- College of Horticulture, South China Agricultural University, Guangzhou, China
Blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum) is a small pulp shrub, which prefers to grow on a soilless culture. For soilless culture, nutritional management remains typically vital for blueberry production. However, the effect of different nutritional treatments on blueberry growth and production is largely unknown. This study was designed to investigate to formulate a specific nutritional treatment for blueberry. The results showed that NH4+-N: NO3−-N ratios significantly affected the growth, nutrient uptake, physiological characteristics, and flowering, as well as the fruiting characteristics of blueberry plants. The number of shoots and top projection area was increased considerably by 25:75 treatment. In contrast, 50:50 treatment promotes plant height, shoot length, and stem thickness, increasing chlorophyll contents, photosynthetic capacity, and P, Ca, and Mg in leaves. In contrast, 50:50 treatment promotes the flowering fruiting rate and prolongs the blueberry flowering period. The maximum soluble sugar contents were noted in 25:75, while maximum starch contents were reported in the 50:50 treatment. The treatments 100:0 and 75:25 promote early flowering and accelerate fruit set. Notably, NH4+-N: NO3−-N ratios; 50:50 treatment significantly encourages plant growth, nutrient uptake, chlorophyll contents, photosynthetic capacity, and fruit setting rate in blueberry plants. These findings suggested that NH4+-N: NO3−-N ratios 50:50 is the most appropriate treatment that significantly promotes vegetative growth and enhances production in blueberry plants. This study provides valuable information for improved blueberry production under a controlled environment.
1 Introduction
Blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum) is an important perennial shrub fruit plant belonging to the genus Vaccinium of the Ericaceae family (Han et al., 2021; Wu et al., 2022). It’s native to North America (Neugebauer et al., 2024; Wu et al., 2022) and because of its unique flavor and high nutritional value, its rapidly spreading to all over the world (Wu et al., 2022). The fruits of blueberry are oblate or spherical in shape, sift and juicier, having excellent levels of antioxidant active ingredients: polyphenols, anthocyanins, and flavonoids (Liu et al., 2022; Nagasaka et al., 2022). Blueberry fruit has prodigious nutritional and medicinal values, such as improving eyesight, aging, strengthening heart function, anti-cancer, softening blood vessels, and enhancing human immunity (Han et al., 2021; Stull et al., 2024). As the blueberry industry expands, the sustainability of blueberry is continuously threatened by environmental influences, that cause a significant reduction in production and quality (Tamir et al., 2023; Yang et al., 2023).
Blueberry is an oligotrophic plant, and the contents of nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, and magnesium in the tree are shallow compared with other fruit trees (Shen et al., 2020; Ortiz-Delvasto et al., 2023; Yang et al., 2023; Ru et al., 2024). Blueberry is sensitive to fertilization, and improper fertilization will not only affect production but will even cause the leaves of blueberry branches to wilt and physiological dysfunction; in severe cases, it will lead to the whole plant falling and the branches withering and dying (Alt et al., 2017; Shen et al., 2020; Tang et al., 2024). Blueberries are primarily cultivated in soilless substrates culture, and fertilization and water supply are carried out simultaneously through the integrated system (Ortiz-Delvasto et al., 2023). For optimum plant growth, a suitable nutritional solution is required throughout the growth period. Nutrient solution management is a crucial part of soilless substrate cultivation technology. However, the formula composition, concentration, ratio of different nutrients, pH, and daily preparation of nutrient solution directly affect the absorption and utilization of nutrients by crop roots (Tamir et al., 2023). Therefore, these factors are significant for improved crop production and quality under soilless culture (Yang et al., 2022b; Tamir et al., 2023).
Typically, blueberries are cultivated through soilless culture, but up to now, the relevant research on the nutrient solution formula of blueberries remains unclear. Many studies focused on the adaptability of blueberries to nitrogen forms, the effects of nutrient deficiency, and the formulations of different nutrient solutions (Alt et al., 2017; Shen et al., 2020; Yang et al., 2022b; Wu et al., 2024). However, a few reports on the systematic research on the integrated nutrient solution formula of blueberry with water and fertilizer. For the sustainable development of the blueberry industry, it is crucial to optimize and adjust the nutrient solution formula to obtain a nutrient solution formula that is more suitable for cultivating blueberries.
The substrate cultivation is generally called the nutrient substrate, which not only has the primary function of fixing and supporting plants but also has the role of regulating nutrient and water supply (Cocetta et al., 2012; Yang et al., 2022b; Hu et al., 2023). The physicochemical properties of the substrate are crucial for its effective utilization, as it can directly affect the environment in which plant roots grow, thus affecting the growth and development of plants and ultimately determining the yield and quality of fruits to a certain extent (Palencia et al., 2016; Ortiz-Delvasto et al., 2023; Rasool et al., 2024). Soilless substrate cultivation has significant advantages over soil cultivation, which can avoid continuous cropping obstacles, avoid the occurrence of soil-borne diseases, reduce root physiological diseases caused by aeration problems, and make more efficient use of water and fertilizer, increase the planting adaptability of plants, and enable plants to be planted in some soil environments where average growth cannot be achieved (Nunez et al., 2023; Ortiz-Delvasto et al., 2023; Rasool et al., 2024). Blueberry root distribution is shallow, and primarily, it has fine roots without root hairs and weak absorption capacity. Hence, blueberries prefer loose and airy acidic soils with high organic matter content, which have high requirements for a rhizosphere environment (Saad et al., 2020; Nunez et al., 2023; Ortiz-Delvasto et al., 2023).
For the specialized root of the blueberry, the peat and coir can provide a favorable environment and water retention to the rooting system, thus supreme substrates for blueberry cultivation (Cocetta et al., 2012; Alt et al., 2017). In addition, peat with good cation exchange capacity, low content of phytotoxic substances, and perlite, which has good stability and good air permeability and does not produce components that interfere with the balance of nutrient solution, are also one of the most widely used substrates in soilless culture (Shen et al., 2020; Xu et al., 2020; Lu et al., 2022; Yang et al., 2022b; Nunez et al., 2023). Soilless substrate formula has good substrate permeability and water and fertilizer retention ability, which can provide the best rhizosphere environment for blueberry growth and promote the growth and development of blueberry. This study was designed to investigate the nutrient solution formula suitable for blueberry substrate cultivation and then determine the effects of different N and K levels on the growth and adaptability of blueberries. This study aims to explore the optimal nutrient treatment to provide theoretical guidance and practical reference for high-yield, high-quality, and efficient facility substrate cultivation and production of blueberry.
2 Materials and methods
The experiment was carried out in the control growth chamber of the College of Horticulture, South China Agricultural University. The highbush blueberry seedlings of “Nangao Z9”, were used as experimental material. The cultivation substrate was prepared according to peat:cocofen:perlite = 1:1:1 (see Supplementary Table S1 for physical and chemical properties), and planted in square cultivation pots with specifications of 26 cm× 26 cm× 30 cm (length × width × height). Each trial was divided into five treatments, each with 18 blueberry plants. After planting, drip irrigation (8 times a day, 100 ml each time) with water was used for three days. The pH was set to 4.8 (the pH value of the nutrient solution was adjusted by sulfuric acid), and the treatment was started after three days. Growth-related indexes were determined on the 30th, 60th, and 90th days of treatment, and destructive sampling analysis was performed on the 90th day of treatment.
2.1 Experimental I
2.1.1 Effects of different nutrient solution formulations on blueberry
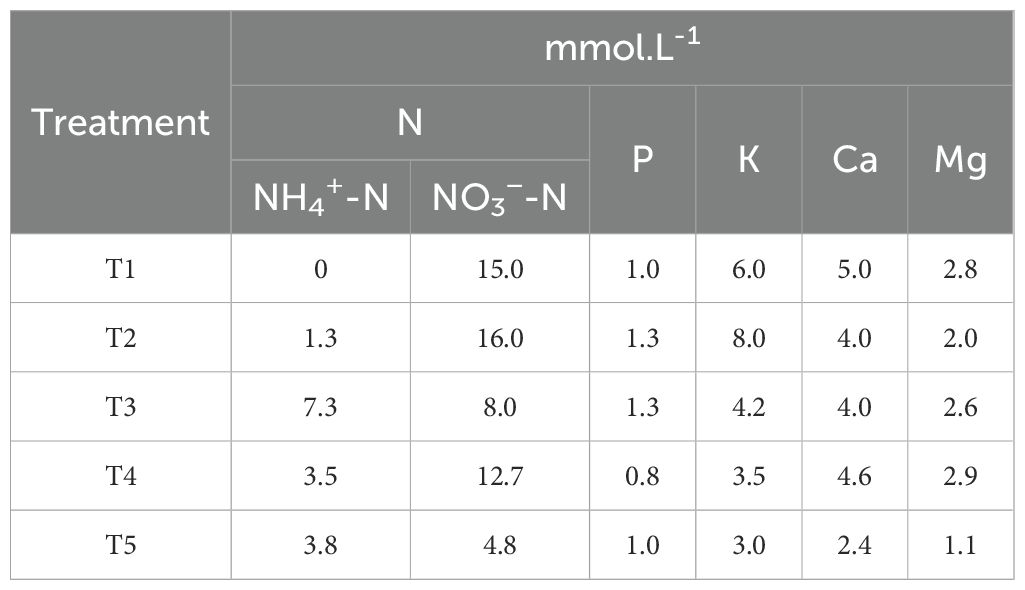
To investigate the effects of different nutrient treatments on blueberry, the three existing blueberry nutrient solution formulas and two standard nutrient solution formulas were selected, shown in Table 1. After the trial, the indicators were measured and analysed, and the formula with the best comprehensive index was chosen as the basic formula for further experiments. The contents of trace elements in each treatment are shown in Supplementary Table S1.
2.2 Experimental II
2.2.1 Effects of different nitrogen and potassium levels on blueberry
In this experiment, the best treatment was selected from the previous, while the concentration of N or K elements was changed, as shown in Table 2. Moreover, the concentration of other elements remained unchanged. There were 5 treatments, while the contents N and K concentrations in CK remained unchanged. The content of trace elements in each treatment is shown in Supplementary Table S1, and the concentration of macro-elements is shown in Table 3.
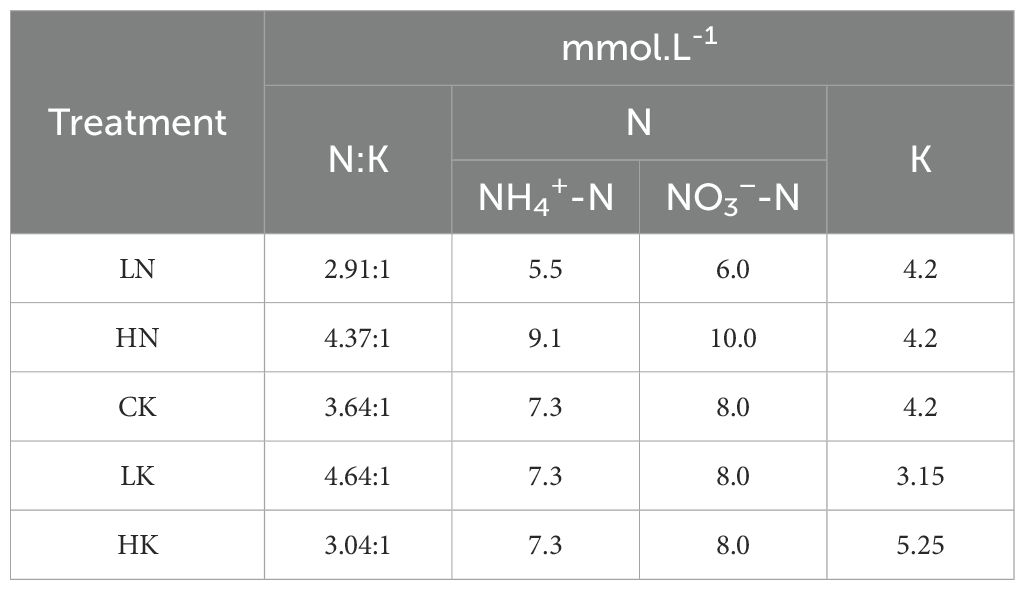
Table 3. Proportion and concentration of nitrogen and potassium at different nitrogen and potassium levels.
2.3 Experimental III
2.3.1 Effects of different levels of NH4 and NO3 on blueberry plants
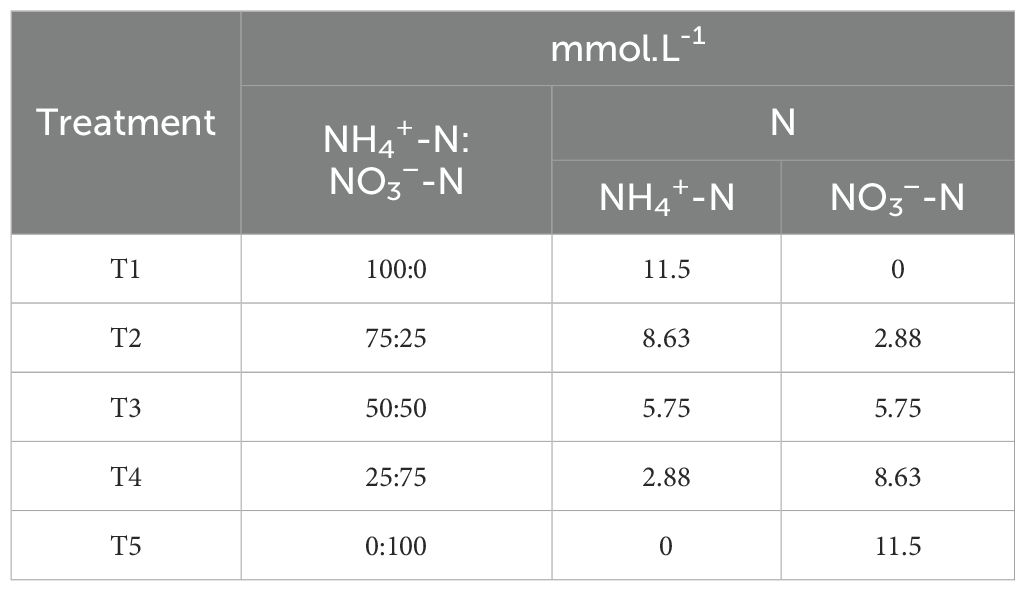
Based on the previous experiment, the excellent treatment was used for further modification to investigate the effect of different ammonium nitrate ratios on blueberries. Under the total nitrogen amount determined in experiment II, five different levels of ammonium nitrate ratio (NH4+-N/NO3-N) were designed, i.e., 100:0, 75:25, 50:50, 25:75, 0:100, where (NH4) 2SO4 and NO3-N provided NH4+-N was provided by Ca (NO3)2 and KNO3, as mentioned in Table 2. The dosage of trace elements in each treatment is shown in Supplementary Table S1, and the concentration of ammonium nitrate nitrogen is shown in Table 2.
2.4 Determination of plant morphological indicators
Nine blueberry plants with uniform growth were labelled in each treatment, and morphological indexes were measured on the 30th, 60th, and 90th days of treatment. Measure the stem thickness of blueberry shoots through a digital vernier calliper and the length of blueberry shoots were measured by measuring tape. The blueberry leaf picture and the whole blueberry picture were taken, and the leaf area and top projection area (cm2) of the blueberry were calculated using Image J (V1.8.0) software.
2.5 Determination of photosynthetic pigments in blueberry leaves
The contents of chlorophylls were determined on 5th-7th leaves of the basal branches from top to bottom were harvested. 0.2g leaf tissue were inserted into 95% ethanol solution and put in dark for 24h, and then chlorophyll a (Chl A), chlorophyll b (Chl B), and carotenoid was measured as previously described. The optical density was recorded at 665, 649 and 470nm using a spectrophotometer (Li et al., 2022; Xing et al., 2022). The calculation formula is as follows:
● Chlorophyll a concentration (mg/L) = 12.7× OD665-2.69×OD649
● Chlorophyll b concentration (mg/L) = 22.9× OD649-4.86×OD665
● Total chlorophyll concentration (mg/L) = 8.02×OD6655+20.20×OD649
● Carotenoid concentration (mg/L) = 4.7×OD447-0.27× total chlorophyll concentration
● Photosynthetic pigment content (mg/g) = (photosynthetic pigment concentration × extraction volume) / sample mass
2.6 Determination of photosynthetic characteristics of blueberry leaves
After 90 days of treatment, 10 plants were randomly selected for each treatment, and the light and parameters of basal functional leaves (top-down 5-7) were measured by LI-6400 portable photosynthetic instrument at 9:00~11:00 a.m. in sunny weather, including net photosynthetic rate (Pn), transpiration rate (E), stomatal conductance (Gs), and intercellular CO2 concentration (Ci) (Zhao et al., 2024).
2.7 Determination of physiological indexes of blueberry leaves
To investigate the physiological indexes of blueberry leaves, the 5th to 7th leaves were harvested. The SOD activity and malondialdehyde contents were determined by the nitrogen blue tetrazolium (NBT) photochemical reduction method and thiobarbituric acid (TBA) reaction method, respectively (Wu et al., 2022).
2.8 Determination of soluble sugar and starch contents
The contents of soluble sugar in blueberry leaves were determined by using previously describe method. Briefly, 1g fresh samples were grounded and rinsed with ddH2O2 and then the extractions were filtered and boiled for 30mints, and the tube and residue were flushed to the final volume (100 ml). 0.5ml extract solution and 1.5ml ddH2O2 were added to 25ml tube and gently mixed with 0.5ml anthrone-ethyl acetate and 5 ml concentrated sulfuric acid, then boiled for 1min. After cooldown at room temperate, the absorbance was measure at 630nm (Wang et al., 2022).
Th contents of starch in blueberry leaves were determined by anthrone method. Briefly, 0.1g samples were homogenized in in 10ml of 80% of ethanol and then water bathed at 80°C for 30 mins. After centrifugation at 6000rmp for 10 mints, the supernatants were combined with 2ml on anthrone regent and biol again for 7mints. Finally, the absorbance was recorded at 620nm as described previously (Clegg, 1956).
2.9 Determination of mineral element contents in blueberry plants tissues
The leaves of blueberries (the third test were roots, stems, and leaves) were washed and dried and placed in an oven at 105°C for 30min, and dried to constant weight at 75°C to obtain dry samples. To determine the total nutrients contents samples were first digested in HNO3 by using a microwave digestion system (Mars X press Microwave Digestion system, CEM, Matthews, NC, USA), and then analysed by ICP-OES (ICP-OES, Optima 5300 DV, Perkin Elmer, Waltham, WA, USA) analyzer, while Jaldal Method was used for N contents determination (Huang et al., 2016; Rodríguez-Vila et al., 2022) The nutrient status of blueberry leaves in this experiment will be evaluated with reference to the previous grading standards for blueberry leaf nutrients (Huang et al., 2016).
2.10 Investigation of blueberry flowering and fruiting habits
From November 2022, the flowering rate was counted, and the first flowering stage, full flowering stage and last flowering stage of shoots were calculated, and 12 blueberry shoots were counted for each treatment. The petals are dehisced, revealing the stigma for which the flower opens. The flowering percentage reaches 20% for the first flowering stage, the flowering percentage reaches 50% for the full flowering stage, and the flowering percentage reaches 90% for the late flowering stage, and the flowering rate = number of flowers/total number of flowers ×100%. After pollination and fertilization, it can grow and develop normally to form young fruits, which is the success of fruit set, and the fruit setting rate = number of fruit sets/number of flowers × 100% (Yang et al., 2022b).
2.11 Data processing
In this experiment, SPSS 26.0 software was used for statistical analysis, and Duncan method was used for multiple comparisons of single factor tests, and P<0.05 reached a significant level of difference, and Origin 2021 software was used for plotting.
3 Results
3.1 The effects of different nutrient solution formulations on the growth form of blueberries
As shown in Figure 1. different nutritional treatments significantly affected on plant height, shoot length, leaf area, stem thickness, number of shoots plant-1, and top projection area of blueberry. The results showed that the plant height, shoot length, leaf area, stem thickness and top projection area on the 30th day among the treatments remained statically the same, whereas on 60 and 90th day of treatment showed significant differences as presented in Figure 1. In particular, the plant height, shoot length, leaf area, stem thickness, no. shoots plant-1 and top projection area were significantly increased by 42.60%, 18.34%, 28.05%, 28.21%, 39.58%% and 32.10% in T3 treatment respectively, when compared to T1. Likewise, on 90th day of treatment, the plant height, shoot length, leaf area, stem thickness, number of shoots plant-1 and top projection area were significantly increased by 30%, 18.06%, 45.51%, 46.47%, 31.57% and 59.81% were improved considerably in T3 treatment respectively, as compared to T1, as presented in Figure 1. Additionally, the different nutrient treatments potentially regulate the blueberry growth as presented in Figure 1G. These results suggested that T3 treatment was more conducive and significantly increased the blueberry plant growth, hence consider for a subsequent experiment.
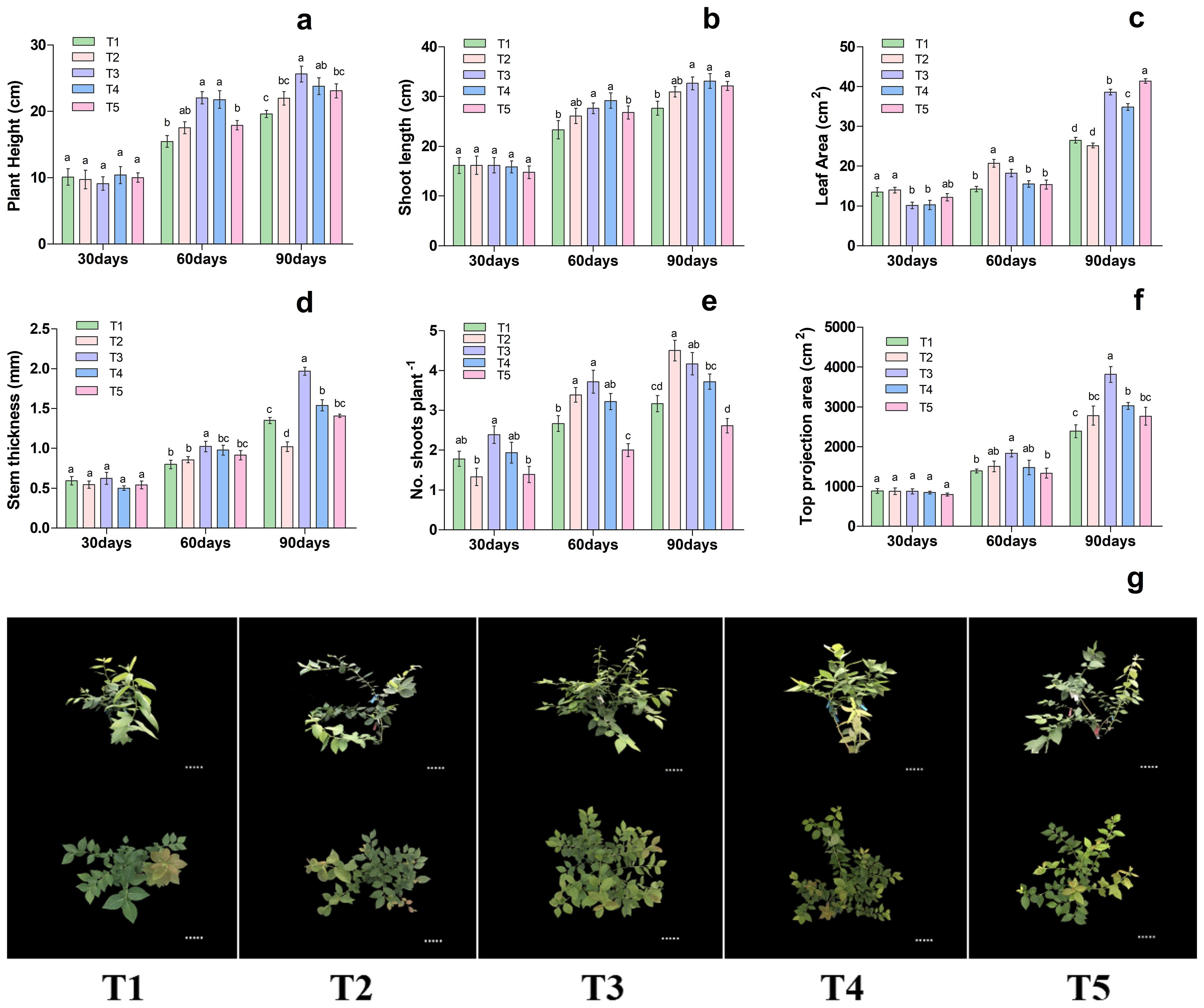
Figure 1. Changes in plant morphological characteristics under different nutritional treatments in blueberry. The growth morphology of the blueberry; (A) plant height, (B) shoot length, (C) leaf area, (D) stem thickness, (E) No od shoots plant-1, (F) top projection area, (G) blueberry shoot growth at different times 30days, 60days and 90days after treatments. The data indicated are the means ± SD. Different letters above the column indicate a significant difference between the treatments (P<0.05).
3.2 Effects of different nitrogen and potassium levels on blueberry growth
Based on previous experiments, treatment T3 was used to investigate the effect of different N and K levels on blueberry growth. As shown in Figure 2, different nitrogen and potassium levels significantly affected on blueberry plant height, shoot length, leaf area, stem thickness, no. of shoots plant-1, and top projection area. The results showed that 30th day of treatment showed no significant difference in shoot length, stem thickness, and leaf area. In contrast, the top projection area in CK (control) and LK treatments was significantly lower than that of HN treatment, as presented in Figure 2. On the 60th and 90th days of treatment, the stem thickness and length were increased first and then decreased with the increase of nitrogen and potassium levels in the nutrient solution, respectively, and reported maximum under CK treatment. On the 60th and 90th days of treatment, the top projection area of plants decreased gradually with the increase of nitrogen level.
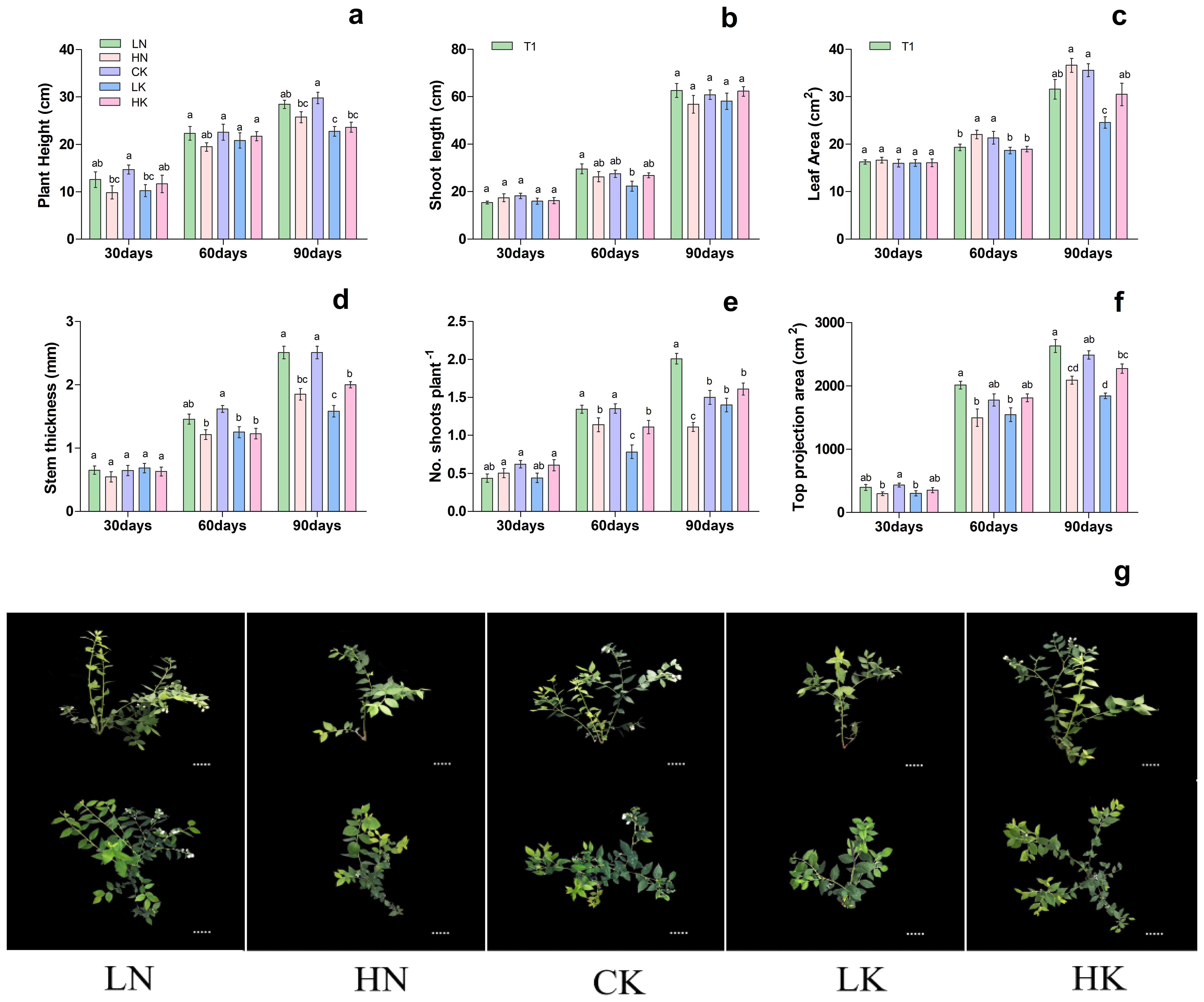
Figure 2. Changes in plant morphological characteristics under nitrogen and potassium levels (LN, HN, CK, LK, and HK) in blueberry. The growth morphology of the blueberry; (A) plant height, (B) shoot length, (C) leaf area, (D) stem thickness, (E) No od shoots plant-1, (F) top projection area, (G) blueberry shoot growth at different times 30days, 60days and 90days after treatments. The data indicated are the means ± SD. Different letters above the column indicate a significant difference between the treatments (P<0.05).
Meanwhile, with the rise in potassium level, the top projection area of the plant increased first and then decreased, reaching a maximum of 2489.34 cm2 in the CK. Likewise, the leaf area was increased gradually with the increase of nitrogen level, while with the rise in potassium levels, the leaf area was increased first and then decreased, and reported maximum at CK; 21.34 and 35.58 cm2, respectively (Figure 2). These results are predicted that, in comparison of CK and LN treatments, the blueberry plant growth of HN, LK and HK treatments was significantly reduced. Based on these findings, it can be concluded that LN and CK treatments were more favorable for the growth of blueberries.
3.3 Effect of different proportions of ammonium nitrate nitrogen on blueberry growth
To further investigate the effect of proportions of ammonium (NH4+) and nitrate (NO3-) (NH4+-N: NO3−-N) on blueberry, then premium treatment LN was modified through NH4+ and NO3- levels. The results showed that, with the increase of treatment time, the effect of different proportions of NH4+ and NO3 levels on the growth morphology of blueberry plants gradually increased, thus significantly affecting the growth morphology of blueberry seedlings (Figure 3). On 30th day of treatment, there were no significant differences in stem thickness, stem length, top projection area and leaf area of each treatment. However, on 60th day of treatment, with the decrease of the ratio of NH4+-N: NO3−-N, the stem diameter growth of the extended branches of the plants increased first and then decreased, and the 75:25 and 50:50 treatments were significantly higher than those of NH4+; 100:0 and NO3; 0:100 treatments. The top projection area of plants also increased first and then decreased with the decrease of the ratio of NH4+-N: NO3−-N, and the 50:50 and 25:75 treatments were significantly higher than those of the other treatments. Moreover, the plant height, stem diameter growth, leaf area, and top projection area of the plants increased first. Then it decreased with the decrease of the ratio of NH4+-N: NO3−-N, reaching the maximum at 50:50 and 25:75 treatments, respectively as presented in Figure 3. In conclusion, on the 90th day of treatment, the growth of plants increased first and then decreased with the decrease of the ratio of NH4+-N: NO3−-N, and compared with the single form of nitrogen, the mixed application of ammonium and nitrate was significantly more conducive to the growth of plants.
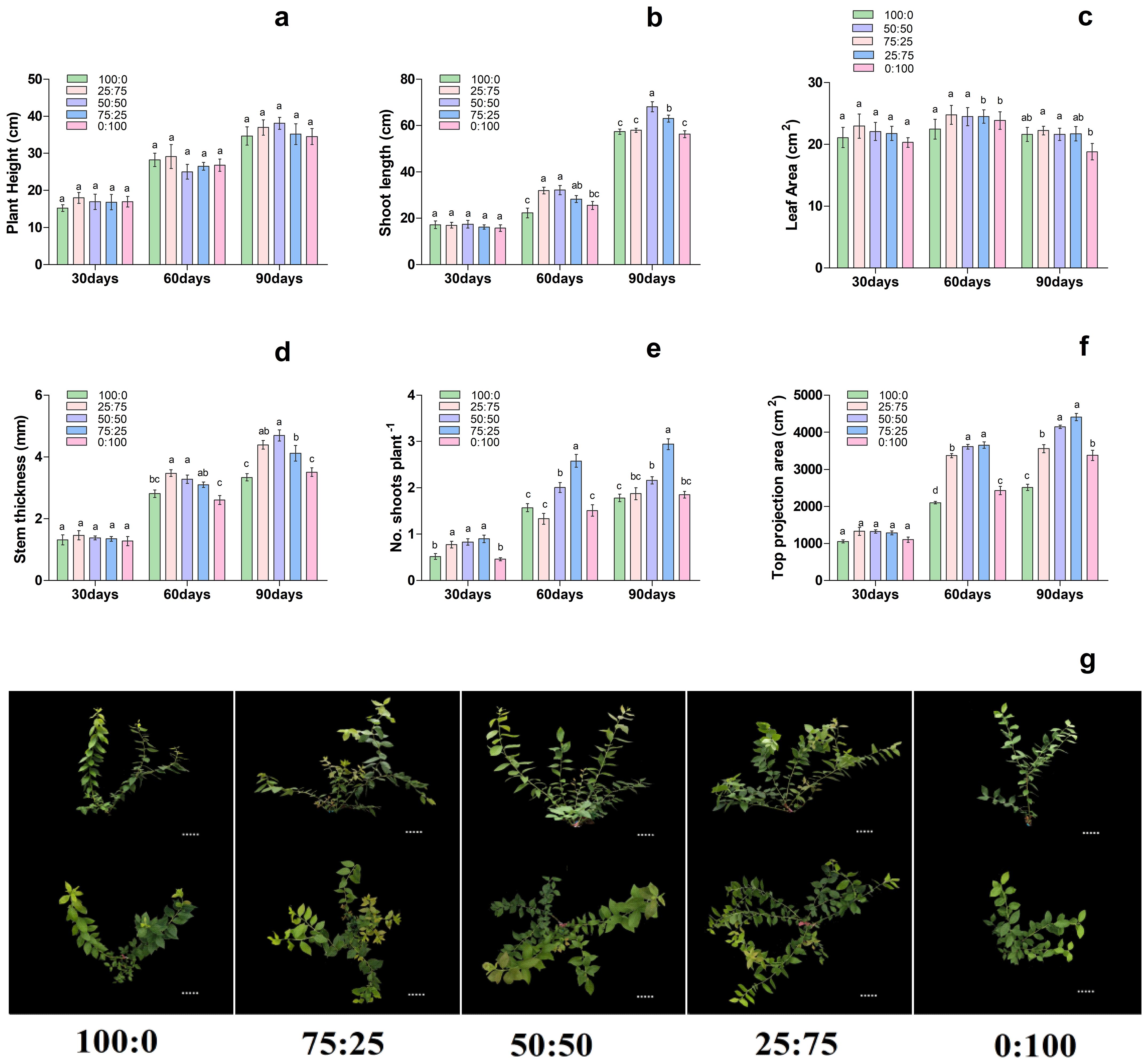
Figure 3. Changes in plant morphological characteristics under nitrogen and potassium levels (LN, HN, CK, LK and HK) in blueberry. Ther growth morphology of the blueberry; (A) plant height, (B) shoot length, (C) leaf area, (D) stem thickness, (E) No od shoots plant-1, (F) top projection area, (G) blueberry shoot growth at different times 30days, 60days, and 90days after treatments. The data indicated are the means ± SD. Different letters above the column indicate a significant difference between the treatments (p<0.05).
3.3.1 Effect of different proportions of NH4+-N: NO3−-N, on photosynthetic pigments in blueberry leaves
Chlorophyll is the most crucial pigment that plays an essential role in plant growth and development; thus considered a key growth indicator. The results of this study showed that the ratios of NH4+-N: NO3−-N caused a significant variation on the accumulation of chlorophyll and carotenoid contents in blueberry (Figure 4). On the 30th and 60th days of treatment, the contents of chlorophyll a (Chl. A), chlorophyll b (Chl. B), total chlorophyll (Chl. A+B) and carotenoids increased first and then decreased with the decrease of the ratio of NH4+-N: NO3−-N, and all reached the maximum at 75:25 treatment. Whereas, at 90th day of treatment, the content of each chlorophyll was increased first and then decreased with the decrease of the ratio of NH4+-N: NO3−-N, but reached the maximum value at 50:50 treatment. These results determine that the application of a higher proportion (75:25) of ammonium/nitrate in the early and middle stages of treatment would promote the accumulation of photosynthetic pigment in blueberry leaves. However, with the increase of treatment time, the application of an appropriate ratio (50:50) of ammonium nitrate nitrogen could promote the accumulation of photosynthetic pigment in leaves. Their findings suggest that the composition NH4+-N: NO3−-N ratio played a crucial role in chlorophyll biosynthesis in blueberry.
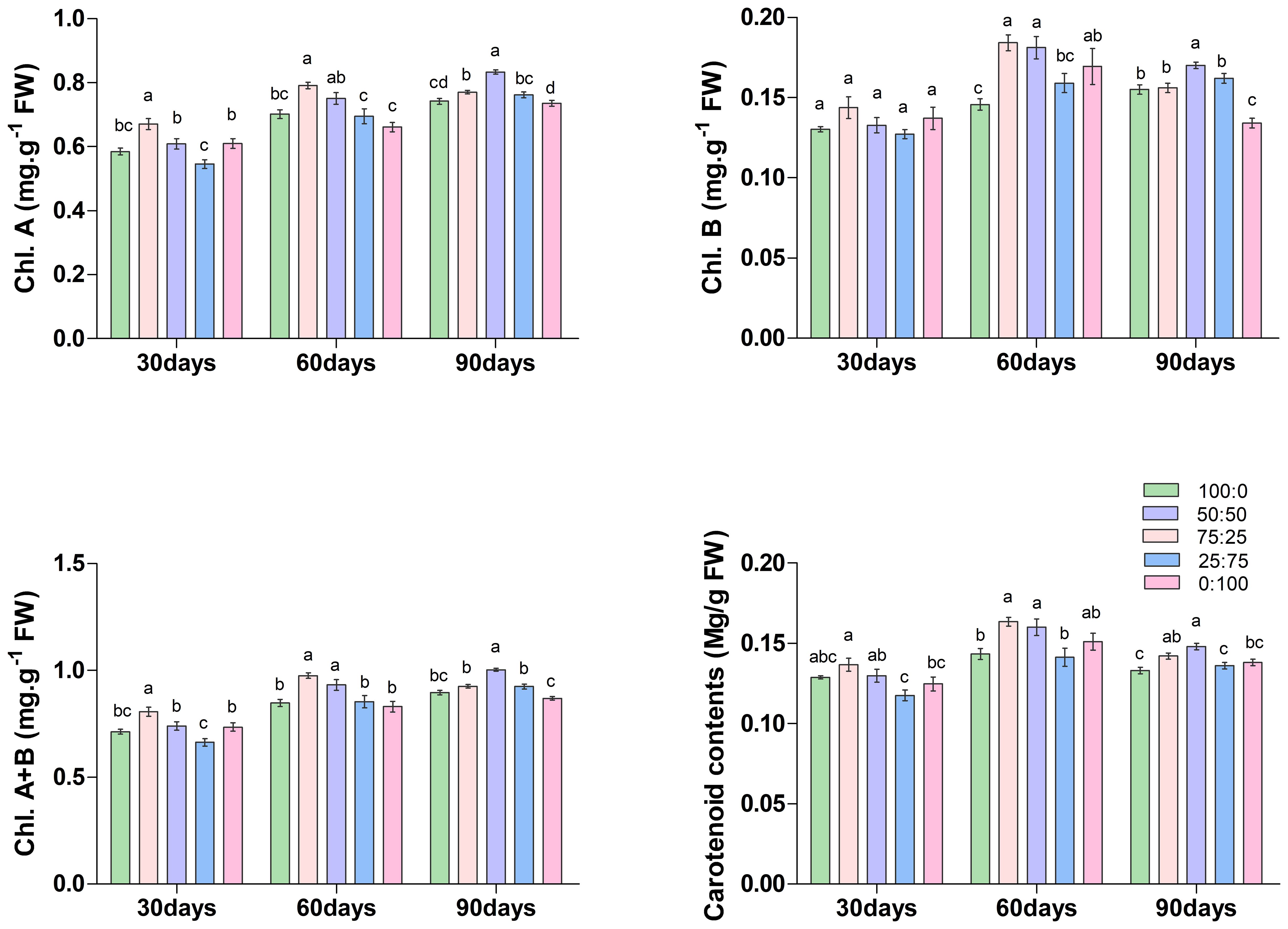
Figure 4. The effect of NH4+-N: NO3−-N levels on chlorophyll content in blueberry. Results are presented as the mean (n=4) and the bars above columns represent the standard deviation (SD). Different letters above the bars indicate significant differences (P< 0.05).
3.3.2 Effect of different proportions of ammonium nitrate nitrogen on photosynthetic parameters of blueberry leaves
The application of different proportions of NH4+-N: NO3−-N had a significant effect on the photosynthetic capacity of blueberry leaves. As presented in Figure 5, the net photosynthetic rate (Pn), transpiration rate (Tr), and stomatal conductance (Gs) of blueberry leaves increased first. Then, it decreased with the decrease of the ratio of NH4+-N: NO3−-N. The Pn rate and Tr reaching the maximum at 50:50, whereas Gs was noted maximum at 50:50, followed by 75:50 treatment as presented in Figure 5D. Similarly, intercellular concentration CO2 (Ci) of blueberry leaves decreased first and then increased with the decrease of the ratio of NH4+-N: NO3−-N, and was the lowest was reported in 50:50 treatment. The results indicated that the application of ammonium nitrate nitrogen in an appropriate ratio (50:50) was more conducive to the photosynthesis of blueberry leaves.
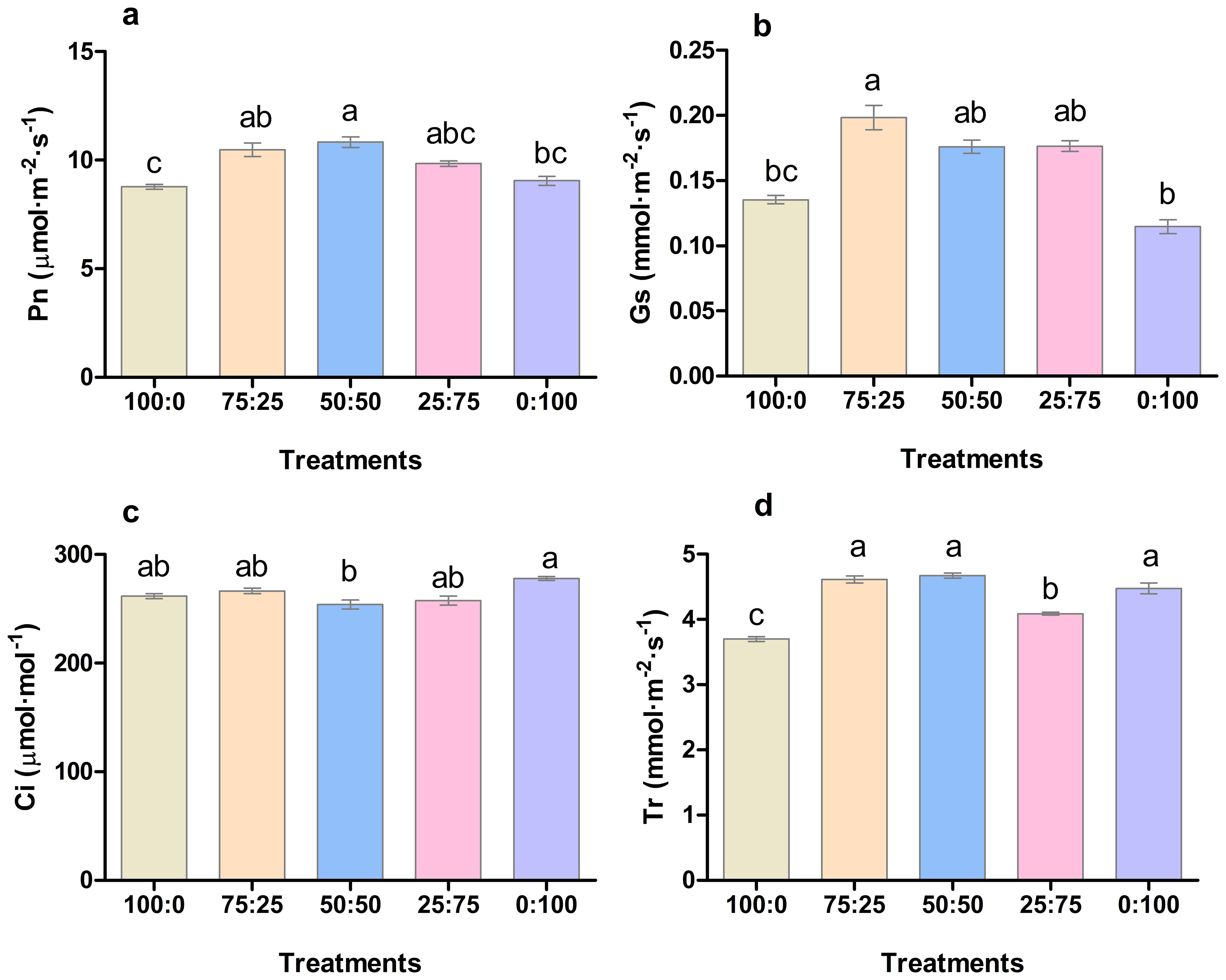
Figure 5. The effect of NH4+-N: NO3−-N levels on photosynthesis (A); net photosynthetic rate (Pn), (B); stomatal conductance (Gs), (C); intercellular CO2 concentration (Ci), and (D); transpiration rate (Tr) in blueberry. Results are presented as the mean (n=4), and the bars above columns represent the standard deviation (SD). Different letters above the bars indicate significant differences (P< 0.05).
3.3.3 Effects of different proportions of NH4+-N: NO3−-N on SOD activity and MDA content in blueberry leaves
Antioxidant enzymes play a crucial role in plant response to environmental hurdles and reduce the harmful effects. The involvement of NH4+-N: NO3−-N in SOD enzyme activity and MDA production was analysed in blueberry leave (Figure 5). The results showed that SOD activity and MDA contents of blueberry leaves changed regularly with the decrease of the ratio of NH4+-N: NO3−-N. The higher the proportion of nitrate application enhanced the SOD activity of leaves and reported the maximum 1:100 treatment. However, the higher proportion of ammonium application resulted in a significant increment in MDA contents, as shown Figure 6. The maximum MDA contents were noted in the whole ammonium treatment 100:0. These results suggest that increasing the proportion of nitrate in the nutrient solution is beneficial to reduce the stress on blueberry plants.
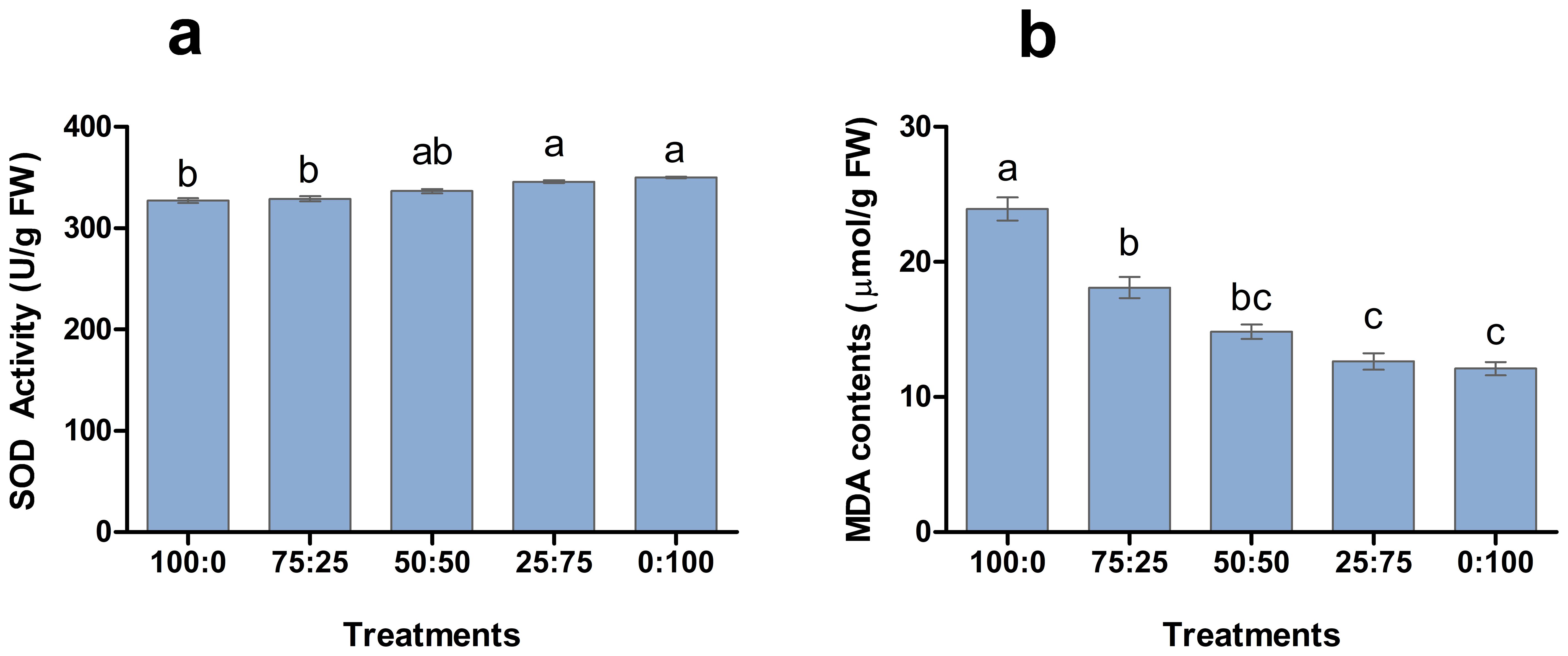
Figure 6. The effect of NH4+-N: NO3−-N levels on SOD activity (A) and MDA contents (B) in blueberry. Results are presented as the mean (n=4) and the bars above columns represent the standard deviation (SD). Different letters above the bars indicate significant differences (P< 0.05).
3.3.4 Effect of different proportions of ammonium nitrate nitrogen on the mineral element content of blueberry leaves
After 90 days of treatment, the application of different proportions of NH4+-N: NO3−-N had a significant effect on the mineral accumulation of blueberry leaves (Figure 7). The contents of N, P, Ca and Mg in blueberry leaves were increased first and then decreased with the increase of nitrate nitrogen application. The N contents were significantly maximum (17.46 mg/g) in 25:75 treatment. In contrast, P, Ma and Ca contents were 1.20 mg/g, 10.58 mg/g, and 3.29 mg/g in 50:50 treatment, respectively, were significantly higher when compared to other treatments. The K contents were considerably higher in 0:100 treatment, while the minimum K was noted in 100:0 treatment. The results showed that K contents were gradually increased with the increase of N contents. While, the Fe contents were significantly higher in 100:0 and 75;25 treatments, whereas minimum Fe was reported in 0;100 treatments. These findings suggest that NH4+-N: NO3−-N ratio was key in nutrient uptake and accumulation, thus improving blueberry growth and production.
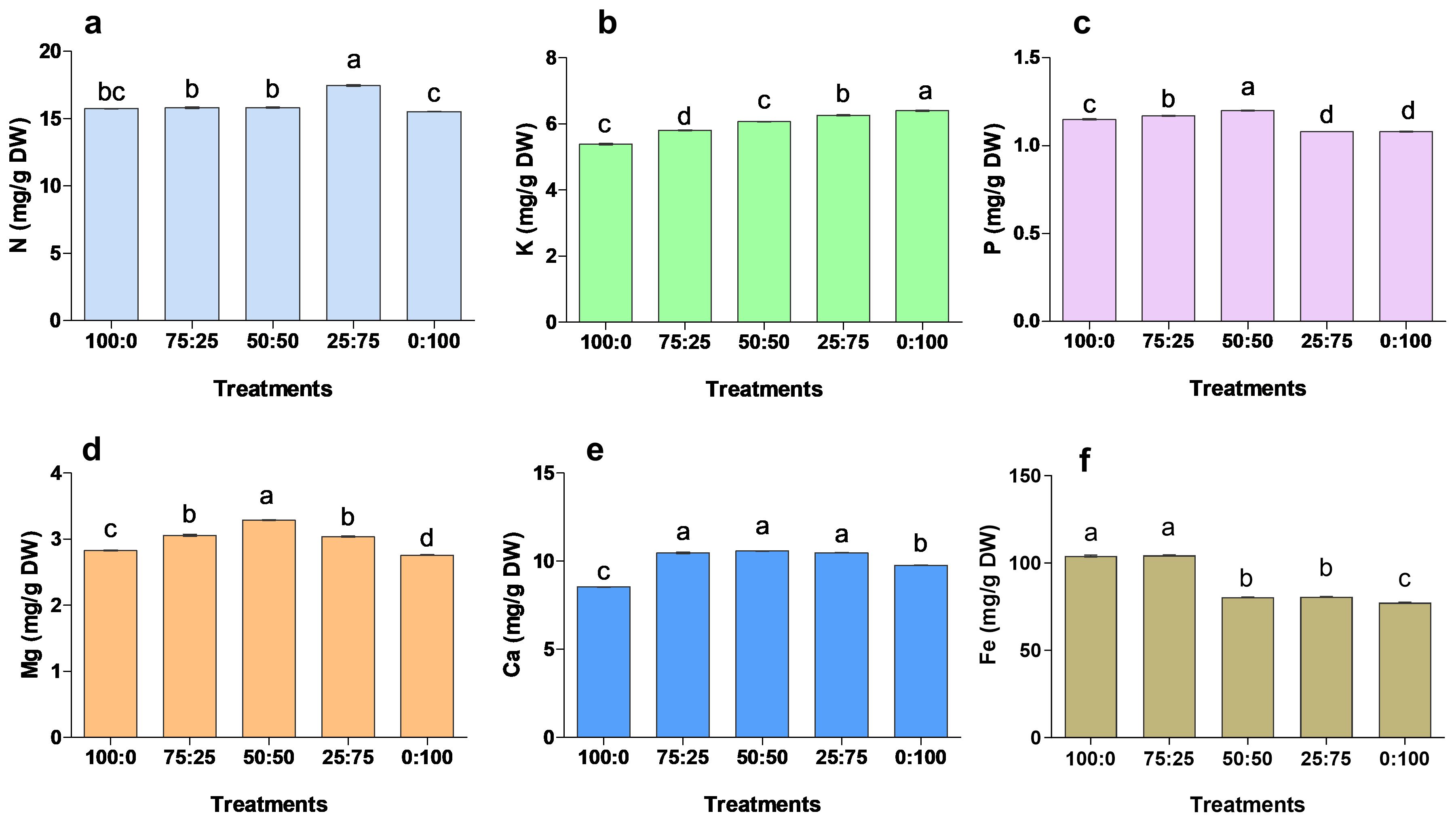
Figure 7. The effect of NH4+-N: NO3−-N levels on nutrient accumulation in blueberry (A–F). Results are presented as the mean (n=4) and the bars above columns represent the standard deviation (SD). Different letters above the bars indicate significant differences (P< 0.05).
3.3.5 Effect of different proportions NH4+-N: NO3−-N on soluble sugar and starch
Nitrogen is the essential macro-nutrient for plant growth and developmental processes, involved in synthesizing amino acids, proteins, carbohydrates, proteins, chlorophyll, and other metabolites. Here, we investigate the effect of NH4+-N: NO3−-N ratio on soluble sugar and starch contents in blueberry leaves, as presented in Figure 8. The results showed that soluble sugar and starch contents of blueberry leaves increased first and then decreased with the increase of NH4+-N: NO3−-N ratio. The maximum soluble sugar content (10.64 mg/g), which was 21.88% higher than that of the all-ammonium treatment, was noted in 25:75 treatment. These results predicted that the application of NH4+-N: NO3−-N ratio in an appropriate ratio (50:50) was more conducive to the occurrence of carbon and nitrogen metabolism in blueberry leaves, hence improving blueberry growth and production.
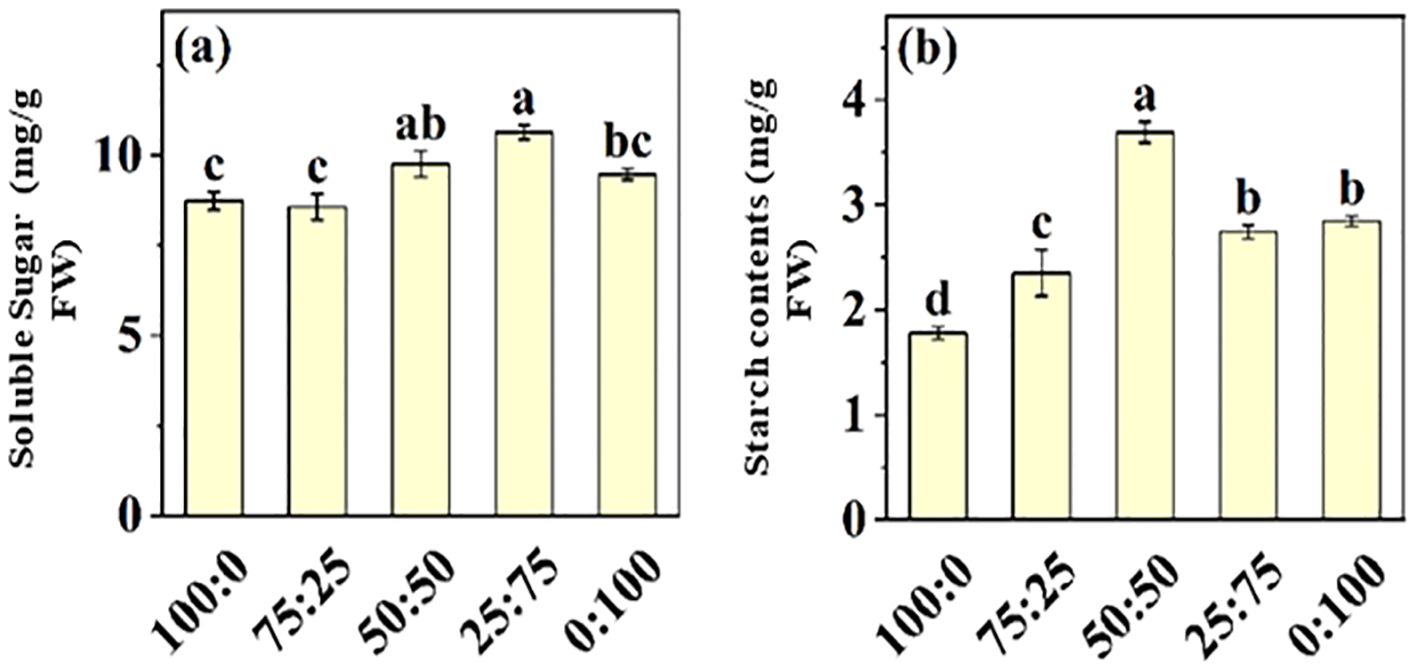
Figure 8. The effect of NH4+-N: NO3−-N levels on soluble sugar (A) and starch contents (B) in blueberry. Results are presented as the mean (n=4) and the bars above columns represent the standard deviation (SD). Different letters above the bars indicate significant differences (P< 0.05).
3.3.6 Effects of different proportions of ammonium nitrate nitrogen treatment on blueberry flowering
For the blueberry plant, flower development, initiation, and inductions are primarily critical, due to its high sensitivity to environmental cues. Here in this study, we reported that NH4+-N: NO3−-N ratio significantly affected on reproductive growth (Figure 9). The results showed that there were differences in the timing, such as first flowering, full flowering and late flowering of blueberries with different NH4+-N: NO3−-N treatment. The 50:50 treatment was the first to enter the early flowering stage, which was four days earlier than the total ammonium (100:0) and 15 days earlier than the total nitrate treatment (0:100). However, 100:0 treatment entered the complete blooming stage significantly earlier than other treatments, which was 2, 3, 6 and 13 days earlier than the other four treatments, respectively. In contrast, the full flowering stage was also delayed with an increased NH4+-N: NO3−-N ratio.
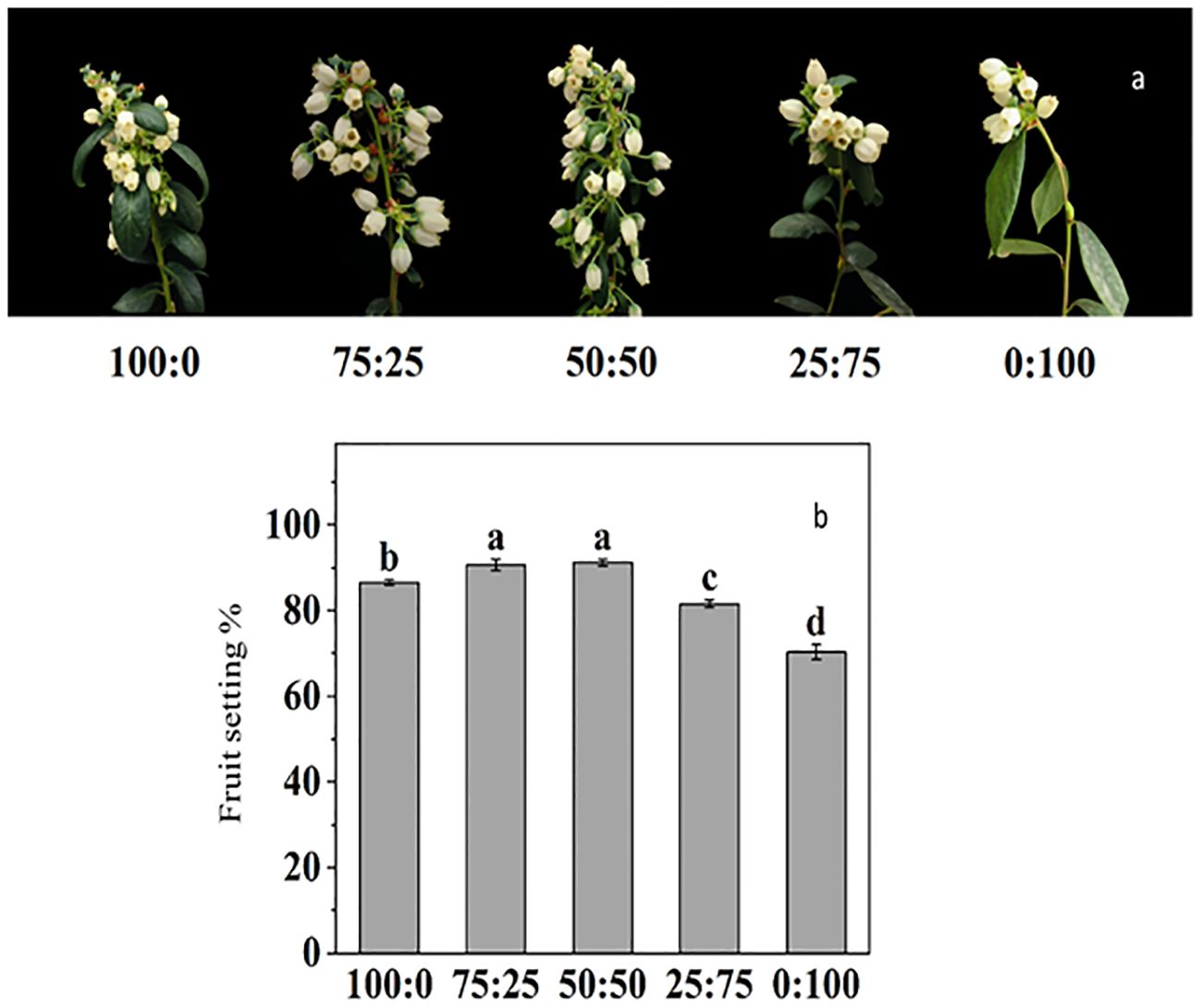
Figure 9. The effect of NH4+-N: NO3−-N levels on flower induction (A) and fruit setting percentage (B) in blueberry. Results are presented as the mean (n=4) and the bars above columns represent the standard deviation (SD). Different letters above the bars indicate significant differences (p< 0.05).
The fruit setting rate of blueberry was significantly affected by NH4+-N: NO3−-N treatments. As presented in Figure 9B, the increase in the proportion of NH4+-N: NO3−-N, the fruit setting rate of blueberry, increased first and then decreased. The maximum fruit-setting rate reported 50:50 treatment reached 91.23%, but there was no difference with 75:25 treatment, while the lowest fruit-setting rate 70.28%, was reported in NO3 (0:100) treatment.
3.3.7 Correlation analysis and principal component analysis and comprehensive evaluation of blueberries treated with ammonium nitrate nitrogen in different proportions
To further investigate and clarify the effect of nitrogen and potassium levels on blueberry growth, the correlation and PCA analysis were carried out as presented in Figures 10, 11, respectively. The correlation analysis suggested that the 100:0 treatment had high antioxidant enzyme activity in ammonium cations, while 75:25 and 50:50 treatments could significantly promote plant growth, chlorophyll contents, and photosynthesis. The 25:75 treatment was conducive to promoting the germination of blueberry basal growth branches and the accumulation of chlorophyll (Figure 10). These results suggest that 50:50 NH4+-N: NO3−-N level resulted in a significant improvement in blueberry growth and production.
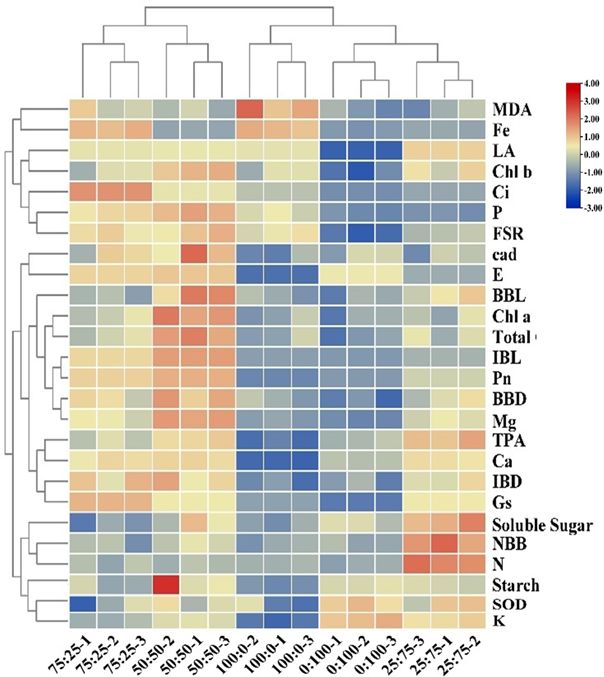
Figure 10. Cluster analysis of blueberry indexes in different proportions of NH4+-N: NO3−-N treatments.
However, the PCA analysis indicated that the cumulative contribution rate is greater than 85%, and the cumulative variance contribution rate of the first four principal components was 91.07%, which contained information on blueberry growth and development. The positive effects on the first principal component are mainly chlorophyll, the growth, branch length, the growth of basal branches, the net photosynthetic rate, and other indicators, and the loading weight is significant. The adverse effects are mainly Fe and intercellular carbon dioxide concentration (Figure 11). The key indexes such as SOD, MDA, soluble sugar, and K content had a positive effect on the second principal component. They had a considerable load weight, among which the leaf area, fruit setting rate, and P content had adverse effects. The distribution between the five treatments was far, indicating a significant difference. These results suggest that NH4+-N: NO3−-N ratio significantly affected blueberry growth and production.
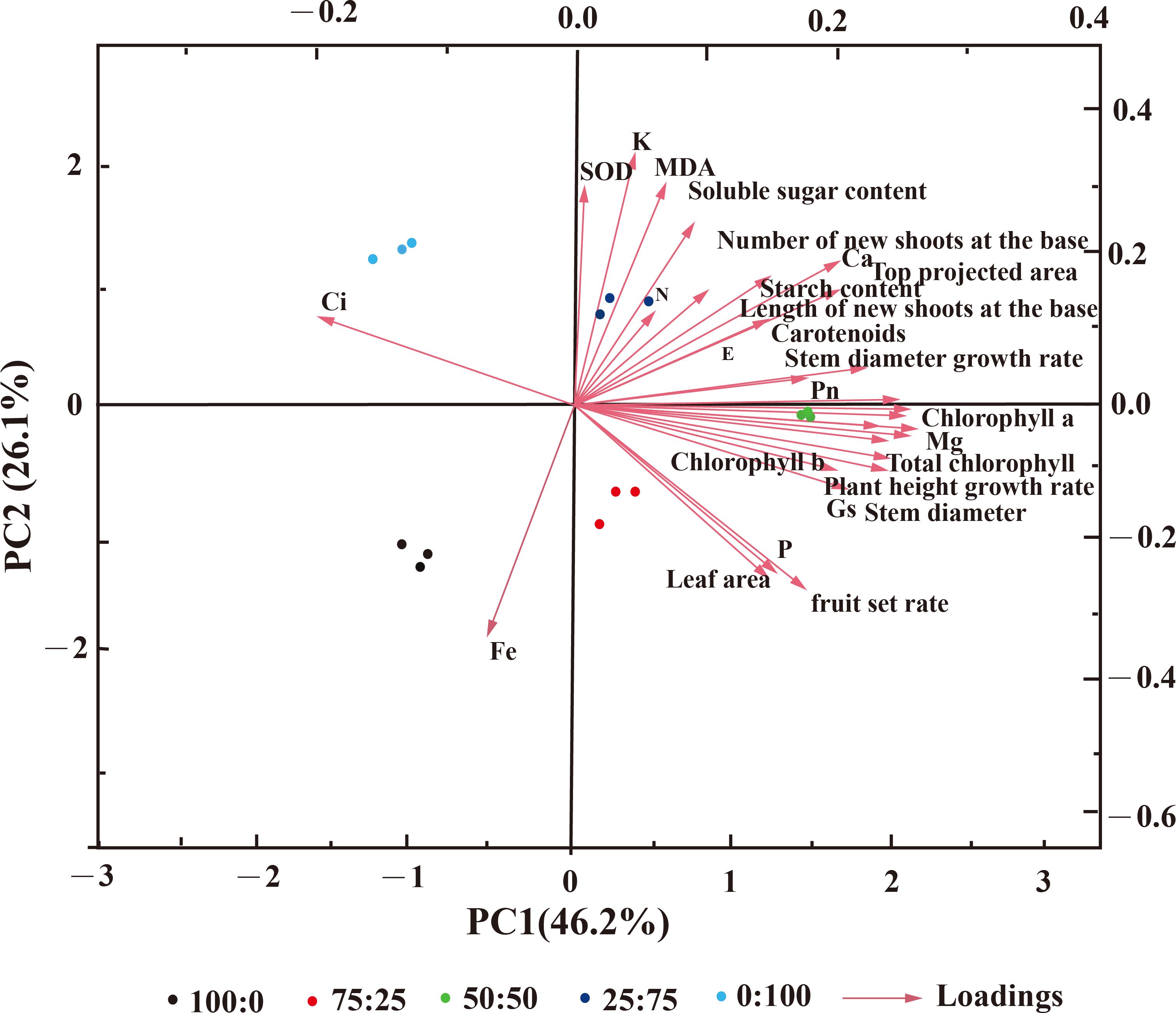
Figure 11. Principal component analysis (PCA) diagram of blueberry treated with NH4+-N: NO3−-N in different proportions.
4 Discussion
N is one of the essential macronutrients that play a role in plant growth and development, as well as crop production (Ye et al., 2022; Fu et al., 2023). Nitrate act as a signalling molecule that directly regulates the expression of key genes involved in regulating root and leaf development, cells expansion, regulating gene expression, and metabolism enzymes (Manoli et al., 2016; Tarkowski et al., 2024). The availability of N in the soil is primarily limited, while the application of additional N fertilizer to improve high crop production which not only increases input cost but also causes soil pollution (Kicklighter et al., 2019; Carillo and Rouphael, 2022; Vitousek et al., 2024). N uptake and accumulation by plants from soil in two forms: ammonium (NH4+) and nitrate (NO3-). In plants, the metabolism of N is followed by three key steps, including ammonia and nitrate transport, nitrate reduction and ammonia assimilation (The et al., 2021). Nitrate and ammonium transporters (low and high-affinity transporters) are involved in the absorption and transportation of NH4+ and NO3- ions on the root surface to the rest of plant tissues (Tarkowski et al., 2024). After absorption, nitrate ions are reduced into nitrite by nitrate reductase (NR) in cytoplasm and then transported into plastid, where it can be reduced into ammonium through nitrite reductase (NiR) enzyme (Tabatabaei et al., 2008; Zhao and Shen, 2018; Morales De Los Ríos et al., 2021). Therefore, the appropriate ratio of NH4+/NO3- might be substantial for plant growth and development by enhancing the uptake rate and accumulation of N in plant tissues (Tabatabaei et al., 2008; Zhu et al., 2021). Previous studies reported that appropriate NH4+/NO3- ratio are important for chlorophyll synthesis, nutrient uptake and optimum plant growth and biomass in rice and Chinese cabbage (Tabatabaei et al., 2008; Zhu et al., 2021; Fu et al., 2023). Moreover, the NH4+/NO3- ratio for plants varies from plant to plant and species. Likewise, 25:75 NH4+/NO3- treatment for tomato, strawberry, and Chinese cabbage (Tabatabaei et al., 2008; Zhu et al., 2021; Gholamnejad et al., 2023)., while 0;100 for wheat and 50:50 is the optimal ratio for soybean (Raza et al., 2021; Yang et al., 2022a).
Herein, in this study the blueberry plant height, shoot length, leaf area, and stem thickness were significantly increased in 50:50 NH4+/NO3- ratio, followed by 75:25 treatment (Figure 3). Moreover, the application of minimum NH4+/NO3- ratio (25:75) promotes the blueberry branches, top projection area, and improve the lateral growth of the plants. However, the maximum plant height, stem length, and diameter of blueberry branches were noted in 50:50 NH4+/NO3- ratio, thus indicating an appropriate ammonium-nitrate ratio (25:75~50:50) may promote the growth of blueberry basal branches (Figure 3). Previous study reported that, under the specific condition of a total nitrogen concentration, the optimal NH4+/NO3- ratio showed better growth characteristics and more significant biomass accumulation in Chinese cabbage seedlings, compared to the treatment with a single nitrogen source (Alt et al., 2017; Yang et al., 2023). Similarly, in this study, the 75:25, 50:50, and 25:75 treatments significantly increased blueberry growth compared to the full ammonium or total nitrate treatments. Likewise, the contents of chlorophyll (Figure 4) and photosynthetic capacity (Figure 5) were enhanced by 75:25, 50:50 treatments, respectively. These results indicate that NH4+ and NO3- combinations maybe beneficial for synthesizing photosynthetic pigments in blueberry leaves and to improve production. Under a specific total nitrogen concentration, the chlorophyll content and net photosynthetic rate of blueberry leaves were increased compared with NH4+ and NO3- alone (Tabatabaei et al., 2008; Alt et al., 2017). These results are supported by previous studies, which reported that the NH4+ and NO3- treatment regulate plant growth, expression of candidate genes of photosynthesis machinery and chlorophyll metabolism in rice and tomato seedlings (Fu et al., 2023; Gholamnejad et al., 2023). Thus, it can be concluded that NH4+ and NO3- treatment 50:50 is most beneficial and hence causes a significant increment in blueberry seedling growth through improving chlorophyll accumulation and photosynthesis (Hao et al., 2023).
The absorption and transportation of NH4+ and NO3- ions in plants are mostly affected by various factors, including soil environment, abiotic stresses, crop species and genotype (Alt et al., 2017; Fu et al., 2023; Chen et al., 2024). Previous studies reported that crops suitable for acidic soils tend to prefer NH4+, while crops ideal for neutral or alkaline soil environments tend to show a preference for NO3- fertilizers (Cui et al., 2017; Zhu et al., 2021), because in acidic soils with low pH, the nitrifying process cannot be carried out generally due to the decrease in nitrifying bacteria. The available nitrogen produced by microorganisms from decomposing organic matter is mainly ammonium nitrogen, while in neutral and alkaline soils, the available nitrogen produced by nitrifying bacteria is mainly nitrate nitrogen (Santos et al., 2018; Goñi et al., 2021). Soil pH mostly change after crops absorb NH4+ and NO3- ions, affecting the availability of other nutrients. Hence, these two forms of nitrogen and other ions have a direct or indirect effect on plant growth (Cui et al., 2017). A previous study reported that the ratio of NH4+ and NO3- had a different impact on the biomass accumulation of various crops. In tomato, the ratio of NH4+ and NO3- treatment, 50:50 and 25:75 was most beneficial for the growth of tomato seedlings (Gholamnejad et al., 2023). Likewise, 75:25 NH4+ and NO3- treatment significantly improve seedling growth and biomass in rice and maize (Wang et al., 2023; Yunchao et al., 2024). Transcriptomic analysis showed that 75:25 treatment regulates the expression of nitrogen metabolism, carbon fixation in the photosystem, photosynthesis, starch and sucrose metabolism, and zeatin synthesis (Wang et al., 2020; Wang et al., 2023). Thus, these findings suggest that the appropriate ratio of NH4+ and NO3- is crucial primarily for plant growth and development.
Blueberry plants are susceptible to environmental cues, which lead to a significant decline in growth and production (Alt et al., 2017; Nunez et al., 2023). The uptake and distribution of essential nutrients are crucial for maintaining homeostasis and plant growth under abiotic stress (Sathee et al., 2021; Carillo and Rouphael, 2022). Abiotic stresses significantly reduced the mineral uptake and accumulation, ultimately causing growth and biomass in cucumber and tomato seedlings (Raj et al., 2021; Ye et al., 2022). Herein, this study the ratio of NH4+ and NO3- treatments regulated the minerals uptake and accumulation in blueberry tissues Figure 7. Previous study showed that the mineral uptake and accumulation of P, K, Ca, Fe, Mn, and B were enhanced by 1:1 ammonium to nitrate ratio (Gholamnejad et al., 2023; Wu et al., 2024) This spectacle may be due to the dynamic equilibrium formed by the antagonism between NH4+ and NO3- ions to promote the absorption of essential elements, therefore resulting in a significant increment in chlorophyll contents and photosynthetic capacity (Figure 5), and enhancing blueberry growth (Figure 3). In this experiment, the application of different proportions of ammonium nitrate nitrogen also significantly affected the accumulation of mineral elements in blueberry roots and stems. The N, P, and K contents in blueberry reached the maximum when the NH4+ and NO3- ratios were 25:75 and 50:50, indicating that ammonium/nitrate mixed application could accumulate more nitrogen in plant leaves.
In plants, sugar and sucrose are the final product of photosynthesis, which are initially transported in the phloem to energize cells for the improvement of plant growth and development and activation of the defense system during abiotic stresses (Mehdi et al., 2024). Under abiotic stress conditions, plants need more energy to survive and protect cells from oxidative damage. Thus, sugars are vital sources of energy (Zhang et al., 2022). The results of this study showed that the soluble sugar and starch contents in blueberry leaves increased first and then decreased with the increase of the proportion NH4+ and NO3- (Figure 8). These results suggest that appropriate NH4+ and NO3- ratios facilitate the minerals uptake and accumulation (Figure 7), thus enhanced photosynthetic capacity and sugar synthesis (Tabatabaei et al., 2008; Alt et al., 2017; Cui et al., 2017; Signore et al., 2020; Morales De Los Ríos et al., 2021; Chen et al., 2024).
To observe the physiological changes of plants during nutritional treatments, the SOD activity and MDA content as essential indicators to reflect plant metabolism and stress resistance (Agarwal et al., 2020; Sathee et al., 2021; Lu et al., 2022). The results showed that the SOD activity of blueberry leaves was the lowest when the N source was only NH4 (100:0), and the highest SOD activity was when the N source was only NO3 (0:100). In contrast, the MDA contents were maximum in 100:0 and minimum in 0:100 treatments as shown in Figure 6, indicating that might be due to increasing of the proportion of NO3 in the N source was conducive to improving the ammonium stress of blueberries. In this experiment, applying different proportions of ammonium nitrate nitrogen affected the flowering time and flowering rate of blueberries (Figure 9). The plants were the first to enter the flowering stage when the ammonium nitrate ratio was 50:50, indicating that the appropriate ratio of ammonium nitrate nitrogen (50:50 treatment) was conducive to early flowering in blueberry. The higher the NH4+-N ratio, the faster the flowering speed and shorter the duration, indicating that the plants had a higher demand for NH4+-N in the nitrogen source after entering the first flowering stage (Figures 10, 11). In contrast, the high proportion of NO3-N significantly reduced the flowering rate of blueberry and delayed flowering initiation, indicating that blueberry was more adaptable to the high proportion of NO3-N in the reproductive growth stage (Figure 11). In this study, the fruit setting rate of blueberry had the same trend as the duration of flowering, and both of them increased first and then decreased with the decrease of the proportion of ammonium nitrate nitrogen applied, indicating that the appropriate proportion of mixed nitrogen (50:50 treatment) was conducive to improving the fruit setting rate of blueberry.
5 Conclusion
Blueberries have different requirements for ammonium and nitrate at various growth stages. The ammonium-to-nitrate ratio of 50:50 is conducive for the growth of shoots and accumulation of mineral elements, thus promoting the formation of flower buds, and fruit setting rate. In contrast, the ammonium-to-nitrate ratio of 100:0~75:25 can promote blueberries to enter the full flowering stage early and accelerate the development process from flower to fruit. In order to achieve the goal of high yield and quality of blueberry cultivated on substrate, reasonable fertilization should be applied according to the needs of different growth and development periods of plants. Considering the growth and nutrient use efficiency of blueberry, the N fertilizer level was reduced based on the improved formula of “Shaoyi Blueberry”, and the nutrient solution formula was formulated with NH4+-N: NO3−-N as 50:50, which could maximize the high-quality and efficient production of blueberry. Future experiment is needed to modify substrate and nutritional formulation corelation for enhanced blueberry production.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
AA: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Software. SS: Data curation, Formal analysis, Project administration, Writing – original draft, Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. CC: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. MC: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. YX: Writing – original draft. JW: Conceptualization, Data curation, Supervision, Writing – original draft. WS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Project administration, Writing – original draft. RC: Conceptualization, Data curation, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – original draft. JZ: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Project administration.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. Guangdong Provincial Science and Technology Plan Project of China (2024B0202010013), Special fund for rural revitalization strategy of Guangdong province, China (2024KJ25).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpls.2024.1438811/full#supplementary-material
References
Agarwal, P., Mitra, M., Banerjee, S., Roy, S. (2020). MYB4 transcription factor, a member of R2R3-subfamily of MYB domain protein, regulates cadmium tolerance via enhanced protection against oxidative damage and increases expression of PCS1 and MT1C in Arabidopsis. Plant Sci. 297, 110501. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2020.110501
Alt, D. S., Doyle, J. W., Malladi, A. (2017). Nitrogen-source preference in blueberry (Vaccinium sp.): Enhanced shoot nitrogen assimilation in response to direct supply of nitrate. J. Plant Physiol. 216, 79–87. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2017.05.014
Carillo, P., Rouphael, Y. (2022). Nitrate uptake and use efficiency: pros and cons of chloride interference in the vegetable crops. Front. Plant Sci. 13, 899522. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.899522
Chen, B., Shi, Y., Lu, L., Wang, L., Sun, Y., Ning, W., et al. (2024). PsNRT2.3 interacts with PsNAR to promote high-affinity nitrate uptake in pea (Pisum sativum L.). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 206, 108191. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2023.108191
Clegg, K. M. (1956). The application of the anthrone reagent to the estimation of starch in cereals. J. Sci. Food Agric. 7, 40–44. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.2740070108
Cocetta, G., Karppinen, K., Suokas, M., Hohtola, A., Häggman, H., Spinardi, A., et al. (2012). Ascorbic acid metabolism during bilberry (Vaccinium myrtillus L.) fruit development. J. Plant Physiol. 169, 1059–1065. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2012.03.010
Cui, J., Yu, C., Qiao, N., Xu, X., Tian, Y., Ouyang, H. (2017). Plant preference for NH4+ versus NO3– at different growth stages in an alpine agroecosystem. Field Crops Res. 201, 192–199. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2016.11.009
Fu, Y., Zhong, X., Lu, C., Liang, K., Pan, J., Hu, X., et al. (2023). Growth, nutrient uptake and transcriptome profiling of rice seedlings in response to mixed provision of ammonium- and nitrate-nitrogen. J. Plant Physiol. 284, 153976. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2023.153976
Gholamnejad, S., Haghighi, M., Etemadi, N., Pessarakli, M. (2023). The effects of N-NO3: N-NH4 ratios and calcium concentration of the nutrient solution on the growth parameters and partitioning of nitrogen and calcium in tomato plants (Solanum lycopersicum L.). J. Plant Nutr. 46, 2827–2840. doi: 10.1080/01904167.2022.2160753
Goñi, O., Łangowski, Ł., Feeney, E., Quille, P., O’connell, S. (2021). Reducing nitrogen input in barley crops while maintaining yields using an engineered biostimulant derived from ascophyllum nodosum to enhance nitrogen use efficiency. Front. Plant Sci. 12, 664682. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.664682
Han, T., Wu, W., Li, W. (2021). Transcriptome analysis revealed the mechanism by which exogenous ABA increases anthocyanins in blueberry fruit during veraison. Front. Plant Sci. 12, 758215. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.758215
Hao, D.-L., Zhou, J.-Y., Li, L., Qu, J., Li, X.-H., Chen, R.-R., et al. (2023). An appropriate ammonium: nitrate ratio promotes the growth of centipedegrass: insight from physiological and micromorphological analyses. Front. Plant Sci. 14, 1324820. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1324820
Hu, L., Wang, X., Liu, H., Wu, Y., Wu, W., Lyu, L., et al. (2023). Mechanisms of exogenous GA3-induced inhibition of seed development in southern highbush blueberry (Vaccinium darrowii). Sci. Hortic. 322, 112430. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2023.112430
Huang, Y., Zhao, L., Kong, Q., Cheng, F., Niu, M., Xie, J., et al. (2016). Comprehensive mineral nutrition analysis of watermelon grafted onto two different rootstocks. Hortic. Plant J. 2, 105–113. doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2016.06.003
Kicklighter, D. W., Melillo, J. M., Monier, E., Sokolov, A. P., Zhuang, Q. (2019). Future nitrogen availability and its effect on carbon sequestration in Northern Eurasia. Nat. Commun. 10, 3024. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-10944-0
Li, C., Ran, M., Liu, J., Wang, X., Wu, Q., Zhang, Q., et al. (2022). Functional analysis of CqPORB in the regulation of chlorophyll biosynthesis in Chenopodium quinoa. Front. Plant Sci. 13, 1083438. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1083438
Liu, L., Zheng, Y., Feng, S., Yu, L., Li, Y., Zong, Y., et al. (2022). Transcriptomic and physiological analysis reveals the responses to auxin and abscisic acid accumulation during vaccinium corymbosum flower bud and fruit development. Front. Plant Sci. 13, 818233. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.818233
Lu, W., Wei, G., Zhou, B., Liu, J., Zhang, S., Guo, J. (2022). A comparative analysis of photosynthetic function and reactive oxygen species metabolism responses in two hibiscus cultivars under saline conditions. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 184, 87–97. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2022.05.023
Manoli, A., Trevisan, S., Voigt, B., Yokawa, K., Baluška, F., Quaggiotti, S. (2016). Nitric oxide-mediated maize root apex responses to nitrate are regulated by auxin and strigolactones. Front. Plant Sci. 6, 1269. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2015.01269
Mehdi, F., Galani, S., Wickramasinghe, K. P., Zhao, P., Lu, X., Lin, X., et al. (2024). Current perspectives on the regulatory mechanisms of sucrose accumulation in sugarcane. Heliyon 10, e27277. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27277
Morales De Los Ríos, L., Corratgé-Faillie, C., Raddatz, N., Mendoza, I., Lindahl, M., De Angeli, A., et al. (2021). The Arabidopsis protein NPF6.2/NRT1.4 is a plasma membrane nitrate transporter and a target of protein kinase CIPK23. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 168, 239–251. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2021.10.016
Nagasaka, K., Nishiyama, S., Fujikawa, M., Yamane, H., Shirasawa, K., Babiker, E., et al. (2022). Genome-wide identification of loci associated with phenology-related traits and their adaptive variations in a highbush blueberry collection. Front. Plant Sci. 12, 793679. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.793679
Neugebauer, K. A., Mattupalli, C., Hu, M., Oliver, J. E., Vanderweide, J., Lu, Y., et al. (2024). Managing fruit rot diseases of Vaccinium corymbosum. Front. Plant Sci. 15, 1428769. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1428769
Nunez, G. H., Buzzi, G., Heller, C. R. (2023). Southern highbush blueberry responses to humic acid application in soilless substrates. Sci. Hortic. 308, 111541. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2022.111541
Ortiz-Delvasto, N., Garcia-Ibañez, P., Olmos-Ruiz, R., Bárzana, G., Carvajal, M. (2023). Substrate composition affects growth and physiological parameters of blueberry. Sci. Hortic. 308, 111528. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2022.111528
Palencia, P., Giné Bordonaba, J., Martínez, F., Terry, L. A. (2016). Investigating the effect of different soilless substrates on strawberry productivity and fruit composition. Sci. Hortic. 203, 12–19. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2016.03.005
Raj, A., Jhariya, M. K., Yadav, D. K., Banerjee, A. (2021). “10 - Nitrogen uptake and dynamics in plants under stress condition,” in Transporters and Plant Osmotic Stress. Eds. Roychoudhury, A., Tripathi, D. K., Deshmukh, R. (Academic Press), 167–194. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-817958-1.00013-X
Rasool, S., Ahmad, I., Ziaf, K., Naveed, M. (2024). Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria incorporated soilless substrates – A potential arena for high quality nursery production of ornamentals. Sci. Hortic. 326, 112745. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2023.112745
Raza, A., Asghar, M. A., Hussain, S., Bin, C., Shafiq, I., Ahmad, I., et al. (2021). Optimal NH4+/NO3- ratios enhance the shade tolerance of soybean seedlings under low light conditions. Plant Biol. (Stuttg) 23, 464–472. doi: 10.1111/plb.13219
Rodríguez-Vila, A., Atuah, L., Abubakari, A. H., Atorqui, D. W., Abdul-Karim, A., Coole, S., et al. (2022). Effect of biochar on micronutrient availability and uptake into leafy greens in two urban tropical soils with contrasting soil pH. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 6, 821397. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2022.821397
Ru, S., Sanz-Saez, A., Leisner, C. P., Rehman, T., Busby, S. (2024). Review on blueberry drought tolerance from the perspective of cultivar improvement. Front. Plant Sci. 15, 1352768. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1352768
Saad, N., Alcalá-Briseño, R. I., Polston, J. E., Olmstead, J. W., Varsani, A., Harmon, P. F. (2020). Blueberry red ringspot virus genomes from Florida inferred through analysis of blueberry root transcriptomes. Sci. Rep. 10, 12043. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-68654-3
Santos, A., Fangueiro, D., Moral, R., Bernal, M. P. (2018). Composts produced from pig slurry solids: nutrient efficiency and N-leaching risks in amended soils. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2, 8. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2018.00008
Sathee, L., Jha, S. K., Rajput, O. S., Singh, D., Kumar, S., Kumar, A. (2021). Expression dynamics of genes encoding nitrate and ammonium assimilation enzymes in rice genotypes exposed to reproductive stage salinity stress. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 165, 161–172. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2021.05.013
Shen, X., Sheng, L., Benedict, C., Kruger, C. E., Su, Y., Schacht, E., et al. (2020). Evaluation of pre-harvest microbiological safety of blueberry production with or without manure-derived fertilizer. Front. Microbiol. 10, 3130. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.03130
Signore, A., Bell, L., Santamaria, P., Wagstaff, C., Van Labeke, M.-C. (2020). Red light is effective in reducing nitrate concentration in rocket by increasing nitrate reductase activity, and contributes to increased total glucosinolates content. Front. Plant Sci. 11, 604. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.00604
Stull, A. J., Cassidy, A., Djousse, L., Johnson, S. A., Krikorian, R., Lampe, J. W., et al. (2024). The state of the science on the health benefits of blueberries: a perspective. Front. Nutr. 11, 1415737. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1415737
Tabatabaei, S. J., Yusefi, M., Hajiloo, J. (2008). Effects of shading and NO3:NH4 ratio on the yield, quality and N metabolism in strawberry. Sci. Hortic. 116, 264–272. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2007.12.008
Tamir, G., Zeng, Q., Eli, D., Zilkah, S., Bar-Tal, A., Dai, N. (2023). Combined effects of alkaline pH and high Ca concentration on root morphology, cell-wall polysaccharide concentrations and blueberry plant performance. Front. Agron. 5, 1121448. doi: 10.3389/fagro.2023.1121448
Tang, Q., Wang, X., Ma, S., Fan, S., Chi, F., Song, Y. (2024). Molecular mechanism of abscisic acid signaling response factor VcbZIP55 to promote anthocyanin biosynthesis in blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 210, 108611. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2024.108611
Tarkowski, Ł.P., Clochard, T., Blein-Nicolas, M., Zivy, M., Baillau, T., Abadie, C., et al. (2024). The nitrate transporter-sensor MtNPF6.8 regulates the branched chain amino acid/pantothenate metabolic pathway in barrel medic (Medicago truncatula Gaertn.) root tip. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 206, 108213. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2023.108213
The, S. V., Snyder, R., Tegeder, M. (2021). Targeting nitrogen metabolism and transport processes to improve plant nitrogen use efficiency. Front. Plant Sci. 11, 628366. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.628366
Vitousek, P. M., Cen, X., Groffman, P. M. (2024). Has nitrogen availability decreased over much of the land surface in the past century? A model-based analysis. Biogeochemistry 167, 793–806. doi: 10.1007/s10533-024-01146-y
Wang, L., Zhang, S., Li, J., Zhang, Y., Zhou, D., Li, C., et al. (2022). Identification of key genes controlling soluble sugar and glucosinolate biosynthesis in Chinese cabbage by integrating metabolome and genome-wide transcriptome analysis. Front. Plant Sci. 13, 1043489. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1043489
Wang, P., Wang, C.-D., Wang, X.-L., Wu, Y.-H., Zhang, Y., Sun, Y.-G., et al. (2023). Increasing nitrogen absorption and assimilation ability under mixed NO3– and NH4+ supply is a driver to promote growth of maize seedlings. J. Integr. Agric. 22, 1896–1908. doi: 10.1016/j.jia.2023.04.037
Wang, Y., Ji, H., Wang, R., Hu, Y., Guo, S. (2020). Synthetic fertilizer increases denitrifier abundance and depletes subsoil total N in a long-term fertilization experiment. Front. Microbiol. 11, 2026. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.02026
Wu, D., Sun, J., Silvennoinen, R., Repo, T. (2024). Root injury detection by impedance loss factor and hydraulic conductance of apple (Malus domestica), blackcurrant (Ribes nigrum) and blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum) nursery plants. Sci. Hortic. 328, 112864. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2024.112864
Wu, Y., Huang, Z., Zhang, C., Shi, C., Lyu, L., Li, W., et al. (2022). Comparative analysis of the morphological, physiological, proteomic, and metabolic mechanisms of the “Biloxi” Blueberry response to shade stress. Front. Plant Sci. 13, 877789. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.877789
Xing, Y., Wang, K., Huang, C., Huang, J., Zhao, Y., Si, X., et al. (2022). Global transcriptome analysis revealed the molecular regulation mechanism of pigment and reactive oxygen species metabolism during the stigma development of carya cathayensis. Front. Plant Sci. 13, 881394. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.881394
Xu, N., Yu, B., Chen, R., Li, S., Zhang, G., Huang, J. (2020). OsNAR2.2 plays a vital role in the root growth and development by promoting nitrate uptake and signaling in rice. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 149, 159–169. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2020.02.004
Yang, D., Zhao, J., Bi, C., Li, L., Wang, Z. (2022a). Transcriptome and proteomics analysis of wheat seedling roots reveals that increasing NH4+/NO3– ratio induced root lignification and reduced nitrogen utilization. Front. Plant Sci. 12, 797260. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.797260
Yang, H., Wei, Z., Duan, Y., Wu, Y., Zhang, C., Wu, W., et al. (2023). Transcriptomic and metabolomic investigation of the adaptation mechanisms of blueberries to nitrogen deficiency stress. Sci. Hortic. 321, 112376. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2023.112376
Yang, H., Wu, Y., Zhang, C., Wu, W., Lyu, L., Li, W. (2022b). Growth and physiological characteristics of four blueberry cultivars under different high soil pH treatments. Environ. Exp. Bot. 197, 104842. doi: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2022.104842
Ye, J. Y., Tian, W. H., Jin, C. W. (2022). Nitrogen in plants: from nutrition to the modulation of abiotic stress adaptation. Stress Biol. 2, 4. doi: 10.1007/s44154-021-00030-1
Yunchao, H., Tiancai, Y., Zhenyu, G., Tiankang, W., Xueli, L., Long, Y., et al. (2024). Appropriate supply of ammonia and ammonium nitrate reduce cadmium content in rice seedlings by inhibiting cadmium uptake and transport. Rice Sci. 31, 2024. doi: 10.1016/j.rsci.2024.02.007
Zhang, H., Zhu, J., Gong, Z., Zhu, J.-K. (2022). Abiotic stress responses in plants. Nat. Rev. Genet. 23, 104–119. doi: 10.1038/s41576-021-00413-0
Zhao, X., Lin, S., Yu, S., Zhang, Y., Su, L., Geng, L., et al. (2024). Exogenous calcium enhances the physiological status and photosynthetic capacity of rose under drought stress. Hortic. Plant J. 10, 853–865. doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2023.01.010
Zhao, X. Q., Shen, R. F. (2018). Aluminum–nitrogen interactions in the soil–plant system. Front. Plant Sci. 9, 807. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.00807
Keywords: nitrogen, potassium, antioxidant, sugar, photosynthesis, blueberry
Citation: Anwar A, Zheng J, Chen C, Chen M, Xue Y, Wang J, Su W, Chen R and Song S (2024) Effects of NH4+-N: NO3−-N ratio on growth, nutrient uptake and production of blueberry (Vaccinium spp.) under soilless culture. Front. Plant Sci. 15:1438811. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1438811
Received: 26 May 2024; Accepted: 23 September 2024;
Published: 17 October 2024.
Edited by:
Marco Betti, Sevilla University, SpainReviewed by:
Surendra Sarsaiya, Zunyi Medical University, ChinaPeter Pal’ove-Balang, Pavol Jozef Šafárik University in Košice, Slovakia
Copyright © 2024 Anwar, Zheng, Chen, Chen, Xue, Wang, Su, Chen and Song. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Shiwei Song, c3dzb25nQHNjYXUuZWR1LmNu; Riyuan Chen, cnljaGVuQHNjYXUuZWR1LmNu
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Ali Anwar
Ali Anwar Junming Zheng†
Junming Zheng† Shiwei Song
Shiwei Song