.7 billion by 2050 (Statistics Database). Cham. Switzerland. Available online at: https://www.un.org/en/desa.
Pulawska, J. (1997). “Detection of agrobacterium tumefaciens in soil using PCR,” in Developments in plant pathology, vol. 11 . Ed. Dehne, H. W., Adam, G., Diekmann, M., Frahm, J., Mauler-Machnik, A., Halteren, P. (Springer, Dordrecht).
Puławska, J., Sobiczewski, P. (2005). Development of a semi-nested PCR based method for sensitive detection of tumorigenicAgrobacteriumin soil. J. Appl. Microbiol. 98, 710–721.
Qinhua, G., Yan, L., Xiuling, S., Yingchao, W. (2011). Isolation and identification of Pseudomonas marginalis and its biological characterization. J. Plant Prot. 38, 183–184.
Savary, S., Willocquet, L., Pethybridge, S. J., Esker, P., McRoberts, N., Nelson, A. (2019). The global burden of pathogens and pests on major food crops. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 3, 430–439. doi: 10.1038/s41559-018-0793-y
Schofield, D. A., Sharp, N. J., Westwater, C. (2012). Phage-based platforms for the clinical detection of human bacterial pathogens. Bacteriophage 2, 105–283. doi: 10.4161/bact.19274
Shao, X., Gan, Q., Zhao, W., Li, Y., Wang, Y., Pang, G. (2009). Detection and identification of Xanthomonas hyacinthi by real-time fluorescent PCR. Plant Quarantine (in Chinese) 23, 25–27.
Shao, X., Gan, Q., Li, Y., Zhao, W., Wu, X., Su, Z. (2011). Detection of Burkholderia caryophylli by TaqMan real-time fluorescent PCR. Acta Phytopathologica Sin. (in Chinese) 41, 24–30.
Sharon, M., Choudhary, A. K., Kumar, R. (2010). Nanotechnology in agricultural diseases and food safety. J. Phytology 2, 83–92.
Shenge, K., Stephan, D., Mabagala, R. B., Mortensen, C. N., Wydra, K. (2008). Molecular characterization ofPseudomonas syringae pv.tomato isolates from Tanzania. Phytoparasitica 36, 338–351. doi: 10.1007/BF02980813
Silva, C. F., Torres, P., Oliveira, N. P. D., Marques, A. S. A., Ferreira, M. A. S. V. (2015). PCR-based methods for detection of Erwinia psidii on guava. Trop. Plant Pathol. 40, 251–259. doi: 10.1007/s40858-015-0020-1
Štajner, N., Cregeen, S., Javornik, B. (2013). Evaluation of reference genes for RT-qPCR expression studies in hop (Humulus lupulus L.) during infection with vascular pathogen verticillium albo-atrum. PloS One 8, e68228. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0068228
Streets, A. M., Zhang, X., Cao, C., Pang, Y., Wu, X., Xiong, L., et al. (2014). Microfluidic single-cell whole-transcriptome sequencing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. United States America 111, 7048–7053. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1402030111
Taylor, R. K., Guilford, P. J., Clark, R. G., Hale, C. N., Forster, R. L. S. (2001). Detection of Erwinia amylovora in plant material using novel polymerase chain reaction (PCR) primers. New Z. J. Crop Hortic. Sci. 29, 35–43. doi: 10.1080/01140671.2001.9514158
Tebaldi, N. D., Peters, J., Chitarra, L., Souza, R., Zouwen, Bergervoet, J. H. W. (2010). Detection of Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. phaseoli in bean seeds by flow cytometry, immunostaining and direct viable counting. Trop. Plant Pathol. 35, 213–222. doi: 10.1590/S1982-56762010000400002
Umesha, S., Jyothi, N., Roohie, R. K. (2015). Detection of bacterial and fusarium wilt pathogens in cabbage by multiplex PCR. J. Plant Sci. 3, 185. doi: 10.11648/J.JPS.20150304.13
Vanhee, L. M. E., Nelis, H. J., Coenye, T. (2009). Rapid detection and quantification of Aspergillus fumigatus in environmental air samples using Solid-phase cytometry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 43, 3233–3239. doi: 10.1021/es803435a
Van Laere, O., De Wael, L., De Mey, J. (1985). Immuno gold staining (IGS) and immuno gold silver staining (IGSS) for the identification of the plant pathogenic bacterium Erwinia amylovora (Burrill) Winslow et al. Histochemistry 83, 397–399. doi: 10.1007/BF00509198
Wang, Y., Ji, Y., Li, Y., Wang, J., Jiang, Q., Gan, Q., et al (2015a). Detection for Alternaria porri using PCR based on Brn1 gene. Plant Prot. (in Chinese) 29, 30–32.
Wang, Y., Gan, Q., Li, Y., Ji, Y., Wu, X., Shao, X.. (2015b). Detection of Embellisia allii using real-time quantitative PCR based on glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene. Scientia Agricultura Sin. (in Chinese) 48, 390–397.
Wang, Y., Huang, W. E., Cui, L., Wagner, M. (2016). Single cell stable isotope probing in microbiology using Raman microspectroscopy. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 41, 34–42. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2016.04.018
Wyatt, G. M., Turner, J. G., Morgan, M. R. A. (1989). Rapid and specific detection of Pseudomonas syringae pv. phaseolicola by immunological methods. Food Agric. Immunol. 1, 53–63. doi: 10.1080/09540108909354674
Yang, L., Sun, Y., Sun, L., Wang Feng, Z. J., Liang, Y. (2025). Application of loop-mediated isothermal amplification in plant pathogen detection. Phytopathology® 115, 6–13. doi: 10.1094/PHYTO-10-23-0391-KC
Yao, K. S., Li, S. J., Tzeng, K. C., Cheng, T. C., Chang, C. Y., Chiu, C. Y., et al. (2009). Fluorescence silica nanoprobe as a biomarker for rapid detection of plant pathogens. Advanced Materials Res. 79-82, 513–516. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.79-82
Yüksel, S., Schwenkbier, L., Pollok, S., Weber, K., Cialla-May, D., Popp, J., et al. (2015). Label-free detection of Phytophthora ramorum using surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Analyst 140, 7254–7262. doi: 10.1039/C5AN01156F.
Zaccardelli, M., Spasiano, A., Bazzi, C., Merighi, M. (2005). Identification and in planta detection of Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato using PCR amplification of hrpZ Pst. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 111, 85–90. doi: 10.1007/s10658-004-2734-7.
Zaccardelli, M., Spasiano, A., Merighi, M., Bazzi, C. (2003). Pseudomonas syringae and related pathogens. Ed. Iacobellis, N. S., Collmer, A., Hutcheson, S., Mansfield, Morris, C., Murillo, J., et al (Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands), 553–558.
Keywords: plant pathogens, morphology-based diagnostic, immunology-based methods, micro-Raman spectroscopy, non-invasive discrimination, single-cell detection
Citation: Wang X, Liang S, Gan Q, Cai B and Liu C (2025) Current status and future perspectives of the diagnostic of plant bacterial pathogens. Front. Plant Sci. 16:1547974. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1547974
Received: 19 December 2024; Accepted: 03 February 2025;
Published: 28 February 2025.
Edited by:
Milan Kumar Lal, National Rice Research Institute (ICAR), IndiaReviewed by:
Chaofeng Wang, University of Nebraska-Lincoln, United StatesCopyright © 2025 Wang, Liang, Gan, Cai and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Qinhua Gan, cWhnYW5AaGFpbmFudS5lZHUuY24=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.