
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Plant Sci. , 27 January 2025
Sec. Plant Abiotic Stress
Volume 15 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2024.1506805
 Yingxin Sun1
Yingxin Sun1 Beier Wang1
Beier Wang1 Lichao Zhang2
Lichao Zhang2 Xiaohan Zheng1
Xiaohan Zheng1 Peng Xu2
Peng Xu2 Meng Zhang1
Meng Zhang1 Meiguang Han1
Meiguang Han1 Peng Di1
Peng Di1 Mei Han1
Mei Han1 Lin Cheng1*
Lin Cheng1* Limin Yang1*
Limin Yang1*The bHLH gene family plays a critical role in regulating internal responses in plants. Although the pharmacological properties of Scutellaria baicalensis have been extensively studied, its bHLH gene family remains poorly investigated. In this study, 142 SbbHLH genes were identified using the complete genome data of S. baicalensis. Phylogenetic and conserved motif analyses were performed. Gene duplication events were analyzed, and cis-element analysis was conducted to explore regulatory factors. The expression patterns of these genes in different tissues and under drought stress were investigated using transcriptome data and qRT-PCR analysis. Phylogenetic and conserved motif analyses revealed that the gene structures within each SbbHLH clade are relatively conserved. Gene duplication analysis identified 29 duplication events in the SbbHLH gene family, most of which involved gene pairs under purifying selection. Cis-element analysis revealed that these genes are regulated by various environmental and hormonal factors. Transcriptomic data and qRT-PCR results demonstrated tissue-specific expression patterns for the 142 SbbHLH genes. Additionally, bHLH genes potentially involved in baicalin biosynthesis were identified under drought stress. The findings suggest that under drought stress, SbbHLH74, SbbHLH98, and SbbHLH142 are regulated by a network centered on SbbHLH53, which enhances baicalin biosynthesis. In conclusion, this study provides a comprehensive analysis of the bHLH gene family in S. baicalensis and identifies 4 potential SbbHLH genes involved in regulating baicalin biosynthesis under drought stress.
Transcription factors (TFs) constitute a crucial class of regulatory factors in plants (Capella et al., 2015). As implied by their name, all bHLH gene families share a conserved bHLH domain (Birkenbihl et al., 2017). The bHLH domain consists of two key regions: the helix-loop-helix region and the basic region. This domain, widely distributed across eukaryotes (Lei et al., 2024). The recognition region of bHLH genes is located at the N-terminus, consisting of a basic region of 10-15 amino acids (aa) that can specifically recognize and bind to G-box and E-box motifs within target sequences (Toledo-Ortiz et al., 2003; Wenjing et al., 2016). In contrast, the amino acid sequence at the C-terminus is longer, spanning 40-50 amino acids, and forms two α-helical structures. The C-terminal region plays a regulatory role, such as enhancing protein interactions or facilitating the formation of protein complexes (Nair and Burley, 2000; Feller et al., 2011a; Huang et al., 2024). Different plant species possess varying numbers of genes within the bHLH gene family. For instance, 127 bHLH genes have been identified in Salvia miltiorrhiza (Zhang et al., 2015), 165 in Oryza sativa (Heim et al., 2003), 85 in Ginkgo biloba (Zhou et al., 2020), 161 in Arabidopsis thaliana (Li et al., 2006), 118 in Juglans mandshurica (Li et al., 2024), and 127 in Panax ginseng (Zhu et al., 2020). These publicly available research findings not only provide a solid foundation for subsequent gene family identification but also offer valuable original data for the functional and evolutionary analysis of these gene families.
Numerous studies have elucidated the fundamental functions of the bHLH gene family. In terms of growth and development, as well as in response to adverse stress, bHLH genes actively participate in metabolic regulation and signal transduction activation (Li et al., 2024). For instance, the first bHLH gene identified was isolated from A. thaliana, where it promotes the growth of roots, stems, leaves, and floral organs (Chen et al., 2024). Additionally, research has shown that the GhDEL65 gene, a member of the bHLH gene family in Gossypium hirsutum, interacts with other genes to form a MYB-bHLH-WD40 complex, which regulates cotton fiber development (Shangguan et al., 2016). In addition, the bHLH gene family plays an important role in regulating plant responses to environmental stresses, including cold (Xue et al., 2022), mechanical damage (Zhang et al., 2023), elevated salinity (Su et al., 2023), and drought (Liang et al., 2023). Studies have shown that OsbHLH148 in rice is activated by drought treatment. The OsbHLH148 gene forms a complex with the OsCOI1 and OsJAZ1 genes to jointly regulate the response to drought stress (Seo et al., 2011). Similarly, the MdCIB1 gene, a member of the bHLH gene family in Malus domestica, exhibits a similar function. Researchers used heterologous expression to transform the gene into A. thaliana and found that it accelerated root growth, resulting in enhanced drought resistance (Ren et al., 2021). Secondary metabolites are an integral part of plant metabolism, and the bHLH gene family also plays a key role in regulating the synthesis of secondary metabolites, such as alkaloids (Singh et al., 2021), terpenoids (Mertens et al., 2016; Mohammad et al., 2023), phenolic acids (Liu et al., 2022), and flavonoids (Jia et al., 2021; Li et al., 2022). For example, the upregulation of the SmbHLH3 gene in S. miltiorrhiza can reduce the synthesis of phenolic acids. Further studies have shown that it regulates phenolic acid biosynthesis by forming a complex with SmHPPR1 and SmTAT1 (Zhang et al., 2020). The biosynthesis of anthocyanins in Vaccinium spp. can be enhanced by upregulating the VcbHLH1 gene (Zhao M. et al., 2019). Collectively, existing studies highlight the broad role of the bHLH gene family and emphasize the importance of further research on its members.
Scutellaria baicalensis has been used for over 2,000 years in traditional Chinese medicine to treat ailments related to the liver and lungs, characterized by its bitter and cold properties (Zhao et al., 2016; Zhao Q. et al., 2019; Geng et al., 2023). Modern pharmacological studies have shown that baicalin, the primary bioactive component of S. baicalensis, possesses beneficial effects, including anti-tumor, anti-viral, and analgesic properties (Wang et al., 2018). It also has potent inhibitory effects on various pathogens (Wang et al., 2022; Jia et al., 2023). The components of S. baicalensis that are responsible for treating diseases are root-specific flavonoids (RSFs), including baicalein, wogonin, baicalin, and wogonoside (Fang et al., 2023). Unlike typical 4-hydroxy flavonoids, such as scutellarein, they lack a hydroxyl group in their chemical structure, classifying them as 4’-deoxy RSFs (Pei et al., 2022). The biosynthetic pathway of RSFs begins with the conversion of phenylalanine to cinnamoyl-CoA by phenylalanine ammonialyase (PAL) and cinnamate-CoA ligase-like 7 (CLL-7). This intermediate is then condensed by a specific chalcone synthase (CHS-2) and isomerized by chalcone isomerase (CHI) to produce pinocembrin, a flavanone lacking a 4’-OH group (Zhao et al., 2016). Subsequently, chrysin is synthesized by flavone synthase II-2 (FNSII-2), while flavone 6-hydroxylase (F6H) converts it to baicalein. Alternatively, it can be acted upon by flavone 8-hydroxylase (F8H) and phenylpropanoid and flavonoid O-methyltransferases (PFOMT) to produce wogonin (Zhao et al., 2018; Zhao Q. et al., 2019). Finally, baicalin and wogonoside are produced through the glucuronidation of wogonin and baicalein by flavonoid 7-O-glucuronosyltransferases (UBGAT) (Nagashima et al., 2000). Notably, the baicalein content in S. baicalensis has been observed to increase under drought stress conditions, with moderate drought typically promoting the accumulation of flavonoids (Cheng et al., 2018). Additionally, transcription factor families play a significant role in regulating baicalin biosynthesis under drought conditions (Cheng et al., 2023). However, studies on bHLH transcription factors in S. baicalensis are still limited, and the molecular kinetics underlying flavonoid synthesis in this species remain poorly understood.
This study performed a comprehensive genome-wide analysis of the bHLH gene family in S. baicalensis. The analysis included the assessment of physicochemical properties, evolutionary relationships, gene structures, chromosomal locations, cis-regulatory elements, and synteny of the bHLH genes. Additionally, transcriptome data were analyzed to assess the tissue-specific expression patterns of bHLH genes and their correlation with flavonoid biosynthesis under drought stress. This approach aimed to elucidate the regulatory mechanisms underlying bHLH genes in S. baicalensis. The findings provide a foundational framework for exploring the biological functions of bHLH genes and offer deeper insights into the molecular regulatory mechanisms of SbbHLH genes.
For drought treatment, two-year-old S. baicalensis plants were cultivated in 7.5 × 45 cm nutrient pots under controlled greenhouse conditions. The culture parameters were set to a 24-hour cycle with the following settings: from 0 to 8 hours, a temperature of 15°C, light intensity of 0 lux, and 50% humidity; from 8 to 24 hours, a temperature of 22°C, light intensity of 30,000 lux, and 50% humidity. We determined the most suitable time and the most suitable concentration of polyethylene glycol (PEG) solution through the experiments of different drought stress time and different drought stress degree in the early stage.The treatment group was irrigated with 120 mL of 20% PEG solution, while the control group received an equal volume of distilled water. Plants were harvested 24 hours after treatment. A total of nine samples were collected from each group, with every three samples pooled together. The pooled samples were wrapped in aluminum foil, snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen, and stored at -80°C. Each treatment was conducted with three biological replicates.
S. baicalensis genome data (GWHAOTO00000000) were obtained from CNCB (https://www.cncb.ac.cn/, accessed on 8 April 2024) (Xu et al., 2020). To identify potential bHLH genes, two complementary approaches were employed. First, the Hidden Markov Model (HMM) for the bHLH domain (PF00010) was retrieved from the InterPro database (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/, accessed on 10 April 2024), and the S. baicalensis protein sequence database was scanned using HMMER 3.0 (Huang et al., 2024). Second, A. thaliana bHLH protein data were downloaded from the Plant Transcription Factor Database (PlantTFDB, https://planttfdb.gao-lab.org/, accessed on 10 April 2024) (Mohammad et al., 2023). BLAST 2.15.0 was performed using A. thaliana bHLH protein sequences as queries, with an e-value <1e−5, to identify potential bHLH protein sequences in S. baicalensis. Redundant protein IDs and sequences were removed, and all identified candidates were further verified using the Pfam (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/, accessed on 15 April 2024) (Mohammad et al., 2023), SMART (https://smart.embl.de/, accessed on 16 April 2024) (Huang et al., 2024), and Batch CD-search (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/cdd/, accessed on 15 April 2024) databases. The physicochemical properties of SbbHLH proteins were analyzed using the ExPASy (https://web.expasy.org/protparam/, accessed on 6 May 2024) (Zhang et al., 2015). Subcellular localization of the SbbHLH proteins was predicted using multiple tools, including WoLF-PSORT (https://wolfpsort.hgc.jp/, accessed on 6 May 2024) (Zhou et al., 2020), CELLO v.2.5 (http://cello.life.nctu.edu.tw/, accessed on 18 November 2024) (Huang et al., 2024), and BUCSA (https://busca.biocomp.unibo.it/, accessed on 18 November 2024) (Liang et al., 2023).
The SbbHLH and AtbHLH protein sequences were aligned using MAFFT v7.520. A phylogenetic tree was then constructed using the Maximum Likelihood (ML) method with 1000 bootstrap replicates and visualized using iTOL (https://itol.embl.de/, accessed on 20 May 2024). The ka/ks ratios were calculated with ka/ks Calculator 2.0 to assess natural purifying selection among target gene pairs. The SbbHLH genes of S. baicalensis were mapped to nine chromosomes using the genome data. Additionally, the collinear relationships between chromosome pairs were analyzed using TBtools v2.025 (Chen et al., 2023).
Gene structure annotation was obtained using the GFF3 file of the S. baicalensis genome, and visualized using TBtools v2.025 (Chen et al., 2023). Conserved motifs within the SbbHLH proteins were identified using the MEME (https://meme-suite.org/meme/ accessed on 8 June 2024). The 2kb region upstream of the start codon of the SbbHLH gene in the S. baicalensis genome was used as the promoter sequence and subjected to analysis in the PlantCARE database (https://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/plantcare/html/ accessed on 10 June 2024) to predict potential cis-elements.
The transcriptome data of S. baicalensis in different tissues were downloaded from public resources (https://ngdc.cncb.ac.cn/bioproject/browse/PRJCA009556 accessed on 30 April 2024) (Hu et al., 2023). The sequence reads were processed using FastQC 0.11.8 to remove adapters and low-quality sequences, then assembled using HISAT2 2.1.0. The expression patterns of SbbHLH genes were analyzed using normalized values expressed as Fragments Per Kilobase Million (FPKM). A heatmap was generated to visualize these expression patterns, with Z-score normalization applied to the data.
Accurately weigh 0.5 g of fresh S. baicalensis root samples. Following the instructions provided in the assay kits from the Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute, measure the activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD, A001-1-1) and peroxidase (POD, A084-3-1), as well as the concentrations of proline (A107-1-1) and soluble protein (A045-2-2). To determine the baicalin content, The root tissues of S. baicalensisto a constant weight. A 0.3 g sample of the dried powder was then combined with 10 mL of 70% ethanol. Microwave extraction was performed at 80°C for 6 minutes using the MARS6 system (CEM, USA). Following extraction, filter the solution and dilute it to a final volume of 50 mL with 70% ethanol. Pass 2 mL of the diluted solution through a 0.22 μm filter membrane to prepare the sample for analysis. The baicalin content was determined using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC, Agilent 1100, USA) according to the elution protocol described by Han et al (Zhong-Ming et al., 2011). The concentration was calculated based on the standard curve equation: y = 2626.76x − 96.06 (R² = 0.9997). Each sample was measured in triplicate, and the average value was reported as the final result, with the standard deviation represented as the error bar.
RNA was extracted from the roots of both control and treatment groups of S. baicalensis. To ensure RNA quality, the total RNA was assessed and quantified using the Qubit fluorescence quantifier and the Qsep400 high-throughput biological fragment analyzer. Breaks intact RNA into short RNA fragments. Then reverse transcribed to form cDNA. The cDNA was purified and Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) amplification to complete the construction of cDNA library. After sequencing, the raw data were obtained. The raw data were filtered using FastQC 0.23.2 and Trimmomatic 0.36.5, and assembled using HISAT2 2.1.0. Normalization of the number of mapped reads against transcript length facilitated the calculation of gene alignment using FeatureCounts 1.6.2. Changes in gene expression were determined based on FPKM values.
The protein interaction network analysis of the differentially expressed genes was performed using the STRING database (https://cn.string-db.org/, accessed on July 27, 2024). Homologous genes from A. thaliana were selected to construct the interaction network, with a prediction score > 0.7 and a p-value < 1e-10. To validate the transcriptome data, 10 SbbHLH genes were randomly selected from the transcriptome data of S. baicalensis. Primers for each SbbHLH gene were designed using Primer Premier 5.0 (Supplementary Table S1). Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) was performed to analyze these genes, with 18S rRNA serving as the reference gene. The qRT-PCR reaction mixture consisted of 10 µL of SYBR Premix Ex Taq (RR820 Takara, China), 1 µL of each primer, 1 µL of cDNA template, and 7 µL of ddH2O, making a total volume of 20 µL. The PCR protocol started with a pre-denaturation step at 95°C for 30 s, followed by 40 cycles of denaturation at 95°C for 5 s, annealing at 56°C for 30 s, and extension at 72°C for 15 s. Finally, the 2-ΔΔCt method was used to normalize the experimental results, with 18S rRNA as the internal reference gene. To ensure the reliability of the data, each sample was repeated three times. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), and different lowercase letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05).
To identify bHLH genes on a genome-wide scale in S. baicalensis, we used the AtbHLH proteins as queries and applied the HMM model containing the bHLH domain to search the complete amino acid database of S. baicalensis. After removing redundant sequences, the candidate SbbHLH genes were screened using the SMART, Batch CD-search, and Pfam databases, resulting in the identification of 142 SbbHLH genes (Supplementary Table S2). Based on their chromosomal locations, the 142 SbbHLH genes were renamed sequentially (SbbHLH1-SbbHLH142) (Supplementary Table S3). Analysis of their physicochemical properties revealed that the amino acid (aa) lengths of the SbbHLH proteins ranged from 91 (SbbHLH97) to 912 (SbbHLH56), with molecular weights (MW) varying from 10,431.7 Da (SbbHLH97) to 99,345.31 Da (SbbHLH56). The isoelectric points (pI) of these proteins ranged from 4.76 (SbbHLH104) to 11.54 (SbbHLH134), with an average pI of 6.94. Notably, 90 SbbHLH proteins had pI values below 7, classifying them as acidic, while 52 proteins exhibited pI values above 7, indicating they are basic. Subcellular localization predictions showed that 134 SbbHLH genes were localized to the nucleus, while the remaining proteins were distributed across other cellular compartments: chloroplasts (SbbHLH42, SbbHLH43, SbbHLH58, SbbHLH66, SbbHLH69, SbbHLH83), extracellular space (SbbHLH95), and mitochondria (SbbHLH52).
A phylogenetic tree was constructed using the protein sequences of 142 SbbHLH genes and 161 AtbHLH genes. The resulting phylogenetic tree was divided into 16 branches based on the homology of bHLH proteins (Figure 1). Significant variation was observed in the number of genes within each branch; branch 4 contained the highest number of members, with 25 SbbHLH genes (17.6%), while branch 7 had the fewest, comprising only one SbbHLH gene. Notably, each branch included bHLH genes from both S. baicalensis and A. thaliana, highlighting the evolutionary conservation of bHLH genes across species. Since genes within the same branch are likely to share similar functions, this phylogenetic analysis provides a foundational framework for predicting the potential functions of SbbHLH genes.
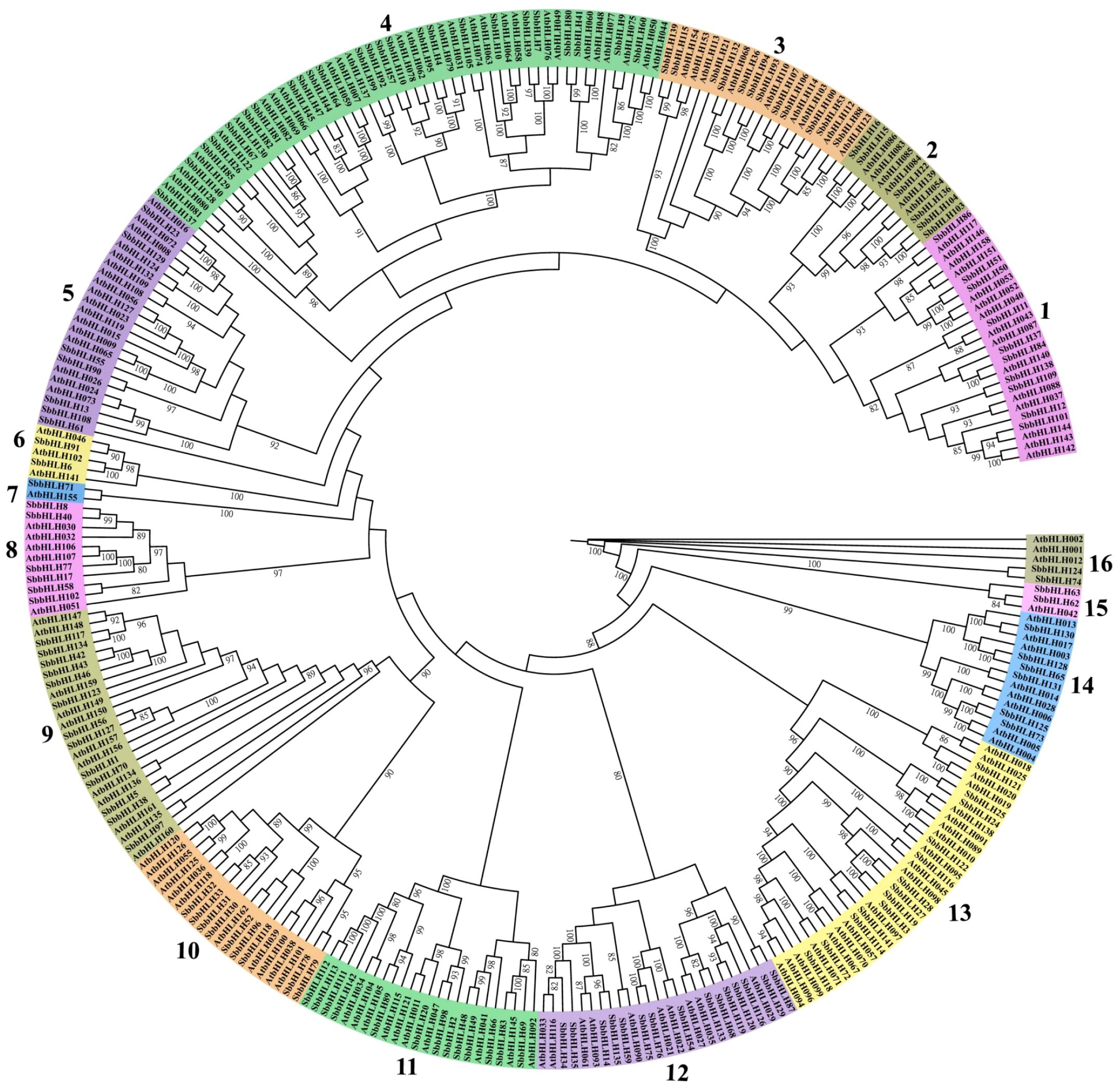
Figure 1. Phylogenetic tree of bHLH proteins in S. baicalensis and A. thaliana. Phylogenetic relationships were derived using the protein sequences by ML method with 1000 bootstrap. The bHLH proteins were grouped into 16 distinct branches, which are represented using various colors.
We constructed a phylogenetic tree to elucidate the relationships among all SbbHLH genes (Figure 2A). Based on the topology of the tree, we further analyzed conserved motifs and gene structures. A total of 10 conserved motifs were identified (Figure 2B). Notably, motifs 1 and 2 were present in all SbbHLH genes, with these two motifs constituting the complete bHLH domain. Specifically, motif 1 corresponds to the partial loop and helix 2 region of the bHLH domain, while motif 2 includes the basic region, helix 1, and part of the loop region. Similar motifs were typically distributed among genes within the same branch. For example, the branch containing SbbHLH112, SbbHLH113, SbbHLH111, and SbbHLH142 displayed motifs 1, 2, 6, 7, and 10. Whereas the branch comprising SbbHLH5, SbbHLH1, SbbHLH70, SbbHLH97, and SbbHLH138 only contained motifs 1 and 2. This distinct motif distribution suggests that these branches may have divergent functions, providing insights into the conservation and diversity of SbbHLH genes while supporting the phylogenetic tree classification. Gene structure analysis provides valuable insights into the phylogenetic relationships among SbbHLH genes. Among the 142 SbbHLH genes analyzed, the number of exons ranged from 1 to 14 (Figure 2C), with the majority containing between 2 and 8 exons. Notably, SbbHLH51 exhibited the highest exon count at 14, while several genes, including SbbHLH11, SbbHLH12, SbbHLH42, SbbHLH43, SbbHLH83, SbbHLH86, SbbHLH101, and SbbHLH123, each contained only a single exon. Such variations likely reflect the unique functional roles and evolutionary trajectories of these genes, suggesting diverse regulatory mechanisms within the SbbHLH gene family. Moreover, the similarity in the number and length of exons within the same branch further supports the phylogenetic tree classification.

Figure 2. Conserved motifs and gene structure based on phylogenetic tree. (A) The phylogenetic tree of 142 SbbHLH genes. Phylogenetic relationships were derived using the protein sequences by ML method with 1000 bootstrap. (B) Conserved motifs were identified in SbbHLH genes. Different motifs are represented by different colors. (C) Schematic diagram of the exon and intron structures of 142 SbbHLH genes. The scale bar for gene sequence length is at the bottom right corner of each graph.
Chromosome localization analysis revealed that the 142 SbbHLH genes are distributed across all nine chromosomes of S. baicalensis (Figure 3A). Chromosome 1 contains the highest number of SbbHLH genes (26, 18.30%), while chromosome 6 has the fewest (7, 0.05%). Gene duplication events are known to facilitate the evolution and expansion of gene families in plants. To investigate the gene duplication events within the SbbHLH gene family, we analyzed a total of 142 SbbHLH genes (Figure 3A). Our analysis identified 26 segmental duplication events and 3 tandem duplication events. These findings were further supported by phylogenetic analysis, indicating the critical role of segmental duplication in the evolution of the SbbHLH gene family. Additionally, a ka/ks analysis was performed on 29 gene pairs (Supplementary Table S4). The results showed that, except for the SbbHLH48/49 gene pair, which is under positive selection, the remaining 28 gene pairs underwent purifying selection. This further supports the notion that the SbbHLH gene family is crucial for environmental adaptation and the emergence of new functions. To clarify the phylogenetic relationships among bHLH gene families across different species, we constructed a collinearity map comparing the bHLH genes of A. thaliana, S. barbata, and S. baicalensis (Figure 3B). The analysis identified 122 homologous gene pairs between S. baicalensis and A. thaliana and 172 homologous gene pairs between the two Scutellaria species. The higher number of homologous gene pairs within Scutellaria indicates a closer evolutionary relationship between these species. Further analysis revealed that S. baicalensis, A. thaliana, and S. barbata had 121, 115, and 78 homologous genes, respectively. Notably, 70 homologous bHLH genes are shared among all three species, accounting for 49.30% of the total SbbHLH genes in S. baicalensis.
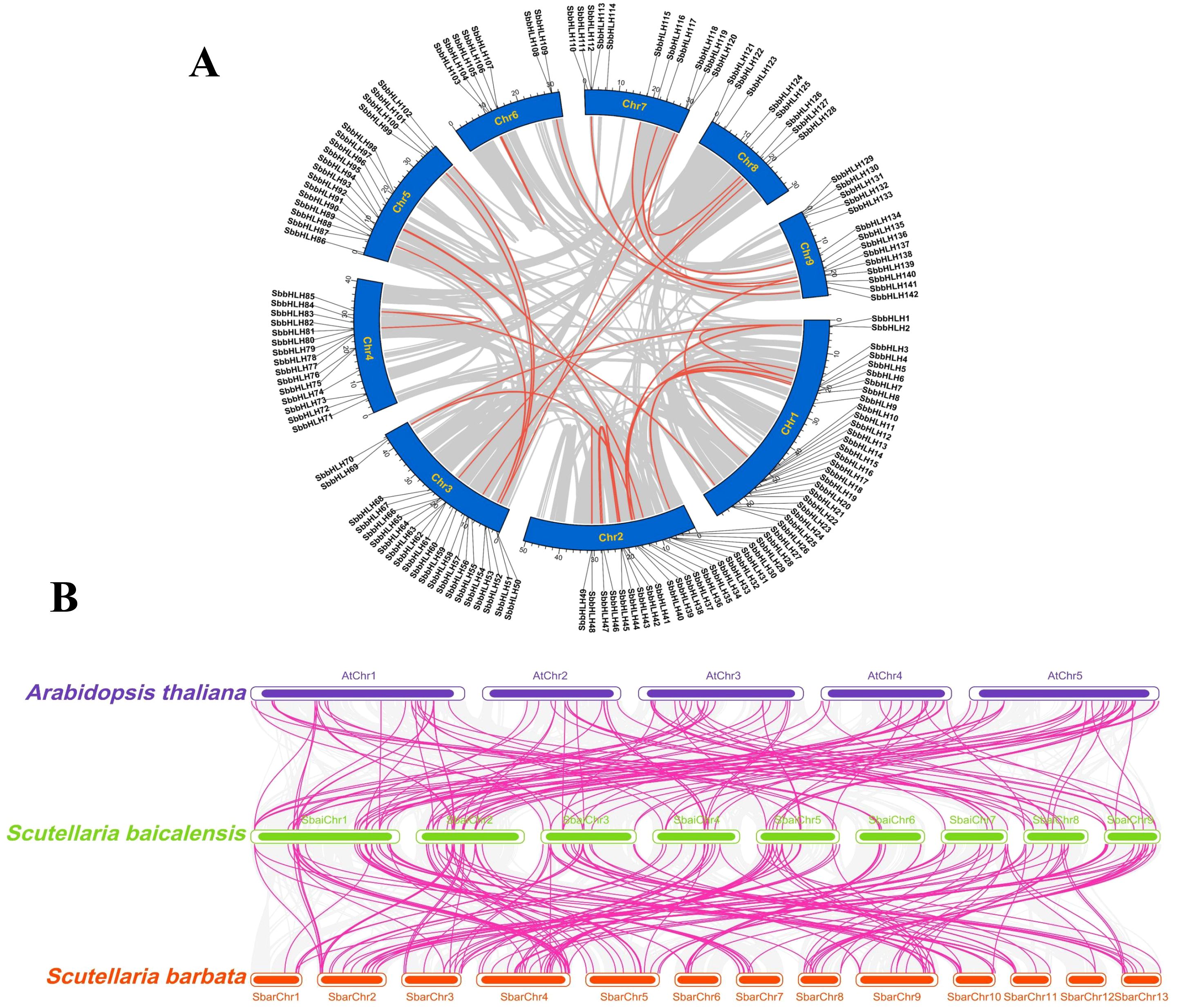
Figure 3. Chromosomal distribution and colinearity analysis of 142 SbbHLH genes. (A) Distribution of 142 SbbHLH genes on 9 chromosomes and collinearity analysis between chromosomes within the species. Chromosomes are represented by blue bars, and collinearity of gene pairs is indicated using red lines. (B) Colinearity analysis of SbbHLH genes among S. baicalensis, S. barbata, and A. thaliana. Collinear relationships of bHLH gene pairs are indicated using pink lines.
A total of 3,521 cis-elements were predicted across the 142 SbbHLH genes (Figure 4). These cis-elements were grouped into 21 types, which were further categorized into three main functional groups: growth and development, hormone response, and stress response. Among them, 2,081 cis-elements (59.10%) were associated with growth and development, followed by 910 (25.85%) linked to hormone responses and 530 (15.05%) related to stress responses. Notably, 138 of the 142 SbbHLH genes contained hormone-responsive elements, including those responsive to salicylic acid, abscisic acid, and gibberellins. This suggests that hormonal regulation plays a significant role in the expression of SbbHLH genes. Notably, although stress response elements constituted a smaller proportion overall, 139 SbbHLH genes were found to contain such elements, including those responsive to anaerobic conditions, low temperatures, and MYB-drought inducibility. Among them, SbbHLH128, SbbHLH71, and SbbHLH135 had the largest number of stress response elements, with 30, 18, and 17 elements, respectively. Furthermore, seven SbbHLH genes were identified to contain MYB regulatory elements associated with flavonoid biosynthesis.
Baicalin is the primary medicinal component of S. baicalensis and classified as an RSF, and is predominantly synthesized in the root tissue. To explore the expression patterns of SbbHLH genes and identify potential genes involved in baicalin biosynthesis, we analyzed transcriptomic data from different tissues of S. baicalensis. Principal component analysis (PCA) revealed that the expression profiles of SbbHLH genes formed distinct clusters corresponding to the four tissue types (Supplementary Figure S1). This clustering was primarily driven by specific SbbHLH genes with high contributions to the principal components, indicating their tissue-specific expression patterns. Almost all SbbHLH genes were expressed in the four tissue types, with the exception of six genes (SbbHLH19, SbbHLH22, SbbHLH84, SbbHLH103, SbbHLH104, and SbbHLH120). We generated a heatmap using the FPKM values of the remaining 136 SbbHLH genes, which were not uniformly expressed across different tissues (Figure 5). Notably, the number of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) was highest in the flowers compared to the root, stem, and leaf tissues. In flower tissue, we identified 13 significant DEGs, of which 9 were upregulated and 4 were downregulated. In root tissue, we found 10 upregulated and 2 downregulated genes, totaling 12 DEGs. In stem tissue, 8 DEGs were observed, while only 2 DEGs were found in leaves. To validate our findings, we measured the expression levels of 10 SbbHLH genes in different tissues by qRT-PCR (Supplementary Table S1), which further confirmed the stability of the transcriptome data (Supplementary Figure S2).
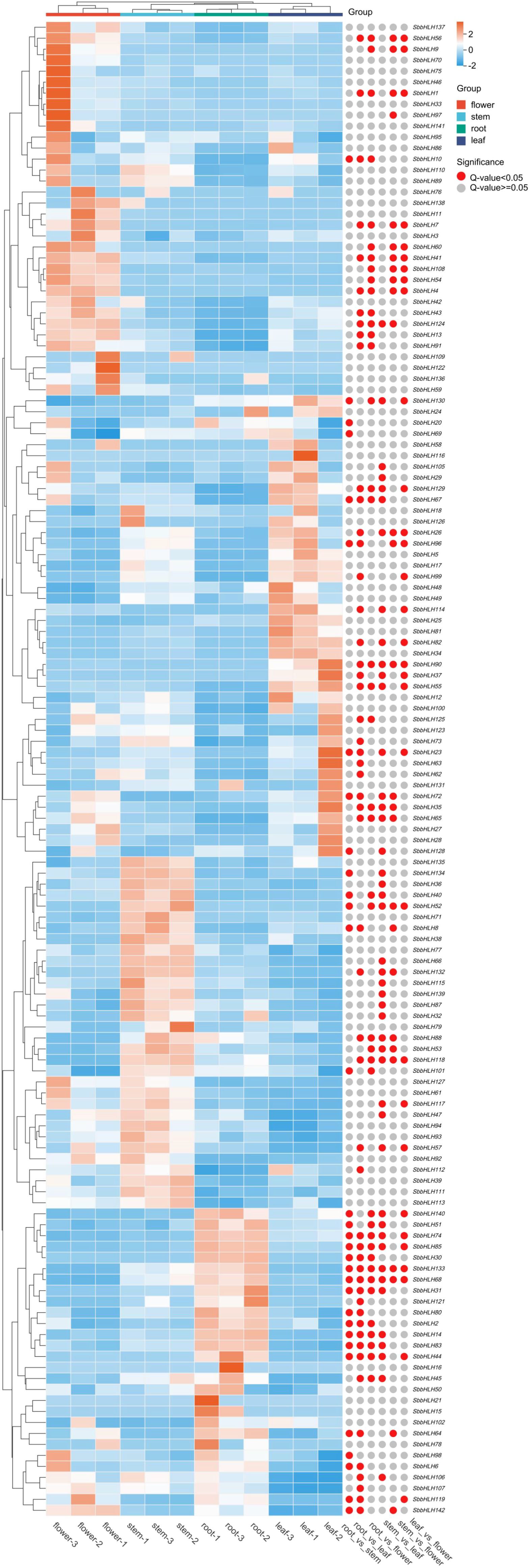
Figure 5. Expression patterns of SbbHLH genes in different tissues of S. baicalensis. Red circles indicate significant differences between the two comparison groups.
To explore the effects of drought stress on the physiological and pharmacological components of S. baicalensis. we measured the activities of SOD and POD, as well as the contents of proline and Soluble Protein (Figure 6A, B). The results indicated that the activities of SOD and POD increased significantly under drought conditions, rising by 159.61% and 29.76%, respectively, compared to the control group. Similarly, the contents of proline and Soluble Protein also exhibited significant increases, with proline rising by 0.9-fold and Soluble Protein by 0.6-fold relative to the control group. Additionally, we assessed the changes in baicalin content under drought treatment. The results demonstrated a significant increase in baicalin content as well (Figure 6C). This increase in baicalin content is particularly beneficial for enhancing the quality of S. baicalensis as a medicinal material. We further analyzed the expression patterns of SbbHLH genes and baicalin biosynthesis genes under drought stress using transcriptomic data. A total of 82 SbbHLH genes and 22 baicalin biosynthesis genes were identified in both the control and drought-treated groups. After normalizing the FPKM values for these genes, a clustered heatmap was generated (Figure 7A). The results showed that the CYP82D-1 and CCL-7 genes were upregulated under drought stress, along with 30 other SbbHLH genes exhibiting similar expression trends. This suggests that CYP82D-1 and CCL-7, together with the 30 SbbHLH genes grouped into one class, may be involved in the biosynthesis of baicalin under drought stress. We divided the 15,179 genes into 11 distinct modules using weighted correlation network analysis (WGCNA) (Figure 7B). The turquoise module, containing 8,839 genes, is the largest, followed by the blue module with 4,981 genes. The purple module is the smallest, with only 75 genes. Notably, the expression pattern of genes in the blue module was strongly positively correlated with baicalin content, with correlations were both greater than 0.85 and p-values<0.01 (Figure 7B, Supplementary Figure S3). Therefore, we analyzed the genes in the blue module and searched for matches based on the original IDs of the 142 SbbHLH genes we identified. Among the blue module genes, we found 32 SbbHLH genes. Additionally, sequence alignment revealed three genes involved in baicalin biosynthesis (Supplementary Table S5). To validate the expression patterns of these genes, we performed qRT-PCR on 10 SbbHLH genes, which confirmed the reliability of the transcriptome data (Supplementary Figure S4).
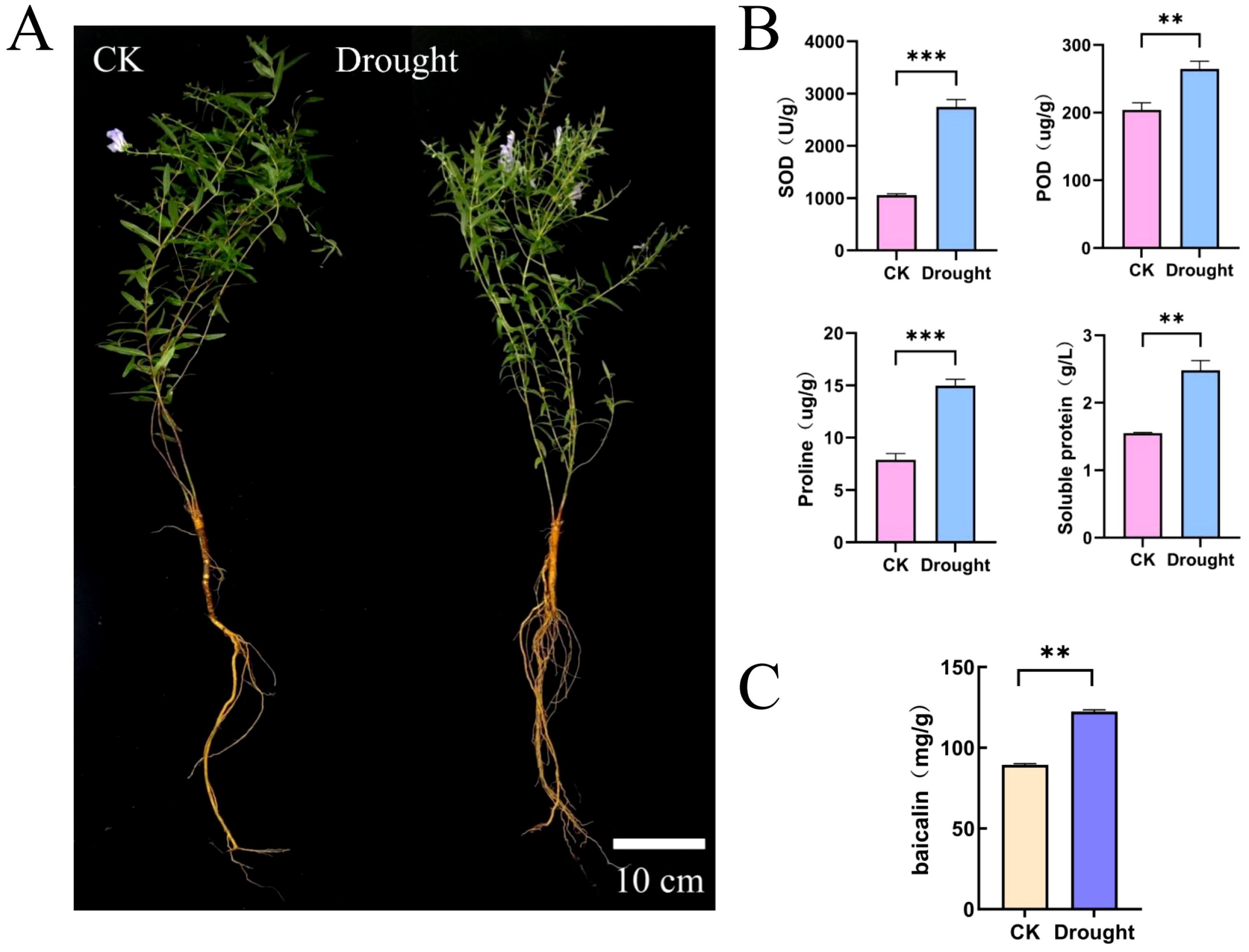
Figure 6. Physiological changes of S. baicalensis under drought stress. (A) The phenotypes of CK and drought treatment. Bar = 10 cm. (B) Protective enzyme activity and osmotic regulating substance content. (C) The baicalin content. Error bars were obtained from three measurements (Mean ± SD). Statistical analysis was conducted with one-way analysis of variance, ** and *** indicate p < 0.05 and p < 0.01.
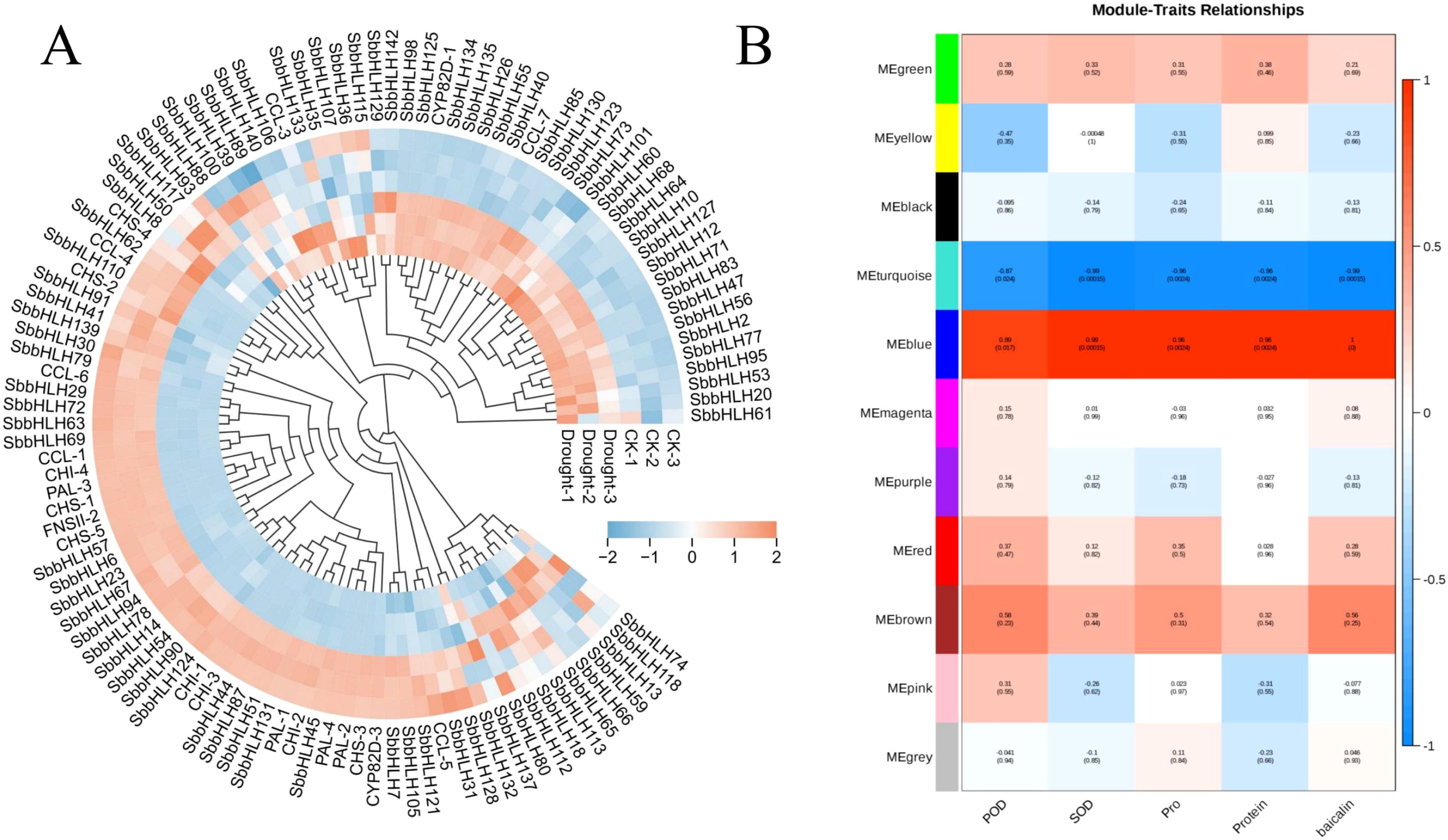
Figure 7. Cluster heatmap and WGCNA analysis of S. baicalensis under drought stress (A) Cluster heatmap of SbbHLH genes and baicalin biosynthesis genes in S. baicalensis. (B) Heatmap of the correlation between modules and physiological changes in S. baicalensis, with correlation coefficients and p-values in every graph.
Baicalin is one of the primary medicinal components of S. baicalensis. Our previous research demonstrated that moderate drought stress activates the stress response in S. baicalensis, inducing physiological changes that enhance baicalin content (Cheng et al., 2018; Cheng et al., 2023). We analyzed the promoter regions of CYP82D-2, CYP82D-1, and CCL-7, which are involved in the biosynthesis of the major secondary metabolite baicalin within the blue module. Our analysis revealed that the promoter regions of these genes in the baicalin biosynthetic pathway contain cis-elements associated with bHLH transcription factors (Figure 8A), suggesting that CYP82D-2, CYP82D-1, and CCL-7 may be regulated by SbbHLH genes. We merged the 30 SbbHLH genes with expression patterns similar to CYP82D-1 and CCL-7 obtained from the clustered heatmap with the 32 SbbHLH genes from the blue module. After removing duplicates, a total of 36 unique SbbHLH genes were identified. Subsequently, we constructed a protein interaction network using the 36 SbbHLH genes and 3 baicalin biosynthesis pathway genes (Supplementary Table S6; Figure 8B; Supplementary Figure S5). The results showed that the CYP82D-1 interacts with SbbHLH142 and SbbHLH98, while CCL-7 interacts with SbbHLH74. Notably, SbbHLH53 emerged as a central node in the protein interaction network, interacting with multiple proteins, including SbbHLH142, SbbHLH140, SbbHLH20, SbbHLH85, SbbHLH40, SbbHLH68, SbbHLH35, and SbbHLH125. Phylogenetic analysis revealed that SbbHLH53 in S. baicalensis shares a high degree of homology with AtbHLH112 in A. thaliana. Previous studies have shown that, under drought conditions, AtbHLH112 in A. thaliana is induced by drought stress and then regulates the expression of genes related to SOD, POD and proline metabolism. Based on previous studies and the findings of this study, we propose that the SbbHLH gene regulates the baicalin biosynthetic pathway under drought stress. Specifically, when S. baicalensis is subjected to drought stress, its physiological state undergoes significant changes, including alterations in SOD activity, POD activity, and proline content. At the genetic level, the expression of SbbHLH53 is upregulated under drought stress, activating a regulatory network centered on this transcription factor and ultimately promoting baicalin biosynthesis. Within this complex regulatory framework, SbbHLH74 may positively regulate the expression of CCL-7. Meanwhile, SbbHLH98 and SbbHLH142 are likely to enhance the expression of CYP82D-1 (F6H), which accelerates the enzymatic conversion of chrysin to baicalein through the action of F6H. Ultimately, these interactions and regulatory mechanisms contribute to an increased biosynthesis rate of baicalin under drought stress conditions.
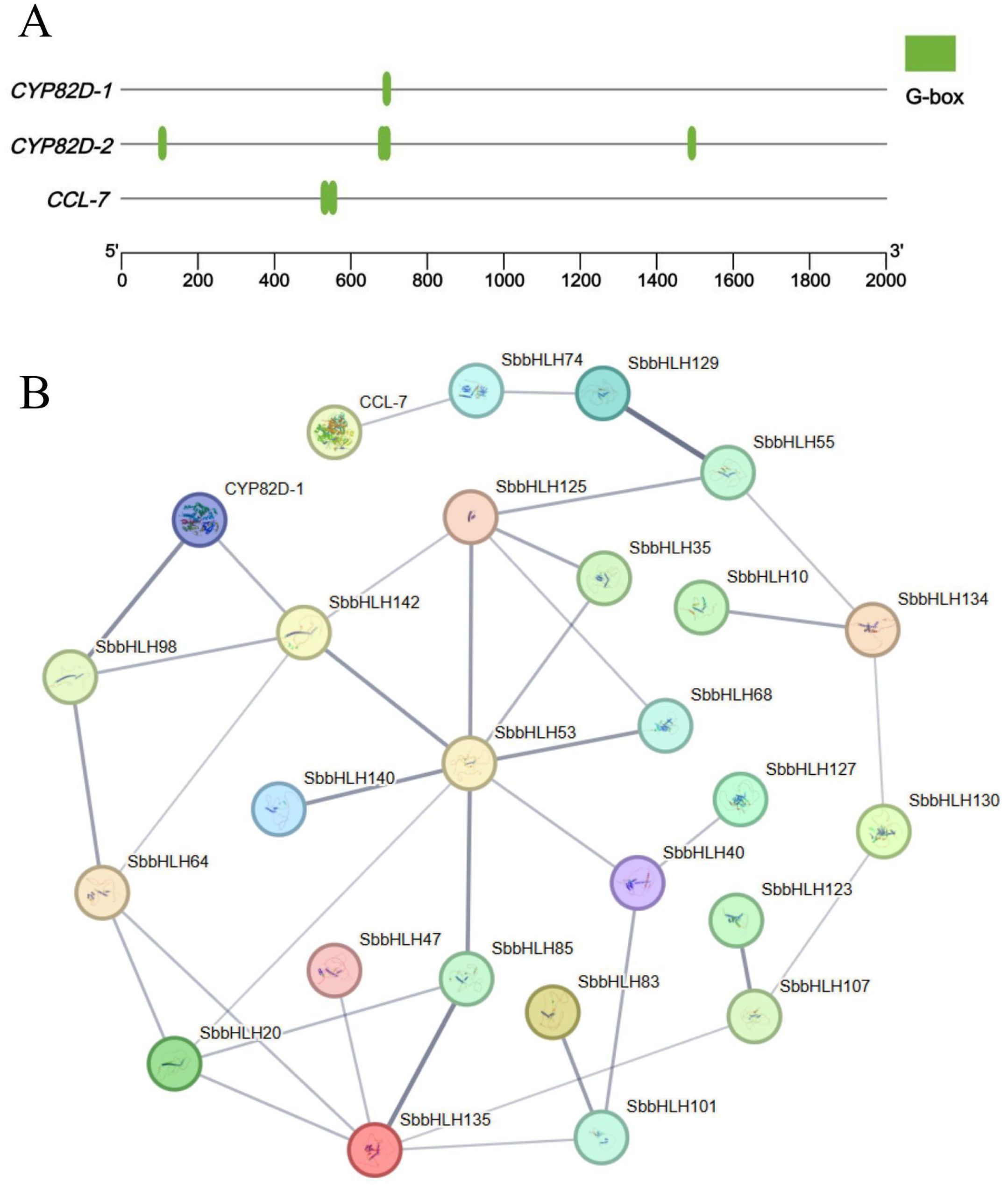
Figure 8. Analysis of cis-elements and protein interaction network. (A) Predicted cis-elements from 2 kb upstream of three key enzyme genes in the baicalin biosynthesis pathway. (B) Protein interaction network analysis. line thickness indicates the strength of data support.
The bHLH gene family play crucial roles in signal transduction networks (Seo et al., 2011; Zhang et al., 2020; Yin et al., 2023). The identification of transcription factor families has been facilitated by the rapid increase in plant genomic data. The bHLH genes had been comprehensively analyzed in multiple species, including Salvia miltiorrhiza (Zhang et al., 2015), Ginkgo biloba (Zhou et al., 2020), A. thaliana (Li et al., 2006), Juglans mandshurica (Li et al., 2024), Passiflora edulis (Liang et al., 2023) and Citrus sinensis (Huang et al., 2024), underscoring the significance of this transcription factor family. However, comprehensive information regarding bHLH gene family in S. baicalensis remains scarce. Therefore, we identified and analyzed 142 SbbHLH genes in S. baicalensis. This number is comparable to that reported in P. edulis (138) (Liang et al., 2023) and C. sinensis (135) (Huang et al., 2024), fewer than in A. thaliana (161), and more than in G. biloba (Zhou et al., 2020) and S. miltiorrhiza (Zhang et al., 2015). The genome size and chromosome number of different species may lead to differences in the number of bHLH genes (Flagel and Wendel, 2009; Kamran et al., 2023).
The phylogenetic tree, comprising the 142 SbbHLH genes and 161 AtbHLH genes, showed that each SbbHLH gene clustered with at least one AtbHLH gene, forming sister branches (Figure 1). This clustering suggests that bHLH genes diversified prior to species evolution, thereby enhancing the reliability of classification and functional predictions for SbbHLH genes in S. baicalensis (Yao et al., 2024). The analysis of the conserved motifs in the 142 SbbHLH genes revealed that genes with similar conserved motifs are generally grouped within the same branch of the phylogenetic tree. This suggests that members within the same branch may share a common ancestor and perform similar functions, further supporting the phylogenetic relationships within S. baicalensis (Figure 2A). All SbbHLH genes contained motifs 1 and 2, indicating that these motifs represent the conserved domains of bHLH genes, forming the DNA-binding domain and the protein dimerization region (Kamran et al., 2023). In contrast, However, the distribution of motifs 2-10 was random but conserved within individual branches, reflecting the specific functions of genes within those branches. Among the 142 SbbHLH genes, the highest number of exons observed was 14, while 134 genes have more than two exons (Figure 2B). These results suggest that exon insertions or deletions may have occurred during evolution, contributing to the expansion of the SbbHLH gene family (Li et al., 2024).
The 142 SbbHLH genes are unevenly distributed across the nine chromosomes of S. baicalensis (Figure 3A), suggesting their involvement in evolutionary development (Reams and Neidle, 2004). Gene duplication events are common in transcription factor families, enabling rapid expansion and contraction in response to environmental changes. This process contributes to the quantitative variation of transcription factor families and promotes genetic diversity (Guo et al., 2024). Gene duplications are typically categorized into segmental and tandem duplications, with segmental duplications being particularly prevalent in plant transcription factor families (Yao et al., 2024). As anticipated, we identified three tandemly duplicated and 26 segmentally duplicated gene pairs in S. baicalensis, suggesting that segmental duplication likely plays a pivotal role in the evolution of bHLH genes and the development of novel functions for environmental adaptation (Figure 3A). Similar conclusions in other species, such as J. mandshurica and C. praecox, further support the idea that segmental duplication is a common mechanism driving the expansion of bHLH gene families (Kamran et al., 2023; Li et al., 2024). Collinearity analysis provided further insights into the origin and evolution of the bHLH gene family (Figure 3B). We identified 122 gene pairs between S. baicalensis and A. thaliana, and 172 gene pairs between Scutellaria species. This indicates a closer phylogenetic relationship within Scutellaria, while still showing 48.45% similarity with A. thaliana. This suggests that bHLH gene diversity may have emerged early in terrestrial plants. The ka/ks analysis revealed that SbbHLH genes primarily underwent purifying selection, reflecting highly conserved evolution (Supplementary Table S4) (Zhan et al., 2023). Additionally, we identified 70 collinear genes among S. baicalensis, S. barbata, and A. thaliana, which are crucial for understanding evolutionary dynamics.
The growth and development of plant are complex processes influenced by both external environmental factors and internal hormone levels (Li et al., 2024). To further clarify the role of SbbHLH genes in S. baicalensis, we identified the cis-elements of 142 SbbHLH genes. The results showed that SbbHLH genes play significant roles in stress tolerance, hormone responses, and growth and development in S. baicalensis (Figure 4). Changes in transcription levels are a primary mode of regulation in organisms. We further examined the expression patterns of these 142 SbbHLH genes in different tissues (Figure 5). Our findings revealed that 136 SbbHLH genes were expressed in at least one tissue, with varying expression levels among different tissues, indicating tissue-specific expression of SbbHLH genes. Notably, 12 genes were highly expressed in the roots, suggesting their potential roles in root growth and development (Zhao et al., 2016; Cheng et al., 2018).
Given the importance of S. baicalensis for its antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties (Wang et al., 2022). Moreover, the yield of S. baicalensis and the content of baicalin are closely linked to its market price, making the understanding of baicalin biosynthesis mechanisms a current research hotspot. Our study demonstrated that appropriate drought treatment could stimulate the production of secondary metabolites in S. baicalensis, including baicalin and baicalein (Cheng et al., 2018; Cheng et al., 2023). Under drought treatment, the physiological state of S. baicalensis undergoes significant changes, including the active removal of harmful substances through increased activity of protective enzyme, and osmotic adjustment via elevated proline and soluble protein content (Figure 6B). The content of the secondary metabolite baicalin also significantly increased, indicating that secondary metabolites help resist drought stress (Figure 6C). A substantial body of literature shows that these processes involve complex signal transduction between the environment, hormones, and transcription factors, ultimately altering the activity of downstream key enzymes and thereby affecting the biosynthesis of plant secondary metabolites (Guo et al., 2024). The bHLH gene family plays a crucial role in plant stress resistance. For example, overexpression of MdCIB1 (cryptochrome-interacting bHLH1) in Malus domestica callus enhanced drought tolerance to PEG6000, while MdCIB1 transgenic A. thaliana exhibited improved root development under drought stress (Ren et al., 2021; Li et al., 2024).
To investigate the potential roles of SbbHLH genes in regulating baicalin biosynthesis under drought treatment, we performed transcriptome data and qRT-PCR analysis on root tissues of S. baicalensis subjected to drought treatment and control treatments. To investigate the potential role of SbbHLH genes in regulating baicalin biosynthesis under drought stress, we performed transcriptome and qRT-PCR analyses on root tissues of S. baicalensis subjected to drought stress and control treatments. A total of 36 SbbHLH genes exhibited expression patterns consistent with the trend in baicalin content (Figure 7A, B). Additionally, we identified cis-elements associated with drought stress and hormone responses in the promoter regions of SbbHLH genes, further supporting their role in regulating the stress response in S. baicalensis (Figure 4). Protein interaction analysis suggested that SbbHLH53 may act as a central component of the regulatory network under drought stress, modulating the expression of downstream genes, including CCL7 and CYP82D-1, in response to drought conditions and hormonal changes (Figure 8B, Supplementary Figure S5). This suggests that these bHLH genes are part of a complex cross-regulatory network involving both drought stress and hormone induction. For instance, ScbHLH5 and ScbHLH65 exhibited significant positive correlations under various hormonal inductions in Secale cereale, indicating a synergistic regulatory effect between different endogenous hormonal metabolic pathways (Chen et al., 2024). Given the conservation of the bHLH gene family, we can predict the functions of SbbHLH genes through homology analysis (Feller et al., 2011b). Many SbbHLH genes have been functionally validated in A. thaliana, allowing us to infer their roles in S. baicalensis. The homologous gene of SbbHLH53 in S. baicalensis is AtbHLH112, which has been shown to mediate physiological responses at the transcriptional level, including proline biosynthesis and ROS scavenging, thereby enhancing the salt and drought tolerance of A. thaliana (Liu et al., 2015).
The bHLH genes may exhibit complex regulatory mechanisms in response to abiotic stress and function by forming both homologous and heterologous complexes (Guo et al., 2024). Previous studies have indicated that the HLH domain facilitates dimer formation, with specific amino acid residues in the helix regions being essential for this process (Carretero-Paulet et al., 2010). Since the biosynthesis pathways of anthocyanins and baicalin share similarities, it is plausible that the SbbHLH gene may also form complexes through protein interactions, playing a crucial role in regulating downstream gene expression in response to drought stress signals. Our study revealed that 36 SbbHLH genes exhibited elevated expression under drought stress. Notably, we identified binding sites for bHLH genes in the promoter regions of key genes involved in baicalin biosynthesis (Figure 8A). The biosynthesis of baicalin may be influenced by drought stress, which can increase the expression of SbbHLH genes and consequently the content of baicalin (Yang et al., 2022; Cheng et al., 2023). Based on our analysis and previous studies, we hypothesize that SbbHLH74, SbbHLH98, and SbbHLH142 play crucial roles in regulating baicalin biosynthesis. Specifically, under drought stress, the regulatory network centered on the SbbHLH53 gene is activated, influencing the expression of SbbHLH74, SbbHLH98, and SbbHLH142, which in turn enhances the activities of CYP82D-1 and CCL-5 and promotes baicalin biosynthesis. Our study aims to further investigate the target genes that regulate baicalin biosynthesis to clarify the role of SbbHLH genes in this process. In future studies, we will validate the functions of SbbHLH genes and their regulatory mechanisms under drought stress.
This study represents the first genome-wide analysis of the SbbHLH gene family in S. baicalensis. We identified a total of 142 SbbHLH genes within the S. baicalensis genome, each corresponding to at least one homologous AtbHLH gene from A. thaliana. Conserved motif analysis indicated that SbbHLH genes are relatively conserved across different branches, further supporting their phylogenetic relationships. Chromosome localization revealed that the 142 SbbHLH genes are unevenly distributed across nine chromosomes. Segmental duplication was identified as the primary mechanism driving the amplification of SbbHLH genes, with 29 pairs of gene duplication events observed. We investigated the expression of SbbHLH genes in response to drought stress and explored their specific roles in regulating baicalin biosynthesis. The results showed that SbbHLH genes are interconnected and exhibit complex regulatory mechanisms under drought stress. Notably, SbbHLH53 may serve as a core component of the regulatory network under drought conditions, while SbbHLH74, SbbHLH98, and SbbHLH142 are potential candidate genes involved in the regulation of baicalin biosynthesis. In summary, our results provide a comprehensive analysis of the SbbHLH genes in S. baicalensis and providing new insights into the regulation of baicalin biosynthesis by SbbHLH genes under drought stress.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
YS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Visualization, Writing – original draft. BW: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft. LZ: Methodology, Resources, Writing – original draft. XZ: Formal Analysis, Visualization, Writing – original draft. PX: Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. MZ: Conceptualization, Software, Validation, Writing – review & editing. MGH: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft. PD: Formal Analysis, Software, Writing – review & editing. MH: Methodology, Project administration, Writing – review & editing, Resources. LC: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Supervision, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. LY: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82204575), the Key R&D Project of Jilin Province Science and Technology Development Plan (20240305001YY) and National Key Research and Development Program of China (2021YFD1600900).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpls.2024.1506805/full#supplementary-material
Birkenbihl, R. P., Kracher, B., Roccaro, M., Somssich, I. E. (2017). Induced genome-wide binding of three arabidopsis WRKY transcription factors during early MAMP-triggered immunity. Plant Cell 29, 20–38. doi: 10.1105/tpc.16.00681
Capella, M., Ribone, P. A., Arce, A. L., Chan, R. L. (2015). Arabidopsis thaliana HomeoBox 1 (AtHB1), a Homedomain-Leucine Zipper I (HD-Zip I) transcription factor, is regulated by PHYTOCHROME-INTERACTING FACTOR 1 to promote hypocotyl elongation. New Phytol. 207, 669–682. doi: 10.1111/nph.13401
Carretero-Paulet, L., Galstyan, A., Roig-Villanova, I., Martinez-Garcia, J. F., Bilbao-Castro, J. R., Robertson, D. L. (2010). Genome-wide classification and evolutionary analysis of the bHLH family of transcription factors in Arabidopsis, poplar, rice, moss, and algae. Plant Physiol. 153, 1398–1412. doi: 10.1104/pp.110.153593
Chen, C., Wu, Y., Li, J. X. Z. J. (2023). TBtools-II: A "one for all, all for one"bioinformatics platform for biological big-data mining. Mol. Plant 16, 1733–1742. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2023.09.010
Chen, X., Yao, C., Liu, J., Liu, J., Fang, J., Deng, H., et al. (2024). Basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) gene family in rye (Secale cereale L.): genome-wide identification, phylogeny, evolutionary expansion and expression analyses. BMC Genomics 25, 67. doi: 10.1186/s12864-023-09911-3
Cheng, L., Han, M., Yang, L. M., Yang, L., Sun, Z., Zhang, T. (2018). Changes in the physiological characteristics and baicalin biosynthesis metabolism of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi under drought stress. Ind. Crop Prod. 122, 473–482. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2018.06.030
Cheng, L., Yu, J., Zhang, L., Yao, Y., Sun, Z., Han, M., et al. (2023). Identification of SbWRKY Transcription Factors in Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi under Drought Stress and Their Relationship with Baicalin. Agronomy 13, 2564. doi: 10.3390/agronomy13102564
Fang, Y., Liu, J., Zheng, M., Zhu, S., Pei, T., Cui, M., et al. (2023). SbMYB3 transcription factor promotes root-specific flavone biosynthesis in Scutellaria baicalensis. Hortic. Res.-England 10, uhac266. doi: 10.1093/hr/uhac266
Feller, A., Machemer, K., Braun, E. L., Grotewold, E. (2011a). Evolutionary and comparative analysis of MYB and bHLH plant transcription factors. Plant J. Cell Mol. Biol. 66, 94–116. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2010.04459.x
Feller, A., Machemer, K., Braun, E. L., Grotewold, E. (2011b). Evolutionary and comparative analysis of MYB and bHLH plant transcription factors. Plant J. 66, 94–116. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2010.04459.x
Flagel, L. E., Wendel, J. F. (2009). Gene duplication and evolutionary novelty in plants. New Phytol. 183, 557–564. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2009.02923.x
Geng, D., Jiang, M., Dong, H., Wang, R., Lu, H., Liu, W., et al. (2023). MeJA regulates the accumulation of baicalein and other 4 '- hydroxyflavones during the hollowed root development in Scutellaria baicalensis. Front. Plant Sci. 13. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1067847
Guo, F., Meng, X., Hong, H., Liu, S., Yu, J., Huang, C., et al. (2024). Systematic identification and expression analysis of bHLH gene family reveal their relevance to abiotic stress response and anthocyanin biosynthesis in sweetpotato. BMC Plant Biol. 24, 156. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-04788-0
Heim, M. A., Jakoby, M., Werber, M., Martin, C., Weisshaar, B., Bailey, P. C. (2003). The basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor family in plants: a genome-wide study of protein structure and functional diversity. Mol. Biol. Evol. 20, 735–747. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msg088
Hu, S., Wang, W., Zhang, C., Zhou, W., Yan, P., Xue, X., et al. (2023). Integrated transcriptomic and metabolomic profiles reveal anthocyanin accumulation in Scutellaria baicalensis petal coloration. Ind. Crop Prod. 194, 116144. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2022.116144
Huang, X., Su, L., Xian, B., Yu, Q., Zhang, M., Fan, J., et al. (2024). Genome-wide identification and characterization of the sweet orange (Citrus sinensis) basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) family reveals a role for CsbHLH085 as a regulator of citrus bacterial canker resistance. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 267, 131442. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.131442
Jia, K., Li, Y., Liu, T., Gu, X., Li, X. (2023). New insights for infection mechanism and potential targets of COVID-19: Three Chinese patent medicines and three Chinese medicine formulas as promising therapeutic approaches. Chin. Herb. Med. 15, 157–168. doi: 10.1016/j.chmed.2022.06.014
Jia, N., Wang, J. J., Liu, J., Jiang, J., Sun, J., Yan, P., et al. (2021). DcTT8, a bHLH transcription factor, regulates anthocyanin biosynthesis in Dendrobium candidum. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 162, 603–612. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2021.03.006
Kamran, H. M., Fu, X., Wang, H., Yang, N., Chen, L. (2023). Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of the bHLH Transcription Factor Family in Wintersweet (Chimonanthus praecox). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 13462. doi: 10.3390/ijms241713462
Lei, P., Jiang, Y., Zhao, Y., Jiang, M., Ji, X., Ma, L., et al. (2024). Functions of basic helix–loop–helix (bHLH) proteins in the regulation of plant responses to cold, drought, salt, and iron deficiency: A comprehensive review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 72, 10692–10709. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c09665
Li, X., Cao, L., Jiao, B., Yang, H., Ma, C., Liang, Y. (2022). The bHLH transcription factor AcB2 regulates anthocyanin biosynthesis in onion (Allium cepa L.). Hortic. Res.-England 9, uhac128. doi: 10.1093/hr/uhac128
Li, X., Duan, X., Jiang, H., Sun, Y., Tang, Y., Yuan, Z., et al. (2006). Genome-wide analysis of basic/helix-loop-helix transcription factor family in rice and arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 141, 1167–1184. doi: 10.1104/pp.106.080580
Li, Y., Fu, Q., Li, X., Zhang, Q., Zhao, Q., Ding, Y., et al. (2024). Exploring the guardian of abiotic stress: Genome-wide identification of the basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor family in Juglans mandshurica. Sci. Hortic. 331, 113154. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2024.113154
Liang, J., Fang, Y., An, C., Yao, Y., Wang, X., Zhang, W., et al. (2023). Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the bHLH gene family in passion fruit (Passiflora edulis) and its response to abiotic stress. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 225, 389–403. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.11.076
Liu, Y., Ji, X., Nie, X., Qu, M., Zheng, L., Tan, Z., et al. (2015). Arabidopsis AtbHLH112 regulates the expression of genes involved in abiotic stress tolerance by binding to their E-box and GCG-box motifs. New Phytol. 207, 692–709. doi: 10.1111/nph.13387
Liu, S., Wang, Y., Shi, M., Maoz, I., Gao, X., Sun, M., et al. (2022). SmbHLH60 and SmMYC2 antagonistically regulate phenolic acids and anthocyanins biosynthesis in Salvia miltiorrhiza. J. Adv. Res. 42, 205–219. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2022.02.005
Mertens, J., Pollier, J., Vanden, B. R., Lopez-Vidriero, I., Franco-Zorrilla, J. M., Goossens, A. (2016). The bHLH Transcription Factors TSAR1 and TSAR2 Regulate Triterpene Saponin Biosynthesis in Medicago truncatula. Plant Physiol. 170, 194–210. doi: 10.1104/pp.15.01645
Mohammad, Hurrah, I. M., Kumar, A., Abbas, N. (2023). Synergistic interaction of two bHLH transcription factors positively regulates artemisinin biosynthetic pathway in Artemisia annua L. Physiol. Plant 175, e13849. doi: 10.1111/ppl.13849
Nagashima, S., Hirotani, M., Yoshikawa, T. (2000). Purification and characterization of UDP-glucuronate: baicalein 7-O-glucuronosyltransferase from Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi. cell suspension cultures. Phytochemistry 53, 533–538. doi: 10.1016/S0031-9422(99)00593-2
Nair, S. K., Burley, S. K. (2000). Recognizing DNA in the library. Nature 404, 717–718. doi: 10.1038/35008182
Pei, T., Yan, M., Huang, Y., Wei, Y., Martin, C., Zhao, Q. (2022). Specific flavonoids and their biosynthetic pathway in scutellaria baicalensis. Front. Plant Sci. 13. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.866282
Reams, A. B., Neidle, E. L. (2004). Selection for gene clustering by tandem duplication. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 58, 119–142. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.58.030603.123806
Ren, Y., Yang, Y., Zhao, Q., Zhang, T., Wang, C., Hao, Y., et al. (2021). MdCIB1, an apple bHLH transcription factor, plays a positive regulator in response to drought stress. Environ. Exp. Bot. 188, 104523. doi: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2021.104523
Seo, J., Joo, J., Kim, M., Kim, Y., Nahm, B. H., Song, S. I., et al. (2011). OsbHLH148, a basic helix-loop-helix protein, interacts with OsJAZ proteins in a jasmonate signaling pathway leading to drought tolerance in rice. Plant J. 65, 907–921. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2010.04477.x
Shangguan, X. X., Yang, C. Q., Zhang, X. F., Wang, L. J. (2016). Functional characterization of a basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) transcription factor GhDEL65 from cotton (Gossypium hirsutum). Physiol. Plant 158, 200–212. doi: 10.1111/ppl.12450
Singh, S. K., Patra, B., Paul, P., Liu, Y., Pattanaik, S., Yuan, L. (2021). BHLH IRIDOID SYNTHESIS 3 is a member of a bHLH gene cluster regulating terpenoid indole alkaloid biosynthesis in Catharanthus roseus. Plant Direct 5, e00305. doi: 10.1002/pld3.305
Su, L., Zhang, Y., Yu, S., Geng, L., Lin, S., Ouyang, L., et al. (2023). RcbHLH59-RcPRs module enhances salinity stress tolerance by balancing Na(+)/K(+) through callose deposition in rose (Rosa chinensis). Hortic. Res.-England 10, uhac291. doi: 10.1093/hr/uhac291
Toledo-Ortiz, G., Huq, E., Quail, P. H. (2003). The Arabidopsis basic/helix-loop-helix transcription factor family. Plant Cell 15, 1749–1770. doi: 10.1105/tpc.013839
Wang, W., Hu, S., Yang, J., Zhang, C., Zhang, T., Wang, D., et al. (2022). Novel R2R3-MYB transcription factor sb MYB12 positively regulates baicalin biosynthesis in scutellaria baicalensis georgi. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 15452. doi: 10.3390/ijms232415452
Wang, Z., Wang, S., Kuang, Y., Hu, Z., Qiao, X., Ye, M. (2018). A comprehensive review on phytochemistry, pharmacology, and flavonoid biosynthesis of Scutellaria baicalensis. Pharm. Biol. 56, 465–484. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2018.1492620
Wenjing, Hao, L., Yang, T., Zhao, Y., Xiao, K., Yao (2016). TabHLH1, a bHLH-type transcription factor gene in wheat, improves plant tolerance to Pi and N deprivation via regulation of nutrient transporter gene transcription and ROS homeostasis. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 104, 99–113. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.03.023
Xu, Z., Gao, R., Pu, X., Xu, R., Wang, J., Zheng, S., et al. (2020). Comparative Genome Analysis of Scutellaria baicalensis and Scutellaria barbata Reveals the Evolution of Active Flavonoid Biosynthesis. Genom. Proteomics Bioinf. 18, 230–240. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2020.06.002
Xue, L., Wei, Z., Zhai, H., Xing, S., Wang, Y., He, S., et al. (2022). The IbPYL8-IbbHLH66-IbbHLH118 complex mediates the abscisic acid-dependent drought response in sweet potato. New Phytol. 236, 2151–2171. doi: 10.1111/nph.18502
Yang, L., Qiao, L., Su, X., Ji, B., Dong, C. (2022). Drought stress stimulates the terpenoid backbone and triterpenoid biosynthesis pathway to promote the synthesis of saikosaponin in bupleurum chinense DC. Roots. Molecules 27, 5470. doi: 10.3390/molecules27175470
Yao, Y., He, Z., Li, X., Xu, J., Han, X., Liang, H., et al. (2024). Genome-wide identification of bHLH gene family and its response to cadmium stress in Populus x canescens. Peerj 12, e17410. doi: 10.7717/peerj.17410
Yin, Y., Yan, Z., Guan, J., Huo, Y., Wang, T., Li, T., et al. (2023). Two interacting basic helix-loop-helix transcription factors control flowering time in rice. Plant Physiol. 192, 205–221. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiad077
Zhan, H., Liu, H., Ai, W., Han, X., Wang, Y., Lu, X. (2023). Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of the bHLH Transcription Factor Family and Its Response to Abiotic Stress in Mongolian Oak (Quercus mongolica). Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 45, 1127–1148. doi: 10.3390/cimb45020075
Zhang, X., Luo, H., Xu, Z., Zhu, Y., Ji, A., Song, J., et al. (2015). Genome-wide characterisation and analysis of bHLH transcription factors related to tanshinone biosynthesis in Salvia miltiorrhiza. Sci. Rep. 5, 11244. doi: 10.1038/srep11244
Zhang, L., Xiang, Z., Li, J., Wang, S., Chen, Y., Liu, Y., et al. (2023). bHLH57 confers chilling tolerance and grain yield improvement in rice. Plant Cell Environ. 46, 1402–1418. doi: 10.1111/pce.14513
Zhang, C., Xing, B., Yang, D., Ren, M., Guo, H., Yang, S., et al. (2020). SmbHLH3 acts as a transcription repressor for both phenolic acids and tanshinone biosynthesis in Salvia miltiorrhiza hairy roots. Phytochemistry 169, 112183. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2019.112183
Zhao, M., Li, J., Zhu, L., Chang, P., Li, L., Zhang, L. (2019). Identification and characterization of MYB-bHLH-WD40 regulatory complex members controlling anthocyanidin biosynthesis in blueberry fruits development. Genes 10, 496. doi: 10.3390/genes10070496
Zhao, Q., Weng, J. K., Chen, X. Y., Martin, C., Cui, M. Y., Levsh, O., et al. (2018). Two CYP82D enzymes function as flavone hydroxylases in the biosynthesis of root-specific 4'-deoxyflavones in scutellaria baicalensis. Mol. Plant 11, 135–148. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2017.08.009
Zhao, Q., Yang, J., Cui, M. Y., Liu, J., Martin, C. (2019). The Reference Genome Sequence of Scutellaria baicalensis Provides Insights into the Evolution of Wogonin Biosynthesis. Mol. Plant 12, 935–950. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2019.04.002
Zhao, Q., Zhang, Y., Wang, G., Hill, L., Weng, J. K., Chen, X. Y., et al. (2016). A specialized flavone biosynthetic pathway has evolved in the medicinal plant, Scutellaria baicalensis. Sci. Adv. 2, e1501780. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1501780
Zhong-Ming, H., Hong-Li, G., Bo, C., Shun-Bo, H. U., Mei, H., Li-Min, Y. (2011). Extracting technology of baicalin by microwave from scutellaria baicalensis georgi. Lishizhen Med. Materia Med. Res. 22, 2840–2841. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0805.2011.12.005
Zhou, X., Liao, Y., Kim, S. U., Chen, Z., Nie, G., Cheng, S., et al. (2020). Genome-wide identification and characterization of bHLH family genes from Ginkgo biloba. Sci. Rep. 10, 13723. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-69305-3
Keywords: Scutellaria baicalensis, bHLH gene family, expression pattern, baicalin biosynthesis, drought stress
Citation: Sun Y, Wang B, Zhang L, Zheng X, Xu P, Zhang M, Han M, Di P, Han M, Cheng L and Yang L (2025) Genome-wide identification of the bHLH gene family in Scutellaria baicalensis and their relationship with baicalin biosynthesis under drought stress. Front. Plant Sci. 15:1506805. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1506805
Received: 06 October 2024; Accepted: 26 December 2024;
Published: 27 January 2025.
Edited by:
Xuwu Sun, Henan University, ChinaReviewed by:
Wenjun Huang, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), ChinaCopyright © 2025 Sun, Wang, Zhang, Zheng, Xu, Zhang, Han, Di, Han, Cheng and Yang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Lin Cheng, MDA3MTA1QGpsYXUuZWR1LmNu; Limin Yang, eWFuZ2xpbWluQGpsYXUuZWR1LmNu
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.