
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Plant Sci. , 21 May 2024
Sec. Plant Physiology
Volume 15 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2024.1431121
This article is a correction to:
Melatonin mitigates cadmium phytotoxicity through modulation of phytochelatins biosynthesis, vacuolar sequestration, and antioxidant potential in Solanum lycopersicum L
 Md. Kamrul Hasan1
Md. Kamrul Hasan1 Golam Jalal Ahammed1
Golam Jalal Ahammed1 Lingling Yin1
Lingling Yin1 Kai Shi1,2
Kai Shi1,2 Xiaojian Xia1,2
Xiaojian Xia1,2 Yanhong Zhou1,2,3
Yanhong Zhou1,2,3 Jingquan Yu1,2,3
Jingquan Yu1,2,3 Jie Zhou1,2*
Jie Zhou1,2*By Hasan MK, Ahammed GJ, Yin L, Shi K, Xia X, Zhou Y, Yu J and Zhou J (2015). Front. Plant Sci. 6:601. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2015.00601
In the published article, there were a couple of errors in Figure 3A and Figure 7A as published. In Figure 3A, the representative images of NBT-stained leaflets (2nd row) after Cd (panel 2), Cd+M250 (panel 6) and Cd+M500 (panel 7) treatments were overwritten by redundant images, respectively. In Figure 7A, ‘Control’ was written in the X-axis legend mistakenly. The corrected Figure 3 and Figure 7 and their captions appear below.
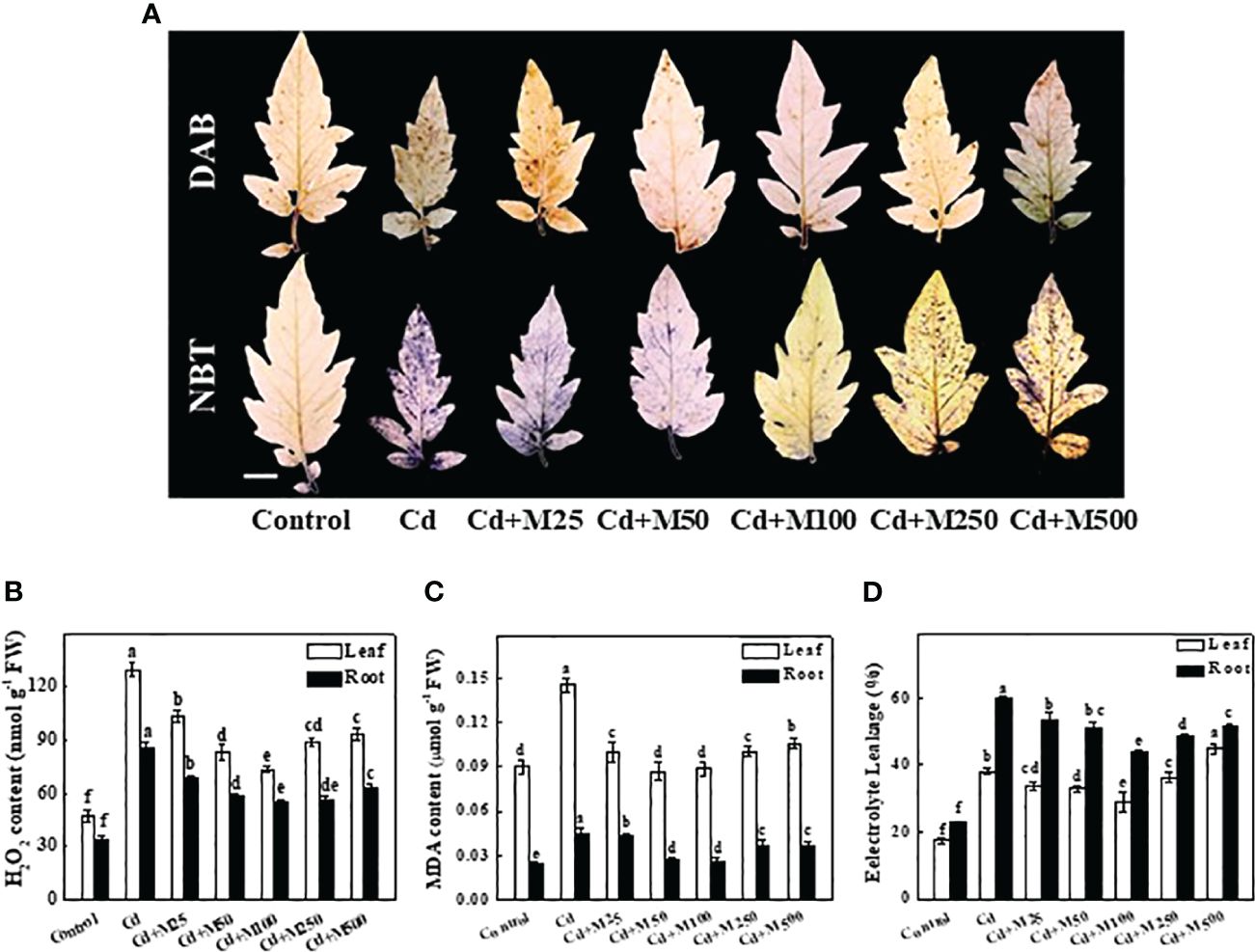
Figure 3 Effects of melatonin on ROS accumulation, lipid peroxidation, and membrane integrity after 14 days long Cd stress. (A) The in situ detection of H2O2 (upper panel) and O2·− (lower panel) in tomato leaves. Bar = 1.0 cm, (B) H2O2 concentrations in tomato leaves and roots, (C) MDA concentrations in tomato leaves and roots, and (D) Electrolyte leakage from tomato leaves and roots. Accumulation of H2O2 and O2·− in leaves was visually detected by staining with 3, 3-diaminobenzidine (DAB) and nitroblue tetrazolium (NBT), respectively. The data shown are the averages of four replicates, with the standard errors indicated by the vertical bars. The means denoted by the same letter within the same color histograms did not significantly differ at a P < 0.05, according to Tukey’s test. Cd, 100 μM cadmium; M25, 25 µM melatonin; M50, 50 µM melatonin; M100, 100 µM melatonin; M250, 250 µM melatonin; M500, 500 µM melatonin; FW, fresh weight.
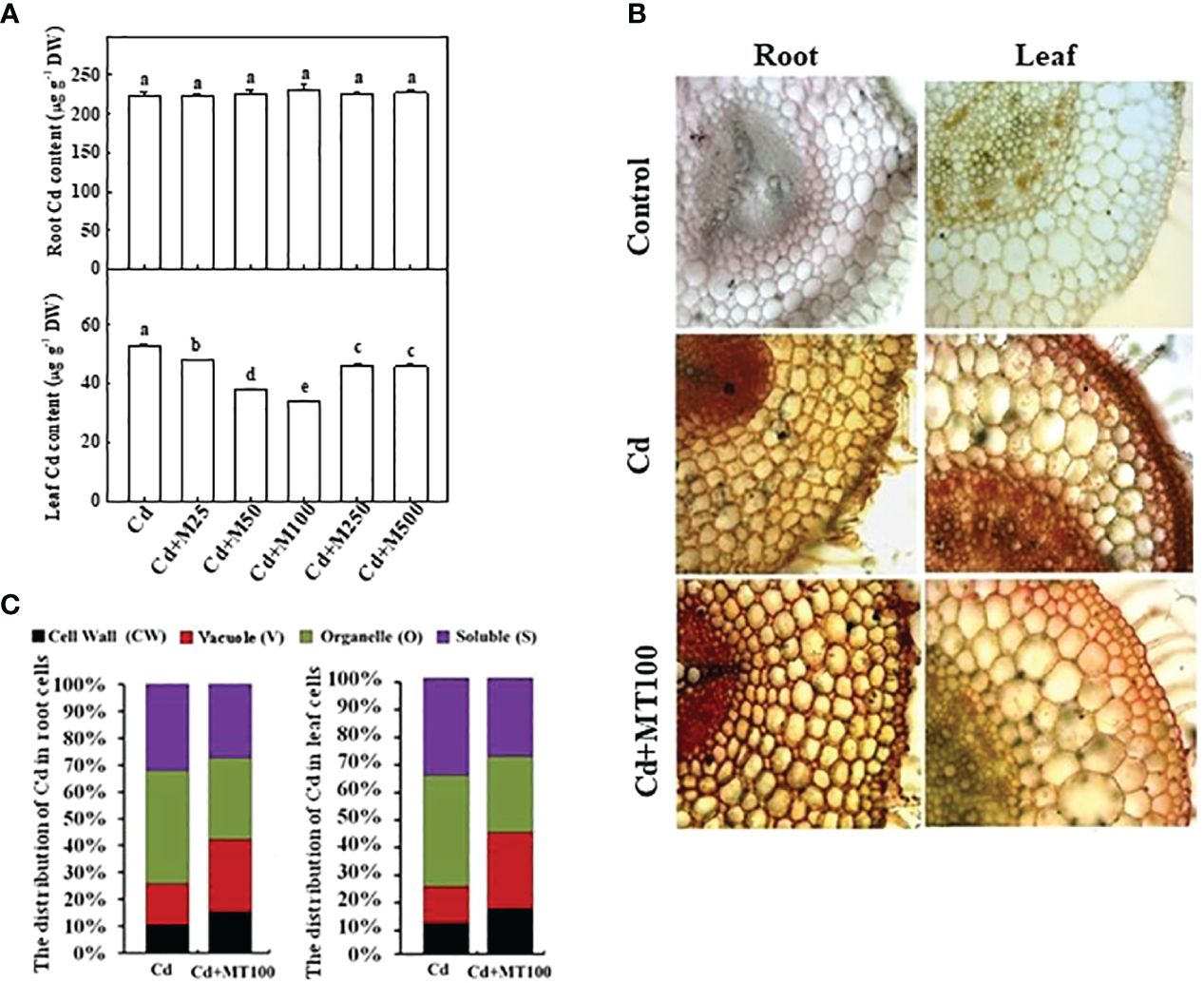
Figure 7 The accumulation of cadmium in tomato plants and its subcellular distribution following 14 days long Cd stress as influenced by melatonin treatments. (A) Cd concentrations in tomato roots and leaves. (B) The in situ detection of Cd in tomato roots and leaves using a dithizone staining-based histochemical method (C) The distribution of Cd in different subcellular compartments. The data shown in (A), are the averages of four replicates, with the standard errors indicated by the vertical bars. The means denoted by the same letter did not significantly differ at a P < 0.05, according to Tukey’s test. Cd, 100 μM cadmium; M25, 25 µM melatonin; M50, 50 µM melatonin; M100, 100 µM melatonin; M250, 250 µM melatonin; M500, 500 µM melatonin; DW, dry weight.
The authors apologize for these errors and state that these do not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: cadmium, food safety, melatonin, phytochelatins, tomato, vacuolar sequestration
Citation: Hasan MK, Ahammed GJ, Yin L, Shi K, Xia X, Zhou Y, Yu J and Zhou J (2024) Corrigendum: Melatonin mitigates cadmium phytotoxicity through modulation of phytochelatins biosynthesis, vacuolar sequestration, and antioxidant potential in Solanum lycopersicum L. Front. Plant Sci. 15:1431121. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1431121
Received: 11 May 2024; Accepted: 13 May 2024;
Published: 21 May 2024.
Approved by:
Frontiers Editorial Office, Frontiers Media SA, SwitzerlandCopyright © 2024 Hasan, Ahammed, Yin, Shi, Xia, Zhou, Yu and Zhou. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jie Zhou, amllQHpqdS5lZHUuY24=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.