
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Plant Sci. , 10 March 2025
Sec. Plant Membrane Traffic and Transport
Volume 16 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2025.1546011
This article is part of the Research Topic Nutritional and Adaptive Aspects of Ion Transport in Plants View all articles
Nitrate signaling coordinates the expression of a broad range of genes involved in nitrate uptake, transport, and assimilation, playing a crucial role in plant growth and development. Notably, nitrate signaling interacts extensively with various messenger molecules, including phytohormones, calcium ions (Ca2+), reactive oxygen species (ROS), peptides, and sucrose. This crosstalk amplifies nitrate signaling and optimizes nutrient uptake, coordinating developmental processes and enhancing stress tolerance. Understanding the interactions between nitrate and these signaling molecules offers valuable insights into improving crop nutrient use efficiency (NUE), stress resilience, and agricultural sustainability. Using Arabidopsis thaliana as a model, this review consolidates current knowledge on nitrate signaling and its interplay with other signaling pathways that regulate plant development and adaptation. Finally, the review highlights potential genetic strategies for enhancing NUE, contributing to more sustainable agricultural practices.
Nitrate (NO3−) is the primary source of nitrogen, an essential element for plants to form key biomolecules like amino acids, proteins, and nucleic acids. In addition to its nutritional role, nitrate also serves as a signaling molecule that regulates plant growth, development, and responses to environmental factors. However, excessive nitrate use in crops with low nitrogen use efficiency (NUE) has led to higher fertilizer costs and environmental issues like nitrate leaching, which causes eutrophication (Yadav et al., 2017; Bijay and Craswell, 2021).
NUE refers to the ability of a plant to utilize available nitrogen for growth and production effectively. It measures how efficiently plants can absorb, assimilate, and utilize nitrogen, especially in relation to the amount of nitrogen provided, such as through fertilizers. NUE is a crucial factor in enhancing agricultural productivity and promoting sustainability in farming practices. One promising strategy to improve NUE is the genetic manipulation of nitrate signaling pathways. Modern molecular breeding techniques, such as marker-assisted selection, genomic selection, and genome-wide association studies, facilitate the identification and selection of genes linked to NUE. Genetic engineering contributes to improving NUE by introducing novel genes or pathways to enhance nitrogen metabolism. In addition, breakthroughs in genome editing technologies provide the possibility to precisely modify genes involved in nitrate signaling. Therefore, a thorough understanding of nitrate signaling and its integration with other cellular networks is crucial for the improvement of NUE via genetic manipulation.
Advances in the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana have provided valuable insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying nitrate signaling and its regulatory processes. Central to nitrate signaling are key events such as nitrate uptake, root-to-shoot transport, allocation within plant tissues, and cellular transport. Many nitrate transporter are involved in these processes, which have been extensively reviewed (Wang et al., 2018b; Islam et al., 2020; Vidal et al., 2020). This signaling pathway is not only regulated at both the transcriptional and post-transcriptional levels but also undergoes extensive crosstalk with other signaling molecules, including phytohormones, calcium ions (Ca2+), reactive oxygen species (ROS), peptides, and sucrose. The interaction with these molecules amplifies nitrate signaling, optimizing nutrient uptake and enhancing plant resilience by remodeling root architecture and shoot growth, highlighting the integrated nature of nutrient signaling in plant physiology. A comprehensive understanding of nitrate signaling and its interactions with other cellular networks is essential for advancing both fundamental plant biology and agricultural applications. This review aims to enhance our understanding of these signaling interactions in Arabidopsis, offering insights that could improve crop NUE and resilience in agricultural systems. We will also explore potential strategies to leverage this knowledge for enhancing NUE in crops.
Environmental nitrate levels fluctuate across space and time, requiring plants to dynamically adjust root and shoot growth to optimize nitrate uptake and acquisition. Information about external nitrate availability and the overall demand of the plant is translated into cellular signals including phytohormones (illustrated in Figure 1). The crosstalk between phytohormones and nitrate signaling is mainly reflected in the developmental plasticity of root system architecture (RSA), referred to as root foraging, which enables plants to efficiently seek out nutrient pools that fluctuate spatially and temporally (illustrated in Figure 1). RSA includes the initiation, emergence, and elongation of primary roots (PR), lateral roots (LR), as well as root hairs (HR) (Jia et al., 2022).

Figure 1. Illustration of the crosstalk between nitrate signaling and phytohormone signaling. Pointed and blunt arrowheads indicate activating and inhibiting interactions, respectively. The thick arrow indicates the root-to-shoot translocation.
The basipetal transport of auxin has long been recognized as a crucial mechanism for transmitting nitrate signals from the shoot to the root, driving the remodeling of RSA (Li, 2024). Nitrate deficiency directly affects auxin transport, with the key nitrate transporter NRT1.1 (Nitrate Transporter 1.1) playing a pivotal role in this process. Notably, NRT1.1 is also identified as an auxin influx facilitator, contributing to auxin transport activity modulated by nitrate (Krouk et al., 2010). Under low nitrate conditions, NRT1.1 prevents auxin accumulation in the root tip, thereby inhibiting LR growth. In contrast, when nitrate levels are high, the auxin transport activity of NRT1.1 is inhibited, leading to auxin accumulation in the root tip and promoting LR outgrowth (Krouk et al., 2010). In the absence of nitrate, NRT1.1 also negatively regulates the auxin influx carrier LAX3 (Like-Aux1-3), reducing auxin levels in the LR and impeding its development (Ma et al., 2014; Maghiaoui et al., 2020). Interestingly, NRT1.1 is essential for modulating protein phosphorylation in response to nitrate. In fact, only 4% of the nitrate-phosphoproteome observed in wild-type plants was retained in the nrt1.1 mutant (Vega et al., 2021). The dephosphorylation of the Ser439 residue in PIN2 (PIN-Formed 2), an auxin efflux carrier, promotes its polar localization in the plasma membrane and modulates auxin flow between adjacent tissues, thereby inhibiting both PR and LR elongation (Vega et al., 2021). Additionally, the auxin transport of PIN7, another auxin efflux carrier, is regulated by NRT2.1 through direct interaction. The nrt2.1 mutant exhibits defects in polar auxin transport, resulting in impaired low-nitrate-mediated suppression of PR growth (Wang et al., 2023).
NRT1.1 also negatively regulates the auxin biosynthetic gene TAR2 (Arabidopsis Tryptophan Aminotransferase-Related 2), which encodes a key enzyme in the tryptophan-dependent auxin biosynthesis pathway, thereby inhibiting LR development (Ma et al., 2014; Maghiaoui et al., 2020). In addition, nitrate deficiency induces the expression of auxin biosynthesis genes YUC3/5/7/8 and TAA1 (Tryptophan Aminotransferase of Arabidopsis 1), leading to increased auxin accumulation at LR tips and influencing root elongation (Jia et al., 2021). It has been shown that RH elongation under nitrogen deficiency relies on TAA1- and YUC8-mediated auxin biosynthesis at the root apex, alongside AUX1 (Auxin Transporter Protein 1)- and PIN2-driven auxin transport toward the shoots (Jia et al., 2023). In the RH zone, auxin transport driven by AUX1 and PIN2 activates the transcription factors ARF6/8 (Auxin Response Factor), thereby promoting RH elongation in response to low nitrogen availability (Jia et al., 2023).
Furthermore, nitrate availability plays a role in auxin signaling by post-transcriptionally regulating related genes. ARF6/8 are the cleavage targets of miR167, a microRNA that promotes mRNA degradation or inhibits translation of its targets (Wu et al., 2006). Under nitrogen deficiency, the expression of miR167 is repressed, thereby relieving its inhibition on ARF8 transcripts, which in turn promotes LR outgrowth and adventitious roots (Gutierrez et al., 2009; Liang et al., 2012). miR160, another microRNA induced under nitrogen deficiency, targets the transcripts of ARF10, ARF16, and ARF17 for degradation, facilitating adventitious root outgrowth by repressing ARF17 (Wang et al., 2005; Gutierrez et al., 2009; Liang et al., 2012). Additionally, miR393 and its cleavage target AFB3 (Auxin Signaling F-box 3) are both nitrate-induced. In addition, both afb3 mutants and miR393-overexpressing lines exhibited a decreased density of emerging and initiating LR compared to wild-type under KNO3 treatment (Vidal et al., 2010). These suggest that the miR393-AFB3 module forms a feed-forward mechanism to regulate RSA in response to nitrogen availability. AFB3 is also found to mediate the degradation of the transcriptional repressor IAA14 (Indole-3-Acetic Acid Inducible 14) to effectively alleviate the repression exerted on ARF7 and ARF19, promoting auxin signaling and LR initiation (Okushima et al., 2005).
CKs are shown to act as long-distance signaling molecules that move between root and shoot. This translocation is facilitated by the xylem transport system driven by transpiration flow and the phloem transport system that delivers photosynthate throughout the body of the plant (Kudo et al., 2010). CKs have been shown to repress all root-specific root-type NRT genes (NRT1.1, NRT1.5, NRT2.1, NRT2.2, NRT2.6, and NAR2.1), an effect that is independent of the nitrogen status of plants, whether under high or low nitrate conditions (Kiba et al., 2011). This suggests that CKs function as a nitrogen satiety signal, inhibiting nitrate uptake in the root. In addition to this repressive role, CKs positively regulate certain NRT genes in the shoot. Specifically, shoot-expressed NRT genes (NRT1.3, NRT1.4, NRT1.7, NRT2.7) are up-regulated by CKs under both high nitrate and low nitrate conditions, indicating that CKs may enhance nitrate distribution and translocation within shoots (Kiba et al., 2011).
In verse, nitrate supply induces CK accumulation, which may subsequently travel through the vascular bundles (Sharma and Zheng, 2019; Li et al., 2021). Studies have shown that nitrate upregulates the expression of IPT3 (Isopentenyl Transferase 3), a phloem companion cell-localized gene encoding adenosine phosphates-isopentenyltransferase, an enzyme that catalyzes the initial step of cytokinin biosynthesis (Takei et al., 2004a; Hirose et al., 2008). Similarly, nitrate enhances the expression of CYP735A2 (Cytochrome P450 735A2), a vascular bundle-localized gene encoding cytokinin hydroxylase, which catalyzes the biosynthesis of trans-zeatin (tZ) cytokinin (Takei et al., 2004b). Nitrate feeding is proposed to stimulate the synthesis of isopentenyl (iP)-type CK in root phloem after IPT3 activation, with CYP735A2 subsequently converting these into trans-zeatin (tZ) (Hirose et al., 2008; Ahmad et al., 2023). This nitrate-induced accumulation of CK regulates both root growth and leaf expansion through root-to-shoot transport.
The link between nitrate and ABA was first identified nearly two decades ago, highlighting the role of ABA in inhibiting LR growth under high nitrate conditions (Signora et al., 2001). In WT plants, high nitrate levels (10 mM) reduced LR formation compared to low nitrate conditions (0.1 mM). In contrast, ABA biosynthesis and ABA-insensitive mutants (abi4 and abi5) displayed a similar number of LR regardless of nitrate concentration (Signora et al., 2001), suggesting that ABA mediates the inhibition of LR growth under elevated nitrate levels. Interestingly, although NRT1.2 functions as both an ABA and nitrate transporter, its ABA transport activity remains unaffected by high nitrate concentrations, suggesting that the physiological linkage between nitrate and ABA signals may be not through NRT1.2 (Kanno et al., 2013). Subsequent studies demonstrated that nitrate induces the expression of the BG1 (Enzyme β-glucosidase 1), which releases ABA from ABA-glucose ester stores in the ER, promoting ABA accumulation in the root meristem and thereby modulating root growth (Ondzighi-Assoume et al., 2016). Besides, ABA Responsive Element Binding Factors 2 and 3 (ABF2 and ABF3) are key regulators of the endodermis response to nitrate, their targets account for more than 50% of the nitrate-responsive transcriptome in the endodermis (Contreras-Lopez et al., 2022). The positive effect of nitrate on LR growth was absent in abf2, abf3, and abf2abf3 mutants, suggesting their roles in LR development in response to nitrate (Contreras-Lopez et al., 2022).
Nitrate supply enhances GA biosynthesis in Arabidopsis (Camut et al., 2021). GAs promote growth by opposing the functions of DELLA growth-repressing proteins (DELLAs), members of the GRAS family of transcription regulators (Davière and Achard, 2013). GA binds to the GA receptors Gibberellin Insensitive 1 (GID1) to trigger its degradation of DELLAs. Usually, DELLA accumulation reduces growth to prioritize resources for defense mechanisms, while GA-mediated DELLA degradation stimulates growth under favorable conditions (Colebrook et al., 2014). It was found that nitrate reduces the abundance of DELLAs by increasing GA contents through activation of GA metabolism gene expression (Camut et al., 2021). Consistent with that, the growth restraint under nitrate deficiency is partially rescued in mutants lacking all DELLAs (Camut et al., 2021).
BRs have been reported to enhance root foraging for nutrients under mild nitrogen deficiency conditions (Jia et al., 2019, Jia et al., 2020). Further studies revealed that nitrogen deficiency specifically upregulates the expression of the BR biosynthesis gene DWARF1 as well as the BR co-receptor BAK1 (BRI1-Associated Receptor Kinase 1) (Jia et al., 2019, Jia et al., 2020). BAK1 further activates downstream BSK3 (Brassinosteroid Signaling Kinase 3), a key protein involved in modulating root elongation (Jia et al., 2019). CML38 (Calmodulin-like-38) and PEPR2 (PEP1 Receptor 2) are induced by exogenous nitrate and BR, they interact at the cell membrane to regulate shared downstream genes involved in both the nitrate and BR signaling pathways. The CML38-PEPR2 complex not only transduces nitrate signals to reduce nitrate uptake and assimilation, but also mediates BR signaling by suppressing BES1 (BRI1-EMS-Suppressor 1) phosphorylation and upregulating BES1-target genes, ultimately inhibiting root growth. As such, it has been identified as a convergence module linking nitrate and BR signaling (Song et al., 2021). Under low-nitrogen conditions, mutants of these genes exhibited enhanced PR growth and increased LR development (Song et al., 2021).
ET production increases in Arabidopsis roots when shifted from low (0.1 mM) to high nitrate concentrations (10 mM) (Tian et al., 2009) or from high (10 mM) to low nitrate concentrations (0.2 mM) (Zheng et al., 2013), indicating enhanced ET biosynthesis during nitrate fluctuations in the root environment. At high nitrate concentrations, the expression of NRT1.1 and NRT2.1 is upregulated and downregulated, respectively. However, this regulatory response is absent in etr1 (Ethylene Resistant 1) and ein2 (Ethylene Insensitive 2) mutants, suggesting a role for ET in nitrate signaling (Tian et al., 2009). Under low-nitrate conditions, NRT2.1 expression is induced to enhance high-affinity nitrate uptake, potentially lowering nitrate levels around the roots and subsequently stimulating ET biosynthesis. The increased ET then downregulates NRT2.1 expression, forming a negative feedback loop (Zheng et al., 2013). These findings imply that ET may interact with nitrate signaling, particularly in response to or during recovery from nitrate deficiency.
Stressors trigger stress-initiated nitrate allocation to roots (SINAR), enhancing root-based nitrate assimilation. This process may be more energy-efficient, as it reduces competition with photosynthesis for reductants and energy, thereby supporting growth under adverse conditions (Zhang et al., 2014). SINAR levels are reduced in ein2 and coi1 (Coronatine Insensitive 1, which encodes a JA receptor) mutants, suggesting that it is primarily regulated by ET and JA signaling pathways (Zhang et al., 2014). In addition, SINAR is mediated by two nitrate transporters, NRT1.5 and NRT1.8, which are responsible for exporting nitrate from pericycle cells into the xylem and for retrieving nitrate from xylem sap back into root cells, respectively (Li et al., 2010; Chen et al., 2012). The expression of NRT1.5 is repressed under Cd/Na stress or MeJA treatment, and this repression is alleviated by disruption of EIN2 or COI1. Conversely, NRT1.8 expression is induced under Cd/Na stress or MeJA treatment, but induction is diminished in erf59erf104 (Ethylene Response Factors) double mutants (Zhang et al., 2014). These findings indicate that ET and JA signaling modulate SINAR by downregulating NRT1.5 and upregulating NRT1.8. Similar to soil stress such as Cd and Na, UV-B radiation can also induce ET production in many plants (Wang et al., 2022b). It was found that UV-B-induced nitrate reallocation from hypocotyls to roots was impaired in ET signaling mutants for EIN2 and EIN3 (Wang et al., 2022b). Further studies indicate that ET activates the expression of genes within the ERFs-NRT1.8 signaling module, promoting NRT1.8-mediated nitrate unloading from hypocotyl to roots (Wang et al., 2022b).
Nitrate triggers Ca2+ fluxes in plant cells, where the resulting calcium signals transduce nitrate cues to downstream effectors, such as protein kinases and transcription factors (TFs), to regulate gene expression and adjust metabolism (illustrated in Figure 2) (Riveras et al., 2015). In nitrate-treated roots, cytosolic Ca2+ levels [Ca2+]cyt are lower in the nrt1.1-AQ line (a cross of nrt1.1 mutant and 35S::aequorin transgenic line) compared to the WT-AQ line, demonstrating that nitrate-triggered increases in [Ca2+]cyt depend on NRT1.1 (Riveras et al., 2015).
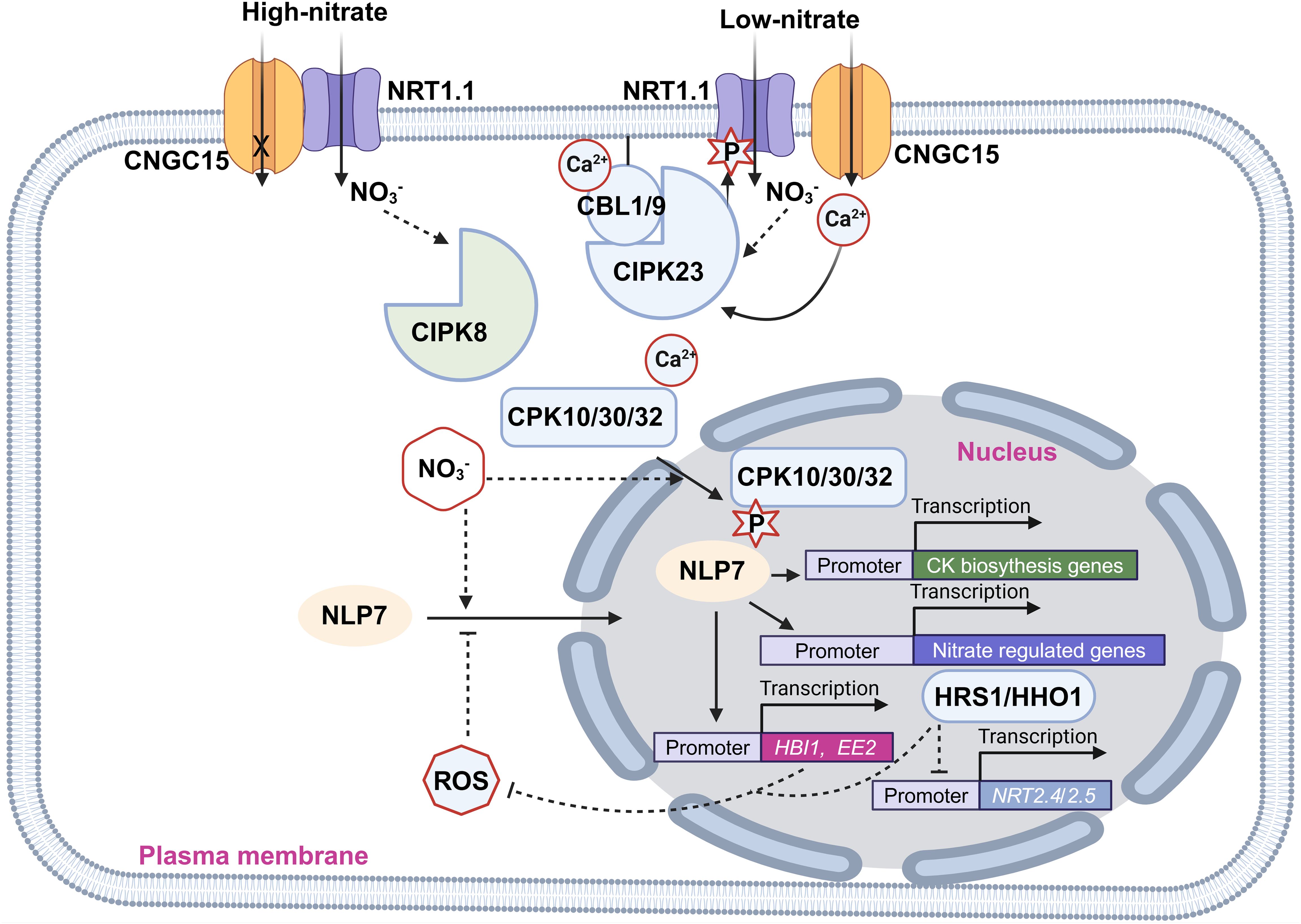
Figure 2. Illustration of the crosstalk between nitrate signaling and calcium as well as ROS signaling. Pointed and blunt arrowheads indicate activating and inhibiting interactions, respectively. The cross mark indicates inhibition of the channel activity of CNGC15.
CNGC (Cyclic Nucleotide-gated Channel) is a class of nonselective cationic channels with permeability to monovalent and divalent cations including Ca2+ (Gao et al., 2016; Zhang et al., 2017). CNGC15 was reported to form a complex with NRT1.1 to control Ca2+ influx in a nitrate-dependent manner (Wang et al., 2021). The Ca2+ channel activity of CNGC15 is inhibited when it forms a heterocomplex with NRT1.1. However, upon nitrate addition, this interaction of CNGC15-NRT1.1 is weakened and the Ca2+ channel activity of CNGC15 is restored (Wang et al., 2021).
CBLs (Calcineurin B-like proteins) are Ca2+-binding proteins that interact with CIPKs (CBL-interacting protein kinases) to phosphorylate the downstream targets (Mao et al., 2023). CIPK8 and CIPK23 are inducible by nitrate. However, their induction is significantly reduced in the nrt1.1 mutant, indicating their function within the NRT1.1-dependent signaling pathway (Ho et al., 2009; Hu et al., 2009). Notably, CIPK23 not only acts downstream in NRT1.1 signaling but also regulates NRT1.1 directly by phosphorylating it at the T101 residue, controlling both its transport and signaling functions (Ho et al., 2009). The CBL1/9-CIPK23 complex regulates the nitrate uptake activity of NRT1.1 by phosphorylating T101 residue. When T101 is phosphorylated, NRT1.1 functions as a high-affinity nitrate transporter, whereas in its dephosphorylated state, it operates as a low-affinity nitrate transporter (Liu and Tsay, 2003). In contrast, CIPK8, while less well characterized, stimulates primary nitrate responses in the low-affinity range. This role is evident from defects in cipk8 null mutants during the low-affinity phase of nitrate-induced expression of NRT2.1 and NIA genes but not in the high-affinity phase (Hu et al., 2009).
CPKs (Ca2+-dependent protein kinases) are Ser/Thr kinases and contain a Ca2+ binding domain, working for both sensing Ca2+ and phosphorylating targets (Schulz et al., 2013). A nitrate-sensitized genomic screen identified CPKs (Ca2+-sensor protein kinases) as key regulators of primary nitrate responses. CPK10, CPK30, and CPK32 phosphorylate the Ser-205 residue in the transcription factor NLP7 (NIN-like Protein 7), a master regulator of nitrate metabolism (Liu et al., 2017). NLP7 orchestrates the expression of 91 genes involved in nitrate uptake and assimilation, including NIA1, NIA2, NRT2.1, and NRT2.2 (Castaings et al., 2009; Konishi and Yanagisawa, 2013; Marchive et al., 2013). Therefore, the nlp7 mutants exhibit longer primary roots and more lateral roots, phenotypic traits characteristic of N-starved plants (Castaings et al., 2009). Nitrate induces both Ca2+ accumulation and CPK translocation in the nucleus, promoting the localization and phosphorylation of NLP7 in the nucleus (Liu et al., 2017). Besides, nitrate-driven activation of NLP7 fine-tunes the biosynthesis of CKs in the roots and their translocation to the shoots, where they enhance the expression of CRFs (Cytokinin Response Factors). CRFs, in turn, promote the flow of auxin by directly regulating the transcription of PIN auxin transporters, promoting the development of shoot organs (Abualia et al., 2022).
Nitrate signaling can influence ROS production, which in turn modulates downstream processes like root nitrate uptake (illustrated in Figure 2) (Shin and Schachtman, 2004; Shin et al., 2005). The growth-related transcription factor HBI1 (Homolog of Brassinosteroid Enhanced Expression 1 Interacting with IBH1) increases the expression levels of antioxidant genes, thereby reducing ROS accumulation in plants (Chu et al., 2021). HBI1 and its homolog BEE2 are rapidly induced by nitrate, though this induction is dramatically reduced in nlp7 mutants. Further analysis revealed that NLP7 directly binds to the promoters of HBI1 and BEE2, and nitrate treatment induces NLP7’s localization to the nucleus (Chu et al., 2021). These findings indicate that nitrate reduces ROS accumulation by promoting NLP7 nuclear localization, which in turn induces HBI expression, boosting antioxidant gene expression. Additionally, H2O2 inhibits the nitrate-promoted nuclear localization of NLP7, a process impaired in hbi mutants (Chu et al., 2021). Thus, these results suggest that nitrate treatment lowers H2O2 levels, while H2O2 inhibits nitrate signaling, creating a feedback loop that regulates plant growth and development (Chu et al., 2021). Furthermore, HRS1 (Hypersensitivity to Low Pi-elicited Primary Root Shortening) and its homolog HHOs are transcription factors that directly bind the promoters of two high-affinity nitrate transporters NRT2.4 and NRT2.5 and repress their expression (Safi et al., 2021). Besides, HHO genetic manipulations (HRS1 overexpression and HHO1 knockout) impair ROS accumulation in plants at early N depletion, indicating their key roles in the control of ROS accumulation in response to N starvation (Safi et al., 2021). These findings suggest that HRS1 and HHOs are also key regulators in the crosstalk between nitrate signaling and ROS signaling.
CEPs (C-terminally Encoded Peptides) are encoded in the stele of LR and are loaded into the xylem vessels to travel to shoots, where they regulate systemic nitrate acquisition responses as a ‘hunger signal’ (Tabata et al., 2014). CEPs contain 15 family members in Arabidopsis (Roberts et al., 2013), seven of which are rapidly and highly upregulated in root directly under low nitrate conditions (Ohkubo et al., 2017). Upon translocation, CEP peptides are perceived by the shoot-localized leucine-rich repeat receptor kinase CEPR1 (CEP Receptor 1), which is expressed in the vascular tissues of leaves (Tabata et al., 2014). The CEP-CEPR1 module upregulates the expression of nitrate transporters such as NRT1.1, NRT2.1, and NAR2.1 (NRT3.1), facilitating nitrate uptake (illustrated in Figure 3) (Tabata et al., 2014). Since root-derived CEP peptides are recognized by CEPR1 in leaf vascular tissue and subsequently regulate the expression of nitrate transporter in roots, the systemic N-demand signaling likely involves a descending shoot-to-root signal activated downstream of CEPR1. This hypothesis led to the identification of two shoot-to-root mobile peptides, CEPD1 and CEPD2 (CEP Downstream 1 and 2), which mediate the descending signal upon the perception of root-derived CEP (Ohkubo et al., 2017). CEPDL2 (CEPD-like 2) contributes to nitrate acquisition cooperatively with CEPD1 and CEPD2, while CEPDL2 is upregulated in the leaf vasculature by the shoot nitrogen deficiency (Ota et al., 2020). In roots, CEPD1/2/CEPDL2 interact with TGA1/4 (TGACG-binding), the TFs playing a global role in root nitrate signaling. TGA1/TGA4 regulate NRT2.1 and NRT2.2 expression by binding to their promoters (Alvarez et al., 2014). The tga1/4 mutants maintain basal nitrate uptake but exhibit impaired nitrate acquisition in response to shoot nitrogen demand (Kobayashi et al., 2024).
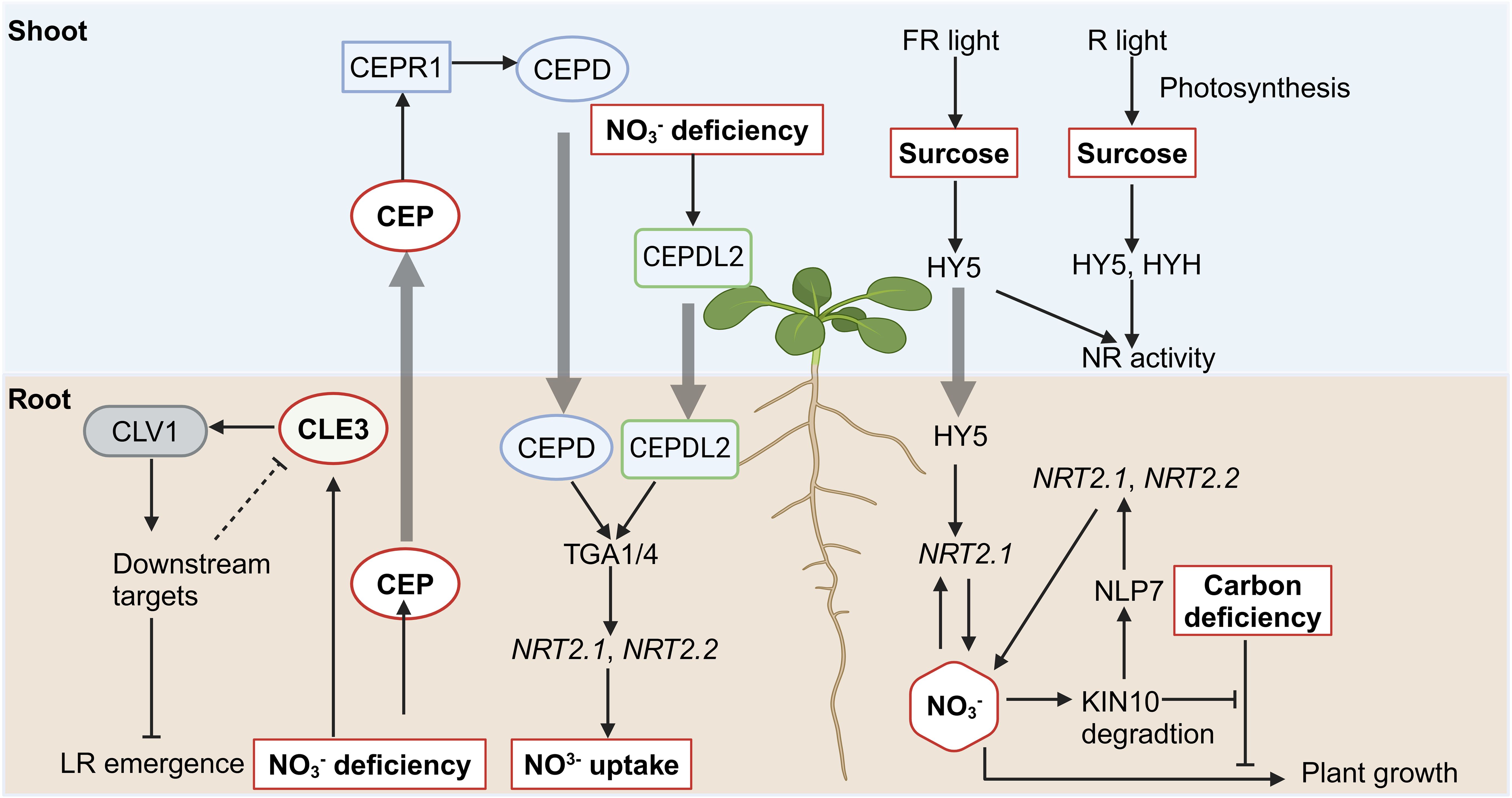
Figure 3. Illustration of the crosstalk between nitrate signaling and peptide as well as sucrose signaling. Pointed and blunt arrowheads indicate activating and inhibiting interactions, respectively. The thick arrow indicates the shoo-to-root or root-to-shoot translocation.
CLEs (Clavata3/Embryo Surrounding Region) peptides control meristem functions in plants (Araya et al., 2014b). CLE1, -3, -4, and -7 have been found to interact with the receptor kinase CLV1 (Clavata1), repressing LR emergence and growth under nitrogen deprivation (Araya et al., 2014a). Since CLE mRNAs are expressed in the pericycle while CLV1 is expressed in phloem companion cells, therefore CLE peptides are also proposed to serve as cell–cell mobile signals, integrating N signals into root responses (Araya et al., 2014a, Araya et al., 2014b).
Nitrate and sugar signaling pathways are tightly interconnected, ensuring that nitrate uptake and assimilation align with the plant’s energy status to optimize growth under varying environmental conditions (illustrated in Figure 3) (Fichtner et al., 2021). Sucrose availability influences nitrate-responsive gene expression and vice versa. NRT2.1 is regulated both transcriptionally and post-transcriptionally by C- and N-derived metabolites (Lejay et al., 1999; Girin et al., 2007; Jong et al., 2014), positioning it as a key integrator in the crosstalk between nitrate and sugar pathways (Fichtner et al., 2021). Its expression is repressed in darkness but is relieved in the presence of sucrose (Lejay et al., 1999). Additionally, intermediates of the oxidative pentose phosphate pathway, such as pyruvate and shikimate, have been shown to induce the expression of NRT2.1 (Jong et al., 2014). KIN10 (SnRK1 Catalytic Subunit Alpha Kinase 10) is identified as another key integrator in the coordination of carbon and nitrogen metabolism (Wang et al., 2022a). It was found that carbon deficiency represses the plant growth induced by nitrate, however, this inhibitory effect is relieved in the mutants of KIN10. Further study showed that nitrate promotes KIN10 degradation, thereby relieving the inhibitory effects of carbon deficiency on nitrate-mediated plant growth. Besides, KIN10 also phosphorylates NLP7 and promotes its cytoplasmic localization and degradation, regulating the nitrate signaling pathways. Thus, ensuring optimal nitrate signaling and the coordination of carbon and nitrogen metabolism in plants (Wang et al., 2022a).
HY5 (Long Hypocotyl 5), a core bZIP TF primarily expressed in shoots, has also been shown to move from shoots to roots upon light exposure (Chen et al., 2016). HY5 and its close homolog HYH regulate light- and sucrose-dependent nitrate reductase (NR) activity (Jonassen et al., 2008). HY5 is required for NR activation by far-red (FR) and red (R) light, as FR and R light fail to induce high NR activity in the hy5 mutant compared to WT. In contrast, while FR light induces NR activity in the hyh mutant, R light does not, indicating that HYH is specifically necessary for R-induced NR activity. The hy5hyh double mutant exhibits reduced white light-induced NR activity compared to the single mutants, suggesting a partially redundant role for HY5 and HYH. Further insights into the role of HY5 come from studies on shoot-to-root signaling. HY5 binds directly to the promoter of NRT2.1, as shown by ChIP assays, and shoot illumination-induced upregulation of root NRT2.1 is largely abolished in the hy5 mutant (Chen et al., 2016). This HY5-mediated enhancement of root NRT2.1 promotes nitrate uptake and depends on shoot carbon photo-assimilate (sucrose) levels. These findings underscore the role of HY5 as a systemic regulator of nitrate uptake and the carbon/nitrogen balance in response to ambient light and sucrose signals (Chen et al., 2016).
The crosstalk between nitrate signaling and other molecular pathways is crucial for optimizing plant growth, development, and stress responses. The interactions between nitrate, phytohormones, ROS, calcium, peptide, and sucrose help plants integrate environmental cues and internal nutrient status to adjust their physiological processes. Understanding these interactions provides strategies for enhancing crop NUE.
Plants exhibit diverse adaptive responses to fluctuating nitrogen availability, including optimizing their RSA under nitrogen-limited conditions to enhance nitrogen acquisition from the soil. Given the intricate crosstalk between phytohormone and nitrate signaling in RSA remodeling, genes within phytohormone signaling pathways serve as promising targets for enhancing the NUE of crops.
For instance, the QTL DRO1 (Deeper Rooting 1) in Oryza sativa, negatively regulated by auxin, promotes deeper rooting, enhancing nitrogen uptake and cytokinin fluxes during later growth stages. The near-isogenic line bearing the allele of DRO1 exhibited more roots within the lower soil layer of the paddy field and approximately 10% higher grain yield (Arai-Sanoh et al., 2014). OsPIN2 plays a critical role in mediating root gravitropic responses and ensuring normal root growth angles in rice (Wang et al., 2018a). The Os-pin2 mutant exhibited a large root growth angle and reduced sensitivity to gravity, leading to a shallower root system. This shallow root architecture likely enhances topsoil foraging, facilitating nutrient acquisition from the upper soil layers while also helping to avoid hypoxic conditions, ultimately promoting rice growth (Wang et al., 2018a). Therefore, PIN2 also represents a promising genetic target for regulating NUE. In Triticum aestivum, overexpression of TaTAR2.1-3A, TaTAR2.1-3B, and TaTAR2.1-3D, orthologs of AtTAR2, enhances LR branching, as well as plant height, spike number, grain yield, and nitrogen accumulation in the aboveground parts under varying nitrogen supply levels (Shao et al., 2017).
Additionally, as previously mentioned, BSK3 is the key kinase in the BR signaling pathway that regulates root elongation. The allelic variation from Leu319 to Pro319 results enhances BR sensitivity, leading to increased root elongation, making BSK3 a promising target for improving root growth under nitrogen-limited conditions (Jia et al., 2019). Exploiting natural allelic variants of BSK3 or generating new variants through precise genome editing could contribute to the development of longer root systems, thereby enhancing nitrate uptake under low nitrogen conditions. These studies illustrate how modulating phytohormone signaling can affect RSA to improve NUE, offering valuable insights into the phytohormone-mediated RSA-NUE relationship in crops.
The application of synthetic chemicals for remodeling RSA involves the use of chemical agents to modify root overall root system development, enhancing the NUE of plants. For instance, foliar application of NAA increased the endogenous IAA content, enhanced the activity of enzymes related to nitrogen assimilation, and boosted the rate of photosynthesis. In addition, NAA promoted root activity, regulated root morphology and structure, and facilitated further nitrogen uptake and plant growth (Jiang et al., 2024). In addition, treatment with ethephon (a direct source of ET) and ACC (an ET precursor) promotes the initiation of LR and enhances nitrogen absorption (Liu et al., 2010). The application of GA3 stimulates cell division and elongation in the root meristem, resulting in longer PR and LR, thereby increasing the nitrogen uptake of maize (Ullah et al., 2022).
Hormones also intersect with CEP receptor signaling to regulate RSA in plants (Chapman et al., 2020). CEP peptides act not only as “N-hunger signals” that are perceived by receptors in the shoot, triggering further signaling that induces the expression of nitrate transporters in the roots, but also interact with hormone signaling, particularly cytokinin, to promote shallower LR growth (Chapman et al., 2024). Furthermore, CEPs have been shown to repress auxin biosynthesis and alter auxin transport in the roots of Medicago and Arabidopsis, affecting gravitropic responses (Chapman et al., 2020). Based on these findings, there have been efforts to exploit synthetic CEPs to enhance nitrate uptake. One study reported that applying synthetic CEP peptides significantly boosted nitrate uptake in both Medicago and Arabidopsis by 70–140% under low nitrate conditions, by modulating the transcription of nitrate transporter genes (Roy et al., 2021).
The crosstalk between sugar and nitrate signaling highlights the close interconnection between carbon and nitrogen metabolism (Aluko et al., 2023). Therefore, genes involved in carbon metabolism also represent promising targets for enhancing NUE. A moderate nitrogen supply can reduce the expression level of OsSTP28 (Sugar Transporter Protein 28), a sugar transporter that negatively regulates nitrogen response during rice tillering, thereby increasing the glucose concentration in the apoplast of the stem base (Zhang et al., 2024). This process inhibits the activity of the transcription factor OSH15 (Oryza Sativa Homeobox 15) by altering the methylation status on histone H3K27 (Histone H3 Lysine 27) and activates the GA degradation pathway, primarily driven by the gibberellin oxidase GA2oxs, which ultimately leads to increased tiller number and higher yield. In addition, the study uncovered a more effective allelic variant of OsSTP28, which enhances modern cultivated rice’s response to nitrogen more efficiently, promoting tillering and ultimately improving yield (Zhang et al., 2024). This provides valuable genetic resources for improving both high yield and NUE in rice.
Recently, two novel carbon-nitrogen metabolism-coupled photorespiratory bypasses were synthesized in rice, which were successfully assembled and expressed efficiently in chloroplasts without releasing carbon dioxide (Chen et al., 2025). The introduction of these bypasses could convert glycolate metabolism in the chloroplasts into glyoxylate, thereby promoting the synthesis of amino acids, energy, and carbohydrates. This, in turn, significantly enhanced both photosynthetic efficiency and NUE in rice. Field trials demonstrated that rice with the carbon-nitrogen metabolism-coupled photorespiratory bypass exhibited a 19.0% yield increase under normal growth conditions compared to the wild-type control, and up to a 44.1% increase under low nitrogen conditions (Chen et al., 2025). This research not only uncovers a new mechanism for regulating carbon-nitrogen metabolism through photorespiratory bypasses but also provides a scientific basis for developing high-yield, fertilizer-efficient, and stress-tolerant rice varieties.
As previously described, ET/JA and NRT1.5/1.8-involved SINAR promote the stress tolerance of plants under cadmium and salt (Zhang et al., 2018). However, reduced nitrate root-to-shoot translocation means low NUE and inhibited plant development, resulting in the trade-off between plant growth and stress tolerance. Recently, with the development of gene-editing techniques and a more comprehensive understanding of SINAR, genetic engineering of SINAR for the most appropriate shoot/root nitrate ratio is promising to improve the NUE of plants in adverse environments.
Specifically, genes involved in root-to-shoot transport can be targeted through genetic engineering, such as NRT1.5, which exports nitrate from pericycle cells into the xylem (Lin et al., 2008), and NRT1.8, which retrieves nitrate from xylem sap back into root cells (Li et al., 2010). Under salt and Cd2+ treatment, the expression of NRT1.8 for xylem nitrate retrieval is upregulated, while the expression of NRT1.5 for xylem loading is downregulated, resulting in increased SINAR to roots in response to these stressors (Zhang et al., 2014). Besides, NPF2.3, co-expressed in pericycle cells with NRT1.5, mediates xylem nitrate loading, particularly under salt stress when NRT1.5 is downregulated (Taochy et al., 2015). Thus, the gene expression alteration or key amino acid substitution of these nitrate transporters could be precisely edited to appropriately regulate the nitrate root-to-shoot ratio. Additionally, considering NRT1.5/1.8-involved SINAR is under the regulation of ET/JA phytohormones, involved genes in the ET/JA signaling module could also be considered to engineer SINAR (Zhang et al., 2017).
Within plant cells, excessive nitrate can be stored in the vacuole, enabling plants to regulate nitrogen levels, avoid toxicity, and maintain a nitrate reservoir for future needs. However, some nitrate-inefficient genotypes exhibit reduced efficiency in remobilizing nitrate into the cytoplasm, leading to excessive nitrate accumulation in the vacuole. This phenomenon is considered “luxury consumption” under conditions of abundant nitrate supply in modern agricultural systems. Studies have shown that reduced root VSC (Vacuolar Sequestration Capacity) of nitrate in the high-NUE genotype enhances nitrate transport to shoots compared to the low-NUE genotype, thereby promoting NUE in Brassica napus (Han et al., 2016). This effect is likely mediated by the upregulation of BnNRT1.5, downregulation of BnNRT1.8, and inhibition of tonoplast proton-pumps activities (Han et al., 2016). This presents an additional strategy to improve NUE through SINAR editing. Furthermore, the CLCa (Chloride Channel a) is the main 2NO3−/1H+ exchanger responsible for vacuolar nitrate accumulation (De Angeli et al., 2006). A mutation in a glutamate residue at position 203 (CLCaE203A) converts the 2NO3−/1H+ exchanger into a NO3− channel (Hodin et al., 2023). When introduced into a clca knockout mutant, this mutation resulted in impaired nitrate accumulation and enhanced NUE compared to both the wild-type and clca mutant (Hodin et al., 2023). Therefore, the root-specific expression of CLCaE203A could also enhance NUE without the growth disruptions caused by CLCa expression in shoots.
The molecular mechanisms governing nitrate nutrition in plants constitute a highly intricate network involving specialized nitrate transporters and signaling molecules. These components work in concert to ensure the efficient uptake, systemic distribution, and metabolic assimilation of nitrate, enabling plants to adapt dynamically to fluctuations in environmental nitrogen levels. This regulatory network not only detects nitrate availability but also coordinates a variety of physiological and developmental processes, such as root architecture remodeling, shoot growth regulation, and metabolic adjustments, all aimed at optimizing nitrogen acquisition and utilization. In this review, we provide a comprehensive analysis of the crosstalk between nitrate and signaling molecules, exploring their direct and indirect effects on NUE and related processes in the model plant Arabidopsis. Establishing a strong link between these signaling molecules and the enhancement of crop NUE is essential for advancing research aimed at improving both NUE and crop yield. Recent breakthroughs in genome editing technologies, such as CRISPR/Cas, offer precise tools for modifying genes involved in nitrate signaling. We anticipate that further discoveries of nitrogen-efficient genes, influenced by the intricate interactions between nitrate and signaling molecules, will pave the way for developing crop varieties with improved NUE.
JM: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. ZT: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. JS: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. DW: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. YY: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. SL: Investigation, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Collaborative Science and Technology Project of JSZY (H202422) and the Tobacco Genome Project and Biological Breeding (110202201014 (JY-14)).
Author(s) JM, ZT, JS, DW, YY and JL were employed by Technology Centre, China Tobacco Jiangsu Industrial Co., Ltd., Nanjing, China.
The author(s) declare that Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript. OpenAI (https://openai.com/index/chatgpt/) was used for language editing and polishing.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abualia, R., Otvos, K., Novak, O., Bouguyon, E., Domanegg, K., Krapp, A., et al. (2022). Molecular framework integrating nitrate sensing in root and auxin-guided shoot adaptive responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. United States America 119, e2122460119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2122460119
Ahmad, N., Jiang, Z., Zhang, L., Hussain, I., Yang, X. (2023). Insights on phytohormonal crosstalk in plant response to nitrogen stress: A focus on plant root growth and development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 3631. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043631
Aluko, O. O., Liu, Z., Sun, X. (2023). The interplay of carbon and nitrogen distribution: Prospects for improved crop yields. Modern Agric. 1, 57–75. doi: 10.1002/moda.v1.1
Alvarez, J. M., Riveras, E., Vidal, E. A., Gras, D. E., Contreras-Lopez, O., Tamayo, K. P., et al. (2014). Systems approach identifies TGA1 and TGA4 transcription factors as important regulatory components of the nitrate response of Arabidopsis thaliana roots. Plant J. 80, 1–13. doi: 10.1111/tpj.2014.80.issue-1
Arai-Sanoh, Y., Takai, T., Yoshinaga, S., Nakano, H., Kojima, M., Sakakibara, H., et al. (2014). Deep rooting conferred by DEEPER ROOTING 1 enhances rice yield in paddy fields. Scientic Rep. 4, 5563. doi: 10.1038/srep05563
Araya, T., Miyamoto, M., Wibowo, J., Suzuki, A., Kojima, S., Tsuchiya, Y. N., et al. (2014a). CLE-CLAVATA1 peptide-receptor signaling module regulates the expansion of plant root systems in a nitrogen-dependent manner. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. United States America 111, 2029–2034. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1319953111
Araya, T., von Wiren, N., Takahashi, H. (2014b). CLE peptides regulate lateral root development in response to nitrogen nutritional status of plants. Plant Signaling Behav. 9, 2029–2034. doi: 10.4161/psb.29302
Bijay, S., Craswell, E. (2021). Fertilizers and nitrate pollution of surface and ground water: an increasingly pervasive global problem. Discover Appl. Sci. 3, 518. doi: 10.1007/s42452-021-04521-8
Camut, L., Gallova, B., Jilli, L., Sirlin-Josserand, M., Carrera, E., Sakvarelidze-Achard, L., et al. (2021). Nitrate signaling promotes plant growth by upregulating gibberellin biosynthesis and destabilization of DELLA proteins. Curr. Biol. 31, 4971–4982. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2021.09.024
Castaings, L., Camargo, A., Pocholle, D., Gaudon, V., Texier, Y., Boutet-Mercey, S., et al. (2009). The nodule inception-like protein 7 modulates nitrate sensing and metabolism in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 57, 426–435. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03695.x
Chapman, K., Ivanovici, A., Taleski, M., Sturrock, C. J., Ng, J. L. P., Mohd-Radzman, N. A., et al. (2020). CEP receptor signalling controls root system architecture in Arabidopsis and Medicago. New Phytol. 226, 1809–1821. doi: 10.1111/nph.v226.6
Chapman, K., Taleski, M., Frank, M., Djordjevic, M. A. (2024). C-TERMINALLY ENCODED PEPTIDE (CEP) and cytokinin hormone signaling intersect to promote shallow lateral root angles. J. Exp. Bot. 75, 631–641. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erad353
Chen, G., Li, Y., Jin, K., Gao, J., Wu, S., Cui, X., et al. (2025). Synthetic photorespiratory bypass improves rice productivity by enhancing photosynthesis and nitrogen uptake. Plant Cell 37 (1), koaf015. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koaf015
Chen, C. Z., Lv, X. F., Li, J. Y., Yi, H. Y., Gong, J. M. (2012). Arabidopsis NRT1.5 is another essential component in the regulation of nitrate reallocation and stress tolerance. Plant Physiol. 159, 1582–1590. doi: 10.1104/pp.112.199257
Chen, X., Yao, Q., Gao, X., Jiang, C., Harberd, N. P., Fu, X. (2016). Shoot-to-root mobile transcription factor HY5 coordinates plant carbon and nitrogen acquisition. Curr. Biol. 26, 640–646. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2015.12.066
Chu, X., Wang, J. G., Li, M., Zhang, S., Gao, Y., Fan, M., et al. (2021). HBI transcription factor-mediated ROS homeostasis regulates nitrate signal transduction. Plant Cell 33, 3004–3021. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koab165
Colebrook, E. H., Thomas, S. G., Phillips, A. L., Hedden, P., Davies, S. A., Dow, J. A. T., et al. (2014). The role of gibberellin signalling in plant responses to abiotic stress. J. Exp. Biol. 217, 67–75. doi: 10.1242/jeb.089938
Contreras-Lopez, O., Vidal, E. A., Riveras, E., Alvarez, J. M., Moyano, T. C., Sparks, E. E., et al. (2022). Spatiotemporal analysis identifies ABF2 and ABF3 as key hubs of endodermal response to nitrate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. United States America 119, e2107879119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2107879119
Davière, J. M., Achard, P. (2013). Gibberellin signaling in plants. Development 140, 1147–1151. doi: 10.1242/dev.087650
De Angeli, A., Monachello, D., Ephritikhine, G., Frachisse, J. M., Thomine, S., Gambale, F., et al. (2006). The nitrate/proton antiporter AtCLCa mediates nitrate accumulation in plant vacuoles. Nature 442 (7105), 939–942.
Fichtner, F., Dissanayake, I. M., Lacombe, B., Barbier, F. (2021). Sugar and nitrate sensing: a multi-billion-year story. Trends Plant Sci. 26, 352–374. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2020.11.006
Gao, Q. F., Gu, L. L., Wang, H. Q., Fei, C. F., Fang, X., Hussain, J., et al. (2016). Cyclic nucleotide-gated channel 18 is an essential Ca2+ channel in pollen tube tips for pollen tube guidance to ovules in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. United States America 113, 3096–3101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1524629113
Girin, T., Lejay, L., Wirth, J., Widiez, T., Palenchar, P. M., Nazoa, P., et al. (2007). Identification of a 150 bp cis-acting element of the AtNRT2.1 promoter involved in the regulation of gene expression by the N and C status of the plant. Plant Cell Environ. 30, 1366–1380. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3040.2007.01712.x
Gutierrez, L., Bussell, J. D., Pacurar, D. I., Schwambach, J., Pacurar, M., Bellini, C. (2009). Phenotypic plasticity of adventitious rooting in Arabidopsis is controlled by complex regulation of AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR transcripts and microRNA abundance. Plant Cell 21, 3119–3132. doi: 10.1105/tpc.108.064758
Han, Y. L., Song, H. X., Liao, Q., Yu, Y., Jian, S. F., Lepo, J. E., et al. (2016). Nitrogen use efficiency is mediated by vacuolar nitrate sequestration capacity in roots of Brassica napus. Plant Physiol. 170, 1684–1698. doi: 10.1104/pp.15.01377
Hirose, N., Takei, K., Kuroha, T., Kamada-Nobusada, T., Hayashi, H., Sakakibara, H. (2008). Regulation of cytokinin biosynthesis, compartmentalization and translocation. J. Exp. Bot. 59, 75–83. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erm157
Ho, C. H., Lin, S. H., Hu, H. C., Tsay, Y. F. (2009). CHL1 functions as a nitrate sensor in plants. Cell 138, 1184–1194. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.07.004
Hodin, J., Lind, C., Marmagne, A., Espagne, C., Bianchi, M. W., De Angeli, A., et al. (2023). Proton exchange by the vacuolar nitrate transporter CLCa is required for plant growth and nitrogen use efficiency. Plant Cell 35, 318–335. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koac325
Hu, H. C., Wang, Y. Y., Tsay, Y. F. (2009). AtCIPK8, a CBL-interacting protein kinase, regulates the low-affinity phase of the primary nitrate response. Plant J. 57, 264–278. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03685.x
Islam, S., Islam, R., Kandwal, P., Khanam, S., Proshad, R., Kormoker, T., et al. (2020). Nitrate transport and assimilation in plants: a potential review. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 68, 133–150. doi: 10.1080/03650340.2020.1826042
Jia, Z., Giehl, R. F. H., Hartmann, A., Estevez, J. M., Bennett, M. J., von Wiren, N. (2023). A spatially concerted epidermal auxin signaling framework steers the root hair foraging response under low nitrogen. Curr. Biol. 33, 3926–3941. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2023.08.040
Jia, Z., Giehl, R. F. H., Meyer, R. C., Altmann, T., von Wiren, N. (2019). Natural variation of BSK3 tunes brassinosteroid signaling to regulate root foraging under low nitrogen. Nat. Commun. 10, 2378. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-10331-9
Jia, Z., Giehl, R. F. H., von Wiren, N. (2020). The root foraging response under low nitrogen depends on DWARF1-mediated brassinosteroid biosynthesis. Plant Physiol. 183, 998–1010. doi: 10.1104/pp.20.00440
Jia, Z., Giehl, R. F. H., von Wiren, N. (2021). Local auxin biosynthesis acts downstream of brassinosteroids to trigger root foraging for nitrogen. Nat. Commun. 12, 5437. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-25250-x
Jia, Z., Giehl, R. F. H., von Wiren, N. (2022). Nutrient-hormone relations: Driving root plasticity in plants. Mol. Plant 15, 86–103. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2021.12.004
Jiang, N., Zou, T., Huang, H., Li, C., Xia, Y., Yang, L. (2024). Auxin synthesis promotes N metabolism and optimizes root structure enhancing N acquirement in maize (Zea mays L.). Planta 259, 46. doi: 10.1007/s00425-023-04327-5
Jonassen, E. M., Lea, U. S., Lillo, C. (2008). HY5 and HYH are positive regulators of nitrate reductase in seedlings and rosette stage plants. Planta 227, 559–564. doi: 10.1007/s00425-007-0638-4
Jong, F. D., Thodey, K., Lejay, L. V., Bevan, M. W. (2014). Glucose elevates NITRATE TRANSPORTER2.1 protein levels and nitrate transport activity independently of its HEXOKINASE1-mediated stimulation of NITRATE TRANSPORTER2.1 expression. Plant Physiol. 164, 308–320. doi: 10.1104/pp.113.230599
Kanno, Y., Kamiya, Y., Seo, M. (2013). Nitrate does not compete with abscisic acid as a substrate of AtNPF4.6/NRT1.2/AIT1 in Arabidopsis. Plant Signaling Behav. 8, e26624. doi: 10.4161/psb.26624
Kiba, T., Kudo, T., Kojima, M., Sakakibara, H. (2011). Hormonal control of nitrogen acquisition: roles of auxin, abscisic acid, and cytokinin. J. Exp. Bot. 62, 1399–1409. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erq410
Kobayashi, R., Ohkubo, Y., Izumi, M., Ota, R., Yamada, K., Hayashi, Y., et al. (2024). Integration of shoot-derived polypeptide signals by root TGA transcription factors is essential for survival under fluctuating nitrogen environments. Nat. Commun. 15, 6903. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-51091-5
Konishi, M., Yanagisawa, S. (2013). Arabidopsis NIN-like transcription factors have a central role in nitrate signalling. Nat. Commun. 4, 1617. doi: 10.1038/ncomms2621
Krouk, G., Lacombe, B., Bielach, A., Perrine-Walker, F., Malinska, K., Mounier, E., et al. (2010). Nitrate-regulated auxin transport by NRT1.1 defines a mechanism for nutrient sensing in plants. Dev. Cell 18, 927–937. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2010.05.008
Kudo, T., Kiba, T., Sakakibara, H. (2010). Metabolism and long-distance translocation of cytokinins. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 52, 53–60. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-7909.2010.00898.x
Lejay, L., Tillard, P., Lepetit, M., Olive, F., Filleur, S., Daniel-Vedele, F., et al. (1999). Molecular and functional regulation of two NO3- uptake systems by N- and C-status of Arabidopsis plants. Plant J. 18, 509–519. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313X.1999.00480.x
Li, S. (2024). Is auxin the key to improve crop nitrogen use efficiency for greener agriculture? New Phytol. 244, 2170–2175. doi: 10.1111/nph.20066
Li, J. Y., Fu, Y. L., Pike, S. M., Bao, J., Tian, W., Zhang, Y., et al. (2010). The Arabidopsis nitrate transporter NRT1.8 functions in nitrate removal from the xylem sap and mediates cadmium tolerance. Plant Cell 22, 1633–1646. doi: 10.1105/tpc.110.075242
Li, H., Testerink, C., Zhang, Y. (2021). How roots and shoots communicate through stressful times. Trends Plant Sci. 26, 940–952. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2021.03.005
Liang, G., He, H., Yu, D. (2012). Identification of nitrogen starvation-responsive microRNAs in Arabidopsis thaliana. PloS One 7, e48951. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0048951
Lin, S. H., Kuo, H. F., Canivenc, G., Lin, C. S., Lepetit, M., Hsu, P. K., et al. (2008). Mutation of the arabidopsis NRT1.5 nitrate transporter causes defective root-to-shoot nitrate transport. Plant Cell 20 (9), 2514–2528.
Liu, J., Liu, G., Hou, L., Liu, X. (2010). Ethylene-induced nitric oxide production and stomatal closure in Arabidopsis thaliana depending on changes in cytosolic pH. Chin. Sci. Bull. 55, 2403–2409. doi: 10.1007/s11434-010-4033-3
Liu, K. H., Niu, Y., Konishi, M., Wu, Y., Du, H., Sun Chung, H., et al. (2017). Discovery of nitrate-CPK-NLP signalling in central nutrient-growth networks. Nature 545, 311–316. doi: 10.1038/nature22077
Liu, KH, Tsay, YF (2003). Switching between the two action modes ofthe dual-af®nity nitrate transporter CHL1 by phosphorylation. EMBO J. 22, 1005–1013. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg118
Ma, W., Li, J., Qu, B., He, X., Zhao, X., Li, B., et al. (2014). Auxin biosynthetic gene TAR2 is involved in low nitrogen-mediated reprogramming of root architecture in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 78, 70–79. doi: 10.1111/tpj.2014.78.issue-1
Maghiaoui, A., Bouguyon, E., Cuesta, C., Perrine-Walker, F., Alcon, C., Krouk, G., et al. (2020). The Arabidopsis NRT1.1 transceptor coordinately controls auxin biosynthesis and transport to regulate root branching in response to nitrate. J. Exp. Bot. 71, 4480–4494. doi: 10.1093/jxb/eraa242
Mao, J., Mo, Z., Yuan, G., Xiang, H., Visser, R. G.F., Bai, Y., et al. (2023). The CBL-CIPK network is involved in the physiological crosstalk between plant growth and stress adaptation. Plant Cell Environ. 46, 3012–3022. doi: 10.1111/pce.v46.10
Marchive, C., Roudier, F., Castaings, L., Brehaut, V., Blondet, E., Colot, V., et al. (2013). Nuclear retention of the transcription factor NLP7 orchestrates the early response to nitrate in plants. Nat. Commun. 4, 1713. doi: 10.1038/ncomms2650
Ohkubo, Y., Tanaka, M., Tabata, R., Ogawa-Ohnishi, M., Matsubayashi, Y. (2017). Shoot-to-root mobile polypeptides involved in systemic regulation of nitrogen acquisition. Nat. Plants 3, 1–6. doi: 10.1038/nplants.2017.29
Okushima, Y., Overvoorde, P. J., Arima, K., Alonso, J. M., Chan, A., Chang, C., et al. (2005). Functional genomic analysis of the AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR gene family members in Arabidopsis thaliana: Unique and overlapping functions of ARF7 and ARF19. Plant Cell 17, 444–463. doi: 10.1105/tpc.104.028316
Ondzighi-Assoume, C. A., Chakraborty, S., Harris, J. M. (2016). Environmental nitrate stimulates abscisic acid accumulation in Arabidopsis root tips by releasing it from inactive stores. Plant Cell 28, 729–745. doi: 10.1105/tpc.15.00946
Ota, R., Ohkubo, Y., Yamashita, Y., Ogawa-Ohnishi, M., Matsubayashi, Y. (2020). Shoot-to-root mobile CEPD-like 2 integrates shoot nitrogen status to systemically regulate nitrate uptake in Arabidopsis. Nat. Commun. 11, 641. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-14440-8
Riveras, E., Alvarez, J. M., Vidal, E. A., Oses, C., Vega, A., Gutierrez, R. A. (2015). The calcium ion is a second messenger in the nitrate signaling pathway of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 169, 1397–1404. doi: 10.1104/pp.15.00961
Roberts, I., Smith, S., De Rybel, B., Van Den Broeke, J., Smet, W., De Cokere, S., et al. (2013). The CEP family in land plants: evolutionary analyses, expression studies, and role in Arabidopsis shoot development. J. Exp. Bot. 64, 5371–5381. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ert331
Roy, S., Griffiths, M., Torres-Jerez, I., Sanchez, B., Antonelli, E., Jain, D., et al. (2021). Application of synthetic peptide CEP1 increases nutrient uptake rates along plant roots. Front. Plant Sci. 12, 793145. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.793145
Safi, A., Medici, A., Szponarski, W., Martin, F., Clement-Vidal, A., Marshall-Colon, A., et al. (2021). GARP transcription factors repress Arabidopsis nitrogen starvation response via ROS-dependent and -independent pathways. J. Exp. Bot. 72, 3881–3901. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erab114
Schulz, P., Herde, M., Romeis, T. (2013). Calcium-dependent protein kinases: hubs in plant stress signaling and development. Plant Physiol. 163, 523–530. doi: 10.1104/pp.113.222539
Shao, A., Ma, W., Zhao, X., Hu, M., He, X., Teng, W., et al. (2017). The auxin biosynthetic TRYPTOPHAN AMINOTRANSFERASE RELATED TaTAR2.1-3A increases grain yield of wheat. Plant Physiol. 174, 2274–2288. doi: 10.1104/pp.17.00094
Sharma, A., Zheng, B. (2019). Molecular responses during plant grafting and its regulation by auxins, cytokinins, and gibberellins. Biomolecules 9, 397. doi: 10.3390/biom9090397
Shin, R., Berg, R. H., Schachtman, D. P. (2005). Reactive oxygen species and root hairs in Arabidopsis root response to nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium deficiency. Plant Cell Physiol. 46, 1350–1357. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pci145
Shin, R., Schachtman, D. P. (2004). Hydrogen peroxide mediates plant root cell response to nutrient deprivation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. United States America 101, 8827–8832. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0401707101
Signora, L., De Smet, I., Foyer, C. H., Zhang, H. (2001). ABA plays a central role in mediating the regulatory effects of nitrate on root branching in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 28, 655–662. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.2001.01185.x
Song, X., Li, J., Lyu, M., Kong, X., Hu, S., Song, Q., et al. (2021). CALMODULIN-LIKE-38 and PEP1 RECEPTOR 2 integrate nitrate and brassinosteroid signals to regulate root growth. Plant Physiol. 187, 1779–1794. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiab323
Tabata, R., Sumida, K., Yoshii, T., Ohyama, K., Shinohara, H., Matsubayashi, Y. (2014). Perception of root-derived peptides by shoot LRR-RKs mediates systemic N-demand signaling. Science 346, 343–346. doi: 10.1126/science.1257800
Takei, K., Ueda, N., Aoki, K., Kuromori, T., Hirayama, T., Shinozaki, K., et al. (2004a). AtIPT3 is a key determinant of nitrate-dependent cytokinin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol. 45, 1053–1062. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pch119
Takei, K., Yamaya, T., Sakakibara, H. (2004b). Arabidopsis CYP735A1 and CYP735A2 encode cytokinin hydroxylases that catalyze the biosynthesis of trans-Zeatin. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 41866–41872. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M406337200
Taochy, C., Gaillard, I., Ipotesi, E., Oomen, R., Leonhardt, N., Zimmermann, S., et al. (2015). The arabidopsis root stele transporter NPF2.3 contributes to nitrate translocation to shoots under salt stress. Plant J. 83 (3), 466–479.
Tian, Q. Y., Sun, P., Zhang, W. H. (2009). Ethylene is involved in nitrate-dependent root growth and branching in Arabidopsis thaliana. New Phytol. 184, 918–931. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2009.03004.x
Ullah, I., Dawar, K., Tariq, M., Sharif, M., Fahad, S., Adnan, M., et al. (2022). Gibberellic acid and urease inhibitor optimize nitrogen uptake and yield of maize at varying nitrogen levels under changing climate. Environ. Sci. pollut. Res. 29, 6568–6577. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-16049-w
Vega, A., Fredes, I., O’Brien, J., Shen, Z., Otvos, K., Abualia, R., et al. (2021). Nitrate triggered phosphoproteome changes and a PIN2 phosphosite modulating root system architecture. EMBO Rep. 22, e51813. doi: 10.15252/embr.202051813
Vidal, E. A., Alvarez, J. M., Araus, V., Riveras, E., Brooks, M. D., Krouk, G., et al. (2020). Nitrate in 2020: thirty years from transport to signaling networks. Plant Cell 32, 2094–2119. doi: 10.1105/tpc.19.00748
Vidal, E. A., Araus, V., Lu, C., Parry, G., Green, P. J., Coruzzi, G. M., et al. (2010). Nitrate-responsive miR393/AFB3 regulatory module controls root system architecture in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. United States America 107, 4477–4482. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0909571107
Wang, Y. Y., Cheng, Y. H., Chen, K. E., Tsay, Y. F. (2018b). Nitrate transport, signaling, and use efficiency. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 69, 85–122. doi: 10.1146/annurev-arplant-042817-040056
Wang, X., Feng, C., Tian, L., Hou, C., Tian, W., Hu, B., et al. (2021). A transceptor-channel complex couples nitrate sensing to calcium signaling in Arabidopsis. Mol. Plant 14, 774–786. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2021.02.005
Wang, L., Guo, M., Li, Y., Ruan, W., Mo, X., Wu, Z., et al. (2018a). LARGE ROOT ANGLE1, encoding OsPIN2, is involved in root system architecture in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 69, 385–397. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erx427
Wang, H., Han, C., Wang, J.-G., Chu, X., Shi, W., Yao, L., et al. (2022a). Regulatory functions of cellular energy sensor SnRK1 for nitrate signalling through NLP7 repression. Nat. Plants 8, 1094–1107. doi: 10.1038/s41477-022-01236-5
Wang, J. W., Wang, L. J., Mao, Y. B., Cai, W. J., Xue, H. W., Chen, X. Y. (2005). Control of root cap formation by MicroRNA-targeted auxin response factors in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 17, 2204–2216. doi: 10.1105/tpc.105.033076
Wang, X. T., Xiao, J. H., Li, L., Guo, J. F., Zhang, M. X., An, Y. Y., et al. (2022b). Ethylene acts as a local and systemic signal to mediate UV-B-induced nitrate reallocation to Arabidopsis leaves and roots via regulating the ERFs-NRT1.8 signaling module. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 9068. doi: 10.3390/ijms23169068
Wang, Y., Yuan, Z., Wang, J., Xiao, H., Wan, L., Li, L., et al. (2023). The nitrate transporter NRT2.1 directly antagonizes PIN7-mediated auxin transport for root growth adaptation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. United States America 120, e2221313120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2221313120
Wu, M. F., Tian, Q., Reed, J. W. (2006). Arabidopsis microRNA167 controls patterns of ARF6 and ARF8 expression, and regulates both female and male reproduction. Development 133, 4211–4218. doi: 10.1242/dev.02602
Yadav, M. R., Kumar, R., Parihar, C. M., Yadav, R. K., Jat, S. L., Ram, H., et al. (2017). Strategies for improving nitrogen use efficiency: A review. Agric. Rev. 38, 29–40. doi: 10.18805/ag.v0iOF.7306
Zhang, G. B., Meng, S., Gong, J. M. (2018). The expected and unexpected roles of nitrate transporters in plant abiotic stress resistance and their regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19, 3535. doi: 10.3390/ijms19113535
Zhang, S., Pan, Y., Tian, W., Dong, M., Zhu, H., Luan, S., et al. (2017). Arabidopsis CNGC14 mediates calcium influx required for tip growth in root hairs. Mol. Plant 10, 1004–1006. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2017.02.007
Zhang, G. B., Yi, H. Y., Gong, J. M. (2014). The Arabidopsis ethylene/jasmonic acid-NRT signaling module coordinates nitrate reallocation and the trade-off between growth and environmental adaptation. Plant Cell 26, 3984–3998. doi: 10.1105/tpc.114.129296
Zhang, J., Zhang, Y., Chen, J., Xu, M., Guan, X., Wu, C., et al. (2024). Sugar transporter modulates nitrogen-determined tillering and yield formation in rice. Nat. Commun. 15, 9233. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-53651-1
Keywords: NUE, nitrate signaling, phytohormones, ROS, calcium, peptides, sucrose, crosstalk
Citation: Mao J, Tian Z, Sun J, Wang D, Yu Y and Li S (2025) The crosstalk between nitrate signaling and other signaling molecules in Arabidopsis thaliana. Front. Plant Sci. 16:1546011. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1546011
Received: 16 December 2024; Accepted: 05 February 2025;
Published: 10 March 2025.
Edited by:
Dong-Wei Di, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), ChinaReviewed by:
Germán Robert, National Institute of Agricultural Technology (INTA), ArgentinaCopyright © 2025 Mao, Tian, Sun, Wang, Yu and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jingjing Mao, bWFvamluZ2ppbmc0MEAxNjMuY29t; Shaopeng Li, bGlzcEBqc3p5Z3MuY29t
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.