
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Plant Sci. , 30 January 2025
Sec. Plant Nutrition
Volume 15 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2024.1404077
 Girijaveni V1*
Girijaveni V1* Sammi Reddy K2
Sammi Reddy K2 Srinivasarao Ch3
Srinivasarao Ch3 Raju B M K1
Raju B M K1 Divya Balakrishnan4
Divya Balakrishnan4 Sumanta Kundu1
Sumanta Kundu1 Pushpanjali1
Pushpanjali1 Jagriti Rohit1
Jagriti Rohit1 Singh V K1
Singh V K1Poor nutrient use efficiency (NUE) and water use efficiency (WUE) is a predominantly faced problem in semi-arid regions that limit the crop production. This problem can be addressed with the application of zeolite that is a naturally available mineral with very high cation exchange and water holding capacity, which aids in improving NUE and WUE. Moreover, zeolites are safe for the environment and living organisms, and their use in agriculture results in improving physical and chemical properties of soil. Yet, its study is very limited in semi-arid regions of India. Thus, a study was conducted with locally available zeolite at CRIDA, Hyderabad. Zeolite was further characterized using X-ray diffraction (XRD) and SEM, as the type of zeolite collected is unknown from local market. The results of XRD and SEM revealed that the zeolite collected was mordenite zeolite. Our study includes laboratory and pot experiment where laboratory includes sorption and leaching column study to evaluate the zeolite capacity to hold and release the nutrients especially NH4+, P, and K. In this study, the adsorption behaviour of the natural mordenite was examined, and it was found that the maximum adsorption capacity for NH4+, P, and K were estimated as 10.6, 1.08, and 2.15 mg g−1, respectively, suggesting the zeolite has good affinity for N. Furthermore, the column study revealed that there was 15.4% reduction in NH4+–N loss with 10 tonnes zeolite ha−1 + N @ 100 kg ha−1 as compared to N alone, while the reduction was 39.6% with 10 tonnes zeolite ha−1 + N @ 500 kg ha−1 compared to N alone, suggesting that the zeolite could control the release of N as compared to the sole application of N, which was supplied through urea. In addition, pot experiment was carried out with three levels of fertiliser rates, four levels of zeolite, and two levels of moisture in randomised complete block design with three replications to evaluate the changes in soil available nutrients and their uptake in tomato. Results revealed that there was a significant positive impact on yield, water use efficiency, nutrient (N, P, and K) uptake, and soil available nutrients. Highest soil available N, P, and K, crop uptake, and yield were observed due to zeolite application @ 200 kg ha−1 along with 100% recommended dose of fertilization in Alfisols. Thus, zeolite application along with chemical fertilisers can improve the nutrient availability by reducing the leaching losses and improving nutrient use efficiency.
Sustainable management of soil and water in the climate change scenario is the key to feed the ever growing human population. Obviously, with the increase in world population at a rapid rate, there would be huge demand for food, shelter, etc. With the limited resources of land and water, which are degrading at faster rate, it is necessary to ensure food security with improved soil health, nutrient use efficiency, and water use efficiency. Moreover, the major soils in semiarid tropics belong to Alfisols. In FAO/UNESCO classification system, Alfisols are comparable to Luvisols. They usually have a base-rich argillic B horizon representing the largest single soil group of the semi-arid tropics. In India, Alfisol soils cover 79.7 m ha, characterized by red, reddish brown to yellowish brown colours. Most of the Alfisol soils are at the verge of degradation, having low cropping intensity, relatively low organic matter status, poor soil physical health, low fertility, etc. Due to poor nutrient use efficiency, nutrient losses due to leaching, volatilization, and denitrification are high in these soils. In India, due to substantial inter-seasonal variations and monsoon disturbances, the crops grown in these soils fail, as these have low water holding capacity. Hence, various measures need to be taken by leveraging the technology towards enhanced nutrient and water use efficiency especially in semi-arid tropics. One such strategy is the use of zeolite. Zeolite is a natural amendment that can be used along with fertilisers to improve their use efficiency and also water use efficiency in soils.
Zeolites are naturally occurring crystalline-hydrated aluminosilicates of framework structure containing pores occupied by water and alkali and alkaline earth cations (Ramesh and Reddy, 2011; Li et al., 2023). Zeolites are well-known ion exchangers in the world. Among 40 different types of natural zeolites, most commonly used in crop production includes clinoptilotile, erionite, and mordenite (Mpanga et al., 2020). Zeolites are known to ensure NH4+ retention in soils, preventing leaching of NH4+ and nitrate (NO3−) and other losses. The mechanism of adsorption of K+ in zeolite similar to NH4+ and to smaller extent can adsorb phosphate (PO43−) being anion. The ability to remove nutrients and their release pattern can be effectively studied through isotherm and leaching column studies. These studies give a clear picture of nutrient supply, as zeolite plays a key role in nutrient cycling through sorption process and leaching when applied to soil. Sorption studies are evaluated using empirical models such as Langmuir, Freundlich, and Temkin isotherms. Langmuir isotherm indicates the amount of nutrients held in the form of a single layer on the surface. Mostly, Langmuir isotherm is suitable to study the single layer surface adsorption reaction for adsorption sites (Kalam et al., 2021). Freundlich isotherm demonstrates the mechanism of adsorbed nutrients and adsorbent surface at different sites or heterogeneous adsorbent surface (Palanivell et al., 2019; Akrawi et al., 2021), while the binding energy involved in adsorbing nutrient is measured by Temkin isotherm (Murphy et al., 2023). Temkin isotherm assumes that heat generation during the process of nutrient adsorption decreases linearly as the adsorbent coverage increases (Ohale et al., 2020). In a study where NH4+, Na+, and K+ ions were provided in the solution, it was found that zeolite could remove more NH4+ and K+ ions in comparison with Na+, which remained in the solution. In the same study, the efficiency of zeolite and vermiculite was evaluated in removing NH4+ and found that it was high for zeolite (85%), while it was almost 70% for vermiculite (Shinzato et al., 2020). Several studies found reduced nitrogen leaching due to soil application of zeolites in combination with chemical fertiliser volatilisation (Aghaalikhani et al., 2012; Vilcek et al., 2013; Omar et al., 2015; Nakhli et al., 2017; Cataldo et al., 2021; Mondal et al., 2021).
Research revealed that zeolite can be best soil amendment for soil types with coarse texture, deficit moisture levels, and low fertility levels (Ghorbani et al., 2022). Additionally, its application helped in balancing pH, improving chemical properties, restoring soil microbial activity, increasing moisture retention, and reducing compaction. Zeolites have high retention ability of ammonium and potassium and help to retain nutrients in the root zone. Recent studies show that use of zeolites is beneficial, as it helps in improving the physical and chemical properties of soils. It is mainly due to its higher cation exchange capacity (CEC), higher specific surface area, internal void structure, higher moisture holding capacity, etc. Thus, these properties of zeolites can help in enhancing the water and nutrient use efficiency. In addition, it reduces the risk of environmental pollution occurring due to reduction in nitrate leaching, emissions of nitrous oxides, and NH3 (Louhar, 2020). Zeolite application improved nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium fertilisers use efficiency in Typic Paleudults (Palanivell et al., 2021). Zeolite application maintained higher mineral and mineralisable N in different types of soils (Saha et al., 2018; Mondal et al., 2021; Hazrati et al., 2022). Moreover, the porous nature of zeolite aids in soil aeration, and moisture maintenance in turn improves the crop performance and production.
Despite the great interest in zeolites as agricultural amendment, few data exist with mordenite, in terms of their use in agriculture. Mordenite is an orthorhombic zeolite of high silica content and is a common alteration product of pyroclastic sediment, sedimentary rock, and lava flows of worldwide distribution (Narayanan et al., 2021). The ideal composition of mordenite is [(Na2K2Ca)4Al8Si40O96] 28H2O. Its characteristics include high heat stability with specific gravity of 2.12–2.15 g cm−3 and bulk density of 1.7 g cm−3 with porosity of 28% (Cataldo et al., 2021). Due to soil application of mordenite zeolite, the soil water infiltration increased by 7%–30% on a gentle slope land, while it was increased by 50% on steep slope land (Xiubin and Zhanbin, 2001). Natural and synthetic zeolitic materials of clinoptilolite and mordenite were used as soil amendment and found that amended soils exhibited higher CEC values compared with unamended soil (Giannatou et al., 2018). Mixtures of zeolite tuff (chabazite- and mordenite-rich tuff) were tested as slow release fertiliser in loamy soil. Even in abandoned quarries in semiarid Mediterranean areas where soil fertility and water availability are highly limited, native plant species (Olea europaea var. Sylvestris, Pistacia lentiscus, Rosmarinus officinalis, and Quercus coccifera) could sustain through the addition of organic (compost derived from horticultural crop residues and poultry manure) and inorganic (three types of zeolites: mordenite, clinoptilolite, and ZeoPro) amendments. Thus, zeolite could play a key role in soil restoration (Ortega et al., 2020). Zeolite addition also improves microbial activity where application of chabazite zeolite showed a positive effect on the scoring of GLU activity, which an indicator of microbial activity in the coarse-textured soil of Perennial-Olive system (Chae et al., 2017; Levakov et al., 2021). In Mediterranean soils, co-addition of 5% compost + 2% zeolite improved the NPK availability over no application of zeolite. The addition of stilbite-zeolite @ 1.25%–10% w/w in a contaminated soil could improve the chemical properties of soil and was effective in remediating the soil; also rye grass studied showed a gradual increase in yield with increase in addition, suggesting that natural zeolite showed a positive impact on crop yield by improving chemical properties and reducing environmental impact of contaminated soil (Amirahmadi et al., 2022). Long-term study with Chabazite-Zeolite @ 5 kg m−2 as amendment improved soil quality in arable and perennial cropping systems with significantly higher scores (lower bulk density and NH3–N emissions) (Ferretti et al., 2024). Thus, the objective of the study was (1) to evaluate the modernite zeolite for ammonium, phosphorus, and potassium removal through sorption and release through leaching column study and (2) to study its application along with chemical fertilisers on crop uptake and soil nutrient dynamics in Alfisols.
Natural zeolite available in the local market was purchased, and the study was carried as given below in Figure 1.
The crystalline phases were identified by X-ray diffraction (XRD) using a D8 Advance X-ray diffractometer. X-ray diffraction analysis (XRD) of the materials was performed using a D8 Advance diffractometer (Bruker AXS) operating at a tube voltage of 40 kV and a tube current of 40 mA. The X-ray beam was filtered with a Ni 0.02-mm filter to select a CuKα wavelength. The specimens were scanned over a 2θ range from 3° to 70° at a scanning speed of 5° min−1 using a coupled two theta/theta scan type (Harrington and Santiso, 2021). The identification of zeolite sample was confirmed by matching the powder XRD patterns of the samples with the diffractograms of single-phase patterns from Powder Data File (PDF), compiled by the International Centre for Diffraction Data (ICDD).
The scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images of the zeolite sample were studied where the samples were fixed in 2.5% gluteraldehyde in 0.1 M phosphate buffer (pH 7.2) for 24 h at 4°C and post-fixed 2% in aqueous osmium tetroxide for 4 h (Sandoval-Molina et al., 2017). The samples were dehydrated in series of graded alcohols and dried to critical point drying with CPD (EMS-850) unit by using liquid carbon dioxide. The processed samples were mounted over the stubs with a double-sided carbon conductivity tape, and a thin layer of gold coat over the samples were done by using an automated sputter coater (Model JEOL JFC-1600, Peabody, Massachusetts, USA) for 3 min and scanned under a scanning electron microscope (SEM, Model JOEL-JSM 5600) at required magnifications as per the standard procedures at RUSKA Lab’s College of Veterinary Science, PVNRTVU, Rajendranagar, Hyderabad, India.
Batch experiments were conducted to evaluate the adsorption capacity of zeolite for ammonical-N, phosphorus, and potassium. Batch experiments were conducted in an array of conical flasks, where 100 mL of graded concentrations of ammonium solutions were added to 250-mL Erlenmeyer flasks with 1 g zeolite, sealed and shaken at a speed of 180 rpm for 2 h in a mechanical shaker at 25°C. The influence factors of ammonium and potassium adsorption were studied with the initial ammonium concentration (25–400 mg L−1) and initial potassium concentration (25–300 mg L−1). An ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) salt was used to make the NH4+ solutions, and potassium chloride (KCl) used to make the K+ solutions. The equilibrium ammonium concentration was measured using Nessler’s reagent and phosphorus through blue colour method in spectrophotometry, measured by a UV-VIS spectrophotometer (UV-1800, Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) and three replicates were performed in parallel for each set of experiments, while the equilibrium potassium concentration was measured using flame photometer. Differences in the concentration between the initial and residual solution were used to calculate the equilibrated adsorption capacity. The data were fit in the Langmuir and Freundlich isotherm equations as given below:
where qe is the adsorbed amount at equilibrium (mg g−1) and Ce represents the equilibrium concentration (mg L−1). KF and n are equilibrium constants indicative of adsorption capacity and adsorption intensity, respectively. If n is greater than 2 and less than 10 (2 < n < 10), the adsorption process is favourable.
where qe and Ce are the adsorption capacity at equilibrium and the equilibrium concentration respectively, qmax represents the maximum adsorption capacity (mg g−1), Ks is the adsorption equilibrium constant, and n is the dissociation parameter.
The removal efficiency (R %) and the adsorption capacities of adsorbents at time (qt, mg/g) and at equilibrium (qe, mg/g) were calculated using the following equations:
where C0 and Ce are the initial and equilibrium concentration of the cation (mg L−1), V is the volume (L) of solution, and m is the mineral mass (g).
A soil leaching experiment was conducted to evaluate the inorganic nitrogen leaching for 45 days in the presence of mordenite zeolite in Alfisol of sandy loam texture. The surface soil (0–15 cm) was collected from Hayathnagar Research Farm, CRIDA for this study. Column study with glass columns of 5 cm internal diameter and 50 cm height was used to investigate the release pattern at field scale situation. Columns were organized with three replications. The treatments comprised of two levels of N (100 kg ha−1 and 500 kg ha−1) and four levels of zeolite (0.2 tonnes ha−1, 0.5 tonnes ha−1, 5 tonnes ha−1, and 10 tonnes ha−1). All treatment combinations were thoroughly mixed and scaled down to the amount of 900 g soil. The pore volume for these columns was found to be 981.25 cm3. The filled columns were saturated with distilled water and then irrigated homogeneously with known volume of distilled water, and the leachate was collected with an interval of 3 days and analysed for ammonical-N content using Nessler reagent for colour development (Krug et al., 1979).
A net house experiment was conducted for 2 years (2017 and 2018) to assess the effect of zeolite amendment along with chemical fertilisers on tomato plant growth. This experiment was carried in the net house of Central Research Institute for Dryland Agriculture (CRIDA), Hyderabad. For this experiment, surface soils (0–15 cm) were collected from Hayathnagar Research farm of CRIDA, Hyderabad. The collected soil samples were air dried, processed, and sieved for taking up the pot experiment. The tomato (PKM-1 variety) was used as test crop.
The experimental setup is presented in Table 1 where there are 12 treatments with a total of 72 pots taken up. The experimental design followed was factorial completely randomised design (CRD) with three replications. The fertiliser and zeolite doses added were scaled down to 10 kg soil taken in the pots. The experiment was laid under two levels of moisture conditions—50% and 100% FC. To maintain the moisture levels, the calculated amount of water was used to irrigate the pots to maintain the field capacity. Fertiliser materials used were urea, diammonium phosphate (DAP), and muriate of potash (MOP). Irrigation and other agronomic practices were carried out as per requirement. Crop yield parameters such as plant height, number of leaves, and biomass yield were recorded, and nutrient status was studied in post-harvest soil samples after the harvest of tomato during both the study years.
The initial soil samples were analysed for mechanical composition, pH, electric conductivity (EC), organic carbon, and available nutrients (N, P, and K) following standard procedures. The physicochemical properties of the initial soil under study are presented in Table 2. Soil water retention at permanent wilting point (PWP) and field capacity (FC) were measured in pressure plate apparatus at −1.5 MPa and −0.033 MPa (Cassel and Nielsen, 1986). The difference between PWP and FC was calculated as available water. A representative portion of each soil sample was air dried, powdered, and passed through a 0.2-mm sieve for the determination of organic carbon (OC) by Walkley and Black’s method (Jackson, 2005). Available soil nitrogen was determined by alkaline–KMnO4 method given by Subbaiah and Asija (1956), which primarily measures easily oxidizable N using Kjeltec Auto 1030 Analyser made by Tecator in Sweden. Available P (Olsen P) was determined by sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) extraction and subsequent colorimetric analysis (Olsen et al., 1954). Exchangeable K was measured using the method suggested by Hanway and Heidal, 1952.
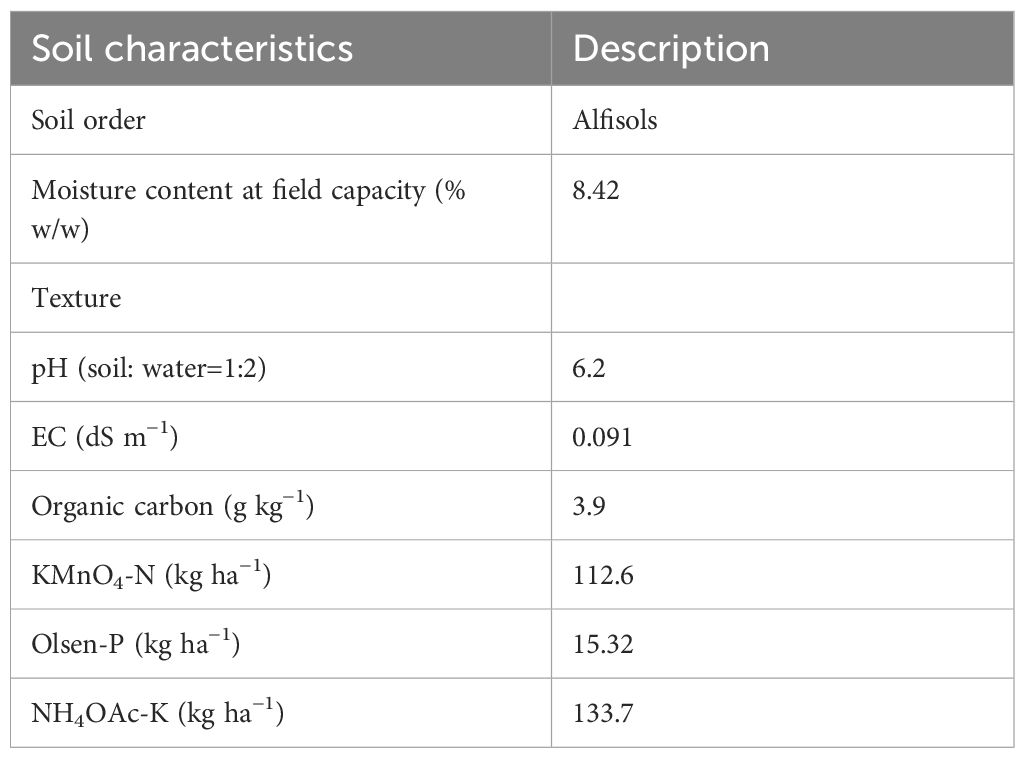
Table 2. Physicochemical properties and fertility status of the experimental soil before taking up the study.
Plant samples collected were dried in oven at 65°CC and powdered by using a plant sample grinder. The powdered samples were packed in polyethylene zip covers for further analysis. These samples were used for the estimation of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium according to the procedure.
Nitrogen content in the plant sample was determined by micro-Kjeldhal distillation method using Kelplus equipment (Jackson, 1973). To a 0.1 g of powdered plant sample in a test tube, 3 ml of concentrated sulphuric acid was added and predigested for 24 h. The black charred contents in the test tube turned into clear supernatant solution by the addition of 1 ml of 30% hydrogen peroxide against flame. The contents were transferred into a Kjeldahl tube for distillation. A 250-ml conical flask containing 25 ml of 4% boric acid with mixed indicator was placed at the end of delivery tube; 15 ml of 40% sodium hydroxide was run into the Kjeldahl tube automatically after placing the Kjeldahl tube in position. After completion of distillation, the conical flask with distillate is titrated against 0.01 N sulphuric acid until the bluish green colour turned into pink colour. A blank was run simultaneously.
One gram of oven-dried and processed plant samples was digested with a 9:3:1 mixture of nitric acid, perchloric acid, and sulphuric acid on a hot plate. The clear digested residue was cooled, diluted to 100 mL with double distilled water, and filtered to remove insoluble silica.
In the digested extract, phosphorus content was determined by Vanado–molybdo phosphoric yellow colour method as described by Piper (1966) using a UV-VIS spectrophotometer (UV-1800, Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) at 420 nm, and P content was expressed as per cent.
Potassium content in the triacid digest was determined using the flame photometer Elico CL 361 (Piper, 1966) and expressed as per cent.
The nutrient uptake was computed using the formula:
Analysis of variance (ANOVA) was estimated for individual environments, and further combined analysis of variance by split–split plot in completely randomized design was carried out using the software, Statistical Tool for Agricultural Research (STAR) (Version 2.0.1, http://bbi.irri.org/products) and R-Packages 1.5 (R Core Team 2013). If the F statistic is significant, further post-hoc pairwise comparison between sample means were computed using least significant difference (LSD) and Tukeys’ honest significant difference (HSD) test. The correlation coefficients and graphs were generated based on the mean data and correlograms were constructed in RStudio using “metan” package (Olivoto and Dal` Col Lucio, 2019) based on Pearson’s correlation matrix between soil chemical properties.
X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis was carried in order to identify the phases present in the zeolite sample as shown in Figure 2. XRD revealed the presence of mixture of phases in the collected zeolite with peaks at 2 that match mordenite, tetracesium tetraaluminosilicate, leucite, octasodium tecto hexagallohexa silicate dibromide, Ga-sodalite, lithosite, and cerium nickel silicon. The lattice parameters (a, b, c) obtained from the XRD for zeolite sample are shown in Table 3. Zeolites found in nature are rarely in their pure form but usually contain impurities such as other types of zeolite, other minerals, or amorphous materials. In this case, quartz impurities were found in mordenite as indicated by the XRD pattern. In our study, quantitative XRD analysis showed that the major component of the natural zeolite was mordenite with minor amounts of others. The diffraction pattern of the zeolite sample was matched with that of the literature, and identified phases are shown in Table 3 along with the chemical formulas and figure of merit of the crystalline phases of zeolite (Table 4).
Scanning electron microscopy is a highly versatile technique that gives detailed surface information of samples and used to obtain high-resolution images. It is a type of electron microscopy that uses a focused beam of electrons to scan the surface of a specimen and generate images at a much greater resolution. The resolution of SEM instruments can range from up to several nanometres. With the help of scanning electron microscopy (SEM) imaging, the shape of zeolite was elucidated. In our study, the photographs at several thousands’ magnification have shown a needle-like structure (Figure 3). According to the reports on natural zeolites, the morphology of natural mordenite with a small amount of impurities was needle- or fibre-like with c-axis elongation (Passaglia and Sheppard, 2001). The SEM results are consistent with the XRD results, suggesting that the sample is mordenite zeolite. The SEM images were matching the images presented by Sakizci and Kilinc (2015).
Plant growth is mainly dependent on nutrients in soil solution and associated with colloid surfaces. In general, adsorbed fractions will be released slowly as the ions in soil solution get depleted. Thus, removal of ammonium nitrogen (NH4+–N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) by zeolite is important to know the nutrient supplying capacity. Therefore, this study was conducted to determine NH4+, P, and K adsorption characteristics of mordenite natural zeolite at high ionic concentrations (0–800 mg L−1) in aqueous solution. Results showed that initial NH4+, P, and K concentration had significant effects on NH4+, P, and K adsorption capacity of zeolite. With the addition of increasing amounts of ammonium (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) to zeolite, the equilibrium concentration of N, P, and K increased (Figure 4). Similarly, with the increasing equilibrium concentration (Ce), an increase in the adsorption of N, P, and K was reported by Shin et al. (2021); Assawasaengrat and Rueangdechawiwat (2019), and Cheng et al. (2017) where the extent of adsorption varies with zeolite type and other conditions. The presence of cages and channels contain cations (usually Na+, Ca2+, K+, and Mg2+) and water molecules within the zeolite matrix will get exchanged with the cations presence in the surroundings. Hence, with supplementation of ammonium/potassium, NH4+-N/K gets exchanged with the cations present in its framework in zeolite in that it helps in nutrient supply to plants. Several factors like the negative charge of its framework structure, concentration, size, and charge of the exchange ions determine the exchange capacity of the zeolite. The extent of exchange capacity needs to be explored for different types of zeolite. Extensive literature is available with respect to ammonium exchange capacity of different zeolites in waste water. Further studies revealed that chemical modification of natural zeolite/clay has increased ammonium exchange capacity (AEC) to the extent of 45–55 g NH4+–N kg−1 (Guida et al., 2020). Zeolites can be modified with different treatments such as thermal treatment, acid treatment, alkaline treatment, surfactant, and even with others. The choice of the treatment depends on the purpose for which it is used; mainly chemical treatment with acids, bases, and salts enhances cation absorption and also is very simple, fast, and accessible. Chemical modification with NaOH, FeCl3, and HCl in clinoptilolite zeolite resulted in an increase in ammonium adsorption by an order of magnitude (Jahani et al., 2023).
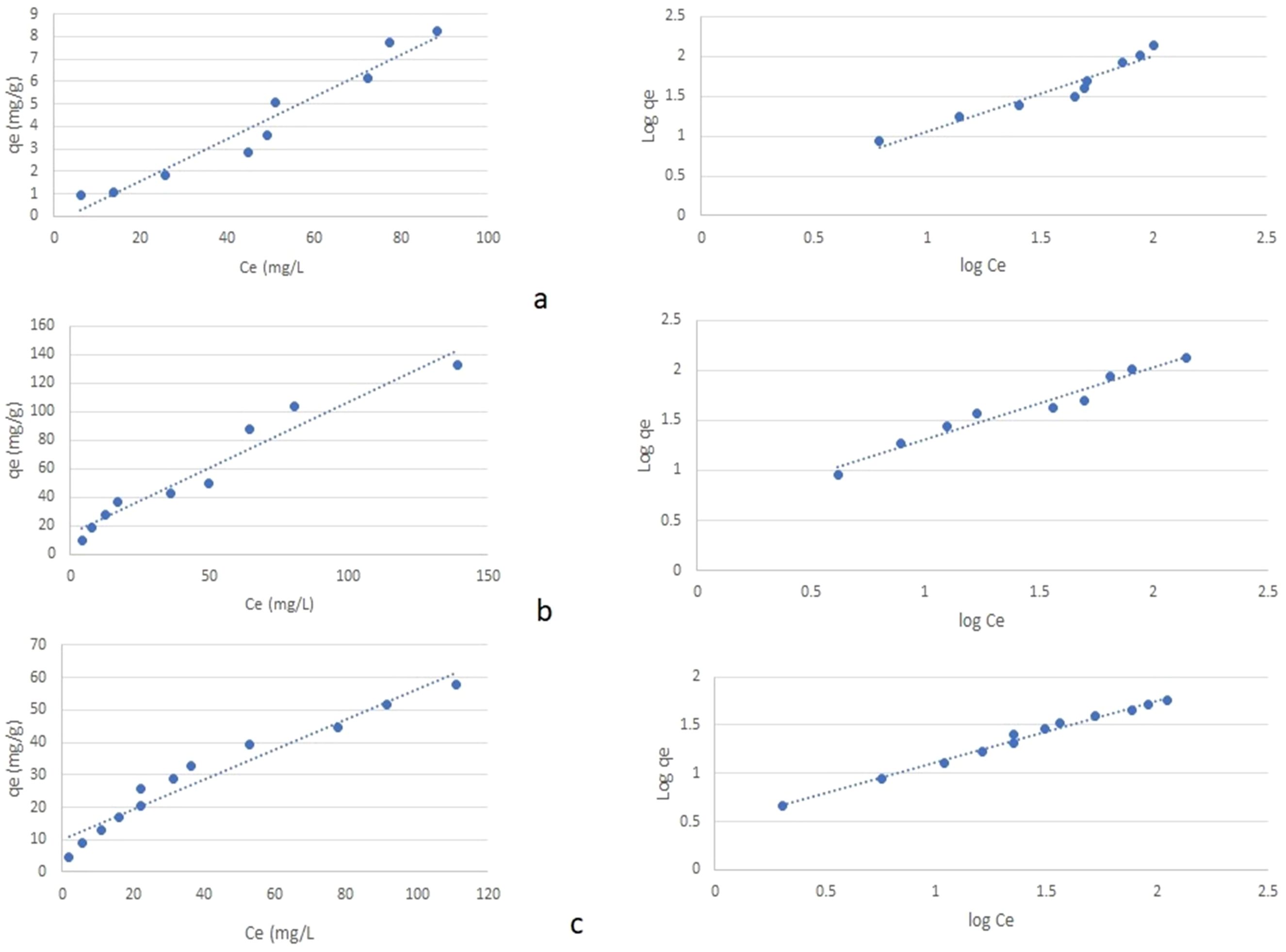
Figure 4. Isotherm plots (qe vs. Ce) and (log qe vs. log Ce) for adsorption of the ions (A) NH4+, (B) P, and (C) K on the natural zeolite.
In our study, adsorption data were fitted to sorption isotherms, Freundlich and Langmuir models, and found that all the three models fitted well with the adsorption process of the studied zeolite; however, the Langmuir model showed best fit for the adsorption process for NH4+–N while Freundlich for P and K (Tables 5, 6). The maximum adsorption capacity of the studied zeolite for NH4+, P, and K were estimated as 10.6 mg g−1, 1.08 mg g−1, and 2.15 mg g−1, respectively. This might be attributed to the highest pore surface area and CEC. Wijesinghe et al. (2016) reported that natural Australian zeolites showed maximum adsorption capacity of NH4+ to the extent of 9.48 mg N g−1and 11.83 mg N g−1, respectively. Xue et al. (2018) employed different types of zeolites in ammonia-rich water to evaluate the ammonia removal efficiency and concluded that mordenite is more efficient in removing ammonia from water. The amount of NH4+ ions removed by zeolite from aqueous solutions increased with increasing concentrations of NH4+ ions in the purified solution (Franus et al., 2015). This suggests that the studied zeolite can be used for improving nutrient use efficiency of chemical fertilisers for crop production.
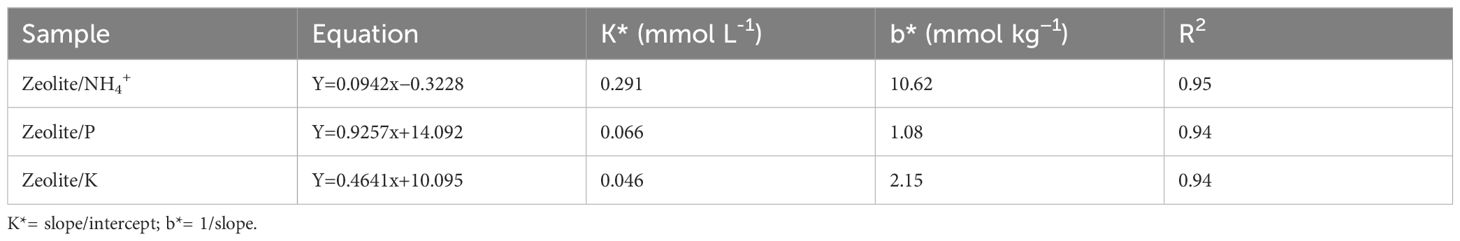
Table 5. Linear forms of Langmuir equations and constants b and k for N, P, and K adsorption by zeolite.
Shin et al. (2021) reported that zeolite-based adsorbents showed the maximum K sorption to the extent of 40–42 mg g−1 by natural zeolite and treated zeolite, which showed higher K sorption rates than the natural zeolite. However, the maximum K sorption rate was found to be 2.15 mg g−1 in our study. At the lowest and highest concentration of NH4+–N, P, and K, a noticeable difference in the adsorption of ammonium, phosphorus, and potassium was reported in the zeolite. As compared to P, N and K were absorbed in large quantities by mordenite zeolite (Tables 5, 6). The adsorption by zeolite followed the order: N>K>P. The adsorption maxima were also found to be high for ammonium followed by K and P (Table 5). The low adsorption maxima for P might be attributed to the negative surface on the zeolite. The surface charge for mordenite is −53 mV; hence, zeolite have poor affinity towards anions sorption. However, several studies state that surface modification of zeolite can increase affinity towards anions (Barczyk et al., 2014).
The percentage of removal capacity ranges between 91% and 60% for ammonical N, P, and K (Figure 5). The removal efficiency is very high with low initial concentration, and as the concentration increased, there was a decline in removal capacity. Initially, the adsorption process is fast, as the ratio of the initial concentration of ammonia to the available surface area is low, and subsequently, the fraction adsorption increases. However, availability of active sites becomes less at higher concentration; hence, the percentage removal decreases. This observation is similar with phosphorus and potassium. As the ammonium concentration and potassium concentration increased, the removal capacity decreased. A similar phenomenon has also been observed in other studies (Kotoulas et al., 2019; Liu et al., 2022). Thus, initial ammonium concentration plays a key role in the adsorption mechanism of cations on zeolite. Sarioglu (2005) studied Dogantepe zeolite with initial ammonium concentration (8.8–885 mg NH4+–N L−1) and found that removal efficiency was achieved in the range of 8.8–40.3 mg NH4+–N L−1. Mordenite samples had an adsorption efficiency of approximately 8.7 mg total ammonia N g− 1 at a total ammonia N of 200 mg L−1 (Zhou et al., 2014), while Muscarella et al. (2023) revealed that the amount of NH4+ adsorbed by mordenite was high as compared to clinoptilolite and heulandite. This might be due to the high specific area of mordenite as compared to clinoptilolite and heulandite that allowed it to hold more of NH4+ ions. In addition, the higher the NH4+–N concentration in the solution, the higher the solute concentration gradient. This provides the necessary driving force so that NH4+–N ions could take the place of cations on the surface of the internal micropores of zeolite within a given contact time (Du et al., 2005; Cyrus and Reddy, 2011; Chai et al., 2021). In this study, experimental results clearly showed that zeolite used in the study can be a suitable adsorbent for the removal of NH4+ ion from aqueous solution, thus can be used to manage nitrogen availability in soils.
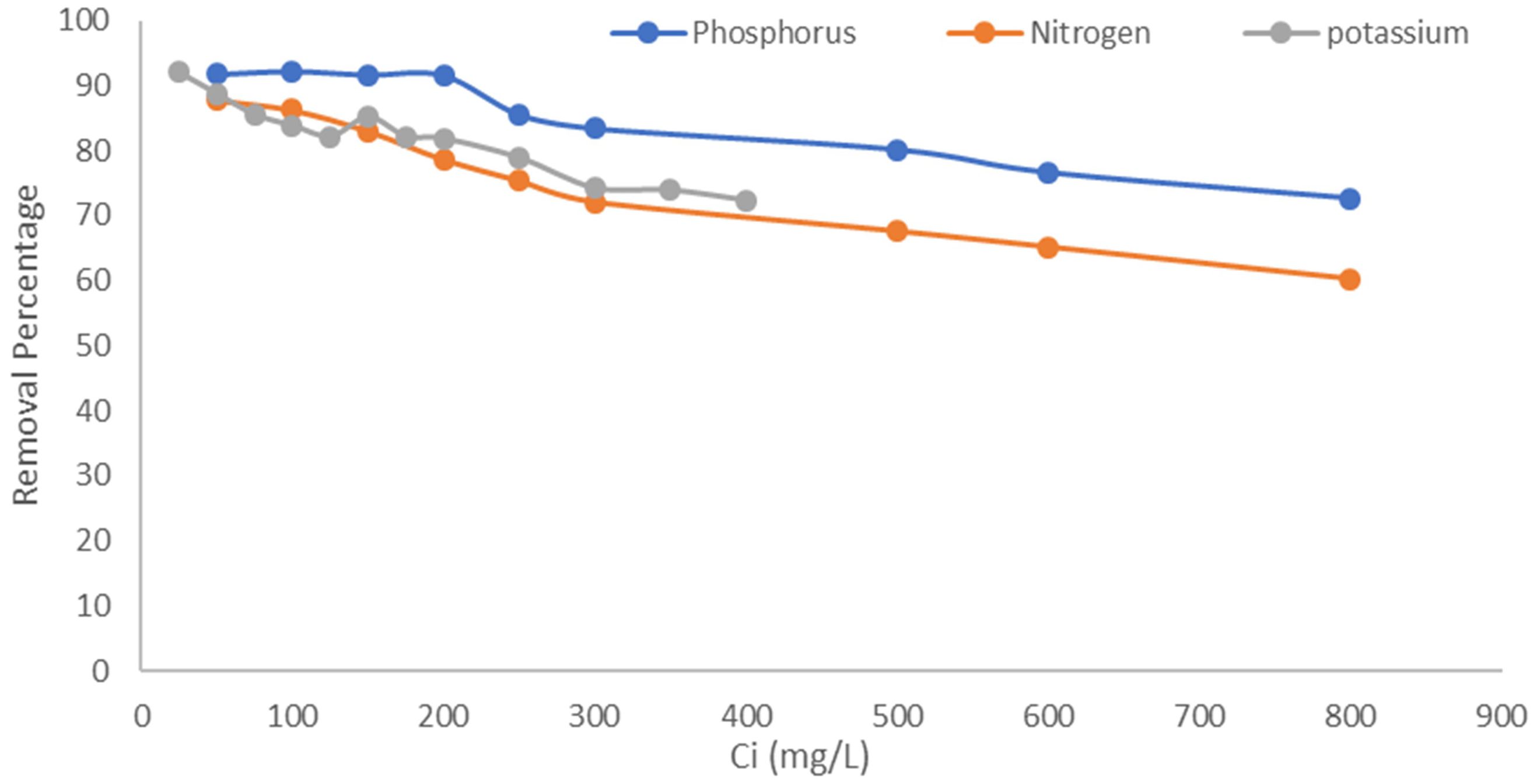
Figure 5. Removal capacity (%) of natural mordenite zeolite under different concentrations of N, P, and K.
Leaching experiment depicts the behaviour of nutrients in soil–water environment in the presence of fertiliser and zeolite. The effects of zeolite and N on ammonical-N leaching at different leaching events in Alfisol were compared with the combination of N with zeolite and without zeolite addition (Figure 6). The amount of NH4–N in leachate was largest in soil treated with N (supplied through urea), as compared to that of all the other treatments from day 3, and it continued to rise in the subsequent leaching events. Leachate ammonium concentration reached to maximum at day 12 with N @ 100 kg ha−1 + zeolite @ 5 tonnes ha−1, while the peak occurred at day 27 with the increase in zeolite application to 10 tonnes ha−1, and the concentration showed a decreasing trend afterwards, regardless of the rate of application (Figure 6A). Similarly, with N @ 500 kg ha−1, the NH4–N concentration was higher at day 3 with sole N supplied through urea as compared with N and zeolite application (Figure 6B). However, peak occurred at day 27 with zeolite application @ 10 tonnes ha−1 and followed a decreasing trend. The zeolite application could reduce the NH4–N losses when applied along with N as compared to sole N application.
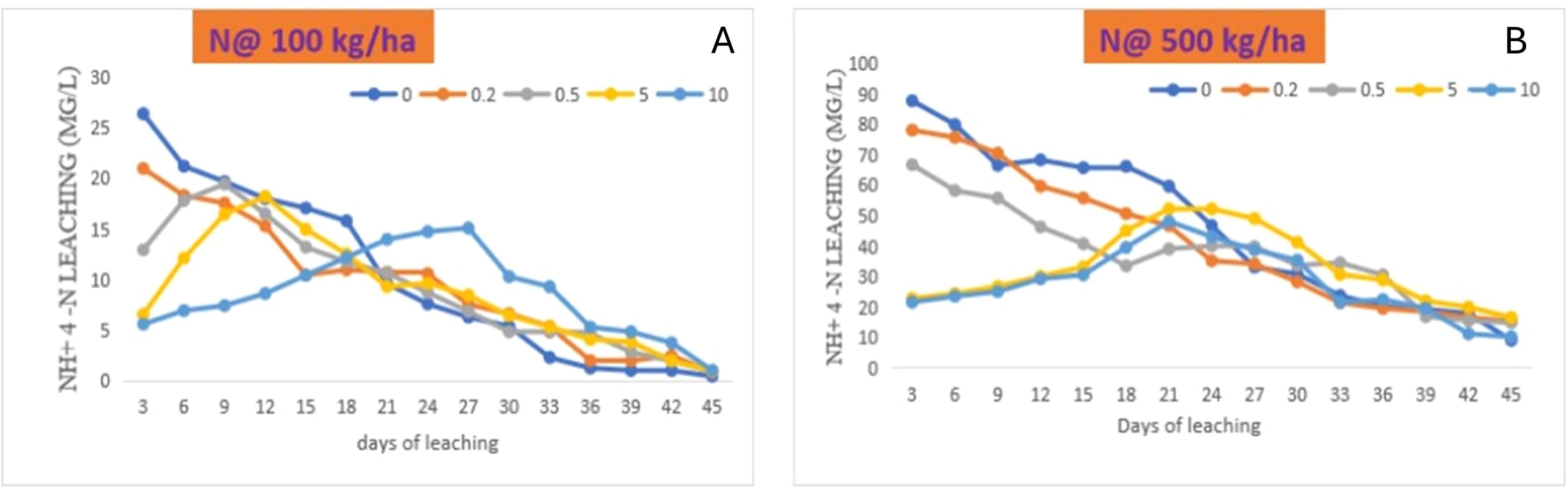
Figure 6. Effects of co-application of N though urea [(A) N @100 kg/ha, (B) N @500 kg/ha] and zeolite on NH4–N leaching at different leaching intervals in Alfisol soil.
During this experiment, cumulative amounts of NH4+–N measured in leachate is shown in Figure 7. In this study, the maximum NH4+–N was lost with N application without zeolite addition in both the case of N application rate @ 100 kg ha−1 and 500 kg ha−1. However, a significant reduction in the loss of NH4–N was observed with the increase in the rate of zeolite application. Similarly, the extent of reduction in the loss of NH4–N was high with N application rate of 500 kg ha−1 as compared to 100 kg ha−1 for Alfisol soil. With application of N @ 500 kg ha−1 + zeolite @ 10 tonnes ha−1 could reduce the loss of NH4–N up to 39.6%, while the application of N @ 100 kg ha−1 + zeolite @ 10 tonnes ha−1 could reduce the loss of NH4–N up to 15.4% as compared to the sole application of N @ 500 kg ha−1 and 100 kg ha−1, respectively. Therefore, zeolite application @ 10 tonnes ha−1 proved to be the most effective treatment in reducing leaching of NH4–N in Alfisol soil. This could be attributed to the specific selectivity of mordenite zeolite for NH4–N as evident from our sorption study; the mordenite zeolite could successfully reduce the leaching losses that in turn depends on the inner channels of zeolite. Upon evaluating the capacity of two natural New Zealand zeolites (clinoptilolite and mordenite) in removing NH4+ from a range of wastewaters, it was found that both zeolites tested, regardless of their particle sizes, were equally effective (87%–98%) at NH4+ removal from domestic wastewaters or synthetic solutions containing NH4+ concentrations of up to 150 g NH4–N m−3. However, mordenite showed more effective NH4+ removal than clinoptilolite for dairy and piggery wastewaters, and for synthetic solutions containing high NH4+ concentrations (350-750 g NH4–N m−3) (Nguyen and Tanner, 1998). In the leaching column experiment study with clinoptilolite zeolite, the leaching of ammonia from urea significantly reduced compared to sole soil alone (Latifah et al., 2017). Colombani et al. (2015) found a high concentration of N content in the leachate, while N content was low and retarded peaks were found in case of amended soil columns. In another study, the application of zeolite @ 10 tonnes ha−1 reduced the loss of nitrate-N, ammonical-N, and total-N by 19.4%, 16.9%, and 16%, respectively, in the leachate (Wang et al., 2023).
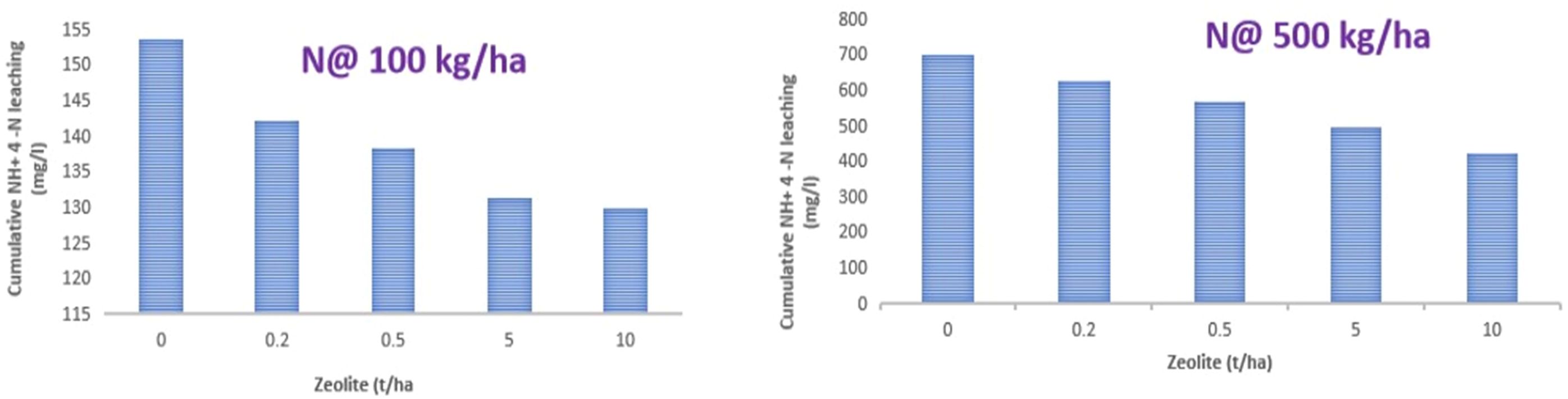
Figure 7. Effect of zeolite dose at two rates of urea application on cumulative losses of NH4–N from Alfisol soil. Means with different letters indicate significant differences among treatments by Tukey’s test at p ≤ 0.05.
In our study, it is clear that zeolite application could maintain a greater number of leaves in combination with fertiliser application as compared to sole application of fertilisers (Figure 8). Without fertiliser addition, the zeolite application alone could not record the highest number of leaves in tomato. This is because zeolite as such does not contain nutrients to adequate levels. It can act as good exchanger and improve the nutrient content of fertilisers added to the soil (Jarosz et al., 2022). The mean values ± margin of error of plant height in tomato are presented in Figure 8. In our study, zeolite application along with fertilisers showed positive influence on the tomato plant height in both the moisture levels (50% FC and 100% FC). The plant height was high when grown under 100% FC with mean of 55.65 cm as compared to 50% FC with mean of 41.45 cm. With increase in zeolite levels, there was an increase in plant height with highest application of zeolite @ 200 kg ha−1 (Z200). In both the moisture levels, it was found that with RDF100 in combination with Z200, it could maintain highest plant height as compared to treatment combinations. Wu et al. (2020) observed that the application of 10 tonnes ha−1 zeolite improved grain filling in rice with increased amount of N accumulation. Hazrati et al. (2017) reported that zeolite application could alleviate water stress and other adverse effects and improved plant height and number of leaves in Aloe vera L. This finding was similar in rice (Wulandari et al., 2019) and maize grown in saline conditions (Aboul-Magd et al., 2020).
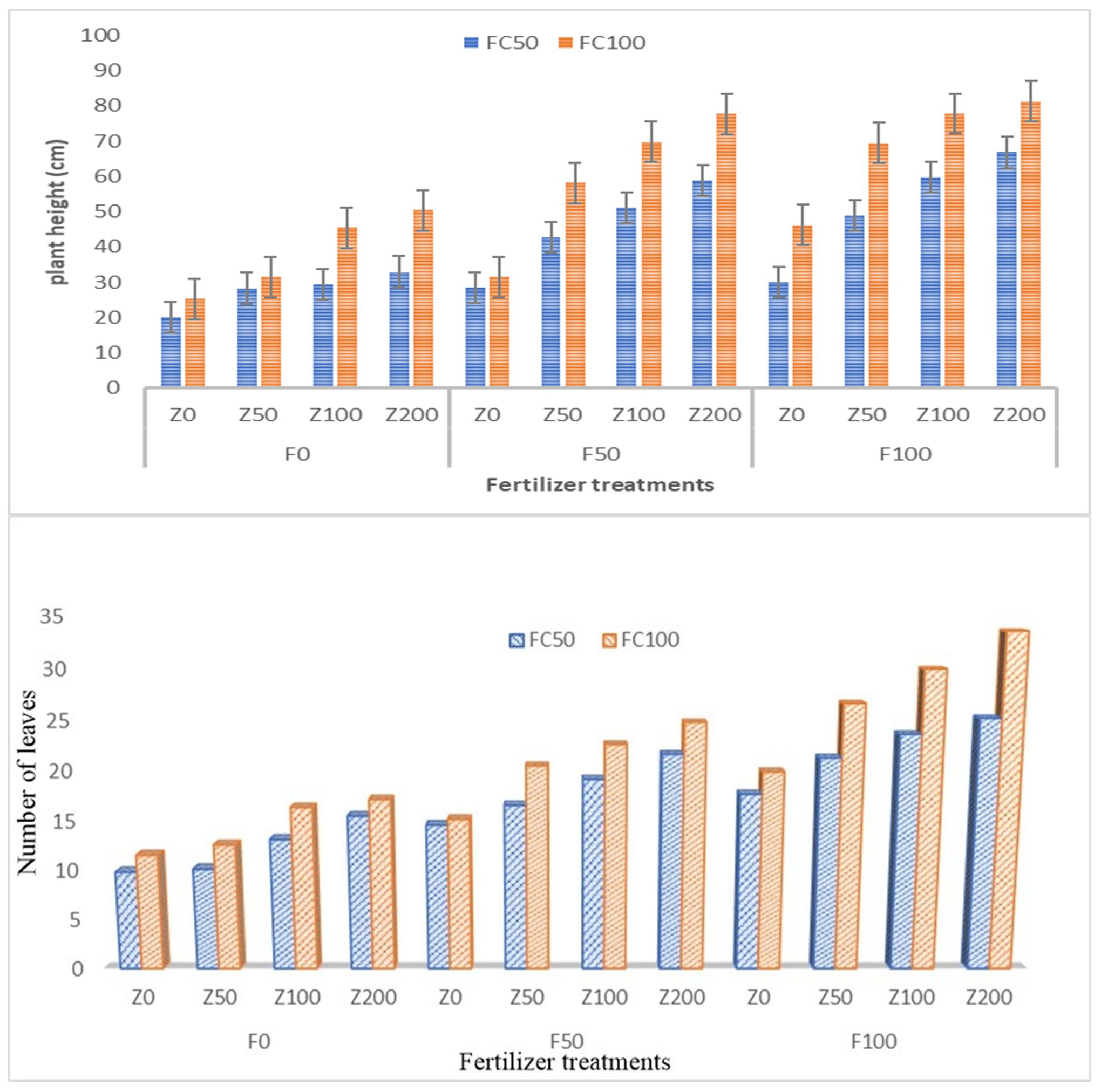
Figure 8. Impact of zeolite application along with fertilisers on (A) plant height and (B) number of leaves in tomato.
At the end of each experimental period, soil available N, P, and K was studied in post-harvest soil samples. The change in soil available nitrogen content of the post-harvest soil at different moisture levels, fertiliser levels, and zeolite levels is presented in Table 7. There was a significant effect (p<0.05%) on the soil available N, P, and K due to the application of zeolite at both the moisture levels and fertiliser levels. The results revealed that fertiliser application along with zeolite application significantly improved soil available N, P, and K content (Table 7). Under two moisture conditions, it was observed that soil available N, P, and K content increased significantly under 100% FC as compared to 50% FC, while under three fertiliser levels studied, 100% RDF could maintain higher soil available N, P, and K content as compared to 50% RDF and control. The soil available N increased with increasing dose of zeolite application. Highest was observed with zeolite application (Z200) of 89.28 mg kg−1 (equivalent to 200 kg zeolite ha−1). The treatment RDF100 + Z4 was most effective in maintaining higher soil available nutrient under both the moisture levels, and the increase in soil available N, P, and K was significantly (p < 0.05%) higher than the rest of the treatments. This suggests that zeolite application improves soil available nutrients if applied along with chemical fertilisers. Legese et al. (2024) impregnated zeolite (phillipsite) with 5% solutions of macro- (P, N, K, Ca, and Mg) and micro-nutrients (Fe, Zn, and Cu) in the form of their salts and evaluated the two samples (UNZC and SMNZC); it was found that total N increased in all amended plots as compared to amended plots. The content was higher where a higher dose was tested. Ravali et al. (2020) observed similar findings due to the application of zeolite @ 7.5 tonnes ha−1 and N @ 200 kg ha−1, which showed a significant effect on soil NPK content at different crop growth stages and at harvest in maize. Under 100% FC, with 100% RDF, the application of zeolite @ 200 kg ha−1, 100 kg ha−1, and 50 kg ha−1 increased the soil N by 48.6%, 40.5%, and 25.1%, respectively, over Z0 (without zeolite application) (Figure 9A). With 50% RDF, the application of zeolite @ 200 kg ha−1, 100 kg ha−1, and 50 kg ha−1 increased the soil N by 62.1%, 44.7%, and 34.9%, respectively, over Z0. Under 50% FC, with 100% RDF, the application of zeolite @ 200 kg ha−1, 100 kg ha−1, and 50 kg ha−1 increased the soil N by 37.5%, 27.8%, and 22.2%, respectively, over Z0 (without zeolite application). With 50% RDF, the application of zeolite @ 200 kg ha−1, 100 kg ha−1, and 50 kg ha−1 increased the soil N by 31.5%, 24.7%, and 4.7%, respectively, over Z0. Zeolite application @ 5 tonnes ha−1 resulted in an increase of 35.13% in total N content in Alfisols (Triatmoko et al., 2019). The soil chemical properties that include soil cation exchange capacity, the soil total nitrogen concentration, and nitrogen use efficiency increased significantly due to the co-application of 150 kg N ha−1 and 200 kg N ha−1 with 10 and 15 tonnes ha−1 of zeolite (Dastbaz et al., 2023).
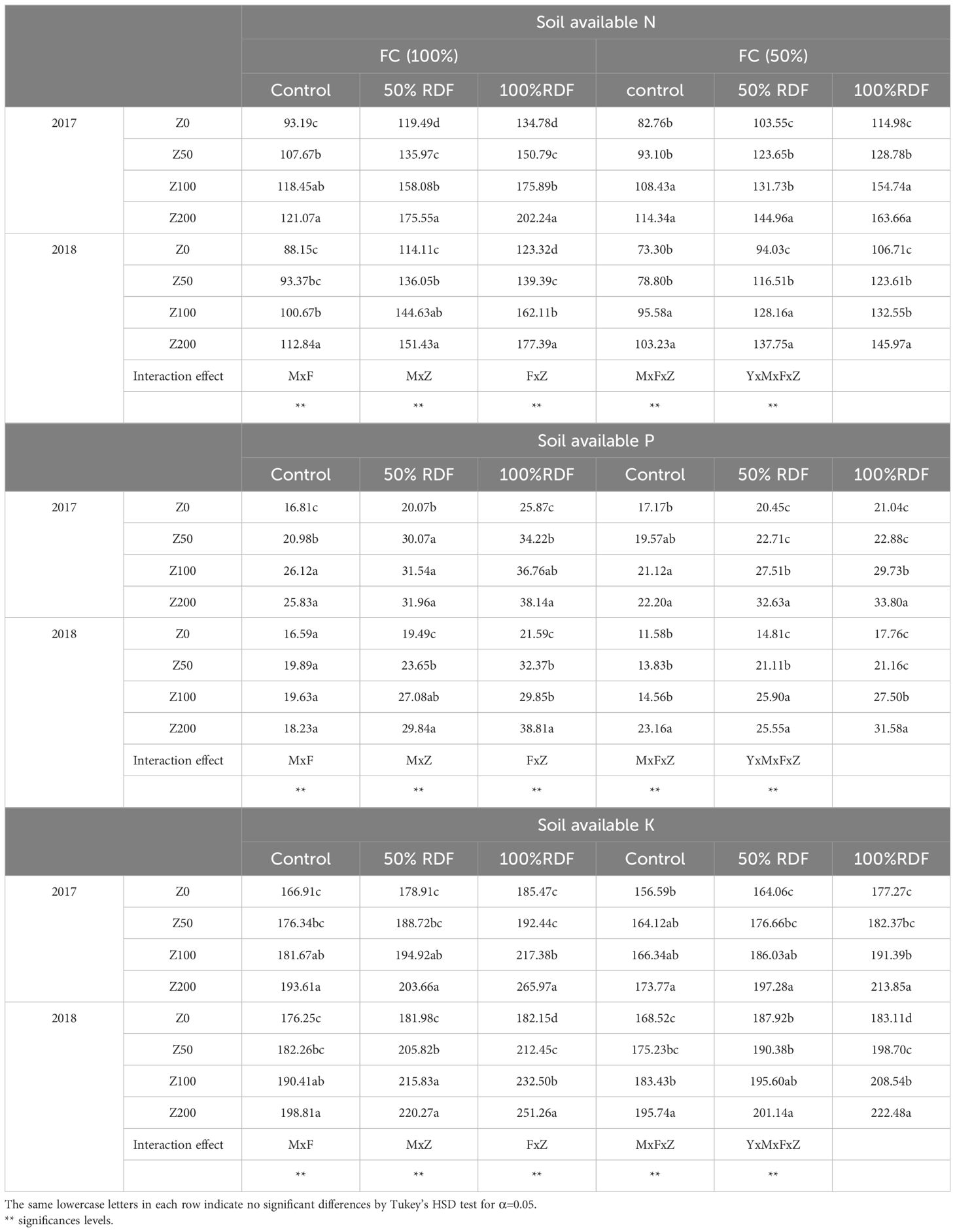
Table 7. Soil available N, P, and K (kg/ha) as affected by different levels of moisture, fertiliser, and zeolite.
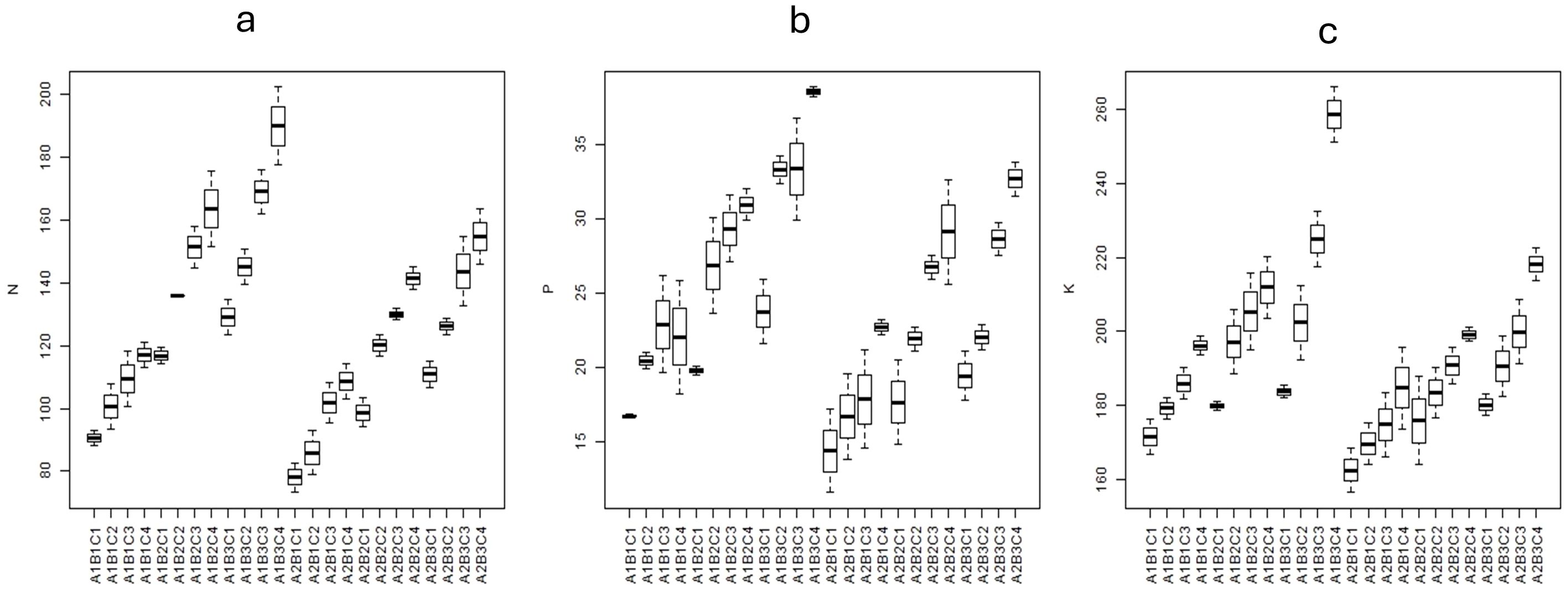
Figure 9. Box plots showing the (A) soil available N, (B) soil available P, and (C) soil available K content (kg/ha) in different treatments. A1 = 100% FC; A2 = 50% FC; B1 = control, B2 = 90: 50: 25 kg NPK/ha, B3 = 180: 100: 50 kg NPK/ha; C1 = control; C2 = 50 kg/ha; C3 = 100 kg/ha; C4 = 200 kg/ha.
Similarly, under 100% FC, with 100% RDF, the application of zeolite @ 200 kg ha−1, 100 kg ha−1, and 50 kg ha−1 increased the soil available P by 48.9%, 27.1%, and 23.7%, respectively, over Z0 (without zeolite application). With 50% RDF, the application of zeolite @ 200 kg ha−1, 100 kg ha−1, and 50 kg ha−1 increased the soil N by 37.8%, 28.4%, and 17.9% respectively, over Z0 (Figure 9B). Under 50% FC, with 100% RDF, the application of zeolite @ 200 kg ha−1, 100 kg ha−1, and 50 kg ha−1 increased the soil N by 44.9%, 29.5%, and 11.6%, respectively, over Z0 (without zeolite application). With 50% RDF, the application of zeolite @ 200 kg ha−1, 100 kg ha−1, and 50 kg ha−1 increased the soil N by 43.9%, 42.1%, and 26.4%, respectively, over Z0. The capacity of zeolite to improve the P availability is found high under 100% FC as compared to 50% FC.
In case of soil available K, under 100% FC, with 100% RDF, the application of zeolite @ 200 kg ha−1, 100 kg ha−1, and 50 kg ha−1 increased the soil available K by 14.1%, 12.4%, and 6.92%, respectively, over Z0 (without zeolite application) (Figure 9C). While with 50% RDF, the application of zeolite @ 200 kg ha−1, 100 kg ha−1, and 50 kg ha−1 increased the soil N by 14.6%, 10.6%, and 6.97%, respectively, over Z0. Under 50% FC, with 100% RDF, the application of zeolite @ 200 kg ha−1, 100 kg ha−1, and 50 kg ha−1 increased the soil N by 21.1%, 15.8%, and 7.53%, respectively, over Z0 (without zeolite application). While with 50% RDF, the application of zeolite @ 200 kg ha−1, 100 kg ha−1, and 50 kg ha−1 increased the soil N by 21.5%, 19.1%, and 7.01%, respectively, over Z0. The capacity of zeolite to improve the nutrient availability is found high under 100% FC as compared to 50% FC. There was significant difference in soil available nutrients in post-harvest soil due to zeolite and fertiliser use. The combined application of zeolite and fertiliser showed improved nutrient status than fertiliser application without zeolite. Some studies reported that N fertiliser requirement was reduced by 33% due to zeolite application in rice (Chen et al., 2017). The two- and three-way interaction effect among moisture, fertiliser rate, zeolite, and even year was significant for soil available N, P, and K contents. Averaged across the three zeolite amendments, topsoil available K increased from 13% (93 DAT, K30) to 31% (55 DAT, K60) in 2017, and from 16% (55 DAT, K30) to 46% (34 DAT, K60) in 2018 due to K30 and K60 applications application in rice (Li et al., 2022). In calcareous soils, it was reported that application of natural zeolite at 10 μg ha−1 (Z10) significantly increased in N, P, and K in post-harvest soil samples with 42.72 mg N kg−1 soil, 20.23 mg P kg−1 soil, and 201.05 mg K kg−1 soil, respectively (Saleh and Al Bahrani, 2023). Application of zeolite along with chemical fertilisers could improve soil N, P, and K content (Banik et al., 2023) and also with organic manures such as vermicompost and biofertilisers, and chemical fertilisers could improve soil N, P, and K content and also resulted in higher soil available N, P, and K in post-harvest soil samples (Rahmani et al., 2023; Idim et al., 2024).
The present study showed higher N, P, and K uptake due to zeolite addition along with chemical fertilisers (Figure 10). Experimental treatments significantly affected N, P, and K uptake in tomato. Among the treatments, control treatment (RDF0Z0) had minimum N, P, and K uptake, whereas maximum N, P, and K uptake was obtained due to application of full recommended dose of fertilisers along with 200 kg zeolite ha−1 (RDF100Z200). The zeolite addition improve,d N, P and K uptake by two times as compared to without zeolite addition under both the moisture conditions. The treatment RDF100+Z200 could maintain higher mean N, P, and K uptake with 560.63 mg pot−1, 85.34 mg pot−1, and 192.87 mg pot−1, respectively, in 100% FC conditions, while least mean N, P, and K uptake with 289.39 mg pot−1, 42.80 mg pot−1, and 83.30 mg pot−1, respectively, in 100% FC conditions in control treatment (RDF0Z0). However, the uptake reduced slightly under 50% FC conditions where the mean N, P, and K uptake was 436.53 mg pot−1, 87.53 mg pot−1, and 192.87 mg pot−1, respectively, in F100+Z200 treatment and 224.90 mg pot−1, 42.80 mg pot−1, and 76.63 mg pot−1, respectively, under RDF0Z0 treatment. Zeolite addition (5 tonnes ha−1) along with manures improved potassium availability and uptake in soybean cultivated in Alfisols (Haniati et al., 2019) and also improved N availability and uptake in soybean (Triatmoko et al., 2019). In Iran, there was significant effect of combined application of zeolite and fertiliser on improved N uptake (Kavoosi, 2007) and K uptake in rice (Chen et al., 2017; Xia et al., 2019). Gholamhoseini et al. (2012) reported that the zeolite application @ 9 tonnes ha−1 improved the N uptake by four times in canola.
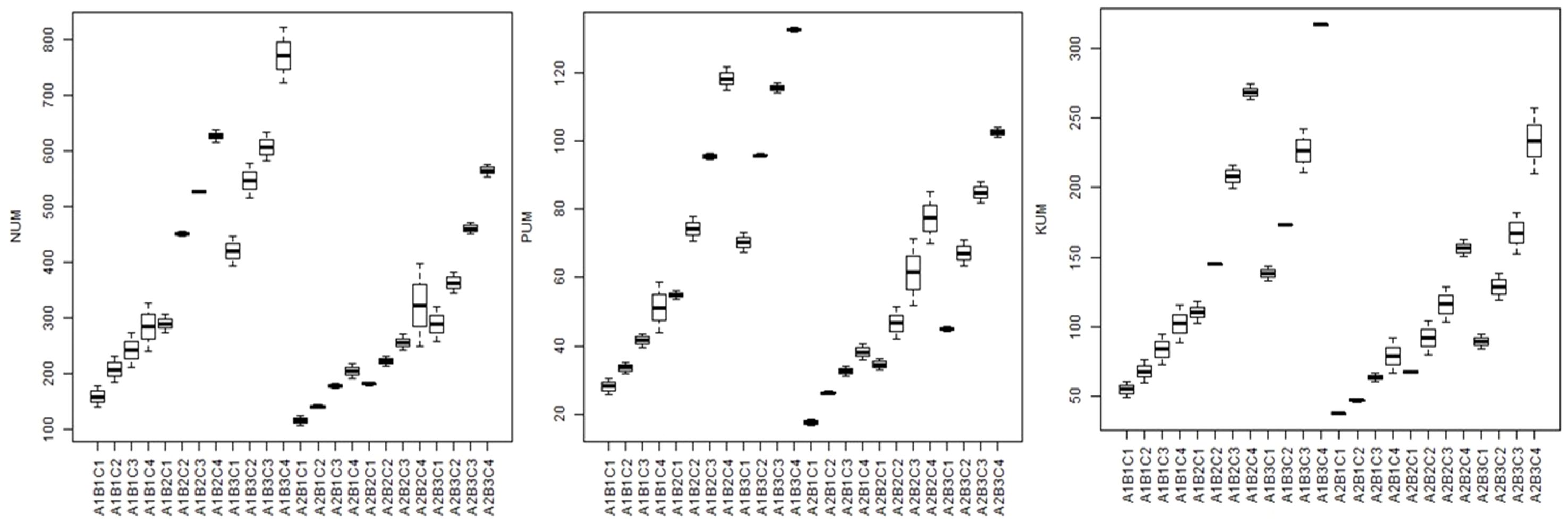
Figure 10. Box plots showing the N, P, and K uptake (mg/pot) in different treatments for both the study years. NUM, nitrogen uptake; PUM, phosphorus uptake; KUM, potassium uptake; A1 = 100% FC; A2 = 50% FC; B1 = control, B2 = 90: 50: 25 kg NPK/ha, B3 = 180: 100: 50 kg NPK/ha; C1 = control; C2 = 50 kg/ha; C3 = 100 kg/ha; C4 = 200 kg/ha.
In the first year of the experiment (2017), zeolite addition to the soil (along with chemical fertiliser) significantly increased the tomato biomass in respect to the control (Table 8). The yield at the highest zeolite dose (Z200) was higher with 34.82 g pot−1 than other doses. This observation was similar in second year of experimentation (2018) where it was 39.99 g pot−1 due to application zeolite @ 200 kg ha−1 (Z200). Result showed that the biomass of tomato was significantly influenced by the treatment applied (Table 8). The greatest mean biomass yield was obtained by supplementing (RDF100Z200) under both moisture levels studied with 49.08 g pot−1 in 100% FC and 38.31 g pot−1 in 50% FC and the least with 26.93 g pot−1 in 100% FC and 26.06 g pot−1 in 50% FC in control (RDF0Z0). On other hand, with the increase in fertiliser rate from RDF0 to RdF100 (100% RDF-180: 100: 50 kg NPK ha−1) and zeolite dose from Z0 to Z200 (0–200 kg ha−1) led to an increase of 36.4% and 48.39% increase in biomass yield, respectively. Kotoulas et al. (2019) reported highest fresh weight of wheat due to zeolite application @ 40 mg kg−1, which was fund to be 74% higher than the control. Another study revealed that combined application of 100 kg ha−1 zeolite and 200 kg ha−1 NPK provided optimal yields of dry shelled maize up to 5.44 tonnes ha−1 grown in Inceptisol (Affendi et al., 2023).
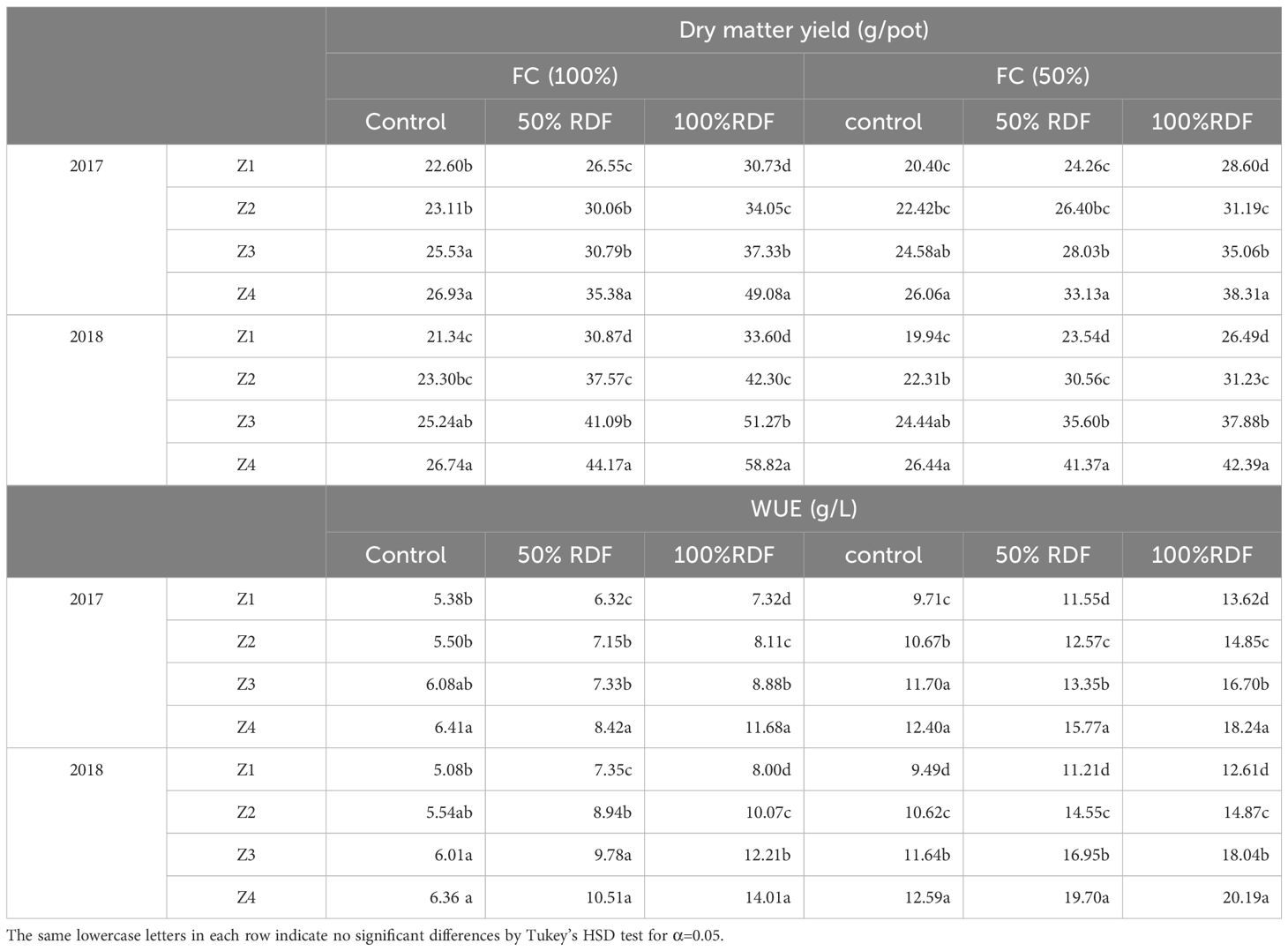
Table 8. Dry matter yield (g/pot) and WUE (g L−1) as affected by different levels of moisture, fertiliser, and zeolite in tomato.
Zeolite addition to the soil (along with chemical fertiliser) significantly increased the WUE as compared to the control (Table 8). The WUE was found high with 50% FC as compared to 100% FC during both the years of experiment. The WUE was found high under 50% FC with 18.24 g L−1 in 2017 and 20.19 g L−1 in 2018 in F100Z200 treatment, while under 100% FC, the WUE was with 11.68 g L−1 in 2017 and 14.01 g L−1 in 2018 in F100Z200 treatment. Under 100% FC, the mean increase in WUE over 2 years with Z4 was 22.17% in control (without any fertiliser application), 38.11% in 50% RDF, and 67.34% in 100% RDF. Research states that zeolite holds water in its extraordinary porous structure and hence improves water availability to crops and enhances WUE (Xiubin and Zhanbin, 2001; Gholamhoseini et al., 2013). Zheng et al. (2018) reported that zeolite application @ 15 tonnes m−2 along with energy-controlled irrigation improved grain yield with less water consumption. According to Kralova et al. (1994), soils enriched with natural zeolite were able to increase the water retention by 18%–19% and for sandy soils even up to 50% (Lancellotti et al., 2014). While Ravali et al. (2020) reported 48.5% increase in water retention capacity due to 7.5 tonnes ha−1 zeolite application in sandy and loamy soils. Hazrati et al. (2022) reported an increase in WUE up to 22.10 g L−1 with the use of 10 tonnes zeolite ha−1 along with an application @ 150 kg ha−1 even under 60% depletion of available soil water content in Salvia officinalis grown in loam sandy soils. The positive effect of zeolite application in increasing yield was observed in maize (Aboul-Magd et al., 2020); sugarcane (Cairo et al., 2017), and tomato (Méndez Argüello et al., 2018).
In most of the studies, clinoptilolite is widely used and tested for improving the soil availability. However, mordenite is also known to improve soil available nutrients and water use efficiency (Stamatakis et al., 2017). Mordenite is a high silicate zeolite and large-pore zeolite with high surface area (Gosselink et al., 2010). In our study, mordenite application could improve the soil available N, P, and K; their uptake; dry matter yield; and WUE in Alfisols. Overall performance for both the years is shown in Figure 11. Uptake of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium by tomato is significantly affected by fertiliser levels and zeolite levels. An increase in fertiliser application leads to a decrease in nitrogen use efficiency and an increase in soil nitrate N accumulation and soil fertility. Combined supplementation of chemical fertilisers with zeolite had a notable effect on the chemical properties of the soil and also on yield. Zeolite prevents nutrients to be lost through leaching (Sun et al., 2019). Our study showed a strong correlation among N, P, and K availability in soil and their uptake in plant and dry matter yield and water use efficiency (Figure 12).
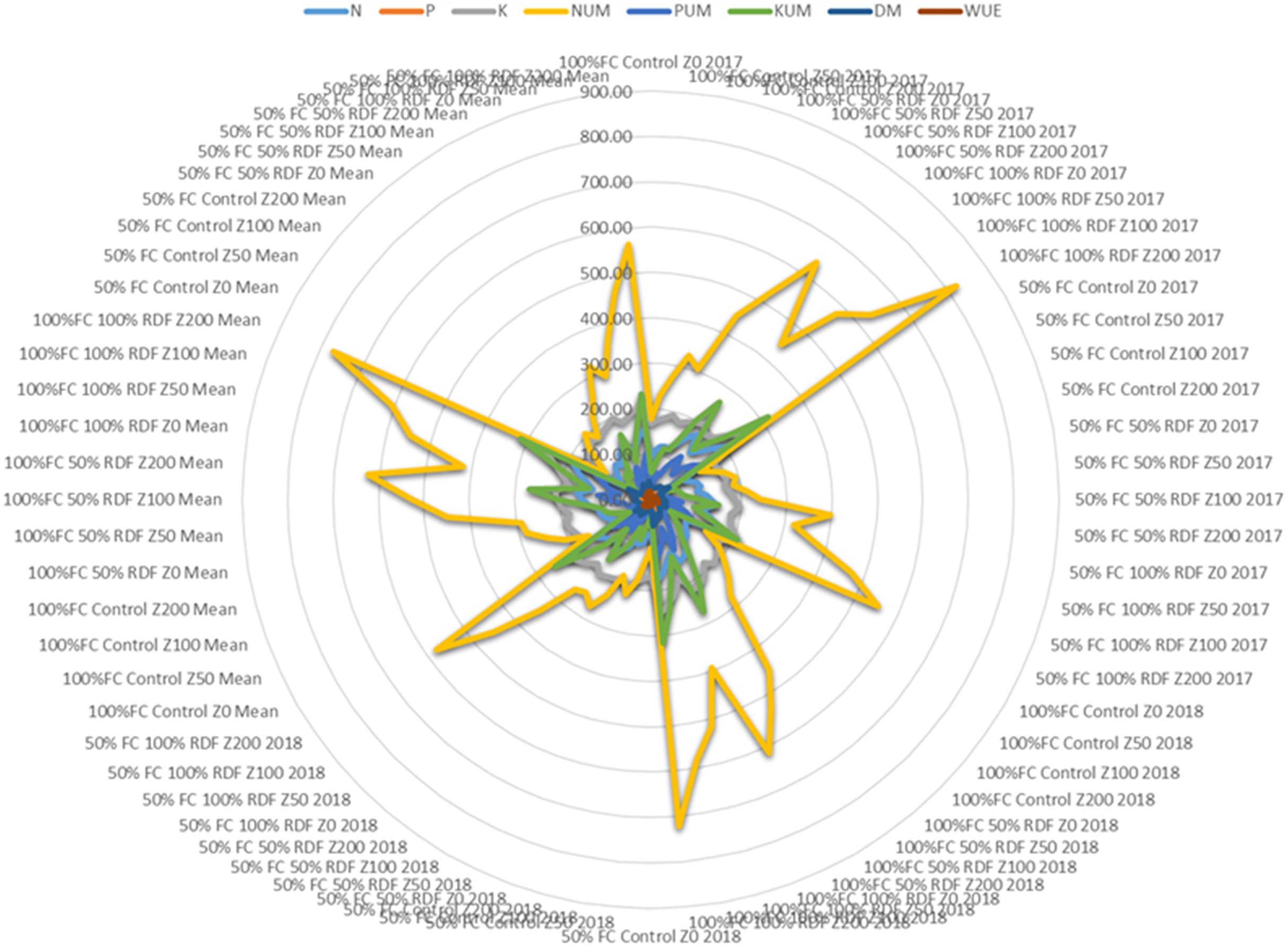
Figure 11. Spider diagram of different treatments on soil available N (denoted as N), P (denoted as P), K (denoted as K); plant uptake of N (denoted as NUM), plant uptake of P (denoted as PUM), plant uptake of K (denoted as KUM); dry matter production (denoted as DM) and water use efficiency (WUE).
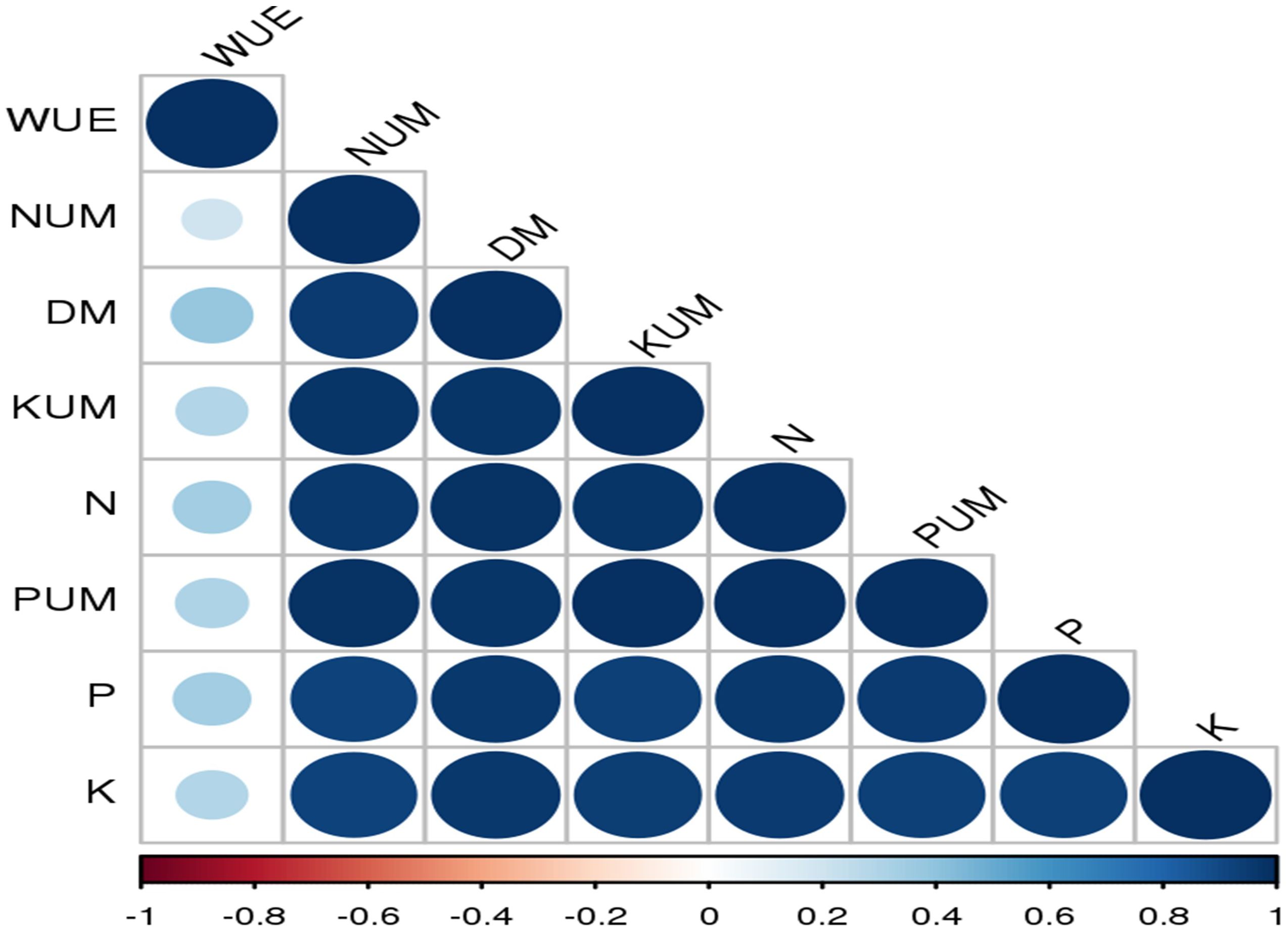
Figure 12. Pearson’s correlation matrix between soil chemical properties (soil available N, P, and K), nutrient uptake (NUM, PUM, and KUM), WUE, and dry matter yield. Correlations are displayed in blue (positive) and red (negative); colour intensity and circle size are proportional to the correlation coefficient. WUE, water use efficiency; NUM, N uptake; DM, dry matter; KUM, potassium uptake; N, soil available N; PUM, P uptake; P, soil available P; K, soil available K.
Application of zeolites in soil has gained importance for reducing N leaching and increase N efficiency. Sepaskhah and Yousefi (2007) reported that application of 2–8 g zeolite kg−1 prevented nutrient leaching in sandy loam soil. MesoLite zeolite has low surface area (9–12 m2 g−1) and very high cation exchange capacity [494 cmol(+)/kg]. The application of mesolite to sandy soil @ 0.4% resulted in reducing the NH4+ to the extent of 90% as compared to unamended soil (Zwingmann et al., 2009). In canola, the application of 270 kg N ha−1 without zeolite resulted in the greatest amount of N leaching loss to the tune of 144.23 kg ha−1 in sandy soils (Gholamhoseini et al., 2012). Due to its multiple positive effects on the chemical soil properties, zeolite contributes to improved nutrient, crop productivity, and crop quality. Water scarcity is a major limiting factor of agricultural production in arid locations mainly due to low precipitation and high evaporation and is aggravated by global climate change through extreme events and prolonged dry seasons. However, studies proved that zeolite improves water and plant nutrients. Recently, it is reported that the positive impact of zeolite application on paddy yield could continue even in the fifth year after its initial application. Moreover, application of zeolite @ 10 tonnes ha−1 (Z10) increased soil NH4+–N by 27%–38% and NO3–N by 14%–22% in 5 years compared to Z0 (control) (Zhao et al., 2023). Thus, zeolite application can last for 5 years. Thus, it can be used along with mineral fertilisers to earn more profits.
Zeolite is a promising amendment in soil management. In this study, natural zeolite sample purchased from local market was characterized using XRD and SEM to known the type of zeolite and found that it is mordenite zeolite. The sorption study revealed that mordenite zeolite has shown good adsorption of ammonical-N and to lesser extent of P and K, which was also found to have a good fit in Langmuir and Freundlich isotherms with high R2. This suggests that mordenite has good affinity for ammonical-N and also, in a little extent, for K. Leaching column study also revealed that it was effective in mitigating the losses under laboratory condition. Mainly, combined application of zeolite and N supplemented through urea could mitigate N leaching loss and ensure slow release availability when applied along with urea. There was a significant impact on soil available nutrients (N, P, and K) due to application of 100% RDF along with zeolite @ 200 kg ha−1 with mean increase of 46.9%, 63.6%, and 40.6%, respectively, under 100% FC, while the mean increase in soil available N, P, and K was up to 39.5%, 68%, and 21%, respectively, under 50% FC over 100% RDF without zeolite. There was also a significant positive impact on plant nutrients (N, P, and K) uptake, dry matter production, and water use efficiency due to application of 100% RDF along with zeolite @ 200 kg ha−1 under 50% and 100% FC as compared to without zeolite application. Thus, mordenite zeolite can also be an option to improve soil’s water-holding capacity and nutrient use efficiency by reducing the leaching losses and improving the crop yield. However, comprehensive studies across different agro climatic conditions and its beneficial effect on soil quality need to explore.
The original contributions presented in the study are included article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
GV: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. SRK: Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. SC: Software, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. RK: Formal analysis, Software, Writing – review & editing. DB: Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. SK: Writing – review & editing. PP: Writing – review & editing. JR: Writing – review & editing. SVK: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
The authors would like to express their gratitude to the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) for their support. I must thank Dr. Arunshanker, Principal scientist working at CRIDA, Hyderabad for english editing.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Aboul-Magd, M., Elzopy, K. A., Zangana, Z. R. M. (2020). Effect of zeolite and urea fertilizer on maize grown under saline conditions. Middle East J. Appl. Sci. 10, 18–25. doi: 10.36632/mejas%2F2020.10.1.3
Affendi, S., Berd, I., Haryoko, W., Utama, Z. H., Novia, P. (2023). The role of zeolite and NPK fertilizer on maize (Zea mays L.) growth in inceptisol, southern solok district. Asian J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 9, 95–103. doi: 10.9734/ajsspn/2023/v9i4195
Aghaalikhani, M., Gholamhoseini, M., Dolatabadian, A., Khodaei-Joghan, A., Sadat, A. K. (2012). Zeolite influences on nitrate leaching, nitrogen-use efficiency, yield and yield components of canola in sandy soil. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 58, 1149–1169. doi: 10.1080/03650340.2011.572876
Akrawi, H. S. Y., Al-Obaidi, M. A., Abdulrahman, C. H. (2021). “Evaluation of Langmuir and Frendlich isotherm equation for Zinc Adsorption in some calcareous soil of Erbil province north of Iraq,” in IOP conference series: earth and environmental science Iraq: INTERNATIONAL COLLABORATIVE CONFERENCE OF MODERN AGRICULTURAL TECHNOLOGIES, 761, 012017. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/761/1/012017
Amirahmadi, E., Ghorbani, M., Moudrý, J. (2022). Effects of zeolite on aggregation, nutrient availability, and growth characteristics of corn (Zea mays L.) in cadmium-contaminated soils. Water Air amp; Soil Pollution. 233, 436. doi: 10.1007/s11270-022-05910-4
Assawasaengrat, P., Rueangdechawiwat, R. (2019). “). Adsorption of ammonia nitrogen in aqueous solution using zeolite A,” in IOP conference series: mater sci eng, vol. 639. (Shenzhen, China: IOP Publishing), 012050. doi: 10.1088/1757-899X/639/1/012050
Banik, C., Bakshi, S., Andersen, D. S., Laird, D. A., Smith, R. G., Brown, R. C. (2023). The role of biochar and zeolite in enhancing nitrogen and phosphorus recovery: A sustainable manure management technology. Chem. Eng. J. 456, 141003. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.141003
Barczyk, K., Mozgawa, W., Król, M. (2014). Studies of anions sorption on natural zeolites. Spectrochim Acta A Mol. Biomol Spectrosc. 133, 876–882. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2014.06.065
Cairo, P. C., de Armas, J. M., Artiles, P. T., Martin, B. D., Carrazana, R. J., Lopez, O. R. (2017). Effects of zeolite and organic fertilizers on soil quality and yield of sugarcane. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 11, 733–738. doi: 10.21475/AJCS.17.11.06.P501
Cassel, D. K., Nielsen, D. R. (1986). “Field capacity and available water capacity,” in Methods of soil analysis, Part 1. Physical and mineralogical methods. Ed. Klute, A. (Wisconsin, Madison), 901–906. doi: 10.2136/sssabookser5.1.2ed.c36
Cataldo, E., Salvi, L., Paoli, F., Fucile, M., Masciandaro, G., Manzi, D., et al. (2021). Application of zeolites in agriculture and other potential uses: A review. Agronomy. 11, 1547. doi: 10.3390/agronomy11081547
Chae, Y., Cui, R., Woong Kim, S., An, G., Jeong, S. W., An, Y. J. (2017). Exoenzyme activity in contaminated soils before and after soil washing: ß-glucosidase activity as a biological indicator of soil health. Ecotoxicol. Environ. 135, 368–374. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.10.007
Chai, Y., Dai, W., Wu, G., Guan, N., Li, L. (2021). Confinement in a zeolite and zeolite catalysis. Accounts Chem. Res. 54, 2894–2904. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.1c00274
Chen, T., Xia, G., Wu, Q., Zheng, J., Jin, Y., Sun, D., et al. (2017). The influence of zeolite amendment on yield performance, quality characteristics, and nitrogen use efficiency of paddy rice. Crop Sci. 57, 2777–2787. doi: 10.2135/cropsci2016.04.0228
Cheng, Q., Li, H., Xu, Y., Chen, S., Liao, Y., Deng, F., et al. (2017). Study on the adsorption of nitrogen and phosphorus from biogas slurry by NaCl-modified zeolite. PloS One 12, e0176109. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0176109
Colombani, N., Mastrocicco., M., Di Giuseppe., D., Faccini., B., Coltorti., M. (2015). Batch and column experiments on nutrient leaching in soils amended with Italian natural zeolitites. Catena. 127, 64–71. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2014.12.022
Cyrus, J. S., Reddy, G. B. (2011). Sorption and desorption of ammonium by zeolite: Batch and column studies. J. Environ. Sci. Health A. 46, 408–414. doi: 10.1080/02773813.2010.542398
Dastbaz, N., Mahmoodi, M. A., Karimi, A., Salavati, S. (2023). Impact of zeolite and nitrogen application on nitrogen use efficiency, growth and yield of maize (Zea mays L.). J. Agric. Eng. 45, 391–408. doi: 10.22055/agen.2023.43010.1655
Du, Q., Liu, S., Cao, Z., Wang, Y. (2005). Ammonia removal from aqueous solution using natural Chinese clinoptilolite. Separ. Purif. Technol. 44, 229–234. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2004.04.011
Ferretti, G., Rosinger, C., Diaz-Pines, E., Faccini, B., Coltorti, M., Keiblinger, K. M. (2024). Soil quality increases with long-term chabazite-zeolite tuff amendments in arable and perennial cropping systems. J. Environ. Manage. 354, 120303. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2024.120303
Franus, M., Wdowin, M., Bandura, L., Franus, W. (2015). ). Removal of environmental pollutions using zeolites from fly ash: A review. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 24, 854–866. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/273482441.
Gholamhoseini, M., AghaAlikhani, M., Malakouti, M. J., Joghan, A. K. (2012). Influence of zeolite application on nitrogen efficiency and loss in canola production under sandy soils conditions. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 43, 1247–1262. doi: 10.1080/00103624.2012.666301
Gholamhoseini, M., Ghalavand, A., Khodaei-Joghan, A., Dolatabadian, A., Zakikhani, H., Farmanbar, E. (2013). Zeolite-amended cattle manure effects on sunflower yield, seed quality, water use efficiency and nutrient leaching. Soil Tillage Res. 126, 193–202. doi: 10.1016/j.still.2012.08.002
Ghorbani, M., Amirahmadi, E., Konvalina, P., Moudrý, J., Bárta, J., Kopecký, M., et al. (2022). Comparative influence of biochar and zeolite on soil hydrological indices and growth characteristics of corn (Zea mays L.). Water. 14, 3506. doi: 10.3390/w14213506
Giannatou, S., Vasilatos, C., Mitsis, I., Koukouzas, N. (2018). Utilization of natural and synthetic zeolitic materials as soil amendments in abandoned mine sites. Bull. Geological Soc. Greece. 53, 78–98. doi: 10.12681/bgsg.18567
Gosselink, R. W., Sagala, S. L., Meeldijk, J. D., de Jongh, P. E., de Jong, K. P. (2010). Alkaline treatment on commercially available aluminum rich mordenite. Appl. Catal A: Gen. 382, 65–72. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2010.04.023
Guida, S., Potter, C., Jefferson, B., Soares, A. (2020). Preparation and evaluation of zeolites for ammonium removal from municipal wastewater through ion exchange process. Sci. Rep. 10, 1–11. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-69348-6
Haniati, I. L., Minardi, S., Nastiti, A. H. L., Harieni, S., Syamsiyah, J., Hartati, S. (2019). The utilizing of zeolite and manures for increasing potassium availability, uptake, and yield on soybean in Alfisols. In IOP Conf. Series: Mater Sci. Eng. 633, 12012. doi: 10.1088/1757-899X/633/1/012012
Hanway, J. J., Heidal, H. (1952). Soil analysis methods as used in Iowa State College Soil Testing Laboratory Vol. 57 (Iowa, United States: Iowa State College of Agriculture Bulletin), 1–31.
Harrington, G. F., Santiso, J. (2021). Back-to-Basics tutorial: X-ray diffraction of thin films. J. Electroceramics. 47, 141–163. doi: 10.1007/s10832-021-00263-6
Hazrati, S., Khurizadeh, S., Sadeghi, A. R. (2022). Application of zeolite improves water and nitrogen use efficiency while increasing essential oil yield and quality of Salvia officinalis under water-deficit stress. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 29, 1707–1716. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.10.059
Hazrati, S., Tahmasebi-Sarvestani, Z., Mokhtassi-Bidgoli, A., Modarres-Sanavy, S. A. M., Mohammadi, H., Nicola, S. (2017). Effects of zeolite and water stress on growth, yield and chemical compositions of Aloe vera L. Agric. Water Management. 181, 66–72. doi: 10.1016/J.AGWAT.2016.11.026
Idim, K. S., Marzi, M., Oyeyiola, A., Kazemian, H. (2024). Enhancing composting efficiency and nutrient retention through zeolite amendment: implications for sustainable soil management and plant growth. ACS Sustain. Resource Management. 1 (7), 1340–1349. doi: 10.1021/acssusresmgt.3c00130
Jackson, M. L. (2005). Soil chemical analysis: advanced course: a manual of methods useful for instruction and research in soil chemistry, physical chemistry of soils, soil fertility, and soil genesis (Madison, WI: UW-Madison Libraries parallel press).
Jahani, F., Sadeghi, R., Shakeri, M. (2023). Ultrasonic-assisted chemical modification of a natural clinoptilolite zeolite: Enhanced ammonium adsorption rate and resistance to disturbing ions. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 11, 110354. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2023.110354
Jarosz, R., Szerement, J., Gondek, K., Mierzwa-Hersztek, M. (2022). The use of zeolites as an addition to fertilisers–A review. Catena. 213, 106125. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2022.106125
Kalam, S., Abu-Khamsin, S. A., Kamal, M. S., Patil, S. (2021). Surfactant adsorption isotherms: A review. ACS omega 6, 32342–32348. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.1c04661
Kavoosi, M. (2007). Effects of zeolite application on rice yield, nitrogen recovery, and nitrogen use efficiency. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 38, 69–76. doi: 10.1080/00103620601093652
Kotoulas, A., Agathou, D., Triantaphyllidou, I. E., Tatoulis, T. I., Akratos, C. S., Tekerlekopoulou, A. G., et al. (2019). Zeolite as a potential medium for ammonium recovery and second cheese whey treatment. Water. 11, 136. doi: 10.3390/w11010136
Kralova, M., Hrozinkova, A., Ruzek, P., Kovanda, F., Kolousek, D. (1994). Synthetic and natural zeolites affecting the physicochemical soil properties (Czech Republic: Rostlinna Vyroba-UZPI).
Krug, F. J., Ruzicka, J., Hansen, E. H. (1979). Determination of ammonia in low concentrations with Nessler’s reagent by flow injection analysis. Analyst. 104, 47–54. doi: 10.1039/AN9790400047
Lancellotti, I., Toschi, T., Passaglia, E., Barbieri, L. (2014). Release of agronomical nutrient from zeolitite substrate containing phosphatic waste. Environ. Sci. pollut. Res. 21, 13237–13242. doi: 10.1007/s11356-014-3334-5
Latifah, O., Ahmed, O. H., Majid, N. M. A. (2017). Enhancing nitrogen availability from urea using clinoptilolite zeolite. Geoderma. 306, 152–159. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2017.07.012
Legese, W., Taddesse, A. M., Kibret, K., Wogi, L. (2024). Effects of natural and modified zeolite based composite fertilizers on slow release and nutrient use efficiency. Heliyon. 10, e25524. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e25524
Levakov, I., Ronen, Z., Siebner, H., Dahan, O. (2021). Continuous in-situ measurement of free extracellular enzyme activity as direct indicator for soil biological activity. Soil Biol. Biochem. 163, 108448. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2021.108448
Li, J., Gao, Z. R., Lin, Q. F., Liu, C., Gao, F., Lin, C., et al. (2023). A 3D extra-large-pore zeolite enabled by 1D-to-3D topotactic condensation of a chain silicate. Sci. 379, 283–287. doi: 10.1126/science.ade1771
Li, Y., Xia, G., Wu, Q., Chen, W., Lin, W., Zhang, Z., et al. (2022). Zeolite increases grain yield and potassium balance in paddy fields. Geoderma. 405, 115397. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2021.115397
Liu, P., Zhang, A., Liu, Y., Liu, Z., Liu, X., Yang, L., et al. (2022). Adsorption mechanism of high-concentration ammonium by Chinese natural zeolite with experimental optimization and theoretical computation. Water. 14, 2413. doi: 10.3390/w14152413
Louhar, G. (2020). Zeolites: A potential source of soil amendments to improve soil properties. Chem Sci Rev Lett 9 (35), 777–785. doi: 10.37273/chesci.CS205108196
Méndez Argüello, B., Vera Reyes, I., Cárdenas Flores, A., Santos Villarreal, G., Ibarra Jiménez, L., Lira Saldivar, R. H. (2018). Water holding capacity of substrates containing zeolite and its effect on growth, biomass production and chlorophyll content of Solanum lycopersicum Mill. Nova scientia. 10, 45–60. doi: 10.21640/ns.v10i21.1413
Mondal, M., Biswas, B., Garai, S., Sarkar, S., Banerjee, H., Brahmachari, S., et al (2021). Zeolites enhance soil health, crop productivity and environmental safety. Agronomy. 11, 448. doi: 10.3390/agronomy11030448
Mpanga, I. K., Braun, H., Walworth, J. (2020). Zeolite application in crop production: Importance to soil nutrient, soil water, soil health, and environmental pollution management (Tucson, USA: The University of Arizona Cooperative Extension), 1–4. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/344258480.
Murphy, O. P., Vashishtha, M., Palanisamy, P., Kumar, K. V. (2023). A review on the adsorption isotherms and design calculations for the optimization of adsorbent mass and contact time. ACS omega. 8, 17407–17430. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c08155
Muscarella, S. M., Laudicina, V. A., Cano, B., Badalucco, L., Conte, P. (2023). Recovering ammonium by treated and untreated zeolitic mixtures: a comprehensive experimental and modelling study. Microporous Mesoporous Materials 349, 112434. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2023.112434
Nakhli, S. A. A., Delkash, M., Bakhshayesh, B. E., Kazemian, H. (2017). Application of zeolites for sustainable agriculture: a review on water and nutrient retention. Water Air Soil Pollution. 228, 1–34. doi: 10.1007/s11270-017-3649-1
Narayanan, S., Tamizhdurai, P., Mangesh, V. L., Ragupathi, C., Ramesh, A. (2021). Recent advances in the synthesis and applications of mordenite zeolite–review. RSC advances. 11, 250–267. doi: 10.1039/d0ra09434j
Nguyen, M. L., Tanner, C. C. (1998). Ammonium removal from wastewaters using natural New Zealand zeolites. New Z. J. Agric. Res. 41, 427–446. doi: 10.1080/00288233.1998.9513328
Ohale, P. E., Onu, C. E., Ohale, N. J., Oba, S. N. (2020). Adsorptive kinetics, isotherm and thermodynamic analysis of fishpond effluent coagulation using chitin derived coagulant from waste Brachyura shell. Chem. Eng. J. Advances. 4, 100036. doi: 10.1016/j.ceja.2020.100036
Olivoto, T., Dal` Col Lucio, A. (2019). Metan: An R package for multi-environment trial analysis. Methods Ecol. Evol. 11, 783–789. doi: 10.1111/2041-210X.13384
Olsen, S. R., Cole, C. L., Wetanabe, P. S., Dean, L. A. (1954). Estimation of available phosphorus in soils by extraction with sodium bicarbonate (Washington DC: United States Department of Agriculture), 939.
Omar, L., Ahmed, O. H., Majid, N. M. A. (2015). Improving Ammonium and Nitrate release from Urea using Clinoptilolite zeolite and compost produced from agricultural wastes. Sci. World J. 574201, 1–12. doi: 10.1155/2015/574201
Ortega, R., Domene, M. A., Soriano, M., Sánchez-Marañón, M., Asensio, C., Miralles, I. (2020). Improving the fertility of degraded soils from a limestone quarry with organic and inorganic amendments to support vegetation restoration with semiarid Mediterranean plants. Soil Tillage Res. 204, 104718. doi: 10.1016/j.still.2020.104718
Palanivell, P., Ahmed, O. H., Latifah, O., Abdul Majid, N. M. (2019). Adsorption and desorption of nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and soil buffering capacity following application of chicken litter biochar to an acid soil. Appl. Sci. 10, 295. doi: 10.3390/app10010295
Palanivell, P., Ahmed, O. H., Omar, L., Abdul Majid, N. M. (2021). Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium adsorption and desorption improvement and soil buffering capacity using clinoptilolite zeolite. Agronomy. 11, 379. doi: 10.3390/agronomy11020379
Passaglia, E., Sheppard, R. A. (2001). The crystal chemistry of zeolites. Rev. mineralogy geochemistry. 45, 69–116. doi: 10.2138/rmg.2001.45.2
Piper, C. S. (1966). A laboratory manual of methods for the examination of soils and the determination of the inorganic constituents of plants. Soil Plant analysis. Hans Publishers, Bombay.
R Core Team. (2013). R: A language and environment for statistical computings. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. http://www.R-project.org/.
Rahmani, R., Khalesro, S., Heidari, G., Mokhatssi-Bidgoli, A. (2023). Vermicompost and zeolite improve yield, nutrient uptake, essential and fixed oil production, and composition of Nigella sativa L. Front. Sustain. Food Systems. 7. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2023.1214691
Ramesh, K., Reddy, D. D. (2011). Zeolites and their potential uses in agriculture. Adv. agronomy. 113, 219–241. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-386473-4.00004-X
Ravali, C., Rao, K. J., Anjaiah, T., Suresh, K. (2020). Effect of zeolite on soil physical and physico-chemical properties. Multilogic Sci. 10, 776–781. doi: 10.9734/cjast/2020/v39i3831090
Saha, B. K., Rose, M. T., Wong, V. N., Cavagnaro, T. R., Patti, A. F. (2018). Nitrogen dynamics in soil fertilized with slow-release brown coal-urea fertilizers. Sci. Rep. 8, 14577. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-32787-3
Sakizci, M., Kilinc, L. O. (2015). Influence of acid and heavy metal cation exchange treatments on methane adsorption properties of mordenite. Turkish J. Chem. 39, 970–983. doi: 10.3906/kim-1501-71
Saleh, Q. O., Al Bahrani, I. Q. (2023). “Effect of zeolite, poultry manure and mineralFertilizers in availability of NPK in calcareous soil,” in IOP conference series: earth and environmental science, vol. Vol. 1262. (Curran Associates, Inc: IOP Publishing), 082002. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315%2F1262%2F8%2F082002
Sandoval-Molina, M. A., Zavaleta-Mancera, H. A., Morales-Rodríguez, S., Janczur, M. K. (2017). Fixation and dehydratation protocol for Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), for the observation of morphology of secretory spiness 1–2. doi: 10.17504/protocols.io.k3vcyn6
Sarioglu, M. E. L. T. E. M. (2005). Removal of ammonium from municipal wastewater using natural Turkish (Dogantepe) zeolite. Separation purification Technol. 41, 1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2004.03.008
Sepaskhah, A. R., Yousefi, F. (2007). Effects of zeolite application on nitrate and ammonium retention of a loamy soil under saturated conditions. Soil Res. 45, 368–373. doi: 10.1071/SR06069
Shin, S., Jho, E. H., Park, H., Lee, S., Kim, J. H. (2021). Potassium recovery from potassium solution and seawater using different adsorbents. Appl. Sci. 11, 8660. doi: 10.3390/app11188660
Shinzato, M. C., Wu, L. F., Mariano, T. O., Freitas, J. G., Martins, T. S. (2020). Mineral sorbents for ammonium recycling from industry to agriculture. Environ. Sci. pollut. Res. 27, 13599–13616. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-07873-7
Stamatakis, M. G., Stamataki, I. S., Giannatou, S., Vasilatos, C., Drakou, F., Mitsis, I., et al. (2017). Characterization and evaluation of chabazite-and mordenite-rich tuffs, and their mixtures as soil amendments and slow-release fertilizers. Arch. Agron. Soil Science. 63, 735–747. doi: 10.1080/03650340.2016.1235268
Subbaiah, B. V., Asija, G. L. (1956). A rapid procedure for the estimation Available N in the soils. Curr. Science. 25, 259.
Sun, Y., Xia, G., He, Z., Wu, Q., Zheng, J., Li, Y., et al. (2019). Zeolite amendment coupled with alternate wetting and drying to reduce nitrogen loss and enhance rice production. Field Crops Res. 235, 95–103. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2019.03.004
Triatmoko, V., Alvernia, P., Haniati, I. L., Minardi, S., Suntoro, W., Ariyanto, D. P. (2019). “Zeolite and manure treatment on the increase of N soil, N absorption and soybean production in alfisols,” in IOP conference series: materials science and engineering, vol. Vol. 633. (Central java, Indonesia: IOP Publishing), 012026. doi: 10.1088/1757-899X/633/1/012026
Vilcek, J., Torma, S., Adamisin, P., Hronec, O. (2013). Nitrogen sorption and its release in the soil after zeolite application. Bulg. J. Agric. Sci. 9, 228–234.
Wang, Y., Chen, J., Sun, Y., Jiao, Y., Yang, Y., Yuan, X., et al. (2023). Zeolite reduces N leaching and runoff loss while increasing rice yields under alternate wetting and drying irrigation regime. Agric. Water Management. 277, 108130. doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2022.108130
Wijesinghe, D. T. N., Dassanayake, K. B., Sommer, S. G., Jayasinghe, G. Y., J. Scales, P., Chen, D. (2016). Ammonium removal from high-strength aqueous solutions by Australian zeolite. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A. 51, 614–625. doi: 10.1080/10934529.2016.1159861
Wu, Q., Wang, Y., Chen, T., Zheng, J., Sun, Y., Chi, D. (2020). Soil nitrogen regulation using clinoptilolite for grain filling and grain quality improvements in rice. Soil Tillage Res. 199, 104547. doi: 10.1016/j.still.2019.104547
Wulandari, R., Hanum, H., Hasanah, Y. (2019). “The effect of nitrogen fertilizer, zeolite and fresh straw to increase total-N, cation exchange capacity (CEC) of rice crop,” in IOP conference series: earth and environmental science, vol. Vol. 260. (Medan, Indonesia: IOP Publishing), 012157. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/260/1/012157
Xia, G., Liu, G., Sha, Y., Zhao, Q., Zhang, F., Chen, T. (2019). ). Impact of zeolite on dynamic of soil available potassium and grain yield in alternate wetting and drying rice system. Nongye Gongcheng Xuebao. 35, 101–109. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2019.18.013
Xiubin, H. E., Zhanbin, H. (2001). Zeolite application for enhancing water infiltration and retention in loess soil. Resources Conserv. recycling. 34, 45–52. doi: 10.1016/S0921-3449(01)00094-5
Xue, R., Donovan, A., Zhang, H., Ma, Y., Adams, C., Yang, J., et al. (2018). Simultaneous removal of ammonia and N-nitrosamine precursors from high ammonia water by zeolite and powdered activated carbon. J. Environ. Sci. 64, 82–91. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2017.02.010
Zhao, Q., Chen, T., Wang, S., Sha, Y., Zhang, F., Sun, Y., et al. (2023). Effects of five-year field aged zeolite on grain yield and reactive gaseous N losses in alternate wetting and drying paddy system. Sci. Total Environment. 904, 166279. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.166279
Zheng, J., Chen, T., Xia, G., Chen, W., Liu, G., Chi, D. (2018). Effects of zeolite application on grain yield, water use and nitrogen uptake of rice under alternate wetting and drying irrigation. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Engineering. 11, 157–164. doi: 10.25165/j.ijabe.20181101.3064
Zhou, L., Boyd, C. E. (2014). Total ammonia nitrogen removal from aqueous solutions by the natural zeolite, mordenite: A laboratory test and experimental study. Aquaculture 432, 252–257.
Keywords: Alfisols, crop production, food security, mordenite zeolite, NUE, WUE
Citation: V G, K SR, Ch S, B M K R, Balakrishnan D, Kundu S, Pushpanjali, Rohit J and V K S (2025) Role of mordenite zeolite in improving nutrient and water use efficiency in Alfisols. Front. Plant Sci. 15:1404077. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1404077
Received: 20 March 2024; Accepted: 30 September 2024;
Published: 30 January 2025.
Edited by:
Asif Naeem, Nuclear Institute for Agriculture and Biology, PakistanReviewed by:
Hanxi Wang, Harbin Normal University, ChinaCopyright © 2025 V, K, Ch, B M K, Balakrishnan, Kundu, Pushpanjali, Rohit and V K. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Girijaveni V, girijgirij3@gmail.com
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.