- 1Department of Agronomy, Faculty of Agriculture, Hasanuddin University, Makassar, Indonesia
- 2Department of Soil Science, Faculty of Agriculture, Hasanuddin University, Makassar, Indonesia
- 3Taiwan International Cooperation and Development Fund (TaiwanICDF), Taipei, Taiwan
- 4International Rice Research Institute, University of the Philippines Los Baños, Los Baños, Philippines
- 5Department of Agronomy and Horticulture, Faculty of Agriculture, IPB University, Bogor, Indonesia
- 6Research Center for Food Crops, Research Organization for Agriculture and Food, National Research and Innovation Agency, Cibinong, Indonesia
- 7Indonesian Cereal Testing Instrument Standard Institute, Maros, South Sulawesi, Indonesia
- 8Food Crops, Horticulture, Plantation and Food Security Office of Soppeng, Soppeng, Indonesia
- 9Department of Crop Sciences, University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, Urbana, IL, United States
- 10Plant Production Department, College of Food and Agriculture Sciences, King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
The genotype evaluation process requires analysis of GxE interactions to ascertain the responsiveness of a genotype to various environments, including the development of early maturing rice. However, the concept of interaction is relatively specific to grain yield. In contrast, grain yield is highly polygenic, so assessment should be carried out with multivariate approaches. Therefore, multivariate assessment in evaluating GxE interactions should be developed, especially for early maturing rice genotypes. The study aimed to develop a comprehensive multivariate approach to improve the comprehensiveness and responsiveness of GxE interaction analysis. The study was conducted in Bone and Soppeng districts, South Sulawesi, Indonesia, in two seasons. The study used a randomized complete block design, where replications were nested across two seasons and locations. Two check varieties and five early maturing varieties were replicated three times in each environment. Based on this study, a new approach to GxE interaction analysis based on multiple regression index analysis, BLUP analysis, factor analysis, and path analysis was considered adequate, especially for evaluating early maturing rice. This approach combined days to harvest, biological yield, and grain yield in multiple linear regression with weighting based on the combination of all analyses. The effectiveness of the GxE interaction assessment was reflected by high coefficient of determination (R2) and gradient (b) values above 0.8 and 0.9, respectively. Inpari 13 (R2 = 0.9; b=1.05), Cakrabuana (R2 = 0.98; b=0.99), and Padjajaran (R2 = 0.95; b=1.07) also have good grain yield with days to harvesting consideration, namely 7.83 ton ha-1, 98.12 days; 7.37 ton ha-1, 95.52 days; and 7.29 ton ha-1, 97.23 days, respectively. Therefore, this index approach can be recommended in GxE interaction analysis to evaluate early maturing rice genotypes. Furthermore, Inpari 13, Cakrabuana, and Padjajaran are recommended as adaptive early maturing varieties.
1 Introduction
Rice is a major food crop that has always been prioritized for development. This crop has the advantage of grain content rich in carbohydrates and several other components, such as vitamins, antioxidants, and minerals (Fukagawa and Ziska, 2019; Sen et al., 2020). These ingredients work synergistically to support the availability of energy and health for humans, so this crop is often consumed as the primary source of carbohydrates for most of the world’s population, including Indonesia. Indonesia belongs to the world’s top five rice production countries, after China, India, and Bangladesh (Yuan et al., 2022; Bin Rahman and Zhang, 2023). According to Statistic Indonesia (2023a), Indonesia’s rice production reached 53.63 million tonnes, a decrease of 2.05% compared to the previous year. This production is considered worrying compared to other countries when looking at the ratio to the population (Rozaki, 2020; Fitrawaty et al., 2023). This is crucial, considering Indonesia’s population growth rate is relatively high at 1.13% Statistic Indonesia (2023b). Therefore, innovations related to the sustainability of rice production must be further developed to maintain food security in Indonesia.
Other factors, such as the issue of climate change, also influence the stability and sustainability of rice production. Climate change is an environmental change due to increased greenhouse gas concentrations (Cassia et al., 2018; Karbi and Chemke, 2023; Simmer et al., 2023). The increase causes the trapping of reflected heat waves like the greenhouse system so that the earth’s temperature increases and has an impact on changing the rhythm of seasons and rainfall patterns in various parts of the world (Cassia et al., 2018; Marx et al., 2021; Karbi and Chemke, 2023). This can induce various plant abiotic stresses, such as drought, salinity, acidity, and other stresses (Sánchez-Bermúdez et al., 2022; Eckardt et al., 2023). However, water-related stress is the main problem due to climate change (Ahmed et al., 2020; Chen et al., 2023; Sato et al., 2024; Yadav et al., 2024). Water, as the main component of climate change, will increase the duration of dry and rainy season patterns, including their intensity, so that seasonal patterns are not more evident per year (Fahad et al., 2017; Ahmed et al., 2020; Haile et al., 2021; Chen et al., 2023; Janni et al., 2023; Yadav et al., 2024). In addition, these effects will also induce the intensity of the El Niño and La Niña effects to be more intense in several locations in the hemisphere (Yang et al., 2018; Geng et al., 2023; Wang et al., 2023), including Indonesia (Nur’utami and Hidayat, 2016; Arjasakusuma et al., 2018; Sulaiman et al., 2023). El Nino-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) is a climatic phenomenon that causes predominant rainfall variability in the tropics. The phenomenon causes severe droughts in many regions, causing many socio-economic losses (Rodysill et al., 2019; Adamson, 2022). On the other side, La Nina events cause an increase in convection and regional precipitation that drives heavy rainfall events. This causes major flooding in the region (Rodysill et al., 2019). Both phenomena effects cause a decrease in rice grain yield per hectare, leading to crop failure (Ansari et al., 2021; Barrios-Perez et al., 2021; Cherian et al., 2021; Haile et al., 2021). This is also the case in Indonesia, where the impact of El Nino and La Nina can reduce Indonesia’s rice production by around 2.9% to 4% (Murniati and Mutolib, 2020; Khairullah et al., 2021). In addition, according to (Sun et al., 2020), these two phenomena have an impact on reducing rice production, slowing down planting, and harvest failure, so they account for 40% of the variability in rice grain yield per hectare in Indonesia. Therefore, preventive measures need to be taken to adapt to the impacts of climate change. One innovation that can be offered is the development of early-maturing rice varieties.
The development of early maturing crop varieties is one of the adaptation strategies that aim to avoid the impact of climate stress (Rohaeni and Ishaq, 2016; Ren et al., 2023). This is in contrast to other adaptation strategies, such as avoidance and tolerance, which directly deal with climate stress (Seleiman et al., 2021; Eckardt et al., 2023; Yun et al., 2023; Anshori et al., 2024). In addition, this approach can optimize planting intensity under normal conditions so that rainfed land can be planted two to three times per year (Sudana, 2016; Subekti and Umar, 2022; Musa et al., 2023; Widiastuti et al., 2023; Sutardi et al., 2023). The development of early maturing varieties has also been conducted in rice and reported by Iftekharuddaula et al. (2016); Fang et al. (2019); Sjahril et al. (2020); Saminadane et al. (2023); Shanmugam et al. (2023). In general, the development of early maturing rice varieties in Indonesia has also been carried out, where there are several early maturing rice varieties that the Ministry of Agriculture has released (Purba and Giametri, 2017; Rismawati et al., 2022; Musa et al., 2023). These varieties have been adapted in several regions. However, specific reports related to interaction analysis, as one of the bases for evaluation, have yet to be published among these early maturing varieties. This includes comparisons of potential with high-yielding varieties in general. Nevertheless, Musa et al. (2023) and Anshori et al. (2024) have reported the potential fertilizer response to NPK dosage and its yield adaptability among five potential early maturing varieties. However, the concept has yet to cover the multivariate comprehensive influence of all growth characters on the stability and recovery responsiveness of the early maturing rice. In general, grain yield per hectare is not a dependent character. In other words, its variability is influenced by other agronomic components (Fellahi et al., 2018; van Eeuwijk et al., 2019; Anshori et al., 2021; Burgess et al., 2023; Hassani et al., 2023). This indicates that rice stability and responsiveness testing require integrated evaluation support criteria (Hashim et al., 2021; Salah et al., 2022; Santos et al., 2022; Hassani et al., 2023). The concept was also reported by (Alsabah et al., 2019; Akbar et al., 2021; Hashim et al., 2021; Salah et al., 2022). Therefore, several supporting characters must be integrated and synergistically included in the evaluation and interaction analysis.
Interaction analysis is an approach to measure a genotype’s response level to environmental changes. This concept is crucial for further evaluating a line or the recommendation process of a variety to be adapted to a region (Saltz et al., 2018; Smith et al., 2021; Gupta et al., 2022). These advantages make this analysis often applied in breeding activities, known as GxE interaction analysis (Yang, 2014; Brown et al., 2020; Gupta et al., 2022). Several concepts of GxE interaction analysis have been reported by several rice studies (Oladosu et al., 2017; Poli et al., 2018; Hashim et al., 2021; Roy et al., 2022; Panda et al., 2023; Ghazy et al., 2024). However, the specific assessment of GxE interactions in early-maturing rice has yet to be widely reported. In addition, analyses of GxE interactions are generally independent between growth characters and even only focused on grain yield per hectare (Yang, 2014; Brown et al., 2020; Hilmarsson et al., 2021; Roy et al., 2022). However, some studies have linked their potential using multivariate analyses (Sitaresmi et al., 2019; Pour-aboughadareh and Sanjani, 2021; Sumuni et al., 2024). Alam et al. (2021); Hashim et al. (2021); Hasan et al. (2022); Roy et al. (2022); Aswidinnoor et al. (2023); Singh et al. (2023), and Panda et al. (2023) used the principal component analysis pattern in analyzing the potential of a rice genotype to several environments. In addition, Sae-Lim et al. (2014); Mengesha et al. (2019), and Smith et al. (2021) also developed the concept of interaction analysis on a genotype through factor analysis. However, both multivariate analysis concepts still emphasize one main characteristic: grain yield per hectare. Meanwhile (Olivoto et al., 2019a, b), Sharifi et al. (2020); Pour-aboughadareh and Sanjani (2021); Panda et al. (2023), and Ahmed et al. (2024) also utilized the potential of various traits through the concept of the weighted average of absolute scores (WAASB), commercial check variety which utilized multivariate analysis and indices. However, these concepts only focus on stability, so the idea is considered less comprehensive in describing the potential for responsiveness between genotypes. Based on this, the development of a new approach that is more comprehensive in assessing the responsiveness of a GxE interaction needs to be done, especially for early maturing rice varieties. This study aims to develop and evaluate the effectiveness of multivariate approaches in analyzing GxE interactions that are more comprehensive and responsive. In addition, this study also aims to assess and determine the interaction potential of early maturing rice varieties that are responsive and have the potential to be developed.
2 Materials and methods
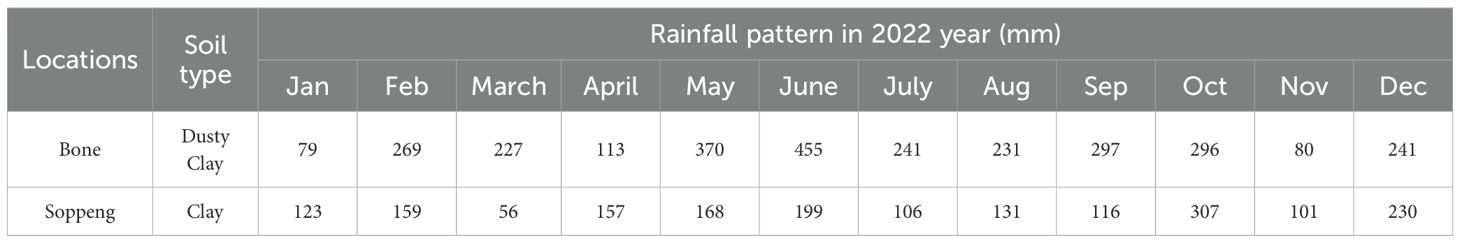
Two districts were chosen for this study: Soppeng Regency, at coordinates of 4°20’44.698 “S, 119°54’54.032 “E, and Bone District, West Sulawesi, Indonesia, at coordinates of 4°36’30.975 “S, 120°17’41.636 “E.” Based on South Sulawesi’s potential for rice production—particularly in the island’s eastern region—both sites were selected. The evaluation activities used two growth seasons: January–April 2022 (1st season) and June–September 2022 (2nd season). Table 1 shows the rainfall trends for each season.
2.1 Experimental design
This study used a randomized complete block design, with replications nested in two seasons and two locations (4 environments). Two commercial check varieties (Ciherang and Inpari 32) and five early maturing varieties (Cakrabuana, Padjajaran, Inpari 13; Inpari 19, and M70D) were grown three times in each environment. The combination of varieties, replications, and environment resulted in 84 experimental units. Based on research by (Barokah et al., 2021; Subekti and Umar, 2022; Musa et al., 2023 and Anshori et al., 2024), five early maturing rice varieties were chosen. In the meantime, the two varieties (Ciherang and Inpari 32) in South Sulawesi potential demand and seed requirements are taken into consideration when selecting check varieties (Sitaresmi et al., 2023; Qadir et al., 2024).
2.2 Research procedure
The research methodology started with plowing and tilling the land to create a muddy environment. After that, the field was organized with a plot system measuring 3.5 m x 3.5 m and 1 m between plots. Simultaneously, the seeds to be planted were pre-soaked for 24 hours. Then, the seeds are mixed into the nursery bed. Seedlings were reared until 15 days old, and then transferred to the field with a spacing of 20 cm x 20 cm, resulting in 416 plants per plot (Anshori et al., 2024).
Seedlings planted are maintained with various activities such as replanting, weeding, watering, fertilizing, and insect control. Weeding is done manually and chemically at 30 days after planting. Dead seedlings are replaced seven days later by replanting according to the variety. Weeds were removed mechanically, followed by herbicide application using a sprayer. Irrigation began six days after the first fertilization or 20 days after planting by adding water to the experimental field about 5 cm above the soil surface. After the second fertilization, irrigation was temporarily stopped to keep the soil moist and clay-like. Watering was resumed five days later, with the water level raised to about 10 cm above the soil surface during the primordial phase to prevent the formation of additional tillers. Fourteen days after transplanting, a fertilizer mixture of 200 kg ha-1 N: 100 kg ha-1 P2O5: 100 kg ha-1 K2O was applied, followed by a second round of urea fertilization 35 days later. Pest and disease control used pesticides adjusted to the type and phenological stage of the rice plant pest or disease. Harvesting is done when two-thirds of the rice panicles have reached physiological maturity (yellowing straw), and the grain at the base of the panicle has hardened. Data were collected throughout the harvesting process before the plant portions were placed into the sample bags.
2.3 Observation parameters and data analysis
This study focused on several agronomic characteristics of rice. These characters include plant height (PH), number of total tillers (NTT), number of productive tillers (NPT), days to harvesting (DH), flag leaf length (FLL), panicle length (PL), biological yield (BY), thousand-grain weight (TGW), and grain yield per hectare (GY). Biological yield means the average grain weight per hill from five sample plants, while grain yield is observed by converting plot weight to weight per hectare. These observational characters were systematically analyzed to evaluate the potential for GxE interactions, especially in early-maturing rice varieties. Meanwhile, the average of all growth traits to all locations and seasons was shown in Supplementary Table 1.
Data analysis began with a nested analysis of variance involving potential season and location interactions as nests in the replicates. The result of the analysis becomes the basis of whether further analysis is needed. If there are complex interactions on the observed characters, especially season x location x variety interactions, then GxE interaction analysis is conducted. The GxE interaction analysis starts with the best linear unbiased prediction (BLUP) analysis (Olivoto et al., 2019a, 2022; Schmidt et al., 2019; Khanna et al., 2022). Characters that did not meet the potential heritability of BLUP were not included in the multivariate analysis. Selected characters in BLUP were analyzed using factor analysis (Rocha et al., 2018; Olivoto et al., 2019a, 2022) and path analysis (Sabouri et al., 2008; Anshori et al., 2021; Fikri et al., 2023) as part of the multivariate analysis. The characters specified in the multivariate analysis were used as selection criteria in the index.
The index’s weighting is based on the combination of the three analyses: BLUP heritability, score on factor analysis, and direct effect of path analysis. The potential of each variety in the index is based on the standardized BLUP value. The standardized values are inputted into the index formulation of the previously developed multiple regression equation (Olivoto et al., 2019b; van Eeuwijk et al., 2019; Anshori et al., 2021, 2022).
Or
Then, the index values were averaged and sorted per environment before regression analysis, like Finlay-Wilkinson’s stability testing, was conducted (Pour-Aboughadareh et al., 2022; Anshori et al., 2024). The interaction analysis results based on the index values were tested for sensitivity through the determination value (R2) and compared with the independent GY potential. This was to see the potential effectiveness between the two approaches.
3 Results
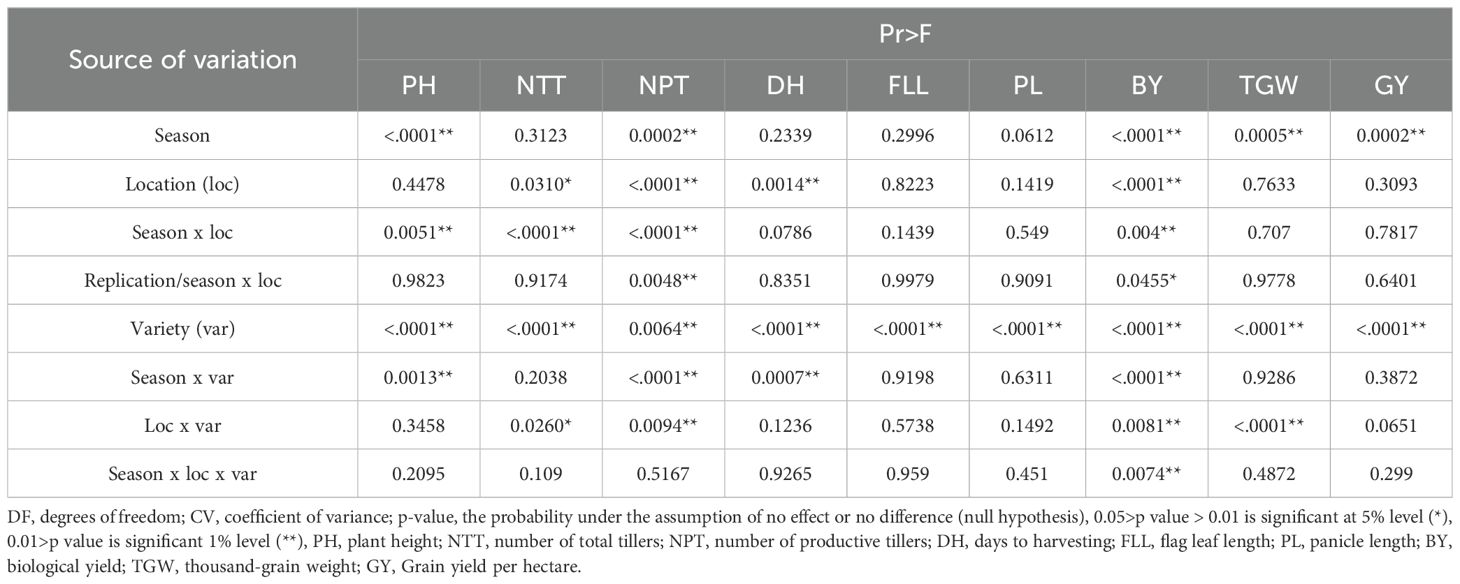
Variance analysis showed that the varietal diversity source significantly affected all growth characters (Table 2). In contrast, season and location-independent sources of diversity only significantly affected some characters, such as PH, NPT, BY, TGW, and grain yield per hectare (GY) influenced by season, and NTT, NPT, and BY influenced by location. Meanwhile, the interaction source of diversity only has a specific effect on several characters. By character, BY is a character significantly affected by all sources of diversity. This is followed by the number of productive tiller characters, which is also influenced by all sources of diversity, except for the season x location x genotype interaction. In contrast, the characters are influenced by a few sources of diversity, such as FLL and PL. Both characters are only influenced by the source of varietal diversity.
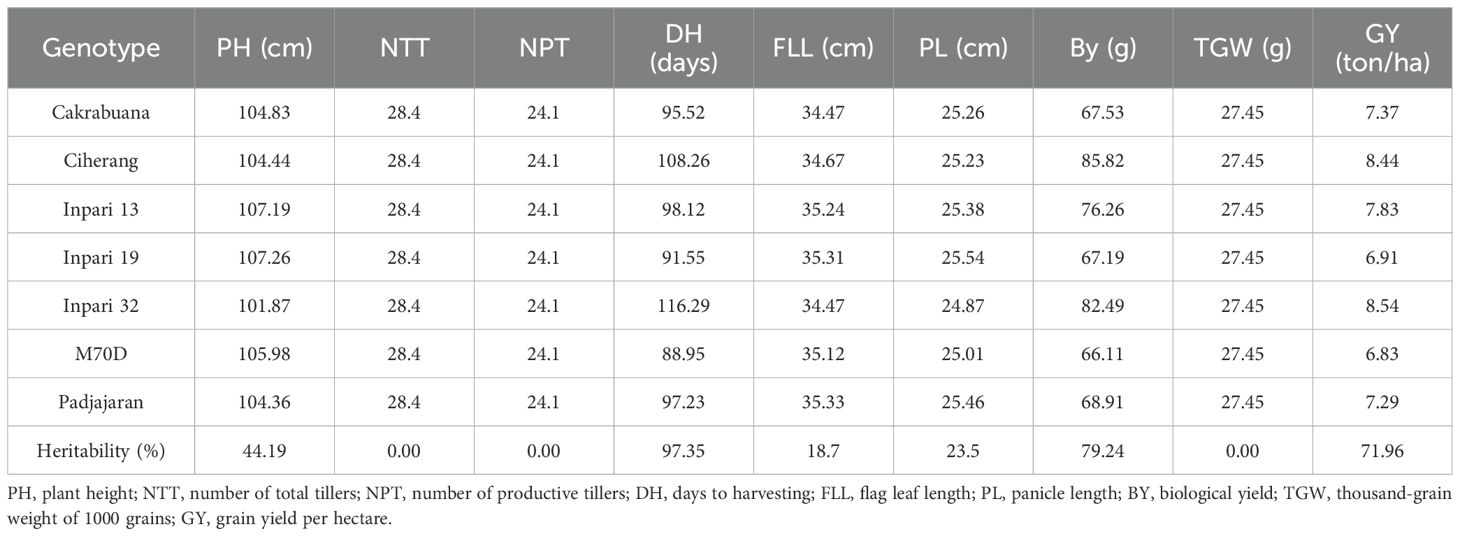
The results of the BLUP analysis show that three characters have the same average BLUP value in each variety, namely NTT, NPT, and TGW (Table 3). This is followed by a heritability value that shows 0. Conversely, other characters have a variance of BLUP values between each variety, followed by heritability values above 0. PH (44.19%) and PL (23.5%) are characters with moderate heritability. Meanwhile, characters classified as high heritability are DH (97.35%), BY (79.24%), and GY (71.96%). Varieties with the highest BLUP GY values were Inpari 32 (8.54 tonnes/ha) and Ciherang (8.44 tonnes/ha) as a commercial check variety and Inpari 13 (7.83 tonnes/ha) as an early maturing rice variety.
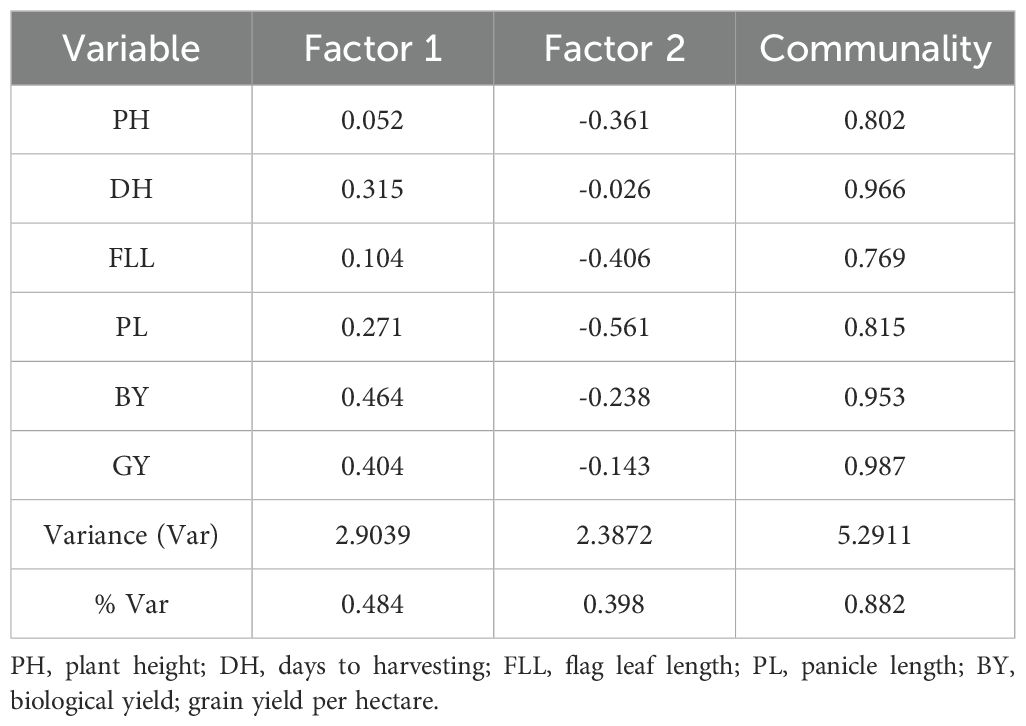
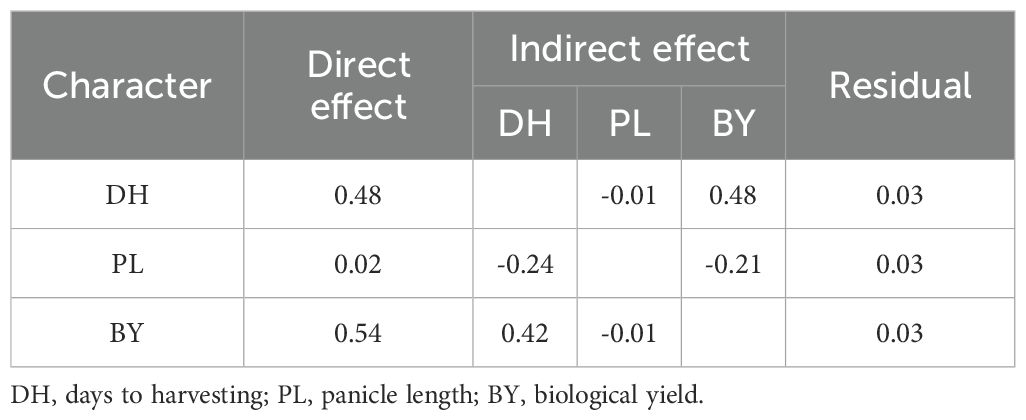
The factor analysis results showed that two dimensions could describe the representative diversity of the diverse characters based on the BLUP value (Table 4). In general, the commonality of all characters has reached 0.8, except for FLL, which only reached 0.769. Based on GY characters, factor 1 is the factor that collects the highest loading factor score for GY characters. In factor 1, the characters PH (0.052) and FLL (0.104) are the characters that have low loading scores. The DH, PL, and BY characters in factor 1 had good factor loading scores of 0.315, 0.271, and 0.464, respectively. Meanwhile, the results of the path analysis are shown in Table 5, which has a determination value of 0.84. DH and BY are two characters with a direct effect of 0.48 and 0.54, respectively. In contrast, PL had a low direct effect of 0.02 and was ineffective as a selection criterion.
The selection index combines standardized BLUP values with the weighting values developed in this study (Table 6). Based on the index value, the Bone_season 1 (E1) environment (1.71) is the environment with the highest average index, followed by Soppeng_season 1 (E3) with a value of 0.76. Inpari 32 (3.94 and 3.01, respectively) and Ciherang (2.93 and 1.96) were the best varieties in the E1 and E3 environments. In addition, Inpari 13 was also rated as the best variety, especially against other early-maturing varieties (1.52 and 1.40, respectively). On the contrary, the lowest average index value belongs to Environment_Soppeng season 2 with a value of (-2.01). Inpari 32, Ciherang, and Inpari 13 had index values of 0.6 -0.44 and -2.18, respectively. In contrast, the M70D variety has the lowest value in almost all environments, especially in the Soppeng season 2 environment.
Based on the regression analysis results (Figures 1A, B), the coefficient of determination (R2) in the multivariate index-based GxE analysis has a high value above 0.8, except for the Ciherang variety. In contrast, the coefficient of determination in GY-based GxE analysis is relatively below 0.8, except for Inpari 13 (0.927), Cakrabuana (0.9615), and Padjajaran (0.8332). Ciherang variety in index-based GxE analysis has the lowest determination value, 0.529, with a regression gradient (b) of 0.786. The gradient is also relatively in the same group as the regression gradient of Inpari 32 (0.868). Regression gradients that have response values ranging from 1 ± 0.1 are Inpari 13 (1.06), Cakrabuana (1.99) and Padjajaran (1.07). In contrast, based on GxE GY, Inpari 32 and Inpari 19 have gradients ranging from 1 ± 0.1. However, both have low determination values of 0.4337 and 0.6733, respectively. Meanwhile, Inpari 13, Cakrabuana, and Padjajaran have regression gradients below 0.9.
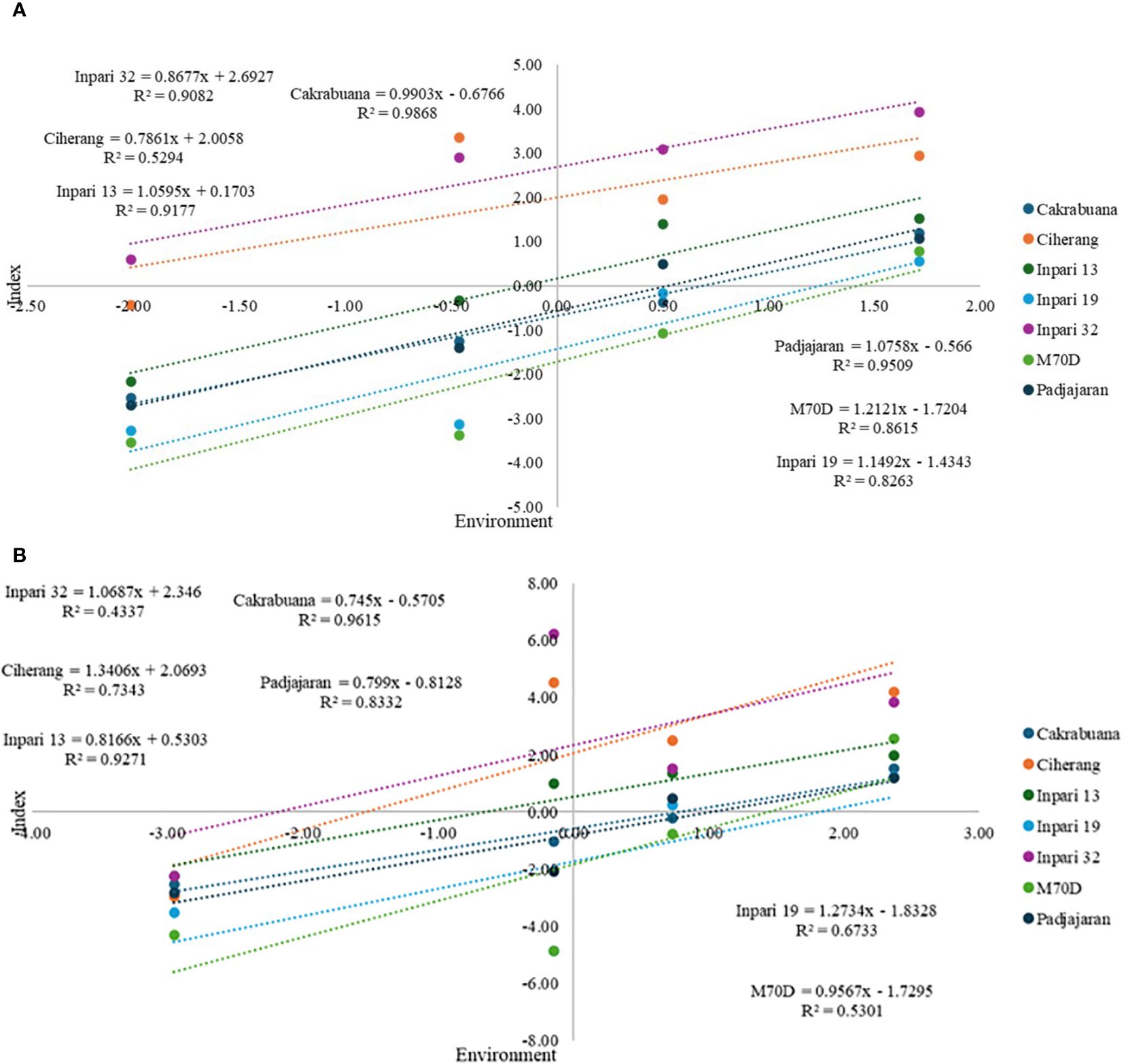
Figure 1. GxE interaction analysis is based on a multivariate index of selection criteria (A), and GxE interaction analysis is based on grain yield per hectare (B).
4 Discussions
The ANOVA results showed that the sources of diversity in this study had specific and diverse patterns of influence among characters. However, one source of variation (variety) significantly affected all growth characters. Significant varietal diversity is due to differences in the types of varieties used, where there are five early maturing rice varieties and two medium maturing varieties as commercial varieties in general. The difference in type will correlate with phenology and agronomic characters (Paiman et al., 2022; Sheng et al., 2022; Afa et al., 2023; Seck et al., 2023), so the difference in growth response will be significant for all characters. As for the effect of interactions, the diversity of interactions is specific depending on the character and interaction pattern. However, in the character of biological yield, all sources of diversity showed a significant effect on the character. In general, biological yield is one of the key characteristics that can represent the potential for GY (Bhati et al., 2015; Li et al., 2019). This is also in line with Li et al. (2019) and Burgess et al. (2023), where biological yield is the accumulation of a potential GY component, so this character is often used as the main supporting criteria for the crop yield (Bhati et al., 2015; Li et al., 2019; Zhao et al., 2020; Dhakal et al., 2021). Based on this, this character can be a consideration in in-depth analysis, especially for more comprehensive interactions. However, in this study, GY was only influenced by independent variance sources of variety and season. Therefore, BLUP and multivariate analysis can be used in this study.
The results of estimating the mean value of BLUP-based characters explain that several characters (NTT, NPT, and TGW) do not have diversity between each genotype. In general, the estimation of the BLUP value is influenced by the potential genetic variation (Molenaar et al., 2018; Schmidt et al., 2019; Khanna et al., 2022). Suppose a character has a low genetic variance. In that case, it will impact the narrow variance and does not have a random effect on the BLUP value. So, the heritability of the three characters is 0 in the BLUP analysis (Molenaar et al., 2018; Sood et al., 2020). However, when comparing these results with the ANOVA, there needs to be more alignment because the varietal diversity source significantly affects all three characters. This indicates good heritability potential in the three characters (Fadhilah et al., 2022; Anshori et al., 2024). The difference is due to the BLUP concept, which is that the combination of season and location is combined into an environment. This will impact the pattern of diversity effects (Johnstone and Manly, 2014), so the heritability of the BLUP pattern will be lower than that of the ANOVA pattern in this study. In addition, according to Jia (2017), the difference in heritability between regular and BLUP has a different approach, where the BLUP heritability value that links cross-validation tends to be lower than the regular heritability value. Based on these two things, the potential in the ANOVA results will be different from the BLUP potential. However, the BLUP potential value is believed to be more effective in assessing the potential of a genotype than the general approach. This is because the BLUP approach can correct the potential value of the genotype to the influence of its environment so that the potential assessment is more accurate, especially for multi-environment experiments (MET) (Molenaar et al., 2018; Schmidt et al., 2019; Sood et al., 2020; Chen et al., 2024). Therefore, NTT, NPT, and TGW characters were not included in subsequent analyses.
The combination of several multivariate analyses is a systematic approach to determining selection or evaluation criteria (Kose et al., 2018; Hashim et al., 2021; Laraswati et al., 2021; Barth et al., 2022; Fadhilah et al., 2022; Habib et al., 2024). These criteria can increase the effectiveness of the selection process. In this study, the combination of multivariate analyses focused on factor analysis and cross-sectional analysis. Both analyses were chosen, given their potential to reduce the diversity of ineffective characters in evaluation judgments (Nayak et al., 2018; Anshori et al., 2022; Farid et al., 2022; Fikri et al., 2023). Generally, factor analysis can reduce diversity in characters with low covariance in a dimension. This makes the character unimportant in influencing the variety of dimensions so that the character can be eliminated in the evaluation process (Nayak et al., 2018; Rocha et al., 2018; Tavakol and Wetzel, 2020; Jia et al., 2022). This concept is also suggested when analyzing the interaction and stability of a genotype. Rocha et al. (2018) and Olivoto et al. (2022) Utilized BLUP values and factor analysis to assess genotype potential. However, the concept still needs to be approached with path analysis that focuses on the direct effect of a character on the total diversity of a main character (Anshori et al., 2022; Fikri et al., 2023). This is due to the importance of a unidirectional evaluation of the main characters that can describe and answer the objectives of an assessment (Fikri et al., 2023; Musa et al., 2023). Therefore, combining factor and path analysis as part of multivariate analysis is considered effective in estimating selection criteria in evaluating GxE interactions.
GxE interaction analyses of DH, BY, and GY can be done independently. The concept of independent assessment of selection or evaluation criteria in rice was also reported by Hilmarsson et al. (2021) and Musa et al. (2023). However, the three characters are related, so the assessment should combine them. One of them is through the index value approach. The utilization of index values in the combination of evaluation and selection criteria has also been reported by (Fadhilah et al., 2022; Sarwendah et al., 2022; Fikri et al., 2023). In general, the index value becomes the midpoint in combining the advantages and disadvantages of a genotype against various selection or evaluation criteria (Olivoto et al., 2019b; van Eeuwijk et al., 2019; Fikri et al., 2023). The combination involves dimensional adjustment so that the three criteria can be combined in a linear equation with balanced values (Sabouri et al., 2008; Anshori et al., 2021, 2022; Batista et al., 2021; Fikri et al., 2023). This assesses the interaction of the three comprehensive and objective (Sabouri et al., 2008; Anshori et al., 2021; Batista et al., 2021). The utilization of index values based on BLUP analysis was also reported by Olivoto et al. (2019b); Pour-aboughadareh and Sanjani (2021), and Panda et al. (2023). However, the combination of the three also considers the priority level of a criterion, so weighting in the index is necessary (Sabouri et al., 2008; van Eeuwijk et al., 2019; Pavithra and Vengadessan, 2020; Anshori et al., 2021; Batista et al., 2021; Rahimi and Debnath, 2023). Consideration of the weighting value can use the heritability approach (Fadhilah et al., 2022; Rahimi and Debnath, 2023; Farid et al., 2024), factor score in factor analysis (Anshori et al., 2022; Farid et al., 2022; Fikri et al., 2023), or direct effect on cross-section (Sabouri et al., 2008; Alsabah et al., 2019; Pavithra and Vengadessan, 2020; Anshori et al., 2021, 2022; Sarwendah et al., 2022; Fikri et al., 2023). The three concepts are considered effective in assessing selected and evaluated genotypes, so combining the three can be a new approach to forming index values for GxE analysis. This is also supported by reports on the effectiveness of combining various genetic and multivariate analyses in forming selection indices (Farid et al., 2022; Fadhilah et al., 2022).
The GxE interaction analysis in this study was combined with the orthogonal-polynomial concept based on regression analysis of several varieties. This concept is very familiar in stability analysis by Finlay-Wilkinson, which focused on simple linear regression (Finlay and Wilkinson, 1963). In addition, the development of regression-based GxE interaction analysis was also reported by Brown et al. (2020); Hilmarsson et al. (2021) and Roy et al., 2022). However, the approach in this study focuses on the index value of the combination of the three selection criteria, so the regression analysis focuses on the concept of multiple regression. This makes the interaction assessment simpler, more structured, and more comprehensive, making the results easy to understand and interpret in the evaluation process.
Based on the interaction index analysis approach, all rice varieties have high determination values reaching > 0.8, except for the Ciherang variety (0.529). In general, the determination value above 0.8 indicates a high level of effectiveness in a model. This is inversely proportional to GY-based GxE analysis, which has a determination value below 0.8. This suggests that the index approach effectively assesses multivariate rice growth interaction responses, especially for early maturing varieties. In addition, in this analysis, Inpari 13, Cakrabuana, and Padjajaran varieties have a stable response to environmental changes. This is characterized by b values close to or equal to 1, like the Finlay-Wilkinson concept (Finlay and Wilkinson, 1963; Piepho and Blancon, 2023; Anshori et al., 2024). In contrast, interactions based solely on GY had b values below 0.9 for all three varieties. These results indicate that the index approach can comprehensively assess rice growth characters’ responsiveness, so the three varieties are considered suitable for planting in various seasons at both test sites. This developed concept is different from the Finlay-Wilkinson interaction analysis and MGIDI, which can only assess partially whether only focusing on the potential responsiveness (Finlay-Wilkinson) or the comprehensive potential assessment (MGIDI) (Sitaresmi et al., 2019; Olivoto et al., 2022; Pour-Aboughadareh et al., 2022; Debsharma et al., 2023). This makes this approach the meeting point of the two interaction analyses, so the picture of responsiveness related to potential GxE interactions can be assessed comprehensively and systematically. Therefore, the orthogonal-polynomial multiple regression approach based on multivariate analysis and BLUP index values can be recommended for analyzing GxE interactions. In addition, Inpari 13, Cakrabuana, and Padjajaran rice varieties are recommended as adaptive varieties, especially in both locations (Bone and Soppeng).
5 Conclusions
In conclusion, the new approach through BLUP-based multiple regression index, factor analysis, and path analysis is considered adequate in analyzing GxE interactions, especially in evaluating early maturing rice. In addition, the approach is also considered to combine the concepts of Finlay-Wilconson and MGIDI stability analysis in the analysis of GxE interactions. Based on this approach, the index formed is 0.147*days to harvesting standardized + 0.199*biological yield standardized +
0.291*grain yield per hectare (GY) standardized. The index approach showed a high determination above 0.8 with a gradient (b) value above 0.9 in the GxE interaction analysis, especially for early maturing rice varieties. This compares favorably with GY-based GxE interaction analysis. Therefore, this index approach can be recommended in GxE interaction analysis, especially in evaluating early maturing rice genotypes. In addition, based on the index-based GxE interaction analysis, the early maturing rice varieties Inpari 13, Cakrabuana, and Padjajaran are recommended to be used as adaptive varieties, especially in both locations (Bone and Soppeng).
5.1 Resource identification initiative
The project uses STAR 2.0.1 from IRRI, META-R from CIMMYT, and the Microsoft Excel 2016 version. Seeds of rice varieties were obtained from rice seed markets in Indonesia.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
MA: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Resources, Software, Writing – original draft. YM: Conceptualization, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. MF: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. MJ: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. RP: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. KK: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. YH: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. MC: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. IB: Supervision, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. WS: Formal analysis, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft. HS: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. BP: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. AN: Data curation, Resources, Writing – review & editing. WW: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. DW: Funding acquisition, Validation, Writing – review & editing. MS: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. Researchers Supporting Project number (RSPD2024R751), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. This study also fund by The International Cooperation and Development Fund (ICDF) Taiwan in 2022-2023 for first stage study. For advance study, this funding is cover by the International Collaboration Research (I-CORE) Program Equity World Class University Indonesia Endowment Fund for Agency (WCU LPDP) 2023-2024 scheme (grant number: 04966/UN4.22/PT.01.03/2023) among Hasanuddin University, International Cooperation and Development Fund (ICDF) Taiwan, and International Rice Research Institute.
Acknowledgments
Researchers Supporting Project number (RSPD2024R751), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, is acknowledged. We are grateful to the International Cooperation and Development Fund (ICDF) Taiwan, the International Rice Research Institute, and the Ministry of Education, Culture, Research, and Technology of the Republic of Indonesia for funding this study over two seasons. Furthermore, we are also thank to the International Collaboration Research (I-CORE) Program Equity World Class University Indonesia Endowment Fund for Agency (WCU LPDP) 2023-2024 scheme (grant number: 04966/UN4.22/PT.01/.03/2023) in supporting for validation of this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpls.2024.1462981/full#supplementary-material
References
Adamson, G. (2022). Situating el ni~no: Toward a critical (physical) geography of ENSO research practice. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 112, 877–892. doi: 10.1080/24694452.2021.1945910
Afa, L. O., Ansi, A., Zulfikar, Z., Muhidin, M., Al Qadri, A. (2023). Growth and yield of local upland rice (Oryza sativa L.) wakawondu cultivar in various plant populations and balanced fertilization. Bul. Penelit. Sos. Ekon. Pertan. Fak. Pertan. Univ. Haluoleo 24, 88–98. doi: 10.37149/bpsosek.v24i2.288
Ahmed, M. S., Majeed, A., Attia, K. A., Javaid, R. A., Siddique, F., Farooq, M. S., et al. (2024). Country-wide, multi-location trials of Green Super Rice lines for yield performance and stability analysis using genetic and stability parameters. Sci. Rep. 14, 1–17. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-55510-x
Ahmed, T., Zounemat-Kermani, M., Scholz, M. (2020). Climate change, water quality, and water-related challenges: A review focusing on Pakistan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 17, 1–22. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17228518
Akbar, M. R., Purwoko, B. S., Dewi, I. S., Suwarno, W. B., Sugiyanta (2021). Genotype × Environment interaction and stability analysis for high yielding doubled haploid lines of lowland rice. Turkish J. F. Crop 26, 218–225. doi: 10.17557/tjfc.1033784
Alam, T., Suryanto, P., Supriyanta, Basunanda, P., Wulandari, R. A., Kastono, D., et al. (2021). Rice cultivar selection in an agroforestry system through gge-biplot and eblup. Biodiversitas 22, 4750–4757. doi: 10.13057/biodiv/d221106
Alsabah, R., Purwoko, B. S., Dewi, I. S., Wahyu, Y. (2019). Selection index for selecting promising doubled haploid lines of black rice. Sabrao J. Breed. Genet. 51, 430–441.
Ansari, A., Lin, Y. P., Lur, H. S. (2021). Evaluating and adapting climate change impacts on rice production in Indonesia: A case study of the keduang subwatershed, Central Java. Environ. - MDPI 8, 1–17. doi: 10.3390/environments8110117
Anshori, M. F., Musa, Y., Farid, M., Jayadi, M., Bahrun, A. H., Yassi, A., et al. (2024). A new concept in assessing adaptability index for superior potential cropping intensity in early-maturing rice. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 8. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2024.1407880
Anshori, M. F., Purwoko, B. S., Dewi, I. S., Ardie, S. W., Suwarno, W. B. (2021). A new approach to select doubled haploid rice lines under salinity stress using indirect selection index. Rice Sci. 28, 368–378. doi: 10.1016/j.rsci.2021.05.007
Anshori, M. F., Purwoko, B. S., Dewi, I. S., Suwarno, W. B., Ardie, S. W. (2022). Salinity tolerance selection of doubled-haploid rice lines based on selection index and factor analysis. AIMS Agric. Food 7, 520–535. doi: 10.3934/agrfood.2022032
Arjasakusuma, S., Yamaguchi, Y., Hirano, Y., Zhou, X. (2018). ENSO-and rainfall-sensitive vegetation regions in Indonesia as identified from multi-sensor remote sensing data. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Information 7, 1–19. doi: 10.3390/ijgi7030103
Aswidinnoor, H., Listiyanto, R., Rahim, S., Holidin, Setiyowati, H., Nindita, A., et al. (2023). Stability analysis, agronomic performance, and grain quality of elite new plant type rice lines (Oryza sativa L.) developed for tropical lowland ecosystem. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 7. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2023.1147611
Barokah, U., Nugroho, R. J., Huda, M. (2021). Uji adaptasi varietas unggul baru padi sawah berbasis penerapan teknologi terpadu di kecamatan karangsambung kabupaten kebumen. CERMIN J. Penelit. 5, 36. doi: 10.36841/cermin_unars.v5i1.764
Barrios-Perez, C., Okada, K., Varón, G. G., Ramirez-Villegas, J., Rebolledo, M. C., Prager, S. D. (2021). How does El Niño Southern Oscillation affect rice-producing environments in central Colombia? Agric. For. Meteorol. 306, 1–14. doi: 10.1016/j.agrformet.2021.108443
Barth, E., de Resende, J. T. V., Mariguele, K. H., de Resende, M. D. V., da Silva, A. L. B. R., Ru, S. (2022). Multivariate analysis methods improve the selection of strawberry genotypes with low cold requirement. Sci. Rep. 12, 1–12. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-15688-4
Batista, L. G., Gaynor, R. C., Margarido, G. R. A., Byrne, T., Amer, P., Gorjanc, G., et al. (2021). Long-term comparison between index selection and optimal independent culling in plant breeding programs with genomic prediction. PLoS One 16, 1–5. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0235554
Bhati, M., Babu, G. S., Rajput, A. S. (2015). Genetic variability, correlation and path coefficient for grain yield and quantitative traits of elite rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes at Uttar Pradesh. Electron. J. Plant Breed. 6, 586–591.
Bin Rahman, A. N. M. R., Zhang, J. (2023). Trends in rice research: 2030 and beyond. Food Energy Secur. 12, 1–17. doi: 10.1002/fes3.390
Brown, D., Van den Bergh, I., de Bruin, S., Machida, L., van Etten, J. (2020). Data synthesis for crop variety evaluation. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 40, 1–20. doi: 10.1007/s13593-020-00630-7
Burgess, A. J., Masclaux-Daubresse, C., Strittmatter, G., Weber, A. P. M., Taylor, S. H., Harbinson, J., et al. (2023). Improving crop yield potential: Underlying biological processes and future prospects. Food Energy Secur. 12, 1–29. doi: 10.1002/fes3.435
Cassia, R., Nocioni, M., Correa-Aragunde, N., Lamattina, L. (2018). Climate change and the impact of greenhouse gasses: CO2 and NO, friends and foes of plant oxidative stress. Front. Plant Sci. 9. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.00273
Chen, H., Wu, Y. C., Cheng, C. C., Teng, C. Y. (2023). Effect of climate change-induced water-deficit stress on long-term rice yield. PLoS One 18, 1–14. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0284290
Chen, R., Li, D., Fu, J., Fu, C., Qin, P., Zhang, X., et al. (2024). Exploration of quality variation and stability of hybrid rice under multi-environments. Mol. Breed. 44, 1–21. doi: 10.1007/s11032-024-01442-3
Cherian, S., Sridhara, S., Manoj, K. N., Gopakkali, P., Ramesh, N., Alrajhi, A. A., et al. (2021). Impact of el niño southern oscillation on rainfall and rice production: A micro-level analysis. Agronomy 11, 1–18. doi: 10.3390/agronomy11061021
Debsharma, S. K., Syed, M. A., Ali, M. H., Maniruzzaman, S., Roy, P. R., Brestic, M., et al. (2023). Harnessing on genetic variability and diversity of rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes based on quantitative and qualitative traits for desirable crossing materials. Genes (Basel). 14, 1–21. doi: 10.3390/genes14010010
Dhakal, K., Yadaw, R. B., Baral, B. R., Pokhrel, K. R., Rasaily, S. (2021). Agro-morphological and genotypic diversity among rice germplasms under rainfed lowland condition. Agrivita 43, 466–478. doi: 10.17503/agrivita.v43i3.3026
Eckardt, N. A., Cutler, S., Juenger, T. E., Marshall-Colon, A., Udvardi, M., Verslues, P. E. (2023). Focus on climate change and plant abiotic stress biology. Plant Cell 35, 1–3. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koac329
Fadhilah, A. N., Farid, M., Ridwan, I., Anshori, M. F., Yassi, A. (2022). Genetic parameters and selection index of high-yielding tomato F2 populations. SABRAO J. Breed. Genet. 54, 1026–1036. doi: 10.54910/sabrao2022.54.5.6
Fahad, S., Bajwa, A. A., Nazir, U., Anjum, S. A., Farooq, A., Zohaib, A., et al. (2017). Crop production under drought and heat stress: Plant responses and management options. Front. Plant Sci. 8. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.01147
Fang, J., Zhang, F., Wang, H., Wang, W., Zhao, F., Li, Z., et al. (2019). Ef-cd locus shortens rice maturity duration without yield penalty. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 116, 18717–18722. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1815030116
Farid, M., Anhsori, M. F., Ridwan, I. (2022). Tomato F3 lines development and its selection index based on narrow sense heritability and factor analysis. Biodiversitas 23, 5790–5797. doi: 10.13057/biodiv/d231132
Farid, M., Anshori, M. F., Mantja, K., Ridwan, I., Adnan, A., Subroto, G. (2024). Selection of lowland tomato advanced lines using selection indices based on pca, path analysis, and the smith-hazel index. Sabrao J. Breed. Genet. 56, 708–718. doi: 10.54910/sabrao2024.56.2.22
Fellahi, Z. E. A., Hannachi, A., Bouzerzour, H. (2018). Analysis of direct and indirect selection and indices in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) segregating progeny. Int. J. Agron. 2018, 1–11. doi: 10.1155/2018/8312857
Fikri, M., Farid, M., Musa, Y., Anshori, M. F., Padjung, R., Nur, A. (2023). Multivariate analysis in the development of technology packages for corn cultivation by adding fertilizer to compost. Chil. J. Agric. Res. 83, 471–483. doi: 10.4067/S0718-58392023000400471
Finlay, K. W., Wilkinson, G. N. (1963). The analysis of adaptation in a plant-breeding programme and G. N. Wilkinson? By K. W. Finlay*. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 14, 742–754. doi: 10.1071/AR9630742
Fitrawaty, Hermawan, W., Yusuf, M., Maipita, I. (2023). A simulation of increasing rice price toward the disparity of income distribution: An evidence from Indonesia. Heliyon 9, e13785. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e13785
Fukagawa, N. K., Ziska, L. H. (2019). Rice: importance for global nutrition. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. (Tokyo). 65, S2–S3. doi: 10.3177/jnsv.65.S2
Geng, T., Jia, F., Cai, W., Wu, L., Gan, B., Jing, Z., et al. (2023). Increased occurrences of consecutive La Niña events under global warming. Nature 619, 774–781. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-06236-9
Ghazy, M. I., Abdelrahman, M., El-Agoury, R. Y., El-hefnawy, T. M., EL-Naem, S. A., Daher, E. M., et al. (2024). Exploring genetics by environment interactions in some rice genotypes across varied environmental conditions. Plants 13, 1–17. doi: 10.3390/plants13010074
Gupta, V., Kumar, M., Singh, V., Chaudhary, L., Yashveer, S., Sheoran, R., et al. (2022). Genotype by Environment Interaction Analysis for Grain Yield of Wheat (Triticum aestivum (L.) em.Thell) Genotypes. Agric. 12, 1–15. doi: 10.3390/agriculture12071002
Habib, M. A., Azam, M. G., Haque, M. A., Hassan, L., Khatun, M. S., Nayak, S., et al. (2024). Climate-smart rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes identification using stability analysis, multi-trait selection index, and genotype-environment interaction at different irrigation regimes with adaptation to universal warming. Sci. Rep. 14, 1–23. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-64808-9
Haile, B. T., Zeleke, T. T., Beketie, K. T., Ayal, D. Y., Feyisa, G. L. (2021). Analysis of El Niño Southern Oscillation and its impact on rainfall distribution and productivity of selected cereal crops in Kembata Alaba Tembaro zone. Clim. Serv. 23, 100254. doi: 10.1016/j.cliser.2021.100254
Hasan, M. J., Kulsum, M. U., Sarker, U., Matin, M. Q. I., Shahin, N. H., Kabir, M. S., et al. (2022). Assessment of GGE, AMMI, regression, and its deviation model to identify stable rice hybrids in Bangladesh. Plants 11, 1–26. doi: 10.3390/plants11182336
Hashim, N., Rafii, M. Y., Oladosu, Y., Ismail, M. R., Ramli, A., Arolu, F., et al. (2021). Integrating multivariate and univariate statistical models to investigate genotype–environment interaction of advanced fragrant rice genotypes under rainfed condition. Sustain. 13, 1–15. doi: 10.3390/su13084555
Hassani, M., Mahmoudi, S. B., Saremirad, A., Taleghani, D. (2023). Genotype by environment and genotype by yield*trait interactions in sugar beet: analyzing yield stability and determining key traits association. Sci. Rep. 13, 1–16. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-51061-9
Hilmarsson, H. S., Rio, S., Y Sánchez, J. I. (2021). Genotype by environment interaction analysis of agronomic spring barley traits in Iceland using ammi, factorial regression model and linear mixed model. Agronomy 11, 1–15. doi: 10.3390/agronomy11030499
Iftekharuddaula, K. M., Ahmed, H. U., Ghosal, S., Amin, A., Moni, Z. R., Ray, B. P., et al. (2016). Development of early maturing submergence-tolerant rice varieties for Bangladesh. F. Crop Res. 190, 44–53. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2015.12.001
Janni, M., Maestri, E., Gullì, M., Marmiroli, M., Marmiroli, N. (2023). Plant responses to climate change, how global warming may impact on food security: a critical review. Front. Plant Sci. 14. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1297569
Jia, W., Sun, M., Lian, J., Hou, S. (2022). Feature dimensionality reduction: a review. Complex Intell. Syst. 8, 2663–2693. doi: 10.1007/s40747-021-00637-x
Jia, Z. (2017). Controlling the overfitting of heritability in genomic selection through cross validation. Sci. Rep. 7, 1–9. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-14070-z
Johnstone, P., Manly, B. F. J. (2014). Analysis of variance through examples. Wiley StatsRef Stat. Ref. Online 1–16. doi: 10.1002/9781118445112.stat07533
Karbi, I., Chemke, R. (2023). A shift towards broader and less persistent Southern Hemisphere temperature anomalies. NPJ Clim. Atmos. Sci. 6, 1–7. doi: 10.1038/s41612-023-00526-9
Khairullah, I., Alwi, M., Annisa, W., Mawardi (2021). The fluctuation of rice production of tidal swampland on climate change condition (Case of South Kalimantan Province in Indonesia). IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 724, 0–7. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/724/1/012009
Khanna, A., Anumalla, M., Catolos, M., Bartholomé, J., Fritsche-Neto, R., Platten, J. D., et al. (2022). Genetic trends estimation in IRRIs rice drought breeding program and identification of high yielding drought-tolerant lines. Rice 15, 1–14. doi: 10.1186/s12284-022-00559-3
Kose, A., Onder, O., Bilir, O., Kosar, F. (2018). Application of multivariate statistical analysis for breeding strategies of spring safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.). Turkish J. F. Crop 23, 12–19. doi: 10.17557/tjfc.413818
Laraswati, A. A., Padjung, R., Farid, M., Nasaruddin, N., Anshori, M. F., Nur, A., et al. (2021). Image based-phenotyping and selection index based on multivariate analysis for rice hydroponic screening under drought stress. Plant Breed. Biotechnol. 9, 272–286. doi: 10.9787/PBB.2021.9.4.272
Li, R., Li, M., Ashraf, U., Liu, S., Zhang, J. (2019). Exploring the relationships between yield and yield-related traits for rice varieties released in China from 1978 to 2017. Front. Plant Sci. 10. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.00543
Marx, W., Haunschild, R., Bornmann, L. (2021). Heat waves: a hot topic in climate change research. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 146, 781–800. doi: 10.1007/s00704-021-03758-y
Mengesha, W., Menkir, A., Meseka, S., Bossey, B., Afolabi, A., Burgueno, J., et al. (2019). Factor analysis to investigate genotype and genotype × environment interaction effects on pro-vitamin A content and yield in maize synthetics. Euphytica 215, 1–15. doi: 10.1007/s10681-019-2505-3
Molenaar, H., Boehm, R., Piepho, H. P. (2018). Phenotypic selection in ornamental breeding: It’s better to have the BLUPs than to have the BLUEs. Front. Plant Sci. 871. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.01511
Murniati, K., Mutolib, A. (2020). The impact of climate change on the household food security of upland rice farmers in Sidomulyo, Lampung province, Indonesia. Biodiversitas 21, 3487–3493. doi: 10.13057/biodiv/d210809
Musa, Y., Farid, M., Nasaruddin, N., Anshori, M. F., Adzima, A. F., Maricar, M. F., et al. (2023). Sustainability approach in cropping intensity (CI) 400 through optimizing the dosage of compost and chemical fertilizers to early-maturing rice varieties based on multivariate analysis. J. Agric. Food Res. 14, 100907. doi: 10.1016/j.jafr.2023.100907
Nayak, P., Mukherjee, A. K., Pandit, E., Pradhan, S. K. (2018). Application of statistical tools for data analysis and interpretation in rice plant pathology. Rice Sci. 25, 1–18. doi: 10.1016/j.rsci.2017.07.001
Nur’utami, M. N., Hidayat, R. (2016). Influences of IOD and ENSO to Indonesian rainfall variability: role of atmosphere-ocean interaction in the indo-pacific sector. Proc. Environ. Sci. 33, 196–203. doi: 10.1016/j.proenv.2016.03.070
Oladosu, Y., Rafii, M. Y., Abdullah, N., Magaji, U., Miah, G., Hussin, G., et al. (2017). Genotype × Environment interaction and stability analyses of yield and yield components of established and mutant rice genotypes tested in multiple locations in Malaysia*. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B Soil Plant Sci. 67, 590–606. doi: 10.1080/09064710.2017.1321138
Olivoto, T., Diel, M. I., Schmidt, D., Lúcio, A. D. (2022). MGIDI: a powerful tool to analyze plant multivariate data. Plant Methods 18, 1–13. doi: 10.1186/s13007-022-00952-5
Olivoto, T., Lúcio, A. D. C., da Silva, J. A. G., Marchioro, V. S., de Souza, V. Q., Jost, E. (2019a). Mean performance and stability in multi-environment trials i: Combining features of AMMI and BLUP techniques. Agron. J. 111, 2949–2960. doi: 10.2134/agronj2019.03.0220
Olivoto, T., Lúcio, A. D. C., da Silva, J. A. G., Sari, B. G., Diel, M. I. (2019b). Mean performance and stability in multi-environment trials II: Selection based on multiple traits. Agron. J. 111, 2961–2969. doi: 10.2134/agronj2019.03.0221
Paiman, Isnawan, B. H., Aziez, A. F., Subeni, Salisu, M. A. (2022). The role of agronomic factors in salibu rice cultivation. Open Agric. J. 16, 1–7. doi: 10.2174/18743315-v16-e2112170
Panda, S., Naveen Kumar, R., Pavani S, L., Ganesan, S., Singh, P. K., Sah, R. P., et al. (2023). Multi-environment evaluation of rice genotypes: impact of weather and culm biochemical parameters against sheath blight infection. Front. Plant Sci. 14. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1280321
Pavithra, S., Vengadessan, V. (2020). Selection for drought tolerance in rice genotypes based on principal components and seletion indices. Electron. J. Plant Breed. 11, 1032–1036. doi: 10.37992/2020.1104.168
Piepho, H. P., Blancon, J. (2023). Extending Finlay–Wilkinson regression with environmental covariates. Plant Breed. 142, 621–631. doi: 10.1111/pbr.13130
Poli, Y., Balakrishnan, D., Desiraju, S., Panigrahy, M., Voleti, S. R., Mangrauthia, S. K., et al. (2018). Genotype × Environment interactions of Nagina22 rice mutants for yield traits under low phosphorus, water limited and normal irrigated conditions. Sci. Rep. 8, 1–13. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-33812-1
Pour-Aboughadareh, A., Khalili, M., Poczai, P., Olivoto, T. (2022). Stability indices to deciphering the genotype-by-environment interaction (GEI) effect: an applicable review for use in plant breeding programs. Plants 11, 1–24. doi: 10.3390/plants11030414
Pour-aboughadareh, A., Sanjani, S. (2021). MGIDI and WAASB indices : The useful approaches for selection of salt-tolerant barley genotype at the early growth and maturity stages. Preprint., 1–31. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-304576/v1
Purba, R., Giametri, Y. (2017). Performance of yields and profits in rice farming with the introduction of varieties in banten. J. Ilmu Pertan. Indones. 22, 13–19. doi: 10.18343/jipi.22.1.13
Qadir, A., Suhartanto, M. R., Widajati, E., Budiman, C., Zamzami, A., Rosyad, A., et al. (2024). Commercial rice seed production and distribution in Indonesia. Heliyon 10, e25110. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e25110
Rahimi, M., Debnath, S. (2023). Estimating optimum and base selection indices in plant and animal breeding programs by development new and simple SAS and R codes. Sci. Rep. 13, 1–8. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-46368-6
Ren, H., Bao, J., Gao, Z., Sun, D., Zheng, S., Bai, J. (2023). How rice adapts to high temperatures. Front. Plant Sci. 14. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1137923
Rismawati, Sadimantara, G. R., Usman, Leomo, S., Erawan, D., Samai, S. (2022). Effectiveness of NPK fertilizer on the growth of several new superior upland rice lines ( Oryza sativa L.) crosses from Southeast Sulawesi. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 977, 1–7. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/977/1/012010
Rocha, J. R., do, A. S., de, C., MaChado, J. C., Carneiro, P. C. S. (2018). Multitrait index based on factor analysis and ideotype-design: proposal and application on elephant grass breeding for bioenergy. GCB Bioenergy 10, 52–60. doi: 10.1111/gcbb.12443
Rodysill, J. R., Russell, J. M., Vuille, M., Dee, S., Lunghino, B., Bijaksana, S. (2019). La Nina-driven ~ flooding in the Indo-Pacific warm pool during the past millennium. Quat. Sci. Rev. 225, 106020. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2019.106020
Rohaeni, W. R., Ishaq, M. I. (2016). Evaluasi varietas padi sawah pada display varietas unggul baru (Vub) di kabupaten karawang, jawa barat. Agric 27, 1. doi: 10.24246/agric.2015.v27.i1.p1-7
Roy, D., Gaur, A. K., Pandey, I. D. (2022). Estimation of G x E Interaction by AMMI Model in ‘Antenna Panel’ Genotypes of Rice [Oryza sativa L. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 65, 1–14. doi: 10.1590/1678-4324-2022220202
Rozaki, Z. (2020). COVID-19, agriculture, and food security in Indonesia. Rev. Agric. Sci. 8, 243–261. doi: 10.7831/ras.8.0_243
Sabouri, H., Rabiei, B., Fazlalipour, M. (2008). Use of selection indices based on multivariate analysis for improving grain yield in rice. Rice Sci. 15, 303–310. doi: 10.1016/S1672-6308(09)60008-1
Sae-Lim, P., Komen, H., Kause, A., Mulder, H. A. (2014). Identifying environmental variables explaining genotype-by-environment interaction for body weight of rainbow trout (Onchorynchus mykiss): Reaction norm and factor analytic models. Genet. Sel. Evol. 46, 1–11. doi: 10.1186/1297-9686-46-16
Salah, A., Faysal, M., Ali, L., Azam, G., Sarker, U., Ercisli, S., et al. (2022). Genetic variability, character association, and path coefficient analysis in transplant aman rice genotypes. Plants 11, 1–15. doi: 10.3390/plants11212952
Saltz, J. B., Bell, A. M., Flint, J., Gomulkiewicz, R., Hughes, K. A., Keagy, J. (2018). Why does the magnitude of genotype-by-environment interaction vary? Ecol. Evol. 8, 6342–6353. doi: 10.1002/ece3.4128
Saminadane, T., Geddam, S., Krishnaswamy, P., Jothiganapathy, K., Tamilselvan, A., Ramadoss, B. R., et al. (2023). Development of early maturing salt-tolerant rice variety KKL(R) 3 using a combination of conventional and molecular breeding approaches. Front. Genet. 14. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1332691
Sánchez-Bermúdez, M., del Pozo, J. C., Pernas, M. (2022). Effects of combined abiotic stresses related to climate change on root growth in crops. Front. Plant Sci. 13. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.918537
Santos, C., Martins, D. C., González-Bernal, M. J., Rubiales, D., Vaz Patto, M. C. (2022). Integrating phenotypic and gene expression linkage mapping to dissect rust resistance in chickling pea. Front. Plant Sci. 13. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.837613
Sarwendah, M., Lubis, I., Junaedi, A., Purwoko, B. S., Sopandie, D., Dewi, A. K. (2022). Application of selection index for rice mutant screening under a drought stress condition imposed at reproductive growth phase. Biodiversitas 23, 5446–5452. doi: 10.13057/biodiv/d231056
Sato, H., Mizoi, J., Shinozaki, K., Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. (2024). Complex plant responses to drought and heat stress under climate change. Plant J. 117, 1873–1892. doi: 10.1111/tpj.16612
Schmidt, P., Hartung, J., Bennewitz, J., Hans-Peter, P. (2019). Heritability in plant breeding on a genotype-difference basis. Genetics 212, 991–1008. doi: 10.1534/genetics.119.302134
Seck, F., Covarrubias-Pazaran, G., Gueye, T., Bartholomé, J. (2023). Realized genetic gain in rice: achievements from breeding programs. Rice 16, 1–22. doi: 10.1186/s12284-023-00677-6
Seleiman, M. F., Al-Suhaibani, N., Ali, N., Akmal, M., Alotaibi, M., Refay, Y., et al. (2021). Drought stress impacts on plants and different approaches to alleviate its adverse effects. Plants 10, 1–25. doi: 10.3390/plants10020259
Sen, S., Chakraborty, R., Kalita, P. (2020). Rice - not just a staple food: A comprehensive review on its phytochemicals and therapeutic potential. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 97, 265–285. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2020.01.022
Shanmugam, A., Manivelan, K., Deepika, K., Nithishkumar, G., Blessy, V., Monihasri, R. B., et al. (2023). Unraveling the genetic potential of native rice (Oryza sativa L.) landraces for tolerance to early-stage submergence. Front. Plant Sci. 14. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1083177
Sharifi, P., Erfani, A., Abbasian, A., Mohaddesi, A. (2020). Stability of some of rice genotypes based on WAASB and MTSI indices. Iran. J. Genet. Plant Breed. 9, 1–11. doi: 10.30479/ijgpb.2021.14432.1283
Sheng, R. T. C., Huang, Y. H., Chan, P. C., Bhat, S. A., Wu, Y. C., Huang, N. F. (2022). Rice growth stage classification via RF-based machine learning and image processing. Agric. 12, 1–23. doi: 10.3390/agriculture12122137
Simmer, R. A., Jansen, E. J., Patterson, K. J., Schnoor, J. L. (2023). Climate change and the sea: A major disruption in steady state and the master variables. ACS Environ. Au 3, 195–208. doi: 10.1021/acsenvironau.2c00061
Singh, G., Khanna, R., Kaur, R., Kaur, K., Kaur, R., Sharma, N., et al. (2023). Performance under multi-environment trial for quantitative traits of rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes in North-West India (Punjab). Ecol. Genet. Genom. 28, 100190. doi: 10.1016/j.egg.2023.100190
Sitaresmi, T., Hairmansis, A., Widyastuti, Y., Susanto, U., Pramono, B., Landep, M., et al. (2023). Advances in the development of rice varieties with better nutritional quality in Indonesia. J. Agric. Food Res. 12, 100602. doi: 10.1016/j.jafr.2023.100602
Sitaresmi, T., Willy, S., Gunarsih, C., Nafisah, N., Nugraha, Y., Sasmita, P., et al. (2019). Comprehensive stability analysis of rice genotypes through multi-location yield trials using pbstat-ge. Sabrao J. Breed. Genet. 51, 355–372. Available at: https://data.cimmyt.org.
Sjahril, R., Trisnawaty, A. R., Riadi, M., Rafiuddin, Sato, T., Toriyama, K., et al. (2020). Selection of early maturing and high yielding mutants of Toraja local red rice grown from M2-M3 population after ion beam irradiation. Hayati J. Biosci. 27, 166–173. doi: 10.4308/hjb.27.2.166
Smith, A., Norman, A., Kuchel, H., Cullis, B. (2021). Plant variety selection using interaction classes derived from factor analytic linear mixed models: models with independent variety effects. Front. Plant Sci. 12. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.737462
Sood, S., Bhardwaj, V., Kaushik, S. K., Sharma, S. (2020). Prediction based on estimated breeding values using genealogy for tuber yield and late blight resistance in auto-tetraploid potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Heliyon 6, e05624. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e05624
Statistic Indonesia. (2023a). Catalog : 1101001. Stat. Indones. Available online at: https://www.bps.go.id/publication/2020/04/29/e9011b3155d45d70823c141f/statistik-Indonesia-2020.html (accessed July 3, 2024)
Statistic Indonesia (2023b). Luas Panen dan Produksi Padi di Indonesia 2023 (Angka Tetap). Jakarta: Stat. Indonesia, 1–8. Available at: https://www.bps.go.id/pressrelease/2023/10/16/2037 (accessed [July 3, 2024]).
Subekti, A., Umar, A. (2022). Keragaan dua belas varietas unggul baru padi pada agroekosistem lahan pasang surut di kalimantan barat. Agrica Ekstensia 16, 8–13. doi: 10.55127/ae.v16i1.112
Sudana, W. (2016). Pola penelitin vs pola tanam petani Response to IP Padi 400 Policy : The Improved vs the Existing Cropping Patterns. Anal. Kebijak. Pertan. 8, 103–117. Available at: https://epublikasi.pertanian.go.id/berkala/akp/article/view/745.
Sulaiman, A., Osaki, M., Takahashi, H., Yamanaka, M. D., Susanto, R. D., Shimada, S., et al. (2023). Peatland groundwater level in the Indonesian maritime continent as an alert for El Niño and moderate positive Indian Ocean dipole events. Sci. Rep. 13, 1–12. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-27393-x
Sumuni, S. M., Kaur, R., Kaur, R., Khanna, R., Kaur, K., Lore, J. S., et al. (2024). Multivariate analysis for morpho-physiological and milling traits along with molecular profiling of known bacterial blight resistance genes in advanced breeding lines of rice. Cereal Res. Commun. 52, 759–775. doi: 10.1007/s42976-023-00412-3
Sun, R., Li, J., Feng, J., Hou, Z., Zhang, Y. (2020). Contrasting impacts of two types of El Niño on productivitys of early rice in Southern China. Agron. J. 112, 1084–1100. doi: 10.1002/agj2.20014
Sutardi, Apriyana, Y., Rejekiningrum, P., Alifia, A. D., Ramadhani, F., Darwis, V., et al. (2023). The transformation of rice crop technology in Indonesia: innovation and sustainable food security. Agronomy 13, 1–14. doi: 10.3390/agronomy13010001
Tavakol, M., Wetzel, A. (2020). Factor Analysis: a means for theory and instrument development in support of construct validity. Int. J. Med. Educ. 11, 245–247. doi: 10.5116/ijme.5f96.0f4a
van Eeuwijk, F. A., Bustos-Korts, D., Millet, E. J., Boer, M. P., Kruijer, W., Thompson, A., et al. (2019). Modelling strategies for assessing and increasing the effectiveness of new phenotyping techniques in plant breeding. Plant Sci. 282, 23–39. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2018.06.018
Wang, B., Sun, W., Jin, C., Luo, X., Yang, Y. M., Li, T., et al. (2023). Understanding the recent increase in multiyear La Niñas. Nat. Clim. Change 13, 1075–1081. doi: 10.1038/s41558-023-01801-6
Widiastuti, N. N., Lestari, E., Permatasari, P. (2023). Farmer participation in IP400 rice cultivation in kebakkramat district karanganyar regency. Indones. J. Soc Responsib. Rev. 2, 128–139. doi: 10.55381/ijsrr.v2i2.188
Yadav, M., Vashisht, B. B., Jalota, S. K., Jyolsna, T., Singh, S. P., Kumar, A., et al. (2024). Improving Water efficiencies in rural agriculture for sustainability of water resources: A review. Water Resour. Manage. 38, 3505–3526. doi: 10.1007/s11269-024-03836-6
Yang, R. C. (2014). Analysis of linear and non-linear genotype × environment interaction. Front. Genet. 5. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2014.00227
Yang, S., Li, Z., Yu, J. Y., Hu, X., Dong, W., He, S. (2018). El Niño-Southern Oscillation and its impact in the changing climate. Natl. Sci. Rev. 5, 840–857. doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwy046
Yuan, S., Stuart, A. M., Laborte, A. G., Rattalino Edreira, J. I., Dobermann, A., Kien, L. V. N., et al. (2022). Southeast Asia must narrow down productivity gap to continue to be a major rice bowl. Nat. Food 3, 217–226. doi: 10.1038/s43016-022-00477-z
Yun, Y., Kim, G., Cho, G., Lee, Y., Yun, T., Kim, H. (2023). Effect of nitrogen application methods on yield and grain quality of an extremely early maturing rice variety. Agric. 13, 1–14. doi: 10.3390/agriculture13040832
Keywords: BLUP, early-maturity rice, GxE analysis, index regression, oryza sativa
Citation: Anshori MF, Musa Y, Farid M, Jayadi M, Padjung R, Kaimuddin K, Huang YC, Casimero M, Bogayong I, Suwarno WB, Sembiring H, Purwoko BS, Nur A, Wahyuni W, Wasonga DO and Seleiman MF (2024) A comprehensive multivariate approach for GxE interaction analysis in early maturing rice varieties. Front. Plant Sci. 15:1462981. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1462981
Received: 11 July 2024; Accepted: 13 September 2024;
Published: 01 October 2024.
Edited by:
Linghe Zeng, United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), United StatesReviewed by:
Antônio Teixeira Do Amaral, State University of Northern Rio de Janeiro, BrazilGurjeet Singh, Texas A and M University, United States
Copyright © 2024 Anshori, Musa, Farid, Jayadi, Padjung, Kaimuddin, Huang, Casimero, Bogayong, Suwarno, Sembiring, Purwoko, Nur, Wahyuni, Wasonga and Seleiman. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Muhammad Fuad Anshori, ZnVhZC5hbnNob3JpQHVuaGFzLmFjLmlk
 Muhammad Fuad Anshori
Muhammad Fuad Anshori Yunus Musa1
Yunus Musa1 Madonna Casimero
Madonna Casimero Willy Bayuardi Suwarno
Willy Bayuardi Suwarno Hasil Sembiring
Hasil Sembiring Bambang Sapta Purwoko
Bambang Sapta Purwoko Mahmoud F. Seleiman
Mahmoud F. Seleiman