
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Plant Sci. , 12 March 2025
Sec. Plant Abiotic Stress
Volume 16 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2025.1523636
This article is part of the Research Topic Salinity and Drought Stress in Plants: Understanding Physiological, Biochemical and Molecular Responses Volume II View all 26 articles
 Zhiying Wang1,2
Zhiying Wang1,2 Baorui Cao2,3
Baorui Cao2,3 Yueyue Ma2
Yueyue Ma2 Weifan Xu2
Weifan Xu2 Jialei Fu4
Jialei Fu4 Zhongwen Zhang5
Zhongwen Zhang5 Jinxin Du2
Jinxin Du2 Tingting Deng3
Tingting Deng3 Jingxiang Pang2
Jingxiang Pang2 Meina Yang1,2*†
Meina Yang1,2*† Jinxiang Han1,2†
Jinxiang Han1,2†Introduction: Isatidis Folium, derived from the dried leaves of Isatis indigotica Fort, has been used for centuries as a traditional Chinese herb with antibacterial and antiviral properties. However, both the cultivation conditions and the growth status of Isatis indigotica Fort have been negatively affected by climatic and environmental degradation, which has made it challenging to accurately assess the quality of Isatidis Folium. The current quality control system for Isatidis Folium lacks precision and comprehensive identification indices, and importantly, the cultivation process has not been integrated into this system.
Methods: In this study, we proposed a novel method to distinguish between different stress subtypes in Isatis indigotica Fort based on biophoton emission and attempted to explore the potential relationship between the biophoton characteristics of fresh Isatis indigotica Fort leaves and the quality of Isatidis Folium. The delayed luminescence (DL) and spontaneous photon emission (SPE) characteristics of fresh Isatis indigotica Fort leaves under different stress conditions were detected using a biophoton detection system. An attempt was made to differentiate samples subjected to various stress treatments using biophoton characteristic parameters. Additionally, the content of active ingredients was determined by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography, and the inhibitory activity against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus was evaluated to identify the quality of Isatidis Folium. Several physiological indicators of fresh Isatis indigotica Fort leaves, including the photosynthetic pigment content, relative electrical conductivity, and reactive oxygen species production rate were also determined.
Result: The differences in physiological indices, active ingredient content, and inhibitory activity indicated that the stress conditions significantly inhibited the growth status of Isatis indigotica Fort leaves and the herbal quality. Meanwhile, biophoton characteristic parameters were obtained that could accurately and efficiently distinguish fresh Isatis indigotica Fort leaves between different stress subtypes: initial intensity of DL and counts per second of SPE. Both characteristic parameters were highly correlated with the physiological indicators and quality of Isatidis Folium.
Discussion: This study has preliminarily demonstrated the feasibility of utilizing biophoton detection technology for the quality evaluation of Isatidis Folium during cultivation for the first time and provided an improved method for distinguishing samples of various qualities.
The traditional Chinese herb, Isatidis Folium, belongs to the cruciferous plant Isatis indigotica Fort [Brassicaceae], specifically the leaf part of the entire plant, which has been extensively utilized in Eastern countries for centuries. Isatis indigotica Fort has been officially recognized as the only source of Isatidis Folium since the 1985 edition of the Chinese Pharmacopoeia. Isatis indigotica Fort primarily produced in the Yellow River basin north of the Yangtze River (Chen et al., 2022). It is cold-resistant, warmth-favoring, and relatively drought-tolerant, but does not tolerate waterlogging (Commission, C. P, 2020). Isatidis Folium has the effects of clearing heat, detoxicating, cooling blood, and eliminating spots. It has been proven to have various pharmacological activities including antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, anti-endotoxin, and anticancer effects (Chung et al., 2024), and is frequently used to alleviate the symptoms of colds, fevers, sore throats, viral hepatitis, and epidemic encephalitis B in clinical (Wu et al., 2018; Chen et al., 2022). Previous studies have shown that Isatidis Folium primarily contains active ingredients such as alkaloids (Liu et al., 2018; Ji et al., 2013; Xiong et al., 2022; Yuan et al., 2023), flavonoids (Jiang et al., 2015; Yu et al., 2018), organic acids (Mao, 2018; Yan et al., 2024), and polysaccharides (Guo et al., 2016). Among these, alkaloids, especially indole alkaloids, have been extensively studied and have been found to have significant biological activities, and are often used as quality control indicators for Isatidis Folium. Indole alkaloids mainly include indigo, indirubin, and tryptanthrin (Xu et al., 2021). Indirubin is the main active ingredient of Isatidis Folium (Chen et al., 2022), which has been demonstrated to have excellent antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, anti-leukemic, and immune-enhancing activities (Wu et al., 2016; Chuang et al., 2024). Indigo has been proven to be liver-protective, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial (Zhang et al., 2020). Tryptanthrin is an alkaloid with an indole-quinazoline structure that has pharmacological activities including antibacterial, antiviral, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer (Alam et al., 2025).
The quality control of Isatidis Folium is challenging due to the influence of several factors, including its origin, germplasm, the growing environment, and the harvest season. Environmental factors are the core external factors affecting the formation of herbal quality and are crucial for the efficacy of Chinese herbs. Isatis tinctoria Fort is susceptible to external conditions such as soil, moisture, salinity, etc., which can affect the quality of Isatidis Folium. Due to the current global warming, soil desertification, and increased salinization, salt stress and drought are the two major abiotic stresses on herbal plants, significantly limiting the quality of Chinese herbs. Additionally, the use of artificial organic pesticides and fertilizers has increased the levels of organic phosphorus, organic nitrogen, heavy metal ions, microorganisms, and other residues in Isatidis Folium, which can result in a reduction in herbal quality (Gao and Dong, 2010). Fourteen batches of Isatidis Folium and corresponding tablets from different origins and environments were investigated and the results showed that Isatidis Folium samples had high ash content and significantly insufficient active ingredient content (La and Hu, 2009). This indicates that the quality of Isatidis Folium products in the market is inconsistent and below the required standard. As a result, traditional Chinese herbal preparations based on Isatidis Folium, such as Qinghuo tablets, Xiaowen Jiedu oral liquid, and Fufangdaqingye mixture, failed to meet the required quality standards. Therefore, the clinical efficacy would be negatively affected.
According to the Chinese Pharmacopoeia 2020, the indirubin content of Isatidis Folium should be determined using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) as the quality evaluation method (Commission, C. P, 2020). Currently, reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC) is the primary method used to quantify the primary active ingredients in Isatidis Folium (Xiao et al., 2015). In related literature, the Box-Behnken response surface method was used to optimize the indices and strategies for the determination of the quality standard content of Isatidis Folium in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia, and the contents of indigo and indirubin were simultaneously quantified by HPLC, which provided a new method for the quality control of Isatidis Folium and tablets (Wang et al., 2024). The contents of 4-hydroxyquinazoline, 2,4-hydroxyquinazoline, syringic acid, tryptanthrin, indigo, and indirubin of Isatidis Folium were quantified based on the multi-component content determination, and the quality evaluation method based on HPLC fingerprinting was then established (Li et al., 2019). Due to the extreme complexity of the chemical composition of Chinese herbs, it is tough to base quality control on a clear study of all the components. The current quality measurement therefore typically relies more on some ingredients with significant pharmacological activity (Sun et al., 2021), which is still the most common and universal consensus in herbal quality control. Pharmacological activity testing can directly reflect the potential efficacy of certain aspects of Chinese herbs and is the more widely used and recognized quality identification method. However, it is more cumbersome and time-consuming than quantification of medicinal composition, and is also difficult to explore all the efficacy completely. Therefore, it is crucial to reinforce the quality control of Isatidis Folium and establish a simpler quality evaluation method that agrees with the holistic view of traditional Chinese medicine and is tailored to the specific attributes of Isatidis Folium. This will help enhance the quality evaluation system for this Chinese herb.
Biophoton emission is a universal phenomenon in living organisms (Zhou, 2019). It is believed to be generated during the transition from high-energy to low-energy states of biological molecules and conveys intricate information about the internal dynamics of the living system (Popp et al., 1988; Gu, 2012). It changes with the physiological state of the organism and is highly sensitive to various physiological and biochemical conditions within the organism and the external environment. Biophoton emission can closely reflect cell division, cell death, information transfer, functional regulation, photosynthesis, and other physiological processes (Wang et al., 2015). Two different types of biophoton emission have been identified. The first is the autonomous luminescence of organisms, known as spontaneous photon emission (SPE). Its luminosity is remarkably low, with a photon emission rate of only hundreds to thousands per unit time and area, depending on the intrinsic properties of the sample tested. The other is delayed luminescence (DL), which occurs when a sample in a steady state is suddenly exposed to a stimulus such as a light source, its luminescence intensity suddenly increases, followed by a trend similar to hyperbolic decay until the luminescence intensity returns to the initial steady state. Biological samples from different sources exhibit different SPE and DL characteristics due to their inherent properties. Therefore, the biophoton characteristics of the biological samples can be used to determine the exact state and comprehensive internal information of the samples. Previous studies (Sun et al., 2021) have revealed that DL is related to the contents of anthraquinone derivatives, suggesting that the DL might be able to reflect the impact of environmental factors on the quality of Rhei Radix Et Rhizoma and be used to evaluate the quality of Chinese herbs. Before this, relevant laboratory studies were conducted on screening different varieties of fresh Chinese herbs at different growth ages using SPE analysis (Zhao et al., 2017). The research results showed that SPE can be used to characterize the active substance content in Chinese herbs of different growth ages and varieties. Therefore, this evaluation could contribute to achieving quality control for Chinese herbs in the future.
In this study, we established two types of stress models: salt stress and drought stress. The biophoton characteristics of fresh Isatis indigotica Fort leaves were subjected to systematic analysis to ascertain their behavior under different stress conditions. By combining the biophoton characteristic parameters with physiological indicators, the content of active ingredients, and minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC), we investigated the underlying reasons for the differences in the biophoton characteristics of Isatis indigotica Fort leaves and its intrinsic relationship with the quality of Isatidis Folium under varying stress conditions. We obtained the biophoton characteristic index parameters that can characterize the different attributes of Isatis indigotica Fort leaves and clarified the feasibility of the biophoton technology for the quality prediction of Isatidis Folium.
Isatis indigotica Fort was planted in planting boxes (0.4 m × 1.2 m × 0.5 m) in the herbal garden of Shandong First Medical University (116° 8’ 6” N, 116° 8’ 6” E, Jinan, Shandong Province, China) on August 20, 2022. Before sowing, the soil was turned to a depth of 30 cm, and sheep manure was applied as a base fertilizer. Then, 3-4 cm deep trenches were dug for sowing, with a spacing of 5-8 cm between plants and 15 cm between rows. A transparent thermal insulation shed was constructed outside of the boxes. No shading treatment was applied throughout the planting process and 24-hour ventilation was maintained. Drought stress and salt stress were applied to Isatis indigotica Fort and each stress condition followed the principle of a single control. Seeds were purchased from the Bozhou Changnong Chinese Medicinal Materials Planting Co., Ltd, and Isatis indigotica Fort was identified by researcher Fu Jialei, confirming that they met the identification standards as specified in the 2020 edition of the Chinese Pharmacopoeia (Commission, C. P, 2020). The technical specifications for planting, collection, storage, and primary processing were conducted by the Law of the People’s Republic of China on Traditional Chinese Medicine and other relevant regulations (Committee, N. S, 2017).
After sowing, Isatis indigotica Fort was grown under the same conditions. Twenty days after the seedling emergence, four boxes of uniformly grown and healthy Isatis indigotica Fort were selected for subsequent cultivation. Four different salinity gradients of 0 mmol/L (the control group), 60 mmol/L (low salinity), 120 mmol/L, and 180 mmol/L (high salinity) were established for the salt stress treatment. Each box of Isatis indigotica Fort was fixed at approximately 50 plants after seedling and interplanting. To avoid excessive osmotic stress, the salinity was gradually increased, starting at 1/3 of the predetermined concentration for the first stress, 2/3 for the second stress, and reaching the full predetermined concentration for the third stress. Salt stress was applied once a week for one month, with each injection of twice the amount of water held by the soil (Mi et al., 2018). To maintain soil salinity at the respective gradient levels throughout the stress period, soil samples were collected daily from each treatment group and air-dried. Soil salinity was then determined using the conductivity method (Song, 2011).
This experimental study was carried out from 1 September to 1 November. After seed emergence, two boxes of Isatis indigotica Fort with consistent growth status were selected for subsequent cultivation. Each box contained approximately 50 plants. Two irrigation treatments were established: the control group (adequate water supply) with a soil water content of 70-90% and drought stress with a soil relative water content of 30-50%. The control group was irrigated three to four times a week with 3 L of well water and the drought stress group was irrigated two to three times a week with 1 L. To maintain the soil water content within the set range, daily evaporation was compensated for by measuring soil moisture each evening through the gravimetric method (Ma, 2022) and adjusting water application accordingly. This approach ensured that all treatments adhered to their designated moisture conditions. The drought stress treatment lasted for two months.
Isatis indigotica Fort plants grown under different stress conditions were utilized as the experimental samples, collected from the boxes in the herbal garden. Fresh samples were collected in the morning and afternoon to avoid exposure to the midday sun and to prevent the sampling and experiments during extreme weather conditions. This was done to ensure the natural environment was as consistent as possible when collecting experimental samples. Samples were randomly collected and immediately stored in ice boxes after collection. The fresh samples were cleaned with double distilled water, blotted dry on blotting paper, and photographed for recording. Subsequently, the samples were placed in the darkroom of the instrument for one hour for dark adaptation. Each experiment maintained a consistent time interval between sample collection and dark adaptation.
Before the measurements, a constant room temperature of 20°C was established and the YPMS-2 biophoton detector (Miluna, the Netherlands) was switched on for a two-hour cooling period. This system consists of a black chamber, a photomultiplier tube (PMT), a photomultiplier tube high-voltage power supply type PMS20S (Sens-Tech), a photon counting unit C9744 (Hamamatsu Photonics K.K., Iwata, Japan), a thermoelectric cooler and a computer equipped with photon counting data software (Figure 1). The core component of this detection system is the PMT with a shutter in front of it to avoid any interference from external light. After dark adaptation, the SPE characteristics of the sample were examined. The measurement time for each detection point was set at one second, with a continuous measurement period of ten minutes and a total of 600 detection points. The DL characteristics and the excitation were conducted using a light-emitting diode (LED) (7 mm, 10 W, type LZ4-00MD00; LED Engine Inc., United States). The samples were illuminated by the LED for 15 seconds and then detected continuously for 5 minutes. Three replicate DL experiments were performed for each sample. After the DL detection, the background noise was detected for 10 min, the sample weight was weighed and the thickness was also measured. To minimize contingency effects, six independent experimental replications were conducted for each group, with all six replicates completed within a single day.
To find the parameters representing the biophoton characteristics and then to quantitatively compare the differences under various stress conditions, we characterized the SPE properties with counts per second (CPS). In addition, to calculate the DL characteristics of the samples, all the photon counts measured during the 300 s of each decay curve were used according to the Gu parameter function (Equation 1). Six parameters were obtained from the Gu parameter equation. They are the three “Gu parameters” (A, B, C), the initial intensity (I0) of DL, the average intensity of the entire DL process (IW), and the decay time (T). The values of A, B, and C are derived while fitting the DL kinetic curves using the Gu parameter equation. While I0, IW, and T are macroscopic quantities calculated based on A, B, and C. These parameters can well express the characteristics of the DL decay curve. Subsequently, we used the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) to screen pivotal parameters that could be utilized to characterize the biophoton characteristics of fresh Isatis indigotica Fort leaves. The Gu parameter equation (Equation 1) and the equations for each parameter (Equations 2–5) are provided blow (Gu, 2012; Sun et al., 2017):
In Equation 1, t is the time; A is an intensity parameter dependent on the sample’s nature, system structure, and illumination conditions; B is a characteristic time, related only to the nature of the sample itself; and C is a phase factor determining the initial state of the sample, which is sensitive to the I0 of the DL. In Equation 2, N is the average count rate of the sample, and n is the background count rate of the instrument without a sample. The light intensity decays to It = I0/m when the time is T. The value of the factor “m” ranges from 2 to 4 and in this study m = 3. In Equation 5, W is the total measurement time. The strength indicators I0, IW, and CPS were homogenized by multiplying the thickness and dividing by the weight of the corresponding sample.
After the fresh leaves were collected, they were washed with double distilled water, blotted with absorbent papers, and dried in a drying box (HAIYU) at 60°C for 24 hours. The dried leaves were then ground using an 800C multifunction grinder (Dongguan Fanta Electrical Co., Ltd.) and sieved through a 65-mesh Chinese medicine sieve (0.212 mm aperture). Finally, they were placed in centrifuge tubes and stored in a cool and dry place.
A total of 3 g of Isatidis Folium powder was accurately weighed and transferred to a beaker. 50 mL of chloroform was added and the mixture was thoroughly shaken and weighed. The sample was then heated and refluxed for 30 minutes, cooled, and reweighed and chloroform was added to make up for the loss in weight. The mixed solution was then thoroughly shaken, filtered, and concentrated to dryness. An appropriate amount of methanol-chloroform mixture (8:2, v/v) was added to dissolve the residue. The solution was then transferred to a 10 mL volumetric flask, diluted to the mark with the same solvent, and thoroughly mixed to obtain the test solution of Isatidis Folium.
The UPLC analysis was performed using a Waters Acquity UPLC (Waters, Milford, MA, USA) that was equipped with an ACQUITY UPLC sample organizer, a chromatographic column manager, a column temperature box with heating and cooling functions, a binary solvent manager and sample manager, a photodiode array, and an evaporative light scattering detector. The chromatographic analysis was performed using an ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18 column (150 mm × 2.1 mm, 1.7 μm) with a mobile phase of 0.1% phosphoric acid solution (A) - methanol (B). A gradient elution was used as follows: 0 min-3.5 min, 75% A-74% A; 3.5 min-5 min, 74% A-65% A; 5 min-6 min, 65% A-65% A; 6 min-10 min, 65% A-55% A; 10 min-18.5 min, 55% A-30% A; 18.5 min-25 min, 30% A-12% A; 25 min-26 min, 12% A-12% A; 26 min-26.01 min, 12% A-75% A; 26.01 min-33 min, 75% A-75% A. The detection time was 35 min. The injection volume was 10 μL and the flow rate was 0.3 mL/min. The column temperature was maintained at 35°C and the sample cell temperature was set at 25°C.
Escherichia coli (E. coli) and Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) were removed from the -80℃ refrigerator and streaked on solid LA culture media on an ultra-clean workbench. The bacterial strains with similar morphology to be determined were picked up with an inoculation loop and inoculated onto a liquid LB media. Bacterial strains were incubated at 37°C for 2-6 h to OD600 = 0.7, containing approximately 1-2×108 CFU/mL (calibrated with sterile 0.85% saline). The bacterial solution was diluted 100-fold to obtain a solution containing approximately 1-2 × 106 bacteria.
A sample of 40.96 g of Isatidis Folium and 200 mL of double-distilled water were placed in a casserole, soaked together for 30 min, and decocted on a 2200 W induction cooker. After cooling, the power was reduced to 800 W, and the total decoction time was 15 min. At the end of the decoction, the decoction was filtered through a 6-layer gauze. The filter residue was placed in a casserole, 200 mL of double-distilled water was added, and the above process of decoction and filtration was repeated. The two filter liquors were combined and placed in a casserole, and the power of the induction cooker was set at 2200 W for decoction. After boiling, the power was reduced to 800 W. Then the heating process was continued until the decoction volume was concentrated to 10 mL, i.e., the final concentration was 4.96 g/mL. The decoction was filtered using a 0.22 μm sterile filter membrane in an ultra-clean bench to remove bacteria and large particles and then stored in a refrigerator at 4°C.
100 μL of LB medium was added to each of 8 adjacent wells of the 96-well plate respectively. 100 μL of the drug solution was added to the first well and mixed thoroughly, then 100 μL of the mixture was taken and added to the second well. The mixture of the second well was mixed thoroughly and then 100 μL of the mixture was taken and added to the third well, and so on. The mixture of the eighth well was mixed thoroughly and 100 μL of the mixture was taken and discarded. Then, 100 μL of bacterial solution was added to each of the eight wells respectively, thus creating samples to be tested with different drug concentration gradients: 1024, 512, 256, 128, 64, 32, 16, 8 μg/mL. 100 μL of LB medium and 100 μL of bacterial solution were added to the ninth well as a positive control group. 100 μL of LB medium and 100 μL of drug solution were added to the tenth well as a negative control. Four samples were prepared in parallel for four replicates. The 96-well plate was incubated in a shaker incubator at 37 ℃ for 18 h. The absorbance at 600 nm of each well was detected with an enzyme marker, and 80% of the bacterial concentration of the positive control group was used as the endpoint for determining the MIC value, and the concentration of the drug solution which was closest to this endpoint was the MIC value of Isatidis Folium.
Fresh samples were collected, washed with double distilled water, and dried with absorbent papers. The leaves were cut into pieces, avoiding the main veins, and 0.1000 g of the crushed leaves were accurately weighed and transferred to a 50 mL centrifuge tube. 15 mL of extract (a 1:1 volume mixture of ethanol and acetone) was added to the centrifuge tube. The mixture was then placed in complete darkness for 24 hours until the leaves had completely faded. During this period, the mixture was shaken two to three times. The absorbance of the extract at 474, 642, and 665 nm was later determined using a U-3900H UV/VIS spectrophotometer (Hitachi High-Tech Science Corporation, Tokyo, Japan). Three biological replicates were made for each treatment. The contents of chlorophylls and carotenoids were determined according to the method of Huang and were calculated using Equations 6–9 (Huang et al., 2013):
Ca, Cb, and Cc are the concentrations (mg/L) of chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, and carotenoids, respectively. As represents the absorbance of the extraction solution at the corresponding wavelength. In Equation 9, C is the content (mg/g) of the photosynthetic pigment, C’ is the concentration of the corresponding photosynthetic pigment, V is the volume (L) of the extraction solution, and m is the weight (g) of the leaf samples.
The freshly collected samples were washed with double distilled water and subsequently dried with absorbent papers. Ten leaf discs were quickly punched from different parts of the same leaf using a 6 mm punch, avoiding the main veins. These leaf discs were then placed in a conical flask containing 30 mL of ultrapure water (Millipore, Boston, MA, USA). This mixture was shaken on a shaker at 150 rpm for 12 h and the conductivity was then measured using a DDS-11A conductivity meter. After boiling in a water bath for 30 min and cooling to room temperature, the mixture was shaken to re-determine the conductivity. Three replicate experiments were performed for each treatment. The REC was calculated using Equation 10:
E1, E2, and E3 represent the conductivity of double distilled water, samples, and samples after boiling water bath, respectively.
0.1 g of fresh samples were weighed and placed in a mortar, to which 1 mL of Tris-HCl buffer 1 (containing sucrose and EDTA) and 10 μL of PMSF solution were added. The leaf pieces were ground and homogenized, and the mixture was centrifuged at 600 rpm for 5 min at 4°C. The supernatant was transferred to a new centrifuge tube and centrifuged at 11,000 rpm for 10 min at 4°C. The precipitate was resuspended in 200 μL of Tris-HCl buffer 2 (containing potassium chloride, magnesium chloride hexahydrate, and glucose) and gently mixed with a pipette gun. 50 μL of malic acid, 50 μL of pyruvic acid, 50 μL of succinic acid, and 30 of μL DCFH-DA were added to the determination tube and the blank tube, respectively. In addition, 20 μL of mitochondrial suspension was added to the determination tube and 20 μL of Tris-HCl buffer 2 was added to the blank tube. They were mixed well and incubated at 37°C for 15 min in the dark. The Tristar²S LB 942 multifunctional enzyme labeler (Berthold, Bad Wildbad, Germany) was preheated for 30 min, and the excitation and emission wavelengths were set to 499 nm and 521 nm, respectively. Fluorescence intensity was measured at 37°C within 10 min. Three replicate experiments were performed for each treatment. The change in fluorescence intensity over time was analyzed by fitting a linear regression to calculate the slope (k). The actual rate of mitochondrial ROS production (u/s/g) was then determined using Equation 11:
v represents the production rate of ROS; k1 and k2 represent the slope of the linear regression line for the data points pertaining to the fluorescence intensity of the sample in the detection tube and the blank tube over time, respectively; g represents the weight of the samples.
Principal component analysis (PCA) was used to indicate the degree of discrimination between the biophoton characteristics of the control group and stress groups. The mean ± standard deviation (SD) values of the samples were statistically analyzed using GraphPad Prism 9.5.0 for Windows (GraphPad Software, La Jolla, CA, USA, www.graphpad.com). Data from samples under different stress conditions were compared using a two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test. Spearman correlation analysis was performed to explore the potential relationships between biophoton signature parameters and active ingredient content, MIC values, and physiological indices. In all statistical tests, P ≤ 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Figure 2 shows the fresh Isatis indigotica Fort leaves under different stress conditions. Under these stressors, the growth of leaves exhibited varying degrees of inhibition. In the salt stress groups, the increasing salinity gradually inhibited the leaf development, resulting in gradual chlorosis, marginal curling, withering, and even the emergence of sporadic necrotic spots. In the drought stress group, the leaves were small and thin, excessively soft, and wrinkled.
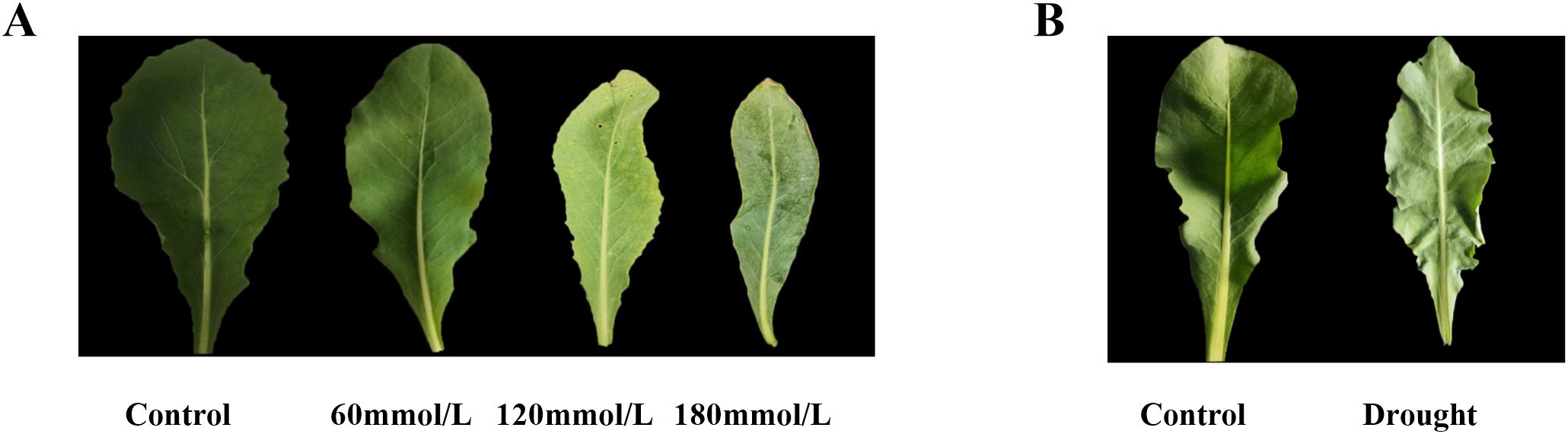

Figure 2. The fresh Isatis indigotica Fort leaves under different stress conditions. (A) Salt stress. (B) Drought stress.
Figure 3 shows different DL kinetic curves and SPE characteristics of Isatis indigotica Fort leaves samples under different stress conditions. Both salt and drought stresses significantly altered the SPE characteristics, which was mainly reflected in the biophoton intensity at the steady state. The biophoton intensity of samples was significantly lower in the high salinity and drought stress groups compared to the control group. In addition, the T and I0 of the DL characteristics varied with different samples, and the intensity of DL after stimulation of biological systems tended to be much higher than that of SPE at the steady state. The DL characteristics of samples exposed to both salt and drought stress treatments also significantly changed, especially the parameter I0, which shows the most obvious changes. The initial photon emission intensity of the samples under the stress treatments was approximately half that of the control group.
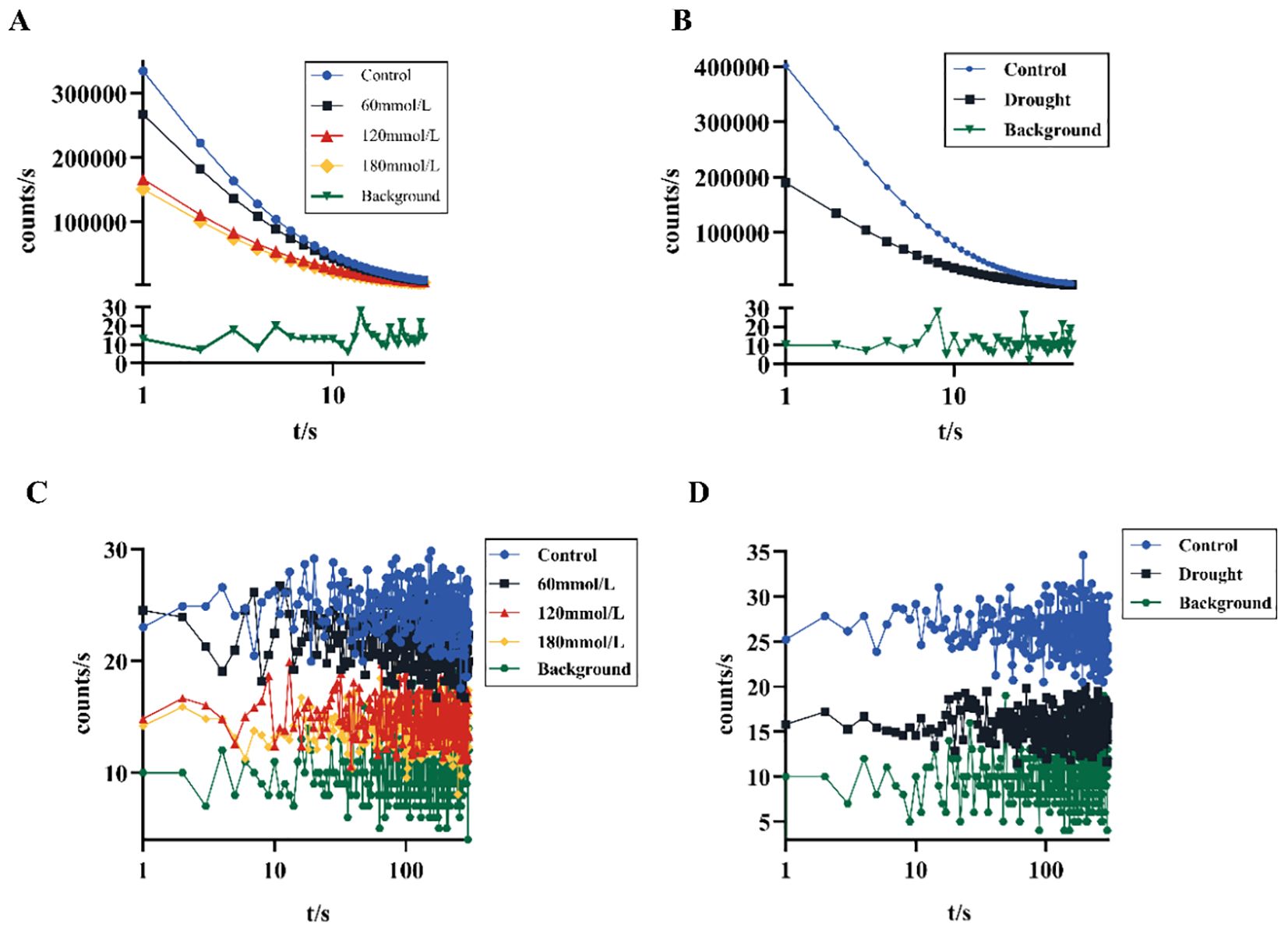
Figure 3. Biophoton characteristics of fresh Isatis indigotica Fort leaves under different stress conditions. (A, B) DL kinetic curves of samples under salt and drought stress treatment groups, respectively. (C, D) SPE characteristics of samples under salt and drought stress treatment groups, respectively.
To differentiate between the control and stress groups, LASSO regression was used to screen for characteristic parameters. In LASSO regression, the range of values of the penalty coefficient is usually gradually reduced from a series of larger values, and the smaller the cross-validated mean square error, the better the model fits. As the penalty coefficients change, the more important the variable, the later the coefficients are compressed to zero. Seven relevant characteristic variables were considered in this study. Based on the training cohort data, three potential indicator parameters were identified: CPS, I0, and T. These parameters exhibited relatively high importance coefficients in the LASSO regression model (Figure 4).
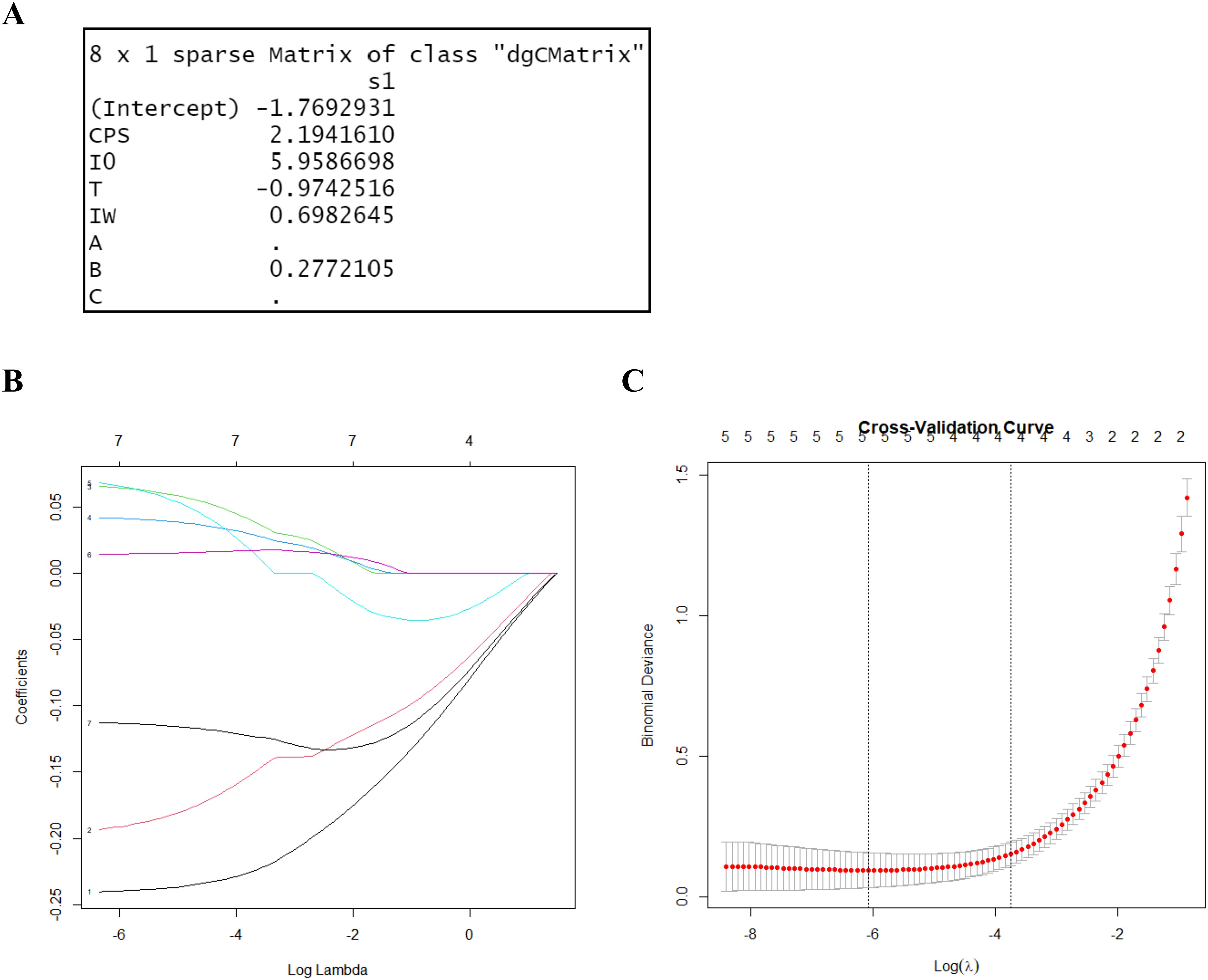
Figure 4. LASSO regression for variable selection. (A) LASSO output characteristic coefficients. (B) LASSO coefficient path plot. It reflects the relationships between the coefficients of the variables and the value of log lambda. Each curve represents the trajectory of the coefficients of a feature as a function of λ. The horizontal axis represents the value of λ on a logarithmic scale, the vertical axis represents the coefficient of the feature, and different colors represent different features. (C) Cross-validation results of the LASSO regression. By verifying the optimal parameter (λ) in the LASSO model, the partial likelihood binomial deviation was plotted against log (λ). The dashed line was determined using the minimum criterion and the one standard error of the minimum criteria (the 1-SE criteria) in selecting the optimal log (λ) values of the features. The best lambda value from cross-validation is 0.002297955.
Figure 5 shows the three biophoton characteristic parameters of Isatis indigotica Fort leaves under different stress conditions. High salinity and drought stress conditions induced significant changes in the biophoton parameters. Compared to the control group, both I0 and CPS showed a highly significant decrease under these stress conditions, while the low salinity stress group had a relatively minimal effect. The variation trend of T under different stress conditions was not significant.
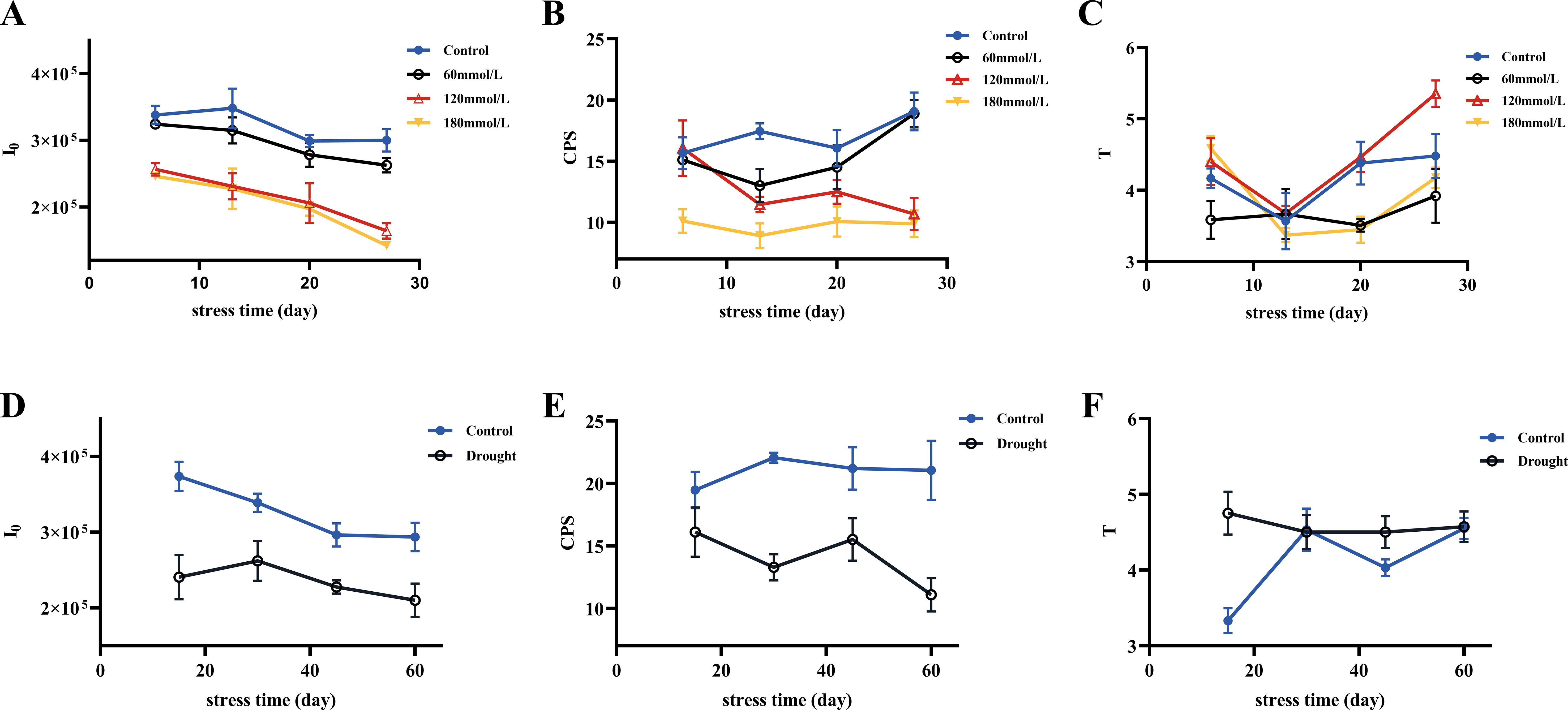
Figure 5. Three selected biophoton characteristic parameters (I0, CPS, and T) of fresh Isatis indigotica Fort leaves under different stress conditions with stress time. (A–C) The changing trends of I0, CPS, and T in the salt stress group with stress time, respectively. (D–F) The changing trends of I0, CPS, and T in the drought stress group with stress time, respectively.
PCA was then applied to provide a focused view of the variance in the biophoton characteristic parameters (I0 and CPS) to differentiate the stress subtypes. The results indicated that the biophoton characteristics could reasonably stratify the samples between the control group and the high salinity and drought stress groups (Figure 6).
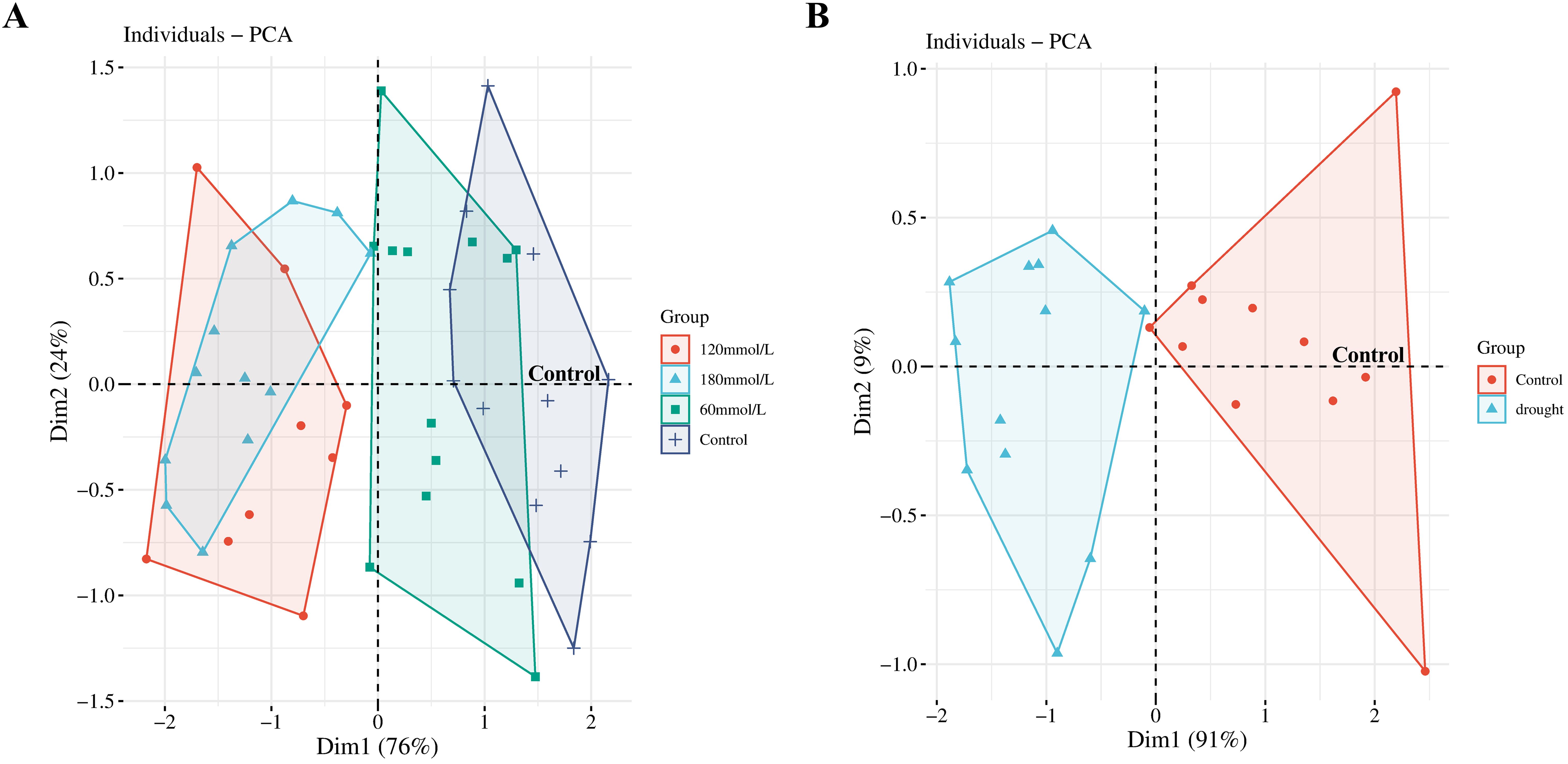
Figure 6. PCA scores obtained from the biophoton data. (A) PCA score plots of the biophoton characteristic obtained from samples at different salinities. (B) PCA score plots of the biophoton characteristic obtained from drought stress group.
A two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test was used to compare the differences in biophoton parameters between the control group and the stress treatment groups. The analysis results indicated significant differences in both I0 and CPS between the control group and the high salinity groups. The control group showed higher I0 and CPS than the high salinity groups, as shown in Figures 7A, B. Similar results were observed under drought stress groups, where I0 and CPS were significantly lower in the drought stress group compared to the control group (Figures 7D, E). However, there were no significant differences in T between any of these groups (Figures 7C, F).
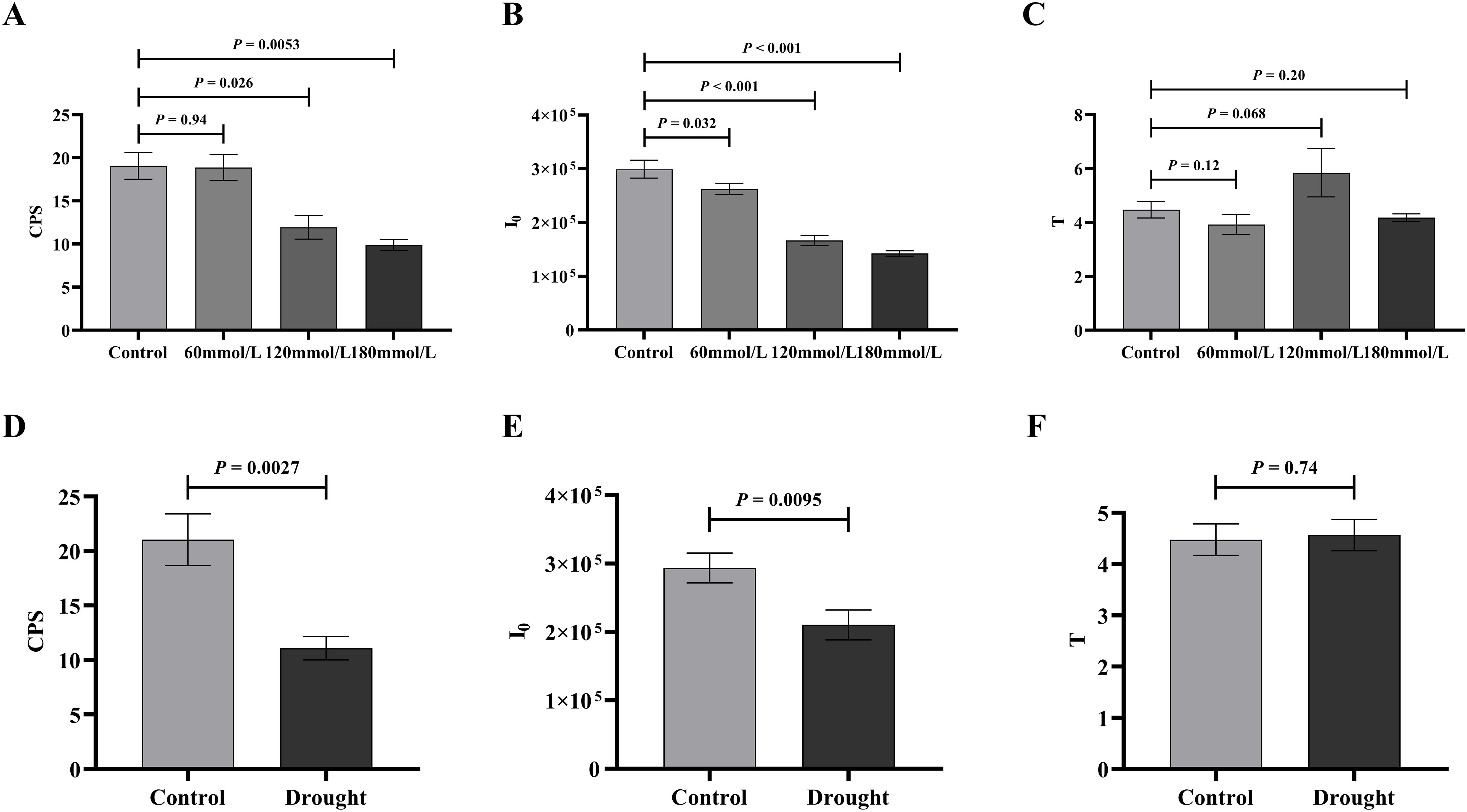
Figure 7. The t-test analysis of the biophoton parameters under different stress conditions. (A–C) The t-test analysis results of I0, CPS, and T among different salt concentration. (D–F) The t-test analysis results of I0, CPS, and T in different drought stress treatment group.
The active ingredient content in Isatidis Folium was determined by UPLC. Five peaks were identified by comparing the retention times of the samples (Figure 8B) with those of the standards (Figure 8A), including 4-hydroxyquinazoline, syringic acid, tryptanthrin, indigo, and indirubin. The precision ranged from 0.99% to 2.59% and the RSD of the reproducibility test ranged from 0.976% to 3.246%. The stability test was performed by analyzing the sample solution at six different time points after the preparation of the test sample (0, 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, and 24 hours) at room temperature, with RSDs ranging from 1.395% to 2.085%. Standard solutions at 0.5, 1, and 1.5 times the sample concentration were added to the samples, and the recovery test was then conducted according to the method described in Section “2.3.2”. The average recoveries ranged from 99.29% to 100.66% with RSDs from 1.72% to 4.32%. These results indicate the good performance and data reliability of the UPLC method.
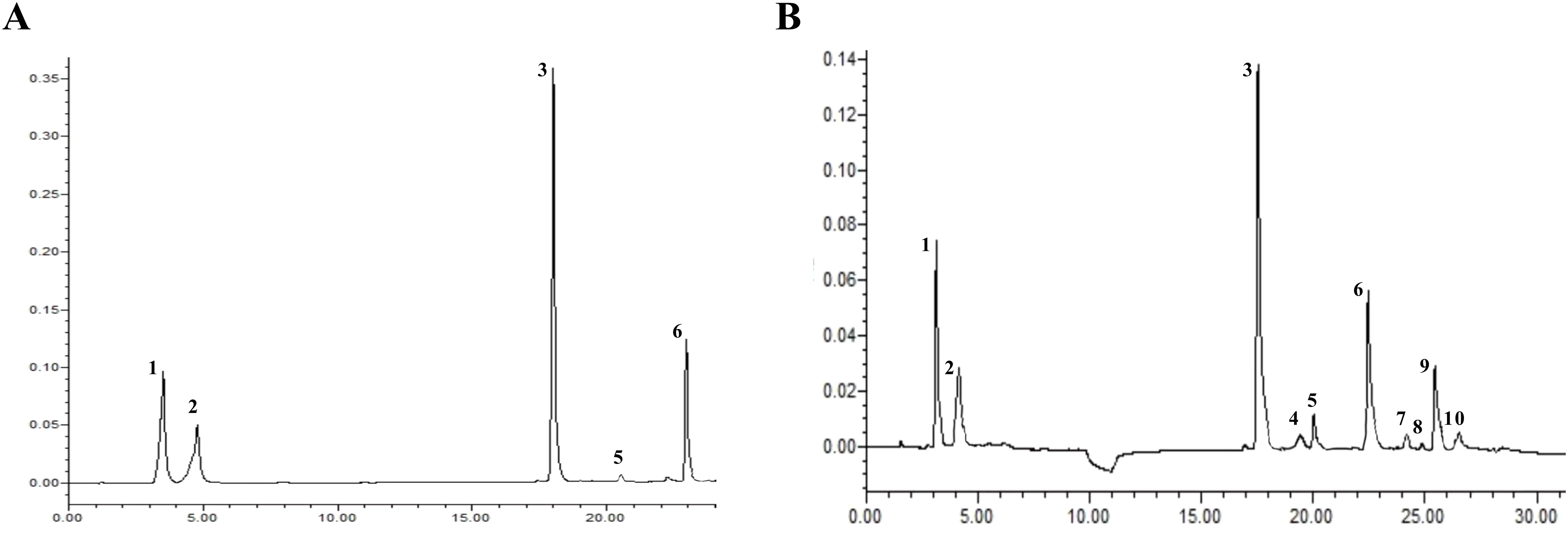
Figure 8. The UPLC chromatograms of Isatidis Folium. (A) The standard chromatogram. (B) The sample chromatogram. 1: 4-hydroxyquinazoline; 2: syringic acid; 3: tryptanthrin; 5: indigo; 6: indirubin. However, compounds 4, 7, 8, 9, and 10 were uncertain.
Figure 9A illustrates the differences in the levels of the five active ingredients under different salinity conditions. The t-test analysis results showed that except for the content of 4-hydroxyquinazoline, the levels of both tryptanthrin, syringic acid, indigo, and indirubin in the high salinity stress groups were significantly lower than those in the control group. Although the levels of certain constituents in the low salinity group also differed to some extent from those in the control group, the variability was small and the difference was not significant compared with the control group. Figure 9B illustrates the differences in the levels of the five active ingredients under different drought stress conditions. The t-test analysis results showed that the levels of syringic acid, tryptanthrin, indigo, and indirubin were all significantly lower in the drought stress group than in the control group. According to the 2020 edition of the Chinese Pharmacopoeia, the standard content of indirubin was 0.02%. The indirubin content was 0.1% in the control group, 0.046% in the drought group, 0.095% in the low salinity stress group, and about 0.018% in the high salinity stress group. Based on the levels of these five active ingredients, it can be concluded that the quality of Isatidis Folium varies under different environmental conditions. This suggests that Isatis indigotica Fort possesses a certain tolerance to salt and drought, while the accumulation of most of the active ingredients was strongly inhibited under severe salt stress.
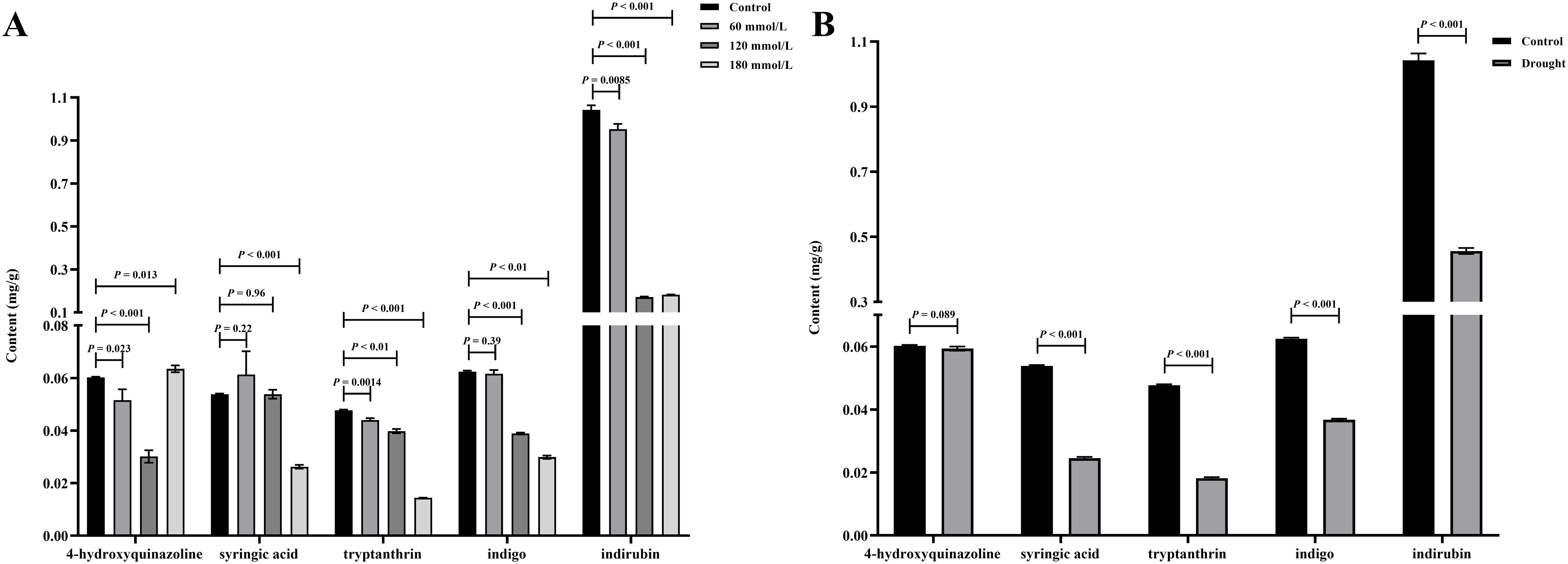
Figure 9. The t-test analysis results of the active ingredient content in Isatidis Folium under different stress conditions. (A) Salt stress; (B) Drought stress.
Table 1 shows the inhibitory activity of the Isatidis Folium decoction against E. coli and S. aureus under different stress conditions. In the control group, the decoction of Isatidis Folium was able to significantly inhibit the growth of E. coli and S. aureus at a concentration of 128-256 μg/mL, whereas in the high salinity and drought stress groups, a concentration of 512 μg/mL was required, and especially under drought stress, a concentration of 1024 μg/mL was required to inhibit the growth of S. aureus. The MIC values of both the high salinity group and the drought group were all significantly higher than those of the control group, indicating that the antibacterial activity of Isatidis Folium was significantly reduced under more severe stresses, implying that the medicinal effects were also severely inhibited.
As the salt stress progressed, the total chlorophyll and carotenoid contents of the control group all showed increasing trends, whereas the high salinity groups showed clear decreasing trends. At the same time, those of the high salinity groups were all lower than those of the control and the low salinity groups (Figures 10A–C). The contents of photosynthetic pigments in the low salinity group showed no difference compared to the control group in the early stage of stress, but the continuous accumulation of salt led to a decreasing trend in the later stage of stress. Based on the t-test analysis, in the later stage of stress, the contents of photosynthetic pigments of the control group were all significantly higher than those of the high salinity groups, as shown in Figure 11A. In addition, at the later stage of stress, the contents of photosynthetic pigments of the low salinity group were also lower than those of the control group, but the decreasing trend was relatively insignificant compared to those of the high salt stress groups. Under drought stress, the contents of photosynthetic pigments in both control and drought groups showed continuously increasing trends, but those of the control group were always significantly higher than those of the drought stress group (Figures 10D–F). Figure 11B shows the t-test analysis results that the contents of photosynthetic pigments were significantly different between the drought group and the control group, with the control group having significantly higher levels.
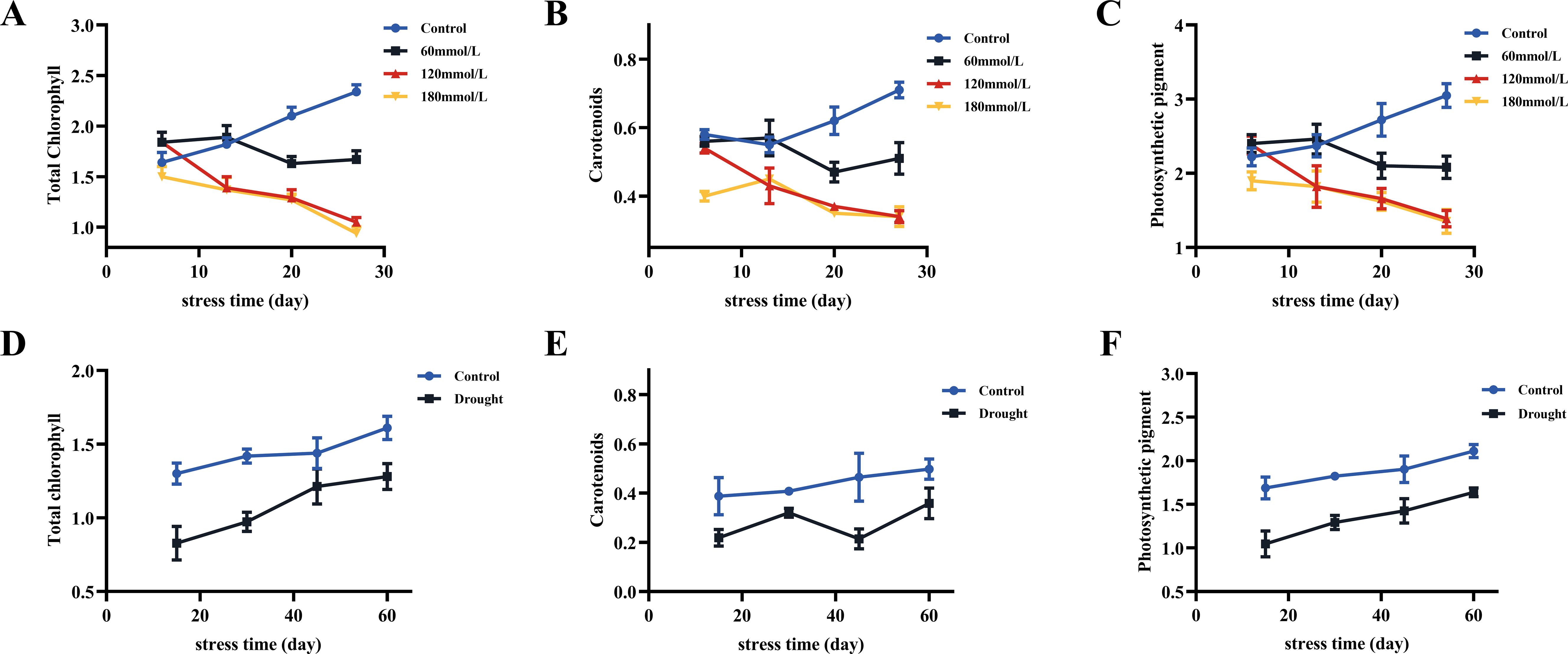
Figure 10. The content of total chlorophyll, carotenoids, and photosynthetic pigments in fresh Isatis indigotica Fort leaves under different stress conditions. (A–C) Salt stress. (D–F) Drought stress.
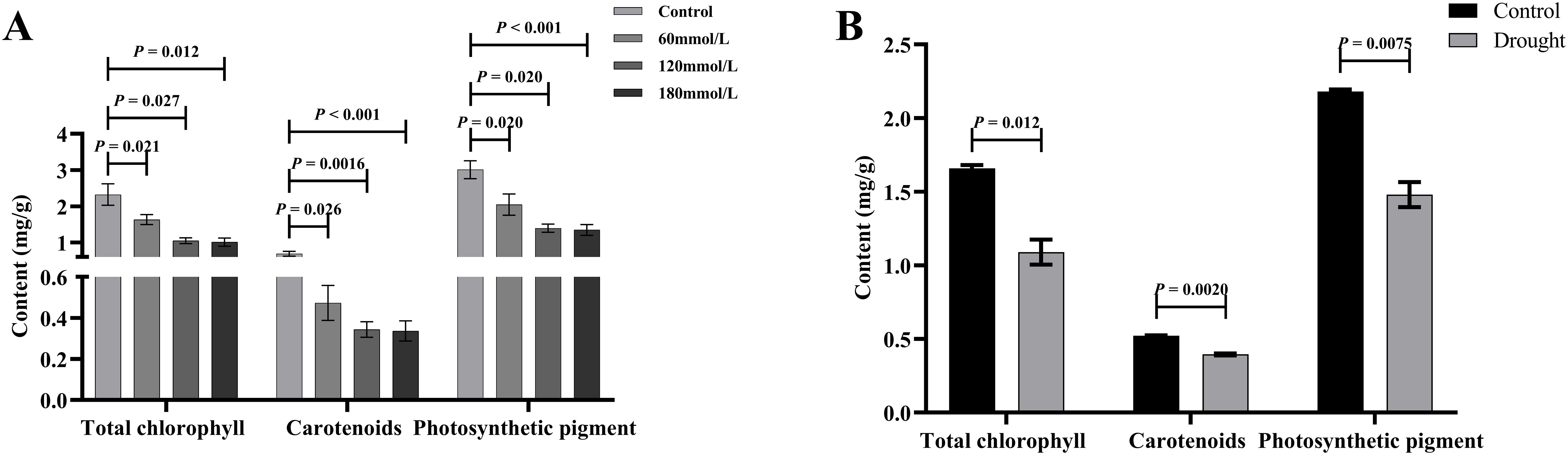
Figure 11. The t-test analysis results of total chlorophyll, carotenoids, and photosynthetic pigments content under different stress conditions. (A) Salt stress. (B) Drought stress.
Figures 12A, B illustrate the variations in REC under different stress conditions. As the stress progressed, the REC of the stress groups exhibited different degrees of increase, whereas the REC of the control group remained consistently lower than those observed in the stressed groups and were stable over time. Figures 12C, D show the results of the t-test analysis, indicating that the REC of the control group was significantly lower than that of the high salinity and drought groups. Specifically, the REC of the high salinity and drought groups were approximately 136.33%, 200.78%, and 167.67% higher than that of the control group.
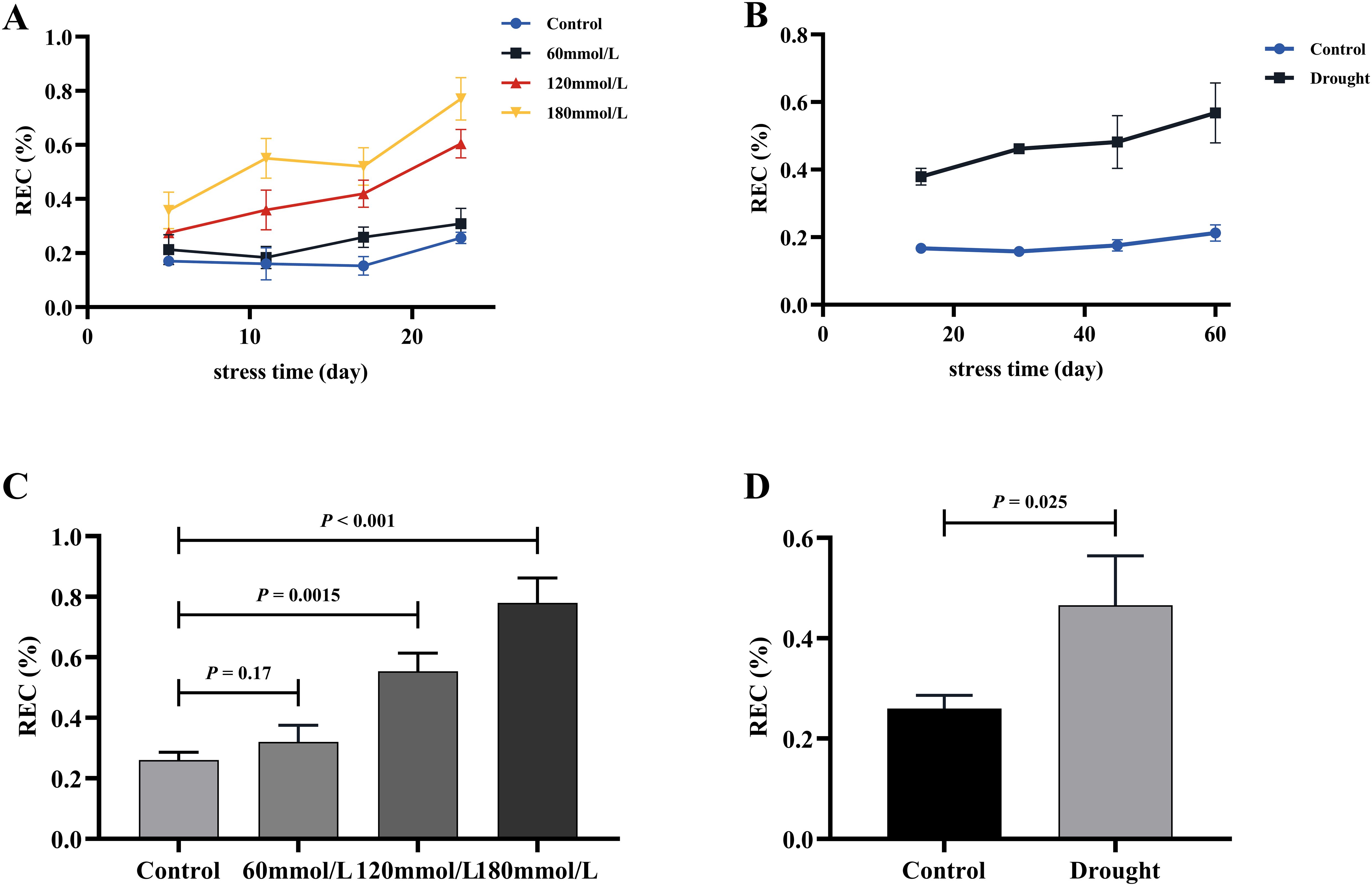
Figure 12. The REC of fresh Isatis indigotica Fort leaves under the two different treatment factors. (A, B) The variation of REC treated with salt stress and drought stress with the treatment time. (C, D) The t-test analysis results of REC in salt and drought stress groups.
Among the salt stress groups, the control and 180 mmol/L groups differed significantly and were selected for the t-test analysis. Figure 13 illustrates the differences in the production rate of ROS in the different stress groups: the rates in both the 180 mmol/L group and the drought group were all significantly higher than those in the control group.
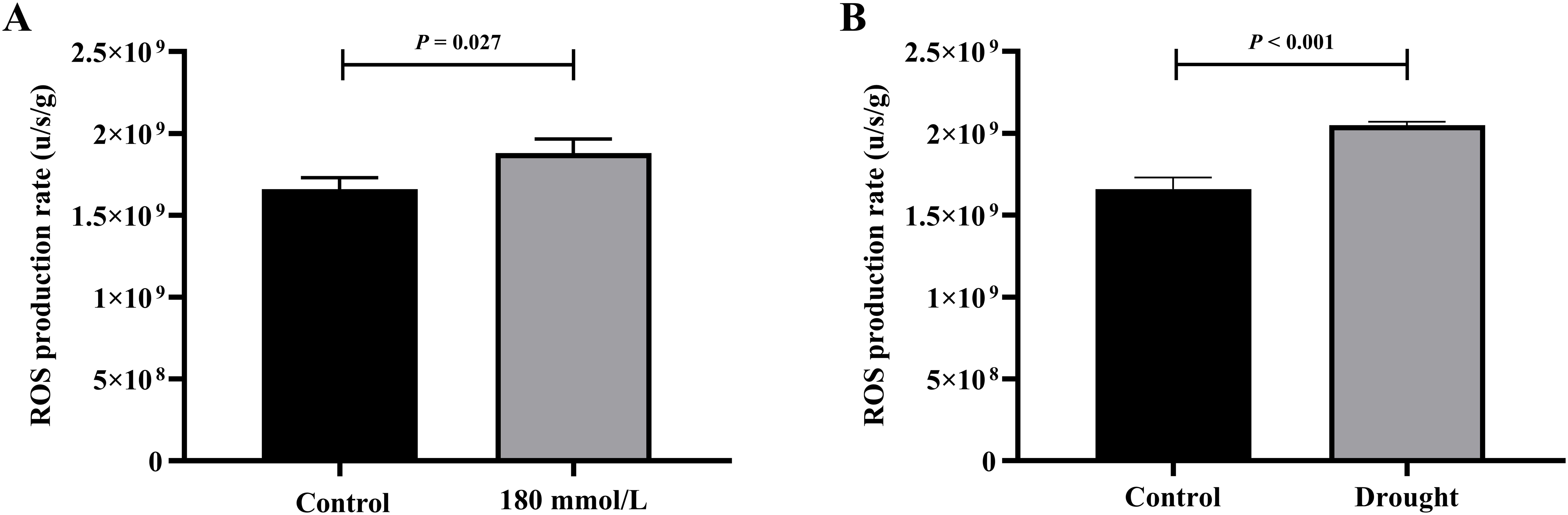
Figure 13. The t-test analysis results of ROS production rate under different stress conditions. (A) Salt stress. (B) Drought stress.
Based on the preceding results, the correlation between biophoton parameters and other indices was analyzed. The correlation analysis results are presented in Table 2 and Figure 14 provides a more intuitive view of the correlation network. The results indicated a positive correlation between the biophoton parameters (I0 and CPS) and the content of photosynthetic pigments and active ingredients such as syringic acid, tryptanthrin, indigo, and indirubin under different stress treatments. In addition, I0 and CPS were negatively correlated with REC, ROS generation rate, and MIC values. However, the correlation between T and other indicators was basically not significant.
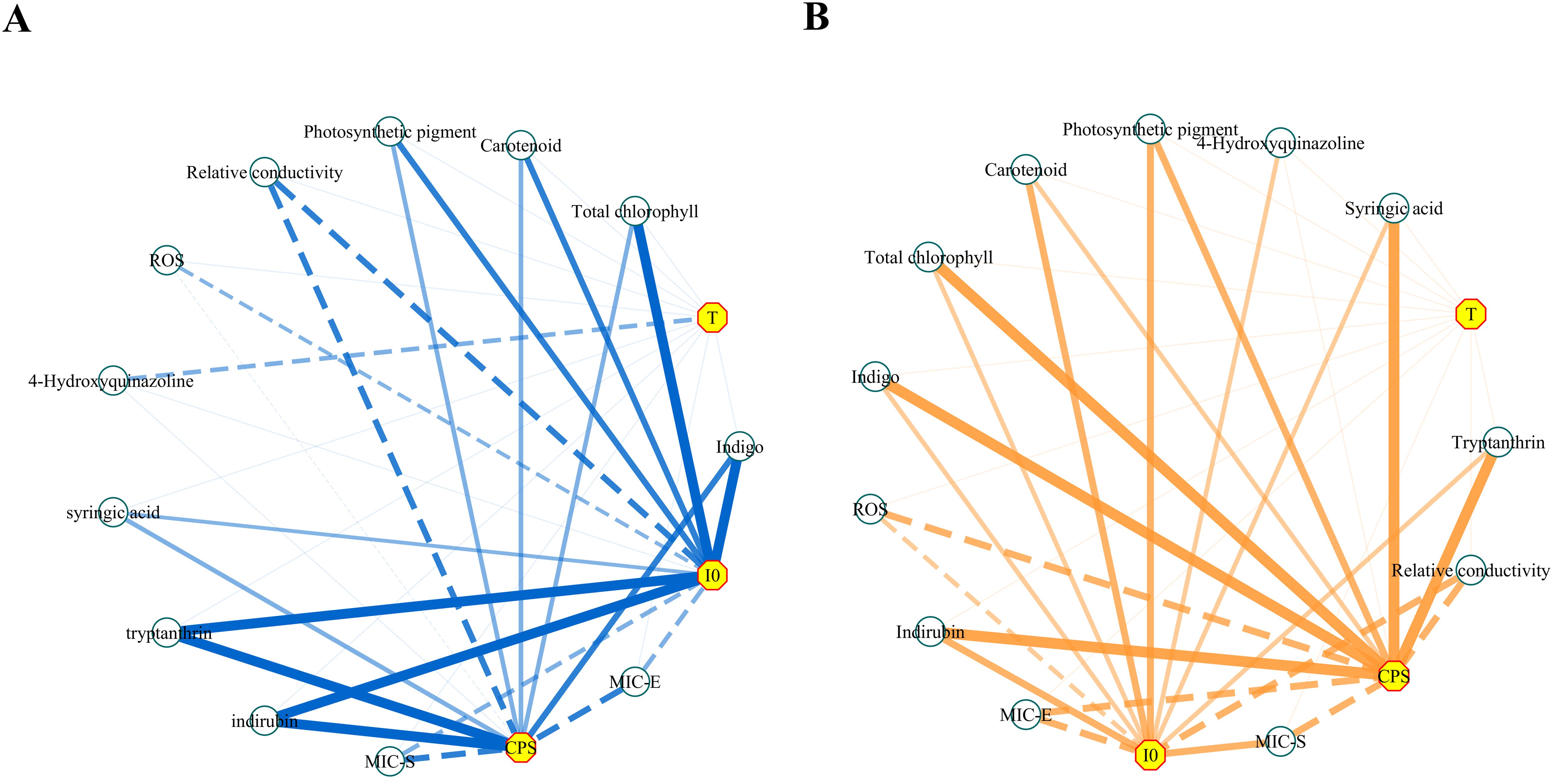
Figure 14. The network diagrams of the correlation analysis. (A) Salt stress. (B) Drought stress. Negative correlations were indicated by dotted lines and positive correlations were indicated by solid lines; the thicker lines indicated a higher correlation (i.e., a larger Spearman’s |ρ|). The length of each line had no meaning. MIC-E and MIC-S represent the minimum concentration at which the decoction of Isatidis Folium significantly inhibited the growth of E. coli and S. aureus, respectively.
According to the metabolic luminescence theory, redox reactions in biological systems produce highly reactive peroxyl radicals, which can then be oxidized into excited-state biomolecules. These inherently unstable biomolecules must return to the ground state, releasing excess energy in the form of photons during these transitions (Cifra and Pospísil, 2014). It is reasonable to assume that a biological system with higher metabolic activity will contain more biomolecules in the excited state. The greater the energy released by these active biomolecules during energy level transitions, the greater the intensity of the biophoton emission. Plant stress exposure leads to ROS accumulation, disrupting cell membrane structure and function, and promoting the formation of harmful compounds like superoxide anion and MDA. Such disruptions can lead to metabolic disruption and, ultimately, a decrease in the intensity of biophoton emission (Bu et al., 2022). It was found that the initial delayed fluorescence of winter wheat decreased by an order of magnitude under stress conditions (Jócsák et al., 2024). Consistent findings were obtained in our study: under high salinity and drought stress, the I0 of Isatis indigotica Fort leaves was approximately halved relative to the control group. Additionally, evidence indicates that I0 levels can reflect the metabolic strength of biological systems (Xi et al., 2011; Gang et al., 2015), which supports our previous view regarding the correlation between metabolic strength and biophoton emission intensity. Thus, it can be postulated that high salt and drought stresses likely caused significant cellular damage, inhibiting metabolic activity in Isatis indigotica Fort leaves. In the study of the DL characteristics, in addition to the intensity parameter, the time parameter T, introduced by Professor Gu, serves as an important macroscopic indicator reflecting the decay rate of the DL kinetic curve. Mathematical analysis of the DL decay kinetics revealed no significant differences in T between different stress conditions. This implies that different stress conditions had minimal impact on the decay characteristics of the DL kinetic curves of samples. Similar results were observed in a related study (Gu, 2012), where Europe Aloe vera samples showed a 30% higher I0 than South America samples, yet their T values remained nearly identical. This indicates that Aloe vera samples from these two regions differed in the “density” category, but were similar in the “composition” category. Consequently, we infer that Isatis indigotica Fort leaves subjected to different stress conditions maintained a similar level of “composition”, resulting in stable T values. However, stress influenced the “density”, such as the content of constituent substances, leading to a significant difference in I0 values. Therefore, we believe that, although parameter T cannot be used as a sensitive indicator to distinguish Isatis indigotica Fort leaves under various stress conditions, it can still reflect this valuable information.
These two severe abiotic stresses can promote the excessive accumulation of ROS and lead to oxidative stress damage. Such perturbations can lead to the extravasation of intracellular substances and the degradation of chlorophyll, thereby affecting physiological and metabolic processes such as photosynthesis (Sun et al., 2012). Chloroplasts are the sites of photosynthesis and can use photosynthetic pigments to convert light energy into chemical energy and store it in organic matter, which is the energy source for all life activities in green plants. The structure of the chloroplast remains relatively stable under normal physiological conditions (Qu et al., 2024). However, under stress conditions, the normal structure of the chloroplast is disrupted, leading to a series of abnormal phenomena, including plasmalemma separation, disorganization of internal components, and rupture of the membrane system (Long and Deng, 2019). This leads to the degradation of chlorophyll, disruption of physiological functions, and inhibition of photosynthesis. Consequently, the destruction of chloroplast structure and function will inevitably weaken the metabolic activities of green plants and inhibit their normal growth. Therefore, in this study, we developed these two stress models to investigate the potential relationship between biophoton emission characteristics, physiological state, and herbal quality. The test results showed that the photosynthetic pigment content of Isatis indigotica Fort leaves decreased significantly under stress conditions. This suggests that salt and drought stress could damage the chloroplasts, resulting in reduced energy production and unfavorable secondary metabolite synthesis. The study also showed that the REC of samples under both high salinity stress and drought stress were all significantly higher than that of the control group. This suggests that under stress conditions, the cell membrane structure suffers severe damage, resulting in a loss of the ability to regulate the entry and exit of substances. At the same time, the stress disrupts the dynamic balance between ROS generation and consumption in the leaves, leading to membrane rupture and metabolic disorders (Meng et al., 2022). As a result, plant growth is inhibited, inevitably affecting the accumulation of active ingredients.
The correlation analysis revealed a strong correlation between the physiological indicators and the biophoton parameters (I0 and CPS). Compared to the control group, there was a significant decrease tread in photosynthetic pigment content with increasing stress levels. I0 and CPS positively correlated with photosynthetic pigment content, consistent with prior research findings (Sun et al., 2023b). Lower chlorophyll content correlates with reduced photosynthesis, indicating weakened metabolic activity and decreased biophoton emission intensity. In contrast, both I0 and CPS showed a significant negative correlation with the rate of ROS production, which seems to contradict some reports in the literature. This discrepancy may be due to the source of biophoton emission in Isatis indigotica Fort leaves differing from that observed in other sample types. It is well known that ROS is one of the major sources of ultra-weak luminescence and that the ultra-weak luminescence of biological samples is positively correlated with oxidative stress. However, ROS may not be the only or direct source of the changes in biophoton emission. On the contrary, some studies (Sun et al., 2023b; Bai et al., 2018b) have reported that the ultra-weak luminescence of green plants was negatively correlated with ROS, which is consistent with our results. This is because salt stress severely inhibits the photosystem (PS) activity and the oxygen-evolving complex in leaves, damages the integrity of the thylakoid membrane, decreases the photochemical efficiency of PSII, and hinders the QA-QB electron transfer (Sun et al., 2023a). This change inhibits photosynthesis and reduces the metabolic strength of the system. At the same time, the large accumulation of ROS under stress will damage the cell membrane system, causing extravasation of intracellular tissue and disorganization of tissue structure, leading to metabolic disorders, reduced growth and vigor, and ultimately reflected in the weakening of the CPS (Bai et al., 2018a). REC serves as a crucial physiological indicator of plant resistance, exhibiting a negative correlation with the structural integrity of cell membranes. The significant negative correlation between biophoton parameters and REC indicates that biophoton emission could reflect the extent of cell membrane damage in Isatis indigotica Fort leaves under stress. In conclusion, the results demonstrate that biophoton parameters can be used as effective indicators for reflecting the physiological status of Isatis indigotica Fort leaves.
Chinese herbs are composed of a variety of complex chemical components. Some of these components, such as alkaloids, flavonoids, glycosides, volatile oils, amino acids, possess specific biological activities and are collectively termed the active ingredients of Chinese herbs. Relevant studies have shown that, in addition to growth, appearance, and physiological indices, stressors can also affect the accumulation of active ingredients in medicinal plants (Tang et al., 2018; Yang et al., 2023). For medicinal plants, the content of active ingredients plays a crucial role in determining their quality. Consequently, excessive stress will inevitably affect the quality of the herbs. The results of the UPLC-based determination of active ingredients indicated that the effect of low salinity stress on the total active ingredient content of Isatidis Folium was not discernible. In contrast, under high salinity and drought stress conditions, a significant reduction in the content of the four main active ingredients was observed, which is consistent with the results reported in the literature (Zhou et al., 2019; Cheng, 2018). Similar results were also obtained in the determination of antibacterial activity: the MIC values of E. coli and S. aureus were significantly higher than those of the control group in both high salinity and drought stress groups, indicating that excessive stress also inhibited the antibacterial activity of Isatidis Folium. Combining the results of UPLC and MIC determination, we tentatively conclude that stress conditions, especially excessive abiotic stresses, can seriously reduce the herbal quality. Therefore, there is a significant difference between the herbal quality of our established stress models and the control group.
It is known that the form of excitation energy generated by light irradiation depends on the absorption of this energy by molecules within the body. Changes in the chemical composition and content of the herbs will alter the internal structure of the herbs, which in turn will alter the ability of the molecules to interact, absorb, and store excitation energy, resulting in different DL kinetics. In addition, some studies (Xi et al., 2015) have shown that SPE mainly occurs during the redox metabolism and protein synthesis processes in Chinese herbs, and the differences in the active ingredient content will affect the protein synthesis mechanism and related energy metabolism in the plants, thereby affecting the CPS of the Chinese herbs. The findings indicated that the content of the active components of Isatidis Folium under both two types of stress was positively correlated with the biophoton parameters (I0 and CPS). The levels of the active ingredients of Isatidis Folium under high salt and drought stress decreased significantly compared to the control group. It is important to note that Isatidis Folium contains mainly indigo, indirubin, tryptanthrin, and syringic acid, as active compounds, which may directly influence the pharmacological action and thus affect its therapeutic properties.
The DL technique has previously been identified as an effective method for quality control of Chinese herbal medicines, based on studies analyzing the DL characteristics, active ingredient content, and pharmacological activity. These studies have demonstrated an obvious correlation between biophoton parameters and quality indicators (Jia et al., 2020; Sun et al., 2019b, a, Sun et al., 2016b, a, Sun et al., 2020). Existing literature further indicates potential correlations between the biophoton emission characteristics and the herbal content of the active ingredients in fresh samples of several Chinese herbal plants, such as the roots of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge and Platycodon grandiflorus (Jacq.) A.DC (Zhao et al., 2017), Lonicera japonica Thunb. buds (Zhao, 2014), and Leonurus japonicus Houtt. leaves and Carthamus tinctorius L. flowers (Cao et al., 2023). All these studies provide a solid foundation for our exploration. Our study reveals that the biophoton characteristics of fresh Isatis indigotica Fort leaves of different stress conditions were significantly different and correlated with the active ingredient content, antibacterial activity, and physiological indices. Therefore, we preliminary believe it is feasible to use the biophoton characteristics of fresh Isatis indigotica Fort leaves to predict and evaluate the quality of Isatidis Folium during cultivation. Specifically, the biophoton detection technology enables real-time monitoring of Isatidis Folium quality during the growth of Isatis indigotica Fort. This allows for the timely removal of poor-quality plants or the implementation of corrective measures, thereby improving overall yield and quality.
In addition, other existing quality control methods of Chinese herbs, although mainstream, lack complete and accurate characterization. These methods rely on the analysis of dried Chinese herbs after processing, involving complex procedures that result in irreversible damage and waste. Additionally, they struggle to effectively monitor herbal quality during cultivation. Conversely, biophoton emission captures comprehensive intrinsic information from biological samples, aligning with the holistic view of traditional Chinese medicine and offering a more thorough reflection of herbal quality. Moreover, quality evaluation of Chinese herbs based on biophoton technology will not damage the structure or efficacy of the samples. The measurement of specific parameters by this technique allows quality to be determined immediately post-harvest. Therefore, biophoton detection technology has the advantages of rapidity, sensitivity, and non-invasiveness, simplifying the evaluation process compared to the traditional methods and requiring lower operational techniques and testing costs. However, given the limited sample diversity and size, further extensive experimental investigation is required to validate the generalizability and applicability of these findings. Due to the large equipment, many components, and complicated wiring, the current biophoton detectors can only be fixed in one place, making it impossible to detect fresh samples directly in the planting fields without removing the samples from the plants. The diversity of DL kinetic curve fitting methods results in a wide range of biophoton parameters and the lack of agreement in this domestic and international research field, which also leads to uncertainty and complexity in parameter selection. Spectroscopic detection techniques are also of great value in the characterization and identification of Chinese herbs (Yao et al., 2022; Qi et al., 2022), and when combined with modern scientific techniques such as chromatography and mass spectrometry, they can evaluate the properties of Chinese herbs more comprehensively. By combining HPLC with near-infrared technology and chemometric modeling, a comprehensive evaluation of Danshen medicines was achieved, from active ingredient quantification to overall quality variation (Li et al., 2022). The creation of a comprehensive analysis process of multispectral data enables the traceability of the origin of Chinese herbs (Qi et al., 2020). It not only helps to evaluate herbal quality but also facilitates similar quality assessment efforts for other natural medicines. Moreover, the spectroscopic method has the advantages of high sensitivity, high accuracy, and intelligence, which can achieve rapid, non-destructive, and environmentally friendly detection of Chinese herbs without affecting their quality and utility as well. Therefore, further identification of the most applicable fitting methods and characteristic parameters, as well as the development of portable instrumentation that can detect the light intensity and spectrum concurrently, is crucial for the real promotion of this technology for quality prediction and monitoring during herbal cultivation. If this technology is to be truly promoted and applied to quality prediction and monitoring during the cultivation of Chinese herbs, future research should focus on establishing mathematical models of biophoton parameters based on multiple sources and large samples, to better guide practical applications.
The quality of Chinese herbs represents a pivotal concern in the modernization and internationalization of traditional Chinese medicine. Currently, the quality of Isatidis Folium varies, and the evaluation system requires improvement. In this study, we proposed a novel method to identify different stress subtypes of Isatis indigotica Fort using biophoton technology and preliminarily verified its feasibility in the quality evaluation of Isatidis Folium, which aligns with the holistic perspective of traditional Chinese medicine and is also simple and rapid. This study revealed significant differences in the biophoton parameters (I0 and CPS) and physiological indices of fresh Isatis indigotica Fort leaves and in the active ingredient content and antibacterial activity of Isatidis Folium under various stress conditions. I0 and CPS were able to accurately differentiate between stress subtypes and the growth status of Isatis indigotica Fort and were correlated with the quality of Isatidis Folium. Thus, we believe that the biophoton detection technique has good potential as a rapid technique to predict and evaluate the quality of Isatidis Folium. Furthermore, I0 and CPS may serve as effective indicator parameters with significant potential for herbal quality monitoring.
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
ZW: Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. BC: Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YM: Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. WX: Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. JF: Methodology, Writing – original draft. ZZ: Methodology, Writing – original draft. JD: Investigation, Writing – original draft. TD: Investigation, Writing – original draft. JP: Methodology, Writing – original draft. MY: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. JH: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82004212), the Project of Shandong Traditional Chinese Medicine Plan (No. M-2022259), and the Co-construction Project of National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine (No.GZY-KJS-SD-2023-084).
The authors would like to thank all those who contributed to this study.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Alam, K., Hossain, M. S., Zhao, Y., Zhang, Z., Xu, S., Hao, J., et al. (2025). Tryptanthrins as multi-bioactive agents: discovery, diversity distribution and synthesis. Bioorganic Chem. 154, 108071. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2024.108071
Bai, Y., Yan, Y. T., Guo, J. L., Liang, S., Shao, C. F. (2018a). Relationship between ultraweak luminescence and reactive oxygen under salt stress of sedum plants. Northern Horticulture, 82–87. doi: 10.11937/bfyy.20173121
Bai, Y., Yan, Y. T., Liang, S., Guo, J. L. (2018b). The relationship between ultraweak luminescence and photosynthesis under salt stress of Sedum hybridum. J. Anhui Agric. University. 45, 526–531. doi: 10.13610/j.cnki.1672-352x.20180620.006
Bu, L., Chen, Z., Liu, Z. (2022). Effects of salt stress on physiological and biochemical indices of rob hemp and ultra-faint luminescence. Mol. Plant Breed., 1–15.
Cao, B., Wang, Z., Zhang, J., Fu, J., Zhang, Z., Du, J., et al. (2023). A biophoton method for identifying the quality states of fresh Chinese herbs. Front. Pharmacol. 14, 1140117. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1140117
Chen, J., Zhu, Z., Gao, T., Chen, Y., Yang, Q., Fu, C., et al. (2022). Isatidis Radix and Isatidis Folium: A systematic review on ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry and pharmacology. J. Ethnopharmacol. 283, 114648. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114648
Cheng, L. (2018). Physiological and ecological changes of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi under drought stress and mlecular ecological mechanism of baicalin biosynthesis (Jilin: Dr, Jilin Agricultural University).
Chuang, H. C., Chuang, K. J., Cheng, P. C., Hsieh, C. L., Fan, Y. Y., Lee, Y. L. (2024). Indirubin induces tolerogenic dendritic cells via aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation and ameliorates allergic asthma in a murine model by expanding Foxp3-expressing regulatory T cells. Phytomedicine. 135, 156013. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.156013
Chung, Y. C., Lee, A., Jang, C. H., Ryuk, J. A., Ha, H., Hwang, Y. H. (2024). Isatidis folium represses dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis and suppresses the inflammatory response by inhibiting inflammasome activation. Nutrients. 16, 3323. doi: 10.3390/nu16193323
Cifra, M., Pospísil, P. (2014). Ultra-weak photon emission from biological samples: Definition, mechanisms, properties, detection and applications. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B-Biology. 139, 2–10. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2014.02.009
Commission, C. P (2020). Chinese pharmacopoeia (Beijing: The Medicine Science and Technology Press of China).
Committee, N. S (2017). “Law of the people’s republic of China on traditional chinese medicine,” in Gazette of the Standing Committee of the National People’s Congress of the People’s Republic of China (Beijing: Gazette of the Standing Committee of the National People’s Congress of the People’s Republic of China), 5–11. Available at: https://flk.npc.gov.cn/detail2.html?MmM5MDlmZGQ2NzhiZjE3OTAxNjc4YmY4MzgyODA5YWI%3D.
Gang, X., Zhao, Y. Y., Liu, K., He, R. R. (2015). Changes of ultraweak photon emission of corn during germination under NaCl stress. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Engineering. 31, 308–314. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2015.11.044
Gao, G. X., Dong, Z. (2010). Exploration of Chinese medicine quality standardization and modernization development of Chinese medicine. China Med. Herald. 7, 76–77. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7210.2010.02.046
Guo, X., Hu, X. L., Wang, Y. R., Yang, Z. F., Wang, Y. T., Li, Z. T., et al. (2016). Systematic separation, purification and composition analysis of polysaccharides from isatis indigotica. J. Chin. Medicinal Materials. 47, 1508–1514. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2016.09.010
Huang, Q. C., Xu, Y. M., Wei, Y. H., Liang, Y. Z. (2013). Comparison of carotenoid content in dark leaf plants. Hubei Agric. Sci. 52, 2573–2574. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0439-8114.2013.11.028
Ji, Z. Q., Li, Y. L., Zhang, Y. F., Shi, L. (2013). Studies on chemical constituents of folium isatidis. China Pharmacist. 16, 1467–1469. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-049X.2013.10.010
Jia, Y. S., Sun, M. M., Shi, Y. H., Zhu, Z. H., Van Wijk, E., Van Wijk, R., et al. (2020). A comparative study of aged and contemporary Chinese herbal materials by using delayed luminescence technique. Chin. Med. 15, 6. doi: 10.1186/s13020-020-0287-0
Jiang, L. L., Lu, Y. L., Jin, J. H., Dong, L. L., Xu, F. L., Chen, S. S., et al. (2015). n-Butanol extract from Folium isatidis inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory cytokine production in macrophages and protects mice against lipopolysaccharide-induced endotoxic shock. Drug Design Dev. Ther. 9, 5601–5609. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S89924
Jócsák, I., Lukács, H., Varga-Visi, É., Somfalvi-Tóth, K., Keszthelyi, S. (2024). Identification and investigation of barley powdery mildew (Blumeria graminis f. sp. tritici) infection in winter wheat with conventional stress reactions and non-invasive biophoton emission parameters. J. Biosciences. 49, 6.
La, F. Y., Hu, H. B. (2009). Study on the quality analysis of isatidis folium and its pieces. Jiangsu Jouranl Traditional Chin. Med. 41, 59–60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-397X.2009.08.039
Li, Q., Qi, L., Zhao, K., Ke, W., Li, T., Xia, L. (2022). Integrative quantitative and qualitative analysis for the quality evaluation and monitoring of Danshen medicines from different sources using HPLC-DAD and NIR combined with chemometrics. Front. In Plant Science. 13, 932855. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.932855
Li, Y., Zhang, M. M., Zhang, X., Zhang, N., Xie, Z. M. (2019). Evaluation of the quality of isatis indigotica from different origins by multi-component content determination and HPLC fingerprint. China Pharmaceuticals. 28, 15–18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4931.2019.17.004
Liu, S. F., Zhang, Y. Y., Zhou, L., Lin, B., Huang, X. X., Wang, X. B., et al. (2018). Alkaloids with neuroprotective effects from the leaves of Isatis indigotica collected in the Anhui Province, China. Phytochemistry. 149, 132–139. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2018.02.016
Long, H. Y., Deng, L. X. (2019). Response and adaptation of plant morphology to drought stress. Hubei Agric. Sci. 58, 5–7. doi: 10.14088/j.cnki.issn0439-8114.2019.08.001
Ma, Y. E. (2022). Effect of soil moisture content on the growth and physiological characteristics of sphagnum pine seedlings. J. Green Sci. Technology. 24, 150–153. doi: 10.16663/j.cnki.lskj.2022.23.017
Mao, X. F. (2018). Research on extraction and isolation of folium isatidis’ogranic acids and its acute toxic experiment. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University.
Meng, X. C., Li, X. Y., Yao, J., Kong, L., Guan, Y. (2022). Mechanism of ecological stress enhancing quality of genuine medicinal materials and its quality evaluation idea. Chin. Traditional Herbal Drugs 53, 1587–1594. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2022.05.034
Mi, Y. W., Wang, G. X., Gong, C. W., Cai, Z. P., Wu, W. G. (2018). Effect of salt stress on the growth and resistance physiology of young woad seedlings. Acta Prataculturae Sinica. 27, 43–51. doi: 10.11686/cyxb2017282
Popp, F. A., Li, K. H., Mei, W. P., Galle, M., Neurohr, R. (1988). Physical aspects of biophotons. Experientia. 44, 576–585. doi: 10.1007/BF01953305
Qi, L., Zhong, F., Chen, Y., Mao, S., Yan, Z., Ma, Y. (2020). An integrated spectroscopic strategy to trace the geographical origins of emblic medicines: Application for the quality assessment of natural medicines. J. Pharm. Analysis. 10, 356–364. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2019.12.004
Qi, L., Zhong, F., Liu, N., Wang, J., Nie, K., Tan, Y., et al. (2022). Characterization of the anti-AChE potential and alkaloids in Rhizoma Coptidis from different Coptis species combined with spectrum-effect relationship and molecular docking. Front. In Plant Science. 13, 1020309. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1020309
Qu, H. X., Liang, S., Hu, L. F., Yu, L., Liang, P. X., Hao, Z. D., et al. (2024). Overexpression of hybrid in leads to excessive chlorophyll synthesis and improved growth. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25, 13.
Song, S. W. (2011). Study on response characteristics of six mulberry varieties under salt stress. Taian: Shandong Agricultural University. Thesis.
Sun, M., Chang, W. T., Van Wijk, E., He, M., Koval, S., Lin, M. K., et al. (2017). Characterization of the therapeutic properties of Chinese herbal materials by measuring delayed luminescence and dendritic cell-based immunomodulatory response. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B. 168, 1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2017.01.018
Sun, M. M., He, M., Korthout, H., Halima, M., Kim, H. K., Yan, Y., et al. (2019a). Characterization of ginsenoside extracts by delayed luminescence, high-performance liquid chromatography, and bioactivity tests. Photochemical Photobiological Sci. 18, 1138–1146. doi: 10.1039/c8pp00533h
Sun, Q., Leng, J., Tang, L., Wang, L., Fu, C. (2021). A comprehensive review of the chemistry, pharmacokinetics, pharmacology, clinical applications, adverse events, and quality control of indigo naturalis. Front. Pharmacol. 12, 664022. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.664022
Sun, C., Li, X., Guo, J. (2023a). Relationship between photosystem activity and ultraweak luminescence excitation in Cerasus humilis leaves under salt stress. Plant Physiol. Biochemistry: PPB. 196, 1032–1045. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2023.03.005
Sun, M., Li, L., Wang, M., Van Wijk, E., He, M., Van Wijk, R., et al. (2016a). Effects of growth altitude on chemical constituents and delayed luminescence properties in medicinal rhubarb. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B. 162, 24–33. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2016.06.018
Sun, M. M., Van Wijk, R., Van Wijk, E., Wang, M., Van Wietmarschen, H., Hankemeier, T., et al. (2016b). Delayed luminescence: an experimental protocol for Chinese herbal medicines. Luminescence. 31, 1220–1228. doi: 10.1002/bio.v31.6
Sun, M. M., Wang, S. P., Jing, Y., Li, L., He, M., Jia, Y. S., et al. (2019b). Application of delayed luminescence measurements for the identification of herbal materials: a step toward rapid quality control. Chin. Med. 14, 47. doi: 10.1186/s13020-019-0269-2
Sun, M., Wu, H., He, M., Jia, Y., Wang, L., Liu, T., et al. (2020). Integrated assessment of medicinal rhubarb by combination of delayed luminescence and HPLC fingerprint with emphasized on bioactivities based quality control. Chin. Med. 15, 72. doi: 10.1186/s13020-020-00352-8
Sun, M. C., Yin, Z. P., Ma, X. L., Zhou, L. J., Ren, J., Song, X. S. (2012). Effects of salt stress on physiological characteristics and ion contents in Cerasus humilis seedlings. Nonwood For. Res. 30, 33–37. doi: 10.14067/j.cnki.1003-8981.2012.02.012
Sun, C., Zhu, C., Li, D. F., Zhang, J., Guo, J. L. (2023b). Relationship between Chloroplast Structure and Function and Ultraweak Luminescence Excitation of Cerasus humilis Leaves under Salt Stress. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica. 43, 2049–2059. doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-4025.2023.12.2049
Tang, X. Q., Liu, Y., Yang, R., Li, L. H., Wang, Y., Shi, S. L., et al. (2018). Effects of salt stress on physiology and active component of Silybum marianum at seedling stage. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 46, 135–139. doi: 10.15889/j.issn.1002-1302.2018.21.033
Wang, W. H., Pang, J. X., Huang, J. Z., Han, J. X. (2015). Development and application of biophoton. J. Biomed. Eng. Res. 34, 196–200. doi: 10.19529/j.cnki.1672-6278.2015.03.015
Wang, X. L., Sun, H. Z., Liu, X. M., Su, J., Liu, Y. L. (2024). Optimization of determination method and difference analysis of Isatidis folium in Chinese Pharmacopoeia by response surface method. Chin. J. Hosp. Pharmacy. 44, 557–563. doi: 10.13286/j.1001-5213.2024.05.11
Wu, X., Chen, X., Jia, D., Cao, Y., Gao, S., Guo, Z., et al. (2016). Corrigendum: Characterization of anti-leukemia components from Indigo naturalis using comprehensive two-dimensional K562/cell membrane chromatography and in silico target identification. Sci. Rep. 6, 30103. doi: 10.1038/srep30103
Wu, B., Wang, L., Jiang, L., Dong, L., Xu, F., Lu, Y., et al. (2018). n-butanol extract from Folium isatidis inhibits the lipopolysaccharide-induced downregulation of CXCR1 and CXCR2 on human neutrophils. Mol. Med. Rep. 17, 179–185. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.7870
Xi, G., Zhang, X., Liu, K., Li, S. (2011). Evaluation method of UV-B radiation damage on plant cell based on photonic technology. Chin. J. Luminescence. 32, 398–403. doi: 10.3788/fgxb20113204.0398
Xi, G., Zhao, Y. Y., Liu, K., He, R. R. (2015). Effect of protein synthesis inhibitors on ultraweak photon emission of germinated maize. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agricultural. 303-308, 10.
Xiao, Y. H., Xia, Y., Cheng, P. P., Fang, Y., Da, G. Z., Huang, J., et al. (2015). Simultaneous determination of indigo and indirubin in folium isatidis by RP-HPLC. Herald Med. 34, 1506–1508. doi: 10.3870/j.issn.1004-0781.2015.11.024
Xiong, X. L., Yuan, M. M., Wu, L. F., Li, K. C., Zhong, R. J. (2022). Studies on the chemical constituents of folium isatidis. J. Chin. Medicinal Materials 45, 2637–2642. doi: 10.13863/j.issn1001-4454.2022.11.019
Xu, Z. Q., Cai, Y. N., Chen, Y. D., Zhao, Z. M., Ma, Q., Yang, D. P., et al. (2021). Studies on the chemical constituents of the leaves of kalanchoe. J. Chin. Medicinal Materials. 44, 1875–1879. doi: 10.13863/j.issn1001-4454.2021.08.016
Yan, Z. H., Li, W. S., Liang, B. Y., Wu, H., Peng, W., Li, C. Y., et al. (2024). Comparison of chemical constituents of Isatidis Radix and Isatidis Folium based on UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS. Chin. Traditional Herbal Drugs 55, 3956–3965. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2024.12.004
Yang, Q. Y., Luo, Y. Z., Yang, Y., Ruan, B. L., Huang, M. J. (2023). Influences of drought stress on physiology and active components of different parts of Dendrobium officinale. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 51, 142–149. doi: 10.15889/j.issn.1002-1302.2023.13.022
Yao, C., Qi, L., Zhong, F., Li, N., Ma, Y. (2022). An integrated chemical characterization based on FT-NIR, GC-MS and LC-MS for the comparative metabolite profiling of wild and cultivated agarwood. J. Chromatography. B Analytical Technol. In Biomed. Life Sci. 1188, 123056. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2021.123056
Yu, Y. P., Gong, D. D., Zhu, Y., Wei, W., Sun, G. X. (2018). Quality consistency evaluation of combined with equal weight quantified ratio fingerprint method and determination of antioxidant activity. J. Chromatogr. B-Analytical Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 1095, 149–156. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2018.07.031
Yuan, M. M., Li, K. C., Dai, M., Zhou, L. G., Zhou, G. P., Wu, L. F. (2023). Chemical constituents from folium isatidis. Chin. Traditional Patent Med. 45, 2923–2929. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2023.09.020
Zhang, Y. M., Huang, Y. Z., Wan, H. H., Li, Z. X., Sun, W., Wu, S. S., et al. (2020). Advances in biosynthesis of indigo in plants. China J. Chin. Materia Medica. 45, 491–496. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20191204.102
Zhao, X. L. (2014). The preliminary study on characteristics of biophoton emission of Chinese herbs in the process of growth. Jinan: University of Jinan. Master.
Zhao, X., Pang, J., Fu, J., Yang, M., Van Wijk, E., Liu, Y., et al. (2017). Application of spontaneous photon emission in the growth ages and varieties screening of fresh Chinese herbal medicines. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017, 2058120. doi: 10.1155/2017/2058120
Zhou, B. C. (2019). Preliminary study on the properties of traditional Chinese medicine based on the detection of palisade and mouse ultraweak luminescence. Jinan: Jinan University. master.
Zhou, B. Q., Lu, H., Liu, F., Wang, X., Geng, Y. L., Liu, W., et al. (2019). Effects of different temperature stress on cell membrane permeability,active oxygen metabolism and accumulation of effective substances in Lonicera japonicea. Chin. J. Chin. Mater Med. 44, 3935–3941. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20190701.110
Keywords: Isatis indigotica Fort, Isatidis Folium, biophoton emission, stress condition, quality evaluation, active ingredient content, antibacterial activity
Citation: Wang Z, Cao B, Ma Y, Xu W, Fu J, Zhang Z, Du J, Deng T, Pang J, Yang M and Han J (2025) Exploration of biophoton characteristics of fresh Isatis indigotica fort leaves under salt and drought stresses and the feasibility analysis for the quality prediction of Isatidis Folium. Front. Plant Sci. 16:1523636. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1523636
Received: 06 November 2024; Accepted: 19 February 2025;
Published: 12 March 2025.
Edited by:
Sunil Kumar Sahu, Beijing Genomics Institute (BGI), ChinaReviewed by:
Chenghao Fei, Nanjing Agricultural University, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Wang, Cao, Ma, Xu, Fu, Zhang, Du, Deng, Pang, Yang and Han. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Meina Yang, eHoxOTU2MDY1OTE5M0AxNjMuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share last authorship
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.