- Institute of Medicinal Plant Development, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, China
Excessive utilization of chemical fertilizers degrades the quality of medicinal plants and soil. Bio-organic fertilizers (BOFs) including microbial inoculants and microalgae have garnered considerable attention as potential substitutes for chemical fertilizer to enhance yield. In this study, a field experiment was conducted to investigate the effects of BOF partially substituting chemical fertilizer on the growth and quality of medicinal plant Polygala tenuifolia. The growth parameters, bioactive component contents, soil properties and composition of rhizosphere microorganisms were measured. The results indicated that substituting 40% of chemical fertilizer with microalgae showed the most pronounced growth-promoting effect, leading to a 29.30% increase in underground biomass and a 19.72% increase in 3,6’-disinapoylsucrose (DISS) content. Substituting 20% of chemical fertilizer with microalgae improved soil quality, significantly increasing soil organic matter content by 15.68% (p<0.05). Microalgae addition significantly affected the rhizosphere bacterial community composition of P. tenuifolia, reducing the relative abundance of Cladosporium by 33.33% and 57.93%, while increasing the relative abundance of Chloroflexi by 31.06% and 38.27%, under 20% and 40% chemical fertilizer reduction, respectively. The relative abundance of Chloroflexi positively correlated with both the underground biomass and DISS content (p<0.05), indicating that microalgae may stimulate Chloroflexi species associated with carbon cycling, thereby enhancing soil fertility, nutrient absorption, and ultimately leading to increased biomass accumulation and production of bioactive components in P. tenuifolia. In addition, there was no significant difference in underground growth and bioactive component contents between reduced chemical fertilizer dosage combined with solid microbial inoculant (SMI) and polyglutamic microbial inoculant (PMI), compared with 100% chemical fertilizer. Correlation analysis revealed that PMI could increase soil phosphorus availability through Streptomyces recruitment. In conclusion, our findings demonstrated that bio-organic fertilizers can partially substitute chemical fertilizer to improve soil properties and microorganisms, enhancing the growth and quality of P. tenuifolia. This provides a theoretical basis for increasing medicinal plant productivity under chemical fertilizer reduction.
1 Introduction
Polygala tenuifolia, which uses the roots for medicinal purposes, is commonly employed for treating insomnia, memory disorders, and neurosis. This perennial medicinal plant holds potential as a preventive and therapeutic agent against Alzheimer’s disease, leading to high market demands (Deng et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2023). The increasing demand for P. tenuifolia has promoted a drive for higher yields, thus resulting in the overuse of agrochemicals. However, it was reported that over 50% of nitrogen in fertilizers applied cannot be absorbed by crops (Saud et al., 2022). On the other hand, agrochemical overuse may lead to a decline in soil organic matter content, as well as soil microbial diversity and abundance, result in soil compaction, acidification, and imbalanced nutrient structure, ultimately compromising both the quality of P. tenuifolia and soil health (Guo et al., 2010; Liu et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2020). Therefore, it is necessary to reduce chemical fertilizer usage and improve utilization rate. Currently in agriculture, there is a conscious effort being made to develop and utilize bio-organic fertilizers (BOFs) as substitutes for chemical fertilizers and pesticides to reduce harm to crops and soil (Waltz, 2017).
Microalgae fertilizers (MFs) and microbial inoculants (MIs) have been commercially available as BOFs, biopesticides and soil amendments (Renuka et al., 2018; Klimasmith and Kent, 2022; Parmar et al., 2023). MIs contain single or multiple strains of live or dormant microorganisms, including plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPRs) and beneficial fungi, such as Azotobacter sp., Azospirillum sp., Bacillus sp., Rhizobium sp., Sphingobium sp., Streptomyces sp., and Pseudomonas sp., which could interact with plants and exert conducive influence on the composition and structure of soil microbial communities (Zhuang et al., 2007; Berendsen et al., 2012; Ambrosini et al., 2016; Sousa et al., 2016). Bacillus sp., such as Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, B. subtilis, and B. mucilaginosus, are PGPRs commonly used in bio-fertilizers, and also constitute the primary constituents of the MIs utilized in this study (Abou-El-Seoud and Abdel-Megeed, 2012; Sun et al., 2020; Xue et al., 2021). The underlying mechanisms responsible for their growth-promoting effects can be summarized into the following three points: (1) improving plant nutrient utilization through nitrogen fixation and phosphorus solubilization (Klimasmith and Kent, 2022); (2) producing plant growth hormones and enzymes (Trabelsi and Mhamdi, 2013); (3) providing biocontrol against filamentous fungi and pathogens (Cao et al., 2011; Wang et al., 2021; Deng et al., 2022; Luo et al., 2022). Microalgae primarily promote plant growth and enhance soil fertility through nitrogen fix, carbon sequester through photosynthesis, and synthesis of metabolites (Marks et al., 2017; Abinandan et al., 2019; Sido et al., 2022). Additionally, PGPRs and nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria can also assist in phytoremediation by removing toxic metals and organic pollutants from soil and fostering a more ordered and efficient microbial community (Kong et al., 2019; Rezasoltani and Champagne, 2023). Both Bacillus MI and microalgae can reduce NO and N2O emissions or sequester CO2 from the atmosphere, thereby mitigating the greenhouse effect, global warming, and climate change (Calvo et al., 2013; Cheah et al., 2015; Calvo et al., 2016; Wu et al., 2018).
The combination of bio-organic fertilizer and chemical fertilizer has been found to result in superior crop yield and quality compared to using only bio-organic fertilizer (Zhang et al., 2024). As mentioned earlier, both MIs and MFs have the potential to enhance plant nutrient uptake and reduce nitrogen loss, thus increasing the efficiency of chemical fertilizer utilization (Xue et al., 2021). Studies have demonstrated that the co-application of Bacillus MIs or microalgae with chemical fertilizer can regulate the structure of soil microbial communities to achieve coordination and supplementation of chemical fertilizer, leading to enhanced soil nutrient content and ultimately increasing crop yield (Cao et al., 2023). Under deficit irrigation regimes, reducing chemical fertilizer application in conjunction with MI can enhance fenugreek yield while minimizing chemical fertilizer consumption (Dadrasan et al., 2015). Microalgae biomass grown in domestic wastewater can be partially substituted for chemical fertilizer in the cultivation of basil crops (Ocimum basilicum L.) (Álvarez-González et al., 2022). It is noteworthy that BOFs can serve as a viable strategy to maintain or improve crop yields. However, insufficient application of chemical fertilizer or sole reliance on BOF may result in yield reduction (Ye et al., 2020). Studies have shown that a substitution rate of 20%-40% with chemical fertilizer is more beneficial in promoting nutrient absorption and increasing crop yields, while reducing environmental pollution and improving soil microenvironment (Adesemoye et al., 2009; Lei et al., 2012; Jin et al., 2022; Yuan et al., 2023). Therefore, BOFs hold promising potential in partially substituting agrochemicals for sustainable crop and medicinal plant production.
However, the current research has primarily focused on the application of BOFs in crop production, with limited studies conducted on their effects in medicinal plants (Renuka et al., 2018; Shahwar et al., 2023). Medicinal plants, particularly, differ from general crops as their quality directly impacts efficacy and safety. Therefore, the objectives of this study were (1) to investigate the effects of chemical fertilizer reduction and application of different bio-organic fertilizers on the growth and quality of P. tenuifolia, and (2) to explore the mechanism of bio-organic fertilizers partially substituting chemical fertilizer by analyzing soil properties and microorganisms, in order to provide theoretical basis for eco-friendly fertilizer applications in medicinal plant cultivation.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Experimental sites
Field experiment was conducted in Wenxi County, Yuncheng City, Shanxi Province (111°13’27’’ E, 35°26’26’’ N), the primary production region for Polygala tenuifolia. A biennial P. tenuifolia field with consistent growth was selected. The cultivated P. tenuifolia was identified by Professor Jianping Han of the Institute of Medicinal Plant Development, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College following the standards outlined in the Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China (PPRC-2020). The specimens were preserved at the same institution. The region has a temperate continental monsoon climate, with an average annual temperature of 12.5 °C. The annual precipitation is 506 mm, and this region is susceptible to drought. The tested soil type is sandy loam soil. The plowing layer soil (0-20 cm) had a pH of 8.11, an organic matter content of 15.80 g/kg, a total nitrogen content of 1.08 g/kg, a total phosphorus content of 0.59 g/kg, a total potassium content of 25.70 g/kg, an alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen content of 74.19 mg/kg, an available phosphorus content of 11.50 mg/kg, and an available potassium content of 215.00 mg/kg.
2.2 Experimental treatments and maintenance
Seven treatments were established as shown in Table 1: (1) CF: 100% chemical fertilizer; (2) PMI1: -20% chemical fertilizer + polyglutamic acid microbial inoculant; (3) PMI2: -40% chemical fertilizer + polyglutamic acid microbial inoculant; (4) SMI1: -20% chemical fertilizer + solid microbial inoculant; (5) SMI2: -40% chemical fertilizer + solid microbial inoculant; (6) MF1: -20% chemical fertilizer + microalgae fertilizer; (7) MF2: -40% chemical fertilizer + microalgae fertilizer. The chemical fertilizer (N: P: K = 16: 5: 24) was purchased from Liuguo Chemical Co. Ltd (Anhui, China) with an application rate of 750 kg/ha. The application rate of chemical fertilizer used in treatments with a 20% and 40% reduction in chemical fertilizer is 600 kg/ha and 450 kg/ha, respectively. The Gulefeng 8.8 billion® polyglutamic acid microbial inoculant (PMI, viable count ≥ 8.8×109/mL) was purchased from Xuankai Biotechnology (Xuankai Biotechnology Co. Ltd., Nanjing, China) and utilized in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions, at a dosage of 75L diluted microbial inoculant per hectare (diluted at a ratio of 1:100). PMI primarily consists of polyglutamic acid (PGA), Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, B. subtilis and Brevibacillus laterosporu. The solid microbial inoculant (SMI, viable count ≥ 2.0×108/g) was produced by Jintu Biotechnology (Jintu Biotechnology Co. Ltd., Hebei, China) and utilized at a dosage of 150 kg/ha. Its main components are Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and Brevibacillus laterosporu. The Titubang® microalgae fertilizer (MF, viable count ≥ 1.0×105/mL) was purchased from Bailing Biotechnology (Bailing Biotechnology Co. Ltd., Beijing, China) and utilized at a dosage of 50 L diluted microbial inoculant per hectare (diluted at a ratio of 1:100). Chlorella pyrenoidosa, nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria and Tolypothrix tenuis are the main components. Each treatment consisted of three biological replicates, with each replicate covering an area of 12 m2 (2 m×6 m). To minimize the marginal effect, protection lines (0.5 m) were placed between each replicate cell. The experiment was initiated in April 2023 with the first application of biennial P. tenuifolia, followed by subsequent applications of the same dosage of BOFs administered every two months, for a total of three times.
2.3 Determination of underground biomass and quality of P. tenuifolia
After six months, P. tenuifolia were sampled, and plant traits were collected from at least ten plants in each biological replicate. The underground biomass of each P. tenuifolia root was determined, while the root diameter was measured using vernier scale. All root samples were processed by removing the woody core (xylem), dried at 55 °C, powdered, and sieved through a 50-mesh sieve. The contents of polygalaxanthone III (POL) and 3,6’-disinapoylsucrose (DISS) in P. tenuifolia were determined by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). 0.5 g of P. tenuifolia powder was mixed with 10 mL of 70% methanol, weighed, and subjected to ultrasonic extraction (400 W, 40 kHz) for 45 min. After cooling and re-weighing, any weight loss was compensated by adding additional 70% methanol. The mixture was centrifuged at a speed of 5000 r/min for 5 min, and the supernatant was filtered through a 0.22 μm filter membrane. A Shimadzu LC-2030 HPLC system (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) equipped with an Agilent ZORBAX Extend-C18 column (46×250 mm, 5 μm) was employed for isocratic elution. The mobile phase consisted of acetonitrile and 0.05% phosphoric acid solution at a ratio of 18:82 (v/v) with a flow rate of 1.0 mL/min. Detection was conducted at a wavelength of 320 nm, while the column temperature was 30 °C and the injection volume was 10 μL. A series of working standard solutions were set up with a mixed standard solution comprising POL and DISS, both of which were purchased from Yuanye Biotechnology Co., Ltd (Shanghai, China).
2.4 Soil sampling and determination
When harvesting P. tenuifolia plants, rhizosphere soil tightly adhering to the root surface were collected. One sample of P. tenuifolia rhizosphere soil was collected per replicate, with three replicates per treatment. Each sample represented a composite of soil collected from the rhizosphere of plants within its respective replicate plot. All rhizosphere soil samples were sieved and stored at -80 °C for microbial analysis. In each replicated plot, bulk soil samples weighing approximately 500 g were collected using a five-point sampling method at depths ranging from 0 to 20 cm around the plants. Three replicates were taken for each treatment. The collected soil samples were air-dried, sieved through a 100-mesh sieve, and subjected to analysis for pH and the contents of soil organic matter (SOM), alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen (AN), available potassium (AK) and available phosphorus (AP). The soil pH was tested by the potentiometric method, while the organic matter content was determined using the K2CrO7/H2SO4 oxidation method (Marks et al., 2017; Shrestha et al., 2022). The alkaline hydrolysis diffusion method was employed to determine the soil alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen content (Wang et al., 2022). The molybdenum antimony anti-colorimetric method was used to measure the soil available phosphorus content (Chu and Grogan, 2010). The flame spectrophotometer technique was utilized to assess the soil available potassium content (Li et al., 2022).
2.5 Sequencing
Total genome DNA from all rhizosphere soil samples were extracted using CTAB method (Kamdem et al., 2023; Zheng et al., 2024). DNA concentration and purity was monitored on 1% agarose gels. The 16S rRNA gene of bacteria was amplified using the primers 341F (5’-CCTAYGGGRBGCASCAG-3’)/806R (5’-GGACTACNNGGGTATCTAAT-3’), and the ITS region of the fungi was amplified with ITS1F (5’-CTTGGTCATTTAGAGGAAGTAA-3’)/ITS2R (5’-GCTGCGTTCTTCATCGATGC-3’) primers (Wei et al., 2021). The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) system was composed as follows: 15 μL of Phusion® High – Fidelity PCR Master Mix (New England Biolabs), 0.2 μM of forward and reverse primers, and about 10 ng template DNA. Thermal cycling consisted of initial denaturation at 98°C for 1 min, followed by 30 cycles of denaturation at 98°C for 10 s, annealing at 50°C for 30 s, elongation at 72°C for 30 s; then ended with an extension at 72°C for 5 min. The integrity and concentration of PCR products were verified by 2% agarose gel electrophoresis. PCR products were purified with Qiagen Gel Extraction Kit (Qiagen, Germany). Sequencing libraries were generated using TruSeq® DNA PCR-Free Sample Preparation Kit (Illumina, USA) and index codes were added. The library quality was assessed on the Qubit@ 2.0 Fluorometer (Thermo Scientific) and Agilent Bioanalyzer 2100 system. At last, the library was sequenced on an Illumina NovaSeq platform by Novogene Co., Ltd (Beijing, China) and 250 bp paired-end reads were generated.
2.6 Bioinformatics analysis
Paired-end reads were first assigned to samples based on unique barcodes, then trimmed to remove barcode and primer sequences, and merged using FLASH. Quality filtering was done with Fastp (v. 0.23.1) to obtain high-quality clean tags. These tags were compared against the Silva database (16S) and Unite database (ITS) using the UCHIME Algorithm to detect and remove chimera sequences, resulting in effective tags. Denoising was then performed using the DADA2 module in QIIME2 (Version QIIME2-202202) to obtain initial amplicon sequence variants (ASVs). Species annotation was conducted using the Silva database (16S) and Unite database (ITS) within QIIME2. Multiple sequence alignment was done using QIIME2 to investigate phylogenetic relationships and differences in predominant species among sample groups. The absolute abundance of ASV was normalized based on the sample with the fewest sequences. Subsequent alpha and beta diversity analyses were performed using the normalized data.
GraphPad Prism (V10.0.3) was used to plot histograms representing the average values of the parameters, with bars indicating the standard error of the mean (SEM). The statistical differences were analyzed using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with SPSS V26.0 statistical software (IBM, USA). Alpha diversity indices were measured through QIIME2 to analyze the diversity and richness. Principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) of rhizosphere microbial community composition were performed using Bray-Curtis distance. Biomarkers were identified by the Linear discriminant analysis effect size (LefSe) with a linear discriminant analysis (LDA) score > 2.0 and p < 0.05. Redundancy analysis (RDA) was used to explore the relationships between soil properties and microbial composition using R (V4.3.1). R (V4.3.1) was also used to estimate the correlation among plant growth indicators, quality indicators, soil properties and rhizosphere microbial communities by Pearson and Mantel correlation analysis.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 P. tenuifolia growth
In this study, combined application of reduced chemical fertilizer and BOF increased P. tenuifolia underground growth traits including underground biomass and root diameter (Figure 1). MF showed the greatest efficacy in promoting both underground biomass and root diameter of P. tenuifolia (Figure 1B). The underground biomass of P. tenuifolia increased by 23.05% and 29.30% under MF1 and MF2 respectively, while the root diameter experienced respective increments of 6.82% and 4.78%. Reducing the application of chemical fertilizer and combining it with SMI and PMI did not result in a significant difference in the underground growth of P. tenuifolia when compared to applying 100% chemical fertilizer.
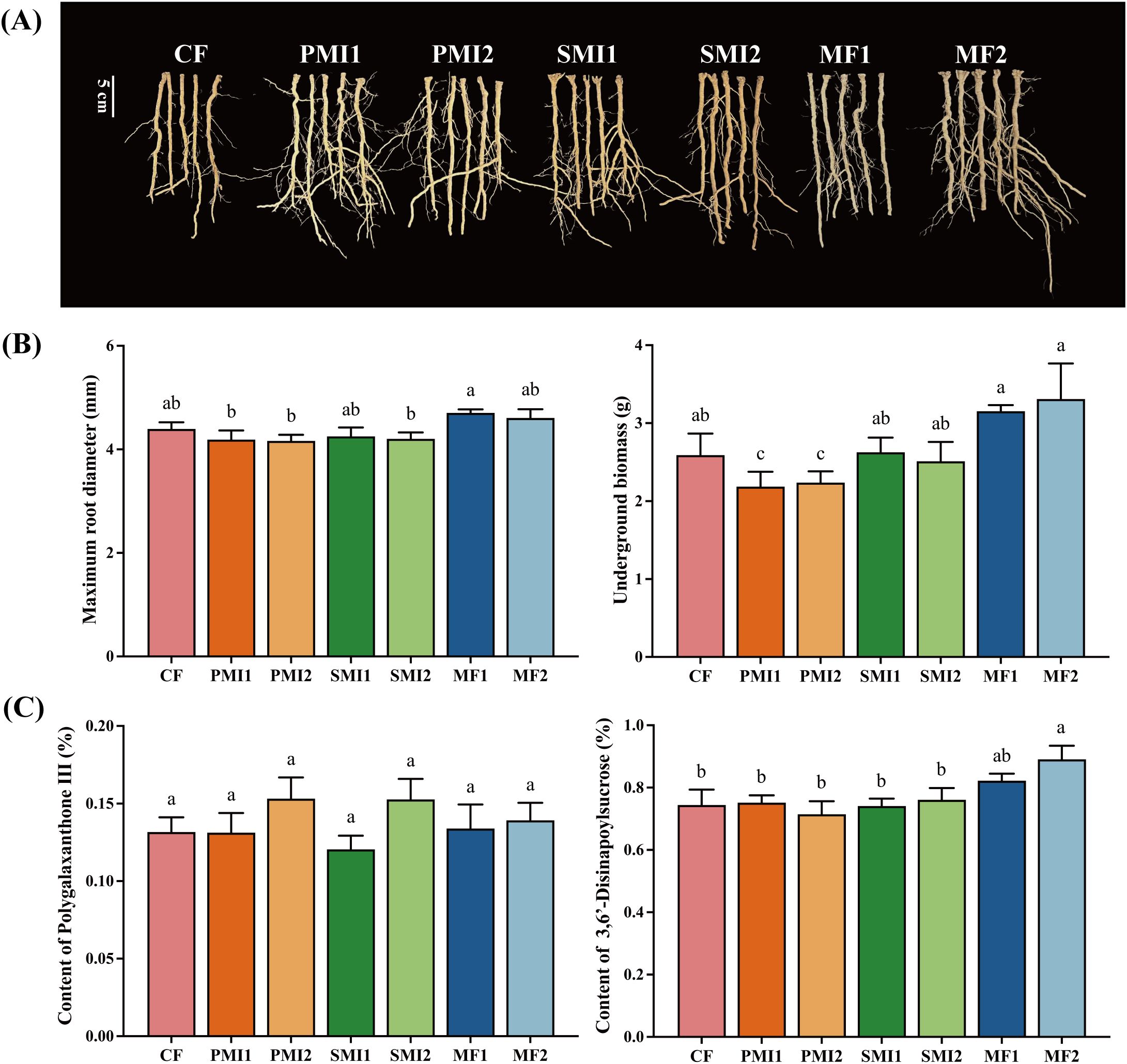
Figure 1. Effect of partial substitution of BOFs for chemical fertilizer on root phenotype (A), underground growth (B) and bioactive component contents (C). CF, 100% chemical fertilizer; PMI1, -20% chemical fertilizer + polyglutamic acid microbial inoculant; PMI2, -40% chemical fertilizer + polyglutamic acid microbial inoculant; SMI1, -20% chemical fertilizer + solid microbial inoculant; SMI2, -40% chemical fertilizer + solid microbial inoculant; MF1, -20% chemical fertilizer + microalgae fertilizer; MF2, -40% chemical fertilizer + microalgae fertilizer. The different lowercase letters indicated the significant difference among the different groups at p<0.05 level.
Microbial inoculants with Bacillus as the core microorganism exert a significant effect on increasing production (Chen et al., 2021; Shi et al., 2022). In this study, the underground biomass of P. tenuifolia in PMI and SMI groups were comparable to CF under reduced chemical fertilizer usage conditions, indicating that MIs partially substituting chemical fertilizer can ensure efficient production (Figure 1B). This effect may be attributed to the nitrogen fixation and phosphorus solubilization functions of the main functional bacteria including Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, and Bacillus mucilaginosus added in MIs, as well as their abilities to release growth-promoting hormones. Furthermore, poly-γ-glutamic (γ-PGA), a novel fertilizer synergist and one of the main components in PMI, not only exhibits remarkable water and fertilizer retention abilities but also enhances plant nutrient absorption by increasing root biomass and activity (Yin et al., 2018; Bai et al., 2022). Researchers had also discovered that the combination of microalgae with organic fertilizers or their partial substitution for chemical fertilizer can improve crop yield (Álvarez-González et al., 2022; Cao et al., 2023). This study confirmed that among different BOFs applied in this study, co-application of microalgae and chemical fertilizer has the best promotion effects on P. tenuifolia growth compared to 100% chemical fertilizer group (Figure 1B). Additionally, as shown in Figure 1A, MF significantly enhanced the growth of lateral and fibrous roots. This may be attributed to the pivotal role of indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) produced by various microalgae in primary and lateral root development (Zhang et al., 2024). Overall, partial substitution of chemical fertilizer with BOF provided a feasible strategy to reduce chemical fertilizer usage, thereby promoting underground growth of P. tenuifolia and increasing yield.
3.2 Bioactive component contents
As shown in Figure 1C, MF significantly increased the content of DISS in the roots of P. tenuifolia, MF1 and MF2 increased the content of DISS by 10.45% and 19.72%, respectively, with the increase in MF2 being statistically significant (p < 0.05). While other BOFs treatments as partial substitutes for chemical fertilizer achieved comparable effectiveness to 100% chemical fertilizer in terms of DISS and POL contents in P. tenuifolia.
POL has anti-inflammatory properties, and DISS is known for its significant anxiolytic and antidepressant effects (Hu et al., 2011; Yang et al., 2022; Zhang et al., 2022). They are major bioactive components of P. tenuifolia, playing a crucial role in determining the clinical efficacy of P. tenuifolia roots, which serve as important quality control indicators (Xu et al., 2016). The content of oligosaccharide esters including DISS in P. tenuifolia is significantly influenced by soil type and origin, while there is minimal variation in xanthones (Pu et al., 2017; Ji et al., 2023). This suggested a close relationship between the accumulation of DISS during the growth process of P. tenuifolia and environmental factors such as climate, soil properties, and rhizosphere microbial communities. These findings supported our experimental results and confirmed that the application of MF may create more favorable conditions for DISS accumulation in P. tenuifolia. Our previous investigations have demonstrated that Bacillus sp. can facilitate the accumulation of total tanshinone in Salvia miltiorrhiza (Wei et al., 2023). Furthermore, many studies had shown that MF can increase the nutrient contents of crops, vegetables and fruits, including soluble sugars, vitamin C, protein, chlorophyll and carotenoids (Coppens et al., 2016, 2016; Zhang et al., 2024). MF also has the ability to increase the content of secondary metabolites in plants (Díaz et al., 2024). For instance, applying Coelastrella sp. can elevate most organic acids and phenolic compounds in strawberries by more than 10% (Žunić et al., 2024). The above results demonstrated that microalgae could improve plant quality while promoting plant growth, indicating its potential for further study and application in the cultivation of medicinal plants (Figure 1C). Meanwhile, based on the results of this study, further research is needed to investigate the mechanism by which microalgae promote DISS accumulation in P. tenuifolia.
3.3 Soil properties
As shown in Figure 2, the partial substitution of chemical fertilizer with BOFs had a significant impact on soil physicochemical properties. PMI2 and MF1 exhibited a substantial increase in SOM by 11.32% and 15.68%, respectively (p < 0.05). CF group displayed the highest AN content, while soils treated with 80% chemical fertilizer application demonstrated higher AN level than those treated with 60% chemical fertilizer application, suggesting that inorganic nutrients provided by chemical fertilizer are primarily responsible for increasing inorganic nitrogen content in the soil. All the six treatments with BOFs showed a higher availability of P in soils as compared to CF. Among them, the AP content processed by PMI1 and PMI2 is 1.92 times and 2.27 times that of CF, respectively (p < 0.05).
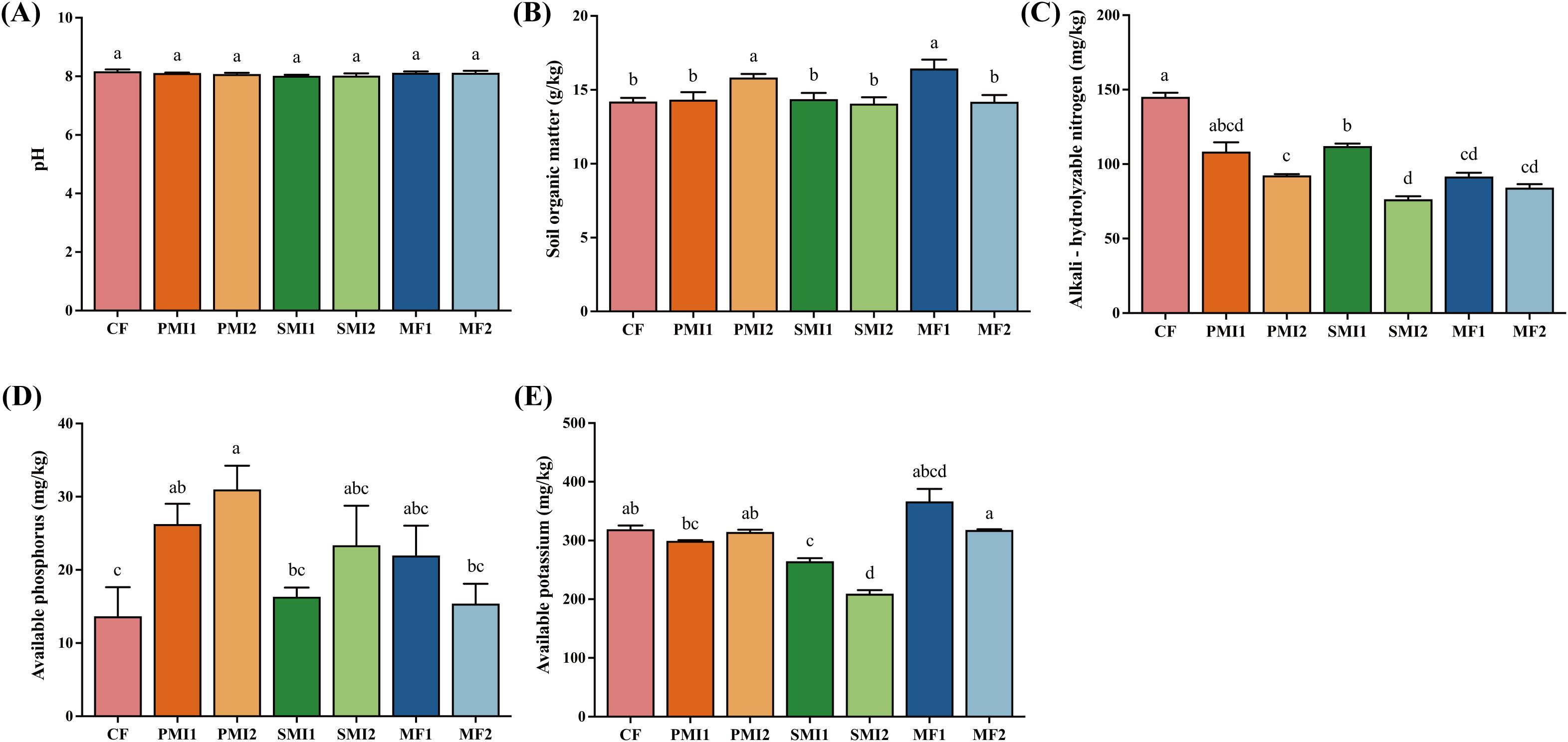
Figure 2. Soil physicochemical properties under different fertilization treatments. (A) pH; (B) soil organic matter; (C) alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen; (D) available phosphorus; (E) available potassium. CF, PMI1, PMI2, SMI1, SMI2, MF1, and MF2 were as defined in the footnote to Figure 1. The different lowercase letters indicated the significant difference among the different groups at p<0.05 level.
In addition to the reduction in chemical fertilizer usage, the decrease of AN may also be attributed to the incorporation of BOFs, which enhanced nitrogen absorption by P. tenuifolia (Zhou et al., 2023). Beneficial microorganisms present in MIs can effectively colonize soils and secrete organic acids that dissolve and release nitrogen nutrients adsorbed onto soil particles, while also modifying indigenous bacterial communities involved in nitrogen cycling (van der Heijden et al., 2008; Lei et al., 2012; Huang et al., 2022). Application of microalgae can enhance soil enzyme activity and promote life activities of microorganisms related to nitrogen cycling, while nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria can provide fixed-nitrogen through biological fixation or conversion between different forms of nitrogen fertilizers (Renuka et al., 2018; Zhou et al., 2023). Hence, the synergistic application of chemical fertilizer and MIs confers greater advantages on nitrogen uptake by plants compared to their individual applications. In addition to N nutrition, the inoculation of BOFs can augment the availability and translocation of various micro- and macronutrients, including Zn, Cu, Fe, C, P, K within the soils and plants (Coppens et al., 2016; Renuka et al., 2018). Various BOFs including Bacillus sp. and microalgae have been found to possess phosphate solubilization ability, which can lower soil pH and convert soil-bound phosphorus into soluble forms that are readily accessible for plant growth. This transformation is also facilitated by metabolites released during microbial metabolism and low molecular weight organic acids. The partial substitution of chemical fertilizer with BOFs primarily stimulate plant growth through microbial activities and interactions with soil or plants rather than directly supplying various nutrients to the soil. Consequently, changes in properties of the soil may be influenced by factors such as fertilization amount, fertilizer ratio, and duration of application. In conclusion, the partial substitution of chemical fertilizer with BOFs have shown potential to enhance nitrogen nutrient uptake by P. tenuifolia in soil and can significantly improve the availability of phosphorus, which is closely related to the beneficial effects of microorganisms.
3.4 Rhizosphere microbial community
3.4.1 Rhizosphere microbial diversity of P. tenuifolia
After quality control filtering, a total of 20,178 bacterial ASVs and 2,995 fungal ASVs were detected. PCoA analysis based on rhizosphere bacterial community composition revealed that samples within the same BOF treatment groups clustered together and MF groups showed distinct separation from other groups (Figure 3). This indicated that the addition of MF significantly influenced bacterial community composition. Furthermore, a more pronounced impact observed on bacterial communities compared to fungal communities (Supplementary Figure S1). The application of BOFs may altered soil environmental conditions and promoted an enrichment of specific functional microbial groups within the rhizosphere, thereby diminishing species biodiversity (Yang et al., 2022). Additionally, the introduction of exogenous microorganisms can potentially disturb native microbial communities, resulting in either antagonistic or synergistic effects (Qiu et al., 2009; Ambrosini et al., 2016). It should also be noted that the influence exerted by external additions like BOFs on soil microflora has strong temporal dependency (Nguyen et al., 2018).
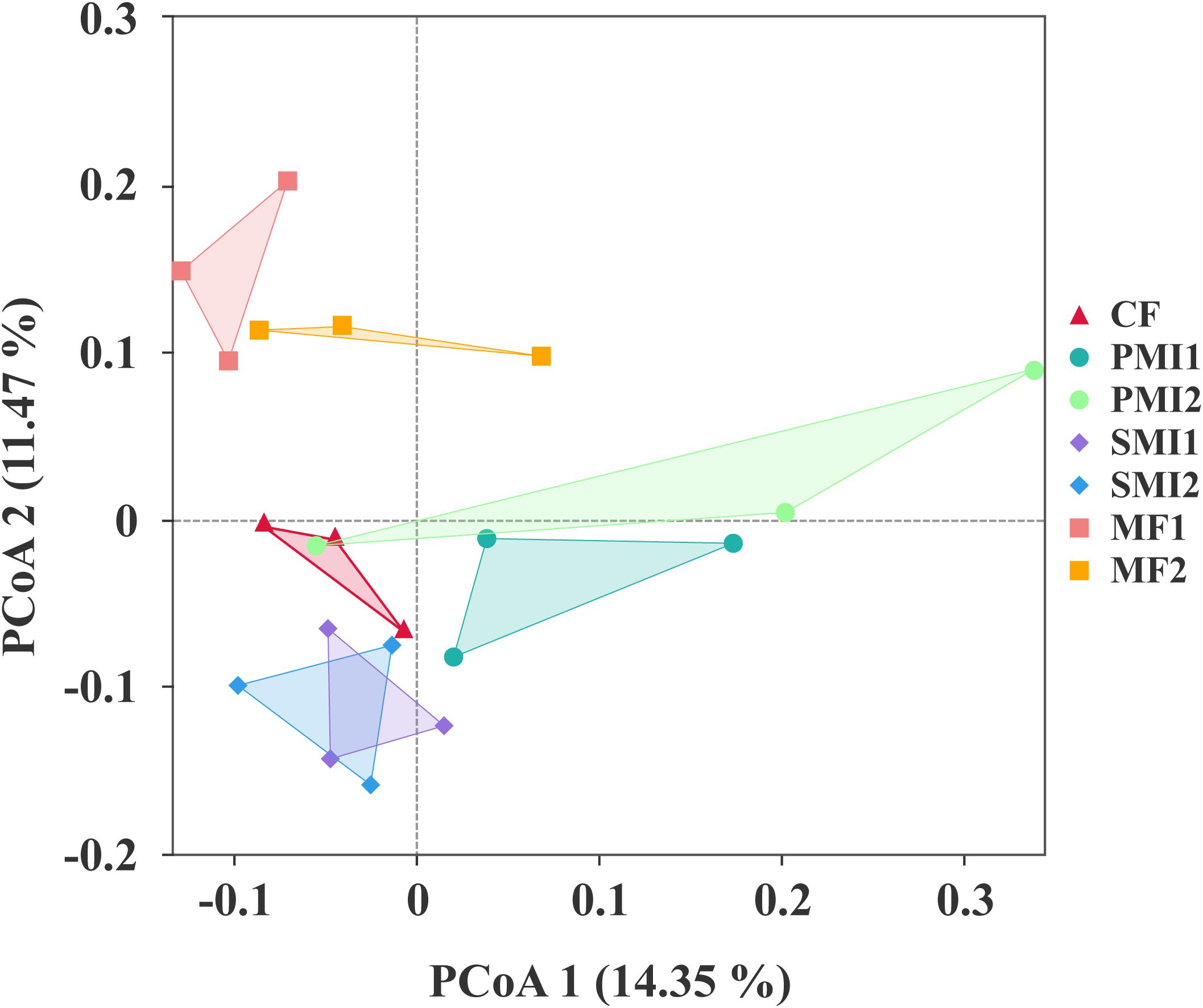
Figure 3. Principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) plot based on the rhizosphere bacterial community composition. CF, PMI1, PMI2, SMI1, SMI2, MF1, and MF2 were as defined in the footnote to Figure 1.
3.4.2 Composition of the rhizosphere bacterial community
The clustering results revealed that the bacterial communities of different fertilization treatments belonged to 41 phyla, 98 classes, 216 orders, 298 families and 547 genera based on the detected ASVs. At each taxonomic level, there were certain ASVs that remain unidentified. Actinobacteriota, Proteobacteria, Acidobacteriota, Chloroflexi and Gemmatimonadota were identified as the dominant phyla with a combined relative abundance (RA) exceeding 80% in the bacterial community (Figure 4A), which was consistent with previous study (Gu et al., 2023). Compared to CF, both SMI and MF groups showed an increased RA of Chloroflexi. Therefore, it can be concluded that the application of SMI and MF alleviated the decline in Chloroflexi caused by chemical fertilizer.
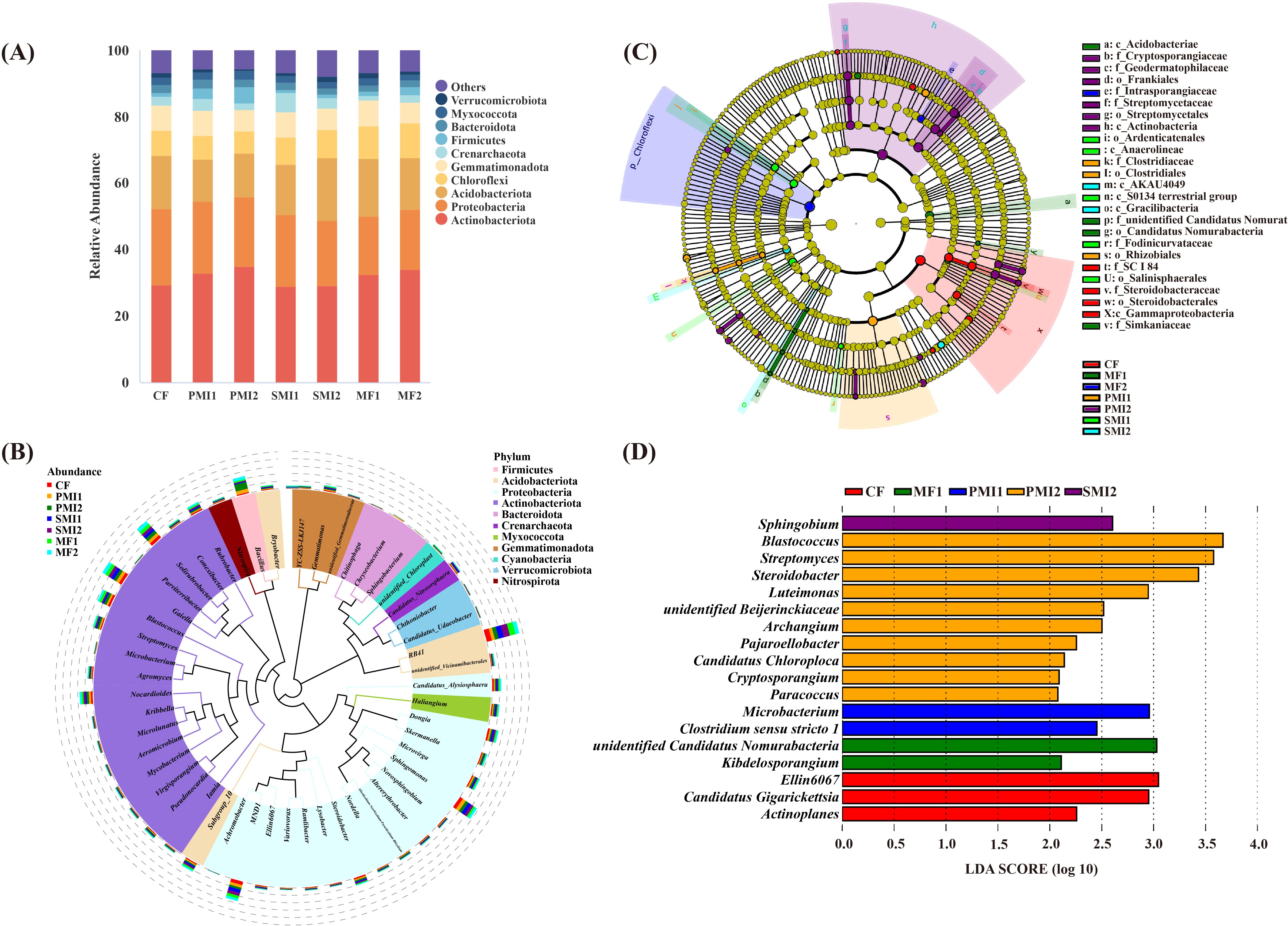
Figure 4. Composition of rhizosphere bacterial communities in P. tenuifolia. (A) The relative abundance of top 10 bacterial phyla. (B) Phylogenetic tree of top 50 bacterial genera based on relative abundance. (C) Significantly enriched bacterial taxa showed by cladograms based on linear discriminant (LEfSe) analysis. (D) Scores for the bacterial genera showed by bar chart based on LEfSe analysis. CF, PMI1, PMI2, SMI1, SMI2, MF1, and MF2 were as defined in the footnote to Figure 1.
The predominant genera were identified as RB41 (RA: 2.12-4.06%), Sphingomonas (1.32-2.35%), MND1 (1.36-2.39%), Solirubrobacter (1.73-2.30%), and Gaiella (1.84-2.24%) (Figure 4B). The PMIs groups showed the greatest promotional effect in the RA of Bacillus. This could be attributed to the substantial proliferation and recruitment of Bacillus in soil after their application. Unexpectedly, the RA of Bacillus in SMIs groups was found to be lower compared to that in CF. It is possible that Bacillus, as endophytes colonizing within P. tenuifolia plants, negatively affected the RA of rhizosphere Bacillus (Wang et al., 2020). Another plausible explanation arised from differences in fertilization methods. Bacterial movement between ecological niches primarily relies on rainfall. In this experiment, both PMI and MF were applied through spraying techniques; however, SMI employed furrow application due to its solid-state fertilizer nature. Despite timely watering after fertilization, this application method might hinder microorganisms from transferring effectively from fertilizer into soil, thereby potentially contributing to a low survival rate of exogenous microbial communities (Semenov et al., 2021). The result indicated that Streptomyces significantly increased in PMI2 (p<0.05). A limited number of bacterial genera, including Streptomyces, were primarily responsible for the release of carbon dioxide from soil (Stone et al., 2021). Moreover, Streptomyces contribute to enhanced resistance against biotic and abiotic stresses in plants. Apart from acting as biocontrol agents through antibiotic production, Streptomyces promotes plant growth by solubilizing phosphorus and producing plant growth hormone-like substances such as IAA (Kim et al., 2011; Vurukonda et al., 2018; Omar et al., 2022). In summary, the partial substitution of chemical fertilizer with BOFs can alter the composition of rhizosphere bacterial communities and increase the RAs of plant growth-promoting bacteria.
According to the LEfSe analysis, the application of BOFs caused significant changes in specific taxonomic groups, thereby exerting a profound influence on rhizosphere ecological functions (Figures 4C, D). At the genus level, functional classification of specific biomarkers in each treatment revealed that BOFs can enrich beneficial bacteria capable of promoting plant growth and participating in soil bioremediation. Firstly, PGPRs were enriched. Samples of the PMI2 group detected the highest abundance of Streptomyces. Kibdelosporangium was the biomarker of MF1, which possesses 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase acid (ACCD) activity, enabling it to reduce ethylene concentration in plants under stress conditions, improve plant stress resistance, and thereby promote the growth of host plants (Xing et al., 2012; Qin et al., 2015; Ali and Kim, 2018; Xiong et al., 2019). Microbacterium and Sphingobium, which possess soil bioremediation capabilities, were significantly enriched in PMI1 and SMI2, respectively. Microbacterium sp. is capable of producing plant hormones such as IAA, which can remediate heavy metal pollution and enhance plant growth under multi-heavy metal stress (Ren et al., 2019; Sun et al., 2019). Furthermore, the volatiles produced by root-associated bacteria of Microbacterium can promote plant growth without requiring direct and prolonged contact with plants, which is likely achieved through the regulation of sulfur and nitrogen metabolism (Cordovez et al., 2018; Liu et al., 2022). There are multiple PGPRs present in Sphingobium, which exhibit resistance to heavy metals and possess the ability to degrade aromatic pollutants (Thomas et al., 2019; Boss et al., 2022; Liu et al., 2023; Zou et al., 2023). Overall, both MIs and MFs can optimize rhizosphere bacterial communities by regulating soil microbial activity and recruiting agricultural beneficial microorganisms (Xiao and Zheng, 2016; Wang et al., 2021).
3.4.3 Composition of the rhizosphere fungal community
The fungal community of P. tenuifolia rhizosphere is taxonomically classified into 13 phyla, 46 classes, 83 orders, 179 families and 350 genera. At each taxonomic level, there were some ASVs that cannot be identified. The combined of Ascomycota (RA: 68.83%-76.72%), Basidiomycota (14.42%-20.78%), and Mortierellomycota (4.46%-11.24%) accounted for over 94% of the total ASVs in all treatments, making them the dominant fungal phyla in the rhizosphere of P. tenuifolia (Figure 5A). Ascomycota are the dominant fungal species in global soil, followed by Basidiomycota (Egidi et al., 2019). The dominant genera in each treatment were Alternaria (RA: 7.30%-15.57%), Solicoccozyma (4.81%-7.72%), Didymella (3.28-6.78%), Mortierella (3.43-8.26%), Fusarium (4.54-7.58%), Neocosmospora (2.50-4.86%), Cladosporium (1.70-4.65%) and Papiliotrema (1.88-3.92%), respectively (Figure 5B). The RAs of Mortierella were significantly increased in SMI2 (p<0.05). Mortierella has been reported as a phosphate-solubilizing fungus with the ability to mobilize P from insoluble forms and protect crops from pathogen invasion (Sharma et al., 2013; Alori et al., 2017; Ozimek and Hanaka, 2021; Ning et al., 2022). The abundance of the genus Cladosporium, which contains various plant and human pathogenic fungi, decreased in MFs, with reductions of 33.33% in MF1 and 57.93% in MF2.
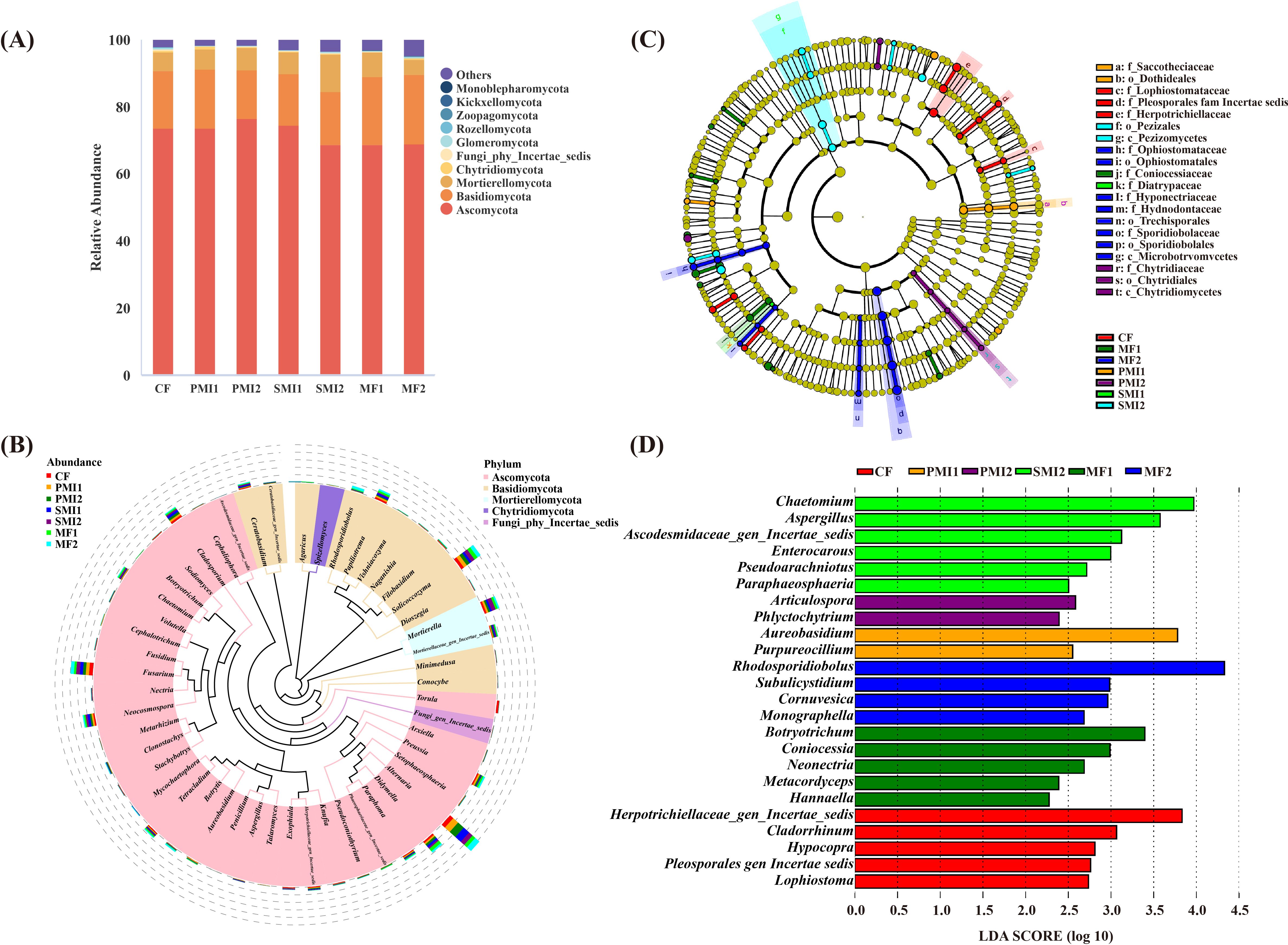
Figure 5. Composition of rhizosphere fungal communities in P. tenuifolia. (A) The relative abundance of top 10 fungal phyla. (B) Phylogenetic tree of top 50 fungal genera based on relative abundance. (C) Significantly enriched fungal taxa showed by cladograms based on linear discriminant (LEfSe) analysis. (D) Scores for the fungal genera showed by bar chart based on LEfSe analysis. CF, PMI1, PMI2, SMI1, SMI2, MF1, and MF2 were as defined in the footnote to Figure 1.
According to LEfSe analysis, there were also differences in fungal biomarkers of P. tenuifolia rhizosphere across different groups (Figures 5C, D). Cladorrhinum, which was enriched in CF, was found to be detrimental to plants or humans. However, this negative effect was significantly inhibited in BOF groups, suggesting that the application of BOFs reduced the RAs of certain harmful fungal genera in P. tenuifolia rhizosphere soil. Furthermore, different groups also demonstrated enrichment of beneficial fungal genera in the soil. For instance, Aureobasidium and Purpureocillium enriched in PMI1 group, which can serve as plant growth promoters and biological control agents (Bao et al., 2022; Rensink et al., 2024). The biomarker MF1, Hannaella, exhibits the biocontrol effect, and Hannaella sp. capable of inducing plant disease resistance (Lin et al., 2022; Yang et al., 2023).
3.5 Correlation analysis of plant traits, soil properties, and rhizosphere microbial communities
Pearson correlation analysis were conducted to investigate the relationship among plant traits (growth parameters and bioactive components contents) and soil properties (Supplementary Figure S2). A significant positive correlation was observed between the content of DISS and both underground biomass and root diameter of P. tenuifolia (p < 0.05). Studies on the active components and medicinal specifications of P. tenuifolia have shown that the content of DISS was positively correlated with root length but highly negatively correlated with plant height (Zhang et al., 2022). Saponins in P. tenuifolia are mainly distributed in the root parenchyma and stored within the secondary phloem (Teng et al., 2009). This may explain the significant correlation between the active components content in P. tenuifolia and its underground parts, especially the biomass of phloem. Based on our research findings, it can be inferred that the application of microalgae may enhance the medicinal quality by increasing the underground biomass of P. tenuifolia.
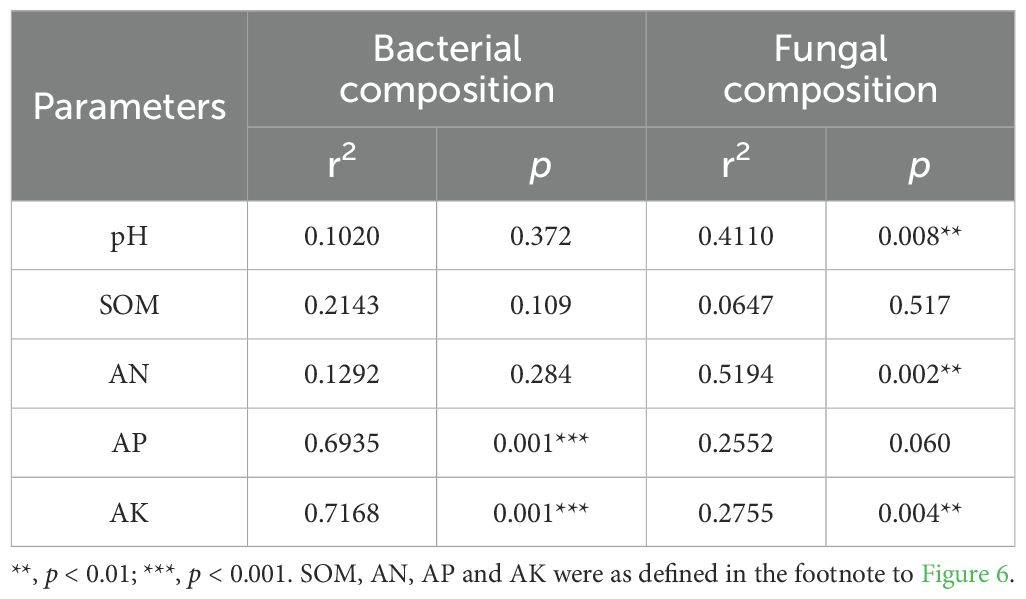
The effects of soil properties on the rhizosphere microbial community of P. tenuifolia upon fertilizer application were investigated by RDA analysis. It was found that soil properties had more significant effects on rhizosphere bacterial structure than fungi (Figures 6A, B). AP and AK significantly influenced soil bacterial community composition, while pH, AN and AK had a remarkable impact on soil fungal community composition (Table 2). In conclusion, pH and available nutrients were all important factors influencing the structure of rhizosphere microbial communities. Further analysis revealed a close association between certain rhizosphere microorganisms and available soil nutrients (Figures 6C, D). The content of AP showed a significant positive correlation with Streptomyces (p < 0.05), which had the highest RAs in PMIs and were identified as biomarkers for PMI2. These microorganisms are capable of solubilizing nutrients sequestered in the crystalline lattice of soil mineral fraction through the secretion of low molecular weight organic acids such as gluconic acid, citric acid, succinic acid, and oxalic acid (Rajput et al., 2013; Timofeeva et al., 2022). As a result, the AP content of PMI1 and PMI2 were significantly increased (p < 0.05). Consequently, the application of PMIs promoted the growth of P. tenuifolia by recruiting Streptomyces to enhance phosphorus availability in soil. The content of pH and AN exhibited positive correlation with the RAs of Agromyces, which related to nitrogen-converting. Some Agromyces sp. have been identified to possess the nitrogen fixation gene (nifH) and have been experimentally verified to exhibit nitrogen-fixing ability (Zhou et al., 2014). AK was significantly positively correlated with Blastococcus and Solirubrobacter (p < 0.05). Solirubrobacter acts as a PGPR and also facilitates the mobilization of potentially toxic elements (Jiang et al., 2023; Cebekhulu et al., 2024). In short, using bio-organic fertilizer as a partial substitution for chemical fertilizer can recruit beneficial microorganisms and improve soil fertility, with complex interactions observed between rhizosphere microbial activity and soil properties.
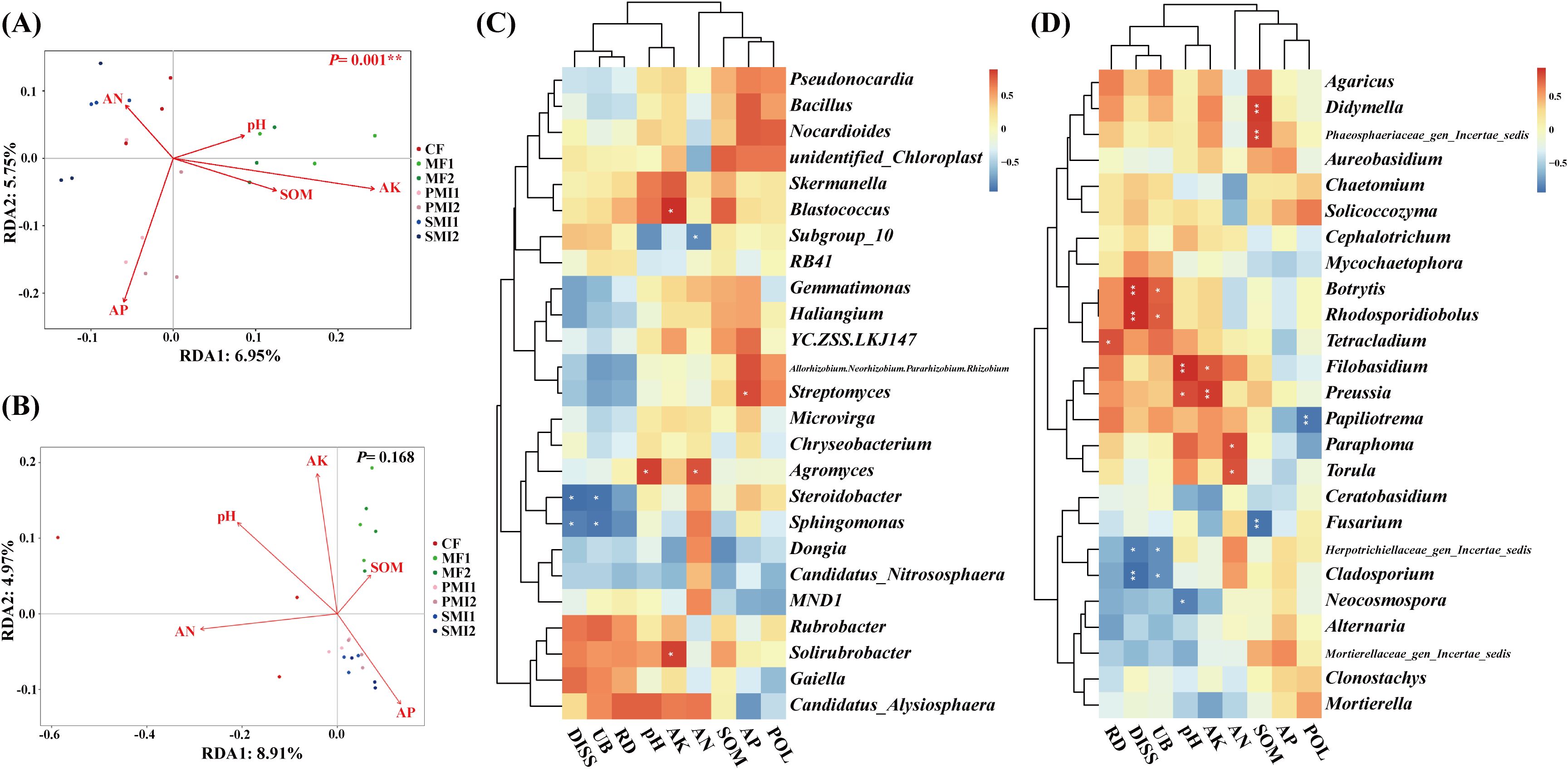
Figure 6. Relationship among plant traits, soil properties, and rhizosphere microbial communities. Redundancy analysis (RDA) reveals relative importance of soil properties on the rhizosphere bacterial community (A) and fungal community (B). Heatmap analysis of the correlation among the composition of rhizosphere bacteria (C) and fungi (D) at the genus level, soil properties and plant traits. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01. SOM, soil organic matter; AN, alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen; AK, available potassium; AP, available phosphorus; POL, polygalaxanthone III; DISS, 3,6’-disinapoylsucrose. CF, PMI1, PMI2, SMI1, SMI2, MF1, and MF2 were as defined in the footnote to Figure 1.
According to the Pearson test between plant traits and microbial community, underground biomass and DISS content were positively correlated with the RA of Chloroflexi (p < 0.01) and negatively correlated with the RA of Proteobacteria (p < 0.05) (Supplementary Figure S3). Rhizosphere microbial communities exhibited a response to reduced chemical fertilizer application and the utilization of BOFs by promoting the proliferation of oligotrophs (e.g., some Chloroflexi) while suppressing copiotrophs (e.g., some Proteobacteria) (Dai et al., 2018). Oligotrophs such as Chloroflexi exhibited a pronounced substrate affinity and preferentially decompose resistant carbon (Hug et al., 2013; Banerjee et al., 2016). Chloroflexi plays a central role in the symbiotic relationships between soil bacteria, fungi, and plants. Specifically, Chloroflexi can fix CO2 and convert inorganic carbon into biodegradable organic matter, and it also acts as producers of nutrients such as phosphorus and nitrogen (Narsing Rao et al., 2022; Freches and Fradinho, 2024). In this study, Chloroflexi exhibited the highest RAs in MFs, showing a significant increase of 31.06% and 38.27% compared to CF in MF1 and MF2, respectively. Additionally, SOM content in MF1 was significantly higher than CF (p < 0.05). Therefore, the application of microalgae may positively stimulate specific species within Chloroflexi, thereby improving soil carbon cycling, enhancing soil fertility, promoting nutrient absorption by plants, and ultimately increasing biomass accumulation and bioactive component production in P. tenuifolia.
4 Conclusion
This study focused on P. tenuifolia, assessing the impact of substituting chemical fertilizer with BOFs on its underground growth, bioactive component contents, soil properties, rhizosphere bacterial and fungal communities. The objective is to determine how BOF application affects P. tenuifolia’s growth, quality, soil fertility, and the rhizosphere microenvironment. The results showed that BOFs maintained the quality and yield of P. tenuifolia while reducing chemical fertilizer application by 20% and 40%. Among them, MF not only exhibited the greatest growth-promoting effect but also significantly enhanced the accumulation of bioactive components in P. tenuifolia. Substituting 40% chemical fertilizer with microalgae resulted in a 29.30% increase in underground biomass and a 19.72% increase in 3,6’-disinapoylsucrose content. microalgae partially substituting chemical fertilizer also significantly altered the composition of rhizosphere microbial communities, with a greater impact on bacterial community rather than fungal community. MF and PMI partially substituting for chemical fertilizer enhanced soil fertility by increasing organic matter and available phosphorus levels, respectively. Cholorflexi exhibited the highest relative abundances in MFs, and correlation analysis revealed a positive association between plant traits and Cholorflexi, indicating that microalgae partial substitution for chemical fertilizer may stimulate Chloroflexi species associated with carbon cycling, thereby enhancing both growth and quality of P. tenuifolia. Moreover, Streptomyces had the highest relative abundances in PMIs and was identified as biomarker for PMI2, and correlation analysis also revealed a positive association between available phosphorus content and Streptomyces, indicating that PMI may recruit Streptomyces to increase the soil available phosphorus content without compromising the underground growth and bioactive component contents of P. tenuifolia. In conclusion, these findings underscore the potential of microalgae and microbial inoculant as chemical fertilizer substitutes to enhance the growth and quality P. tenuifolia by improving soil microorganisms. This study provides a theoretical foundation for the utilization of microalgae and microbial inoculants as partial substitutes for chemical fertilizer to enhance productivity and improve soil quality in medicinal plants.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are publicly available. This data can be found here: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioproject/PRJNA1206537.
Author contributions
YS: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YR: Resources, Writing – review & editing. GW: Resources, Writing – review & editing. JL: Writing – review & editing. HZ: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. YY: Writing – review & editing. XP: Writing – review & editing. JH: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by grants from the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2022YFC3501503).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpls.2024.1499966/full#supplementary-material
References
Abinandan, S., Subashchandrabose, S. R., Venkateswarlu, K., Megharaj, M. (2019). Soil microalgae and cyanobacteria: the biotechnological potential in the maintenance of soil fertility and health. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 39, 981–998. doi: 10.1080/07388551.2019.1654972
Abou-El-Seoud, I. I., Abdel-Megeed, A. (2012). Impact of rock materials and biofertilizations on P and K availability for maize (Zea Maize) under calcareous soil conditions. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 19, 55–63. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2011.09.001
Adesemoye, A. O., Torbert, H. A., Kloepper, J. W. (2009). Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria allow reduced application rates of chemical fertilizers. Microb. Ecol. 58, 921–929. doi: 10.1007/s00248-009-9531-y
Ali, S., Kim, W.-C. (2018). Plant growth promotion under water: decrease of waterlogging-induced ACC and ethylene levels by ACC deaminase-producing bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 9. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.01096
Alori, E. T., Glick, B. R., Babalola, O. O. (2017). Microbial phosphorus solubilization and its potential for use in sustainable agriculture. Front. Microbiol. 8. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00971
Álvarez-González, A., Uggetti, E., Serrano, L., Gorchs, G., Ferrer, I., Díez-Montero, R. (2022). Can microalgae grown in wastewater reduce the use of inorganic fertilizers? J. Environ. Manage 323, 116224. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.116224
Ambrosini, A., de Souza, R., Passaglia, L. M.P. (2016). Ecological role of bacterial inoculants and their potential impact on soil microbial diversity. Plant Soil 400, 193–207. doi: 10.1007/s11104-015-2727-7
Bai, N., Zhang, H., He, Y., Zhang, J., Zheng, X., Zhang, H., et al. (2022). Effects of Bacillus subtilis A-5 and its fermented γ-polyglutamic acid on the rhizosphere bacterial community of Chinese cabbage. Front. Microbiol. 13. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.954489
Banerjee, S., Kirkby, C. A., Schmutter, D., Bissett, A., Kirkegaard, J. A., Richardson, A. E. (2016). Network analysis reveals functional redundancy and keystone taxa amongst bacterial and fungal communities during organic matter decomposition in an arable soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 97, 188–198. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2016.03.017
Bao, Z.-X., Liu, R., Li, C.-Q., Pan, X.-R., Zhao, P.-J. (2022). Pathogenicity and Metabolites of Purpureocillium lavendulum YMF1.00683 against Meloidogyne incognita. Pathogens 11, 795. doi: 10.3390/pathogens11070795
Berendsen, R. L., Pieterse, C. M. J., Bakker, P. A. H. M. (2012). The rhizosphere microbiome and plant health. Trends Plant Sci. 17, 478–486. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2012.04.001
Boss, B. L., Wanees, A. E., Zaslow, S. J., Normile, T. G., Izquierdo, J. A. (2022). Comparative genomics of the plant-growth promoting bacterium Sphingobium sp. strain AEW4 isolated from the rhizosphere of the beachgrass Ammophila breviligulata. BMC Genomics 23, 508. doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-08738-8
Calvo, P., Watts, D. B., Ames, R. N., Kloepper, J. W., Torbert, H. A. (2013). Microbial-based inoculants impact nitrous oxide emissions from an incubated soil medium containing urea fertilizers. J. Environ. Qual 42, 704–712. doi: 10.2134/jeq2012.0300
Calvo, P., Watts, D. B., Kloepper, J. W., Torbert, H. A. (2016). Application of microbial-based inoculants for reducing N2O emissions from soil under two different ammonium nitrate–based fertilizers. Soil Sci. 181, 427. doi: 10.1097/SS.0000000000000176
Cao, T. N.-D., Mukhtar, H., Le, L.-T., Tran, D. P.-H., Ngo, M. T. T., Pham, M.-D.-T., et al. (2023). Roles of microalgae-based biofertilizer in sustainability of green agriculture and food-water-energy security nexus. Sci. Total Environ. 870, 161927. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.161927
Cao, Y., Zhang, Z., Ling, N., Yuan, Y., Zheng, X., Shen, B., et al. (2011). Bacillus subtilis SQR 9 can control Fusarium wilt in cucumber by colonizing plant roots. Biol. Fertil. Soils 47, 495–506. doi: 10.1007/s00374-011-0556-2
Cebekhulu, S., Gómez-Arias, A., Matu, A., Alom, J., Valverde, A., Caraballo, M. A., et al. (2024). Role of indigenous microbial communities in the mobilization of potentially toxic elements and rare-earth elements from alkaline mine waste. J. Hazard. Mater. 466, 133504. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2024.133504
Cheah, W. Y., Show, P. L., Chang, J.-S., Ling, T. C., Juan, J. C. (2015). Biosequestration of atmospheric CO2 and flue gas-containing CO2 by microalgae. Biores. Technol. 184, 190–201. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2014.11.026
Chen, Y., Li, S., Liu, N., He, H., Cao, X., Lv, C., et al. (2021). Effects of different types of microbial inoculants on available nitrogen and phosphorus, soil microbial community, and wheat growth in high-P soil. Environ. Sci. pollut. Res. Int. 28, 23036–23047. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-12203-y
Chu, H., Grogan, P. (2010). Soil microbial biomass, nutrient availability and nitrogen mineralization potential among vegetation-types in a low arctic tundra landscape. Plant Soil 329, 411–420. doi: 10.1007/s11104-009-0167-y
Coppens, J., Grunert, O., Van Den Hende, S., Vanhoutte, I., Boon, N., Haesaert, G., et al. (2016). The use of microalgae as a high-value organic slow-release fertilizer results in tomatoes with increased carotenoid and sugar levels. J. Appl. Phycol. 28, 2367–2377. doi: 10.1007/s10811-015-0775-2
Cordovez, V., Schop, S., Hordijk, K., Dupré de Boulois, H., Coppens, F., Hanssen, I., et al. (2018). Priming of plant growth promotion by volatiles of root-associated microbacterium spp. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 84, e01865–e01818. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01865-18
Dadrasan, M., Chaichi, M. R., Pourbabaee, A. A., Yazdani, D., Keshavarz-Afshar, R. (2015). Deficit irrigation and biological fertilizer influence on yield and trigonelline production of fenugreek. Ind. Crops Prod. 77, 156–162. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2015.08.040
Dai, Z., Su, W., Chen, H., Barberán, A., Zhao, H., Yu, M., et al. (2018). Long-term nitrogen fertilization decreases bacterial diversity and favors the growth of Actinobacteria and Proteobacteria in agro-ecosystems across the globe. Glob. Chang. Biol. 24, 3452–3461. doi: 10.1111/gcb.14163
Deng, X., Zhang, N., Li, Y., Zhu, C., Qu, B., Liu, H., et al. (2022). Bio-organic soil amendment promotes the suppression of Ralstonia solanacearum by inducing changes in the functionality and composition of rhizosphere bacterial communities. New Phytol. 235, 1558–1574. doi: 10.1111/nph.18221
Deng, X., Zhao, S., Liu, X., Han, L., Wang, R., Hao, H., et al. (2020). Polygala tenuifolia: a source for anti-Alzheimer’s disease drugs. Pharm. Biol. 58, 410–416. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2020.1758732
Díaz, L. E., Gonzalez, J. D., Morales-Gonzalez, M. P., Garzón-Castro, C. L. (2024). Harnessing the power of microalgae consortia for sustainable crop production: case study on lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.). J. Appl. Phycol. 36, 3273–3286. doi: 10.1007/s10811-024-03308-9
Egidi, E., Delgado-Baquerizo, M., Plett, J. M., Wang, J., Eldridge, D. J., Bardgett, R. D., et al. (2019). A few Ascomycota taxa dominate soil fungal communities worldwide. Nat. Commun. 10, 2369. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-10373-z
Freches, A., Fradinho, J. C. (2024). The biotechnological potential of the Chloroflexota phylum. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 90, e01756–e01723. doi: 10.1128/aem.01756-23
Gu, Y.-Y., Liang, X.-Y., Zhang, H.-Y., Fu, R., Li, M., Chen, C.-J. (2023). Effect of biochar and bioorganic fertilizer on the microbial diversity in the rhizosphere soil of Sesbania cannabina in saline-alkaline soil. Front. Microbiol. 14. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1190716
Guo, J. H., Liu, X. J., Zhang, Y., Shen, J. L., Han, W. X., Zhang, W. F., et al. (2010). Significant acidification in major Chinese croplands. Science 327, 1008–1010. doi: 10.1126/science.1182570
Hu, Y., Liu, M., Liu, P., Guo, D.-H., Wei, R.-B., Rahman, K. (2011). Possible mechanism of the antidepressant effect of 3,6’-disinapoylsucrose from Polygala tenuifolia Willd. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 63, 869–874. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.2011.01281.x
Huang, Z., Ruan, S., Sun, Y., Cheng, X., Dai, J., Gui, P., et al. (2022). Bacterial inoculants improved the growth and nitrogen use efficiency of Pyrus betulifolia under nitrogen-limited conditions by affecting the native soil bacterial communities. Appl. Soil Ecol. 170, 104285. doi: 10.1016/j.apsoil.2021.104285
Hug, L. A., Castelle, C. J., Wrighton, K. C., Thomas, B. C., Sharon, I., Frischkorn, K. R., et al. (2013). Community genomic analyses constrain the distribution of metabolic traits across the Chloroflexi phylum and indicate roles in sediment carbon cycling. Microbiome 1, 22. doi: 10.1186/2049-2618-1-22
Ji, H. Y., Luo, Y., Jing, Y. Y., Tan, K., Peng, L., Hu, B. X. (2023). Effects of different soils on accumulation of landmark components, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities and inhibitory ability of acetylcholinesterase in Polygala. Lishizhen Med. Mater. Med. Res. 34, 166–169. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0805.2023.01.45
Jiang, Z.-M., Mou, T., Sun, Y., Su, J., Yu, L.-Y., Zhang, Y.-Q. (2023). Environmental distribution and genomic characteristics of Solirubrobacter, with proposal of two novel species. Front. Microbiol. 14. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1267771
Jin, N., Jin, L., Wang, S., Li, J., Liu, F., Liu, Z., et al. (2022). Reduced chemical fertilizer combined with bio-organic fertilizer affects the soil microbial community and yield and quality of lettuce. Front. Microbiol. 13. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.863325
Kamdem, C. N., Fogue, P. S., Tiofack, A. A. Z., Mewamba, E. M., Womeni, H. M., Koffi, M., et al. (2023). Assessment of cetyl-trimethyl-ammonium bromide (CTAB) based method for the extraction of soil-transmitted helminth DNAs from stools for molecular dagnostic of soil-transmitted helminthiasis. J. Microbiol. Methods 204, 106661. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2022.106661
Kim, Y. C., Leveau, J., McSpadden Gardener, B. B., Pierson, E. A., Pierson, L. S., Ryu, C.-M. (2011). The multifactorial basis for plant health promotion by plant-associated bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 77, 1548–1555. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01867-10
Klimasmith, I. M., Kent, A. D. (2022). Micromanaging the nitrogen cycle in agroecosystems. Trends Microbiol. 30, 1045–1055. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2022.04.006
Kong, Z., Wu, Z., Glick, B. R., He, S., Huang, C., Wu, L. (2019). Co-occurrence patterns of microbial communities affected by inoculants of plant growth-promoting bacteria during phytoremediation of heavy metal-contaminated soils. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 183, 109504. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109504
Lei, X. D., Li, J. W., Xu, X. L., Zhang, H. L., Cao, L. K. (2012). Effect of microbial inoculants on spinach growth characteristics and soil microbial diversity. zgstnyxb 20, 488–494. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1011.2012.00488
Li, Q., Zhang, D., Song, Z., Ren, L., Jin, X., Fang, W., et al. (2022). Organic fertilizer activates soil beneficial microorganisms to promote strawberry growth and soil health after fumigation. Environ. pollut. 295, 118653. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.118653
Lin, R., Yang, Q., Xiao, J., Solairaj, D., Ngea, G. L. N., Zhang, H. (2022). Study on the biocontrol effect and physiological mechanism of Hannaella sinensis on the blue mold decay of apples. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 382, 109931. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2022.109931
Liu, Z.-S., Wang, K.-H., Cai, M., Yang, M.-L., Wang, X.-K., Ma, H.-L., et al. (2023). Agromyces chromiiresistens sp. nov., Novosphingobium album sp. nov., Sphingobium arseniciresistens sp. nov., Sphingomonas pollutisoli sp. nov., and Salinibacterium metalliresistens sp. nov.: five new members of Microbacteriaceae and Sphingomonadaceae from polluted soil. Front. Microbiol. 14. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1289110
Liu, L., Zhang, X., Xu, W., Liu, X., Li, Y., Wei, J., et al. (2020). Ammonia volatilization as the major nitrogen loss pathway in dryland agro-ecosystems. Environ. pollut. 265, 114862. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114862
Liu, C., Zhuang, J., Wang, J., Fan, G., Feng, M., Zhang, S. (2022). Soil bacterial communities of three types of plants from ecological restoration areas and plant-growth promotional benefits of Microbacterium invictum (strain X-18). Front. Microbiol. 13. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.926037
Luo, L., Zhao, C., Wang, E., Raza, A., Yin, C. (2022). Bacillus amyloliquefaciens as an excellent agent for biofertilizer and biocontrol in agriculture: An overview for its mechanisms. Microbiol. Res. 259, 127016. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2022.127016
Marks, E. A. N., Miñón, J., Pascual, A., Montero, O., Navas, L. M., Rad, C. (2017). Application of a microalgal slurry to soil stimulates heterotrophic activity and promotes bacterial growth. Sci. Total Environ. 605–606, 610–617. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.06.169
Narsing Rao, M. P., Luo, Z. H., Dong, Z. Y., Li, Q., Liu, B. B., Guo, S. X., et al. (2022). Metagenomic analysis further extends the role of Chloroflexi in fundamental biogeochemical cycles. Environ. Res. 209, 112888. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2022.112888
Nguyen, T. T. N., Wallace, H. M., Xu, C.-Y., Zwieten, L., Weng, Z. H., Xu, Z., et al. (2018). The effects of short term, long term and reapplication of biochar on soil bacteria. Sci. Total Environ. 636, 142–151. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.04.278
Ning, Q., Chen, L., Li, F., Zhang, C. Z., Ma, D. H., Cai, Z. J., et al. (2022). Effects of mortierella on nutrient availability and straw decomposition in soil. Acta Pedol. Sin. 59, 206–217. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0805.2023.01.45
Omar, A. F., Abdelmageed, A. H. A., Al-Turki, A., Abdelhameid, N. M., Sayyed, R. Z., Rehan, M. (2022). Exploring the plant growth-promotion of four streptomyces strains from rhizosphere soil to enhance cucumber growth and yield. Plants (Basel) 11, 3316. doi: 10.3390/plants11233316
Ozimek, E., Hanaka, A. (2021). Mortierella species as the plant growth-promoting fungi present in the agricultural soils. Agriculture. 11, 7. doi: 10.3390/agriculture11010007
Parmar, P., Kumar, R., Neha, Y., Srivatsan, V. (2023). Microalgae as next generation plant growth additives: Functions, applications, challenges and circular bioeconomy based solutions. Front. Plant Sci. 14. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1073546
Pu, Y. J., Wang, D. D., Yan, Y., Tian, H. L., Peng, B., Qin, X. M., et al. (2017). Analysis of influencing factors of secondary metabolites contents in cultivated Polygala tenuifolia. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 42, 3167–3177. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.2017.0125
Qin, S., Miao, Q., Feng, W. W., Wang, Y., Zhu, X., Xing, K., et al. (2015). Biodiversity and plant growth promoting traits of culturable endophytic actinobacteria associated with Jatropha curcas L. growing in Panxi dry-hot valley soil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 93, 47–55. doi: 10.1016/J.APSOIL.2015.04.004
Qiu, Y., Pang, H., Zhou, Z., Zhang, P., Feng, Y., Sheng, G. D. (2009). Competitive biodegradation of dichlobenil and atrazine coexisting in soil amended with a char and citrate. Environ. pollut. 157, 2964–2969. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2009.06.003
Rajput, M. S., Naresh Kumar, G., Rajkumar, S. (2013). Repression of oxalic acid-mediated mineral phosphate solubilization in rhizospheric isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae by succinate. Arch. Microbiol. 195, 81–88. doi: 10.1007/s00203-012-0850-x
Ren, X.-M., Guo, S.-J., Tian, W., Chen, Y., Han, H., Chen, E., et al. (2019). Effects of plant growth-promoting bacteria (PGPB) inoculation on the growth, antioxidant activity, cu uptake, and bacterial community structure of rape (Brassica napus L.) grown in cu-contaminated agricultural soil. Front. Microbiol. 10. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01455
Rensink, S., van Nieuwenhuijzen, E. J., Sailer, M. F., Struck, C., Wösten, H. A. B. (2024). Use of Aureobasidium in a sustainable economy. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 108, 202. doi: 10.1007/s00253-024-13025-5
Renuka, N., Guldhe, A., Prasanna, R., Singh, P., Bux, F. (2018). Microalgae as multi-functional options in modern agriculture: current trends, prospects and challenges. Biotechnol. Adv. 36, 1255–1273. doi: 10.1016/j.bioteChadv.2018.04.004
Rezasoltani, S., Champagne, P. (2023). An integrated approach for the phycoremediation of Pb (II) and the production of biofertilizer using nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria. J. Hazard Mater 445, 130448. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.130448
Saud, S., Wang, D., Fahad, S. (2022). Improved nitrogen use efficiency and greenhouse gas emissions in agricultural soils as producers of biological nitrification inhibitors. Front. Plant Sci. 13. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.854195
Semenov, M. V., Krasnov, G. S., Semenov, V. M., Ksenofontova, N., Zinyakova, N. B., van Bruggen, A. H. C. (2021). Does fresh farmyard manure introduce surviving microbes into soil or activate soil-borne microbiota? J. Environ. Manage 294, 113018. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113018
Shahwar, D., Mushtaq, Z., Mushtaq, H., Alqarawi, A. A., Park, Y., Alshahrani, T. S., et al. (2023). Role of microbial inoculants as bio fertilizers for improving crop productivity: A review. Heliyon 9, e16134. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e16134
Sharma, S. B., Sayyed, R. Z., Trivedi, M. H., Gobi, T. A. (2013). Phosphate solubilizing microbes: sustainable approach for managing phosphorus deficiency in agricultural soils. Springerplus 2, 587. doi: 10.1186/2193-1801-2-587
Shi, H., Lu, L., Ye, J., Shi, L. (2022). Effects of two bacillus velezensis microbial inoculants on the growth and rhizosphere soil environment of prunus davidiana. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 13639. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113639
Shrestha, R. C., Ghazaryan, L., Poodiack, B., Zorin, B., Gross, A., Gillor, O., et al. (2022). The effects of microalgae-based fertilization of wheat on yield, soil microbiome and nitrogen oxides emissions. Sci. Total Environ. 806, 151320. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.151320
Sido, M. Y., Tian, Y., Wang, X., Wang, X. (2022). Application of microalgae Chlamydomonas applanata M9V and Chlorella vulgaris S3 for wheat growth promotion and as urea alternatives. Front. Microbiol. 13. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1035791
Sousa, J. A., de, J., Olivares, F. L. (2016). Plant growth promotion by streptomycetes: ecophysiology, mechanisms and applications. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 3, 24. doi: 10.1186/s40538-016-0073-5
Stone, B. W., Li, J., Koch, B. J., Blazewicz, S. J., Dijkstra, P., Hayer, M., et al. (2021). Nutrients cause consolidation of soil carbon flux to small proportion of bacterial community. Nat. Commun. 12, 3381. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-23676-x
Sun, B., Bai, Z., Bao, L., Xue, L., Zhang, S., Wei, Y., et al. (2020). Bacillus subtilis biofertilizer mitigating agricultural ammonia emission and shifting soil nitrogen cycling microbiomes. Environ. Int. 144, 105989. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2020.105989
Sun, W., Xiong, Z., Chu, L., Li, W., Soares, M. A., White, J. F., et al. (2019). Bacterial communities of three plant species from Pb-Zn contaminated sites and plant-growth promotional benefits of endophytic Microbacterium sp. (strain BXGe71). J. Hazard Mater 370, 225–231. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.02.003
Teng, H. M., Cai, X., Hu, Z. H. (2009). The relationship between morphological development and accumulation of saponins in the root of Polygala tenuifolia Willd. Planta Med. 75, 1033–1033. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1234820
Thomas, F., Corre, E., Cébron, A. (2019). Stable isotope probing and metagenomics highlight the effect of plants on uncultured phenanthrene-degrading bacterial consortium in polluted soil. ISME J. 13, 1814–1830. doi: 10.1038/s41396-019-0394-z
Timofeeva, A., Galyamova, M., Sedykh, S. (2022). Prospects for using phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms as natural fertilizers in agriculture. Plants (Basel) 11, 2119. doi: 10.3390/plants11162119
Trabelsi, D., Mhamdi, R. (2013). Microbial inoculants and their impact on soil microbial communities: a review. BioMed. Res. Int. 2013, 863240. doi: 10.1155/2013/863240
van der Heijden, M. G. A., Bardgett, R. D., van Straalen, N. M. (2008). The unseen majority: soil microbes as drivers of plant diversity and productivity in terrestrial ecosystems. Ecol. Lett. 11, 296–310. doi: 10.1111/j.1461-0248.2007.01139.x
Vurukonda, S. S. K. P., Giovanardi, D., Stefani, E. (2018). Plant growth promoting and biocontrol activity of streptomyces spp. as endophytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19, 952. doi: 10.3390/ijms19040952
Waltz, E. (2017). A new crop of microbe startups raises big bucks, takes on the establishment. Nat. Biotechnol. 35, 1120–1122. doi: 10.1038/nbt1217-1120
Wang, T., Cheng, K., Huo, X., Meng, P., Cai, Z., Wang, Z., et al. (2022). Bioorganic fertilizer promotes pakchoi growth and shapes the soil microbial structure. Front. Plant Sci. 13. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1040437
Wang, X., Ji, C., Song, X., Liu, Z., Liu, Y., Li, H., et al. (2021). Biocontrol of two bacterial inoculant strains and their effects on the rhizosphere microbial community of field-grown wheat. BioMed. Res. Int. 2021, 8835275. doi: 10.1155/2021/8835275
Wang, B., Wan, C.-X., Zeng, H. (2020). Colonization on cotton plants with a GFP labeled strain of bacillus axarquiensis. Curr. Microbiol. 77, 3085–3094. doi: 10.1007/s00284-020-02071-7
Wei, X., Bai, X., Cao, P., Wang, G., Han, J., Zhang, Z. (2023). Bacillus and microalgae biofertilizers improved quality and biomass of Salvia miltiorrhiza by altering microbial communities. Chin. Herb Med. 15, 45–56. doi: 10.1016/j.chmed.2022.01.008
Wei, X., Cao, P., Wang, G., Liu, Y., Song, J., Han, J. (2021). CuO, ZnO, and γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles modified the underground biomass and rhizosphere microbial community of Salvia miltiorrhiza (Bge.) after 165-day exposure. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 217, 112232. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112232
Wu, S., Zhuang, G., Bai, Z., Cen, Y., Xu, S., Sun, H., et al. (2018). Mitigation of nitrous oxide emissions from acidic soils by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, a plant growth-promoting bacterium. Glob. Chang. Biol. 24, 2352–2365. doi: 10.1111/gcb.14025
Xiao, R., Zheng, Y. (2016). Overview of microalgal extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) and their applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 34, 1225–1244. doi: 10.1016/j.bioteChadv.2016.08.004
Xing, K., Bian, G.-K., Qin, S., Klenk, H.-P., Yuan, B., Zhang, Y.-J., et al. (2012). Kibdelosporangium phytohabitans sp. nov., a novel endophytic actinomycete isolated from oil-seed plant Jatropha curcas L. containing 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid deaminase. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 101, 433–441. doi: 10.1007/s10482-011-9652-4
Xiong, Y., Jiang, J., Qin, S. (2019). Research progress of kibdelosporangium. Acta Microbiol. Sin. 59, 799–808. doi: 10.13343/j.cnki.wsxb.20180298
Xu, X. S., Zhang, Y. H., Wang, D. D., Zhang, F. S., Qin, X. M., Peng, B., et al. (2016). UPLC/Q-TOF MS-based metabolomics in analyzing the key factors affecting the quality of commercial Polygala tenuifolia. J. Shanxi Med. Univ. 47, 255–263. doi: 10.13753/j.issn.1007-6611.2016.03.014
Xue, L., Sun, B., Yang, Y., Jin, B., Zhuang, G., Bai, Z., et al. (2021). Efficiency and mechanism of reducing ammonia volatilization in alkaline farmland soil using Bacillus amyloliquefaciens biofertilizer. Environ. Res. 202, 111672. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2021.111672
Yang, Y., Li, G., Min, K., Liu, T., Li, C., Xu, J., et al. (2022). The potential role of fertilizer-derived exogenous bacteria on soil bacterial community assemblage and network formation. Chemosphere 287, 132338. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132338
Yang, X., Xiong, B., Yuan, Z., Liao, H., Liu, X., Wu, Y., et al. (2022). Polygalaxanthone III, an Active Ingredient in Polygala japonica Houtt., Repaired Malassezia-Stimulated Skin Injury via STAT3 Phosphorylated Activation. Molecules 27, 7520. doi: 10.3390/molecules27217520
Yang, Q., Zhang, X., Solairaj, D., Lin, R., Wang, K., Zhang, H. (2023). TMT-based proteomic analysis of hannaella sinensis-induced apple resistance-related proteins. Foods 12, 2637. doi: 10.3390/foods12142637
Ye, L., Zhao, X., Bao, E., Li, J., Zou, Z., Cao, K. (2020). Bio-organic fertilizer with reduced rates of chemical fertilization improves soil fertility and enhances tomato yield and quality. Sci. Rep. 10, 177. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-56954-2
Yin, A., Jia, Y., Qiu, T., Gao, M., Cheng, S., Wang, X., et al. (2018). Poly-γ-glutamic acid improves the drought resistance of maize seedlings by adjusting the soil moisture and microbial community structure. Appl. Soil Ecol. 129, 128–135. doi: 10.1016/j.apsoil.2018.05.008
Yuan, X., Zhang, J., Chang, F., Wang, X., Zhang, X., Luan, H., et al. (2023). Effects of nitrogen reduction combined with bio-organic fertilizer on soil bacterial community diversity of red raspberry orchard. PloS One 18, e0283718. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0283718
Zhang, X., Guo, J., Vogt, R. D., Mulder, J., Wang, Y., Qian, C., et al. (2020). Soil acidification as an additional driver to organic carbon accumulation in major Chinese croplands. Geoderma 366, 114234. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2020.114234
Zhang, R., Wu, C. J., Zhang, L. J., Guo, S. H., Tian, H. L. (2022). Genetic diversity and comprehensive evaluation of polygala tenuifolia based on morphological traits and indicative components. J. Nucl. Agric. Sci. 36, 2381–2390. doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2022.12.2381
Zhang, J., Xie, J., Liang, Y., Li, Y., Zhang, Y., Wang, C., et al. (2022). Anxiolytic effects, metabolism and plasma pharmacokinetics of 3, 6’ -disinapoylsucrose. BioMed. Pharmacother. 149, 112913. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112913
Zhang, Z., Xu, M., Fan, Y., Zhang, L., Wang, H. (2024). Using microalgae to reduce the use of conventional fertilizers in hydroponics and soil-based cultivation. Sci. Total Environ. 912, 169424. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.169424
Zhang, L., Yong, Y.-Y., Deng, L., Wang, J., Law, B. Y.-K., Hu, M.-L., et al. (2023). Therapeutic potential of Polygala saponins in neurological diseases. Phytomedicine 108, 154483. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154483
Zheng, Y., Yu, C., Xiao, Y., Ye, T., Wang, S. (2024). The impact of utilizing oyster shell soil conditioner on the growth of tomato plants and the composition of inter-root soil bacterial communities in an acidic soil environment. Front. Microbiol. 14. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1276656
Zhou, L., Liu, W., Duan, H., Dong, H., Li, J., Zhang, S., et al. (2023). Improved effects of combined application of nitrogen-fixing bacteria Azotobacter beijerinckii and microalgae Chlorella pyrenoidosa on wheat growth and saline-alkali soil quality. Chemosphere 313, 137409. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.137409
Zhou, G.-C., Wang, Y., Ma, Y., Zhai, S., Zhou, L.-Y., Dai, Y.-J., et al. (2014). The metabolism of neonicotinoid insecticide thiamethoxam by soil enrichment cultures, and the bacterial diversity and plant growth-promoting properties of the cultured isolates. J. Environ. Sci. Health B 49, 381–390. doi: 10.1080/03601234.2014.894761
Zhuang, X., Chen, J., Shim, H., Bai, Z. (2007). New advances in plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria for bioremediation. Environ. Int. 33, 406–413. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2006.12.005
Zou, Y., An, Z., Chen, X., Zheng, X., Zhang, B., Zhang, S., et al. (2023). Effects of co-applied biochar and plant growth-promoting bacteria on soil carbon mineralization and nutrient availability under two nitrogen addition rates. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 266, 115579. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2023.115579
Keywords: chemical fertilizer reduction, bio-organic fertilizer, rhizosphere microorganism, medicinal plant cultivation, Polygala tenuifolia
Citation: Su Y, Ren Y, Wang G, Li J, Zhang H, Yang Y, Pang X and Han J (2025) Microalgae and microbial inoculant as partial substitutes for chemical fertilizer enhance Polygala tenuifolia yield and quality by improving soil microorganisms. Front. Plant Sci. 15:1499966. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1499966
Received: 22 September 2024; Accepted: 20 December 2024;
Published: 16 January 2025.
Edited by:
Guangxin Yuan, Beihua University, ChinaReviewed by:
Shobhit Raj Vimal, University of Allahabad, IndiaZhaoqiang Han, Nanjing Agricultural University, China
Copyright © 2025 Su, Ren, Wang, Li, Zhang, Yang, Pang and Han. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jianping Han, aGFwcHlteXJhMjAwN0AxNjMuY29t
 Yuying Su
Yuying Su Ying Ren
Ying Ren Gang Wang
Gang Wang Xiaohui Pang
Xiaohui Pang Jianping Han
Jianping Han