- 1School of Life Sciences, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China
- 2School of Modern Agriculture and Biotechnology, Ankang University, Ankang, China
Brassica crops, well known for their nutritional and medicinal value, encompass a diverse range of species and varieties, many of which are rich in anthocyanins. These flavonoid pigments not only contribute to the vibrant colors of Brassica plants but also possess significant antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and neuroprotective properties. This review provides an in-depth analysis of the distribution, composition, and health benefits of anthocyanins in Brassica crops, highlighting their potential applications in the food industry and medicine. We discuss the accumulation patterns of anthocyanins in various Brassica tissues, the influence of genetic and environmental factors on their concentration, and the impact of acylation on their stability and biological activities. This review also explores the antioxidant capacity and cardioprotective effects of Brassica anthocyanins, as well as their roles in protecting against hepatic and renal injury and promoting neuroprotection. Furthermore, we examine the use of anthocyanins as natural food colorants and their integration into intelligent packaging for the real-time monitoring of food freshness. Our findings underscore the multifaceted benefits of Brassica anthocyanins, positioning them as key components in the development of functional foods and sustainable food systems.
1 Introduction
Brassica is an important genus of the Brassicaceae family that has been used as a food source and medicinal compound in Eurasia since ancient times (Cheng et al., 2014). Brassica plants are currently used in vegetable and oil production in more than 150 countries; provide edible roots, leaves, stems, buds, flowers, and seed products; and play important roles in agricultural production (Velasco et al., 2017; Rakow, 2004).
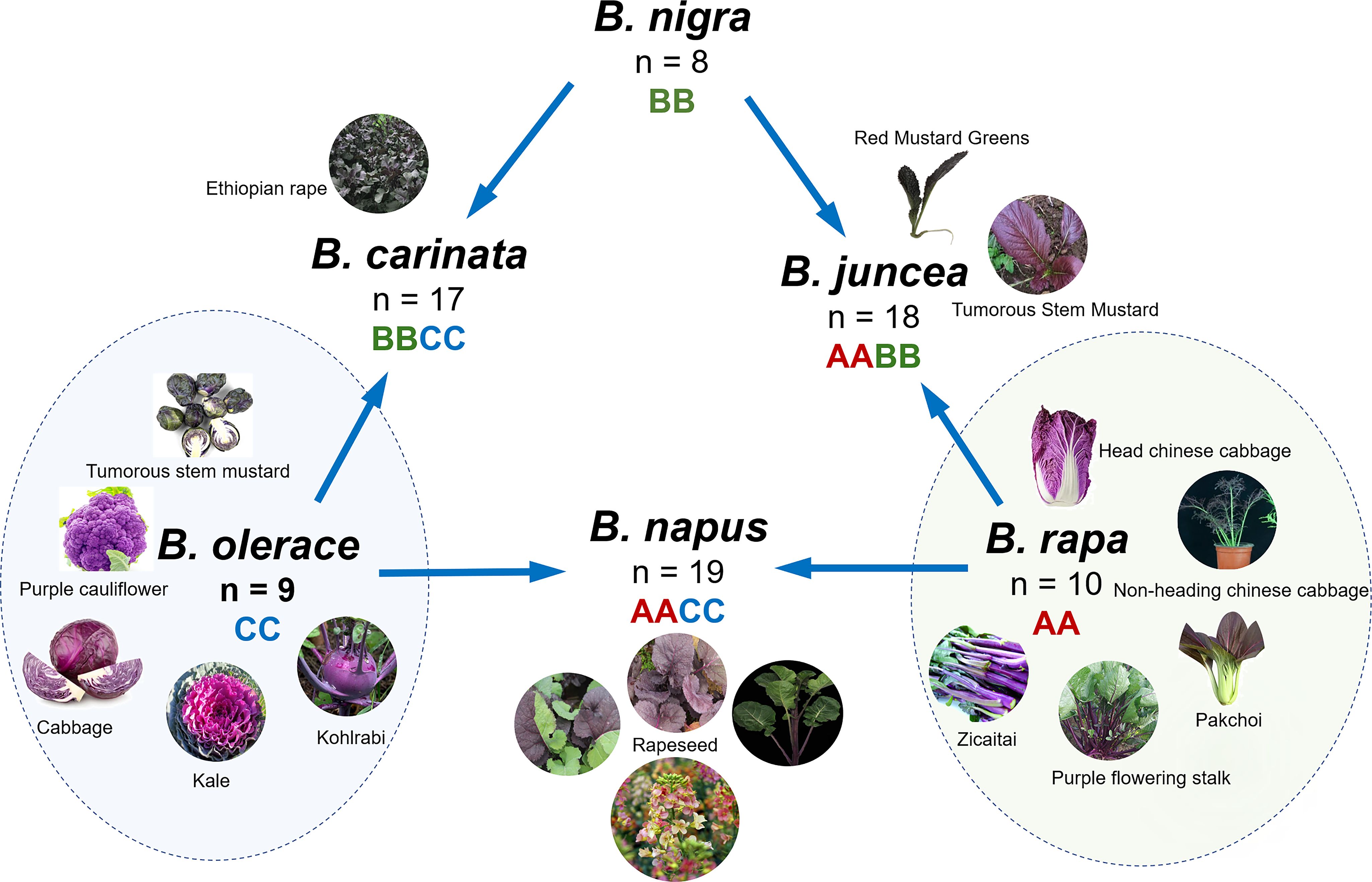
The genus Brassica consists of six widely cultivated species: Brassica rapa L., Brassica oleracea L., Brassica napus L., Brassica nigra(L.) K. Koch, Brassica carinata A. Braun, and Brassica juncea(L.) Czern. These species are utilized globally as vegetables, oilseed crops, condiments and fodder. B. napus, B. carinata and B. juncea are allotetraploid species that evolved from the natural hybridization of three diploid progenitors (B. oleracea, B. rapa, and B. nigra). The versatile B. oleracea, a cornerstone of vegetable cultivation, encompasses an array of distinct varieties, notably broccoli (var. italica), cauliflower (var. botrytis), kale (var. acephala), cabbage (var. capitata), kohlrabi (var. gongylodes), and Brussels sprouts (var. gemmifera) (Šamec et al., 2016). B. rapa encompasses diverse forms of vegetables, including the versatile turnip, the highly popular Chinese cabbage, and the delicate pak choi, in addition to varieties utilized as forage crops and for oilseed production (Escribano-Bailón et al., 2004). This species displays remarkable versatility, accommodating various culinary and agricultural purposes. They are not only delicious but also rich in nutrients and constitute an important part of people’s daily diet (Nagaharu, 1935). Some Brassica seeds can be used to extract oil, such as rapeseed, which produces high-quality oil with a variety of nutritional benefits. In addition, B. carinata and B. juncea are two important Brassica crops. The B. carinata seed, a unique nonedible oil crop, is cultivated primarily for the production of oil-derived products, notably in the synthesis of biodiesel (Mekuriaw and Abera, 2024). Notably, B. carinata has traditional medicinal value and is well known for its therapeutic potential in addressing wounds and alleviating gastrointestinal disturbances (Nakakaawa et al., 2023). The vitamin A content in B. juncea is important for maintaining good vision and contributes to healthy skin. Furthermore, the dietary fiber in B. juncea helps promote intestinal health, prevent constipation, help lower serum cholesterol levels, and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease.
In addition to agriculture, studies have shown that Brassica crops have a wide range of applications in the food industry and medicine. For example, B. campestris L., B. juncea(L.) Czern., B. campestris var. purpuraria, and B. oleracea var. italica have medicinal value, and B. alboglabra L. H. Bailey and B. rapa ssp. pekinensis can be used to treat certain diseases or as health foods (Kapusta-Duch et al., 2012; Zhao A. et al., 2022; Zhao Y. et al., 2022; Mahn and Reyes, 2012). Brassica species are well known for their abundant accumulation of essential nutrients and bioactive phytochemicals, encompassing a diverse array of vitamins, minerals, and compounds such as indole phytoalexins, phenolic acids, and glucosinolates (Salehi et al., 2021). These constituents confer a multitude of biological benefits to Brassica plants, particularly in safeguarding cardiovascular health and mitigating cancer risk. The antimicrobial properties of these compounds (Vale et al., 2015), coupled with their potent antioxidant (Bhandari and Kwak, 2015; Soengas et al., 2012) and anticancer activities (Hafidh et al., 2013; Thangam et al., 2013), underscore their importance in promoting overall wellness. Extensive epidemiological investigations involving human subjects have revealed a compelling inverse correlation between increased consumption of Brassica vegetables and the incidence of cancer, specifically highlighting their chemoprotective potential against malignancies of the lung, stomach, colon, and rectum (Avato and Argentieri, 2015).
A variety of natural pigments exist in nature, including chlorophylls, carotenoids, flavonoids, and quinone derivatives, which provide rich colors and play important physiological roles in living organisms (Honda and Moriya, 2018). Owing to their unique natural properties and healthy and harmless characteristics, natural plant pigments have gradually replaced some chemically synthesized pigments and have become important coloring agents in modern industry. Anthocyanins are a class of flavonoid pigments that are widely found in plants and give them vibrant colors ranging from blue to purple. The basic structure of anthocyanins consists of two benzene rings connected by a pyran ring with multiple substituents, and their color-forming principle is affected by a variety of factors, such as pH, cochromatism, and molecular modification (Francis F. J., 1989; Roy and Rhim, 2021; Lv et al., 2022), which work together to make anthocyanins colorful in plants. Anthocyanins have a variety of biological activities, such as antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and free radical scavenging and antiaging activities (Zhang et al., 2020), which has positive implications for the prevention and treatment of certain diseases (Escribano-Bailón et al., 2004). In addition, it has also been shown that anthocyanins can promote the regeneration of retinal cells, prevent myopia, improve vision, and have multiple benefits for human health (Alappat and Alappat, 2020).
In Brassica crops, a very large number of varieties are characterized by the accumulation of rich anthocyanins. These varieties usually have a bright red–blue–purple color and are highly ornamental, nutritional, and medicinal value (Favela-Gonzalez et al., 2020). Considering the universality of anthocyanin accumulation in the Brassica genus and the biological value of anthocyanins, this review aims to provide an overview for a better understanding of the organizational distribution, composition, and health benefits of anthocyanins in Brassica crops and their potential applications in the food industry and medicine.
2 Anthocyanin accumulation in Brassica crops
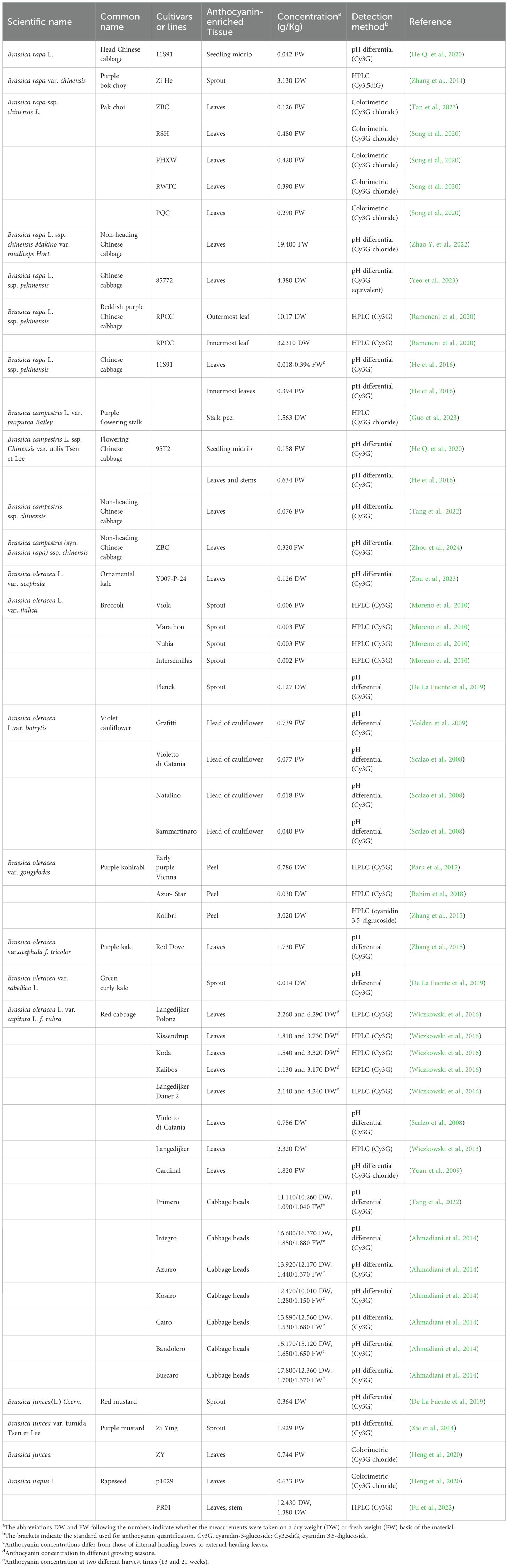
Anthocyanins accumulate in tissues and parts that often appear red or purple and are the main pigments responsible for the coloration of plant petals, leaves, stems, and fruits (Escribano-Bailón et al., 2004). In species of the Brassica genus, numerous varieties with anthocyanin accumulation have been discovered (Table 1; Figure 1). B. oleracea, a major vegetable species, includes the most purple or red varieties/cultivars, the most studied of which are red cabbage (var. capitata) (Song et al., 2018; Ghareaghajlou et al., 2021), purple broccoli (Liu et al., 2020; Rahim et al., 2019) and purple cauliflower (Chiu and Li, 2012), purple kale (var. acephala) (Zhang et al., 2012), purple kohlrabi, and purple Brussels sprouts (var. gemmifera), which have anthocyanin accumulation. For B. rapa, a diverse array of purple-hued cultivars showcase remarkable anthocyanin pigmentation, including the purple flowering stalk (Campestris var. purpurea Bailey) (Guo et al., 2023), purple head Chinese cabbage (He Q. et al., 2020), B. rapa L. ssp. chinensis (He Q. et al., 2020), nonheading Chinese cabbage (ssp. Chinensis Makino var. mutliceps Hort.) (Zhao Y. et al., 2022), B. rapa ssp. Parachinensis (He et al., 2016), B. rapa subsp. chinensis (Jeon et al., 2018), bok choy (var. chinensis) (Zhang et al., 2014), and B. rapa L. ssp. chinensis var. purpurea (Guo et al., 2015). In addition, purple tumorous stem mustard (var. tumida Tsen et Lee) (Xie et al., 2014) and red mustard greens (Coss variety) (Lin et al., 2011) have been reported for B. juncea, and mustard with only purple leaf veins and leaf edge cracks has also been studied and reported in B. juncea(Zhang et al., 2022). B. napus has several anthocyanin-enriched variants, including purple-leaved B. napus(Huang et al., 2024) and purple-stemmed B. napus(Chen et al., 2022), and variants with diversely colored petals resulting from anthocyanin accumulation have been developed for ornamental purposes (Yin et al., 2019; Zeng et al., 2023; Cui et al., 2024). Additionally, B. carinata with purple leaves has gradually gained attention because of its ornamental and nutritional value (Mushtaq et al., 2016).
In these purple Brassica crops, anthocyanins accumulate mostly in nutrient-containing organs, i.e., leaves and stems (Figure 1). In the case of leaves, the deposition forms of anthocyanins are diverse, and their presence results in red, purple, blue, pink, and other colors (Ren and Zemel, 2015). Ornamental kale, a horticultural variety of B. oleracea, has leaves in a range of colors, such as white, purple, pink, yellow, and red, leading to high ornamental value. Red cabbage is well known for its bright purple leaves, and its bright color and high nutritional value make it a common healthy ingredient in salads (Hanschen, 2020). Purple ornamental cabbage (B. oleracea var. acephala) is characterized by green outer leaves and purple inner leaves, which are attributed to the specific accumulation of anthocyanins in the inner leaves (Jin et al., 2019). Moreover, purple kale has dark purple leaf veins resulting from the special accumulation of anthocyanins (Barcena et al., 2019). Similarly, in the anthocyanin-enriched varieties, the entire aboveground parts of the flowering stalk, especially the stems, exhibit a vibrant purple color, making them widely favored by consumers. Bok choy (Zhang et al., 2014), non-heading Chinese cabbage (Zhao Y. et al., 2022), and red flat cabbage (B. rapa L. subsp. narinosa) (Park et al., 2021) primarily accumulate anthocyanins on the surface of their leaf blades, which mix with chlorophyll to produce a dark purple hue. The accumulation of anthocyanins in the stem bark results in purple stems, which is also a relatively common phenomenon in Brassica crops. In addition to purple-stalked Chinese kale (B. oleracea var. alboglabra), which displays a rich purple color only in its stem (Tang et al., 2024), rapeseed with purple flower stalks resulting from the specific accumulation of anthocyanins has increased its value as a vegetable (Chen D. et al., 2023). In particular, purple kohlrabi shows abundant anthocyanin accumulation in the epidermis of swollen stems (Zhang et al., 2015). In the two cabbage varieties, broccoli and cauliflower, anthocyanin accumulation was observed only in the flower buds of certain cultivars. To date, colored petals caused by anthocyanin accumulation have been reported only in rapeseed (Cui et al., 2024; Zeng et al., 2023; Yin et al., 2019). In general, anthocyanins most commonly accumulate in the epidermal layers of various aboveground organs in Brassica crops, including the upper and lower sides of the leaves, stems, swollen stems, and buds (Chiu and Li, 2012), which is due to the exposure of the epidermis of these tissues to light.
The concentrations of anthocyanins reported in Brassica crops vary greatly among varieties, and the levels of these anthocyanins are summarized herein (Table 1). Ahmadiani et al. (2014) reported that the anthocyanin content of seven red cabbage cultivars ranged from 11.110 to 17.800 g/kg dry weight (DM), and these values for fresh matter were approximately 1.090 and 1.700 g/kg fresh weight (FM), respectively, and did not increase with time. The total anthocyanin content was found to be 0.739 g/kg for the head of cauliflower in Violet cauliflower and 3.02 g/kg dry weight for the swollen stem peel in Kolibri (Park et al., 2012; Zhang et al., 2015). Although anthocyanins are absent in adults, the sprouts of broccoli and kale are rich in anthocyanins (0.127 and 0.014 g/kg DW, respectively) (De La Fuente et al., 2019). The anthocyanin accumulation in the purple stem bark of purple flowering stalks, highly valued by consumers for its vibrant color, reaches 1.563 g/kg Dw (Guo et al., 2023).
The levels of anthocyanin accumulation vary across different plant growth stages and are influenced by genetic factors, environmental conditions, physiological stress responses, and the nutritional state of the plant (Kim et al., 2021; Chalker-Scott, 2008). The anthocyanin content in Brassica crops has been shown to fluctuate depending on the cultivar (Moreno et al., 2010), specific plant organ (Park et al., 2012; Rahim et al., 2018), season of growth (Guarise et al., 2019; Wiczkowski et al., 2014), and environmental growth conditions (Baenas et al., 2015), even within the same species. The most common phenomenon of anthocyanin accumulation is in the organ epidermis (Guo et al., 2023; Park et al., 2012; Zhang et al., 2015; Rahim et al., 2018; Fu et al., 2022), possibly due to the regulation of anthocyanin accumulation by light. In the red cabbage variety ‘Langedijer Polona’, the anthocyanin content measured in 2009 (6.290 g/kg DW) was threefold greater than that measured in 2008 (2.260 g/kg DW) (Wiczkowski et al., 2014), likely due to differences in cultivar characteristics and growing conditions. The outermost and innermost leaves of reddish purple Chinese cabbage have clearly different anthocyanin contents (10.170 and 32.310 g/kg DW, respectively) due to tissue differences (Rameneni et al., 2020). After exposure to low temperatures, anthocyanins are significantly promoted to accumulate in purple veins, particularly in the midribs (He Y. et al., 2020). These differences are often influenced by environmental factors due to the variations in cultivar and growing conditions.
3 Anthocyanin compositions and characteristics in Brassica crops
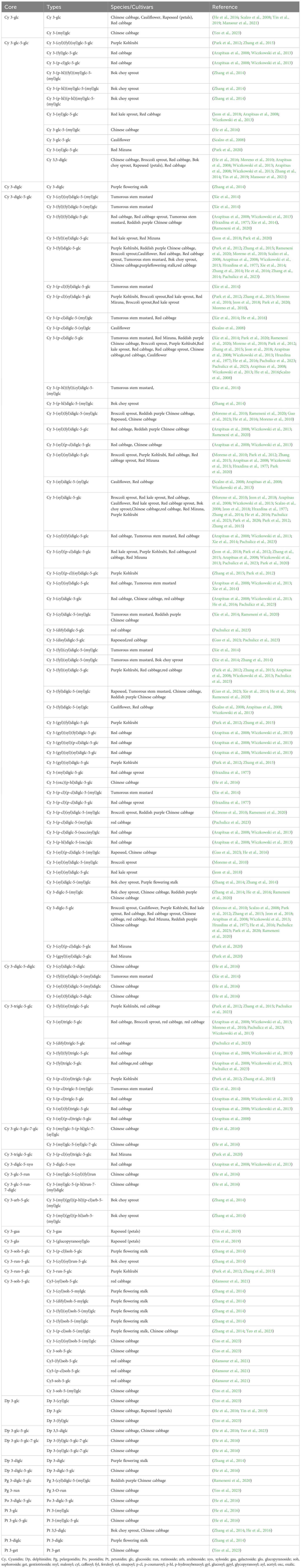
Anthocyanins are glycosides of hydroxyl and/or methoxy derivatives of 2-phenylbenzopyrylium or flavylium salts based on a C6-C3-C6 carbon skeleton structure (Kong et al., 2003). To date, more than twenty naturally occurring anthocyanidins have been identified, with six cyanidin, peonidin, delphinidin, petunidin, malvidin and pelargonidin—most commonly found in fruits and vegetables (Castañeda-Ovando et al., 2009). In various Brassica crop species, anthocyanins, including the colorful petals of the oilseed crop B. napus, which has high ornamental potential, have been systematically identified and analyzed. Glycosylation of anthocyanins at the 3-, 5-, and 7-positions of the anthocyanidin core has been observed in Brassica crops (Table 2). The sugars added to anthocyanins include glucose, xylose, rutinose, arabinose, galactose, sophorose, gentiotriose and glucopyranose. In Brassica crops, the primary anthocyanins are cyanidin 3-diglucoside-5-glucoside derivatives, which are acylated with various aromatic acids, aliphatic acids, glucosides and xylose (Table 2). For example, all the anthocyanins in seven red cabbage cultivars—Kosaro, Cairo, Integro, Azurro, Buscaro, Primero, and Bandolero—at two maturity stages (harvested at 13 and 21 weeks posttransplantation) consisted of nonacylated, monoacylated, and diacylated cyanidin-3-diglucoside-5-glucoside derivatives, which were acylated with sinapic, ferulic, and p-coumaric acids (Ahmadiani et al., 2014). Additionally, the sinapoyl- and feruloyl-esterified forms of cyanidin 3-diglucoside-5-glucoside are predominant in red Mizuna (Rameneni et al., 2020), whereas p-coumaryl and feruloyl esters are predominant in mustard (Xu et al., 2019). In the purple stem bark of B. napus, cyanidin 3-(feruloyl)diglucoside-5-(malonyl)glucoside was found to be the predominant anthocyanin. However, in the pink and red petals of rapeseed, petunidin and delphinidin derivatives are often identified as the main anthocyanin components rather than just cyanidin (Yin et al., 2019; Zeng et al., 2023), which is distinctly different from the composition found in leaves and stems.
In general, the predominant anthocyanins are acylated cyanidin 3-glucoside/diglucoside-5-glucoside. However, anthocyanin profiles vary considerably among Brassica crops, particularly with respect to the types and degrees of acylation modifications present (Table 2; Figure 2). The acyl groups commonly linked to the anthocyanins in Brassica include aromatic acids such as p-coumaric, ferulic, sinapic, caffeic and p-hydroxybenzoic acids, as well as aliphatic acids such as oxalic, acetic, succinic, and malonic acids, in addition to glucoside, glycopyranoside and xylose (Figure 2).
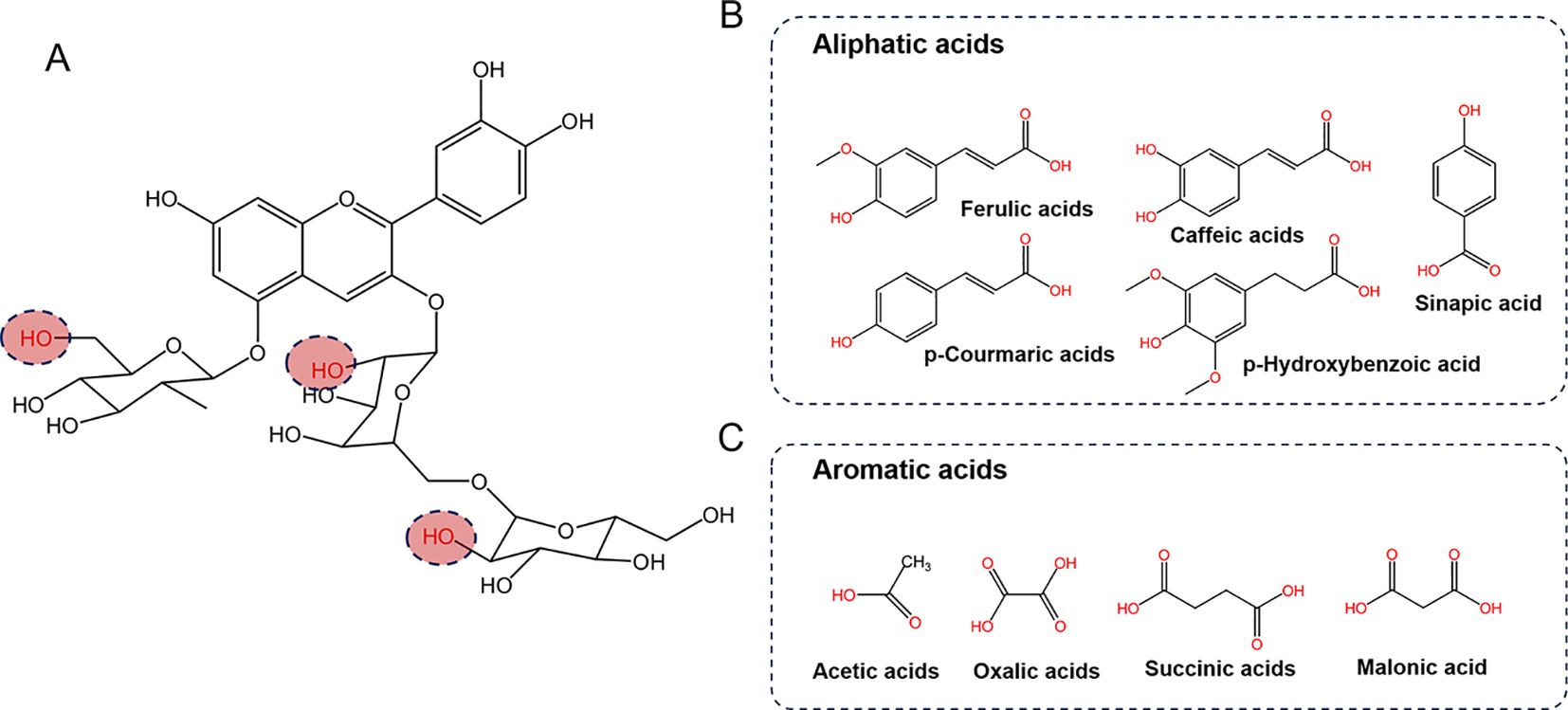
Figure 2. The primary anthocyanins detected in Brassica crops. (A) Chemical structures of the primary anthocyanins core, and the red dashed circles highlight the potential attachment site for acyl groups. (B, C) show common organic acids that acylate the sugar moiety of anthocyanins.
The resilience of anthocyanins is often determined by the quantity and nature of their acyl substituents, and many studies have shown that anthocyanins with acyl groups tend to be more stable than those without such modifications (Matsufuji et al., 2007). The addition of acyl groups to anthocyanins increases their stability via both intramolecular and/or intermolecular copigmentation effects, as well as through self-association processes (Fenger et al., 2019; Cortez et al., 2017). Brassica anthocyanins, which feature intricate acylation patterns, display exceptional stability against thermal processing, fluctuations in pH, light exposure, and storage (Zhang et al., 2022). Prietto et al. (2017) reported that anthocyanins from red cabbage demonstrated greater stability than those from black beans when exposed to light. Leveraging this stability, they developed a pH-sensitive film utilizing extracts from red cabbage anthocyanin extracts. The extracts from red cabbage were thermostable and produced a coloring effect over a broader pH range compared to their non-acylated counterparts, such as the commercial Hibiscus-based colorant (Steingass et al., 2023). Moreover, the study of Pereira et al. (2024) suggested that the degree of acylation affects anthocyanin thermostability since extracts containing mono- and diacylated anthocyanins extracted from red cabbage are more stable than hibiscus calyxes (nonacylated) extracts are, which supports the application of polyacylated anthocyanins as natural color additives for food products.
Compared with their nonacylated forms, anthocyanins whose glycosyl moieties are acylated by hydroxycinnamic acid (HCA) residues, including caffeic, p-coumaric, ferulic, and sinapic acids, are recognized for their greater color stability (Malien-Aubert et al., 2001; Trouillas et al., 2016; Steingass et al., 2023). Purple Brassica crops represent promising vegetable sources for the recovery of acylated anthocyanins carrying aromatic acyl moieties such as hydroxycinnamic acids (McDougall et al., 2005). The prevailing anthocyanins in red cabbage include cyanidin-3-O-sophoroside-5-O-glucoside and its forms with one to two hydroxycinnamoyl groups attached through acetylation, which are derived primarily from p-coumaric, caffeic, ferulic, and sinapic acids (Idaka et al., 2006; Moloney et al., 2018), and red cabbage anthocyanins have been reported to be less sensitive to thermal degradation than grape, black currant, and elderberry anthocyanins are (Dyrby et al., 2001; Trouillas et al., 2016).
4 Biological activity and health benefits of anthocyanins from Brassica crops
4.1 Antioxidant activity of Brassica anthocyanins
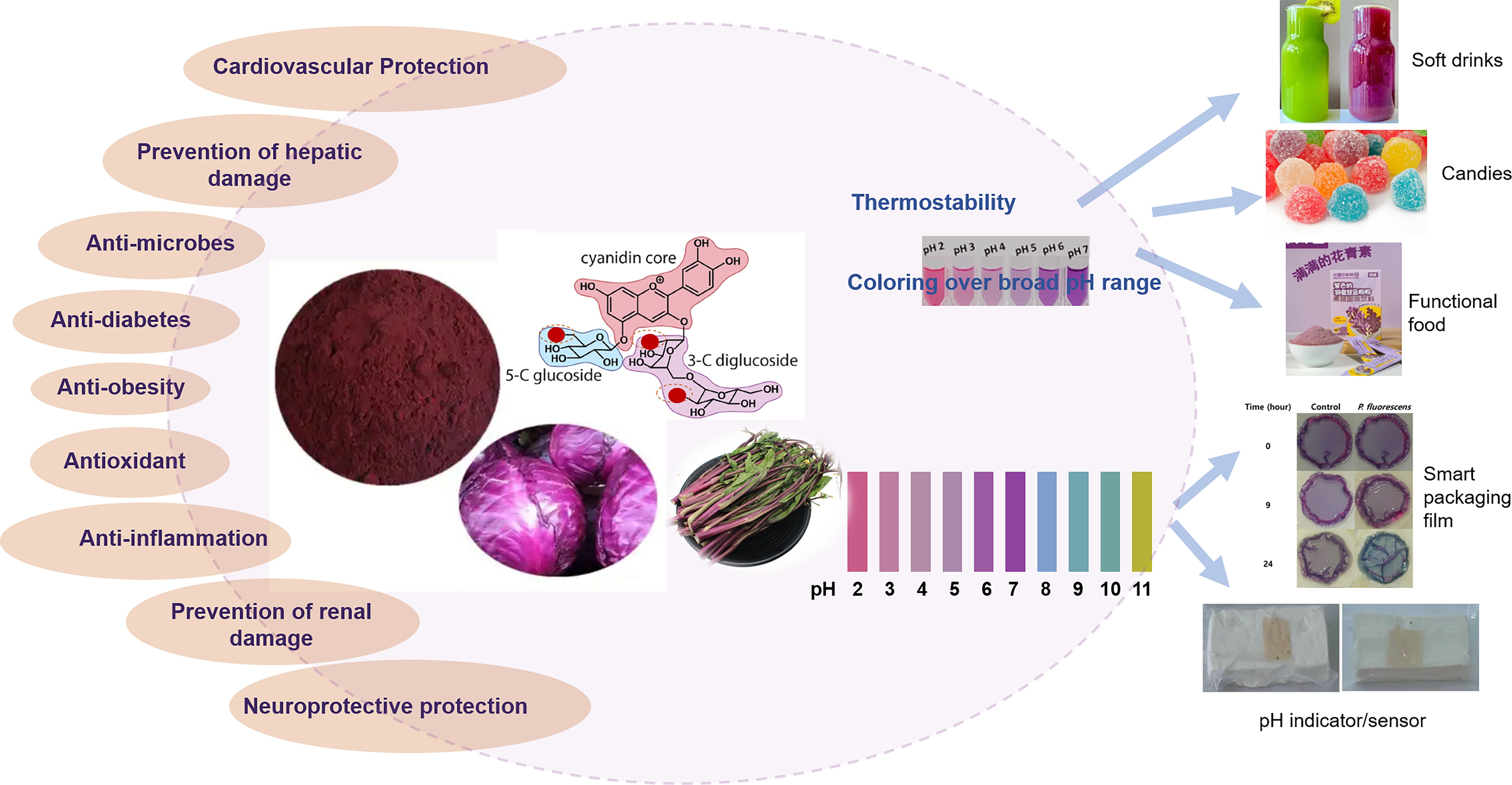
Anthocyanins are known for their strong antioxidant activity, a property primarily attributed to their phenolic structure, which allows them to scavenge reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reduce oxidative stress. By donating hydrogen atoms or electrons, anthocyanins effectively neutralize free radicals, protecting against oxidative stress and potentially reducing the risk of aging and various diseases linked to an imbalance of free radicals and antioxidants (Lee et al., 2011). Anthocyanins from Brassica crops have been reported to exhibit strong antioxidant properties to protect the body from oxidative damage. In vitro analysis demonstrated that the extract of Hon Tsai Tai (purple Brassica chinensis) presented significantly greater antioxidant activity than did anthocyanin-lacking varieties such as Pak Choi and Choi Sum, as evidenced by the 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical scavenging ability, reducing power, and 2’,7’-dichlorofluorescin (DCF) activity, and measurements of the intracellular superoxide dismutase activity and malondialdehyde content further confirmed its antioxidant protective effect (Chen et al., 2016). Studies on in vivo models have demonstrated that Brassica anthocyanins mitigate oxidative stress and exhibit protective effects on cellular components. For example, red cabbage anthocyanins reduce oxidative stress markers in liver mitochondria and protect plasma lipids from peroxidation in rat models (Igarashi et al., 2000; Kolodziejczyk et al., 2011).
Brassica anthocyanins have also been reported to prevent oxidative imbalance in brain tissue, as shown in mouse studies, where anthocyanins preserve glutathione levels in the brain under oxidative stress (Lee et al., 2002). Research also suggests that anthocyanins may modulate inflammatory responses in blood platelets, potentially through interactions with Toll-like receptor 4, which may reduce oxidative damage in inflammation-induced conditions (Saluk et al., 2015). In cellular models, such as HepG2 cells, red cabbage anthocyanins reduce H2O2-induced oxidative stress, improving cell survival and reducing apoptosis (Fang et al., 2018). Additionally, they demonstrated antioxidative effects against lipid peroxidation in rat plasma under stress, indicating broad protective effects across different biological systems (Veber et al., 2020). These findings collectively highlight the significant antioxidant potential of Brassica anthocyanins, which not only combat oxidative agents but also provide cellular protection, making them promising compounds for functional foods and health-promoting applications.
The effectiveness of Brassica anthocyanins varies across cultivars and is particularly influenced by acylation. For example, anthocyanins from the red cabbage cultivar “Langedijker Polona” presented the highest oxygen radical absorbance capacity (ORAC) value, underscoring cultivar-specific antioxidant capacities (Wiczkowski et al., 2014). Studies have shown that diacylated anthocyanins tend to be more stable and have higher antioxidant potential than monoacylated anthocyanins because of their enhanced stability and reactivity with free radicals (McDougall et al., 2007; Pereira et al., 2024). A study by Wiczkowski, Szawara-Nowak, and Topolska (Wiczkowski et al., 2013) specifically evaluated red cabbage anthocyanins and reported that compared with their nonacylated counterparts, acylated cyanidin glycosides presented greater antioxidant capacities. Additionally, the antioxidant potency of acylated anthocyanins varies depending on the type and extent of acylation (Wiczkowski et al., 2016). Among those modified with different hydroxycinnamic acids, those that are acylated with sinapic acid displayed the highest antioxidant activity (McDougall et al., 2007). Recent studies have further supported these findings, indicating that anthocyanins with multiple acyl groups, especially when bound to hydroxycinnamic acids, have not only enhanced radical-scavenging abilities but also improved stability, potentially leading to better health benefits when incorporated into diets (Zhang et al., 2021).
4.2 Cardiovascular protection
Anthocyanins contribute to cardiovascular health through mechanisms involving low-density lipoprotein (LDL) antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, as well as improvements in endothelial function. Research indicates that anthocyanins can help lower the levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) under hyperlipidemic conditions and lower the risk of atherosclerosis by inhibiting lipid peroxidation and protecting vascular integrity. Al-Dosari (2014) reported that red cabbage extract decreased serum lipid levels while increasing high-density lipoprotein (HDL) levels in rats fed a cholesterol-rich diet, further supporting its hypocholesterolemic activity. Cruz et al. (2016) demonstrated that aqueous extracts of red cabbage ameliorated lipid alterations in rats induced by Triton WR-1339, leading to improved cardiovascular health. Additionally, anthocyanins from red cabbage exhibit significant hypocholesterolemic effects by influencing cholesterol metabolism (Liang et al., 2019; Zhang et al., 2022).
Moreover, studies by Sankhari et al. (2012) and Jana et al. (2017) highlighted the cardioprotective effects of anthocyanin-rich red cabbage extract, which not only preserved enzymatic and nonenzymatic antioxidants in atherogenic diet-fed rats but also provided protection against oxidative stress in myocardial infarction models. These findings underscore the potential of Brassica anthocyanins as functional food components for enhancing cardiovascular health. The cardioprotective effects of red cabbage anthocyanins are further supported by their ability to inhibit platelet activation, a critical factor in cardiovascular disease development. Saluk et al. (2012) reported that anthocyanins mitigate platelet hyperactivation, thereby reducing the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which are associated with cardiovascular risk. Overall, the consumption of Brassica anthocyanins appears to offer a multifaceted approach to cardiovascular protection, encompassing lipid metabolism regulation, antioxidant enhancement, and platelet activity modulation.
4.3 Protection against hepatic and renal injury
Brassica anthocyanins are valuable for combating liver and kidney damage. For example, studies have shown that red cabbage anthocyanins can alleviate liver impairment caused by high-cholesterol diets (Duchnowicz et al., 2012; Ashfaq et al., 2019). Sankhari et al. (2012) further illustrated that these anthocyanins reduced hepatic injury in rats fed an atherogenic diet by lowering triglyceride, total cholesterol, and LDL levels while increasing HDL and antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase. Turnip extracts containing anthocyanins have been shown to have hepatoprotective effects on CCl4-induced hepatotoxicity in rats by reducing the levels of serum glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase, glutamate pyruvate transaminase, and alkaline phosphatase (Sharef et al., 2019). Al-Dosari (2014) reported that red cabbage extracts effectively inhibited liver damage and demonstrated cytoprotective effects in HepG2 cells.
In addition to liver protection, red cabbage anthocyanins have also been reported to exhibit nephroprotective effects. Research by Shiyan et al. (2018) revealed that anthocyanin-rich extracts improved kidney function in rat models of gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity. Moreover, Rezq (2018) reported that the administration of red cabbage extract to NDEA- and CCl4-treated rats resulted in decreased serum levels of urea nitrogen, uric acid, and creatinine, thereby improving kidney function. The protective role of these anthocyanins is further supported by findings from Sharef et al. (2019), who demonstrated that red cabbage extracts could safeguard renal tissues against gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity. These findings suggest that incorporating anthocyanin-rich foods from Brassica crops into the diet may contribute positively to liver and kidney health and highlight their potential as natural therapeutic agents for managing related diseases.
4.4 Neuroprotective protection
Anthocyanins from Brassica crops also exhibit significant neuroprotective effects, primarily through the suppression of neuroinflammation and oxidative stress. Research by Lee et al. (2002) demonstrated that red cabbage extract was among the top vegetable sources that exhibited neuroprotective effects against oxidative stress in the brains of mice treated with NMDA, reinforcing the potential of these compounds in maintaining central nervous system health. Research by Heo and Lee (2006) highlighted that pretreatment with red cabbage phenolics notably inhibited amyloid-beta peptide-induced cytotoxicity in PC12 cells, indicating a protective mechanism against neurotoxicity linked to Alzheimer’s disease. Zhang et al. (2019) supported the hypothesis that red cabbage anthocyanins play a critical role in protecting neuronal cells by suppressing neuroinflammation and mitigating oxidative damage. Recently, Platosz et al. (2020) reported that the blood–cerebrospinal fluid barrier is selective for red cabbage anthocyanins and that only nonacylated derivatives are present in the cerebrospinal fluid. Furthermore, Zhang and Jing (2023) reported that extracts rich in red cabbage anthocyanins and cyanidin-3-diglucoside-5-glucoside potentially alleviated the cognitive decline associated with aging by decreasing inflammation in the nervous system, increasing antioxidant capabilities, and regulating the gut−brain axis. Collectively, these findings suggest that Brassica anthocyanins can serve as effective agents for neuroprotection, highlighting their importance in dietary interventions for improving cognitive health.
4.5 Other biological activities
In addition, anthocyanins have been linked to various health benefits, such as anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, antidiabetic and antiobesity effects (Figure 3). Zielińska et al. (2015) reported that red cabbage extracts attenuated inflammation in a mouse model of acute and chronic Crohn’s disease. Moreover, studies have demonstrated that red cabbage anthocyanins can protect against heavy metal toxicity in lymphocytes (Posmyk et al., 2009) and mitigate intestinal injuries caused by irinotecan, highlighting their potential in gastrointestinal health (Tong et al., 2017). Additionally, red cabbage extracts have shown efficacy in inhibiting pancreatic lipase, which is crucial for fat absorption, thereby assisting in weight management (Xie et al., 2018). The extracts have also been identified as effective α-glucosidase and α-amylase inhibitors, with a stronger effect against α-glucosidase, contributing to better blood glucose control and a reduced risk of diabetes-related complications (Posmyk et al., 2009). With respect to antiaging effects, research has shown that, compared with cultivars without anthocyanins, such as Pak Choi and Choi Sum, only the anthocyanin-enriched Hon Tsai Tai extract significantly prolonged the lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans, resulting in an 8% increase in the mean lifespan over that of the controls (Chen et al., 2016). These diverse health benefits underscore the potential of Brassica anthocyanins as functional food components that may enhance overall health and prevent various diseases.
Additionally, the biological activities of anthocyanins are significantly influenced by their interactions within the colonic environment. Furthermore, bioavailability, the proportion of a nutrient that reaches systemic circulation, is a critical factor affecting the biological activity of Brassica anthocyanins. These aspects should be given particular attention and further investigated.
5 Application of Brassica anthocyanins
The shift toward natural colorants has been driven by consumer awareness regarding the potential adverse effects of artificial pigments on health and the environment (Rodriguez-Amaya, 2016; Francis M., 1989). Anthocyanins derived from Brassica crops, particularly red cabbage, have garnered attention as natural food colorants because of their vibrant hues and health benefits (Giusti and Wrolstad, 2003) (Figure 3). Steingass et al. (2023) recently demonstrated that, compared with commercial Hibiscus-based colorants, acylated anthocyanins from Brassica plants were more thermostable and produced a coloring effect over a broader pH range. Numerous studies have emphasized the suitability of Brassica anthocyanins as food colorants, and red cabbage-derived anthocyanins have been used in candies, soft drinks and other food products (Patras, 2019). In a recent study, Saberian et al. (2021) optimized the extraction process of red cabbage anthocyanins and explored their use as natural colorants in low-calorie gummy candies.
Owing to excellent stability and color differences across various pH values, such as pink at pH 3, violet at pH 5, and blue at pH 7 (Zhang and Jin, 2022; Dyrby et al., 2001), anthocyanins extracted from red cabbage have been widely used in the development of pH indicators for determining the freshness of food. In 2015, Silva-Pereira et al. (2015) and Pereira et al. (2015) developed pH indicators based on red cabbage anthocyanins. One of these indicators functions as a visual sign of fish decay, with superior optical and morphological characteristics. The other was designed to identify alterations in food quality by monitoring pH shifts in packaged items that had been subjected to unsuitable storage conditions. Kuswandi et al. (2020) created an edible pH sensor utilizing red cabbage anthocyanins fixed onto a bacterial cellulose membrane designed for determining pH levels in beverages and monitoring milk freshness. Moreover, Sezgin and Ocsoy (2023) developed novel colorimetric biosensors consisting of anthocyanin-rich black carrot or red cabbage extracts for rapid, sensitive, and economical detection of Helicobacter pylori.
Additionally, incorporating red cabbage anthocyanins in intelligent food packaging can be used to monitor the freshness of food products in real time, further contributing to food preservation (Abedi-Firoozjah et al., 2022). Nascimento Alves et al. (2020) developed biodegradable films that integrate green banana starch, gelatin, and alginate with red cabbage anthocyanins to monitor the freshness of sheep meat. These smart films are designed to detect changes in color parameters as indicators of meat quality reflected by pH changes resulting from the formation of volatile alkaline compounds during storage. Liu et al. (2021) developed colorimetric films based on polyvinyl alcohol/sodium carboxymethyl cellulose doped with red cabbage anthocyanins and demonstrated the potential of these films as indicators of freshness and intelligent packaging by monitoring the freshness of pork. Additionally, Park et al. (2022) investigated the antimicrobial activity and indicator properties of edible chitosan-based films prepared with red cabbage anthocyanins (as spoilage indicators) and clove bud oil (as antimicrobial agents), and the results indicated that the color change of the films reflected the growth process of the fish-spoiling bacteria.
Nevertheless, like anthocyanins from other species, the utilization of Brassica anthocyanins in the food and medical sectors has been significantly hindered by their inadequate stability and bioavailability (Chen Y. et al., 2023; González-Barrio et al., 2010). To enhance the stability of ACNs, a variety of approaches have been employed. These include encapsulation techniques such as spray-drying, freeze-drying, and the hard-panned coating method, as well as co-pigmentation and innovative enzymatic methods (Cortez et al., 2017), with nanoencapsulation also emerging as a promising strategy (Liang et al., 2024). Wagh et al. (2023) fabricated a new generation of carbon dot-based active and intelligent packaging films with antibacterial, UV blocking and real-time sensing potential via B. oleracea(BO) extract. The packaging trials demonstrated that the developed film operated effectively and without causing damage, enabling real-time monitoring of the freshness of ground pork, fish, and shrimp. The film indicated freshness through a visible transition from red to colorless/yellow, indicating its potential as a multifaceted packaging solution. This material can signal quality deterioration and prolong the shelf-life of perishable packaged goods.
Overall, the versatility of Brassica anthocyanins as natural colorants, coupled with their application in food monitoring and smart packaging solutions, position them as valuable components in the food industry, promoting health, safety, and sustainability.
6 Conclusion
This review underscores the multifaceted significance of anthocyanins in Brassica crops, which are not only rich in these pigments but also exhibit a broad spectrum of biological activities and health benefits. From their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties to their potential in cardiovascular health and neuroprotection, anthocyanins have emerged as vital components in functional foods. Moreover, their application extends beyond nutrition, serving as natural colorants and integral to smart packaging solutions for real-time food freshness monitoring. The stability and pH-responsive color changes of these anthocyanins make them ideal for developing indicators in food technology, emphasizing their role in enhancing food safety and quality. This comprehensive overview highlights the potential of Brassica anthocyanins as key players in the food industry, contributing to health, sustainability, and technological advancement.
Author contributions
XL: Writing – original draft. FW: Writing – review & editing. NT: Writing – review & editing. JH: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the Key Research and Development Program of Shaanxi Province (2024NC2-GJHX-03) and the Youth Innovation Team of Shaanxi Universities (2023AYTD01).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abedi-Firoozjah, R., Yousefi, S., Heydari, M., Seyedfatehi, F., Jafarzadeh, S., Mohammadi, R., et al. (2022). Application of red cabbage anthocyanins as pH-sensitive pigments in smart food packaging and sensors. Polymers 14, 1629. doi: 10.3390/polym14081629
Ahmadiani, N., Robbins, R., Collins, T., Giusti, M. (2014). Anthocyanins contents, profiles, and color characteristics of red cabbage extracts from different cultivars and maturity stages. J. Agr Food Chem. 62, 7524–7531. doi: 10.1021/jf501991q
Alappat, B., Alappat, J. (2020). Anthocyanin pigments: beyond aesthetics. Molecules 25. doi: 10.3390/molecules25235500
Al-Dosari, M. S. (2014). Red cabbage (Brassica oleracea L.) mediates redox-sensitive amelioration of dyslipidemia and hepatic injury induced by exogenous cholesterol administration. Am. J. Chin. Med. 42, 189–206. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X1450013X
Arapitsas, P., Sjoberg, P. J., Turner, C. (2008). Characterisation of anthocyanins in red cabbage using high resolution liquid chromatography coupled with photodiode array detection and electrospray ionization-linear ion trap mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 109, 219–226. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2007.12.030
Ashfaq, F., Butt, M. S., Bilal, A., Tehseen, S., Suleria, H. A. R. (2019). Bioefficacy of red cabbage against hypercholesterolemic diet mediated oxidative stress. Clin. Phytoscience 5, 33. doi: 10.1186/s40816-019-0126-y
Avato, P., Argentieri, M. P. (2015). Brassicaceae: a rich source of health improving phytochemicals. Phytochem. Rev. 14, 1019–1033. doi: 10.1007/s11101-015-9414-4
Baenas, N., Ferreres, F., García-Viguera, C., Moreno, D. A. (2015). Radish sprouts—Characterization and elicitation of novel varieties rich in anthocyanins. Food Res. Int. 69, 305–312. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2015.01.009
Barcena, A., Martinez, G., Costa, L. (2019). Low intensity light treatment improves purple kale (Brassica oleracea var. sabellica) postharvest preservation at room temperature. Heliyon 5, e02467. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02467
Bhandari, S. R., Kwak, J. H. (2015). Chemical composition and antioxidant activity in different tissues of brassica vegetables. Molecules 20, 1228–1243. doi: 10.3390/molecules20011228
Castañeda-Ovando, A., Pacheco-Hernández, M. D. L., Páez-Hernández, M. E., Rodríguez, J. A., Galán-Vidal, C. A. (2009). Chemical studies of anthocyanins: A review. Food Chem. 113, 859–871. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.09.001
Chalker-Scott, L. (2008). Environmental significance of anthocyanins in plant stress responses. Photochem. Photobiol. 70, 1–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1999.tb01944.x
Chen, Y., Belwal, T., Xu, Y., Ma, Q., Li, D., Li, L., et al. (2023). Updated insights into anthocyanin stability behavior from bases to cases: Why and why not anthocyanins lose during food processing. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 63, 8639–8671. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2022.2063250
Chen, D., Jin, Q., Pan, J., Liu, Y., Tang, Y., E, Y., et al. (2023). Fine mapping of genes controlling pigment accumulation in oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.). Mol. Breed 43, 19. doi: 10.1007/s11032-023-01365-5
Chen, W., Miao, Y., Ayyaz, A., Hannan, F., Huang, Q., Ulhassan, Z., et al. (2022). Purple stem Brassica napus exhibits higher photosynthetic efficiency, antioxidant potential and anthocyanin biosynthesis related genes expression against drought stress. Front. Plant Sci. 13. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.936696
Chen, J., Zhang, J., Xiang, Y., Xiang, L., Liu, Y., He, X., et al. (2016). Extracts of Tsai Tai (Brassica chinensis): enhanced antioxidant activity and anti-aging effects both in vitro and in Caenorhabditis elegans. Food Funct. 7, 943–952. doi: 10.1039/c5fo01241d
Cheng, F., Wu, J., Wang, X. W. (2014). Genome triplication drove the diversification of plants. Horticulture Res. 1. doi: 10.1038/hortres.2014.24
Chiu, L. W., Li, L. (2012). Characterization of the regulatory network of BoMYB2 in controlling anthocyanin biosynthesis in purple cauliflower. Planta 236, 1153–1164. doi: 10.1007/s00425-012-1665-3
Cortez, R., Luna-Vital, D. A., Margulis, D., Gonzalez de Mejia, E. (2017). Natural pigments: stabilization methods of anthocyanins for food applications. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 16, 180–198. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.12244
Cruz, A. B., Pitz, H. D., Veber, B., Bini, L. A., Maraschin, M., Zeni, A. L. (2016). Assessment of bioactive metabolites and hypolipidemic effect of polyphenolic-rich red cabbage extract. Pharm. Biol. 54, 3033–3039. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2016.1200633
Cui, C., Zhang, K., Chai, L., Zheng, B., Zhang, J., Jiang, J., et al. (2024). Unraveling the mechanism of flower color variation in Brassica napus by integrated metabolome and transcriptome analyses. Front. Plant Sci. 15. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1419508
De La Fuente, B., Lopez-Garcia, G., Manez, V., Alegria, A., Barbera, R., Cilla, A. (2019). Evaluation of the bioaccessibility of antioxidant bioactive compounds and minerals of four genotypes of brassicaceae microgreens. Foods 8. doi: 10.3390/foods8070250
Duchnowicz, P., Bors, M., Podsedek, A., Koter-Michalak, M., Broncel, M. (2012). Effect of polyphenols extracts from Brassica vegetables on erythrocyte membranes (in vitro study). Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 34, 783–790. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2012.09.008
Dyrby, M., Westergaard, N., Stapelfeldt, H. (2001). Light and heat sensitivity of red cabbage extract in soft drink model systems. Food Chem. 72, 431–437. doi: 10.1016/S0308-8146(00)00251-X
Escribano-Bailón, M. T., Santos-Buelga, C., Rivas-Gonzalo, J. C. (2004). Anthocyanins in cereals. J. Chromatogr A 1054, 129–141. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2004.08.152
Fang, S., Lin, F., Qu, D., Liang, X., Wang, L. (2018). Characterization of purified red cabbage anthocyanins: improvement in HPLC separation and protective effect against H(2)O(2)-induced oxidative stress in hepG2 cells. Molecules 24. doi: 10.3390/molecules24010124
Favela-Gonzalez, K. M., Hernandez-Almanza, A. Y., De-la-Fuente-Salcido, N. M. (2020). The value of bioactive compounds of cruciferous vegetables (Brassica) as antimicrobials and antioxidants: A review. J. Food Biochem. 44, e13414. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.13414
Fenger, J. A., Moloney, M., Robbins, R. J., Collins, T. M., Dangles, O. (2019). The influence of acylation, metal binding and natural antioxidants on the thermal stability of red cabbage anthocyanins in neutral solution. Food Funct. 10, 6740–6751. doi: 10.1039/c9fo01884k
Francis, F. J. (1989). Food colorants: anthocyanins. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 28, 273–314. doi: 10.1080/10408398909527503
Francis, M. (1989). “Control as a Dimension of Public-Space Quality,” in Public Places and Spaces. Eds. Altman, I., Zube, E. H.(Springer US, Boston, MA).
Fu, H., Chao, H., Zhao, X., Wang, H., Li, H., Zhao, W., et al. (2022). Anthocyanins identification and transcriptional regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis in purple Brassica napus. Plant Mol. Biol. 110, 53–68. doi: 10.1007/s11103-022-01285-6
Ghareaghajlou, N., Hallaj-Nezhadi, S., Ghasempour, Z. (2021). Red cabbage anthocyanins: Stability, extraction, biological activities and applications in food systems. Food Chem. 365, 130482. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130482
Giusti, M. M., Wrolstad, R. E. (2003). Acylated anthocyanins from edible sources and their applications in food systems. Biochem. Eng. J. 14, 217–225. doi: 10.1016/S1369-703X(02)00221-8
González-Barrio, R., Borges, G., Mullen, W., Crozier, A. (2010). Bioavailability of anthocyanins and ellagitannins following consumption of raspberries by healthy humans and subjects with an ileostomy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 58, 3933–3939. doi: 10.1021/jf100315d
Guarise, M., Borgonovo, G., Bassoli, A., Ferrante, A. (2019). Evaluation of two wild populations of hedge mustard (Sisymbrium officinale(L.) scop.) as a potential leafy vegetable. Horticulturae 5, 13. doi: 10.3390/horticulturae5010013
Guo, N., Wu, J., Zheng, S., Cheng, F., Liu, B., Liang, J., et al. (2015). Anthocyanin profile characterization and quantitative trait locus mapping in zicaitai (Brassica rapa L. ssp. chinensis var. purpurea). Mol. Breed. 35. doi: 10.1007/s11032-015-0237-1
Guo, P., Zhang, B., Hu, Z., Zhou, S., Wang, Y., Xie, Q., et al. (2023). Anthocyanin accumulation and transcriptional regulation in purple flowering stalk (Brassica campestris L. var. purpurea Bailey). Plant Mol. Biol. 111, 57–72. doi: 10.1007/s11103-022-01311-7
Hafidh, R. R., Abdulamir, A. S., Abu Bakar, F., Jalilian, F. A., Jahanshiri, F., Abas, F., et al. (2013). Novel anticancer activity and anticancer mechanisms of Brassica oleracea L. var. capitata f. rubra. Eur. J. Integr. Med. 5, 450–464. doi: 10.1016/j.eujim.2013.06.004
Hanschen, F. S. (2020). Domestic boiling and salad preparation habits affect glucosinolate degradation in red cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata f. rubra). Food Chem. 321, 126694. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.126694
He, Q., Ren, Y., Zhao, W., Li, R., Zhang, L. (2020). Low temperature promotes anthocyanin biosynthesis and related gene expression in the seedlings of purple head chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa L.). Genes (Basel) 11. doi: 10.3390/genes11010081
He, Q., Zhang, Z., Zhang, L. (2016). Anthocyanin Accumulation, Antioxidant Ability and Stability, and a Transcriptional Analysis of Anthocyanin Biosynthesis in Purple Heading Chinese Cabbage (Brassica rapa L. ssp. pekinensis). J. Agric. Food Chem. 64, 132–145. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.5b04674
He, Y., Zhu, M., Wu, J., Ouyang, L., Wang, R., Sun, H., et al. (2020). Repurposing of anthocyanin biosynthesis for plant transformation and genome editing. Front. Genome Ed 2. doi: 10.3389/fgeed.2020.607982
Heng, S., Cheng, Q., Zhang, T., Liu, X., Huang, H., Yao, P., et al. (2020). Fine-mapping of the BjPur gene for purple leaf color in Brassica juncea. Theor. Appl. Genet. 133, 2989–3000. doi: 10.1007/s00122-020-03634-9
Heo, H. J., Lee, C. Y. (2006). Phenolic phytochemicals in cabbage inhibit amyloid β protein-induced neurotoxicity. LWT 39, 331–337. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2005.02.018
Honda, C., Moriya, S. (2018). Anthocyanin biosynthesis in apple fruit. Horticulture J. 87, 305–314. doi: 10.2503/hortj.OKD-R01
Hrazdina, G., Iredale, H., Mattick, L. R. (1977). Anthocyanin composition of Brassica oleracea cv. Red Danish. Phytochemistry 16, 297–299. doi: 10.1016/S0031-9422(00)86817-X
Huang, L., Lin, B., Hao, P., Yi, K., Li, X., Hua, S. (2024). Multi-omics analysis reveals that anthocyanin degradation and phytohormone changes regulate red color fading in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) petals. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25. doi: 10.3390/ijms25052577
Idaka, E., Suzuki, K., Yamakita, H., Ogawa, T., Kondo, T., Goto, T. (2006). Structure of monoacylated anthocyanins isolated from red cabbage, brassica oleracea. Chem. Lett. 16, 145–148. doi: 10.1246/cl.1987.145
Igarashi, K., Kimura, Y., Takenaka, A. (2000). Preventive effects of dietary cabbage acylated anthocyanins on paraquat-induced oxidative stress in rats. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 64, 1600–1607. doi: 10.1271/bbb.64.1600
Jana, S., Patel, D., Patel, S., Upadhyay, K., Thadani, J., Mandal, R., et al. (2017). Anthocyanin rich extract of Brassica oleracea L. alleviates experimentally induced myocardial infarction. PloS One 12, e0182137. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0182137
Jeon, J., Lim, C. J., Kim, J. K., Park, S. U. (2018). Comparative metabolic profiling of green and purple pakchoi (Brassica rapa subsp. Chinensis). Molecules 23. doi: 10.3390/molecules23071613
Jin, S. W., Rahim, M. A., Jung, H. J., Afrin, K. S., Kim, H. T., Park, J. I., et al. (2019). Abscisic acid and ethylene biosynthesis-related genes are associated with anthocyanin accumulation in purple ornamental cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. acephala). Genome 62, 513–526. doi: 10.1139/gen-2019-0038
Kapusta-Duch, J., Kopeć, A., Piatkowska, E., Borczak, B., Leszczyńska, T. (2012). The beneficial effects of brassica vegetables on human health. Rocz Panstw Zakl Hig. 63, 389–395.
Kim, H. S., Yoo, J. H., Park, S. H., Kim, J. S., Chung, Y., Kim, J. H., et al. (2021). Measurement of Environmentally Influenced Variations in Anthocyanin Accumulations in Brassica rapa subsp. Chinensis (Bok Choy) Using Hyperspectral Imaging. Front. Plant Sci. 12. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.693854
Kolodziejczyk, J., Saluk-Juszczak, J., Posmyk, M. M., Janas, K. M., Wachowicz, B. (2011). Red cabbage anthocyanins may protect blood plasma proteins and lipids. Cent Eur. J. Biol. 6, 565–574. doi: 10.2478/s11535-011-0037-5
Kong, J. M., Chia, L. S., Goh, N. K., Chia, T. F., Brouillard, R. (2003). Analysis and biological activities of anthocyanins. Phytochemistry 64, 923–933. doi: 10.1016/s0031-9422(03)00438-2
Kuswandi, B., Asih, N. P.N., Pratoko, D. K., Kristiningrum, N., Moradi, M. (2020). Edible pH sensor based on immobilized red cabbage anthocyanins into bacterial cellulose membrane for intelligent food packaging. Packaging Technology and Science, 33 (8), 321–332. doi: 10.1002/pts.v33.810.1002/pts.2507
Lee, S., Park, Y., Zuidema, M. Y., Hannink, M., Zhang, C. (2011). Effects of interventions on oxidative stress and inflammation of cardiovascular diseases. World J. Cardiol. 3, 18–24. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v3.i1.18
Lee, K.-J., Sok, D.-E., Kim, Y.-B., Kim, M. R. (2002). Protective effect of vegetable extracts on oxidative stress in brain of mice administered with NMDA. FRI 35, 55–63. doi: 10.1016/S0963-9969(01)00119-3
Liang, T., Jing, P., He, J. (2024). Nano techniques: an updated review focused on anthocyanin stability. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 64, 11985–12008. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2023.2245893
Liang, T., Sun, G., Cao, L., Li, J., Wang, L. (2019). A pH and NH3 sensing intelligent film based on Artemisia sphaerocephala Krasch. gum and red cabbage anthocyanins anchored by carboxymethyl cellulose sodium added as a host complex. Food Hydrocolloids 87, 858–868. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2018.08.028
Lin, L. Z., Sun, J., Chen, P., Harnly, J. (2011). UHPLC-PDA-ESI/HRMS/MS(n) analysis of anthocyanins, flavonol glycosides, and hydroxycinnamic acid derivatives in red mustard greens (Brassica juncea Coss variety). J. Agric. Food Chem. 59, 12059–12072. doi: 10.1021/jf202556p
Liu, D., Cui, Z., Shang, M., Zhong, Y. (2021). A colorimetric film based on polyvinyl alcohol/sodium carboxymethyl cellulose incorporated with red cabbage anthocyanin for monitoring pork freshness. Food Packaging Shelf 28, 100641. doi: 10.1016/j.fpsl.2021.100641
Liu, C., Yao, X., Li, G., Huang, L., Xie, Z. (2020). Transcriptomic profiling of purple broccoli reveals light-induced anthocyanin biosynthetic signaling and structural genes. PeerJ 8, e8870. doi: 10.7717/peerj.8870
Lv, X., Li, L., Lu, X., Wang, W., Sun, J., Liu, Y., et al. (2022). Effects of organic acids on color intensification, thermodynamics, and copigmentation interactions with anthocyanins. Food Chem. 396, 133691. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.133691
Mahn, A., Reyes, A. (2012). An overview of health-promoting compounds of broccoli (Brassica oleracea var. italica) and the effect of processing. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 18, 503–514. doi: 10.1177/1082013211433073
Malien-Aubert, C., Dangles, O., Amiot, M. J. (2001). Color stability of commercial anthocyanin-based extracts in relation to the phenolic composition. Protective effects by intra- and intermolecular copigmentation. J. Agr Food Chem. 49, 170–176. doi: 10.1021/jf000791o
Mansour, K. A., Moustafa, S. F., Abdelkhalik, S. M. (2021). High-Resolution UPLC-MS Profiling of Anthocyanins and Flavonols of Red Cabbage (Brassica oleracea L. var. capitata f. rubra DC.) Cultivated in Egypt and Evaluation of Their Biological Activity. Molecules 26, 7567. doi: 10.3390/molecules26247567
Matsufuji, H., Kido, H., Misawa, H., Yaguchi, J., Otsuki, T., Chino, M., et al. (2007). Stability to Light, Heat, and Hydrogen Peroxide at Different pH Values and DPPH Radical Scavenging Activity of Acylated Anthocyanins from Red Radish Extract. J. Agr Food Chem. 55, 3692–3701. doi: 10.1021/jf063598o
McDougall, G. J., Dobson, P., Smith, P., Blake, A., Stewart, D. (2005). Assessing potential bioavailability of raspberry anthocyanins using an in vitro digestion system. J. Agric. Food Chem. 53, 5896–5904. doi: 10.1021/jf050131p
McDougall, G. J., Fyffe, S., Dobson, P., Stewart, D. (2007). Anthocyanins from red cabbage – stability to simulated gastrointestinal digestion. Phytochemistry 68, 1285–1294. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2007.02.004
Mekuriaw, T. A., Abera, M. K. (2024). CaO -catalyzed trans-esterification of brassica carinata seed oil for biodiesel production. Heliyon 10, e33790. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e33790
Moloney, M., Robbins, R. J., Collins, T. M., Kondo, T., Yoshida, K., Dangles, O. (2018). Red cabbage anthocyanins: The influence of d-glucose acylation by hydroxycinnamic acids on their structural transformations in acidic to mildly alkaline conditions and on the resulting color. Dyes Pigments 158, 342–352. doi: 10.1016/j.dyepig.2018.05.057
Moreno, D. A., Pérez-Balibrea, S., Ferreres, F., Gil-Izquierdo, Á., García-Viguera, C. (2010). Acylated anthocyanins in broccoli sprouts. Food Chem. 123, 358–363. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.04.044
Mushtaq, M. A., Pan, Q., Chen, D., Zhang, Q., Ge, X., Li, Z. (2016). Comparative leaves transcriptome analysis emphasizing on accumulation of anthocyanins in brassica: molecular regulation and potential interaction with photosynthesis. Front. Plant Sci. 7. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.00311
Nagaharu, U. (1935). Genome analysis in Brassica carinata with special reference to the experimental formation of Brassica napus, a peculiar mode of fertilization. J. Japanese Bot. 7, 389–452.
Nakakaawa, L., Gbala, I. D., Cheseto, X., Bargul, J. L., Wesonga, J. M. (2023). Oral acute, sub-acute toxicity and phytochemical profile of Brassica carinata A. Braun microgreens ethanolic extract in Wistar rats. J. Ethnopharmacol 305, 116121. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.116121
Nascimento Alves, R., Lorranne Santos Lima, T., Silva Chaves, K., Albuquerque Meireles, B. R. L. (2020). Biodegradable films withBrassica Oleracea Capitataextract as a quality indicator in sheep meat. J. Food Process. Preservation 45. doi: 10.1111/jfpp.14997
Pachulicz, R. J., Yu, L., Jovcevski, B., Bulone, V., Pukala, T. L. (2023). Structural analysis and identity confirmation of anthocyanins in brassica oleracea extracts by direct injection ion mobility-mass spectrometry. ACS Meas Sci. Au 3, 200–207. doi: 10.1021/acsmeasuresciau.2c00058
Patras, D. (2019). Stability and color evaluation of red cabbage waste hydroethanolic extract in presence of different food additives or ingredients. Food Chem. 275, 539–548. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.09.100
Park, C. H., Bong, S. J., Lim, C. J., Kim, J. K., Park, S. U. (2020). Transcriptome Analysis and Metabolic Profiling of Green and Red Mizuna (Brassica rapa L. var. japonica). Foods 9, 1079. doi: 10.3390/foods9081079
Park, W. T., Kim, J. K., Park, S., Lee, S.-W., Li, X., Kim, Y. B., et al. (2012). Metabolic Profiling of Glucosinolates, Anthocyanins, Carotenoids, and Other Secondary Metabolites in Kohlrabi (Brassica oleracea var. gongylodes). J. Agr Food Chem. 60, 8111–8116. doi: 10.1021/jf301667j
Park, K. J., Lee, J.-S., Jo, H. J., Kim, E. S., Lee, H. G. (2022). Antimicrobial and indicator properties of edible film containing clove bud oil-loaded chitosan capsules and red cabbage for fish preservation. Int. J. Biol. Macromolecules 196, 163–171. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.12.027
Park, S., Lee, H., Min, M. K., Ha, J., Song, J., Lim, C. J., et al. (2021). Functional characterization of brF3'H, which determines the typical flavonoid profile of purple chinese cabbage. Front. Plant Sci. 12. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.793589
Pereira, V. A., De Arruda, I. N. Q., Stefani, R. (2015). Active chitosan/PVA films with anthocyanins from Brassica oleraceae(Red Cabbage) as Time–Temperature Indicators for application in intelligent food packaging. Food Hydrocolloids 43, 180–188. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2014.05.014
Pereira, A. R., Fernandes, V. C., Delerue-Matos, C., de Freitas, V., Mateus, N., Oliveira, J. (2024). Exploring acylated anthocyanin-based extracts as a natural alternative to synthetic food dyes: Stability and application insights. Food Chem. 461, 140945. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2024.140945
Platosz, N., Baczek, N., Topolska, J., Szawara-Nowak, D., Misztal, T., Wiczkowski, W. (2020). The blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier is selective for red cabbage anthocyanins and their metabolites. J. Agric. Food Chem. 68, 8274–8285. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.0c03170
Posmyk, M. M., Janas, K. M., Kontek, R. (2009). Red cabbage anthocyanin extract alleviates copper-induced cytological disturbances in plant meristematic tissue and human lymphocytes. BioMetals 22, 479–490. doi: 10.1007/s10534-009-9205-8
Prietto, L., Mirapalhete, T. C., Pinto, V. Z., Hoffmann, J. F., Vanier, N. L., Lim, L.-T., et al. (2017). pH-sensitive films containing anthocyanins extracted from black bean seed coat and red cabbage. LWT 80, 492–500. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2017.03.006
Rahim, M. A., Afrin, K. S., Jung, H. J., Kim, H. T., Park, J. I., Hur, Y., et al. (2019). Molecular analysis of anthocyanin biosynthesis-related genes reveal BoTT8 associated with purple hypocotyl of broccoli (Brassica oleracea var. italica L.). Genome 62, 253–266. doi: 10.1139/gen-2018-0173
Rahim, M. A., Robin, A. H. K., Natarajan, S., Jung, H.-J., Lee, J., Kim, H., et al. (2018). Identification and characterization of anthocyanin biosynthesis-related genes in kohlrabi. Appl. Bioch 184, 1120–1141. doi: 10.1007/s12010-017-2613-2
Rakow, G. (2004). “Species Origin and Economic Importance of Brassica,” in Brassica. Eds. Pua, E. C., Douglas, C. J.(Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin, Heidelberg).
Rameneni, J. J., Choi, S. R., Chhapekar, S. S., Kim, M. S., Singh, S., Yi, S. Y., et al. (2020). Red chinese cabbage transcriptome analysis reveals structural genes and multiple transcription factors regulating reddish purple color. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21. doi: 10.3390/ijms21082901
Ren, R. K., Zemel, R. S. (2015). “Exploring models and data for image question answering.” in Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. 28. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1505.02074
Rezq, A. (2018). Antioxidant role of cabbage (Brassica oleracea) ethanolic extract in hepatoprotective of N-nitrosodiethylamine induced initiation of hepatocellular carcinoma in rat liver. Egypt J. Nutr. 32, 1–53.
Rodriguez-Amaya, D. B. (2016). Natural food pigments and colorants. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 7, 20–26. doi: 10.1016/j.cofs.2015.08.004
Roy, S., Rhim, J. W. (2021). Anthocyanin food colorant and its application in pH-responsive color change indicator films. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 61, 2297–2325. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2020.1776211
Saberian, H., Esmailian, A., Hosseini, F. (2021). Optimization of anthocyanin extraction from red cabbage and its application in low calorie gummy candy. Food Sci Technol Int. 18, 129–140. doi: 10.29252/fsct.18.01.12
Salehi, B., Quispe, C., Butnariu, M., Sarac, I., Marmouzi, I., Kamle, M., et al. (2021). Phytotherapy and food applications from Brassica genus. Phytother. Res. 35, 3590–3609. doi: 10.1002/ptr.7048
Saluk, J., Bijak, M., Kołodziejczyk-Czepas, J., Posmyk, M., Janas, K., Wachowicz, B. (2012). Anthocyanins from red cabbage extract — evidence of protective effects on blood platelets. Open Life Sci. 7, 655–663. doi: 10.2478/s11535-012-0057-9
Saluk, J., Bijak, M., Posmyk, M. M., Zbikowska, H. M. (2015). Red cabbage anthocyanins as inhibitors of lipopolysaccharide-induced oxidative stress in blood platelets. Int. J. Biol. Macromol 80, 702–709. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2015.07.039
Šamec, D., Pavlović, I., Salopek-Sondi, B. (2016). White cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata f. alba): botanical, phytochemical and pharmacological overview. Phytochem. Rev. 16, 117–135. doi: 10.1007/s11101-016-9454-4
Sankhari, J. M., Thounaojam, M. C., Jadeja, R. N., Devkar, R. V., Ramachandran, A. V. (2012). Anthocyanin-rich red cabbage (Brassica oleracea L.) extract attenuates cardiac and hepatic oxidative stress in rats fed an atherogenic diet. J. Sci. Food Agric. 92, 1688–1693. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.5532
Scalzo, R. L., Genna, A., Branca, F., Chedin, M., Chassaigne, H. (2008). Anthocyanin composition of cauliflower (Brassica oleracea L. var. botrytis) and cabbage (B. oleracea L. var. capitata) and its stability in relation to thermal treatments. Food Chem. 107, 136–144. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2007.07.072
Sezgin, G. C., Ocsoy, I. (2023). Anthocyanin-rich black carrot (Daucus carota ssp. sativus var. atrorubens Alef.) and red cabbage (Brassica oleracea) extracts incorporated biosensor for colorimetric detection of Helicobacter pylori with color image processing. Braz. J. Microbiol. 54, 897–905. doi: 10.1007/s42770-023-00989-1
Sharef, M., Aljamali, N., Jawd, D. S., Jawd, S., Aljamali, S. (2019). Evaluation for the effectiveness of Red Cabbage extract against hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity induced by gentamicin antibiotic in male Albino rats. Int. J. Pharm. Res. 11, 1636.
Shiyan, S., Herlina, H., Sari, L. R. (2018). Nephroprotective of anthocyanin pigments extract from red cabbage (Brassica Oleracea L. Var. Capitata F. Rubra) against gentamicin-capopril-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 11, 432–436. doi: 10.22159/ajpcr.2018.v11i4.20373
Silva-Pereira, M. C., Teixeira, J. A., Pereira-Júnior, V. A., Stefani, R. (2015). Chitosan/corn starch blend films with extract from Brassica oleraceae(red cabbage) as a visual indicator of fish deterioration. LWT 61, 258–262. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2014.11.041
Soengas, P., Cartea, M. E., Francisco, M., Sotelo, T., Velasco, P. (2012). New insights into antioxidant activity of Brassica crops. Food Chem. 134, 725–733. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.02.169
Song, B., Xu, H., Chen, L., Fan, X., Jing, Z., Chen, S., et al. (2020). Study of the relationship between leaf color formation and anthocyanin metabolism among different purple pakchoi lines. Molecules 25, 4809. doi: 10.3390/molecules25204809
Song, H., Yi, H., Lee, M., Han, C. T., Lee, J., Kim, H., et al. (2018). Purple Brassica oleracea var. capitata F. rubra is due to the loss of BoMYBL2-1 expression. BMC Plant Biol. 18, 82. doi: 10.1186/s12870-018-1290-9
Steingass, C. B., Burkhardt, J., Bäumer, V., Kumar, K., Mibus-Schoppe, H., Zinkernagel, J., et al. (2023). Characterisation of acylated anthocyanins from red cabbage, purple sweet potato, and Tradescantia pallida leaves as natural food colourants by HPLC-DAD-ESI(+)-QTOF-MS/MS and ESI(+)-MSn analysis. Food Chem. 416, 135601. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2023.135601
Tan, C., Chen, H., Dai, G., Liu, Y., Shen, W., Wang, C., et al. (2023). Identification and characterization of the gene BraANS.A03 associated with purple leaf color in pak choi (Brassica rapa L. ssp. chinensis). Planta 258, 19. doi: 10.1007/s00425-023-04171-7
Tang, K., Karamat, U., Li, G., Guo, J., Jiang, S., Fu, M., et al. (2024). Integrated metabolome and transcriptome analyses reveal the role of BoGSTF12 in anthocyanin accumulation in Chinese kale (Brassica oleracea var. alboglabra). BMC Plant Biol. 24, 335. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-05016-5
Tang, L., Xiao, D., Yin, Y., Wang, H., Wang, J., Liu, T., et al. (2022). Comparative transcriptome analysis of purple and green non-heading chinese cabbage and function analyses of bcTT8 gene. Genes (Basel) 13. doi: 10.3390/genes13060988
Thangam, R., Suresh, V., Rajkumar, M., Vincent, J. D., Gunasekaran, P., Anbazhagan, C., et al. (2013). Antioxidant and in vitro anticancer effect of 2-pyrrolidinone rich fraction of Brassica oleracea var. capitata through induction of apoptosis in human cancer cells. Phytother. Res. 27, 1664–1670. doi: 10.1002/ptr.4908
Tong, T., Niu, Y. H., Yue, Y., Wu, S. C., Ding, H. (2017). Beneficial effects of anthocyanins from red cabbage (Brassica oleracea L. var. capitata L.) administration to prevent irinotecan-induced mucositis. J. Funct. Foods 32, 9–17. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2017.01.051
Trouillas, P., Sancho-García, J. C., De Freitas, V., Gierschner, J., Otyepka, M., Dangles, O. (2016). Stabilizing and modulating color by copigmentation: insights from theory and experiment. Chem. Rev. 116, 4937–4982. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00507
Vale, A. P., Santos, J., Melia, N., Peixoto, V., Brito, N. V., Oliveira, M. B. P. P. (2015). Phytochemical composition and antimicrobial properties of four varieties of sprouts. Food Control 55, 248–256. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2015.01.051
Veber, B., Camargo, A., Dalmagro, A. P., Bonde, H. L. P., Magro, D. D. D., Lima, D. D., et al. (2020). Red cabbage (Brassica oleracea L.) extract reverses lipid oxidative stress in rats. Acad. Bras. Cienc 92, e20180596. doi: 10.1590/0001-3765202020180596
Velasco, P., Rodríguez, V. M., Francisco, M., Cartea, M. E., Soengas, P. (2017). “Genetics and breeding of Brassica crops. Glucosinolates.” in Reference Series in Phytochemistry, eds. Mérillon, J.M., Ramawat, K., 61–86. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-25462-3_2
Volden, J., Bengtsson, G. B., Wicklund, T. (2009). Glucosinolates, l-ascorbic acid, total phenols, anthocyanins, antioxidant capacities and colour in cauliflower (Brassica oleracea L. ssp. botrytis); effects of long-term freezer storage. Food Chem. 112, 967–976. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.07.018
Wagh, R. V., Khan, A., Priyadarshi, R., Ezati, P., Rhim, J.-W. (2023). Cellulose nanofiber-based multifunctional films integrated with carbon dots and anthocyanins from Brassica oleracea for active and intelligent food packaging applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromolecules 233, 123567. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.123567
Wiczkowski, W., Szawara-Nowak, D., Romaszko, J. (2016). The impact of red cabbage fermentation on bioavailability of anthocyanins and antioxidant capacity of human plasma. Food Chem. 190, 730–740. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.06.021
Wiczkowski, W., Szawara-Nowak, D., Topolska, J. (2013). Red cabbage anthocyanins: Profile, isolation, identification, and antioxidant activity. Food Res. Int. 51, 303–309. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2012.12.015
Wiczkowski, W., Topolska, J., Honke, J. (2014). Anthocyanins profile and antioxidant capacity of red cabbages are influenced by genotype and vegetation period. J. Funct. Foods 7, 201–211. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2014.02.011
Xie, Q., Hu, Z., Zhang, Y., Tian, S., Wang, Z., Zhao, Z., et al. (2014). Accumulation and molecular regulation of anthocyanin in purple tumorous stem mustard (Brassica juncea var. tumida Tsen et Lee). J. Agric. Food Chem. 62, 7813–7821. doi: 10.1021/jf501790a
Xie, L., Su, H., Sun, C., Zheng, X., Chen, W. (2018). Recent advances in understanding the anti-obesity activity of anthocyanins and their biosynthesis in microorganisms. Trend Food Sci. Technol. 72, 13–24. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2017.12.002
Xu, W., Zhang, N., Zhang, Z., Jing, P. (2019). Effects of dietary cyanidin-3-diglucoside-5-glucoside complexes with rutin/Mg(II) against H(2)O(2)-induced cellular oxidative stress. Food Res. Int. 126, 108591. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2019.108591
Yeo, H. J., Ki, W. Y., Lee, S., Kim, C. Y., Kim, J. K., Park, S. U., et al. (2023). Metabolite profiles and biological activities of different phenotypes of Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa ssp. Pekinensis). Food Res. Int. 174, 113619. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2023.113619
Yin, N. W., Wang, S. X., Jia, L. D., Zhu, M. C., Yang, J., Zhou, B. J., et al. (2019). Identification and characterization of major constituents in different-colored rapeseed petals by UPLC-HESI-MS/MS. J. Agric. Food Chem. 67, 11053–11065. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.9b05046
Yuan, Y., Chiu, L.-W., Li, L. (2009). Transcriptional regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis in red cabbage. Planta 230, 1141–1153. doi: 10.1007/s00425-009-1013-4
Zeng, H., Zheng, T., Li, Y., Chen, Q., Xue, Y., Tang, Q., et al. (2023). Characterization variation of the differential coloring substances in rapeseed petals with different colors using UPLC-HESI-MS/MS. Molecules 28. doi: 10.3390/molecules28155670
Zhang, Y., Chen, G., Dong, T., Pan, Y., Zhao, Z., Tian, S., et al. (2014). Anthocyanin accumulation and transcriptional regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis in purple bok choy (Brassica rapa var. chinensis). J. Agric. Food Chem. 62, 12366–12376. doi: 10.1021/jf503453e
Zhang, B., Hu, Z., Zhang, Y., Li, Y., Zhou, S., Chen, G. (2012). A putative functional MYB transcription factor induced by low temperature regulates anthocyanin biosynthesis in purple kale (Brassica Oleracea var. acephala f. tricolor). Plant Cell Rep. 31, 281–289. doi: 10.1007/s00299-011-1162-3
Zhang, Y., Hu, Z., Zhu, M., Zhu, Z., Wang, Z., Tian, S., et al. (2015). Anthocyanin Accumulation and Molecular Analysis of Correlated Genes in Purple Kohlrabi (Brassica oleracea var. gongylodes L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 63, 4160–4169. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.5b00473
Zhang, N., Jing, P. (2022). Anthocyanins in Brassicaceae: composition, stability, bioavailability, and potential health benefits. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 62, 2205–2220. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2020.1852170
Zhang, N., Jing, P. (2023). Red cabbage anthocyanins attenuate cognitive impairment by attenuating neuroinflammation and regulating gut microbiota in aging mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 71, 15064–15072. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c03183
Zhang, J., Wu, J., Liu, F., Tong, L., Chen, Z., Chen, J., et al. (2019). Neuroprotective effects of anthocyanins and its major component cyanidin-3-O-glucoside (C3G) in the central nervous system: An outlined review. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 858, 172500. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.172500
Zhang, H., Xu, Z., Zhao, H., Wang, X., Pang, J., Li, Q., et al. (2020). Anthocyanin supplementation improves anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory capacity in a dose-response manner in subjects with dyslipidemia. Redox Biol. 32, 101474. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2020.101474
Zhang, K., Yang, D., Hu, Y., Njogu, M. K., Qian, J., Jia, L., et al. (2022). Integrated Analysis of Transcriptome and Metabolome Reveals New Insights into the Formation of Purple Leaf Veins and Leaf Edge Cracks in Brassica juncea. Plants 11. doi: 10.3390/plants11172229
Zhang, N., Zhang, Z., Xu, W., Jing, P. (2021). TMT-based quantitative proteomic analysis of hepatic tissue reveals the effects of dietary cyanidin-3-diglucoside-5-glucoside-rich extract on alleviating D-galactose-induced aging in mice. J. Proteomics 232, 104042. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2020.104042
Zhao, A., Jeffery, E. H., Miller, M. J. (2022). Is bitterness only a taste? The expanding area of health benefits of brassica vegetables and potential for bitter taste receptors to support health benefits. Nutrients 14, 1434. doi: 10.3390/nu14071434
Zhao, Y., Qi, X., Liu, Z., Zheng, W., Guan, J., Liu, Z., et al. (2022). Transcriptome and Metabolome Profiling to Explore the Causes of Purple Leaves Formation in Non-Heading Chinese Cabbage (Brassica rapa L. ssp. chinensis Makino var. mutliceps Hort.). Foods 11. doi: 10.3390/foods11121787
Zhou, Q., Xu, X., Li, M., Yang, X., Wang, M., Li, Y., et al. (2024). Laser capture microdissection transcriptome (LCM RNA-seq) reveals BcDFR is a key gene in anthocyanin synthesis of non-heading Chinese cabbage. BMC Genomics 25, 425. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10341-y
Zielińska, M., Lewandowska, U., Podsędek, A., Cygankiewicz, A. I., Jacenik, D., Sałaga, M., et al. (2015). Orally available extract from Brassica oleracea var. capitata rubra attenuates experimental colitis in mouse models of inflammatory bowel diseases. J. Funct. Foods 17, 587–599. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2015.05.046
Keywords: Brassica crops, anthocyanin, acylation, natural colorants, health benefit
Citation: Li X, Wang F, Ta N and Huang J (2025) The compositions, characteristics, health benefits and applications of anthocyanins in Brassica crops. Front. Plant Sci. 16:1544099. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1544099
Received: 12 December 2024; Accepted: 20 January 2025;
Published: 17 February 2025.
Edited by:
Yongtai Yin, Temasek Life Sciences Laboratory, SingaporeReviewed by:
Jianwei Gu, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, ChinaDao-Zong Chen, Gannan Normal University, China
Copyright © 2025 Li, Wang, Ta and Huang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Na Ta, dGF0YW5hbmExMjE2QDE2My5jb20=; Jinyong Huang, amlueWh1YW5nQHp6dS5lZHUuY24=
 Xinjie Li1
Xinjie Li1 Jinyong Huang
Jinyong Huang