
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Plant Sci., 26 March 2025
Sec. Functional and Applied Plant Genomics
Volume 16 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2025.1526700
 Sucharita Mohapatra1,2
Sucharita Mohapatra1,2 S. R. Prabhukarthikeyan1*
S. R. Prabhukarthikeyan1* Gayatri Biswal2
Gayatri Biswal2 Mihira Kumara Mishra2
Mihira Kumara Mishra2 Soumya Shephalika Dash1
Soumya Shephalika Dash1 Gyanisha Nayak1
Gyanisha Nayak1 U. Keerthana1
U. Keerthana1 C. Parameswaran1
C. Parameswaran1 P. Panneerselvam1
P. Panneerselvam1 S. D. Mohapatra1
S. D. Mohapatra1Rice blast, caused by Magnaporthe oryzae, is one of the most devastating diseases affecting rice crops. We investigated effectiveness of Streptomyces spp. against M. oryzae. The results revealed that among the Streptomyces spp., Streptomyces caeruleatus strain S14 demonstrated superior effectiveness in inhibiting the mycelial growth of M. oryzae (74.7%). The strain was identified by sequencing 16S rRNA region. Further, the complete genome sequence of this highly effective strain was acquired using the Illumina NovaSeq 6000 (PE 150), revealing a total genome length of 9,750,804 base pairs (9.7 Mb). The genome comprises 9,191 protein-coding sequences (CDS), 68 transfer RNA (tRNA) genes, 6 ribosomal RNA (rRNA) genes, with an average G+C content of 71.03%. The Streptomyces caeruleatus S14 genome, annotated with RASTtk and genetic code 11, falls under the superkingdom Bacteria. According to annotation statistics from PATRIC, it is a high-quality genome with 97.9% coarse consistency, 93.7% fine consistency, and completeness of 99.9%. The genome included genes related to metabolism, protein processing, defense, virulence, energy, stress response, membrane transport, regulation, cell signaling, cell envelope, DNA processing, cellular activities, RNA processing, and miscellaneous. The complete genome sequence of S. caeruleatus suggests that it offers valuable insights into its antimicrobial activity and provide key genetic traits responsible for pathogen suppression. Incidentally this is the first whole genome sequencing report of S. caeruleatus isolated from rice rhizosphere soil in India.
Rice (Oryza sativa L.) is a vital food crop and a staple diet for people worldwide, particularly in Asia. However, its production is affected by various biotic and abiotic stresses (Chaiharn et al., 2009). Rice blast, caused by the filamentous, ascomycetous fungus M. oryzae, is a major biotic stress for rice crops. The yield losses from rice blast vary between 10-30% in different rice-producing countries, with losses potentially reaching up to 50% during severe disease outbreaks (Asibi et al., 2019; Luh Suriani et al., 2020). To increase agricultural production, modern agriculture often depends on fungicides. However, the usage of fungicides result in environmental pollution, pesticide resistance, residual issues, soil quality degradation, and damages the natural ecosystems (Pooja and Katoch, 2014; Law et al., 2017). To mitigate the detrimental effects of these toxic chemicals, biocontrol agents could be regarded as essential candidates for promoting sustainable agriculture (Kenawy et al., 2019; Kalam et al., 2020; Basu et al., 2021; Naz et al., 2022; Vinothini et al., 2024). Biocontrol of plant diseases is a time-consuming process with little immediate profits, but it offers long-lasting, cost-effective, and safe solutions for managing plant health (Prabhukarthikeyan et al., 2019; Sawant et al., 2023, 2024). Nowadays biological control by using potential actinomycetes is receiving greater attention all over the world. Many of them belong to the group of Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) (Jones and Elliot, 2017).
Actinobacteria, commonly known as actinomycetes is a phylum of Gram-positive, filamentous bacteria with a high % G+C content and they are found in larger range of habitats, which include both terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems (Amin et al., 2019; Rego et al., 2019; Omar et al., 2022). Because of its effective secondary metabolite synthesis, this phylum is important in the sectors of agriculture, medicine, and industry (Harir et al., 2018; Ferraiuolo et al., 2021). Actinobacteria have attracted a lot of attention from the scientific community for their ability to produce a wide range of bioactive compounds with antimicrobial, antitumoral, and immunosuppressant activities, making them a key focus of research (Barka et al., 2016; Sudha et al., 2022). Actinobacteria play a crucial role in suppressing fungal pathogens in both controlled environments and living organisms by triggering key genes involved in systemic acquired resistance (SAR) and the jasmonate/ethylene (JA/ET) pathways (Conn et al., 2008). They employ diverse antagonistic strategies, including competition for space and nutrients, antibiotic production, siderophore secretion, lytic enzyme release, volatile organic compound (VOC) emission and stimulation of host resistance (Gong et al., 2022; Kaari et al., 2022).
Streptomyces are known to be the largest genus of phylum Actinobacteria, which are ubiquitous in soil. They are essential in the biological buffering of soils and are integral to the decomposition of organic matter, which is essential for promoting crop production. The production of antifungal compounds and extracellular hydrolytic enzymes by various Streptomyces spp. has been extensively studied, highlighting their significant role in biocontrol, particularly against phytopathogens including rice blast disease (Gonzalez-Franco and Robles-Hernandez, 2009; Dave et al., 2024). For this reason, the isolation, characterization and identification of novel and efficient Streptomyces strains from natural resources is an important achievement. Bacterial genomes can be examined using whole genome sequencing (WGS), which is essential for genome annotation, revealing numerous genes with homology to known transporters, drug targets, virulence factors, and antibiotic resistance genes. Streptomyces spp. are known to have a linear chromosome ranging in size from 5.1 to 10.1 Mbp (Kirby et al., 2012; Lee et al., 2020). There are many different types of sequencing have been used for Whole genome sequencing. WGS of Streptomyces bacteria has been done using both PacBio and Illumina. PacBio provides long reads and relatively expensive, while Illumina is cost-effective and produces short reads. But by far the most practical microbial genomics sequencing platform is Illumina (Shin et al., 2013; Rhoads and Au, 2015).
In this study, we reported the complete genome sequence of S. caeruleatus, which was isolated from rhizosphere soil of rice from Cuttack district, Odisha, India. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first WGS report of S. caeruleatus which was isolated from rice rhizosphere soil in India.
Streptomyces spp. were isolated from rice rhizosphere soil of Odisha, India (Supplementary Table S1). Soil sample was serially diluted and spread evenly over the surface of SCA (Starch Casein Agar) media treated with nystatin (50 μg/ml) and rifampicin (2.5 μg/ml) in a Petridish to prevent fungal growth. After seven days of incubation at 30°C, the morphologically different Streptomyces colonies were collected and inoculated into International Streptomyces Project (ISP2) agar medium, which was then incubated for seven days at 28°C (Shirling and Gottlieb, 1966). Then the Streptomyces isolates were stored at -20°C in glycerol stocks for further use.
M. oryzae isolate RLB 06 (NCBI accession number- MT093385) was obtained from Plant pathology, Division of Crop protection, ICAR- National Rice Research Institute, Cuttack, Odisha, India.
The dual culture method was used to assess the antifungal activity of Streptomyces spp. against M. oryzae (Khare et al., 2010). Streptomyces isolates were cultured on ISP2 medium for seven days, and a loopful of each antagonistic isolate was inoculated 1 cm from the edge of a petri plate containing Potato Dextrose Agar (PDA) medium. A 7-day-old mycelial disc (5 mm in diameter) of M. oryzae was placed on the opposite side of the PDA plate (9 cm in diameter). The PDA Petridish containing only M. oryzae was used as control. All plates were incubated at 28°C for 7 days. Following seven days of incubation period at 28°C, the diameter of the M. oryzae culture in the control and dual culture plates was measured in order to calculate the percentage of inhibition of radial growth (PIRG) using the formula below:
where I represent inhibition of mycelial growth, C represents fungal colony growth in the control plate, and T is the fungal colony growth in the dual culture plate.
Biochemical characterization including gram staining, catalase test, gelatin hydrolysis, citrate utilization test, starch hydrolysis, indole test, HCN test, casein hydrolysis and cellulase test was performed for the effective strains in our previous study (Mohapatra et al., 2023).
The genomic DNA of the most effective strain, S. caeruleatus was extracted using the Cetyl Trimethyl Ammonium Bromide (CTAB) (Hopwood, 2000). Extracted DNA was treated with RNase A to remove any RNA in the preparation and purified. Bacterial identification was conducted by 16S rRNA gene sequences through PCR using two universal primers, 27F (5′-AGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG-3′) and 1492R (5′-GGTTACCTTGTTACGACTT-3′), followed by Sanger sequencing. The amplification was performed using an automated thermocycler (Takara) with the following conditions: an initial denaturation at 94°C for three minutes, followed by 40 cycles of denaturation at 94°C for thirty seconds, annealing at 50°C for one minute, and elongation at 72°C for ten minutes. DNA quality and quantity were assessed by gel electrophoresis and NanoDrop respectively. The identified 16S rRNA sequences were aligned with the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) database using BLAST. Sanger sequencing of the partial 16S rRNA gene allowed for genus-level identification before proceeding with whole-genome sequencing. For whole-genome sequencing (WGS), the PCR product of the bacterial DNA was sent to Novelgene Technologies Pvt. Ltd. in Hafeezpet, Hyderabad. WGS was conducted on the Illumina NovaSeq6000 (PE 150) following standard Illumina protocols.
The genome of the bacterial strain S. caeruleatus was comprehensively analyzed by submitting the sequencing reads to the Pathosystems Resource Integration Center (PATRIC) (Wattam et al., 2017). The sequencing data, containing adapter sequences and low-quality reads, was pre-processed using FASTP v0.23.4 to obtain high-quality reads, with a quality threshold of Q20. Reads with a mapping quality below Q20 were excluded from further analysis. The quality-trimmed reads were subsequently de novo assembled using SPAdes v3.15.5 with error correction (Bankevich et al., 2012). Scaffolding of the assembled contigs was performed using RagTag v2.1.0, employing a reference genome (GCF_001514235.1). The assembled genome’s contiguity and completeness were assessed using single-copy orthologs with QUASTv5.1 (Quality Assessment Tool for Genome Assemblies) (Gurevich et al., 2013) and BUSCO v5.7.0 (Benchmarking Universal Single-Copy Orthologs) (Simao et al., 2015). The BUSCO pipeline, run against the bacteria_odb10 database, was used for quantitative analysis of the assembly’s completeness.
The RASTtk v1.3.0 was used to annotate the genome of S. caeruleatus (Brettin et al., 2015) and genetic code 11. This process involved comparing the genome to others in PATRIC to identify gene functions, classify them into functional categories (Subsystems), and perform phylogenetic analysis. The Gene Ontology (GO) assignments, Enzyme Commission (EC) numbers, and KEGG pathways were determined using the blastKOALA server to annotate gene functions and pathways. The genome of Streptomyces was also annotated for genus-specific protein families (PLFams) and cross-genus protein families (PGFams) (Davis et al., 2016). Additionally, eggNOG-mapper v2.1.11 was used to identify clusters of orthologous groups (COG) for the predicted protein sequences. The complete genome was screened against known sequences in databases like CARD, NDARO, DrugBank, TTD, TCDB, PATRIC-VF, and Victors in order to identify antibiotic resistance genes, transporters, drug targets, and virulence factors. The Genome Annotation Service in PATRIC uses a k-mer-based method for detecting antimicrobial resistance (AMR) genes, using PATRIC’s curated collection of representative AMR gene sequences. A subsystem consists of a collection of proteins that collaborate to carry out a particular biological activity or create a structural complex. PATRIC annotation comprises the analysis of subsystems unique to each genome (Overbeek et al., 2005).
The phylogenetic tree was generated using the complete genome sequence of the S. caeruleatus S14, with additional whole genome sequences downloaded from the NCBI database. Using Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis software (MEGA-XI), the Neighbor-Joining technique, aligned with MUSCLE, was used to deduce the evolutionary history (Saitou and Nei, 1987). The branches are accompanied with the percentage of replicate trees in which the linked taxa clustered together in the bootstrap test (1000 replicates) (Felsenstein, 1985). This analysis involved total 19 different strains of Streptomyces which included an outgroup Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain PPF-1. The genetic distance was analyzed using the Kimura 2-parameter model in MEGA software.
A total of 85 isolates of Streptomyces spp. were isolated from different rice growing areas of Odisha, Eastern India. All the isolates were tested against M. oryzae. The result demonstrated that the S. caeruleatus S14 isolate exhibited a high level of inhibition, with an average inhibition area of 74.7% compared to other isolates. The untreated control displayed no inhibitory activity against M. oryzae, indicating the maximum growth of fungus (Figure 1; Table 1). PCR amplification of 16S rRNA gene showed an amplicon size of 1500bp (Figure 2).
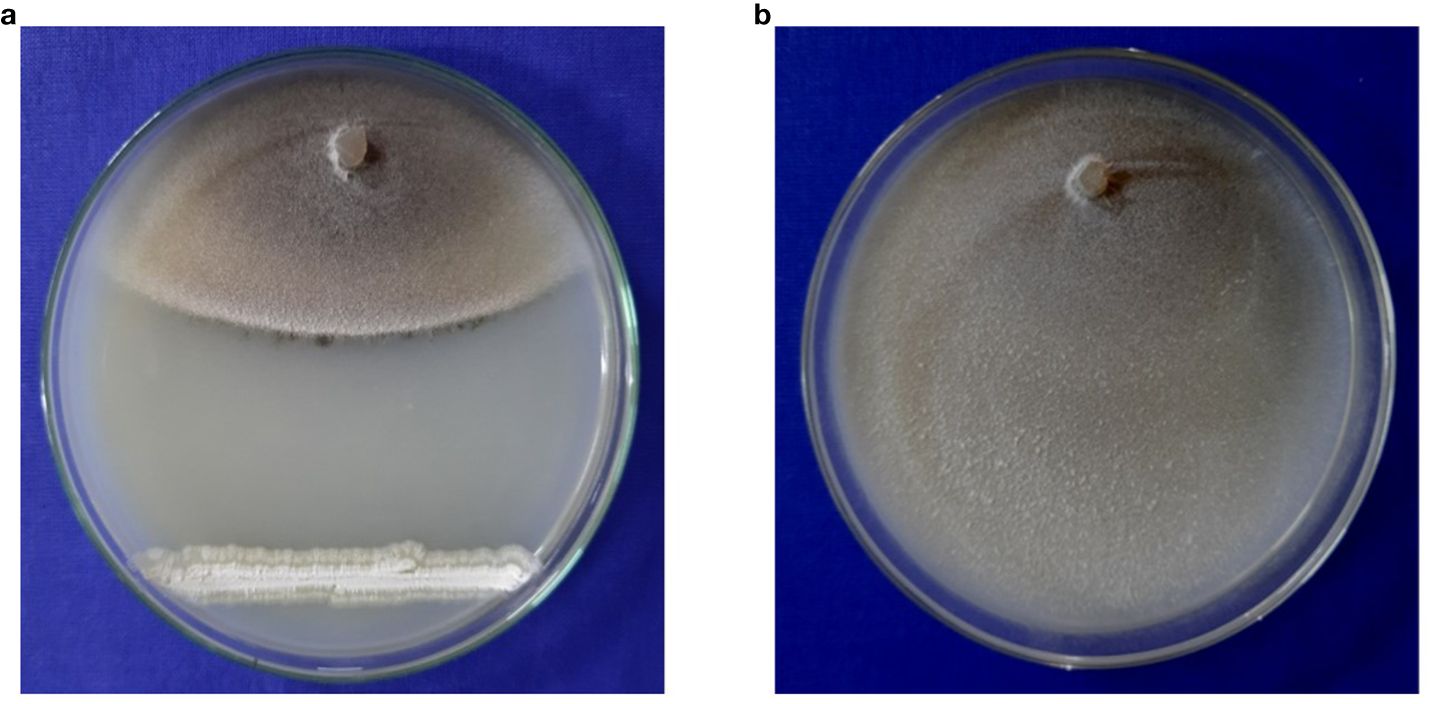
Figure 1. Antifungal activity of Streptomyces caeruleatus (a) Dual culture experiment of streptomyces caeruleatus against Magnaporthe oryzae (b) Isolate of Magnaporthe oryzae without biocontrol agent as control.
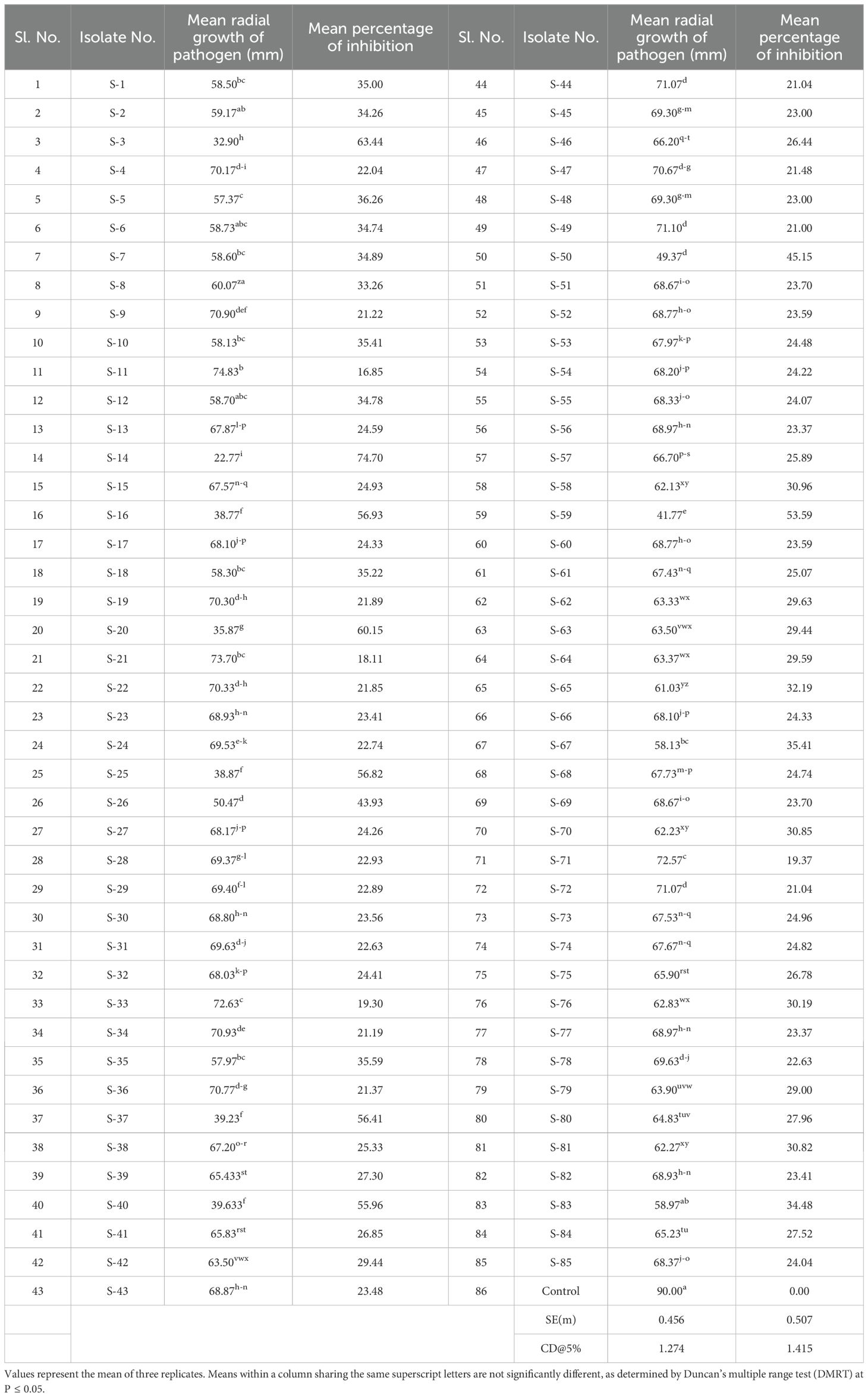
Table 1. Screening of different Streptomyces spp. against M. oryzae for antifungal activity in vitro..
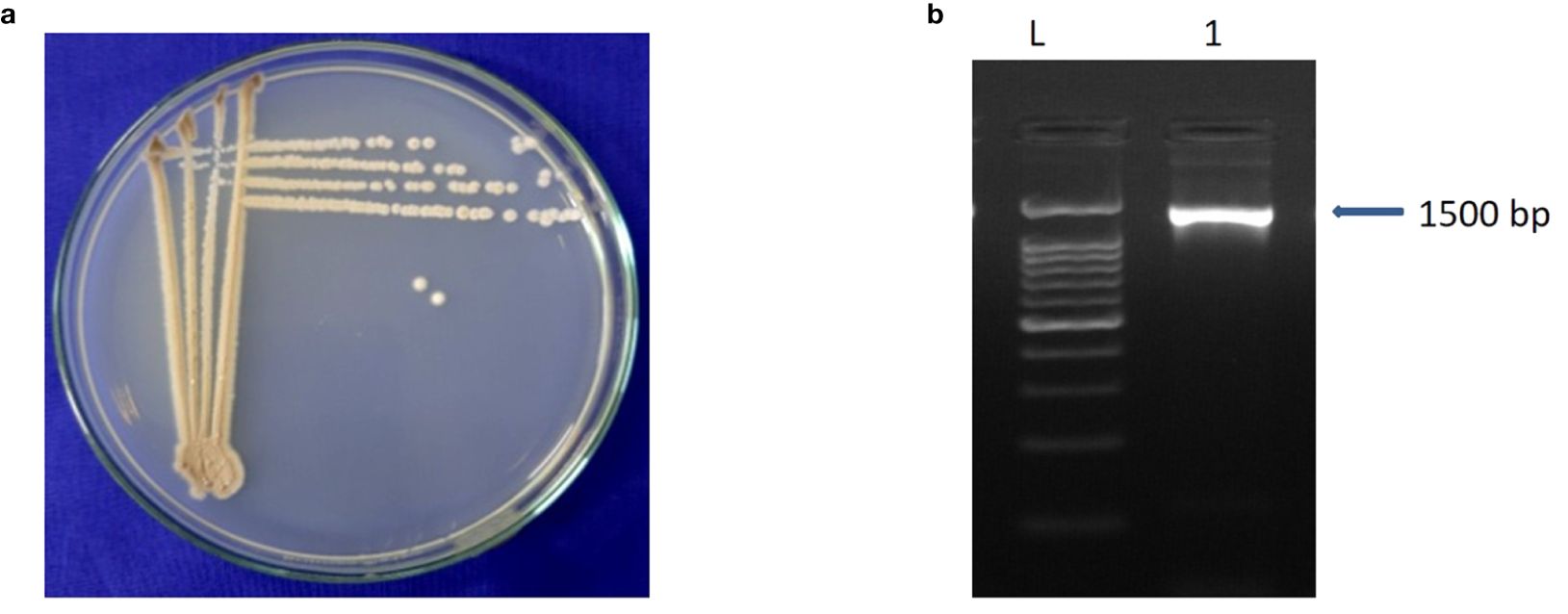
Figure 2. Characteristics of Streptomyces caeruleatus (a) colony morphology (b) PCR amplicons of 16S rRNA (L- 100 bps Ladder, 1- Streptomyces caeruleatus). Forward primer 27F (5’AGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG-3’) and reverse primer 1492R (5’ GGTTACCTTGTTACGACTT-3).
Whole genome sequencing analysis of the S. caeruleatus strain S14 revealed 186 contigs, with a total length of 9,750,804 bp (9.7 Mb). The N50 contig length, representing the shortest sequence length that accounts for 50% of the genome, is 603,168 bp. The genome has an average coverage of 119X and a G+C content of 71.03%. The L50 value, indicating the minimum number of contigs that together represent 50% of the genome’s length, is 7. Annotation statistics and comparisons with other genomes of the same species in PATRIC demonstrated that the genome quality is excellent, with a coarse consistency of 97.9%, fine consistency of 93.7%, and completeness of 99.9% (Supplementary Table S2). The S. caeruleatus S14 genome was annotated with the RAST toolkit (RASTtk), assigned the unique genome identifier 661399.5. The genome was annotated with genetic code 11 and categorized within the superkingdom Bacteria. This genome is classified as follows: cellular organisms > Bacteria > Terrabacteria group > Actinomycetota> Actinomycetes > Streptomycetales> Streptomycetaceae> Streptomyces >Streptomyces caeruleatus.
The genome of S.caeruleatus strain S14 comprises 9,191 protein-coding sequences (CDS) (Supplementary Table S3), 68 transfer RNA (tRNA) genes, and 6 ribosomal RNA (rRNA) genes (Figure 3). Additionally, the genome contains 2,992 hypothetical proteins and 6,199 proteins with functional assignments. Among these, 1,562 proteins have Enzyme Commission (EC) numbers, 1,365 have Gene Ontology (GO) assignments, and 1,208 proteins are mapped with pathway assignments. The genome also includes 8,020 proteins belonging to genus-specific protein families (PLfams) and 8,199 proteins belonging to cross-genus protein families (PGFams) (Supplementary Table S4; Table 2).
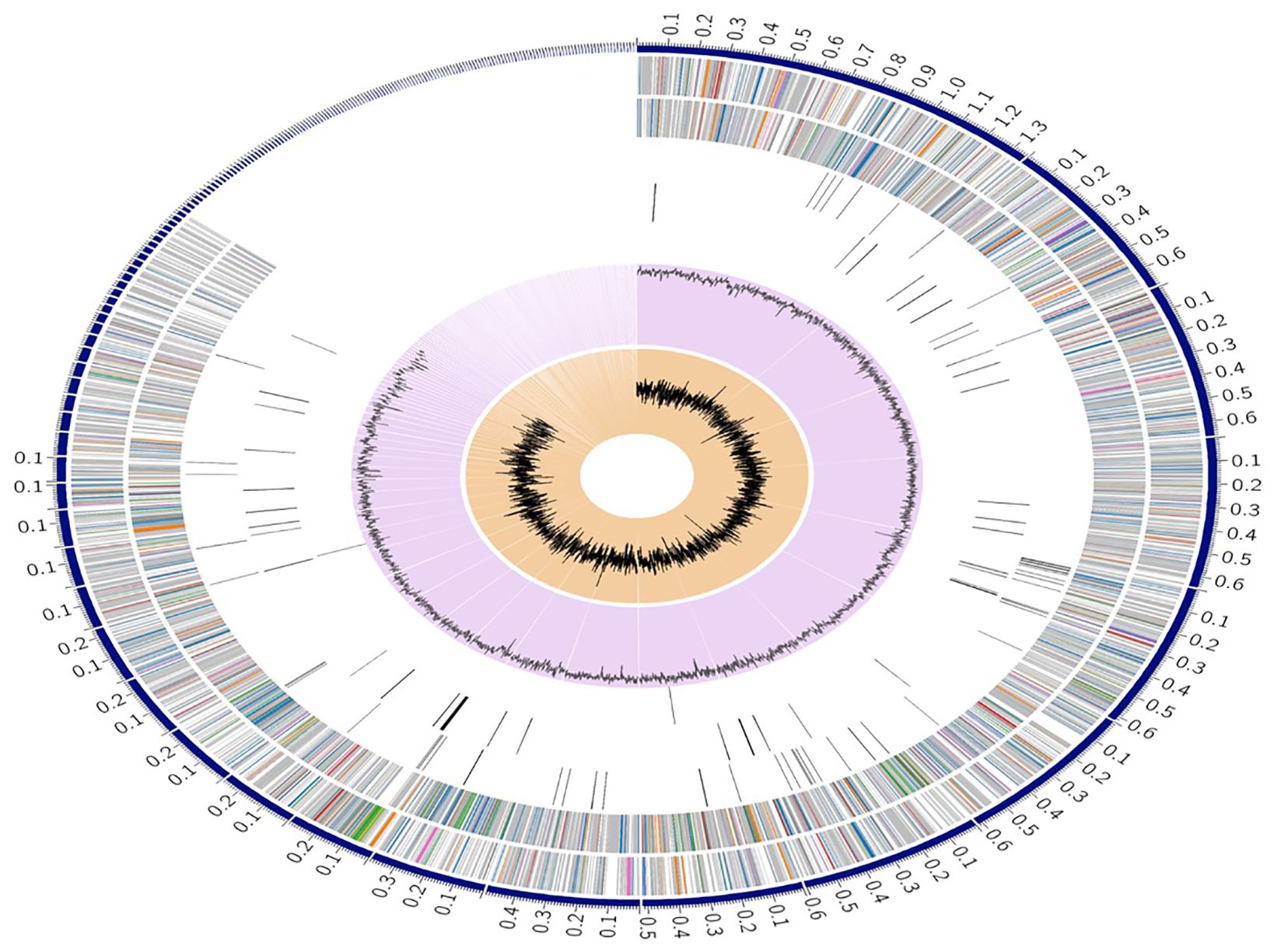
Figure 3. A circular graphical display of the distribution of the genome annotations. This includes, from outer to inner rings, the contigs, CDS on the forward strand, CDS on the reverse strand, RNA genes, CDS with homology to known antimicrobial resistance genes, CDS with homology to known virulence factors, GC content and GC skew. The colors of the CDS on the forward and reverse strand indicate the subsystem that these genes belong to.
Quantitative analysis of the assembly’s completeness was performed using the BUSCO pipeline against the bacteria_odb10 database, identifying 99.2% of orthologous genes present, with only 1 gene fragmented. The BUSCO score was C:99.2% [S:96.8%, D:2.4%], F:0.8%, M:0.0%, n:124 (Supplementary Table S5; Figure 4). All of the protein-coding genes were allocated to clusters of orthologous groups (COGs) and classified into different functional categories using EggNOG mapper (Supplementary Table S6). In addition to these features, the genome annotation identified various biosynthetic gene clusters, which are crucial for the production of secondary metabolites. This highlights the potential of S. caeruleatus S14 for producing novel antibiotics and other bioactive compounds. The detailed analysis of regulatory elements and signaling pathways also provides insights into the complex regulatory networks governing the organism’s metabolic processes and environmental interactions. The comprehensive genomic characterization of S. caeruleatus S14 underscores its significance in biotechnology and its potential applications in agriculture, particularly in biocontrol and plant growth promotion.
The genome of S.caeruleatus includes specialty genes viz., antibiotic resistance-54 from (PATRIC), antibiotic resistance-6 (CARD), antibiotic resistance -2 (NDARO), drug target -6 (TTD), drug target-18 (Drug Bank), transporter-64 (TCDB), virulence factor -5 (Victors), and virulence factor -7 (Patric VF) (Table 3).
The analysis of S. caeruleatus for the presence of subsystems revealed the occurrence of superclasses, each containing varying numbers of subsystems (SS) and associated families/genes, as detailed in (Figure 5). The genome of S. caeruleatus contains several distinct superclasses, including: metabolism (104 SS, 1059 Genes), stress response, virulence, defense (37 SS, 187 Genes), protein processing (42 SS, 274 Genes), energy (33 SS, 387 Genes), DNA processing (18 SS, 101 Genes) cellular processes (15 SS, 143 Genes), RNA processing (10 SS, 46 Genes), membrane transport (9 SS, 49 Genes), regulation and cell signaling (6 SS, 89 Genes), cell envelope (6 SS, 23 Genes), and miscellaneous (4 SS, 16 Genes).
Groups of genes potentially contributing to the antimicrobial activity of bacterial strains were explored. The S. caeruleatus genome was annotated with various genes associated with different AMR mechanisms including those involved in efflux pump, genes conferring resistance, antibiotic target, enzymatic activation and inactivation and protein alteration. This comprehensive annotation offers insights into the potential antimicrobial resistance (AMR) mechanisms in S. caeruleatus, enhancing the understanding of its antimicrobial properties (Table 4).
Whole genome sequencing of the bacterial strain was identified as S. caeruleatus S14. Its evolutionary relationship was ascertained by constructing a phylogenetic tree with 1000 bootstrap replicates using the Neighbor-Joining method in the MEGA XI application, as illustrated in (Figure 6). According to the derived phylogenetic tree, Streptomyces coelicolorA3(2) and S. caeruleatus S14 have the closest genetic relationship, indicating a strong evolutionary connection between the two strains. Based on this analysis, it is proposed that S. caeruleatus S14 is a novel member of the Streptomyces genus.
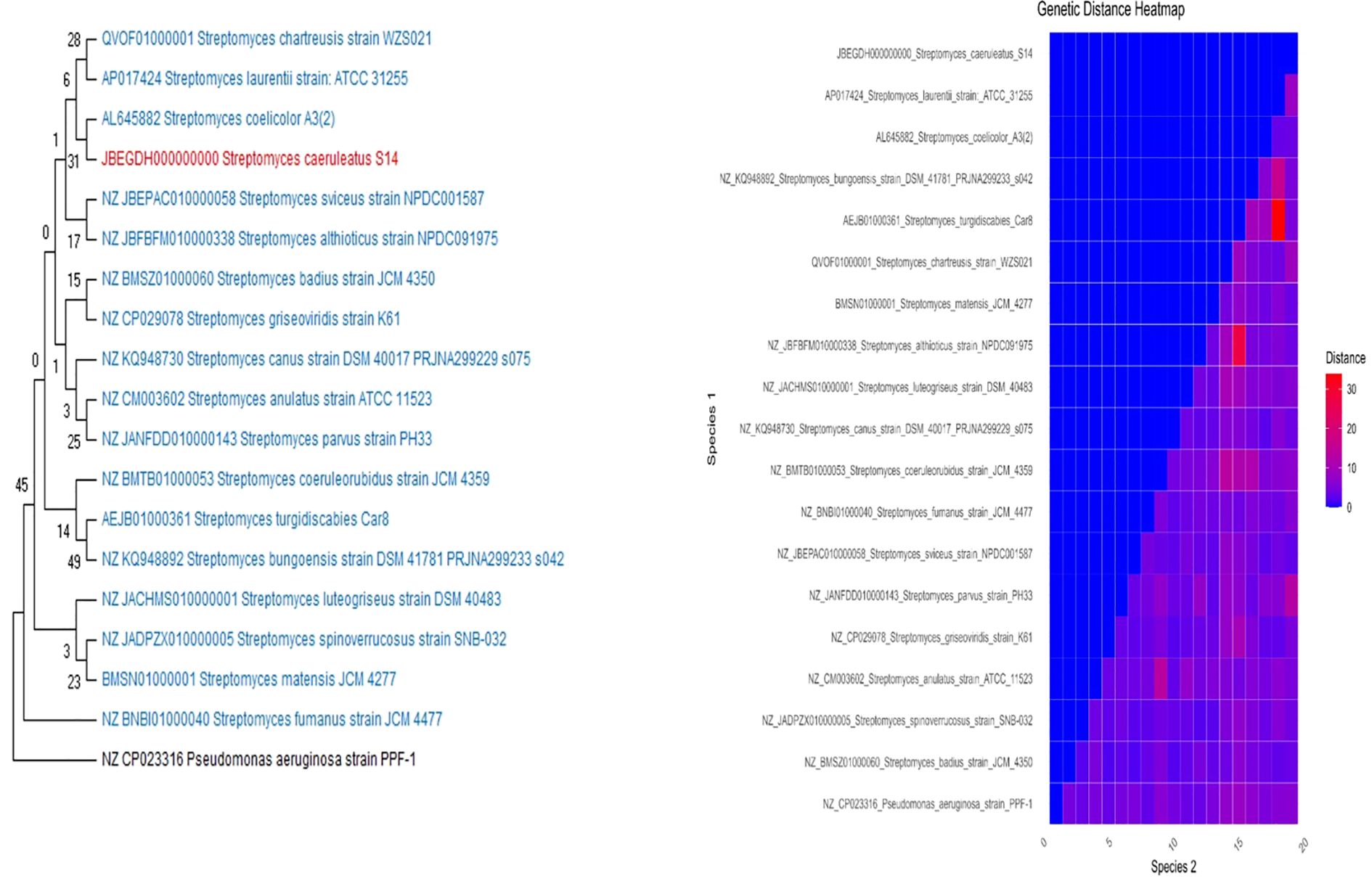
Figure 6. Phylogenetic analysis of the genome of Streptomyces caeruleatus S14. The neighbour joining tree was computed with Mega 11.0 with 1000 boot strap replications and a cut off value of 90%. The genetic distance heatmap was generated using Kimura 2 parameter model in MEGA.
Rice blast, caused by M. oryzae, is the most destructive disease affecting rice crops in rice-growing regions across the globe (Asibi et al., 2019). In sustainable agriculture, biocontrol agents offer an environmentally safe alternative to synthetic fungicides. This study offers a detailed genomic and functional analysis of the S. caeruleatus strain S14, isolated from the rice rhizosphere in Cuttack, Odisha and demonstrates significant biocontrol potential against M. oryzae, the pathogen responsible for rice blast disease, which affects rice crops worldwide (Law et al., 2017). The inhibition rate 74.7% recorded in dual culture assays makes S. caeruleatus as a highly effective biocontrol agent. This finding is particularly critical in the context of sustainable agriculture, where the reliance on chemical fungicides has led to environmental degradation, the evolution of fungicide-resistant strains, and concerns over food safety. Our findings are in concurrence with other workers who reported that Streptomyces vinaceusdrappus, isolated from Loktak lake sediment, inhibited the mycelial growth of M. oryzae by 53.5% (Ningthoujam et al., 2009). Similarly, Streptomyces philanthi RM-1-138, isolated from the chili pepper rhizosphere soil in southern Thailand, was found to inhibit the in-vitro growth of M. oryzae PTRRC-18 (Boukaew and Prasertsan, 2014). The mode of action of biological control agents are typically classified into four categories viz., the activity of substances, parasitism, competition, and antibiosis (Weller, 1988). However, the superior performance of S. caeruleatus in our study could be attributed to its unique genomic composition.
The complete genome analysis of S. caeruleatus S14 revealed a genome size of 9.7 Mb with 9191 protein-coding genes, including several associated with antimicrobial resistance, stress response, and virulence factors. These findings underscore the genetic basis for the strain’s biocontrol activity and provide insights into its potential to produce secondary metabolites, including antibiotics. Notably, genes encoding antibiotic resistance mechanisms, such as efflux pumps and antibiotic-inactivating enzymes, were identified, suggesting that S. caeruleatus could survive in competitive microbial environments. The high GC content (71.03%) of S. caeruleatus suggests an adaptation to soil environments, where high-GC content genomes are often correlated with the production of bioactive compounds. Notably, genome annotation identified several biosynthetic gene clusters (BGCs) responsible for the production of secondary metabolites, reinforcing the potential of strain for novel bioactive compound discovery. These BGCs are essential in the synthesis of antimicrobial compounds, which likely contribute to the observed inhibition of M. oryzae. A circular map of the genome was generated in GC View (Stothard and Wishart, 2005). The subsystems of genome were analyzed to gain insight into the precise role of a group of proteins responsible for a certain biological function or structural complex. Annotation entails examining the subsystems unique to each genome, which aligns well with the findings reported by (Settu et al., 2024). CDS from S.caeruleatus were analyzed and assigned to Clusters of Orthologous Groups (COG) by EggNOG (Huerta-Cepas et al., 2019).
Phylogenetic analysis confirmed the classification of the strain as a novel member of the genus Streptomyces. Its distinct genetic makeup compared to closely related species such as S. coelicolor further supports the uniqueness of this strain. This distinctiveness, combined with its biocontrol potential, makes S. caeruleatus as a viable option for subsequent exploration in sustainable agriculture practices. Streptomyces species carry antibiotic resistance genes, which contribute to their potential bioactive properties. Many Streptomyces species are known for producing secondary metabolites, including antibiotics. The genome of S. caeruleatus was annotated with genes homologous to known antibiotic-resistance genes. This resistance is considered as natural, consistently inherited trait specific to certain bacterial genera or species. The majority of shared genes are linked to various antimicrobial resistance mechanisms, such as antibiotic-target-modifying enzymes (RlmA(II)), antibiotic-inactivating enzymes (CatA family, FosB, Vgb(A)), replacement proteins (FabK, FabL), protection proteins (Lsa(B)), proteins involved in antibiotic sequestration (FabK-like), and regulators that modulate the expression of antibiotic resistance genes (BceR, BceS, LiaF, LiaR, LiaS) (Settu et al., 2024).
Given the promising results of this study, further research should focus on field trials to validate the efficacy of S. caeruleatus under natural environmental conditions. Additionally, studies on the formulation and delivery methods of this biocontrol agent will be crucial for its successful adoption in agriculture. The genetic data generated from this study also pave the way for exploring the metabolic pathways involved in secondary metabolite production, which could result in the discovery of novel compounds with agricultural and pharmaceutical applications.
S. caeruleatus strain S14 is a potent biocontrol agent with significant promise for managing rice blast disease. Its comprehensive genomic profile, including antimicrobial resistance mechanisms, and stress response genes, highlights its adaptability and effectiveness. Biocontrol agents provide a sustainable alternative to chemical pesticides, contributing to both crop protection and environmental preservation. As global agricultural practices shift toward sustainability, the role of microbial agents like S. caeruleatus will become increasingly important in achieving food security and environmental health.
The Genbank accession number for the 16S rRNA gene sequence is PP439819. The Genbank accession number for the whole genome sequence is JBEGDH000000000. The data were submitted in NCBI as name of SRA (Sequence Read Archieve) submission- (Accession No. SRR29262195, SRP511307). This whole-genome shotgun (WGS) project has been deposited at Gen-Bank under the accession BioProject- PRJNA1117618, BioSample- SAMN41577059.
SM: Methodology, Writing – original draft. SP: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing. GB: Validation, Writing – review & editing. MM: Validation, Writing – review & editing. SD: Formal Analysis, Software, Writing – review & editing. GN: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing – review & editing. UK: Data curation, Validation, Writing – review & editing. CP: Formal Analysis, Software, Writing – review & editing. PP: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. SM: Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research work was supported by ICAR-National Rice Research Institute, Cuttack, Odisha.
Authors are thankful to the Director, ICAR-NRRI, Cuttack, Odisha, India for facilitating the requirements of the study. We are also grateful to the Biju Patnaik Research Fellowship (BPRF) for providing financial support for the Ph.D.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be constructed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpls.2025.1526700/full#supplementary-material
Amin, D. H., Abolmaaty, A., Borsetto, C., Tolba, S., Abdallah, N. A., Wellington, E. M. H. (2019). In silico genomic mining reveals unexplored bioactive potential of rare actinobacteria isolated from Egyptian soil. Bull. Natl. Res. Cent 43, 1–9. doi: 10.1186/s42269-019-0121-y
Asibi, A. E., Chai, Q., Coulter, J. A. (2019). Rice blast: A disease with implications for global food security. Agronomy 9, 451. doi: 10.3390/agronomy9080451
Bankevich, A., Nurk, S., Antipov, D., Gurevich, A. A., Dvorkin, M., Kulikov, A. S., et al. (2012). SPAdes: a new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 19, 455–477. doi: 10.1089/cmb.2012.0021
Barka, E. A., Vatsa, P., Sanchez, L., Gaveau-Vaillant, N., Jacquard, C., Meier-Kolthoff, J. P., et al. (2016). Taxonomy, physiology, and natural products of Actinobacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 80, 1–43. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00019-15
Basu, A., Prasad, P., Das, S. N., Kalam, S., Sayyed, R. Z., Reddy, M. S., et al. (2021). Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) as green bioinoculants: recent developments, constraints, and prospects. Sustainability 13, 1140. doi: 10.3390/su13031140
Boukaew, S., Prasertsan, P. (2014). Suppression of rice sheath blight disease using a heat stable culture filtrate from Streptomycesphilanthi RM-1-138. Crop Prot 61, 1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.cropro.2014.02.012
Brettin, T., Davis, J. J., Disz, T., Edwards, R. A., Gerdes, S., Olsen, G. J., et al. (2015). RASTtk: A modular and extensible implementation of the rast algorithm for building custom annotation pipelines and annotating batches of genomes. Sci. Rep. 5, 8365. doi: 10.1038/srep08365
Chaiharn, M., Chunhaleuchanon, S., Lumyong, S. (2009). Screening siderophore producing bacteria as potential biological control agent for fungal rice pathogens in Thailand. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 25, 1919–1928. doi: 10.1007/s11274-009-0090-7
Conn, V. M., Walker, A. R., Franco, C. M. M. (2008). Endophytic actinobacteria induce defense pathways in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 21, 208–218. doi: 10.1094/mpmi-21-2-0208
Dave, A., Ingle, S., Perveen, K., Bukhari, N. A., Sayyed, R., Mastinu, A. (2024). Harnessing plant growth–promoting and wilt-controlling biopotential of a consortium of actinomycetes and mycorrhizae in pigeon pea. J. Phytopathol. 172, e13399. doi: 10.1111/jph.13399
Davis, J. J., Gerdes, S., Olsen, G. J., Olson, R., Pusch, G. D., Shukla, M., et al. (2016). PATtyFams: protein families for the microbial genomes in the PATRIC database. Front. Microbiol. 7. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00118
Felsenstein, J. (1985). Confidence Limits on Phylogenies: An approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39, 783–791. doi: 10.1111/j.1558-5646.1985.tb00420.x
Ferraiuolo, S. B., Cammarota, M., Schiraldi, C., Restaino, O. F. (2021). Streptomycetes as platform for biotechnological production processes of drugs. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 105, 551–568. doi: 10.1007/s00253-020-11064-2
Gong, Y., Liu, J. Q., Xu, M. J., Zhang, C. M., Gao, J., Li, C. G., et al. (2022). Antifungal volatile organic compounds from Streptomyces setonii WY228 control black spot disease of sweet potato. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 88, e02317–e02321. doi: 10.1128/aem.02317-21
Gonzalez-Franco, A. C., Robles-Hernandez, L. (2009). Actinomycetes as biological control agents of phytopathogenic fungi. Tecnociencia Chihuahua 3, 64–73. doi: 10.54167/tecnociencia.v15i2.837
Gurevich, A., Saveliev, V., Vyahhi, N., Tesler, G. (2013). QUAST: quality assessment tool for genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 29, 1072–1075. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btt086
Harir, M., Bendif, H., Bellahcene, M., Fortas, Z., Pogni, R. (2018). Streptomyces secondary metabolites. Basic Biol. Appl. Actinobact 6, 99–122. doi: 10.5772/intechopen.79890
Hopwood, D. A. (2000). Practical Streptomyces Genetics Vol. 518 (Norwich, England: John Innes Foundation), 170–171.
Huerta-Cepas, J., Szklarczyk, D., Heller, D., Hernandez-Plaza, A., Forslund, S. K., Cook, H., et al. (2019). eggNOG 5.0: a hierarchical, functionally and phylogenetically annotated orthology resource based on 5090 organisms and 2502 viruses. Nucleic Acids Res. 47, 309–314. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky10
Jones, S. E., Elliot, M. A. (2017). Streptomyces exploration: competition, volatile communication and new bacterial behaviours. Trends Microbiol. 25, 522–531. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2017.02.001
Kaari, M., Joseph, J., Manikkam, R., Sreenivasan, A., Venugopal, G., Alexander, B., et al. (2022). Anti-Biofilm activity and biocontrol potential of streptomyces cultures against Ralstonia solanacearum on tomato plants. Indian J. Microbiol. 62, 32–39. doi: 10.1007/s12088-021-00963-1
Kalam, S., Basu, A., Ahmad, I., Sayyed, R. Z., El-Enshasy, H. A., Dailin, D. J., et al. (2020). Recent understanding of soil acidobacteria and their ecological significance: a critical review. Front. Microbiol. 11. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.580024
Kenawy, A., Dailin, D. J., Abo-Zaid, G. A., Malek, R. A., Ambehabati, K. K., Zakaria, K. H. N., et al. (2019). Biosynthesis of antibiotics by PGPR and their roles in biocontrol of plant diseases. Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria for sustainable stress management: volume 2: rhizobacteria in biotic stress management. Microorganisms for Sustainability, Springer, Singapore. 13, 1–35. doi: 10.1007/978-981-13-6986-5-1
Khare, A., Singh, B. K., Upadhyay, R. S. (2010). Biological control of Pythium aphanidermatum causing damping-off of mustard by mutants of Trichoderma viridae 1433. J. Agric. Technol. 6, 231–243.
Kirby, R., Sangal, V., Tucker, N. P., Zakrzewska-Czerwinska, J., Wierzbicka, K., Herron, P. R., et al. (2012). Draft genome sequence of the human pathogen Streptomyces somaliensis, a significant cause of actinomycetoma. J. Bacteriol. 194, 3544–3545. doi: 10.1128/JB.00534-12
Law, J. W. F., Ser, H. L., Khan, T. M., Chuah, L. H., Pusparajah, P., Chan, K. G., et al. (2017). The potential of Streptomyces as biocontrol agents against the rice blast fungus, Magnaporthe oryzae (Pyricularia oryzae). Front. Microbiol. 8. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00003
Lee, N., Kim, W., Hwang, S., Lee, Y., Cho, S., Palsson, B., et al. (2020). Thirty complete Streptomyces genome sequences for mining novel secondary metabolite biosynthetic gene clusters. Sci. Data 7, 55. doi: 10.1038/s41597-020-0395-9
Luh Suriani, N., Ngurah Suprapta, D., Nazir, N., Made Susun Parwanayoni, N., Agung Ketut Darmadi, A., Andya Dewi, D., et al. (2020). A mixture of piper leaves extracts and rhizobacteria for sustainable plant growth promotion and bio-control of blast pathogen of organic Bali rice. Sustainability 12, 8490. doi: 10.3390/su13031140
Mohapatra, S., Biswal, G., Prabhukarthikeyan, S. R., Mishra, M. K. (2023). Biochemical characterization of Streptomyces spp. isolated from rhizosphere soils of rice in Odisha. Biol. Forum 15, 765–772.
Naz, R., Khushhal, S., Asif, T., Mubeen, S., Saranraj, P., Sayyed, R. Z. (2022). “Inhibition of bacterial and fungal phytopathogens through volatile organic compounds produced by Pseudomonas sp,” in Secondary metabolites and volatiles of PGPR in plant-growth promotion (Springer International Publishing, Cham), 95–118. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-07559-9_6
Ningthoujam, D. S., Sanasam, S., Tamreihao, K., Nimaichand, S. (2009). Antagonistic activities of local actinomycete isolates against rice fungal pathogens. Afr J. Microbiol. Res. 3, 737–742.
Omar, A. F., Abdelmageed, A. H., Al-Turki, A., Abdelhameid, N. M., Sayyed, R. Z., Rehan, M. (2022). Exploring the plant growth-promotion of four Streptomyces strains from rhizosphere soil to enhance cucumber growth and yield. Plants 11, 3316. doi: 10.3390/plants11233316
Overbeek, R., Begley, T., Butler, R. M., Choudhuri, J. V., Chuang, H. Y., Cohoon, M., et al. (2005). The subsystems approach to genome annotation and its use in the project to annotate 1000 genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 33, 5691–5702. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki866
Pooja, K., Katoch, A. (2014). Past, present and future of rice blast management. Plant Sci. Today 1, 165–173. doi: 10.14719/pst.2014.1.3.24
Prabhukarthikeyan, S. R., Yadav, M. K., Anandan, A., Aravindan, S., Keerthana, U., Raghu, S., et al. (2019). Bio-protection of brown spot disease of rice and insight into the molecular basis of interaction between Oryza sativa, Bipolaris oryzae and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. Biol. Control 137, 104018. doi: 10.1016/j.biocontrol.2019.104018
Rego, A., Raio, F., Martins, T. P., Ribeiro, H., Sousa, A. G., Seneca, J., et al. (2019). Actinobacteria and cyanobacteria diversity in terrestrial antarctic microenvironments evaluated by culture-dependent and independent methods. Front. Microbiol. 10. doi: 10.3389/fmicb
Rhoads, A., Au, K. F. (2015). PacBio sequencing and its applications. Genom. Proteom Bioinform. 13, 278–289. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2015.08.002
Saitou, N., Nei, M. (1987). The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 4, 406–425. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454
Sawant, S. B., Prabhukarthikeyan, S. R., Mishra, M. K., Parameswaran, C., Keerthana, U., Senapati, A. K. (2023). Induction of defense-related enzymes and enhanced disease resistance in rice against Sarocladium oryzae by Bacillus cereus RBS-57. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 128, 102168. doi: 10.1016/j.pmpp.2023.102168
Sawant, S. B., Prabhukarthikeyan, S. R., Mishra, M. K., Parameswaran, C., Keerthana, U., Senapati, A. K. (2024). Understanding the molecular basis of biocontrol effect of Bacillus cereus rbs-57 on sheath rot disease of rice through protein profiling. J. Plant Growth Regul. 43, 4753–4769. doi: 10.1007/s00344-024-11431-7
Settu, V., Annaiyan, S., Mannu, J. (2024). Revealing the genetic arsenal of Bacillus firmus TNAU1: Unleashing nematicidal and plant growth promotion traits. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 129, 102177. doi: 10.1016/j.pmpp.2023.102177
Shin, S. C., Ahn, D. H., Kim, S. J., Lee, H., Oh, T. J., Lee, J. E., et al. (2013). Advantages of single-molecule real-time sequencing in high-GC content genomes. PloS One. 8, e68824. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0068824
Shirling, E. B., Gottlieb, D. (1966). Methods for characterization of Streptomyces species. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 16, 313–340. doi: 10.1099/00207713-16-3-313
Simao, F. A., Waterhouse, R. M., Ioannidis, P., Kriventseva, E. V., Zdobnov, E. M. (2015). BUSCO: assessing genome assembly and annotation completeness with single-copy orthologs. Bioinformatics 31, 3210–3212. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btv351
Stothard, P., Wishart, D. S. (2005). Circular genome visualization and exploration using CGView. Bioinformatics 21, 537–539. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bti054
Sudha, A., Durgadevi, D., Archana, S., Muthukumar, A., Suthin Raj, T., Nakkeeran, S., et al. (2022). Unraveling the tripartite interaction of volatile compounds of Streptomyces rochei with grain mold pathogens infecting sorghum. Front. Microbiol. 13. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.923360
Vinothini, K., Nakkeeran, S., Saranya, N., Jothi, P., Richard, J. I., Perveen, K., et al. (2024). Rhizosphere engineering of biocontrol agents enriches soil microbial diversity and effectively controls root-knot nematodes. Microb. Ecol. 87, 120. doi: 10.1007/s00248-024-02435-7
Wattam, A. R., Davis, J. J., Assaf, R., Boisvert, S., Brettin, T., Bun, C., et al. (2017). Improvements to PATRIC, the all-bacterial bioinformatics database and analysis resource center. Nucleic Acids Res. 45, 535–542. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw1017
Keywords: actinobacteria, biocontrol, genome annotation, genome sequence, rice blast, Streptomyces caeruleatus, whole genome sequence
Citation: Mohapatra S, Prabhukarthikeyan SR, Biswal G, Mishra MK, Dash SS, Nayak G, Keerthana U, Parameswaran C, Panneerselvam P and Mohapatra SD (2025) Comprehensive genome analysis of Streptomyces caeruleatus S14 isolated from rice rhizosphere. Front. Plant Sci. 16:1526700. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1526700
Received: 12 November 2024; Accepted: 27 February 2025;
Published: 26 March 2025.
Edited by:
Abdul Kader Jailani Amirudeen, University of Arkansas, United StatesReviewed by:
Ni Luh Suriani, Udayana University, IndonesiaCopyright © 2025 Mohapatra, Prabhukarthikeyan, Biswal, Mishra, Dash, Nayak, Keerthana, Parameswaran, Panneerselvam and Mohapatra. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: S. R. Prabhukarthikeyan, cHJhYmh1a2FydGhpcGF0QGdtYWlsLmNvbQ==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.