
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Plant Sci. , 17 December 2024
Sec. Plant Genetics, Epigenetics and Chromosome Biology
Volume 15 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2024.1512047
Plant microRNAs (miRNAs) are small non-coding RNA molecules that usually negatively regulate gene expression at the post-transcriptional level. Recent data reveal that plant miRNAs are not limited to individual plants but can transfer across different species, allowing for communication with the plant, animal, and microbial worlds in a cross-kingdom approach. This review discusses the differences in miRNA biosynthesis between plants and animals and summarizes the current research on the cross-species regulatory effects of plant miRNAs on nearby plants, pathogenic fungi, and insects, which can be applied to crop disease and pest resistance. In particular, this review highlights the latest findings regarding the function of plant miRNAs in the transboundary regulation of human gene expression, which may greatly expand the clinical applicability of plant miRNAs as intriguing tools in natural plant-based medicinal products in the future.
MicroRNAs (miRNAs), a category of non-coding RNAs, share a conserved single-stranded RNA structure with a length between 18 and 24 nucleotides. These miRNAs regulate target gene expression in eukaryotes at the post-transcriptional level. The first miRNA was identified as lin-4 in Caenorhabditis elegans. Since then, miRNAs have been found in an ever-expanding family across animals, plants, and other eukaryotic species. Plant miRNAs were initially identified in Arabidopsis thaliana (Llave et al., 2002). Subsequently, miRNAs in other plant species have been identified one after another. Due to advances in next-generation sequencing (NGS) technology, tens of thousands of miRNAs have been discovered in various plants. For instance, 10,414 mature miRNA sequences and 8,615 hairpin precursors from 82 plant organisms have been reported present in the most recent version of miRbase (miRbase v22, https://mirbase.org/index.shtml) (Kozomara et al., 2019). Approximately 16,438 miRNA sequences from 121 plant species have been cataloged in the plant non-coding RNA database (PNRD, http://structuralbiology.cau.edu.cn/PNRD/index.php) (Yi et al., 2015). Additionally, about 38,186 miRNA sequences from 179 plants have been documented in the second version of Plant miRNA database (PmiREN v2.0, https://pmiren.com/) (Guo et al., 2022). Current understanding of plant miRNA function mainly focuses on regulating the expression of target genes during plant development and in response to stress. However, mounting evidence suggests that plant miRNAs not only function within plant bodies but also cross-regulate the expression of genes in viruses, fungi, insects, and mammals (Wang et al., 2017c; Chen and Rechavi, 2022; Sun et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2022; Li et al., 2023). This paper reviews recent research progress on the transfer mechanisms of plant miRNAs and cross-kingdom miRNA/target gene regulation systems. In particular, examples of cross-boundary transmission and regulation of plant miRNAs, along with their possible target genes, are summarized here, along with their potential applications in developing new drugs.
MiRNAs are produced through several steps, including transcription of miRNA encoding genes (MIR genes), primary miRNA (pri-miRNA) processing, and mature miRNA export (Ameres and Zamore, 2013). The processes of miRNA biosynthesis in both plants and animals are illustrated in Figure 1. In plants, the pri-miRNAs are mostly synthesized by RNA polymerase II (Pol II). Then, the DICER-LIKE 1 (DCL1) protein processes pri-miRNAs, removing the poly-A tail and producing short precursors known as pre-miRNAs. DCL1 further processes the secondary structure of pre-miRNAs to produce the imperfect miRNA-miRNA* duplexes. Consequently, the miRNA-miRNA* duplexes are methylated at the 3’ terminal by HUA enhancer 1 (HEN1) in plants and then transported from nucleus to cytoplasm, associated with HASTY (HST). Finally, the duplexes separate, and only one strand is integrated into the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) to identify target mRNAs (Yu et al., 2017). In animals, the MIR genes are transcribed as pri-miRNAs by RNA polymerase II and III (Pol II/III). Then RNase III enzyme Drosha cleaves the poly-A tails from pri-miRNAs in the nucleus to produce pre-miRNAs with a 2 nt overhang at the 3’ end and a 5’ phosphate. The pre-miRNAs are subsequently processed and transferred to the cytoplasm concurrently by Ran-GTP dependent EXPORTIN 5 (EXP5). Dicer finally cleaves the pre-miRNAs to produce ~22 bp mature miRNA duplexes, which combine with ARGONAUTE (AGO) proteins to form RISC (Figure 1).
Based on the diversity in biosynthesis processes, there are several differences between animal miRNAs and plant miRNAs: (1) Compared to animal miRNAs, plant miRNAs have longer and more varied stem-loop precursors (ranging from 100 to 900 nt in plants vs. predominantly less than 100 nt in animals) (Zhu et al., 2016). (2) The length of plant miRNAs shows a tighter distribution around 21 nt (Cao et al., 2023), while animal miRNAs typically range from 22 to 23 nt (Ha and Kim, 2014). Interestingly, abnormal miRNA isoforms with 1-nt-shorter 3’ends are widely accumulated in many human primary tumors and ectopic expression of plant RNA-dependent RNA polymerase 1 (RDR1) enables broad antitumor response by rescuing miRNA deficiency (Qi et al., 2022). (3) At the 5’ terminus, plant miRNAs tend to favor uracil (U). Additionally, the 3’ terminal ribose of plant miRNAs is methylated at the 2′-hydroxyl group by HEN1, providing molecular stability, which is a crucial step for miRNA biosynthesis in plants but not in animals (Baranauske et al., 2015). (4) Animals and plants exhibit distinct miRNA genetic structures. About 50% of genes encoding animal miRNAs are located in clusters, which frequently comprise different mature miRNAs. For example, one of the most deeply conserved clusters is the mir-100~let-7~mir-125 cluster, which has an important role in the development of bilaterian animals (Roush and Slack, 2008). In contrast, there are fewer instances of miRNA clusters in plants, which almost exclusively encode miRNAs that share high homology. An example of high homology of plant miRNAs is the miR159/miR319 family in Arabidopsis, which share identical sequence at 17 of 21 nucleotides, yet evolve to target two distinct gene families (Palatnik et al., 2007). (5) Differences can also be found in miRNA target recognition and location, as well as their mode of action. In animals, miRNA complementary sites are often found in the 3’ untranslated regions (3’ UTR), whereas in most plants, they are nearly exclusively present within the open reading frame regions. Plant miRNAs usually have single binding sites, and exhibit high or perfect complementarity to their target sites (less than 4 mismatches), whereas animal miRNAs can bind to multiple target sites with less complementarity. Moreover, plant miRNAs primarily repress gene expression by directly cleaving target mRNAs at the post-transcriptional level (Rogers and Chen, 2013), whereas animal miRNAs mainly repress the translation of target genes by preventing translational initiation or elongation. Despite differences in target recognition, plant miRNAs can also induce translational repression in addition to target cleavage (Gandikota et al., 2007; Iwakawa and Tomari, 2015). Notably, the miRNA regulatory mechanisms of gene expression are complicated and vary in different organisms and different tissues (Fabian et al., 2010). In some situations, miRNAs can also increase mRNA stability or translation efficiency (Henke et al., 2008; Orom et al., 2008). For instance, mammalian miR-10a interacts with 5’ UTR of ribosomal protein mRNAs and enhances their translation in response to stress or nutrient shortage (Orom et al., 2008). MiR-122 enhances the replication of the hepatitis C virus (HCV) by binding to 5’UTR and stabilizing the RNA of HCV (Jopling et al., 2005; Henke et al., 2008).
The cross-kingdom regulation by plant miRNAs was first reported in 2012 when it was discovered that rice-derived miR168a existed in mouse sera and functioned in the liver by targeting low-density lipoprotein receptor adapter protein 1 (LDLRAP1) (Zhang et al., 2012). Notably, some plant miRNAs are highly homologous to animal miRNAs (Bellato et al., 2019; Avsar et al., 2020; Cao et al., 2023; Huang et al., 2023), and many biological processes mediated by miRNAs are shared between plants and other organisms (Arda and Doganlar, 2022), therefore facilitating plant miRNAs’ capacity for cross-kingdom modulation of gene expression (Xu et al., 2024b). Recent research has demonstrated that small RNAs, especially miRNAs, can move not only within the cells and tissues of a single plant but also between distinct species, enabling cross-kingdom communication (Knip et al., 2014; Bellato et al., 2019; Zeng et al., 2019; Gualtieri et al., 2020; Chen and Rechavi, 2022; Urzi et al., 2022). The trans-species transfer and regulation of miRNAs have been documented between plants and other organisms, including plants-plants, plants-viruses, plants-fungi, plants-insects, plants-animals, and plants-humans (Zeng et al., 2019; Zhang et al., 2019; Chi et al., 2023; Li et al., 2023). Several recent findings regarding the role of plant miRNAs in mediating cross-species gene regulation are reviewed as follows. Additionally, this review provides a mechanistic understanding of miRNA regulation, including plant miRNA transfer carriers, plant miRNA absorption, plant miRNA activity at the destination, and the future application of plant miRNAs.
It has been reported that trans-species miRNA communication occurs naturally between the parasitic and host plants (Shahid et al., 2018). Cuscuta campestris obtains nutrients from host plants by using the feeding structure known as ‘haustoria’. In the haustoria, C. campestris generates 22-nt miRNAs that are also found in the stems of its host plants (Figure 2A) (Shahid et al., 2018). These parasitic plant 22-nt miRNAs function in host plants, causing the host target genes to be silenced, suggesting a natural inter-species miRNA regulatory relationship between the parasitic plant and its host (Shahid et al., 2018). Recent studies have confirmed that plant miRNAs can be secreted and taken up by the nearby plants (Betti et al., 2021; Marzec, 2022). Arabidopsis miR399 and miR156 are shown to target PHO2 and SPL genes, respectively (Pant et al., 2008; Bhogale et al., 2014). Exogenous administration of chemically synthesized miR399 or miR156 has been shown to trigger the silencing of their target genes in plants (Betti et al., 2021). The observed silencing effect was even more dramatic when endogenous miRNA extracts from plants overexpressing miR399 or miR156 were used instead of synthetic products, demonstrating that miRNAs can be absorbed and modulate target gene expression in receiving plants (Betti et al., 2021). To further investigate whether miRNAs are delivered between different plant individuals, overexpressing miR399/miR156 lines and wild-type were cultured in the same liquid medium. The results showed that a higher concentration of miR399/miR156 was detected in the medium, and the target genes in wild-type plants were down-regulated (Figure 2B), suggesting that miRNAs were secreted outside of plants and functioned in their neighbors (Betti et al., 2021). This study demonstrated that miRNAs function as novel signaling molecules in plant-to-plant communication.
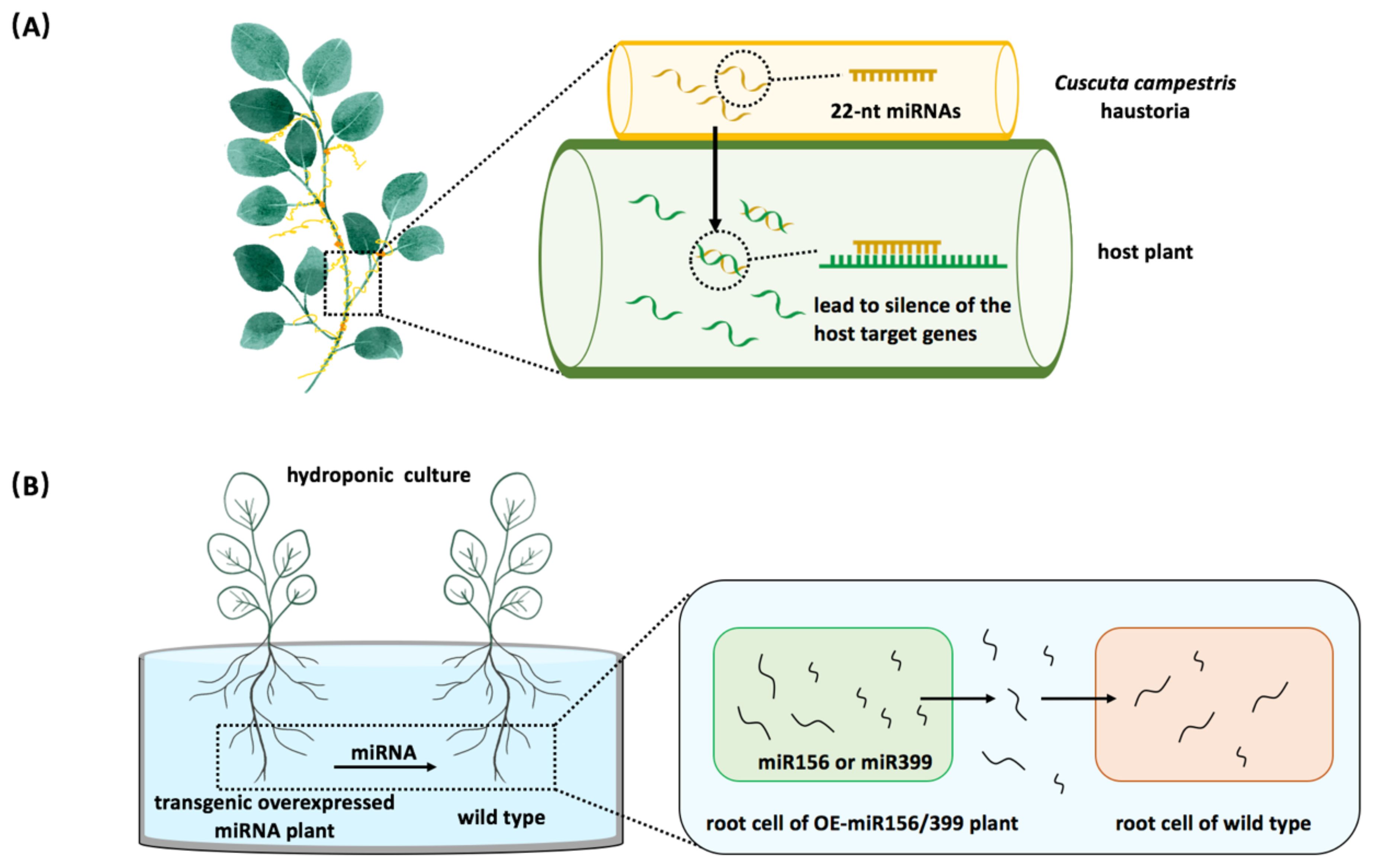
Figure 2. Plant miRNAs serve as regulatory molecules between plants. (A) The inter-species miRNA regulation occurs between the parasitic plant dodder (Cuscuta campestris) and its host. Cuscuta campestris utilizes haustoria to facilitate the movement of miRNAs into host plant cells. (B) Plant miRNAs act as signaling molecules affecting nearby plants. When wild-type plants are co-cultivated with overexpressing miR156 or miR399 plants, the expression levels of miRNA target genes are decreased in wild-type plants.
Apart from miRNA communication within and across plant species, miRNAs also transfer between plants and their microbial pathogens. Cross-kingdom miRNA regulation between plants and fungal pathogens is bidirectional (Wang et al., 2016; Huang et al., 2019a). One way that microbial pathogens alter the expression of host genes involved in immunity is by delivering small RNAs into host plants (Wang et al., 2016; Huang et al., 2019a). For instance, the gray mold Botrytis cinerea causes gene silencing in different host plant species by introducing a variety of small RNAs into plant cells (Weiberg et al., 2013). The miRNA-like RNA 1 from Puccinia striiformis (Pst) was found to inhibit gene expression in host wheat (Triticum aestivum), reducing the host plants’ resistance to Pst (Wang et al., 2017a). However, the miRNAs from plant hosts may also be reciprocally transported into pathogens to silence genes linked to virulence (Wang et al., 2016; Cai et al., 2018b; Huang et al., 2019a). In response to pathogen Verticilium dahlia, cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) miR159 and miR166 were transferred into fungal hyphae, where they silenced the virulence genes (Zhang et al., 2016c). Another study showed that Arabidopsis-derived miR166 was transferred to fungal pathogen B. cinerea. to inhibit pathogen gene expression (Cai et al., 2018b). Since these plant miRNAs are delivered into microbial pathogens and efficiently silence the virulence-related genes, they can be applied to protect crops. Several major crops, including barley, wheat, and soybean, have been genetically engineered to produce these cross-kingdom plant miRNAs to regulate pathogenic diseases caused by viruses, viroids, fungi, oomycetes, and bacteria (Niu et al., 2021). Additionally, it has been proven that some pathogenic microorganisms can absorb external small RNAs from their surroundings (Wang et al., 2016; Cai et al., 2018a), making the direct application of small RNA spay to protect plants against the microbial pathogens. For example, it has been found that rice can be effectively protected against blast disease by spaying small RNAs that target Magnaporthe oryzae MoDES1 gene (Sarkar and Roy-Barman, 2021). Similarly, the application of exogenous small RNAs confers plant protection against the pathogens B. cinerea and Sclerotinia sclerotiorum (McLoughlin et al., 2018). Therefore, the transboundary regulation of miRNAs between plants and microorganisms inspires the development and application of innovative methods for crop disease control in agriculture (Niu et al., 2021; Qiao et al., 2021).
The cross-kingdom transmission of miRNAs has also been demonstrated in plant-insect interactions (Chi et al., 2023). Some herbivorous insects utilize foliar, root, or phloem resources as their food, which facilitate the transport of host plant miRNAs into their bodies (Figure 3). Several cereal miRNAs, including 13 miRNAs from Sorghum bicolor and 3 miRNAs from Hordeum vulgare, have been found in two grain aphid species (Schizaphis graminum and Sipha flava), indicating that plant miRNAs are transferred into the herbivorous insects (Wang et al., 2017b). Plant miRNAs have also been identified in the bodies of cotton-melon aphid Aphis gossypii during feeding on melon phloem sap (Sattar et al., 2012). Similarly, mulberry (Morus alba) miRNAs were discovered in silkworm hemolymph and multiple tissues after feeding on mulberry leaves, confirming that plant miRNAs are taken up by insects orally and transported into various tissues (Jia et al., 2015). Intriguingly, plant miRNAs are involved in transboundary regulation through plant-pollinator interactions. An excellent example illustrating the pollen-derived miRNA regulatory process is honey bee caste formation (Masood et al., 2016; Zhu et al., 2017). Plant miRNAs have been found to delay development, decrease body weight and length, and reduce the reproductive capacity of honeybees, thus promoting worker bee formation (Zhu et al., 2017). Mechanically, pollen miR162a inhibits the expression of the amTOR gene in bees, which determines caste development (Figure 3) (Zhu et al., 2017).
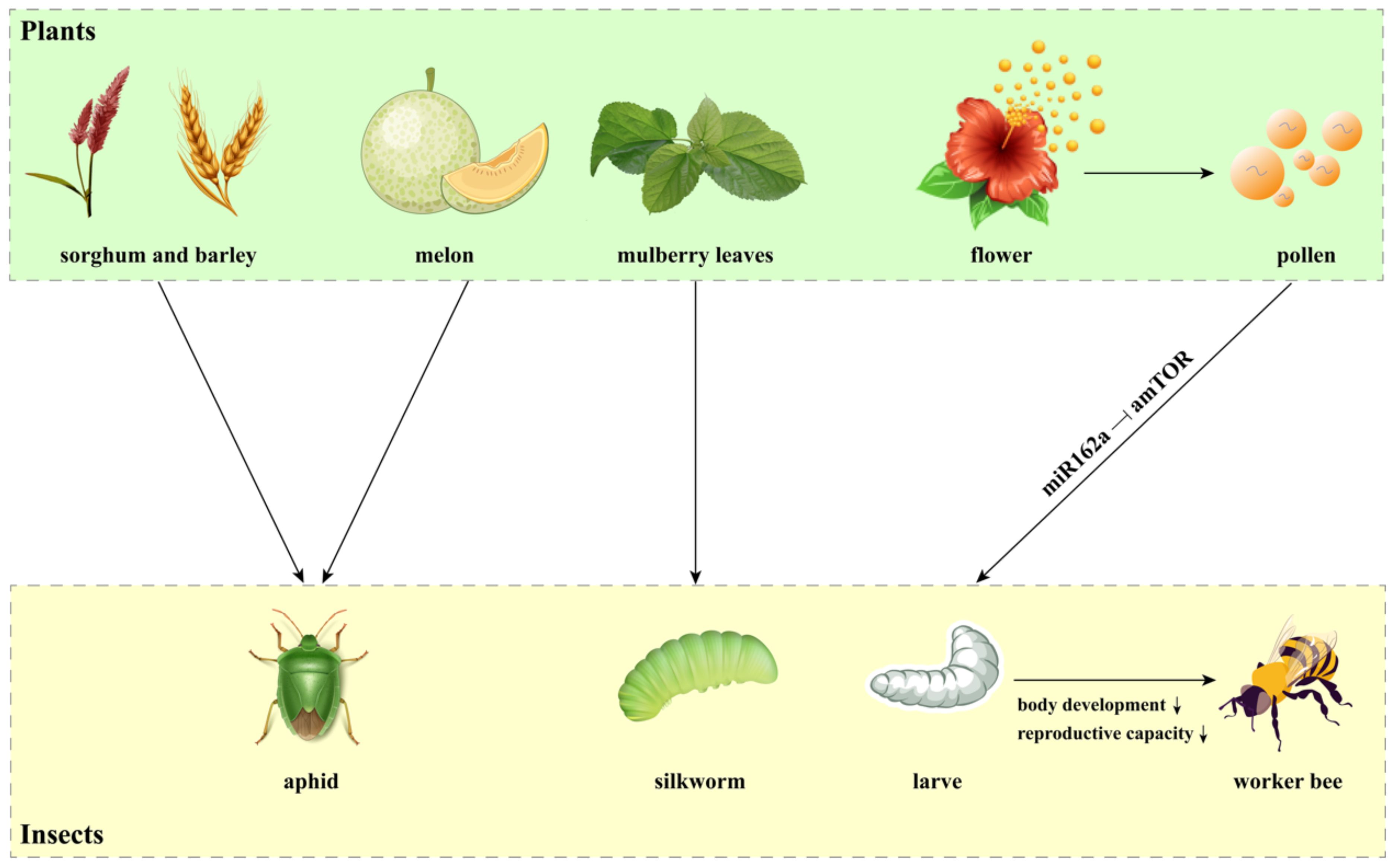
Figure 3. Cross-kingdom miRNAs in plant-insect interactions. This figure illustrates how miRNAs derived from specific plants are transferred and act as regulatory molecules in the bodies of herbivorous insects. Notably, miRNAs from sorghum, barley, and melon have been detected in various aphid species, while miRNAs from mulberry leaves have been identified in silkworms. Additionally, pollen-derived miR162a plays a key role in the regulatory process of honey bee caste formation by targeting amTOR gene.
Now the transboundary regulation of miRNAs from plants to mammals is the focus of attention, as the plant-derived miRNAs may be used as novel agents to improve human health (Li et al., 2023; Xu et al., 2024b). As early as 2012, it was discovered that rice-derived miR168a could target the mRNA of murine low-density lipoprotein receptor adapter protein 1 (LDLRAP1), reducing its protein level in the liver (Zhang et al., 2012). This was the first scientific proof of the transboundary regulation by plant miRNAs in mammals, implying that mammals can take up functional miRNAs from dietary plant food. In 2015, it was discovered that honeysuckle (Lonicera japonica) miR2911 could be consumed by mice and directly targeted to influenza A virus (IAV) (Zhou et al., 2015). Honeysuckle miR2911 effectively inhibited IAV’s PB2 and NS1 gene expression in vivo and in vitro (Zhou et al., 2015). This research proved that the plant-derived miRNAs suppressed viral proliferation in mammals, which suggested the promising application of plant miRNAs as antiviral drugs. Later, plant miR159 was identified in human bodies and recognized for its potential to inhibit breast tumor cell growth by targeting the transcription factor 7 (TCF7). TCF7 is important for tumor initiation by mediating Wnt/β-catenin signaling (Chin et al., 2016). Similarly, miR156a was found to be enriched in broccoli and the synthetic miR156a mimics inhibited epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) cells by specifically targeting the 3’ UTR of the junctional adhesion molecular A (JAM-A) in vitro (Tian et al., 2016). Plant miR159a and miR156c from nut exhibit anti-inflammatory properties via suppressing TNF superfamily member 1a (Tnfrsf1a) expression in macrophages and adipocytes (Aquilano et al., 2019). In 2020, clinical data showed that honeysuckle-derived miR2911 can prevent the replication of SARS-CoV-2, accelerating recovery from COVID-19 infection (Zhou et al., 2020). Ginger-derived miRNA (aly-miR396a-5p) was reported to decrease SARS-CoV-2-induced lung inflammation in mice by repressing the expression of the Nsp12 gene (Teng et al., 2021). Additionally, the plant miR171 was found to modulate the mTOR pathway by targeting G protein subunit alpha 12 (GNA12) (Gismondi et al., 2021). The plant miR167e-5p has the ability to influence adipogenesis via negative regulation of β-catenin in 3T3-L1 cells (Chen et al., 2022b). Garlic-derived miRNA (Han-miR3630-5p) can bind to and inhibit toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), thus alleviating DSS-induced colitis (Zhu et al., 2023b). Previous work in our lab showed that honeysuckle-derived miR2911 inhibits HPV-positive cervical cancer cell proliferation via directly targeting the oncogenes of HPV E6 and E7 (Chi et al., 2024). So far, examples of cross-kingdom gene regulation of plant miRNAs are still being discovered. The following table summarizes the existing examples of transboundary regulation of plant miRNAs in mammals (Table 1).
Exosomes, which store bioactive chemicals such as proteins and RNA molecules, have been well characterized in mammalian cells. Recently, plant miRNAs have been discovered to mediate communication within the plant kingdom and cross kingdoms by being stably packaged into plant-derived exosome-like nanoparticles (PENs) (Zhang et al., 2016b; Chen et al., 2022a; Cieslik et al., 2022; Urzi et al., 2022). PENs can be extracted from various plants and serve as nanocarriers for the delivery of biological cargo, including plant-derived miRNAs. For instance, a study identified a range of miRNAs in edible PENs from 11 different species, with numbers ranging from 32 to 127 (Xiao et al., 2018). PENs from grapes have been shown to contain 96 miRNAs (Ju et al., 2013), while ginger-derived PENs contain 125 distinct miRNAs (Zhang et al., 2016a). Approximately 398 miRNAs have been identified in PENs from ginseng (Xu et al., 2021). Several studies have demonstrated that PENs exert biological effects mediated by bioactive miRNAs (Xiao et al., 2018; Potesta et al., 2020; Kalarikkal and Sundaram, 2021; Teng et al., 2021; Xu et al., 2021). The mechanism by which plant miRNAs selectively load into PENs has been discovered (He et al., 2021). Appropriate small RNA packaging requires the involvement of RNA binding proteins, such as AGO1, RNA helicases, and annexins (He et al., 2021). The PENs share structural and functional similarities with mammal exosomes (Cai et al., 2021; Teng et al., 2021). The phospholipid bilayer and surface polysaccharides of PENs protect the encapsulated cargo from degradation in the gastrointestinal tract, resulting in higher stability and bioavailability of the miRNAs (Yang et al., 2018; Kalarikkal and Sundaram, 2021). Notably, the miRNAs packed in the PENs are highly resistant to RNase and tolerant to both acidic and alkaline environments (Wang et al., 2020; Umezu et al., 2021; Qin et al., 2022), enabling the transfer of plant miRNAs through the digestive tract after oral intake.
The PENs can be absorbed by intestinal macrophages via micropinocytosis and clathrin-dependent endocytosis (Wang et al., 2014; Umezu et al., 2021). Importantly, a recent study confirmed that plant miRNAs in PENs are more easily absorbed by mammals (Teng et al., 2018). A study indicated that miRNAs from vegetables or fruits are generally absorbed in the gastric mucosal cells of the stomach (Chen et al., 2021a). In detail, the SID1 transmembrane family member 1 (SIDT1), which is rich in the stomach, functions as an essential transporter that facilitates the absorption of dietary miRNAs into these cells (Figure 4) (Chen et al., 2021a). Besides, it is worth noting that the uptake of mature plant miRNA by SIDT1 was significantly increased under acidic culture conditions (Chen et al., 2021a). Following absorption, the plant miRNAs enter the bloodstream and circulate to various tissues such as the stomach, intestine, lung, liver, and bladder, where they modulate target genes in recipient mammalian cells (Figure 4) (Zhang and Hong, 2019; Chen et al., 2021a). In particular, the gas-miR36-5p from Gastrodia elata was found to prevent Alzheimer’s disease in a mouse model through targeted inhibition of GSK-3 activity, suggesting plant miRNAs can cross the blood-brain barrier and treat central nervous system diseases (Lu et al., 2023).
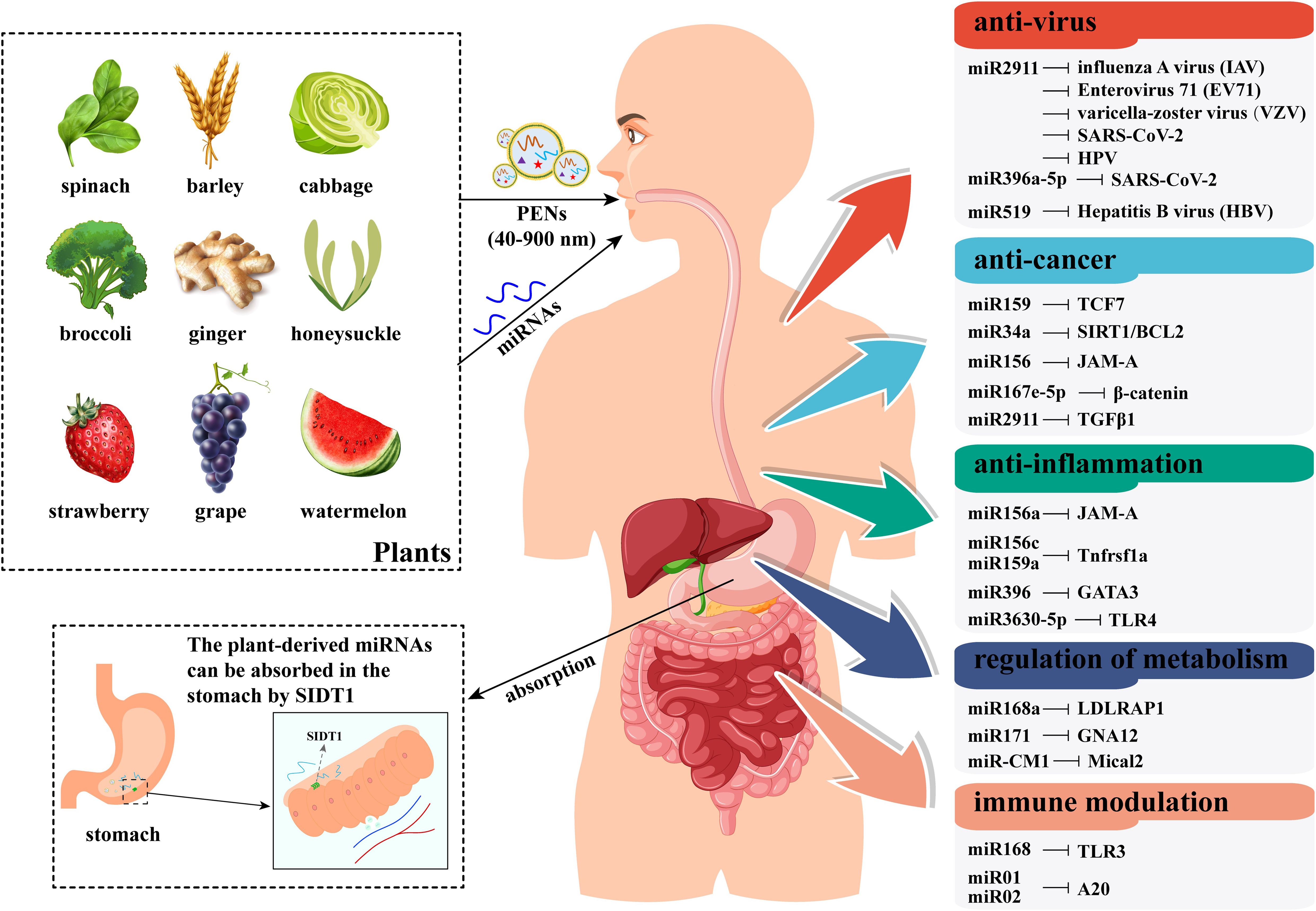
Figure 4. A schematic model of plant miRNAs’ transport, uptake, and effects in human bodies. This figure illustrates the process by which plant miRNAs (either naked or encapsulated in PENs) are obtained orally through diet. After passing through the gastrointestinal tract, plant miRNAs are absorbed by the SIDT1 protein in the stomach. These absorbed miRNAs are transported to target organs and cells via the circulatory system. Ultimately, plant miRNAs regulate disease-related gene expression in a cross-kingdom manner, acting as novel active substances that benefit human health. The information in the right boxes lists plant miRNAs and their primary targets in humans.
In addition to oral uptake, PENs can also be administered via other routes, including intranasal administration, intraperitoneal administration, intravenous administration, and transdermal administration (Feng et al., 2023). This suggests that cargo miRNAs can reach target organs or cells through multiple administration methods. Thus, plant-derived miRNAs may represent a promising therapeutic strategy against various diseases, including viral infections, tumors, inflammation, metabolic disorders, and immune modulation (Figure 4). The transportation and administration of plant miRNAs in mammals are then achieved through a PEN-mediated mode. In fact, PENs have been used to deliver exogenous small RNAs to disrupt gene expression of multiple diseases. For instance, grapefruit–derived PENs were deployed to deliver miR17 to mouse brain tumor via intranasal route (Zhuang et al., 2016). Similarly, ginger-derived PENs were able to transfer exogenous small RNAs to intestinal epithelial tissue (Zhang et al., 2017) or subcutaneous tumor cells (Li et al., 2018b). Recently, PENs from four foods have been shown to serve as effective nanocarriers for exogenous miRNAs (Lopez de Las Hazas et al., 2023). The result suggested that PENs can enhance the biological stability of exogenous miRNAs against RNase degradation and ferry miRNAs toward cellular uptake (Lopez de Las Hazas et al., 2023). Furthermore, it was found that host plants transferred miRNAs to the fungal pathogen Botrytis cinerea primarily through PENs (Cai et al., 2018b). Therefore, PENs may serve as vehicles for delivering plant miRNAs from donor plants to other recipient organisms.
Growing evidence suggests that plant miRNAs may serve as an ‘RNA language’ to interact various organisms, including plants, microorganisms, insects, and mammals. Despite the increasing knowledge about cross-kingdom regulation of plant miRNAs, many questions remain unanswered. For instance, how are miRNAs secreted from donor plants and absorbed by recipient plants during interspecies transfer? Which types of plant miRNAs—those associated with AGO proteins, miRNA duplexes, or mature single strands—are mobile across species? Additionally, do plant miRNAs enter receiving plants via transporter proteins similar to SID-1 in nematodes (Shih and Hunter, 2011) or SIDT1 in mammals (Chen et al., 2021a)? While evidence suggests that plant miRNAs are effectively encapsulated and transported via PENs, how do these miRNAs retain functionality in different organisms during cross-kingdom regulation? This is particularly important given that most plant miRNAs are 3’ methylated, which differs from animal miRNAs, and mammalian AGO proteins generally do not bind to methylated small RNAs. Moreover, the process by which plant miRNAs are packaged into PENs requires further clarification. Several studies indicate that absorbed plant miRNAs are packaged into extracellular vesicles in mammalian circulation (Zhang et al., 2012; Luo et al., 2017; Chen et al., 2021a). However, it remains unclear whether these enclosed plant miRNAs are repackaged into mammalian exosomes in the intestine or retained in their original PENs. Addressing these questions through further experimentation will significantly enhance our understanding of RNA biology and facilitate practical applications.
Pathogenic fungi and pests pose serious threats to crop production. Given the transboundary regulation of plant miRNAs in combating these threats, plant miRNAs could be valuable tools for crop protection against diseases (Mahanty et al., 2023). The host-induced gene silencing (HIGS) strategy involves genetically engineered plants producing small RNAs to target virulence-related genes, proving effective against various fungal pathogens and pests (Qi et al., 2019). However, HIGS raises concerns regarding transgenic implementations in agriculture. To address this, spray-induced gene silencing (SIGS) has been developed, where RNAs are directly applied to plant leaves. Using stable nanovesicles, RNA sprays conjugated with nanoparticles can enhance the efficacy of pathogen gene silencing (Qiao et al., 2021). Nevertheless, SIGS faces challenges related to RNA uptake efficiency and production costs.
As research uncovers the roles of plant miRNAs in regulating disease-related genes in mammals, their potential applications in therapeutic interventions—particularly in anti-cancer and anti-viral contexts—are becoming increasingly evident (Zhang et al., 2023). Numerous miRNAs have been identified as tumor suppressors or oncogenic in human contexts (Slack and Chinnaiyan, 2019), leading to a burgeoning field of miRNA therapeutics against cancer (Rupaimoole and Slack, 2017; Diener et al., 2022). As highlighted in Table 1 and Figure 4, several plant miRNAs influence cancer cell cycles, proliferation, and apoptosis, suggesting their potential as anti-cancer agents. Interestingly, unusual 1-nt shorter miRNA isoforms are prevalent in cancers, and ectopic expression of plant RDR1 can inhibit cancer cell proliferation by modifying defective miRNAs (Qi et al., 2022), indicating shared editing processes of small RNAs between plants and animals.
On the anti-viral front, plant miRNAs have garnered attention for their efficacy against various viruses, including honeysuckle miR2911, which targets influenza A, varicella-zoster virus, and enterovirus 71. Notably, during the COVID-19 pandemic, honeysuckle-derived miR2911 was found to prevent the replication of SARS-CoV-2, promoting recovery from infection. Additionally, ginger-derived aly-miR396a-5p and rlcv-miR-rL1-28-3p have shown potential in inhibiting SARS-CoV-2 gene expression (Teng et al., 2021). Houttuynia cordata-derived miRNAs have also been validated for targeting respiratory RNA viruses, such as miR858a and miR858b against H1N1 and miR166a-3p against SARS-CoV-2 (Zhu et al., 2023a). Recently, the plant beverage Amrtan Ocean 2911, rich in honeysuckle miR2911, has been approved for market entry. These advancements suggest significant translational medicine applications for plant miRNA-based bioengineering.
Moreover, the role of plant miRNAs may extend to herbal medicine. Historically, research on active pharmacological components in herbal medicine has focused on secondary metabolites. However, with the recognition of transboundary roles, herb-derived miRNAs could emerge as novel active ingredients. A recent study established the Bencao small RNA Atlas by sequencing small RNA libraries from 265 traditional Chinese medicines, identifying 21,757 miRNAs, of which 17,509 (80.4%) were predicted to target at least one human gene. Furthermore, 39.1% of human genes were predicted to be targeted by these herbal miRNAs (Cao et al., 2023).
Despite the promising potential of plant miRNAs, their inherent risks must be carefully considered. Due to conserved sequences, a single plant miRNA may target a broad spectrum of genes in mammals, potentially impacting entire cellular pathways even with moderate effects on individual targets. Off-target effects also warrant attention. Thus, comprehensive analyses of target genes for individual plant miRNAs are essential. Proper dosages and administration strategies should be tailored to specific tissues and cell types. Finally, multidimensional validation of the effects of plant miRNAs on cells and animals must be conducted prior to clinical trials to mitigate unforeseen interactions.
LS: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft. YS: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. CG: Writing – original draft. MF: Writing – original draft. YY: Writing – original draft. FY: Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Open Program of International Joint Research Laboratory for Recombinant Pharmaceutical Protein Expression System of Henan (KFKTYB202201), Natural Science Foundation of Henan Province (242300420172), the Key Scientific Research Project Plans of Higher Education Institutions in Henan Province (24A350011, 24B310009), and National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31500982).
We are grateful to Prof. Juan Du from Karolinska Institute for critically reviewing the manuscript.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
AGO, Argonaute; BCL2, B-cell lymphoma-2; DCL1, DICER-LIKE 1; EXP5, EXPORTIN 5; GATA3, GATA binding protein 3; GNA12, G protein subunit alpha 12; HCV, hepatitis C virus; HEN1, HUA enhancer 1; HIGS, host-induced gene silencing; HST, HASTY; IAV, influenza A virus; JAM-A, junctional adhesion molecular A; LDLRAP1, low-density lipoprotein receptor adapter protein 1; Mical2, microtubule-associated monooxygenase, calponin, and LIM domain containing 2; miRNA, microRNA; MIR, microRNA encoding gene; NGS, next-generation sequencing; PENs, plant-derived exosome-like nanoparticles; Pol II, RNA polymerase II; pri-miRNA, primary miRNA; RDR1, RNA-dependent RNA polymerase 1; RISC, RNA-induced silencing complex; SIDT1, SID1 transmembrane family member 1; SIRT1, Sirtuin 1; SIGS, spray-induced gene silencing; TCF7, transcription factor 7; TGF-β, transforming growth factor β; TLR3, Toll-like receptor 3; Tnfrsf1, TNF superfamily member 1a; UTR, untranslated regions.
Akao, Y., Kuranaga, Y., Heishima, K., Sugito, N., Morikawa, K., Ito, Y., et al. (2022). Plant hvu-MIR168-3p enhances expression of glucose transporter 1 (SLC2A1) in human cells by silencing genes related to mitochondrial electron transport chain complex I. J. Nutr. Biochem. 101, 108922. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2021.108922
Ameres, S. L., Zamore, P. D. (2013). Diversifying microRNA sequence and function. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 14, 475–488. doi: 10.1038/nrm3611
Aquilano, K., Ceci, V., Gismondi, A., De Stefano, S., Iacovelli, F., Faraonio, R., et al. (2019). Adipocyte metabolism is improved by TNF receptor-targeting small RNAs identified from dried nuts. Commun. Biol. 2, 317. doi: 10.1038/s42003-019-0563-7
Arda, H., Doganlar, O. (2022). Stress-induced miRNAs isolated from wheat have a unique therapeutic potential in ultraviolet-stressed human keratinocyte cells. Environ. Sci. pollut. Res. Int. 29, 17977–17996. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-17039-8
Avsar, B., Zhao, Y., Li, W., Lukiw, W. J. (2020). Atropa belladonna Expresses a microRNA (aba-miRNA-9497) Highly Homologous to Homo sapiens miRNA-378 (hsa-miRNA-378); both miRNAs target the 3’-Untranslated Region (3’-UTR) of the mRNA Encoding the Neurologically Relevant, Zinc-Finger Transcription Factor ZNF-691. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 40, 179–188. doi: 10.1007/s10571-019-00729-w
Baranauske, S., Mickute, M., Plotnikova, A., Finke, A., Venclovas, C., Klimasauskas, S., et al. (2015). Functional mapping of the plant small RNA methyltransferase: HEN1 physically interacts with HYL1 and DICER-LIKE 1 proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 43, 2802–2812. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv102
Bellato, M., De Marchi, D., Gualtieri, C., Sauta, E., Magni, P., Macovei, A., et al. (2019). A bioinformatics approach to explore microRNAs as tools to bridge pathways between plants and animals. Is DNA damage response (DDR) a potential target process? Front. Plant Sci. 10, 1535. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.01535
Betti, F., Ladera-Carmona, M. J., Weits, D. A., Ferri, G., Iacopino, S., Novi, G., et al. (2021). Exogenous miRNAs induce post-transcriptional gene silencing in plants. Nat. Plants 7, 1379–1388. doi: 10.1038/s41477-021-01005-w
Bhogale, S., Mahajan, A. S., Natarajan, B., Rajabhoj, M., Thulasiram, H. V., Banerjee, A. K. (2014). MicroRNA156: a potential graft-transmissible microRNA that modulates plant architecture and tuberization in Solanum tuberosum ssp. andigena. Plant Physiol. 164, 1011–1027. doi: 10.1104/pp.113.230714
Cai, Q., He, B., Kogel, K. H., Jin, H. (2018a). Cross-kingdom RNA trafficking and environmental RNAi-nature’s blueprint for modern crop protection strategies. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 46, 58–64. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2018.02.003
Cai, Q., He, B., Wang, S., Fletcher, S., Niu, D., Mitter, N., et al. (2021). Message in a bubble: shuttling small RNAs and proteins between cells and interacting organisms using extracellular vesicles. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 72, 497–524. doi: 10.1146/annurev-arplant-081720-010616
Cai, Q., Qiao, L., Wang, M., He, B., Lin, F. M., Palmquist, J., et al. (2018b). Plants send small RNAs in extracellular vesicles to fungal pathogen to silence virulence genes. Science 360, 1126–1129. doi: 10.1126/science.aar4142
Cao, Y., Lin, Y., Sun, N., Du, X., Dong, Y., Mei, S., et al. (2023). A comprehensive analysis of the Bencao (herbal) small RNA Atlas reveals novel RNA therapeutics for treating human diseases. Sci. China Life Sci. 66, 2380–2398. doi: 10.1007/s11427-022-2181-6
Cavalieri, D., Rizzetto, L., Tocci, N., Rivero, D., Asquini, E., Si-Ammour, A., et al. (2016). Plant microRNAs as novel immunomodulatory agents. Sci. Rep. 6, 25761. doi: 10.1038/srep25761
Chen, X., Dai, G. H., Ren, Z. M., Tong, Y. L., Yang, F., Zhu, Y. Q. (2016). Identification of dietetically absorbed rapeseed (Brassica campestris L.) bee pollen microRNAs in serum of mice. BioMed. Res. Int. 2016, 5413849. doi: 10.1155/2016/5413849
Chen, X., Liu, B., Li, X., An, T. T., Zhou, Y., Li, G., et al. (2021b). Identification of anti-inflammatory vesicle-like nanoparticles in honey. J. Extracell. Vesicles 10, e12069. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12069
Chen, T., Ma, F., Peng, Y., Sun, R., Xi, Q., Sun, J., et al. (2022b). Plant miR167e-5p promotes 3T3-L1 adipocyte adipogenesis by targeting beta-catenin. In Vitro Cell Dev. Biol. Anim. 58, 471–479. doi: 10.1007/s11626-022-00702-w
Chen, X., Rechavi, O. (2022). Plant and animal small RNA communications between cells and organisms. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 23, 185–203. doi: 10.1038/s41580-021-00425-y
Chen, N., Sun, J., Zhu, Z., Cribbs, A. P., Xiao, B. (2022a). Edible plant-derived nanotherapeutics and nanocarriers: recent progress and future directions. Expert Opin. Drug Delivery 19, 409–419. doi: 10.1080/17425247.2022.2053673
Chen, X., Wu, R. Z., Zhu, Y. Q., Ren, Z. M., Tong, Y. L., Yang, F., et al. (2018). Study on the inhibition of Mfn1 by plant-derived miR5338 mediating the treatment of BPH with rape bee pollen. BMC Complement Altern. Med. 18, 38. doi: 10.1186/s12906-018-2107-y
Chen, Q., Zhang, F., Dong, L., Wu, H., Xu, J., Li, H., et al. (2021a). SIDT1-dependent absorption in the stomach mediates host uptake of dietary and orally administered microRNAs. Cell Res. 31, 247–258. doi: 10.1038/s41422-020-0389-3
Chi, Y., Shi, L., Lu, S., Cui, H., Zha, W., Shan, L., et al. (2024). Inhibitory effect of Lonicera japonica-derived exosomal miR2911 on human papilloma virus. J. Ethnopharmacol. 318, 116969. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116969
Chi, X., Wang, Z., Wang, Y., Liu, Z., Wang, H., Xu, B. (2023). Cross-kingdom regulation of plant-derived miRNAs in modulating insect development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 7978. doi: 10.3390/ijms24097978
Chin, A. R., Fong, M. Y., Somlo, G., Wu, J., Swiderski, P., Wu, X., et al. (2016). Cross-kingdom inhibition of breast cancer growth by plant miR159. Cell Res. 26, 217–228. doi: 10.1038/cr.2016.13
Cieslik, M., Nazimek, K., Bryniarski, K. (2022). Extracellular vesicles-oral therapeutics of the future. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 7554. doi: 10.3390/ijms23147554
Diener, C., Keller, A., Meese, E. (2022). Emerging concepts of miRNA therapeutics: from cells to clinic. Trends Genet. 38, 613–626. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2022.02.006
Du, J., Liang, Z., Xu, J., Zhao, Y., Li, X., Zhang, Y., et al. (2019). Plant-derived phosphocholine facilitates cellular uptake of anti-pulmonary fibrotic HJT-sRNA-m7. Sci. China Life Sci. 62, 309–320. doi: 10.1007/s11427-017-9026-7
Fabian, M. R., Sonenberg, N., Filipowicz, W. (2010). Regulation of mRNA translation and stability by microRNAs. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 79, 351–379. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-060308-103103
Feng, J., Xiu, Q., Huang, Y., Troyer, Z., Li, B., Zheng, L. (2023). Plant-derived vesicle-like nanoparticles as promising biotherapeutic tools: present and future. Adv. Mater. 35, e2207826. doi: 10.1002/adma.202207826
Gandikota, M., Birkenbihl, R. P., Hohmann, S., Cardon, G. H., Saedler, H., Huijser, P. (2007). The miRNA156/157 recognition element in the 3’ UTR of the Arabidopsis SBP box gene SPL3 prevents early flowering by translational inhibition in seedlings. Plant J. 49, 683–693. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2006.02983.x
Gismondi, A., Nanni, V., Monteleone, V., Colao, C., Di Marco, G., Canini, A. (2021). Plant miR171 modulates mTOR pathway in HEK293 cells by targeting GNA12. Mol. Biol. Rep. 48, 435–449. doi: 10.1007/s11033-020-06070-6
Gualtieri, C., Leonetti, P., Macovei, A. (2020). Plant miRNA cross-kingdom transfer targeting parasitic and mutualistic organisms as a tool to advance modern agriculture. Front. Plant Sci. 11, 930. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.00930
Guo, Z., Kuang, Z., Zhao, Y., Deng, Y., He, H., Wan, M., et al. (2022). PmiREN2.0: from data annotation to functional exploration of plant microRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 50, D1475–D1482. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab811
Ha, M., Kim, V. N. (2014). Regulation of microRNA biogenesis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 15, 509–524. doi: 10.1038/nrm3838
Han, J., Wu, T., Jin, J., Li, Z., Cheng, W., Dai, X., et al. (2022). Exosome-like nanovesicles derived from Phellinus linteus inhibit Mical2 expression through cross-kingdom regulation and inhibit ultraviolet-induced skin aging. J. Nanobiotechnol. 20, 455. doi: 10.1186/s12951-022-01657-6
He, B., Cai, Q., Qiao, L., Huang, C. Y., Wang, S., Miao, W., et al. (2021). RNA-binding proteins contribute to small RNA loading in plant extracellular vesicles. Nat. Plants 7, 342–352. doi: 10.1038/s41477-021-00863-8
Henke, J. I., Goergen, D., Zheng, J., Song, Y., Schuttler, C. G., Fehr, C., et al. (2008). microRNA-122 stimulates translation of hepatitis C virus RNA. EMBO J. 27, 3300–3310. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2008.244
Hou, D., He, F., Ma, L., Cao, M., Zhou, Z., Wei, Z., et al. (2018). The potential atheroprotective role of plant MIR156a as a repressor of monocyte recruitment on inflamed human endothelial cells. J. Nutr. Biochem. 57, 197–205. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2018.03.026
Huang, Y., Liu, H., Sun, X., Ding, M., Tao, G., Li, X. (2019b). Honeysuckle-derived microRNA2911 directly inhibits varicella-zoster virus replication by targeting IE62 gene. J. Neurovirol. 25, 457–463. doi: 10.1007/s13365-019-00741-2
Huang, F., Qiao, X., Mei, S., Zhang, C., Jiang, C. (2023). Analysis of non-coding small RNA similarity/sharing between plant and animal genomes. Sci. China Life Sci. 66, 2437–2440. doi: 10.1007/s11427-022-2373-8
Huang, C. Y., Wang, H., Hu, P., Hamby, R., Jin, H. (2019a). Small RNAs - big players in plant-microbe interactions. Cell Host Microbe 26, 173–182. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2019.07.021
Iwakawa, H. O., Tomari, Y. (2015). The functions of microRNAs: mRNA decay and translational repression. Trends Cell Biol. 25, 651–665. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2015.07.011
Jia, L., Zhang, D., Xiang, Z., He, N. (2015). Nonfunctional ingestion of plant miRNAs in silkworm revealed by digital droplet PCR and transcriptome analysis. Sci. Rep. 5, 12290. doi: 10.1038/srep12290
Jopling, C. L., Yi, M., Lancaster, A. M., Lemon, S. M., Sarnow, P. (2005). Modulation of hepatitis C virus RNA abundance by a liver-specific MicroRNA. Science 309, 1577–1581. doi: 10.1126/science.1113329
Ju, S., Mu, J., Dokland, T., Zhuang, X., Wang, Q., Jiang, H., et al. (2013). Grape exosome-like nanoparticles induce intestinal stem cells and protect mice from DSS-induced colitis. Mol. Ther. 21, 1345–1357. doi: 10.1038/mt.2013.64
Kalarikkal, S. P., Sundaram, G. M. (2021). Edible plant-derived exosomal microRNAs: Exploiting a cross-kingdom regulatory mechanism for targeting SARS-CoV-2. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 414, 115425. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2021.115425
Kasarello, K., Kohling, I., Kosowska, A., Pucia, K., Lukasik, A., Cudnoch-Jedrzejewska, A., et al. (2022). The anti-inflammatory effect of cabbage leaves explained by the influence of bol-miRNA172a on FAN expression. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 846830. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.846830
Knip, M., Constantin, M. E., Thordal-Christensen, H. (2014). Trans-kingdom cross-talk: small RNAs on the move. PloS Genet. 10, e1004602. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004602
Kozomara, A., Birgaoanu, M., Griffiths-Jones, S. (2019). miRBase: from microRNA sequences to function. Nucleic Acids Res. 47, D155–D162. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky1141
Kumar, D., Kumar, S., Ayachit, G., Bhairappanavar, S. B., Ansari, A., Sharma, P., et al. (2017). Cross-kingdom regulation of putative miRNAs derived from happy tree in cancer pathway: A systems biology approach. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 18, 1191. doi: 10.3390/ijms18061191
Kumazoe, M., Ogawa, F., Hikida, A., Shimada, Y., Yoshitomi, R., Watanabe, R., et al. (2023). Plant miRNA osa-miR172d-5p suppressed lung fibrosis by targeting Tab1. Sci. Rep. 13, 2128. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-29188-6
Li, M., Chen, T., He, J. J., Wu, J. H., Luo, J. Y., Ye, R. S., et al. (2019). Plant MIR167e-5p inhibits enterocyte proliferation by targeting beta-catenin. Cells 8, 1385. doi: 10.3390/cells8111385
Li, X., Huang, Y., Sun, M., Ji, H., Dou, H., Hu, J., et al. (2018a). Honeysuckle-encoded microRNA2911 inhibits Enterovirus 71 replication via targeting VP1 gene. Antiviral Res. 152, 117–123. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2018.02.015
Li, Y., Teng, Z., Zhao, D. (2023). Plant-derived cross-kingdom gene regulation benefits human health. Trends Plant Sci 28, 626–629. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2023.03.004
Li, Z., Wang, H., Yin, H., Bennett, C., Zhang, H. G., Guo, P. (2018b). Arrowtail RNA for ligand display on ginger exosome-like nanovesicles to systemic deliver siRNA for cancer suppression. Sci. Rep. 8, 14644. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-32953-7
Liang, H., Zhang, S., Fu, Z., Wang, Y., Wang, N., Liu, Y., et al. (2015). Effective detection and quantification of dietetically absorbed plant microRNAs in human plasma. J. Nutr. Biochem. 26, 505–512. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2014.12.002
Liang, G., Zhu, Y., Sun, B., Shao, Y., Jing, A., Wang, J., et al. (2014). Assessing the survival of exogenous plant microRNA in mice. Food Sci. Nutr. 2, 380–388. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.113
Liu, Y. C., Chen, W. L., Kung, W. H., Huang, H. D. (2017). Plant miRNAs found in human circulating system provide evidences of cross kingdom RNAi. BMC Genomics 18, 112. doi: 10.1186/s12864-017-3502-3
Liu, C., Xu, M., Yan, L., Wang, Y., Zhou, Z., Wang, S., et al. (2021). Honeysuckle-derived microRNA2911 inhibits tumor growth by targeting TGF-beta1. Chin. Med. 16, 49. doi: 10.1186/s13020-021-00453-y
Llave, C., Kasschau, K. D., Rector, M. A., Carrington, J. C. (2002). Endogenous and silencing-associated small RNAs in plants. Plant Cell 14, 1605–1619. doi: 10.1105/tpc.003210
Lopez de Las Hazas, M. C., Tome-Carneiro, J., Del Pozo-Acebo, L., Del Saz-Lara, A., Chapado, L. A., Balaguer, L., et al. (2023). Therapeutic potential of plant-derived extracellular vesicles as nanocarriers for exogenous miRNAs. Pharmacol. Res. 198, 106999. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2023.106999
Lu, Z., Fu, J., Wu, G., Yang, Z., Wu, X., Wang, D., et al. (2023). Neuroprotection and mechanism of gas-miR36-5p from gastrodia elata in an Alzheimer’s disease model by regulating glycogen synthase kinase-3beta. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 17295. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417295
Luo, Y., Wang, P., Wang, X., Wang, Y., Mu, Z., Li, Q., et al. (2017). Detection of dietetically absorbed maize-derived microRNAs in pigs. Sci. Rep. 7, 645. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-00488-y
Mahanty, B., Mishra, R., Joshi, R. K. (2023). Cross-kingdom small RNA communication between plants and fungal phytopathogens-recent updates and prospects for future agriculture. RNA Biol. 20, 109–119. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2023.2195731
Marzec, M. (2022). MicroRNA: a new signal in plant-to-plant communication. Trends Plant Sci. 27, 418–419. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2022.01.005
Masood, M., Everett, C. P., Chan, S. Y., Snow, J. W. (2016). Negligible uptake and transfer of diet-derived pollen microRNAs in adult honey bees. RNA Biol. 13, 109–118. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2015.1128063
McLoughlin, A. G., Wytinck, N., Walker, P. L., Girard, I. J., Rashid, K. Y., de Kievit, T., et al. (2018). Identification and application of exogenous dsRNA confers plant protection against Sclerotinia sclerotiorum and Botrytis cinerea. Sci. Rep. 8, 7320. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-25434-4
Niu, D., Hamby, R., Sanchez, J. N., Cai, Q., Yan, Q., Jin, H. (2021). RNAs - a new frontier in crop protection. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 70, 204–212. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2021.06.005
Orom, U. A., Nielsen, F. C., Lund, A. H. (2008). MicroRNA-10a binds the 5’UTR of ribosomal protein mRNAs and enhances their translation. Mol. Cell 30, 460–471. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.05.001
Palatnik, J. F., Wollmann, H., Schommer, C., Schwab, R., Boisbouvier, J., Rodriguez, R., et al. (2007). Sequence and expression differences underlie functional specialization of Arabidopsis microRNAs miR159 and miR319. Dev. Cell 13, 115–125. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2007.04.012
Pant, B. D., Buhtz, A., Kehr, J., Scheible, W. R. (2008). MicroRNA399 is a long-distance signal for the regulation of plant phosphate homeostasis. Plant J. 53, 731–738. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03363.x
Potesta, M., Roglia, V., Fanelli, M., Pietrobono, E., Gismondi, A., Vumbaca, S., et al. (2020). Effect of microvesicles from Moringa oleifera containing miRNA on proliferation and apoptosis in tumor cell lines. Cell Death Discovery 6, 43. doi: 10.1038/s41420-020-0271-6
Qi, Y., Ding, L., Zhang, S., Yao, S., Ong, J., Li, Y., et al. (2022). A plant immune protein enables broad antitumor response by rescuing microRNA deficiency. Cell 185, 1888–1904 e1824. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2022.04.030
Qi, T., Guo, J., Peng, H., Liu, P., Kang, Z., Guo, J. (2019). Host-induced gene silencing: A powerful strategy to control diseases of wheat and barley. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20, 206. doi: 10.3390/ijms20010206
Qiao, L., Lan, C., Capriotti, L., Ah-Fong, A., Nino Sanchez, J., Hamby, R., et al. (2021). Spray-induced gene silencing for disease control is dependent on the efficiency of pathogen RNA uptake. Plant Biotechnol. J. 19, 1756–1768. doi: 10.1111/pbi.13589
Qin, X., Wang, X., Xu, K., Zhang, Y., Ren, X., Qi, B., et al. (2022). Digestion of Plant Dietary miRNAs Starts in the Mouth under the Protection of Coingested Food Components and Plant-Derived Exosome-like Nanoparticles. J. Agric. Food Chem. 70, 4316–4327. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.1c07730
Qiu, F. S., Wang, J. F., Guo, M. Y., Li, X. J., Shi, C. Y., Wu, F., et al. (2023). Rgl-exomiR-7972, a novel plant exosomal microRNA derived from fresh Rehmanniae Radix, ameliorated lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury and gut dysbiosis. BioMed. Pharmacother. 165, 115007. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115007
Rogers, K., Chen, X. (2013). Biogenesis, turnover, and mode of action of plant microRNAs. Plant Cell 25, 2383–2399. doi: 10.1105/tpc.113.113159
Roush, S., Slack, F. J. (2008). The let-7 family of microRNAs. Trends Cell Biol. 18, 505–516. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2008.07.007
Rupaimoole, R., Slack, F. J. (2017). MicroRNA therapeutics: towards a new era for the management of cancer and other diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 16, 203–222. doi: 10.1038/nrd.2016.246
Sarkar, A., Roy-Barman, S. (2021). Spray-induced silencing of pathogenicity gene moDES1 via exogenous double-stranded RNA can confer partial resistance against fungal blast in rice. Front. Plant Sci. 12. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.733129
Sattar, S., Addo-Quaye, C., Song, Y., Anstead, J. A., Sunkar, R., Thompson, G. A. (2012). Expression of small RNA in Aphis gossypii and its potential role in the resistance interaction with melon. PloS One 7, e48579. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0048579
Shahid, S., Kim, G., Johnson, N. R., Wafula, E., Wang, F., Coruh, C., et al. (2018). MicroRNAs from the parasitic plant Cuscuta campestris target host messenger RNAs. Nature 553, 82–85. doi: 10.1038/nature25027
Sharma, A., Sahu, S., Kumari, P., Gopi, S. R., Malhotra, R., Biswas, S. (2017). Genome-wide identification and functional annotation of miRNAs in anti-inflammatory plant and their cross-kingdom regulation in Homo sapiens. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 35, 1389–1400. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2016.1185381
Shih, J. D., Hunter, C. P. (2011). SID-1 is a dsRNA-selective dsRNA-gated channel. RNA 17, 1057–1065. doi: 10.1261/rna.2596511
Slack, F. J., Chinnaiyan, A. M. (2019). The role of non-coding RNAs in oncology. Cell 179, 1033–1055. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.10.017
Sun, M., Xu, S., Mei, Y., Li, J., Gu, Y., Zhang, W., et al. (2022). MicroRNAs in medicinal plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 10477. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810477
Teng, Y., Ren, Y., Sayed, M., Hu, X., Lei, C., Kumar, A., et al. (2018). Plant-derived exosomal microRNAs shape the gut microbiota. Cell Host Microbe 24, 637–652 e638. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2018.10.001
Teng, Y., Xu, F., Zhang, X., Mu, J., Sayed, M., Hu, X., et al. (2021). Plant-derived exosomal microRNAs inhibit lung inflammation induced by exosomes SARS-CoV-2 Nsp12. Mol. Ther. 29, 2424–2440. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2021.05.005
Tian, Y., Cai, L., Tian, Y., Tu, Y., Qiu, H., Xie, G., et al. (2016). miR156a mimic represses the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of human nasopharyngeal cancer cells by targeting junctional adhesion molecule A. PloS One 11, e0157686. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0157686
Umezu, T., Takanashi, M., Murakami, Y., Ohno, S. I., Kanekura, K., Sudo, K., et al. (2021). Acerola exosome-like nanovesicles to systemically deliver nucleic acid medicine via oral administration. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 21, 199–208. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2021.03.006
Urzi, O., Gasparro, R., Ganji, N. R., Alessandro, R., Raimondo, S. (2022). Plant-RNA in extracellular vesicles: the secret of cross-kingdom communication. Membranes (Basel) 12, 352. doi: 10.3390/membranes12040352
Wang, J., Li, C., Ruan, J., Yang, C., Tian, Y., Lu, B., et al. (2024a). Cross-kingdom regulation of ginseng miRNA156 on immunity and metabolism. Int. Immunopharmacol. 138, 112577. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112577
Wang, X., Liu, Y., Dong, X., Duan, T., Wang, C., Wang, L., et al. (2024b). peu-MIR2916-p3-enriched garlic exosomes ameliorate murine colitis by reshaping gut microbiota, especially by boosting the anti-colitic Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron. Pharmacol. Res. 200, 107071. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2024.107071
Wang, Y., Pruitt, R. N., Nurnberger, T., Wang, Y. (2022). Evasion of plant immunity by microbial pathogens. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 20, 449–464. doi: 10.1038/s41579-022-00710-3
Wang, X., Ren, X., Ning, L., Wang, P., Xu, K. (2020). Stability and absorption mechanism of typical plant miRNAs in an in vitro gastrointestinal environment: basis for their cross-kingdom nutritional effects. J. Nutr. Biochem. 81, 108376. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2020.108376
Wang, B., Sun, Y., Song, N., Zhao, M., Liu, R., Feng, H., et al. (2017a). Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici microRNA-like RNA 1 (Pst-milR1), an important pathogenicity factor of Pst, impairs wheat resistance to Pst by suppressing the wheat pathogenesis-related 2 gene. New Phytol. 215, 338–350. doi: 10.1111/nph.14577
Wang, M., Weiberg, A., Lin, F. M., Thomma, B. P., Huang, H. D., Jin, H. (2016). Bidirectional cross-kingdom RNAi and fungal uptake of external RNAs confer plant protection. Nat. Plants 2, 16151. doi: 10.1038/nplants.2016.151
Wang, W., Yang, J., Xiang, Y. Y., Pi, J., Bian, J. (2017c). Overexpression of hsa-miR-320 is associated with invasion and metastasis of ovarian cancer. J. Cell Biochem. 118, 3654–3661. doi: 10.1002/jcb.26009
Wang, H., Zhang, C., Dou, Y., Yu, B., Liu, Y., Heng-Moss, T. M., et al. (2017b). Insect and plant-derived miRNAs in greenbug (Schizaphis graminum) and yellow sugarcane aphid (Sipha flava) revealed by deep sequencing. Gene 599, 68–77. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2016.11.014
Wang, B., Zhuang, X., Deng, Z. B., Jiang, H., Mu, J., Wang, Q., et al. (2014). Targeted drug delivery to intestinal macrophages by bioactive nanovesicles released from grapefruit. Mol. Ther. 22, 522–534. doi: 10.1038/mt.2013.190
Weiberg, A., Wang, M., Lin, F. M., Zhao, H., Zhang, Z., Kaloshian, I., et al. (2013). Fungal small RNAs suppress plant immunity by hijacking host RNA interference pathways. Science 342, 118–123. doi: 10.1126/science.1239705
Xia, C., Zhou, H., Xu, X., Jiang, T., Li, S., Wang, D., et al. (2020). Identification and Investigation of miRNAs From Gastrodia elata Blume and Their Potential Function. Front. Pharmacol. 11, 542405. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.542405
Xiao, J., Feng, S., Wang, X., Long, K., Luo, Y., Wang, Y., et al. (2018). Identification of exosome-like nanoparticle-derived microRNAs from 11 edible fruits and vegetables. PeerJ 6, e5186. doi: 10.7717/peerj.5186
Xu, Q., Li, Y., Qin, X., Xin, Y., Wang, J., Zhang, Y., et al. (2024a). osa-miR168a, a plant miRNA that survives the process of in vivo food digestion, attenuates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice by oral administration. J. Agric. Food Chem. 72, 25146–25160. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.4c07283
Xu, Q., Qin, X., Zhang, Y., Xu, K., Li, Y., Li, Y., et al. (2023). Plant miRNA bol-miR159 Regulates Gut Microbiota Composition in Mice: In Vivo Evidence of the Crosstalk between Plant miRNAs and Intestinal Microbes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 71, 16160–16173. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c06104
Xu, X. H., Yuan, T. J., Dad, H. A., Shi, M. Y., Huang, Y. Y., Jiang, Z. H., et al. (2021). Plant exosomes as novel nanoplatforms for microRNA transfer stimulate neural differentiation of stem cells in vitro and in vivo. Nano Lett. 21, 8151–8159. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.1c02530
Xu, T., Zhu, Y., Lin, Z., Lei, J., Li, L., Zhu, W., et al. (2024b). Evidence of cross-kingdom gene regulation by plant microRNAs and possible reasons for inconsistencies. J. Agric. Food Chem. 72, 4564–4573. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c09097
Yang, C., Zhang, M., Merlin, D. (2018). Advances in plant-derived edible nanoparticle-based lipid nano-drug delivery systems as therapeutic nanomedicines. J. Mater. Chem. B 6, 1312–1321. doi: 10.1039/C7TB03207B
Yi, X., Zhang, Z., Ling, Y., Xu, W., Su, Z. (2015). PNRD: a plant non-coding RNA database. Nucleic Acids Res. 43, D982–D989. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku1162
Yu, W. Y., Cai, W., Ying, H. Z., Zhang, W. Y., Zhang, H. H., Yu, C. H. (2021). Exogenous Plant gma-miR-159a, Identified by miRNA Library Functional Screening, Ameliorated Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation and Inflammation via Inhibiting GSK-3beta-Mediated Pathways. J. Inflammation Res. 14, 2157–2172. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S304828
Yu, Y., Jia, T., Chen, X. (2017). The ‘how’ and ‘where’ of plant microRNAs. New Phytol. 216, 1002–1017. doi: 10.1111/nph.14834
Zeng, J., Gupta, V. K., Jiang, Y., Yang, B., Gong, L., Zhu, H. (2019). Cross-kingdom small RNAs among animals, plants and microbes. Cells 8, 371. doi: 10.3390/cells8040371
Zhang, S., Hong, Z. (2019). Mobile RNAs—the magical elf traveling between plant and the associated organisms. ExRNA 1, 1–6. doi: 10.1186/s41544-019-0007-z
Zhang, L., Hou, D., Chen, X., Li, D., Zhu, L., Zhang, Y., et al. (2012). Exogenous plant MIR168a specifically targets mammalian LDLRAP1: evidence of cross-kingdom regulation by microRNA. Cell Res. 22, 107–126. doi: 10.1038/cr.2011.158
Zhang, W. J., Li, Y. Y., Xiang, Z. H., Deng, J., Li, W., Lin, Q. L., et al. (2023). Emerging evidence on the effects of plant-derived microRNAs in colorectal cancer: a review. Food Funct. 14, 691–702. doi: 10.1039/d2fo03477h
Zhang, B., Li, W., Zhang, J., Wang, L., Wu, J. (2019). Roles of small RNAs in virus-plant interactions. Viruses 11, 827. doi: 10.3390/v11090827
Zhang, M., Viennois, E., Prasad, M., Zhang, Y., Wang, L., Zhang, Z., et al. (2016a). Edible ginger-derived nanoparticles: A novel therapeutic approach for the prevention and treatment of inflammatory bowel disease and colitis-associated cancer. Biomaterials 101, 321–340. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2016.06.018
Zhang, M., Viennois, E., Xu, C., Merlin, D. (2016b). Plant derived edible nanoparticles as a new therapeutic approach against diseases. Tissue Barriers 4, e1134415. doi: 10.1080/21688370.2015.1134415
Zhang, M., Wang, X., Han, M. K., Collins, J. F., Merlin, D. (2017). Oral administration of ginger-derived nanolipids loaded with siRNA as a novel approach for efficient siRNA drug delivery to treat ulcerative colitis. Nanomed. (Lond) 12, 1927–1943. doi: 10.2217/nnm-2017-0196
Zhang, T., Zhao, Y. L., Zhao, J. H., Wang, S., Jin, Y., Chen, Z. Q., et al. (2016c). Cotton plants export microRNAs to inhibit virulence gene expression in a fungal pathogen. Nat. Plants 2, 16153. doi: 10.1038/nplants.2016.153
Zhou, Z., Li, X., Liu, J., Dong, L., Chen, Q., Liu, J., et al. (2015). Honeysuckle-encoded atypical microRNA2911 directly targets influenza A viruses. Cell Res. 25, 39–49. doi: 10.1038/cr.2014.130
Zhou, L. K., Zhou, Z., Jiang, X. M., Zheng, Y., Chen, X., Fu, Z., et al. (2020). Absorbed plant MIR2911 in honeysuckle decoction inhibits SARS-CoV-2 replication and accelerates the negative conversion of infected patients. Cell Discovery 6, 54. doi: 10.1038/s41421-020-00197-3
Zhu, H., Chang, M., Wang, Q., Chen, J., Liu, D., He, W. (2023a). Identifying the Potential of miRNAs in Houttuynia cordata-Derived Exosome-Like Nanoparticles Against Respiratory RNA Viruses. Int. J. Nanomed. 18, 5983–6000. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S425173
Zhu, Z., Liao, L., Gao, M., Liu, Q. (2023b). Garlic-derived exosome-like nanovesicles alleviate dextran sulphate sodium-induced mouse colitis via the TLR4/MyD88/NF-kappaB pathway and gut microbiota modulation. Food Funct. 14, 7520–7534. doi: 10.1039/d3fo01094e
Zhu, K., Liu, M., Fu, Z., Zhou, Z., Kong, Y., Liang, H., et al. (2017). Plant microRNAs in larval food regulate honeybee caste development. PloS Genet. 13, e1006946. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006946
Zhu, R., Zhang, Z., Li, Y., Hu, Z., Xin, D., Qi, Z., et al. (2016). Discovering numerical differences between animal and plant microRNAs. PloS One 11, e0165152. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0165152
Keywords: plant miRNAs, miRNA biosynthesis, cross-kingdom regulation, miRNA transfer, plant-derived exosome-like nanoparticles
Citation: Shi L, Guo C, Fang M, Yang Y, Yin F and Shen Y (2024) Cross-kingdom regulation of plant microRNAs: potential application in crop improvement and human disease therapeutics. Front. Plant Sci. 15:1512047. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1512047
Received: 16 October 2024; Accepted: 03 December 2024;
Published: 17 December 2024.
Edited by:
Anca Macovei, University of Pavia, ItalyReviewed by:
Ruirui Huang, University of San Francisco, United StatesCopyright © 2024 Shi, Guo, Fang, Yang, Yin and Shen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yuan Shen, eXVhbi5zaGVuQHlhaG9vLmNvbQ==; Fei Yin, eWluZmVpQG5idS5lZHUuY24=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.