
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Plant Sci. , 04 November 2024
Sec. Functional Plant Ecology
Volume 15 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2024.1459058
Vegetation serves as a crucial indicator of ecological environment and plays a vital role in preserving ecosystem stability. However, as urbanization escalates rapidly, natural vegetation landscapes are undergoing continuous transformation. Paradoxically, vegetation is pivotal in mitigating the ecological and environmental challenges posed by urban sprawl. The middle and lower Yangtze River Basin (MLYRB) in China, particularly its economically thriving lower reaches, has witnessed a surge in urbanization. Consequently, this study explored the spatiotemporal variations of normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) in the MLYRB, with an emphasis on elucidating the impact of climate change and urbanization on vegetation dynamics. The results indicate that a significant increasing trend in NDVI across the MLYRB from 2000 to 2020, a pattern that is expected to persist. An improvement in vegetation was observed in 94.12% of the prefecture-level cities in the study area, predominantly in the western and southern regions. Temperature and wind speed stand out as dominant contributors to this improvement. Nevertheless, significant vegetation degradation was detected in some highly urbanized cities in the central and eastern parts of the study area, mainly attributed to the negative effects of escalating urbanization. Interestingly, a positive correlation between NDVI and the urbanization rate was observed, which may be largely related to proactive ecological preservation policies. Additionally, global climatic oscillations were identified as a key force driving periodic NDVI variations. These findings hold significant importance in promoting harmonious urbanization and ecological preservation, thereby providing invaluable insights for future urban ecological planning efforts.
Climate warming stands as one of the pressing environmental concerns globally, posing a substantial challenge to achieving the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The greenhouse effect, primarily caused by CO2 emissions, is a significant contributor to this warming (IPCC, 2014)., Notably, vegetation performs a critical function in sequestering carbon within the global carbon cycle (Chen et al., 2020; Wu et al., 2023), thereby assisting in climate warming mitigation. Meanwhile, the health and distribution of vegetation are paramount in attaining the SDGs. Hence, monitoring vegetation dynamics aids not just in evaluating ecosystem functions but also furnishes vital insights for formulating and executing effective ecological management tactics (Gao et al., 2022).
Under the combined influences of climate change and human intervention, vegetation cover of the underlying surface has undergone substantial transformation (Huang et al., 2021b; Piao et al., 2019). Specifically, there has been a general upward trend in vegetation cover in the mid-latitudes of the Northern Hemisphere (Myneni et al., 1997; Zheng et al., 2021). Likewise, Africa has witnessed a slight increase in vegetation greenness (Umuhoza et al., 2023). A greening trend is also evident in karst areas globally (Huang et al., 2022). In contrast, North America and Southwest Asia have experienced severe vegetation degradation (Lotsch et al., 2005). In China, while there is an overall increase in vegetation, certain areas such as Northeast China, northern Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, and the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau have seen notable vegetation degradation (Zhou et al., 2020). Alarmingly, there are indications that vegetation browning may become a more prevalent phenomenon in the foreseeable future (Liu et al., 2023b). Evidently, the intricate interactions between climate change and anthropogenic activities are responsible for the conspicuous regional disparities in vegetation dynamics.
Despite the widespread recognition that both climate change and human intervention affects vegetation dynamics, quantifying the relative contributions of these factors to vegetation changes remains a challenge. Currently, scholars primarily utilize statistical methods such as Pearson correlation (Chu et al., 2019), partial correlation (Xie et al., 2022), and multiple linear regression (Long et al., 2023) to establish a direct linear connection between vegetation patterns and climatic conditions. This process aids in determining the specific role played by climatic variables in vegetation dynamics. In terms of assessing the impact of human intervention on vegetation, common quantitative techniques include the use of geographic detector (Zheng et al., 2021) and residual analysis (Lamchin et al., 2020; Liu et al., 2022; Qi et al., 2019). However, given that the multifaceted nature of anthropogenic impacts, these methods often struggle to precisely distinguish the contribution of specific human-induced factors to vegetation changes, which may lead to potential biases in estimating the influence of anthropogenic activities. Additionally, as spatial distance from human activity areas gradually increases, the impact of anthropogenic factors on vegetation tends to progressively weaken until it disappears completely (Bernier et al., 2017; Yi et al., 2021a).
In recent years, climate change has emerged as the primary driving force behind changes in global vegetation greenness (Lamchin et al., 2020; Lawal et al., 2019). To some extent, increasing temperature can enhance vegetation photosynthesis and extend the growing season (Shen et al., 2014). Meanwhile, precipitation serves as an crucial water source for vegetation growth (Wang et al., 2022b). Nevertheless, the impact and magnitude of temperature and precipitation on vegetation vary greatly across diverse eco-geographical regions. For instance, vegetation growth in arid regions is mainly limited by soil moisture (Du et al., 2019b), whereas temperature plays a pivotal role in high-altitude regions (Li et al., 2019). Importantly, the effect of temperature and precipitation on vegetation does not follow a linear enhancement pattern. Extreme climatic conditions, resulting from excessively high temperatures and heavy precipitation, can negatively affect vegetation growth (Zhang, 2020).
The relationship between urbanization and vegetation evolution is intimate. Rapid urban expansion has resulted in a notable surge of impervious surfaces, thereby exerting a conspicuous negative influence on vegetation (Yan et al., 2019). This phenomenon is evident in numerous cities worldwide (De Carvalho and Szlafsztein, 2019; De La Barrera and Henríquez, 2017; Wu et al., 2019). Conversely, changes in vegetation serve as a mirror, reflecting urbanization’s imprint on the terrain and ecological ambiance. To illustrate, the demolition of vegetation has the potential to spark urban environmental challenges (IPCC, 2014), ultimately impinging on the stability and service functions of urban ecosystems (Alpaidze and Salukvadze, 2023). However, cities ironically offer novel habitats for vegetation. Research indicates that urbanization bears an indirect positive effect on vegetation, evident in the amplified growth of vegetation within urban boundaries over time (Zhang et al., 2022a). In addition, this indirect effect is further shaped by a blend of climatic and anthropogenic factors, which, to a certain degree, counteract the negative direct impact of urbanization.
Previous studies on vegetation dynamics in China primarily focused on geographically delimited areas, particularly emphasizing specific regions such as the Yangtze River Basin (Wang et al., 2022a), the Yellow River Basin (Liu et al., 2023a), the Loess Plateau (Li et al., 2021a), and the Tibetan Plateau (Li et al., 2019). Nevertheless, these macroscopic studies often overlook intricate details concerning vegetation changes. The middle and lower Yangtze River Basin (MLYRB), a densely populated and highly urbanized area in China, highlights the importance of understanding the effects of urban sprawl on vegetation. Additionally, quantitative investigations into the impact of urbanization on vegetation remains scarce. Therefore, the primary goals of this study were to: (1) reveal the unique regional and municipal patterns of past and future vegetation variations in the MLYRB; (2) explore the interplay between vegetation and climate variability; and (3) analyze the impact of urbanization on vegetation changes.
The MLYRB, situated between 24°30′−34°10′ N and 105°52′−122°25′ E, lies in the southern parts of the central and eastern China. This vast region encompasses 13 provincial-level and 68 city-level administrative regions (Figure 1), with a total area of approximately 78.64×104 km2. By 2020, the urbanization rate in the basin had surpassed 58%, making it as one of China’s most urbanized levels and densely populated areas. The terrain of the MLYRB is predominantly flat, featuring plains such as the Jianghan-Dongting Lake Plain (also known as the Lianghu Plain), Poyang Lake Plain, and Central Anhui Riverside Plain. The MLYRB boasts a dense network of rivers and abundant water resources, including freshwater lakes like Dongting Lake, Poyang Lake, Taihu Lake, and Chaohu Lake. Characterized by a subtropical monsoon climate, the basin experiences moderate temperature and abundant rainfall. The annual average temperature ranges from 8.79 to 20.50 °C, while the yearly precipitation varies between 643.19 mm and 2358.40 mm. These climatic conditions foster healthy vegetation growth, favoring both forests and croplands. However, from August to October every year, as the East Asian summer monsoon shifts southward, abnormal monsoon rain belts can cause floods in MLYRB (Li et al., 2022). Correspondingly, excessive precipitation in the study area can trigger hypoxia in the root systems of surface vegetation, hindering their growth or even causing plant death. Additionally, excessively high summer temperature can elevate vegetation evaporation, potentially leading to droughts that inhibit vegetation growth in the study area (Huang et al., 2021a).
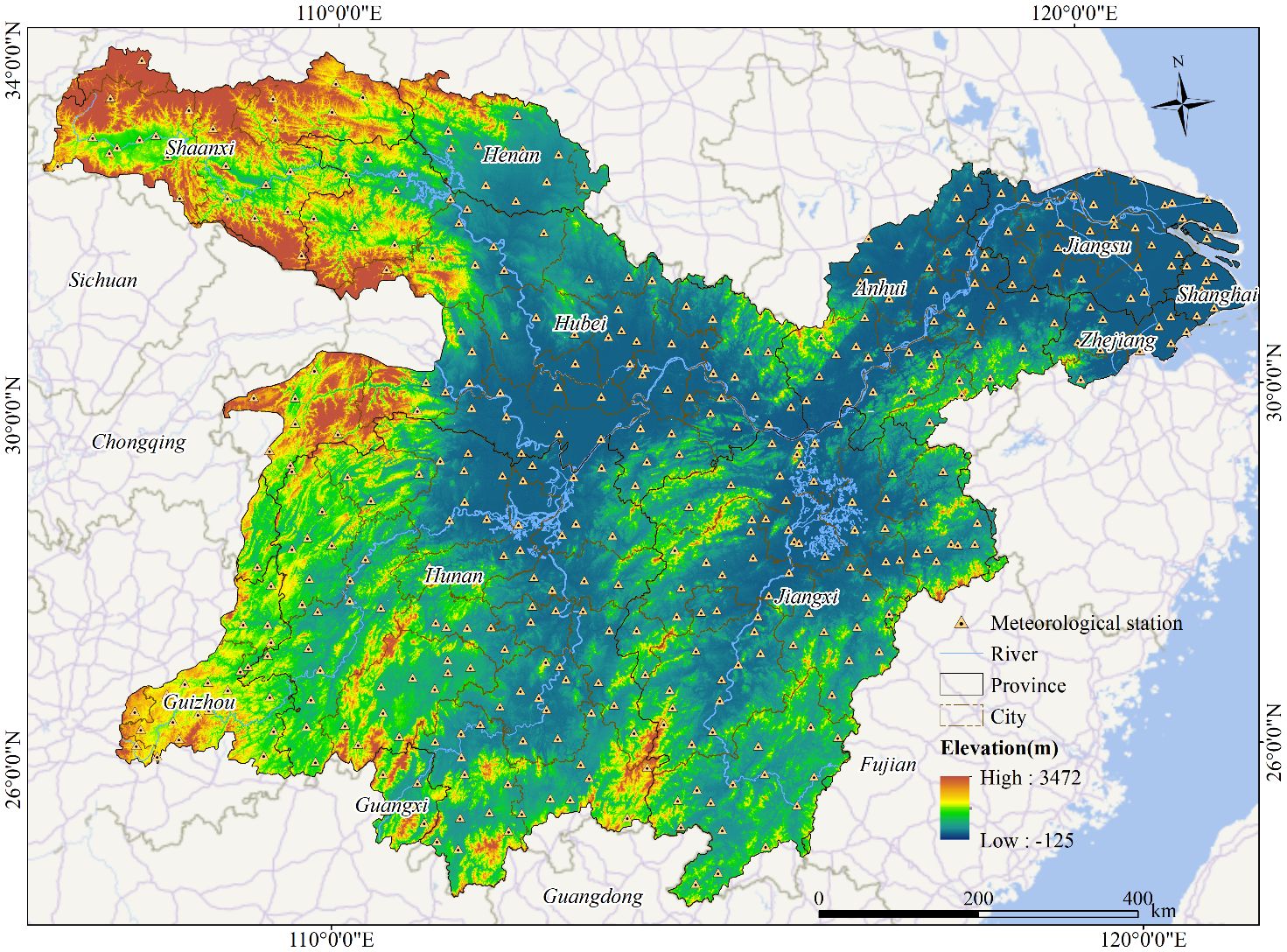
Figure 1. Spatial distribution of provinces, cities, meteorological stations, main rivers, and digital elevation model in the middle and lower Yangtze River Basin, China.
The MODIS normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) time series data utilized in this study, spanning from 2000 to 2020, were sourced from the Land, Atmosphere Near-real-time Capability for EOS (LANCE) system, accessible at https://ladsweb.modaps.eosdis.nasa.gov/. These data were archived in the HDF format, featuring a temporal resolution of 16 days and a spatial resolution of 250 meters. The MODIS Reprojection Tool, provided by the United States Geological Survey (USGS), facilitated the mosaicking, format conversion, and projection of the MODIS data. To account for missing data in January and February of 2000, multi-year synchronous average values were utilized. Monthly NDVI datasets were created using the maximum-value composites procedure to minimize the effects of cloud cover, atmospheric conditions, and solar zenith angle variability. Subsequently, the mean method was applied to generate annual NDVI datasets, aiming to mitigate the impact of climatic anomalies on NDVI in certain months as much as possible.
Generally, the calculation of NDVI is highly correlated with near-infrared and red bands. Falling within the range of [−1, 1], this index effectively indicates vegetation growth status. Specifically, a negative NDVI value signifies the presence of ground cover, such as clouds, water, or snow. Conversely, a positive value denotes vegetation cover, with values closer to 1 exhibiting a greater degree of coverage. Furthermore, an NDVI nearing 0 suggests the existence of rocks, bare soil, or other unvegetated surfaces.
The meteorological data utilized in this study were obtained from the Hunan Meteorological Bureau. It encompassed various climatic variables for the MLYRB during 2000−2020, including the annual average temperature (°C), annual average relative humidity (%), annual average wind speed (m·s−1), annual total precipitation (mm), and annual total sunshine duration (h). This dataset was derived from the climate records of 410 Chinese national meteorological stations within the study area. Also, this dataset was interpolated by the Inverse Distance Weighting (IDW) method to generate meteorological raster data with the same projection and resolution as the NDVI dataset, enabling an analysis of the contribution of climatic variables to NDVI changes.
Additionally, this study delved into the influence of global-scale climate oscillations on the periodic variations in NDVI. The specific climate indices examined include the Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation (AMO), North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO), Pacific Decadal Oscillation (PDO), and Southern Oscillation Index (SOI). These data were sourced from the Physical Science Laboratory of National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) (https://psl.noaa.gov/) and National Climate Prediction Center of NOAA (https://www.cpc.ncep.noaa.gov/).
The Digital Elevation Model (DEM) was accessed from the Geospatial Data Cloud Platform (http://www.gscloud.cn/). Administrative division vector data was procured from the Data Center for Resource and Environment Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences (http://www.resdc.cn/). Details of El Niño and La Niña events occurring since 2000 were gathered from the National Climate Center of China website (http://cmdp.ncc-cma.net/). In addition, the annual urbanization rate data for each county from 2003 to 2020 was extracted from the China Statistical Yearbook, published by the China National Bureau Statistics (http://www.stats.gov.cn/).
The integration of Sen’s slope estimator (SSE) and Mann-Kendall (M-K) significance test has proven highly effective in discerning trends in vegetation cover, be it increasing or decreasing. This combined approach has gained widespread application in hydrological and meteorological research (Tong et al., 2018; Zhang and Jin, 2021). SSE, recognized as a robust non-parametric statistical method (Sen, 1968; Theil, 1992), excels at minimizing the influence of error and outliers in the raw data on statistical outcomes. In this research, this method was applied to estimate the trend in NDVI. A positive or negative value of the estimated result indicates corresponding upward or downward trend in NDVI, respectively. Additionally, the M-K test (Kendall, 1975; Mann, 1945) was leveraged to determine the statistical significance of these NDVI trends. In the context of a two-tailed trend test, if the standardized test statistic meets or exceeds the thresholds of 1.96 and 2.58, it signifies that the observed trend has passed the significance test, corresponding to confidence levels of and , respectively.
The Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average (ARIMA) model, originally introduced by Box and Jenkins (Box and Jenkins, 1970), stands as a prevalent time series forecasting model. Given that time series data often exhibits patterns of periodicity or seasonality, the ARIMA model can be extended to the Seasonal Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average (SARIMA) model. This method is denoted as , wherein p and P represent the autoregressive order and the seasonal autoregressive order, respectively. Similarly, d and D indicate the trend differences and the seasonal difference order, while q and Q signify the moving average order and the seasonal moving average order, respectively. Additionally, S depicts the seasonal cycle length. Regarding the NDVI time series training set employed in this study, the SARIMA model can be expressed as follows:
where refers to the d-order difference; is the D-order seasonal difference with S as the period; denotes the q-order moving average coefficient polynomial, B represents the lag operator, and ; signifies the p-order autoregressive coefficient polynomial; corresponds to the Q-order seasonal moving average coefficient polynomial; depicts the P-order seasonal autoregressive coefficient polynomial; and indicates the random disturbance of error term at time t.
Compared to the single-factor correlation, multi-factor analysis offers a more comprehensive understanding of the relationship between NDVI and diverse climatic factors. The multiple linear regression (MLR) model is instrumental in examining the interplay between a dependent variable and multiple independent variables (Fu et al., 2022, 2024). In this study, the model was employed to evaluate how temperature, precipitation, relative humidity, sunshine duration, and wind speed affect NDVI. To neutralize the impacts caused by the different dimensions of climatic variables, it is necessary to standardize these variables before applying the MLR. The formula for MLR can be described below:
where refers to the NDVI time series; , , , , and represent the time series for temperature, precipitation, relative humidity, sunshine duration, and wind speed, respectively; denotes a constant; is the standard regression coefficients. The absolute values of these coefficients indicate the significance of each climatic variable to NDVI. A larger absolute value of the coefficient implies a greater impact of that particular climatic variable. The relative contribution of various climatic variables to NDVI can be determined by computing the ratio of the absolute value of each variable’s coefficient to the sum of the absolute values of all climatic variable coefficients.
Cross wavelet transform (XWT) integrates wavelet transform (WT) with cross-spectrum analysis, enabling the precise identification of the significant interactions between two time series across various time-frequency domains. Furthermore, XWT reveals the correlation consistency among sequences and elucidates their phase relationships in the time-frequency space. Assuming and represent the XWT of two time series, X and Y respectively, and their cross wavelet power spectrum (CWPS) was defined as (Torrence and Compo, 1998)
where the absolute value of the left-hand side of the equation corresponds to the density of the CWPS. A larger absolute value indicates a more significant correlation between the high-energy regions of two time series.
Provided that the expected spectra of both time series X and Y are red noise spectra, denoted as and respectively, the distribution relationship of the CWPS can be expressed as follows:
where , represent the standard deviations of time series X and Y, respectively; v denotes the degrees of freedom for the Morlet wavelet transform, specifically set at 2. If the left-hand side of the equation exceeds the upper confidence limit of the 95% red noise power spectrum, it is considered to have passed the significance level test at . Furthermore, refers to the confidence level linked to the probability p, and at the significance level of .
Wavelet coherence (WTC) addresses the limitations of cross wavelet in detecting correlations between time series, particularly in low-energy region. The WTC can be written as
where S refers to the smoother; s signifies the companion scaling of wavelet function; represents modulus for a complex number; denotes the cross product of wave amplitude at certain frequency from two time series; and are the amplitudes of vibration waves in two time series.
Pearson correlation analysis is a wide-used statistical method. The Pearson correlation coefficient can effectively express the degree and direction of a relationship, thereby reflecting connections between different elements (Pearson, 1920). In this research, this method was utilized to analyze the correlation between the urbanization rate and NDVI from 2003 to 2020. The formula for the calculation is as follows:
where represents the correlation coefficient; , signify the annual urbanization rate and NDVI, respectively, while , correspond to the average urbanization rate and average NDVI over the study period; i refers to the year index (ranging from 1 to 18); n indicates the duration of the research, and n =18. Generally, if > 0, it suggests a positive correlation between the two variables; conversely, a negative coefficient describes a negative correlation. Also, the closer the absolute value of approaches 1, the stronger the positive (or negative) correlation. Additionally, when the correlation coefficient meets the significance test criteria with a significance level of 95% or above, it demonstrates a statistically significant correlation between NDVI and the urbanization rate.
The annual average NDVI in the MLYRB rose from 0.54 to 0.62, stabilizing at approximately 0.59. This upward trend was highly significant, with an increment of 0.0034 year−1 (P < 0.01) (Figure 2). The NDVI peaked in 2018. By referencing the 2018 China Ecological Meteorological Bulletin and the meteorological data of this study, it becomes evident that the majority of the study area enjoyed ample water and warmth in 2018, while meteorological disasters such as droughts and heavy rains had minimal impact. Such climatic conditions are conducive to vegetation growth, and China’s ecological projects have borne positive outcomes. This could explain why the NDVI attained the highest value in 2018. Conversely, the lowest NDVI was occurred in 2000. This can be attributed to the heavy emphasis on economic development during that period, coupled with the lack of comprehensive environmental safeguards and the overexploitation of vegetation resources. The most rapid growing phase of NDVI occurred between 2012 and 2018 (0.0067 year−1), followed by the period during 2000−2007 (0.0042 year−1). In contrast, the steepest decline in NDVI was witnessed from 2018 to 2020 (−0.0025 year−1), preceded by a milder drop from 2007 to 2012 (−0.0017 year−1).
As shown in Figure 3, five cities in the MLYRB with the highest NDVI over the past 21 years were Huangshan, Jingdezhen, Ganzhou, Enshi Tujia and Miao Autonomous Prefecture (ETMAP), and Huaihua in China. These cities boasted NDVI values of 0.705, 0.664, 0.662, 0.658, 0.655, respectively. In contrast, the lowest NDVI values were observed in Suzhou and Wuxi, at 0.311 and 0.392, respectively. Notably, the NDVI in the central-western region of the study area is significantly higher than that in the eastern region.
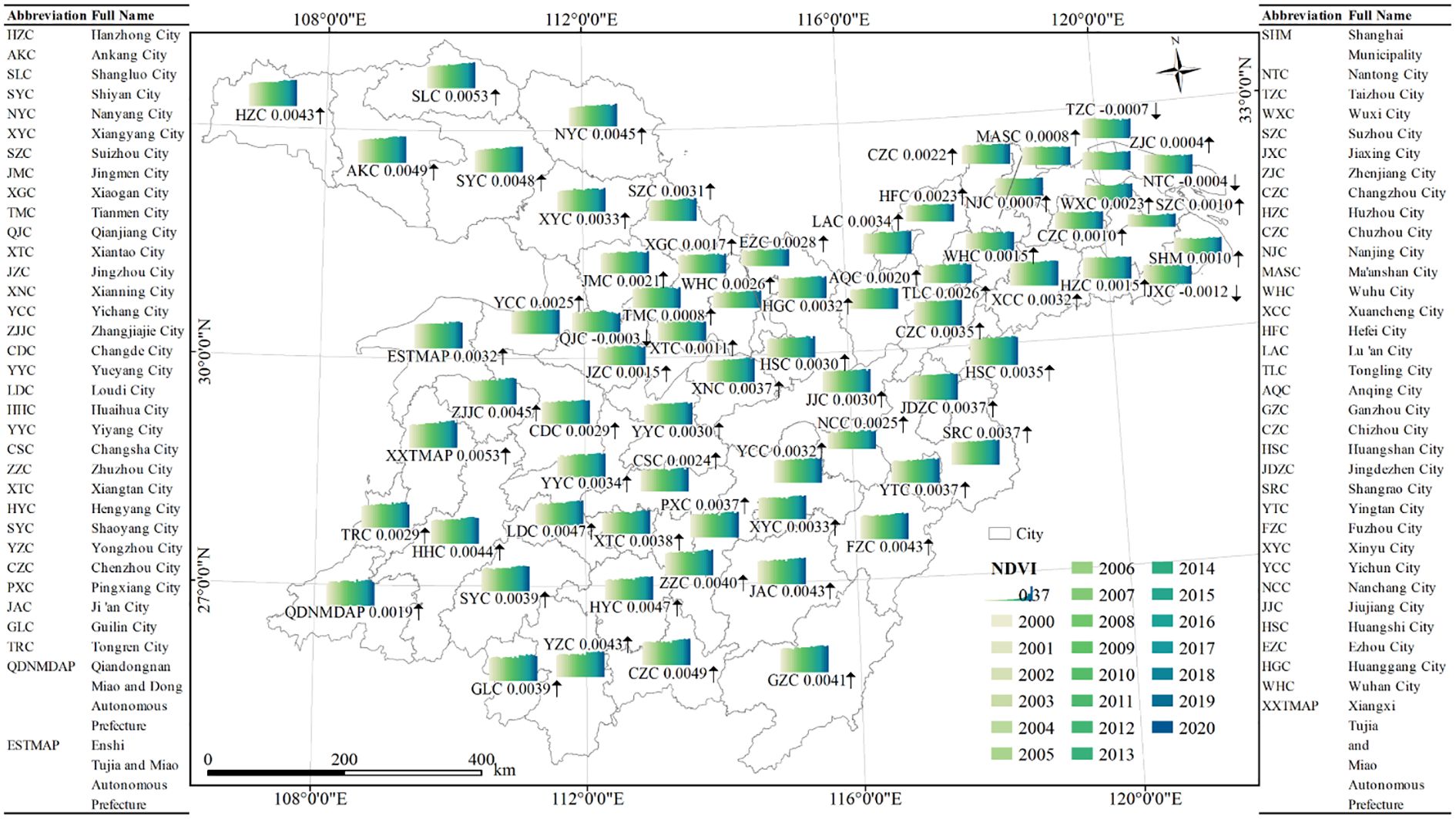
Figure 3. Temporal variations of NDVI at the city scale in the study area, 2000−2020. The arrow symbols, specifically ↑ and ↓, denote upward and downward trends, respectively. HZC stands for Hangzhou City, with similar abbreviations employed for the other cities represented.
Regarding the growth rate of NDVI, most cities displayed an upward trend, accounting for 94.12% of the total cities in the study area. Specifically, Shangluo, Xiangxi Tujia and Miao Autonomous Prefecture, Chenzhou, Ankang, and Shiyan exhibited pronounced growth trends, with rates of 0.0053 year−1, 0.0053 year−1, 0.0049 year−1, 0.0049 year−1, and 0.0048 year−1, respectively. The Yangtze River Delta region (YRD) stands out for its high urbanization level and consequent vegetation degradation. Within this region, Jiaxing experienced the steepest NDVI decline at −0.0012 year−1, followed by Taizhou (−0.0007 year−1) and Nantong (−0.0004 year−1). In addition, Qianjiang also manifested a downward trend in NDVI with a decrease rate of −0.0003 year−1.
Overall, the majority of the MLYRB was well-covered with vegetation (Figure 4A). Spatially, NDVI predominantly adhered to a “high in the west and low in the east, high in the south and low in the north” pattern, primarily attributed to the advanced urbanization along the Yangtze River and in the lower reaches of the Yangtze River Basin (Zheng et al., 2021). The areas with high NDVI values (> 0.6) accounted for 51.83% of the study area (Figure 4A). Precisely 22 cities exhibited an NDVI between 0.60 and 0.65, mainly located in the western part of the study area and central-southern part of eastern region (Figure 4B). Among these, Huangshan boasted the highest NDVI, followed by Jingdezhen, then Ganzhou, the ETMAP, and Huaihua. The areas with low NDVI values (< 0.2) comprised 1.87% of the study area (Figure 4A). On the city scale, NDVI was relatively lower in Wuhan urban circle and the YRD (Figure 4B).
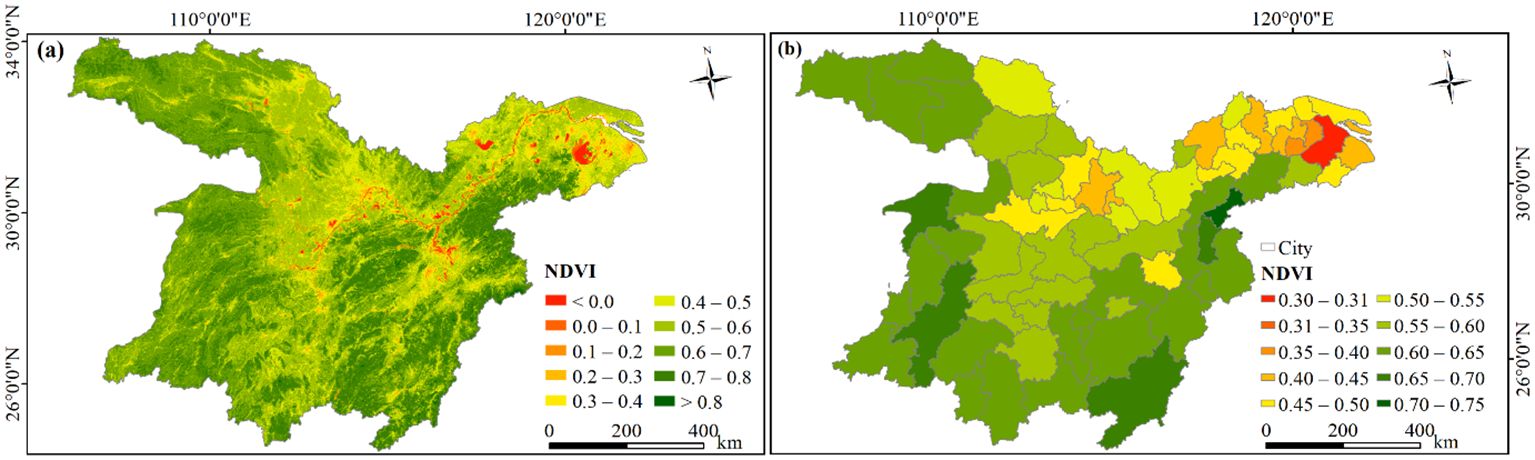
Figure 4. (A) Spatial pattern of the average annual NDVI in the study area, 2000−2020. (B) Pixel-based statistics of average NDVI at the city scale.
As shown in Figure 5A, the NDVI kernel density gradually decreased from the southwest to the northeast. Regions with high kernel density were predominantly situated in the central and southern parts of the MLYRB. Characterized by robust vegetation growth and dense vegetation cover, these regions were primarily composed of forests and croplands. Between 2000 and 2020, the geographic center of NDVI in the MLYRB continuously migrated (Figure 5B). The longitude of the centroid ranged between 113°10′23.78′′ E and 113°15′56.20′′ E, and the latitude extended from 29°22′1.01′′ N to 29°26′32.91′′ N. Overall, the NDVI centroid coordinates moved from 113°15′56.20′′ E, 29°23′40.29′′ N in 2000 to 113°14′5.85′′ E, 29°24′44.14′′ N in 2020, following a fluctuating trajectory. This migratory trend indicates significant interannual variability in NDVI in the study area. Notably, the migrations during 2005−2006, 2011−2012, 2012−2013, and 2019−2020 were particularly pronounced, covering distances of approximately 5.92 km, 5.54 km, 8.20 km, and 6.25 km, respectively. These distances exhibit an expansion in vegetation cover across a wide area of the study area during these specific periods.
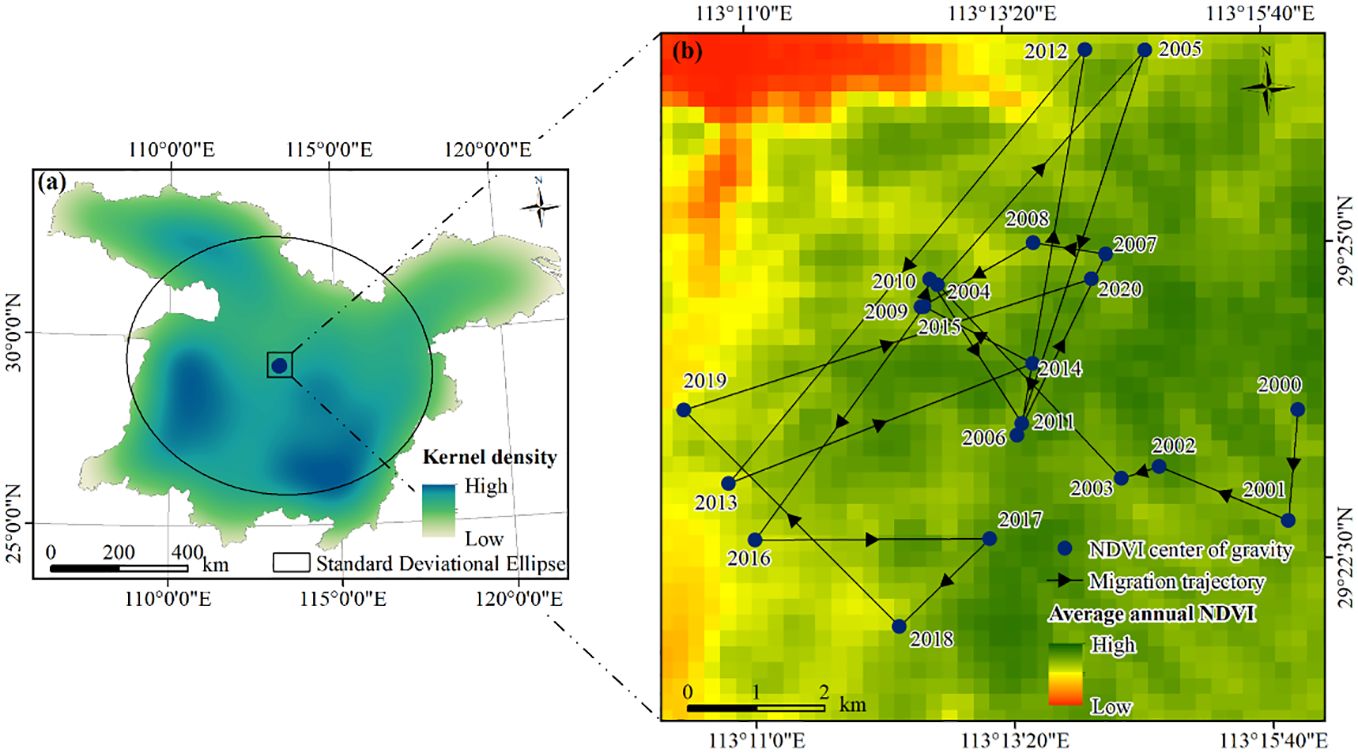
Figure 5. (A) Kernel density and standard deviational ellipse of annual NDVI. (B) Spatial variations in NDVI centroid migration within the study area, 2000−2020.
As shown in Figure 6A, the change rate of NDVI in the MLYRB during 2000−2020 ranged from −0.0362 to 0.0365 per year. The majority of the study area, specifically 89.28%, demonstrated an upward trend in NDVI. These areas were mainly observed in the Qinling-Daba mountainous area and its adjacent areas (southern Shaanxi, southern Henan, and northwestern Hubei), as well as the Wuling-Xuefeng Mountain ranges (western Hunan), and Jiangnan Hills. Conversely, the areas where NDVI showed a downward trend accounted for 10.72%, primarily concentrated in central Hubei, northern Hunan, southern Anhui, and highly urbanized regions in Jiangsu, Zhejiang, and Shanghai Municipality.
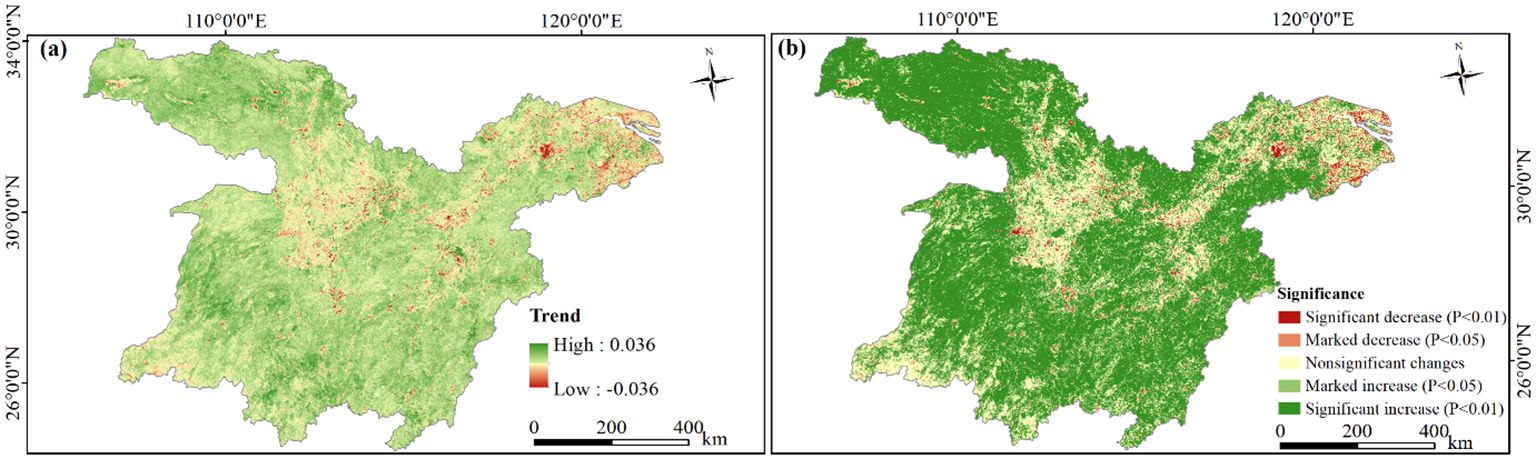
Figure 6. Variability and trends of NDVI in the study area, 2000−2020. (A) Spatial patterns of pixel-by-pixel NDVI variations; (B) significance of NDVI trends.
According to Figure 6B, the majority of the study area (62.65%) exhibited a significant increase in NDVI, followed by regions showing nonsignificant changes (23.81%) and marked increases (9.97%). Conversely, areas with significant decreases and marked decreases only accounted for 3.57%. Specifically, the Dongting Lake Basin (DLB), Poyang Lake Basin (PLB), and Han River Basin (HRB) predominantly featured a significant upward NDVI trend. Regions with marked NDVI increases were dispersed across the study area. Significant NDVI decreases were primarily identified in Lixian and Linli Counties of Changde, Dantu County of Ma’anshan, Xuanzhou District of Xuancheng, Gaochun District of Nanjing, and the vicinity of Taihu Lake. Notably, the Wuhan Metropolitan Area (WMA), Changsha-Zhuzhou-Xiangtan urban agglomeration (CZTUA), Poyang Lake urban agglomeration (PLUA), and the YRD predominantly exhibited a marked decreasing NDVI trend.
The regression coefficients indicate a correlation between NDVI and climatic variables, highlighting notable spatial differences among cities. For example, excluding Qianjiang and Chuzhou, the NDVI of the other 66 cities showed a positive correlation with temperature (Figure 7A). Similarly, the NDVI of 62% of the cities positively correlated with precipitation, with Huangshi exhibiting the strongest positive correlation (Figure 7B). Notably, the NDVI of 81% of the cities demonstrated a negative correlation with sunshine duration, Loudi exhibiting the strongest negative one (Figure 7C). Evidently, the correlation between NDVI and wind speed was negative in cities situated along the southeast-northwest axis, while being positive on both sides of the axis (Figure 7D). Regarding relative humidity (Figure 7E), 54% of the cities indicated a negative correlation with NDVI, with Xiantao presenting the strongest correlation; and the other cities exhibited a positive correlation, with Xinyu and Chenzhou showing strong correlations.
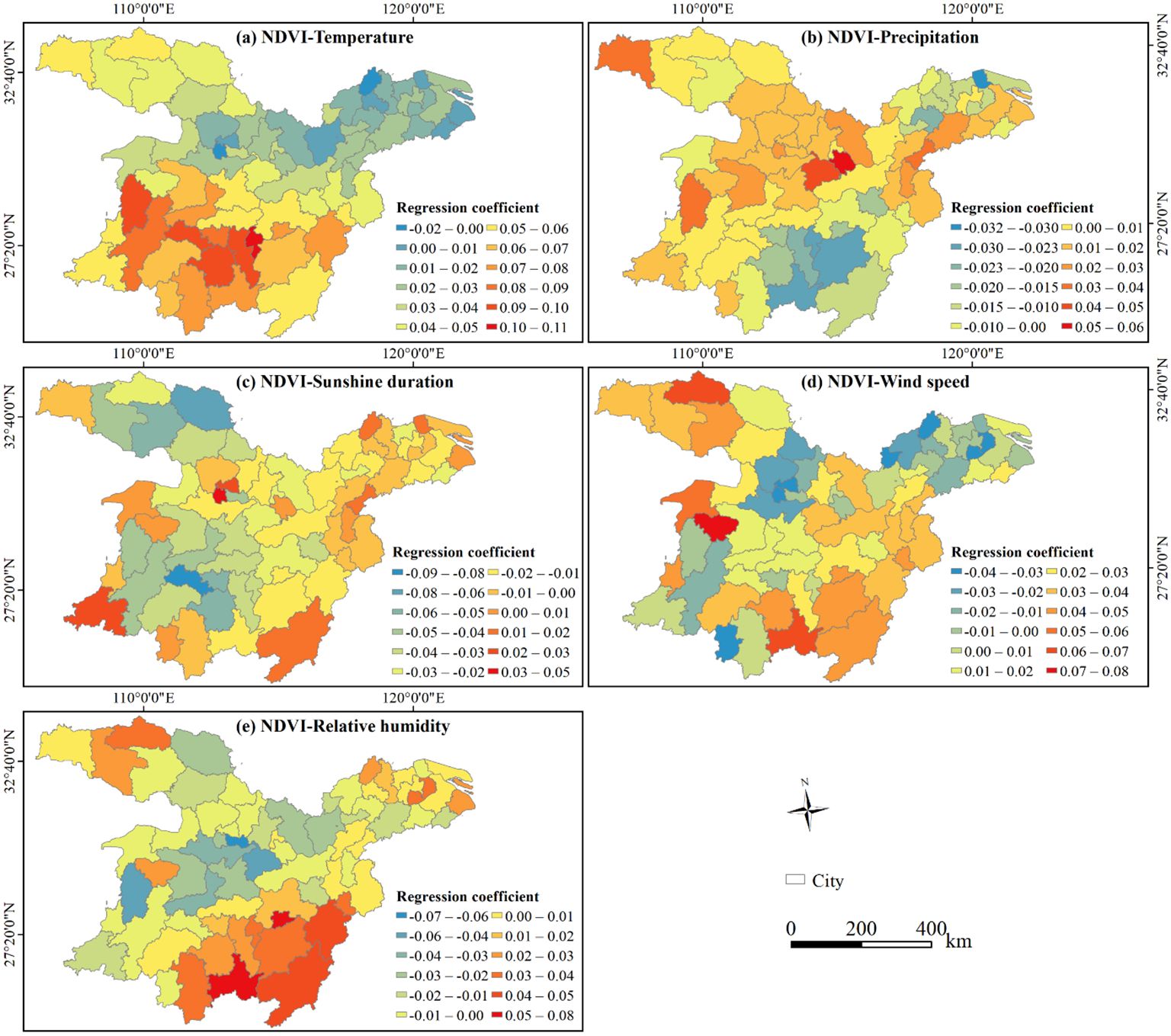
Figure 7. Spatial distribution of regression coefficients between NDVI and climatic variables at the city scale in the study area, 2000−2020. (A) Correlation between NDVI and Temperature; (B) correlation between NDVI and precipitation; (C) correlation between NDVI and sunshine duration; (D) correlation between NDVI and wind speed; and (E) correlation between NDVI and relative humidity.
As shown in Figure 8, the areas where NDVI demonstrated a positive correlation with climatic variables accounted for 71.20% of the study area. Aside from sunshine duration, the correlations between other variables (i.e., temperature, wind speed, sunshine duration, relative humidity, and precipitation) and NDVI were mainly positive. Specifically, temperature exerted the most significant influence on vegetation changes, affecting 33.33% of the study area. The regions where NDVI positively correlated with temperature were mainly distributed in the DLB, PLB, Hanzhong, certain parts of Shangluo, Suizhou, Xiaogan, and northern Huanggang. Wind speed ranked as the second dominated factor of NDVI, encompassing 27.71%. The positive correlation areas of NDVI and temperature were primarily found in Shanghai, the ETMAP, parts of Shiyan, central Huanggang, Chizhou, and Shaoyang, western Xiangyang and Huangshan, southern Chenzhou, and eastern Shangrao.

Figure 8. (A) Spatial pattern of the dominant factors influencing vegetation changes in the study area, 2000−2020. (B) Proportions of positive and negative dominant areas for climatic variables based on pixel statistics.
Additionally, sunshine duration, relative humidity, and precipitation also exerted notable effects on NDVI, accounting for 15.47%, 14.48% and 9.01% of the study area, respectively. NDVI negatively correlated with Sunshine duration in specific areas like central Huaihua and Xinhua County of Loudi, Shiyan, central Ankang, Nanyang, and the intersection of Yichun, and Nanchang. The areas where NDVI positively correlated with relative humidity were mainly observed in Quanjiao and Dingyuan Counties of Chuzhou, Shushan District of Hefei, Jing County of Xuancheng, Lishui District of Nanjing, Pucheng County of Nanping, Zixi County of Fuzhou, Guidong County and Zixing City of Chenzhou, Yongding District of Zhangjiajie, Jingshan of Jingmen, Liuba County of Hanzhong, Zhashui County of Shangluo. The positively correlated areas of NDVI and precipitation were mainly located in southern Xi’an, western and central Hanzhong, eastern Xianning and Huangshi, and southern Xuancheng.
The cross-wavelet energy spectrum revealed a remarkable resonance period of 10.5 to 13.1 months (2001−2019) between NDVI and AMO in the MLYRB. The period between 2008 to 2012 notably exhibited a high-energy region, and the phase difference pointed towards a positive correlation between NDVI and AMO (Figure 9A). Moreover, there were two distinct resonance periods identified between NDVI and NAO: 9.0 to 12.5 months (2001−2009) and 9.2 to 12.7 months (2010−2019). Predominantly, the high-energy region was evident from 2011 to 2017, and the phase difference indicated a negative correlation between NDVI and NAO (Figure 9B). Furthermore, there were two significant resonance periods uncovered between NDVI and PDO: 8.8 to 14.7 months (2001−2008) and 8.6 to 12.9 months (2009−2019). The year 2005 primarily witnessed a high-energy region, and the phase difference implied that NDVI responded with a delay to alterations in PDO (Figure 9C). Lastly, two significant resonance periods were identified between NDVI and SOI: 11.8 to 13.0 months (2001−2003) and 10.3 to 11.8 months (2005−2016). The former high-energy region was primarily observed from 2001 to 2002, while the latter was focused in 2007. The phase difference hinted at a negative correlation between NDVI and SOI (Figure 9D).
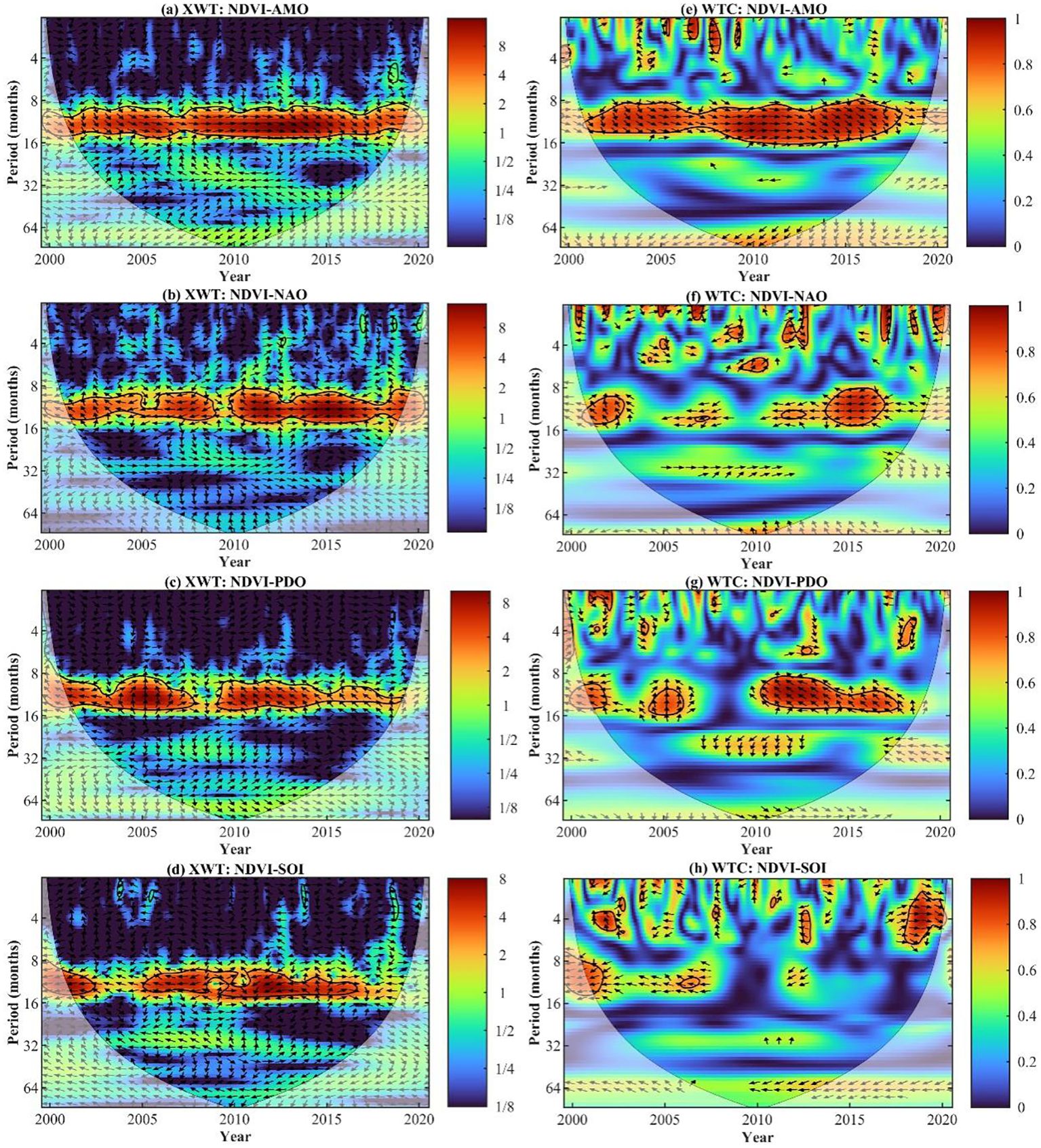
Figure 9. (A−D) Cross wavelet power spectrum and (E−H) wavelet coherence between NDVI and climate indices (i.e., AMO, Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation; NAO, North Atlantic Oscillation; PDO, Pacific Decadal Oscillation; and SOI, Southern Oscillation Index). The thick black contours depict the 5% significance level, highlighting the areas of strongest correlation. Here, WTC and XWT denote wavelet coherence and cross wavelet transform, respectively.
In the low-energy region of the wavelet coherence power spectrum, NDVI exhibited a significant resonance period with AMO, spanning from 10.3 to 13.5 months (2008−2012). Notably, the phase difference was predominantly positive (Figure 9E), suggesting that a positive influence of AMO on the periodic variation of NDVI. Similarly, NDVI demonstrated a pronounced resonance period with NAO between 8.3 and 13.0 months (2014−2017). The phase difference was significantly negative (Figure 9F), implying that NDVI was strongly impacted by the counteracting effects of the NAO. Notably, a significant resonance period was observed between NDVI and PDO for a duration of 10.4 to 15.7 months (2005). This resonance was characterized by an upward phase difference, indicating that NDVI responded with a lag to PDO changes (Figure 9G). Additionally, NDVI displayed a significant resonance period with SOI from 3.3 to 4.7 months (2018−2019) (Figure 9H). The phase difference was markedly positive, showing that SOI facilitated the enhancement of NDVI.
The correlation between urbanization and NDVI exhibited notable spatial heterogeneity. Among the examined areas, 86.43% demonstrated a positive correlation between NDVI and urbanization rate, whereas 13.57% showed a negative correlation (Figure 10A). Specifically, 65.18% of these areas displayed a marked or significant positive correlation (Figure 10B). Notably, 54.32% presented a significant positive correlation, predominantly distributed in regions like Qinling-Daba Mountains, Wuling-Xuefeng Mountains, Dabie Mountains, Jiangnan Hills, Southern Anhui Mountainous Areas, and Western Zhejiang Hills. The remaining 10.86% had a marked positive correlation scattered across the study area. These mountainous regions had relatively lower urbanization rates. Simultaneously, the Chinese government’s emphasis on ecological environment protection has led to the implementation of various ecological preservation such as natural forest conservation and converting farmland back to forests, positively impacting NDVI.
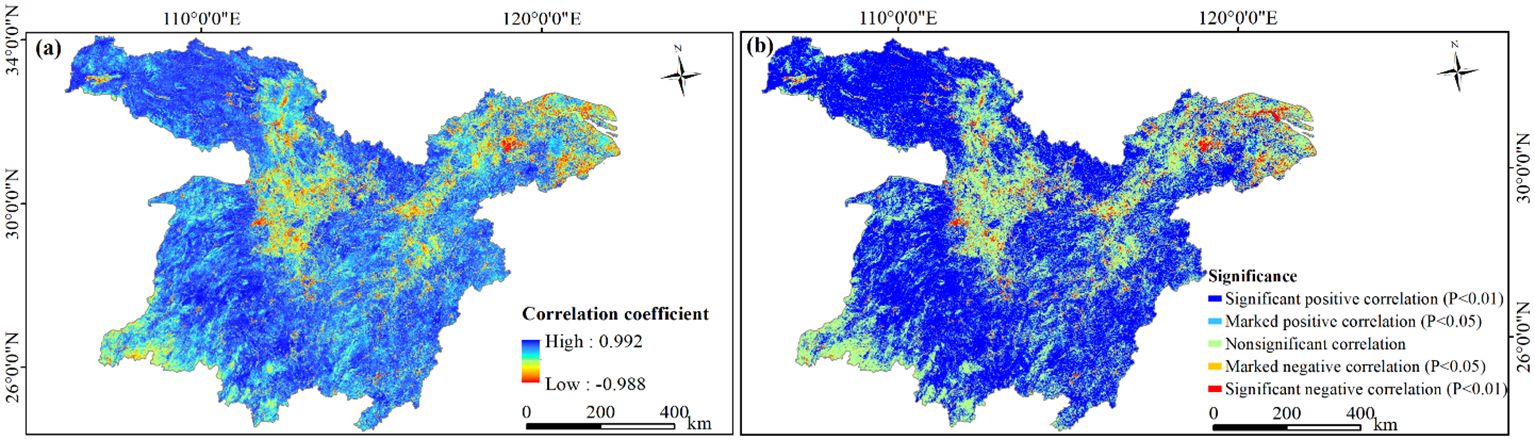
Figure 10. Correlation between NDVI and urbanization rate in the study area, 2003−2020. (A) Correlation coefficient; (B) significance of correlation.
Areas exhibiting a significant or marked negative correlation accounted for 4.30% (Figure 10B). Specifically, 2.73% showed a significant negative correlation, mainly distributed in the WMA, the CZTUA, the PLUA, and the YRD urban agglomeration. The 1.57% areas with a marked negative correlation were primarily concentrated in Lianghu Plain and along the Yangtze River. With urban expansion and rapid population growth, these regions saw rising urbanization rates, leading to the conversion of natural vegetation into urban land. This transformation resulted in reduced vegetation cover. Consequently, NDVI is negatively correlated with the urbanization rate.
This study focused on the provincial capital cities of Wuhan (Figure 11B), Changsha (Figure 11C), Nanchang (Figure 11D), and Nanjing (Figure 11E) within the study area (Figure 11A) to examine effects of urban expansion on vegetation. By monitoring the NDVI change rate, it was observed that the NDVI generally exhibited a negative trend in the outskirts of each provincial capital. Specifically, the western region of Wuhan, the central area of Changsha, and the southern part of Nanjing all displayed a decreasing NDVI. Similarly, most areas in Nanchang also demonstrated a decline in NDVI, suggesting significant vegetation degradation in these regions. With the accelerating pace of urbanization, urban development continued to encroach upon the periphery of these cities. This haphazard expansion often came at the expense of the surrounding vegetation. Consequently, this destruction led to direct changed in land cover, resulting in a decrease in NDVI. This observation underscores the contribution of urban expansion to vegetation degradation.
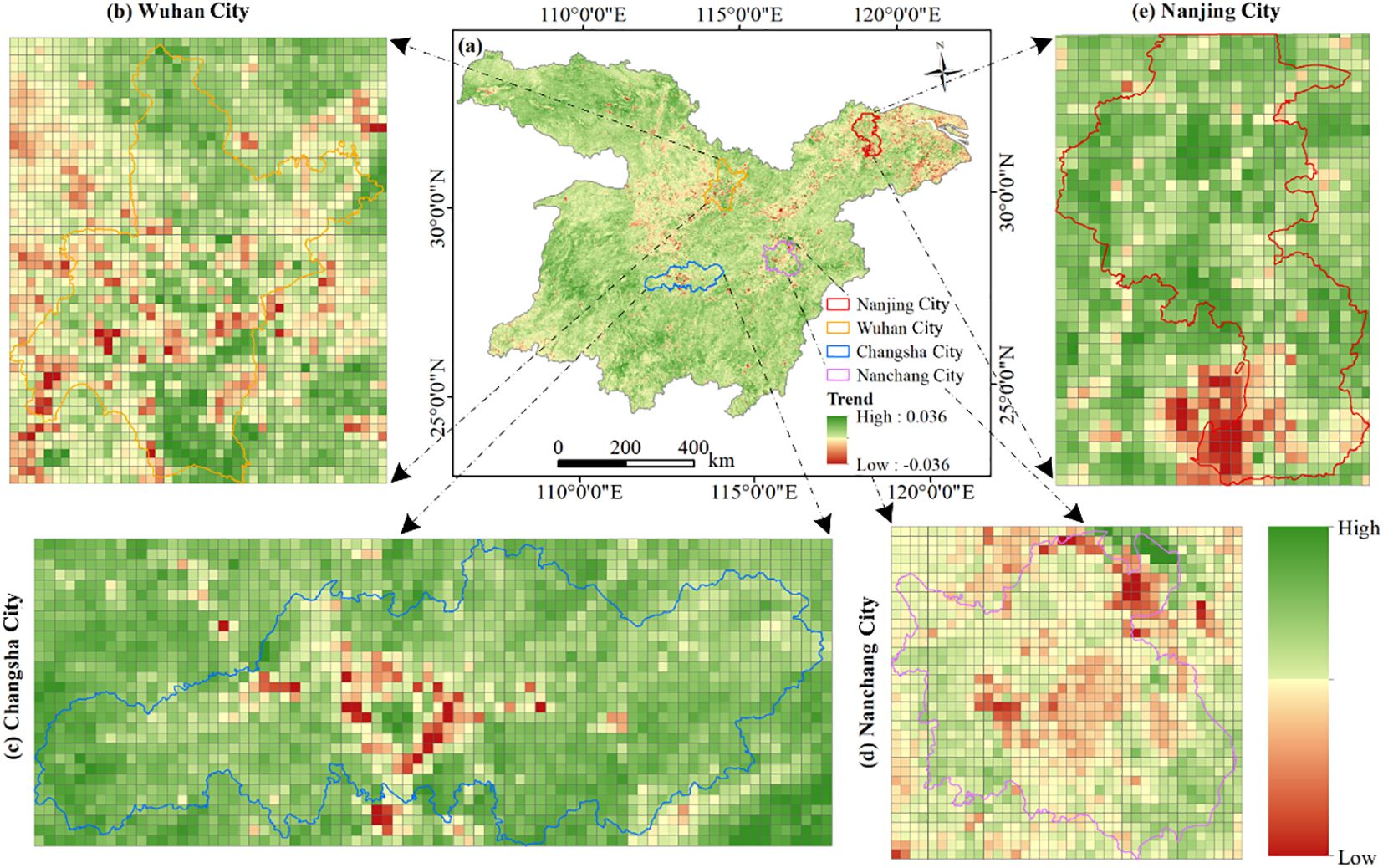
Figure 11. Impact of urban expansion on NDVI change rate. (A) Variations in NDVI, as well as exemplary cities such as (B) Wuhan; (C) Changsha; (D) Nanchang; and (E) Nanjing.
The proportions of regions with high NDVI values (> 0.6) within the study area are 67.35%, 72.72%, and 76.02% for the periods of 2021−2030 (Figure 12A), 2031−2040 (Figure 12B), and 2041−2050 (Figure 12C), respectively. These proportions suggest that the vegetation coverage in the study area is projected to continue on a greening trend, especially in the western region and Jiangnan Hills. This trend holds great significance not only for maintaining regional ecological balance and regulating climate but also offering robust support towards achieving China’s dual carbon goals. Areas with lower vegetation coverage are mainly located in the urban agglomeration in the middle reaches of Yangtze River, the Chaohu Lake Basin, the Taihu Lake Basin, and the YRD. These locations are characterized by rapid economic progress, a sizable population, and a relatively advanced level of urbanization, resulting in a degradation in vegetation (Qu et al., 2020).
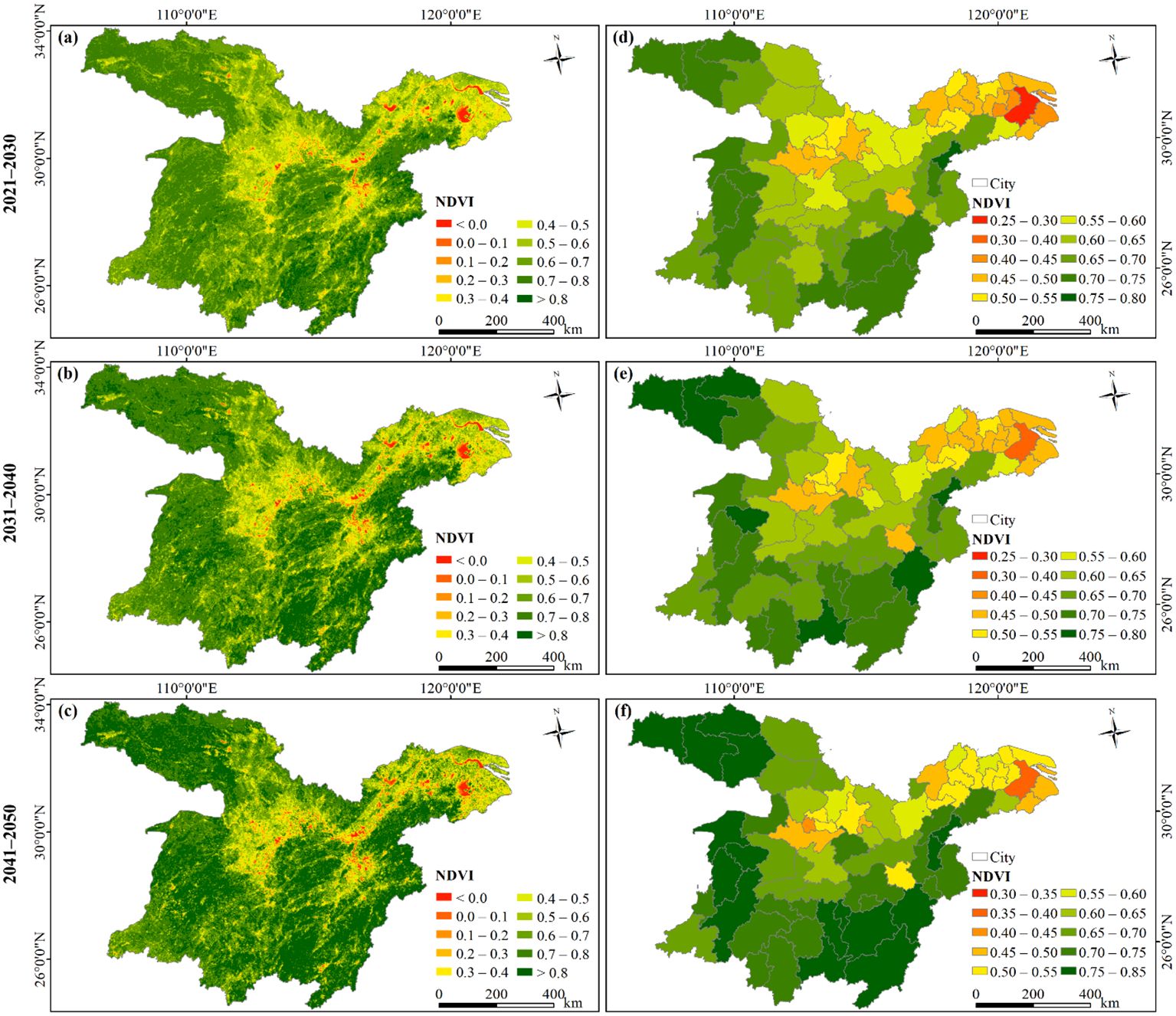
Figure 12. Spatial patterns of future NDVI based on (A−C) the whole-domain scale and (D−F) the city scale for the periods of 2021−2030, 2031−2040, and 2041−2050, respectively.
Figures 12D–F illustrate a steady growth trend in NDVI across all cities spanning from 2021 to 2050. The proportions of cities where the NDVI exceeds 0.6 stand at 58.82%, 63.24%, and 66.18% for the decades 2021−2030, 2031−2040 and 2041−2050, respectively. Throughout the study period referenced, the NDVI of Huangshi consistently tops the list with the highest NDVI, followed by Ganzhou, Chenzhou, and Shangluo. In contrast, Suzhou persistently registers the lowest NDVI. Other highly urbanized areas, such as Shanghai Municipality, Wuxi, and Jiaxing, also exhibit relatively low NDVI values.
This study explores the spatiotemporal variations of vegetation in the MLYRB using multi-temporal remote sensing data. The results indicate a significant improvement in vegetation over the past 21 years, corroborating the conclusions of previous studies (Yi et al., 2021b; Zhang et al., 2023). Specifically, there has been a marked enhancement in vegetation coverage, particularly in the western and central regions of the study area. As suggested by some researchers, this pronounced trend can be attributed to the conversion of a significant portion of croplands into forests (Zhu et al., 2016). Also, climatic factors and ecological conservation efforts have positively contributed to this vegetation growth (Zhang et al., 2020). The NDVI has shown significant improvement in areas constituting 62.65% of the study area, especially in the DLB, PLB, and HRB. Since these three basins are pivotal commodity grain production centers in China, the observed NDVI dynamics align with changes in crop patterns (Han et al., 2020; Liu et al., 2021; Long et al., 2021). However, vegetation degradation accounted for merely 3.57% of the study area, primarily affecting urban areas. This result underscores the profound negative impact of urban expansion on vegetation coverage (Guan et al., 2019).
In this study, the SARIMA model was utilized to project future NDVI trends over multiple periods. The model relies on multiple non-seasonal and seasonal parameters. Notably, their estimation is solely based on a historical dataset, which may be influenced by factors such as sample size, data quality, and data distribution characteristics. Consequently, these estimations inherently carry a certain degree of uncertainty, thereby affecting the predictive accuracy. Nonetheless, the SARIMA model has been verified to exhibit high stability, and its predictive approach integrates both numerical values and noise, resulting in simulated values remarkably close to the actual ones (Jiang et al., 2010). This conclusion indicates that parameter estimation has a negligible effect on the model’s predictive accuracy.
A thorough comprehension of the relationship between climatic factors and NDVI is crucial for predicting vegetation dynamics and managing ecological restoration projects. Among various climatic factors, temperature and precipitation play a vital role in shaping regional NDVI variations (Li et al., 2021a, 2021). Numerous studies have predominantly focused on exploring the effects of temperature and precipitation on NDVI by calculating correlation coefficients (Gao et al., 2022; Yu et al., 2020). This research reveals a predominantly positive correlation between NDVI and temperature, echoing previous research findings (Hua et al., 2017; Zhang et al., 2020). Furthermore, moderate wind speeds expedite the transpiration rate of plant leaves, elevate CO2 levels within plant cells, enhance the net photosynthetic rate, and subsequently foster vegetation growth (Zhang et al., 2022b). Conversely, excessive precipitation can lead to vegetation root rot, while rainy conditions diminish solar radiation reaching the earth’s surface, ultimately impeding vegetation growth (Hussien et al., 2023).
Urban expansion profoundly impacts vegetation dynamics (Du et al., 2019a). As depicted in Figure 12, the vegetation in the primary provincial capitals and adjacent regions of the MLYRB exhibits a marked degradation trend. This degradation is largely attributed to the adverse effects of urban expansion. The negative correlation between urban development and vegetation can be ascribed to factors such as environmental deterioration, habitat loss, and changes in land cover during the urbanization process (He et al., 2014; Kowarik, 2011). Furthermore, vegetation changes are associated with different stages of urbanization (Fu et al., 2018). Cities in their early development stage often reduce vegetation cover to meet residential space demands (Wu et al., 2019). Conversely, more mature cities may prioritize increasing urban green spaces, which could facilitate vegetation regeneration. Hence, as the demand for better urban living standards persists, vegetation degradation will gradually give way to improvement (Li et al., 2020).
Climatic variables, including temperature, precipitation, wind speed, relative humidity, and sunshine duration, directly shape the growth cycle, water demand, and light conditions of vegetation (Wang et al., 2024). Meanwhile, human activities primarily impact vegetation changes through land use/cover changes (Yin et al., 2018), population migrations (Inderjit et al., 2017), urban expansion (De La Barrera and Henríquez, 2017), and artificial afforestation (Fu et al., 2024). These anthropogenic effects are often localized and direct, intricately tied to the intensity and patterns of human intervention. In summary, vegetation change is a multifaceted phenomenon influenced by various factors, and the degree of this influence varies across regions. Notably, climatic factors exert a long-term influence on vegetation changes, whereas human activities typically have a more immediate and visible impact. Consequently, it is imperative to separately explore the effects of climate factors and human activities on vegetation changes to gain a deeper understanding of their respective mechanisms and impact levels.
Examining the regional patterns of vegetation dynamics and their responses to climate change aids in gaining a better understanding of the driving forces behind vegetation variability. Nevertheless, in exploring the impacts of climate change on vegetation, this study neglected the time lag and cumulative effects of climatic factors on vegetation growth. Obviously, the significance of these time lags and cumulative effects has been verified in numerous studies (Wu et al., 2015; Zuo et al., 2021). Meanwhile, this research has not fully considered other potential factors influencing vegetation dynamics, such as CO2 fertilization (Zhu et al., 2016), extreme climatic events (Zscheischler et al., 2014), and anthropogenic activities (Jiang et al., 2017). Additionally, the period for the urbanization rate used in this study spans from 2003 to 2020, with missing statistical information for the preceding three years (2000−2002), might undermine the reliability of evaluating the impact of urbanization on vegetation changes. Consequently, future research could endeavor to develop a comprehensive model capable of quantifying most relevant factors to explore the driving mechanisms of vegetation dynamics at regional and even global scales.
This study investigated the impact of climate change and urbanization on NDVI variations in the MLYRB, and projected future NDVI trends. The primary findings are summarized below:
1. The annual average NDVI in the study area exhibited a significant upward trend from 2000 to 2020. This growing trend was evident in 89.38% of the area, with western and southern cities boasting significantly higher NDVI values than their counterparts. Meanwhile, 67.76% of the area underwent significant NDVI changes, with extremely significant increases and decreases accounting for 53.56% and 2.59%, respectively. Over the study period, the centroid of NDVI consistently displaced, with the migration distance progressively increasing, underscoring the significant NDVI variations.
2. Temperature and wind speed positively impacted 32.54% and 20.92% of the study area, respecti vely. Conversely, 11.63% of the area was adversely affected by sunshine duration. Precipitation and relative humidity exerted a comparatively minor effect on vegetation. Global climate oscillations are capable of influencing periodic variations in NDVI. Additionally, despite urbanization being a pivotal contributor to NDVI decline, a positive correlation between the two was noted.
3. Vegetation is anticipated to sustain its greening trend in the foreseeable future, evident in the increasing NDVI values across all cities. Nevertheless, areas with low vegetation cover remain predominantly in highly urbanized zones.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
JL: Writing – original draft, Software, Funding acquisition. JF: Writing – review & editing, Funding acquisition, Formal Analysis, Conceptualization. JQ: Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Project administration. BS: Writing – original draft, Visualization, Software, Methodology. YH: Writing – original draft, Validation, Data curation.
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research received supports from Hunan Provincial Education Department (grant numbers CX20221269, 22C0408) and Hunan Key Laboratory of Geospatial Big Data Mining and Application (grant number 2020-01).
The authors would like to thank the editors and reviewers for their valuable comments on this paper.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Alpaidze, L., Salukvadze, J. (2023). Green in the city: Estimating the ecosystem Services Provided by Urban and Peri-Urban Forests of Tbilisi Municipality, Georgia. Forests 14, 121. doi: 10.3390/f14010121
Bernier, P. Y., Paré, D., Stinson, G., Bridge, S. R. J., Kishchuk, B. E., Lemprière, T. C., et al. (2017). Moving beyond the concept of “primary forest” as a metric of forest environment quality. Ecol. Appl. 27, 349–354. doi: 10.1002/eap.1477
Box, G. E. P., Jenkins, G. M. (1970). Time series Analysis, Forecasting, and Control (San Francisco: Holden-Day).
Chen, J., Fan, W., Li, D., Liu, X., Song, M. (2020). Driving factors of global carbon footprint pressure: Based on vegetation carbon sequestration. Appl. Energ. 267, 114914. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2020.114914
Chu, H., Venevsky, S., Wu, C., Wang, M. (2019). NDVI-based vegetation dynamics and its response to climate changes at Amur-Heilongjiang River Basin from 1982 to 2015. Sci. Total. Environ. 650, 2051–2062. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.09.115
De Carvalho, R. M., Szlafsztein, C. F. (2019). Urban vegetation loss and ecosystem services: The influence on climate regulation and noise and air pollution. Environ. pollut. 245, 844–852. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.10.114
De La Barrera, F., Henríquez, C. (2017). Vegetation cover change in growing urban agglomerations in Chile. Ecol. Indic. 81, 265–273. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2017.05.067
Du, J., Fu, Q., Fang, S., Wu, J., He, P., Quan, Z. (2019a). Effects of rapid urbanization on vegetation cover in the metropolises of China over the last four decades. Ecol. Indic. 107, 105458. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.105458
Du, J., He, Z., Piatek, K. B., Chen, L., Lin, P., Zhu, X. (2019b). Interacting effects of temperature and precipitation on climatic sensitivity of spring vegetation green-up in arid mountains of China. Agr. Forest. Meteorol. 269-270, 71–77. doi: 10.1016/j.agrformet.2019.02.008
Fu, J., Gong, Y., Zheng, W., Zou, J., Zhang, M., Zhang, Z., et al. (2022). Spatial-temporal variations of terrestrial evapotranspiration across China from 2000 to 2019. Sci. Total. Environ. 825, 153951. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153951
Fu, J., Liu, J., Qin, J., Yang, L., Zhang, Z., Deng, Y., et al. (2024). Monitoring long-term vegetation dynamics over the Yangtze River Basin, China, using multi-temporal remote sensing data. Ecosphere 15, e4809. doi: 10.1002/ecs2.4809
Fu, W., Lü, Y., Harris, P., Comber, A., Wu, L. (2018). Peri-urbanization may vary with vegetation restoration: A large scale regional analysis. Urban. For. Urban. Gree. 29, 77–87. doi: 10.1016/j.ufug.2017.11.006
Gao, W., Zheng, C., Liu, X., Lu, Y., Chen, Y., Wei, Y., et al. (2022). NDVI-based vegetation dynamics and their responses to climate change and human activities from 1982 to 2020: A case study in the Mu Us Sandy Land, China. Ecol. Indic. 137, 108745. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.108745
Guan, X., Shen, H., Li, X., Gan, W., Zhang, L. (2019). A long-term and comprehensive assessment of the urbanization-induced impacts on vegetation net primary productivity. Sci. Total. Environ. 669, 342–352. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.361
Han, Y., Guo, X., Jiang, Y., Xu, Z., Li, Z. (2020). Environmental factors influencing spatial variability of soil total phosphorus content in a small watershed in Poyang Lake Plain under different levels of soil erosion. Catena 187, 104357. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2019.104357
He, C., Liu, Z., Tian, J., Ma, Q. (2014). Urban expansion dynamics and natural habitat loss in China: a multiscale landscape perspective. Global. Change. Biol. 20, 2886–2902. doi: 10.1111/gcb.12553
Hua, W., Chen, H., Zhou, L., Xie, Z., Qin, M., Li, X., et al. (2017). Observational quantification of climatic and human influences on vegetation greening in China. Remote. Sens. 9, 425. doi: 10.3390/rs9050425
Huang, W., Duan, W., Chen, Y. (2021b). Rapidly declining surface and terrestrial water resources in Central Asia driven by socio-economic and climatic changes. Sci. Total. Environ. 784, 147193. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.147193
Huang, J., Ge, Z., Huang, Y., Tang, X., Shi, Z., Lai, P., et al. (2022). Climate change and ecological engineering jointly induced vegetation greening in global karst regions from 2001 to 2020. Plant Soil. 475, 193–212. doi: 10.1007/s11104-021-05054-0
Huang, L., Zhou, P., Cheng, L., Liu, Z. (2021a). Dynamic drought recovery patterns over the Yangtze River Basin. Catena 201, 105194. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2021.105194
Hussien, K., Kebede, A., Mekuriaw, A., Beza, S. A., Erena, S. H. (2023). Spatiotemporal trends of NDVI and its response to climate variability in the Abbay River Basin, Ethiopia. Heliyon 9, e14113. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e14113
Inderjit, C., Kalisz, S., Simberloff, D., Wardle, D. A. (2017). A framework for understanding human-driven vegetation change. Oikos 126, 1687–1698. doi: 10.1111/oik.2017.v126.i12
IPCC (2014). Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis Working Group I Contribution to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press).
Jiang, L., ·Jiapaer, G., Bao, A., Guo, H., Ndayisaba, F. (2017). Vegetation dynamics and responses to climate change and human activities in Central Asia. Sci. Total. Environ. 599, 967–980. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.05.012
Jiang, B., Liang, S., Wang, J., Xiao, Z. (2010). Modeling MODIS LAI time series using three statistical methods. Remote. Sens. Environ. 114, 1432–1444. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2010.01.026
Kowarik, I. (2011). Novel urban ecosystems, biodiversity, and conservation. Environ. pollut. 159, 1974–1983. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2011.02.022
Lamchin, M., Wang, S. W., Lim, C.-H., Ochir, A., Pavel, U., Gebru, B. M., et al. (2020). Understanding global spatio-temporal trends and the relationship between vegetation greenness and climate factors by land cover during 1982–2014. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 24, e01299. doi: 10.1016/j.gecco.2020.e01299
Lawal, S., Lennard, C., Hewitson, B. (2019). Response of southern African vegetation to climate change at 1.5 and 2.0° global warming above the pre-industrial level. Clim. Serv. 16, 100134. doi: 10.1016/j.cliser.2019.100134
Li, M., Chu, R., Sha, X., Xie, P., Ni, F., Wang, C., et al. (2022). Monitoring 2019 drought and assessing Its effects on vegetation using solar-induced chlorophyll fluorescence and vegetation indexes in the Middle and Lower Reaches of Yangtze River, China. Remote. Sens. 14, 2569. doi: 10.3390/rs14112569
Li, P., Wang, J., Liu, M., Xue, Z., Bagherzadeh, A., Liu, M. (2021a). Spatio-temporal variation characteristics of NDVI and its response to climate on the Loess Plateau from 1985 to 2015. Catena 203, 105331. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2021.105331
Li, D., Wu, S., Liang, Z., Li, S. (2020). The impacts of urbanization and climate change on urban vegetation dynamics in China. Urban. For. Urban. Gree. 54, 126764. doi: 10.1016/j.ufug.2020.126764
Li, S., Xu, L., Jing, Y., Yin, H., Li, X., Guan, X. (2021b). High-quality vegetation index product generation: A review of NDVI time series reconstruction techniques. Int. J. Appl. Earth. Obs. 105, 102640. doi: 10.1016/j.jag.2021.102640
Li, L., Zhang, Y., Wu, J., Li, S., Zhang, B., Zu, J., et al. (2019). Increasing sensitivity of alpine grasslands to climate variability along an elevational gradient on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Sci. Total. Environ. 678, 21–29. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.04.399
Liu, Y., Liu, H., Chen, Y., Gang, C., Shen, Y. (2022). Quantifying the contributions of climate change and human activities to vegetation dynamic in China based on multiple indices. Sci. Total. Environ. 838, 156553. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.156553
Liu, Q., Peng, C., Schneider, R., Cyr, D., Liu, Z., Zhou, X., et al. (2023b). Vegetation browning: global drivers, impacts, and feedbacks. Trends. Plant Sci. 28, 1014–1032. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2023.03.024
Liu, X., Wang, Z., Zhang, L., Fan, W., Yang, C., Li, E., et al. (2021). Inconsistent seasonal variation of antibiotics between surface water and groundwater in the Jianghan Plain: Risks and linkage to land uses. J. Environ. Sci. 109, 102–113. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2021.03.002
Liu, J., Wei, L., Zheng, Z., Du, J. (2023a). Vegetation cover change and its response to climate extremes in the Yellow River Basin. Sci. Total. Environ. 905, 167366. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.167366
Long, X., Liu, F., Zhou, X., Pi, J., Yin, W., Li, F., et al. (2021). Estimation of spatial distribution and health risk by arsenic and heavy metals in shallow groundwater around Dongting Lake plain using GIS mapping. Chemosphere 269, 128698. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128698
Long, Q., Wang, F., Ge, W., Jiao, F., Han, J., Chen, H., et al. (2023). Temporal and spatial change in vegetation and its interaction with climate change in Argentina from 1982 to 2015. Remote. Sens. 15, 1926. doi: 10.3390/rs15071926
Lotsch, A., Friedl, M. A., Anderson, B. T., Tucker, C. J. (2005). Response of terrestrial ecosystems to recent Northern Hemispheric drought. Geophys. Res. Lett. 32, L06705. doi: 10.1029/2004GL022043
Mann, H. B. (1945). Nonparametric tests against trend. Econometrica 13, 245–259. doi: 10.2307/1907187
Myneni, R. B., Keeling, C. D., Tucker, C. J., Asrar, G., Nemani, R. R. (1997). Increased plant growth in the northern high latitudes from 1981 to 1991. Nature 386, 698–702. doi: 10.1038/386698a0
Pearson, K. (1920). Notes on the history of correlation. Biometrika 13, 25–45. doi: 10.1093/biomet/13.1.25
Piao, S., Zhang, X., Chen, A., Liu, Q., Lian, X., Wang, X., et al. (2019). The impacts of climate extremes on the terrestrial carbon cycle: A review. Sci. China. Earth. Sci. 62, 1551–1563. doi: 10.1007/s11430-018-9363-5
Qi, X., Jia, J., Liu, H., Lin, Z. (2019). Relative importance of climate change and human activities for vegetation changes on China’s silk road economic belt over multiple timescales. Catena 180, 224–237. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2019.04.027
Qu, S., Wang, L., Lin, A., Yu, D., Yuan, M. (2020). Distinguishing the impacts of climate change and anthropogenic factors on vegetation dynamics in the Yangtze River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 108, 105724. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.105724
Sen, P. K. (1968). Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall’s tau. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 63, 1379–1389. doi: 10.1080/01621459.1968.10480934
Shen, M., Cong, N., Cao, R. (2014). Temperature sensitivity as an explanation of the latitudinal pattern of green-up date trend in Northern Hemisphere vegetation during 1982–2008. Int. J. Climatol 35, 3707–3712. doi: 10.1002/joc.4227
Theil, H. (1992). “A rank-invariant method of linear and polynomial regression analysis,” in Henri Theil’s contributions to economics and econometrics, eds. B., Raj, J., Koerts (Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands), 345–381. doi: 10.1007/978-94-011-2546-8_20
Tong, S., Zhang, J., Bao, Y., Lai, Q., Lian, X., Li, N., et al. (2018). Analyzing vegetation dynamic trend on the Mongolian Plateau based on the Hurst exponent and influencing factors from 1982–2013. J. Geogr. Sci. 28, 595–610. doi: 10.1007/s11442-018-1493-x
Torrence, C., Compo, G. P. (1998). A practical guide to wavelet analysis. B. Am. Meteorol. Soc 79, 61–78. doi: 10.1175/1520-0477(1998)079<0061:APGTWA>2.0.CO;2
Umuhoza, J., Jiapaer, G., Tao, Y., Jiang, L., Zhang, L., Gasirabo, A., et al. (2023). Analysis of fluctuations in vegetation dynamic over Africa using satellite data of solar-induced chlorophyll fluorescence. Ecol. Indic. 146, 109846. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.109846
Wang, Q., Ju, Q., Wang, Y., Fu, X., Zhao, W., Du, Y., et al. (2022a). Regional patterns of vegetation dynamics and their sensitivity to climate variability in the yangtze river basin. Remote. Sens. 14, 5623. doi: 10.3390/rs14215623
Wang, S., Li, R., Wu, Y., Zhao, S. (2022b). Vegetation dynamics and their response to hydrothermal conditions in Inner Mongolia, China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 34, e02034. doi: 10.1016/j.gecco.2022.e02034
Wang, Z., Liu, Y., Wang, Z., Zhang, H., Chen, X., Wen, Z., et al. (2024). Quantifying the spatiotemporal changes in evapotranspiration and its components driven by vegetation greening and climate change in the northern foot of yinshan mountain. Remote. Sens. 16, 357. doi: 10.3390/rs16020357
Wu, S., Liang, Z., Li, S. (2019). Relationships between urban development level and urban vegetation states: A global perspective. Urban. For. Urban. Gree. 38, 215–222. doi: 10.1016/j.ufug.2018.12.010
Wu, L., Zhang, Y., Luo, G., Chen, D., Yang, D., Yang, Y., et al. (2023). Characteristics of vegetation carbon sink carrying capacity and restoration potential of China in recent 40 years. Front. For. Glob. Change 6. doi: 10.3389/FFGC.2023.1266688
Wu, D., Zhao, X., Liang, S., Zhou, T., Huang, K., Tang, B., et al. (2015). Time-lag effects of global vegetation responses to climate change. Global. Change. Biol. 21, 3520–3531. doi: 10.1111/gcb.12945
Xie, X., He, B., Guo, L., Huang, L., Hao, X., Zhang, Y., et al. (2022). Revisiting dry season vegetation dynamics in the Amazon rainforest using different satellite vegetation datasets. Agr. Forest. Meteorol. 312, 108704. doi: 10.1016/j.agrformet.2021.108704
Yan, Z., Teng, M., He, W., Liu, A., Li, Y., Wang, P. (2019). Impervious surface area is a key predictor for urban plant diversity in a city undergone rapid urbanization. Sci. Total. Environ. 650, 335–342. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.09.025
Yi, Y., Wang, B., Shi, M., Meng, Z., Zhang, C. (2021b). Variation in vegetation and its driving force in the middle reaches of the yangtze river in China. Water 13, 2036. doi: 10.3390/w13152036
Yi, L., Yu, Z., Qian, J., Kobuliev, M., Chen, C., Xing, X. (2021a). Evaluation of the heterogeneity in the intensity of human interference on urbanized coastal ecosystems: Shenzhen (China) as a case study. Ecol. Indic. 122, 107243. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.107243
Yin, H., Pflugmacher, D., Li, A., Li, Z., Hostert, P. (2018). Land use and land cover change in Inner Mongolia - understanding the effects of China’s re-vegetation programs. Remote. Sens. Environ. 204, 918–930. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2017.08.030
Yu, L., Liu, Y., Liu, T., Yan, F. (2020). Impact of recent vegetation greening on temperature and precipitation over China. Agr. Forest. Meteorol. 295, 108197. doi: 10.1016/j.agrformet.2020.108197
Zhang, C. (2020). Moisture sources for precipitation in Southwest China in summer and the changes during the extreme droughts of 2006 and 2011. J. Hydrol. 591, 125333. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125333
Zhang, X., Jin, X. (2021). Vegetation dynamics and responses to climate change and anthropogenic activities in the Three-River Headwaters Region, China. Ecol. Indic. 131, 108223. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.108223
Zhang, M., Liu, H., Wang, K., Chen, Y., Ren, Y., Yue, Y., et al. (2023). Nonlinear trends of vegetation changes in different geomorphologic zones and land use types of the Yangtze River basin, China. Land. Degrad. Dev. 34, 2548–2559. doi: 10.1002/ldr.4627
Zhang, W., Wang, L., Xiang, F., Qin, W., Jiang, W. (2020). Vegetation dynamics and the relations with climate change at multiple time scales in the Yangtze River and Yellow River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 110, 105892. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.105892
Zhang, T., Xu, X., Jiang, H., Qiao, S., Guan, M., Huang, Y., et al. (2022b). Widespread decline in winds promoted the growth of vegetation. Sci. Total. Environ. 825, 153682. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153682
Zhang, L., Yang, L., Zohner, C. M., Crowther, T. W., Li, M., Shen, F., et al. (2022a). Direct and indirect impacts of urbanization on vegetation growth across the world’s cities. Sci. Adv. 8, eabo0095. doi: 10.1126/SCIADV.ABO0095
Zheng, K., Tan, L., Sun, Y., Wu, Y., Duan, Z., Xu, Y., et al. (2021). Impacts of climate change and anthropogenic activities on vegetation change: Evidence from typical areas in China. Ecol. Indic. 126, 107648. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.107648
Zhou, Z., Ding, Y., Shi, H., Cai, H., Fu, Q., Liu, S., et al. (2020). Analysis and prediction of vegetation dynamic changes in China: Past, present and future. Ecol. Indic. 117, 106642. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.106642
Zhu, Z., Piao, S., Myneni, R. B., Huang, M., Zeng, Z., Canadell, J. G., et al. (2016). Greening of the Earth and its drivers. Nat. Clim. Change. 6, 791–795. doi: 10.1038/nclimate3004
Zscheischler, J., Mahecha, M. D., von Buttlar, J., Harmeling, S., Jung, M., Rammig, A., et al. (2014). A few extreme events dominate global interannual variability in gross primary production. Environ. Res. Lett. 9, 35001. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/9/3/035001
Keywords: vegetation, spatiotemporal patterns, influencing factors, future trend, middle and lower Yangtze River basin
Citation: Liu J, Fu J, Qin J, Su B and Hong Y (2024) Effects of climate variability and urbanization on spatiotemporal patterns of vegetation in the middle and lower Yangtze River Basin, China. Front. Plant Sci. 15:1459058. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1459058
Received: 03 July 2024; Accepted: 14 October 2024;
Published: 04 November 2024.
Edited by:
Mohammad Ibrahim Khalil, University College Dublin, IrelandReviewed by:
Meng Zhang, Central South University Forestry and Technology, ChinaCopyright © 2024 Liu, Fu, Qin, Su and Hong. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jing Fu, ZnVqaW5nNzU3OUBoeW51LmVkdS5jbg==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.