- Department of Biological Sciences, California State Polytechnic University, Pomona, CA, United States
Famously referred to as “Darwin’s abominable mystery,” the rapid diversification of angiosperms over the last ~140 million years presents a fascinating enigma. This diversification is underpinned by complex genetic pathways that evolve and rewire to produce diverse and sometimes novel floral forms. Morphological innovations in flowers are shaped not only by genetics but also by evolutionary constraints and ecological dynamics. The importance of model organisms in addressing the long-standing scientific questions related to diverse floral forms cannot be overstated. In plant biology, Arabidopsis thaliana, a core eudicot, has emerged as a premier model system, with its genome being the first plant genome to be fully sequenced. Similarly, model systems derived from crop plants such as Oryza sativa (rice) and Zea mays (maize) have been invaluable, particularly for crop improvement. However, despite their substantial utility, these model systems have limitations, especially when it comes to exploring the evolution of diverse and novel floral forms. The order Ranunculales is the earliest-diverging lineage of eudicots, situated phylogenetically between core eudicots and monocots. This group is characterized by its exceptional floral diversity, showcasing a wide range of floral morphologies and adaptations that offer valuable insights into the evolutionary processes of flowering plants. Over the past two decades, the development of at least five model systems including, Aquilegia, Thalictrum, Nigella, Delphinium and Eschscholzia within the Ranunculales order has significantly advanced our understanding of floral evolution. This review highlights the conservation and divergence of floral organ identity programs observed among these models and discusses their importance in advancing research within the field. The review also delves into elaborate petal morphology observed in Aquilegia, Nigella, and Delphinium genera, and further discusses the contributions, limitations, and future research directions for Ranunculales model systems. Integrating these diverse models from the early-diverging eudicot order has enhanced our understanding of the complex evolutionary pathways that shape floral diversity in angiosperms, bridging the knowledge gaps essential for a comprehensive understanding of floral evolution.
1 Introduction
The evolution of flower morphology is a multifaceted and nuanced process shaped by the interplay of genetic, environmental, ecological, and evolutionary factors (Becker et al., 2011). This complex interaction has given rise to the remarkable diversity of floral forms observed in angiosperms, which have diversified into over 350,000 species (Endress, 2011; Moyroud and Glover, 2017). These diverse species of angiosperms are categorized into major clades, including early-diverging angiosperms (ANA clade), magnoliids, monocots, early-diverging eudicots, and core eudicots, based on a combination of morphological, genetic, phylogenetic, and evolutionary criteria (Soltis and Soltis, 2013; Li et al., 2021).
Over the past three decades, research on floral organ identity has been fundamental in elucidating the mechanisms driving the evolution of floral morphology. Central to this body of research is the seminal ABC model, established more than thirty years ago (Coen and Meyerowitz, 1991). This model was initially developed through studies on two core eudicot model systems, Arabidopsis thaliana, a member of the Brassicaceae family from the Rosid clade, and Antirrhinum majus, belonging to the Plantaginaceae family from the Asterid clade. The ABC model was later expanded to the more comprehensive ABCDE model (Colombo et al., 1995; Pelaz et al., 2000), which provides a framework for understanding how floral organ identities are specified through the combinatorial function of A, B, C, D, and E class genes. According to this model, the A+E specifies sepal identity, A+B+E specifies petal identity, B+C+E specifies stamen identity, C+E specifies carpel identity, and the D class genes are crucial for ovule identity (Bowman et al., 1991; Ma and dePamphilis, 2000; Soltis et al., 2006).
The flower structure of A. thaliana exemplifies a typical simple flower, consisting of four concentric whorls: sepals (4), petals (4), stamens (6), and carpels (2-fused) (Figures 1A–D). Over the years, A. thaliana has become an impressive model system, it has a short life cycle, and availability of many functional tools including stable transformations, and a small genome size (Meyerowitz and Pruitt, 1985). The genome of Arabidopsis thaliana was sequenced nearly a quarter century ago in 2000, marking it the first plant genome to be fully sequenced (The Arabidopsis Genome Initiative, 2000) The simplicity of this floral structure and ease of genetic work has made Arabidopsis an indispensable core eudicot model system.
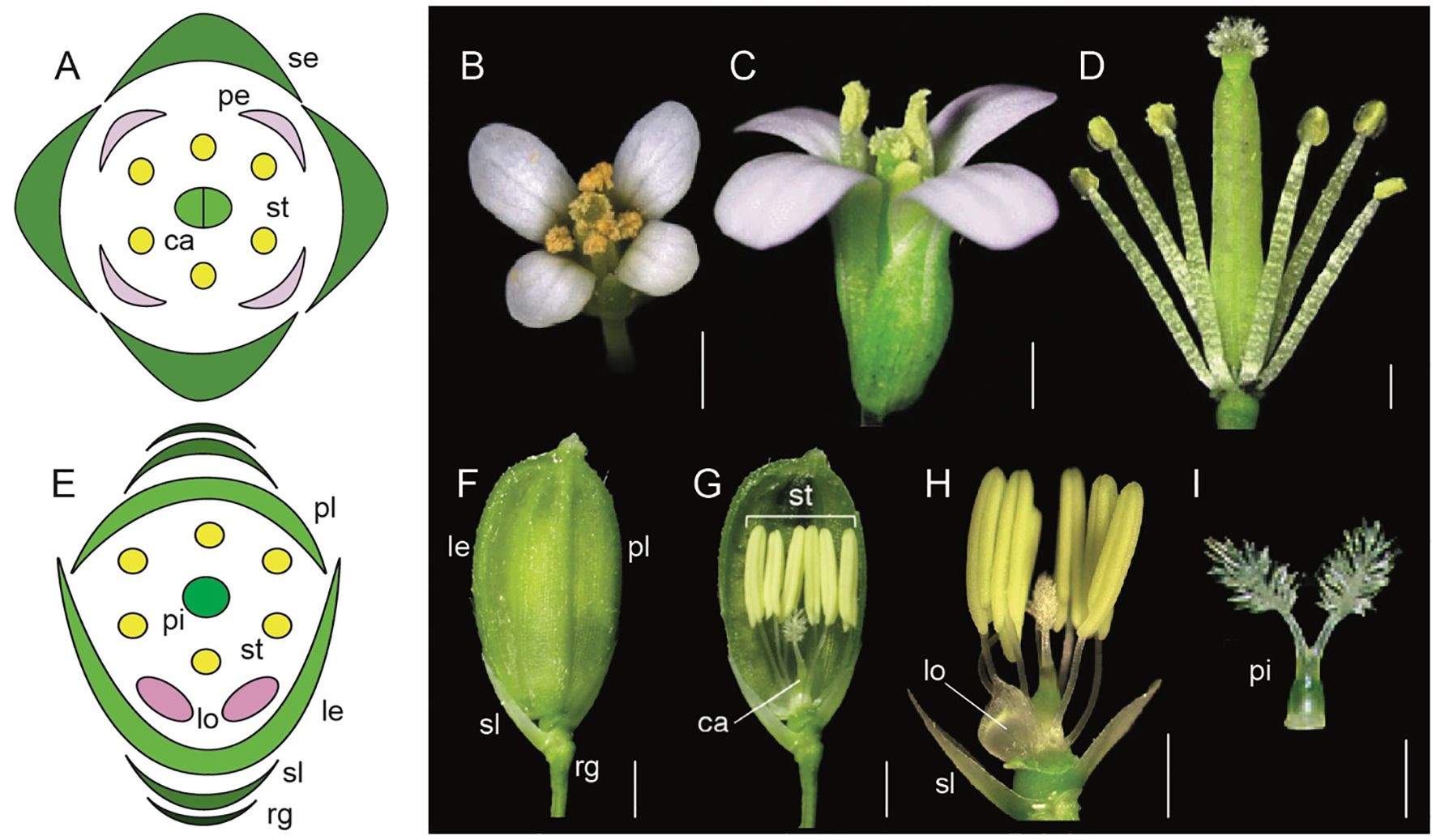

Figure 1. Comparative floral morphology of Arabidopsis thaliana and Oryza sativa (Adapted from Xue et al., 2020; Krämer, 2015; Tanaka et al., 2017; Sugiyama et al., 2019; Dreni, 2023; Logacheva et al., 2008; Hirano et al., 2014). (A) A. thaliana floral diagram (B) A. thaliana wild-type flower top view (C) A. thaliana wild-type side view (D) A. thaliana androecium and gynoecium attached to the receptacle (E) Oryza sativa floral diagram (F) mature O. sativa spikelet (rg, rudimentary glume; sl, sterile lemma; le, lemma; pl, palea) (G) O. sativa androecium, gynoecium, sterile lemma and lodicules attached to the receptacle (H) O. sativa syncarpic ovary, stamens, lodicule, and sterile lemma attached to the receptacle. (I) O. sativa syncarpic ovary. Scale bars: (B) 1 mm, (C) 200 μm, (D) 500 μm, (F) 1 mm, (G) 1 mm, (H) 1 mm, (I) 1 mm.
Equally remarkable has been the research in monocots with model systems like Oryza sativa (rice), Zea mays (maize), and Sorghum bicolor (sorghum). Flowers in grasses have perianth organs that are morphologically distinct from those in core eudicots. For example, rice flowers contain sterile organs the lemma (1), palea (1), and lodicules (2), as well as fertile organs stamens (6), and a syncarpic ovary with two styles and a feathery stigma (Figures 1E–I, Yoshida and Nagato, 2011; Dreni, 2023). Many aspects of the ABC model are conserved, however there are also unique genetic players in monocots that fulfill the A function differently compared to Arabidopsis. This highlights the evolutionary diversification of floral organ identity mechanisms across angiosperms.
While Arabidopsis and rice have been indispensable model organisms for research, addressing comprehensive evolutionary inquiries, particularly pertaining to the origins and diversification of distinct floral structures and observed developmental pathways, is limited. The incorporation of early-diverging eudicots, such as those within the Ranunculales order, into eco-evo-devo studies has offered critical insights into floral organ evolution. Positioned at the evolutionary midpoint between core eudicots and monocots, several genera within Ranunculales, such as Aquilegia, Thalictrum, Nigella, Delphinium, and Eschscholzia, serve as excellent model systems for studying floral development and organ identity (Figures 2A, B, The RanOmics group et al., 2024). These genera exhibit a range of floral morphologies that provide insights into the evolutionary and genetic mechanisms underlying flower development.
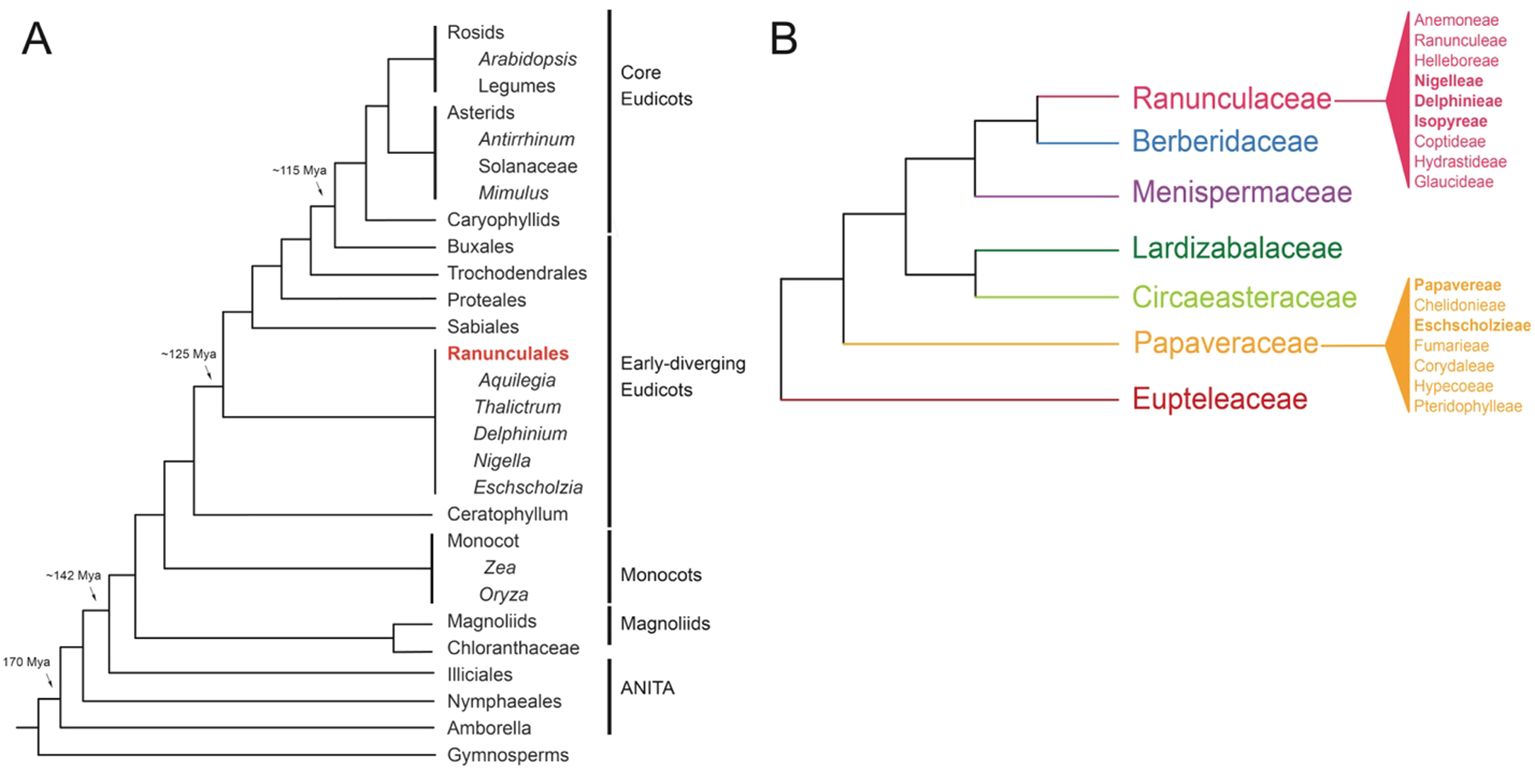
Figure 2. Phylogenies (A) Simplified angiosperm phylogeny based on Moore et al., 2007 and adapted from Kramer, 2009, showing genera with notable resources available (B) Simplified Ranunculales phylogeny, showing tribes within the Raunculaceae and Papaveraceae, based on The RanOmics group et al., 2024; Delpeuch et al., 2022; Zhai et al., 2019; Peng et al., 2023; Peng et al., 2024.
One of the central themes of evo-devo studies is understanding morphological evolution, particularly within the scope of organ identity establishment. What are the genetic factors and developmental pathways that drive the formation and diversification of floral organs? Studies in these early-diverging eudicots within the framework of the ABC model not only expand the taxonomic breadth of research but also provide comparative data crucial for deciphering evolutionary transitions in floral morphology. By bridging insights from core eudicots and monocots with those from early-diverging eudicots, genomic researchers can uncover conserved genetic networks and adaptive innovations that have shaped the remarkable diversity of angiosperm flowers. This review comprehensively focuses on morphological innovations and organ identity research in the major emerging model systems in Ranunculales, with a particular focus on the petal elaborations in genera Aquilegia, Nigella, and Delphinium. We also discuss how gene duplications have influenced the evolution of floral forms within the framework of the ABC model. Additionally, the review seeks to highlight the significance of these model systems in understanding broader evolutionary patterns and mechanisms in angiosperms.
2 Morphological diversity and distribution
The species-rich order Ranunculales, which emerged ~115 million years ago (Mya), consists of approximately 4500 species distributed in seven families, including Ranunculaceae (~2500 sp), Berberidaceae (~700 sp), Menispermaceae (~440 sp), Lardizabalaceae (~40 sp), Circeasteraceae (~2 sp), Papaveraceae (~430-825), and Eupteleaceae (~2 sp) (Figure 2B, Damerval and Becker, 2017; The RanOmics group et al., 2024). Several genera within the Ranunculales order have emerged as valuable model systems for studying floral development and organ identity. Notably, Aquilegia, Thalictrum, Nigella, Delphinium, and Eschscholzia from the Ranunculales order, offer diverse floral morphologies that provide crucial insights into the genetic mechanisms driving flower development (Kramer et al., 2007; Drea et al., 2007; Di Stilio et al., 2010; Jabbour and Renner, 2012b; Gonçalves et al., 2013; Wang et al., 2015; Zhao et al., 2023). In the following section, we discuss the geographical distribution and distinctive floral morphology of each model system offering a concise overview of their evolution and adaptation to diverse environments and pollinators (Figures 3A-ix, Supplementary Table 1).
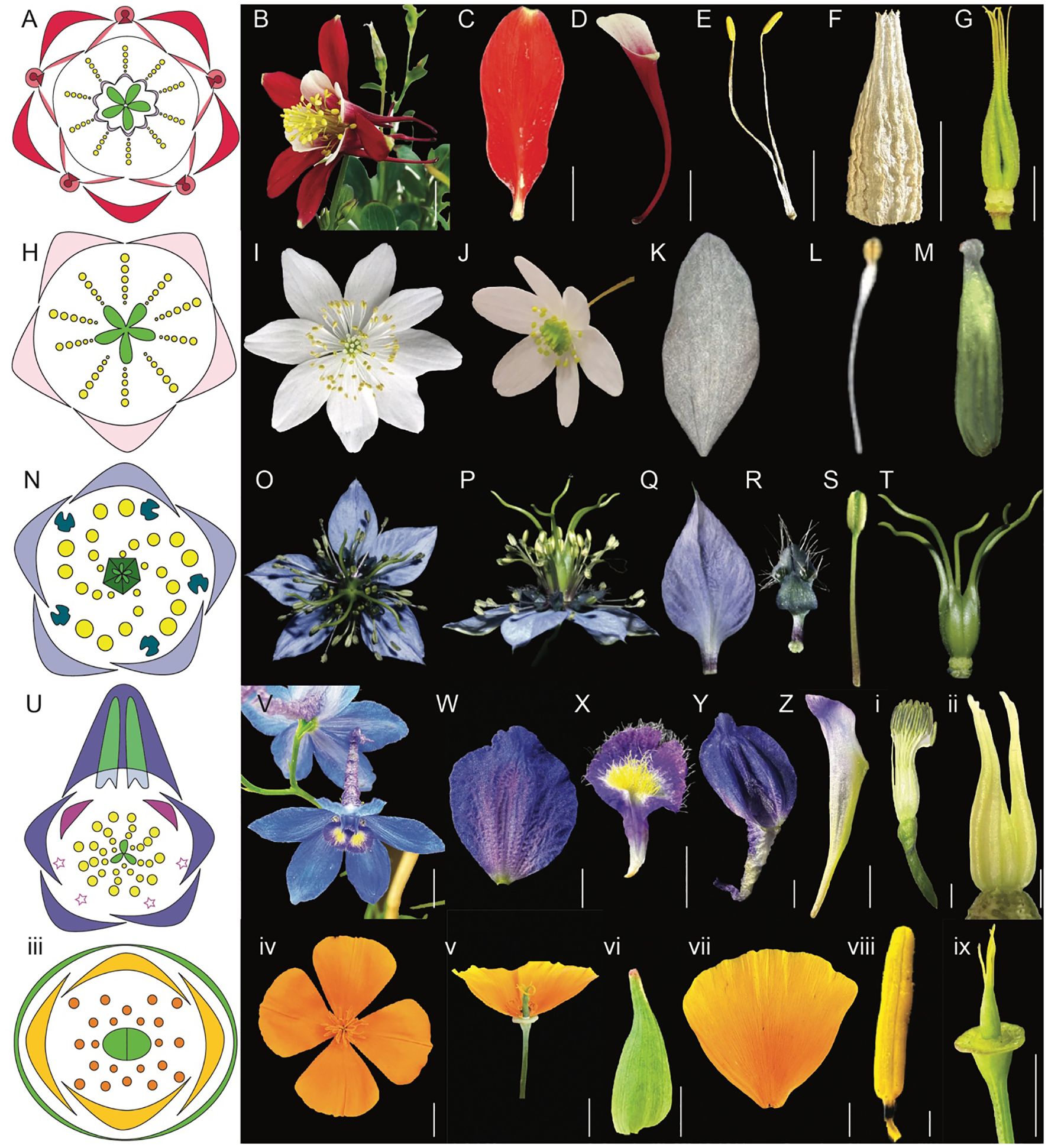

Figure 3. Comparative morphology of five Ranunculales models, Aquilegia, Thalictrum, Nigella, Delphinium, and Eschscholzia (Adapted from Sharma et al., 2024; Sharma et al., 2014; Galimba et al., 2012; Arias et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2015; Jabbour et al., 2009; Becker et al., 2023; Di Stilio et al., 2009). (A–G) Aquilegia coerulea (A) floral diagram (B) flower side view (C) sepal (D) spurred petal (E) mature stamens (F) staminodia (G) carpels attached to receptacles (H–M) Thalictrum (H) floral diagram (I) flower top view (J) flower side view (K) sepal (L) stamen (M) carpel (N–T) Nigella damascena (N) floral diagram (O) flower top view (P) flower side view (Q) sepal (R) petal (S) stamen (T) carpels attached to receptacle (U-ii) Delphinium x belladona ‘Bellamosum’ (U) floral diagram (V) flower top view (W) sepal (X) lateral petal (Y) dorsal spurred sepal (Z) spurred petal i. stamens attached to receptacle ii. carpels attached to receptacle iii-ix Eschscholzia californica iii. floral diagram iv. flower top view v. flower side view vi. sepal vii. petal viii. anther ix. carpel attached to receptacle. Scale bars: (B) 1 cm, (C) 5 mm, (D) 1 cm, (E) 5 mm, F. 5 mm, (G) 5 mm, (W) 5 mm, (X) 5 mm, (Y) 5 mm, (Z) 5 mm, ii. 1 mm, iv. 1 cm, v. 1 cm, vi. 5 mm, vii. 5 mm, viii. 1 mm, ix. 5 mm (The images for Thalictrum (H–M) and Nigella (N–T) are adapted from the sources mentioned above. Since the original pictures did not have scale bars, we were unable to provide that information in this figure).
2.1 Aquilegia
The genus Aquilegia, consisting of around 70-80 species (Munz, 1946; Whittemore and Parfitt, 1997; Nold, 2003), is a classic example of adaptive radiation (Hodges and Derieg, 2009; Kramer, 2009; Kramer and Hodges, 2010; Sharma et al., 2014). Aquilegia originated in Eastern Asia around 6 to 6.9 Mya and subsequently diversified into Europe and North America between 1 to 3 Mya. This diversification involved two distinct radiation events, leading to the development of species in Europe and North America (Bastida et al., 2010; Fior et al., 2013). The genus is now distributed across Asia (23 species), Europe (21 species), and North America (22 species) (Bastida et al., 2010). Interestingly, the diversification of Aquilegia was primarily driven by allopatric speciation through geographic isolation in Europe (Bastida et al., 2010). In contrast, sympatric speciation, likely influenced by pollinator specialization, played a significant role in the diversification of species in North America. This divergence in speciation mechanisms underscores the contrasting evolutionary pressures experienced by the genus in these two regions (Bastida et al., 2010). These distinct evolutionary trajectories position Aquilegia as a key model genus for exploring adaptive radiation and speciation processes.
The actinomorphic perianth of Aquilegia comprises five types of floral organs (Figures 3A, B). The outermost whorl consists of petaloid sepals (5) (Figure 3C). The second whorl includes nectariferous, spurred petals (5) (Figure 3D, Ren et al., 2011). Inner to the petals are stamens, in 10 orthostichies, that are either opposite to sepals or petals (Figure 3E, Tucker and Hodges, 2005; Sharma et al., 2014). The fourth organ identity features the novel organ, thin and papery staminodes arranged in two whorls of five surrounding the gynoecium, consisting of 10 sterile structures (Figure 3F). The innermost whorl comprises unfused green carpels (4-7) (Figure 3G, Sharma et al., 2014), with the ovary being broader and tapering into a straight style.
Within the genus Aquilegia, significant morphological variation is observed. For example, the Asian species A. ecalcarata is notable for being spurless and lacking nectaries (Figure 4A, Geng et al., 2021), whereas A. jonesii, a North American species which is found at high altitudes, lacks the novel organ staminodes (Figure 4B, Johns et al., 2024). Variations in petal spur length in Aquilegia species are particularly well-studied in North America species, where the spur lengths range from ~5-150 mm (Figures 5A–K). This variation in spur length is closely linked to the pollinator specialization, which has played a significant role in the diversification of the genus within the region (Bastida et al., 2010; Puzey et al., 2011).
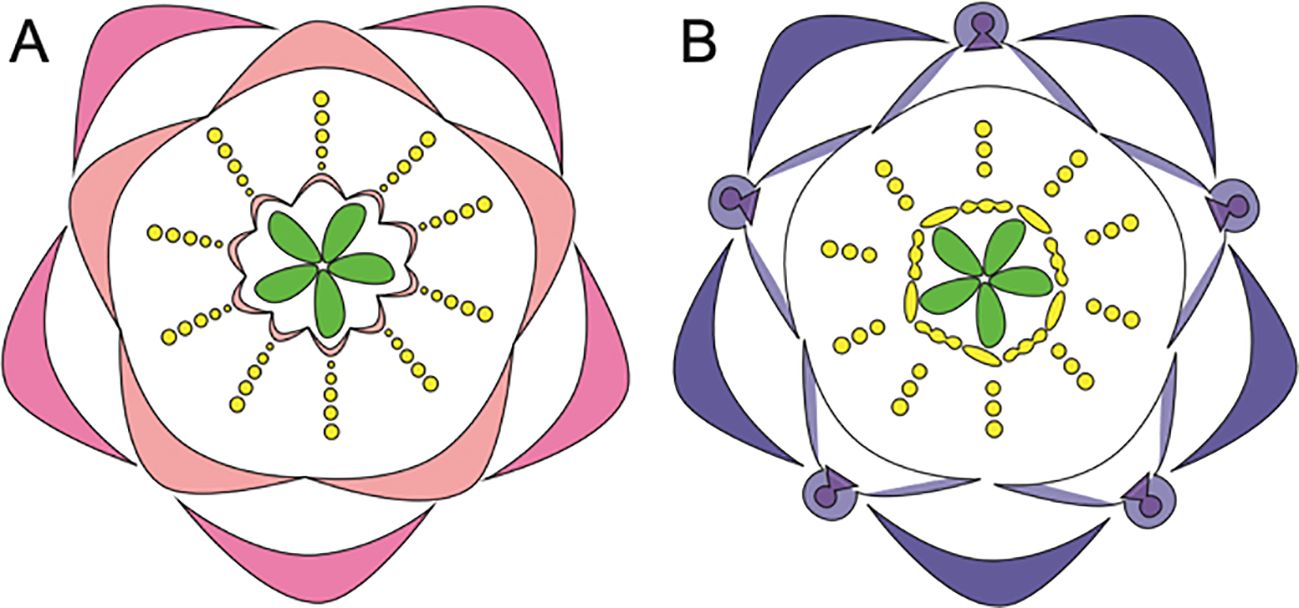
Figure 4. Floral diagrams illustrating species with variations from the typical Aquilegia perianth structure (A) A. ecalcarata, lacks spurs and (B) A. jonesii, lacks staminodia (Adapted from Tucker and Hodges, 2005; Kramer, 2009; Johns et al., 2024).
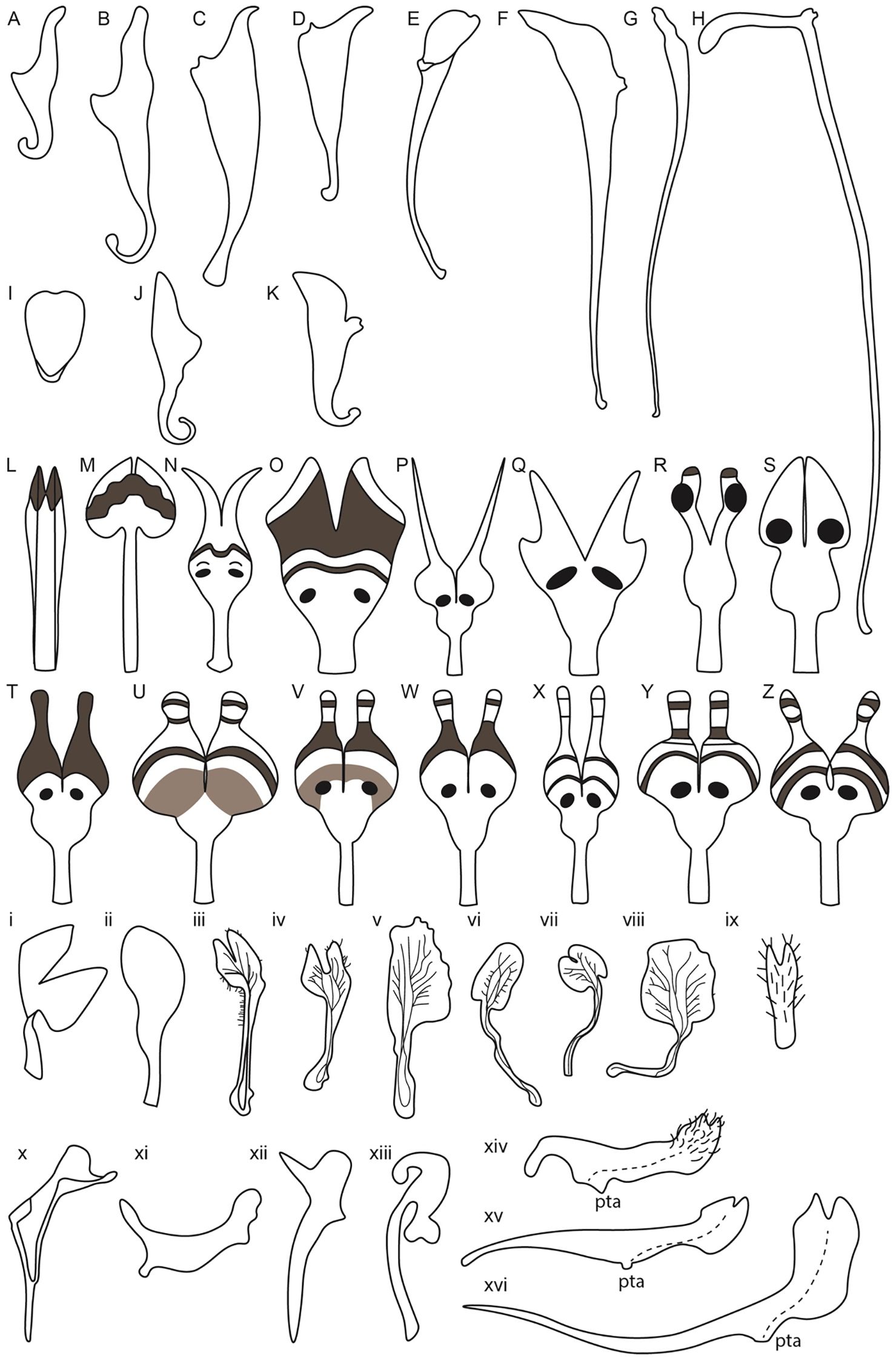
Figure 5. Petal diversity of Ranunculales models, Aquilegia, Nigella, Delphinium along with related Delphinieae species, Staphisagria and Aconitum. (Adapted from Ballerini et al., 2019; Edwards et al., 2022; Munz, 1967; Kramer and Hodges, 2010; Bosch et al., 1997; Zhang et al., 2022; Delpeuch et al., 2022; Yao et al., 2019) Aquilegia petals (A–K) (A) A. brevistyla (B) A. saximontana (C) A. canadensis (D) A. formosa (E) A. coerulea (F) A. chrysantha (G) A. pinetorum (H) A. longissima (I) A. ecalcarata (J) A. flabellata (K) A. sibirica; Nigella petals from simple to complex (L–Z) (L) N. integrifolia (M) N. unguicularis (N) N. nigellastrum (O) N. orientalis (P) N. oxypetala (Q) N. ciliaris (R) N. elata (S) N. damascena (T) N. stricta (U) N. d. ssp. jenny (V) N. dengii ssp. dengii (W) N. carpatha (X) N. a. spp. brevifolia (Y) N. a. spp. aristata (Z) N. a. spp. arvensis; Lateral petals of Delphinium and related Staphisagria (i-ix) i. D. anthriscifolium ii. S. macrosperma iii. D. montanum iv. D. bolosii v. S. pictum vi. D. gracile vii. D. verdunense viii. D. obcordatum ix. D. leroyi; Dorsal petals in Delphinium and its related genera Staphisagria and Aconitum (x-xvi) x. D. anthriscifolium xi. S. macrosperma xii. D. balanse xiii. Aconitum xiv. D. dasycaulon xv. D. sylvaticum xvi. D. leroyi.
In addition to spur length, spur shape also varies, with some species exhibiting curved spurs and others straight. For instance, A. sibirica (Figure 5K) and A. vulgaris have curved spurs, while A. chrysantha and A. longissima exhibit the straight ones (Figures 5F, H, Stubben and Milligan, 2007; Puzey et al., 2011; Ballerini et al., 2019). Differences in the shape and length of the blade are also noted (Figures 5A–K). The evolution of petal spurs is considered a key innovation within the genus Aquilegia, facilitating adaptive radiation by attracting specific pollinators (Hodges and Arnold, 1995; Edwards et al., 2021).
This diversity in morphological characteristics raises numerous questions about the functional relevance and genetic basis of these traits. Particularly intriguing are the genetic and evolutionary mechanisms behind the loss of staminodes in A. jonesii and the absence of petal spurs in A. ecalcarata (Ballerini et al., 2019; Geng et al., 2021; Johns et al., 2024). Understanding these variations not only sheds light on the evolutionary history of Aquilegia but also contributes to broader insights into the processes driving floral diversity and specialization.
2.2 Thalictrum
The genus Thalictrum, encompassing approximately 150–200 species, exemplifies the complexity and diversity found within the Ranunculaceae family (Boivin, 1944). Distributed throughout temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere, Thalictrum displays a broad spectrum of morphological and ecological adaptations. This genus has experienced considerable diversification, with species adapting to different pollination syndromes and habitats (Kaplan and Mulcahy, 1971).
The divergence of Thalictrum from Aquilegia is estimated to have occurred approximately 28.7–24.5 Mya, followed by events that contributed to its present widespread distribution (Soza et al., 2013). Notably, Thalictrum species exhibit a variety of sexual systems, including hermaphroditism, dioecy (separate male and female plants), andromonoecy (male and hermaphroditic flowers on one plant), gynomonoecy (female and hermaphroditic flowers on one plant) and polygamy with hermaphroditic and unisexual flowers on the same or different individuals (Kaplan and Mulcahy, 1971; LaRue et al., 2013).
The actinomorphic perianth of Thalicturm has a calyx composed of deciduous sepals (4-5) that are white or purplish (Figures 3H–K). Thalictrum lacks petals and nectaries, and the flowers have numerous stamens (34-40) and carpels (4-5) (Figures 3L, M, Kaplan and Mulcahy, 1971; Ren et al., 2011). The pistils are unfused and uniovulate, with a stigma that is papillionate (signifying butterfly shape). The flowers produce pollen as the primary attractant for pollinators. Both insect and/or wind pollination have been noted depending on the species (Kaplan and Mulcahy, 1971). For example, T. thalictroides is primarily insect-pollinated (entomophilous), T. polygamum utilizes both insect and wind pollination (anemophilous), while T. dioicum and T. revolutum are generally wind-pollinated (Kaplan and Mulcahy, 1971). Insect-pollinated species of Thalictrum are characterized by short styles and small anthers, while wind-pollinated species display long styles and large anthers (Martínez-Gómez et al., 2023). This variation in pollination strategies is mirrored in the diverse floral morphologies and sexual systems found within the genus (Kaplan and Mulcahy, 1971).
Thalictrum has undergone multiple polyploidy transitions, with chromosome numbers ranging from 2n=2x=14 to 2n=24x=168 (Löve, 1982; Tamura, 1995; Soza et al., 2013). While a study by Soza et al. (2013) found no correlation between changes in ploidy and the evolution of dioecy, they identified a strong association between polyploidy and wind pollination. This diversity in floral structures and pollination strategies not only emphasizes the adaptability of Thalictrum species to their environments but also highlights the complex evolutionary processes influencing plant-pollinator interactions. The study suggests that the evolution of dioecy in Thalictrum likely involved other pathways beyond polyploidy. Understanding these variations offers valuable insights into the mechanisms driving floral diversity and reproductive success within the genus.
2.3 Nigella damascena L.
The genus Nigella comprises of approximately 18–22 species (Yao et al., 2019; Lubna et al., 2024) These species exhibit an annual life cycle and have a broad biogeographical distribution, native from Macaronesia, Europe to Mediterranean, North Africa, and Central Asia (Kew Science). There is sparse distribution in Oceania region and South America (Nigella L. @ in GBIF Secretariat, 2023). The highest species diversity is found in the Aegean region, where six species of the N. arevensis complex are found (Strid, 1970; Bittkau and Comes, 2009; Jaros et al., 2018; Dönmez et al., 2021; Lubna et al., 2024). The genus Nigella s. lat. (Nigella L. and Garidella L.) originated approximately, 43.2-8.9 Mya and has predominantly undergone allopatric speciation. The diversification within the genera approximately began during the Oligocene through the Messinian (29.0-6.0 Mya). The major shift within the genus occurred when the N. arevensis complex underwent non-adaptive radiation. The complex probably originated in the Messinian to mid-Pleistocene period (6.2-1.3 Mya) and its diversification began in the Late Pleistocene (0.8-0.2 Mya) (Bittkau and Comes, 2009). This regional event significantly accelerated the diversification rate on the species-level log lineages-through-time (LTT) plot, which is usually linear and constant under the standard constant-rates birth-death (CR-BD) model of diversification. Considering the spatio-temporal scale, it is predicted that the (palaeo) geographical complexity of the Aegean region along with changes in the climate and sea level during the Late Pleistocene are primary factors that led to a rapid increase in speciation within the complex (Bittkau and Comes, 2009). This recent diversification event makes Nigella an interesting model system to explore and to further gain insights into the underlying mechanisms that led to such rapid speciation.
The actinomorphic and bipartite perianth of Nigella is composed of four kinds of floral organs (Deroin et al., 2015) arranged in an ontogenic spiral (Figures 3N–P, Jabbour et al., 2009). The calyx varies in petaloid sepal number (4 –7), with 5 being the most predominant (Figure 3Q, Gonçalves et al., 2013; Wang et al., 2015; Zhang et al., 2020). The corolla comprises of bilabiate nectariferous petals (5 - 10) attaching to the receptacle via rod-like stalk (Figure 3R, Liao et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2020). The Nigella genus is noted for its elaborated petal morphology (Figures 5L–Z). The doubly geniculated petals have a laminar upper lip, bifurcate lower lip covered with short trichomes and long hairs along the pair of pseudonectaries and lobes, respectively (Yao et al., 2019). The true nectary can be found sandwiched between the upper and lower lip of the petal (Liao et al., 2020). The sepals and petals surround the androecium made of stamens (20-25) organized in eight parastichies (Figure 3S) and the gynoecium is composed five carpels (Figure 3T, Gonçalves et al., 2013; Deroin et al., 2015). Nigella also has an apetalous [T] morph, which lacks petals and instead, possesses sepal-like organs. Other floral organs such as sepals, stamens and carpels are similar in structure and cellular composition, however sepal-like organs can vary in shapes ranging from petaloid to bifid or trifid apices to mixed organs with sepal and stamen characteristics (Gonçalves et al., 2013). The pollinators of N. damascena include honeybees, which are the most common followed by bumblebees and wasps (Liao et al., 2020).
2.4 Delphinium
The species-rich genus was comprehensively reviewed by Sharma et al. (2024); therefore, we provide a brief overview here to maintain context. The highly diverse Delphinieae tribe, comprising approximately 750 species, is characterized by complex zygomorphic flowers that achieve almost perfect monosymmetry through dorsoventral differentiation, with floral organs arranged in a spiral phyllotaxy (Endress, 1999; Jabbour and Renner, 2012a; Novikoff and Jabbour, 2014).
This tribe includes Delphinium (~365 species) (Yin et al., 2020) along with the three genera Aconitum (~400, species) (Ali et al., 2023), Gymnaconitum (1 species) (Wang et al., 2013), and Staphisagria (3 species) (Jabbour and Renner, 2011). The members of this group mostly inhabit cold and temperate regions across four continents in the Northern Hemisphere (Bosch et al., 2016) as well as high mountains within tropical Africa (Warnock, 1997; Jabbour and Renner, 2012a; DuPasquier et al., 2021). The tribe originated between 29–31.4 Mya (Jabbour and Renner, 2012a; Wang et al., 2016; Xiang et al., 2017) with the genus Delphinium originating about 24 Mya in East Asia. It diversified across the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau (QTP) where the perennial life cycle emerged and eventually diversified into North America ~3 Mya (Jabbour and Renner, 2012a).
The perianth organs of Delphinium are very characteristic, forming a spur(s)-in-spur configuration referred to as a hyperorgan (Figures 3U, V, Jabbour and Renner, 2012b; Jabbour et al., 2021; Sharma et al., 2024). The outermost perianth whorl of Delphinium flower is denoted by petaloid sepals (5) (Figure 3W, Kosuge, 1994; Endress, 1995), two of which are lateral, another two are ventral, and a single dorsal spurred (Figure 3Y). The second whorl includes lateral non-spurred trichome-rich showy petals (0-2) except for the subgenus Consolida (Figure 3X) and nectariferous dorsal spurred petals (1-2) that grow within the dorsal sepal spur cavity (Figure 3Z, Jabbour et al., 2021) in synorganization (Chen et al., 2018) forming a hyperorgan (Jabbour et al., 2021). Innermost whorls are composed of stamens (13-40) (Figure 3i, Novikoff and Jabbour, 2014; Zhang et al., 2022) surrounding a variable number of carpels (1-5) (Figure 3ii, Jabbour and Renner, 2012b; Blanché, 1990; Espinosa et al., 2021; Zhang et al., 2022; Sharma et al., 2024). The distinctive floral structures of these plants are not only aesthetically remarkable but also functionally significant in their interactions with pollinators. The most common pollinators of Delphinium are bees, although hawkmoths, hummingbirds, flies and wind pollination are also observed (Jabbour and Renner, 2012b). This genus exhibits a variety of floral morphologies that elucidate their evolutionary relationships, reproductive strategies, and ecological adaptations.
2.5 Papaver and Eschscholzia
The Papaveraceae family holds a pivotal position in the phylogeny of flowering plants, as it is sister to the rest of the Ranunculales, which is sister to the rest of the Eudicots (Peng et al., 2023). This family offers significant insights into the evolution of more complex floral organ morphology (Hidalgo and Gleissberg, 2010). Comprising 45 genera and ~ 850 species, 70% of which are regional endemics, this family is predominantly found from sea level to altitudes of ~ 6000m across temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere. They inhabit forest understories, alpine meadows, tundra, and deserts (Peng et al., 2023). The Papaveraceae family ancestral habitat is inferred to be a forest understory with partial canopy in Asia (Peng et al., 2023). A divergence of the family occurred during the Lower-Mid Cretaceous resulting in four subfamilies, Hypecoideae, Pteridophylloideae, Fumarioideae, and Papaveroideae (Hoot et al., 2015; Becker et al., 2023; Peng et al., 2024).
The Papaveroideae subfamily originated in Asia. The interconnectivity of western North America via the Bering Land Bridge is hypothesized to be a facilitator for the subsequent dispersal into western North America twice, between 121-101 Mya and 95- 82 Mya (Peng et al., 2023). The Papaveroideae tribe Eschscholzieae includes Eschscholzia californica ssp. californica (California poppy) (Figures 3iii–v), and Papavereae tribe includes Papaver somniferum (opium poppy) (Hoot et al., 2015). The genera Eschscholzia and Papaver serve as model systems for understanding the genetic and evolutionary mechanisms underlying floral development (Hidalgo and Gleissberg, 2010; Becker et al., 2023).
The globally identifiable species within this family is P. somniferum, commonly known as the opium poppy. It is native to Northern African countries— Morrocco, Algeria, and Tunisia, and European countries— Portugal, Spain, France and Italy (Jesus et al., 2021). P. somniferum is uniquely situated as a close sister group to the core eudicots, making it a prime candidate for comparative studies (Drea et al., 2007; Hong et al., 2022). The flowers of P. somniferum are actinomorphic and contain 4 types of floral organs (Hidalgo and Gleissberg, 2010), including sepals (2), followed by two alternating whorls of petals (4, 2 in each whorl) (Hidalgo and Gleissberg, 2010). The next whorl contains numerous stamens (25–223) and carpels (8-12) that fuse to form the capsule (Prajapati et al., 2001; Drea et al., 2007).
E. californica also has an actinomorphic perianth, composed of fused sepals (2) arranged in a cap-like structure in the outermost whorl (Figure 3vi). The cap dehisces to reveal the brightly colored silky petals (4) that are arranged in two concentric whorls where two outer petals surround two inner petals perpendicularly (Figure 3vii, Becker et al., 2005). The color of petals can vary across natural populations. Moving from northern to southern populations, hues will shift from more yellow in the north to orange in central and southern populations (Cook, 1962). Inner to petal whorls are stamens (16–39) that have golden yellow anthers that darken at the base, they attach to the receptacle by a short filament (Figure 3viii, Cook, 1962; Becker et al., 2023). The innermost whorl comprises of bicarpellate gynoecium (Figure 3ix, Becker et al., 2005, 2023). From the gynoecium, long stigmatic extensions (Becker et al., 2005) protrude in a prong-like fashion.
3 Morphological and evolutionary innovations in petal structure and implications for plant-pollinator interactions
Petals can be simple, characterized by flat surfaces, smooth margins, and simple color patterns, as seen in Arabidopsis, roses, lilies, and tulips. However, petals can also be elaborate, featuring protrusions, spurs, appendages, trichomes, pouches, fringes, and teeth (Endress and Matthews, 2006; Fu et al., 2022). Such elaborations are prominent in many members of the Ranunculaceae family, including Aquilegia, Delphinium, and Nigella (Figure 5). Petal elaboration is observed in at least 35 orders of angiosperms (Fu et al., 2022). This elaboration on petaloid organs enhances plant-pollinator interactions, thereby contributing to reproductive success and promoting evolutionary radiation (Whittall and Hodges, 2007; Yao et al., 2019; Fu et al., 2022). Petal elaborations have been classified into four main types: marginal, ventral, dorsal, and surface elaborations (Endress and Matthews, 2006; Fu et al., 2022). Petal elaborations are generally achieved through morphogenetic transformation which includes deformation and the addition of decorations and details such as those described above to the petal surface (Figure 6, Endress and Mathews, 2006; Fu et al., 2022);.
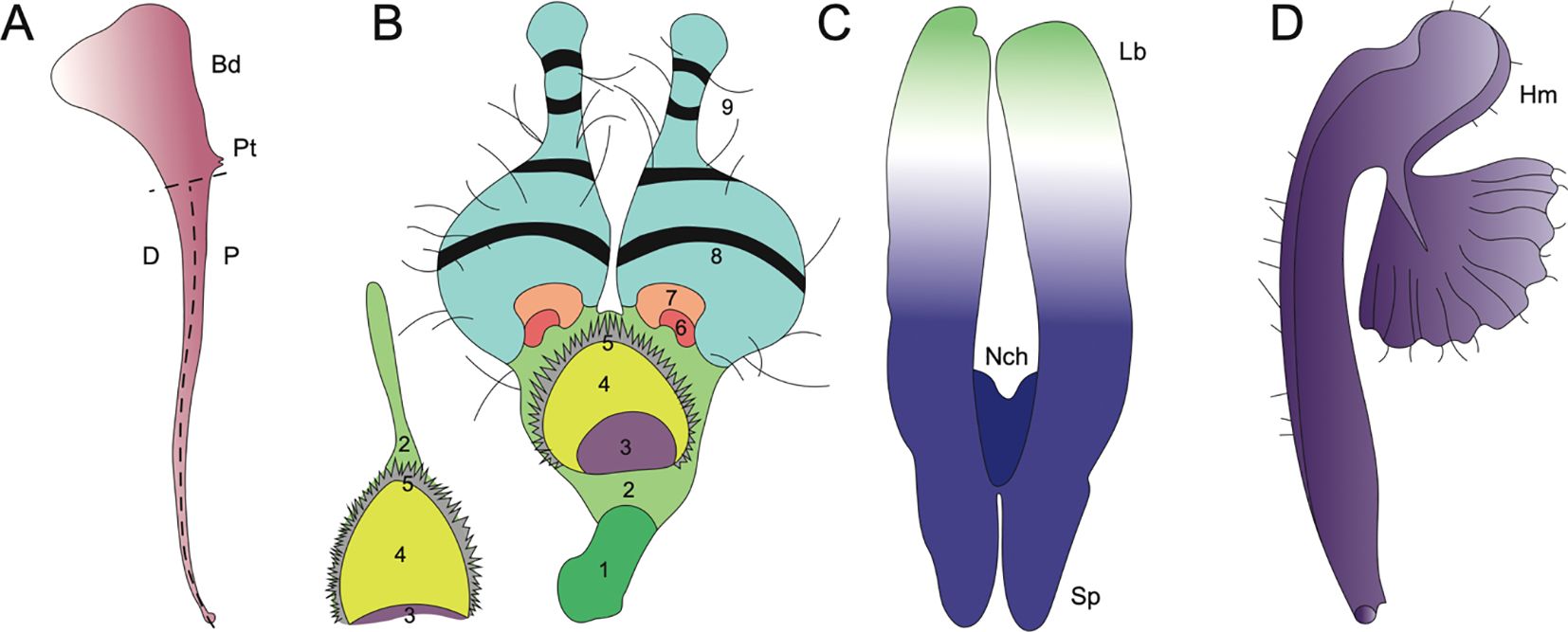
Figure 6. Evolutionary innovations in petal structure for Aquilegia, Nigella, and Delphinieae. (Adapted from Puzey et al., 2011; Yao et al., 2019; Zalko et al., 2021; MNHN and Chagnoux, 2024) (A) A. coerulea spurred petal distal (D), proximal (P), point of attachment (Pt), blade (Bd) adapted from Puzey et al., 2011. (B) N. arvensis and its epidermal cell zones 1-9. (1) rectangular cells, (2) irregular cells, (3) secretory, (4) oblong cells, (5) short trichomes, (6) polygonal cells with grainy surfaces, (7) polygonal cells with smooth surfaces, (8) conical cells, (9) long trichomes, and (10) pavement cells (not shown). Adapted from Yao et al., 2019. (C) Staphisagria notch (Nch), spur (Sp), labium (Lb). Adapted from Zalko et al., 2021. (D) Gymnoaconitum gynandrum (Hm) helmet adapted from MNHN and Chagnoux, 2024.
A study by Carrive et al. (2020) cautiously reported insights into the ancestral state of Ranunculales flowers. This study proposed that the ancestral flower was actinomorphic, with trimerous whorls and a differentiated perianth. The study also noted the nectar-storing organs had a single origin. In Ranunculaceae, the nectar is produced and stored by the petals. The ancestral state of petals in the family is characterized as flat petals with short claws, suggesting that the elaboration in petals in various taxa within this family have evolved independently (Delpeuch et al., 2022). Endress and Matthews (2006) mention that within the core Ranunculales, which includes four families, Ranunculaceae, Berberidaceae, Menispermaceae, and Lardizabalaceae, the elaborate and complicated petal morphology is associated with the presence of nectaries in petals. Petal elaboration in Ranunculales, particularly within genera such as Aquilegia, Nigella, and Delphinium, showcases the remarkable morphological diversity and complexity driven by developmental repatterning, heterochrony, genetic regulation and by co-option of existing genetic programs (Figure 6, Yao et al., 2019). The study of these complex interactions within an eco-evo-devo framework highlights how ecological interactions, evolutionary processes, and developmental mechanisms converge to shape the elaborate and complex petal morphologies observed in these genera.
3.1 The spurred and nectariferous petals of Aquilegia
Aquilegia, commonly known as columbines, are cherished as ornamentals for their uniquely beautiful flowers, highlighted by petaloid perianth organs and particularly their spurred petals. As mentioned above, the length of these spurs can vary from as short as ~5 mm to as long as 180 mm reflecting the adaptation to different pollinator species with varying tongue lengths (Figures 5A–K). The shortest spurs are typically associated with bee pollination, while medium-length spurs are adapted for hummingbirds, and the longest spurs are designed for pollination by hawkmoths (Bastida et al., 2010; Puzey et al., 2011). The elaborate spurs consist of two parts - a laminar blade that grows and extends upwards from its point of attachment to the receptacle, and the spur with the nectary at its tip growing downwards (Figure 6A, Edwards et al., 2022). In Aquilegia, bee-pollinated species, such as A. brevistyla, A. jonesii, A. saximontana, have purple flowers with short, curved spurs. This curvature results from differential cell division and elongation on the distal versus proximal sides of the spur (Figures 5A, B, Edwards et al., 2022).
The North American radiation event, approximately 1-3 Mya, resulted in shifts in pollinators, including hummingbirds and hawkmoths (Bastida et al., 2010). These shifts were associated with distinct morphological traits compared to bee-pollinated species. For instance, hummingbird-pollinated species exhibit reduced blade length, red perianths, and long, straight spurs (example, A. canadensis, A. formosa) (Figures 5C, D, Hodges et al., 2004; Edwards et al., 2022). Notably, there have been two independent transitions to hummingbird pollination. In contrast, hawkmoth-pollinated species also have long, straight spurs but have lost anthocyanins and floral scent (A.longissma, A. pubescens), with five documented transitions to hawkmoth pollination (Figure 5H, Hodges et al., 2004; Stubben and Milligan, 2007).
Whittall and Hodges (2007) propose that the absence of the hawkmoth pollination syndrome in Europe, despite the presence of hawkmoths, can be attributed to the intermediate role of hummingbird pollination. The tongue length of hummingbirds is intermediate between that of bees and hawkmoths, facilitating a gradual evolutionary transition (Whittall and Hodges, 2007). Spurs are lost in A. ecalcarata, a species that is native from central China, and is pollinated by syrphid flies (Figure 5I, Huang et al., 2018; Geng et al., 2021). Although the spurless trait in A. ecalcarata appears to have evolved from a single evolutionary event, the species itself shows evidence of multiple independent origins, as demonstrated by several studies (Huang et al., 2018; Xue et al., 2020; Geng et al., 2021; Geng et al., 2024). Moreover, recent findings by Geng et al. (2024) present strong evidence that gene flow has played a crucial role in the parallel evolution observed within A. ecalcarata. The comparison of gene expression patterns between spurred Aquilegia species by Ballerini et al. (2019) and the spurless A. ecalcarata reveals a significant heterochronic shift in petal development (Geng et al., 2021). In spurred species, the transition from cell division to differentiation is delayed; this developmental delay allows for the extended formation of the spur (Puzey et al., 2011). The complex relationship between the floral morphology of Aquilegia and its diverse pollinators underscores the evolutionary adaptability of this genus. The variations in petal spur length and curvature reflect not only the specialized pollination mechanisms but also the dynamic evolutionary history shaped by geographical and ecological factors.
3.2 Distinctly elaborate and complex petals of Nigella
The genus Nigella is noted for its elaborate petal morphology, showcasing significant variation in micromorphological characters of petals such as upper and bifurcated lower lips, pseudonectaries, nectary chamber, long hairs, short trichomes, and eyebrow-like stripes, etc (Yao et al., 2019; Strid, 1970; Tamura, 1995; Endress and Matthews, 2006; Zhao et al., 2011; Gonçalves et al., 2013). The complex and elaborate petal formation occurred via the deformation of old characters as well as de novo formation of new characters (Yao et al., 2019). The developmental basis of petal elaboration in Nigella involves both marginal and ventral elaboration. Marginal elaboration is evident from the presence of lobes along the petal edges, while ventral elaboration includes structures such as scales, protrusions, and the development of features like lips and appendages (Endress and Matthews, 2006; Erbar et al., 1999; Yao et al., 2019).
The study by Yao et al. (2019) explores the morphological, genetic, and evolutionary aspects of petal elaboration in Nigella, highlighting its complexity and adaptive significance. The evolution of Nigella petals exemplifies evolutionary gradualism, where initially simple ancestral petals gradually developed new characters such as long stalks, geniculate bends, and eyebrow-like stripes over time, leading to increased complexity (Figures 5L–Z, Yao et al., 2019). The study also highlights the presence of at least ten different types of epidermal cells that contribute to the detailed petal structures in N. arvensis. These include rectangular cells, irregular cells, secretory cells, oblong cells, short trichomes, polygonal cells with both grainy and smooth surfaces, conical cells, long trichomes, and pavement cells (Figure 6B). Each type of cell has unique micromorphological characteristics, locations, and roles, which collectively enhance the complexity and functionality of the petals (Yao et al., 2019).
In their 2019 study, Yao et al. grouped Nigella species into three major categories based on petal morphology and micromorphological characteristics. The ancestral Nigella species, N. integrifolia is the single species in category 1 (Figure 5L). The petals in this category are relatively simple and tubular in structure. Key features include the presence of an upper lip, nectary and ridges, a bifurcate lower lip, and specific epidermal cell types (2,3, 4, 9, and 10). These features represent the ancestral state from which more complex structures evolved. Category 2 includes two species - N. unguicularis and N. nigellastrum (Figures 5M, N). The petals in these species exhibit more complexity compared to Category 1, featuring elongated stalks and geniculate bends, eyebrow-like stripes, and short trichomes. In addition to the cell types in category 1, cell types 1 and 5 are also observed in category 2. N. nigellastrum also displays type 11 epidermal cells. Interestingly, type 11 epidermal cells are the characteristic feature of only this species and are not found in other species within the genus. The introduction of these characters increased complexity in the petal structure, creating a clear distinction between the upper and lower lips, as well as the stalk. Consequently, the nectar-bearing petals were directly exposed to pollinators (Yao et al., 2019). These new characters mark an intermediate evolutionary stage, leading to enhanced functionality in pollinator attraction.
Continued evolutionary changes led to the formation of Category 3, which includes all the remaining species within the genus Nigella. The species in category 3, exhibit the most elaborate petal structures with highly specialized modifications. In this category, species such as N. orientalis, N. oxypetala, N. ciliaris, N. elata, and N. damascena exhibit additional new characteristics such as pseudonectaries, type 7 and type 8 epidermal cells (Figures 5O–S). Notably, N. ciliaris, N. oxypetala, and N. damascena independently lost eyebrow-like stripes. Furthermore, epidermal cell type 6 emerged in all species of category 3 except in N. ciliaris, N. oxypetala, N. orientalis. Besides, caudate lobes are observed in all catagory 3 species except in N. ciliaris, N. orientalis, N. elata and N. damascena Interestingly, pseudonectaries were secondarily lost in N. degenii ssp. jenny, and in some populations of N. degenii subspecies. degenii and N. degenii subspecies. barbro (Figures 5U, V).
Within Nigella, the origination of the new characters in the petal structure has led to significant functional innovation and complexity. One of the distinguishing features of Nigella is the pseudonectaries, or false nectaries. Studies by Liao et al. (2020) suggest that pseudonectaries may play crucial role in pollination success. When observed under the UV light, pesudonectaries appear shiny and reflective, while all the other floral regions are dark black (Liao et al., 2020). Interestingly, bees can view these pseudonectaries as shiny, however, they observe the other flower parts and petals to be dark green, thus indicating the role of pseudonectaries in attracting the bees. Liao et al. (2020) also reported that flowers without pseudonectaries experience significant reduction in the visiting frequency and probing time of honeybees. Besides, the eyebrow like stripes which look like concentric rings on the open flower can serve as tracks that guide the pollinators. Along with the pseudonectaries, they further help the pollinator to locate entrance to the nectary chamber (Weber, 1995).
Notably, the short trichomes are thought to serve a role of protecting the nectar since the nectar chamber is formed by the upper and lower lips, and the short trichomes are found at the chewing surface of the upper and lower lips. Additionally, they also may play role in reducing the evaporation of water as the flowers usually bloom in hot and dry seasons (Strid, 1970; Zohary, 1983).
3.3 The lateral flat and dorsal spurred petal (s) in Delphinieae
Within the Delphinieae tribe, remarkable diversity in petal morphology is observed including three distinct types of petals–lateral, dorsal- spurred, and reduced ventral. Lateral petals are observed in genera Staphisagria and Delphinium, except in its subgenus Consolida (Jabbour et al., 2021; Zalko et al., 2021). Spurred petals (1–2) are observed in all the species, except in the taxa D. ecalcarata and D. turcicum (Figure 7, Espinosa et al., 2017; Xiang et al., 2017). The reduced petals are present in all species within the tribe, vary in their ranging from 4–6 (Espinosa et al., 2017; Zalko et al., 2021).
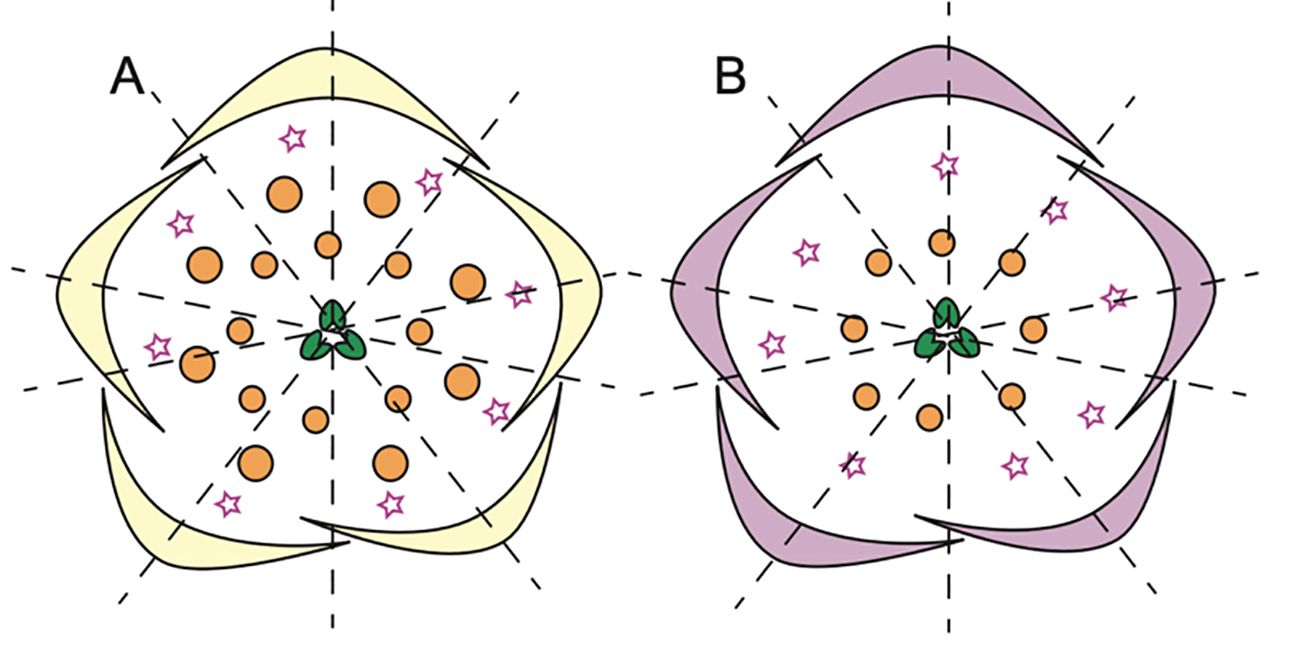
Figure 7. Floral diagrams illustrating species with variations from the typical Delphinium perianth structure and actinomorphy. (A) D. turccium and (B) D. ecalcarata (Adapted from Espinosa et al., 2017, 2021; Luo et al., 2023), stars in whorl 2 represent reduced petals.
The study by Munz (1967) provides a foundational examination of Delphinium species, highlighting their unique floral morphologies, including the characteristics of the dorsal spurred and lateral flat petals (Figures 5i–xvi). In his meticulous documentation, Munz referred to the spurred petals as “upper pair” with nectariferous spurs and lateral petals as “lower pair” with an expanded lamina and basal claw. These illustrations and descriptions reveal significant diversity in petal morphology across different Delphinium species. For instance, the spurred petals, or upper petals, vary in length and curvature while the lower petals, also show considerable diversity in shape and size (Munz, 1967; Jabbour and Renner, 2012b). The variations in petal structure, particularly spur length and shape, are likely adaptations to attract specific pollinators, underscoring the evolutionary significance of these traits in facilitating effective plant-pollinator interactions.
Building on Munz’s observation, the evolution of floral traits within Delphinium further illustrates adaptations to various pollinators. For example, the lateral petals in D. anthriscifolium, act as visual cues to attract and guide pollinators and function as a biomechanical filter to ensure that effective pollinators access the nectar (Muller, 1883; Blanché, 1990; Hou et al., 2022). Lateral petals are bilobed and twisted helically, providing a stable landing platform for pollinators and partially cover the spurred petals to protect the nectar from desiccation (Zhang et al., 2022; Zhang H. et al., 2024). The dorsal petals possess a nectar spur with a widened tip, designed to accommodate the tongue length of specific pollinators, enhancing pollination specialization (Zhang et al., 2022). Within the tribe, bee-pollinated species typically exhibit shorter, curved spurs, while those pollinated by hummingbirds or hawkmoths tend to have longer, straight spurs (Zalko et al., 2021). In Delphinium subgenus Consolida flowers possess a single dorsal nectariferous petal, resulting from the fusion of the two superior petals. This structural simplification is seen as an evolutionary adaptation to different ecological niches and pollinator availability. The lateral petals, prominent in the other subgenra of Delphinium, are absent in Consolida, indicating a trend toward floral simplification (Blanché, 1990).
The Aconitum genus showcases a high-galeate upper sepal, forming a hood that protects the nectar-producing parts of the flower (Figure 5xiii). The short nectar-spurs of the petals are located at the apex of an elongated pedicel (Jabbour et al., 2021). Bumblebees must enter the hooded sepal to access the nectar spurs, during which their abdomen and legs inevitably brush against the anthers, facilitating pollen transfer (Fukuda et al., 2001; Jabbour and Renner, 2012b). Recently, Gymnaconitum, that consists of a single species G. gymnandrum, was elevated to the genus level (Wang et al., 2013). This was previously, classified under the genus Aconitum. G. gymnandrum, is characterized by several unique features, including clawed sepals, large flabellate petal lobes, multiple carpels and an exposed stigma (Figure 6D).
In Staphisagria, petal primordia of dorsal petals are fused, the petals become notched and share a common cavity (Figure 6C, Payer, 1857; Jabbour and Renner, 2012b; Zalko et al., 2021). Besides, the inner epidermis of inner spur, this shared cavity at the entrance also showcases nectar secretory tissues. The mechanisms of nectar secretion and release exhibit significant variation among species within the tribe (Antoń and Kamińska, 2015; reviewed by Sharma et al., 2024). These varied floral morphologies across the Delphinieae tribe underscore the complex evolutionary dynamics driving adaptation and speciation within the Ranunculaceae family, highlighting the nuanced interplay between floral traits and pollinator interactions.
4 Model systems in Ranunculales, key organ identity developments, and potential for studying evolutionary developmental genetics
One of the key strengths of these Ranunculales models is the feasibility of functional genetics studies. Techniques such as RNA interference (RNAi) and Virus-Induced Gene Silencing (VIGS) are applicable across these species, enabling detailed investigations into gene function and regulation. Tissue culture and stable transformation systems are available for E. californica, P. somniferum, and T. thalictroides (Nessler, 1982; Park and Facchini, 2000; Samanani et al., 2002; Chitty et al., 2003; Lotz et al., 2022). While N. damascena can be cultured in vitro, stable transformation techniques have not yet been established for this species. Notably, the genomes of all these species, except for Nigella, have been sequenced or are being assembled. Within the Delphinieae tribe, the genome of S.picta is being assembled (The RanOmics group et al., 2024). The continued development of these genetic and genomic resources has facilitated elegant and informative research. Especially, the research on understanding the floral organ identity programs both the conservation and divergence of the ABC model of floral organ identity within closely related species. One particularly intriguing aspect of this research is the role of gene duplication in shaping unique floral morphologies. Below we discuss some selected developments.
4.1 Genetic studies in Aquilegia
In Aquilegia, there are three copies of the B gene homolog APETALA-3, AqAP3-1, AqAP3-2, and AqAP3-3. The AP3 lineage experienced two gene duplication events that occurred before the diversification of Ranunculaceae; these are independent of the B gene duplications in core eudicots. Kramer et al. (2007) hypothesized the role of B genes in contributing to the elaborate petal spur identity and a possible role in establishing staminodium identity. The expression of three AqAP3 paralogs detected through in situ hybridization was discrete in floral meristems at mid-late developmental stages. Expression of AqAP3-1 was observed only in staminodia, a strong expression of AqAP3-2 was noted in the stamen whorl and AqAP3-3 was strongly detected in petal primordia (Kramer et al., 2007), however, a broader expression for AP3-1, AP3-2 was noted in other floral organs in semi quantitative RT-PCR (Supplementary Table 2.1). Knockdown studies using the virus-induced gene silencing (VIGS) approach demonstrated the functional role of the three AP3 paralogs (Figure 8). AqAP3-1 knockdown resulted in the homeotic conversion of staminodia into carpels, inferring the neo-functionalization of this paralog in the establishment of staminodia identity (Figures 8A, B). AqAP3-2 knockdown in severe cases resulted in stamen necrosis but not complete loss of stamen identity (Figure 8C). A double knockdown of AqAP3-1 and AqAP3-2 resulted in a complete loss of stamen and staminodia identity, resulting in homeotic carpels replacing stamens and staminodes (Figure 8D, Sharma and Kramer, 2013). A reduction in petal size was also observed, but the petal identity was not lost. The double knockdown results implicate that AqAP3-1 to some degree and AqAP3-2 in a major capacity promote stamen identity. Downregulation of AqAP3-3 resulted in the loss of petal identity, implicating a petal-specific sub-functionalization (Figure 8E, Sharma et al., 2011). Dissection of the roles of the APETALA-3 homologs in organ identity establishment in Aquilegia is an example of the functional evolution of gene paralogs post duplication.
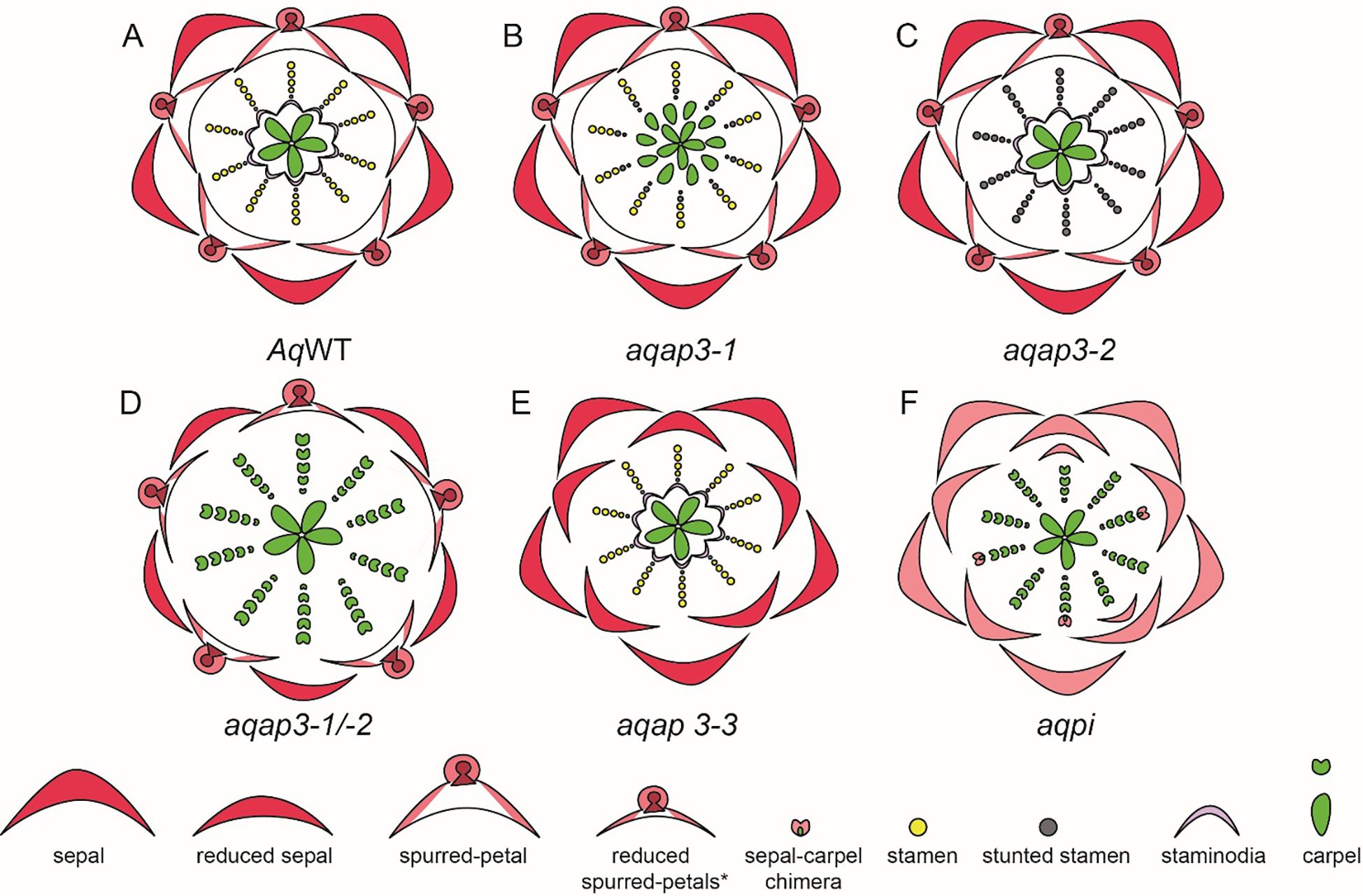
Figure 8. A. coerulea and its homeotic RNAi phenotypes (Adapted from Sharma et al., 2014). (A) Wildtype (WT) floral diagram displaying five organ identities from outer to inner most whorl: sepals, petals, stamens, staminodia, and carpels. (B) AqAP3-1 silenced flower (aqap3-1) show a strong transformation of the staminodia into carpels and stunted, sterile stamens in the inner stamen whorls, indicated in grey. (C) AqAP3-2 silenced flower (aqap3-2) display stunted, sterilized stamens in all stamen whorls with no effect on the other floral organs. (D) The double knockdown of AqAP3-1 and AqAP3- 2 silenced flower (aqap3-1/2) exhibits a reduction in petal and sepal size and a full transformation of the staminodia and stamens into carpels. (E) In AqAP3-3 silenced flower (aqap3-3) spurred petals are replaced by sepals. (F) AqPI-silenced flower (aqpi) phenotype shows petals replaced by sepals and stamens and staminodia by carpels as well as color loss in sepals and sepal-carpel chimeric organs.
A single homolog of the PISTILLATA, AqAPI, was detected in Aquilegia. PISTILLATA is also a B class gene. AqPI is expressed broadly in younger floral meristems but then gets localized in stamen, petal, and staminodia in the late stages (Supplementary Table 2.1). The expression pattern of AqPI, encompassed the complete expression domain of all three APETALA 3 paralogs. The AqPI expression indicated a conserved canonical role in establishing stamen and petal identity and contributing to staminodia identity; this was confirmed by the initial knockdown studies done in the Aquilegia vulgaris (Kramer et al., 2007). Later studies in A. coerulea identified a novel role of AqPI in the maintenance of the C domain boundary. The AqPI knockdown was repeated without the AqANS marker; the knockdown not only resulted in the loss of anthocyanin pigment in petals but also a loss of determinacy in the outer stamen whorls (Figure 8F). The range of phenotypes included multiple whorls of homeotic sepals or petals instead of stamens, various petal/stamen, or sepal/carpel chimeric organs. These phenotypes indicated that the expression of AqPI in outer stamens whorls might be necessary for maintaining the spatial expression domain of AqAG homologs (Sharma and Kramer, 2017). Although the role of B genes in the maintenance of petaloidy in sepals was established, we did not observe any phenotype in which the sepal identity was altered.
The A-class gene duplications in core eudicots have resulted in two major lineages, the AP1 and the FUL. Both lineages have some overlap of function, particularly their roles of floral meristem identity, AP1 also has a role in perianth identity, while FUL homologs functions also include inflorescence identity, leaf, and fruit development. Outside the core eudicots, pre-duplication ancestors of AP1, and FUL gene lineage are the FUL-like genes; these genes are more similar to FUL than to AP1 (Litt and Kramer, 2010). In Aquilegia, there are two copies of FUL-like genes AqFUL1A and AqFUL1B, the two copies are a result of tandem duplication. Outside the core eudicots, or even outside Arabidopsis, there is no conservation of the A class role in promoting sepal identity. In Aquileia, AqFUL genes are broadly expressed in leaves both pre- and post-vernalization. In young floral meristems, expression can be detected during sepal initiation and in petal, and stamen primordia (Supplementary Table 2.1). Knockdown of AqFUL results in branched inflorescences with simple cauline leaves coming off laterally from the nodes. The phenotype indicates AqFUL has a role in the repression of axillary meristem activity and in leaf morphogenesis (Pabón-Mora et al., 2013). No floral phenotype was observed in the AqFUL silenced plants. Functional studies of ABC genes in the non-conventional model system Aquilegia have provided valuable insights into the genetic foundations of petal spur development and the genetic mechanisms that define the identity of the novel staminodium.
4.2 Genetic bases of organ identity and elaboration beyond ABC genes in Aquilegia
Organ identity beyond ABC genes and elaboration mechanism has also been explored in Aquilegia. Developmental, transcriptomic, and QTL studies have shed light on the unique characteristics and evolutionary mechanisms of staminodia in Aquilegia (Meaders et al., 2020; Johns et al., 2024). Research has demonstrated that staminodia, sterile stamens, evolved approximately 20-22 Mya in the common ancestor of Aquilegia and its close relatives, Semiaquilegia and Urophysa (Bastida et al., 2010; Meaders et al., 2020). Unlike fertile stamens, staminodia lack anthers and feature ruffled lamina that expands to be 2-3 times broader than stamen filaments at maturity. These organs undergo post-genital fusion along their lateral margins to form a protective sheath around the carpels, with lamina expansion identified as a novel developmental mechanism. Asymmetric lignification across adaxial surface is observed in staminodes (Meaders et al., 2020). Key genes related to abaxial/adaxial identity, such as YABBY family transcription factors (AqFIL and AqCRC), were differentially expressed and were upregulated in staminodium compared to stamen, indicating their role in laminar expansion. Besides these, two other genes HOTHEAD and DEFECTIVE IN CUTICLE FORMATION were enriched in the staminodium implicating their possible role in the adherence mechanism that keeps the 10 staminodium organs attached to each other (Meaders et al., 2020). Within the genus Aquilegia, A. jonesii, is the only species that lack staminodium. A QTL analysis of an outcrossed F2 population of cross between A. jonesii, and A. coerulea “Origami” revealed a polygenic basis for staminode loss in A. jonesii (Johns et al., 2024).
The elaborate petal spurs in Aquilegia bear nectaries at their tips, exhibiting significant variation in length and shape within the genus, with A. longissima having the longest spurs (Edwards et al., 2021, 2022). A QTL analysis on the F2 generation from a cross between A. canadensis and A. brevistyla by Edwards et al. (2021) analyzed 17 floral traits, including spur-related traits such as spur curvature, spur length, and blade length. All traits except spur curvature were controlled by multiple loci (Edwards et al., 2021). In another study, Ballerini et al. (2020) crossed the spurless species A. ecalcarata with the spurred species A. sibirica and identified a single gene, located under the POP QTL and designated as POPOVICH, strongly associated with nectar spurs. POPOVICH is a C2H2 zinc-finger transcription factor. Knocking down this gene in A. coerulea (the rapid cycling model) resulted in flowers with short or no spurs and without nectaries (Ballerini et al., 2020). Additionally, the role of TCP4 in petal development was reported by Yant et al. (2015). TCP4 expression is initially observed in the blade margin of young petals but later shifts to the developing spur. Downregulation of TCP4 led to spurs with increased curvature and ectopic outgrowths due to cell proliferation. Furthermore, the role of STYLISH homologs was also reported in Aquilegia. STY genes in Aquilegia not only have a conserved role in carpel development, but also showed a role in nectary development. Downregulation of all three STY homologs resulted in petals without or distorted nectaries (Min et al., 2019).
Building on the insights from the above experiments, Zhang et al. (2020) explored the role of AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR (ARF) homologs, AqARF6 and AqARF8, which are highly expressed in developing petal spurs (Yant et al., 2015). The simultaneous knockdown of both ARF homologs in A. coerulea resulted in a significant reduction in spur length and the absence of nectar production due to the failure of nectaries to mature and become functional. This work provided evidence for the involvement of ARF6/8 homologs in promoting cell expansion and suggested a regulatory connection with STY homologs (Zhang et al., 2020). The studies described above contributes to a comprehensive understanding of petal spur development in Aquilegia.
4.3 Genetic studies in Thalictrum
The apetalous genus Thalictrum is a very dynamic and elegant model system noted for its diverse sexual system and extensive variability in ploidy. Functional studies conducted using VIGS have unraveled the function of B, C, and E class genes in T. thalictroides (Figure 9). There are three AP3 homologs, AP3-1, AP3-2a, and AP3-2b, and one or two PI homologs depending on the species. The AP3-3 homolog which has been implicated to have a role in establishment of petal identity (Kramer et al., 2007; Sharma et al., 2011; Zhang et al., 2013) is not detected in Thalictrum (Di Stilio et al., 2005). All B class genes are broadly expressed in sepals and stamens (Supplementary Table 2.2, Di Stilio et al., 2005). All three AP3 homologs were silenced individually (Galimba et al., 2018, Supplementary Table 2.2). The common knockdown phenotypes of the AP3 homologs included defects in sepal shape and number and proper establishment of sepal stamen boundary, presence of some chimeric organs such as such as sepal with ectopic anthers or stigmatic tips in stamen whorls and, stunting in stamens showing small anthers and short filaments (Figures 9A–D). TthAP3-1 and TthAP3-2b knockdown phenotypes also included reduction in size and width of sepals. Additionally, in both TthAP3-2a, and TthAP3-2b knockdown phenotypes included lobed sepals (Galimba et al., 2018). These phenotypes indicate a conserved role of B genes in stamen development. Additionally, a role of AP3-1 and Ap3-2b homologs in petaloidy of sepals and proper stigma development in carpels (Galimba et al., 2018).
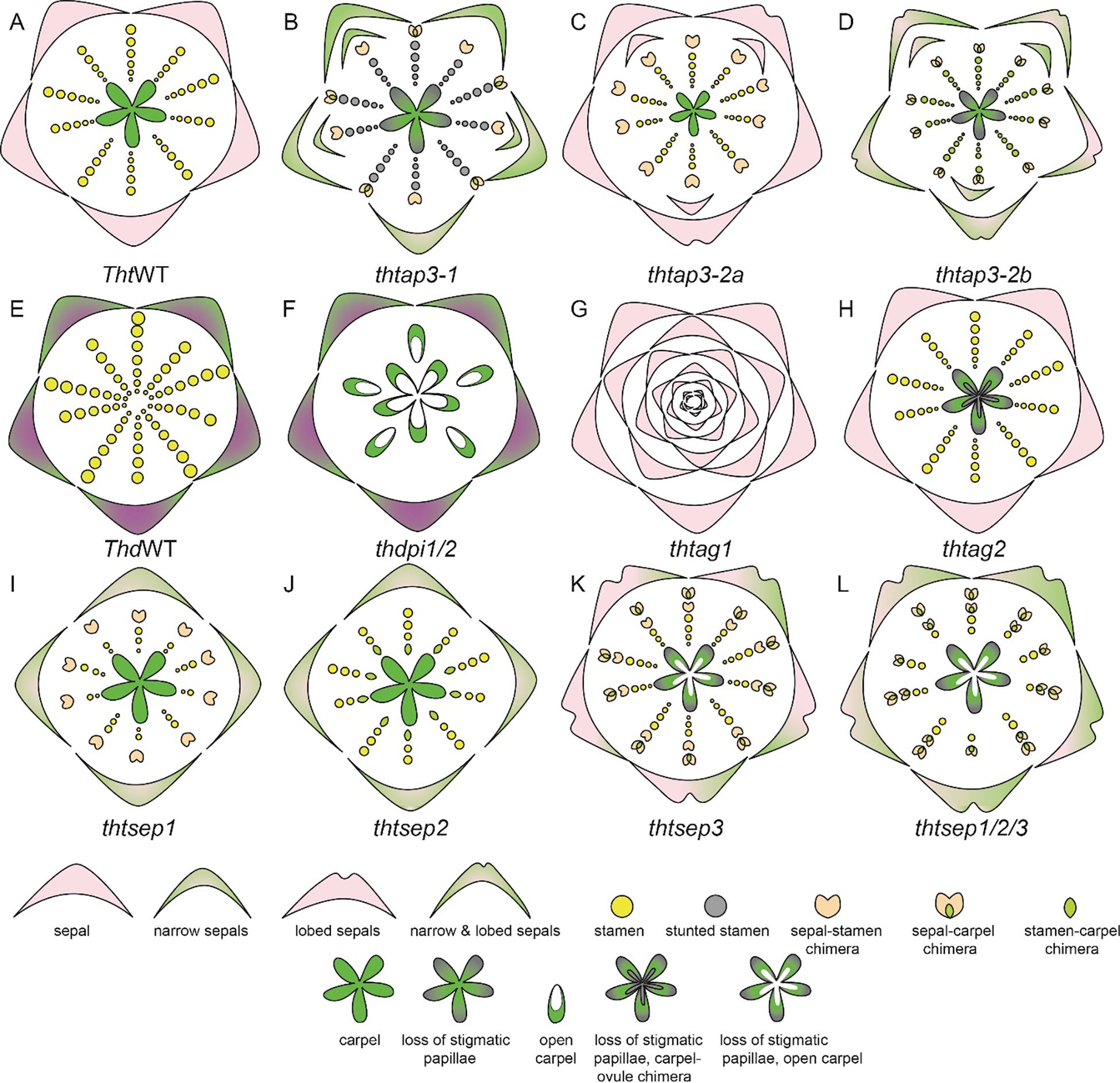
Figure 9. T. thalictroides and T. dioicum floral diagrams illustrated based on floral phenotype description in Galimba and Di Stilio, 2015; Galimba et al., 2012; LaRue et al., 2013; Di Stilio et al., 2005; Soza et al., 2016; Martínez-Gómez et al., 2020; Galimba et al., 2018. (A) Wildtype (WT) floral diagram for T. thalictroides displaying three organ identities: sepals, stamen, and carpels (B) thtap3-1 phenotype exhibits a reduction of sepal size and width, extra sepals and chimeric organs in the outer stamen whorls, carpels showing improper stigmatic development (C) thtap3-2a sepals retain their size but are lobed, extra sepals and chimeric organs observed in the outer stamen whorl (D) thtap3-2b show a combination of the other two ap3 knockdowns, reduction of sepal size and width, lobed sepals, extra sepals and chimeric organs in stamen whorls a carpels showing improper stigmatic development. (E) Wildtype (WT) floral diagram for a male T. dioicum male flower with outer whorl sepals and large stamens. (F) thdpi1/2 downregulation produced female flowers in which the stamens are replaced by carpels. (G) thtag1 flowers display stamens and carpels fully transformed into sterile sepal-like organs and floral indeterminacy. (H) thtag2 flowers exhibit ovules transformed into carpel-like structures. (I) thtsep1 displayed reduced or narrowed green-tipped sepals, with modified stamens that are shorter and wider, and sepal-carpel-stamen chimeric organs (J) thtsep2 similar to the phenotype of thtsep1, but with carpel-stamen chimeric organs where the inner two whorls meet (K) thtsep3 sepals have irregular edges, green patches and an array of chimeric organs (L) thtsep1/2/3 flowers exhibited a combination of the defects present in the single knockdowns such as patchy sepals, a reduction of stamens, a transformation of stamens to sepaloid stamens, glabrous papillae, and open sterile carpels.
Expression and functional analysis of PI homolog(s) have also been performed in Thalictrum. In T. thalictroides there is one copy of PI homolog that is expressed in sepal and in stamens (Di Stilio et al., 2005; Martínez-Gómez et al., 2020). In the tetraploid, T. dioicum, a dioecious species, two transcripts of PI homolog have been identified, ThdPI-1 and ThdPI-2; both copies are expressed in the perianth organs of carpellate and staminate flowers, as well as in the stamens of staminate flowers (Supplementary Table 2.2, Di Stilio et al., 2005; Martínez-Gómez et al., 2020). Downregulation of ThdPI-1 and ThdPI-2 with one construct that targeted both copies in T. dioicum resulted in female flowers in male inflorescences (Figures 9E, F, LaRue et al., 2013). In these flowers the stamens were homeotically transformed into carpels. Female plants that were treated with the VIGS did not show any visible phenotype. VIGS treatment was also carried out in T. thalictroides, whose flowers are hermaphroditic exhibiting both stamens and carpels. The knockdown flower phenotype was the homeotic conversion of all stamens to carpels. On the basis of these results, LaRue et al. (2013) hypothesized that B genes are a target of mutation, which leads to dioecy in Thalictrum.
In Thalictrum, the C class expression and functional analysis have yielded very interesting results. In T. dioicum, ThdAG-1 is expressed in both carpels and stamens whereas ThdAG-2 is strictly expressed in the carpels of female flowers (Di Stilio et al., 2005). ThtAG-1 was found to be expressed in stamens, carpels, and ovules, whereas ThtAG-2 was only slightly expressed in the carpel and ovule (Supplementary Table 2.2). Knockdown of ThtAG1 exhibited homeotic floral phenotypes, including complete conversion of stamens and carpels to sterile organs resembling sepals (Figure 9G). Down-regulation of ThtAG2 resulted in a homeotic conversion of ovules into carpel-like structures (Figure 9H, Galimba et al., 2012; Galimba and Di Stilio, 2015). This result indicates a sub-functionalization of ThtAG2 to an ovule identity gene.
The expression and analysis of E-class gene homologs, ThtSEP1, ThtSEP2, and ThtSEP3, in T. thalictroides have been reported (Supplementary Table 2.2, Soza et al., 2016; Martínez-Gómez et al., 2020). All three homologs are broadly expressed in all floral organs in both young and mature flowers. However, ThtSEP3 shows more prominent expression across all floral organs, while ThtSEP1 is predominantly expressed in the sepals of mature flowers. The knockdown of ThtSEP1 resulted in flowers with missing and narrowed sepals, and sepals with green tips, short and widened stamens, and some sepal-carpel-stamen chimeric organs (Figure 9I, Soza et al., 2016). Knockdown of ThtSEP2 produced flowers with similar sepal defects, including missing sepals and green patches, as well as fewer stamens, abnormal stamen filaments, and carpel-stamen chimeras at the boundary of the inner two whorls (Figure 9J, Soza et al., 2016). The knockdown of ThtSEP3 led to flowers with irregular sepal edges, green patches, and a range of chimeric organs (Figure 9K). Abnormal carpels were observed, including open structures, smooth stigmas lacking papillae, sepaloid stamens, and arrested carpels. Double gene knockdowns of two homologs subsequently such as ThtSEP1 and ThtSEP2, ThtSEP1 and ThtSEP3, and ThtSEP2 and ThtSEP3 resulted in enhanced phenotypes, combining the defects seen in single knockdowns (Soza et al., 2016). The triple knockdown of ThtSEP1, ThtSEP2, and ThtSEP3 produced flowers with severe defects, including large green patches on sepals, fewer stamens, sepaloid stamens, open and sterile carpels, and smooth stigmas without papillae (Figure 9L, Soza et al., 2016). These findings underscore a certain level of redundancy in the functional roles of SEP homologs and their role in sepal and stamen development while also contributing to the petaloidy of sepals. Additionally, SEP3 was implicated in conferring carpel identity, whereas SEP1 and SEP2 homologs have a role in maintaining sepal, stamen, and stamen-carpel boundaries (Soza et al., 2016).
4.4 Genetic studies in Nigella damascena
A study by Gonçalves et al. (2013) specifically reported the role of B gene homolog AP3-3 in N. damascena petalous (P) and apetalous (T) morphs. Wang et al. (2015), also in an in-depth study, reported the expression of floral organ function of organ identity genes in N. damascena (Supplementary Table 2.3). There are three copies of APETALA-3, NdAP3-1, NdAP3-2, and NdAP3-3. NdAP3-3 is prominently expressed in petals and slightly in stamens. The other two AP3 homologs, NdAP3-1 and NdAP3-2 show broader expression patterns, with stronger expression in the stamens and moderate-to-weak expression in petals and carpels (Supplementary Table 2.3). NdAP3-3 plays a crucial role in the petal identity, and also controls the petal-stamen boundary (Wang et al., 2015). Gonçalves et al. (2013), in their study, show a comparative analysis of B gene expression in the petalous and apetalous morph. Notably, AP3-3 homolog was not expressed in the T morph while other B genes had similar expression patterns in both morphs (Gonçalves et al., 2013). When NdAP3-3 was knocked down in petalous morph, flowers with the strongest phenotype produce flowers with ‘double sepals’ as the petals transform into sepals (Figures 10A, B). It is interesting to note that the count of sepals was bigger than the sum of petals and sepals observed in the wild-type flowers. This indicated that the petal-stamen boundary was shifted inwards, additionally, AP3-3 also plays a role in meristem patterning (Gonçalves et al., 2013; Wang et al., 2015).
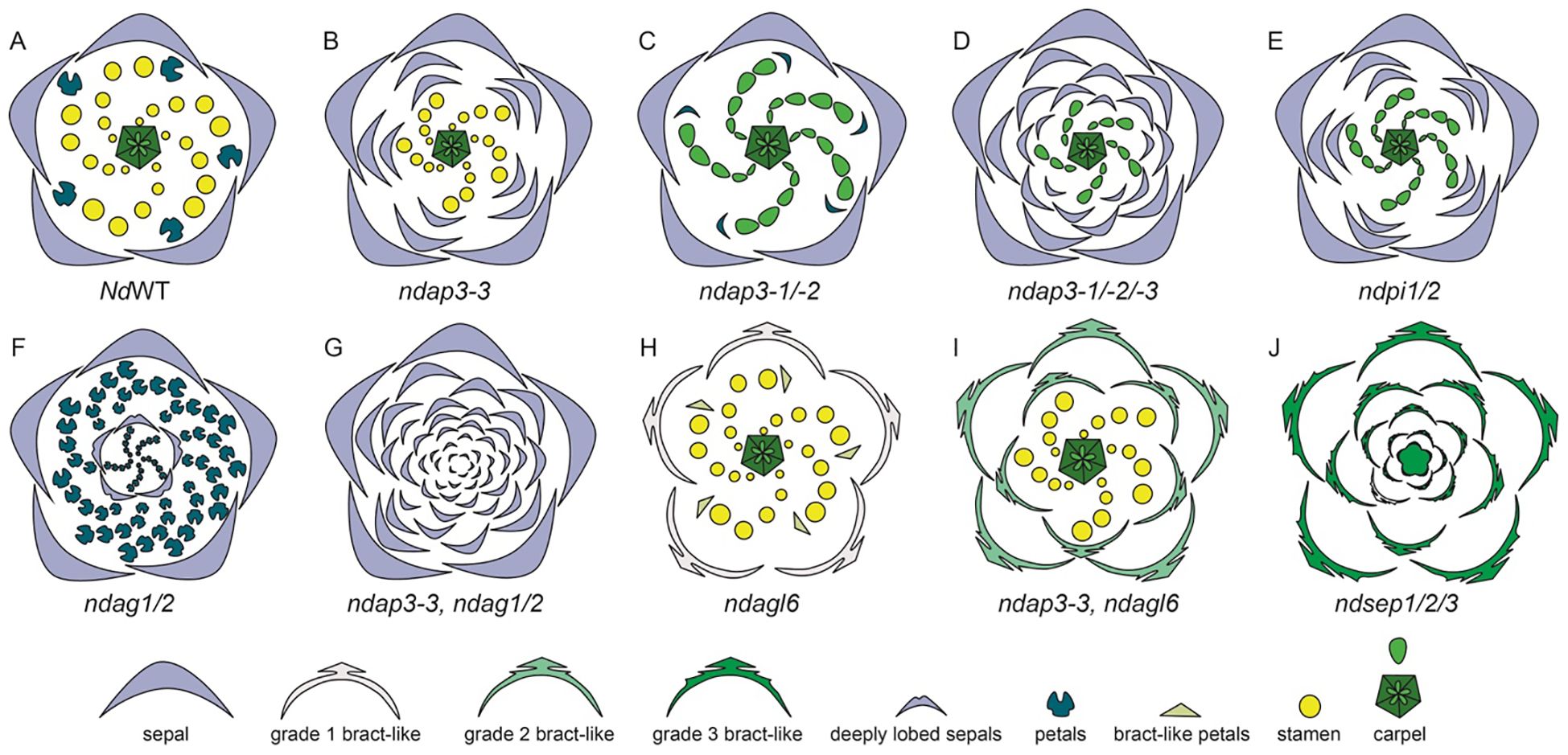
Figure 10. Knockdown phenotypes for wild-type, VIGS-treated, and ‘Double Sepals’ N. damascena flowers (Adapted from Gonçalves et al., 2013; Wang et al., 2015). A strong phenotype is shown for each treatment. (A) Floral diagram for a wild-type (WT) flower. Gene knockdown performed in the wild type plants: (B) ndap3-3-silenced flower in which petals are replaced by sepals, extra sepals observed (C) ndap3-1/2-silenced flower in which petals are reduced, resemble sepals and stamens are replaced by carpels (D) ndap3-1/2/3-silenced flower in which petals and outer stamens transform into sepals, while inner stamens are replaced by carpels (E) ndpi1/2-silenced flower in which petals have homeotically transformed into sepals and stamens into carpels (F) ndag1/2-silenced flower in which “flower-within-flower” structure is observed, where stamens are replaced by petals, carpels replaced by sepals, and floral determinacy is lost. Gene knockdown performed in the ‘Double Sepals’ flower (T morph): (G) (T-morph) ndap3-3, ndag1/2 silenced flower produces unlimited number of sepals (H) Knockdown phenotype in the wild type flower for ndagl6 silenced flower comprises of bract-like sepals with lobed margins, simplified petal structure, and unchanged stamens and carpels and (I) T morph, ndap3-3, ndagl6 silenced flower shows bract-like sepals, unchanged stamens and carpels. (J) ndsep1/2/3 silenced flower shows only bracts, the flower determinacy is lost, and flower inside flower phenotype is observed.
In their study Gonçalves et al. (2013) suggested that a single mutation event is responsible for the dimorphism, leading to apetalous and petalous flower forms in N. damascena. The authors suggest that the insertion of MITE (miniature inverted-repeat transposable element) at the same locus as the AP3-3 gene has led to the apetalous morphology, the segregation analysis suggest that the same locus is responsible for dimorphism (Gonçalves et al., 2013). The presence of this mutant allele, containing MITE, has been found to be homozygous in the T morph plants, however, it is either heterozygous or absent in the P morph flowers (Zhang et al., 2013). However, other researchers suggest that the MITE insertion is an effect, rather than a cause itself. Interestingly, a recent study by Conde e Silva et al. (2023) confirms the MITE as the major candidate polymorphism that can potentially inactivate NdAP3-3 in T morph. There are other changes observed in the T morph, such as the presence of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), however, none of these were cis-regulatory in nature (Conde e Silva et al., 2023).
When either of the other two NdAP3 homologs, NdAP3-1 or NdAP3-2 is silenced individually, there are no significant phenotypic changes except that the petals are reduced slightly. However, when both NdAP3-1 and NdAP3-2 were knocked down simultaneously, the petals resembled sepals which were reduced in size and a stamen to carpel transformation was also observed (Figure 10C). This indicated that NdAP3-1 and NdAP3-2 together specify the stamen identity, while also controlling the petal development specifically its shape. When all three homologs, NdAP3-1, NdAP3-2, and NdAP3-3 were knocked down simultaneously, the flowers with strong phenotypes only showed sepals and carpels (Figure 10D). Interestingly, the number of sepals was even larger than what was observed in the AP3-3 knockdown phenotype, implicating that the petal-stamen boundary was further shifted inward. Wang et al. (2015) suggested that NdAP3-1 and NdAP3-2 may enhance the function of NdAP3-3 in determining the petal-stamen boundary.
Furthermore, the expression of PI-like genes was also analyzed (Supplementary Table 2.3, Wang et al., 2015). Both PI1 and PI2 homologs were consistently expressed in sepals, petals, and stamens. When both the PI homologs were knocked down simultaneously, the flowers showed only sepals and carpels, implying that PI-like and AP3-like genes are dependent on each other for proper functionality (Figure 10E). However, unlike AP3-like genes, In PI knockdown flowers the sepal count was not as large as it was observed in flowers when all three AP3 were knocked down together.
Additionally, the expression and knockdown studies were conducted on AG1 and AG2 homologs (Supplementary Table 2.3, Wang et al., 2015). In terms of expression, both the genes, NdAG1 and NdAG2, are expressed in carpels, however, NdAG1, is also expressed in stamens. When each of the copies was knocked down individually, no significant phenotype change was observed. However, when both the copies were knocked down simultaneously, a “flower-within-flower” structure was observed with five sepals followed by a precarious number of petals which were a result of stamens being homeotically transformed (Figure 10F, Wang et al., 2015). The carpels that homeotically transformed into sepals in the inner whorls were deeply lobed and floral determinacy was lost. Additionally, the petal-stamen boundary was shifted inward as the number of petals was larger than the sum of petals and stamens. Taking all the results into consideration, authors concluded that NdAG1 seems to play a role as a C-function gene, controlling stamen and carpel identity, and may also be involved in repressing the expression of NdAP3-3 due to the inward shift of petal-stamen boundary. Additionally, NdAG2 also specifies carpel identity, plays a role in floral determinacy, and may control the stamen-carpel boundary by potentially regulating B gene expression (Figure 10G; Wang et al., 2015). Since single knockdowns for either homolog did not yield any phenotypes, this suggests a redundancy in both homologs’ functional repertoire.
Furthermore, the expression and function of AP1 homologs, NdFL1 and NdFL2, was determined in N. damascena (Supplementary Table 2.3). Both homologs were found to be broadly expressed at low levels in all the floral organs. When both the homologs were knocked down simultaneously, no floral phenotype was observed. The expression and function of NdAGL6 was also studied by Wang et al. (2015) (Supplementary Table 2.3). NdAGL6 is expressed in all floral organs. Knockdown of NdAGL6 resulted in morphological changes in the sepals, which became bract-like with narrow, linear-lobed margins (Figure 10H). Additionally, petals exhibited a linear-to-obovate structure, lacking pseudonectaries, long hairs, and short trichomes, while stamens and carpels remained unchanged. The same phenotype was observed when both FUL-like and AGL6 homologs were knocked down simultaneously, further confirming that AGL6, rather than AP1-lineage members NdFL1/2, plays a crucial role in sepal and petal identity determination.
NdAGL6 is a dosage-dependent gene that works with AP3-like genes to determine basic petal structure (Wang et al., 2015). Wang et al. (2015) also performed VIGS on the T-morph N. damascena to further elucidate the function of AGL6. In the ‘Double Sepals’ flowers, ndap3-3-TRV2-NdAGL6, the resulting floral phenotype included bract-like, pinnately lobed sepals, whose number was higher compared to the NdAGL6-silenced flowers, indicating that some of the outer stamens, along with the petals, were converted to bract-like organs (Figure 10I). Carpels remained unchanged, demonstrating that NdAGL6 plays a crucial role in forming margined and petaloid sepals and works with NdAP3-3 to control petal structure (Wang et al., 2015). The AGL6 homolog in N. damascena is thus implicated in functioning as an A-function gene, determining sepal and petal identity (Wang et al., 2015).
In N. damascena, three SEP-like genes, NdSEP1, NdSEP2, and NdSEP3 have been identified. NdSEP1 is expressed in the early stages in sepals and petals; NdSEP2 expression was not detected in any floral organ at any developmental stage (Supplementary Table 2.3). NdSEP3 is broadly expressed in all floral organs across all developmental stages. When all three homologs were knocked down simultaneously, the silenced flowers developed only bracts, and the floral organ determinacy was lost, resulting in a ‘flower-within-flower’ phenotype (Figure 10J). Wang et al., 2015 also reported that all SEP proteins in N. damascena form heterodimers with NdAGL6, NdAG1, and NdAG2. The findings of this study highlight a crucial role of SEP-like genes, functioning as E-class genes, in N. damascena and having a function in both floral organ identity and ensuring floral organ determinacy (Wang et al., 2015).
4.5 Genetic bases of organ identity and elaboration beyond ABC genes in Nigella
Liao et al. (2020) performed RNA sequencing to identify candidate genes involved in pseudonectary formation. In their study, they identified NidaYAB5 as a critical candidate gene. mRNA in situ hybridization studies detected the expression of NidaYAB5 in developing pseudonectaries, with the expression becoming progressively more pronounced at later stages of development. When NidaYAB5 was downregulated using VIGS, the petals in the silenced flowers did not produce pseudonectaries, confirming the key role of NidaYAB5 in this process.
Zhang et al. (2020) published a study in which they investigated the function of NidaLMI1 in relation to petal elaboration. NidaLMI1 was expressed in petals specifically at developmental stages 8 and 9, in the region between the two pseudonectaries, within the forked lamina, and became more pronounced in areas with short trichomes. Downregulation of NidaLMI1 resulted in a phenotype where the two petal lobes of the lower lip were fused, and short trichomes were absent. Based on these findings, the authors proposed that NidaLMI1 plays a crucial role in the differentiation of short trichomes and is essential for the bifurcation of the lower lip.
Together, these findings underscore the complex genetic interactions that drive petal elaboration and organ identity in N. damascena.
4.6 Genetic studies in Delphinium
The genetic studies in Delphinium were reviewed by Sharma et al. (2024), hence we briefly provide some of the major findings in this section, to maintain the necessary context. In Delphinium, the B genes AP3 has three paralogs, DeajAP3-1, DeajAP3-2, and DeajAP3-3 and two PI homologs DeajPI1 and DeajPI2 (Supplementary Table 2.4). Functional study by Zhao et al. (2023), in D. ajacis implicate a redundant role of AP3-1 and AP3-3 homologs in determining reduced petal identity and in maintaining petal stamen boundary. Gene knockdown of AP3-3 homolog was reported in two Delphinium species, first, by Zhao et al. (2023), in D. ajacis and then by Zhang et al. (2024) in D. anthriscifolium, the results were distinct (Figures 11A–D). It is important to note. D. ajacis, lacks lateral petals and has only one spurred fused dorsal petal, while D. anthriscifolium a species has two lateral petals, and two dorsal nectariferous spurred petals. Zhao et al. (2023) implicate AP3-3 homolog primarily confers dorsal spurred-petal identity while in D. anthricifolium AP3-3 may control the identity of dorsal, lateral, and reduced petals (Zhang P. et al., 2024). This distinction in phenotype might be due to a stronger knockdown observed in D. anthricifolium or, alternatively, in D. anthriscifolium the functional repertoire of AP3-3 homolog is broader. The triple knockdown of DeajAP3-1, DeajAP3-2, and DeajAP3-3 in D. ajacis resulted in flowers with the fused single-spurred dorsal petal transformed into a fused double-spurred sepal, and all reduced petals, along with some outer stamens, were converted into non-spurred sepals (Figure 11E). Furthermore, the remaining stamens were transformed into carpels.
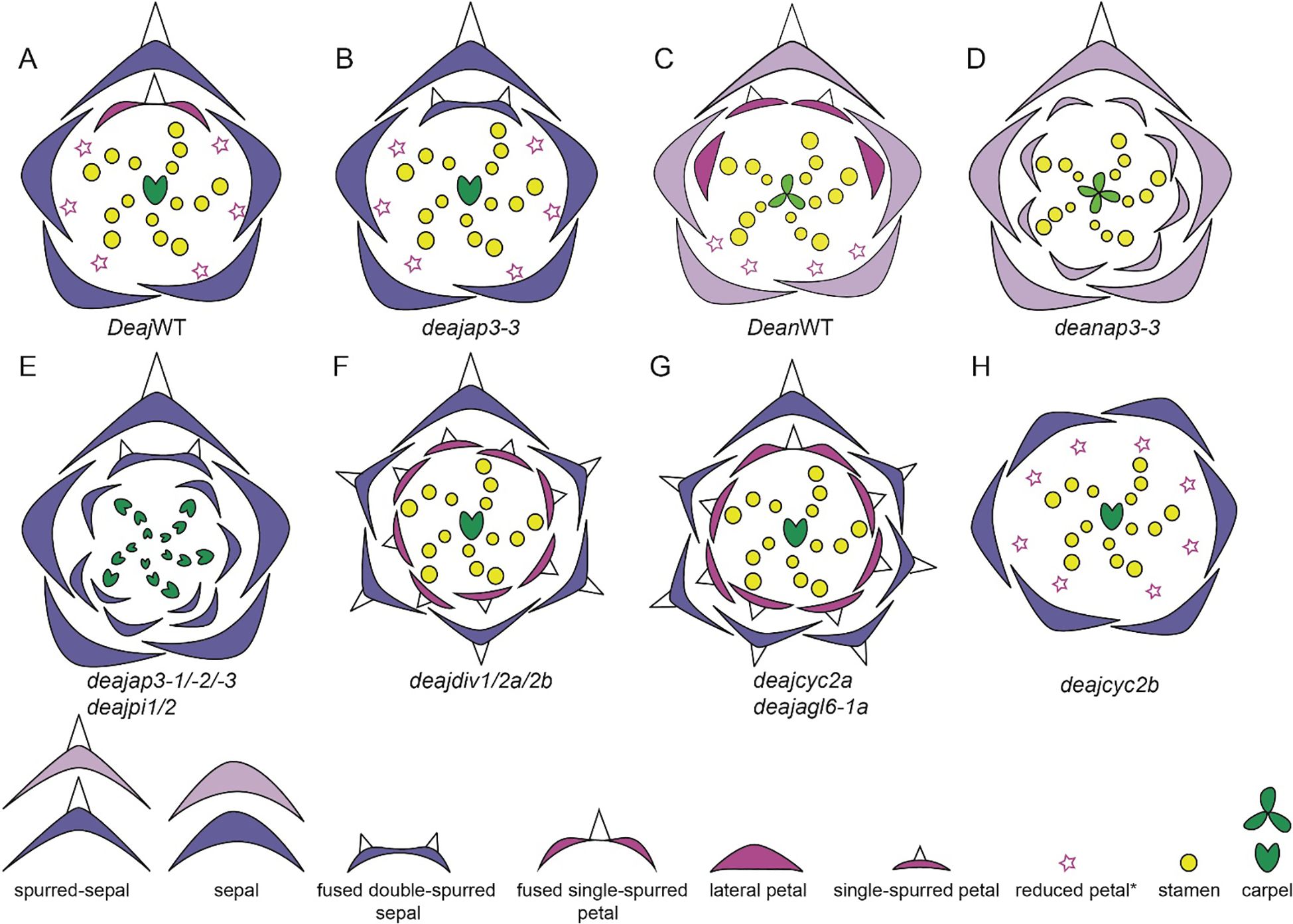
Figure 11. Phenotypes of wild-type, and VIGS-treated Delphinium flowers (Adapted from Zhao et al., 2023; Zhang P. et al., 2024). (A) Wildtype (WT) floral diagram of D. ajacis: outer whorl with non-spurred sepals, spurred sepals, the inner whorl single-spurred petal, reduced petals, followed by stamens, and carpels (B) deajap3-3: fused double-spurred sepals replace single-spurred petal in second whorl, without affecting the floral identity of other organs (C) Wildtype (WT) floral diagram of D. anthricifolium (D) deanap3-3: spurred, lateral and reduced petals homeotically transform into sepals in the second whorl (E) Phenotype observed when all AP3-3 homologs are silenced, deajap3-1, deajap3-2, and deajap3-3 is similar to when both PI homologs are silenced simultaneously: single-spurred petal transforms to fused double-spurred sepals, reduced petals, and some outer stamens to non-spurred sepals, and stamens to carpels. (F) deajdiv1, deajdiv2a, and deajdiv2b triple knockdown: single-spurred sepals replace non-spurred sepals, and all reduced petals and fused single-spurred petals become single-spurred petals. Floral symmetry shifts from zygomorphy to actinomorphy (G) Phenotype observed when deajcyc2a and deajajl6-1a are knocked down individually, the silenced flowers in first whorl have sepals, and all have spurs; in whorl 2 lateral and reduced petals get homeotically transformed into spurred petals; the dorsal fused spurred petal identity is not changed (H) deajcyc2b silenced flowers: the dorsal spurred sepal in whorl 1 transform into flat sepal; in whorl 2, lateral, dorsal spurred petals become reduced and floral symmetry shifts from zygomorphy to actinomorphy.
The simultaneous knockdown of DeajP11 and DeajPI2 genes resulted in similar phenotypes to those observed when all homologs are AP3 homologs are simultaneously knocked down (Figure 11E). These classic B phenotypes highlight the functional interdependence of AP3 and PI proteins for floral organ identity determination (Zhao et al., 2023).
4.7 Genetic bases of organ identity and elaboration beyond ABC genes in Delphinium
Delphinium flowers are zygomorphic, the study by Zhao et al. (2023) did functional studies to disentangle the role of CYCLOIDIA (CYC) and DIVARICATA (DIV) homologs. The CYC homolog was implicated to be a dorsal identity gene promoting spur formation in dorsal petal and sepal, alternatively, CYC2a, homolog suppresses spur formation in sepals and reduced petals and is implicated to have a role in establishing lateral and ventral identity in perianth organs (Zhao et al., 2023). Additionally, simultaneous knocked down of DIV homologs DeajDIV1, DeajDIV2a, DeajDIV2b yielded very similar phenotypes as DeajCYC2a. The most intriguing result was DeajAGL61a knockdown phenotype was also similar to DeajCYC2a, implicating a complex feedback loop between CYC2a, AGL61a and DIV homologs working jointly to regulate the lateral and ventral development of sepals and petals (Figures 11F–H).
In Delphinium, the lateral petals are composed of two distinct parts, a distal blade and a proximal stalk. Prior to anthesis, the stalk undergoes a 180° twist, a phenomenon known as resupination. Interestingly, at the junction where the stalk meets the blade, the petal exhibits a unique 90° asymmetric bend. This helical rotation, combined with the bending, plays a crucial role in shaping the complex floral morphology of the plant (Zhang et al., 2022; Zhang H. et al., 2024). RNA-sequencing studies conducted on the lateral petals of D. anthriscifolium identified a key candidate gene, DeanLMI1, a member of the class I HD-Zip family of transcription factors. Zhang et al. (2024) demonstrated that DeanLMI1 is essential for the development of asymmetric bending in the lateral petals. When DeanLMI1 expression was knocked down using VIGS, the lateral petals failed to bend and did not cover the reproductive organs, as seen in wild-type flowers. This study highlights the role of DeanLMI1 in promoting cell expansion in width and influencing the organization of cell wall nanostructures on the adaxial epidermis, which together contribute to the overall three-dimensional petal shape and asymmetric bending (Zhang H. et al., 2024).
4.8 Genetic studies in poppy
The characterization, expression and functional analysis of ABC genes have been done in P. somniferum and E. californica. In P. somniferum, two AP3 homologs, PapsAP3-1 and PapsAP3-2 were identified. PapsAP3-1 has a prominent expression in stamens and petals throughout all developmental stages and weak expression in sepals and carpels at later developmental stages (Supplementary Table 2.5, Drea et al., 2007). PapsAP3-2, is more prominent in stamens at all developmental stages and becomes prominent expression in petals while a weak expression in sepals and carpels at late developmental stages. Silencing of both homologs individually produced distinct phenotypes. PapsAP3-1 knockdown resulted in the transformation of petals to sepaloid organs with no visible effect on stamens (Figures 12A, B). The silencing PapsAP3-2 yielded stamen-to-carpel transformations (Figure 12C). Silencing both the homologs simultaneously resulted in homeotic transformations of petals to sepal and a severe stamen to carpel transformation as compared to single gene knockdown (Figure 12D, Drea et al., 2007). These results exemplify sub-functionalization of B gene homologs, with PapsAP3-1 and PapsAP3-2 having roles in establishing petal and stamen identities respectively (Drea et al., 2007).
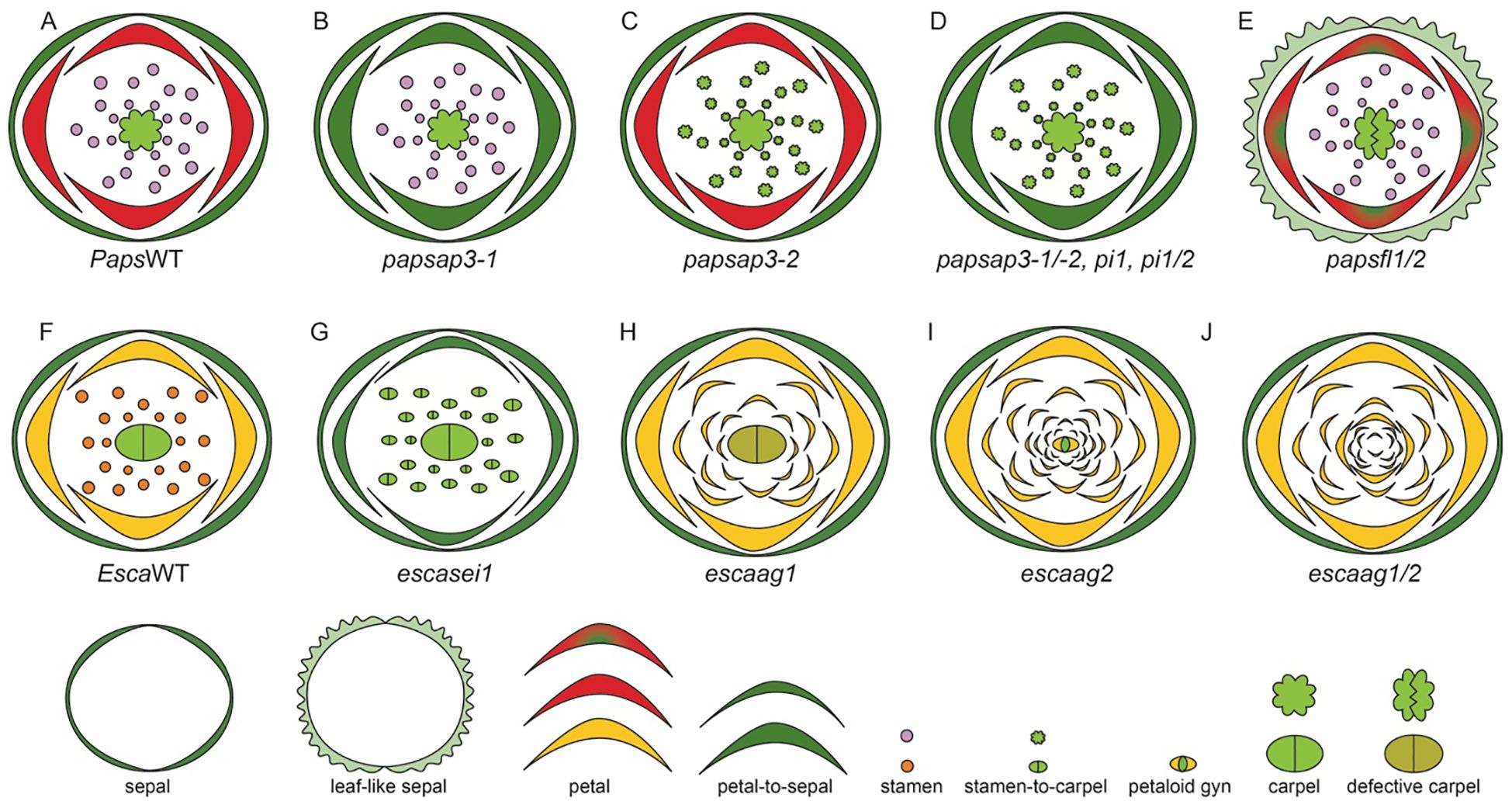
Figure 12. Wild-type and VIGS treated P. somniferum, and E. californica flowers. (Adapted from Becker et al., 2023; Hidalgo and Gleissberg, 2010; Pabón-Mora et al., 2012; Lange et al., 2013; Drea et al., 2007; Yellina et al., 2010; Sauquet et al., 2015). (A) P. somniferum, wildtype (WT) floral diagram displaying five organ identities: sepal cap, petals, stamen, and carpels. (B) In papsap3-1 homeotic transformation of petals to sepaloid organs is observed. (C) In papsap3-2 a stamen-carpel transformation is observed. (D) The phenotypes of papsap3 1 and 2 together, papspi-1 single gene knockdown and papspi-1 and 2 together are similar resulting in a classic petal-sepal and stamen- carpel homeotic transformation. (E) The papsfl-1 and 2 simultaneous knockdown the phenotype is sepal to leaflike transformation, the petals have green patches, and the fruit is elongated and cracked. (F) E. californica, wildtype (WT) floral diagram displaying five organ identities: sepal cap, two petal whorls, several stamen whorls, and bicarpellate gynoecium. (G) In escasei silenced flowers, petals are transformed into sepals and stamens into carpels. (H) In esca-ag1 silenced flowers stamens are transformed into petals, petal-stamen mosaic structures, malformed stamens and an undifferentiated gynoecium lacking ovules and placenta. (I) In esca-ag2 silenced flowers stamens and carpels are transformed into petal-like structures. (J) In esca-ag1/2 silenced flowers, stamens transform into petals, and the determinacy is lost with strongly silenced flowers showing flower-within-flower phenotype.
The two PISTILLATA homologs in P. somniferum are PapsPI-1 and PapsPI-2. PapsPI-1 is expressed in petals and stamens throughout all developmental stages however, PapsPI-2 is broadly expressed in all floral organs is only weakly expressed in stamens and carpels at late developmental stages (Supplementary Table 2.5). Silencing PapsPI-1 results in the classic PI phenotype yielding homeotic transformation of stamens to carpeloid structures and petals to sepaloid organs. Simultaneous knockdown of both PI had a similar phenotype as PapsPI-1 with more severe stamen to carpel transformation (Figure 12D, Drea et al., 2007). These phenotypes exemplify a broader conserved role of PapsPI-1 in petal and stamen development while a possible redundantly role of PapsPI-2 with PapsPI-1 in stamen conferring stamen identity (Drea et al., 2007).
P. somniferum, FUL-like gene homologs are PapsFL1 and PapsFL2 are broadly expressed in all floral organs throughout young and mature developmental stages additionally they are also expressed in leaves and fruits (Supplementary Table 2.5, Pabón-Mora et al., 2012). Knockdown studies of PapsFL1 yielded phenotypes the homeotic transformation of sepal into leaf-like organs that were lobed and had waxy cuticle, the petals had green patches and the most striking results was the asymmetrical elongation and premature rupture of the carpel (Pabón-Mora et al., 2012). The plants that had silenced flowers also had other phenotypes such as branched inflorescences, altered leaf morphology, indicating a conserved function in repressing axillary meristem activity and promoting proper floral development. PapsFL2 knockdown had very similar phenotypes with the exception that petals were unaffected. Simultaneous knockdown of both copies yielded similar results as seen in both individual knockdowns however, in petals big green patches were observed (Figure 12E). These phenotypes implicate that FUL like genes in opium poppy fulfill the A function (Pabón-Mora et al., 2012).
Expression and function of FUL-like genes was also reported in E. californica, EscaFL1 is broadly expressed in all floral organs except petals, whereas EscaFL2 is expressed ubiquitously in all (Supplementary Table 2.5, Pabón-Mora et al., 2012). Both paralogs are also expressed in leaves and fruits. Knockdown studies indicate that disrupting EscaFL1-2 results in branched inflorescences with simple cauline leaves, demonstrating their role in repressing axillary meristem activity. The floral phenotype of leaf-like sepals observed in EscaFL-silenced plants suggests that the A-class role in promoting sepal identity is conserved in Eschscholzia californica as it is in core eudicots (Pabón-Mora et al., 2012).
The DEFICIENS/APETALA like homologs in E. californica include EscaDEF1, EscaDEF2, and EscaDEF3, which are B-class genes essential for specifying petal and stamen identity. EScaDEF1 is an ortholog of APETALA3-2 (AP3-2) and is primarily expressed in petals, while EscaDEF2 and EscaDEF3 are orthologs of APETALA3-1 (AP3-1) and are expressed in stamens and both petals and stamens, respectively (Supplementary Table 2.5, Lange et al., 2013). In E. californica, SEI, was identified as the PI homolog. The (VIGS) of the SEI gene in E. californica resulted in phenotypes that closely resembled those observed in the sei-1 mutant (Lange et al., 2013; Figures 12F, G). Specifically, VIGS-treated plants showed partial homeotic conversion of petals into sepals, where the altered petals retained some orange coloration but exhibited a broad green stripe in the center, making them sepaloid in size and shape. Additionally, the stamens in the outer whorls were transformed into reduced-sized petaloid organs, and in place of the inner whorl stamens, single, unfused carpel-like structures developed. Lange et al. (2013) proposed that B class genes expression possibly have a reinforcing effect on C class genes, specifically in species that have multiple stamen whorls.
In E. californica there are two AGAMOUS homologs, expression and functional analysis has been reported for these. EscaAG1 highly expressed in stamens and carpels and low expression is observed in the perianth organs (Yellina et al., 2010). EScaAG2 is carpels and more prominently in stamens (Supplementary Table 2.5). The study by Yellina et al. (2010) explores the functional role of the AGAMOUS (AG) homologs using virus-induced gene silencing (VIGS). Knockdown of EscaAG1 results in flowers showing transformation of stamens into petal-like organs (Figure 12H). Most flowers exhibited partial conversion, affecting only the outer whorl of stamens. The gynoecium also displayed alterations, transforming into flattened green structures or petaloid organs with orange pigmentation, indicating a loss of carpel identity. Similarly, knockdown of EscaAG2 resulted in homeotic conversion of stamens and carpels. The gynoecium in these cases also exhibited petaloid features, further indicating a loss of carpel identity (Figure 12I).
The simultaneous knockdown of both EscaAG1 and EscaAG2 produced the strongest phenotypes, of flowers showing homeotic conversions of stamens into petals. Additionally, the gynoecium showed more pronounced petaloid transformations, emphasizing the combined role of both genes in maintaining carpel identity (Figure 12J). Beyond changes in organ identity, VIGS treatment also caused defects in floral meristem termination, resulting in increased stamen numbers and prolonged meristematic activity, leading to the development of ectopic floral structures within the gynoecium. These findings highlight the essential roles of EscaAG1 and EscaAG2 in specifying stamen and carpel identity, as well as in ensuring proper floral meristem termination in E. californica (Yellina et al., 2010).
5 Conclusions and synthesis
Ranunculales model systems provide invaluable insights into plant evolution and development, owing to their diverse and distinctive morphological traits and important phylogenetic position. Through the review of eco-evo-devo studies in these model systems it is clear that morphological diversification is shaped by ecological, evolutionary and genetic factors. However, the underlying mechanisms driving this diversification differ significantly among the model systems. The significance of gene duplication is profound, as gene orthologs and paralogs in closely related species show both conserved and diverged functions. For example, in Aquilegia AP3-1 has been neo-functionalized and establishes the identity of the novel organ staminodia (Sharma and Kramer, 2013), whereas in Thalictrum AP3-1 homolog controls the size, width, and petaloidy of sepals and proper stigmatic development (Galimba et al., 2018). Furthermore, in Aquilegia, Delphinium and Nigella, AP3-2 homolog has a role in conferring stamen identity (Sharma and Kramer, 2013; Wang et al., 2015; Zhao et al., 2023), however, in Thalictrum it controls sepal shape and petaloidy of sepals (Galimba et al., 2018).
Another example is the case of Thalictrum, where SEP3 homolog has a more pronounced role in carpel identity, however, in Delphinium and Nigella, SEP genes broadly control organ identity of all floral organs. Another interesting difference lies in the role of AGL6 in Delphinium and Nigella. AGL6 homologs, AGL6-1a and AGL6-1b, establish spur identity in Delphinium and work redundantly to determine sepal and petal identity, however, in Nigella, AGL6 functions as an A class gene playing role in sepal and petal identity (Wang et al., 2015). Furthermore, the gene knockdown studies in Aquilegia and Nigella suggest negligible role of FUL-like genes in floral organ identity, however, in Poppy, FL1 and FL2 homologs play role in promoting sepal identity. Another interesting example is the diversification of AG2 homologs, in Thalictrum AG2 has been implicated to have a D function conferring proper ovule development.
Research in the recent years have not only enhanced our understanding of floral evolution but it also acknowledges several caveats that must be considered. Below we outline key advantages and realistic caveats associated with for eco-evo-devo research using these model systems.
5.1 Advantages
● The model systems described in this study provide unique insights into early-diverging eudicot lineage and the molecular changes level that contributed to rapid angiosperm diversification. For example, Aquilegia that has undergone recent adaptive radiation, with interfertile species showing low genetic divergence.
● Availability of flower mutants in Aquilegia, Nigella, Delphinium and Thalictrum provides an opportunity for comparative developmental and genetic studies.
● Opportunity to study the morphological evolution of elaborated and novel floral organs in conjunction with their ecological and molecular bases.
● The growing availability of genetics and genomic resources, such as provided by the RanOmics group, enable in-depth omics-studies and accelerates research.
5.2 Challenges
● Diversity of habitats and limited availability of some species can constrain comparative studies.
● Some species, like Delphinium have large genomes which can make assembly and analysis challenging.
● Rapid transformation and efficient systems are not available for all models (reviewed by The RanOmics group et al., 2024).
● Comparatively longer lifecycles than Arabidopsis.
● In some species like Aquilegia inbreeding depression can pose challenges in maintaining both pure and mutant lines.
● Unavailability of mutant seed banks limits broad genetic screening studies.
6 Future directions
The wealth of floral morphological diversity in early-diverging Ranunculales presents a great opportunity to understand the molecular bases and evolutionary transitions and innovations. Below are a few future directions research in this field.
● Adaptive and non-adaptive radiation within the Ranunculales, play crucial roles in shaping floral diversity. Adaptive radiation, driven by natural selection and pollinator interactions, leads to specialized floral traits that enhance reproductive success in specific ecological niches, as seen in genera like Aquilegia. Conversely, non-adaptive radiation, influenced by genetic drift and geographical isolation, contributes to the broad spectrum of floral forms, as exemplified by Nigella. Future research should focus on elucidating the genetic and developmental pathways underlying these processes. By integrating genomic and ecological approaches, we can deepen our understanding of how evolutionary forces interact to drive speciation and floral diversification in Ranunculales.
● Studies in Aquilegia have demonstrated that many floral traits are polygenic, with QTLs distributed across different chromosomes. This discovery lays a robust groundwork for future investigations into the genetic interactions and regulatory mechanisms underlying these traits. Future studies can build on this foundation to explore the genetic networks that govern floral development and diversification.
● Investigating the genetic and environmental factors driving the evolution of diverse sexual systems within Thalictrum, such as hermaphroditism, dioecy, and andromonoecy. Future studies could involve studying the genetic regulatory networks that regulate sex determination and the ecological and evolutionary implications of different sexual systems on reproductive success and fitness.
Author contributions
BS: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Visualization, Validation, Supervision, Project administration, Investigation, Funding acquisition, Formal analysis, Conceptualization. MP: Visualization, Validation, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Investigation, Funding acquisition, Formal analysis. AA: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Visualization, Validation, Investigation, Funding acquisition, Formal analysis. MB: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Visualization, Validation, Investigation, Funding acquisition, Formal analysis. RR: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Visualization, Validation, Investigation, Funding acquisition, Formal analysis. SR: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Visualization, Validation, Investigation, Funding acquisition, Formal analysis.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. BS is supported by the Provost Teacher-Scholar Award, Strategic Interdisciplinary Research Grant, and Agriculture Research Institute grants 20-04-122 and 23-04-119. This project was supported by an USDA NIFA Hispanic Serving Institution grant to the California State University Agricultural Research Institute, award number 2019-38422-30208 to MP and RR. MP and RR are also supported by the CPP STARS Program. MB was supported by the McNair Scholars Program. MP, RR, AA acknowledge the support of Projects Hatchery at CPP. Research reported in this publication was supported by the National Institute of General Medical Sciences of the National Institutes of Health under Award Number T32GM137812, to AA and SR through the B2D program.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank members of the Sharma lab, especially undergraduate student Christian Suarez and the reviewers for their comments on the manuscript. The authors sincerely apologize to authors whose work we were not able to review because of space limitations. The authors also acknowledge a minor use of ChatGPT -4 for correcting grammatical errors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Author disclaimer
The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpls.2024.1486301/full#supplementary-material
References
Ali, S., Chouhan, R., Sultan, P., Hassan, Q. P., Gandhi, S. G. (2023). A comprehensive review of phytochemistry, pharmacology and toxicology of the genus Aconitum L. Adv. Tradit Med. (ADTM) 23, 299–320. doi: 10.1007/s13596-021-00565-8
Antoń, S., Kamińska, M. (2015). Comparative floral spur anatomy and nectar secretion in four representatives of Ranunculaceae. Protoplasma 252, 1587–1601. doi: 10.1007/s00709-015-0794-5
Arias, T., Riaño-Pachón, D. M., Di Stilio, V. S. (2021). Genomic and transcriptomic resources for candidate gene discovery in the Ranunculids. Appl. Plant Sci. 9, e11407. doi: 10.1002/aps3.11407
Ballerini, E. S., Kramer, E. M., Hodges, S. A. (2019). Comparative transcriptomics of early petal development across four diverse species of Aquilegia reveal few genes consistently associated with nectar spur development. BMC Genomics 20, 668. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-6002-9
Ballerini, E. S., Min, Y., Edwards, M. B., Kramer, E. M., Hodges, S. A. (2020). POPOVICH, encoding a C2H2 zinc-finger transcription factor, plays a central role in the development of a key innovation, floral nectar spurs, in Aquilegia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 117, 22552–22560. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2006912117
Bastida, J. M., Alcántara, J. M., Rey, P. J., Vargas, P., Herrera, C. M. (2010). Extended phylogeny of Aquilegia: the biogeographical and ecological patterns of two simultaneous but contrasting radiations. Plant Syst. Evol. 284, 171–185. doi: 10.1007/s00606-009-0243-z
Becker, A., Alix, K., Damerval, C. (2011). The evolution of flower development: current understanding and future challenges. Ann. Bot. 107, 1427–1431. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcr122
Becker, A., Gleissberg, S., Smyth, D. R. (2005). Floral and vegetative morphogenesis in california poppy (Eschscholzia californica cham.). Int. J. Plant Sci. 166, 537–555. doi: 10.1086/429866
Becker, A., Yamada, Y., Sato, F. (2023). California poppy (Eschscholzia californica), the Papaveraceae golden girl model organism for evodevo and specialized metabolism. Front. Plant Sci. 14. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1084358
Bittkau, C., Comes, H. P. (2009). Molecular inference of a Late Pleistocene diversification shift in Nigella s. lat. (Ranunculaceae) resulting from increased speciation in the Aegean archipelago. J. Biogeography 36, 1346–1360. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2699.2008.02003.x
Blanché, C. (1990). Delphinium L. Subgen. Delphinium: origin and evolutionary trends. Collect. Bot. 19, 75–96. doi: 10.3989/collectbot.1990.v19.118
Boivin, B. (1944). American Thalictra and their Old-World allies. Contributions Gray Herbarium Harvard Univ. no. 147-153, 1943-45,337–487. doi: 10.5962/p.336293
Bosch, M., Blanché, C., Molero, J. (1997). Pollination ecology in the Tribe Delphineae (Ranunculaceae) in W mediterranean area: Floral visitors and pollinator behaviour. Lagascalia 19, 545–562.
Bosch, M., Simon, J., López-Pujo, J., Blanché, C. (2016). DCDB: an updated online database of chromosome numbers of tribe Delphinieae (Ranunculaceae). Fl. Medit. 26, 191–201. doi: 10.7320/FlMedit26.191
Bowman, J. L., Smyth, D. R., Meyerowitz, E. M. (1991). Genetic interactions among floral homeotic genes of Arabidopsis. Development 112, 1–20. doi: 10.1242/dev.112.1.1
Carrive, L., Domenech, B., Sauquet, H., Jabbour, F., Damerval, C., Nadot, S. (2020). Insights into the ancestral flowers of Ranunculales. Botanical J. Linn. Soc. 194, 23–46. doi: 10.1093/botlinnean/boaa031
Chen, Y., Jabbour, F., Novikov, A., Wang, W., Gerber, S. (2018). A study of floral shape variation in Delphinieae (Ranunculaceae) using geometric morphometrics on herbarium specimens. Bot. Lett. 165, 368–376. doi: 10.1080/23818107.2018.1427145
Chitty, J. A., Allen, R. S., Fist, A. J., Larkin, P. J. (2003). Genetic transformation in commercial Tasmanian cultivars of opium poppy, Papaver somniferum, and movement of transgenicpollen in the field. Funct. Plant Biol. 30, 1045–1058. doi: 10.1071/FP03126
Coen, E. S., Meyerowitz, E. M. (1991). The war of the whorls: genetic interactions controlling flower development. Nature 353, 31–37. doi: 10.1038/353031a0
Colombo, L., Franken, J., Koetje, E., van Went, J., Dons, H. J., Angenent, G. C., et al. (1995). The petunia MADS box gene FBP11 determines ovule identity. Plant Cell 7, 1859–1868. doi: 10.1105/tpc.7.11.1859
Conde e Silva, N., Leguilloux, M., Bellec, A., Rodde, N., Aubert, J., Manicacci, D., et al. (2023). A MITE insertion abolishes the AP3-3 self-maintenance regulatory loop in apetalous flowers of Nigella damascena. J. Exp. Bot. 74, 1448–1459. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erac489
Cook, S. A. (1962). Genetic system, variation, and adaptation in eschscholzia Californica. Evolution 16, 278–299. doi: 10.1111/j.1558-5646.1962.tb03220.x
Damerval, C., Becker, A. (2017). Genetics of flower development in Ranunculales – a new, basal eudicot model order for studying flower evolution. New Phytol. 216, 361–366. doi: 10.1111/nph.14401
Delpeuch, P., Jabbour, F., Damerval, C., Schönenberger, J., Pamperl, S., Rome, M., et al. (2022). A flat petal as ancestral state for Ranunculaceae. Front. Plant Sci. 13. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.961906
Deroin, T., Damerval, C., Le Guilloux, M., Jabbour, F. (2015). Floral vascular patterns of the double-flowered and wild-type morphs of nigella damascena L. (Ranunculaceae). Modern Phytomorphology 7, 13–20. doi: 10.5281/ZENODO.160356
Di Stilio, V. S., Kramer, E. M., Baum, D. A. (2005). Floral MADS box genes and homeotic gender dimorphism in Thalictrum dioicum (Ranunculaceae) – a new model for the study of dioecy. Plant J. 41, 755–766. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02336.x
Di Stilio, V. S., Kumar, R. A., Oddone, A. M., Tolkin, T. R., Salles, P., McCarty, K. (2010). Virus-induced gene silencing as a tool for comparative functional studies in thalictrum. PloS One 5, e12064. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012064
Di Stilio, V. S., Martin, C., Schulfer, A. F., Connelly, C. F. (2009). An ortholog of MIXTA-like2 controls epidermal cell shape in flowers of Thalictrum. New Phytologist 183, 718–728. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2009.02945.x
Dönmez, A. A., Uğurlu Aydin, Z., Oybak Dönmez, E. (2021). Taxonomic monograph of the tribe Nigelleae (Ranunculaceae): a group including ancient medicinal plants. Turk J. Bot. 45, 468–502. doi: 10.3906/bot-2105-39
Drea, S., Hileman, L. C., De Martino, G., Irish, V. F. (2007). Functional analyses of genetic pathways controlling petal specification in poppy. Development 134, 4157–4166. doi: 10.1242/dev.013136
Dreni, L. (2023). “The ABC of flower development in monocots: the model of rice spikelet,” in Flower Development: Methods and Protocols. Eds. Riechmann, J. L., Ferrándiz, C. (Springer US, New York, NY), 59–82. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3299-4_3
DuPasquier, P.-E., Andro-Durand, V., Batory, L., Wang, W., Jabbour, F. (2021). Nomenclatural revision of Delphinium subg. Consolida (DC.) Huth (Ranunculaceae). PK 180, 81–110. doi: 10.3897/phytokeys.180.67126
Edwards, M. B., Ballerini, E. S., Kramer, E. M. (2022). Complex developmental and transcriptional dynamics underlie pollinator-driven evolutionary transitions in nectar spur morphology in Aquilegia (columbine). Am. J. Bot. 109, 1360–1381. doi: 10.1002/ajb2.16046
Edwards, M. B., Choi, G. P. T., Derieg, N. J., Min, Y., Diana, A. C., Hodges, S. A., et al. (2021). Genetic architecture of floral traits in bee- and hummingbird-pollinated sister species of Aquilegia (columbine). Evolution 75, 2197–2216. doi: 10.1111/evo.14313
Endress, P. K. (1995). “Floral structure and evolution in Ranunculanae,” in Systematics and Evolution of the Ranunculiflorae. Eds. Jensen, U., Kadereit, J. W. (Springer, Vienna), 47–61. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-6612-3_5
Endress, P. K. (1999). Symmetry in flowers: diversity and evolution. Int. J. Plant Sci. 160, S3–S23. doi: 10.1086/314211
Endress, P. K. (2011). Evolutionary diversification of the flowers in angiosperms. Am. J. Bot. 98, 370–396. doi: 10.3732/ajb.1000299
Endress, P. K., Matthews, M. L. (2006). Elaborate petals and staminodes in eudicots: Diversity, function, and evolution. Organisms Diversity Evol. 6, 257–293. doi: 10.1016/j.ode.2005.09.005
Erbar, C., Kusma, S., Leins, P. (1999). Development and interpretation of nectary organs in Ranunculaceae1. Flora 194, 317–332. doi: 10.1016/S0367-2530(17)30920-9
Espinosa, F., Deroin, T., Malécot, V., Wang, W., Pinedo, M., Nadot, S., et al. (2021). Historical note on the taxonomy of the genus Delphinium L. (Ranunculaceae) with an amended description of its floral morphology. Adansonia 43, 9–18. doi: 10.5252/adansonia2021v43a
Espinosa, F., Deroin, T., Xiang, K.-L., Wang, W., Castro, M. P., Byng, J. W., et al. (2017). The Turkish endemic pseudodelphinium turcicum (Ranunculaceae): an unusual population of delphinium with peloric flowers that has persisted in the wild for 20 years. Int. J. Plant Sci. 178, 546–555. doi: 10.1086/692764
Fior, S., Li, M., Oxelman, B., Viola, R., Hodges, S. A., Ometto, L., et al. (2013). Spatiotemporal reconstruction of the Aquilegia rapid radiation through next-generation sequencing of rapidly evolving cp DNA regions. New Phytol. 198, 579–592. doi: 10.1111/nph.12163
Fu, X., Shan, H., Yao, X., Cheng, J., Jiang, Y., Yin, X., et al. (2022). Petal development and elaboration. J. Exp. Bot. 73, 3308–3318. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erac092
Fukuda, Y., Suzuki, K., Murata, J. (2001). The function of each sepal in pollinator behavior and effective pollination in Aconitum japonicum var. montanum. Plant Species Biol. 16, 151–157. doi: 10.1046/j.1442-1984.2001.00059.x
Galimba, K. D., Di Stilio, V. S. (2015). Sub-functionalization to ovule development following duplication of a floral organ identity gene. Dev. Biol. 405, 158–172. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2015.06.018
Galimba, K. D., Martínez-Gómez, J., Di Stilio, V. S. (2018). Gene duplication and transference of function in the paleoAP3 lineage of floral organ identity genes. Front. Plant Sci. 9, E2267–E2275. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.00334
Galimba, K. D., Tolkin, T. R., Sullivan, A. M., Melzer, R., Theißen, G., Di Stilio, V. S. (2012). Loss of deeply conserved C-class floral homeotic gene function and C- and E-class protein interaction in a double-flowered ranunculid mutant. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 109. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1203686109
Geng, F., Xie, J., Xue, C., Sun, L., Li, J., Niu, C., et al. (2021). Loss of innovative traits underlies multiple origins of Aquilegia ecalcarata. J. Sytematics Evol. 60, 1291–1302. doi: 10.1111/jse.12808
Geng, F. D., Liu, M. Q., Zhang, X. D., Wang, L. Z., Lei, M. F. (2024). Genomics of hybrid parallel origin in Aquilegia ecalcarata. BMC Ecology and Evolution 24, 75. doi: 10.1186/s12862-024-02266-7
Gonçalves, B., Nougué, O., Jabbour, F., Ridel, C., Morin, H., Laufs, P., et al. (2013). An APETALA 3 homolog controls both petal identity and floral meristem patterning in Nigella damascenaL. (Ranunculaceae). Plant J. 76, 223–235. doi: 10.1111/tpj.12284
Hidalgo, O., Gleissberg, S. (2010). Evolution of the reproductive architecture in the bleeding hearts and poppies (Papaveraceae s.l.). Int. J. Plant Dev. Biol. 4, 76–85.
Hirano, H.-Y., Tanaka, W., Toriba, T. (2014). “Grass Flower Development,” in Flower Development, eds. Riechmann, J. L., Wellmer, F. (New York, NY: Springer New York), 57–84. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-9408-9_3
Hodges, S. A., Arnold, M. L. (1995). Spurring plant diversification: are floral nectar spurs a key innovation? Proceedings: Biol. Sci. 262, 343–348. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1995.0215
Hodges, S. A., Derieg, N. J. (2009). Adaptive radiations: from field to genomic studies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 106 Suppl 1, 9947–9954. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0901594106
Hodges, S. A., Fulton, M., Yang, J. Y., Whittall, J. B. (2004). Verne Grant and evolutionary studies of Aquilegia. New Phytol. 161, 113–120. doi: 10.1046/j.1469-8137.2003.00950.x
Hong, U. V. T., Tamiru-Oli, M., Hurgobin, B., Okey, C. R., Abreu, A. R., Lewsey, M. G. (2022). Insights into opium poppy (Papaver spp.) genetic diversity from genotyping-by-sequencing analysis. Sci. Rep. 12, 111. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-04056-3
Hoot, S. B., Wefferling, K. M., Wulff, J. A. (2015). Phylogeny and Character Evolution of Papaveraceae s. l. (Ranunculales). Systematic Bot. 40, 474–488. doi: 10.1600/036364415X688718
Hou, Q.-Z., Shao, W.-J., Ehmet, N., Yang, G., Zhong, Y.-Q., Min, W.-R., et al. (2022). The biomechanical screening game between visitor power and staminode operative strength of delphinium caeruleum (Ranunculaceae). Plants 11, 2319. doi: 10.3390/plants11172319
Huang, L., Geng, F. D., Fan, J. J., Xue, C., Zhang, X. Y., Kang, J. Q., et al. (2018). Genetic diversity and evolutionary history of four closely related Aquilegia species revealed by 10 nuclear gene fragments. J. Syst. Evol. 56, 129–138. doi: 10.1111/jse.12298
Jabbour, F., Renner, S. (2011). Resurrection of the genus Staphisagria J. Hill, sister to all the other Delphinieae (Ranunculaceae). Phytokeys 7, 21. doi: 10.3897/phytokeys.7.2010
Jabbour, F., Renner, S. S. (2012a). A phylogeny of Delphinieae (Ranunculaceae) shows that Aconitum is nested within Delphinium and that Late Miocene transitions to long life cycles in the Himalayas and Southwest China coincide with bursts in diversification. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 62, 928–942. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2011.12.005
Jabbour, F., Renner, S. S. (2012b). Spurs in a spur: perianth evolution in the delphinieae (Ranunculaceae). Int. J. Plant Sci. 173, 1036–1054. doi: 10.1086/667613
Jabbour, F., Ronse De Craene, L. P., Nadot, S., Damerval, C. (2009). Establishment of zygomorphy on an ontogenic spiral and evolution of perianth in the tribe Delphinieae (Ranunculaceae). Ann. Bot. 104, 809–822. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcp162
Jabbour, F., Zalko, J., Morel, A., Frachon, S., Bouchart-Dufay, I. (2021). “Ontogeny and evolution of the hyperorgan of delphinieae,” in Systematics and the Exploration of Life. Eds. Grandcolas, P., Maurel, M. (John Wiley & Sons, Ltd), 171–184. doi: 10.1002/9781119476870.ch9
Jaros, U., Tribsch, A., Comes, H. P. (2018). Diversification in continental island archipelagos: new evidence on the roles of fragmentation, colonization and gene flow on the genetic divergence of Aegean Nigella (Ranunculaceae). Ann. Bot. 121, 241–254. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcx150
Jesus, A., Bonhomme, V., Evin, A., Ivorra, S., Soteras, R., Salavert, A., et al. (2021). A morphometric approach to track opium poppy domestication. Sci. Rep. 11, 9778. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-88964-4
Johns, J. W., Min, Y., Ballerini, E. S., Kramer, E. M., Hodges, S. A. (2024). Loss of staminodes in Aquilegia jonesii reveals a fading stamen–staminode boundary. EvoDevo 15, 6. doi: 10.1186/s13227-024-00225-3
Kaplan, S. M., Mulcahy, D. L. (1971). Mode of pollination and floral sexuality in thalictrum. Evolution 25, 659–668. doi: 10.2307/2406946
Kew Science. Available online at: http://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:33199-1 (Accessed August 21, 2024).
Kosuge, K. (1994). “Petal evolution in ranunculaceae,” in Early Evolution of Flowers. Eds. Endress, P. K., Friis, E. M. (Springer Vienna, Vienna), 185–191. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-6910-0_11
Kramer, E. M. (2009). Aquilegia: A new model for plant development, ecology, and evolution. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 60, 261–277. doi: 10.1146/annurev.arplant.043008.092051
Krämer, U. (2015). Planting molecular functions in an ecological context with Arabidopsis thaliana. eLife 4, e06100. doi: 10.7554/eLife.06100
Kramer, E. M., Hodges, S. A. (2010). Aquilegia as a model system for the evolution and ecology of petals. Phil. Trans. R. Soc B 365, 477–490. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2009.0230
Kramer, E. M., Holappa, L., Gould, B., Jaramillo, M. A., Setnikov, D., Santiago, P. M. (2007). Elaboration of B gene function to include the identity of novel floral organs in the lower eudicot aquilegia. Plant Cell 19, 750–766. doi: 10.1105/tpc.107.050385
Lange, M., Orashakova, S., Lange, S., Melzer, R., Theißen, G., Smyth, D. R., et al. (2013). The seirena B class floral homeotic mutant of California Poppy (Eschscholzia californica) reveals a function of the enigmatic PI motif in the formation of specific multimeric MADS domain protein complexes. Plant Cell 25, 438–453. doi: 10.1105/tpc.112.105809
LaRue, N. C., Sullivan, A. M., Di Stilio, V. S. (2013). Functional recapitulation of transitions in sexual systems by homeosis during the evolution of dioecy in Thalictrum. Front. Plant Sci. 4. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2013.00487
Li, H.-T., Luo, Y., Gan, L., Ma, P.-F., Gao, L.-M., Yang, J.-B., et al. (2021). Plastid phylogenomic insights into relationships of all flowering plant families. BMC Biol. 19, 232. doi: 10.1186/s12915-021-01166-2
Liao, H., Fu, X., Zhao, H., Cheng, J., Zhang, R., Yao, X., et al. (2020). The morphology, molecular development and ecological function of pseudonectaries on Nigella damascena (Ranunculaceae) petals. Nat. Commun. 11, 1777. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-15658-2
Litt, A., Kramer, E. M. (2010). The ABC model and the diversification of floral organ identity. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 21, 129–137. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2009.11.019
Logacheva, M. D., Fesenko, I. N., Fesenko, A. N., Penin, A. A. (2008). Genetic and morphological analysis of floral homeotic mutants tepal-like bractand fagopyrum apetalaof Fagopyrum esculentum. Botany 86, 367–375. doi: 10.1139/B08-010
Lotz, D., Imani, J., Ehlers, K., Becker, A. (2022). Towards a genetic model organism: an efficient method for stable genetic transformation of Eschscholzia californica (Ranunculales). Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 149, 823–832. doi: 10.1007/s11240-021-02223-y
Löve, Á. (1982). Iopb chromosome number reports lxxiv. TAXON 31, 119–128. doi: 10.1002/j.1996-8175.1982.tb02346.x
Lubna, L., Asaf, S., Khan, I., Jan, R., Asif, S., Bilal, S., et al. (2024). Genetic characterization and phylogenetic analysis of the Nigella sativa (black seed) plastome. Sci. Rep. 14, 14509. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-65073-6
Luo, X.-Y., Nie, T.-J., Liu, H., Ding, X.-F., Huang, Y., Guo, C.-C., et al. (2023). Karyotype and genome size variation in Delphinium subg. anthriscifolium (Ranunculaceae). PK 234, 145–165. doi: 10.3897/phytokeys.234.108841
Ma, H., dePamphilis, C. (2000). The ABCs of floral evolution. Cell 101, 5–8. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80618-2
Martínez-Gómez, J., Galimba, K. D., Coté, E. Y., Sullivan, A. M., Di Stilio, V. S. (2020). Spontaneous homeotic mutants and genetic control of floral organ identity in a ranunculid. Evol. Dev. 23, 197–214. doi: 10.1111/ede.12357
Martínez-Gómez, J., Park, S., Hartogs, S. R., Soza, V. L., Park, S. J., Di Stilio, V. S. (2023). Flower morphology as a predictor of pollination mode in a biotic to abiotic pollination continuum. Ann. Bot. 132, 61–76. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcad069
Meaders, C., Min, Y., Freedberg, K. J., Kramer, E. (2020). Developmental and molecular characterization of novel staminodes in Aquilegia. Ann. Bot. 126, 231–243. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcaa029
Meyerowitz, E. M., Pruitt, R. E. (1985). Arabidopsis thaliana and plant molecular genetics. Science 229, 1214–1218. doi: 10.1126/science.229.4719.1214
Min, Y., Bunn, J. I., Kramer, E. M. (2019). Homologs of the STYLISH gene family control nectary development in Aquilegia. New Phytol. 221, 1090–1100. doi: 10.1111/nph.15406
MNHN, Chagnoux, S. (2024). The vascular plants collection (P) at the Herbarium of the Muséum national d’Histoire Naturelle (MNHN - Paris). Version 69.375 (MNHN - Museum national d’Histoire naturelle). Occurrence dataset. Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF). doi: 10.15468/nc6rxy
Moore, M. J., Bell, C. D., Soltis, P. S., Soltis, D. E. (2007). Using plastid genome-scale data to resolve enigmatic relationships among basal angiosperms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 104, 19363–19368. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0708072104
Moyroud, E., Glover, B. J. (2017). The evolution of diverse floral morphologies. Curr. Biol. 27, R941–R951. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2017.06.053
Munz, P. A. (1967). A synopsis of african species of delphinium and consolida. Arnold Arboretum Harvard Univ. 48, 30–55. doi: 10.5962/p.67865
Nessler, C. L. (1982). Somatic embryogenesis in the opium poppy, Papaver somniferum. Physiologia Plantarum 55, 453–458. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3054.1982.tb04526.x
Nigella L. @ in GBIF Secretariat. (2023). GBIF backbone taxonomy. doi: 10.15468/39omei (accessed July 22, 2024).
Novikoff, A., Jabbour, F. (2014). Floral anatomy of delphinieae (Ranunculaceae): comparing flower organization and vascular patterns. Modern Phytomorphology 5, 35–44. doi: 10.5281/ZENODO.161001
Pabón-Mora, N., Ambrose, B. A., Litt, A. (2012). Poppy APETALA1/FRUITFULL orthologs control flowering time, branching, perianth identity, and fruit development. Plant Physiol. 158, 1685–1704. doi: 10.1104/pp.111.192104
Pabón-Mora, N., Sharma, B., Holappa, L. D., Kramer, E. M., Litt, A. (2013). The Aquilegia FRUITFULL-like genes play key roles in leaf morphogenesis and inflorescence development. Plant J. 74, 197–212. doi: 10.1111/tpj.12113
Park, S.-U., Facchini, P. J. (2000). Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of opium poppy, Papaver somniferum, via shoot organogenesis. J. Plant Physiol. 157, 207–214. doi: 10.1016/S0176-1617(00)80192-3
Pelaz, S., Ditta, G. S., Baumann, E., Wisman, E., Yanofsky, M. F. (2000). B and C floral organ identity functions require SEPALLATA MADS-box genes. Nature 405, 200–203. doi: 10.1038/35012103
Peng, H.-W., Xiang, K.-L., Erst, A. S., Lian, L., Ortiz, R. D. C., Jabbour, F., et al. (2023). A complete genus-level phylogeny reveals the Cretaceous biogeographic diversification of the poppy family. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 181, 107712. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2023.107712
Peng, H., Xiang, K., Lian, L., Liu, B., Erst, A. S., Gao, T., et al. (2024). A revised tribal classification of Papaveraceae (poppy family) based on molecular and morphological data. Taxon 73, 762–783. doi: 10.1002/tax.13175
Prajapati, S., Bajpai, S., Gupta, M. M., Kumar, S. (2001). The floral androcarpel organ (ACO) mutation permits high alkaloid yields in opium poppy Papaver somniferum. Current Science 81, 1109–1112.
Puzey, J. R., Gerbode, S. J., Hodges, S. A., Kramer, E. M., Mahadevan, L. (2011). Evolution of spur-length diversity in Aquilegia petals is achieved solely through cell-shape anisotropy. Proc. R. Soc B. 279, 1640–1645. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2011.1873
Ren, Y., Gu, T., Chang, H. (2011). Floral development of dichocarpum, thalictrum, and aquilegia (Thalictroideae, ranunculaceae). Plant Syst. Evol. 292, 203–213. doi: 10.1007/s00606-010-0399-6
Samanani, N., Park, S.-U., Facchini, P. J. (2002). In vitro regeneration and genetic transformation of the berberine-producing plant, Thalictrum flavum ssp. glaucum. Physiol. Plant 116, 79–86. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-3054.2002.1160110.x
Sauquet, H., Carrive, L., Poullain, N., Sannier, J., Damerval, C., Nadot, S. (2015). Zygomorphy evolved from disymmetry in Fumarioideae (Papaveraceae, Ranunculales): new evidence from an expanded molecular phylogenetic framework. Ann. Bot. 115, 895–914. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcv020
Sharma, B., Guo, C., Kong, H., Kramer, E. M. (2011). Petal-specific subfunctionalization of an APETALA3 paralog in the Ranunculales and its implications for petal evolution. New Phytol. 191, 870–883. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2011.03744.x
Sharma, B., Kramer, E. M. (2013). “Virus-induced gene silencing in the rapid cycling columbine aquilegia coerulea ‘Origami,’,” in Virus-Induced Gene Silencing. Ed. Becker, A. (Humana Press, Totowa, NJ), 71–81. doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-278-0_6
Sharma, B., Kramer, E. M. (2017). Aquilegia B gene homologs promote petaloidy of the sepals and maintenance of the C domain boundary. EvoDevo 8, 22. doi: 10.1186/s13227-017-0085-7
Sharma, B., Pandher, M. K., Alcaraz Echeveste, A. Q., Romo, R. K., Bravo, M. (2024). Delphinium as a model for development and evolution of complex zygomorphic flowers. Front. Plant Sci. 15. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1453951
Sharma, B., Yant, L., Hodges, S. A., Kramer, E. M. (2014). Understanding the development and evolution of novel floral form in Aquilegia. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 17, 22–27. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2013.10.006
Soltis, P. S., Soltis, D. E. (2013). “Angiosperm phylogeny: A framework for studies of genome evolution,” in Plant Genome Diversity Volume 2: Physical Structure, Behaviour and Evolution of Plant Genomes. Eds. Greilhuber, J., Dolezel, J., Wendel, J. F. (Springer, Vienna), 1–11. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-1160-4_1
Soltis, P. S., Soltis, D. E., Kim, S., Chanderbali, A., Buzgo, M. (2006). Expression of floral regulators in basal angiosperms and the origin and evolution of ABC-function. Adv. Botanical Res. 44, 483–506. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2296(06)44012-X
Soza, V. L., Haworth, K. L., Di Stilio, V. S. (2013). Timing and consequences of recurrent polyploidy in meadow-rues (Thalictrum, ranunculaceae). Mol. Biol. Evol. 30, 1940–1954. doi: 10.1093/molbev/mst101
Soza, V. L., Snelson, C. D., Hewett Hazelton, K. D., Di Stilio, V. S. (2016). Partial redundancy and functional specialization of E-class SEPALLATA genes in an early-diverging eudicot. Dev. Biol. 419, 143–155. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2016.07.021
Strid, A. (1970). Studies in the Aegean flora. XVI. Biosystematics of the Nigella arvensis complex. With special reference to the problem of non-adaptive radiation. Opera Bot. 28, 1–169.
Stubben, C. J., Milligan, B. G. (2007). Conservation implications of spur length variation in long-spur columbines (Aquilegia longissima). (Department of Biology, New Mexico State University, Las Cruces, New Mexico 88003).
Sugiyama, S.-H., Yasui, Y., Ohmori, S., Tanaka, W., Hirano, H.-Y. (2019). Rice flower development revisited: regulation of carpel specification and flower meristem determinacy. Plant Cell Physiol. 60, 1284–1295. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcz020
Tamura, M. (1995). “Die natürlichen pflanzenfamilien,” in Angiospermae: Ordnung Ranunculales Fam. Ranunculaceae (Berlin: Duncker & Humblot), vol. 17. , 412–435.
Tanaka, W., Toriba, T., Hirano, H. (2017). Three TOB 1-related YABBY genes are required to maintain proper function of the spikelet and branch meristems in rice. New Phytol. 215, 825–839. doi: 10.1111/nph.14617
The Arabidopsis Genome Initiative (2000). Analysis of the genome sequence of the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature 408, 796–815. doi: 10.1038/35048692
The RanOmics group, Becker, A., Bachelier, J. B., Carrive, L., Conde E Silva, N., Damerval, C., et al. (2024). A cornucopia of diversity— Ranunculales as a model lineage. J. Exp. Bot. 75, 1800–1822. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erad492
Tucker, S. C., Hodges, S. A. (2005). Floral ontogeny of aquilegia, semiaquilegia, and enemion (Ranunculaceae). Int. J. Plant Sci. 166, 557–574. doi: 10.1086/429848
Wang, P., Liao, H., Zhang, W., Yu, X., Zhang, R., Shan, H., et al. (2015). Flexibility in the structure of spiral flowers and its underlying mechanisms. Nat. Plants 2, 15188. doi: 10.1038/nplants.2015.188
Wang, W., Lin, L., Xiang, X.-G., Ortiz, R., del, C., Liu, Y., et al. (2016). The rise of angiosperm-dominated herbaceous floras: Insights from Ranunculaceae. Sci. Rep. 6, 27259. doi: 10.1038/srep27259
Wang, W., Liu, Y., Yu, S.-X., Gao, T.-G., Chen, Z.-D. (2013). Gymnaconitum, a new genus of Ranunculaceae endemic to the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau. TAXON 62, 713–722. doi: 10.12705/624.10
Warnock, M. J. (1997). Delphinium. In flora of North America editorial committee (Ed.). Flora North America North Mexico 3, 167–182.
Weber, A. (1995). “Pollination of Nigella arvensis (Ranunculaceae) (film presentation),” in Systematics and Evolution of the Ranunculiflorae. Eds. Jensen, U., Kadereit, J. W. (Springer, Vienna), 325–326. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-6612-3_34
Whittall, J. B., Hodges, S. A. (2007). Pollinator shifts drive increasingly long nectar spurs in columbine flowers. Nature 447, 706–709. doi: 10.1038/nature05857
Whittemore, A. T., Parfitt, B. D. (1997). “Aquilegia in Flora of North America,” in Flora of North America Editorial Committee (Eds.) (New York: Oxford University Press), vol. 3.
Xiang, K.-L., Aytaç, Z., Liu, Y., Espinosa, F., Jabbour, F., Byng, J. W., et al. (2017). Recircumscription of Delphinium subg. Delphinium (Ranunculaceae) and implications for its biogeography. Taxon 66, 554–566. doi: 10.12705/663.3
Xue, L., Wu, H., Chen, Y., Li, X., Hou, J., Lu, J., et al. (2020). Evidences for a role of two Y-specific genes in sex determination in Populus deltoides. Nat. Commun. 11, 5893. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-19559-2
Yant, L., Collani, S., Puzey, J., Levy, C., Kramer, E. M. (2015). Molecular basis for three-dimensional elaboration of the Aquilegia petal spur. Proc. R. Soc. B: Biol. Sci. 282, 20142778. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2014.2778
Yao, X., Zhang, W., Duan, X., Yuan, Y., Zhang, R., Shan, H., et al. (2019). The making of elaborate petals in Nigella through developmental repatterning. New Phytol. 223, 385–396. doi: 10.1111/nph.15799
Yellina, A. L., Orashakova, S., Lange, S., Erdmann, R., Leebens-Mack, J., Becker, A. (2010). Floral homeotic C function genes repress specific B function genes in the carpel whorl of the basal eudicot California poppy (Eschscholzia californica). EvoDevo 1, 13. doi: 10.1186/2041-9139-1-13
Yin, T., Cai, L., Ding, Z. (2020). An overview of the chemical constituents from the genus Delphinium reported in the last four decades. RSC Adv. 10, 13669–13686. doi: 10.1039/D0RA00813C
Yoshida, H., Nagato, Y. (2011). Flower development in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 62, 4719–4730. doi: 10.1093/jxb/err272
Zhai, W., Duan, X., Zhang, R., Guo, C., Li, L., Xu, G., et al. (2019). Chloroplast genomic data provide new and robust insights into the phylogeny and evolution of the Ranunculaceae. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 135, 12–21. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2019.02.024
Zalko, J., Frachon, S., Morel, A., Deroin, T., Espinosa, F., Xiang, K.-L., et al. (2021). Floral organogenesis and morphogenesis of staphisagria (Ranunculaceae): implications for the evolution of synorganized floral structures in delphinieae. Int. J. Plant Sci. 182, 59–70. doi: 10.1086/711471
Zhang, R., Fu, X., Zhao, C., Cheng, J., Liao, H., Wang, P., et al. (2020). Identification of the key regulatory genes involved in elaborate petal development and specialized character formation in nigella damascena (Ranunculaceae). Plant Cell 32, 3095–3112. doi: 10.1105/tpc.20.00330
Zhang, R., Guo, C., Zhang, W., Wang, P., Li, L., Duan, X., et al. (2013). Disruption of the petal identity gene APETALA3-3 is highly correlated with loss of petals within the buttercup family (Ranunculaceae). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 110, 5074–5079. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1219690110
Zhang, W.-G., Liu, Y.-G., Nie, T.-J., Guo, C.-C., Qiu, L.-H., Yang, G.-Y., et al. (2022). Floral ontogeny of Delphinium anthriscifolium (Ranunculaceae) and development of intrafloral and symmetrical resupinated organs. Botanical J. Linn. Soc. 198, 86–98. doi: 10.1093/botlinnean/boab041
Zhang, P., Xie, Y., Xie, W., Li, L., Zhang, H., Duan, X., et al. (2024). Roles of the APETALA3–3 ortholog in the petal identity specification and morphological differentiation in Delphinium anthriscifolium flowers. Horticulture Res. 11, uhae097. doi: 10.1093/hr/uhae097
Zhang, H., Xue, F., Guo, L., Cheng, J., Jabbour, F., DuPasquier, P.-E., et al. (2024). The mechanism underlying asymmetric bending of lateral petals in Delphinium (Ranunculaceae). Curr. Biol. 34, 755–768. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2024.01.004
Zhao, H., Liao, H., Li, S., Zhang, R., Dai, J., Ma, P., et al. (2023). Delphinieae flowers originated from the rewiring of interactions between duplicated and diversified floral organ identity and symmetry genes. Plant Cell 35, 994–1012. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koac368
Zhao, L., Liu, P., Che, X.-F., Wang, W., Ren, Y. (2011). Floral organogenesis of Helleborus thibetanus and Nigella damascena (Ranunculaceae) and its systematic significance. Botanical J. Linn. Soc. 166, 431–443. doi: 10.1111/j.1095-8339.2011.01142.x
Keywords: Ranunculales, floral evolution, evo-devo, petal elaboration, organ identity, key model systems
Citation: Sharma B, Pandher MK, Alcaraz Echeveste AQ, Bravo M, Romo RK and Ramirez SC (2024) Comparative case study of evolutionary insights and floral complexity in key early-diverging eudicot Ranunculales models. Front. Plant Sci. 15:1486301. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1486301
Received: 25 August 2024; Accepted: 27 September 2024;
Published: 30 October 2024.
Edited by:
Elena M. Kramer, Harvard University, United StatesReviewed by:
Rui Zhang, Northwest A&F University, ChinaCharlie Scutt, Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique (CNRS), France
Copyright © 2024 Sharma, Pandher, Alcaraz Echeveste, Bravo, Romo and Ramirez. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Bharti Sharma, YnNoYXJtYUBjcHAuZWR1
 Bharti Sharma
Bharti Sharma Mankirat Kaur Pandher
Mankirat Kaur Pandher Marianellie Bravo
Marianellie Bravo Rene Kenny Romo
Rene Kenny Romo Sarah Christine Ramirez
Sarah Christine Ramirez