- 1School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Xianyang Normal University, Xianyang, China
- 2State Key Laboratory of Cotton Biology, Institute of Cotton Research, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Anyang, China
- 3College of Life Sciences, Shaanxi Normal University, Xi’an, China
Hexokinase (HXK) is involved in hexose phosphorylation, sugar sensing, and signal transduction, all of which regulate plant growth and adaptation to stresses. Gossypium hirsutum L. is one of the most important fiber crops in the world, however, little is known about the HXKs gene family in G. hirsutum L. We identified 17 GhHXKs from the allotetraploid G. hirsutum L. genome (AADD). G. raimondii (DD) and G. arboreum (AA) are the diploid progenitors of G. hirsutum L. and contributed equally to the At_genome and Dt_genome GhHXKs genes. The chromosomal locations and exon-intron structures of GhHXK genes among cotton species are conservative. Phylogenetic analysis grouped the HXK proteins into four and three groups based on whether they were monocotyledons and dicotyledons, respectively. Duplication event analysis demonstrated that HXKs in G. hirsutum L. primarily originated from segmental duplication, which prior to diploid hybridization. Experiments of qRT-PCR, transcriptome and promoter cis-elements demonstrated that GhHXKs’ promoters have auxin and GA responsive elements that are highly expressed in the fiber initiation and elongation stages, while the promoters contain ABA-, MeJA-, and SA-responsive elements that are highly expressed during the synthesis of the secondary cell wall. We performed a comprehensive analysis of the GhHXK gene family is a vital fiber crop, which lays the foundation for future studies assessing its role in fiber development.
Introduction
Carbohydrates produced by photosynthesis are eventually stored as sugar. Sugar has an important influence on various stages of the plant life cycle, and can be converted to fructose and glucose in the reservoir tissue (Desnoues et al., 2014). Fructose and glucose are essential six-carbon sugars in plants, which are also known as hexose. Hexose can be phosphorylated by the enzyme of hexokinases (HXKs) (Jang et al., 1997; Halford et al., 1999). Phosphorylated hexose has diverse functions, including the following: phosphorylated hexose is in an activated form that readily participates in metabolic reactions; phosphorylated glucose molecules have a robust polar group and can effectively prevent intracellular hexose extravasation; phosphorylated glucose can store the phosphate group, which could be converted to the terminal high-energy phosphate group of adenosine diphosphate (ADP) (Etienne et al., 2002; Desnoues et al., 2014). Therefore, typical HXKs contain glucose binding domain and adenosine phosphate binding domain (Karve et al., 2008). HXKs play diverse roles in regulating plant growth and function as sugar sensors, regulate sugar signal transduction, and cooperate with phytohormones.
Recent studies have demonstrated that hexokinase is involved in sugar sensing and signal transduction in plants, while AtHXK1 functions as a glucose sensor. The plants of 35S:sense-AtHXK1 is hypersensitive to glucose with small cotyledons, hypocotyls, and roots; 35S-antisense-AtHXK1 transgene plants are hypersensitive to glucose and are typically grown with green, expanded cotyledons and root elongation under glucose treatment (Jang et al., 1997). The mutant ScHXK1 showed that hexokinase had a glucose-sensing function, independent of its enzymic activity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Mayordomo and Sanz, 2001).
Sugar functions as a potential signaling molecules throughout a plant’s life cycle (Hanson and Smeekens, 2009), which is independent of its enzymatic role in converting glucose to glucose 6-phosphate (Smeekens et al., 2010). AtHXK1 is involved in programmed cell death in Arabidopsis, which is mediated by myo-inositol accumulation (Bruggeman et al., 2015). Sugar induced during cell death depends on the rate of AtHXKs-induced sugar phosphorylation; while in yeast, the affinity of AtHXK is higher for glucose than for fructose (Granot and Dai, 1997).
Sugars are a signal in regulating plant growth and cooperate with phytohormones (Smeekens, 2000). The autophagy regulating AtHXK1-dependent glucose signaling-mediated root meristem activity functions by modulating the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in Arabidopsis (Huang et al., 2019). ABA application can improve the expression of sucrose synthases (SuSys) and cell wall invertase (CWINV), and block the glucose-induced repression of two genes, which are insensitive to glucose treatment in CsHXK1 or CsHXK2 mutants (Wang et al., 2017).
In tomato plants, the SlHXK1 mutant showed enhanced leaf senescence and repressed plant growth by affecting starch turnover (Li et al., 2020). OsHXK1-CRISPR/Cas9 plants showed increased plant light tolerance, photosynthetic products, and rice yields along with a significantly increased expression of photosynthesis-related genes (Zheng et al., 2021). The exogenous application of glucose to Arabidopsis can promote true leaf expansion in an AtHXK1-dependent manner; however, the increased expression of AtHXK1 inhibited leaf expansion (Xiao et al., 2000). The upregulation of OsHXK1 increased glucose and ROS levels and promoted programmed cell death (PCD) and leaf senescence (Zheng et al., 2021). HXKs are involved in the steady-state recycling of ADP, while ADP content also regulates H2O2 formation on the mitochondrial inner membrane (Valluru and Van den Ende, 2011).
As sequencing technology develops, the economic value of cotton fibers increases and the genomes of Gossypium hirsutum L. (AADD, 2n = 4X = 52) (Paterson et al., 2012; Li et al., 2015; Hu et al., 2019; Wang et al., 2019), G. anomalum (BB, 2n = 2X = 26) (Grover et al., 2021a), G. stocksii (EE, 2n = 2X = 26) (Grover et al., 2021b), G. longicalyx (FF, 2n = 2X = 26) (Grover et al., 2020), and G. rotundifolium (KK, 2n = 2X = 26) (Wang et al., 2021), etc. have all been sequenced.
Gossypium hirsutum L. is the most widely spread cotton species; it accounts for 90% of all cotton species produced in the world (Li et al., 2015). G. hirsutum L. fibers are highly specialized epidermal hair cells formed on the surface of a seed. They have a single cell structure formed by the protuberance, differentiation and elongation of epidermal cells inside and outside the ovary of the ovule. Cotton fiber differentiation and development can be divided into four stages: the fiber initiation stage, which occurs 3 days before flowering to 3 days post-anthesis (−3 to 3 DPA); the rapid elongation stage, which occurs in the fiber cells from 5 to 25 DPA (Qin and Zhu, 2011); the thickening stage of the cell wall (20–45 DPA); and the fiber dehydration and maturation stage (45–50 days) (Wu et al., 2017).
Studies assessing the development of cotton fibers have demonstrated that hexokinase is involved in glucose-mediated fiber elongation, that low glucose levels promoted cotton fiber elongation, and that treatment with hexokinase inhibitor N-acetyl-glucosamine (NAG) inhibited fiber elongation (Li et al., 2021). Considering the essential functions of GhHXKs in sugar conversion and signal transduction during fiber elongation process in cotton, we performed a genome-wide analysis of GhHXKs and characterized the structure and expression patterns of GhHXKs.
Materials and Methods
Plant Growth and Treatment
A G. hirsutum cultivar, Xuzhou 142, was planted in the greenhouse with a 16 h light, 30°C/8 h dark, 30°C cycle, as previously reported (He et al., 2017). For phytohormone treatment, 0 DPA fresh ovules were collected from cotton bolls, sterilized, and cultured in previously reported liquid culture medium (Shi et al., 2006), which added with 5 μM 1-Naphthylacetic acid (NAA, Sigma) and 1 μM gibberellin acid (GA3, Sigma) for the indicated time (He et al., 2019), respectively. After treatment, the ovules were collected for quantitative real-time (qRT-PCR) experiments. For RNA extraction, fresh cotton seed fibers were harvested from 0, 5, 10, 15, 20, and 25 DPA, and then immediately frozen in liquid nitrogen.
Molecular Databases
The genome sequences of G. hirsutum L. genome (NDM8), G. raimondii (JGI_v2.1), G. arboreum (CRI_v3.0), G. anomalum (NSF_v1), G. stocksii (NSF_v1), G. longicalyx (NSF_v1), and G. rotundifolium (HAU v1) were downloaded from CottonGen1 (Ma et al., 2021). The genome sequence of Arabidopsis thaliana was downloaded from The Arabidopsis Information Resource (TAIR2) database (Lamesch et al., 2012). The HXK sequences from O. sativa (Cho et al., 2006), Phyllostachys edulis (Moso Bamboo) (Zheng et al., 2020), and Manihot esculenta (Cassava) (Geng et al., 2017) were downloaded from the Nucleotide database.3 The genome sequence (Chalhoub et al., 2014) of Brassica napus was downloaded from the Brassicaceae Database (BRAD4). The genome size, sequences and taxonomy ID of Ostreococcus lucimarinus, Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, Volvox carteri, Coccomyxa subellipsoidea, Chlorella variabilis, and Selaginella moellendorffii were downloaded from the Genome database of NCBI.5
Identification of Hexokinase Members
Two HXK Pfam domains (PF03727 and PF00349) were used to search against the G. hirsutum L., G. raimondii, G. arboreum, G. anomalum, G. stocksii, G. longicalyx, and G. rotundifolium genomes using the hidden Markov model (HMM) with HMMER 3.0 (Prakash et al., 2017). The candidate GhHXKs, GaHXKs, GrHXKs, GanHXKs, GstHXKs, GloHXKs, and GroHXKs were submitted to the SMART software (Letunic et al., 2021)6 and the Conserved Domain Database (Lu et al., 2020) (CDD7) to confirm that all candidate HXK proteins contained the Hexokinase domain.
We used the general feature format (GFF) file of the genomes to determine the relative position of HXKs on chromosomes, and visualized the locations with the online software MG2C (Jiangtao et al., 2015). Furthermore, the gene structures of HXKs were also analyzed according to the GFF files, and the “exon-intron” structure was shown by the Gene Structure Display Server (Hu et al., 2015) (GSDS 2.08).
Sequence Analysis
Protein motif analysis was performed using MEME9 with a maximum of eight motifs and using other default parameters.
The physicochemical properties, including molecular weight (MW), isoelectric point (pI), instability index, and grand average of hydropathicity (GRAVY), were analyzed using the online software ExPASy ProtParam tool (Artimo et al., 2012)10 in GhHXKs, GaHXKs, GrHXKs, GanHXKs, GstHXKs, GloHXKs, and GroHXKs, respectively.
The subcellular localization of the candidate HXKs were predicted by the online software, WoLF PSORT (Horton et al., 2007).11
Phylogenetic Tree Construction
The HXK protein sequences of G. hirsutum L., G. raimondii, G. arboreum, A. thaliana, O. sativa, P. edulis, M. esculenta, and B. napus were aligned using ClustalW, and the evolutionary tree was constructed using the neighbor-joining method with MEAG 7.0 (Kumar et al., 2016). To evaluate the reliability of the phylogenetic tree, the bootstrap value was set as 1,000.
Evolutionary Analysis
The duplication types of GhHXKs, GaHXKs, and GrHXKs were analyzed using the Multiple Collinearity Scan (MCScanX) toolkit under the Linux system (Yupeng et al., 2012). The orthologous- and homologous-gene pairs were visualized by the CIRCOS software (Krzywinski et al., 2009). The synonymous substitution rate (Ks), non-synonymous substitution rate (Ka), and Ka/Ks ratios were calculated using the KaKs_Calculator software (Wang et al., 2010). The divergence time between the homologous- and orthologous–gene pairs was calculated according to previously used methods (Yang et al., 2006).
Cis-Acting Element Analysis of Promoter
The sequence 2,000 bp upstream of the initiation codon was extracted as the candidate promoters with the “fastacmd –d database –s chromosome –L start location, end location –o result” using the local BLAST software (Camacho et al., 2009). The Cis-elements in the candidate promoter sequence were analyzed by Plant Cis-acting Regulatory Element (Plant CARE12) (Lescot et al., 2002).
Spatial and Temporal Expression Analysis of GhHXK Genes
The allotetraploid cotton cultivar, Xuzhou 142, was grown in Shaanxi Normal University under controlled conditions (He et al., 2017). A total of 30 ovules were used for each phytohormone and were performed in triplicate. Cotton ovules were collected at one DPA, sterilized with sodium hypochlorite (NaClO, 10%), and cultivated as previously reported (Shi et al., 2006). Five μM 1-Naphthylacetic acid (NAA, Sigma, Germany) and 1 μM GA3 (Sigma, Germany) were added to the culture medium. The ovules treated with phytohormones were used to perform RNA-seq, while the data was conserved in our lab (He et al., 2019).
To illustrate the spatial and temporal expression patterns of GhHXKs, the transcriptomes of various tissues (stamen, anther, seed, fiber, ovule, petal, calycle, torus, leaf, stem, root, cotyledon, stigma, and pistil) and a successive fiber developmental stages (0, 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, and 35 DPA) were downloaded from NCBI (accession NO. PRJNA680449) (Ma et al., 2021). The expression data were normalized and visualized using Omicshare tools.13
RNA Extraction and qRT-PCR Analysis
The total RNA extraction was performed according the instructions for the RNAprep Pure Plant Plus Kit (Code No. DP441, TIANGEN, China), and the cDNA was reverse-transcribed from 2 μg total RNA (Xiao et al., 2016). The qRT-PCR was conducted with three biological and three technical replicates as the following reaction parameters: 95°C for 30 s, followed by 40 cycles of 95°C for 5 s, 60°C for 15s, and 72°C for 20 s. A melting curve was generated from 65 to 95°C. The ubiquitin gene GhUBQ7 (GenBank accession no. AY189972) was used as the internal control for each qPCR experiment. Primers for qRT-PCR experiments were listed in Supplementary Table 1.
Results
Identification and Characterization of hexokinase Genes From Cotton Species
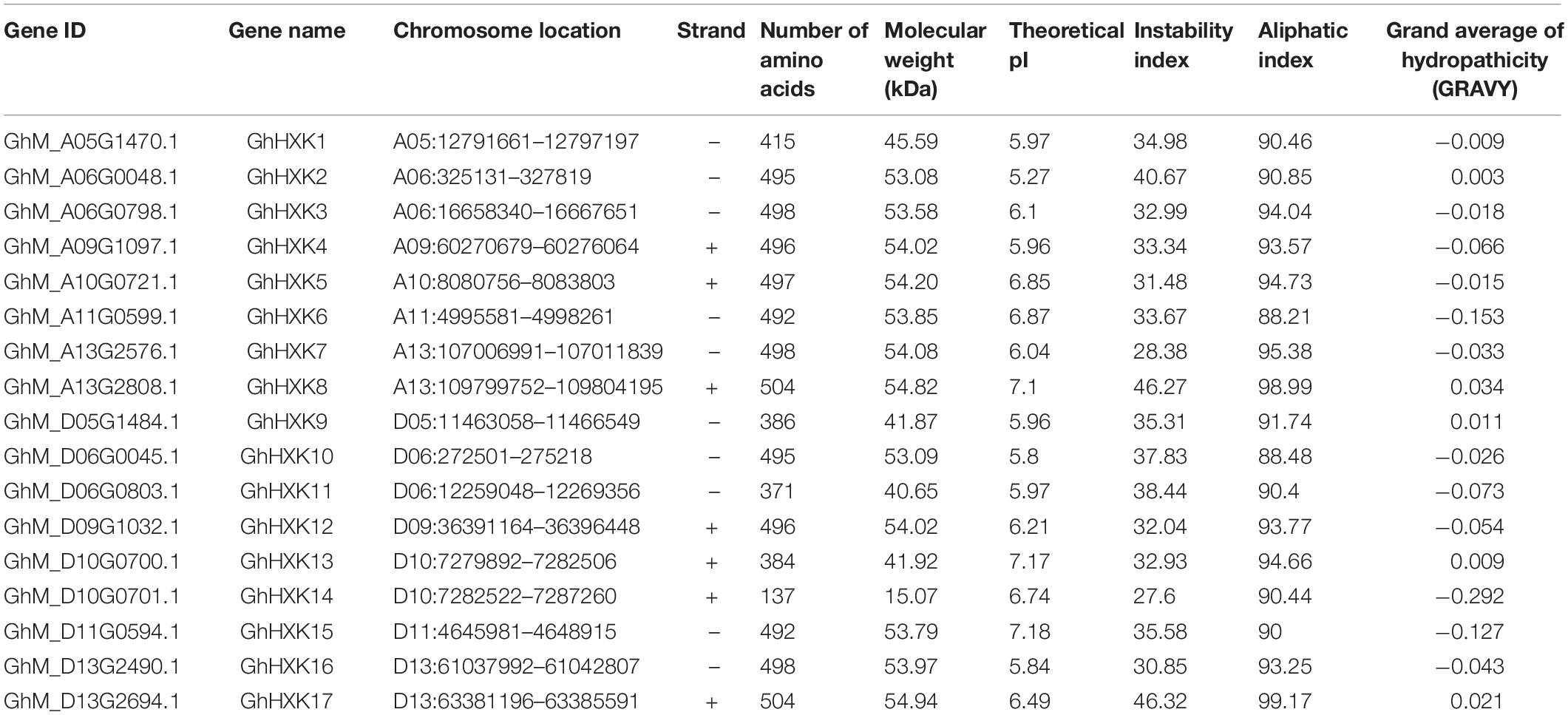
To identify HXK genes in cotton species, two hexokinase domains (PF03727 and PF00349) were used as the query domains with the HMMER 3.0 software (on a Windows system) to search against the genomes of G. hirsutum L. (NDM8), G. arboreum (CRI_v3.0), G. raimondii (JGI_v2.1), G. anomalum (NSF_v1), G. stocksii (NSF_v1), G. longicalyx (NSF_v1), and G. rotundifolium (HAU_v1). There were 17 GhHXKs, 9 GaHXKs, 8 GrHXKs, 8 GanHXKs, 8 GstHXKs, 7 GloHXKs, and 8 GroHXKs retrieved from G. hirsutum L., G. arboreum, G. raimondii, G. anomalum, G. stocksii, G. longicalyx, and G. rotundifolium, respectively (Table 1 and Supplementary Table 2).
The amino acids ranged from 137 (GhHXK14) to 504 (GhHXK8 and GhHXK17). The molecular weight of GhHXKs ranged from 15.07 kDa (GhHXK14) to 54.94 kDa (GhHXK17). According to isoelectric point (pI) analysis, 14 GhHXKs had pI less than 7.0 (with an average of 6.15) and were acidic proteins. In contrast, three GhHXKs were predicted to encode proteins more than 7.0 (average of 7.15) and were basic. Grand average of hydropathicity (GRAVY) analysis found that 12 GhHXKs with GRAVY scores less than zero were hydrophilic proteins; and that five GhHXKs with GRAVY scores more than zero were hydrophobic proteins. Based on the instability index analysis, 14 GhHXK proteins have instability index values less than 40.0 and three GhHXK proteins have instability index values greater than 40.0 (GhHXK2, GhHXK8, and GhHXK17). The detailed physicochemical properties of GaHXKs, GrHXKs, GanHXKs, GstHXKs, GloHXKs, and GroHXKs are listed in Supplementary Table 2.
Chromosomal Location Analysis of HXKs in Cotton Species
According to the GFF files of G. hirsutum L. (NDM8), the 17 GhHXKs are distributed on 12 G. hirsutum L. chromosomes. The 17 GhHXKs genes were named GhHXK1 to GhHXK17 from chromosomes At01 to Dt13 based on their relative chromosomal locations from the chromosome top to bottom (Figures 1, 2). There are eight GhHXKs distributed on six At_subgenomes (At05, At06, At09, At10, At11, and At13) and nine GhHXKs distributed on six Dt_subgenomes (Dt05, Dt06, Dt09, Dt10, Dt11, and Dt13). The GhHXK genes are evenly distributed on At_ and Dt_subgenomes, except for GhHXK14. Nine GaHXKs are distributed on seven G. arboreum genomes. The distribution of GaHXK genes across chromosomes was similar to that of GhHXKs on At_subgenome in G. hirsutum L., while there was an extra on Ga_Chr02 of G. arboreum. Eight GrHXKs were distributed on six chromosomes, which was similar to the distribution of GhHXKs on the Dt_subgenome in G. hirsutum L. At the same time, there is one more gene distributed on the chromosome Gr_Chr07 and one lost gene on the chromosome Gr_Chr05 in G. raimondii (Supplementary Figure 1). This indicated that their gene loss or duplicated evince existed in the G. hirsutum L. genome.
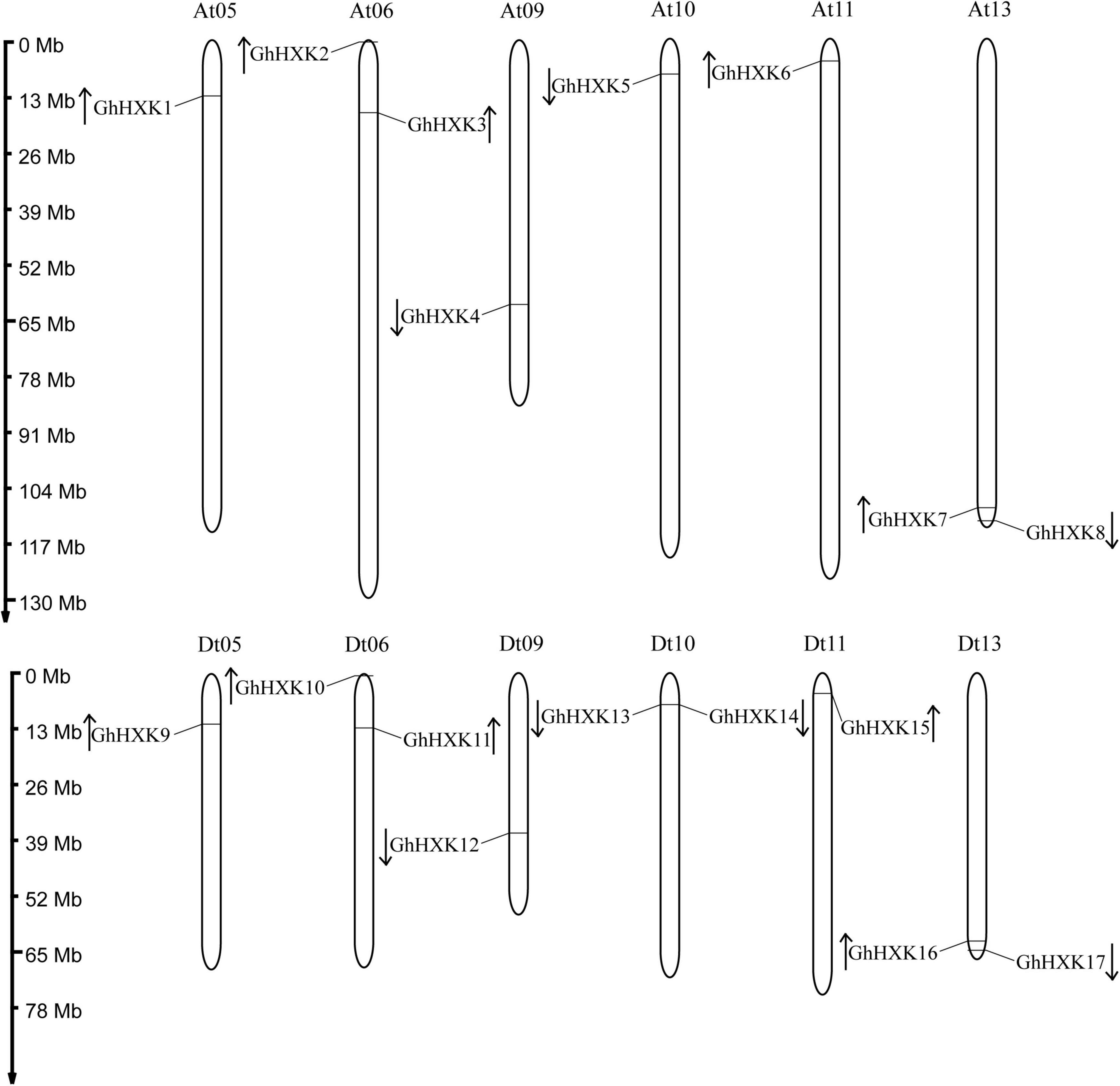
Figure 1. Chromosomal distribution of GhHXKs. The chromosome number is shown above each chromosome. The chromosomal location of each GhHXKs is shown from the top to the bottom of the corresponding chromosome. The scale bars beside the chromosome indicate the length of megabases (Mb). The arrows show the transcription directions of GhHXK genes.
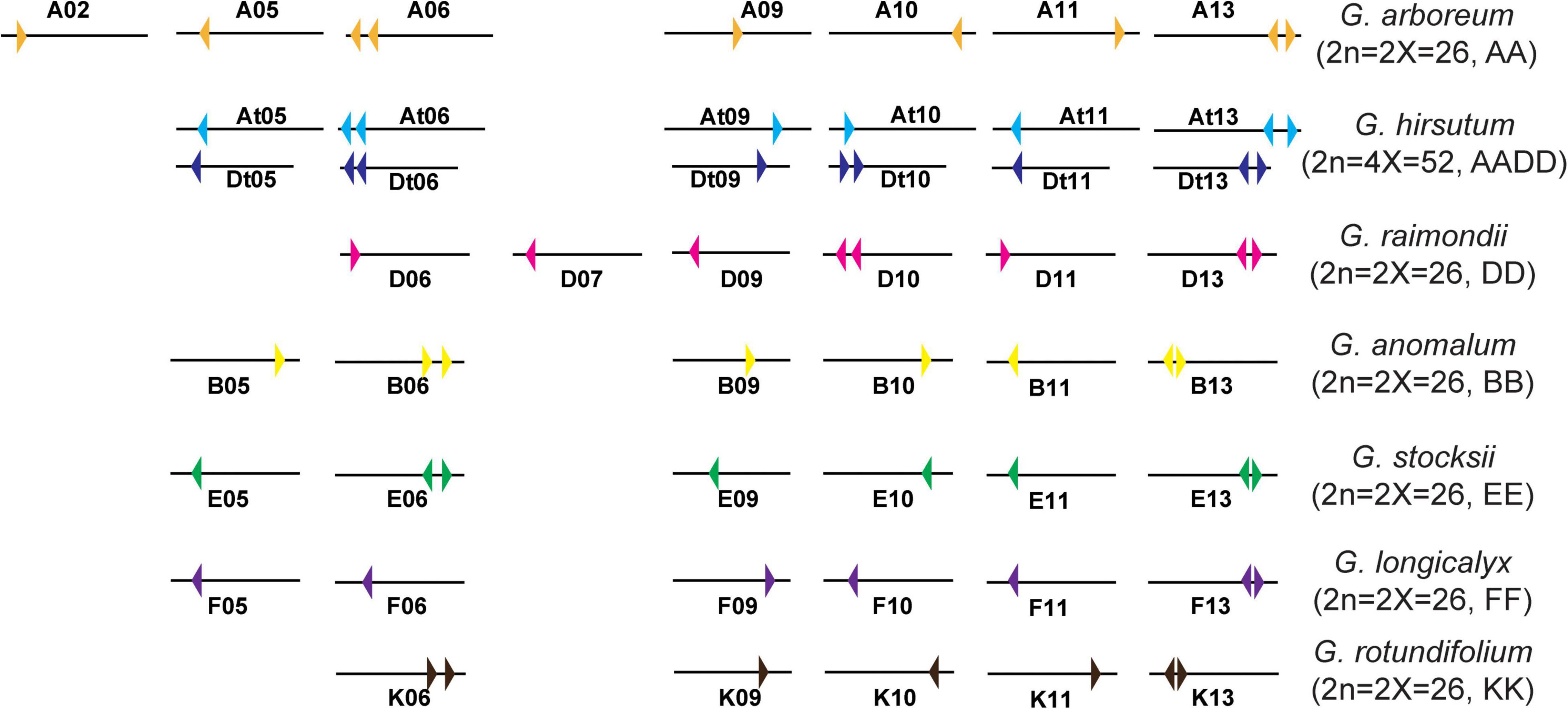
Figure 2. Chromosome distribution diagram of HXK genes in G. hirsutum L., G. arboreum, and G. raimondii. Colorful triangles represent the HXK genes and their transcription direction.
Furthermore, combined with GFF annotation files for other cotton species, the eight GanHXKs were distributed on six G. anomalum (2n = 2X = 26, BB) chromosomes, including B05, B06, B09, B10, B11, and B13, while there were eight GstHXKs distributed on six G. stocksii (2n = 2X = 26, EE) chromosomes, including E05, E06, E09, E10, E11, and E13. The seven GloHXKs were distributed on the identical chromosomes of G. longicalyx (2n = 2X = 26, FF) and were also distributed across the identical chromosomes of G. rotundifolium (2n = 2X = 26, KK), except for K05 (Figure 2). The distribution analysis demonstrated that the HXKs were conservatively distributed on the 5th, 6th, 9th, 10th, 11th, and 13th chromosomes among cotton species. According to the detailed distribution and transcription direction of HXKs between cotton species (Figure 2 and Supplementary Figures 1, 2), inversion and segmental duplication existed in the chromosomes of these cotton species’.
Gene Phylogenetic and Structure of GhHXKs
In general, nucleic acid sequences are more variable than protein sequences. To well illustrate the evolutionary relationships among GhHXKs, a CDS phylogenetic tree was constructed by MEGA 7.0 (Figure 3A). According to the phylogenetic tree in Figure 3A, the GhHXK genes could be clustered into three groups.
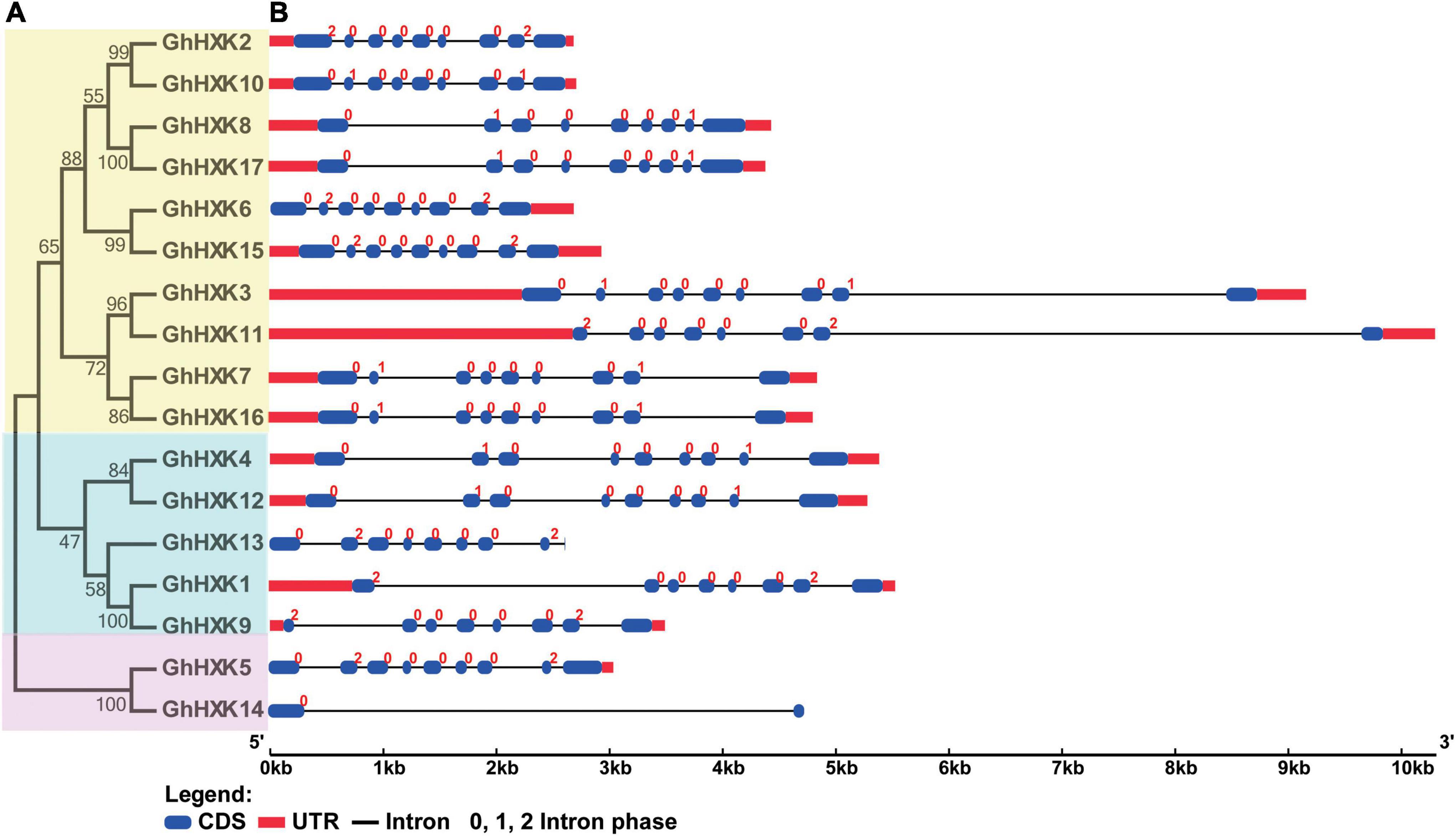
Figure 3. The phylogenetic tree (A) and gene structure (B) of GhHXKs. The phylogenetic tree was constructed with the CDS sequences of GhHXKs by MEGA 7.0 software with default parameters. The exons, UTR, and introns are indicated by blue ovals, red rectangles, and black lines, respectively.
The gene structures of GhHXKs were determined by assessing the annotation information of the GFF files in the G. hirsutum L. genome (NDM8), which were visualized using the GSDS 2.0 online software. The results demonstrated that most GhHXKs contained nine exons and eight introns, and four GhHXKs contained eight exons and seven introns, including GhHXK1, GhHXK9, GhHXK11, and GhHXK13. GhHXK14 contained two exons and one intron. The 13 GhHXKs genes include both 5′- and 3′-UTRs, two GhHXKs contain 3′-UTR, while the remaining two genes (GhHXK13 and GhHXK14) have no UTR region (Figure 3B). Studies assessing the gene structure of other cotton species (Supplementary Figure 3B) demonstrated that most HXKs in cotton species are conservative and have “intron-exon” structures.
Phylogenetic Analysis of GhHXK Proteins
To illustrate the phylogenetic relationships between the HXKs proteins in G. hirsutum L. and those of other species, including G. arboreum, G. raimondii, O. sativa, A. thaliana, P. edulis, M. esculenta, and B. napus, an unrooted neighbor-joining tree was created using the MEGA 7.0 software based on their entire length of the amino acid sequences.
According to the phylogenetic tree of HXKs from multiple species (Figure 4 and Supplementary Figure 4), the HXKs protein sequences were divided into four groups (Clade I, II, III, and IV). Two GhHXKs were classed into Clade I, four GhHXKs was classed into Clade II, 11 GhHXKs were grouped in Clade IV. However, no GhHXK were grouped in Clade III; only HXKs from monocotyledons O. Sativa and P. edulis were grouped into Clade III.
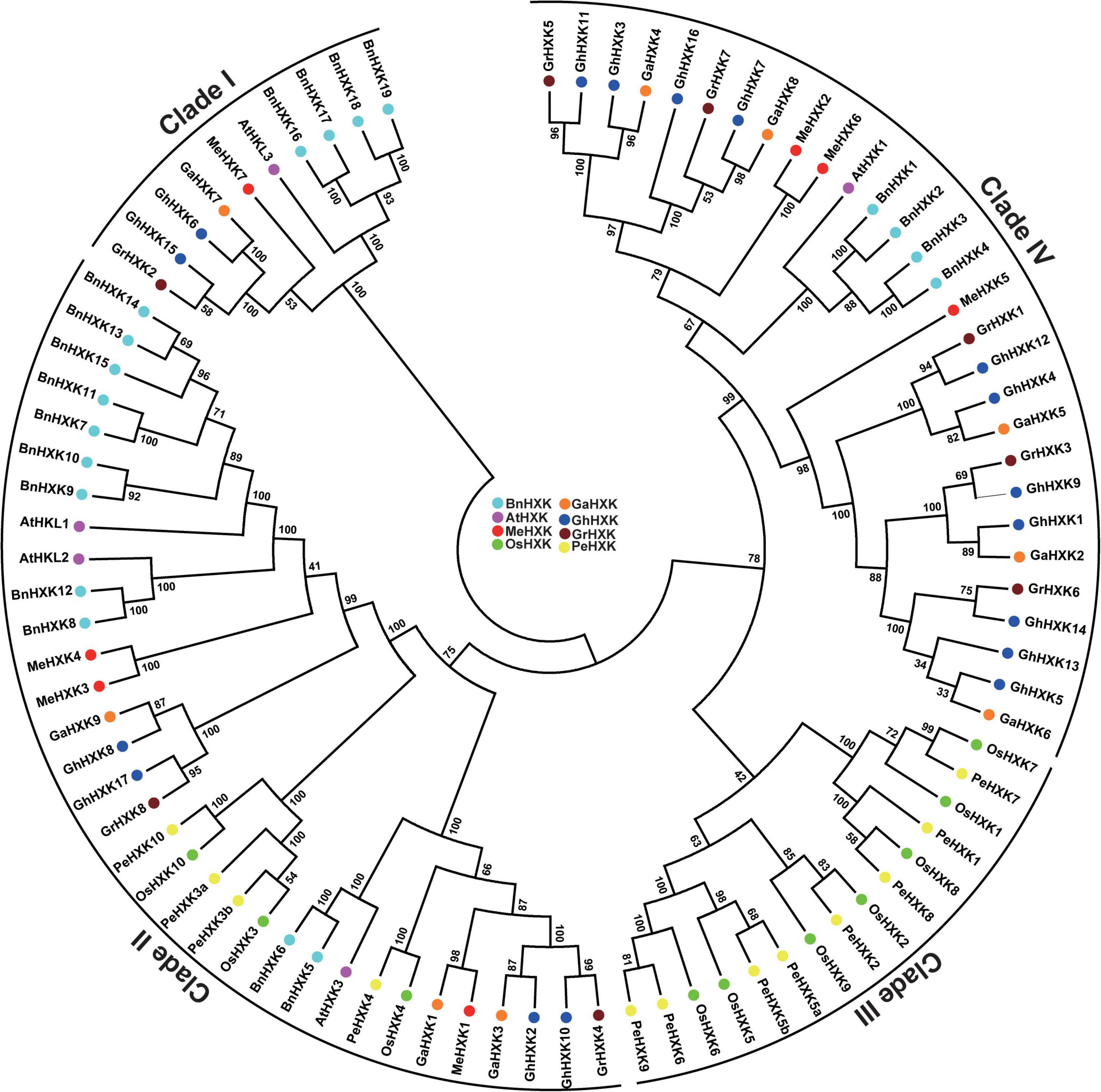
Figure 4. Phylogenetic analysis of GhHXK proteins in G. hirsutum L. An unrooted phylogenetic tree was constructed using HXK protein sequences from A. thaliana (AtHXK), O. sativa (OsHXK), P. edulis (PeHXK), M. esculenta (MeHXK), B. napus (BnHXK), G. hirsutum L. (GhHXK), G. raimondii (GrHXK), and G. arboreum (GaHXK), and are displayed in purple, green, yellow, red, light blue, dark blue, dark red, and orange, respectively.
Protein Features of GhHXKs
The protein sequence of GhHXKs was aligned using ClustalW software to characterize the protein structures. The amino acid sequence alignment showed 39–99% identity between GhHXKs members (Supplementary Figure 4), based on previous work analyzing HXK proteins in A. thaliana, O. sativa, P. edulis, M. esculenta, and B. napus (Cho et al., 2006; Geng et al., 2017; Zheng et al., 2020). The adenosine phosphate binding domain (Supplementary Table 3) and glucose-binding domain were found in most GhHXKs (Supplementary Figure 4 and Supplementary Table 4). The core glucose-binding domain of GhHXKs was conservative as “I/L-GFT-F/V-S-F/S-P/G-V/D” (Figure 5A). There is no glucose-binding domain in GhHXK14 (Supplementary Figure 4), while an intact adenosine phosphate binding domain exists in GhHXK14 (Figure 5B). The adenosine phosphate binding domain has a conserved motif of “RX2R-V/L-X3GX3-I/L/V” in GhHXKs, except for GhHXK9, GhHXK11, and GhHXK13 (Figure 5B). Sequences alignment showed that most of the GhHXKs are conservative with adenosine phosphate and glucose-binding domain.
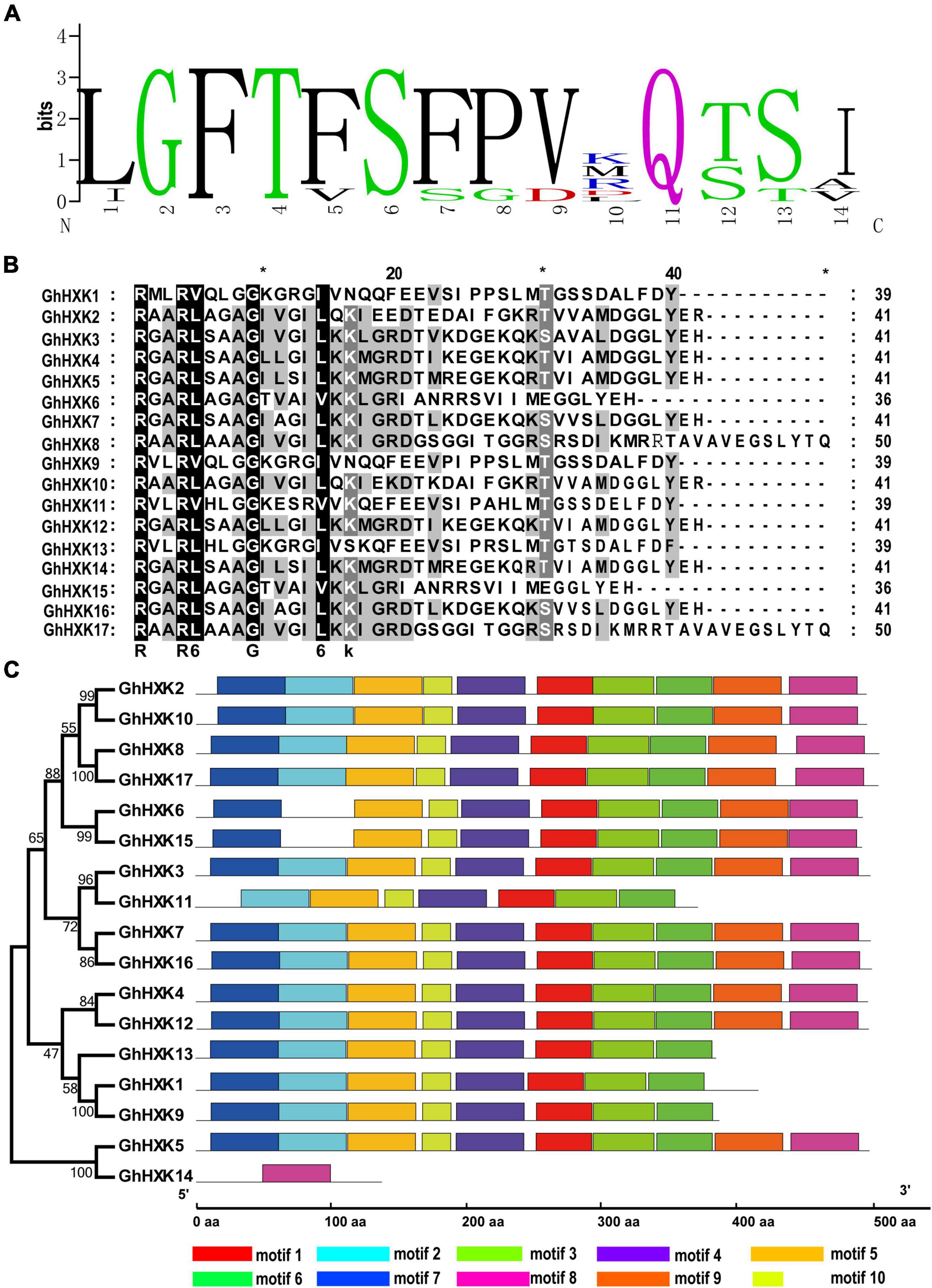
Figure 5. Protein features of HXKs in G. hirsutum L. (A) The weblogo of GhHXK protein glucose-binding sites. (B) The conserved adenosine binding sites of GhHXKs. (C) The motifs of HXK sequences from G. hirsutum L.
Furthermore, the GhHXK protein motif characteristics were analyzed using the MEME online software, and ten conservative motifs were identified in the GhHXK gene family (Figure 5C). The majority of GhHXK proteins contain at least eight motifs, except for GhHXK11 and GhHXK14, which have seven and one motifs, respectively.
Duplication Analysis of GhHXKs
By searching the HXK domain against the genomes from chlorophyta to lycophytes plant species (Supplementary Figure 5), we found that HXK gene family members increased from low to high plant species. The chlorophyta species have less than two HXKs; however, lycophytes plants have more HXKs numbers than five.
Therefore, to illustrate the duplication events of the HXKs gene on chromosome segments, the evolution of GhHXK genes was analyzed in G. hirsutum L., G. arboreum and G. raimondii, respectively, using MCScanX software. The results demonstrated that 16 GhHXK genes were derived from segmental duplication (accounting for 94.12%) of GhHXK gene family members, while only GhHXK14 was derived from dispersed distribution on the chromosomes. Five GaHXKs were derived from segmental duplication, accounting for 55.56% of the total gene family members. Three GaHXKs were derived from dispersed distribution (accounting for 33.33%), and one GaHXK was a singleton gene. There are four GrHXKs derived from segmental duplication (accounting for 50%), three GrHXKs derived from tandem duplication events, and only one derived from dispersed distribution (Figure 6 and Supplementary Table 5). Duplication analysis demonstrated that segmental duplication is the leading cause of HXK genes duplication in cotton species.
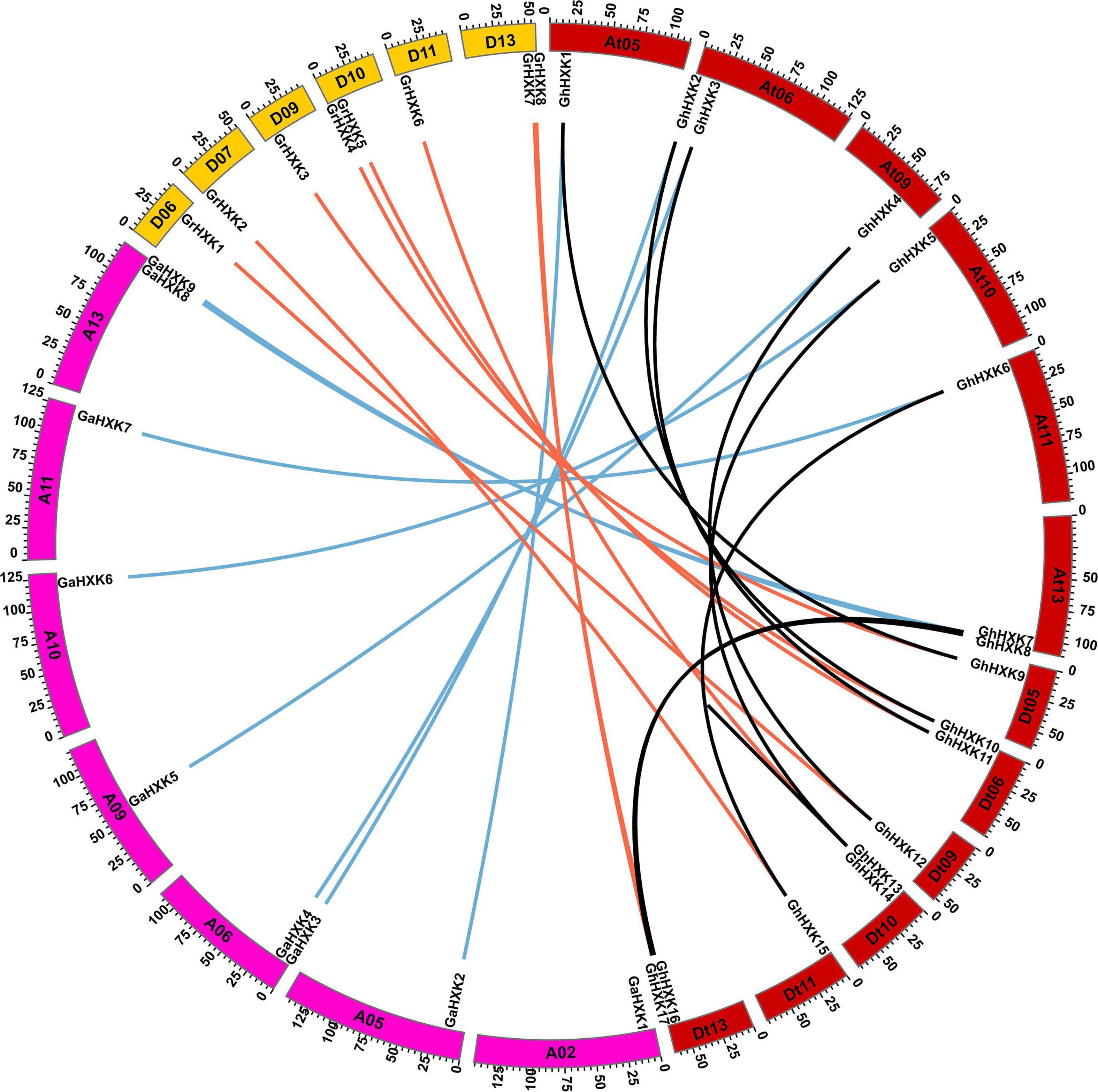
Figure 6. Circos plot showing GhHXKs paralogous gene pairs and orthologous gene pairs. Black lines connect the paralogous GhHXKs gene pairs. Red lines connect the paralogous gene pairs between GhHXKs and GrHXKs. Blue lines connect the paralogous gene pairs between GhHXKs and GaHXKs.
Selection pressure refers to the evolutionary force of natural selection, which dictates the survival and reproduction of adaptive organisms. We further analyzed the Ka, Ks, and Ka/Ks ratios of the orthologous gene pairs in G. hirsutum L., paralogous gene pairs between G. arboreum and G. hirsutum L., and G. raimondii and G. hirsutum L. (Supplementary Table 6). The Ka/Ks ratios for the GhHXKs versus GaHXKs orthologous pairs ranged from 0.0784 to 0.819 and the Ks ranged from 0.00571 to 0.0510, suggesting that the orthologous pairs diverged 1.10 million years ago (MYA). The Ka/Ks ratios for the GhHXKs versus GrHXKs orthologous pairs ranged from zero to 1.917 and the Ks ranged from 0.0055 to 0.0317, suggesting that the orthologous pairs diverged from 1.06 MYA.
Cis-Promoter Analysis of GhHXKs
We further analyzed the cis-regulatory elements in the promoter regions of GhHXKs. The cis-acting elements that we identified in GhHXKs promoters were classified into three categories, including light-, hormone- and abiotic stress-responsive promoters (Figure 7). Light-responsive elements were identified in all GhHXKs’ promoters. Of them, G-box was the most abundant (54) and was found in the promoters of 17 GhHXKs. Analysis of hormone-related elements demonstrated that the number of abscisic acids (ABA)-responsive elements were highest (43), followed by methyl jasmonate (MeJA)-responsive elements (32). Except for GhHXK9, all GhHXK promoters contain ABA-responsive elements (ABRE). Cis-acting elements involved in MeJA (TGACG-motif and CGTCA motif) were found in the promoters of 12 GhHXKs. The promoters of 11, 6, and 3 GhHXKs contain SA-, GA-, and Auxin-responsive elements, respectively. Additionally, all GhHXK promoters had at least two hormone-responsive elements, and GhHXK14 contained all five hormone-responsive elements.
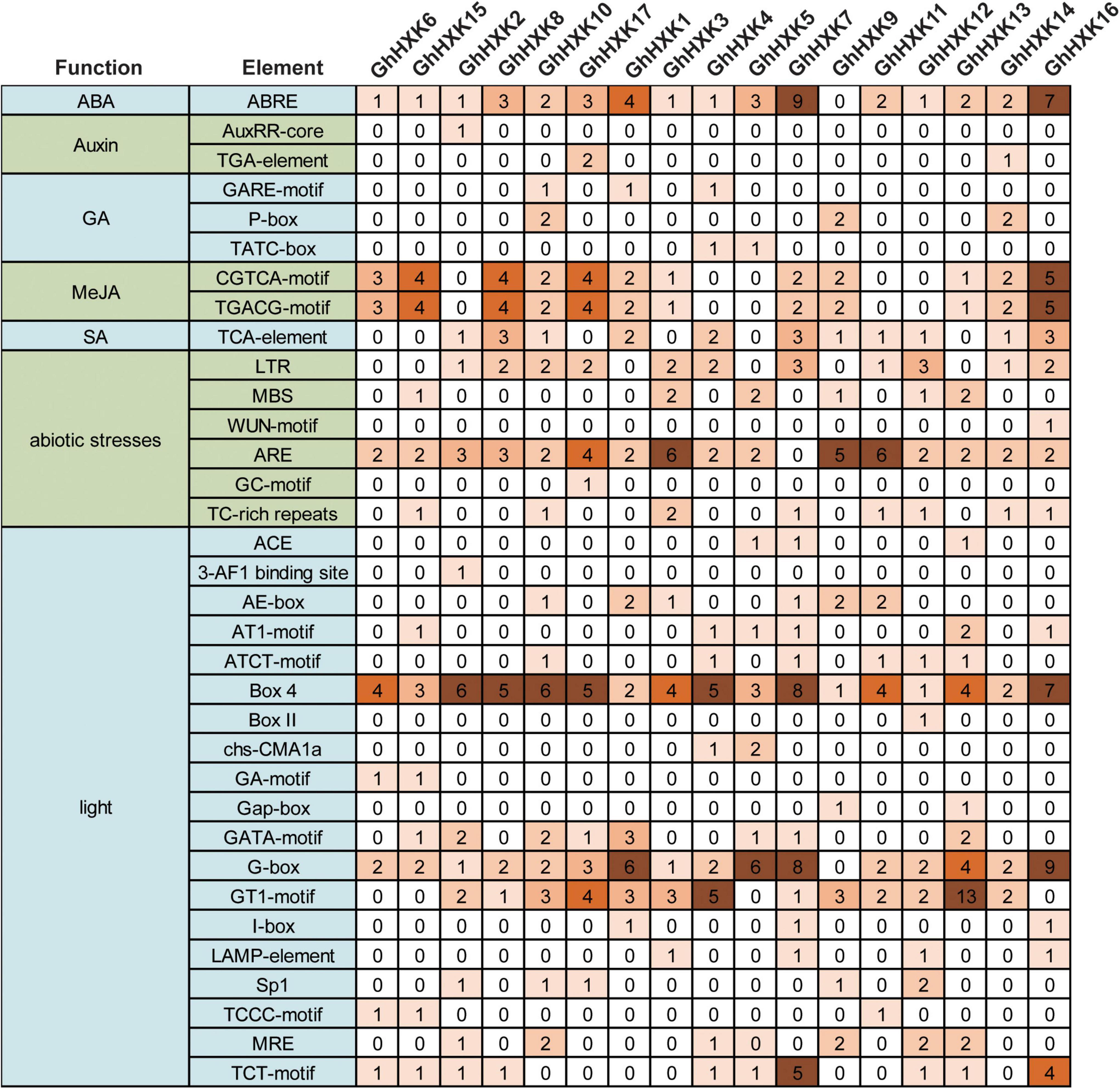
Figure 7. Cis-elements in the promoters of GhHXK genes. Numbers in the box are the number of cis-elements.
GhHXKs Genes Differentially Expressed in Different Tissues and Fiber Developmental Stages
To illustrate the spatial expression patterns of GhHXKs genes, we analyzed the transcriptomes of various tissues (stamen, anther, seed, fiber, ovule, petal, calycle, torus, leaf, stem, root, cotyledon, stigma, and pistil) in G. hirsutum L. Transcripts of GhHXKs were detected in all tissues (Supplementary Figure 6), while their expressions exhibit a tissue-specific expression pattern in G. hirsutum L.
Gossypium hirsutum L. is one of the most important textile crops in the world. Considering its importance, we investigated the expression profiles of GhHXK genes during the fiber developmental stages at 0, 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, and 35 DPA (Figure 8A). According to the expression patterns of GhHXKs during the fiber development process, GhHXKs expression patterns were classified into three groups: (i) secondary cell wall synthesis, where GhHXK6, GhHXK7, GhHXK11, GhHXK15, and GhHXK16 were highly expressed 20–45 DPA, the; (ii) the elongation process during fiber development, where GhHXK4, GhHXK7, GhHXK10, GhHXK12, and GhHXK16 had higher expression levels in fibers from 10 DPA to 20 DPA; and (iii) the fiber initiation and elongation process, where GhHXK1, GhHXK2, GhHXK3, GhHXK5, GhHXK8, GhHXK9, GhHXK14, and GhHXK17 were highly expressed at 0 and 5 DPA. These transcriptome data were also verified by qRT-PCR experiments in Figure 9. GhHXKs have similar expression pattern both in qRT-PCR experiments and transcriptome data during fiber developmental stages.
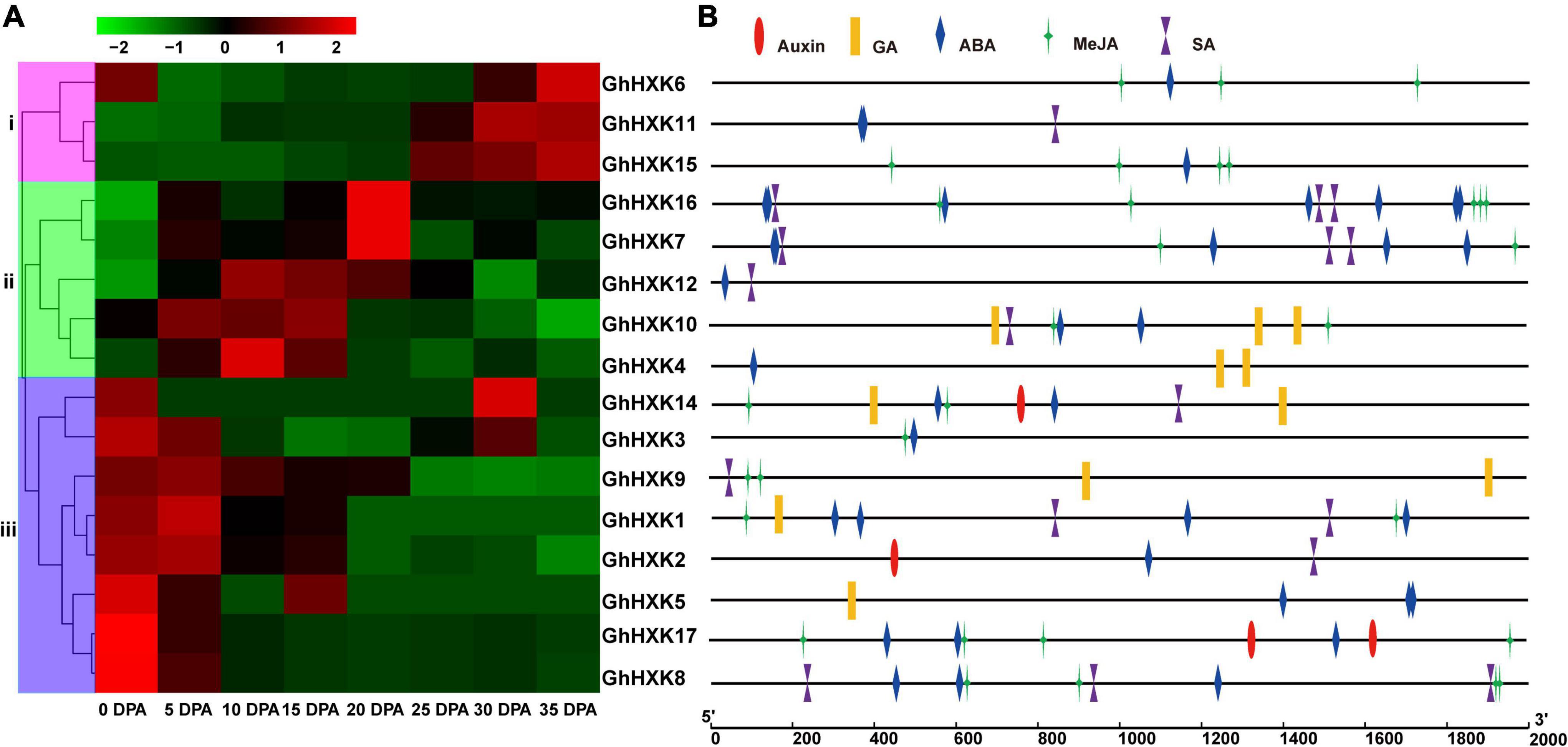
Figure 8. RNA-seq analysis of GhHXKs genes during fiber development at 0, 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30 and 35 DPA (A), and plant hormone-related cis-elements in the GhHXK promoter regions (B). The transcriptome data were normalized by fragments per kilobase of transcript per million mapped reads (FPKM) and visualized using the pheatmap software (https://www.omicshare.com/tools/Home/Soft/heatmap). The colorful bars from green to red indicate the expression levels from low to high, respectively.
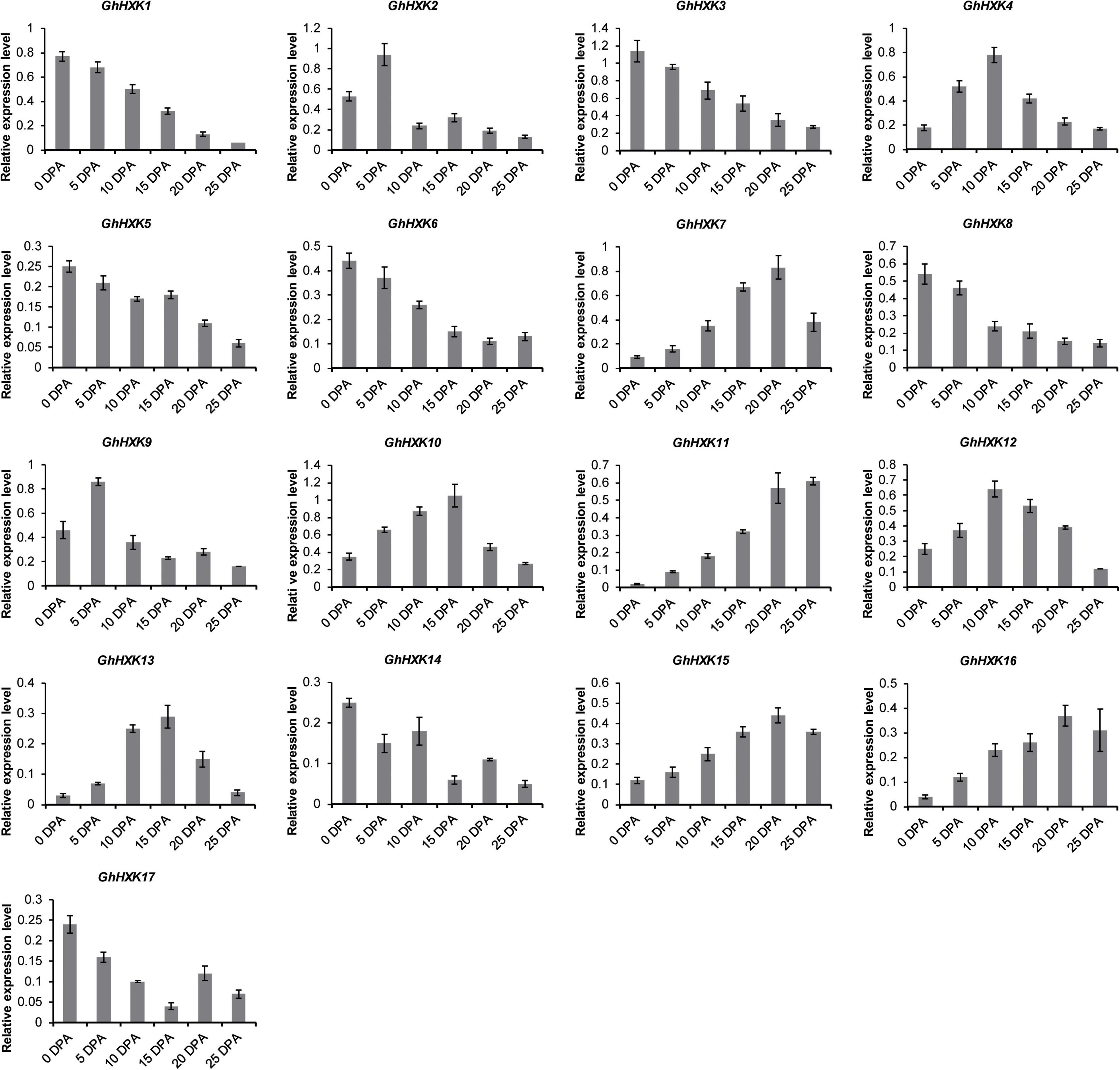
Figure 9. The expression levels of GhHXKs during fiber developmental stages (0, 5, 10, 15, 20, and 25 DPA) analyzed by qRT-PCR. Error bars represent means ± SE from three independent biological repetition. The relative expression level was calculated by using GhUBQ7 as the internal control.
The promoters of GhHXK1, GhHXK4, GhHXK5, GhHXK9, GhHXK10, and GhHXK14 contain GA-responsive cis-elements, while the promoters of GhHXK2, GhHXK14, and GhHXK17 have auxin-responsive cis-elements that are highly expressed from 5 to 20 DPA (Figure 8B). These genes can also be induced by GA and auxin treatment (Figure 10). Our results indicated that GhHXKs are involved in regulating the fiber development process and that the promoters of GhHXKs (i and ii) contain auxin- and GA-responsive elements.
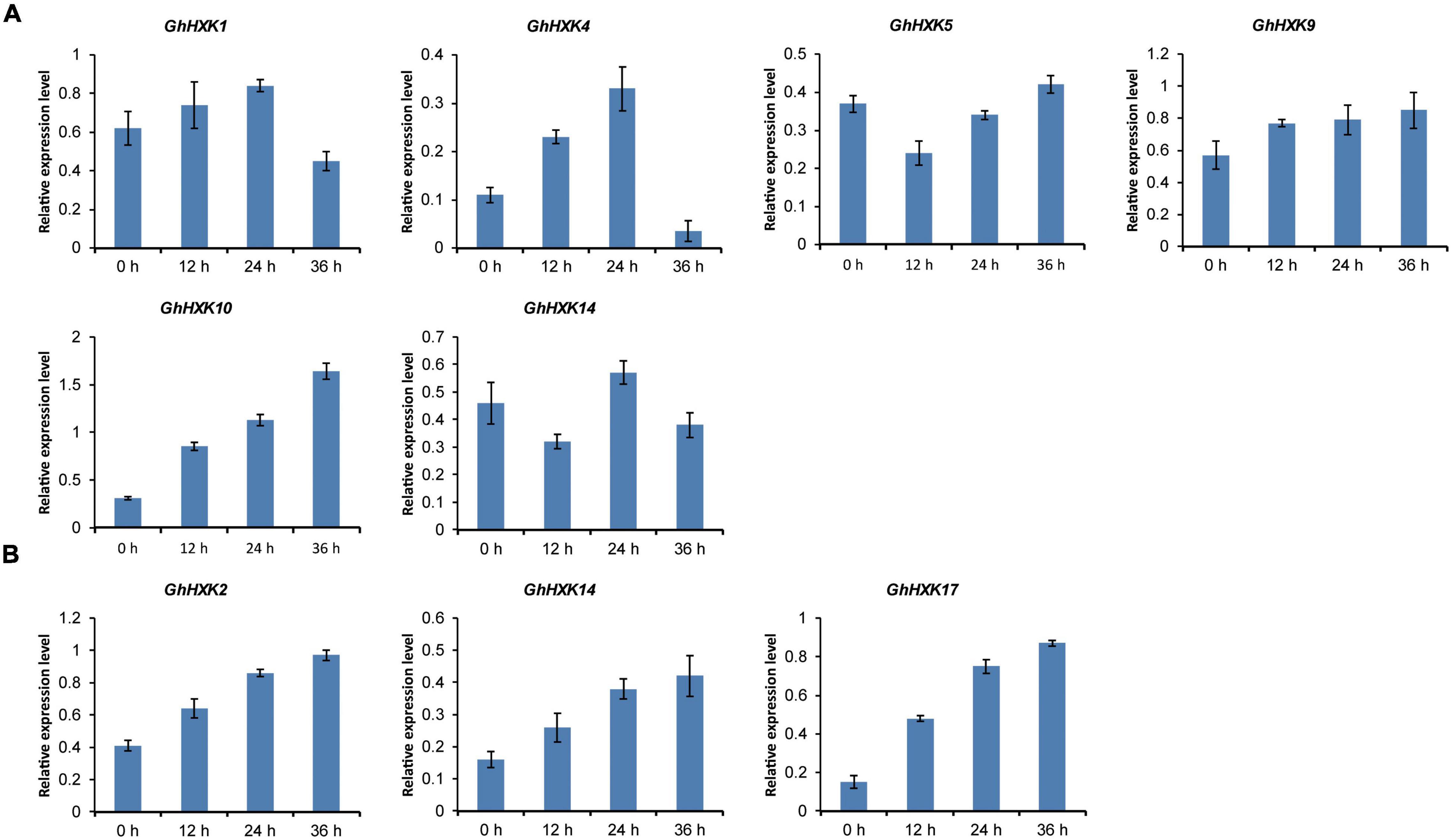
Figure 10. GhHXKs expression levels are induced by GA (A) and auxin (B) analyzed by qRT-PCR. GA treatment induced expression of most GhHXKs with GARE-motif, P-box or TATC-box in their promoter regions (A). The relative expression levels of GhHXKs with AuxRR-core or TGA-element in their promoter regions (B). The error bars represent means ± SE from three independent biological repetition. The y-axis represents the relative expression level. The x-axis represents the 0 DPA ovules treated with GA or IAA for 0, 12, 24, and 36 h, respectively.
Discussion
Hexokinase (HXK) is an enzyme that catalyzes hexose phosphorylation during the metabolism of sugar, which functions as an energy substance and signal during plant growth. In this work, we identified 17, nine, and eight HXKs from G. hirsutum L., G. arboreum, and G. raimondii, respectively, and analyzed the GhHXKs chromosomal locations, phylogeny, gene structure, conservative motifs, duplicated types, cis-elements, and expression patterns during fiber development.
GhHXKs Are Conservative Both in Nucleotide and Protein Sequence Levels
Gossypium hirsutum L. (2n = 4X = 52) is an allotetraploid cotton species. It originated approximately 1–2 MYA after the hybridization of two diploid cotton species, G. arboreum (2n = 2X = 26) and G. raimondii (2n = 2X = 26) (Galau and Wilkins, 1989). In this work, we identified 17, 9, and 8 HXKs from G. hirsutum L., G. arboreum, and G. raimondii, respectively. The total numbers of GaHXK and GrHXK equal that in G. hirsutum L.
Duplication events are the primary reason for the expansion of each gene family member. Analysis of the synteny and phylogeny of HXKs in the G. hirsutum L. genome demonstrated that GhHXKs, GaHXKs, and GrHXKs duplicated due to segmental duplication. The Ks and Ka were more significant in paralogous gene pairs (GhHXKs) than in orthologous gene pairs (GhHXKs vs. GaHXKs and GhHXKs vs. GrHXKs), and in the divergence time in paralogous gene pairs (GhHXKs) than between orthologous gene pairs. This indicates that duplication events in GaHXKs, GrHXKs, and GhHXKs occurred before the divergence of G. raimondii and G. arboreum. Additionally, the HXK sequences were conservative among cotton species.
Hexokinases in higher plants typically contain nine exons, such as PeHXKs (Zheng et al., 2020), OsHXKs (Cho et al., 2006), and MeHXKs (Geng et al., 2017). These nine exons were also found in most GhHXKs. Phylogenetic analysis of HXK proteins found more clade numbers among monocotyledons and fewer clade numbers among dicotyledons. The GhHXKs, GaHXKs, GrHXKs, AtHXKs, MeHXKs, and BnHXKs were clustered into three clades (I, II, and IV), while OsHXKs, PeHXKs were clustered into four clades (I, II, III, and IV). This indicates that the HXKs of monocotyledonous plants had a higher mutation level than that of dicotyledons.
The Central Hypothesis Role of GhHXKs in Sugar Signal Transduction During Fiber Development
Sucrose is the primary photosynthesis produce and is transported to growing cells, such as fiber cells. Sucrose is a disaccharide made up of glucose and fructose, and functions as an osmotic substance and raw material for the synthesis of cell wall cellulose. Sucrose synthase (SuSy) and invertase are involved in the first step of sucrose degradation by cleaving the glycosidic bond between glucose and fructose (Cabello et al., 2014). SuSy helps break down sucrose into fructose and UDP-glucose for cellulose biosynthesis. A SuSy protein, SusC, is highly expressed during the synthesis of the secondary cell wall in fibers and the cell wall fraction. The subcellular location of the protein demonstrated that SusC is localized on the cell wall, which could indicate the presence of UDP-glucose function in cellulose and callose synthesis (Brill et al., 2011). Jiang et al. (2012) demonstrated that over-expressing GhsusA1, a cotton SuSy gene, increased the thickness of the secondary cell wall and overall fiber strength, which indicates that a sucrose signal is involved in controlling cellulose biosynthesis in the development of cotton fiber (Jiang et al., 2012). When this synthetic SuSy gene is overexpressed in cotton, the transgenic cotton plants showed longer fiber length, enhanced fiber strength, and increased cellulose contents (Ahmed et al., 2020). The cell wall invertase (CWIN) is responsible for sucrose cleaving into fructose and glucose, while the expression levels of GhCWIN are significantly more highly expressed at 5 and 10 DPA than 15 and 20 DPA (Wang and Ruan, 2012). During the fiber development process, the sucrose content decreased from fiber initiation (0 DPA) to fiber elongation (12 DPA), and was accompanied by increasing in glucose and fructose in fiber content (Sun et al., 2019). Both SuSy and CWIN can catalyze sucrose into monosaccharides and contribute to cotton fiber development by providing component hexoses for cellulose synthesis. Additionally, the production of hexoses can increase the content of osmotic substances content, which contributes to turgor pressure for fiber elongation (Weschke et al., 2003).
The synthesis and elongation of cotton fiber cell could be required to obtain higher energy. Studies have found significantly higher ATP synthase activity in 10 DPA wild-type fiber cells than in ovule samples and leaf samples. Additionally, exogenously applying the inhibitors of ATP synthase, piceatannol (PA), and oligomycin (OM) decreased fiber length and lowered the ATP/ADP ratio (Pang et al., 2010). Other studies demonstrated that phosphorylated glucose participated in the pentose phosphate pathway, which provides NADPH for cellular respiration (Lu et al., 2016), and that HXKs catalyzes the irreversible step of glycolysis, which provides energy for cell growth (Aguilera-Alvarado and Sanchez-Nieto, 2017).
Transcriptome analysis demonstrated that the hexokinase inhibitor NAG, which repressed cotton fiber elongation, depends on the glucose signal transduced by HXKs (Li et al., 2021). Glucose phosphorylation is also involved in the synthesis of inositol, a signal molecule (Loewus et al., 1982), which positively regulates cotton fiber length. The inositol synthase enzyme, myo-inositol-1-phosphate synthase, positively regulates fiber elongation. The GhMIPS1D gene was ectopically expressed in the Arabidopsis mips1 mutant showed longer root cells and a higher plant height (Ma et al., 2019). RNAi MdMIPS1/2 in apple promoted programmed cell death and necrosis, while apple necrosis was directly caused by the excessive accumulation of reactive oxygen species. Therefore, apple necrosis could be associated with salicylic acid, which increased the polysaccharide-mediated cell wall (Hu et al., 2020).
Crosstalk About IAA, GA, Glucose, and GhHXKs in Fiber Development
Gibberellin and auxin are two plant hormones that promote fiber elongation. Analysis of promoter cis-elements and expression data of expression profile and qRT-PCR experiments demonstrated that some GhHXKs are regulated by GA and IAA.
Gibberellin (GA) plays two roles when regulating the content of intracellular glucose. GA3 treatment can promote the accumulation of sugar in potato tubers under low-temperature conditions by inducing changes in the expression of genes involved in sugar accumulation, ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase (AGPase) (Xie et al., 2018). In the presence of glucose, the GA synthesis enzyme, GA20ox1, can significantly up-regulated by KNO3 (Ikeya et al., 2020).
In the daytime, cytochrome C (Cyt C)-deficient Arabidopsis accumulates glucose with lower levels of GA, while GA treatment complements this reduction of glucose accumulation in Cyt C-deficient plants (Racca et al., 2018). GA synthesis was suppressed by glucose, and the application of mevalonic acid could break down this suppression. Therefore, the key enzyme of the isoprenoid pathway was the target of C-catabolite suppression (Bruckner, 1992). GA3 repressed the transcriptional levels of HXK1 and HXK2, which negatively interfered with the transduction of glucose signals, depending on hexokinase phosphorylation in grape berries (Zhang et al., 2014).
Abscisic acids negatively regulates cotton fiber development, and other studies demonstrated that ABA crosstalked with glucose signal transduction. During the germination process of rice seeds, high glucose concentrations delayed seed germination by repressing ABA catabolism (Zhu et al., 2009). The enzyme UGT73C14 utilized UDP-glucose as sugar donors for ABA glycosylation in G. hirsutum L., and the UDP-glucose can be synthesized by UTP and phosphorylated glucose (Glc-Pi) (Gilbert et al., 2013).
The glucose sensor HXK mutant gin 2 is also resistant to exogenous auxin (Moore et al., 2003). Glucose affects most of the genes regulated by auxin metabolism (Mishra et al., 2009). High glucose concentrations reduced the root meristem zone by repressing the auxin transporters, PIN1 accumulation, and reducing auxin levels in Arabidopsis roots (Yuan et al., 2014). Most IAA-regulated genes were transcriptionally regulated by glucose alone; however, glucose antagonistically functions on IAA-regulated genes (Gupta et al., 2009).
Above all, glucose functions as a molecular signal that crosstalks with IAA, GA, and ABA, while HXK-catalyzed glucose-phosphate is the core of glucose signal transduction. Analysis of the promoter cis-elements analysis and RNA-seq data demonstrated that GhHXKs contain GA- and IAA-related cis-elements can also be regulated by these phytohormones. This indicates that various hormones can crosstalk HXKs with sugar signals when regulating the development of cotton fiber (Figure 11).
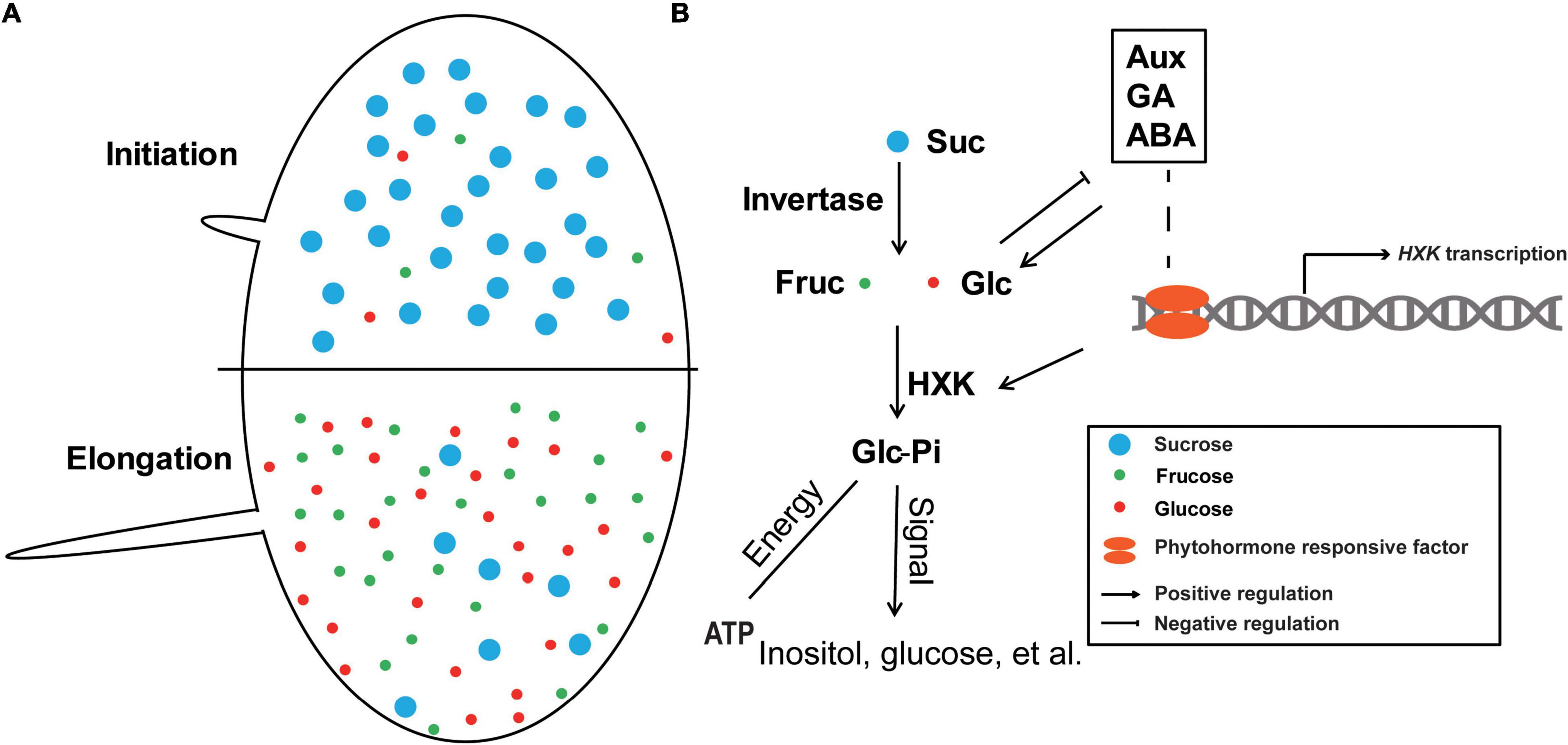
Figure 11. A hypothesis about the roles of GhHXKs in cotton fiber development. (A) During fiber developmental stages, from initiation to elongation, the sucrose content decreased, and the fructose and glucose content increased. (B) The phosphorylated hexose functions in energy supply and signal transduction in fiber development; Meanwhile, intracellular hexose levels are regulated by IAA, GA, and ABA, and GhHXK is the center of this pathway. The blue, red and green dots represent sucrose, glucose and fructose, respectively. The arrows and blunt arrows indicate positive and negative regulation of the specific processes, respectively.
Conclusion
We performed a genome-wide characterization of the GhHXK gene family in cotton research by identifying chromosomal distribution, gene structure, phylogenetic analysis, duplication events, promoter cis-elements, and spatial-temporal expression of the GhHXKs, which provides a comprehensive analysis of the GhHXK gene family.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/Supplementary Material.
Author Contributions
GX and XZ: conceptualization. LD: writing – reviewing. ZL and HL: software and methodology. HW: perform experiments, revise, and writing sections of the manuscript. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Funding
This study was supported by the Natural Science Basic Research Project of Shaanxi Province (2021JQ-817), the Comprehensive Scientific Research Fund Project of the Xianyang Normal University (XSYK20002), the National Key R&D Program (2021YFF1000100), Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund (Y2021XK12), the Project of Introduction High-Level Talents in Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region Flexible Talents (2020), the Key Laboratory Open Fund Program of Shanxi Province (Grant No. MHKF202103), and Key Scientific and Technological Project of Anyang City (2022C01NY012).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The reviewer JG declared a shared affiliation with the author XZ to the handling editor at the time of review.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpls.2022.882587/full#supplementary-material
Supplementary Figure 1 | Chromosomal distribution of GaHXKs and GrHXKs. The arrows show the direction of the transcription of HXK genes.
Supplementary Figure 2 | Chromosomal distribution of GanHXKs, GstHXKs, GloHXKs, and GroHXKs. The arrows show the transcript direction of HXK genes.
Supplementary Figure 3 | Phylogenetic relationships and gene structures of HXKs in cotton species. (A) Phylogenetic tree of HXKs from G. hirsutum L., G. arboreum, G. raimondii, G. anomalum, G. stocksii, G. longicalyx, and G. rotundifolium. The tree was constructed by MEGA 7.0 with default parameters with 1,000 bootstraps. (B) Gene structure. The blue oval and black lines represent exons and introns, respectively.
Supplementary Figure 4 | Amino acid alignment analysis of GhHXKs. The red lines indicate the regions with different functions. The red arrow directs the eight conserved amino acids (counting the amino acid residues based on GhHXK2, the eight amino acids are Asp-106, Thr-110, Lys-196, Asp-231, Gly-253, Asp-438, Gly-440, and Ser-473), which are the active residues of hexokinases (HXKs). The alignment was performed with ClustalW and displayed by GeneDoc.
Supplementary Figure 5 | Distribution of the HXK family genes in plantae. The phylogenetic tree of 18 plant species was shown on the left (A). The genome size (B) and number of HXK genes (C) found in each genome are indicated on the right.
Supplementary Figure 6 | Expression heatmap of the GhHXKs at various tissues (stamen, anther, seed, fiber, ovule, petal, calycle, torus, leaf, stem, root, cotyledon, stigma, and pistil).
Footnotes
- ^ http://www.cottongen.org
- ^ https://www.arabidopsis.org/
- ^ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore
- ^ http://brassicadb.cn/#/
- ^ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genome
- ^ http://smart.embl.de/
- ^ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/cdd
- ^ http://gsds.gao-lab.org/
- ^ https://meme-suite.org/meme/tools/meme
- ^ https://web.expasy.org/protparam/
- ^ https://wolfpsort.hgc.jp/
- ^ http://sphinx.rug.ac.be:8080/PlantCARE
- ^ https://www.omicshare.com/tools/Home/Soft/heatmap
References
Aguilera-Alvarado, G. P., and Sanchez-Nieto, S. (2017). Plant hexokinases are multifaceted proteins. Plant Cell Physiol. 58, 1151–1160. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcx062
Ahmed, M., Iqbal, A., Latif, A., Din, S. U., Sarwar, M. B., Wang, X., et al. (2020). Overexpression of a sucrose synthase gene indirectly improves cotton fiber quality through sucrose cleavage. Front. Plant Sci. 11:476251. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.476251
Artimo, P., Jonnalagedda, M., Arnold, K., Baratin, D., Csardi, G., de Castro, E., et al. (2012). ExPASy: SIB bioinformatics resource portal. Nucleic Acids Res. 40, W597–W603. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks400
Brill, E., van Thournout, M., White, R. G., Llewellyn, D., Campbell, P. M., Engelen, S., et al. (2011). A novel isoform of sucrose synthase is targeted to the cell wall during secondary cell wall synthesis in cotton fiber. Plant Physiol. 157, 40–54. doi: 10.1104/pp.111.178574
Bruckner, B. (1992). Regulation of gibberellin formation by the fungus Gibberella fujikuroi. Ciba Found Symp. 171, 129–137. doi: 10.1002/9780470514344.ch8
Bruggeman, Q., Prunier, F., Mazubert, C., de Bont, L., Garmier, M., Lugan, R., et al. (2015). Involvement of Arabidopsis Hexokinase 1 in cell death mediated by myo-inositol accumulation. Plant Cell. 27, 1801–1814. doi: 10.1105/tpc.15.00068
Cabello, S., Lorenz, C., Crespo, S., Cabrera, J., Ludwig, R., Escobar, C., et al. (2014). Altered sucrose synthase and invertase expression affects the local and systemic sugar metabolism of nematode-infected Arabidopsis thaliana plants. J. Exp. Bot. 65, 201–212. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ert359
Camacho, C., Coulouris, G., Avagyan, V., Ma, N., Papadopoulos, J., Bealer, K., et al. (2009). BLAST+: architecture and applications. BMC Bioinformatics 10:421. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-10-421
Chalhoub, B., Denoeud, F., Liu, S., Parkin, I. A., Tang, H., Wang, X., et al. (2014). Plant genetics. Early allopolyploid evolution in the post-Neolithic Brassica napus oilseed genome. Science 345, 950–953. doi: 10.1126/science.1253435
Cho, J. I., Ryoo, N., Ko, S., Lee, S. K., Lee, J., Jung, K. H., et al. (2006). Structure, expression, and functional analysis of the hexokinase gene family in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Planta 224, 598–611. doi: 10.1007/s00425-006-0251-y
Desnoues, E., Gibon, Y., Baldazzi, V., Signoret, V., Genard, M., and Quilot-Turion, B. (2014). Profiling sugar metabolism during fruit development in a peach progeny with different fructose-to-glucose ratios. BMC Plant Biol. 14:336. doi: 10.1186/s12870-014-0336-x
Etienne, C., Rothan, C., Moing, A., Plomion, C., Bodenes, C., Svanella-Dumas, L., et al. (2002). Candidate genes and QTLs for sugar and organic acid content in peach [ Prunus persica (L.) Batsch]. Theor. Appl. Genet. 105, 145–159. doi: 10.1007/s00122-001-0841-9
Galau, G. A., and Wilkins, T. A. (1989). Alloplasmic male sterility in AD allotetraploid Gossypium hirsutum upon replacement of its resident A cytoplasm with that of D species G. harknessii. Theor. Appl. Genet. 78, 23–30. doi: 10.1007/BF00299748
Geng, M. T., Yao, Y., Wang, Y. L., Wu, X. H., Sun, C., Li, R. M., et al. (2017). Structure, expression, and functional analysis of the hexokinase gene family in Cassava. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 18:1041. doi: 10.3390/ijms18051041
Gilbert, M. K., Bland, J. M., Shockey, J. M., Cao, H., Hinchliffe, D. J., Fang, D. D., et al. (2013). A transcript profiling approach reveals an abscisic acid-specific glycosyltransferase (UGT73C14) induced in developing fiber of Ligon lintless-2 mutant of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). PLoS One 8:e75268. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0075268
Granot, D., and Dai, N. (1997). Sugar induced cell death in yeast is dependent on the rate of sugar phosphorylation as determined by Arabidopsis thaliana hexokinase. Cell Death Differ. 4, 555–559. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4400280
Grover, C. E., Pan, M., Yuan, D., Arick, M. A., Hu, G., Brase, L., et al. (2020). The Gossypium longicalyx genome as a resource for cotton breeding and evolution. G3 10, 1457–1467. doi: 10.1534/g3.120.401050
Grover, C. E., Yuan, D., Arick, M. A., Miller, E. R., Hu, G., Peterson, D. G., et al. (2021a). The Gossypium anomalum genome as a resource for cotton improvement and evolutionary analysis of hybrid incompatibility. G3 11:jkab319. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkab319
Grover, C. E., Yuan, D., Arick, M. A., Miller, E. R., Hu, G., Peterson, D. G., et al. (2021b). The Gossypium stocksii genome as a novel resource for cotton improvement. G3 11:jkab125. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkab125
Gupta, A., Singh, M., Mishra, B. S., Kushwah, S., and Laxmi, A. (2009). Role of glucose in spatial distribution of auxin regulated genes. Plant Signal. Behav. 4, 862–863. doi: 10.4161/psb.4.9.9421
Halford, N. G., Purcell, P. C., and Hardie, D. G. (1999). Is hexokinase really a sugar sensor in plants? Trends Plant Sci. 4, 117–120. doi: 10.1016/s1360-1385(99)01377-1
Hanson, J., and Smeekens, S. (2009). Sugar perception and signaling–an update. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 12, 562–567. doi: 10.1186/s12870-019-1932-6
He, P., Yang, Y., Wang, Z., Zhao, P., and Xiao, G. (2019). Comprehensive analyses of ZFP gene family and characterization of expression profiles during plant hormone response in cotton. BMC Plant Biol. 19:329.
He, P., Zhao, P., Wang, L., Zhang, Y., Wang, X., Xiao, H., et al. (2017). The PIN gene family in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum): genome-wide identification and gene expression analyses during root development and abiotic stress responses. BMC Genomics 18:507. doi: 10.1186/s12864-017-3901-5
Horton, P., Park, K. J., Obayashi, T., Fujita, N., Harada, H., Adams-Collier, C. J., et al. (2007). WoLF PSORT: protein localization predictor. Nucleic Acids Res. 35, W585–W587. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm259
Hu, B., Jin, J., Guo, A. Y., Zhang, H., Luo, J., and Gao, G. (2015). GSDS 2.0: an upgraded gene feature visualization server. Bioinformatics 31, 1296–1297. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu817
Hu, L., Zhou, K., Ren, G., Yang, S., Liu, Y., Zhang, Z., et al. (2020). Myo-inositol mediates reactive oxygen species-induced programmed cell death via salicylic acid-dependent and ethylene-dependent pathways in apple. Hortic. Res. 7:138. doi: 10.1038/s41438-020-00357-2
Hu, Y., Chen, J., Fang, L., Zhang, Z., Ma, W., Niu, Y., et al. (2019). Gossypium barbadense and Gossypium hirsutum genomes provide insights into the origin and evolution of allotetraploid cotton. Nat. Genet. 51, 739–748. doi: 10.1038/s41588-019-0371-5
Huang, L., Yu, L. J., Zhang, X., Fan, B., Wang, F. Z., Dai, Y. S., et al. (2019). Autophagy regulates glucose-mediated root meristem activity by modulating ROS production in Arabidopsis. Autophagy 15, 407–422. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2018.1520547
Ikeya, S., Aoyanagi, T., Ishizuka, I., Takeuchi, A., and Kozaki, A. (2020). Nitrate promotes germination under inhibition by NaCl or high concentration of glucose. Plants 9:707. doi: 10.3390/plants9060707
Jang, J. C., Leon, P., Zhou, L., and Sheen, J. (1997). Hexokinase as a sugar sensor in higher plants. Plant Cell 9, 5–19. doi: 10.1105/tpc.9.1.5
Jiang, Y., Guo, W., Zhu, H., Ruan, Y. L., and Zhang, T. (2012). Overexpression of GhSusA1 increases plant biomass and improves cotton fiber yield and quality. Plant Biotechnol. J. 10, 301–312. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-7652.2011.00662.x
Jiangtao, C., Yingzhen, K., Qian, W., Yuhe, S., Daping, G., Jing, L., et al. (2015). MapGene2Chrom, a tool to draw gene physical map based on Perl and SVG languages. Yi Chuan 37, 91–97. doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.2015.01.013
Karve, A., Rauh, B. L., Xia, X., Kandasamy, M., Meagher, R. B., Sheen, J., et al. (2008). Expression and evolutionary features of the hexokinase gene family in Arabidopsis. Planta 228, 411–425. doi: 10.1007/s00425-008-0746-9
Krzywinski, M., Schein, J., Birol, I., Connors, J., Gascoyne, R., Horsman, D., et al. (2009). Circos: an information aesthetic for comparative genomics. Genome Res. 19, 1639–1645. doi: 10.1101/gr.092759.109
Kumar, S., Stecher, G., and Tamura, K. (2016). MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 33:1870. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msw054
Lamesch, P., Berardini, T. Z., Li, D., Swarbreck, D., Wilks, C., Sasidharan, R., et al. (2012). The Arabidopsis Information Resource (TAIR): improved gene annotation and new tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 40, D1202–D1210. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr1090
Lescot, M., Déhais, P., Thijs, G., Marchal, K., Moreau, Y., Van de Peer, Y., et al. (2002). PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 30, 325–327. doi: 10.1093/nar/30.1.325
Letunic, I., Khedkar, S., and Bork, P. (2021). SMART: recent updates, new developments and status in 2020. Nucleic Acids Res. 49, D458–D460. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa937
Li, F., Fan, G., Lu, C., Xiao, G., Zou, C., Kohel, R. J., et al. (2015). Genome sequence of cultivated Upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum TM-1) provides insights into genome evolution. Nat. Biotechnol. 33, 524–530. doi: 10.1038/nbt.3208
Li, J., Chen, G., Zhang, J., Shen, H., Kang, J., Feng, P., et al. (2020). Suppression of a hexokinase gene, SlHXK1, leads to accelerated leaf senescence and stunted plant growth in tomato. Plant Sci. 298:110544. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2020.110544
Li, X., Liu, W., Ren, Z., Wang, X., Liu, J., Yang, Z., et al. (2021). Glucose regulates cotton fiber elongation by interacting with brassinosteroid. J. Exp. Bot. 73, 711–726. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erab451
Loewus, M. W., Sasaki, K., Leavitt, A. L., Munsell, L., Sherman, W. R., and Loewus, F. A. (1982). Enantiomeric Form of myo-Inositol-1-Phosphate Produced by myo-Inositol-1-Phosphate Synthase and myo-Inositol Kinase in Higher Plants. Plant Physiol. 70, 1661–1663. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.6.1661
Lu, S., Wang, J., Chitsaz, F., Derbyshire, M. K., Geer, R. C., Gonzales, N. R., et al. (2020). CDD/SPARCLE: the conserved domain database in 2020. Nucleic Acids Res. 48, D265–D268. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz991
Lu, X., Huan, L., Gao, S., He, L., and Wang, G. (2016). NADPH from the oxidative pentose phosphate pathway drives the operation of cyclic electron flow around photosystem I in high-intertidal macroalgae under severe salt stress. Physiol. Plant. 156, 397–406. doi: 10.1111/ppl.12383
Ma, R., Song, W., Wang, F., Cao, A., Xie, S., Chen, X., et al. (2019). A Cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) Myo-Inositol-1-Phosphate Synthase (GhMIPS1D) Gene Promotes Root Cell Elongation in Arabidopsis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20:1224. doi: 10.3390/ijms20051224
Ma, Z., Zhang, Y., Wu, L., Zhang, G., Sun, Z., Li, Z., et al. (2021). High-quality genome assembly and resequencing of modern cotton cultivars provide resources for crop improvement. Nat. Genet. 53, 1385–1391. doi: 10.1038/s41588-021-00910-2
Mayordomo, I., and Sanz, P. (2001). Hexokinase PII: structural analysis and glucose signalling in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 18, 923–930. doi: 10.1002/yea.737
Mishra, B. S., Singh, M., Aggrawal, P., and Laxmi, A. (2009). Glucose and auxin signaling interaction in controlling Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings root growth and development. PLoS One 4:e4502. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0004502
Moore, B., Zhou, L., Rolland, F., Hall, Q., Cheng, W. H., Liu, Y. X., et al. (2003). Role of the Arabidopsis glucose sensor HXK1 in nutrient, light, and hormonal signaling. Science 300, 332–336. doi: 10.1126/science.1080585
Pang, Y., Wang, H., Song, W. Q., and Zhu, Y. X. (2010). The cotton ATP synthase delta1 subunit is required to maintain a higher ATP/ADP ratio that facilitates rapid fibre cell elongation. Plant Biol. 12, 903–909. doi: 10.1111/j.1438-8677.2009.00313.x
Paterson, A. H., Wendel, J. F., Gundlach, H., Guo, H., Jenkins, J., Jin, D., et al. (2012). Repeated polyploidization of Gossypium genomes and the evolution of spinnable cotton fibres. Nature 492, 423–427. doi: 10.1038/nature11798
Prakash, A., Jeffryes, M., Bateman, A., and Finn, R. D. (2017). The HMMER Web Server for Protein Sequence Similarity Search. Curr. Protoc. Bioinformatics 60, 3.15.1–3.15.23. doi: 10.1002/cpbi.40
Qin, Y. M., and Zhu, Y. X. (2011). How cotton fibers elongate: a tale of linear cell-growth mode. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 14, 106–111. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2010.09.010
Racca, S., Welchen, E., Gras, D. E., Tarkowska, D., Tureckova, V., Maurino, V. G., et al. (2018). Interplay between cytochrome c and gibberellins during Arabidopsis vegetative development. Plant J. 94, 105–121. doi: 10.1111/tpj.13845
Shi, Y. H., Zhu, S. W., Mao, X. Z., Feng, J. X., Qin, Y. M., Zhang, L., et al. (2006). Transcriptome profiling, molecular biological, and physiological studies reveal a major role for ethylene in cotton fiber cell elongation. Plant Cell 18, 651–664. doi: 10.1105/tpc.105.040303
Smeekens, S. (2000). Sugar-Induced Signal Transduction in Plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 51, 49–81. doi: 10.1146/annurev.arplant.51.1.49
Smeekens, S., Ma, J., Hanson, J., and Rolland, F. (2010). Sugar signals and molecular networks controlling plant growth. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 13, 274–279. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2009.12.002
Sun, W., Gao, Z., Wang, J., Huang, Y., Chen, Y., Li, J., et al. (2019). Cotton fiber elongation requires the transcription factor GhMYB212 to regulate sucrose transportation into expanding fibers. New Phytol. 222, 864–881. doi: 10.1111/nph.15620
Valluru, R., and Van den Ende, W. (2011). Myo-inositol and beyond–emerging networks under stress. Plant Sci. 181, 387–400. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2011.07.009
Wang, D., Zhang, Y., Zhang, Z., Zhu, J., and Yu, J. (2010). KaKs_Calculator 2.0: a toolkit incorporating gamma-series methods and sliding window strategies. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics 8, 77–80. doi: 10.1016/S1672-0229(10)60008-3
Wang, L., and Ruan, Y. L. (2012). New insights into roles of cell wall invertase in early seed development revealed by comprehensive spatial and temporal expression patterns of GhCWIN1 in cotton. Plant Physiol. 160, 777–787. doi: 10.1104/pp.112.203893
Wang, M., Li, J., Wang, P., Liu, F., Liu, Z., Zhao, G., et al. (2021). Comparative genome analyses highlight transposon-mediated genome expansion and the evolutionary architecture of 3D genomic folding in cotton. Mol. Biol. Evol. 38, 3621–3636. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msab128
Wang, M., Tu, L., Yuan, D., Zhu, D., Shen, C., Li, J., et al. (2019). Reference genome sequences of two cultivated allotetraploid cottons, Gossypium hirsutum and Gossypium barbadense. Nat. Genet. 51, 224–229. doi: 10.1038/s41588-018-0282-x
Wang, X. Q., Zheng, L. L., Lin, H., Yu, F., Sun, L. H., and Li, L. M. (2017). Grape hexokinases are involved in the expression regulation of sucrose synthase- and cell wall invertase-encoding genes by glucose and ABA. Plant Mol. Biol. 94, 61–78. doi: 10.1007/s11103-017-0593-9
Weschke, W., Panitz, R., Gubatz, S., Wang, Q., Radchuk, R., Weber, H., et al. (2003). The role of invertases and hexose transporters in controlling sugar ratios in maternal and filial tissues of barley caryopses during early development. Plant J. 33, 395–411. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.2003.01633.x
Wu, Z., Yang, Y., Huang, G., Lin, J., Xia, Y., and Zhu, Y. (2017). Cotton functional genomics reveals global insight into genome evolution and fiber development. J. Genet. Genom. 44, 511–518. doi: 10.1016/j.jgg.2017.09.009
Xiao, G. H., Wang, K., Huang, G., and Zhu, Y. X. (2016). Genome-scale analysis of the cotton KCS gene family revealed a binary mode of action for gibberellin a regulated fiber growth. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 58, 577–589. doi: 10.1111/jipb.12429
Xiao, W., Sheen, J., and Jang, J. C. (2000). The role of hexokinase in plant sugar signal transduction and growth and development. Plant Mol. Biol. 44, 451–461. doi: 10.1023/a:1026501430422
Xie, Y., Onik, J. C., Hu, X., Duan, Y., and Lin, Q. (2018). Effects of (S)-carvone and gibberellin on sugar accumulation in potatoes during low temperature storage. Molecules 23:3118. doi: 10.3390/molecules23123118
Yang, X., Tuskan, G. A., and Cheng, M. Z. (2006). Divergence of the Dof gene families in poplar, Arabidopsis, and rice suggests multiple modes of gene evolution after duplication. Plant Physiol. 142, 820–830. doi: 10.1104/pp.106.083642
Yuan, T. T., Xu, H. H., Zhang, K. X., Guo, T. T., and Lu, Y. T. (2014). Glucose inhibits root meristem growth via ABA insensitive 5, which represses PIN1 accumulation and auxin activity in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Environ. 37, 1338–1350. doi: 10.1111/pce.12233
Yupeng, W., Haibao, T., Debarry, J. D., Xu, T., Jingping, L., Xiyin, W., et al. (2012). MCScanX: a toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity. Nucleic Acids Res. 40:e49. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr1293
Zhang, Y., Zhen, L., Tan, X., Li, L., and Wang, X. (2014). The involvement of hexokinase in the coordinated regulation of glucose and gibberellin on cell wall invertase and sucrose synthesis in grape berry. Mol. Biol. Rep. 41, 7899–7910. doi: 10.1007/s11033-014-3683-7
Zheng, S., Ye, C., Lu, J., Liufu, J., Lin, L., Dong, Z., et al. (2021). Improving the rice photosynthetic efficiency and yield by editing OsHXK1 via CRISPR/Cas 9 system. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22:9554. doi: 10.3390/ijms22179554
Zheng, W., Zhang, Y., Zhang, Q., Wu, R., Wang, X., Feng, S., et al. (2020). Genome-wide identification and characterization of hexokinase genes in Moso Bamboo (Phyllostachys dullish). Front. Plant Sci. 11:600. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.00600
Keywords: Gossypium hirsutum, hexokinase, sequence analysis, the evolutionary, expression pattern
Citation: Dou L, Li Z, Wang H, Li H, Xiao G and Zhang X (2022) The hexokinase Gene Family in Cotton: Genome-Wide Characterization and Bioinformatics Analysis. Front. Plant Sci. 13:882587. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.882587
Received: 24 February 2022; Accepted: 21 April 2022;
Published: 16 May 2022.
Edited by:
Baohua Wang, Nantong University, ChinaReviewed by:
Juwu Gong, Institute of Cotton Research (CAAS), ChinaMing Luo, Southwest University, China
Yanying Qu, Xinjiang Agricultural University, China
Copyright © 2022 Dou, Li, Wang, Li, Xiao and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Guanghui Xiao, guanghuix@snnu.edu.cn; Xianliang Zhang, zxliang1000@163.com
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Lingling Dou
Lingling Dou