- State Key Laboratory for Crop Stress Resistance and High-Efficiency Production, College of Agronomy, Northwest A & F University, Yangling, Shaanxi, China
Background: Blending controlled-release nitrogen fertilizer (CRNF) with ordinary nitrogen fertilizer (ONF) is a strategic approach to improve winter wheat nutrient management. This blend provides nitrogen (N) to winter wheat in a balanced and consistent manner, ensuring long-term growth, reducing nutrient loss due to leaching or volatilization, and increasing N use efficiency (NUE).
Aims: CRNF aims to enhance N application suitability, optimizes soil nutrient dynamics, and its widespread use can boost crop NUE and yield. The study investigates how different CRNF and ONF blending ratios affect soil N content, winter wheat growth, and yield.
Methods: The experiment used two N application rates of 192(N1) and 240(N2) kg ha-1 of ONF, with five different blending ratios CRNF. The proportions of CRNF were 0%(F1), 30%(F2), 50%(F3), 70%(F4), and 100%(F5), respectively. The effects of changes in soil nitrate concentration, dry matter accumulation, N uptake, and transportation at various growth stages and yield were analyzed.
Results: CRNF at the jointing and anthesis stages helps maintain nitrate N levels throughout the growth cycle. Compared to full CRNF application at different N rates, this method also reduces nitrate N leaching in the soil. The 0-60 cm soil layer was primarily influenced by increasing the proportion of CRNF, especially from jointing to maturity. CRNF promotes a higher plant population during the turning green and jointing stages by increasing soil N content, thereby establishing a strong yield foundation for winter wheat. It increases winter wheat N accumulation and correlates positively with soil N content during key growth stages.
Conclusion: Winter wheat grain yield has increased, with significant yield increases observed at 70% blending with a higher amount of N at 240 kg ha-1 and achieved a 2.8% increase in NUE and a 3.0%-15.3% increase in grain yield. In order to improved winter wheat yields through effective N utilization, N2 application (240 kg ha-1) with the combination of (F4) 30% ONF + 70% CRNF would be recommended for northwest region of Shaanxi province in China. By increasing the amount of N accumulation at the anthesis stage, N transport is significantly increased after anthesis, and N accumulation and distribution ratio in grains are significantly increased at maturity.
Highlights
● Increasing CRNF increased soil nitrate N content and reduced leaching across winter wheat growth.
● Combination of CRNF and ONF increased DM accumulation from jointing to maturity in winter wheat.
● CRNF at 70% combined with ONF increased N accumulation, N uptake and N use efficiency of winter wheat.
● Using 70% CRNF combined with ONF at 240 kg ha-1 overcame the bottleneck of increasing the yield and NUE.
1 Introduction
Farmers were using fertilizers from the ancient time itself, but the long-term use of fertilizers had affected the soil fertility which led to pollution of water, air, and soil. Nitrogen (N), particularly in the form of urea, is an essential nutrient fertilizer, which has been critical for increasing plant growth and yield and is widely used to maintain soil fertility (Dimkpa et al., 2020). China is the largest user of urea, which has been used to increase crop production and address food security challenges (Snapp et al., 2023; Gu, 2023). According to statistics, synthetic N input to field crops in China has increased by 215% since 1980 (Zhang et al., 2022a). However, crop N uptake has only increased by 109% in the last 30 years, resulting in lower N fertilizer recovery efficiency (Yan et al., 2014). When urea is applied to farmland, nutrients are rapidly released, and a significant portion is lost due to ammonia volatilization and nitrate N leaching, which are the primary causes of low N utilization efficiency (NUE) (Hussain et al., 2022; Xiao et al., 2019). Furthermore, applying more N than the crop requirement may disturb groundwater, surface water, and atmosphere via N leaching, runoff, and volatilization (Ntinyari et al., 2022), resulting in a waste of resources and energy, as well as an increase in environmental pollution and production costs (Hussain et al., 2023b). Additionally, low NUEs lead to lower economic returns for growers from their fertilizer investments (Snapp et al., 2023).
Global reliance on winter wheat as a primary food source is increasing, with demand expected to double in the 21st century, exceeding current production requirements (Wu et al., 2023; Erenstein et al., 2022). Wheat production is reducing due to numerous factors such as environmental stresses, late sowing, lack of high-quality seeds, climate variability, and insect pests. Fertilizer use must be optimized to address environmental concerns while ensuring global food security (Anderson et al., 2020). The Chinese Ministry of Agriculture introduced the ‘Zero Increase Action Plan’ a strategy to boost crop yields and mitigate environmental issues without increasing fertilizer usage (Liu et al., 2016). This policy proposed several management practices for optimal N fertilizer application, one of which is the development of a controlled-release N fertilizer (CRNF), which provides a new theoretical method for simple and efficient fertilization technology for field crops (Vejan et al., 2021).
Controlled-release urea (CRU) is a new type of urea fertilizer with a physical coating that ensures controlled N release into the soil over time to ensure a continuous supply of N, thereby improving crop N demand and supply coordination (Zhang et al., 2022; Vejan et al., 2021). It is frequently used as a basal fertilizer because it saves labor costs for split application compared to regular urea and improves the synchronization of N supply to soil (Geng et al., 2015; Ma et al., 2021). Various studies have confirmed that the application of CRU significantly increased the NUE and yield of winter wheat (Yang et al., 2011; Zhang et al., 2022; Ma et al., 2021; Zheng et al., 2016; Zhu et al., 2020). For example, Zhou et al. (2023) proposed CRU optimization and stated that CRU proportion was more critical than CRU longevity, reporting that under N treatments of 157.5, 180, and 225 kg ha-1, the optimal ranges of CRU proportion were 41~64%, 38~64%, and 24~40% for wheat yield, respectively. In another study, Li et al. (2020) reported that irrigation management and CRU significantly impacted maize growth and development, enhancing plant dry matter (DM) accumulation and N uptake. Similarly, Zheng et al. (2016) reported in a 5-year study of CRU in a wheat-maize cropping system that the application of CRU as a basal fertilizer outperformed normal urea (NU) applied as split fertilization with the same quantity of N application.
Winter wheat has a more extended growing season and requires more labor, which is becoming expensive, so it is vital to promote the use of CRU in wheat cultivation and save labor costs. The CRU application is sub-optimal, so the combination of CRU and NU can make soil N supply more consistent with winter wheat N demand, increase N absorption, and affect wheat grain quality characteristics (Zhang et al., 2018; Zhou et al., 2019). A combination of CRU and NU should be used as a base fertilizer for winter wheat for winter wheat balances N supply, overcoming initial slow release and ensuring long-term availability (Zhang et al., 2022; Li et al., 2018). As a result, this combination is a potential N fertilizer management strategy for increasing wheat grain yield and protein content, and its mechanism should be thoroughly investigated.
Previous research has primarily focused on the release timing of CRNF related to crop N uptake and the resulting yield benefits. However, more research is needed to understand how CRNF responds to variations in soil N availability and N supply capacity. We hypothesized that combining CRNF and ONF would make the soil N supply more consistent with the N demand of winter wheat, increase N absorption in winter wheat, and possibly affect grain yield. Based on this, the current experiment used different blending ratios of CRNF and ONF to explore the soil N supply situation during the entire growth period of winter wheat. The current study aims to investigate winter wheat growth under different soil N supply conditions and to analyze how different blending ratios of CRNF and ONF can affect soil nutrient dynamics and winter wheat productivity. The regulatory pathways and mechanisms of different CRNF and ONF mixing ratios on N accumulation and transport, and the physical properties of winter wheat will be investigated, in order to develop high-quality, appropriate, and effective fertilization solutions.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Experimental site and materials
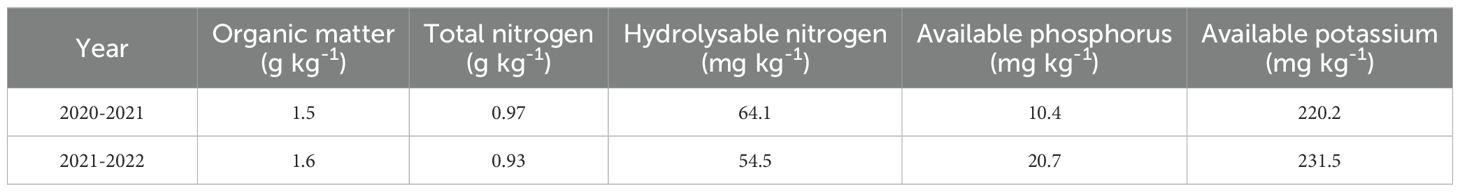
The experiment was conducted during two wheat growing seasons from 2020 to 2022 at the an experimental demonstration site of Northwest A&F University, in Liangma Village, Wugong County, Xianyang City, Shaanxi Province (34°21’N, 108°02’E). The experimental site has an altitude of 443 m, with an average annual rainfall of 504.6 mm and a temperature of 14.37°C. The cropping system of the experimental site was summer maize-winter wheat rotation. All maize residue was crushed during the experiment and returned to the field after harvest. The average daily temperature and rainfall in the two-winter wheat cropping season (2020-2022) are shown in Figure 1. The physical and chemical properties of the soil (0-20 cm) in the soil layer before sowing for the two years are shown in Table 1.
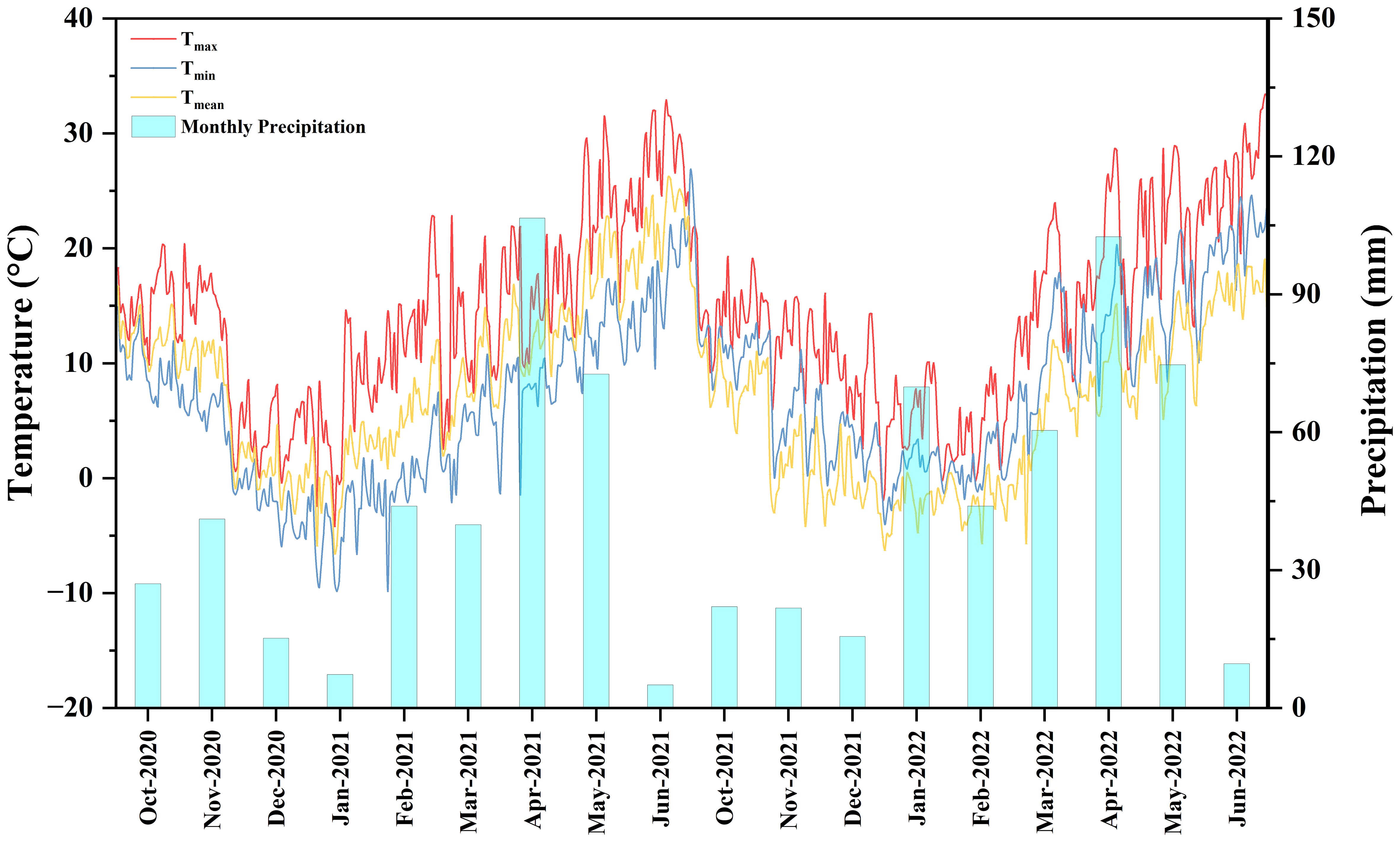
Figure 1. Daily precipitation and temperature during the winter wheat growing season from 2020-2022.
This study used the winter wheat cultivar ‘Xinong 20’, which is widely grown locally. The N fertilizers included in this study were resin-coated urea (CRNF 44%, N) and ordinary urea (ONF 46.4% N). The controlled-release period was 90 days, and it was supplied by Weituoer Company, Yangling District, Shaanxi Province. Potassium chloride (K2O 60%) and heavy superphosphate fertilizer (P2O5 46%) were utilized as potassium and phosphate fertilizer, respectively.
2.2 Experimental design
The experiment used a randomized complete block design with two factors and three replications. The factors include two N application rates (N1, 192 kg ha-1; N2 240 kg ha-1) of ONF and different blending ratios of CRNF and ONF are set under two N application rates, which were 100% ONF (F1), 70% ONF + 30% CRNF (F2), and 50% ONF + 50% CRNF (F3), 30% ONF + 70% CRNF (F4), and 100% CRNF (F5). The N2 (240 kg ha-1) is the local conventional N application amount while N1 (192 kg ha-1) is a 20% reduction in N. The application rate of phosphorus and potassium fertilizers in all treatments was the same, 120 kg ha-1. Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium fertilizers were applied as basal fertilizers in every treatment. The area of the test plots was 10 m length × 2 m width (20 m2). The winter wheat for 2020-2021 was planted on October 26 and harvested on June 11, while the winter wheat for 2021-2022 was planted on October 17 and harvested on June 9. Irrigation, weeding, and other management practices during the growth period of winter wheat are the same as those of local farmers.
2.3 Sampling and measurements
2.3.1 Soil nitrogen dynamics
Two core soil samples were collected from the 0-10, 10-20, 20-30 and 30-40 cm soil layers using an auger having an inner diameter of 4.0 cm. Soil samples were collected and stored in a labeled plastic bag from each plot during the overwintering, greening, jointing, and anthesis stages of winter wheat. Soil samples were collected from the 0-200 cm soil layer at maturity stage. After air drying, the soil sample was sieved and weighed 5.0 g (accurate to 0.001), were extracted with 50 mL of 1 mol L-1 KCl, shaken for 30 minutes, then filtered, and the soil nitrate N and ammonium N content were measured using the continuous flow analyzer (Model AA3-A001-02E, Bran-Luebbe, Germany) in the laboratory (Markus et al., 1985).
2.3.2 Dry matter accumulation and distribution
Plant samples were taken during the overwintering, greening, jointing, anthesis, and maturity stages to determine the aboveground DM accumulation and distribution. Stem, leaves, and spike were sampled at overwintering, greening, jointing, and anthesis stages, while stem, leaves, rachis+glume, and grain were sampled at the maturity stage. The separated plants were placed in an oven at 105°C for 30 minutes and dried at 70°C to a constant weight. The samples were then weighed separately. The calculation formulas for each indicator are as follows:
2.3.3 Nitrogen accumulation and transport in plants
The N content of dried plant samples was determined using the semi-micro Kjeldahl N determination method after they were crushed with a plant crusher and passed through a 100-mesh sieve. The following were the calculation formula for the related indicators of N absorption, accumulation, distribution, and utilization of winter wheat:
The calculation formula for NUE related indicators is as follows:
2.3.4 Yield and its components
Plants were harvested at the maturity stage from a 2.0 m2 area from each plot. After threshing, impurities were removed, and the grains were air-dried, and adjusted standard moisture content (12%) to calculate the grain yield per hectare. In each plot, a sample of 1.0 m2 area is used for calculating number of spikes per unit area and grains number per spike. The 1000-grain weight was calculated from 1000 grains of the yield measurement samples taken for each plot to measure the yield components.
2.4 Statistical analysis
The data were recorded, analyzed and plotted using Microsoft Excel 2016, IBM SPSS 16.0 ((https://www.ibm.com/products/spss-statistics) and Origin 2023b (https://www.originlab.com/index.aspx?go=PRODUCTS/Origin), respectively. Duncan’s test was used for multiple comparisons (P < 0.05). The structural equation (SEM) model is an extension of factor analysis used to test entity theory from empirical data. It is an advanced and robust multivariate statistical method for testing complex path relationship networks. This study assumes that CRNF and ONF application directly or indirectly affect yield components; it was conducted using the ‘plspm’ package of R software, version 3.5.1. model, and report the standardization coefficient of each path in each component model. Significance tests were conducted based on the path coefficients between latent variables.
3 Results
3.1 Soil nitrogen dynamics
3.1.1 Nitrate nitrogen
Nitrate N is essential for amino acid synthesis, protein production, and promotes tillering in winter wheat. The CRNF fertilizer treatments significantly increased soil N availability. Compared to N1, the N2 application rate for soil nitrate N was significantly higher at the greening, jointing, and anthesis stages in the 0-20 cm soil layer. During the wintering period, under various CRNF treatments, the F1 and F2 treatments had significantly higher nitrate N content in the 0-40 cm soil layer (Figure 2). At the anthesis and maturity stages, the F1, F2, and F3 treatments were significantly lower than the F4 and F5 treatments. In 2021-2022, there were no significant differences in the nitrate N content in the 0-40 cm soil layer between treatments (Figure 2). Notably, the proportion of CRNF with F4 provides a more sustained supply of soil nitrate N from the regreening stage to the anthesis stage of winter wheat compared to the sole application of ONF.

Figure 2. Dynamics of soil nitrate nitrogen (NO3–N) concentrations in the 0-40 cm soil layer under various combinations of ONF and CRNF treatments at before wintering stage (WS), regreening stage (RGS), jointing stage (JS), anthesis stage (AS) and maturity stage (MS) for the winter wheat planted a) 2020-2021 and b) (2021-2022) growing season. CRNF and ONF are set under two N application rates N1 (192 kg ha-1) N2 (240 kg ha-1) of ONF (F1) 100% ONF, (F2) 70% ONF + 30% CRNF, (F3) 50% ONF + 50% CRNF, (F4) 30% ONF + 70% CRNF, and (F5) 100% CRNF.
3.1.2 Ammonium nitrogen
Ammonium N promotes and stimulates root growth and development, enhancing water and nutrient uptake. The soil ammonium N content in the 0-40 cm soil layer was lower in 2020-2021 than in 2021-2022 (Figure 3). There was no significant difference in ammonium N content between the two N application rates at the wintering, regreening, and jointing stages. When the proportion of CRNF was increased to 70%, higher ammonium N content was observed at the regreening and jointing stages in the 0-20 cm soil layer among different CRNF treatments (Figure 3). At jointing stage, the performance of ammonium N in soil was ranked as follow: F4> F3, F5> F1, F2. The results show that the ammonium N content in 0-40 cm soil is generally lower than the nitrate N content, as the proportion of CRNF increases in the winter wheat regreening and jointing stages.
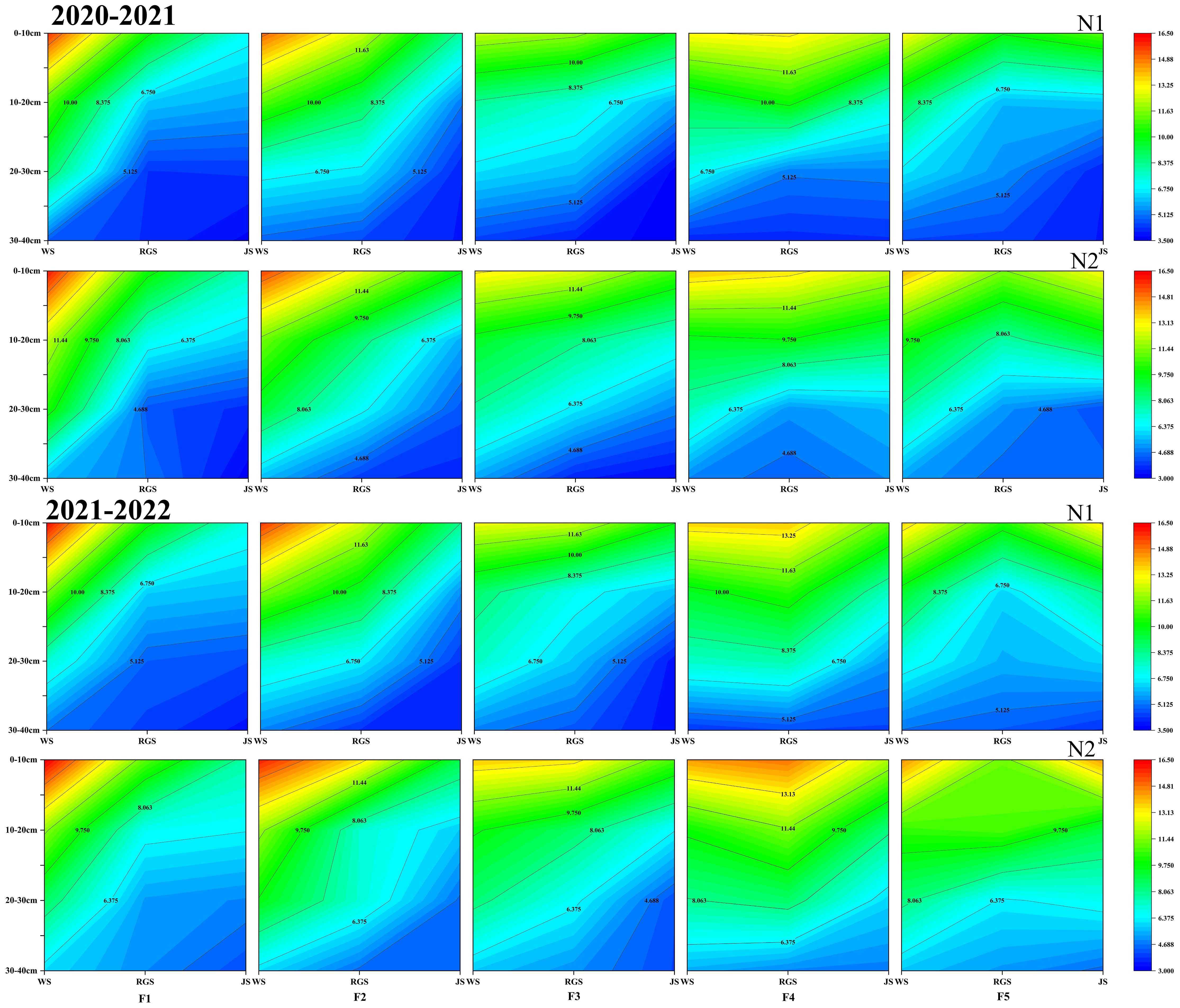
Figure 3. Dynamics of soil ammonium N (NH4+-N) concentration in 0-40 cm soil layer under various combinations of ONF and CRNF treatments at before wintering stage (WS), regreening stage (RGS) and jointing stage (JS) for the winter wheat planted a) 2020-2021 and b) (2021-2022) growing season. CRNF and ONF are set under two N application rates N1 (192 kg ha-1) N2 (240 kg ha-1) of ONF (F1) 100% ONF, (F2) 70% ONF + 30% CRNF, (F3) 50% ONF + 50% CRNF, (F4) 30% ONF + 70% CRNF, and (F5) 100% CRNF.
3.1.3 Soil nitrate nitrogen at maturity stage
The soil nitrate N content at 0-100 cm during the winter wheat maturity period in 2021-2022 was generally higher than in 2020-2021 (Figure 4). The nitrate N accumulation in the 100-200 cm soil layer was significantly higher in the N2 application of N rates, when the proportion of CRNF is 0%, 30%, and 50%. The nitrate N accumulation in the 100-200 cm soil layer showed no significant difference between N1 and N2 application rates when the proportion of CRNF is 70% and 100% (Figure 4). Overall, nitrate levels are relatively low, but notable increases are observed between 80-120 cm depth, likely originating from previous seasons’ excessive rainfall and irrigation. The results showed that increasing the amount of ONF applied promotes downward leaching of soil nitrate N, which is detrimental to winter wheat absorption and utilization. CRNF leaches less soil nitrate N and can provide more soil N supply than ONF due to its slower release rate in the early stage. The amount of CRNF applied should be increased appropriately.
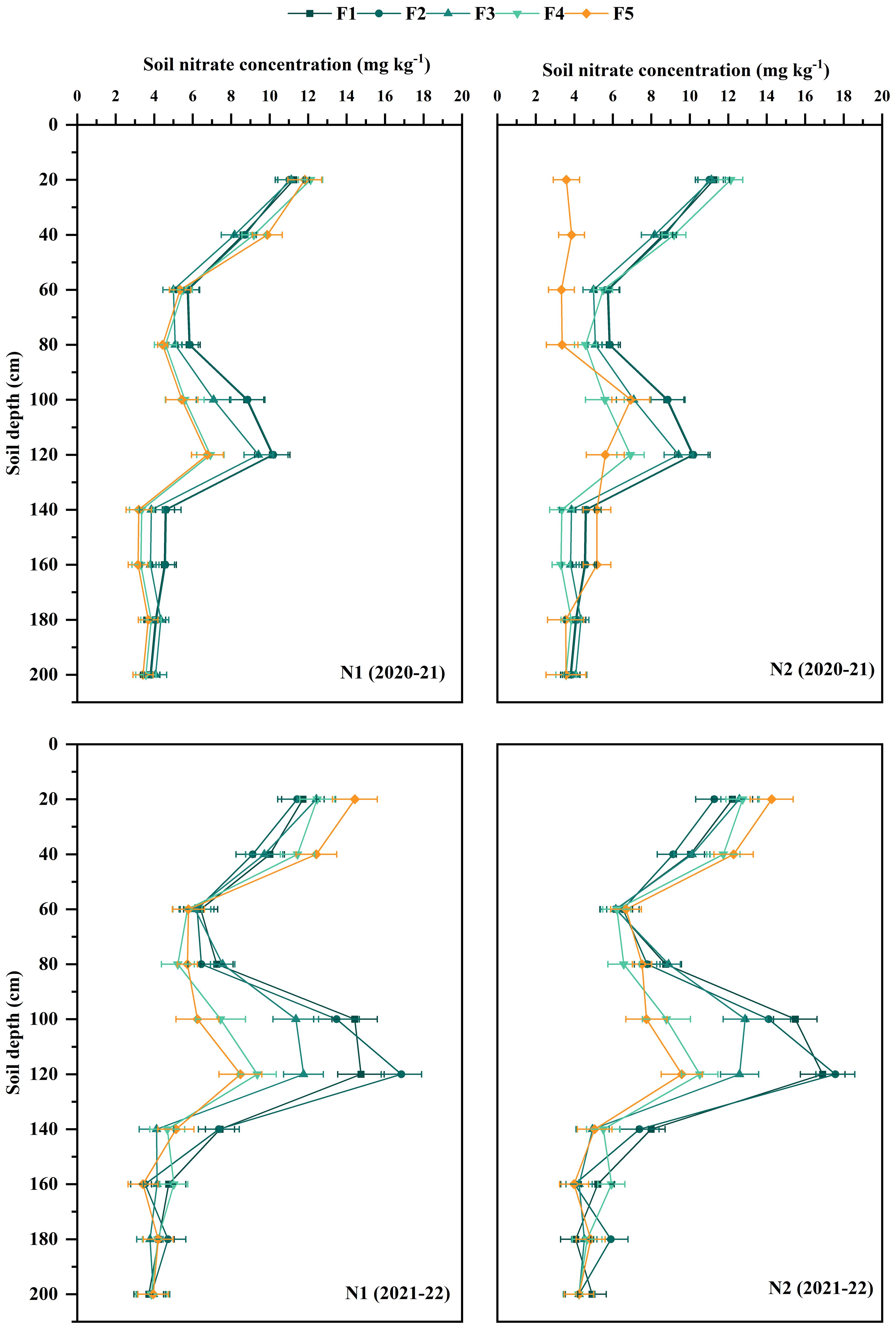
Figure 4. Nitrate N concentration in 0-200 cm soil layer at maturity stages under various combinations of ONF and CRNF treatments for the winter wheat planted (2020-2022) growing season. CRNF and ONF are set under two N application rates N1 (192 kg ha-1) N2 (240 kg ha-1) of ONF (F1) 100% ONF, (F2) 70% ONF + 30% CRNF, (F3) 50% ONF + 50% CRNF, (F4) 30% ONF + 70% CRNF, and (F5) 100% CRNF.
3.2 Dry matter accumulation and transport
3.2.1 Dry matter accumulation dynamics
Dry matter (DM) accumulation and transport play pivotal roles in winter wheat development and yield, progressively increasing throughout the growth period. The DM accumulation in 2021-2022 was overall higher than that in 2020-2021. Under the two ONF application rates, the N2 nitrogen application rate was significantly more significant than the N1 nitrogen application rate during the entire growth stages of winter wheat (Figure 5). For the proportions of CRNF, there was no significant difference between the blending ratio treatments at the wintering and greening stage; the DM accumulation of winter wheat was higher in the F2 and F3 treatments than in the other treatments. At the jointing stage, the N1 ONF application rate and the F4 and F5 treatments were significantly higher than others. Under the N2 ONF application rate, the F4 treatment was significantly higher than the other treatments. At the anthesis and maturity stages, the differences in DM accumulation between different treatments were consistent with the dynamics of the winter wheat population. As the proportion of CRNF increases, the DM accumulation of winter wheat at the anthesis and maturity stages increases. It shows that ONF treatment has obvious advantages before the jointing stage. In contrast, applying CRNF has increased DM accumulation at the anthesis and maturity stages.
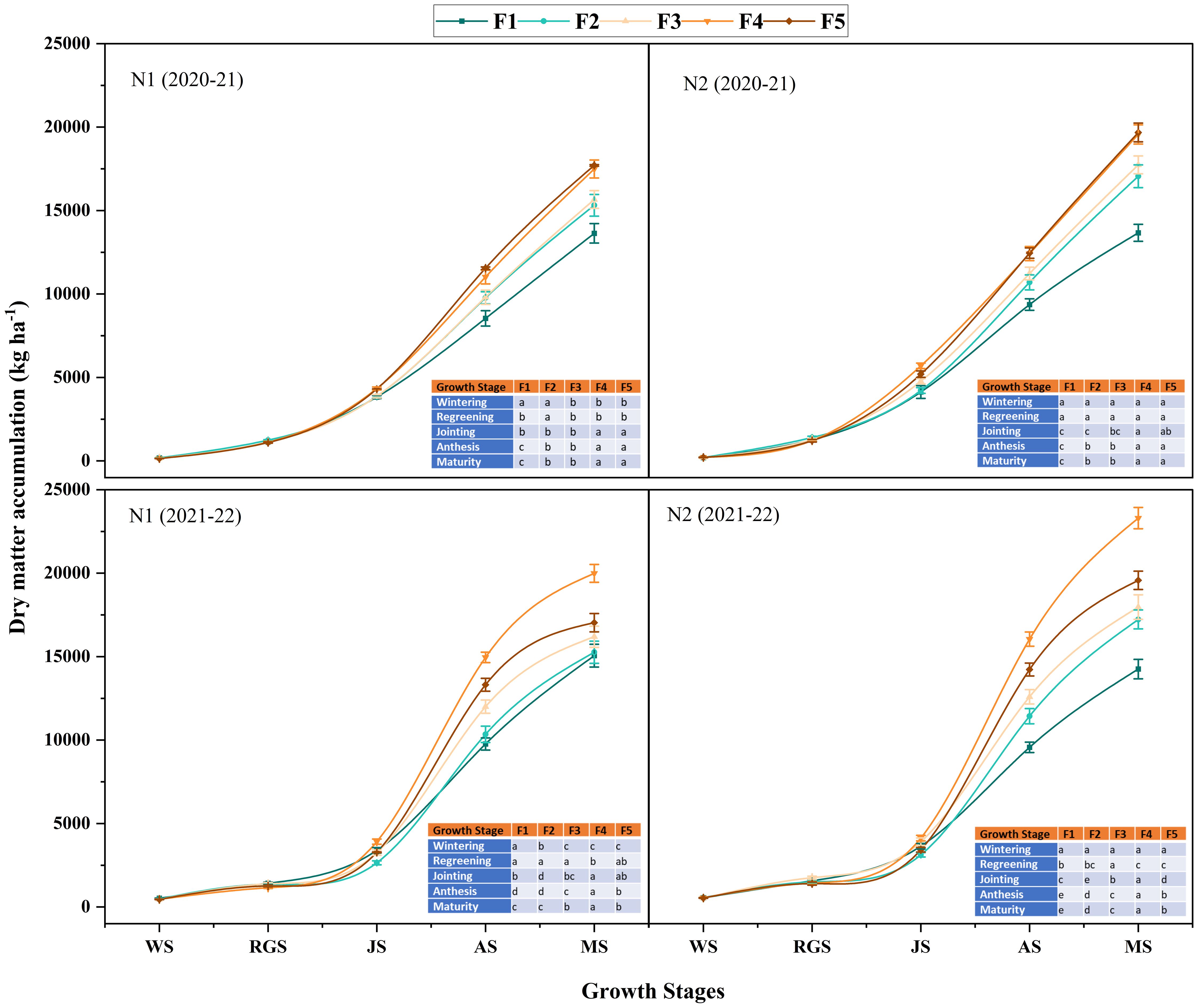
Figure 5. Dynamic changes of dry matter accumulation amounts of winter wheat under various combinations of ONF and CRNF treatments at before wintering stage (WS), regreening stage (RGS) and jointing stage (JS) for the winter wheat planted a) 2020-2021 and b) (2021-2022) growing season. Small letters indicate a significant level of 5% difference. CRNF and ONF are set under two N application rates N1 (192 kg ha-1) N2 (240 kg ha-1) of ONF (F1) 100% ONF, (F2) 70% ONF + 30% CRNF, (F3) 50% ONF + 50% CRNF, (F4) 30% ONF + 70% CRNF, and (F5) 100% CRNF.
3.2.2 Dry matter distribution in various organs
The ranking of DM accumulation and distribution ratio among different organs at maturity for both years was as follows: grain > stem and sheath > spike axis and glume > leaf (Figure 6A). When comparing the F4 treatment of CRNF to the other treatments, the DM accumulation of grains at the maturity stage was significantly higher in the F4 treatment. The DM content in the stem + leaf sheath, spike axis + glume, and leaves was significantly higher in the F4 treatment (Figure 6). It suggests that increasing the amount of N application can significantly increase the DM distribution of each organ during the maturity stage without significant changes in the distribution ratio (Figure 6B). A high proportion of CRNF is beneficial for increasing DM accumulation in each organ during the maturity stage, which is helpful for winter wheat.
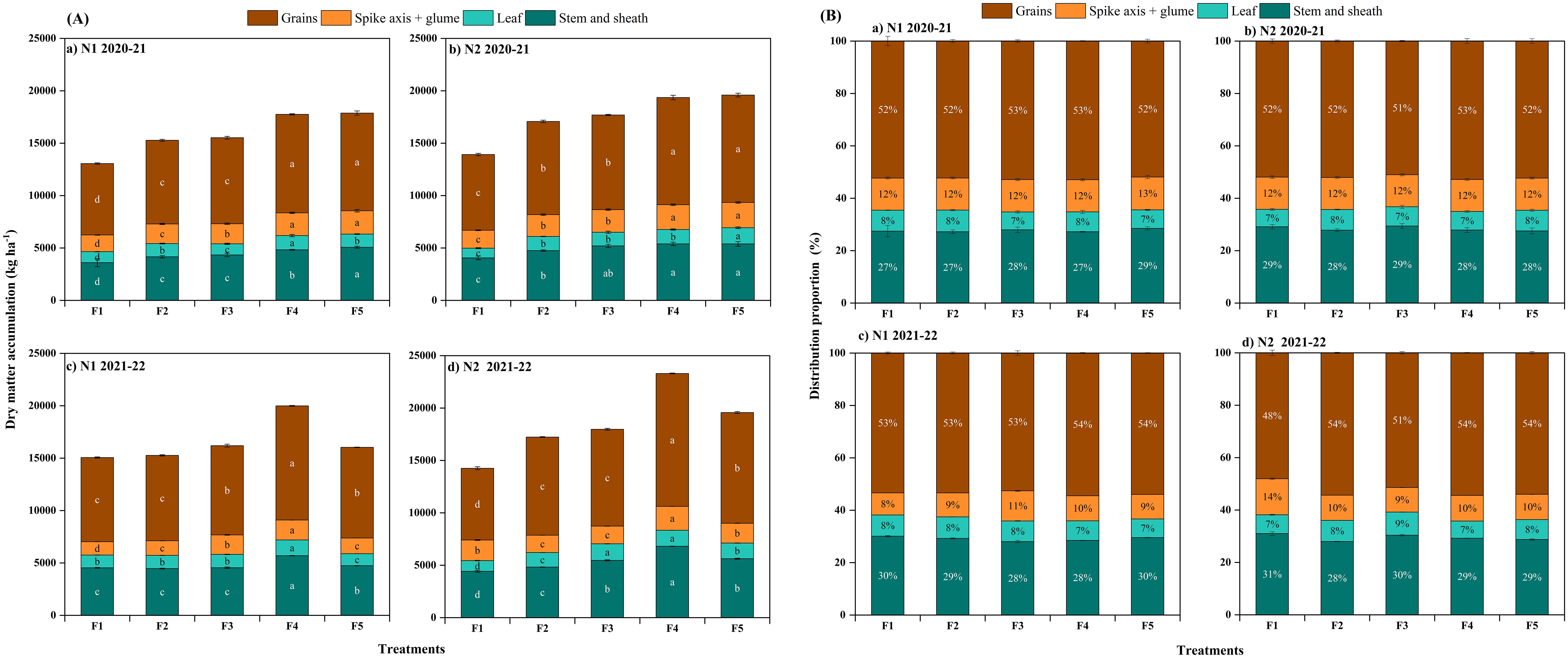
Figure 6. Plant dry matter accumulation (A) and distribution proportion (B) in different organs of winter wheat under various combinations of ONF and CRNF treatments at anthesis stage for the winter wheat planted in 2020-2021 and 2021-2022 growing seasons. Small letters indicate a significant level of 5% difference; CRNF and ONF are set under two N application rates N1 (192 kg ha-1) N2 (240 kg ha-1) of ONF (F1) 100% ONF, (F2) 70% ONF + 30% CRNF, (F3) 50% ONF + 50% CRNF, (F4) 30% ONF + 70% CRNF, and (F5) 100% CRNF.
The translocation amount, transport efficiency, and contribution rate of assimilates stored in vegetative organs before anthesis of winter wheat in 2021-2022 are significantly higher than in 2020-2021, while post-anthesis assimilates in the grains and their contribution rate to the grains was significantly lower in 2020-2021 (Table 2). The results show that increasing the amount of N can increase the distribution of assimilates in the grains after anthesis; appropriately increasing the proportion of CRNF can increase the assimilates amount stored in the vegetative organs before anthesis and the distribution of assimilates in the grains after anthesis. There is no significant difference in the contribution rate of DM to grains before and after anthesis. Among CRNF treatments, the transfer amount of assimilates stored in vegetative organs before anthesis was significantly higher in the F4 and F5 treatments than in other treatments; the distribution amount of assimilates in the grains after anthesis was significantly higher in the F4 treatment.

Table 2. Dry matter assimilation and its contribution to grain of winter wheat after anthesis under different treatments.
3.3 Nitrogen accumulation and transport
3.3.1 Nitrogen accumulation dynamics
Under different N application rates, N accumulation at different growth stages in 2021-2022 was significantly higher than in 2020-2021. During winter wheat’s anthesis and maturity stages, the treatment N2 accumulated more N than N1 (Figure 7). There was no significant difference between treatments with different proportions of CRNF at the wintering, regreening, and jointing stages (Figure 7). At the anthesis and maturity stages, the F4 treatment was significantly higher than other treatments, and the overall performance was F4>F5, F3>F2, and F1, with significant differences between treatments. The rules for each treatment’s blending ratio were consistent with the anthesis stage. The results showed that increasing the amount of N applied can increase the N accumulation in winter wheat at the anthesis and maturity stages.
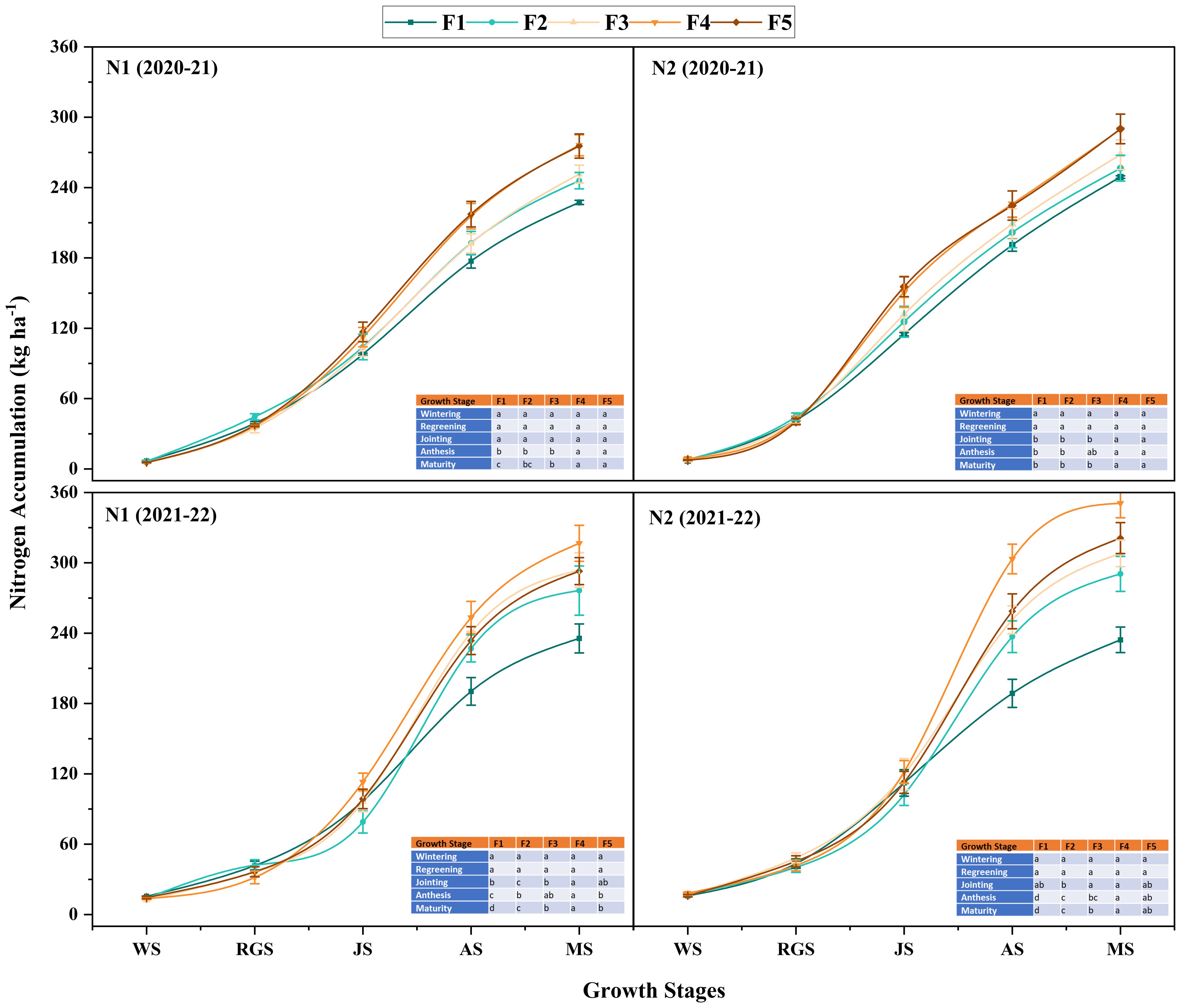
Figure 7. Dynamic changes of nitrogen accumulation amount of winter wheat under various combinations of ONF and CRNF treatments at before wintering stage (WS), regreening stage (RGS) and jointing stage (JS) for the winter wheat planted a) 2020-2021 and b) (2021-2022) growing season. Small letters indicate a significant level of 5% difference; CRNF and ONF are set under two N application rates N1 (192 kg ha-1) N2 (240 kg ha-1) of ONF (F1) 100% ONF, (F2) 70% ONF + 30% CRNF, (F3) 50% ONF + 50% CRNF, (F4) 30% ONF + 70% CRNF, and (F5) 100% CRNF.
3.3.2 Nitrogen distribution in various organs
The N accumulation in mature winter wheat grains did not differ significantly between the two years; however, the N distribution amount and distribution ratio of the stem + sheath, rachis + glume, and leaves were significantly higher in 2021-2022 (Figure 8A). The amount of N distributed in the grains at maturity was significantly higher in the F4 treatment of CRNF. The overall performance was F4>F5>F3>F2>F1, with significant differences between treatments (Figure 8). The results showed that appropriately increasing the amount of N can increase the amount of N distributed and the distribution ratio in winter wheat grains during the maturity stage while decreasing the amount of N distributed and the distribution ratio in leaves (Figure 8B). Increasing the proportion of CRNF improves the N distribution of vegetative organs. The grain N accumulation and distribution ratio reaches its maximum when the proportion of CRNF is at 70%.
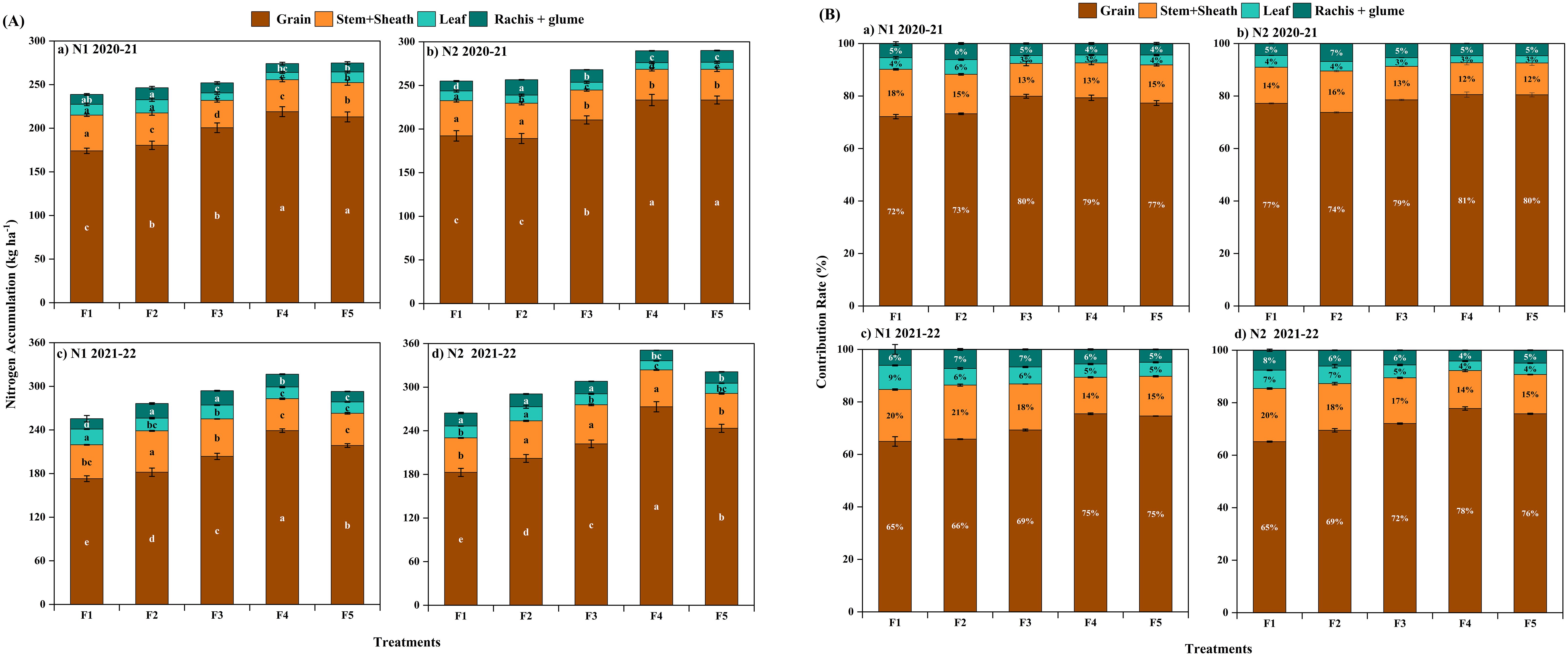
Figure 8. Nitrogen accumulation (A) and distribution proportion (B) in different organs of winter wheat under various combinations of ONF and CRNF treatments at anthesis stage for the winter wheat planted in 2020-2021 and 2021-2022 growing season. Note: Small letters indicate a significant level of 5% difference; CRNF and ONF are set under two N application rates N1 (192 kg ha-1) N2 (240 kg ha-1) of ONF (F1) 100% ONF, (F2) 70% ONF + 30% CRNF, (F3) 50% ONF + 50% CRNF, (F4) 30% ONF + 70% CRNF, and (F5) 100% CRNF.
3.3.3 Nitrogen redistribution
The contribution rate of post-anthesis N to grain N, the transport efficiency of pre-anthesis N in winter wheat, and the contribution of pre-anthesis N to grain N were given in Table 3. The pre-anthesis N transfer amount and post-anthesis N accumulation amount of N application N2 were significantly higher than those of N application N1. The amount of pre-anthesis N transport in the F4 treatment of CRNF was significantly higher than others. The overall performance was F4>F5>F3>F2>F1, and have significant differences between treatments (Table 3). The contribution rate of pre-anthesis N to grain N was significantly lower in the F1 treatment. The F1 treatment has the lowest post-anthesis N accumulation, and the F1 treatment has a significantly higher post-anthesis N contribution rate to the grains. The results show that increasing the N application rate can increase the N accumulation in winter wheat grains during maturity by increasing pre-anthesis N transport and post-anthesis N accumulation. Increasing the grain accumulation of winter wheat at maturity relied on enhancing both the amount and efficiency of N transport before anthesis.
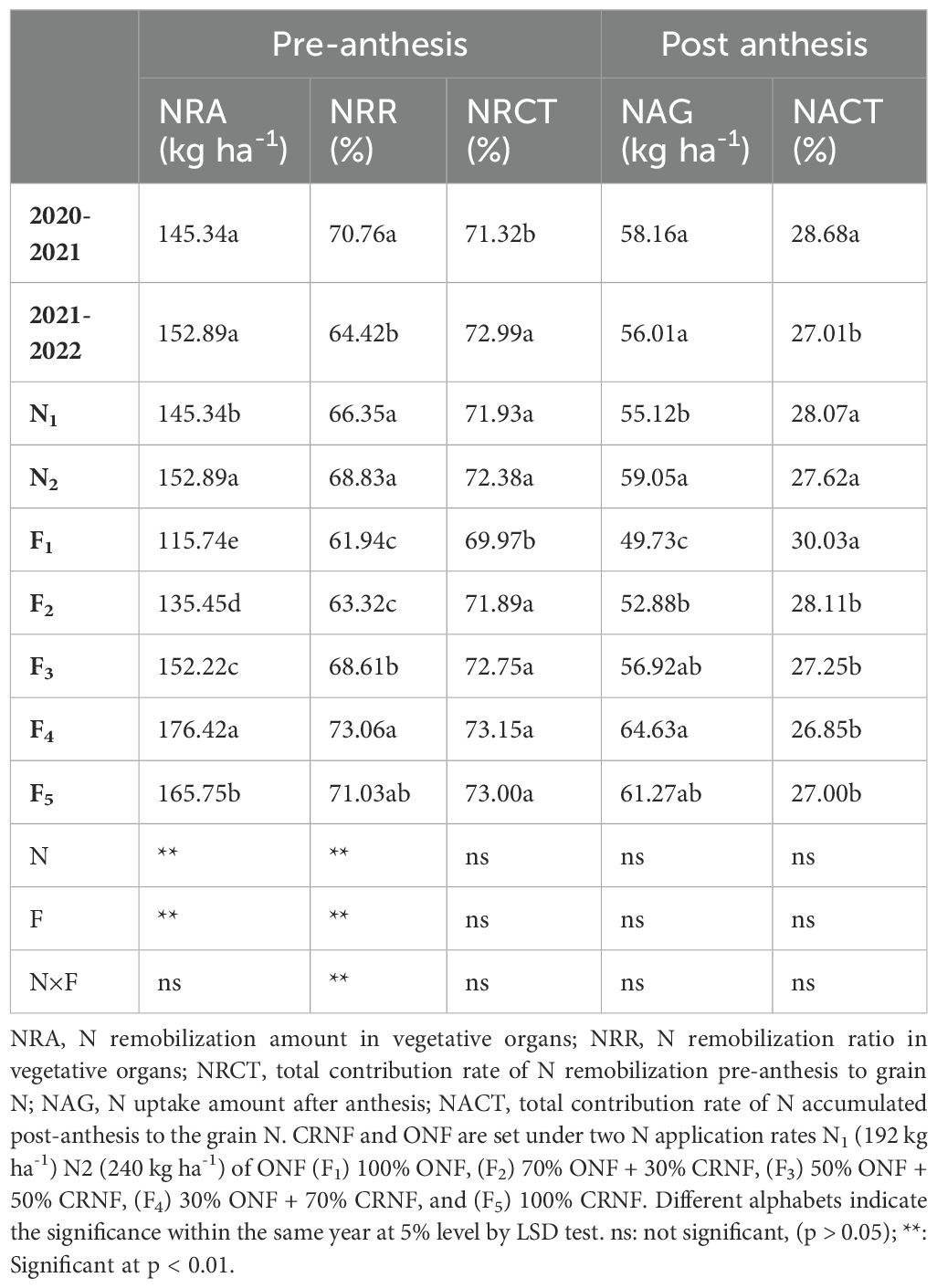
Table 3. Effects of different ONF and CRNF treatments on nitrogen redistribution in winter wheat plants.
3.4 Nitrogen utilization efficiency
The N use efficiency (NUE), N uptake efficiency (NUpE), and N fertilizer partial productivity (NFPP) in 2021-2022 are significantly higher than that in 2020-2021. The NUE revealed no significant difference in N1 and N2 application amounts of ONF when the proportion of CRNF was F4 (70%) and F5 (100%) (Figure 9). For both years, the CRNF treatment F4 combined with ONF at N2 had the highest NUpE and NFPP, significantly higher than the other treatments. There was no significant difference in NUE between N1 and N2 of ONF for the CRNF for F4 treatment, although when the N application amount increased, the NUE did not change significantly. Appropriately increasing the proportion of CRNF can improve winter wheat’s NUE, NUpE, and NFPP in comparison to the F1 of CRNF; the NUE of the F4 treatment increased by an average of 2.14% under the N2 application of ONF in both years.
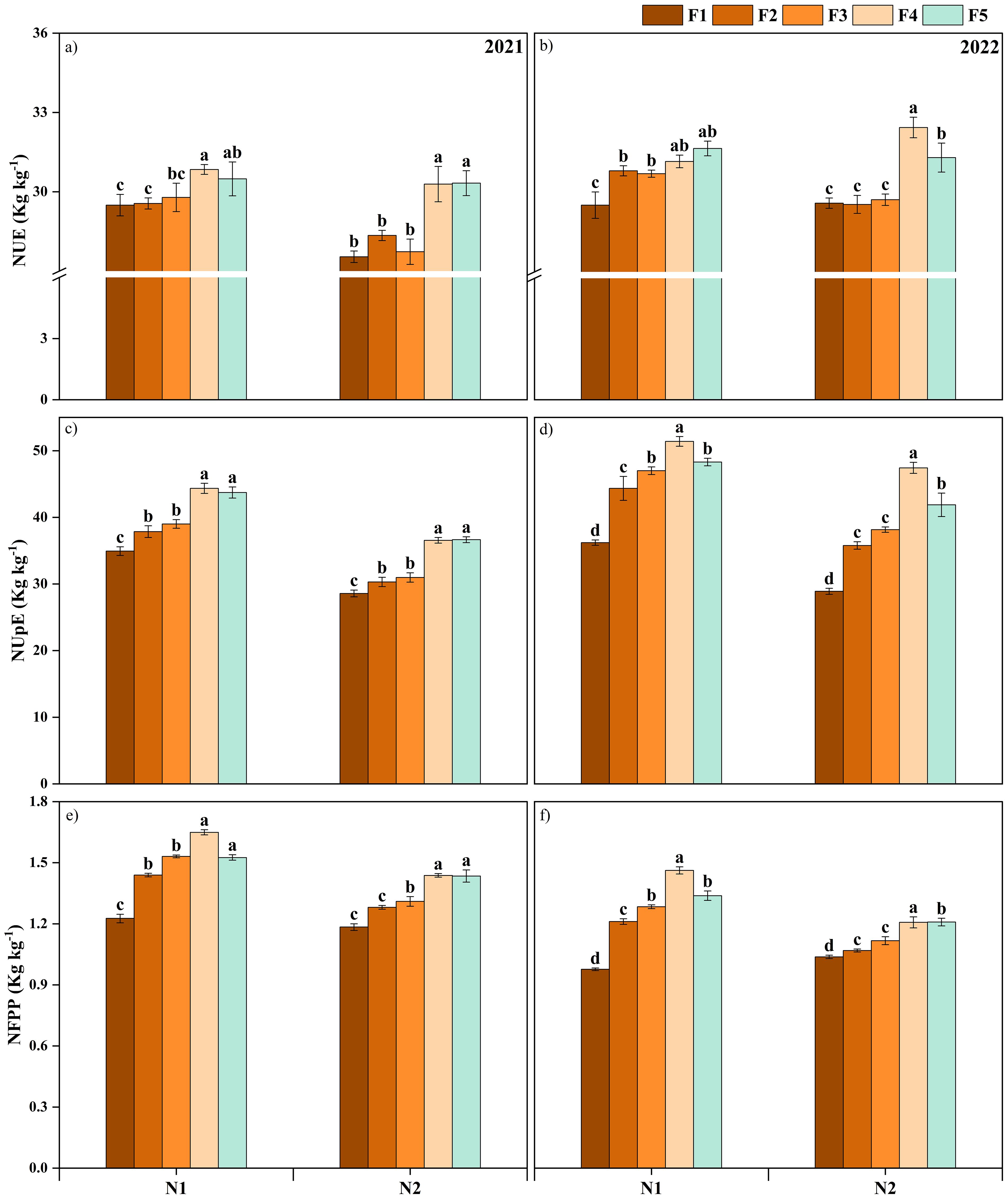
Figure 9. Nitrogen use efficiency (a, b) nitrogen uptake efficiency (c, d) nitrogen fertilizer partial productivity (e, f); winter wheat under various combinations of ordinary nitrogen fertilizer and controlled released nitrogen fertilizer treatments for the winter wheat planted 2020-2022 growing season. CRNF and ONF are set under two N application rates N1 (192 kg ha-1) N2 (240 kg ha-1) of ONF (F1) 100% ONF, (F2) 70% ONF + 30% CRNF, (F3) 50% ONF + 50% CRNF, (F4) 30% ONF + 70% CRNF, and (F5) 100% CRNF. Vertical bars are means ± standard deviation. Different letters mean that the difference of the means between treatments was significant (LSD test, P < 0.05).
3.5 Yield and its components
Winter wheat yield and its components were significantly enhanced by the combination of CRNF with ONF for both years (p < 0.05). Compared to 2020-2021, the number of spikes, grains per spike, and grain yield in 2021-2022 were significantly higher, while the 1000-grain weight was higher in 2020-2021 than in 2021-2022 (Table 4). Winter wheat yield gradually increased in all blended treatments of CRNF. There was no significant difference in the number of grains per spike or 1000-grain weight between the two N application rates when the proportion of CRNF was 0%, 30%, or 50%. The results showed that appropriately increasing the amount of applied N can increase grain yield by increasing the number of spikes. Compared to other fertilizer applications, the maximum number of spikes, grains per spike, and grain yield were observed with treatment of CRNF 70% combined with N2 of ONF.
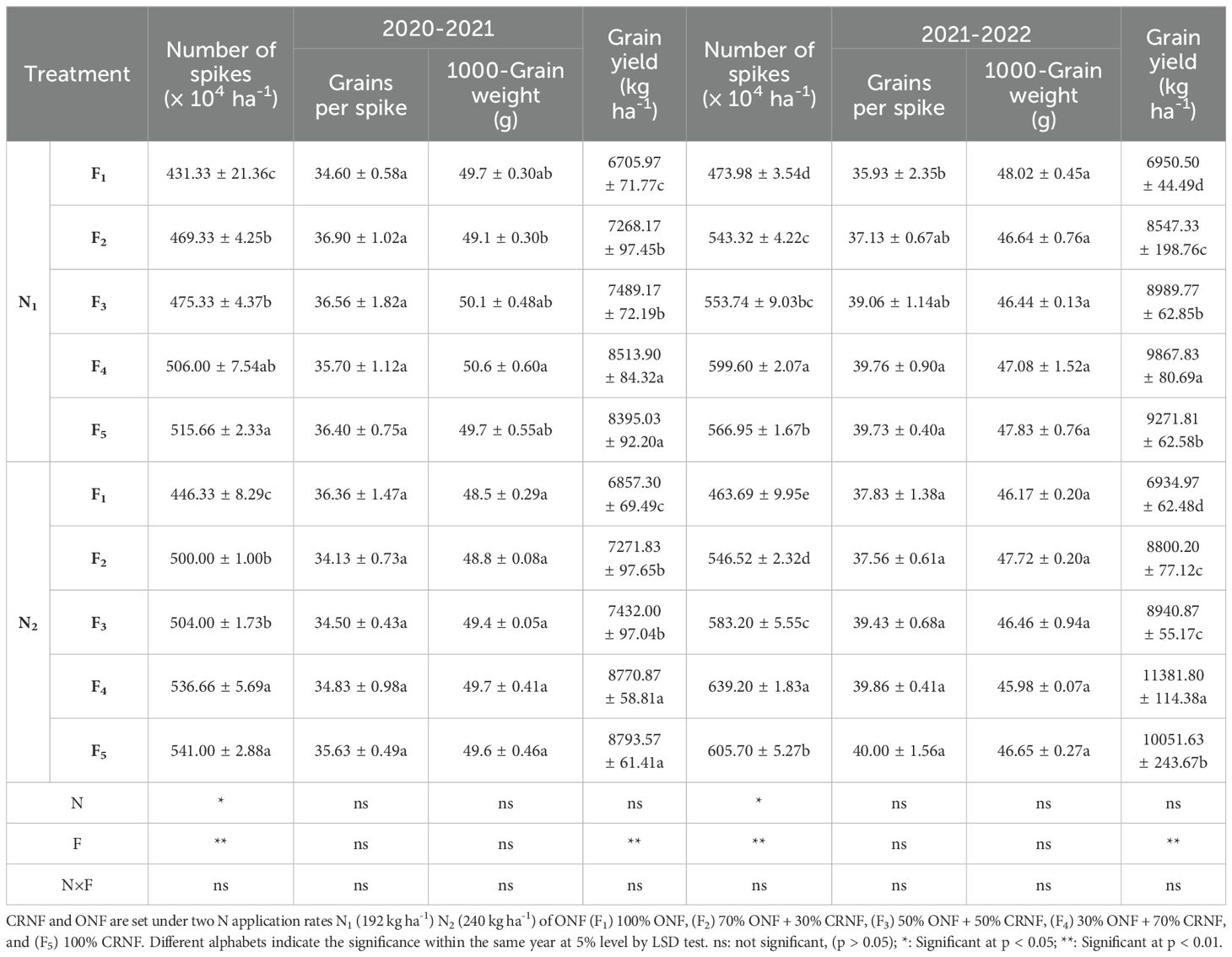
Table 4. Winter wheat grain yield and its components under various treatments of ONF combined with CRNF.
3.6 Relationship between nitrogen fertilizer dynamics to yield and its components
The linear relationship between ordinary N fertilizer (ONF), controlled released N fertilizers (CRNF), N use efficiency (NUE), uptake efficiency (NUpE), partial fertilizer productivity (NPFP) with yield and its components (Grain Number, 1000 Grain Weight, Spikes Number) combined for both the 2020–2022 growing seasons was fitted using structural equation modelling as illustrated in Figures 10A,B. The results showed that CRNF has a positive impact on NUE, NUpE, and NPFP with path coefficients (λ) of 0.704, 0.897, 0.891 respectively and indirectly increased winter wheat yield by increasing the number of grains in spikes (Figure 10). While, ONF directly affected winter wheat and increased yield (λ: 0.774), while CRNF positively impacted yield (λ: -0.064). The N application also indirectly increased yield by increasing spike number (λ: 0.686). The three N-related indexes have a direct positive effect on winter wheat yield was mainly due to the significant increase in spikes number.
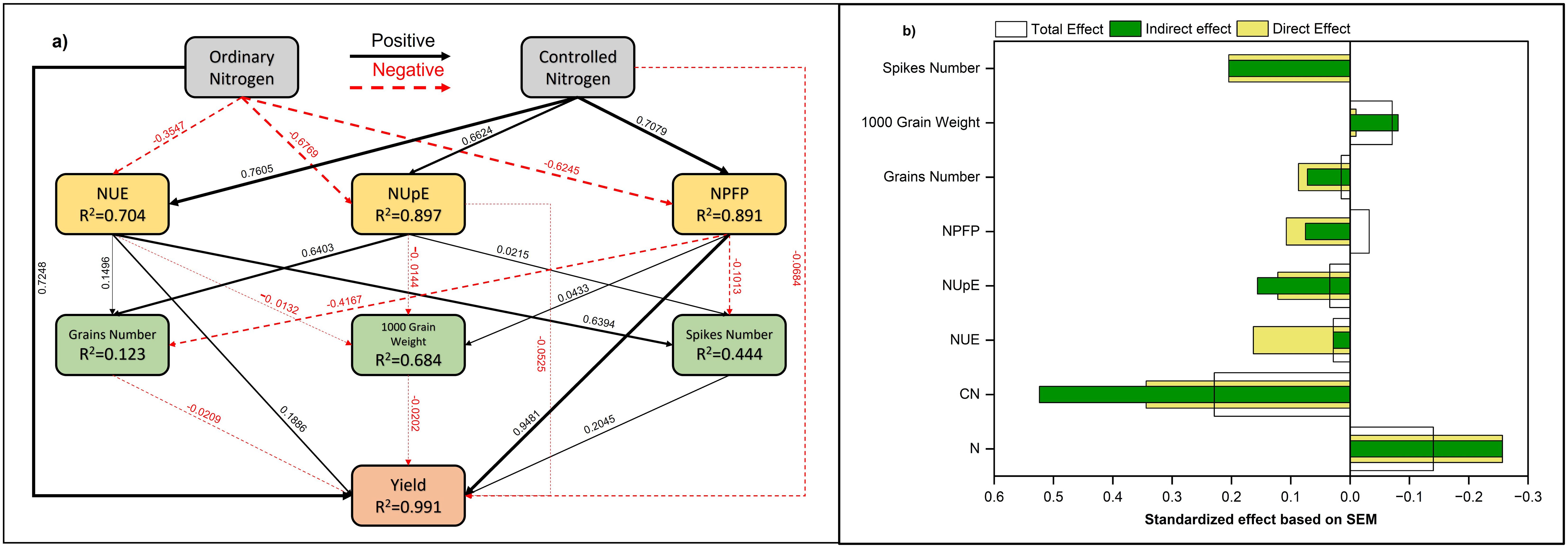
Figure 10. Relationship between ONF and CRNG and yield components of winter wheat. (A) The structural equational model (SEM) framework describing ONF and CRNF, NUE, NUpE, NPFP, grain number, 1000 grain weight, spike number, and grain yield. The red dotted lines and black solid lines are indirect and direct effects. Numbers above/below the arrow line indicate correlation. The interpretation variance (R2) ratio appears next to each indicator in the model. (B) The direct, indirect, and total effects of different potential variables on winter wheat yield are based on SEM data. N, Ordinary nitrogen; CN, Controlled nitrogen; NUE, Nitrogen use efficiency; NUpE, Nitrogen uptake efficiency; and NPFP, Nitrogen fertilizer partial productivity.
4 Discussion
4.1 Impact of CRNF on soil nitrogen supply and dry matter accumulation
Nitrogen is essential for plant growth and development, so its availability is critical for crop productivity and applying ONF combined with CRNF offers a simple and efficient framework to improve fertilizer utilization efficiency. Slowly releasing nutrients from the CRNF over time can effectively prevent N accumulation in the soil quickly, reduce nutrient loss to the environment, and thus increase nutrient availability for crops (Vejan et al., 2021; Ma et al., 2021). The results showed that the soil nitrate N and ammonium N content in the jointing and anthesis stages were higher in the CRNF treatments by 70% when combined with the N2 application of ONF. A high amount of CRNF can provide a sufficient supply of soil N in the late growth period of winter wheat. Because the N-release characteristics of CRNF are greatly affected by soil moisture content and temperature, the early nutrient release of CRNF will be too slow, and a one-time basal application will result in insufficient soil nutrient supply in the early stages of winter wheat growth (Geng et al., 2015; Ma et al., 2021). When the proportion of CRNF is 70% and ONF at N2, it can not only ensure the soil nitrate N and ammonium N content in the early growth period of winter wheat but also significantly increase the soil nitrate N and ammonium N content in the jointing stage. In this way, one-time fertilization of CRNF can meet the N demand of crops throughout the growth stages, thereby increasing grain yield and NUE, minimizing N leaching and volatilization losses, and reducing the impact on the environment (Azeem et al., 2014).
In the current study, compared to the application of ONF, the application of CRNF increases the nitrate N accumulation in the 0-40 cm soil layer of winter wheat during the maturity period, and when the proportion of CRNF is 70%, it can reduce nitrate N content in the 60-100 cm soil layer and reducing N leaching. Our study shows no significant difference in the nitrate N content in the 0-40 cm soil layer during the winter wheat maturity stage, while the nitrate N content in the 1-2 m soil layer is significantly higher than that of other treatments (Figure 4). The lowest N-releasing proportions were CRNF at 70% and 100%, and there was no significant difference in nitrate N accumulation in the 1-2 m soil layer with ONF N2 application, indicating that winter wheat requires more N in the late growth period. The soil N release in the later growth period of winter wheat is more consistent with the N uptake of winter wheat when the proportion of CRNF is 70%, thereby increasing the N accumulation during the maturity period of winter wheat while reducing N leaching risk.
Nitrogen fertilizer significantly impacts the number of tillers in the early growth stage of winter wheat. Stem and tiller dynamics are essential for regulating winter wheat population dynamics and achieving the maximum yield. Nutrient release is too slow in the early growth stage, but increasing the dosage of CRNF can increase soil nutrients before and after the jointing stage of winter wheat, significantly increasing the number of spikes at maturity (Ma et al., 2021, Ma et al., 2022a, Ma et al., 2022b). The application of CRNF at 70% combined with ONF can significantly increase the DM accumulation of winter wheat from regreening to anthesis stages compared with the other proportions of CRNF. Nishimura et al. (2022) reported a similar finding that CRNF can regulate the population size of winter wheat and increase the number of spikes per plant to varying degrees, thus increasing the number of spikes at maturity. The application of CRNF maintains a higher tiller number in the late growth stage, laying the foundation for increased yield.
Winter wheat yield formation depends on DM accumulation, particularly post-anthesis DM accumulation, which can significantly improve harvest index and grain yield (Ercoli et al., 2008; Lijuan et al., 2023). In this study, CRNF combined with ONF has increased the DM accumulation from the greening to the maturity stages by increasing the population number. The amount of stored assimilates transported by vegetative organs before anthesis increased when the CRNF (70%) was combined with ONF (N2). However, the distribution of DM in the grains following anthesis was significantly reduced (Table 2). The distribution amount was significantly higher than that of other treatments. However, there was no significant difference among the blending ratio treatments in the contribution rate of assimilates stored in vegetative organs before anthesis and assimilates after anthesis to grains. It shows that the soil nutrient supply in the treatment with CRNF (70%) is more consistent with the nutrient absorption of winter wheat. The DM accumulation increased to varying degrees during the vegetative and reproductive growth stages, thereby increasing the grain yield of winter wheat. The results are consistent with the findings of Cui et al. (2022).
4.2 Impact of CRNF on nitrogen accumulation and transport
Understanding the dynamics of nutrient accumulation in crops is essential to obtain optimum yield. The ability of a crop to accumulate nutrients varies according to the nutrients used. The translocation of pre-anthesis N to the grain is essential for winter wheat to get maximum yield (Xu et al., 2005). Our results showed that the N accumulation of CRNF (100%) combined with ONF (N2) at the greening stage of winter wheat is low. In contrast, the N accumulation increases rapidly after the jointing stage. The N accumulation of winter wheat has been significantly increased at winter wheat’s anthesis and maturity stages by improving the soil N supply at later growth stages. The N accumulation in grains includes the transfer of N from vegetative organs to the grain and N accumulation in grains after anthesis (Kong et al., 2016). Our results align with the previous findings of Abid et al. (2016), which show that increasing soil N during the early growth period increases the N content of vegetative organs. Increasing soil N in the late growth period can improve the distribution of N in grains after anthesis, resulting in higher grain N content (Chen et al., 2015). The N uptake during the maturity stage was significantly lower in combination with CRNF and ONF. As ONF releases fertilizer efficiency quickly, one-time basal fertilization of ONF cannot meet the N requirement in the later crop growth stages (Zhang et al., 2022a). The amount of N released in the early stage of CRNF is small, making N absorption by vegetative organs difficult, which is not conducive to the transport of N to the grain (Ma et al., 2023). Our findings showed that CRNF (70%) combined with ONF (N2) not only ensured the soil N supply during the greening and jointing stages of winter wheat, but also significantly increased the soil N content at the anthesis stage.
In winter wheat, the N uptake by grains has been affected by N accumulation during anthesis. When N accumulation is increased during anthesis, it can promote the transfer of N from pre-anthesis vegetative organs to the grain and inhibit post-anthesis N absorption (Wu et al., 2021). Our results showed that when the N accumulation during the anthesis period is 272.8 kg ha-1, the contribution rate of pre-anthesis N to grain N reaches the maximum. When it is lower than 272.8 kg ha-1, increasing N accumulation during the anthesis period increased the contribution rate of pre-anthesis N to grain N. The treatment with CRNF (70%) combined with ONF (N2) has increased N accumulation during the anthesis stage of winter wheat and significantly increased the transfer of N from vegetative organs to the grain, resulting in higher grain N content during the maturity stage. Although the input of assimilated N into grains after anthesis showed an increasing trend, the contribution rate of post-anthesis N to grain N showed a decreasing trend. It showed that CRNF at 70% combined with ONF (N2) can provide a good supply of soil nutrients during the reproductive growth stage of winter wheat; because winter wheat accumulates more N during the vegetative growth stage, the N in the grain is transported from the vegetative organs.
4.3 Impact of CRNF on yield and nitrogen use efficiency
Nitrogen fertilizer application is critical to the growth of winter wheat, and its management is the key to improving crop yields (Duan et al., 2019; Hussain et al., 2023a). Our results showed that increasing soil N supply after the greening stage with CRNF (70%) increased plant populations at the jointing and anthesis stages, significantly increasing wheat spikes at maturity and hence increasing the yield. Our experiment also found that when the proportion of CRNF was 0%, 30%, and 50%, there was no significant difference in yield between ONF 192 kg ha-1 and 240 kg ha-1. However, when the proportion of CRNF (70%) was combined with ONF (N2), the yield was significantly improved. Our results are in line with Yang et al. (2011) for the winter wheat yield. Compared to the sole ONF, the CRNF treatment has increased the grain yield with an average of 6.64% for both years. CRNF was applied twice (at the sowing and re-greening stage) and synchronized with the N demand of winter wheat, which has several advantages, such as significantly improved grain yield and NUE. It shows that appropriately increasing the proportion of CRNF can further unleash the potential of N fertilizer input to increase production and efficiency and break the bottleneck of increasing N without increasing production to a certain extent.
The judicious application of fertilizers ensures the supply of nutrients required for crop growth and development, reduces fertilizer losses and improves fertilizer use efficiencies (Dimkpa et al., 2020). Because the application cost of CRNF is higher than ONF’s, the cost can be reduced by combining CRNF with ONF, and the benefits of CRNF can be enhanced. In our experiment, CRNF at 70% combined with ONF (N2) application rates significantly improved N accumulation in the aboveground portion, thus improving grain yield and NUE during the maturity period. The effects of combining CRNF and ONF on NUE were variable and may be related to essential soil fertility and N fertilizer type. The results of our experiments show that a 70% CRNF combined with ONF (N2) outperforms a 20% improvement in NUE. For the improvement of NUE, our results are those of (Ma et al, 2021; Ma et al., 2022a) and Duan et al. (2019).
Our findings support the initial hypothesis, as discussed in the results and discussion sections, a combination of CRNF and ONF has numerous advantages, including 1) can provide a sufficient supply of soil N in the late growth period of winter wheat; 2) can significantly increase the dry matter accumulation of winter wheat from regreening to anthesis stages 3) synchronized the N demand of winter wheat and improved the NUE and grain yield; 4) improved the soil nutrient structure and effectively promote crop yield. Our results indicate that a combination of CRNF and ONF in different soils may be adjusted to meet crop demand for nutrients according to crop type. However, soil type and climate differences among cropping regions must be considered when changing the combination of ONF and CRNF application. Furthermore, special attention should be given to differences in types of available CRNF among crop species. This necessitates the development of predictive models that integrate climate, soil, and crop factors to optimize CRNF application and ensure maximum efficacy. Furthermore, investigating potential synergies between CRNF and other sustainable agricultural practices, such as conservation tillage and integrated pest management, can unlock new opportunities for environmentally conscious and productive farming systems.
5 Conclusion
This study examined the combinations of ONF and CRNF to investigate the soil N supply, winter wheat growth and productivity over two consecutive growing seasons. It has been found that increased CRNF application provides adequate soil N for winter wheat throughout its late growth period. When the N application rate is 240 kg ha-1, a combination of (CRNF: ONF =70:30), have increased soil N supply after the regreening stage, improved plant populations in the jointing and anthesis stages, and significantly increase the number of spikes, thereby increasing yield. This combination of CRNF with ONF have increased N accumulation during the anthesis stage, the transfer of N to the grain prior to anthesis is significantly increased, as is the grain N content and distribution ratio. It has been concluded that a controlled-release mixed N fertilizer application plan strategy is beneficial for improving grain characteristics is used to achieve high winter wheat yield and efficient N utilization.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, on request.
Author contributions
MA: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. RH: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. XL: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. DW: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Key Research and Development Technology Projects in Shaanxi Province (2023-ZDLNY-01), the Xi’an Science and Technology Plan Projects (23NYGG0001), the Key Research and Development Technology Projects in Shandong Province (2022LZGCQY002), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2022YFD2300802).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
N, Nitrogen; NUE, Nitrogen utilization efficiency; CRNF, controlled-release nitrogen fertilizer; CRU, controlled-release urea; DM, dry matter; NU, normal urea; ONF, ordinary nitrogen fertilizer; NUpE, nitrogen uptake efficiency; NFPP, nitrogen fertilizer partial productivity.
References
Abid, M., Tian, Z., Ata-Ul-Karim, S. T., Cui, Y., Liu, Y., Zahoor, R., et al. (2016). Nitrogen nutrition improves the potential of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) to alleviate the effects of drought stress during vegetative growth periods. Front. Plant Sci. 7, 981. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.00981
Anderson, R., Bayer, P. E., Edwards, D. (2020). Climate change and the need for agricultural adaptation. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 56, 197–202. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2019.12.006
Azeem, B., KuShaari, K., Man, Z. B., Basit, A., Thanh, T. H. (2014). Review on materials & methods to produce controlled release coated urea fertilizer. J. Controlled release 181, 11–21. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2014.02.020
Chen, Y., Xiao, C., Wu, D., Xia, T., Chen, Q., Chen, F., et al. (2015). Effects of nitrogen application rate on grain yield and grain nitrogen concentration in two maize hybrids with contrasting nitrogen remobilization efficiency. Eur. J. Agron. 62, 79–89. doi: 10.1016/j.eja.2014.09.008
Cui, P., Chen, Z., Ning, Q., Wei, H., Zhang, H., Lu, H., et al. (2022). One-time nitrogen fertilizer application using controlled-release urea ensured the yield, nitrogen use efficiencies, and profits of winter wheat. Agronomy 12, 1792. doi: 10.3390/agronomy12081792
Dimkpa, C. O., Fugice, J., Singh, U., Lewis, T. D. (2020). Development of fertilizers for enhanced nitrogen use efficiency–Trends and perspectives. Sci. Total Environ. 731, 139113. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139113
Duan, J., Shao, Y., He, L., Li, X., Hou, G., Li, S., et al. (2019). Optimizing nitrogen management to achieve high yield, high nitrogen efficiency and low nitrogen emission in winter wheat. Sci. Total Environ. 697, 134088. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134088
Ercoli, L., Lulli, L., Mariotti, M., Masoni, A., Arduini, I. (2008). Post-anthesis dry matter and nitrogen dynamics in durum wheat as affected by nitrogen supply and soil water availability. Eur. J. Agron. 28, 138–147. doi: 10.1016/j.eja.2007.06.002
Erenstein, O., Jaleta, M., Mottaleb, K. A., Sonder, K., Donovan, J., Braun, H. J. (2022). “Global trends in wheat production, consumption and trade,” in Wheat improvement: food security in a changing climate (Springer International Publishing, Cham), 47–66.
Geng, J., Ma, Q., Zhang, M., Li, C., Liu, Z., Lyu, X., et al. (2015). Synchronized relationships between nitrogen release of controlled release nitrogen fertilizers and nitrogen requirements of cotton. Field Crops Res. 184, 9–16. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2015.09.001
Gu, J. (2023). Optimizing irrigation and nitrogen regimes in rice plants can contribute to achieving sustainable rice productivity. Agronomy 13, 2495. doi: 10.3390/agronomy13102495
Hussain, T., Gollany, H. T., Hussain, N., Ahmed, M., Tahir, M., Duangpan, S. (2022). Synchronizing nitrogen fertilization and planting date to improve resource use efficiency, productivity, and profitability of upland rice. Front. Plant Sci. 13. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.895811
Hussain, T., Gollany, H. T., Mulla, D. J., Ben, Z., Tahir, M., Ata-Ul-Karim, S. T., et al. (2023a). Assessment and application of EPIC in simulating upland rice productivity, soil water, and nitrogen dynamics under different nitrogen applications and planting windows. Agronomy 13, 2379. doi: 10.3390/agronomy13092379
Hussain, T., Mulla, D. J., Hussain, N., Qin, R., Tahir, M., Liu, K., et al. (2023b). Optimizing nitrogen fertilization to enhance productivity and profitability of upland rice using CSM–CERES–rice. Plants 12, 3685. doi: 10.3390/plants12213685
Kong, L., Xie, Y., Hu, L., Feng, B., Li, S. (2016). Remobilization of vegetative nitrogen to developing grain in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Field Crops Res. 196, 134–144. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2016.06.015
Li, G., Zhao, B., Dong, S., Zhang, J., Liu, P., Lu, W. (2020). Controlled-release urea combining with optimal irrigation improved grain yield, nitrogen uptake, and growth of maize. Agric. Water Manage. 227, 105834. doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2019.105834
Li, J., Wan, Y., Wang, B., Waqas, M. A., Cai, W., Guo, C., et al. (2018). Combination of modified nitrogen fertilizers and water saving irrigation can reduce greenhouse gas emissions and increase rice yield. Geoderma 315, 1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2017.11.033
Lijuan, M., Ali, M. F., Xiaohu, H., Zili, P., Zulfiqar, U., Rui, W. (2023). Changes in nitrogen-related performance attributes of winter wheat varieties released between 1950 and 2020 in dryland region of China. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr. 23, 5404–5418. doi: 10.1007/s42729-023-01410-4
Liu, X., Vitousek, P., Chang, Y., Zhang, W., Matson, P., Zhang, F. (2016). Evidence for a historic change occurring in China. Environmental Science & Technology, 50, 505–506. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.5b05972
Ma, Q., Qian, Y., Yu, Q., Cao, Y., Tao, R., Zhu, M., et al. (2023). Controlled-release Nitrogen fertilizer application mitigated N losses and modified microbial community while improving wheat yield and N use efficiency. Agriculture Ecosyst. Environ. 349, 108445. doi: 10.1016/j.agee.2023.108445
Ma, Q., Sun, Q., Zhang, X., Li, F., Ding, Y., Tao, R., et al. (2022a). Controlled-release nitrogen fertilizer management influences grain yield in winter wheat by regulating flag leaf senescence post-anthesis and grain filling. Food Energy Secur. 11, e361. doi: 10.1002/fes3.v11.2
Ma, Q., Tao, R., Ding, Y., Zhang, X., Li, F., Zhu, M., et al. (2022b). Can split application of slow-release fertilizer improve wheat yield, nitrogen efficiency and their stability in different ecological regions? Agronomy 12, 407. doi: 10.3390/agronomy12020407
Ma, Q., Wang, M., Zheng, G., Yao, Y., Tao, R., Zhu, M., et al. (2021). Twice-split application of controlled-release Nitrogen fertilizer met the nitrogen demand of winter wheat. Field Crops Research. 267 108163, 1–9. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2021.108163
Markus, D. K., McKinnon, J. P., Buccafuri, A. F. (1985). Automated analysis of nitrite, nitrate, and ammonium nitrogen in soils. Soil Sci. Soc. America J. 49, 1208–1215. doi: 10.2136/sssaj1985.03615995004900050028x
Nishimura, S., Yoshimura, M., Yamane, T., Oka, N. (2022). Effects of coated slow-release fertilizers on nitrous oxide emission from winter wheat field in a cool-temperate region in Japan. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 68, 305–316. doi: 10.1080/00380768.2022.2038521
Ntinyari, W., Giweta, M., Mutegi, J., Masso, C., Gweyi-Onyango, J. P. (2022). “Managing agricultural nitrogen losses in crop production and mitigation of climate change effects,” in Agriculture, livestock production and aquaculture: advances for smallholder farming systems, vol. Volume 1. (Springer International Publishing, Cham), 21–41.
Snapp, S., Sapkota, T. B., Chamberlin, J., Cox, C. M., Gameda, S., Jat, M. L., et al. (2023). Spatially differentiated nitrogen supply is key in a global food–fertilizer price crisis. Nat Sustain 6, 1268–1278. doi: 10.1038/s41893-023-01166-w
Vejan, P., Khadiran, T., Abdullah, R., Ahmad, N. (2021). Controlled release fertilizer: A review on developments, applications and potential in agriculture. J. Controlled Release 339, 321–334. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2021.10.003
Wu, B., Lin, X., Ali, M. F., Wang, D. (2023). Development of an irrigation regime for winter wheat to save water resources by avoiding irrigation at anthesis stage. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 209, 188–203. doi: 10.1111/jac.v209.1
Wu, B., Shang, Y., Wang, S., Hu, X., Zhang, R., Zhang, B., et al. (2021). Response of nitrogen redistribution to irrigation at jointing in winter wheat. Agron. J. 113, 381–396. doi: 10.1002/agj2.v113.1
Xiao, Y., Peng, F., Zhang, Y., Wang, J., Zhuge, Y., Zhang, S., et al. (2019). Effect of bag-controlled release fertilizer on nitrogen loss, greenhouse gas emissions, and nitrogen applied amount in peach production. J. cleaner production 234, 258–274. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.06.219
Xu, Z. Z., Yu, Z. W., Wang, D., Zhang, Y. L. (2005). Nitrogen accumulation and translocation for winter wheat under different irrigation regimes. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 191, 439–449. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-037X.2005.00178.x
Yan, X., Ti, C., Vitousek, P., Chen, D., Leip, A., Cai, Z., et al. (2014). Fertilizer nitrogen recovery efficiencies in crop production systems of China with and without consideration of the residual effect of nitrogen. Environ. Res. Lett. 9, 095002. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/9/9/095002
Yang, Y. C., Zhang, M., Zheng, L., Cheng, D. D., Liu, M., Geng, Y. Q. (2011). Controlled release urea improved nitrogen use efficiency, yield, and quality of wheat. Agron. J. 103, 479–485. doi: 10.2134/agronj2010.0343
Zhang, G., Liu, S., Dong, Y., Liao, Y., Han, J. (2022). A nitrogen fertilizer strategy for simultaneously increasing wheat grain yield and protein content: Mixed application of controlled-release urea and normal urea. Field Crops Res. 277, 108405. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2021.108405
Zhang, S., Shen, T., Yang, Y., Li, Y. C., Wan, Y., Zhang, M., et al. (2018). Controlled-release urea reduced nitrogen leaching and improved nitrogen use efficiency and yield of direct-seeded rice. J. Environ. Manage. 220, 191–197. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.05.010
Zheng, W., Zhang, M., Liu, Z., Zhou, H., Lu, H., Zhang, W., et al. (2016). Combining controlled-release urea and normal urea to improve the nitrogen use efficiency and yield under wheat-maize double cropping system. Field Crops Res. 197, 52–62. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2016.08.004
Zhou, H., Zhang, M., Liu, Z., Zheng, W., Zhu, Q., Wan, Y. (2019). Maize yield and economic return with controlled-release urea. Nutrient Cycling Agroecosystems 115, 427–440. doi: 10.1007/s10705-019-10020-5
Zhou, X., Yang, X., Feng, S., Zhang, J., Wu, J., Liu, J., et al. (2023). Optimization of controlled-release urea application based on the winter wheat yield. Eur. J. Agron. 151, 126987. doi: 10.1016/j.eja.2023.126987
Keywords: controlled released nitrogen fertilizer, grain yield, nitrogen accumulation, soil nitrogen supply, winter wheat
Citation: Ali MF, Han R, Lin X and Wang D (2025) Controlled-release nitrogen combined with ordinary nitrogen fertilizer improved nitrogen uptake and productivity of winter wheat. Front. Plant Sci. 15:1504083. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1504083
Received: 30 September 2024; Accepted: 29 November 2024;
Published: 07 January 2025.
Edited by:
Khurram Shahzad, Lasbela University of Agriculture, Water and Marine Sciences, PakistanReviewed by:
Yunshan Yang, Shihezi University, ChinaHassan Karim, Department of Agricultural and Forest Sciences and Engineering, University of Lleida, Spain
Abu Zar Ghafoor, Warsaw University of Life Sciences, Poland
Copyright © 2025 Ali, Han, Lin and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Dong Wang, wangd@nwafu.edu.cn; Xiang Lin, sdslinxiang@163.com
 Muhammad Fraz Ali
Muhammad Fraz Ali