
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Plant Sci. , 19 December 2024
Sec. Plant Bioinformatics
Volume 15 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2024.1496351
 Zefeng Li1,2
Zefeng Li1,2 Peijian Cao1,2
Peijian Cao1,2 Huabing Liu3
Huabing Liu3 Jianfeng Zhang1,2
Jianfeng Zhang1,2 Zhaopeng Luo1,2
Zhaopeng Luo1,2 Hui Zhang1,2
Hui Zhang1,2 Mingzhu Wu1,2
Mingzhu Wu1,2 Xiaodong Xie1,2*
Xiaodong Xie1,2*The INDETERMINATE DOMAIN (IDD) gene family, encoding a class of C2H2 transcription factor, played diverse roles in land plants. The IDD family in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) has not been characterized. In this study, 26 NtIDDs were identified in the tobacco genome. Phylogenetic analysis showed that NtIDDs were divided into five groups. Motif analysis revealed that the ID domain was conserved in NtIDDs. Gene duplication analysis demonstrated that segmental/whole-genome duplication and dispersed duplication would have occurred in NtIDDs. Cis-element analysis predicted that hormone-, stress-, and development-related elements are located in NtIDD promoters. Expression analysis revealed tissue preference patterns and differential hormone responses in NtIDDs. Further investigations on the function of NtIDD9 exhibited increased leaf angle degrees in RNA silencing plants. Cellular localization suggested that NtIDD9 expressed in the endodermis of the leaf petiole base. Subcellular localization analysis revealed that the NtIDD9 protein was located in the nucleus. Hormone quantification found that the levels of auxin, ABA, JA, and GA were significantly changed in NtIDD9-silenced plants. Thus, the study suggested that NtIDD9 played a crucial role in modulation of leaf angle development. Overall, these findings lay foundations for future function and mechanism research on IDDs in tobacco.
Transcription factors (TFs) are proteins involved in the process of gene transcription. TFs function through binding on DNA sequences and activating or repressing the transcription of downstream target genes. TFs are critical components in gene regulatory networks, governing gene expression in various circumstances. A number of TF families have been discovered in plants (Hong, 2016). Cys2His2 (C2H2) zinc finger transcription factors form one of the most significant and expansive families of transcription factors identified to date. The INDETERMINATE DOMAIN (IDD) family, encoding a class of C2H2 transcription factors, constitutes a conserved group across terrestrial plants. IDD genes are characterized by the INDETERMINATE (ID) domain. The ID domain is composed of two C2H2 and two Cys2CysHis (C2CH) zinc finger motifs (ZF1–ZF4) (Colasanti et al., 2006). Prior studies confirmed the involvement of IDDs in transcription regulation, in which C2H2 ZFs are important for DNA binding, whereas C2CH ZFs are necessary for protein–protein interaction (Kozaki et al., 2004; Hirano et al., 2017). In recent studies, with thousands of binding sites captured in the Arabidopsis genome, IDDs were also implied in widespread and complex transcriptional networks (O’Malley et al., 2016).
The IDD family proteins have been shown to participate in diverse processes, including plant development, metabolism, hormone signaling, and environmental stresses (Kumar et al., 2019). The first IDD gene, ZmIDD1, was cloned in maize. Analysis indicated that ZmIDD1 controls the transition to flowering in maize (Singleton, 1946; Colasanti et al., 1998). In rice, OsID1/Ehd2/RID1 has also been reported to act as a key regulator from vegetative to floral switches (Wu et al., 2008). Gain of function of OsIDD4 or OsIDD6 restored flowering of the rid1 mutant (Deng et al., 2017). OsIDD10 was found involved in ammonium uptake and nitrogen metabolism in the roots (Xuan et al., 2013a, 2013b). In Arabidopsis, there were 16 IDD genes identified. AtIDD1 was involved in seed maturation (Feurtado et al., 2011). AtIDD3 and AtIDD8 are involved in root development (Ingkasuwan et al., 2012). AtIDD10 controls root hair cell patterning in the epidermis (Hassan et al., 2010). AtIDD9 contributes to specifications of epidermal cell fate (Long et al., 2015a, 2015b). AtIDD8, AtIDD14, and AtIDD15 play an important role in sugar and starch metabolism (Tanimoto et al., 2008; Ingkasuwan et al., 2012). AtIDD2, AtIDD3, AtIDD4, AtIDD5, AtIDD9, and AtIDD10 regulates genes in gibberellin signaling (Fukazawa et al., 2014; Yoshida et al., 2014). AtIDD14, AtIDD15 and AtIDD16 cooperatively control organ morphogenesis and gravitropic responses by regulating auxin biosynthesis and transport (Cui et al., 2013). AtIDD14 could respond to cold stress via regulation of Qua-quine starch (QQS) expression (Li et al., 2009). AtIDD14 can also interact with ABFs/AREBs, pivotal genes in the abscisic acid signaling pathway, and positively regulate drought tolerance (Liu et al., 2022). AtIDD4 acts as a repressor of salt stress in Arabidopsis, and mutations in AtIDD4 confer enhanced salt tolerance (Rawat et al., 2023).
Leaf angle refers to the inclination formed between the leaf midvein and the stem, which is an important trait of plant architecture. The leaf angle has direct impacts on plant density, photosynthetic light use efficiency, stress tolerance, and, consequently, the overall yield of the plant (Cao et al., 2022). Until date, numerous genes have been reported to regulate leaf angle in plants. Among them, IDD genes are recognized to exert essential roles in leaf angle regulation. For example, in Arabidopsis, SHOOT GRAVITROPISM5 (SGR5), also named as AtIDD15, was initially detected able to change the shoot growth orientation by altering gravity sensing (Morita et al., 2006). Further characterization on its close homologs revealed that AtIDD14, AtIDD15, and AtIDD16 cooperatively regulate the orientation angles of both branches and siliques (Cui et al., 2013). In rice, the homologue of AtIDD15, OsIDD14/Loose Plant Architecture1 (LPA1) modulates rice tiller and leaf angle by controlling the adaxial growth at the tiller node and lamina joint (Wu et al., 2013).
Tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) is an important economic crop and cultivated widely. Growth and development, metabolism, and stress resistance are all key aspects for tobacco plant production. As versatile functions disclosed in model plants, the IDD family is deemed as a potential target for crop improvement (Coelho et al., 2018). At present, genome-wide identification and analysis of IDD family have been carried out in several plant species, such as rice, maize, cotton, rapeseed, pear, and apple (Fan et al., 2017; Ali et al., 2019; Su et al., 2019; Zhang et al., 2020; Sun et al., 2022; Feng et al., 2023). However, the IDD family in tobacco has not been characterized and reports on their functions are quite rare. Tobacco is also known as a leaf-harvesting crop. Adjusting the size of the leaf angle is a crucial strategy for managing both the yield and quality of tobacco leaf production. Nevertheless, studies on the genetic basis of leaf angle regulation in tobacco are limited. Although leaf angle regulatory roles of IDDs were characterized in Arabidopsis and rice, they were not fully investigated in tobacco yet.
In the current study, IDD members were identified in tobacco genome; their phylogeny, gene structures, protein motifs, chromosome distributions, duplications, and promoter cis-elements were analyzed. IDD gene expression profiles in different tissues and hormone treatments were also investigated. In addition, the role of NtIDD9 in leaf angle regulation was further explored. These results provide extensive understanding of the IDD family in tobacco and will facilitate the investigation of functions and regulatory mechanisms associated with IDD members.
AtIDD protein sequences were used as queries to search homologous genes in tobacco genome (Edwards et al., 2017) with BLASTP (E value<100) (Camacho et al., 2009). InterPro (v93, https://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/) (Paysan-Lafosse et al., 2023) was used to predict the ID domain (IPR031140). Sequences were subjected to manual curation. Genes with incomplete ID domains were removed. The molecular weights and isoelectric points were calculated with EMBOSS (Rice et al., 2000).
IDD protein sequences in Arabidopsis thaliana, rice, and maize were collected from Phytozome (v10, https://phytozome-next.jgi.doe.gov/) (Goodstein et al., 2012). Multiple-sequence alignments were carried out by MAFFT (v7.520) (Katoh and Standley, 2013). A phylogenetic tree was constructed by MEGA (v7.0.21) (Kumar et al., 2016) using the maximum likelihood (ML) method with bootstrap value 1,000. The tree was edited on iTOL (https://itol.embl.de/) (Letunic and Bork, 2021).
Gene structure annotations were obtained from the GFF3 file of tobacco genome annotation. MEME (v4.9.1) (Bailey et al., 2015) was used to discover motifs in NtIDD protein sequences with parameters (minw = 8, maxw = 50, nmotifs = 10). The gene structure and motifs were plotted with the custom Python script.
The genomic locations of NtIDDs were retrieved from the tobacco genome GFF3 file (Edwards et al., 2017 version, http://solgenomics.net/ftp/genomes/Nicotiana_tabacum/edwards_et_al_2017). Synteny analysis was performed using MCScanX (Wang et al., 2012); minimum five genes were required to call a syntenic block. The types of duplication were identified using the duplicate_gene_classifier program resided in the MCScanX package. Genome distributions and syntenic blocks were visualized using Circos software (Krzywinski et al., 2009).
For cis-element prediction, 1.5-kb upstream sequences of NtIDD genes were extracted and submitted to PlantCARE (https://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/plantcare/html/) (Lescot et al., 2002). NtIDD1 was not performed, due to too many ambiguous bases (N) in its promoter region. After prediction, filtering was further carried out, and elements involved in three categories (hormone responsive, stress responsive, and development related) were considered for analysis.
Public RNA-Seq data generated by a previous study (GenBank accession code: SRP029183) (Sierro et al., 2014) were used for tissue expression analysis. The data were mapped to tobacco genome with HISAT2 (v2.1.0) (Kim et al., 2019). Gene expression levels (FPKM, Fragments Per Kilobase of transcript per Million mapped reads) were estimated using StringTie2 (v2.1.7) (Pertea et al., 2015).
Tobacco plants intended for hormone treatments were cultivated in a greenhouse maintained at temperatures of 28/24°C, with regulated light conditions of 16 h of light and 8 h of darkness. 3-week-old tobacco seedlings were soaked into liquid medium containing 50 μM methyl jasmonate (MeJA), 10 μM abscisic acid (ABA), 10 μM salicylic acid (SA), 10 μM gibberellin acid (GA), 10 μM 6-benzylaminopurine (6-BA, cytokinin, CK), and 5 μM GR24 (strigolactone, SL), where they were cultured for a duration of 5 h. Control seedlings were treated with a 1% (v/v) dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) solution.
Samples were collected with three biological replicates. Total RNA of different samples was extracted with RNA Kit (Imagene, Beijing, China) according to the instruction. The DNA was firstly removed using RNase-free DNase I (Takara, Beijing, China). Then, high-quality RNA was used for cDNA synthesis using Reverse Transcriptase M-MLV (Takara). The quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) was quantified on a LightCycler® 96 Real-Time PCR System. The reaction program was set as the following: 95°C for 30 s, 40 cycles of 95°C for 10 s, 60°C for 30 s. The NtGAPDH gene was used as reference gene to standardize the expression level with the 2−△△CT method. The primer sequences are listed in Supplementary Table 6.
To construct RNA interference (RNAi) plants, the full-length coding sequence (CDS) of the NtIDD9 gene was firstly amplified. Subsequently, the derived PCR fragment was connected to the pBWA(V)HS vector through homologous recombination. The constructs were then transformed into tobacco with the help of Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain GV3101.
For cellular localization, RNA in situ hybridization was conducted according to the manufacturer’s protocol (Servicebio, Wuhan, China). The leaf petiole base tissue was fixed with in situ hybridization fixative (plant) and embedded in wax. Paraffin blocks were sliced 6 μm thick using a slicing machine. The slides were then dewaxed, dehydrated, digested, and hybridized to probes. After washing and dropping anti-Digoxin antibody, BCIP/NBT solution was used for chromogenic staining. Under microscopic observation, blue and blue-purple were interpreted as positive hybridization.
To verify the subcellular location of NtIDD9 protein, the full-length coding sequence (CDS) without stop codon was cloned into the pC1300 and C-terminal fused with enhanced green fluorescent protein (GFP). The product was reclaimed from the recombination ligation gel, and the recombinant plasmid obtained from the ligation was introduced into Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain GV3101. The vector harboring 35S::GFP-NtIDD9 and control vector were infiltrated into Nicotiana benthamiana leaves. After 24 h, fluorescence images were observed using a confocal microscope (FV1200 Olympus, Japan).
The samples were frozen in liquid nitrogen and crushed into fine powder. 50 mg of powdered samples was used to extract endogenous hormones with 1 mL of methyl−tert−butyl−ether (MTBE) solution containing MTBE, methanol, and water in a ratio of 15:4:1. After centrifugation, supernatant was collected to perform liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) analysis. The data were captured on instrument system UPLC (ExionLC™ AD) coupled with MS/MS (QTRAP® 6500+). By using each standard hormone calibration curve, the levels of seven endogenous hormones including auxins, cytokinins (CKs), gibberellin acids (GAs), methyl jasmonates (MeJAs), salicylic acids (SAs), abscisic acids (ABAs), and ethylenes (ETHs) were quantified. To get statistically meaningful results, three biological replicates were carried out. The differential analysis were determined using t-test with false discovery rate (FDR) < 0.05 and |log2(fold change)| ≥1.
Based on homology searching and ID domain prediction, 36 potential tobacco IDD genes were firstly screened (Supplementary Table 1). After removing genes without complete ID domains, totally 26 IDDs were identified in the tobacco genome. The characteristics of NtIDD genes are listed in Table 1 and Supplementary Table 2. In brief, the peptide lengths were ranged from 382 to 542. The molecular weights (Mw) were distributed from 44 kDa to 59.5 kDa. The isoelectric points (pI) were between 8.5 and 10.1. NtIDD protein sequences, together with IDDs from Arabidopsis thaliana, rice, and maize, were used to construct phylogenetic tree (Figure 1). Based on the tree, NtIDDs could be classified into five groups: group I (NtIDD11/20/18), group II (NtIDD12/2/19/10), group III (NtIDD17/14/26/8), group IV (NtIDD24/7/15/5/4/23/1/16/13), and group V (NtIDD25/3/22/21/6/9).
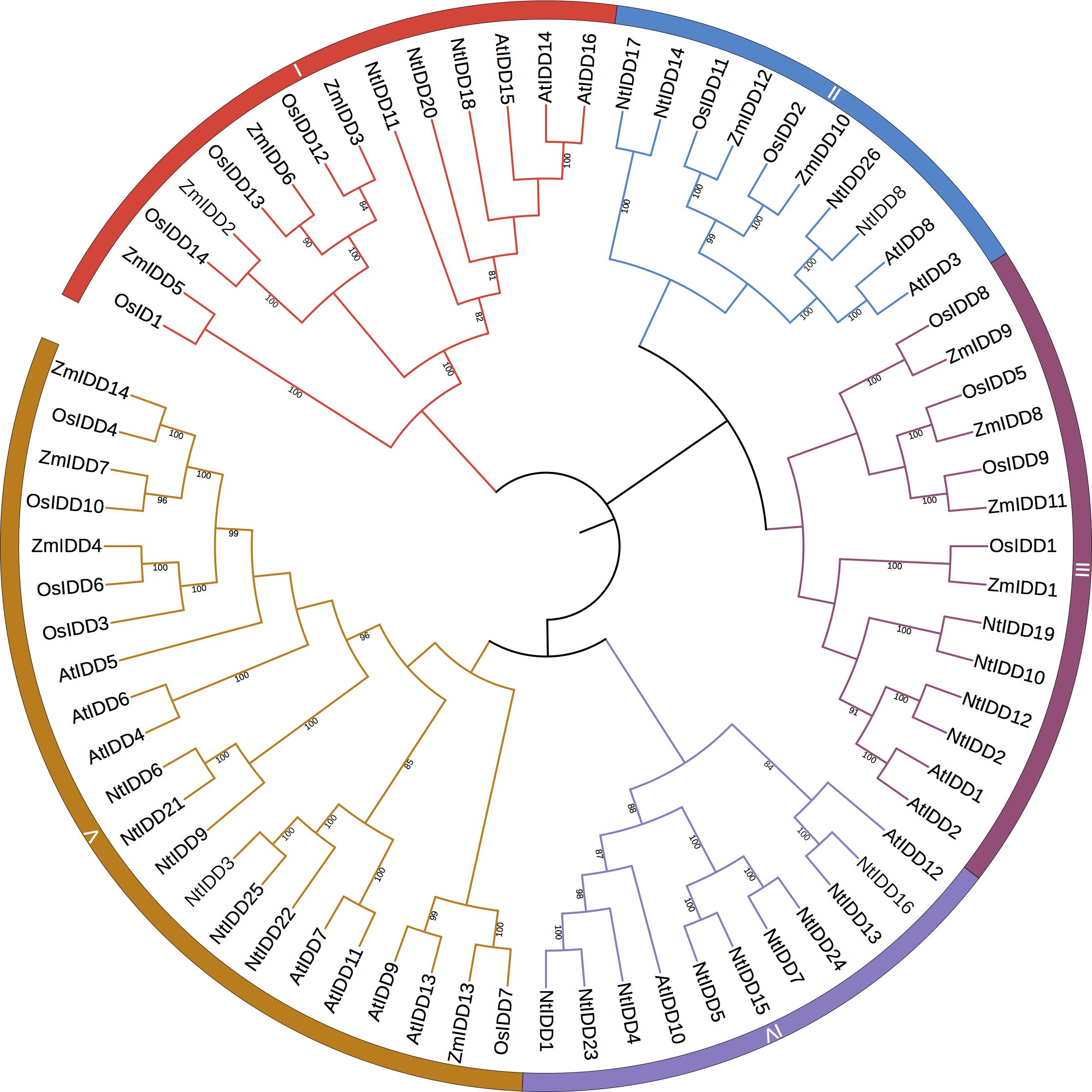
Figure 1. Phylogenetic tree of NtIDDs. Nt, Nicotiana tabacum; At, Arabidopsis thaliana; Zm, Zea mays; Os, Oryza sativa.
Most of NtIDD genes comprised three to four exons (Figure 2A). NtIDD15 contains five exons, whereas NtIDD1, NtIDD6, and NtIDD21 possess only two exons. The intron length of NtIDD genes varied greatly. The shortest and longest introns were found in NtIDD25 and NtIDD15, respectively. Using MEME, 10 motifs were identified in NtIDD protein sequences (Figure 2B). Among them, motif 1/3 were found in all NtIDDs, motif 2/4/5/6/7 were distributed in most of NtIDDs, motif 8 was specifically found in NtIDD1/9/6/21, motif 9 was found in NtIDD5/15/7/24/1/23/4, and motif 10 was found in NtIDD5/15/7/24/1/23/6/21/22. Motifs 1/2/3/8 were associated with the ID domain, which consists of two C2H2 zinc fingers and two C2CH zinc fingers (Figure 3).
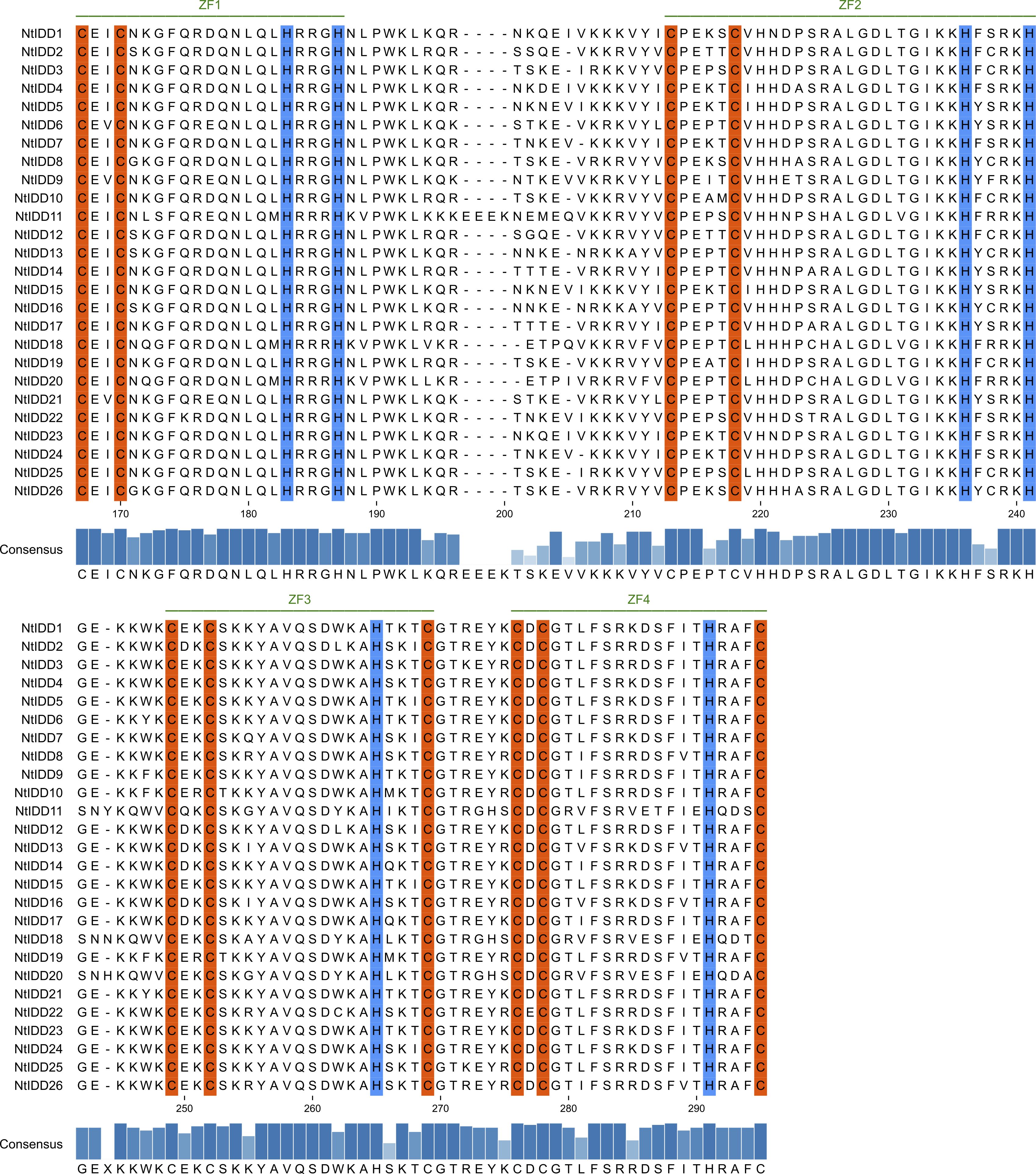
Figure 3. Multiple-sequence alignment of NtIDD proteins. Zinc finger motifs (ZF1, ZF2, ZF3, ZF4) are marked with green lines. The conserved amino acids cysteine and histidine are highlighted with orange and blue colors, respectively.
By investigating distributions of NtIDDs in the genome, 17 genes were positioned on chromosomes, and 9 genes were located on scaffolds (Figure 4). Using MCScanX, syntenic blocks were identified and the types of duplication were classified. There were 14 NtIDDs that were found involved in syntenic blocks (Figure 4) and therefore were deemed as segmental and/or whole-genome duplications (WGD). There were six syntenic gene pairs detected among these NtIDDs (NtIDD2/12, NtIDD5/15, NtIDD6/9, NtIDD7/15, NtIDD10/19, NtIDD13/16). The other 12 NtIDDs distributed out of synteny, and they were categorized as dispersed duplications.
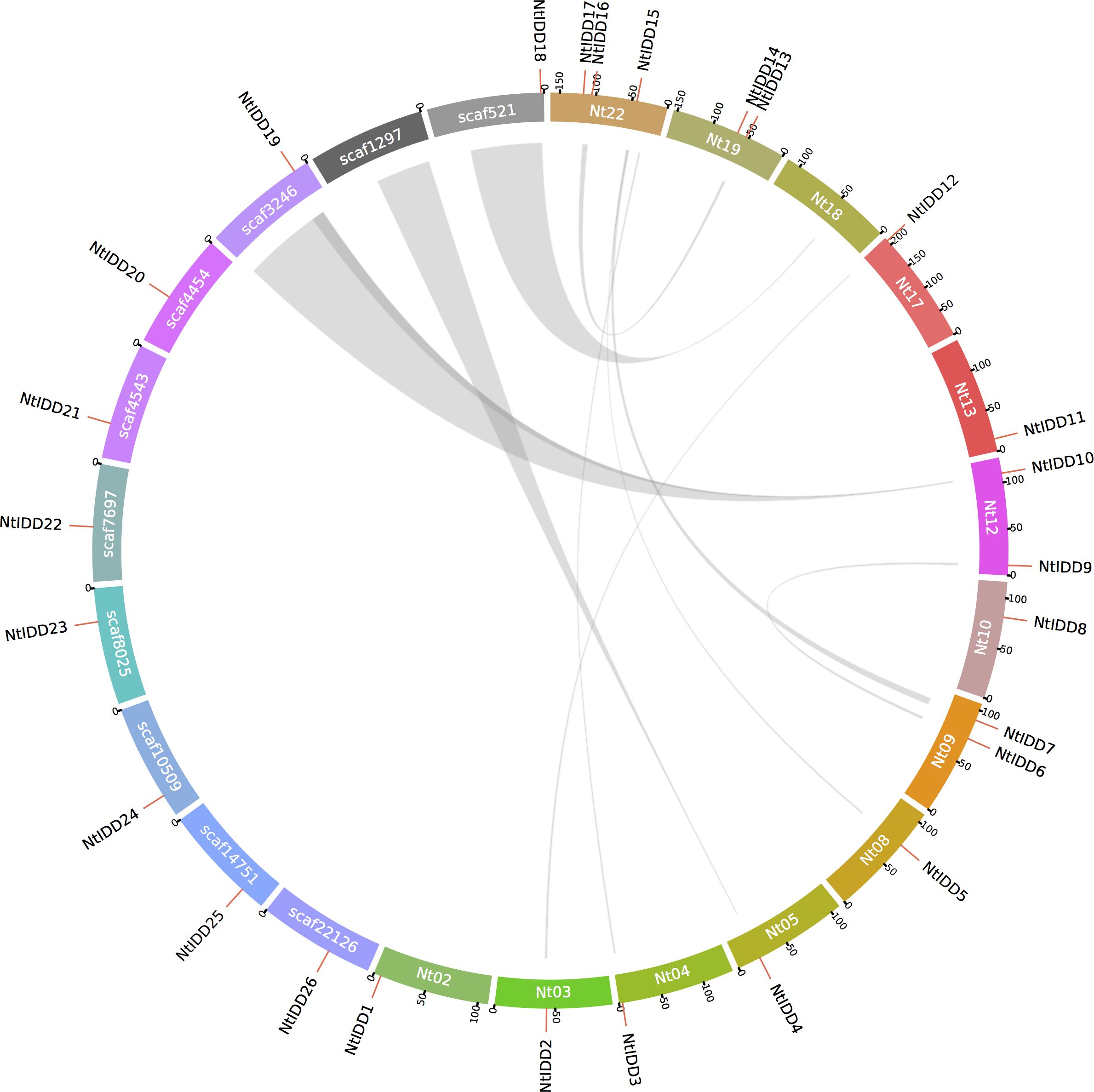
Figure 4. Genome distribution and synteny among NtIDDs. Nt, chromosome; scaf, scaffold. Gray links represent syntenic blocks.
In order to gain more insights on regulatory mechanism, the 1.5-kb upstream sequences of NtIDDs were extracted, and their cis-elements were predicted. There were total 42 elements identified (Figure 5; Supplementary Table 3). Among them, 10 elements were hormone responsive, 27 elements were stress responsive, and 5 elements were development related.
In the hormone-responsive elements, ABRE (abscisic acid responsive), CGTCA-motif/TGACG-motif (MeJA responsive), and TCA-element (salicylic acid responsive) were detected in most of NtIDDs. TGA-element/TGA-box (auxin responsive), TATC-box/GARE-motif/P-box (gibberellin responsive), and SARE (salicylic acid responsive) were discovered in few NtIDDs, such as NtIDD2 and NtIDD10.
In the stress-responsive elements, ARE (anaerobic induction), TC-rich repeats (defense and stress responsive), and G-box/GT1-motif/Box 4/TCT motif (light responsive) were identified in most of NtIDDs. GC-motif (anoxic induction), MBS (drought inducibility), LTR (low-temperature responsive), WUN-motif (wound responsive), and the remaining elements (light responsive) were distributed in several NtIDDs, like NtIDD2 and NtIDD4.
For the development-related elements, MSA-like (cell cycle regulation) was identified in NtIDD6/14/21, circadian (circadian control) was found in NtIDD3 and NtIDD17, GCN4_motif/AACA_motif (endosperm expression) were detected in NtIDD10/20/23, and CAT-box (meristem expression) was discovered in NtIDD9/12/13/17/18/26.
Utilizing public RNA-Seq data, their expressions in nine tissues (Dry Capsule, Root, Stem, Young Leaf, Mature Leaf, Senescent Leaf, Immature Flower, Mature Flower, Senescent Flower) were investigated. In general, NtIDDs expressed throughout all the nine tissues (Figure 6; Supplementary Table 4). Most of NtIDDs expressed in multiple tissues. The expression patterns for NtIDDs were distinct. Figure 7 shows that members with similar expression profiles were clustered together. NtIDD16/13/11 preferentially expressed in the immature flower. NtIDD9/21/6/24/3/25/4/22 expressed higher in leaf. NtIDD10/19 dominantly expressed in capsule. NtIDD12/2 expressed in all tissues, but still higher in capsule. NtIDD17/14/8/26 expressed more specifically in root. NtIDD23 expressed in all tissues, but the expression level in root was the highest. NtIDD20/18/7 expressed higher in stem. NtIDD5/15/1 expressed higher in root, stem, and young leaf.
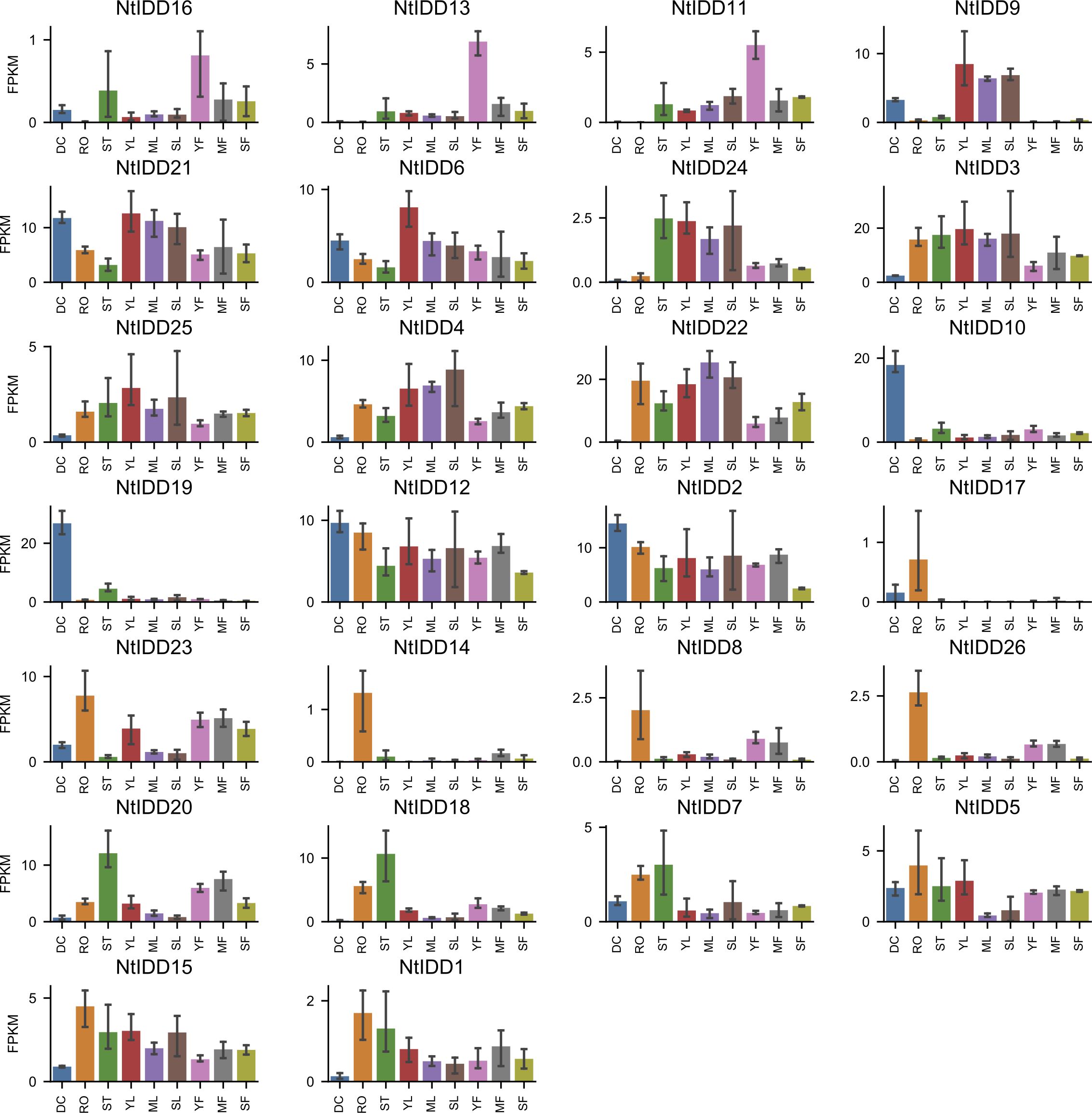
Figure 6. Tissue expression levels of NtIDDs. DC, dry capsule; RO, root; ST, stem; YL, young leaf; ML, mature leaf; SL, senescent leaf; YF, young flower; MF, mature flower; SF, senescent flower. The error bar represents the mean ± SE.
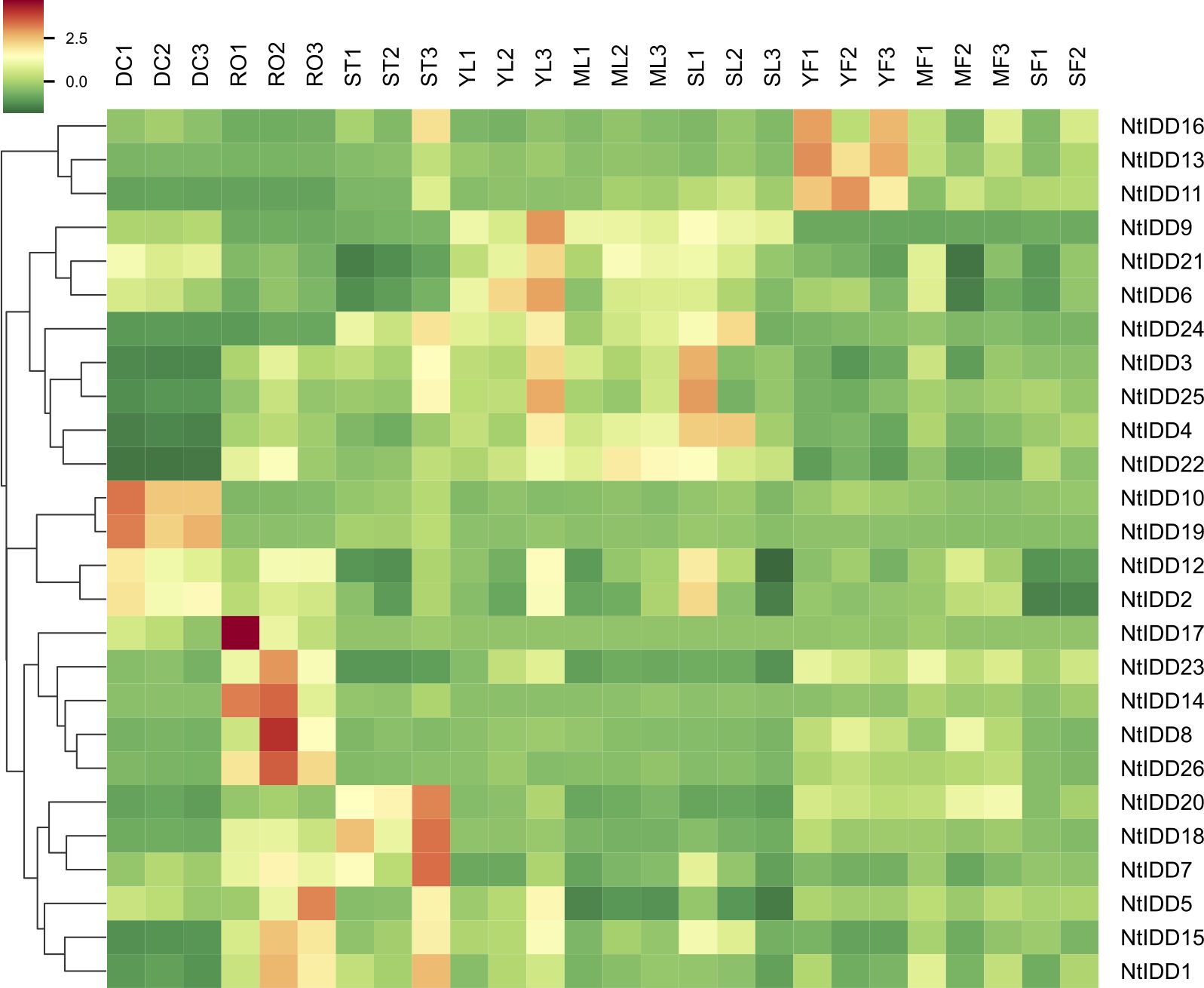
Figure 7. Heatmap of NtIDD tissue expression clustering. DC, dry capsule; RO, root; ST, stem; YL, young leaf; ML, mature leaf; SL, senescent leaf; YF, young flower; MF, mature flower; SF, senescent flower. The numbers (1–3) represent biological replicates.
Under conditions with six exogenous hormones, qRT-PCR expression levels of NtIDDs were measured. Compared with the controls, nine NtIDDs showed significant differential expressions under hormone treatments (Figure 8). NtIDD6/11/12/21 differentially expressed under ABA treatment. NtIDD5/6/11/20/21 were disturbed by GA. NtIDD5/21 and NtIDD19/21 responded in CK and MeJA conditions, respectively. NtIDD5/21/24 were fluctuated by SA application. NtIDD10/11/20/21 were found mediated under SL treatment.
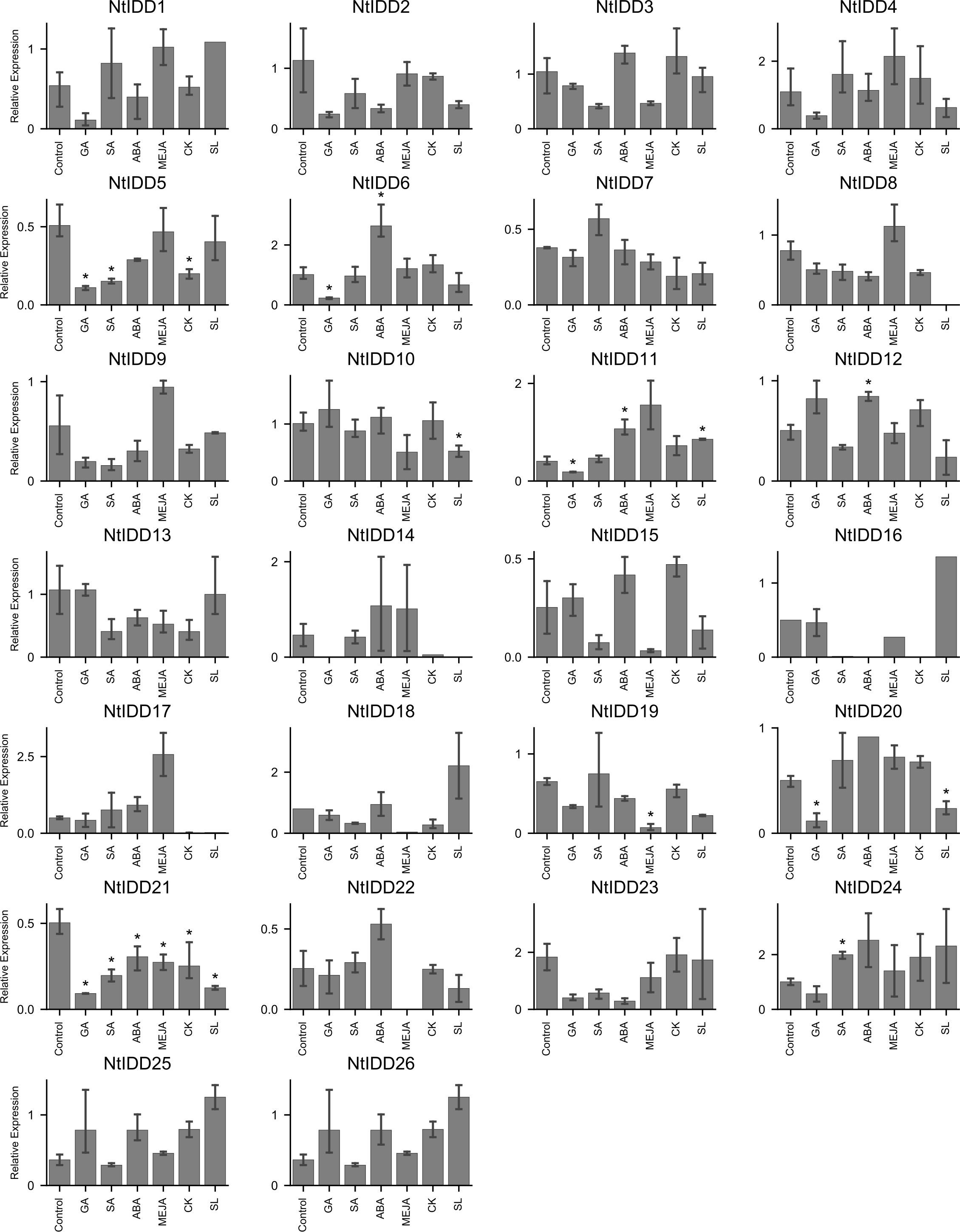
Figure 8. Expression of NtIDDs under exogenous hormone treatments. The error bar represents the mean ± SE. Asterisks show significant differences with t-test (P < 0.05).
IDDs were reported functioning in leaf angle regulation. Earlier studies in Arabidopsis characterized the roles of AtIDD14, AtIDD15, and AtIDD16 in leaf angle regulation (Cui et al., 2013). Later studies pinpointed AtIDD4 acting as a direct regulator on AtIDD14 expression (Völz et al., 2019). Thereby, AtIDD4 was also implicated in regulating leaf angle. In order to investigate roles of NtIDDs in leaf angle regulation, the ortholog of AtIDD4 was identified and analyzed.
Based on phylogenetic relationship and sequence similarity, NtIDD9 was determined as the ortholog of AtIDD4. Expression studies in Arabidopsis showed that AtIDD14 specifically expressed in leaves, AtIDD15 mainly presented in leaf petioles and stems, and AtIDD16 and AtIDD4 highly expressed in leaves and other tissues. In tobacco, as shown above, NtIDD9 also exhibited high and preferential expression in the leaves. Thus, NtIDD9 may carry on conserved functions.
To further test its functions in leaf angle, RNA silencing was then performed and NtIDD9-RNAi transgenic plants were generated. Quantitative RT-PCR showed that the transcripts of NtIDD9 were dramatically reduced (Figure 9A) in the transgenic RNAi lines, suggesting successful silencing. Further examining the phenotype, it is noticed that the orientation angles of leaves were obviously increased in the RNAi plants (Figure 9C). Degree measurement showed that the average leaf angle in the wild type (WT) was 33.8°, whereas it expanded to 76.6° in the RNAi plants (Figure 9B). Therefore, the experiment validated NtIDD9 engaging in leaf angle regulation in tobacco.
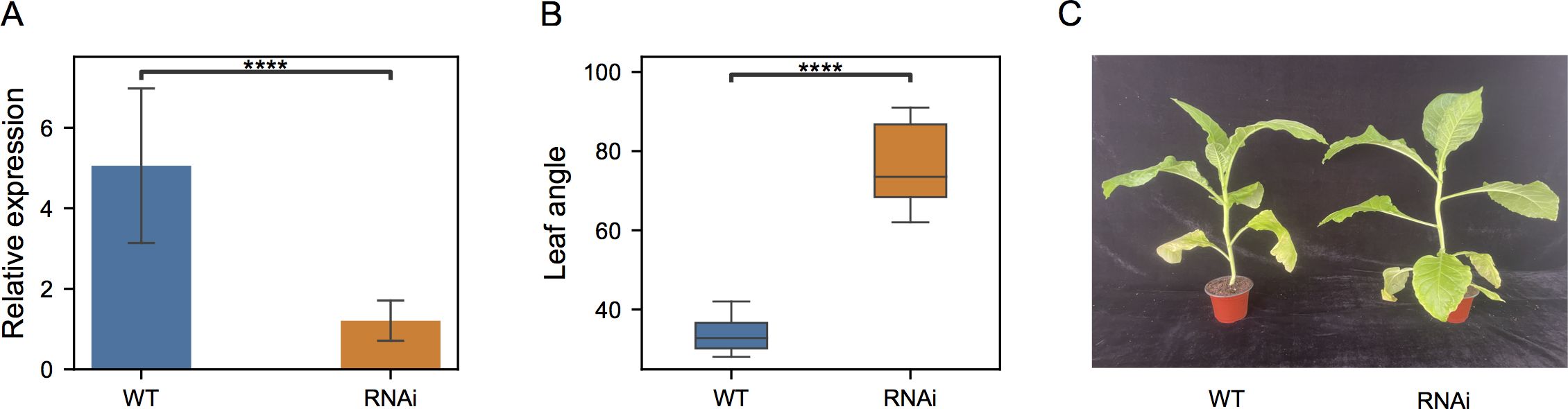
Figure 9. Comparison between wild-type (WT) and NtIDD9-RNAi plants. (A) qRT-PCR expression levels of NtIDD9 in wild-type and RNAi plants. The error bar represents the mean ± SE. Asterisks show significant differences with t-test (P < 1e−4). (B) Statistics of leaf angle degrees in wild-type and RNAi plants. The wild-type and transgenic strains in T0 generation were grown in a greenhouse. After 6 weeks, eight plants in each group were selected for measurement. The angles between stem and leaf were determined using a digital angle meter with the unit degrees (°). Asterisks show significant differences with t-test (P < 1e–4). (C) Phenotypes of wild-type and RNAi plants.
In order to investigate the expression characteristics of NtIDD9 at the cellular level, RNA in situ hybridization technology was used for localization analysis. Results showed that a dense hybridization signal corresponding to NtIDD9 mRNA concentrated in the endodermis at the base of leaf petiole, which is the site that perceives gravity (Tasaka et al., 1999) (Figure 10A).
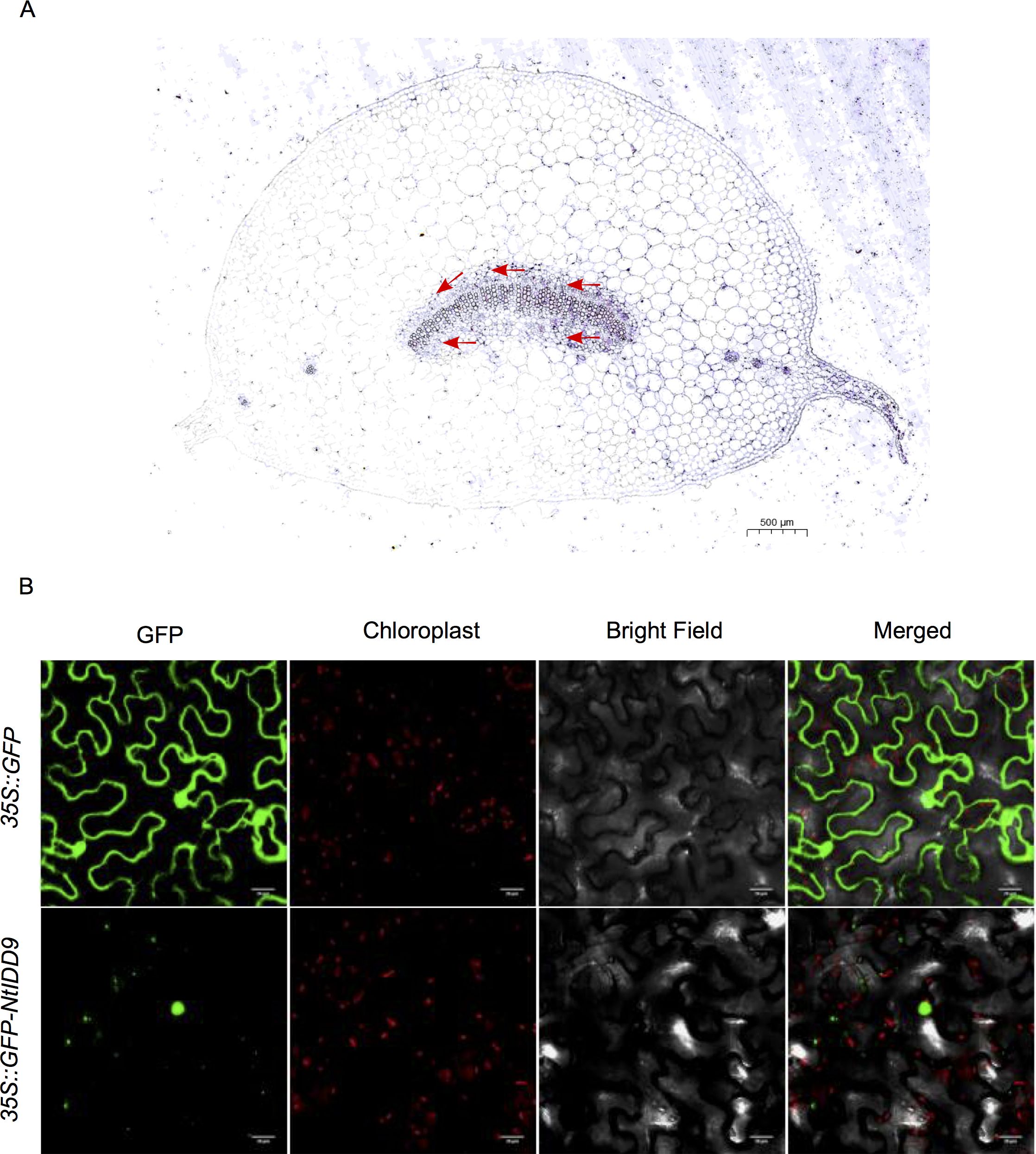
Figure 10. Localization of NtIDD9. (A) RNA in situ hybridization assay of NtIDD9. Red arrows indicate endodermis of leaf petiole base. (B) Subcellular localization of NtIDD9 protein.
The subcellular localization of NtIDD9 protein was predicted by using the online tool Cell-PLoc (Chou and Shen, 2010), and it was found located in the nucleus. To determine the actual subcellular localization, NtIDD9 protein fused with green fluorescent protein (GFP) was transiently expressed in tobacco leaves. As shown in Figure 10B, the fluorescent signal of 35S::GFP-NtIDD9 fusion protein was restricted to the nucleus, suggesting that the NtIDD9 protein is indeed located in the nucleus.
Hormone levels were further quantified in wild-type and NtIDD9-RNAi plants. Utilizing LC-MS/MS, total 37 compounds belonging to seven hormones were quantified (Supplementary Table 5). Further comparison analysis revealed that 11 compounds were significantly different between wild-type and NtIDD9-RNAi plants (Figure 11). The concentrations of ABA (abscisic acid), JA (jasmonic acid), JA-ILE (jasmonoyl-L-isoleucine), and OPDA (cis(+)-12-oxophytodienoic acid) decreased in RNAi plants. In contrast, the levels of TRP (tryptamine), Indole (indole), and cZROG (cis-zeatin-O-glucoside riboside) increased in RNAi plants. In addition, ABA-ald (abscisic aldehyde), IAA-Ala (N-(3-indolylacetyl)-L-alanine), GA12-ald (gibberellin A12 aldehyde), and MeSAG (2-methoxycarbonylphenyl beta-D-glucopyranoside) were specifically detected in RNAi plants.
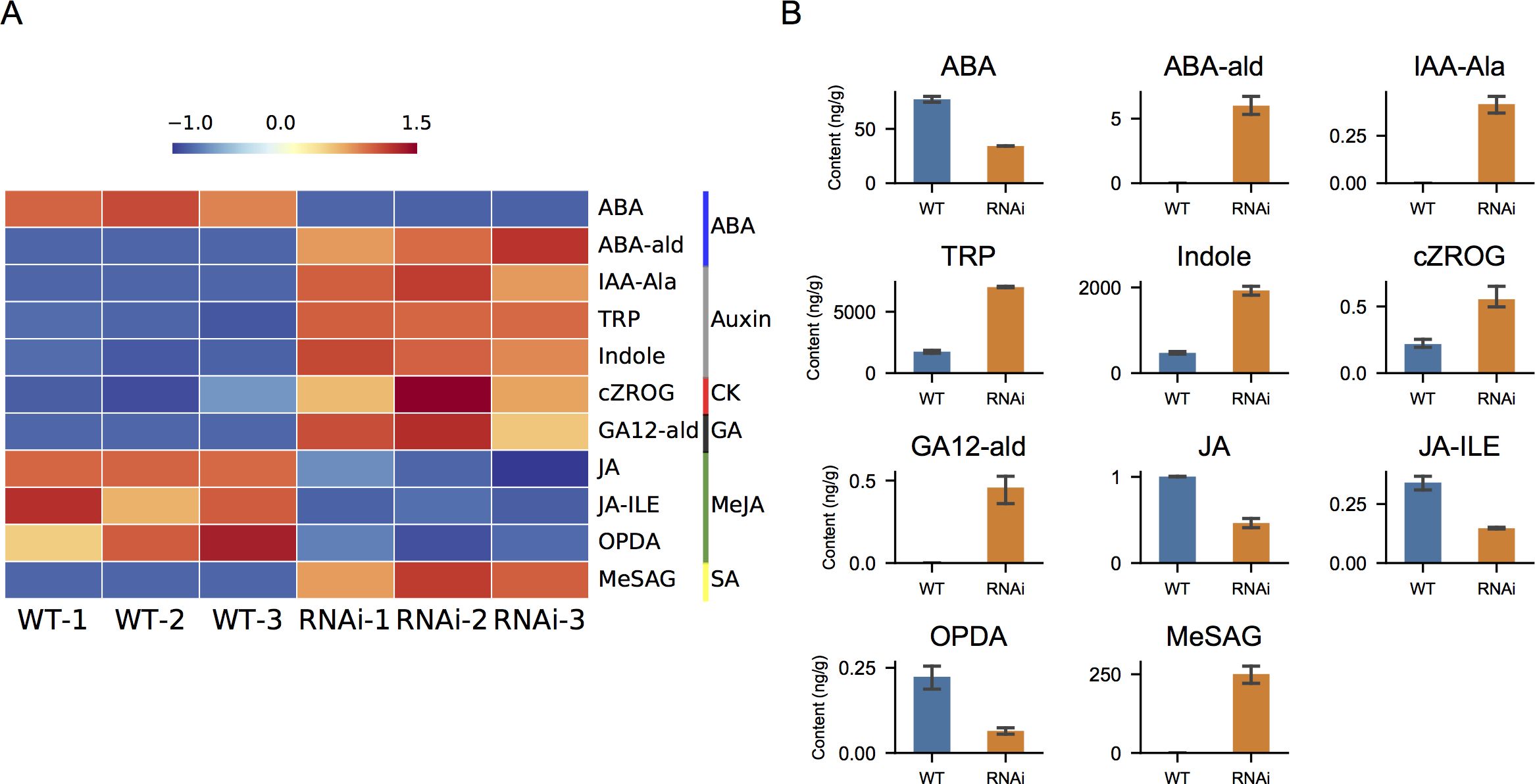
Figure 11. Hormone quantification. (A) Heatmap of differential hormone compounds in wild-type and RNAi plants. The color bars on the right denote different hormone classes. (B) Levels of differential hormone compounds in wild-type and RNAi plants. The error bar represents the mean ± SE. ABA, abscisic acid; ABA-ald, abscisic aldehyde; IAA-Ala, N-(3-indolylacetyl)-L-alanine; TRP, tryptamine; Indole, indole; cZROG, cis-zeatin-O-glucoside riboside; GA12-ald, gibberellin A12 aldehyde; JA, jasmonic acid; JA-ILE, jasmonoyl-L-isoleucine; OPDA, (cis(+)-12-oxophytodienoic acid; MeSAG, 2-methoxycarbonylphenyl beta-D-glucopyranoside.
In this study, 26 IDDs were identified in tobacco genome. The phylogenetic tree showed that NtIDDs could be classified into five groups. In each group, IDDs from tobacco, Arabidopsis, rice, and maize were clustered. This result indicated that IDDs originated before dicot and monocot speciation. In each group, the numbers of NtIDDs were different with other species. For most cases, there were more NtIDDs in each group than other species, implying that duplications occurred in tobacco.
Gene structure analysis found that most of NtIDDs possessed three to four exons, the intron length varied broadly. Similar results were also found in OsIDDs (Zhang et al., 2020) and ZmIDDs (Feng et al., 2023). Motif scanning showed that motif 1/3 were found in all NtIDDs, motif 2/4/5/6/7 were distributed in most of NtIDDs, while motif 8/9/10 were only found in the subset of NtIDDs. The distribution pattern of motifs revealed conservation and diversification of NtIDD sequences. Motif 1/2/3/8 were associated with the ID domain; thus, these motifs were critical parts for functioning. The functions of other motifs were not clear, however.
Genome location analysis demonstrated that NtIDDs located on 12 chromosomes and 9 scaffolds, revealing scatter distribution of the NtIDD family in the tobacco genome. Based on synteny analysis, 14 NtIDDs were identified involved in segmental and/or WGD duplications, and 12 NtIDDs were classified as dispersed duplications. Tobacco was known as an allopolyploid; thus, the expansion of NtIDDs would be affected by the WGD event. This is common in polyploidy species, such as IDDs in cotton (Ali et al., 2019) and rapeseed (Sun et al., 2022). Dispersed duplications happened with unclear mechanisms but were prevalent in plant genomes (Qiao et al., 2019). Tandem duplications are another type of duplication. It was discovered in cotton IDDs, but not in tobacco, suggesting different duplication modes existed in NtIDDs.
Cis-element analysis showed that elements in various stimulus (hormone responsive, stress responsive, and development related) were found in NtIDD promoters. Hormone-responsive elements were associated with abscisic acid, auxin, gibberellin, jasmonate, and salicylic acid; thus, NtIDDs might be coordinated by various hormones. Stress-responsive elements included defense, low-temperature, wounding, drought, and light. This indicated NtIDDs might be affected by external biotic and abiotic stresses. Moreover, development-related elements such as cell cycle and circadian were also detected, implying possible roles of NtIDDs in tobacco growth and development.
RNA-Seq expression analysis showed that NtIDDs expressed widely in tobacco tissues. Most of NtIDDs expressed in multiple tissues. Functional studies on AtIDDs demonstrated distinguished roles in tissues or organs for each member (Prochetto and Reinheimer, 2020). In tobacco, tissue preferential expression patterns were also observed among NtIDDs. NtIDD16/13/11 might function preferring in young flower. NtIDD9/21/6/24/3/25/4/22 might play more roles in leaves. NtIDD10/19/12/2 might participate specific functions in seeds. NtIDD17/23/14/8/26 might engage in specific roles in roots. NtIDD20/18/7 might take more functions in stems. NtIDD5/15/1 might tend to function in roots, stem, and young leaves. These results indicated diversified functions for NtIDDs.
Hormones are important regulators for plant growth and environment stress. Under exogenous hormone applications, several NtIDDs exhibited differential expressions. Among them, NtIDD10/12/19/24 were found specifically responding in SL, ABA, MeJA, and SA, respectively, suggesting their specific roles in certain hormone signaling, while others, such as NtIDD5/6/11/20/21, were disturbed by multiple hormones. For example, NtIDD20 was affected by both GA and SL. NtIDD5 was repressed by GA, SA, and CK. Notably, NtIDD21 was found mediated under all six hormones. Regulating by different hormones indicated their pleiotropic functions in hormone signaling.
AtIDD14, AtIDD15, and AtIDD16 were reported to play roles in leaf angle regulation (Cui et al., 2013). AtIDD4 was also associated due to its direct control on AtIDD14 expression (Völz et al., 2019). As an ortholog of AtIDD4, NtIDD9 was inferred performing similar functions. In the following experiment, RNA silencing of NtIDD9 resulted in phenotype of increased leaf angle degree, indicating its involvement in leaf angle regulation in tobacco. Previous studies have shown that the size of the leaf angle is largely determined by gravitropism, which is a gravity-directed growth process (Chen et al., 1999). The process of gravitropism comprises steps such as gravity perception, signal transduction, and growth response (Baldwin et al., 2013). In leaves, endodermis in the basal part of petiole was discovered responsible for gravity perception (Tasaka et al., 1999; Mano et al., 2006). Recent single-cell transcriptome study also found gravitropism-related genes, LAZY1 (LA1), TILLER ANGLE CONTROL1 (TAC1), and SHOOT GRAVITROPISM6 (SGR6) were enriched in the endodermis (Zhang et al., 2021). Analysis in the current study revealed that NtIDD9 localized in the same cellular part, which suggested its potential role in gravity response. Studies on leaf angle also demonstrated that plant hormones played key roles in regulating angle size (Li et al., 2020; Cao et al., 2022). Endodermis is an important center for hormone signaling. The growth control role for hormones such as auxin, GA, ABA, and SL were gradually illuminating (Dinneny, 2014). In the current study, hormone quantification revealed that concentrations of several classes of hormones were significantly changed in NtIDD9-RNAi plants. For instance, auxins (TRP, Indole) were substantially increased in NtIDD9-RNAi plants. ABA and JA were significantly reduced in NtIDD9-RNAi plants. Meanwhile, GA (GA12-ald) was upregulated in NtIDD9-RNAi plants, either. Hence, NtIDD9 may modulate signal transductions through multiple hormone pathways. Taken together, these findings suggested that NtIDD9 performed a pivotal role in regulating leaf angle development.
In summary, a total of 26 IDD genes were identified in tobacco at the genome-scale level. Their phylogenetic relationship, gene structure, sequence motif, genome distribution, duplication mode, and cis-elements were systematically analyzed. Tissue expression profiles of NtIDDs showed putative important function in tobacco reproductive and vegetative organs. Exogenous hormone treatment implied their roles under hormone signaling. Functional study revealed NtIDD9 participated in leaf angle regulation. Taken together, these results lay important foundations for further function and mechanism research for IDDs in tobacco.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
ZFL: Data curation, Formal analysis, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. PC: Formal analysis, Supervision, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. HL: Investigation, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. JZ: Methodology, Resources, Validation, Writing – review & editing. ZPL: Methodology, Resources, Validation, Writing – review & editing. HZ: Methodology, Resources, Validation, Writing – review & editing. MW: Methodology, Resources, Validation, Writing – review & editing. XX: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by Beijing Life Science Academy Science and Technology Program [grant nos. 2023000CC0100 and 2023200CB0080], the CNTC Research Program [grant no. 110202001020 (JY-03)], the Science and Technique Programs of China Tobacco Zhejiang Industrial [grant no. ZJZY2021B009], and the Natural Science Foundation of Henan, China [grant no. 242300420179].
The authors thank Metware Biotechnology for plant hormone quantification and acknowledge colleagues in CTGRC/BLSA who provided assistance for management, computing, experiment, and writing.
Author HL was employed by the company China Tobacco Zhejiang Industrial, Co Ltd.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpls.2024.1496351/full#supplementary-material
Supplementary Table 1 | Genes screened by homology and InterPro.
Supplementary Table 2 | List of NtIDDs information.
Supplementary Table 3 | List of cis-elements in NtIDD promoters.
Supplementary Table 4 | Tissue expression values(FPKM) of NtIDDs.
Supplementary Table 5 | Hormone levels quantified in wild-type and NtIDD9-RNAi plants.
Supplementary Table 6 | Primer sequences used for qRT-PCR.
TF, transcription factor; IDD, INDETERMINATE DOMAIN; ZF, zinc finger; WGD, whole-genome duplication; FPKM, fragments per kilobase of transcript per million mapped reads; ABA, abscisic acid; CK, cytokinin; ETH, ethylene; GA, gibberellin acid; JA, jasmonic acid; MeJA, methyl jasmonate; SA, salicylic acid; SL, strigolactone; RNAi, RNA interference.
Ali, F., Qanmber, G., Li, Y., Ma, S., Lu, L., Yang, Z., et al. (2019). Genome-wide identification of Gossypium INDETERMINATE DOMAIN genes and their expression profiles in ovule development and abiotic stress responses. J. Cotton Res. 2, 3. doi: 10.1186/s42397-019-0021-6
Bailey, T. L., Johnson, J., Grant, C. E., Noble, W. S. (2015). The MEME suite. Nucleic Acids Res. 43, W39–W49. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv416
Baldwin, K. L., Strohm, A. K., Masson, P. H. (2013). Gravity sensing and signal transduction in vascular plant primary roots. Am. J. Bot. 100, 126–142. doi: 10.3732/ajb.1200318
Camacho, C., Coulouris, G., Avagyan, V., Ma, N., Papadopoulos, J., Bealer, K., et al. (2009). BLAST+: architecture and applications. BMC Bioinf. 10, 421. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-10-421
Cao, Y., Zhong, Z., Wang, H., Shen, R. (2022). Leaf angle: a target of genetic improvement in cereal crops tailored for high-density planting. Plant Biotechnol. J. 20, 426–436. doi: 10.1111/pbi.13780
Chen, R., Rosen, E., Masson, P. H. (1999). Gravitropism in higher plants1. Plant Physiol. 120, 343–350. doi: 10.1104/pp.120.2.343
Chou, K.-C., Shen, H.-B. (2010). Cell-PLoc 2.0: an improved package of web-servers for predicting subcellular localization of proteins in various organisms. Natural Sci. 2, 1090–1103. doi: 10.4236/ns.2010.210136
Coelho, C. P., Huang, P., Lee, D.-Y., Brutnell, T. P. (2018). Making roots, shoots, and seeds: IDD gene family diversification in plants. Trends Plant Sci. 23, 66–78. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2017.09.008
Colasanti, J., Tremblay, R., Wong, A. Y., Coneva, V., Kozaki, A., Mable, B. K. (2006). The maize INDETERMINATE1 flowering time regulator defines a highly conserved zinc finger protein family in higher plants. BMC Genomics 7, 158. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-7-158
Colasanti, J., Yuan, Z., Sundaresan, V. (1998). The indeterminate gene encodes a zinc finger protein and regulates a leaf-generated signal required for the transition to flowering in maize. Cell 93, 593–603. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81188-5
Cui, D., Zhao, J., Jing, Y., Fan, M., Liu, J., Wang, Z., et al. (2013). The arabidopsis IDD14, IDD15, and IDD16 cooperatively regulate lateral organ morphogenesis and gravitropism by promoting auxin biosynthesis and transport. PLoS Genet. 9, e1003759. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003759
Deng, L., Li, L., Zhang, S., Shen, J., Li, S., Hu, S., et al. (2017). Suppressor of rid1 (SID1) shares common targets with RID1 on florigen genes to initiate floral transition in rice. PLoS Genet. 13, e1006642. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006642
Dinneny, J. R. (2014). A gateway with a guard: How the endodermis regulates growth through hormone signaling. Plant Sci. 214, 14–19. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2013.09.009
Edwards, K. D., Fernandez-Pozo, N., Drake-Stowe, K., Humphry, M., Evans, A. D., Bombarely, A., et al. (2017). A reference genome for Nicotiana tabacum enables map-based cloning of homeologous loci implicated in nitrogen utilization efficiency. BMC Genomics 18, 448. doi: 10.1186/s12864-017-3791-6
Fan, S., Zhang, D., Xing, L., Qi, S., Du, L., Wu, H., et al. (2017). Phylogenetic analysis of IDD gene family and characterization of its expression in response to flower induction in Malus. Mol. Genet. Genomics 292, 755–771. doi: 10.1007/s00438-017-1306-4
Feng, X., Yu, Q., Zeng, J., He, X., Ma, W., Ge, L., et al. (2023). Comprehensive analysis of the INDETERMINATE DOMAIN (IDD) gene family and their response to abiotic stress in zea mays. IJMS 24, 6185. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076185
Feurtado, J. A., Huang, D., Wicki-Stordeur, L., Hemstock, L. E., Potentier, M. S., Tsang, E. W. T., et al. (2011). The Arabidopsis C2H2 zinc finger INDETERMINATE DOMAIN1/ENHYDROUS promotes the transition to germination by regulating light and hormonal signaling during seed maturation. Plant Cell 23, 1772–1794. doi: 10.1105/tpc.111.085134
Fukazawa, J., Teramura, H., Murakoshi, S., Nasuno, K., Nishida, N., Ito, T., et al. (2014). DELLAs function as coactivators of GAI-ASSOCIATED FACTOR1 in regulation of gibberellin homeostasis and signaling in arabidopsis. Plant Cell 26, 2920–2938. doi: 10.1105/tpc.114.125690
Goodstein, D. M., Shu, S., Howson, R., Neupane, R., Hayes, R. D., Fazo, J., et al. (2012). Phytozome: a comparative platform for green plant genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 40, D1178–D1186. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr944
Hassan, H., Scheres, B., Blilou, I. (2010). JACKDAW controls epidermal patterning in the Arabidopsis root meristem through a non-cell-autonomous mechanism. Development 137, 1523–1529. doi: 10.1242/dev.048777
Hirano, Y., Nakagawa, M., Suyama, T., Murase, K., Shirakawa, M., Takayama, S., et al. (2017). Structure of the SHR-SCR heterodimer bound to the BIRD/IDD transcriptional factor JKD. Nat. Plants 3, 17010. doi: 10.1038/nplants.2017.10
Hong, J. C. (2016). “General aspects of plant transcription factor families,” in Plant Transcription Factors (Amsterdam: Elsevier), 35–56. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-800854-6.00003-8
Ingkasuwan, P., Netrphan, S., Prasitwattanaseree, S., Tanticharoen, M., Bhumiratana, S., Meechai, A., et al. (2012). Inferring transcriptional gene regulation network of starch metabolism in Arabidopsis thaliana leaves using graphical Gaussian model. BMC Syst. Biol. 6, 100. doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-6-100
Katoh, K., Standley, D. M. (2013). MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 30, 772. doi: 10.1093/molbev/mst010
Kim, D., Paggi, J. M., Park, C., Bennett, C., Salzberg, S. L. (2019). Graph-based genome alignment and genotyping with HISAT2 and HISAT-genotype. Nat. Biotechnol. 37, 907–915. doi: 10.1038/s41587-019-0201-4
Kozaki, A., Hake, S., Colasanti, J. (2004). The maize ID1 flowering time regulator is a zinc finger protein with novel DNA binding properties. Nucleic Acids Res. 32, 1710–1720. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh337
Krzywinski, M., Schein, J., Birol, İ., Connors, J., Gascoyne, R., Horsman, D., et al. (2009). Circos: An information aesthetic for comparative genomics. Genome Res. 19, 1639–1645. doi: 10.1101/gr.092759.109
Kumar, M., Le, D. T., Hwang, S., Seo, P. J., Kim, H. U. (2019). Role of the INDETERMINATE DOMAIN genes in plants. IJMS 20, 2286. doi: 10.3390/ijms20092286
Kumar, S., Stecher, G., Tamura, K. (2016). MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 33, 1870–1874. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msw054
Lescot, M., Déhais, P., Thijs, G., Marchal, K., Moreau, Y., Van de Peer, Y., et al. (2002). PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 30, 325–327. doi: 10.1093/nar/30.1.325
Letunic, I., Bork, P. (2021). Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL) v5: an online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 49, W293–W296. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab301
Li, L., Foster, C. M., Gan, Q., Nettleton, D., James, M. G., Myers, A. M., et al. (2009). Identification of the novel protein QQS as a component of the starch metabolic network in Arabidopsis leaves. Plant J. 58, 485–498. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2009.03793.x
Li, X., Wu, P., Lu, Y., Guo, S., Zhong, Z., Shen, R., et al. (2020). Synergistic interaction of phytohormones in determining leaf angle in crops. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21, 5052. doi: 10.3390/ijms21145052
Liu, J., Shu, D., Tan, Z., Ma, M., Guo, N., Gao, S., et al. (2022). The Arabidopsis IDD14 transcription factor interacts with bZIP-type ABFs/AREBs and cooperatively regulates ABA-mediated drought tolerance. New Phytol. 236, 929–942. doi: 10.1111/nph.18381
Long, Y., Goedhart, J., Schneijderberg, M., Terpstra, I., Shimotohno, A., Bouchet, B. P., et al. (2015a). SCARECROW-LIKE23 and SCARECROW jointly specify endodermal cell fate but distinctly control SHORT-ROOT movement. Plant J. 84, 773–784. doi: 10.1111/tpj.13038
Long, Y., Smet, W., Cruz-Ramírez, A., Castelijns, B., de Jonge, W., Mähönen, A. P., et al. (2015b). Arabidopsis BIRD zinc finger proteins jointly stabilize tissue boundaries by confining the cell fate regulator SHORT-ROOT and contributing to fate specification. Plant Cell 27, 1185–1199. doi: 10.1105/tpc.114.132407
Mano, E., Horiguchi, G., Tsukaya, H. (2006). Gravitropism in leaves of arabidopsis thaliana (L.) heynh. Plant Cell Physiol. 47, 217–223. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pci237
Morita, M. T., Sakaguchi, K., Kiyose, S.-I., Taira, K., Kato, T., Nakamura, M., et al. (2006). A C2H2-type zinc finger protein, SGR5, is involved in early events of gravitropism in Arabidopsis inflorescence stems. Plant J. 47, 619–628. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2006.02807.x
O’Malley, R. C., Huang, S. C., Song, L., Lewsey, M. G., Bartlett, A., Nery, J. R., et al. (2016). Cistrome and epicistrome features shape the regulatory DNA landscape. Cell 165, 1280. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.04.038
Paysan-Lafosse, T., Blum, M., Chuguransky, S., Grego, T., Pinto, B. L., Salazar, G. A., et al. (2023). InterPro in 2022. Nucleic Acids Res. 51, D418–D427. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac993
Pertea, M., Pertea, G. M., Antonescu, C. M., Chang, T.-C., Mendell, J. T., Salzberg, S. L. (2015). StringTie enables improved reconstruction of a transcriptome from RNA-seq reads. Nat. Biotechnol. 33, 290–295. doi: 10.1038/nbt.3122
Prochetto, S., Reinheimer, R. (2020). Step by step evolution of Indeterminate Domain (IDD) transcriptional regulators: from algae to angiosperms. Ann. Bot. 126, 85–101. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcaa052
Qiao, X., Li, Q., Yin, H., Qi, K., Li, L., Wang, R., et al. (2019). Gene duplication and evolution in recurring polyploidization–diploidization cycles in plants. Genome Biol. 20, 38. doi: 10.1186/s13059-019-1650-2
Rawat, A., Völz, R., Sheikh, A., Mariappan, K. G., Kim, S.-K., Rayapuram, N., et al. (2023). Salinity stress-induced phosphorylation of INDETERMINATE-DOMAIN 4 (IDD4) by MPK6 regulates plant growth adaptation in Arabidopsis. Front. Plant Sci. 14. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1265687
Rice, P., Longden, I., Bleasby, A. (2000). EMBOSS: the european molecular biology open software suite. Trends Genet. 16, 276–277. doi: 10.1016/s0168-9525(00)02024-2
Sierro, N., Battey, J. N. D., Ouadi, S., Bakaher, N., Bovet, L., Willig, A., et al. (2014). The tobacco genome sequence and its comparison with those of tomato and potato. Nat. Commun. 5, 3833. doi: 10.1038/ncomms4833
Singleton, W. R. (1946). Inheritance of indeterminate growth in maize. J. Hered 37, 61–64. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a105582
Su, X., Meng, T., Zhao, Y., Li, G., Cheng, X., Abdullah, M., et al. (2019). Comparative genomic analysis of the IDD genes in five Rosaceae species and expression analysis in Chinese white pear ( Pyrus bretschneideri ). PeerJ 7, e6628. doi: 10.7717/peerj.6628
Sun, B., Fan, Y., Duan, H., Liu, X., Chen, Y., Shang, G., et al. (2022). Genome-wide characterization of Brassica napus INDETERMINATE DOMAIN genes reveals a negative role for BnA08.IDD7 in plant development. Ind. Crops Products 175, 114263. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2021.114263
Tanimoto, M., Tremblay, R., Colasanti, J. (2008). Altered gravitropic response, amyloplast sedimentation and circumnutation in the Arabidopsis shoot gravitropism 5 mutant are associated with reduced starch levels. Plant Mol. Biol. 67, 57–69. doi: 10.1007/s11103-008-9301-0
Tasaka, M., Kato, T., Fukaki, H. (1999). The endodermis and shoot gravitropism. Trends Plant Sci. 4, 103–107. doi: 10.1016/s1360-1385(99)01376-x
Völz, R., Kim, S.-K., Mi, J., Rawat, A. A., Veluchamy, A., Mariappan, K. G., et al. (2019). INDETERMINATE-DOMAIN 4 (IDD4) coordinates immune responses with plant-growth in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS Pathog. 15, e1007499. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007499
Wang, Y., Tang, H., Debarry, J. D., Tan, X., Li, J., Wang, X., et al. (2012). MCScanX: a toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity. Nucleic Acids Res. 40, e49. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr1293
Wu, X., Tang, D., Li, M., Wang, K., Cheng, Z. (2013). Loose Plant Architecture1, an INDETERMINATE DOMAIN protein involved in shoot gravitropism, regulates plant architecture in rice. Plant Physiol. 161, 317–329. doi: 10.1104/pp.112.208496
Wu, C., You, C., Li, C., Long, T., Chen, G., Byrne, M. E., et al. (2008). RID1, encoding a Cys2/His2-type zinc finger transcription factor, acts as a master switch from vegetative to floral development in rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 105, 12915–12920. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0806019105
Xuan, Y. H., Priatama, R. A., Huang, J., Je, B. I., Liu, J. M., Park, S. J., et al. (2013a). I ndeterminate domain 10 regulates ammonium-mediated gene expression in rice roots. New Phytol. 197, 791–804. doi: 10.1111/nph.12075
Xuan, Y. H., Priatama, R. A., Kumar, V., Han, C. (2013b). Regulatory role of indeterminate domain 10 (IDD10) in ammonium-dependent gene expression in rice roots. Plant Signal Behav. 8, e24139. doi: 10.4161/psb.24139
Yoshida, H., Hirano, K., Sato, T., Mitsuda, N., Nomoto, M., Maeo, K., et al. (2014). DELLA protein functions as a transcriptional activator through the DNA binding of the indeterminate domain family proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 111, 7861–7866. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1321669111
Zhang, T.-Q., Chen, Y., Wang, J.-W. (2021). A single-cell analysis of the Arabidopsis vegetative shoot apex. Dev. Cell 56, 1056–1074.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2021.02.021
Keywords: IDD family, evolutionary analysis, expression analysis, leaf angle, Nicotiana tabacum
Citation: Li Z, Cao P, Liu H, Zhang J, Luo Z, Zhang H, Wu M and Xie X (2024) Genome-wide analysis of Nicotiana tabacum IDD genes identifies NtIDD9 as a regulator of leaf angle. Front. Plant Sci. 15:1496351. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1496351
Received: 14 September 2024; Accepted: 03 December 2024;
Published: 19 December 2024.
Edited by:
Alla Yemets, National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine (NAN Ukraine), UkraineReviewed by:
Cunmin Qu, Southwest University, ChinaCopyright © 2024 Li, Cao, Liu, Zhang, Luo, Zhang, Wu and Xie. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiaodong Xie, ZGQtOTlAMTYzLmNvbQ==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.