
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Plant Sci., 07 February 2025
Sec. Plant Symbiotic Interactions
Volume 16 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2025.1510196
This article is part of the Research TopicCross-Kingdom Communications Among Plants, Fungi and Bacteria: From Molecules to Ecological FactorsView all 10 articles
Introduction: WRKY transcription factors are essential for plant growth, health, and responses to biotic and abiotic stress.
Methods: In this study, we performed a deep in silico characterization of the WRKY gene family in the genome of Eucalyptus grandis. We also analyzed the expression profiles of these genes upon colonization by the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus (AMF) Rhizophagus irregularis (Ri) and infection with the bacterial pathogen Ralstonia solanacearum (Rs).
Results: A total of 117 EgWRKYs were identified. Phylogenetic analysis divided the EgWRKY proteins into three groups: group I (21 proteins, 17.95%), group II (65 proteins, 55.56%), and group III (24 proteins, 20.51%). Additionally, seven EgWRKY proteins (5.98%) were categorized into group IV due to the absence of the WRKY domain or zinc-finger structure. All EgWRKY genes are distributed irregularly across the 11 chromosomes, with 25 pairs identified as segmental duplicates and four as tandem duplicates. The promoter regions of 50% of members of each subfamily contain plant hormone-related cis-elements associated with defense responses, such as ABREs, TGACG motifs, and CGTCA motifs. All subfamilies (except for group IV-b and IV-c) contain AW-boxes, which are related to mycorrhizal induction. Furthermore, transcriptomic analysis revealed that 21 EgWRKYs were responsive to the AMF Ri, with 13 and 8 genes strongly up- and downregulated, respectively. Several genes (including EgWRKY116, EgWRKY62, and EgWRKY107) were significantly induced by Ri; these genes might enhance the defense of E. grandis against Rs.
Discussion: Therefore, we identified E. grandis WRKY genes that are regulated by AMF colonization, some of which might improve the defense of E. grandis against R. solanacearum. These findings provide insights into E. grandis WRKY genes involved in interactions among the host plant, AMFs, and R. solanacearum.
Eucalyptus grandis, a globally planted tree species, is known for its exceptional growth rate and diverse characteristics (Mao et al., 2024). This plant is highly productive, adaptable, versatile, and valuable (Yu et al., 2019; Mao et al., 2024). However, Eucalyptus trees are susceptible to a wide range of pathogens, which lead to substantial losses (Yang et al., 2022; Ahmad et al., 2024). More than 80% of Eucalyptus species are prone to disease. In particular, the incidence of bacterial wilt ranges from 60.6% to 72.4%, leading to severe economic damage to Eucalyptus nurseries (Ferreira et al., 2018).
Bacterial wilt disease, one of the most destructive plant diseases worldwide, is caused by the soil-born pathogen Ralstonia solanacearum (Rs). This disease poses a major constraint to the production of more than 250 plants worldwide, including forest trees, such as Eucalyptus species (Ferreira et al., 2018; Vailleau and Genin, 2023). Rs can survive for extended periods under natural conditions (Grey and Steck, 2001). Rs penetrates plants through wounds, root tips, and secondary root emergence spots and grows and multiplies within the intercellular gelatinous layer of the plant. This process leads to plasmolysis of epidermal cells, forming cavities, and colonization within the root cortex (Monther et al., 2012; Xue et al., 2020). Rs further invades the xylem ducts from plant epidermal cells. The growth cycle of this pathogen within vascular bundles is regulated by the quorum sensing system (Li et al., 2023a). This system mediates the transition of Rs from the early stages of rapid division to later stages of slow growth, where the pathogen uses fewer nutrients and produces and disperses virulence factors (Lowe-Power et al., 2018). Rs invasion severely impairs water transport and nutrient metabolism in the plant, ultimately leading to the blockage of the water transport system (Yu et al., 2024). Consequently, plants affected by bacterial wilt disease show withering and premature death (Yu et al., 2024). Since chemical measures are not effective in protecting plants from this disease, biological control methods might represent a feasible approach for Rs control in the future (Yuliar et al., 2015; Ferreira et al., 2018).
Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMFs) are plant symbionts with beneficial effects on plant growth and health, as they provide plants with nutrients and induce host resistance to pathogens (Fiorilli et al., 2024; Duan et al., 2024; Martin and van der Heijden, 2024). On one hand, AMFs occupy the ecological niche of pathogenic bacteria, altering the microbial composition in the rhizosphere and promoting the growth of beneficial microorganisms, such as Pseudomonas fluorescens (Li et al., 2023b). This improves the antagonistic effects of the soil against pathogenic bacteria (Lahlali et al., 2022; Basiru et al., 2023). On the other hand, AMFs induce host plant defense responses, such as mycorrhizal-induced resistance and the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascade, to enhance plant stress tolerance (Cameron et al., 2013; Tian et al., 2021). Furthermore, AMFs trigger a robust and rapid immune response in the host plant, improving plant disease resistance by activating defense genes, including WRKY transcription factors (TFs) (Gallou et al., 2012).
WRKY TFs are a widely studied class of plant defense-responsive proteins that regulate stress resistance and plant-specific growth and development (Yan et al., 2022; Javed and Gao, 2023; Wang et al., 2023). SlWRKY75 in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) positively regulates the plant defense response against Pseudomonas syringae by maintaining the homeostasis of plant growth hormones. SlWRKY75 directly activates the expression of SlGH3.3 by binding to the W-box element in its promoter (Yang et al., 2024). In chili pepper (Capsicum annuum), silencing CaWRKY22, CaWRKY27, or CaWRKY40 enhanced plant susceptibility to R. solanacearum (Dang et al., 2013, 2014; Hussain et al., 2018); CaWRKY27b, CaWRKY40, and CaWRKY22 might form a module that regulates plant tolerance to high temperatures and high humidity as well as resistance to R. solanacearum (Hussain et al., 2018; Yang et al., 2022). WRKY TFs also play important roles in plant–AMF–bacterium interactions (Wang et al., 2022; Silvestri et al., 2024). MdWRKY40 provides protection against Fusarium solani infection in mycorrhizal apple (Malus domestica Borkh) seedlings (Wang et al., 2022). Furthermore, MtWRKY69 is associated with AMF colonization levels in Medicago truncatula (Silvestri et al., 2024).
WRKY proteins possess a conserved WRKY motif (WRKYGQK) and a zinc-finger structure following the C2H2, C2HC motif (Rushton et al., 2010; Yan et al., 2022). WRKY proteins can be categorized into four groups, I–IV. Group I members possess two WRKY motifs and one C2H2-type zinc finger. Group II and group III members possess a single WRKY motif. However, group II members are characterized by a C2H2-type zinc finger, while group III members possess a C2HC-type zinc finger. Group II WRKYs are further classified into five subgroups (IIa–IIe) based on the sequences of their DNA-binding domains and the structures of their zinc fingers, while group III is divided into subgroups III-a and III-b. Group IV members have incomplete or partial WRKY structural domains and do not possess zinc-finger motifs, suggesting that these proteins may have lost their roles as WRKY transcription factors (Zhang and Wang, 2005; Chen et al., 2019; Javed et al., 2022; Yan et al., 2022). Analyzing EgWRKY genes for their potential induction by AMF to enhance disease resistance could open new possibilities for Eucalyptus disease control and breeding programs.
We previously demonstrated that inoculating E. grandis with the AMF Funneliformis mosseae or Rhizophagus irregularis drastically increased the activities of defense-related enzymes and enhanced the defense of E. grandis against R. solanacearum (Huang et al., 2023). In this study, we performed a genome-wide analysis of WRKY genes in E. grandis. We used a tripartite system involving E. grandis–AMF–R. solanacearum to identify E. grandis WRKY genes that are induced by AMF and R. solanacearum. These genes might play roles in enhancing the defense of E. grandis against bacterial pathogens.
All E. grandis genome sequences and annotation were obtained from the NCBI nucleotide sequence repository (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/datasets/taxonomy/71139/). The Pfam database (http://pfam.sanger.ac.uk/) was used to obtain an HMM file of predicted WRKY structural domain (PF03106). A basic HMM search using TBtools v2.086 was conducted to identify WRKY family proteins in the E. grandis protein database with an e-value cutoff of 1 × 10−5 (Chen et al., 2023). The NCBI CDD (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/cdd/) and SMART databases (http://smart.embl.de/) were used to confirm the existence of the WRKY domain in all Eucalyptus WRKY proteins.
The Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) WRKY (AtWRKY) protein sequences were downloaded from Phytozome (https://phytozome-next.jgi.doe.gov/) (Goodstein et al., 2012). Multiple sequence alignment of AtWRKY and EgWRKY proteins was performed using ClustalW with MEGA11.0 software (Tamura et al., 2021) with default parameters and used to construct a maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree of AtWRKY and EgWRKY protein sequences.
TBtools (Chen et al., 2023) was used to confirm the chromosomal locations and gene structures of the EgWRKYs and to generate a chromosome distribution map and gene structures for all EgWRKYs. To gain a better understanding of the functions of the EgWRKYs, the deduced protein sequences were analyzed using MEME (Multiple Expectation Maximization for Motif Elicitation: http://meme-suite.org/tools/meme/) to identify and examine conserved motifs, with the following parameters: the repeat count was adjusted to zero or one, with a maximum of ten motifs (Bailey et al., 2009). TBtools was also utilized to generate Circos plots. The One Step MCScanX program in TBtools was used to identify and investigate duplication types and collinear blocks and to build Circos plots.
The isoelectric point (pI) and molecular weight (Mw) functions in ExPASy (https://web.expasy.org/protparam/) were used to estimate the pI and Mw of full-length EgWRKY proteins (Gasteiger et al., 2003). TBtools was used to harvest 2,000 base-pair (bp) sequences upstream of the start codon (ATG) of each EgWRKY gene in the Eucalyptus genome (Chen et al., 2023). After analyzing sequences with PlantCARE online (Lescot et al., 2002) and New PLACE (https://www.dna.affrc.go.jp/PLACE/?action=newplace), cis-acting elements were identified and their distribution in each promoter was determined using TBtools.
E. grandis seeds were surface sterilized with 1% NaClO for 15 min and placed on sterilized quartz sand for germination. After 14 days, seedlings with uniform growth status were transferred to individual pots and inoculated with R. irregularis 197198 (Ri) at the roots using 400 spores per plant. At 45 days post inoculation (dpi) with Ri, mycorrhizal colonization was detected in E. grandis roots after WGA488 staining and observed under a fluorescence microscope (Trouvelot et al., 1986). At 90 dpi, the roots were watered with 20 mL of a 1 × 109 CFU/mL suspension of R. solanacearum. The plants were placed in an artificial climatic chamber with 16 h of light, 30°C, 80% relative humidity, light intensity of 100–200 Wm–2, and 8 h of darkness at 28°C, 80% relative humidity. Mycorrhizal and non-mycorrhizal E. grandis root samples were collected at 0, 24, 48, and 96 hours post-infection (hpi) with Rs, flash-frozen in liquid nitrogen, and stored at –80°C.
Total RNA was extracted from the samples using a Plant RNA Kit (BIO-TEK R6827, OMEGA). The integrity of the total RNA was assessed using 1.5% agarose gel electrophoresis, while its concentration and quality were evaluated using an ultra microspectrophotometer (Nanophotometer N50 Touch, Implem). RNAs from the roots of non-mycorrhizal and mycorrhizal E. grandis seedlings infected with Rs at 0, 24, 48, and 96 hpi were sent to Lianchuan Biotechnology, Hangzhou for cDNA library construction and double-end sequencing of the cDNA library using the Illumina NovaSeq™ 6000 platform (LC-Bio Technologies Co., Ltd., Hangzhou, China). The RNA-Seq (PRJNA893422) data were annotated based on the E. grandis reference genome. The ballgown package was used for segmental per kilobase million (FPKM) quantification. FPKM = all exon sequences/matched sequences × exon length (KB). At the same time, TBtools was used to perform normalization analysis of the FPKM data and to identify significant differences (|log2FC ≥ 1| was considered to be significant). The heatmap diagram was also constructed with log2 values using TBtools.
We identified 117 WRKY sequences in the E. grandis genome (Figure 1, Supplementary Table S1). The EgWRKYs encode proteins ranging from 139 (EgWRKY7) to 1,831 (EgWRKY63) amino acids long. The molecular weights of the EgWRKYs range from 15.796 kDa (EgWRKY72) to 204.607 kDa (EgWRKY63), with the majority falling between 20 and 85 kDa. The calculated isoelectric points (pI) range from 4.75 (EgWRKY85) to 11 (EgWRKY80), with an average of 7.11. The pI values of 48 EgWRKYs are greater than 7, while the pI values of 69 EgWRKYs are less than 7.
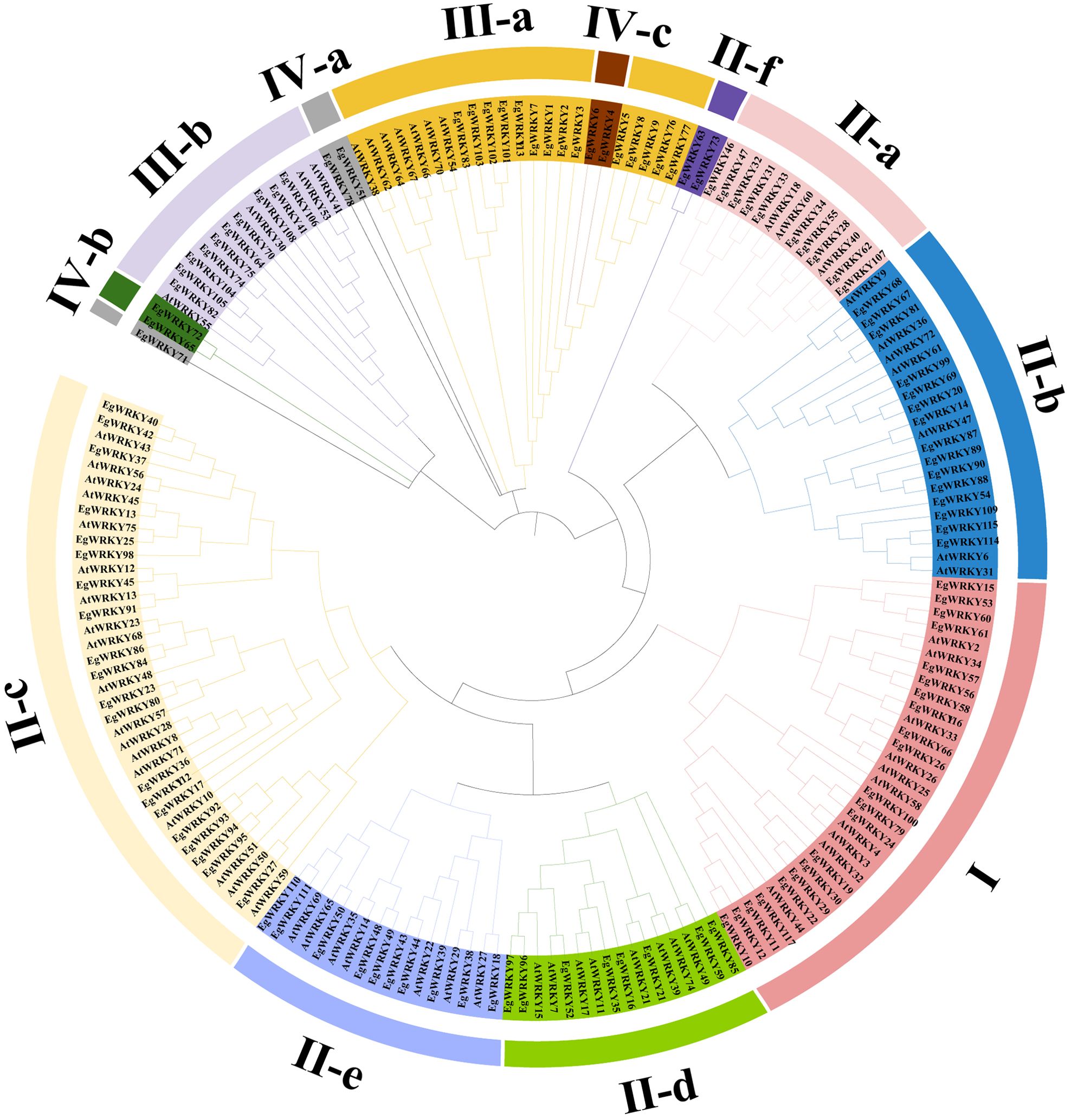
Figure 1. Phylogenetic tree of WRKY proteins in E. grandis and A. thaliana. The tree was constructed with MEGA11.0 using the Maximal likelihood (ML) method following ClustalW alignment of all full-length protein sequences. Different colors denote group I, group II-a–II-f, group III-a–III-b, and group IV-a–IV-c.
Sequence analysis revealed a highly conserved middle WRKY domain (WD) in the EgWRKY proteins (Figure 2), covering approximately 60 amino acid residues. The WRKY proteins were classified into four types based on the specific zinc-finger motifs and the number of WDs. Group I members possess two WRKY motifs, while group II and III members possess a single WRKY motif (Figure 1). Group I and II members harbor a C2H2 zinc-finger motif following the WRKY structural domain, whereas group III WRKY proteins contain a C2HC zinc-finger motif (Figure 2). By combining the results of phylogenetic analysis and analysis of zinc-finger structures, we further classified the EgWRKYs into subgroups. Cluster II was classified into six subgroups (II-a–II-f): II-a (C-X5-C-X23-H-X1-H), II-b (C-X5-C-X23-H-X1-H), II-c (C-X4-C-X23-H-X1-H), II-d (C-X4/5-C-X23-H-X1-H), II-e (C-X5-C-X23-H-X1-H), and II-f (C-X4-C-X22-H-X1-H). Group III was subdivided into two subgroups: III-a (C-X7-C-X23-H-X1-C) and IIIb (C-X5/7-C-X25-H-X1-C) (Figures 1, 2). By contrast, the presence of incomplete WRKY domains (KQVQ) or zinc fingers in group IV (Figure 2) suggests that EgWRKY65, EgWRKY72, EgWRKY78, EgWRKY51, and EgWRKY71 may have lost WRKY TF function. In addition to variations in the zinc-finger motif, mutations in the WRKYGQK sequence were also observed in E. grandis, including WKKHGQK (II-a), WRKYGKK (II-c), WRKYGQR (II-f), WRKYAQE (III-a), WRKYGSK (III-a), WRKYDQK (III-b), and WTMYRQR(III-b). Since EgWRKY3 and EgWRKY7 each contain a zinc-finger motif, they were classified into group III-a rather than group IV, although their zinc fingers exhibit minor differences with those of other group III-a members.
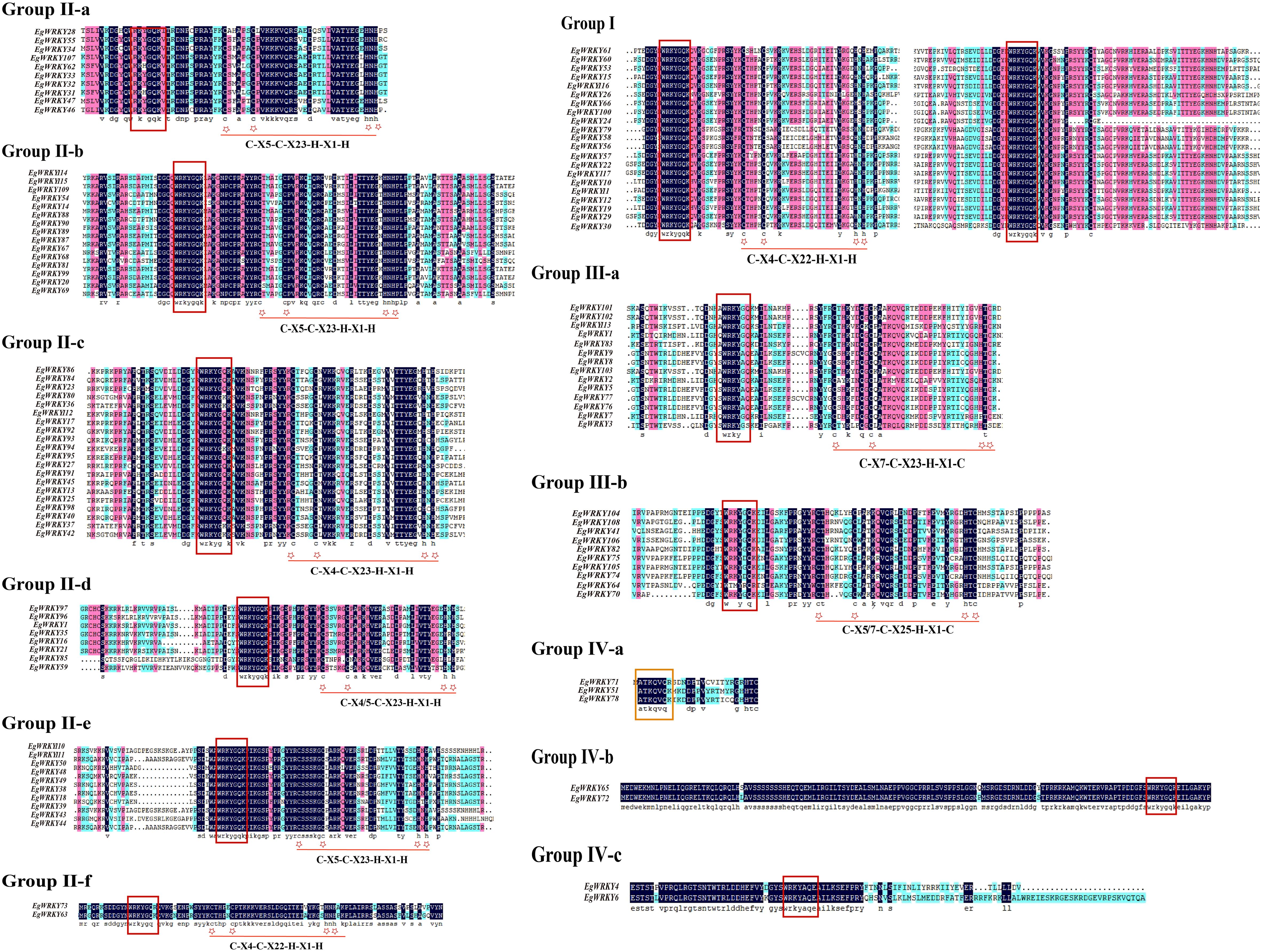
Figure 2. Multiple sequence alignment of the conserved domains of EgWRKY proteins from E. grandis. Black shading indicates identical amino acid sequences in various WRKYs. The zinc-finger structure is denoted by an asterisk and is underlined, while the WRKY motif is denoted by a red box.
The 117 EgWRKYs are unevenly distributed across all 11 chromosomes of E. grandis (Figure 3). Most of these EgWRKY genes are located on chromosomes 1 and 7, accounting for 15.38% (18 genes) and 23.08% (21 genes) of the total number of genes, respectively. Six EgWRKY genes are dispersed on chromosomes 2 and 4, each accounting for 5.12%. Chromosome localization mapping also revealed that EgWRKYs exist in multiple gene clusters on different chromosomes, such as EgWRKY87–EgWRKY90 on chromosome 8 and EgWRKY91–EgWRKY95 on chromosome 9, with most members of the same cluster categorized in the same subfamilies.
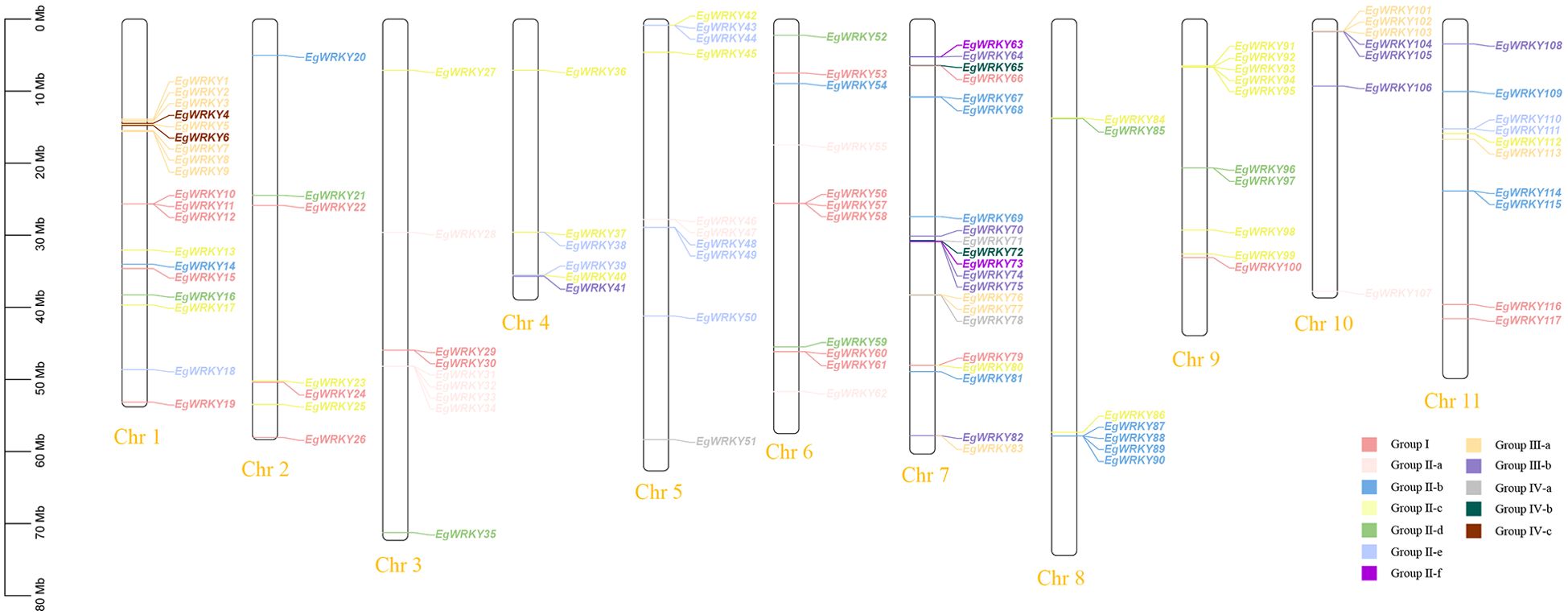
Figure 3. Chromosome mapping of the EgWRKYs. The scale represents an 80-Mb chromosomal distance. Groups I, II-a, II-b, II-c, II-d, II-e, II-f, III-a, III-b, IV-a, IV-b, and IV-c are denoted by dark pink, light pink, blue, light green, medium green, cyan, fuchsia, orange, purple, gray, dark green, and brown, respectively.
Collinearity analysis revealed 21 pairs of segmental duplicates and 4 tandem duplicates among the 117 EgWRKYs. The four tandem duplicates include EgWRKY4 with EgWRKY5, EgWRKY2 with EgSCL8 (encoding scarecrow-like protein 8), EgWRKY1 with EgWRKY7, and EgWRKY74 with E. grandis “Probable Disease Resistance Protein” (XM_039316797.1) (Figure 4A, Supplementary Table S2). Additionally, we identified 68 pairs of segmental duplicates between E. grandis and Arabidopsis WRKYs (Figure 4B, Supplementary Table S3).
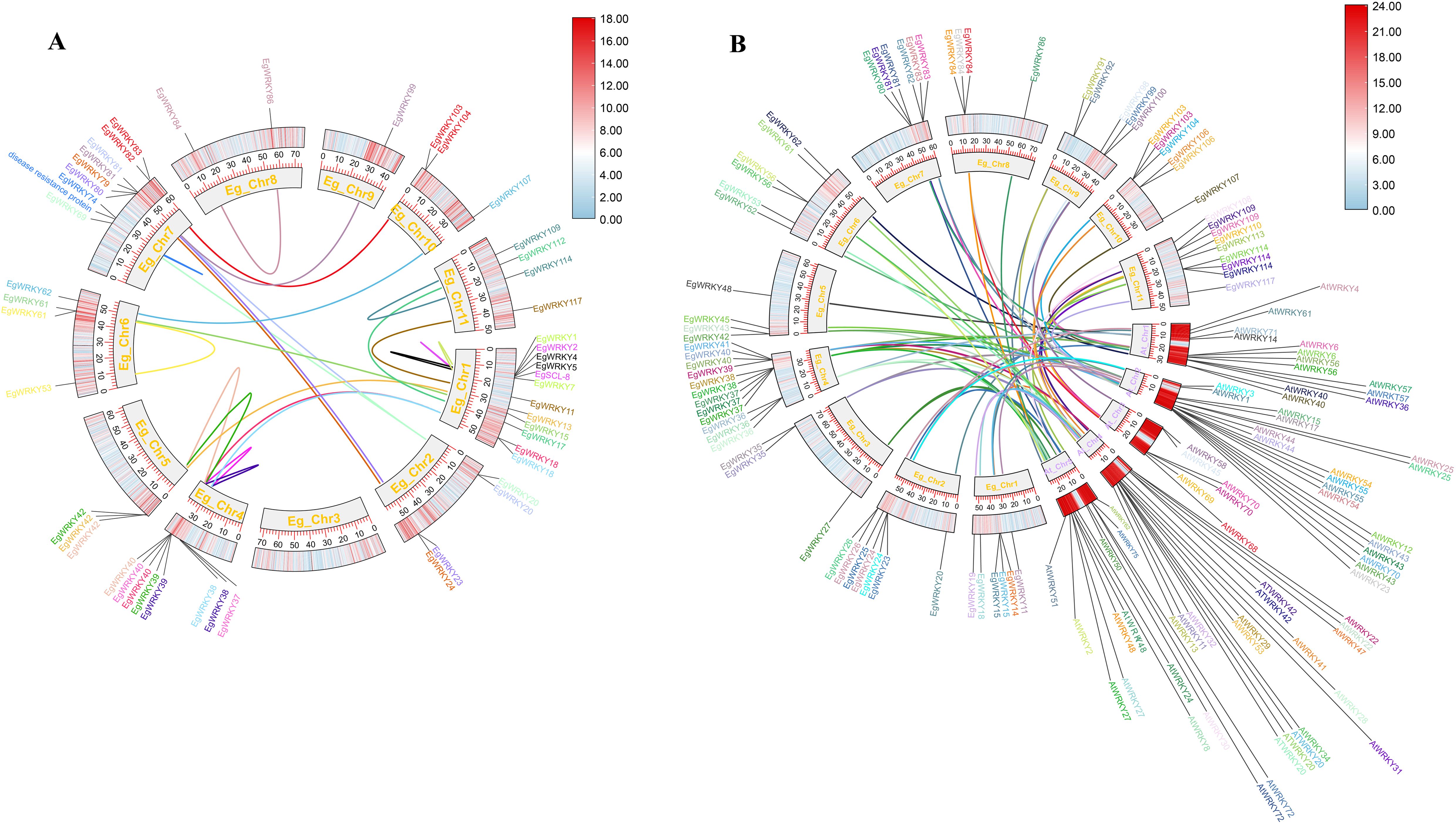
Figure 4. Circos plots of the chromosomal locations of EgWRKYs with duplication links. (A) Duplication of EgWRKYs within the E. grandis genome. (B) Duplication of EgWRKY orthologs within the Arabidopsis genome. A pair of genes with the same color connected by a line represents a duplication relationship. The outer ring shows the density of genes on the chromosome, with redder colors representing greater density.
The quantity of introns and exons differ among the EgWRKYs. Specifically, EgWRKY family genes contain one to twelve introns and two to nine exons. In terms of exon length and intron number, members of the same subfamily exhibit comparable exon/intron distribution patterns. For example, most members of subfamilies II-c, II-d, and II-e have only one to two introns, while most members of subfamilies I, II-a, and IV possess three or more introns. Notably, subfamily IV members EgWRKY51 and EgWRKY6 contain an intron of more than 18,000 bp, and subfamily IIIa members EgWRKY5 and EgWRKY9 possess an even larger intron of ~38,000 bp (Figure 5B, Supplementary Table S1).

Figure 5. Gene structures and conserved motif analysis of EgWRKYs. (A) The conserved motifs of the EgWRKYs. (B) The exon–intron structures of the EgWRKYs. UTRs are denoted by green boxes, CDSs by yellow boxes, and introns by narrow black lines. Rectangles of varying colors are used to depict each conserved motif. The length of the box is equivalent to the length of the motif. (C) WebLogos of the amino acid composition of each motif.
Ten motifs were predicted in the EgWRKYs, with two to six motifs present in each EgWRKY except for some members of group IV (Figures 5A–C). Some motifs are shared by most members of groups I–III, such as motif 1 and motif 2, while others are specific to the subfamily. For example, motif 3 and motif 5 are present only in groups I and II-f. However, members of group I contain motif 4, motif 1, and motif 2, whereas group II-f members lack these motifs. This unique structure may cause members of subfamily group II-f to be outliers in the evolutionary tree (Figures 1, 5A). Most group II-a and group II-b members possess motif 7 and motif 6, while group II-a members contain an additional motif 4 linked to motif 1 than group II-b; groups II-d, II-e, and III-b only contain motif 1 and motif 2. In addition, groups III-a, IV-a, and IV-c contain similar motifs in terms of number and arrangement, which could explain why they were grouped in the same branch (Figure 1), whereas EgWRKY4, EgWRKY6, EgWRKY51, and EgWRKY78 were classified in subfamily IV based on the structures of their zinc fingers (Figure 2).
To investigate the putative regulatory mechanisms of EgWRKY genes, we identified the cis-elements in the 2-kb sequences upstream of their translation start sites (ATGs) and visualized them using TBtools (Figure 6A). The cis-elements ABREs (abscisic acid responsive), TGACG motifs (MeJA responsive), and CGTCA motifs (MeJA responsive), which are associated with defense hormones, accounted for more than 50% of all EgWRKY subfamilies members (Figure 6B). Abscisic acid and jasmonic acid are important phytohormones in the spatio-temporal dynamics of AMF-induced resistance (Cameron et al., 2013). These findings suggest that these EgWRKYs might be involved in the mycorrhiza-induced resistance of Eucalyptus against Rs. The presence of auxin-responsive elements, such as TGA-box and AuxRR-core elements (Lescot et al., 2002), suggests that some EgWRKYs may play a role in regulating plant growth. Notably, 60% of subgroup II-b members contain GC-motif elements, whereas 80% and 100% of subgroup II-b and IV-b members contain MBS elements, 73% and 100% of subgroup II-b and II-e members contain LTR elements, and 14% and 5% subgroup I and II-c members contain SARE elements, respectively. Finally, whereas subgroup II-f members lack ARE elements, all subgroup III-b, IV-a, IV-b, and IV-c members contain this element.
In addition, we identified cis-acting elements associated with mycorrhizal symbiosis in the EgWRKYs, such as P1BS (GNATATNC), CTTC-motif (NTTCTTGTTN), and AW-box (CG(N)7CNANG) (Shi et al., 2023; Duan et al., 2024). Members of all subfamilies except groups IV-b and IV-c contain AW-boxes. In addition more than 20% of members of groups II-a and II-c contain P1BS, CTTC-motif, and AW-boxes, suggesting that these two subfamilies may have a role in the AMF symbiosis. The W-box has been implicated in plant resistance to Rs (Dang et al., 2014; Phukan et al., 2016; Mukhi et al., 2021; Yang et al., 2021). A relatively high number of family members contain W-box elements (71%, 83%, 90%, 85%, 50%, and 67% of group I, II-a, II-b, II-c, II-e, and IV-a members contain W-box elements, respectively, and in other subfamilies, 100% of members contain W-boxes), suggesting that EgWRKYs play important roles in the E. grandis–AMF–R. solanacearum system (Figure 6B). In addition, 7 EgWRKY genes that exhibited significant differences in expression at different time points between mycorrhizal and non-mycorrhizal E. grandis contain W-boxes (Figures 6C, 7).
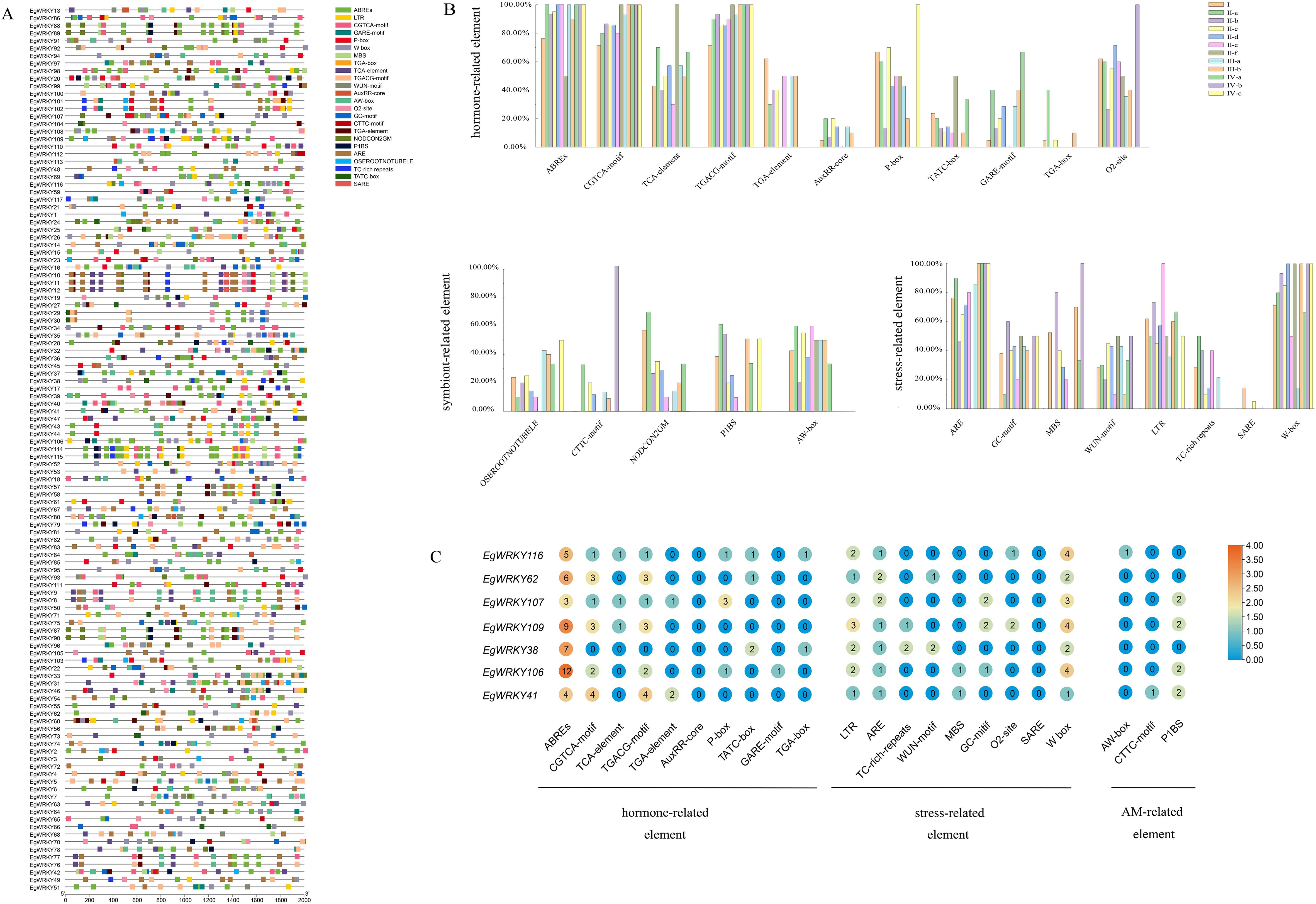
Figure 6. Identification of cis-acting elements in the promoter regions of EgWRKY genes. (A) Each element is depicted by a colored rectangle. The length of the rectangle is equivalent to the length of the element. Different colors correspond to different members of the group. (B) Proportional distribution of individual cis-acting elements within the promoter regions of EgWRKYs. (C) Number of cis-acting elements in EgWRKYs that exhibited a response to Rs infection and inoculation with AMFs.
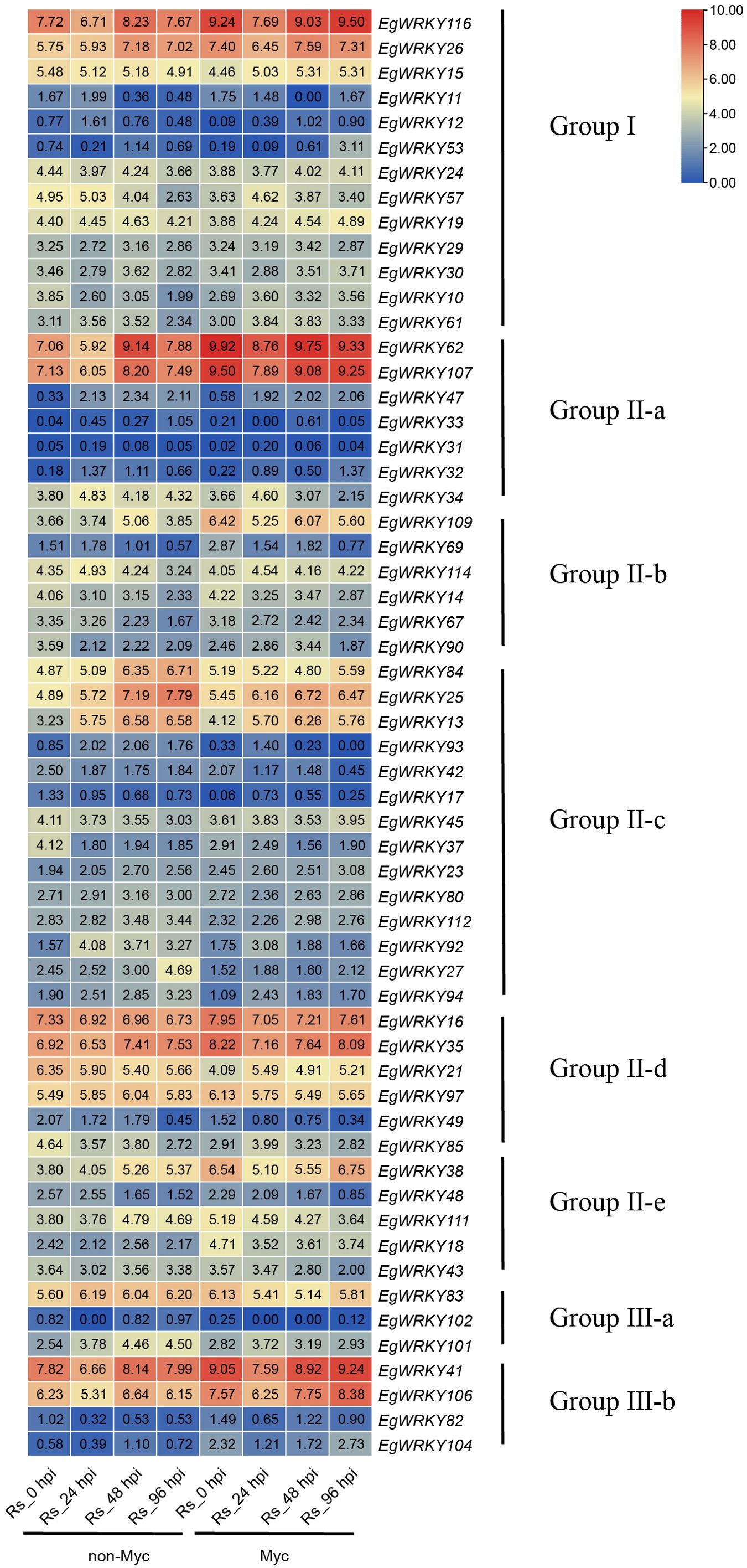
Figure 7. Heatmap of EgWRKY gene expression determined by RNA-seq. Log2-fold differences in gene expression (FPKM values) were used to create the heatmap. Myc, mycorrhized with R. irregularis; Rs, Infected with R. solanacearum.
During the Rs infection process, EgWRKY genes showed different expression patterns in the roots of Ri mycorrhizal and non-mycorrhizal E. grandis plants (Figure 7). Among the 58 EgWRKYs, 21 genes responded to R. irregularis in the absence of Rs infection. In detail, eight genes were downregulated in response to this treatment, including three from group I (EgWRKY10, EgWRKY15, and EgWRKY57) and five from group II (EgWRKY90, EgWRKY17, EgWRKY37, EgWRKY21, and EgWRKY85). The remaining 13 EgWRKYs were upregulated by this treatment, including two from group I (EgWRKY26 and EgWRKY116), eight from group II (EgWRKY18, EgWRKY35, EgWRKY38, EgWRKY62, EgWRKY69, EgWRKY107, EgWRKY109, and EgWRKY111), and three from group III-b (EgWRKY41, EgWRKY106, and EgWRKY104). Notably, EgWRKY116, EgWRKY62, EgWRKY107, EgWRKY109, EgWRKY38, EgWRKY41, and EgWRKY106 were expressed at higher levels in mycorrhizal plants compared to non-mycorrhizal plants. This trend was observed not only in the absence of the pathogen (at 0 h of Rs infection), but also at other time points of the pathogenic interaction. These results suggest that the expression of these seven genes is influenced by AMF symbiosis and might enhance E. grandis resistance against Rs.
Additionally, during Rs infection, EgWRKY116, EgWRKY62, EgWRKY107, EgWRKY41, and EgWRKY106 showed a significant decrease in expression at 24 hpi, regardless of mycorrhization, followed by an increase at 48–96 hpi; this trend was observed for EgWRKY26 only in the mycorrhizal roots of E. grandis. In the absence of mycorrhizal treatment, EgWRKY57 and EgWRKY114 showed slowly upregulated expression before 24 hpi followed by downregulation at 48 hpi and reached the lowest expression level at 96 hpi. EgWRKY27 expression increased after infection with Rs and was quickly and significantly upregulated at 96 hpi. EgWRKY109 was quickly upregulated at 48 hpi with Rs, and at 96 hpi, its expression level returned to that at 24 hpi. These results indicate that these EgWRKYs have different expression patterns following infection by Rs. EgWRKY47, EgWRKY84, EgWRKY13, and EgWRKY25 generally showed sustained increases in expression during Rs infection. Additionally, the expression of EgWRKY37, EgWRKY42, and EgWRKY90 significantly decreased after Rs infection compared to the uninfected controls.
WRKY TFs, which play crucial roles in plant responses to abiotic and biotic stress, constitute one of the largest and most important TF families (Rushton et al., 2010; Javed et al., 2022). While the WRKY family has been extensively studied in model plants, the characterization of the WRKY family in the E. grandis–AMF–R. solanacearum tripartite interaction is missing. The first version of the E. grandis genome contained 79 WRKY genes; the responses of these genes to plant hormonal and abiotic stress treatments were previously studied (Fan et al., 2018). However, in the present study, based on the E. grandis genome version released in 2021 (ASM1654582v1), we identified 117 EgWRKYs, representing an increase of 38 genes in the genome compared to the previous report (Fan et al., 2018). Furthermore, our analysis focused on EgWRKY gene expression in the E. grandis–R. irregularis interaction. Our findings provide insight into EgWRKY genes in the context of symbiotic interactions and biotic stress responses.
The prevalence of mutations and deletions in plant WRKY domains has been documented in various studies (Yao et al., 2015; Jiang et al., 2017; Song et al., 2018; Chen et al., 2019). In sunflower (Helianthus annuus), five WRKY proteins were found to lack one WRKY structural domain (Li et al., 2020). In maize (Zea mays), nine WRKY proteins lack one WRKY structural domain, seven lack WRKY zinc fingers, and three lack one WRKY motif (Hu et al., 2021). The WRKY motif of WRKY genes in eggplant (Solanum melongena) was also reported to be mutated (Yang et al., 2020). In C. annuum, due to the replacement of Q by M in the conserved motif WRKYGQK, CaWRKY27b in the nucleus failed to bind to W-boxes in the promoters of immunity- and thermotolerance-related marker genes (Yang et al., 2022). In the current study, 21 EgWRKYs were found to harbor mutations in WRKY structural domains, suggesting that different EgWRKYs may confer different resistance responses or susceptibility traits. Furthermore, the zinc finger at the C-terminus of EgWRKY3, classified as III-a, was found to be mutated to H-X1-S, while the zinc finger at the C-terminus of EgWRKY7 was mutated from H-X1-C to H-X2-C. Lastly, the structure of the zinc finger at the N-terminus of EgWRKY85, classified as II-d, was mutated from C-X5-C to C-X4-C. These findings suggest that the zinc finger is subject to a substantial number of mutations in group III-a and III-b, potentially leading to the generation of new functions among its members.
The tremendous diversity of WRKY TFs and their unpredictable numbers across plant species might be related to a variety of evolutionary processes, including genome-wide duplications. The success of duplicated genes, whether in tandem or segmental form, during genome-wide duplications could potentially explain ongoing evolutionary shifts and crop domestication (Bertioli et al., 2016; Van De Peer et al., 2017; Bohra et al., 2022). Gene duplication is known to play a major role in the amplification and evolution of plant gene families (Bertioli et al., 2016; Van De Peer et al., 2017). In this study, we observed duplications involving EgWRKY83, EgWRKY103 with AtWRKY54, and EgWRKY106 with AtWRKY41 (Figures 4A, B). Notably, Rs specifically targets AtWRKY54 to suppress plant immune responses to AvrRp4 and PopP2 (Kim et al., 2024). Furthermore, AvrRps4(C) associates with the WRKY domains of the related but distinct RRS1B/RPS4B NLR pair and the DNA-binding domain of AtWRKY41, with similar binding affinities, and effector binding interferes with WRKY-W-box DNA interactions (Mukhi et al., 2021). These results suggest that the orthologs EgWRKY83, EgWRKY103, and EgWRKY106 may have similar functions in E. grandis during interactions with pathogens, making them interesting targets for further investigation.
While introns are not directly involved in the proteome, they often contain regulatory elements that can modulate protein isoform production, RNA stability, and translational efficiency, thereby amplifying the protein-coding potential of the genome through post-transcriptional splicing of introns (Jacob and Smith, 2017; Keane and Seoighe, 2016; Parenteau et al., 2019; Morgan et al., 2019). Due to their very long introns, EgWRKY6, EgWRKY8, EgWRKY9, and EgWRKY51 may play important roles in regulating gene transcription and translation; this concept deserves further investigation.
Predictive analysis of the cis-acting elements of EgWRKYs revealed the presence of many light-associated, plant hormone-associated, tissue-specific, stress-associated, and mycorrhiza-associated elements in the promoters of EgWRKY genes (Figure 6), which might be involved in a variety of biological processes. In E. grandis, more than 50% of the members of subfamilies other than subfamily III-a contain W-box cis-acting elements (Figure 6B). The W-box flanking regions of its sequence may contribute to the molecular recognition mechanism of EgWRKY genes (Cheng et al, 2019; Hsin et al, 2022; Mukhi et al, 2021), which bind to and are activated by other TFs upon the invasion of plants by Rs (Mukhi et al., 2021; Phukan et al., 2016; Dang et al., 2014; Yang et al., 2021).
Eucalyptus WRKY genes are rich in mycorrhizal-induced cis-acting elements such as P1BS, CTTC, and AW-box elements. EgWRKY41, which contains both an AW-box and P1BS, was significantly up-regulated in response to AMF inoculation, while EgWRKY37 and EgWRKY85 were down-regulated by this treatment, suggesting that different EgWRKYs employ different pathways to regulate mycorrhizal interactions in Eucalyptus. In M. truncatula, MtWRKY69 was also shown to be associated with AMF colonization levels (Silvestri et al., 2024). At the transcriptional level, EgWRKY37, EgWRKY84, EgWRKY13, and EgWRKY25 from the II-c family showed a sustained increase in expression during Rs infection, while EgWRKY37 and EgWRKY42 showed a significant decrease in expression after Rs infection. Therefore, in the E. grandis–AMF–R. solanacearum interaction system, EgWRKYs, encoding core transcription factors, can respond to AMF and Rs at the same time. We propose that after mycorrhizal-colonized E. grandis is infected by Rs, the host reinforces AMF symbiosis by regulating the expression of EgWRKYs, thereby enhancing seedling growth while inducing the salicylic acid/jasmonate signaling pathway to enhance host defense against Rs.
We identified 117 EgWRKY genes in the Eucalyptus grandis genome. The predicted EgWRKY proteins were classified into four groups based on phylogenetic analysis and multiple sequence alignment. Collinearity analysis showed that 25 and 4 of these genes were segmental and tandem duplicates, respectively. All subfamilies contain plant hormone-related cis-acting elements (ABREs, TGACG motifs, and CGTCA motifs), which are associated with defense responses. In addition, the majority of subfamilies contain P1BS, CTTC, and AW-box elements; these elements are induced by AMFs. These results suggest that these EgWRKYs respond to AMFs and/or Rs. We identified 23 and 58 EgWRKYs that respond to R. irregularis and R. solanacearum, respectively, in the E. grandis-Ri-Rs interaction system at the transcriptional level. Several EgWRKY genes showed differential expression patterns in mycorrhizal and non-mycorrhizal E. grandis roots during R. solanacearum infection, and EgWRKY62, EgWRKY107, and EgWRKY116 were responsive to the AMF R. irregularis. These results provide insights into the characteristics of E. grandis EgWRKYs and their potential roles in AMF-mediated defense against R. solanacearum.
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/Supplementary Material.
JZ: Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. XY: Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. CH: Formal analysis, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. XF: Data curation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. QL: Software, Writing – review & editing. ZL: Visualization, Writing – review & editing. YS: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. ZC: Conceptualization, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31800541); the Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (2021A1515010561; Molecular Regulatory Mechanisms of Carbon and Nitrogen Nutrient Exchange Balance in Eucalyptus Arbuscular Mycorrhiza); the Social Development Project of Guangzhou Municipal Science and Technology Bureau (202206010058); and the Innovation and Entrepreneurship Program for University Students (2024105641209).
We thank professor Ming Tang for supplying us with the Ri resources, to professor Xiaoyong Mo for providing the Eucalyptus seeds, and to Dr. Jennifer M. Mach for her invaluable guidance in revising and enhancing the quality of our manuscript.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpls.2025.1510196/full#supplementary-material
Ahmad, I., Mazhar, K., Atiq, M., Khalaf, A. K., Rashid, M. H. U., Asif, M., et al. (2024). Epidemiology and management of Fusarium wilt of Eucalyptus camaldulensis through systemic acquired resistance. PeerJ 12, e17022. doi: 10.7717/peerj.17022
Bailey, T. L., Boden, M., Buske, F. A., Frith, M., Grant, C. E., Clementi, L., et al. (2009). MEME SUITE: tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 37, W202–W208. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp335
Basiru, S., Ait Si Mhand, K., Hijri, M. (2023). Disentangling arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and bacteria at the soil-root interface. Mycorrhiza 33, 119–137. doi: 10.1007/s00572-023-01107-7
Bertioli, D. J., Cannon, S. B., Froenicke, L., Huang, G., Farmer, A. D., Cannon, E. K., et al. (2016). The genome sequences of Arachis duranensis and Arachis ipaensis, the diploid ancestors of cultivated peanut. Nat. Genet. 48, 438–446. doi: 10.1038/ng.3517
Bohra, A., Tiwari., A., Kaur, P., Ganie, S. A., Raza, A., Roorkiwal, M., et al. (2022). The key to the future lies in the past: insights from grain legume domestication and improvement should inform future breeding strategies. Plant Cell Physiol. 63, 1554–1572. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcac086
Cameron, D. D., Neal, A. L., Wees, S. C. M. V., Ton, J. (2013). Mycorrhiza-induced resistance: More than the sum of its parts? Trends Plant Sci. 18, 10. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2013.06.004
Chen, C., Wu, Y., Li, J., Wang, X., Zeng, Z., Xu, J., et al. (2023). TBtools-II: A “one for all, all for one” bioinformatics platform for biological big-data mining. Mol. Plant 16, 1733–1742. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2023.09.010
Chen, X. J., Cheng, L., Wang, H., Guo, Z. J. (2019). WRKY transcription factors: evolution, binding, and action. Phytopathol. Res. 1, 13. doi: 10.1186/s42483-019-0022-x
Cheng, X., Zhao, Y., Jiang, Q., Yang, J., Zhao, W., Taylor, I. A., et al. (2019). Structural basis of dimerization and dual W-box DNA recognition by rice WRKY domain. Nucleic Acids Res. 47, 4308–4318. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz113
Dang, F., Wang, Y., She, J., Lei, Y., Liu, Z., Eulgem, T., et al. (2014). Overexpression of CaWRKY27, a subgroup IIe WRKY transcription factor of Capsicum annuum, positively regulates tobacco resistance to Ralstonia solanacearum infection. Physiol. Plant 150, 397–411. doi: 10.1111/ppl.12093
Dang, F. F., Wang, Y. N., Yu, L., Eulgem, T., Lai, Y., Liu, Z. Q., et al. (2013). CaWRKY40, a WRKY protein of pepper, plays an important role in the regulation of tolerance to heat stress and resistance to Ralstonia solanacearum infection. Plant Cell Environ. 36, 757–774. doi: 10.1111/pce.12011
Duan, S., Feng, G., Limpens, E., Bonfante, P., Xie, X. A., Zhang, L. (2024). Cross-kingdom nutrient exchange in the plant–arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus–bacterium continuum. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 22, 773–790. doi: 10.1038/s41579-024-01073-7
Fan, C., Yao, H., Qiu, Z., Ma, H., Zeng, B. (2018). Genome-wide analysis of Eucalyptus grandis WRKY genes family and their expression profiling in response to hormone and abiotic stress treatment. Gene 678, 38–48. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.08.003
Ferreira, M. A., Mafia, R. G., Alfenas, A. C. (2018). Ralstonia solanacearum decreases volumetric growth of trees and yield of kraft celulose of Eucalyptus spp. For. Pathol. 48, 12376–12381. doi: 10.1111/efp.12376
Fiorilli, V., Martínez-Medina, A., Pozo, M. J., Lanfranco, L. (2024). Plant immunity modulation in arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis and its impact on pathogens and pests. Annu. Rev. phytopathol. 62, 127–156. doi: 10.1146/annurev-phyto-121423-042014
Gallou, A., Declerck, S., Cranenbrouck, S. (2012). Transcriptional regulation of defence genes and involvement of the wrky transcription factor in arbuscular mycorrhizal potato root colonization. Funct. Integr. Genomics 12, 183–198. doi: 10.1007/s10142-011-0241-4
Gasteiger, E., Gattiker, A., Hoogland, C., Ivanyi, I., Appel, R. D., Bairoch, A. (2003). ExPASy: the proteomics server for in-depth protein knowledge and analysis. Nucleic Acids Re. 31, 3784–3788. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg563
Goodstein, D. M., Shu, S., Howson, R., Neupane, R., Hayes, R. D., Fazo, J., et al. (2012). Phytozome: a comparative platform for green plant genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 40, D1178–D1186. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr944
Grey, B. E., Steck, T. R. (2001). The viable but nonculturable state of Ralstonia solanacearum may be involved in long-term survival and plant infection. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 67, 3866–3872. doi: 10.1128/AEM.67.9.3866-3872.2001
Hsin, K. T., Hsieh, M. C., Lee, Y. H., Lin, K. C., Cheng, Y. S. (2022). Insight into the phylogeny and binding ability of WRKY transcription factors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 2895. doi: 10.3390/ijms23052895
Hu, W., Ren, Q., Chen, Y., Xu, G., Qian, Y. (2021). Genome-wide identification and analysis of WRKY gene family in maize provide insights into regulatory network in response to abiotic stresses. BMC Plant Biol. 21, 427. doi: 10.1186/s12870-021-03206-z
Huang, D., Chen, Y., Zhong, L. Y., Liang, J. J., Wang, Z. M., Chen, Z. J. (2023). Growth and defense-related enzymes of Eucalyptus in responses to Funneliformis mosseae and Ralstonia solanacearum. Scientia Silvae Sinicae 59, 68–75. doi: 10.13344/j.microbiol.china.221024
Hussain, A., Li, X., Weng, Y., Liu, Z., Ashraf, M. F., Noman, A., et al. (2018). CaWRKY22 Acts as a positive regulator in pepper response to Ralstonia solanacearum by constituting networks with CaWRKY6, CaWRKY27, CaWRKY40, and CaWRKY58. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19, 1426. doi: 10.3390/ijms19051426
Jacob, A. G., Smith, C. W. J. (2017). Intron retention as a component of regulated gene expression programs. Hum. Genet. 136, 1043–1057. doi: 10.1007/s00439-017-1791-x
Javed, T., Gao, S. J. (2023). WRKY transcription factors in plant defense. Trends Genet. 39, 787–801. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2023.07.001
Javed, T., Zhou, J. R., Li, J., Hu, Z. T., Wang, Q. N., Gao, S. J. (2022). Identification and expression profiling of WRKY family genes in sugarcane in response to bacterial pathogen infection and nitrogen implantation dosage. Front. Plant Sci. 13. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.917953
Jiang, C., Shen, Q. J., Wang, B., He, B., Xiao, S., Chen, L., et al. (2017). Transcriptome analysis of WRKY gene family in Oryza officinalis wall ex watt and WRKY genes involved in responses to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae stress. PloS One 12, e0188742. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0188742
Keane, P. A., Seoighe, C. (2016). Intron length coevolution across mammalian genomes. Mol. Biol. Evol. 33, 2682–2691. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msw151
Kim, H., Kim, J., Choi, D. S., Kim, M. S., Deslandes, L., Jayaraman, J., et al. (2024). Molecular basis for the interference of the Arabidopsis WRKY54-mediated immune response by two sequence-unrelated bacterial effectors. Plant J. 118, 839–855. doi: 10.1111/tpj.16639
Lahlali, R., Ezrari, S., Radouane, N., Kenfaoui, J., Esmaeel, Q., El Hamss, H., et al. (2022). Biological control of plant pathogens: A global perspective. Microorganisms 10, 596. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10030596
Lescot, M., Déhais, P., Thijs, G., Marchal, K., Moreau, Y., Van de Peer, Y., et al. (2002). PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 30, 325–327. doi: 10.1093/nar/30.1.325
Li, J., Islam, F., Huang, Q., Wang, J., Zhou, W., Xu, L., et al. (2020). Genome- wide characterization of WRKY gene family in Helianthus annuus L. and their expression profiles under biotic and abiotic stresses. PLoS One 15, e0241965. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0241965
Li, X., Yin, W., Lin, J. D., Zhang, Y., Guo, Q., Wang, G. (2023a). Regulation of the physiology and virulence of Ralstonia solanacearum by the second messenger 2′,3′-cyclic guanosine monophosphate. Nat. Commun. 14, 7654. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-43461-2
Li, X., Zhao, R., Li, D., Wang, G., Bei, S., Ju, X., et al. (2023b). Mycorrhiza-mediated recruitment of complete denitrifying Pseudomonas reduces N2O emissions from soil. Microbiome 11, 45. doi: 10.1186/s40168-023-01466-5
Lowe-Power, T. M., Khokhani, D., Allen, C. (2018). How Ralstonia solanacearum exploits and thrives in the flowing plant xylem environment. Trends Microbiol. 26, 929–942. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2018.06.002
Mao, X., Zheng, H., Luo, G., Liao, S., Wang, R., Tang, M., et al. (2024). Climate change favors expansion of three Eucalyptus species in China. Front. Plant Sci. 15. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1443134
Martin, F. M., van der Heijden, M. G. A. (2024). The mycorrhizal symbiosis: research frontiers in genomics, ecology, and agricultural application. New Phytol. 242, 1486–1506. doi: 10.1111/nph.19541
Monther, M., Tahat, M. M., Sijam, K., Othman, R. (2012). Ultrastructural changes of tomatoes (Lycopersicon esculentum) root colonized by Glomus mosseae and Ralstonia solanacearum. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 11, 409–434. doi: 10.5897/AJB11.2960
Morgan, J. T., Fink, G. R., Bartel, D. P. (2019). Excised linear introns regulate growth in yeast. Nature 565, 606–611. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0828-1
Mukhi, N., Brown, H., Gorenkin, D., Ding, P., Bentham, A. R., Stevenson, C. E. M., et al. (2021). Perception of structurally distinct effectors by the integrated WRKY domain of a plant immune receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 118, e2113996118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2113996118
Parenteau, J., Maignon, L., Berthoumieux, M., Catala, M., Gagnon, V., Abou Elela, S. (2019). Introns are mediators of cell response to starvation. Nature 565, 612–617. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-085
Phukan, U. J., Jeena, G. S., Shukla, R. K. (2016). WRKY Transcription Factors: Molecular regulation and stress responses in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 7. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.00760
Rushton, P. J., Somssich, I. E., Ringler, P., Shen, Q. J. (2010). WRKY transcription factors. Trends Plant Sci. 15, 247–258. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2010.02.006
Shi, J., Wang, X., Wang, E. (2023). Mycorrhizal symbiosis in plant growth and stress adaptation: from genes to ecosystems. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 22, 74:569–74:607. doi: 10.1146/annurev-arplant-061722-090342
Silvestri, A., Ledford, W. C., Fiorilli, V., Votta, C., Scerna, A., Tucconi, J., et al. (2024). A fungal sRNA silences a host plant transcription factor to promote arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis. New Phytol. doi: 10.1111/nph.20273
Song, H., Sun, W., Yang, G., Sun, J. (2018). WRKY transcription factors in legumes. BMC Plant Biol. 18, 243. doi: 10.1186/s12870-018-1467-2
Tamura, K., Stecher, G., Kumar, S. (2021). MEGA11: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 38, 3022–3027. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msab120
Tian, L., Zou, Y. N., Wu, Q. S., Kamil, Kuča (2021). Mycorrhiza-induced plant defence responses in trifoliate orange infected by Phytophthora parasitica. Acta Physiol. Plant 43, 45. doi: 10.1007/s11738-021-03216-2
Trouvelot, A., Kough, J. L., Gianinazzipearson, V. (1986). Measure du taux de mycorhization VA d’un systeme radiculaire. Recherch de methodes d’estimation ayant une signification fonctionnelle. INRA, 1986, 217–221.
Vailleau, F., Genin, S. (2023). Ralstonia solanacearum: An arsenal of virulence strategies and prospects for resistance. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 61, 25–47. doi: 10.1146/annurev-phyto-021622-104551
Van De Peer, Y., Mizrachi, E., Marchal, K. (2017). The evolutionary significance of polyploidy. Nat. Rev. Genet. 18, 411–424. doi: 10.1038/nrg.2017.26
Wang, H., Chen, W., Xu, Z., Chen, M., Yu, D. (2023). Functions of WRKYs in plant growth and development. Trends Plant Sci. 28, 630–645. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2022.12.012
Wang, M., Tang, W., Xiang, L., Chen, X., Shen, X., Yin, C., et al. (2022). Involvement of MdWRKY40 in the defense of mycorrhizal apple against fusarium solani. BMC Plant Biol. 22, 385. doi: 10.1186/s12870-022-03753-z
Xue, H., Lozano-Durán, R., Macho, A. P. (2020). Insights into the Root Invasion by the Plant Pathogenic Bacterium Ralstonia solanacearum. Plants (Basel). 9, 516. doi: 10.3390/plants9040516
Yan, L., Jin, H. T., Raza, A., Huang, Y., Gu, D. P., Zou, X. Y. (2022). WRKY genes provide novel insights into their role against Ralstonia solanacearum infection in cultivated peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Front. Plant Sci. 13. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.986673
Yang, M., Wang, Y., Chen, C., Xin, X., Dai, S., Meng, C., et al. (2024). Transcription factor WRKY75 maintains auxin homeostasis to promote tomato defense against Pseudomonas syringae. Plant Physiol. 20, kiae025. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiae025
Yang, S., Cai, W., Shen, L., Cao, J., Liu, C., Hu, J., et al. (2022). A CaCDPK29-CaWRKY27b module promotes CaWRKY40-mediated thermotolerance and immunity to Ralstonia solanacearum in pepper. New Phytol. 233, 1843–1863. doi: 10.1111/nph.17891
Yang, S., Zhang, Y., Cai, W., Liu, C., Hu, J., Shen, L., et al. (2021). CaWRKY28 Cys249 is Required for Interaction with CaWRKY40 in the regulation of pepper immunity to Ralstonia solanacearum. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 34, 733–745. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-12-20-0361-R
Yang, Y., Liu, J., Zhou, X., Liu, S., Zhuang, Y. (2020). Identification of WRKY gene family and characterization of cold stress-responsive WRKY genes in eggplant. PeerJ 8, e8777. doi: 10.7717/peerj.8777
Yao, Q. Y., Xia, E. H., Liu, F. H., Gao, L. Z. (2015). Genome-wide identification and comparative expression analysis reveal a rapid expansion and functional divergence of duplicated genes in the WRKY gene family of cabbage, Brassica oleracea var.capitata. Gene 557, 35–42. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2014.12.005
Yu, G., Lu, Z., Hao, X., Yu, j., Chen, X. L., Carlos del Pozo, J., et al. (2024). Cell wall-mediated root development is targeted by a soil-borne bacterial pathogen to promote infection. Cell Rep. 43, 114179. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114179
Yu, F., Van Truong, T., He, Q., Hua, L., Su, Y., Li, J. (2019). Dry season irrigation promotes leaf growth in Eucalyptus urophylla × E.grandis under fertilization. Forests 10, 67. doi: 10.3390/f10010067
Yuliar, Nion, Y. ,. A., Toyota, K. (2015). Recent trends in control methods for bacterial wilt diseases caused by Ralstonia solanacearum. Microbes Environ. 30, 1–11. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-82060-3
Keywords: WRKY, arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMFs), Rhizophagus irregularis, Eucalyptus grandis, Ralstonia solanacearum, plant-AMF-bacterium interaction
Citation: Zhang J, Yang X, Huo C, Fan X, Liu Q, Liu Z, Su Y and Chen Z (2025) Eucalyptus grandis WRKY genes provide insight into the role of arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis in defense against Ralstonia solanacearum. Front. Plant Sci. 16:1510196. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1510196
Received: 12 October 2024; Accepted: 22 January 2025;
Published: 07 February 2025.
Edited by:
Luisa Lanfranco, University of Turin, ItalyReviewed by:
Shuangchen Chen, Henan University of Science and Technology, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Zhang, Yang, Huo, Fan, Liu, Liu, Su and Chen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zujing Chen, enVqaW5nY2hlbkBzY2F1LmVkdS5jbg==; Yu Su, c3V5dTExMEAxNjMuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.